Biomarkers in Gingival Crevicular Fluid
|
|
|
- Ursula Neal
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: , p-issn: Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver. IX (Oct. 2015), PP Biomarkers in Gingival Crevicular Fluid Dr Priyanka A. Kurdukar 1, Dr Abhishek A. Kurdukar 2, Dr Swapna A. Mahale 3 Dr Amol M. Beldar 4 1 ( Senior lecturer, Dept of Periodontology, MGV`S K.B.H Dental College, Nashik, India) 2 ( Assistant Professor, Dept of Dentistry, SMBT Medical College, Dhamangaon,India) 3 ( Prof & HOD, Dept of Periodontology, MGV`S K.B.H Dental College, Nashik, India) 4 (Reader, Dept of Periodontology, MGV`S K.B.H Dental College, Nashik, India) Abstract: Conventional clinical and radiographical methods of periodontal diagnosis are only capable of retrospective diagnosis of attachment and bone loss. These are unable to either detect or predict periodontal disease activity (PDA). For these reasons a large proportion of recent periodontal research has been concerned with finding and testing potential markers of PDA. The existence of gingival crevice fluid (GCF), which emerges between the surface of the tooth and the epithelial integument, has been recognized for over 100years. Since it can be easily collected and contains locally and systemically derived markers of periodontal disease, they may offer the basis for a patient-specific biomarker assessment for periodontitis and other systemic diseases. This article reviews the various biomarkers in GCF used for assessing periodontal disease activity. Keywords: Biomarkers, Exudate, GCF. I. Introduction A biomarker is defined as a Parameter that is objectively measured and evaluated as an indicator of normal biological or pathological processes, or pharmacological responses to a therapeutic intervention (NIH 1998). Gingival crevice fluid (GCF) is an inflammatory exudate that seeps into gingival crevices or periodontal pockets around teeth with inflamed gingiva [1]. The diagnostic potential of GCF has been studied over 50 years. In 1960, it was first suggested that analysis of GCF might be a way to quantitatively evaluate the inflammatory status of gingival and periodontal tissues [2]. Presence and function of proteins especially enzymes in GCF were first explored by Seleda, Bang and Cimasoni [3]. It was soon understood that enzymes released from damaged periodontal tissue possessed an enormous potential for periodontal diagnosis. Ohlsson [4], Golub [5] & Uitto [6] discovered that collagenase and elastase in GCF are derived primarily from human cells most notably neutrophils and that their activity is correlated with gingival inflammation and gingival pocket depth. GCF contains a rich array of cellular and biochemical factors which have been shown to indicate the metabolic status of various tissue components of the periodontium (Fig 1). Such factors are now finding value as potential diagnostic or prognostic markers of the periodontium in health and disease [7]. The identification of high-risk and low-risk patient groups in relationship to current disease activity and progression and the initiation of preventive measures are at the heart of much current study. Over 65 GCF components have been preliminarily examined as possible markers for the progression of periodontitis [2] (Table- 1, 2, 3). These components fall into three general categories: 1.1 Host-derived enzymes and their inhibitors 1.2 Inflammatory mediators and host-response modifiers 1.3 Tissue breakdown products DOI: / Page
2 Fig 1: Potential marker sources [7] HOST DERIVED ENZYMES AND THEIR INHIBITORS IN GCF [2] Aspartate aminotransferase Glucosidase Alkaline phosphatase Dipeptidylpeptidase Acid phosphate Nonspecific neutral proteinases Collagenases Matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) ß- Glucoronidase Matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) Matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) Matrix metalloproteinase-13 (MMP-13) Gelatinases Elastase Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) Matrix metalloproteinase- 9 (MMP-9) Elastase inhibitors α2 -macroglobulin Tissue inhibitor of MMP-1 (TIMP-1) α1- proteinase inhibitor Cathepsins Cysteine proteinases Stromyelysins & Myeloperoxidases Serine proteinase Cathepsin D Trypsin like enzymes Lactate dehydrogenases & ß-N-acetyl-hexosaminidase Immunoglobulin- degrading enzymes Acrylsulfatases & Creatinine kinase Table 1: Host derived enzymes and their inhibitors in GCF INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS AND HOST RESPONSE MODIFIERS IN GCF [2] CYTOKINES IN-1α, IL-1ß, IL-1ra, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, Substance P Tumor necrosis factor α Interferon α RANTES (chemoattractant & activator of macrophages and Vasoactive intestinal peptide lymphocytes) PROSTAGLANDIN E2 Neurokinin A LEUCOTRIENE B4 Neopterin ACUTE PHASE REACTANTS Lactoferrin, transferring, α2- macroglobulin, α1- proteinase Platelet-activating factor inhibitor, C- reactive protein Auto antibodies CD-14 Anti-desmosomal antibodies Antibacterial antibodies IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4 Cystatins IgM, IgA Plasminogen activator (PA) Calgranulin A (MRP-8) Table- 2: Inflammatory mediators and host response modifiers in GCF DOI: / Page
3 TISSUE BREAKDOWN IN GCF [2] Glycosaminoglycan Hyaluronic acid Chondroitin-4-sulfate Chondroitin-6-sulfate Dermatan sulfate Laminin Hydroxyproline Fibronectin fragments Connective tissue and bone proteins Osteonectin, Osteocalcin, Type 1 collagen peptides, Osteopontin Calprotectin Hemoglobin ß- chain peptides Pyridinoline crosslinks Table -3: Tissue breakdown in GCF The advantage of collecting GCF as a biomarker is that it is noninvasive, site-specific about teeth, comparatively easy to perform, and offers one of the most accessible entrees of any tissue in the body as a means of assessing the disease state. II. Biomarkers from microbial plaque Presence of lipopolysaccharides (endotoxins) has been positively correlated with gingival inflammation [8]. Patients with localized aggressive periodontitis have increased antibody levels to the lipopolysaccharide of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and interleukin-1 inhibitor. The bacterial proteinases are usually of the serine endopeptidase type and have formed the basis of diagnostic L-BANA test. Similar trypsin-like enzymes are also associated with Treponema denticola. The metabolic end products of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins which include H 2 S, butyrate and proprionate show a positive correlation exists among the degree of inflammation, GCF volume and H 2 S generating potential of GCF fluid. III. Biomarkers from host cells Alkaline phosphatase correlates with increasing inflammation in an experimental gingivitis model. In serum, the enzyme is associated with bone disease, and its elevation in GCF could well reflect changes of alveolar bone in localized area [7]. Extensive studies reviewed by Lamster et al. (1991) [9] on glycogen-degrading enzymes like β- glucuronidase have indicated a significant increase above baseline values some two to four weeks following initiation of inflammation. Wide range of proteolytic enzymes has been detected in GCF; many of host cell origin. Ishikawa et al. (1972) [10] demonstrated 10-fold increase in cathepsin D levels in GCF by comparison with serum, an observation correlated with pocket depth. Also elastase has demonstrated a significant promise as a marker of periodontal disease. Lactoferrin showed better correlation with clinical indices than PMNs and was found to be increased twofold in GCF in sites showing gingivitis, periodontitis, and localized aggressive periodontitis. Glycosaminoglycan concentrations were found to be elevated in aggressive periodontal diseases, and associations have been made with periodontal pathogens such as P. gingivalis. IV. Biomarkers from host tissue damage host tissue damage Collagen represents the most important structural protein of periodontium. Collagen is usually measured by the hydroxyproline assay. Hara and Takahashi (1975) [11] assayed the hydroxyproline levels of serum and GCF in patients before, one month after, and six months after periodontal surgery and found the levels to be significantly lower in both serum and GCF after six months. Collagenase-3 (MMP-13) rather than collagenase-2 (MMP-8) secreted by neutrophils, is a significant enzyme because it appears to be released from fibroblasts and pocket epithelial cells during tissue destruction. Gelatinases are prevalent enzymes in periodontitis and they are released from fibroblasts (MMP-2), epithelial cells (MMP-9 and MMP-2) and neutrophils (MMP-9). Proteoglycans have the ability to bind most collagens as well as fibronectin. Upon degradation of periodontal tissues, glycosaminoglycans are released, making their way into the GCF. Chondroitin-4-sulfate appears to be the major glycosaminoglycan in untreated chronic periodontitis sites, as shown in both animal [12,13] and human [14,15] studies. DOI: / Page
4 V. Host factors: immune response and associated inflammatory mediators The work of Reinhardt et al. (1989) [16] showed higher levels of IgG, IgG1 and IgG4 in GCF from active sites by comparison with stable or healthy sites. The presence of IL-1 in GCF has been shown by Charon et al. (1982) [17], to be higher in inflamed sites than in normal sites. Reports have been noted of raised levels of TNF-α in GCF from diseased sites and of an order similar to IL-1β. Prostaglandin E 2 has been found in elevated quantities in GCF from patients with periodontitis by comparison with gingivitis patients only. PGE 2 levels were also higher in aggressive periodontitis patients by comparison with those in adult periodontitis patients. A review by Offenbacher et al. (1991) indicated the diagnostic potential of PGE2 in GCF. They found that the GCF levels in humans, dogs, and monkeys increased 2- and 3- fold in inflammation and 5- to 6-fold during periods of active attachment loss and bone resorption. In addition, patients with high PGE2 levels are at high risk of attachment loss. He reported higher levels of LTB 4 in GCF obtained from clinical sites associated with adult periodontitis, alveolar bone loss, and aggressive periodontitis. VI. Proteolysis host cell enzymes and their inhibitors in GCF MMP-8 and MMP-9 are the main collagen-degrading enzymes in GCF and they are believed to be mainly responsible for collagen degradation in inflamed tissue during gingivitis and adult periodontitis. MMP-8 and MMP-9 are considered as good indicators for periodontal inflammation. Cathepsin B levels are reduced after periodontal therapy. Both before and after therapy total amounts of cathepsin B in gingival crevice fluid correlate significantly with clinical parameters making cathepsin B a promising factor and potential chair-side diagnostic marker. VII. Matrix molecules and growth factors as indicators of periodontal disease Collagen degradation products have emerged as valuable markers of bone turnover in a multitude of osteolytic and osseous metabolic diseases (Tables 4 & 5)). BONE FORMATION MARKERS [18] 1) Type I protocollagen propeptide proliferation a) C- terminal propeptide fragment (PICP) b) N- terminal propeptide fragment (PINP) 2) Alkaline phosphatase matrix formation a) Total alkaline phosphatase (Al-p) b) Bone alkaline phosphatase (BAL-p) 3) Osteocalcin, bone Gla proteinmineralization (BGP) a) C-terminal fragment b) Mid portion c) Intact Table-4 Bone formation markers BONE RESORPTION MARKERS [18] 1) Pyridinium cross-link a) Urine pyridinoline (PYP), deoxypyridinoline (DPD), HPLC method b) Urine free deoxypyridinoline 2) Pyridinium cross-linked collagen peptide fragment a) Serum C- terminal telopeptide (ICTP) b) Urine C-terminal telopeptide (CTx, crosslaps) c) Urine N-terminal telopeptide (NTx, osteomark) 3) Tartrate- resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) 4) Galactosyl hydroxylysine (GHYL) 5) Hydroxyproline 6) N-terminal osteocalcin fragment 7) Glycosaminoglycans (GAG`s) Table 5 Bone resorption markers Pyridinium cross-link collagen peptide fragment (ICTP) has been shown by various studies to be a good predictor of future alveolar bone and attachment loss. A longitudinal study using an experimental periodontitis model in beagle dogs reported strong correlation between GCF osteocalcin levels and active bone turnover [19]. Diagnostic tools have also been applied to evaluate the response to active periodontal therapy. Golub et al. (1997) [20] found that treatment of 18 chronic periodontitis patients with scaling and root planing and matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor (sub-antimicrobial doxycycline hyclate) resulted in a 70% reduction in GCF ICTP levels after 1month, concomitant with a 30% reduction in collagenase levels. Rapid reductions in GCF ICTP levels in periodontitis subjects after scaling root planing and local delivery of minocycline were also found. DOI: / Page
5 The future suggests that bone-specific biomarkers in GCF will become sensitive enough to give accurate and predictable diagnoses, thus enabling practitioners to serve their periodontal patients better. Furthermore, the elucidation of biomarkers of active periodontitis will greatly add to our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of the progression of periodontal diseases to give real-time measures of bone metabolism. VIII. Futuristic chairside diagnostic test based on GCF sampling: Considering the GCF fluid as a potential analyte for the screening of multiple biomarkers, a rapid, chairside diagnostic tool or a mini-lab could be used by clinicians for risk assessment and decision making on treatment planning. The advantages of such a tool would be enhanced predictability of clinical outcomes and well-informed patients regarding personalized treatment needs. A simple clinical procedure for GCF collection could be used, followed by extraction of analytes from the test strip. The fluid present on the test strip would be subjected to volumetric quantification. Fig- 2: Micro-analyser or Mini-lab There is a plethora of possibilities for the future use of oral fluids in biotechnology and health care applications, especially in the field of diagnostics. A tremendous amount of research activity is currently under way to explore the role of oral fluids as a possible medium in a variety of applications. Recent advances in HIV diagnosis have been made using oral fluids. IX. Conclusion The search for markers of periodontal disease activity will progress with the refinement and application of specific detection techniques for selected factors. GCF will continue to be a vehicle for monitoring tissue and cell products and allows a degree of non-invasive access to the periodontium, unlike the majority of other tissues in the body. Several products show potential benefit, particularly those directly from specific regions of the periodontium which give a clue as to which tissue components are at risk. It is clear that no single marker will fulfill all the criteria necessary for assessment of the clinical state of the periodontium, and future research should be directed at the production of "marker packages". References [1]. Veli-Jukka Uitto. GCF- An introduction. Periodontology 2000, Vol. 31,2003: [2]. Gary Armitage. Analysis of gingival crevice fluid and risk of progression of periodontitis. Periodontology 2000; Vol. 34, 2004: [3]. Bang JS, Cimasoni G. Total protein in human crevicular fluid. J Dent Res 1971: 50: [4]. Golub LM, Siegel K, Ramamurthy NS, Mandel ID. Some characteristics of collagenase activity in gingival crevicular fluid and its relationship to gingival diseases in human. J Dent Res 1976: 55: [5]. Ohlsson K, Olsson I, Tynelius-Bratthall G. Neutrophil leukocyte collagenase, elastase and serum protease inhibitors in human gingival crevices. Acta Odontol Scand 1973:31: [6]. Uitto VJ, Raeste AM. Activation of latent collagenase of human leukocytes and gingival fluid by bacterial plaque. J Dent Res 1978: 57: [7]. G. Embery, R. Waddington. GCF- Biomarkers of periodontal disease activity. Adv Dent Res 1994; 8(2): [8]. Simon B, Goldman H, Ruben M, Baker E. The role of endotoxins in periodontal disease. III. Correlation of the quantity of endotoxin in human gingival exudate with the histologic degree of inflammation. J Periodontol 1971; 42: DOI: / Page
6 [9]. Ira B. Lamster & John T Grbic, Diagnosis of periodontal disease based on analysis of host response. Periodontology 2000; 1995: [10]. Ishikawa I, Cimasoni G, Ahmad-Zadeh C. Possible role of lysosomal enzymes in the pathogenesis of periodontitis. A study on cathepsin D in human gingival fluid. Arch Oral Biol 1972; 17: [11]. Hara K, Takahashi T. Hydroxyproline content in gingival exudate before and after periodontal surgery. J Periodontal Res 1975:10: [12]. Bowers MA, Fisher LW, Termine JD, Somerman MJ. Connective tissue-associated proteins in crevicular fluid: potential markers for periodontal diseases. J Periodontol 1989:60: [13]. Kaufman E, Lamster IB. Analysis of saliva for periodontal diagnosis a review [In Process Citation]. J Clin Periodontol 2000: 27: [14]. Shibutani T, NishinoW, Shiraki M, Iwayama Y. ELISA detection of glycosaminoglycan (GAG) -linked proteoglycans in gingival crevicular fluid. J Periodontal Res 1993: 28: [15]. Embery G, Last KS. Biochemical markers of periodontal tissue destruction. Dent Update 1989: 16: [16]. Reinhardt RA, McDonald TL, Bolton RW, Dubois LM, Kaldahl WB. IgG subclasses in gingival crevicular fluid from active versus stable periodontal sites. J Periodontol 1989:60: [17]. Charon JA, LugerTA, Mergenhagen SE, Oppenheim JJ. Increased thymocyte-activating factor in human gingival fluid during gingival inflammation. Infect Immun 1982; 38: [18]. William V. Giannobile, Khalaf F. AL-Shammari & David P. Sharment. Matrix molecules and growth factors as indicators of periodontal disease activity. Periodontology 2000, 2003, Vol [19]. Giannobile WV, Lynch SE, Denmark RG, Paquette DW, Fiorellini JP, Williams RC. Crevicular fluid osteocalcin and pyridinoline cross-linked carboxyterminal telopeptide of type I collagen (ICTP) as markers of rapid bone turnover in periodontitis. A pilot study in beagle dogs. J Clin Periodontol 1995: 22: [20]. Golub LM, Lee HM, Greenwald RA, Ryan ME, Sorsa T, SaloT, Giannobile WV. A matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor reduces bone-type collagen degradation fragments and specific collagenases in gingival crevicular fluid during adult periodontitis. Inflamm Res 1997: 46: DOI: / Page
CRITICAL BIOMARKERS IN PERIODONTICS
 Review Article CRITICAL BIOMARKERS IN PERIODONTICS Dr. Shivani Sachdeva*, Dr. Harish Saluja*, Dr.Ameet Mani**, Dr.Parul Tandon***, Dr. S. Anuraga**** Abstract: Traditional periodontal diagnostic parameters
Review Article CRITICAL BIOMARKERS IN PERIODONTICS Dr. Shivani Sachdeva*, Dr. Harish Saluja*, Dr.Ameet Mani**, Dr.Parul Tandon***, Dr. S. Anuraga**** Abstract: Traditional periodontal diagnostic parameters
Biomarkers: A Critical Update
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 8, Issue 6 (Jul.- Aug. 2013), PP 74-78 Biomarkers: A Critical Update Promod Kr Rathore 1, Anoop Bhushan
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 8, Issue 6 (Jul.- Aug. 2013), PP 74-78 Biomarkers: A Critical Update Promod Kr Rathore 1, Anoop Bhushan
Gingival crevicular fluid as a periodontal diagnostic indicator- I: Host derived enzymes and tissue breakdown products
 , pp.390 397 Gingival crevicular fluid as a periodontal diagnostic indicator- I: Host derived enzymes and tissue breakdown products Gupta G Department of Periodontics, Institute of Dental Studies and Technologies,
, pp.390 397 Gingival crevicular fluid as a periodontal diagnostic indicator- I: Host derived enzymes and tissue breakdown products Gupta G Department of Periodontics, Institute of Dental Studies and Technologies,
Oral Fluid Based Biomarkers of Alveolar Bone Loss in Periodontitis
 Oral Fluid Based Biomarkers of Alveolar Bone Loss in Periodontitis JANET S. KINNEY, a CHRISTOPH A. RAMSEIER, a AND WILLIAM V. GIANNOBILE a,b a Department of Periodontics and Oral Medicine and Michigan
Oral Fluid Based Biomarkers of Alveolar Bone Loss in Periodontitis JANET S. KINNEY, a CHRISTOPH A. RAMSEIER, a AND WILLIAM V. GIANNOBILE a,b a Department of Periodontics and Oral Medicine and Michigan
Evaluating the levels of salivary enzymes as biochemical markers in periodental disease
 Original article: Evaluating the levels of salivary enzymes as biochemical markers in periodental disease *P.Krushna Kishore, ** Dr.Yuvarajparmar, ***Satishkumar. S 1Reader & H O D, Department of Biochemistry,
Original article: Evaluating the levels of salivary enzymes as biochemical markers in periodental disease *P.Krushna Kishore, ** Dr.Yuvarajparmar, ***Satishkumar. S 1Reader & H O D, Department of Biochemistry,
Focal Infection Theory
 Paradigm Shift Focal Infection Theory 1900, British physician William Hunter first developed the idea that oral microorganisms were responsible for a wide range of systemic conditions that were not easily
Paradigm Shift Focal Infection Theory 1900, British physician William Hunter first developed the idea that oral microorganisms were responsible for a wide range of systemic conditions that were not easily
State of the Art Review
 Mediators of Periodontal Osseous Destruction and Remodeling: Principles and Implications for Diagnosis and Therapy Laurie K. McCauley* and Rahime M. Nohutcu Osteoclastic bone resorption is a prominent
Mediators of Periodontal Osseous Destruction and Remodeling: Principles and Implications for Diagnosis and Therapy Laurie K. McCauley* and Rahime M. Nohutcu Osteoclastic bone resorption is a prominent
Protein biomarkers of periodontitis in saliva
 Protein biomarkers of periodontitis in saliva John J Taylor Institute of Cellular Medicine & Centre for Oral Health Research, School of Dental Sciences, Newcastle University, Framlington Place, Newcastle
Protein biomarkers of periodontitis in saliva John J Taylor Institute of Cellular Medicine & Centre for Oral Health Research, School of Dental Sciences, Newcastle University, Framlington Place, Newcastle
The use of antimicrobial
 Antimicrobial mouthrinses and the management of periodontal diseases Introduction to the supplement Ira B. Lamster, DDS, MMSc The use of antimicrobial mouthrinses is an approach to limiting the accumulation
Antimicrobial mouthrinses and the management of periodontal diseases Introduction to the supplement Ira B. Lamster, DDS, MMSc The use of antimicrobial mouthrinses is an approach to limiting the accumulation
Effect of Orthodontic Tooth Movement on Gingival Crevicular Fluid Infiltration; a Preliminary Investigation
 Original Article Effect of Orthodontic Tooth Movement on Gingival Crevicular Fluid Infiltration; a Preliminary Investigation A. Dannan 1, MA. Darwish 2, MN. Sawan 3 1 Assistant Clinical Specialist, Department
Original Article Effect of Orthodontic Tooth Movement on Gingival Crevicular Fluid Infiltration; a Preliminary Investigation A. Dannan 1, MA. Darwish 2, MN. Sawan 3 1 Assistant Clinical Specialist, Department
Evaluation of aspartate aminotransferase enzyme levels in saliva and gingival crevicular fluid with periodontal disease progression - A pilot study
 J. Int Oral Health 2011 Case Report All right reserved Evaluation of aspartate aminotransferase enzyme levels in saliva and gingival crevicular fluid with periodontal disease progression - A pilot study
J. Int Oral Health 2011 Case Report All right reserved Evaluation of aspartate aminotransferase enzyme levels in saliva and gingival crevicular fluid with periodontal disease progression - A pilot study
ASSESSMENT OF SALIVARY ENZYMES- ALANINE AMINOPEPTIDASE(ALAP) AND DIPEPTIDYL PEPTIDASE IV (DPP IV) IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Original Research ASSESSMENT OF SALIVARY ENZYMES- ALANINE AMINOPEPTIDASE(ALAP) AND DIPEPTIDYL PEPTIDASE IV (DPP IV) IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Original Research ASSESSMENT OF SALIVARY ENZYMES- ALANINE AMINOPEPTIDASE(ALAP) AND DIPEPTIDYL PEPTIDASE IV (DPP IV) IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS
Assessment of IL 6, IL 8 and TNF α levels in the gingival tissue of patients with periodontitis
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 847-851, 2013 Assessment of IL 6, IL 8 and TNF α levels in the gingival tissue of patients with periodontitis MIN KI NOH 1, MIN JUNG 1, SOO HWAN KIM 1, SEO RA LEE
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 847-851, 2013 Assessment of IL 6, IL 8 and TNF α levels in the gingival tissue of patients with periodontitis MIN KI NOH 1, MIN JUNG 1, SOO HWAN KIM 1, SEO RA LEE
Are the GCF levels of MCP-1 and RANTES elevated in Peri-partum women with periodontitis as compared to healthy controls?
 Are the GCF levels of MCP-1 and RANTES elevated in Peri-partum women with periodontitis as compared to healthy controls? E. Ashley Martin, BSDH, RDH A thesis submitted to the faculty of the University
Are the GCF levels of MCP-1 and RANTES elevated in Peri-partum women with periodontitis as compared to healthy controls? E. Ashley Martin, BSDH, RDH A thesis submitted to the faculty of the University
Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) ISSN: 2279-0853, ISBN: 2279-0861. Volume 1, Issue 4 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 36-41 Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool 1 Ashu Bhardwaj,
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) ISSN: 2279-0853, ISBN: 2279-0861. Volume 1, Issue 4 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 36-41 Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool 1 Ashu Bhardwaj,
Diabetes is one of the risk factors
 J Periodontol February 2006 Collagenases in Gingival Crevicular Fluid in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Bedia Safkan-Seppälä,* Timo Sorsa,* Taina Tervahartiala,* Arzu Beklen, and Yrjö T. Konttinen i Background:
J Periodontol February 2006 Collagenases in Gingival Crevicular Fluid in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Bedia Safkan-Seppälä,* Timo Sorsa,* Taina Tervahartiala,* Arzu Beklen, and Yrjö T. Konttinen i Background:
Estimation of Serum Alkaline Phosphatase in Chronic Periodontitis in Smokers and Non- Smokers with Healthy Individuals: A Pilot Study
 Estimation of Serum Alkaline Phosphatase in Chronic Periodontitis in Smokers and Non- Smokers with Healthy Individuals: A Pilot Study Nishant Agrawal 1, Abhishek Singhvi 2, Manoj Upadhyay 3, Navneet Kaur
Estimation of Serum Alkaline Phosphatase in Chronic Periodontitis in Smokers and Non- Smokers with Healthy Individuals: A Pilot Study Nishant Agrawal 1, Abhishek Singhvi 2, Manoj Upadhyay 3, Navneet Kaur
Slide 1 Inflammation. Slide 2 WHAT IS AN EXPERT? Slide 3 FOCAL INFECTION HYPOTHESIS
 Slide 1 Inflammation The Oral Systemic Connection By Alexander H Malick, DMD, FAGD Private Practice, General Restorative Dentistry Dental Sleep Medicine Comprehensive Dentistry under General Anesthesia
Slide 1 Inflammation The Oral Systemic Connection By Alexander H Malick, DMD, FAGD Private Practice, General Restorative Dentistry Dental Sleep Medicine Comprehensive Dentistry under General Anesthesia
Diabetes and Periodontal Disease. Brianne Neelis & Katie Torres. Literature Review 1 11/4/08
 1 Diabetes and Periodontal Disease Brianne Neelis & Katie Torres Literature Review 1 11/4/08 2 Introduction Diabetes is a cardiovascular condition that effects an estimated 20 million people in the United
1 Diabetes and Periodontal Disease Brianne Neelis & Katie Torres Literature Review 1 11/4/08 2 Introduction Diabetes is a cardiovascular condition that effects an estimated 20 million people in the United
THE EFFECT OF DIETARY NUTRIENTS ON OSTEOCHONDROSIS IN SWINE AND EVALUATION OF SERUM BIOMARKERS TO PREDICT ITS OCCURRENCE. NOLAN ZEBULON FRANTZ
 THE EFFECT OF DIETARY NUTRIENTS ON OSTEOCHONDROSIS IN SWINE AND EVALUATION OF SERUM BIOMARKERS TO PREDICT ITS OCCURRENCE. by NOLAN ZEBULON FRANTZ B.S., Tabor College, 2001 B.S., Kansas State University,
THE EFFECT OF DIETARY NUTRIENTS ON OSTEOCHONDROSIS IN SWINE AND EVALUATION OF SERUM BIOMARKERS TO PREDICT ITS OCCURRENCE. by NOLAN ZEBULON FRANTZ B.S., Tabor College, 2001 B.S., Kansas State University,
Inflammation has been studied
 Periodontal Inflammation: Simplified Dr. Fay Goldstep, DDS, FACD, FADFE Inflammation has been studied since ancient times. It was observed that as a result of irritation, injury or infection, tissues throughout
Periodontal Inflammation: Simplified Dr. Fay Goldstep, DDS, FACD, FADFE Inflammation has been studied since ancient times. It was observed that as a result of irritation, injury or infection, tissues throughout
Evaluation of aspartate aminotransferase levels in saliva of patients with different periodontal conditions - a biochemical study
 INDIAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL ADVANCEMENTS Journal homepage: www. nacd. in ORIGINAL RESEARCH Quick Response Code doi: 10.5866/4.1.757 Evaluation of aspartate aminotransferase levels in saliva of patients with
INDIAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL ADVANCEMENTS Journal homepage: www. nacd. in ORIGINAL RESEARCH Quick Response Code doi: 10.5866/4.1.757 Evaluation of aspartate aminotransferase levels in saliva of patients with
Microbiota and Oral Disease Prof. Dennis Cvitkovitch
 1 Professor Dennis Cvitkovitch Faculty of Dentistry Dental Research Institute University of Toronto The human microbiome We are a composite species: eukaryotic, bacterial, archeal Every human harbors over
1 Professor Dennis Cvitkovitch Faculty of Dentistry Dental Research Institute University of Toronto The human microbiome We are a composite species: eukaryotic, bacterial, archeal Every human harbors over
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators
 Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
C-TELOPEPTIDE AS DIAGNOSTIC MARKER FOR ACTIVE PERIODONTAL DESTRUCTION- A REVIEW P.R.GANESH
 International Journal of Dental Research & Development (IJDRD) ISSN(P): 2250-2386; ISSN(E): 2321-0117 Vol. 6, Issue 2, Apr 2016, 1-10 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. C-TELOPEPTIDE AS DIAGNOSTIC MARKER FOR ACTIVE PERIODONTAL
International Journal of Dental Research & Development (IJDRD) ISSN(P): 2250-2386; ISSN(E): 2321-0117 Vol. 6, Issue 2, Apr 2016, 1-10 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. C-TELOPEPTIDE AS DIAGNOSTIC MARKER FOR ACTIVE PERIODONTAL
Systemic antibiotics Vs Local antibiotics in the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases BY: ABRAHEEM JAMAL ABRAHEEM & AYOUB NAGIBB BURWEISS
 Systemic antibiotics Vs Local antibiotics in the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases BY: ABRAHEEM JAMAL ABRAHEEM & AYOUB NAGIBB BURWEISS Guidelines for use of antibiotics in periodontal therapy 1. The clinical
Systemic antibiotics Vs Local antibiotics in the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases BY: ABRAHEEM JAMAL ABRAHEEM & AYOUB NAGIBB BURWEISS Guidelines for use of antibiotics in periodontal therapy 1. The clinical
Evaluation of Systemic Inflammatory Markers in Clinically Healthy Subjects and Chronic Periodontitis Patients
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 3 Ver. III (Mar. 2015), PP 01-06 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of Systemic Inflammatory Markers
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 3 Ver. III (Mar. 2015), PP 01-06 www.iosrjournals.org Evaluation of Systemic Inflammatory Markers
Assessment of Knowledge And Attitude Among Diabetic Patients About Their Oral Health- A Questionnaire Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. I January. (2017), PP 28-33 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Knowledge And Attitude
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. I January. (2017), PP 28-33 www.iosrjournals.org Assessment of Knowledge And Attitude
MATRIX METALLOPROTEINASES AND THEIR ROLE IN ORAL DISEASES: A REVIEW
 MATRIX METALLOPROTEINASES AND THEIR ROLE IN ORAL DISEASES: A REVIEW 1 2 3 Varun BR Bindu J Nair Sivakumar TT Anna P Joseph 1 2 3 Senior Lecturer, Professor & HOD, Professor, Reader, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial
MATRIX METALLOPROTEINASES AND THEIR ROLE IN ORAL DISEASES: A REVIEW 1 2 3 Varun BR Bindu J Nair Sivakumar TT Anna P Joseph 1 2 3 Senior Lecturer, Professor & HOD, Professor, Reader, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial
Markers of bone turnover in DENTISTRY
 Markers of bone turnover in DENTISTRY Ioana MOZOŞ, MD, PhD Department of Functional Sciences, Discipline of Pathophysiology Victor Babeș University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara, Romania ioanamozos@umft.ro
Markers of bone turnover in DENTISTRY Ioana MOZOŞ, MD, PhD Department of Functional Sciences, Discipline of Pathophysiology Victor Babeș University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara, Romania ioanamozos@umft.ro
Host Modulatory Therapy: A Novel Approach in Periodontal Therapy
 IOSR Journal Of Pharmacy (e)-issn: 2250-3013, (p)-issn: 2319-4219 Www.Iosrphr.Org Volume 3, Issue 4 (May 2013), Pp 09-13 Host Modulatory Therapy: A Novel Approach in Periodontal Therapy Dr. Raju Anarthe
IOSR Journal Of Pharmacy (e)-issn: 2250-3013, (p)-issn: 2319-4219 Www.Iosrphr.Org Volume 3, Issue 4 (May 2013), Pp 09-13 Host Modulatory Therapy: A Novel Approach in Periodontal Therapy Dr. Raju Anarthe
Correlation of Levels of Interleukin-1β in Gingival Crevicular Fluid to the Clinical Parameters of Chronic Periodontitis
 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1010 AU Chaudhari et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation of Levels of Interleukin-1β in Gingival Crevicular Fluid to the Clinical Parameters of Chronic Periodontitis AU Chaudhari,
10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1010 AU Chaudhari et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation of Levels of Interleukin-1β in Gingival Crevicular Fluid to the Clinical Parameters of Chronic Periodontitis AU Chaudhari,
JMSCR Volume 2 Issue 7 Page July
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 1.1147 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Clinical Evaluation of Locally Delivered 10% Doxycycline Hyclate Gel as An Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing in the Treatment of Chronic
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 1.1147 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Clinical Evaluation of Locally Delivered 10% Doxycycline Hyclate Gel as An Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing in the Treatment of Chronic
Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases. Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary
 Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary Calcium homeostasis Ca 1000g in adults 99% in bones (extracellular with Mg, P) Plasma/intracellular
Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary Calcium homeostasis Ca 1000g in adults 99% in bones (extracellular with Mg, P) Plasma/intracellular
Biochemistry #01 Bone Formation Dr. Nabil Bashir Farah Banyhany
 Biochemistry #01 Bone Formation Dr. Nabil Bashir Farah Banyhany Greetings This lecture is quite detailed, but I promise you will make it through, it just requires your 100% FOCUS! Let s begin. Today s
Biochemistry #01 Bone Formation Dr. Nabil Bashir Farah Banyhany Greetings This lecture is quite detailed, but I promise you will make it through, it just requires your 100% FOCUS! Let s begin. Today s
Use of aspartate aminotransferase in diagnosing periodontal disease: a comparative study of clinical and microbiological parameters
 33 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 45, No. 1, 33-38, 2003 Original Use of aspartate aminotransferase in diagnosing periodontal disease: a comparative study of clinical and microbiological parameters Emílio
33 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 45, No. 1, 33-38, 2003 Original Use of aspartate aminotransferase in diagnosing periodontal disease: a comparative study of clinical and microbiological parameters Emílio
Host Modulation Therapy: A Novel Approach In The Treatment Of Periodontal Diseases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 9 Number 1 Host Modulation Therapy: A Novel Approach In The Treatment Of Periodontal Diseases S Masamatti, M Virdi, A Kumar Citation S Masamatti,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 9 Number 1 Host Modulation Therapy: A Novel Approach In The Treatment Of Periodontal Diseases S Masamatti, M Virdi, A Kumar Citation S Masamatti,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Comparative Evaluation of Salivary Flow Rate, Ph, Buffering Capacity, Total Protein and Albumin
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Comparative Evaluation of Salivary Flow Rate, Ph, Buffering Capacity, Total Protein and Albumin
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
From Gums to Guts: Periodontal Medicine KEY SLIDES. UCSF Osher Mini-Medical School October 15, /8/2015. environmental factors (smoking)
 From Gums to Guts: Medicine KEY SLIDES UCSF Osher Mini-Medical School October 15, 2015 Tooth Enamel (Crown) Dental Biofilm (Dental Plaque and Calculus) Pocket (with ulcerated wall) Mark I. Ryder DMD Professor
From Gums to Guts: Medicine KEY SLIDES UCSF Osher Mini-Medical School October 15, 2015 Tooth Enamel (Crown) Dental Biofilm (Dental Plaque and Calculus) Pocket (with ulcerated wall) Mark I. Ryder DMD Professor
Received: 15 th May-2012 Revised: 17 th May-2012 Accepted: 21 st May-2012 Review article
 Received: 15 th May-2012 Revised: 17 th May-2012 Accepted: 21 st May-2012 Review article HOST MODULATION AND HOST MODULATING AGENTS IN PERIODONTAL THERAPY 1 Dr. Amit Bhardwaj, MDS, Senior Lecturer, Department
Received: 15 th May-2012 Revised: 17 th May-2012 Accepted: 21 st May-2012 Review article HOST MODULATION AND HOST MODULATING AGENTS IN PERIODONTAL THERAPY 1 Dr. Amit Bhardwaj, MDS, Senior Lecturer, Department
Volume 2 Issue
 Volume 2 Issue 2 2017 Page 333 to 340 Research Article Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 The Anti-Inflammatory Actions of an Intra-Oral Adhesive Patch Containing Botanical Extracts Exert Inhibitory
Volume 2 Issue 2 2017 Page 333 to 340 Research Article Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 The Anti-Inflammatory Actions of an Intra-Oral Adhesive Patch Containing Botanical Extracts Exert Inhibitory
Dental Research Journal
 Dental Research Journal Original Article Plasma levels of N-telopeptide of Type I collagen in periodontal health, disease and after treatment Ganganna Aruna Department of Periodontology, JSS Dental College
Dental Research Journal Original Article Plasma levels of N-telopeptide of Type I collagen in periodontal health, disease and after treatment Ganganna Aruna Department of Periodontology, JSS Dental College
Current Chemotherapeutic Modalities Available in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease
 Current Chemotherapeutic Modalities Available in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Paul Tolmie, D.D.S. Kenneth Rasenberger, D.D.S. Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. The Changing Views of Plaque and Periodontal
Current Chemotherapeutic Modalities Available in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Paul Tolmie, D.D.S. Kenneth Rasenberger, D.D.S. Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. The Changing Views of Plaque and Periodontal
Advances in the Relationship between Periodontitis and Systemic Diseases
 Advances in the Relationship between Periodontitis and Systemic Diseases Andrija Boπnjak Darije PlanËak Zvonimir CuriloviÊ Department of Periodontology School of Dental Medicine University of Zagreb Summary
Advances in the Relationship between Periodontitis and Systemic Diseases Andrija Boπnjak Darije PlanËak Zvonimir CuriloviÊ Department of Periodontology School of Dental Medicine University of Zagreb Summary
Comparison of Bone Scintigraphy with Bone Markers in the Diagnosis of Bone Metastasis in Lung Carcinoma Patients
 Comparison of Bone Scintigraphy with Bone Markers in the Diagnosis of Bone Metastasis in Lung Carcinoma Patients W. EBERT 1, TH. MULEY 1, K.P. HERB 1 and H. SCHMIDT-GAYK 2 1 Thoraxklinik Heidelberg ggmbh,
Comparison of Bone Scintigraphy with Bone Markers in the Diagnosis of Bone Metastasis in Lung Carcinoma Patients W. EBERT 1, TH. MULEY 1, K.P. HERB 1 and H. SCHMIDT-GAYK 2 1 Thoraxklinik Heidelberg ggmbh,
Research Article. INTRODUCTION. Journal of Periodontal JPIS & Implant Science. Dong-Seok Shin, Jin-Woo Park, Jo-Young Suh, Jae-Mok Lee*
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2010;40:33-38 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.1.33 The expressions of inflammatory factors and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in human chronic periodontitis
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2010;40:33-38 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.1.33 The expressions of inflammatory factors and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in human chronic periodontitis
Journal of American Science 2015;11(4)
 Expression of Platelet-Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule PECAM -1 in Gingival Tissue of Patients with Chronic Periodontitis Ghada Bassiouny Department of periodontology and oral medicine, college of Dentistry,
Expression of Platelet-Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule PECAM -1 in Gingival Tissue of Patients with Chronic Periodontitis Ghada Bassiouny Department of periodontology and oral medicine, college of Dentistry,
Gingival enlargement originating from medication and tooth migration
 CLINICAL REPORT 109 Publication Frédéric Duffau Gingival enlargement originating from medication and tooth migration Frédéric Duffau 26 Avenue Kléber, 75116 Paris France KEY WORDS drug-induced gingival
CLINICAL REPORT 109 Publication Frédéric Duffau Gingival enlargement originating from medication and tooth migration Frédéric Duffau 26 Avenue Kléber, 75116 Paris France KEY WORDS drug-induced gingival
Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient. Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club
 Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club Periodontal Maintenance for Natural Teeth and Implants What is Periodontal Maintenance?
Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club Periodontal Maintenance for Natural Teeth and Implants What is Periodontal Maintenance?
CrossLaps and -glucuronidase in Peri-implant and Gingival Crevicular Fluid
 CrossLaps and -glucuronidase in Peri-implant and Gingival Crevicular Fluid Ulrike Schubert 1 /Bernd-Michael Kleber, Prof Dr med dent 2 / Frank Peter Strietzel, Dr med dent 3 /Peter Dörfling, Prof Dr med
CrossLaps and -glucuronidase in Peri-implant and Gingival Crevicular Fluid Ulrike Schubert 1 /Bernd-Michael Kleber, Prof Dr med dent 2 / Frank Peter Strietzel, Dr med dent 3 /Peter Dörfling, Prof Dr med
Gingiva and gingival sulcus
 Gingiva and gingival sulcus Zsolt Lohinai DMD, PhD university adjunct Semmelweis University Dept. of Conservative Dentistry lohinai@elet2.sote.hu Periodontium Gingiva Periodontal ligaments Root cementum
Gingiva and gingival sulcus Zsolt Lohinai DMD, PhD university adjunct Semmelweis University Dept. of Conservative Dentistry lohinai@elet2.sote.hu Periodontium Gingiva Periodontal ligaments Root cementum
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
Stem cell factor in gingival crevicular fluid in periodontal health and disease
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 2 April 2010; 281-287 Original article Stem cell factor in gingival crevicular fluid in periodontal health and disease Sittisak Honsawek a, Wannee Unwerawattana b a Department
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 2 April 2010; 281-287 Original article Stem cell factor in gingival crevicular fluid in periodontal health and disease Sittisak Honsawek a, Wannee Unwerawattana b a Department
ROLE OF INTERCELLULAR INTERACTIONS BETWEEN MAST CELLS AND GINGIVAL FIBROBLASTS IN MEDIATING INFLAMMTION
 ROLE OF INTERCELLULAR INTERACTIONS BETWEEN MAST CELLS AND GINGIVAL FIBROBLASTS IN MEDIATING INFLAMMTION by Reza Termei A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of
ROLE OF INTERCELLULAR INTERACTIONS BETWEEN MAST CELLS AND GINGIVAL FIBROBLASTS IN MEDIATING INFLAMMTION by Reza Termei A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of
orophenol A blend of polyphenols, from Canadian wild blueberries, cranberries, and strawberries, developed for the support of oral health.
 ORAL HEALTH orophenol A blend of polyphenols, from Canadian wild blueberries, cranberries, and strawberries, developed for the support of oral health. Orophenol : promoter of your health What is Orophenol
ORAL HEALTH orophenol A blend of polyphenols, from Canadian wild blueberries, cranberries, and strawberries, developed for the support of oral health. Orophenol : promoter of your health What is Orophenol
Advances in periodontal diagnosis
 Advances in periodontal diagnosis Periodontitis: is a dynamic disease process characterized by periods of disease progression, remission and exacerbation. Diagnosis of periodontal disease includes different
Advances in periodontal diagnosis Periodontitis: is a dynamic disease process characterized by periods of disease progression, remission and exacerbation. Diagnosis of periodontal disease includes different
Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:1234-1240, 2002 Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars Raymond P. White, Jr, DDS, PhD,* Phoebus N. Madianos,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:1234-1240, 2002 Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars Raymond P. White, Jr, DDS, PhD,* Phoebus N. Madianos,
Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters
 Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters REVIEWED PAPER Most patients visiting dental surgeries suffer from various types of periodontopathies. Since
Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters REVIEWED PAPER Most patients visiting dental surgeries suffer from various types of periodontopathies. Since
Zeyad Nazar Majeed, 1,2 Koshy Philip, 3 A. M. Alabsi, 4 Saravanan Pushparajan, 1 and Dasan Swaminathan Introduction
 Disease Markers Volume 2016, Article ID 1804727, 23 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1804727 Review Article Identification of Gingival Crevicular Fluid Sampling, Analytical Methods, and Oral Biomarkers
Disease Markers Volume 2016, Article ID 1804727, 23 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1804727 Review Article Identification of Gingival Crevicular Fluid Sampling, Analytical Methods, and Oral Biomarkers
Periodic exacerbation of gingival inflammation during the menstrual cycle
 159 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 3, 159-164, 2005 Case report Periodic exacerbation of gingival inflammation during the menstrual cycle Nobuko Koreeda 1), Yoshihiro Iwano 1), Mamoru Kishida 1),
159 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 3, 159-164, 2005 Case report Periodic exacerbation of gingival inflammation during the menstrual cycle Nobuko Koreeda 1), Yoshihiro Iwano 1), Mamoru Kishida 1),
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Periodontol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 August 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Periodontol. 2008 August ; 79(8): 1409 1418. doi:10.1902/jop.2008.070623. Subantimicrobial-Dose Doxycycline Modulates Gingival Crevicular
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Periodontol. 2008 August ; 79(8): 1409 1418. doi:10.1902/jop.2008.070623. Subantimicrobial-Dose Doxycycline Modulates Gingival Crevicular
Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Framework and Proposal of a New Classification and Case Definition. By: Kimberly Hawrylyshyn
 Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Framework and Proposal of a New Classification and Case Definition By: Kimberly Hawrylyshyn Background Periodontitis is a microbe induced inflammatory disease that
Staging and Grading of Periodontitis: Framework and Proposal of a New Classification and Case Definition By: Kimberly Hawrylyshyn Background Periodontitis is a microbe induced inflammatory disease that
Bone metabolic markers as gauges of metastasis to bone: a review
 REVIEW Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 3, 161 168, 2002 Bone metabolic markers as gauges of metastasis to bone: a review Mitsuru KOIZUMI* and Etsuro OGATA** Departments of *Nuclear Medicine and
REVIEW Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 3, 161 168, 2002 Bone metabolic markers as gauges of metastasis to bone: a review Mitsuru KOIZUMI* and Etsuro OGATA** Departments of *Nuclear Medicine and
Locally delivered doxycycline improves the healing following non-surgical periodontal therapy in smokers
 J Clin Periodontol 4; : 589 595 doi:./j.-5x.4.54.x Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 4 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Locally delivered doxycycline improves the healing following non-surgical periodontal
J Clin Periodontol 4; : 589 595 doi:./j.-5x.4.54.x Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 4 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Locally delivered doxycycline improves the healing following non-surgical periodontal
J Bagh College Dentistry Vol. 25(1), March 2013 Evaluation of salivary
 Evaluation of salivary levels of Proteinaceous biomarkers Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP-8) and C-Reactive Protein (CRP) in type 2 diabetic patients with periodontitis Afrah A. Abbas, B.D.S (1) Raja Al-
Evaluation of salivary levels of Proteinaceous biomarkers Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP-8) and C-Reactive Protein (CRP) in type 2 diabetic patients with periodontitis Afrah A. Abbas, B.D.S (1) Raja Al-
Biology of the Salivary Glands 513 (KEY) FINAL Examination June 26, 1997 To see correct answers, show hidden text (C) (B)
 Biology of the Salivary Glands 513 (KEY) FINAL Examination June 26, 1997 To see correct answers, show hidden text 1. With increased age, the following event does not occur in the major salivary glands:
Biology of the Salivary Glands 513 (KEY) FINAL Examination June 26, 1997 To see correct answers, show hidden text 1. With increased age, the following event does not occur in the major salivary glands:
Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement
 Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement Abstract Aim: The purpose of this article is to report a case of conditioned gingival enlargement managed by nonsurgical periodontal therapy.
Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement Abstract Aim: The purpose of this article is to report a case of conditioned gingival enlargement managed by nonsurgical periodontal therapy.
Chapter 1 Herpesviruses in Periodontal Disease
 Chapter 1 Herpesviruses in Periodontal Disease Miriam Ting 1 and Jørgen Slots 2 * 1 Specialty Clinic in Periodontology, USA 2 University of Southern California, USA * Corresponding Author: Jørgen Slots,
Chapter 1 Herpesviruses in Periodontal Disease Miriam Ting 1 and Jørgen Slots 2 * 1 Specialty Clinic in Periodontology, USA 2 University of Southern California, USA * Corresponding Author: Jørgen Slots,
Bone Turnover Markers for the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis and Diseases Associated with High Bone Turnover. Original Policy Date
 MP 2.04.10 Bone Turnover Markers for the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis and Diseases Associated with High Bone Turnover Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013
MP 2.04.10 Bone Turnover Markers for the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis and Diseases Associated with High Bone Turnover Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013
Collagenase Assay Kit
 Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen types
Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen types
Dissertation for the degree of philosophiae doctor (PhD) at the University of Bergen. Dissertation date:
 Dissertation for the degree of philosophiae doctor (PhD) at the University of Bergen Dissertation date: Copyright [Hasaan G. Mohamed] The material in this publication is protected by copyright law. Year:
Dissertation for the degree of philosophiae doctor (PhD) at the University of Bergen Dissertation date: Copyright [Hasaan G. Mohamed] The material in this publication is protected by copyright law. Year:
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder
 ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
Topics. Humoral Immune Response Part II Accessory cells Fc Receptors Opsonization and killing mechanisms of phagocytes NK, mast, eosynophils
 Topics Humoral Immune Response Part II Accessory cells Fc Receptors Opsonization and killing mechanisms of phagocytes NK, mast, eosynophils Immune regulation Idiotypic network 2/15/2005 MICR 415 / 515
Topics Humoral Immune Response Part II Accessory cells Fc Receptors Opsonization and killing mechanisms of phagocytes NK, mast, eosynophils Immune regulation Idiotypic network 2/15/2005 MICR 415 / 515
After this presentation and discussion, the participants should be able to:
 Tissue Repair Robert F. Diegelmann, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After this presentation and discussion, the participants should be able to: 1. Define the biochemical responses to tissue injury 2. Describe the mechanisms
Tissue Repair Robert F. Diegelmann, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After this presentation and discussion, the participants should be able to: 1. Define the biochemical responses to tissue injury 2. Describe the mechanisms
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers. A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs
 Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
 The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) An introduction to adaptive immune system before we discuss MHC B cells The main cells of adaptive immune system are: -B cells -T cells B cells: Recognize antigens
The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) An introduction to adaptive immune system before we discuss MHC B cells The main cells of adaptive immune system are: -B cells -T cells B cells: Recognize antigens
Cell Walls, the Extracellular Matrix, and Cell Interactions (part 1)
 14 Cell Walls, the Extracellular Matrix, and Cell Interactions (part 1) Introduction Many cells are embedded in an extracellular matrix which is consist of insoluble secreted macromolecules. Cells of bacteria,
14 Cell Walls, the Extracellular Matrix, and Cell Interactions (part 1) Introduction Many cells are embedded in an extracellular matrix which is consist of insoluble secreted macromolecules. Cells of bacteria,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
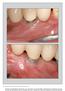 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 91 Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 Levels in Peri-implant Sulcus Fluid Adjacent to Titanium and Zirconium Nitride Surfaces Richard Meissen,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 91 Matrix Metalloproteinase-8 Levels in Peri-implant Sulcus Fluid Adjacent to Titanium and Zirconium Nitride Surfaces Richard Meissen,
Periodontal disease is characterized by progressive periodontal pathogens. It is known that coronary heart disease is
 ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com PREVALENCE OF PERIODONTAL DISEASES IN PATIENTS WITH CORONARY HEART DISEASE Niha Naveed* BDS student, Saveetha
ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com PREVALENCE OF PERIODONTAL DISEASES IN PATIENTS WITH CORONARY HEART DISEASE Niha Naveed* BDS student, Saveetha
European Journal of Endocrinology (1997) ISSN
 European Journal of Endocrinology (1997) 137 167 171 ISSN 0804-4643 Change in C-terminal cross-linking domain of type I collagen in urine, a new marker of bone resorption, during and after gonadotropin-releasing
European Journal of Endocrinology (1997) 137 167 171 ISSN 0804-4643 Change in C-terminal cross-linking domain of type I collagen in urine, a new marker of bone resorption, during and after gonadotropin-releasing
ORAL HEALTH COMPLICATIONS?
 ORAL HEALTH COMPLICATIONS? Your pathway to a better oral health ORAL HEALTH AND PERIODONTAL (GUM) DISEASE Dental cavities are a multifactorial disease of bacterial origin that is characterized by acid
ORAL HEALTH COMPLICATIONS? Your pathway to a better oral health ORAL HEALTH AND PERIODONTAL (GUM) DISEASE Dental cavities are a multifactorial disease of bacterial origin that is characterized by acid
REVIEW ARTICLE NEWER BIOMARKERS IN EARLY DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY
 JCD REVIEW ARTICLE NEWER BIOMARKERS IN EARLY DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY SAPTARSHI MUKHOPADHYAY* *FACULTY (DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE), B R SINGH HOSPITAL (EASTERN RAILWAY), KOLKATA. INTRODUCTION renal disease. It
JCD REVIEW ARTICLE NEWER BIOMARKERS IN EARLY DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY SAPTARSHI MUKHOPADHYAY* *FACULTY (DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE), B R SINGH HOSPITAL (EASTERN RAILWAY), KOLKATA. INTRODUCTION renal disease. It
Point of Care. Q u e s t i o n 1. JCDA February 2008, Vol. 74, No. 1 53
 Point of Care The Point of Care section answers everyday clinical questions by providing practical information that aims to be useful at the point of patient care. The responses reflect the opinions of
Point of Care The Point of Care section answers everyday clinical questions by providing practical information that aims to be useful at the point of patient care. The responses reflect the opinions of
Bone Levels - From Hypothesis To Facts
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 6, Issue 5 (May.- Jun. 2013), PP 19-23 Bone Levels - From Hypothesis To Facts Savitha B 1, Priyanka
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 6, Issue 5 (May.- Jun. 2013), PP 19-23 Bone Levels - From Hypothesis To Facts Savitha B 1, Priyanka
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences PERIODONTAL DISEASE-SYSTEMIC DISEASE INTER RELATIONSHIP QUESTIONNAIRE STUDY ABSTRACT
 Research Article Periodontology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 PERIODONTAL DISEASE-SYSTEMIC DISEASE INTER RELATIONSHIP QUESTIONNAIRE STUDY MEENAKSHI PRIYANKA V 1* AND DR.
Research Article Periodontology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 PERIODONTAL DISEASE-SYSTEMIC DISEASE INTER RELATIONSHIP QUESTIONNAIRE STUDY MEENAKSHI PRIYANKA V 1* AND DR.
Autoimmune Diseases. Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic
 Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Correspondence should be addressed to Mariana Caires Sobral de Aguiar;
 Hindawi BioMed Research International Volume 2017, Article ID 3257235, 7 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3257235 Review Article The Gingival Crevicular Fluid as a Source of Biomarkers to Enhance Efficiency
Hindawi BioMed Research International Volume 2017, Article ID 3257235, 7 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3257235 Review Article The Gingival Crevicular Fluid as a Source of Biomarkers to Enhance Efficiency
Biochemistry #02. The biochemical basis of skeletal muscle and bone disorders Dr. Nabil Bashir Bara Sami. 0 P a g e
 ]Type text[ ]Type text[ ]Type text[ Biochemistry #02 The biochemical basis of skeletal muscle and bone disorders Dr. Nabil Bashir Bara Sami 0 P a g e Greetings everyone, ladies and gentlemen The biochemical
]Type text[ ]Type text[ ]Type text[ Biochemistry #02 The biochemical basis of skeletal muscle and bone disorders Dr. Nabil Bashir Bara Sami 0 P a g e Greetings everyone, ladies and gentlemen The biochemical
Morphology of periodontal defects, indications of periodontal surgery
 Morphology of periodontal defects, indications of periodontal surgery Dr. Ferenc Dőri PhD Semmelweis University Dept. of Periodontology Periodontium Gingiva + Cementum PDL (periodontal ligament) Alveolar
Morphology of periodontal defects, indications of periodontal surgery Dr. Ferenc Dőri PhD Semmelweis University Dept. of Periodontology Periodontium Gingiva + Cementum PDL (periodontal ligament) Alveolar
The Role of the Laboratory in Metabolic Bone Disease
 The Role of the Laboratory in Metabolic Bone Disease Howard Morris PhD, FAACB, FFSc(RCPA) President, IFCC Professor of Medical Sciences, University of South Australia, Clinical Scientist, SA Pathology
The Role of the Laboratory in Metabolic Bone Disease Howard Morris PhD, FAACB, FFSc(RCPA) President, IFCC Professor of Medical Sciences, University of South Australia, Clinical Scientist, SA Pathology
Specific Egg Yolk Antibody (Ovalgen PG) as a Novel Supportive Immunotherapy for Periodontitis
 7 th Vietnam International Dental Exhibition and congress (VIDEC) Aug 7-9, 2014 Specific Egg Yolk Antibody (Ovalgen PG) as a Novel Supportive Immunotherapy for Periodontitis Nguyen Van Sa, Ph.D Immunology
7 th Vietnam International Dental Exhibition and congress (VIDEC) Aug 7-9, 2014 Specific Egg Yolk Antibody (Ovalgen PG) as a Novel Supportive Immunotherapy for Periodontitis Nguyen Van Sa, Ph.D Immunology
Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
IDENTIFICATION OF C-REACTIVE PROTEIN FROM GINGIVAL CREVICULAR FLUID IN SYSTEMIC DISEASE
 IDENTIFICATION OF C-REACTIVE PROTEIN FROM GINGIVAL CREVICULAR FLUID IN SYSTEMIC DISEASE Amelia S * Department of Periodontology, Faculty of Dental Medicine University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Grigore
IDENTIFICATION OF C-REACTIVE PROTEIN FROM GINGIVAL CREVICULAR FLUID IN SYSTEMIC DISEASE Amelia S * Department of Periodontology, Faculty of Dental Medicine University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Grigore
Immunity. Chapter 38 Part 1
 Immunity Chapter 38 Part 1 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1
Immunity Chapter 38 Part 1 Impacts, Issues Frankie s Last Wish Infection with a common, sexually transmitted virus (HPV) causes most cervical cancers including the one that killed Frankie McCullogh 38.1
1 PERIODONTIUM: THE TOOTH SUPPORTING STRUCTURES 1 2 MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY OF THE PERIODONTIUM 21
 Contributors xiii Preface for Course Instructors xv Acknowledgments xviii PART 1: THE PERIODONTIUM IN HEALTH 1 PERIODONTIUM: THE TOOTH SUPPORTING STRUCTURES 1 Tissues of the periodontium 3 Nerve supply,
Contributors xiii Preface for Course Instructors xv Acknowledgments xviii PART 1: THE PERIODONTIUM IN HEALTH 1 PERIODONTIUM: THE TOOTH SUPPORTING STRUCTURES 1 Tissues of the periodontium 3 Nerve supply,
Australian Dental Journal
 Australian Dental Journal The official journal of the Australian Dental Association SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2012; 57: 45 50 doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2011.01650.x Association between
Australian Dental Journal The official journal of the Australian Dental Association SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2012; 57: 45 50 doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2011.01650.x Association between
Gingival crevicular fluid protein content and alkaline phosphatase activity in relation to pubertal growth phase
 Original Article Gingival crevicular fluid protein content and alkaline phosphatase activity in relation to pubertal growth phase Giuseppe Perinetti a ; Lorenzo Franchi b ; Attilio Castaldo c ; Luca Contardo
Original Article Gingival crevicular fluid protein content and alkaline phosphatase activity in relation to pubertal growth phase Giuseppe Perinetti a ; Lorenzo Franchi b ; Attilio Castaldo c ; Luca Contardo
SALIVARY INFLAMMATORY BIOMARKERS IN A STENT-INDUCED BIOFILM OVERGROWTH MODEL. Michael Stella. Chapel Hill 2013
 SALIVARY INFLAMMATORY BIOMARKERS IN A STENT-INDUCED BIOFILM OVERGROWTH MODEL Michael Stella A thesis submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of
SALIVARY INFLAMMATORY BIOMARKERS IN A STENT-INDUCED BIOFILM OVERGROWTH MODEL Michael Stella A thesis submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of
