Microleakage of Repaired Amalgam
|
|
|
- Barrie Earl Booker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISSN: Microleakage of Repaired Amalgam Nawfal A. Zakaria BDS, M.Sc. (Assist Prof.) Neam N. Al Yousifany BDS, MSc (Lect) Department of Conservative Dentistry College of Dentistry, University of Mosul Raghad A. Al Askry BDS, M.Sc. (Assist Lect) ABSTRACT Aims: This invitro study designed to investigate the effect of bonding agent on amalgam repaired with either spherical or admixed alloy. Material and Methods: Cl I cavity preparations were made on the occlusal surface of hundred and twelve extracted human premolars. The teeth were randomly divided into two groups, 56 cavities filled with spherical amalgam and the other 56 cavities filled with admixed amalgam, after aging of restorations, buccal half of the previously placed restorations were removed and each group was divided into two subgroup according to the lining material used. The final number were eight groups of 14 teeth in each. All specimens were thermocycled for 500 times with 15 second dwell time. The samples were stained with 2% methylene blue, sectioned and evaluated for dye penetration. The data were analyzed by Fisher Freeman Halton test.results: There was a significant differences in microleakage of bonded and non bonded specimens, the use of bonding agent significantly increase the microleakage of repaired amalgam. Repairing amalgam with similar alloy type significantly reduce the microleakage.conclusions: Within the limitation of this study, repairing amalgam with bonding agent is acceptable but significantly less microleakage can observed when amalgam repaired without bonding agents. malgam alloy can repaired with different types of alloy, but better marginal seal accomplished when the same types of alloy used for repair Zakaria NA, Al Yousifany NN, Al Askry RA. Microleakage of repaired amalgam. Al Rafidain Dent J. 2008; 8(1): Received: 28/1/2007 Sent to Referees: 17/2/2007 Accepted for Publication: 24/4/2007 INTRODUCTION Studies on durability of repaired amalgam restoration need to evaluate the amount of microleakage of repaired specimens. Microleakage is defined as the passage of bacteria, fluids, molecules or ions between cavity wall and the restorative material applied to it (1). Amalgam restorations sometimes fracture due to the faults made during cavity preparations and restorations procedures or where recurrent caries has rendered a portion of them defective (2, 3). Dentists are frequently facing with a clinical decision to replace or repair an amalgam restoration. These situations involve amalgam or cuspal fracture, inadequate marginal integrity and inadequate interproximal contact. The complete replacement of large restorations is time consuming, technically difficult and may be potentially damaging to the pulp (4, 5). There are many factors play a role in the quality of the amalgam repair these factors are time of repair, type of amalgam alloy used in repair, the effect of roughening the fracture surface and the use of adhesive resin. Each of these factors has been evaluated by researchers with little agreement studies. The important factors in the quality of the amalgam repair are the strength of the joined amalgam surfaces and the microleakage at the interface. Microleakage has been recognized as a major clinical problem with direct filled dental restorations (3, 5 7). Because microleakage can cause an extensive damage, much effort has recently been directed toward developed ways to reduce the microleakage including the application of dentinal bonding agents (4). The purpose of this invitro study was to observe the effects of certain variables, including bonding materials and types of alloy spherical or admixed) on the microleakage between original amalgam and repair interface. 44
2 Zakaria NA, Al Yousifany NN, Al Askry RA. MATERIALS AND METHODS A total of one hundred twelve extracted human maxillary premolar teeth free of cracks (examined by fiber optic light), free of caries and restorations on the visual inspection were selected for the experiment. All teeth were cleaned and polished using scalars and pumice, then stored in distilled water at room temperature prior to use. The root apex of each tooth was sealed with a self cured composite restorative material, two coats of nail varnish were applied to the entire external surface of the root, each tooth was mounted in cold curing acrylic resin to the level of cemento enamel junction. A diamond bur No. 556 in a high speed hand piece with air/water coolant was used to prepare a conventional CL I cavities of 2 mm width and 2 mm depth extending to include the mesial and distal pits without undermining the marginal ridges. The specimens were randomly divided into two groups of fifty six teeth according to the type of amalgam alloy used. Each tooth was washed with water and dried with a compressed air, restored with corresponding amalgam. Fifty six cavities were filled with a precapsulated spherical alloy ( Vivacap, Vivadent, Ets., Germany) and another group of (56) cavities were filled with a precapsulated admixed alloy ( Septalloy NG 70, Specialites Septodont, France). The precapsulated amalgams were triturated with a mechanical amalgamator (Silamat, Vivadent, Schaan/ Liechtenstein, Germany) according to the manufacture instructions. Amalgam immediately condensed into the corresponding cavities by using a mechanical condensation technique with ultra sonic condenser ( Piezon master 400, EMS SA, CH 1260 Nyon, Switzerland). Amalgam was placed incrementally, each increment was condensed against the cavity walls for 20 second with a circular flat ultrasonic condenser tip at the medium power until the cavity was over filled, carved to cavosurface margins of the preparation, then finished and burnished. The specimens were stored in distilled water at 37 c in an incubator for 30 days. After aging of the restorations, each group was randomly divided into two subgroups of twenty eight teeth according to the amalgam used in repairing procedure, each sub group was divided into two groups of fourteen teeth according to the lining materials used The number of final groups were eight groups as shown in table (1). Table (1): Diagrammatic illustration of the experimental groups design for the study. Group No. Type of exist amalgam Bonding use Type of fresh amalgam 1 Spherical No Spherical 2 Spherical No Admixed 3 Spherical Alloy bond Spherical 4 Spherical Alloy bond Admixed 5 Admixed No Admixed 6 Admixed No Spherical 7 Admixed Alloy bond Admixed 8 Admixed Alloy bond Spherical 45
3 Microleakage of repaired amalgam For all specimens half of the previously placed amalgam restorations were removed with a No. 556 diamond bur in a high speed hand piece with water coolant, the depth of these new preparations also measured 2 mm in depth ( new diamond bur were replaced after each 6 samples) all preparations were thoroughly washed with water and air dried, each group was treated before insertion of the new amalgam. For group with lining material used 37% phosphoric acid for 20 seconds were applied to the prepared cavity and the exist amalgam in each tooth, washed thoroughly with water and air dried gently to keep moist surfaces, alloybond primer applied to the both tooth and previously placed amalgam surfaces, dry with air gently for 2 seconds to evaporate solvent and leave surfaces glossy, light cured for 10 seconds. One drop of alloy bond base mixed with one drop of alloybond catalyst, the mixture was placed in a thin layer on all walls of the preparations, as well as to the previously placed amalgam surface using brush. Freshly triturated amalgam condensed into the non bonded and bonded cavities immediately using ultra sonic condenser, the restorations were carved and finished to the cavosurface margins of the preparation. All specimens were thermocycled for 500 times at temperature ranging from 5 c ± 2 c to 55 c ± 2 c each cycle lasted 45 second with a dwell time of 15 seconds in each bath, and 15 seconds intervals between baths, for all specimens the entire tooth surfaces were painted with two coats of nail varnish, except for an area of 1 mm away from the cavity margins and restoration, to prevent dye penetration anywhere other than the restoration margins. Each layer of varnish was allowed to dry before the next layer was applied. The samples were immersed in 2% solution of methylene blue at 37 c for (48) hours. After the removal of the teeth from the dye they were washed with copious amount of water to remove any surface traces of dye, dried and were sectioned through the middle of restoration by using a diamond sectioning disks. The dye penetration at the old new amalgam interface was evaluated blind and independently by two evaluators under stereomicroscope (Hamilton by AI- TAY International Italy) at a magnification level of x10 and scored according to the criteria described by Going etal (8). (Figure.1) Degree 0 no penetration of dye. Degree 1 penetration of dye up to half of the wall depth. Degree 2 penetration of dye to the floor of the cavity but not including it. Degree 3 penetration of dye completely surrounding the filling including the cavity floor. Degree 4 diffusion of dye into the dentin under the floor or base of the cavity. Degree 5 penetration of dye through the dentin to the pulp chamber. Figure (1): Diagram illustrated the degree of dye penetration Data were subjected to the Fisher Freeman Halton statistical test at confidence level of 95 % (p<0.05) RESULTS Table (2) shows the distribution of leakage scores between previously placed amalgam and fresh amalgam of the eight test groups. In general, all specimens show a lower percentage of dye penetration, the microleakage score of all groups were either zero (no dye penetration) or score one (that is mean the dye not reach more than half of the cavity depth).(figure 2). Fisher Freeman Halton test shows that there was a significant differences in the microleakage between the bonded and non bonded repaired amalgam, at p value of Table (3) Similar statistical analyses were under taken in comparing the two types of alloy used for repair, there was a significant decrease in microleakage at p value of when the same type of alloy used for repair. Table (4) 46
4 Zakaria NA, Al Yousifany NN, Al Askry RA. DISCUSSION Numerous investigations have used a variety of research tools to evaluate the extent of microleakage at marginal integrity of restorations, stereomicroscopic examination of dye penetration most commonly used methods. (9) The results of the present study indicated that the microleakage between the new and existing amalgam surfaces was of score zero (no microleakage) or score one (not more than half of the cavity depth). Table (2): The frequency of microleakage scores for the eight tested groups. Site of leakage Total no. of teeth p value Group No. Experimental groups S + S S + A S + B + S S + B + A A + A A + S A + B + A A + B + S Using Fisher Freeman Halton test <0.001 Figure (2): sectioned tooth showing the degree of dye penetration. Table (3) Statistical analysis comparing the frequency of bonded and non bonded amalgam. Score Repair with bonded amalgam Repair without bonded p value No. % No. % Using Fisher Freeman Halton test Table (4) Statistical analysis for types of amalgam used in repair
5 Microleakage of repaired amalgam Score Repair with the same type Repair with different type No. % No. % Using Fisher Freeman Halton test p value The exact mechanism is not understood, but the cause may be due to the linear coefficient of thermal expansion of amalgam is about two to three times that of surrounding tooth structure, thus thermal changes not affect the sealing capacity between the fresh and existing amalgam. The bonding between the two amalgam probably cause from free mercury in fresh amalgam combine with the unconsumed gamma particles in older alloy, this cause a union between them, by the formation of new intermetalic compound. (10,11) Ozer et al. (3) concluded that microleakage of repaired restoration was lower in the amalgam groups than microleakage in the resin composite and composer groups. A clinical study on survival of repaired amalgam, concluded that repair of local defects in amalgam restoration was an effective alternative to restoration replacement especially up to five years. (12) Shirani et al. study the effect of adhesive system on the microleakage at the amalgam repaired, the results indicated a decrease in the microleakage only when composite resin used for repair. (13) The stress rising from the polymerization shrinkage may results in bond failure and show a greater effects on the marginal adaptation. (14) The intermediate materials and substrate have a significant effect on sealing ability of amalgam restoration. (15) Our results agree with the results of Fruite et al. who found that strongest repair of amalgam material can accomplished without the use of any bonding agents. (16) The proper technique of condensing amalgam to the surface of an old amalgam important to establish a bond between the new and old alloy. (17) The results indicated better marginal seal when the same type of alloy used for repair. Dispers alloy had the least microleakage and tytin amalgam had the highest microleakage. (10) Spherical alloy has coarse grained texture that formed surface channels through which microleakage can more rapidly occur. Also may have more inter volumetric space which may contribute to more microleakage. (18,19) In clinical practice it is not always possible for clinician to determine the specific type of dental amalgam. The leakage around amalgam does not depend solely on the shape of particles, condensation force was reported as the most important factor influencing adaptation of amalgam alloy to cavity walls and as well as to the old amalgam. (11) Heavy and constant condensational force in the present study was due to the use of ultrasonic condenser which produced a better adaptation for all types of amalgam alloy. Amalgam alloy show reduce in the microleakage overtime, this reduction has been explained by corrosion products filling the interface gap in order to seal the restoration. (20) Amalgam restoration is still the best material used for amalgam repair even without bonding material. From clinical point, repair cause less damage than complete replacement of amalgam and it is therefore preferred. CONCLUSION The bonding agent significantly increase the microleakage so it is preferable not to use bonding in amalgam repair. Even with bonding the microleak-age is accepted. 48
6 Zakaria NA, Al Yousifany NN, Al Askry RA. The use of the same amalgam alloy is preferable because it gives better marginal adaptation. Although this invitro study designed to simulate the clinical environment, but further testing need, especially (clinical investigations) to assess the real longevityof repair restorations. REFERENCES 1. Kimuro Y. Yonago K, Yokoyama, Matsuoka, Saki K and Matsumoto K. Apical leakage of obturated canals prepared by Er. YAG laser. Am Assoc Endod 2001; 27: Walker AC and Reese SB. Bond strength of amalgam to amalgam in a high copper amalgam. Oper Dent. 1983; 8: Ozer F, Unlu N, Ozturk B and Sengun A. Amalgam repair: evaluation of bond strength and microleakage. Oper Dent. 2002; 27: Hadavi F, Hey JH, Ambrose ER and Elbadrawy HE. Repair of high copper amalgam with and without an adhesive system: Invitro assessment of microleakage and shear bond strength. General Dent. 1993; 41: Jessup JP, Vandewalle KS, Hermesch CB and Buikema DJ. Effect of surface treatment on amalgam repair. Oper Dent. 1998; 23: El Housseiny AA and Farsi N. Sealing ability of a single adhesive in primary teeth: an in vivo study. Int J Paediat Dent. 2002; 12: Giannini M, Paulillo LA and Ambrosano GM. Effect of surface roughness on amalgam repair using adhesive systems. Braz Dent J 2002; 13: Going RE, Massler M and Dute HL. Marginal penetration of dental restoration as studied by crystal violet dye. J Am Dent Assoc. 1960; 61: Delnero MO and Dela Macorra JC. Sealing and dentin bond strength of adhesive system. Oper Dent. 1999; 24: Chang J, Chan J, Cheda H and Iglesias A. Microleakage of a 4 methacryloxyethyl trimellitate anhydride bonding agent with amalgam. J. Prosthet Dent. 1996; 75: Korale ME and Meiers JG. Microleakage of dentin bonding systems used with spherical and admixed amalgams. Am J Dent. 1996; Smales J, Howthorne WS. Long term survival of repaired amalgam, recemted crowns and gold casting. Oper Dent. 2004; 29: Shirani F, Malekipour MR, Zakouchaki PM and Zia P. Effect of different adhesive system on microleakage at the amalgam. J Isfahan Dent School. 2005; (1)304: Smales RJ, Wetherell JD. Review of bonded amalgam restorations and assessment in a general practice over five years. Oper Dent. 2000; 25: Dasilva AF, Piva E, Demarco FF, Corrersobrinho L, Osinga PW. Microleakage in conventional and bonded amalgam restorations influence of cavity volume. Oper Dent. 2006; 31(3): Fruits TJ, Duncanson MGJR and Coury TL. Interfacial bond strength of amalgam bonded to amalgam and resin composite bonded to amalgam. Quintessence Int. 1998; 29(5): Shen C. Speigel J. and Major LA, Repair strength of dental amalgam. Oper Dent. 2006; 31(1): Fayyad MA and Ball PC. Cavity sealing ability of lath cut, blend and spherical amalgam alloy: a laboratory study. Oper Dent. 1984; 9: Mahler DB. The high copper dental amalgam alloy. J Dent Res. 1997; 76: Osborne JW. Creep as a mechanism for sealing amalgam. Oper Dent. 2006; 31(2):
Repair Strength of Dental Amalgams
 Operative Dentistry, 2006, 31-1, 122-126 Repair Strength of Dental Amalgams C Shen J Speigel IA Mjör Clinical Relevance The proper technique of condensing amalgam to the surface of an old amalgam is critical
Operative Dentistry, 2006, 31-1, 122-126 Repair Strength of Dental Amalgams C Shen J Speigel IA Mjör Clinical Relevance The proper technique of condensing amalgam to the surface of an old amalgam is critical
Pelagia Research Library. Comparison of microleakage in bonded amalgam restrorations using different adhesive materials: An invitro study
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2011, 1 (2):92-96 ISSN: 2248 9215 Comparison of microleakage in bonded amalgam restrorations using different
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2011, 1 (2):92-96 ISSN: 2248 9215 Comparison of microleakage in bonded amalgam restrorations using different
Filling materials are used to replace missing parts of the tooth.
 Filling materials are used to replace missing parts of the tooth. 1- Dental caries. 2- Trauma. 3- Abrasion. Parts of teeth which require replacement by restorative materials vary in size of cavity, shape,
Filling materials are used to replace missing parts of the tooth. 1- Dental caries. 2- Trauma. 3- Abrasion. Parts of teeth which require replacement by restorative materials vary in size of cavity, shape,
Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin
 Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin Bright Chang D2 Dental Student UAB School of Dentistry Final report (revision) July 26, 2017 Mentors: Nathaniel Lawson,
Microleakage around zirconia crowns after ultrasonic scaling around their margin Bright Chang D2 Dental Student UAB School of Dentistry Final report (revision) July 26, 2017 Mentors: Nathaniel Lawson,
Results:Mean microleakage score of group G1, G2 and G3 was 2.86 ± 1.43, 1.86 ± 1.65 and 2.46 ± 1.50 respectively.
 Journal of Oral Health & Community Dentistry original article Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage in Class 2 Cavities Restored with A Nanohybrid Composite Using Three Different Increment Techniques-
Journal of Oral Health & Community Dentistry original article Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage in Class 2 Cavities Restored with A Nanohybrid Composite Using Three Different Increment Techniques-
Evaluation of Microleakage in Composite-Composite and Amalgam-Composite Interfaces in Tooth with Preventive Resin Restoration (Ex-viva)
 Original Article Evaluation of Microleakage in Composite-Composite and Amalgam-Composite Interfaces in Tooth with Preventive Resin Restoration (Ex-viva) H. Afshar 1, A. Jafari 2, M. R. Khami 2,3, S. Razeghi
Original Article Evaluation of Microleakage in Composite-Composite and Amalgam-Composite Interfaces in Tooth with Preventive Resin Restoration (Ex-viva) H. Afshar 1, A. Jafari 2, M. R. Khami 2,3, S. Razeghi
Nanoionomer: Evaluation of microleakage
 Original Article Nanoionomer: Evaluation of microleakage Abstract Background: Glass ionomer cements are widely used in pediatric practice due to their advantage of fluoride release and chemical bond to
Original Article Nanoionomer: Evaluation of microleakage Abstract Background: Glass ionomer cements are widely used in pediatric practice due to their advantage of fluoride release and chemical bond to
General dentists in private practice place numerous
 PROACTIVE INTERVENTION DENTISTRY Incorporating Glass Ionomers into Everyday Dental Practice Todd Snyder, DDS, FAACD, FIADFE Introduction General dentists in private practice place numerous direct tooth
PROACTIVE INTERVENTION DENTISTRY Incorporating Glass Ionomers into Everyday Dental Practice Todd Snyder, DDS, FAACD, FIADFE Introduction General dentists in private practice place numerous direct tooth
Operative dentistry. Lec: 10. Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE):
 Operative dentistry Lec: 10 د.عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE): There are 2 types: 1) Unreinforced ZOE (ordinary type): supplied as powder (zinc oxide + some additives like zinc acetate, white
Operative dentistry Lec: 10 د.عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE): There are 2 types: 1) Unreinforced ZOE (ordinary type): supplied as powder (zinc oxide + some additives like zinc acetate, white
how to technique How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. Disadvantages. 1 Issue Full coverage crown. >>
 Issue 37 2013 How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. 1 Full coverage crown. >> Advantages. A full crown can splint all sections of the tooth together. 1 Disadvantages. 1 Encircles crown and acts
Issue 37 2013 How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. 1 Full coverage crown. >> Advantages. A full crown can splint all sections of the tooth together. 1 Disadvantages. 1 Encircles crown and acts
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations The outline form
 Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland School of Dentistry
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry-Biomaterials Structures, chemical properties, physical properties BASIC CONCEPTS ON HOW DENTAL MATERIALS WORK! Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry-Biomaterials Structures, chemical properties, physical properties BASIC CONCEPTS ON HOW DENTAL MATERIALS WORK! Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland
Class I Cavity Preparation. Alaa Sabrah, BDS, MSD, PhD Nov,
 بسم اهلل الرحمن الرحيم Class I Cavity Preparation Alaa Sabrah, BDS, MSD, PhD Nov, 2015 15 Goals and Objectives?Define class I carious lesion.1 Describe the clinical technique for treating class I?carious
بسم اهلل الرحمن الرحيم Class I Cavity Preparation Alaa Sabrah, BDS, MSD, PhD Nov, 2015 15 Goals and Objectives?Define class I carious lesion.1 Describe the clinical technique for treating class I?carious
Microleakage of class II packable resin composite lined with flowable composite and resin modified glass ionomer cement: An in vitro study
 Microleakage of class II packable resin composite lined with flowable composite and resin modified glass ionomer cement: An in vitro study Dr. Haitham J. AL-Azzawi, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Dr. Nagham A. AL-Hyali,
Microleakage of class II packable resin composite lined with flowable composite and resin modified glass ionomer cement: An in vitro study Dr. Haitham J. AL-Azzawi, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Dr. Nagham A. AL-Hyali,
Original Article. in depth, 4 mm in mesiodistal width and 3 mm occlusogingival
 Original Article A Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage in Class V Composite Restorations using a Fifth Generation Adhesive and a Glass Ionomer Bonding Agent - An In Vitro Dye Leakage Study Dipali Shah
Original Article A Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage in Class V Composite Restorations using a Fifth Generation Adhesive and a Glass Ionomer Bonding Agent - An In Vitro Dye Leakage Study Dipali Shah
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary Vol.:9 No.:2 2012
 MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (3), 457:461 September, 2008
 Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (3), 457:461 September, 2008 An In Vitro Assessment of The Marginal Leakage of Compomer, Amalgam and Bonded Amalgam Restoration Salah Eldin Mostafa Elbehery; 1 Naguib Mahmoud
Cairo Dental Journal (24) Number (3), 457:461 September, 2008 An In Vitro Assessment of The Marginal Leakage of Compomer, Amalgam and Bonded Amalgam Restoration Salah Eldin Mostafa Elbehery; 1 Naguib Mahmoud
ALL-BOND 2. Bisco. Instructions for Use. Universal Dental Adhesive
 Bisco 0459 ALL-BOND 2 Universal Dental Adhesive Instructions for Use IN-0005R8 Rev. 2/16 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Road Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 847-534-6000 1-800-247-3368 Caution: U.S. Federal
Bisco 0459 ALL-BOND 2 Universal Dental Adhesive Instructions for Use IN-0005R8 Rev. 2/16 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Road Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 847-534-6000 1-800-247-3368 Caution: U.S. Federal
Clinical report. Drs Paul and Alexandre MIARA and F. CONNOLLY COMPOSITE POSTERIOR FILLINGS. How to control. layering? 8 - Dentoscope n 124
 COMPOSITE POSTERIOR FILLINGS How to control layering? 8 - Dentoscope n 124 CV FLASH Dr Paul MIARA Dental surgeon Dr Alexandre MIARA Dental surgeon Dr F. CONNOLLY Dental surgeon Thanks to continuous improvements
COMPOSITE POSTERIOR FILLINGS How to control layering? 8 - Dentoscope n 124 CV FLASH Dr Paul MIARA Dental surgeon Dr Alexandre MIARA Dental surgeon Dr F. CONNOLLY Dental surgeon Thanks to continuous improvements
Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice
 Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up
 Case 1 This case study focuses on the restoration of an upper molar. Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up The existing, inadequate restoration led to the development
Case 1 This case study focuses on the restoration of an upper molar. Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up The existing, inadequate restoration led to the development
CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATION 36MO
 INTERNATIONAL PEER REVIEW CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATION 36MO Leung Kwan Yu, Steve BDS II - Class 2019, The University of Hong Kong instruments Mirror Periodontal probe Hatchets Gingival margin trimmers
INTERNATIONAL PEER REVIEW CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATION 36MO Leung Kwan Yu, Steve BDS II - Class 2019, The University of Hong Kong instruments Mirror Periodontal probe Hatchets Gingival margin trimmers
Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core
 Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core A post and core is a dental restoration used to sufficiently buildup tooth structure for future restoration with a crown when there is not enough tooth
Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core A post and core is a dental restoration used to sufficiently buildup tooth structure for future restoration with a crown when there is not enough tooth
International J. of Healthcare & Biomedical Research, Volume: 2, Issue: 1, October 2013, Pages 43-47
 Original article: Effect of cavity disinfection with chlorhexidine on microleakage of composite restorations using total etch and self etch single bottle adhesive systems: an in-vitro study 1Dr. Neha Agrawal
Original article: Effect of cavity disinfection with chlorhexidine on microleakage of composite restorations using total etch and self etch single bottle adhesive systems: an in-vitro study 1Dr. Neha Agrawal
SMALL PINS AND LARGE RESTORATIONS: A CASE REPORT
 Indian Journal of Medical s ISSN: 2319 3832(Online) SMALL PINS AND LARGE RESTORATIONS: A CASE REPORT Tejolatha B. 1, Nandakumar K. 1, *Sasidhar Reddy V. 2, Sandeep S. 1 and Sirisha Devi K. 1 1 Department
Indian Journal of Medical s ISSN: 2319 3832(Online) SMALL PINS AND LARGE RESTORATIONS: A CASE REPORT Tejolatha B. 1, Nandakumar K. 1, *Sasidhar Reddy V. 2, Sandeep S. 1 and Sirisha Devi K. 1 1 Department
values is of great interest.
 User Report Dr. Ralph Schönemann, May 21, 2008 There are numerous self-etchbonding systems on the market that sometimes differ very much from one another with regards to their chemical composition. It
User Report Dr. Ralph Schönemann, May 21, 2008 There are numerous self-etchbonding systems on the market that sometimes differ very much from one another with regards to their chemical composition. It
DH220 Dental Materials
 DH220 Dental Materials Lecture #5 Prof. Lamanna RDH, MS Restorative Dentistry: Glass Ionomer Bird & Robinson p.740-741 I. Use Liner Base Luting agent Restorative material: Class III, V, & eroded/abraded
DH220 Dental Materials Lecture #5 Prof. Lamanna RDH, MS Restorative Dentistry: Glass Ionomer Bird & Robinson p.740-741 I. Use Liner Base Luting agent Restorative material: Class III, V, & eroded/abraded
Short-term Evaluation of Resin Sealing and Rebonding on Amalgam Microleakage: An SEM Observation
 Short-term Evaluation of Resin Sealing and Rebonding on Amalgam Microleakage: An SEM Observation Abstract Aims: The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of two different sealing agents on the microleakage
Short-term Evaluation of Resin Sealing and Rebonding on Amalgam Microleakage: An SEM Observation Abstract Aims: The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of two different sealing agents on the microleakage
Filtek LS. Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System. Techniques and Results. Clinical Cases
 Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Techniques and Results Clinical Cases What a composite that shrinks less than 1% 1 can mean to your practice. When restoring a tooth, a dentist takes great
Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Techniques and Results Clinical Cases What a composite that shrinks less than 1% 1 can mean to your practice. When restoring a tooth, a dentist takes great
RESINOMER Dual- Bisco. Instructions for Use. Cured Amalgam Bonding/Luting System
 Bisco RESINOMER Dual- Cured Amalgam Bonding/Luting System 0459 Instructions for Use IN-029R9 Rev. 10/17 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Road Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 1-847-534-6000 1-800-247-3368 Caution:
Bisco RESINOMER Dual- Cured Amalgam Bonding/Luting System 0459 Instructions for Use IN-029R9 Rev. 10/17 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Road Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 1-847-534-6000 1-800-247-3368 Caution:
Principle Investigators: Overview of Study Methods: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz
 Principle Investigators: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz Overview of Study Methods: Subjects in need of Class I and/or Class II restorations were enrolled in two clinical trials conducted in US dental
Principle Investigators: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz Overview of Study Methods: Subjects in need of Class I and/or Class II restorations were enrolled in two clinical trials conducted in US dental
CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATIONS. Amalgam restorations that restore one or both of the proximal surfaces of the tooth
 CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATIONS Amalgam restorations that restore one or both of the proximal surfaces of the tooth Initial Tooth Preparation Occlusal outline form (occlusal step).the occlusal outline form
CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATIONS Amalgam restorations that restore one or both of the proximal surfaces of the tooth Initial Tooth Preparation Occlusal outline form (occlusal step).the occlusal outline form
Press Release. Press Contact. The concept for Class II restoration Delicate preparation, rapid procedure and reliable results
 Press Release The concept for Class II restoration Delicate preparation, rapid procedure and reliable results by Dr. Arzu Tuna and Dr. Umut Baysal, Attendorn, Germany Composite restorations have always
Press Release The concept for Class II restoration Delicate preparation, rapid procedure and reliable results by Dr. Arzu Tuna and Dr. Umut Baysal, Attendorn, Germany Composite restorations have always
Effect of a Resin-based Desensitizing Agent and a Self-etching Dentin Adhesive on Marginal Leakage of Amalgam Restorations
 Effect of a Resin-based Desensitizing Agent and a Self-etching Dentin Adhesive on Marginal Leakage of Amalgam Restorations Abstract Aim: The purpose of this study was to compare the marginal leakage of
Effect of a Resin-based Desensitizing Agent and a Self-etching Dentin Adhesive on Marginal Leakage of Amalgam Restorations Abstract Aim: The purpose of this study was to compare the marginal leakage of
EQUIA. Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System
 EQUIA EQUIA Fil EQUIA Coat + Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System From the World Leader in Glass Ionomer Technology - A Complete Glass Ionomer Based Bulk Fill Rapid Restorative System Class
EQUIA EQUIA Fil EQUIA Coat + Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System From the World Leader in Glass Ionomer Technology - A Complete Glass Ionomer Based Bulk Fill Rapid Restorative System Class
Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module C: Clinical applications
 Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module C: Clinical applications REST 528A Operative
Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module C: Clinical applications REST 528A Operative
Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Resistance of Dental Amalgam, Z350 Composite Resin and Cention-N Restoration In Class II Cavity
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 4 Ver.1 April. (2018), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Resistance
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 4 Ver.1 April. (2018), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Resistance
illustrated technique guide
 DENTSPLY Caulk 38 West Clarke Avenue Milford, DE 9963 www.dentsply.com www.caulk.com -302-422-45 In Canada call -800-263-437 illustrated technique guide Complete Luting System for: 2006 DENTSPLY International.
DENTSPLY Caulk 38 West Clarke Avenue Milford, DE 9963 www.dentsply.com www.caulk.com -302-422-45 In Canada call -800-263-437 illustrated technique guide Complete Luting System for: 2006 DENTSPLY International.
Restorative Dentistry and it s related to Pulp health. Dr.Ahmed Al-Jobory
 Restorative Dentistry and it s related to Pulp health Dr.Ahmed Al-Jobory Pulp Is a viscous connective tissue of collagen fibers and ground substance supporting the vital cellular, vascular, and nerve structures
Restorative Dentistry and it s related to Pulp health Dr.Ahmed Al-Jobory Pulp Is a viscous connective tissue of collagen fibers and ground substance supporting the vital cellular, vascular, and nerve structures
ÆLITE Composites. Bisco. Instructions for Use. Light- Cured. U.S. Patent: 6,709,271
 Bisco ÆLITE Composites 0459 Light- Cured Instructions for Use U.S. Patent: 6,709,271 IN-131R6 Rev. 4/16 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Road Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 847-534-6000 1-800-247-3368 Caution:
Bisco ÆLITE Composites 0459 Light- Cured Instructions for Use U.S. Patent: 6,709,271 IN-131R6 Rev. 4/16 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Road Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 847-534-6000 1-800-247-3368 Caution:
Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2006;51:(2):175-179 Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique GM Knight,* JM McIntyre,* Mulyani*
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Australian Dental Journal 2006;51:(2):175-179 Bond strengths between composite resin and auto cure glass ionomer cement using the co-cure technique GM Knight,* JM McIntyre,* Mulyani*
Cutting instruments. Instruments
 Instruments أﻧﺲ اﻟﻌﺒﯿﺪي. د The removal and shaping of tooth structure are essential aspects of restorative dentistry. Initially this was a difficult process accomplished entirely by the use of - Hand instruments.
Instruments أﻧﺲ اﻟﻌﺒﯿﺪي. د The removal and shaping of tooth structure are essential aspects of restorative dentistry. Initially this was a difficult process accomplished entirely by the use of - Hand instruments.
Adhese Universal. The universal adhesive. Direct Indirect Total-Etch Selective-Etch Self-Etch Wet & Dry. All in. one click
 Adhese Universal The universal adhesive Direct Indirect Total-Etch Selective-Etch Self-Etch Wet & Dry All in one click 1 Universal Adhesion with advanced delivery Adhese Universal is a singlecomponent,
Adhese Universal The universal adhesive Direct Indirect Total-Etch Selective-Etch Self-Etch Wet & Dry All in one click 1 Universal Adhesion with advanced delivery Adhese Universal is a singlecomponent,
Lec11 يجافخلا معنملاذبع د 0 Dental Amalgam:- Advantages:- Disadvantages:- Composition: -
 Operative dentistry Lec11 د 0 عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Dental Amalgam:-Is a union of mercury (liquid) with amalgam alloys (powder) to give a plastic mass, which, hardens in the cavity. Amalgam alloy:- Is a combination
Operative dentistry Lec11 د 0 عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Dental Amalgam:-Is a union of mercury (liquid) with amalgam alloys (powder) to give a plastic mass, which, hardens in the cavity. Amalgam alloy:- Is a combination
Richard E. Corpron, DDS, MS, PhD Susan H. Carron, DDS, MS
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1984 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 6 Number 4 A clinical evaluation of polished and unpolished amalgams: 36-month results Lloyd H. Straffon, DDS, MS
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1984 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 6 Number 4 A clinical evaluation of polished and unpolished amalgams: 36-month results Lloyd H. Straffon, DDS, MS
SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM
 SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Precision by design PS Instrument [>magnified 8 x ] PIEZON method PIEZON Method} SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Piezon ultrasound instruments for a complete range of treatments } Endodontics
SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Precision by design PS Instrument [>magnified 8 x ] PIEZON method PIEZON Method} SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Piezon ultrasound instruments for a complete range of treatments } Endodontics
SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM
 SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Precision by design PIEZON method PIEZON Method} SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Piezon ultrasound instruments for a complete range of treatments } Endodontics } Scaling } Perio } Cavity preparation
SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Precision by design PIEZON method PIEZON Method} SWISS INSTRUMENTS PM Piezon ultrasound instruments for a complete range of treatments } Endodontics } Scaling } Perio } Cavity preparation
PRO-V IDS Kit. Bisco. Instructions for Use. Provisional Restorative System
 Bisco PRO-V IDS Kit Provisional Restorative System Instructions for Use U.S. Patent: 7,748,980; 8,106,110 IN-199R3 Rev. 5/16 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Rd. Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 847-534-6000
Bisco PRO-V IDS Kit Provisional Restorative System Instructions for Use U.S. Patent: 7,748,980; 8,106,110 IN-199R3 Rev. 5/16 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Rd. Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 847-534-6000
2. Gap closure and replacement of the missing tooth 35 with directly modelled bridge region 34-36
 GrandTEC Test Kit Dear User, This Test Kit has been put together to enable you to test GrandTEC on the model before using it in a clinical situation. GrandTEC is a resin-impregnated glass fibre strip.
GrandTEC Test Kit Dear User, This Test Kit has been put together to enable you to test GrandTEC on the model before using it in a clinical situation. GrandTEC is a resin-impregnated glass fibre strip.
Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control
 Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control REST 528A
Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module D: Pulp capping-caries control REST 528A
Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV.
 Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV. Class V. Cervical defects - Dental caries - Non carious lesions (erosion, abrasion, V shaped defects) Types of defects Caries Erosion Abrasion V shaped
Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV. Class V. Cervical defects - Dental caries - Non carious lesions (erosion, abrasion, V shaped defects) Types of defects Caries Erosion Abrasion V shaped
Microleakage of Root Canal Sealed with Temporary Endodontic Sealing Materials
 Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2013)24-29 Microleakage of Root Canal Sealed with Temporary Endodontic Sealing Materials Rajaa T.Sulieman BDS, MSc. (1) Key words microleakage, glass ionomer cement,
Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2013)24-29 Microleakage of Root Canal Sealed with Temporary Endodontic Sealing Materials Rajaa T.Sulieman BDS, MSc. (1) Key words microleakage, glass ionomer cement,
ENDODONTOLOGY. An in-vitro evaluation of apical sealing of three epoxy resin based commercial preparations INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS ABSTRACT
 An in-vitro evaluation of apical sealing of three epoxy resin based commercial preparations Vishal A. Mahajan * Kamra A. I. ** ABSTRACT The aim of the present in vitro study was to evaluate and compare
An in-vitro evaluation of apical sealing of three epoxy resin based commercial preparations Vishal A. Mahajan * Kamra A. I. ** ABSTRACT The aim of the present in vitro study was to evaluate and compare
stabilisation and surface protection
 Guiding the way to caries stabilisation and surface protection Fissure sealing MI restorations Pulp capping Hypersensitivity Protection Caries stabilisation Fuji Triage from GC. Temporary restorations
Guiding the way to caries stabilisation and surface protection Fissure sealing MI restorations Pulp capping Hypersensitivity Protection Caries stabilisation Fuji Triage from GC. Temporary restorations
Comparative evaluation of micro leakage of four recent resin-based core materials - an in vitro study
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparative evaluation of micro leakage of four recent resin-based core materials - an in vitro study B Rajkumar*, Mohammad Iqbal**, Juhi Hussain***, Amandeep Thind#, Gaurav Jain#, Chitrang
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparative evaluation of micro leakage of four recent resin-based core materials - an in vitro study B Rajkumar*, Mohammad Iqbal**, Juhi Hussain***, Amandeep Thind#, Gaurav Jain#, Chitrang
The Dental Board of California Dental Materials Fact Sheet Adopted by the Board on October 17, 2001
 The following document is the Dental Board of California s Dental Materials Fact Sheet. The Department of Consumer Affairs has no position with respect to the language of the Dental Materials Fact Sheet;
The following document is the Dental Board of California s Dental Materials Fact Sheet. The Department of Consumer Affairs has no position with respect to the language of the Dental Materials Fact Sheet;
J. Int Oral Health 2011 Case Report All right reserved
 J. Int Oral Health 2011 Case Report All right reserved A comparative evaluation of the sealing ability of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, High Copper Silver Amalgam, Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement, and
J. Int Oral Health 2011 Case Report All right reserved A comparative evaluation of the sealing ability of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, High Copper Silver Amalgam, Conventional Glass Ionomer Cement, and
A clinical evaluation of polishing amalgams immediately after insertion: 36-month results
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Copyright 1983 by The American Academy of Pedodontics VoL 5 No. 2 A clinical evaluation of polishing amalgams immediately after insertion: 36-month results Richard E. Corpron, DDS,
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Copyright 1983 by The American Academy of Pedodontics VoL 5 No. 2 A clinical evaluation of polishing amalgams immediately after insertion: 36-month results Richard E. Corpron, DDS,
Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study
 ISSN 0970-4388 Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study BOGRA P a, KASWAN S b ABSTRACT: In the present study, 25% EDTA, in gel form, was used to analyse its micromorphological effects on tooth surfaces with
ISSN 0970-4388 Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study BOGRA P a, KASWAN S b ABSTRACT: In the present study, 25% EDTA, in gel form, was used to analyse its micromorphological effects on tooth surfaces with
Evaluation of Dentin Root Canal Permeability After Instrumentation and Er:YAG Laser Application
 Lasers in Surgery and Medicine 26:277 281 (2000) Evaluation of Dentin Root Canal Permeability After Instrumentation and Er:YAG Laser Application Jesus D. Pecora, DDS, PhD, 1 * Aldo Brugnera-Júnior, DDS,
Lasers in Surgery and Medicine 26:277 281 (2000) Evaluation of Dentin Root Canal Permeability After Instrumentation and Er:YAG Laser Application Jesus D. Pecora, DDS, PhD, 1 * Aldo Brugnera-Júnior, DDS,
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry. Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer)
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Multilink Automix The adhesive cementation system
 Multilink Automix The adhesive cementation system A strong bond, proven performance. Recommended for Multilink Aut Strong hold A wide variety of restorative materials are available today. Due to their
Multilink Automix The adhesive cementation system A strong bond, proven performance. Recommended for Multilink Aut Strong hold A wide variety of restorative materials are available today. Due to their
Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module A: Basic Concepts
 Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module A: Basic Concepts REST 528A Operative #3A
Readings: Fundamentals of Operative Dentistry, 3 nd Edition; Summitt, et al Chapters 5, 6 and 8 Pulpal Protection: bases, liners, sealers, caries control Module A: Basic Concepts REST 528A Operative #3A
DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE
 DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE WORKSHEET Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com Study Guide for Dental Materials Dentalelle Tutoring 1. When completing a large composite restoration, how should the composite
DENTAL MATERIALS STUDY GUIDE WORKSHEET Dentalelle Tutoring www.dentalelle.com Study Guide for Dental Materials Dentalelle Tutoring 1. When completing a large composite restoration, how should the composite
For the Perfect Class V and All Cervical Area Gingival Margins when Placing Direct Composites, Create an Injection Molding Matrix
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report For the Perfect Class V and All Cervical Area Gingival Margins when Placing Direct Composites, Create an Injection Molding Paul C Belvedere* Adjunct Professor,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report For the Perfect Class V and All Cervical Area Gingival Margins when Placing Direct Composites, Create an Injection Molding Paul C Belvedere* Adjunct Professor,
Restorative Resin Cement for Bonding and Masking Tetracycline and Dark Stained Teeth for All Veneers
 Restorative Resin Cement for Bonding and Masking Tetracycline and Dark Stained Teeth for All Veneers Store Under Refrigeration Block-Out by Ultra-Bond is a multi-purpose, photo-initiated, dual-cure, restorative
Restorative Resin Cement for Bonding and Masking Tetracycline and Dark Stained Teeth for All Veneers Store Under Refrigeration Block-Out by Ultra-Bond is a multi-purpose, photo-initiated, dual-cure, restorative
6/1/15. Bonding Ceramic Veneers in What we did? What we do? Using Evidence-Based Dentistry XXXX ?????
 Bonding Ceramic Veneers in 2015 What we did? What we do? Using Evidence-Based Dentistry X XXXX????? 1 Are they etched? Are they properly etched? Are they properly cleaned Are they properly etched? Over
Bonding Ceramic Veneers in 2015 What we did? What we do? Using Evidence-Based Dentistry X XXXX????? 1 Are they etched? Are they properly etched? Are they properly cleaned Are they properly etched? Over
PROPAEDEUTICS OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY
 MEDICAL UNIVERSITY VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY AND ORAL PATHOLOGY QUESTIONNAIRE OF PROPAEDEUTICS OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY Academic year 2016/2017 Questions for
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY VARNA FACULTY OF DENTAL MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY AND ORAL PATHOLOGY QUESTIONNAIRE OF PROPAEDEUTICS OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY Academic year 2016/2017 Questions for
CERASMART. The new leader in hybrid ceramic blocks
 The new leader in hybrid ceramic blocks Introducing, a new force absorbing hybrid ceramic block 20 µm Contains high density of ultra fine homogeneously-dispersed fillers in a highly cross-linked resin
The new leader in hybrid ceramic blocks Introducing, a new force absorbing hybrid ceramic block 20 µm Contains high density of ultra fine homogeneously-dispersed fillers in a highly cross-linked resin
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children
 Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objectives Discuss amalgam restorations Discuss resin restorations Describe the history and evolution of use of silicate cement Discuss the role
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objectives Discuss amalgam restorations Discuss resin restorations Describe the history and evolution of use of silicate cement Discuss the role
Patient demand for esthetic dentistry
 PROFILE Masters of Esthetic Dentistry Keys to Success in Creating Esthetic Class IV Restorations Robert C. Margeas, DDS Current occupation Private Practice Adjunct Professor, Department of Operative Dentistry,
PROFILE Masters of Esthetic Dentistry Keys to Success in Creating Esthetic Class IV Restorations Robert C. Margeas, DDS Current occupation Private Practice Adjunct Professor, Department of Operative Dentistry,
Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1035 CLINICAL ARTICLE Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1035 CLINICAL ARTICLE Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate
DPI Luting Cement. DPI Restorative Cement
 DPI Luting Cement DPI Luting Cement is Type I glass ionomer white luting cement. DPI glass ionomers are remarkably biocompatible and can be safely used in deep cavities provided the pulp is not exposed,
DPI Luting Cement DPI Luting Cement is Type I glass ionomer white luting cement. DPI glass ionomers are remarkably biocompatible and can be safely used in deep cavities provided the pulp is not exposed,
Senior Lecturer, Dept. of Conservative &Endodontics, Geetanjali Dental & Research Institute / Geetanjali University, Udaipur, India 2
 Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 06 COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF MICROLEAKAGE IN CLASS II RESTORATION USING FLOWABLE RESIN COMPOSITE AND RESIN MODIFIED
Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 06 COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF MICROLEAKAGE IN CLASS II RESTORATION USING FLOWABLE RESIN COMPOSITE AND RESIN MODIFIED
A Study of Microleakage in Class II Composite Restorations Using Four Different Curing Techniques
 Operative Dentistry, 2007, 32-4, 336-340 A Study of Microleakage in Class II Composite Restorations Using Four Different Curing Techniques N Gharizadeh K Moradi MH Haghighizadeh Clinical Relevance For
Operative Dentistry, 2007, 32-4, 336-340 A Study of Microleakage in Class II Composite Restorations Using Four Different Curing Techniques N Gharizadeh K Moradi MH Haghighizadeh Clinical Relevance For
Jordi Manauta. Shadeguides Composite onlays. Page 1 of Apr 2012
 Jordi Manauta Shadeguides Composite onlays 25 Apr 2012 Indirect composite restorations in posterior teeth give us advantages to enhance the quality, durability and supreme aesthetics. An Article byâ Jordi
Jordi Manauta Shadeguides Composite onlays 25 Apr 2012 Indirect composite restorations in posterior teeth give us advantages to enhance the quality, durability and supreme aesthetics. An Article byâ Jordi
Amalgam restoration of posterior proximal cavities with deep and concave gingival outlines
 Amalgam restoration of posterior proximal cavities with deep and concave gingival outlines M. Darveniza, MDSc, FRACDS* Abstract A technique for making a matrix and wedges for amalgam restoration of deep
Amalgam restoration of posterior proximal cavities with deep and concave gingival outlines M. Darveniza, MDSc, FRACDS* Abstract A technique for making a matrix and wedges for amalgam restoration of deep
Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA in the Apical Sealing Ability of Lased And Unlased Root Canal Walls - A Pilot Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XIV (June 2016), PP 100-104 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XIV (June 2016), PP 100-104 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA
The Dental Board of California - Dental Materials Fact Sheet Adopted by the Board on October 17, 2001
 The Dental Board of California - Dental Materials Fact Sheet Adopted by the Board on October 17, 2001 As required by Chapter 801, Statutes of 1992, the Dental Board of California has prepared this fact
The Dental Board of California - Dental Materials Fact Sheet Adopted by the Board on October 17, 2001 As required by Chapter 801, Statutes of 1992, the Dental Board of California has prepared this fact
BioCoat Featuring SmartCap Technology
 new! BioCoat Featuring SmartCap Technology Premier s new bioactive pit and fissure sealant provides relentless protection, outstanding adhesion and extended fluoride release. Bioactive Release - Uptake
new! BioCoat Featuring SmartCap Technology Premier s new bioactive pit and fissure sealant provides relentless protection, outstanding adhesion and extended fluoride release. Bioactive Release - Uptake
The Facts About Fillings
 The Facts About Fillings DENTAL BOARD OF CALIFORNIA 1432 Howe Avenue Sacramento, California 95825 www.dbc.ca.gov Dental Materials Fact Sheet What About the Safety of Filling Materials? Patient health and
The Facts About Fillings DENTAL BOARD OF CALIFORNIA 1432 Howe Avenue Sacramento, California 95825 www.dbc.ca.gov Dental Materials Fact Sheet What About the Safety of Filling Materials? Patient health and
OliNano Seal Professional prophylaxis for long-term protection
 Professional prophylaxis for long-term protection NEW The patented formula of silicone polymer NANO Technology General information Dental health is one of the main factors to maintain overall health, and
Professional prophylaxis for long-term protection NEW The patented formula of silicone polymer NANO Technology General information Dental health is one of the main factors to maintain overall health, and
A Step-by-Step Approach to
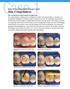
 A Step-by-Step Approach to a Diastema Closure A Dual-Purpose Technique that Manages Black Triangles Marcos Vargas, DDS, MS Figure 1: Preoperative view of a patient who presented with a diastema between
A Step-by-Step Approach to a Diastema Closure A Dual-Purpose Technique that Manages Black Triangles Marcos Vargas, DDS, MS Figure 1: Preoperative view of a patient who presented with a diastema between
Effect of various grit burs on marginal integrity of resin composite restorations
 J Med Dent Sci 2005; 52: 9 15 Original Article Effect of various grit burs on marginal integrity of resin composite restorations Kozo Nishimura 1, Masaomi Ikeda 1, Takako Yoshikawa 1, Masayuki Otsuki 1
J Med Dent Sci 2005; 52: 9 15 Original Article Effect of various grit burs on marginal integrity of resin composite restorations Kozo Nishimura 1, Masaomi Ikeda 1, Takako Yoshikawa 1, Masayuki Otsuki 1
Clinical Technique/Case Report
 Operative Dentistry, 2008, 33-3, 345-349 Clinical Technique/Case Report Modified Matrix Band Design for Ultra-conservative Posterior Restorations S Deliperi Clinical Relevance The combination of minimally
Operative Dentistry, 2008, 33-3, 345-349 Clinical Technique/Case Report Modified Matrix Band Design for Ultra-conservative Posterior Restorations S Deliperi Clinical Relevance The combination of minimally
how to technique Issue How to improve the longevity of porcelain veneers.
 Issue 4 2013 How to improve the longevity of porcelain veneers. 1. Avoid finishing on a resin composite restoration. longer term weak spot Although tempting in the interests of minimal tooth removal, finishing
Issue 4 2013 How to improve the longevity of porcelain veneers. 1. Avoid finishing on a resin composite restoration. longer term weak spot Although tempting in the interests of minimal tooth removal, finishing
Microleakage of different types of temporary restorative materials used in endodontics
 63 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 42, No. 2, 63-67, 2000 Microleakage of different types of temporary restorative materials used in endodontics M.B. Uctasl1 and A.C. Tinaz Department of Endodontics and
63 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 42, No. 2, 63-67, 2000 Microleakage of different types of temporary restorative materials used in endodontics M.B. Uctasl1 and A.C. Tinaz Department of Endodontics and
روپ قداص رتکد ناشخرد یاھدادعتسا رتفد
 CLASS II (pp 658-664 664, 696-708 708) دکتر صادق پور دفتر استعدادھای درخشان Seven Steps of Cavity Preparation 1) Establish the outline form 2) Establish resistance form 3) Establish retention form 4) Provide
CLASS II (pp 658-664 664, 696-708 708) دکتر صادق پور دفتر استعدادھای درخشان Seven Steps of Cavity Preparation 1) Establish the outline form 2) Establish resistance form 3) Establish retention form 4) Provide
Fuji II LC. A Perfect Choice
 A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
RESTORING ENDODONTICALLY TREATED TEETH POST RESTORATIONS CROWNS. Dr. Szabó Enikő associate professor
 RESTORING ENDODONTICALLY TREATED TEETH POST RESTORATIONS CROWNS Dr. Szabó Enikő associate professor Why is the risk of fracture greater? loss of tooth structure large caries trepanation cavity access to
RESTORING ENDODONTICALLY TREATED TEETH POST RESTORATIONS CROWNS Dr. Szabó Enikő associate professor Why is the risk of fracture greater? loss of tooth structure large caries trepanation cavity access to
The Fatigue Behavior of Restorations Used Under the Rest of Removable Partial Denture
 Journal of Dental Biomaterials. 2014;1(1) The Fatigue Behavior of Restorations Used Under the Rest of Removable Partial Denture Farzin M, Bahrani F, Nejabat N, Meshki R Department of Prosthodontics, School
Journal of Dental Biomaterials. 2014;1(1) The Fatigue Behavior of Restorations Used Under the Rest of Removable Partial Denture Farzin M, Bahrani F, Nejabat N, Meshki R Department of Prosthodontics, School
RESTORATIVE MATERIALS
 Position Statement / Media Release RESTORATIVE MATERIALS Dental restorative materials are specially fabricated materials designed for use as dental restorations (fillings). Dental restorations are used
Position Statement / Media Release RESTORATIVE MATERIALS Dental restorative materials are specially fabricated materials designed for use as dental restorations (fillings). Dental restorations are used
Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations:
 1 Lec.7 د.عبد املنعم اخلفاجي CLASS V CAVITY PREPARATION FOR AMAGLAM Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations: 1- Caries:
1 Lec.7 د.عبد املنعم اخلفاجي CLASS V CAVITY PREPARATION FOR AMAGLAM Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations: 1- Caries:
Bisco UNIVERSAL PRIMER
 Bisco UNIVERSAL PRIMER Dual-Cured Adhesive 0459* Instructions for Use IN-219R3 Rev. 3/18 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Rd. Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 847-534-6000 1-800-247-3368 Caution: U.S. Federal
Bisco UNIVERSAL PRIMER Dual-Cured Adhesive 0459* Instructions for Use IN-219R3 Rev. 3/18 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Rd. Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 847-534-6000 1-800-247-3368 Caution: U.S. Federal
Adper Scotchbond SE Self-Etch Adhesive. technical product profile. Adper
 Adper Scotchbond SE Self-Etch Adhesive technical product profile Adper 2 Table of Contents Introduction................................................................5 Product Description.......................................................5
Adper Scotchbond SE Self-Etch Adhesive technical product profile Adper 2 Table of Contents Introduction................................................................5 Product Description.......................................................5
Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative. Filtek. Supreme Plus Universal Restorative
 Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative TM. Multishade
Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative Introduction to Layering with Filtek Supreme Plus Universal Restorative TM. Multishade
DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material. Temrex Corporation October 2009
 DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material Temrex Corporation October 2009 DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material Overview Product Characteristics Physical Properties Case Report Instructions Ordering
DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material Temrex Corporation October 2009 DURATEMP Temporary Crown & Bridge Material Overview Product Characteristics Physical Properties Case Report Instructions Ordering
Multilink Automix The adhesive cementation system
 Multilink Automix The adhesive cementation system A strong bond, proven performance. Clinically proven with Multilink Aut Strong hold A wide variety of restorative materials are available today. Due to
Multilink Automix The adhesive cementation system A strong bond, proven performance. Clinically proven with Multilink Aut Strong hold A wide variety of restorative materials are available today. Due to
BioCoat Featuring SmartCap Technology
 R R Breakthrough! BioCoat Featuring SmartCap Technology The only bioactive pit and fissure sealant that provides relentless protection through daily release of fluoride, calcium and phosphate ions. Bioactive
R R Breakthrough! BioCoat Featuring SmartCap Technology The only bioactive pit and fissure sealant that provides relentless protection through daily release of fluoride, calcium and phosphate ions. Bioactive
