Clinical trials with nanoparticle composite in posterior teeth: a systematic literature review
|
|
|
- Phebe Powell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Literature Review Braz J Oral Sci. July/September 9 - Volume 8, Number 3 Clinical trials with nanoparticle in posterior teeth: a atic literature review Ana Karina Maciel Andrade, Rosângela Marques Duarte, Fábia Danielle Sales da Cunha Medeiros e Silva 3, André Ulisses Dantas Batista, Kenio Costa Lima 4, Marcos Antonio Japiassú Resende Montes 5 DDS, MSc, Assistant Professor, Department of Restorative Dentistry, Federal University of Paraíba, Brazil; Doctorate Student University of Pernambuco, Brazil. DDS, MSc, PhD, Associate Professor, Department of Restorative Dentistry, Federal University of Paraíba, Brazil. 3 DDS, MSc, Assistant Professor, Department of Restorative Dentistry, Federal University of Paraíba, Brazil 4 DDS, MSc, PhD, Associate Professor, Department of Dentistry, Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte,Brazil 5 DDS, MSc, PhD, Associate Professor, Department of Restorative Dentistry, University of Pernambuco, Brazil Abstract Aim: The aim of this article is to evaluate clinical trials with nanoparticle in posterior teeth through a atic review of the literature. Methods: This analysis includes controlled clinical trials with nanoparticle s, with at least 6 months of evaluation, published in the English language between 997 and 9. In vitro and retrospective studies and studies on anterior teeth were excluded. Articles were retrieved from the following full-text electronic journal databases: MEDLINE, LILACS and The Cochrane Library. Results: The largest number of articles was found in the MEDLINE database, but only 4 of them met the inclusion and exclusion criteria. No articles were found in the LILACS database; only two articles were selected from The Cochrane Library databases and they coincided with those already included in MEDLINE. Conclusions: The nanoparticle s give a satisfactory performance for use in posterior teeth for at least years of functional activity, but their performance was not superior to that of the other s. Long-term studies must be conducted to evaluate the performance after years of functional activity. New controlled and randomized clinical trials are necessary. Keywords: controlled clinical trials, resins Received for publication: May 4, 9 Accepted: September 6,9 Correspondence to: Marcos Antonio Japiassú Resende Montes Faculdade de Odontologia de Pernambuco UPE, Departamento de Odontologia Restauradora / Materiais Dentários, Av. Gen. Newton Cavalcanti, 65, CEP: Camaragibe, PE, Brazil. Phone: ; Fax: majrm@uol.com.br Introduction Restorative s have undergone continuous improvement in dental practice for over 4 years, since Bowen incorporated inorganic particles into a resinous matrix. Composites comprise a blend of hard, inorganic particles bound together by a soft, resin matrix, and generally encompass three main components: () the resin matrix comprising: (i) a monomer, (ii) an initiator for free radical polymerization, and (iii) stabilizers to maximize the storage stability of the uncured resin and the chemical stability of the cured resin; () the inorganic filler consisting of particulates such as glass, quartz, and/or fused silica; and (3) the coupling agent, usually an organo-silane, that chemically bonds the reinforcing filler to the resin matrix. The first formulations contained large load particles of up to 5 µm (macrofilled s), and had several unsatisfactory physical and mechanical properties 3. Investigations conducted in the 97s and early 98s concluded that the properties of macrofilled s, particularly wear, color stability and marginal leakage, were clinically unacceptable for posterior teeth. Research indicated that the inorganic content, geometry and load particle dimensions greatly influenced the final properties of the material 4-5. During the last few decades, new formulations have appeared and the mean size of the particles has been drastically reduced. Sub-micrometric particles have been used to
2 Clinical trials with nanoparticle in posterior teeth: a atic literature review 5 improve the physical and mechanical properties, namely reduction of the linear thermal expansion coefficient, greater dimensional stability and greater resistance to abrasion and wear 3,6-7. Microfilled s with a mean filler particle size of.4 µm maintain the gloss produced after polishing. Unfortunately, because of their low tensile strength and fracture toughness, microfilled s are contraindicated for class IV and stress-bearing restorations 8-9. Hybrid s are materials that contain a blend of prepolymerized and inorganic fillers. Microhybrid has been successful to replace missing tooth structure even though hybrids are less polishable than microfilled ; they have excellent mechanical properties -. According to Peutzfeldt, and Walker and Burgess, most improvements in the properties of s are due to the changes in the inorganic particles. These aspects have encouraged the use of various nanometric particles in resin-based materials. Nanotechnology, also known as molecular nanotechnology or molecular engineering, is the production of functional materials and structures in the range of. to nm (the nanoscale) by various physical or chemical methods. The use of nanoparticles is useful for many applications including industry, transport, packaging, high-performance coatings, electronics, biomedicals, where nanoparticles improve the mechanical properties of materials. In dentistry, posterior class I or II restorations require s with high mechanical properties; anterior restorations need s with superior esthetics. The resin that meets all the requirements of both posterior and anterior restorations has not yet emerged 3. Therefore, nanotechnology is of great interest in resin research 3. The nano contains a unique combination of two types of nanofillers (5 75 nm) and nanoclusters. Nanoparticles are discrete nonagglomerated and nonaggregated particles of 75 nm in size. Nanocluster fillers are loosely bound agglomerates of nanosized particles. The agglomerates act as a single unit enabling high filler loading and high strength. Due to the reduced dimension of the particles and the wide size distribution, an increased filler load can be achieved with the consequence of reducing polymerization shrinkage and increasing the mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and compressive strength to fracture. These seem to be equivalent or even sometimes higher than those of hybrid s and significantly higher than microfilled s. As a consequence, s now recommend the use of nanos for both anterior and posterior restorations,3 5. There are also s on the market which are not exclusively nanoparticles, but contain nanometric and micrometric particles, and this has led to better performance. These materials are considered the precursors of nanoparticle s and some refer to them as nanohybrids 3. Within the context of nanotechnology, the aim of this study was to analyze, by means of a ic review of the literature, studies that conducted clinical trials with nanoparticle in posterior teeth in order to verify the performance of these s in real conditions. Material and methods The atic review of the literature was conducted using the following full-text electronic journal databases: MEDLINE (International Literature in Health Sciences), LILACS (Latin American and Caribbean Literature in Health Sciences) and The Cochrane Library. For inclusion in this review, an article had to meet the following specifications: it should be a controlled clinical trial investigating nanoparticle in posterior teeth, with at least 6 months of evaluation, published in the English language between 997 and 9. Articles with the following characteristics were excluded: in vitro studies, retrospective studies and studies on anterior teeth. The search strategy for the MEDLINE and LILACS databases was: nanofiller or (nano) or (nanofill) or (nanofilled) [Words] and CLINICAL TRIAL or CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIAL or CLINICAL TRIAL PHASE I or CLINICAL TRIAL PHASE II or CLINICAL TRIAL PHASE III or CLINICAL TRIAL PHASE IV or RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL or MULTICENTER STUDY or EVALUATION STUDIES [Publication type] and ENGLISH [language]. In The Cochrane Library, the search was conducted as follows: nanofiller or (nano) or (nanofill) or (nanofilled). After aplication of the search strategy, two examiners reviewed the titles and abstracts of the articles and performed the selection by consensus. With the objective of complementing the database searches, non-automated manual searches were also conducted on the References within the selected articles. Results and Discussion Nanoparticle s were developed with the aim of combining high mechanical properties and maximum polishing. Laboratory tests provide useful information on material performance and its manipulation characteristics, but they cannot provide answers about its clinical longevity. Only controlled and randomized clinical trials can provide conclusions on the use of s 6. After application of the search strategy, 79 articles were found in the MEDLINE database, but only four of them met the pre-established criteria; no studies were found in LILACS. Thirteen articles were found in The Cochrane Library, but only two met the inclusion criteria, and these coincided with those selected from MEDLINE database. The searches conducted from within the references of the selected articles yielded no additional articles fulfilling the inclusion requirements. Table explains the objectives, methodology, results and conclusions of the selected articles. Although controlled and randomized clinical trials have a reference pattern, only controlled clinical trials were included in this review, except for Dresch et al. 7 who indicated that randomization was used and explained how it was accomplished. With regard to the sample size, all articles included at least 3 restorations per group, which is considered as a satisfactory number. In the study by Ernst et al. 8, a split mouth design was used and 56 restorations were performed in each group, but the total number of subjects was 5 because some individuals received more than one restoration per group. This contradicts the recommendations of Hickel et al. 9 who affirmed that each research subject must have, at most, one sample unit per group. In the research by Efes et al. 6 each patient received only one restoration, but the ideal condition of all the groups in mouth was not followed. Dresch et al. 7 designed 4 groups in patient, giving a total of 48 restorations and 37 per
3 6 Clinical trials with nanoparticle in posterior teeth: a atic literature review Table Title, author, year, aims, methodology, results and conclusion of articles Title (author, year) Clinical evaluation of a nanofilled in posterior teeth: - month results (Dresch et al., 6) 7 Aims To compare the clinical performance of a nanoparticle with two microhybrid and one compactable in posterior restorations after months Methodology Thirty-seven patients with at least four class I or II cavities and with normal occlusion were selected. A total of 48 restorations were performed, 5% of each material (Filtek Supreme/3M ESPE, St Paul, MN, USA; Pyramid/ Bisco, Schaumburg, IL, USA; Esthet- X/Dentsply, Konstanz, Germany or Tetric Ceram/Ivoclar-Vivadent, Brendererstrasse Liechtenstein, Germany). Two calibrated operators performed the treatment, in accordance with the s instructions. The adhesive s used were from s as the resin, and in the case of deep cavities, calcium hydroxide cement and/or glass ionomer cement was applied. Finishing and polishing were done week later. Two independent examiners assessed the restorations at baseline and months later according to the United States Public Health Service (USPHS) modified criteria Results and conclusions All the patients were assessed months later. At baseline, postoperative sensitivity was observed in seven restorations, which disapeared at the -month evaluation. No secondary caries, marginal discoloration or lack of retention was observed after year. Color match and marginal adaptation were the items that received the highest number of Bravo scores ( and, respectively). Only four restorations were classified as Bravo in the anatomic form item. Six restorations showed poor surface texture after months. No statistically significant difference was observed between materials, and their performance at baseline and after year was statistically similar. The authors concluded that the Filtek Supreme, Pyramid, Esthet-X and Tetric Ceram s exhibited excellent clinical performance after year Clinical evaluation of an ormocer, a nanofill and a hybrid at years (Efes et al., 6 During a period of years evaluate the clinical performance of an ormocer, a nanoparticle, and as control, a hybrid, in small class I cavities in permanent molars Ninety class I cavities were prepared in 9 patients, who had primary caries. The teeth were restored incrementally, in oblique layers with ormocer (Admira/ VOCO, Cuxhaven, Germany), nanoparticle (Filtek Supreme/3M ESPE) or hybrid (Renew/Bisco) by a single operator. The restorations were examined using the Ryge criteria (USPHS modified) at baseline, after 6 months, years and years At the follow-up examinations, %, %, and 97% of 9 restorations were evaluated at 6 months, year and years, respectively. The scores for all the performance criteria were either Alpha or Bravo. None of the restorative materials presented secondary caries or postoperative sensitivity at 6 months, year or years. After years, there were no clinically unacceptable criteria, except in one Admira restoration (ormocer) which failed. According to the cavosurface marginal discoloration and the surface texture criteria, there were no significant differences between the restorative materials. The marginal adaptation rate was % for the nanofill and hybrid and 97% for the ormocer at both and years. There were no significant differences between the restorative materials. The s studied resulted in high clinical performance after years Two-year clinical evaluation of ormocer, nanohybrid and nanofill restorative s in posterior teeth (Mahmoud et al., 8) To evaluate and compare the -year clinical performance of an ormocer, a nanohybrid, and a nanofill resin with that of a conventional microhybrid in restorations of small occlusal cavities made in posterior teeth Forty dental students from the Faculty of Dentistry at Mansoura University were enrolled in this study. The criteria for their inclusion were the presence of primary caries or replacement of existing amalgam for esthetic reasons. Each patient received at least 4 occlusal restorations. A total of 4 restorations was carried out, 5% for each material: ormocer-based, Admira (Voco); a nanohybrid resin, Tetric EvoCeram (Ivoclar-Vivadent); a nanofill resin, Filtek Supreme (3M ESPE); and a microhybrid resin, Tetric Ceram (Ivoclar- Vivadent). Two operators carried out all restorations according to the s instructions. Two independent examiners made all evaluations according to the USPHSmodified Ryge criteria immediately after placement of restorations and after 6 months, year and years All patients attended the -year recall visit. The scores for all the performance criteria were either Alpha or Bravo. Only one ormocer and one microhybrid restoration had failed after years. The color match of 3 microhybrid restorations was scored as Bravo at the baseline examination. This criterion did not change during the -year period. Regarding clinical performance, there were no statistically significant differences among the materials used. After years, the ormocer, nanohybrid, and nanofill s showed acceptable clinical performance similar to that of the microhybrid resin
4 Clinical trials with nanoparticle in posterior teeth: a atic literature review 7 group. Mahmoud et al. placed 4 restorations, 35 for each restorative, with each patient receiving at least 4 occlusal restorations. The studies addressed here were not unanimous with regard to the type of adhesive used. The s of the s recommend the use of an adhesive from. This rule was followed by Efes et al. 6, Dresch et al. 7 and Mahmoud et al.. However, Ernst et al. 8 decided to vary only the and used adhesive for both groups. They reported that the influence of the adhesive on the result of the clinical studies can first be seen in marginal discoloration or in the presence of open margins. These aspects were not verified in this study, which corroborates the clinical evidence that performance might not be compromised when used with an adhesive other than the one recommended. All restorations were assessed blindly, since the examiners did not know the restorative material. Agreement among the examiners was high in all the articles (>.87). The experimental designs of the three studies had some differences, shown in Table, but these particularities did not result in distinct outcomes among the articles. The restorations of the articles selected were evaluated by the Modified USPHS (United States Public Health Service) criteria, which is a long-established method used in clinical trials. The criteria evaluated in common in the 4 articles were color match, retention, marginal adaptation, anatomic form, surface roughness, marginal staining, sensibility and secondary caries. The restorations were classified in Alpha, Bravo, Charlie and Delta. Alpha and Bravo scores mean excellent and clinically acceptable results, while Charlie and Delta scores mean clinically not acceptable, an indication to replace the restoration to prevent future damage or to repair present damage 8. In the research by Dresch et al. 7, no differences were found between the nanoparticle, Filtek Supreme, the compactable Pyramid and two microhybrids (Esthet-X and Tetric Ceram) for the study periods. The majority of the scores were Alpha and Bravo, that is, all the materials exhibited excellent clinical performance after year. No restorations failed. Efes et al. 6 ratified these results as they reported that the scores for color match, marginal discoloration, anatomical form, marginal adaptation and surface texture for all the restorative materials, changed from Alpha to Bravo at most. For the retention criteria, except for one Admira (ormocer) restoration considered clinically unacceptable (score Delta, restoration was partially or totally missing); all the others were Alpha. There was no secondary caries, or postoperative sensitivity in the patients assessed. Consequently, Admira Filtek Supreme (nanoparticle) and Renew (hybrid) resulted in high clinical performance after years. Table Particular characteristics of the selected articles. Study Number of professionals who performed the restorations Sample per group Total number of restorations Reason for performing the restoration Patient age Isolation Type of cavity Pulp capping Followup period Final return rate (%) Number of failures with nanofill Dresch et al, The majority was replacement of existing amalgam for esthetic reasons Not given Rubber dam Classes I and II (AS). In deep cavities: calcium hydroxide and/ or glass ionomer cement before the adhesive year Efes et al., caries 8 48 years Cotton rolls and suction Class I minimally invasive years 97 Ernst et al., caries or deficient restoration Mean 35.7 years (SD.3) Rubber dam Class II One for all the groups years Mahmoud et al., 8 35 caries or replacement of existing amalgam for esthetic reasons Not given Cotton rolls and suction Class I. In cavities extending for more than mm into the dentin, a glass-ionomer cement before AS years
5 8 Clinical trials with nanoparticle in posterior teeth: a atic literature review In the study of Ernst et al. 8, the two s used (Tetric Ceram-hybrid ( fine particles) and Filtek Supreme (nanoparticles) gave acceptable clinical performance at the end of years. According to the USPHS criteria, global clinical success (Alpha and Bravo scores) was 98%. With regard to color match, good performance was 95% for the nanoparticle and 98% for the hybrid. Two fractures of restorations were observed within the observation period of years: one chipping fracture (cohesive-type fracture) of a distal marginal ridge in a Filtek Supreme restoration placed in a mandibular molar and one bulk fracture in the mesial part of a Tetric Ceram restoration placed in a mandibular premolar. The study by Mahmoud et al. also corroborates the findings of the articles mentioned above. The scores for all the performance criteria were either Alpha or Bravo. Only one ormocer and one microhybrid restoration had failed after years, showing secondary caries. Although all the articles included in this review obtained good results, the authors 6 8 warned about the need for longitudinal followup studies in order to obtain long-term answers about this new type of because the trials described were of short duration. Notwithstanding the fact that all the articles included in this review were, in general, well designed, there is the need for additional controlled and randomized clinical trials that could shed light on some of the questions still not completely resolved. The following conclusions may be drawn: The performance of nanoparticle s is satisfactory for use in posterior teeth for at least years of functional activity; Nnanoparticle s can be used in posterior teeth, although their performance was not superior to that of the other s studied; Longer-term studies must be conducted to evaluate performances after years of functional activity.; New controlled and randomized clinical trials are necessary to further evaluate some of the issues and questions that have not been fully addressed by current studies. 5. Yap AUJ, Yap SH, Teo CK, Ng JJ. Comparison of surface finish of new aesthetic restorative materials. Oper Dent. 4; 9: Efes BG, Dörter C, Gömeç Y. Clinical evaluation of an ormocer, a nanofill and a hybrid at years. Am J Dent. 6; 9 : Dresch W, Volpato S, Gomes JC, Ribeiro NR, Reis A, Loguercio AD. Clinical evaluation of a nanofilled in posterior teeth: -month results. Oper Dent. 6; 3: Ernst CP, Brandenbusch M, Meyer G, Canbek K, Gottschalk F, Willershausen B. Two-year clinical performance of a nanofiller vs a fine-particle hybrid resin. Clin Oral Investig. 6; : Hickel R, Roulet JF, Bayne S, Heintze SD, Mjör IA, Peters M et al. Recommendations for conducting controlled clinical studies of dental restorative materials. Clin Oral Investig. 7; : Mahmoud SH, El-Embaby AE, AbdAllah AM, Hamama HH. Two-year clinical evaluation of ormocer, nanohybrid and nanofill restorative s in posterior teeth. J Adhes Dent. 8;: 35-. References. Bowen RL. Properties of a silica-reinforced polymer for dental restorations. J Am Dent Assoc. 963; 66: Peutzfeldt A. Resin s in dentistry: the monomer s. Eur J Oral Sci. 997; 5: Leinfelder KF. Posterior resin: the materials and their clinical performance. J Am Dent Assoc. 995; 6: Adabo GL, Cruz CAS, Fonseca RG, Vaz LG. The volumetric fraction of inorganic particles and the flexural strength of s for posterior teeth. J Dent. 3; 3: Willems G, Lambrechts P, Braem M, Celis JP, Vanherle G. A classification of dental s according to their morphological and mechanical characteristics. Dent Mater. 99; 8: Bryant RW. Direct posterior resin restorations: a review factors influencing case selection. Aust Dent J. 99; 37: Lu H, Lee YK, Oguri M, Powers JM. Properties of a dental resin with a spherical inorganic filler. Oper Dent. 6; 3: Lambrechts P, Ameye C, Vanherle G. Conventional and microfilled resins. Part II. Chip fractures. J Prosthet Dent. 98; 48: Fortin D, Vargas MA. The spectrum of s: new techniques and materials.j Am Dent Assoc. ; 3: 6s-3s.. Walker R, Burgess JO. Comparing resin-based s. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 4; 5: Mitra SB, Wu D, Holmes BN. An aplication of nanotechnology in advanced dental materials. J Am Dent Assoc. 3; 34: Kirk RE, Othmer DF, Kroschwitz J, Howe-Grant M. Encyclopedia of chemical technology. 4th ed. New York: Wiley; 99. p Beun S, Glorieux T, Devaux J, Vreven J, Leloup G. Characterization of nanofilled compared to universal and microfilled s. Dent Mater. 7; 3: Condon JR, Ferracane JL. Reduced polymerization stress through non-bonded nanofiller particles. Biomaterials. ; 3:
Initial 6 months 12 months 24 months Admira Fusion GrandioSO Total
 Clinical study over 2 years VOCO GmbH, Knowledge Communication Department Anton-Flettner-Str. 1-3 27472 Cuxhaven Germany Tel.: +49 ()4721-719-1111 Fax: +49 ()4721-719-19 info@voco.de www.voco.dental With
Clinical study over 2 years VOCO GmbH, Knowledge Communication Department Anton-Flettner-Str. 1-3 27472 Cuxhaven Germany Tel.: +49 ()4721-719-1111 Fax: +49 ()4721-719-19 info@voco.de www.voco.dental With
F i l t e k Z550. Nano Hybrid Universal Restorative. Technical Data Sheet
 F i l t e k Z550 Nano Hybrid Universal Restorative Technical Data Sheet Product Description Filtek Z550 Nano Hybrid Universal Restorative is a visible light-activated nanohybrid composite designed for
F i l t e k Z550 Nano Hybrid Universal Restorative Technical Data Sheet Product Description Filtek Z550 Nano Hybrid Universal Restorative is a visible light-activated nanohybrid composite designed for
EQUIA. Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System
 EQUIA EQUIA Fil EQUIA Coat + Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System From the World Leader in Glass Ionomer Technology - A Complete Glass Ionomer Based Bulk Fill Rapid Restorative System Class
EQUIA EQUIA Fil EQUIA Coat + Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System From the World Leader in Glass Ionomer Technology - A Complete Glass Ionomer Based Bulk Fill Rapid Restorative System Class
Filtek. Any place. Any class. Supreme XTE. It s the one that can do it all. Universal Restorative. Class III. Class IV. Class II. Class I.
 Class III Class IV Class II Class I Class V Any place. Any class. It s the one that can do it all. Designed to be versatile. If you re still using one composite for strong posterior fillings, and another
Class III Class IV Class II Class I Class V Any place. Any class. It s the one that can do it all. Designed to be versatile. If you re still using one composite for strong posterior fillings, and another
lec: Dental material dr. Aseel Mohammed Filling material
 Filling material Filling material: the material that is used to replace a missing part of the tooth which may result from dental caries, trauma or abrasion. It can be divided in to: 1. Direct filling materials:
Filling material Filling material: the material that is used to replace a missing part of the tooth which may result from dental caries, trauma or abrasion. It can be divided in to: 1. Direct filling materials:
Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up
 Case 1 This case study focuses on the restoration of an upper molar. Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up The existing, inadequate restoration led to the development
Case 1 This case study focuses on the restoration of an upper molar. Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up The existing, inadequate restoration led to the development
Amaris. You want outstanding esthetic restorations with the WOW-EFFECT
 The Composite For Simplified Esthetics The Simplified Esthetic Concept You want outstanding esthetic restorations with the WOW-EFFECT You do not have the time to work on a patient for hours You do not
The Composite For Simplified Esthetics The Simplified Esthetic Concept You want outstanding esthetic restorations with the WOW-EFFECT You do not have the time to work on a patient for hours You do not
Clinical Evaluation of a Nanofilled Composite in Posterior Teeth: 12-month Results
 Operative Dentistry, 2006, 31-4, 409-417 Clinical Evaluation of a Nanofilled Composite in Posterior Teeth: 12-month Results W Dresch S Volpato JC Gomes NR Ribeiro A Reis AD Loguercio Clinical Relevance
Operative Dentistry, 2006, 31-4, 409-417 Clinical Evaluation of a Nanofilled Composite in Posterior Teeth: 12-month Results W Dresch S Volpato JC Gomes NR Ribeiro A Reis AD Loguercio Clinical Relevance
EQUIA Forte Glass Hybrid Restorative System. For long term posterior restorations
 EQUIA Forte Glass Hybrid Restorative System For long term posterior restorations The original EQUIA system EQUIA is a self-adhesive posterior restorative system that combines the chemical-bonding, bulk-fill
EQUIA Forte Glass Hybrid Restorative System For long term posterior restorations The original EQUIA system EQUIA is a self-adhesive posterior restorative system that combines the chemical-bonding, bulk-fill
One solution for all. cavity classes. Tetric Evo product line. Tetric EvoCeram. Tetric EvoFlow. Tetric EvoCeram Bulk Fill Tetric EvoFlow Bulk Fill
 One solution for all cavity classes Tetric Evo product line Tetric EvoCeram Tetric EvoFlow Tetric EvoCeram Bulk Fill Tetric EvoFlow Bulk Fill One solution for all cavity classes Posterior region: Class
One solution for all cavity classes Tetric Evo product line Tetric EvoCeram Tetric EvoFlow Tetric EvoCeram Bulk Fill Tetric EvoFlow Bulk Fill One solution for all cavity classes Posterior region: Class
New Nano-Hybrid Technology for your everyday Use
 New Nano-Hybrid Technology for your everyday Use NEW New NANO-HYBRID TECHNOLOGY For Your every Day USE You need a composite that allows you to easily achieve high quality restorations? Polofil NHT, the
New Nano-Hybrid Technology for your everyday Use NEW New NANO-HYBRID TECHNOLOGY For Your every Day USE You need a composite that allows you to easily achieve high quality restorations? Polofil NHT, the
DEPTH PERCEPTION. G-ænial BULK Injectable G-ænial Universal Injectable G-ænial Flo X Family of Injectable Composite Restoratives UP TO TWO MM
 UP TO TWO MM UP TO FOUR MM DEPTH PERCEPTION G-ænial BULK Injectable G-ænial Universal Injectable G-ænial Flo X Family of Injectable Composite Restoratives REDEFINE THE WAY YOU WORK WITH GC INJECTABLES!
UP TO TWO MM UP TO FOUR MM DEPTH PERCEPTION G-ænial BULK Injectable G-ænial Universal Injectable G-ænial Flo X Family of Injectable Composite Restoratives REDEFINE THE WAY YOU WORK WITH GC INJECTABLES!
ÆLITE Composites. Bisco. Instructions for Use. Light- Cured. U.S. Patent: 6,709,271
 Bisco ÆLITE Composites 0459 Light- Cured Instructions for Use U.S. Patent: 6,709,271 IN-131R6 Rev. 4/16 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Road Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 847-534-6000 1-800-247-3368 Caution:
Bisco ÆLITE Composites 0459 Light- Cured Instructions for Use U.S. Patent: 6,709,271 IN-131R6 Rev. 4/16 BISCO, Inc. 1100 W. Irving Park Road Schaumburg, IL 60193 U.S.A. 847-534-6000 1-800-247-3368 Caution:
Discover. the power of fibres. everx Posterior. from GC. sub-structure. Extending the limits. The strongest composite. of direct restorations.
 Discover the power of fibres everx Posterior from GC The strongest composite sub-structure. Extending the limits of direct restorations. Looking for a solution to prevent cracks? Evidence shows that fracture
Discover the power of fibres everx Posterior from GC The strongest composite sub-structure. Extending the limits of direct restorations. Looking for a solution to prevent cracks? Evidence shows that fracture
Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials
 Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials A case study by Ann-Christin Meier, Dr. med. dent., Stapelfeld, Germany When large
Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials A case study by Ann-Christin Meier, Dr. med. dent., Stapelfeld, Germany When large
Indian Journal of Basic & Applied Medical Research; June 2012: Issue-3, Vol.-1, P
 The Effect Of Various Polishing Systems On Surface Roughness Of Nano and Microhybrid Composite Restoratives : An In Vitro Surface Profilometric Study " 1 Dr.Smita Dutta, 2 Dr Rahul Maria.. ABSTRACT: Introduction:
The Effect Of Various Polishing Systems On Surface Roughness Of Nano and Microhybrid Composite Restoratives : An In Vitro Surface Profilometric Study " 1 Dr.Smita Dutta, 2 Dr Rahul Maria.. ABSTRACT: Introduction:
A real leader takes you further.
 A real leader takes you further. The unmatched SDR bulk fill technology In 2009, SureFil SDR flow material with SDR technology was the first product that allowed 4mm bulk placement in flowable consistency.
A real leader takes you further. The unmatched SDR bulk fill technology In 2009, SureFil SDR flow material with SDR technology was the first product that allowed 4mm bulk placement in flowable consistency.
Universal nano-hybrid restorative. Grandio SO
 Universal nano-hybrid restorative SO TOOTH LIKE The perfect filling composite is characterised by a combination of its material properties, to be as similar to the tooth as possible. With the added combination
Universal nano-hybrid restorative SO TOOTH LIKE The perfect filling composite is characterised by a combination of its material properties, to be as similar to the tooth as possible. With the added combination
Clinical use of Filtek Silorane. Low Shrink Posterior Restorative
 Clinical use of Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative In collaboration with Dr. Gabriel Krastl Department of Periodontology, Endodontics and Cariology at the University of Basel Dental Hospital
Clinical use of Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative In collaboration with Dr. Gabriel Krastl Department of Periodontology, Endodontics and Cariology at the University of Basel Dental Hospital
A COMPARATIVE IN VITRO STUDY OF COMPOSITES: COLOUR STABILITY
 A comparative in vitro study of composites: Colour stability A COMPARATIVE IN VITRO STUDY OF COMPOSITES: COLOUR STABILITY STUDY SITE Universitat Internacional de Catalunya School of Dentistry. C/ Josep
A comparative in vitro study of composites: Colour stability A COMPARATIVE IN VITRO STUDY OF COMPOSITES: COLOUR STABILITY STUDY SITE Universitat Internacional de Catalunya School of Dentistry. C/ Josep
Clinical Technique/Case Report
 Operative Dentistry, 2008, 33-3, 345-349 Clinical Technique/Case Report Modified Matrix Band Design for Ultra-conservative Posterior Restorations S Deliperi Clinical Relevance The combination of minimally
Operative Dentistry, 2008, 33-3, 345-349 Clinical Technique/Case Report Modified Matrix Band Design for Ultra-conservative Posterior Restorations S Deliperi Clinical Relevance The combination of minimally
AdperTM FiltekTM EliparTMSof-LexTM
 AdperTM FiltekTM EliparTMSof-LexTM 3M ESPE Composite-Navigator An orientation aid for our composite filling therapy 3M ESPE Composite-Navigator To find the right Solution for your Requirement As one of
AdperTM FiltekTM EliparTMSof-LexTM 3M ESPE Composite-Navigator An orientation aid for our composite filling therapy 3M ESPE Composite-Navigator To find the right Solution for your Requirement As one of
FLUORIDE RELEASING, BIOACTIVE, NANO-HYBRID COMPOSITE
 LS FLUORIDE RELEASING, BIOACTIVE, NANO-HYBRID COMPOSITE V I S I T W W W. S H O F U. C O M O R C A L L 8 0 0. 8 2 7. 4 6 3 8 Create indistinguishable restorations with optical characteristics of natural
LS FLUORIDE RELEASING, BIOACTIVE, NANO-HYBRID COMPOSITE V I S I T W W W. S H O F U. C O M O R C A L L 8 0 0. 8 2 7. 4 6 3 8 Create indistinguishable restorations with optical characteristics of natural
Restorative Solutions. F il t e k Ultimate Universal Restorative. The simplest way to. refl ect reality
 Restorative Solutions F il t e k Ultimate Universal Restorative The simplest way to refl ect reality Outstanding restorations, now easier than ever If you want to emulate nature (and we re sure you do),
Restorative Solutions F il t e k Ultimate Universal Restorative The simplest way to refl ect reality Outstanding restorations, now easier than ever If you want to emulate nature (and we re sure you do),
LOOKING FOR ONLY ONE SIMPLE ANSWER? THE SOLUTION IS
 LOOKING FOR ONLY ONE SIMPLE ANSWER? THE SOLUTION IS the Most Tooth-Like Composite Ever! 89% FILLED UNIVERSAL NANO-HYBRID COMPOSITE THE COMBINATION OF HANDLING, ESTHETICS AND PERFORMANCE 1 FLOWABLE NANO
LOOKING FOR ONLY ONE SIMPLE ANSWER? THE SOLUTION IS the Most Tooth-Like Composite Ever! 89% FILLED UNIVERSAL NANO-HYBRID COMPOSITE THE COMBINATION OF HANDLING, ESTHETICS AND PERFORMANCE 1 FLOWABLE NANO
Fusion Admira Admira NANo-hybrid ormocer restorative MAtEriAls
 Admira Fusion Admira Fusion Nano-hybrid ORMOCER restorative materials Admira Fusion Purely ceramic-based The highly innovative ORMOCER technology developed by the Fraunhofer Institute for Silicate Research
Admira Fusion Admira Fusion Nano-hybrid ORMOCER restorative materials Admira Fusion Purely ceramic-based The highly innovative ORMOCER technology developed by the Fraunhofer Institute for Silicate Research
UAB School of Dentistry
 Wear of a Calcium, Phosphate and Fluoride Releasing Restorative Material Final report -- August 18, 2014 UAB School of Dentistry John Burgess, D.D.S., M.S. Assistant Dean for Clinical Research University
Wear of a Calcium, Phosphate and Fluoride Releasing Restorative Material Final report -- August 18, 2014 UAB School of Dentistry John Burgess, D.D.S., M.S. Assistant Dean for Clinical Research University
A real leader takes you further.
 A real leader takes you further. 2017 Dentsply Sirona. All rights reserved. The unmatched SDR bulk fill technology In 2009, SureFil SDR flow with SDR technology was the first product that allowed 4mm bulk
A real leader takes you further. 2017 Dentsply Sirona. All rights reserved. The unmatched SDR bulk fill technology In 2009, SureFil SDR flow with SDR technology was the first product that allowed 4mm bulk
Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland School of Dentistry
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry-Biomaterials Structures, chemical properties, physical properties BASIC CONCEPTS ON HOW DENTAL MATERIALS WORK! Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry-Biomaterials Structures, chemical properties, physical properties BASIC CONCEPTS ON HOW DENTAL MATERIALS WORK! Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland
< 1% shrinkage! * new record: Low Shrink Posterior Restorative. volumetric. The fi rst direct posterior composite to achieve less than 1 % shrinkage.
 Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative The new record: volumetric < 1% shrinkage! * * < 1 % volumetric shrinkage tested by bonded disc method. The fi rst direct posterior composite to achieve
Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative The new record: volumetric < 1% shrinkage! * * < 1 % volumetric shrinkage tested by bonded disc method. The fi rst direct posterior composite to achieve
Ordering Information.
 Ordering Information Item No. 4911S 4910S 4911D 4910D 4911P 4910P Product Information Single Shade Introductory Kit Capsule Kit includes: 40 0.2 g capsules: 20 each of Body shades A2 and A3; Technique
Ordering Information Item No. 4911S 4910S 4911D 4910D 4911P 4910P Product Information Single Shade Introductory Kit Capsule Kit includes: 40 0.2 g capsules: 20 each of Body shades A2 and A3; Technique
Unique worldwide: Only a single composite for the entire range of tooth shades
 1000 Shades of White... all in 1 Syringe! WORLD TION A V O N IN The Future of Composites: Colour through Light From the Technology Pioneer. Unique worldwide: Only a single composite for the entire range
1000 Shades of White... all in 1 Syringe! WORLD TION A V O N IN The Future of Composites: Colour through Light From the Technology Pioneer. Unique worldwide: Only a single composite for the entire range
THE FIRST ALL CERAMIC-BASED FLOWABLE DIRECT RESTORATIVE
 THE FIRST ALL CERAMIC-BASED FLOWABLE DIRECT RESTORATIVE Admira Fusion Flow FLOWABLE NANO-ORMOCER DIRECT RESTORATIVE Admira Fusion / Admira Fusion Flow THE WORLD S FIRST ALL CERAMIC-BASED FLOWABLE DIRECT
THE FIRST ALL CERAMIC-BASED FLOWABLE DIRECT RESTORATIVE Admira Fusion Flow FLOWABLE NANO-ORMOCER DIRECT RESTORATIVE Admira Fusion / Admira Fusion Flow THE WORLD S FIRST ALL CERAMIC-BASED FLOWABLE DIRECT
Filtek Supreme Ultra Ultra Universal Restorative. One simple shading system. Endless possibilities.
 Filtek Supreme Ultra Ultra Universal Restorative One simple shading system. Endless possibilities. Filtek Supreme Ultra Ultra Universal Restorative Simplicity Exceptionally natural-looking using one shade
Filtek Supreme Ultra Ultra Universal Restorative One simple shading system. Endless possibilities. Filtek Supreme Ultra Ultra Universal Restorative Simplicity Exceptionally natural-looking using one shade
XP BOND IN SELF-CURE MODE USED FOR LUTING PORCELAIN RESTORATIONS:
 XP BOND IN SELF-CURE MODE USED FOR LUTING PORCELAIN RESTORATIONS: 2-YEAR RECALL MARCO FERRARI, IVANOVIC CONIGLIO 2, ELISA MAGNI 2, MARIA CRYSANTI CAGIDIACO Abstract Purpose: The aim of this clinical study
XP BOND IN SELF-CURE MODE USED FOR LUTING PORCELAIN RESTORATIONS: 2-YEAR RECALL MARCO FERRARI, IVANOVIC CONIGLIO 2, ELISA MAGNI 2, MARIA CRYSANTI CAGIDIACO Abstract Purpose: The aim of this clinical study
A Step-by-Step Approach to
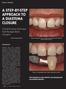 A Step-by-Step Approach to a Diastema Closure A Dual-Purpose Technique that Manages Black Triangles Marcos Vargas, DDS, MS Figure 1: Preoperative view of a patient who presented with a diastema between
A Step-by-Step Approach to a Diastema Closure A Dual-Purpose Technique that Manages Black Triangles Marcos Vargas, DDS, MS Figure 1: Preoperative view of a patient who presented with a diastema between
Fuji II LC. A Perfect Choice
 A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Resistance of Dental Amalgam, Z350 Composite Resin and Cention-N Restoration In Class II Cavity
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 4 Ver.1 April. (2018), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Resistance
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 4 Ver.1 April. (2018), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org Comparative Evaluation of Fracture Resistance
Admira Fusion. Scientific Compendium
 Scientific Compendium Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Technical Data Sheet and Indications... 3 2.1. Technical Data Sheet... 4 2.2. Indications... 5 3. Physical parameters for marginal integrity of...
Scientific Compendium Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Technical Data Sheet and Indications... 3 2.1. Technical Data Sheet... 4 2.2. Indications... 5 3. Physical parameters for marginal integrity of...
Filtek LS. Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System. Techniques and Results. Clinical Cases
 Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Techniques and Results Clinical Cases What a composite that shrinks less than 1% 1 can mean to your practice. When restoring a tooth, a dentist takes great
Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Techniques and Results Clinical Cases What a composite that shrinks less than 1% 1 can mean to your practice. When restoring a tooth, a dentist takes great
Filtek Supreme Ultra Flowable Restorative. technical product profile. Filtek
 Filtek Supreme Ultra technical product profile Filtek TM Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Product Description... 2 Indications for Use... 2 Composition... 2 Shades... 3 Fluorescence... 3 Background...
Filtek Supreme Ultra technical product profile Filtek TM Table of Contents Introduction... 1 Product Description... 2 Indications for Use... 2 Composition... 2 Shades... 3 Fluorescence... 3 Background...
XP Bond in Self-Cure Mode Used for Luting Porcelain Restorations: 4-year Recall
 RESEARCH ARTICLE XP Bond in Self-Cure Mode Used for Luting Porcelain Restorations: 4-year Recall 1 Marco Ferrari, 2 Maria Crysanti Cagidiaco, 3 Cecilia Goracci, 4 Antonella Polimeni 1 Professor and Chair,
RESEARCH ARTICLE XP Bond in Self-Cure Mode Used for Luting Porcelain Restorations: 4-year Recall 1 Marco Ferrari, 2 Maria Crysanti Cagidiaco, 3 Cecilia Goracci, 4 Antonella Polimeni 1 Professor and Chair,
Amaris BeAuTy COmPOse it!
 Beauty Compose it! Natural elegance Two simple steps layers like in nature brilliant results Easy to learn For several decades dentists have used an industry standard designed to facilitate communication
Beauty Compose it! Natural elegance Two simple steps layers like in nature brilliant results Easy to learn For several decades dentists have used an industry standard designed to facilitate communication
cellent adaptation and sculptability
 cellent adaptation and sculptability new: based on VITA is not a registered trademark of DENTSPLY International Inc. universal nano-ceramic restorative The unique SphereTEC technology takes handling comfort
cellent adaptation and sculptability new: based on VITA is not a registered trademark of DENTSPLY International Inc. universal nano-ceramic restorative The unique SphereTEC technology takes handling comfort
Review Article Effect of Recurring Procedure on the Surface Micro hardness Values of Different Composite Resins
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Review Article Effect of Recurring Procedure on the Surface Micro hardness Values of Different Composite Resins Ihab M. Moussa 1 *, Omar A. Alghamdi 2, Ahmed F. Alasraj
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Review Article Effect of Recurring Procedure on the Surface Micro hardness Values of Different Composite Resins Ihab M. Moussa 1 *, Omar A. Alghamdi 2, Ahmed F. Alasraj
Tetric Evo Line. A composite for every indication.
 Tetric Evo Line A composite for every indication. The Tetric Evo Line of Composites Efficient, reliable, esthetic A composite for every indication. Uniquely formulated to be used in any combination, the
Tetric Evo Line A composite for every indication. The Tetric Evo Line of Composites Efficient, reliable, esthetic A composite for every indication. Uniquely formulated to be used in any combination, the
Change the Way You Think About Bulk Fill Composites
 Change the Way You Think About Bulk Fill Composites Are you ready for bulk fill composites? Because the updated edition will blow you away! 1 Foreword by Dr. Joshua Austin, DDS As a general practitioner,
Change the Way You Think About Bulk Fill Composites Are you ready for bulk fill composites? Because the updated edition will blow you away! 1 Foreword by Dr. Joshua Austin, DDS As a general practitioner,
Principle Investigators: Overview of Study Methods: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz
 Principle Investigators: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz Overview of Study Methods: Subjects in need of Class I and/or Class II restorations were enrolled in two clinical trials conducted in US dental
Principle Investigators: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz Overview of Study Methods: Subjects in need of Class I and/or Class II restorations were enrolled in two clinical trials conducted in US dental
The world s first nano-ionomer and. a breakthrough in direct restoratives. Ketac N100. Light-Curing Nano-Ionomer Restorative
 The world s first nano-ionomer and a breakthrough in direct restoratives. Ketac N1 Light-Curing Nano-Ionomer Restorative Ketac N1 The first paste/paste RMGI restorative based on bonded nanofiller technology
The world s first nano-ionomer and a breakthrough in direct restoratives. Ketac N1 Light-Curing Nano-Ionomer Restorative Ketac N1 The first paste/paste RMGI restorative based on bonded nanofiller technology
DH220 Dental Materials
 DH220 Dental Materials Lecture #5 Prof. Lamanna RDH, MS Restorative Dentistry: Glass Ionomer Bird & Robinson p.740-741 I. Use Liner Base Luting agent Restorative material: Class III, V, & eroded/abraded
DH220 Dental Materials Lecture #5 Prof. Lamanna RDH, MS Restorative Dentistry: Glass Ionomer Bird & Robinson p.740-741 I. Use Liner Base Luting agent Restorative material: Class III, V, & eroded/abraded
1 di 5 28/07/
 1 di 5 28/07/2009 0.28 Issue Date: May 2008, Posted On: 5/30/2008 A Clear PVS Matrix Technique for the Placement of Posterior Direct Composites Gabriele Conte, DDS, and Luigi Cianconi, DMD, DDS Full-Text
1 di 5 28/07/2009 0.28 Issue Date: May 2008, Posted On: 5/30/2008 A Clear PVS Matrix Technique for the Placement of Posterior Direct Composites Gabriele Conte, DDS, and Luigi Cianconi, DMD, DDS Full-Text
INN VATION NSISTENCY ABRASI
 INN VATION C LOUR E-M DULUS C NSISTENCY ABRASI N Universal nano-hybrid restorative material Nano-technology: Small particles Big effect Dentists want composite restoratives that have a smooth, non-sticky
INN VATION C LOUR E-M DULUS C NSISTENCY ABRASI N Universal nano-hybrid restorative material Nano-technology: Small particles Big effect Dentists want composite restoratives that have a smooth, non-sticky
Glass ionomer cements in complex oral rehabilitations. A case report.
 Università degli Studi di Milano - Department of Technologies for the Health I.R.C.C.S Istituto Ortopedico Galeazzi Department of Odontology Director: Prof. Roberto Weinstein Glass ionomer cements in complex
Università degli Studi di Milano - Department of Technologies for the Health I.R.C.C.S Istituto Ortopedico Galeazzi Department of Odontology Director: Prof. Roberto Weinstein Glass ionomer cements in complex
Filling materials are used to replace missing parts of the tooth.
 Filling materials are used to replace missing parts of the tooth. 1- Dental caries. 2- Trauma. 3- Abrasion. Parts of teeth which require replacement by restorative materials vary in size of cavity, shape,
Filling materials are used to replace missing parts of the tooth. 1- Dental caries. 2- Trauma. 3- Abrasion. Parts of teeth which require replacement by restorative materials vary in size of cavity, shape,
All Ceramic Inlays - Coming of Age
 CASE REPORT All Ceramic Inlays - Coming of Age Ahmad Naeem 1 & Bashir Taseer 2 Quick Response Code ABSTRACT: In the past decade and a half there has been an explosion in the introduction of restorative
CASE REPORT All Ceramic Inlays - Coming of Age Ahmad Naeem 1 & Bashir Taseer 2 Quick Response Code ABSTRACT: In the past decade and a half there has been an explosion in the introduction of restorative
INN VATION NSISTENCY ABRASI
 INN VATION C LOUR E-M DULUS C NSISTENCY ABRASI N Best of 25, 26, 27 Prefered Product THE NANO-CLASSIC Nano-technology: Small particles Big effect Dentists want composite restoratives that have a smooth,
INN VATION C LOUR E-M DULUS C NSISTENCY ABRASI N Best of 25, 26, 27 Prefered Product THE NANO-CLASSIC Nano-technology: Small particles Big effect Dentists want composite restoratives that have a smooth,
General dentists in private practice place numerous
 PROACTIVE INTERVENTION DENTISTRY Incorporating Glass Ionomers into Everyday Dental Practice Todd Snyder, DDS, FAACD, FIADFE Introduction General dentists in private practice place numerous direct tooth
PROACTIVE INTERVENTION DENTISTRY Incorporating Glass Ionomers into Everyday Dental Practice Todd Snyder, DDS, FAACD, FIADFE Introduction General dentists in private practice place numerous direct tooth
CERASMART. The new leader in hybrid ceramic blocks
 The new leader in hybrid ceramic blocks Introducing, a new force absorbing hybrid ceramic block 20 µm Contains high density of ultra fine homogeneously-dispersed fillers in a highly cross-linked resin
The new leader in hybrid ceramic blocks Introducing, a new force absorbing hybrid ceramic block 20 µm Contains high density of ultra fine homogeneously-dispersed fillers in a highly cross-linked resin
UNIVERSAL SUBMICRON HYBRID COMPOSITE. BRILLIANT EverGlow. Enduring beauty made brilliant
 UNIVERSAL SUBMICRON HYBRID COMPOSITE BRILLIANT EverGlow Enduring beauty made brilliant ENDURING BEAUTY MADE BRILLIANT THE DESIRE TO HAVE AN EASY-TO-HANDLE, AESTHETIC AND DURABLE FILLING MATERIAL IS SIGNIFICANT.
UNIVERSAL SUBMICRON HYBRID COMPOSITE BRILLIANT EverGlow Enduring beauty made brilliant ENDURING BEAUTY MADE BRILLIANT THE DESIRE TO HAVE AN EASY-TO-HANDLE, AESTHETIC AND DURABLE FILLING MATERIAL IS SIGNIFICANT.
RESTORATION OF ENDODONTICALLY TREATED POSTERIOR TEETH WITH DIRECT AND INDIRECT COMPOSITE 6-MONTH RESULTS
 ISS: 1312-773X (Online) http://dx.doi.org/1.5272/jimab.3194.396 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 3, vol. 19, issue 4 RESTORATIO OF EDODOTICALLY TREATED POSTERIOR TEETH WITH DIRECT
ISS: 1312-773X (Online) http://dx.doi.org/1.5272/jimab.3194.396 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 3, vol. 19, issue 4 RESTORATIO OF EDODOTICALLY TREATED POSTERIOR TEETH WITH DIRECT
One Bulk Fill Restorative Technical Product Profile
 Filtek ne Bulk Fill ne Bulk Fill ne Bulk Fill 3 Table of Contents Introduction Introduction...3 Product Description...4 Product Features... 4 Indications for Use... 4 Composition... 5 Shades... 5 Background...6
Filtek ne Bulk Fill ne Bulk Fill ne Bulk Fill 3 Table of Contents Introduction Introduction...3 Product Description...4 Product Features... 4 Indications for Use... 4 Composition... 5 Shades... 5 Background...6
Filtek Supreme Ultra Ultra Universal Restorative. One simple shading system. Endless possibilities.
 Filtek Supreme Ultra Ultra Universal Restorative One simple shading system. Endless possibilities. Everyone has a shade, and you ve just found a simple way to match it. As a leader in groundbreaking restorative
Filtek Supreme Ultra Ultra Universal Restorative One simple shading system. Endless possibilities. Everyone has a shade, and you ve just found a simple way to match it. As a leader in groundbreaking restorative
Filtek. Supreme Plus Supreme. Universal Restorative. A collection of scientific results
 A collection of scientific results Plus Universal Restorative 3M ESPE AG, 3M ESPE Plaz 82229 Seefeld, Germany 3M ESPE Dental Products 3M Center Building 0275-02-SE-03 St. Paul, MN 551-1000 USA The charts
A collection of scientific results Plus Universal Restorative 3M ESPE AG, 3M ESPE Plaz 82229 Seefeld, Germany 3M ESPE Dental Products 3M Center Building 0275-02-SE-03 St. Paul, MN 551-1000 USA The charts
Complex esthetic and functional rehabilitation using glass-ceramic materials - long-term documentation of a restoration
 C L I N I C A L Complex esthetic and functional rehabilitation using glass-ceramic materials - long-term documentation of a restoration Daniel Edelhoff 1 and Oliver Brix 2 1 Prof. Dr Daniel Edelhoff, Munich
C L I N I C A L Complex esthetic and functional rehabilitation using glass-ceramic materials - long-term documentation of a restoration Daniel Edelhoff 1 and Oliver Brix 2 1 Prof. Dr Daniel Edelhoff, Munich
Optra. Innovative accessories for. simplified treatment procedures. Innovative Accessories
 Optra Innovative Accessories Innovative accessories for simplified treatment procedures OptraGate OptraDam Plus OptraSculpt Pad OptraSculpt OptraPol OptraFine OptraStick Simplified isolation relative isolation
Optra Innovative Accessories Innovative accessories for simplified treatment procedures OptraGate OptraDam Plus OptraSculpt Pad OptraSculpt OptraPol OptraFine OptraStick Simplified isolation relative isolation
shrink less than 1 %
 Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System The first composite to shrink less than 1 % Filtek Silorane The first posterior composite to shrink less than 1% 1 Any time you restore a patient
Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System The first composite to shrink less than 1 % Filtek Silorane The first posterior composite to shrink less than 1% 1 Any time you restore a patient
Adper Easy Bond. Self-Etch Adhesive. Technical Product Profile
 Adper Easy Bond Self-Etch Adhesive Technical Product Profile Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction... 4 Product Description... 4 Composition...5-8 Background... 5 Mechanism of Adhesion to Enamel
Adper Easy Bond Self-Etch Adhesive Technical Product Profile Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction... 4 Product Description... 4 Composition...5-8 Background... 5 Mechanism of Adhesion to Enamel
A collection of scientific results. Filtek. Supreme XT Supreme. Universal Restorative
 A collection of scientific results XT Universal Restorative InVivo Clinical Studies InVitro Research 2005 Introduction XT Within one year of introduction, 3M TM ESPE TM TM Universal Restorative became
A collection of scientific results XT Universal Restorative InVivo Clinical Studies InVitro Research 2005 Introduction XT Within one year of introduction, 3M TM ESPE TM TM Universal Restorative became
Lect. 3 operative Dr. Ameer AL-Ameedee
 Lect. 3 operative Dr. Ameer AL-Ameedee Direct composite restorations from Esthetic view: Modern resin materials have opened a huge door of opportunity for both dentists and patients by offering an esthetic
Lect. 3 operative Dr. Ameer AL-Ameedee Direct composite restorations from Esthetic view: Modern resin materials have opened a huge door of opportunity for both dentists and patients by offering an esthetic
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material
 Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
Product Information. Charisma Diamond Discover the next dimension of natural beauty. Giving a hand to oral health.
 Product Information Charisma Diamond Discover the next dimension of natural beauty. Giving a hand to oral health. The new Charisma Diamond Welcome to the next dimension of natural beauty. We commit our
Product Information Charisma Diamond Discover the next dimension of natural beauty. Giving a hand to oral health. The new Charisma Diamond Welcome to the next dimension of natural beauty. We commit our
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry. Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer)
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Heliomolar. Family. Success to the power of three Heliomolar, Heliomolar HB and Heliomolar Flow
 Family Success to the power of three Heliomolar, Heliomolar HB and Heliomolar Flow Restorations in anterior and posterior teeth featuring unmatched aesthetics. Clinically tried-and-tested dental restorative
Family Success to the power of three Heliomolar, Heliomolar HB and Heliomolar Flow Restorations in anterior and posterior teeth featuring unmatched aesthetics. Clinically tried-and-tested dental restorative
The Influence of One-step Polishing Systems on the Surface Roughness and Microhardness of Nanocomposites
 Operative Dentistry, 2008, 33-1, 44-50 The Influence of One-step Polishing Systems on the Surface Roughness and Microhardness of Nanocomposites Y Korkmaz E Ozel N Attar G Aksoy Clinical Relevance One-step
Operative Dentistry, 2008, 33-1, 44-50 The Influence of One-step Polishing Systems on the Surface Roughness and Microhardness of Nanocomposites Y Korkmaz E Ozel N Attar G Aksoy Clinical Relevance One-step
Filtek Supreme XTE Universal Restorative System. technical product profile. Filtek
 Universal Restorative System technical product profile Filtek TM Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction... 1 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION... 2 Indications for Use... 2 Composition... 2 Shades... 3 Fluorescence
Universal Restorative System technical product profile Filtek TM Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction... 1 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION... 2 Indications for Use... 2 Composition... 2 Shades... 3 Fluorescence
Achieving Excellence In Lustre
 Achieving Excellence In Lustre FAM Dr. Suhas Lele is a 1980 graduate of University of Mumbai. He is founder of Vision Invisible Dental academy. Vision Invisible envisage to train practicing dental professionals
Achieving Excellence In Lustre FAM Dr. Suhas Lele is a 1980 graduate of University of Mumbai. He is founder of Vision Invisible Dental academy. Vision Invisible envisage to train practicing dental professionals
esthetics efficiently produced
 Natural-looking esthetics efficiently produced Tetric Evo Composites Bulk Fill Bulk Fill 2005 Conventional composites 2007 2011 PATENTED LIG H T Ivocerin INITIAT O R Bulk Fill Bulk-fi ll composites 2015
Natural-looking esthetics efficiently produced Tetric Evo Composites Bulk Fill Bulk Fill 2005 Conventional composites 2007 2011 PATENTED LIG H T Ivocerin INITIAT O R Bulk Fill Bulk-fi ll composites 2015
values is of great interest.
 User Report Dr. Ralph Schönemann, May 21, 2008 There are numerous self-etchbonding systems on the market that sometimes differ very much from one another with regards to their chemical composition. It
User Report Dr. Ralph Schönemann, May 21, 2008 There are numerous self-etchbonding systems on the market that sometimes differ very much from one another with regards to their chemical composition. It
2011 Dental Materials Clinical Dentistry Survey
 2011 Dental Materials Clinical Dentistry Survey Nov 2011 Dental Evaluation and Consultation Service (DECS) 2011 Federal Dental Service Dental Materials Survey Because of advances in technology, dental
2011 Dental Materials Clinical Dentistry Survey Nov 2011 Dental Evaluation and Consultation Service (DECS) 2011 Federal Dental Service Dental Materials Survey Because of advances in technology, dental
G-COAT PLUS G-COAT PLUS GET THE BEST OF BOTH WORLDS WITH THE STROKE OF A BRUSH
 G-COAT PLUS BEAUTY BRAWN GET THE BEST OF BOTH WORLDS WITH THE STROKE OF A BRUSH 1 Introducing a Revolutionary new Coating G-COAT PLUS gives your restorations the Best of Both Worlds: A beautiful new finish
G-COAT PLUS BEAUTY BRAWN GET THE BEST OF BOTH WORLDS WITH THE STROKE OF A BRUSH 1 Introducing a Revolutionary new Coating G-COAT PLUS gives your restorations the Best of Both Worlds: A beautiful new finish
FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS
 FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS Glass Ionomers Solve Clinicians Quandaries Amalgam fillings have been around for almost two centuries,
FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS FIVE THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GLASS IONOMERS Glass Ionomers Solve Clinicians Quandaries Amalgam fillings have been around for almost two centuries,
ScienceDirect. Influence of Light-Curing Mode on the Mechanical Properties of Dental Resin Nanocomposites
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 69 ( 2014 ) 921 930 24th DAAAM International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation, 2013 Influence of Light-Curing
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 69 ( 2014 ) 921 930 24th DAAAM International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation, 2013 Influence of Light-Curing
Microleakage of Nanofilled Composite Resin Restorative Material
 Journal of Biomaterials and Nanobiotechnology, 2011, 2, 329-334 doi:10.4236/jbnb.2011.23040 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jbnb) 329 Microleakage of Nanofilled Composite Resin
Journal of Biomaterials and Nanobiotechnology, 2011, 2, 329-334 doi:10.4236/jbnb.2011.23040 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/jbnb) 329 Microleakage of Nanofilled Composite Resin
how to technique How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. Disadvantages. 1 Issue Full coverage crown. >>
 Issue 37 2013 How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. 1 Full coverage crown. >> Advantages. A full crown can splint all sections of the tooth together. 1 Disadvantages. 1 Encircles crown and acts
Issue 37 2013 How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. 1 Full coverage crown. >> Advantages. A full crown can splint all sections of the tooth together. 1 Disadvantages. 1 Encircles crown and acts
Alternatives to Amalgam
 Alternatives to Amalgam Introduction: Minemata convention on Mercury The Minamata Convention on Mercury is a global treaty, signed by the UK and over one hundred countries from all over the world in October
Alternatives to Amalgam Introduction: Minemata convention on Mercury The Minamata Convention on Mercury is a global treaty, signed by the UK and over one hundred countries from all over the world in October
Semi-Direct Composite Restorations- A Clinical Report
 MALAYSIAN DENTAL JOURNAL Semi-Direct Composite Restorations- A Clinical Report Berhanuddin Muhamad Asyraf, Tong Wah Lim Faculty of Dentistry, University Teknologi MARA, Malaysia ABSTRACT In nowadays world,
MALAYSIAN DENTAL JOURNAL Semi-Direct Composite Restorations- A Clinical Report Berhanuddin Muhamad Asyraf, Tong Wah Lim Faculty of Dentistry, University Teknologi MARA, Malaysia ABSTRACT In nowadays world,
Excellent temporaries
 Excellent temporaries User report on Structur 2 SC and Structur 2 Premium from VOCO T he use of acrylic and composite type materials for the provisionalisation of crown and bridge work has been well established
Excellent temporaries User report on Structur 2 SC and Structur 2 Premium from VOCO T he use of acrylic and composite type materials for the provisionalisation of crown and bridge work has been well established
Advances in the field of adhesive restorative biomaterials
 DEVELOPMENT OF A PROCESSED COMPOSITE RESIN RESTORATION: PREPARATION AND LABORATORY FABRICATION PART I DOUGLAS A. TERRY 1, KARL F. LEINFELDER 2 Advances in the field of adhesive restorative biomaterials
DEVELOPMENT OF A PROCESSED COMPOSITE RESIN RESTORATION: PREPARATION AND LABORATORY FABRICATION PART I DOUGLAS A. TERRY 1, KARL F. LEINFELDER 2 Advances in the field of adhesive restorative biomaterials
It s more than a denture, It s a smile. IVOCLAR VIVADENT REMOVABLE. More than dentures. Tooth Line Portfolio
 It s more than a denture, It s a smile. IVOCLAR VIVADENT REMOVABLE More than dentures. Tooth Line Portfolio 9458.indd 1 12/8/16 10:28 AM Ivoclar Vivadent Removable Master Class Collection The ultimate
It s more than a denture, It s a smile. IVOCLAR VIVADENT REMOVABLE More than dentures. Tooth Line Portfolio 9458.indd 1 12/8/16 10:28 AM Ivoclar Vivadent Removable Master Class Collection The ultimate
and get a Pentamix TM Lite free *
 Offers valid until 31st October 2014 Spend, Spend, Spend! Spend 450 on any 3M ESPE products and get a Pentamix TM Lite free * Order must include 1 Imprint TM 4 refill Download the free Layar app get.layar.com
Offers valid until 31st October 2014 Spend, Spend, Spend! Spend 450 on any 3M ESPE products and get a Pentamix TM Lite free * Order must include 1 Imprint TM 4 refill Download the free Layar app get.layar.com
Gingiva Solution SR Phonares II, IvoBase, SR Nexco
 Gingiva Solution SR Phonares II, IvoBase, SR Nexco Preface 5 Framework design 6 Framework preparation 8 Finishing of the denture base 10 Gingival modification 12 Mobile mucosa 14 Immobile mucosa 16 Lip
Gingiva Solution SR Phonares II, IvoBase, SR Nexco Preface 5 Framework design 6 Framework preparation 8 Finishing of the denture base 10 Gingival modification 12 Mobile mucosa 14 Immobile mucosa 16 Lip
riva helping you help your patients
 riva helping you help your patients what is a glass ionomer? how will a dentist benefit from using glass ionomers? how will a patient benefit from their glass ionomer? Glass ionomer is the generic name
riva helping you help your patients what is a glass ionomer? how will a dentist benefit from using glass ionomers? how will a patient benefit from their glass ionomer? Glass ionomer is the generic name
Press Release. Press Contact. The concept for Class II restoration Delicate preparation, rapid procedure and reliable results
 Press Release The concept for Class II restoration Delicate preparation, rapid procedure and reliable results by Dr. Arzu Tuna and Dr. Umut Baysal, Attendorn, Germany Composite restorations have always
Press Release The concept for Class II restoration Delicate preparation, rapid procedure and reliable results by Dr. Arzu Tuna and Dr. Umut Baysal, Attendorn, Germany Composite restorations have always
SHOFU BLOCK & DISK CAD/CAM CERAMIC-BASED RESTORATIVE. Visit or call mm x 12mm x 16mm. 98mm x 14mm. 12mm x 14mm x 18mm
 SHOFU BLOCK & DISK CAD/CAM CERAMIC-BASED RESTORATIVE 1mm x 12mm x 16mm 12mm x 14mm x 18mm 98mm x 14mm Visit www.shofu.com or call 8.827.4638 Created through a rigorous manufacturing process, Shofu Blocks
SHOFU BLOCK & DISK CAD/CAM CERAMIC-BASED RESTORATIVE 1mm x 12mm x 16mm 12mm x 14mm x 18mm 98mm x 14mm Visit www.shofu.com or call 8.827.4638 Created through a rigorous manufacturing process, Shofu Blocks
Glass Ionomers. Ingredients. acid. Glass Ionomers
 Glass Ionomers Ingredients The glass should contain strontium too! (This is important) Polyacrylic acid acid Calcium fluoroalumino silicate glass base Glass Ionomers Bioavailable once called bioac/ve Inhibits
Glass Ionomers Ingredients The glass should contain strontium too! (This is important) Polyacrylic acid acid Calcium fluoroalumino silicate glass base Glass Ionomers Bioavailable once called bioac/ve Inhibits
Summary of in-vivo studies. RelyX. Unicem. Self-Adhesive Universal Resin Cement. Clinical studies
 Summary of in-vivo studies RelyX TM Unicem Clinical studies 2003 2006 Table of contents Restorations after 4 years in-vivo................................. 4 Full ceramic inlays and onlays after 12 months
Summary of in-vivo studies RelyX TM Unicem Clinical studies 2003 2006 Table of contents Restorations after 4 years in-vivo................................. 4 Full ceramic inlays and onlays after 12 months
Clinical report. Drs Paul and Alexandre MIARA and F. CONNOLLY COMPOSITE POSTERIOR FILLINGS. How to control. layering? 8 - Dentoscope n 124
 COMPOSITE POSTERIOR FILLINGS How to control layering? 8 - Dentoscope n 124 CV FLASH Dr Paul MIARA Dental surgeon Dr Alexandre MIARA Dental surgeon Dr F. CONNOLLY Dental surgeon Thanks to continuous improvements
COMPOSITE POSTERIOR FILLINGS How to control layering? 8 - Dentoscope n 124 CV FLASH Dr Paul MIARA Dental surgeon Dr Alexandre MIARA Dental surgeon Dr F. CONNOLLY Dental surgeon Thanks to continuous improvements
Finishing and Polishing Procedures of Composite Restorations by Saudi Dentists: A Cross-sectional Study
 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1381 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Finishing and Polishing Procedures of Composite Restorations by Saudi Dentists: A Cross-sectional Study Mohammed Ali AlQarni, Rafi A Togoo, Ibrahim Al Shahrani,
10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1381 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Finishing and Polishing Procedures of Composite Restorations by Saudi Dentists: A Cross-sectional Study Mohammed Ali AlQarni, Rafi A Togoo, Ibrahim Al Shahrani,
