General Health Questionnaire-28: psychometric evaluation of the Slovak version
|
|
|
- Lee Bishop
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 2 General Health Questionnaire-28: psychometric evaluation of the Slovak version Abstract Iveta Nagyova, Boudien Krol, Angela Szilasiova, Roy E. Stewart, Jitse P. van Dijk and Wim J.A. van den Heuvel Studia Psychologica 2000,42,4: The EUropean Research on Incapacitating DIseases and Social Support (EURIDISS) is an international longitudinal study focusing on patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). It elaborates on the impact of the chronic disease on patients daily lives. Rheumatoid arthritis, social support and quality of life are the central concepts within the project. Goldberg and Hillier s 28-item scaled version of the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-28) has been used to measure the psychological aspect of quality of life. The scale is frequently used in Western Europe, but rarely in Central and Eastern Europe. Slovakia, a Central European country, is joining the EURIDISS project since Therefore, the question emerged whether the psychometric properties of the Slovak version of the GHQ-28 are adequate in order to measure the psychological component of quality of life. In the present study the reliability and the validity of the GHQ-28 in Slovak RA-patients are evaluated and the outcomes are discussed in the light of Western European (WE) results. The study examines the internal consistency and the factor structure of the instrument. In general, as far as the reliability figures and the intercorrelations of the scales are concerned, the results indicate that the psychometric qualities of the GHQ-28 in Slovakia are satisfactory. However, when taking into consideration the factor structure of the scale, as pointed out by Principal Component Analysis, this reveals several differences. At least six out of the twentyeight items appear to fit better to another subscale than originally was found. Especially, general health ratings, such as felt recently ill, initially attributed to subscale somatic symptoms, appear to be more closely associated with subscale anxiety/insomnia. More research on GHQ-28 in Central European countries is therefore recommended. 33
2 Introduction By the end of 1990 started a longitudinal study on Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) patients, the EURIDISS project. The study concentrates on the course and consequences of this chronic disease on patients everyday lives. The research project describes the way people cope with their incapacitating disease and the role of psychosocial factors in this coping process. The study started in Western Europe, and in 1994 it was expanded to Central Europe, and in particular to Slovakia. Currently, the project participants are France, Germany, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, Norway, Slovakia and Sweden. Quality of life is considered as an important outcome variable within the project (EURIDISS 1990). According to the literature the concept quality of life comprises several dimensions (Spilker 1990, Krol et al. 1993, Doeglas 2000). The most commonly evaluated are the physical, the psychological and the social dimensions of quality of life. The physical dimension refers to the patient s physical condition as a consequence of the disease or the treatment. The social aspect reflects the patient s satisfaction with participation in social roles and social activities. The psychological aspect refers to the emotional evaluation of a particular situation and is frequently operationalized as anxiety and depression (Blalock et al. 1989, Pincus and Callahan 1993, Krol et al. 1993). Within the EURIDISS study the psychological component of quality of life is considered as an outcome measure. In order to assess the psychological aspect of quality of life the 28-item version of the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-28) can be used. The General Health Questionnaire-28 is frequently used as an indicator of psychological well-being and this latter construct resembles the psychological dimension of quality of life (Goldberg and Hillier 1979, Sanderman and Stewart 1990, EURIDISS 1990, Krol et al. 1994). The GHQ as a self-report instrument was designed for detection and assessment of individuals with an increased likelihood of current psychiatric disorder (Goldberg and Hillier 1979, McDowell and Newell 1987, Goldberg and Williams 1988). The original questionnaire consists of 60 items from which shorter versions of 30, 28, 20 and 12 items were developed. The GHQ-28 scale was derived by factor analysis of the original 60-item version and prepared mainly for research purposes. However, as already mentioned, the scale is often used as a measure of psychological well-being also (Goldberg and Williams 1988, EURIDISS 1990, Krol et al. 1994). The GHQ-28 incorporates four subscales: somatic symptoms, anxiety and insomnia, social dysfunction, and severe depression. The existence of four subscales permits analyses within the subscales and this is an additional advantage of the GHQ-28 scale over the other versions (Goldberg and Hillier 1979, Bowling 1992). Although the GHQ was developed in the United Kingdom during the 1960s and 1970s, there have consequently been many applications in other countries 34 CHAPTER 2
3 as well. In 1988 Goldberg and Williams reported that the GHQ had been translated into about 38 languages, and over 50 validity studies have been published. However, these validity studies were conducted mainly in Western European countries and the USA (Banks 1983, Goldberg and Williams 1988, Sanderman and Stewart 1990, Krol et al. 1994). Some publications exist which refer to the utilisation of the GHQ in Central and Eastern Europe (CEE), particularly in Belarus, Croatia, Hungary, Poland, and Yugoslavia (Radovanovic and Erik 1983, Radovanovic et al. 1988, Erik et al. 1988, Sprusinska 1994, Rathner et al. 1995, Kulenovic et al. 1995, Havenaar et al. 1996a, Havenaar et al. 1996b). Nevertheless, the number of published articles is remarkably small, i.e. only one or two publications from each country. Moreover, apart from Yugoslavia and Belarus the studies are not specifically directed at the psychometric evaluation of the GHQ scales (Radovanovic and Erik 1983, Radovanovic et al. 1988, Havenaar et al. 1996a). In addition, only one of the above-mentioned CEE publications deals with the 28-item version of the GHQ (Sprusinska 1994). On the other hand, as was stated earlier, the GHQ-28 is a frequently used measure of psychological well-being in Western Europe and it has proven to be a valid and reliable instrument for comparisons among patients from different countries (Goldberg and Williams 1988, Krol et al. 1994). Since Slovakia is one of the participating countries of the earlier mentioned international research project (EURIDISS), and since there are nearly no GHQ psychometric studies from Central and Eastern Europe, the question about the psychometric properties of the Slovak version of the GHQ-28 emerged. The purpose of the present study was to determine whether the GHQ-28 can be applied as a measure of psychological well-being also in Central European country or whether there are some differences. The present study is thus directed to the evaluation of the validity and reliability of the GHQ-28 in Slovakia. Method Procedure and sample The results of the present investigation are based on the first wave data of the EURIDISS project. The study with its longitudinal design follows recently diagnosed RA-patients during a four-year-period. The data from the patients are obtained once a year. The total sample in the present study consists of 160 RA-patients from Slovakia, selected according to the international research protocol (EURIDISS, 1990). Due to missing data 12 patients were excluded. Out of the remaining 148 respondents 124 were women and 24 men. Seventy-eight percent of the patients was married and 14% was living alone. The mean age of the respondents was 48.2 years (range 22-70) and the mean disease duration was 22.8 months (range 0-55). 35
4 Between males and females one significant (p.05) difference was found on demographic variables, the percentage of married patients in males was significantly higher than in females. Table 1 illustrates additional demographic characteristics of the Slovak and Western European EURIDISS samples. Table 1 Demographic characteristics of the EURIDISS samples Slovakia France The Netherlands Norway Sweden Number of subjects Age in years (SD) 48.2 (12.0) 53.2 (11.3) 53.5 (11.9) 51.5 (13.1) 47.8 (12.4) Females (%) Married (%) Living alone (%) Disease duration in months (SD) 22.8 (16.0) 31.2 (16.8) 22.5 (14.4) 32.4 (12.0) 58.8 (55.2) Note: The source of Western European result: Krol et al Measures In the GHQ-28 the respondent is asked to compare his recent psychological state with his usual state. For each item four answer possibilities are available (1-not at all, 2-no more than usual, 3-rather more than usual, 4- much more than usual). In the study the Likert scoring procedure (1,2,3,4) is applied and the total scale score ranges from 28 to 112. The higher the score the poorer the psychological well-being of the patient. Statistical methods In the following sections relationships between demographics and the level of psychological well-being will be presented. Then, the subscale correlations, internal consistency figures, and the results from Principal Component Analysis (PCA) follow. The analyses were performed by using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences, SPSS/PC+ (Nie at al. 1975). Results Demographic variables and the GHQ-28 In the sample no relation was found between age and disease duration on the one hand and psychological well-being as measured by the GHQ-28 on the other hand. Generally, on the GHQ-28 no significant differences were found between the married versus not married patients, neither between patients living alone versus not alone. Considering gender, men 36 CHAPTER 2
5 differed from women on the subscale somatic symptoms, women scored significantly higher. This indicates that women experience significantly more somatic symptoms than men do. Intercorrelations between the subscales and the GHQ-28 total scale Table 2 illustrates the correlation coefficients between the GHQ-28 subscales and the total scale. Table 2 Intercorrelations between the GHQ-28 subscales and total scale in the Slovak sample Somatic symptoms Anxiety and insomnia Social dysfunction Severe depression Somatic symptoms - Anxiety/insomnia.62 - Social dysfunction Severe depression GHQ-28 total scale Note: p.001 for all correlation coefficients The intercorrelations between the subscales are rather high, with the mean correlation being about 0.52 (range ). This outcome implies that the subscales are not independent of each other. The correlation coefficients between the subscales and the GHQ-28 total scale, ranging from 0.75 (severe depression) to 0.89 (anxiety and insomnia), indicate the unidimensionality of the scale. The correlation coefficient between the subscale anxiety/insomnia and the GHQ-28 total scale is similar to figures previously reported by Goldberg and Hillier (1979) and support the assumption that anxiety is a core phenomenon of psychological distress. Reliability The internal consistency figures, inter-item correlations, means and standard deviations of the Slovak version of the GHQ-28 in comparison with earlier findings are depicted in Table 3. In the Slovak sample the Cronbach s alpha coefficients of reliability of the subscales vary around 0.82 and the internal consistency of the total scale is The mean inter-item correlations, which can be regarded as an indicator of the homogeneity of the scale, were also computed. In the Slovak sample the mean inter-item correlations are rather high. The highest is for subscale anxiety/insomnia (i-i=0.50). Based on these figures it can be concluded that the Slovak results are comparable with those from Western European countries. 37
6 Table 3 Reliability figures, means, and standard deviations (SD) of the GHQ-28 total scale and subscales in Slovakia and Western European countries participating within the EURIDISS Somatic symptoms Anxiety and insomnia Social dysfunction Severe depression GHQ-28 total scale Slovakia (N=148) Cronbach s alpha i-i correlation Mean SD France (N=115) Cronbach s alpha i-i correlation Mean SD The Netherlands (N=290) Cronbach s alpha i-i correlation Mean SD Norway (N=184) Cronbach s alpha i-i correlation Mean SD Sweden (N=98) Cronbach s alpha i-i correlation Mean SD Note 1: i-i means inter-item correlation Note 2: The source of Western European result: Krol et al Principal component analysis In order to examine the empirical validity of the GHQ-28, Principal Component Analysis (PCA) with varimax rotation and a forced four-factor solution was carried out. PCA is a procedure, which explains the variables by reducing them to a limited number of components. Summarising the variables can be more technically expressed in terms of variance accounted for (Kiers, 1990). As was mentioned earlier, the 28 items of the GHQ total scale can be divided into four subscales (7 items in each). In the present 38 CHAPTER 2
7 study the four factors explained 54% of the variance. When comparing the percentage of explained variance in Slovakia with findings from the Western European countries participating within the EURIDISS, the Slovak figures are slightly lower (Table 4), but are in correspondence with results of the original scale (Goldberg and Hillier 1979). Table 4 Percentages of explained variance by separate PCA in the five countries participating within the EURIDISS Number of components Slovakia (N=148) France (N=115) The Netherlands (N=290) Norway (N=181) Sweden (N=93) Note: The source of Western European result: Krol et al Table 5 presents loadings (item-component correlations) of the 28 items in the sample as obtained by PCA. Below, the factorial matrix (Table 5) will be discussed in more detail in terms of incorrect or suspect items. An item is considered incorrect, if the highest loading is not on the predicted component, but on another, not predicted component. The item is considered suspect, when it contains a high loading on the predicted component, together with a relatively high loading on another, not predicted component (Krol et al. 1994). By performing PCA we tried to retrieve the original factor structure of the scale which was found by Goldberg and Hillier (1979). In Slovakia the factor structure of the scale reveals some differences. The items of the subscale somatic symptoms have a tendency to fall apart in two dimensions. The first four items (1-feeling well, 2-feling in need of a good tonic, 3-run down, 4-feeling ill) contain low loadings on the predicted component, i.e. subscale somatic symptoms and high loadings on a not predicted component, i.e. subscale anxiety/insomnia. The remaining three items of the original subscale somatic symptoms (items: 5, 6, and 7 - headaches and hot or cold spells) contain high loadings on the predicted component, i.e. subscale somatic symptoms. Apart from the above-mentioned four items, two other items are incorrect (items: 10-felt under strain, and 13-found everything getting on top of you). They contain high loadings on subscale severe depression instead of subscale anxiety/ insomnia. Besides, two items are suspect since they contain high loadings 39
8 Table 5 Loadings (item-component correlations) of the 28 items in the Slovak sample (N=148) as obtained by PCA Components Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Item Note: Items 1-7 somatic symptoms, 8-14 anxiety/insomnia, social dysfunction, severe depression 40 CHAPTER 2
9 on the predicted component, together with a relatively high loading on another, not predicted component (items: 12-getting scared or panicky for no good reason, 21-able to enjoy your normal day-to-day activities). Item 12 have high loading on subscale social dysfunctioning and item 21 on subscale severe depression. Finally, item 15 is questionable since it has low loadings on each of the components (item 15: Have you recently been managing to keep yourself busy and occupied ). For more detailed information on items of the GHQ-28 see the appendix. Discussion The present study was directed to the evaluation of the GHQ-28 scale in RA-patients from Slovakia. The objective of the study was to investigate whether the Slovak version of the scale has satisfactory psychometric properties. The question seems to be relevant when considering the scarce studies about the psychometric qualities of this research instrument in Central and Eastern Europe. The rather strong correlations between the subscales, indicating the inter-relatedness of the subscales, are in line with existing publications on the GHQ-28 (Goldberg and Williams 1988, Sanderman and Stewart 1990, Krol et al. 1994). The same holds true for the high correlations between the subscales and the GHQ-28 total scale, indicating the unidimensionality of the instrument (Goldberg and Hillier 1979). The discrepancies on the scoring of the GHQ-28 scale due to gender were also not surprising. According to Goldberg and Williams (1988) the scoring on the GHQ-28 is not influenced by age, marital status and living situation, as opposed to gender. Women usually score higher on the GHQ-28 scale than men (Goldberg and Williams 1988). So far, the results of the correlational analyses and the figures of internal consistency support the presumption about adequate psychometric properties of the scale in Slovakia. PCA was carried out in order to re-examine the factor structure of the scale. The four-factor solution accounted for 54% of the variance. These results are satisfactory and comparable to those of the original scale (Goldberg and Hillier 1979). However, a more detailed inspection of the item-scale correlations (loadings) does present several differences. The items of the subscale somatic symptoms have a tendency to fall apart in two dimensions. The first four questions, which may be described as general illness ratings, contain high loadings on the not predicted component, i.e. subscale anxiety/insomnia, whereas the questions five, six and seven (headaches and hot or cold spells) have high loadings on the predicted component, i.e. subscale somatic symptoms. A number of considerations may explain these results. To a certain extent the higher percentage of females in the sample may account for this finding. Women have a 41
10 tendency to score significantly higher on the subscale somatic symptoms of the GHQ-28 (Goldberg and Williams 1988, Krol et al. 1994). However, the separate PCAs for men and women do not confirm this consideration. Another explanation might be the possible criterion contamination, i.e. the fact that the scale is used in RA-patients with a higher level of somatic symptoms because of the disease. Also the findings of Sanderman and Stewart (1990) with the Dutch version of the GHQ-28 are in line with these considerations. According to their results two out of the first four items of the subscale somatic symptoms are incorrect (items 2 and 3) with high loadings on the subscale anxiety/insomnia and one is suspect (item 1) with high loading on the subscale social dysfunctioning. However, the criterion contamination explanation seems to be not satisfactory since, interestingly, similar results were found when the Turkish version of the GHQ-28 in a community sample of Turkish speaking emigrants in Melbourne was evaluated:... and general illness ratings, such as not feeling perfectly well were not uniquely associated with somatic symptoms (Stuart et al. 1993, p.274). All in all, the results concerning the validity and reliability of the scale are encouraging; however the question associated with subscales somatic symptoms and anxiety/insomnia still has to be answered. More detailed investigations, especially concentrating on the problem with the first subscale (somatic symptoms) may shed more light on this frequently registered difficulty. References Banks M. Validation of the General Health Questionnaire in a young community sample. Psychol Med 1983;13: Bowling A. Measuring health: A review of quality of life measurement scales. Open University Press: Milton Keynes. Philadelphia, Blalock SJ, Devellis RF, Brown GK, Wallston KA. Validity of the centre for epidemiological studies depression scale in arthritis populations. Arthritis Rheum 1989;32: Doeglas D. Functional ability, social support and quality of life: A longitudinal study in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. PhD Thesis. University of Groningen, The Netherlands, Eric L., Radovanovic Z, Jevremovic I, Marinkovic J. Psychiatric disorders and selected variables among medical students in Belgrade (Yugoslavia). Soc Sci Med 1988;27: European Research on Incapacitating Diseases and Social Support (EURIDISS). Int J Health Sci 1990;1: CHAPTER 2
11 Goldberg DP, Hillier VF. A scaled version of the General Health Questionnaire. Psychol Med 1979;9: Goldberg D, Williams P. A user s guide to the General Health Questionnaire. NFER NELSON Publishing company Ltd. Windsor, Havenaar JM, Poelijoe NW, Kasyanenko AP, Bout van den J. Screening for psychiatric disorders in an area affected by the Chernobyl disaster: The reliability and validity of the three psychiatric screening questionnaires in Belarus. Psychol Med 1996a;26: Havenaar JM, Brink van den W, Bout van den J, Kasyanenko AP, Poelijoe NW, Wholfarth T, Meijler Iljina LI. Mental health problems in the Gomel region (Belarus): An analysis of risk factors in an affected area by the Chernobyl disaster. Psychol Med 1996b;26: Kiers HAL. User s manual SCA: A program for simultaneous scale analysis of variables measured in two or more populations. ProGAMMA, Groningen, The Netherlands, Krol B, Sanderman R, Moum T, Suurmeijer T, Doeglas D, Krijnen W, Robinson I, Briançon S, Bjelle A, Heuvel van den W. A comparison of the General Health Questionnaire-28 between patients with rheumatoid arthritis from The Netherlands, France, Sweden, and Norway. Eur J Psychol Assess 1994;10: Krol B, Sanderman R, Suurmeijer T. Social support, rheumatoid arthritis and quality of life: concept, measurement and research. Patient Educ Couns 1993;20: Kulenovic M, Kusevic Z, Grba S. Factor analysis of the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12) on the sample of the unemployed and students. Collegium Anthropologicum 1995;19: McDowell I, Newell C. Measuring Health. New York, Oxford: Oxford University Press, Nie N, Hull CH, Jenkins JG, Steibrenner K, Bent DH. Statistical Package for the Social Sciences. (2nd ed.) New York: McGraw Hill, Pincus T, Callahan LF. Depression scale in rheumatoid arthritis: criterion contamination of patient responses. Patient Educ Couns 1993;20: Radovanovic Z, Eric LJ. Validity of the General Health Questionnaire in a Yugoslav student population. Psychol Med 1983;13: Radovanovic Z, Eric L, Jevremovic I. The effect of re-testing on the validity of the General Health Questionnaire. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 1988;23:36-8. Rathner G, Tury F, Szabo P, Geyer M, Rumpold G, Forgacs A, Sollner W, Plottner G. Prevalence of eating disorders and minor psychiatric morbidity 43
12 in central Europe before the political changes in 1989: A cross-cultural study. Psychol Med 1995;25: Sanderman R, Stewart R. The assessment of psychological distress: Psychometric properties of the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ). Int J Health Sci 1990;1: Sprusinska E. The Family APGAR Index: study on relationship between family function, social support, global stress and mental health perception in women. Int J Occup Med and Env Health 1994;7: Spilker B. Quality of Life Assessments in Clinical Trials. Raven Press, Ltd. New York, Stuart GW, Klimidis S, Minas IH, Tuncer C. The factor structure of the Turkish version of the General Health Questionnaire. Int J Soc Psychiatr 1993;39: CHAPTER 2
13 Appendix The 28-items of the scaled version of the GENERAL HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE (Goldberg and Hillier 1979) HAVE YOU RECENTLY: 1. Been feeling perfectly well and in good health? 2. Been feeling in need of a good tonic? 3. Been feeling run down and out of sorts? 4. Felt that you are ill? 5. Been getting any pains in your head? 6. Been getting a feeling of tightness or pressure in your head? 7. Been having hot or cold spells? 8. Lost much sleep over worry? 9. Had difficulty in staying asleep once you are off? 10. Felt constantly under strain? 11. Been getting edgy and bad-tempered? 12. Been getting scared or panicky for no good reason? 13. Found everything getting on top of you? 14. Been feeling nervous and strung-up all the time? 15. Been managing to keep yourself busy and occupied? 16. Been taking longer over the things you do? 17. Felt on the whole you were doing things well? 18. Been satisfied with the way you ve carried out your task? 19. Felt that you are playing a useful part in things? 20. Felt capable of making decisions about things? 21. Been able to enjoy your normal day-to-day activities? 22. Been thinking of yourself as a worthless person? 23. Felt that life is entirely hopeless? 24. Felt that life isn t worth living? 25. Thought of the possibility that you might make away with yourself? 26. Found at times you couldn t do anything because your nerves were too bad? 27. Found yourself wishing you were dead and away from it all? 28. Found that the idea of taking your own life kept coming into your mind? 45
14
General Health Questionnaire (GHQ12 & GHQ28): psychometric properties and factor structure of the scales in a Turkish primary care sample
 Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol (1997) 32:327-331 9 Springer-Verlag 1997 C. Kdlg-M. Rezaki. B. Rezaki" I. Kaplan" G. 0zgen A. Sa~duyu. M.O. 0ztiirk General Health Questionnaire (GHQ12 & GHQ28): psychometric
Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol (1997) 32:327-331 9 Springer-Verlag 1997 C. Kdlg-M. Rezaki. B. Rezaki" I. Kaplan" G. 0zgen A. Sa~duyu. M.O. 0ztiirk General Health Questionnaire (GHQ12 & GHQ28): psychometric
Citation for published version (APA): Sarkova, M. (2010). Psychological well-being and self-esteem in Slovak adolescents Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Psychological well-being and self-esteem in Slovak adolescents Sarkova, Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
University of Groningen Psychological well-being and self-esteem in Slovak adolescents Sarkova, Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
The impact of pain on psychological well-being in rheumatoid arthritis: the mediating effects of self-esteem and adjustment to disease
 Patient Education and Counseling 58 (2005) 55 62 www.elsevier.com/locate/pateducou The impact of pain on psychological well-being in rheumatoid arthritis: the mediating effects of self-esteem and adjustment
Patient Education and Counseling 58 (2005) 55 62 www.elsevier.com/locate/pateducou The impact of pain on psychological well-being in rheumatoid arthritis: the mediating effects of self-esteem and adjustment
Self-Rated Health and Quality of Life in Slovak Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Nagyova, Iveta
 University of Groningen Self-Rated Health and Quality of Life in Slovak Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Nagyova, Iveta IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
University of Groningen Self-Rated Health and Quality of Life in Slovak Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Nagyova, Iveta IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF)
Disability, Social Support, and Distress in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from a Thirteen- Year Prospective Study
 Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 55, No. 5, October 15, 2006, pp 736 744 DOI 10.1002/art.22231 2006, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Disability, Social Support,
Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 55, No. 5, October 15, 2006, pp 736 744 DOI 10.1002/art.22231 2006, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Disability, Social Support,
Strengthening policies through good information
 1 Strengthening policies through good information FPS PUBLIC HEALTH, SAFETY OF THE FOOD CHAIN AND ENVIRONMENT Belgium Pol Gerits, PH. D. Psychosocial Care Service Department Manager With the kind collaboration
1 Strengthening policies through good information FPS PUBLIC HEALTH, SAFETY OF THE FOOD CHAIN AND ENVIRONMENT Belgium Pol Gerits, PH. D. Psychosocial Care Service Department Manager With the kind collaboration
Factorial Validity and Reliability of 12 items General Health Questionnaire in a Bhutanese Population. Tshoki Zangmo *
 Factorial Validity and Reliability of 12 items General Health Questionnaire in a Bhutanese Population Tshoki Zangmo * Abstract The aim of this study is to test the factorial structure and the internal
Factorial Validity and Reliability of 12 items General Health Questionnaire in a Bhutanese Population Tshoki Zangmo * Abstract The aim of this study is to test the factorial structure and the internal
Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis Scale (QOL-RA Scale)
 Advances in Medical Sciences Vol. 54(1) 2009 pp 27-31 DOI: 10.2478/v10039-009-0012-9 Medical University of Bialystok, Poland Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis
Advances in Medical Sciences Vol. 54(1) 2009 pp 27-31 DOI: 10.2478/v10039-009-0012-9 Medical University of Bialystok, Poland Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis
Citation for published version (APA): Sarkova, M. (2010). Psychological well-being and self-esteem in Slovak adolescents Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Psychological well-being and self-esteem in Slovak adolescents Sarkova, Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
University of Groningen Psychological well-being and self-esteem in Slovak adolescents Sarkova, Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
Measurement of Psychopathology in Populations. William W. Eaton, PhD Johns Hopkins University
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License. Your use of this material constitutes acceptance of that license and the conditions of use of materials on this
Mental Health Status of Female Workers in Private Apparel Manufacturing Industry in Bangalore City, Karnataka, India
 1893 Mental Health Status of Female Workers in Private Apparel Manufacturing Industry in Bangalore City, Karnataka, India Deepthi Shanbhag 1*, Bobby Joseph 2 1 Assistant Professor; Department of Community
1893 Mental Health Status of Female Workers in Private Apparel Manufacturing Industry in Bangalore City, Karnataka, India Deepthi Shanbhag 1*, Bobby Joseph 2 1 Assistant Professor; Department of Community
Health Behavioral Patterns Associated with Psychologic Distress Among Middle-Aged Korean Women
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Health Behavioral Patterns Associated with Psychologic Distress Among Middle-Aged Korean Women Hye-Sook Shin 1, PhD, RN, Jia Lee 2 *, PhD, RN, Kyung-Hee Lee 3, PhD, RN, Young-A Song 4,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Health Behavioral Patterns Associated with Psychologic Distress Among Middle-Aged Korean Women Hye-Sook Shin 1, PhD, RN, Jia Lee 2 *, PhD, RN, Kyung-Hee Lee 3, PhD, RN, Young-A Song 4,
Factor Structure, Validity and Reliability of the Persian version of the Acceptance and Action Questionnaire (AAQ-II-7)
 International Journal of Education and Research Vol. 2 No. 9 September 2014 Factor Structure, Validity and Reliability of the Persian version of the Acceptance and Action Questionnaire (AAQ-II-7) Nezamaddin
International Journal of Education and Research Vol. 2 No. 9 September 2014 Factor Structure, Validity and Reliability of the Persian version of the Acceptance and Action Questionnaire (AAQ-II-7) Nezamaddin
THE VALIDITY OF TWO MALAY VERSIONS OF THE GENERAL HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE (GHQ) IN DETECTING DISTRESSED MEDICAL STUDENTS. Muhamad Saiful Bahri Yusoff
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE VALIDITY OF TWO MALAY VERSIONS OF THE GENERAL HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE (GHQ) IN DETECTING DISTRESSED MEDICAL STUDENTS. Muhamad Saiful Bahri Yusoff Medical Education Department of School
ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE VALIDITY OF TWO MALAY VERSIONS OF THE GENERAL HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE (GHQ) IN DETECTING DISTRESSED MEDICAL STUDENTS. Muhamad Saiful Bahri Yusoff Medical Education Department of School
Factor structure and psychometric properties of the General Health Questionnaire. (GHQ-12) among Ghanaian adolescents
 Factor structure and psychometric properties of the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12) among Ghanaian adolescents Franklin N Glozah 1* and David J Pevalin 1 1 School of Health and Human Sciences, University
Factor structure and psychometric properties of the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ-12) among Ghanaian adolescents Franklin N Glozah 1* and David J Pevalin 1 1 School of Health and Human Sciences, University
PSYCHOMETRIC INDICATORS OF GENERAL HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE IN LATVIA
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PAPER LASE JOURNAL OF SPORT SCIENCE 2013/4/2 205 PSYCHOMETRIC INDICATORS OF GENERAL HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE IN LATVIA Iveta Zelča, Žermēna Vazne, Aleksandra Čuprika, Ingrīda Amantova, Zinta
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PAPER LASE JOURNAL OF SPORT SCIENCE 2013/4/2 205 PSYCHOMETRIC INDICATORS OF GENERAL HEALTH QUESTIONNAIRE IN LATVIA Iveta Zelča, Žermēna Vazne, Aleksandra Čuprika, Ingrīda Amantova, Zinta
Chapter 3 - Does Low Well-being Modify the Effects of
 Chapter 3 - Does Low Well-being Modify the Effects of PRISMA (Dutch DESMOND), a Structured Selfmanagement-education Program for People with Type 2 Diabetes? Published as: van Vugt M, de Wit M, Bader S,
Chapter 3 - Does Low Well-being Modify the Effects of PRISMA (Dutch DESMOND), a Structured Selfmanagement-education Program for People with Type 2 Diabetes? Published as: van Vugt M, de Wit M, Bader S,
Physician you can heal yourself! Cognitive behavioural training reduces stress in GPs
 Family Practice Vol. 21, No. 5 Oxford University Press 04, all rights reserved. Doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmh511, available online at www.fampra.oupjournals.org Printed in Great Britain Physician you can heal
Family Practice Vol. 21, No. 5 Oxford University Press 04, all rights reserved. Doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmh511, available online at www.fampra.oupjournals.org Printed in Great Britain Physician you can heal
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen The measurement of social support in the European Research on incapaciting diseases and social support Suurmeijer, T P B M; Doeglas, D M; Briançon, S; Krijnen, Wilhelmus; Krol,
University of Groningen The measurement of social support in the European Research on incapaciting diseases and social support Suurmeijer, T P B M; Doeglas, D M; Briançon, S; Krijnen, Wilhelmus; Krol,
University of Groningen. Functional ability, social support and quality of life Doeglas, Dirk Maarten
 University of Groningen Functional ability, social support and quality of life Doeglas, Dirk Maarten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
University of Groningen Functional ability, social support and quality of life Doeglas, Dirk Maarten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
The Effect of Expressive Writing on Psychological Distress in Patients with Vitiligo: A Randomized Clinical Trial
 Client-Centered Nursing Care February 2015. Volume 1. Number 1 The Effect of Expressive Writing on Psychological Distress in Patients with Vitiligo: A Randomized Clinical Trial Leili Borimnejad 1*, Alireza
Client-Centered Nursing Care February 2015. Volume 1. Number 1 The Effect of Expressive Writing on Psychological Distress in Patients with Vitiligo: A Randomized Clinical Trial Leili Borimnejad 1*, Alireza
University of Groningen. Functional ability, social support and quality of life Doeglas, Dirk Maarten
 University of Groningen Functional ability, social support and quality of life Doeglas, Dirk Maarten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
University of Groningen Functional ability, social support and quality of life Doeglas, Dirk Maarten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION
 Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 51, No. 5, October 15, 2004, pp 782 791 DOI 10.1002/art.20694 2004, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Are There More Than Cross-Sectional
Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 51, No. 5, October 15, 2004, pp 782 791 DOI 10.1002/art.20694 2004, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Are There More Than Cross-Sectional
Associations between assertiveness, psychological well-being, and self-esteem in adolescents
 bs_bs_banner Journal of Applied Social Psychology 2013, 43, pp. 147 154 Associations between assertiveness, psychological well-being, and self-esteem in adolescents Maria Sarkova 1,2, Maria Bacikova-Sleskova
bs_bs_banner Journal of Applied Social Psychology 2013, 43, pp. 147 154 Associations between assertiveness, psychological well-being, and self-esteem in adolescents Maria Sarkova 1,2, Maria Bacikova-Sleskova
Supplementary Materials:
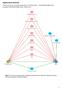 Supplementary Materials: Depression and risk of unintentional injury in rural communities a longitudinal analysis of the Australian Rural Mental Health Study (Inder at al.) Figure S1. Directed acyclic
Supplementary Materials: Depression and risk of unintentional injury in rural communities a longitudinal analysis of the Australian Rural Mental Health Study (Inder at al.) Figure S1. Directed acyclic
SUMMARY AND DISCUSSION
 Risk factors for the development and outcome of childhood psychopathology SUMMARY AND DISCUSSION Chapter 147 In this chapter I present a summary of the results of the studies described in this thesis followed
Risk factors for the development and outcome of childhood psychopathology SUMMARY AND DISCUSSION Chapter 147 In this chapter I present a summary of the results of the studies described in this thesis followed
CBT Intake Form. Patient Name: Preferred Name: Last. First. Best contact phone number: address: Address:
 Patient Information CBT Intake Form Patient Name: Preferred Name: Last Date of Birth: _// Age: _ First MM DD YYYY Gender: Best contact phone number: Email address: _ Address: _ Primary Care Physician:
Patient Information CBT Intake Form Patient Name: Preferred Name: Last Date of Birth: _// Age: _ First MM DD YYYY Gender: Best contact phone number: Email address: _ Address: _ Primary Care Physician:
DEVELOPMENT AND VERIFICATION OF VALIDITY AND RELIABILITY OF
 G. Yao, C.W. Chung, C.F. Yu, et al DEVELOPMENT AND VERIFICATION OF VALIDITY AND RELIABILITY OF THE WHOQOL-BREF TAIWAN VERSION Grace Yao, 1 Chih-Wen Chung, 2 Cheng-Fen Yu, 2 and Jung-Der Wang 2,3 Background
G. Yao, C.W. Chung, C.F. Yu, et al DEVELOPMENT AND VERIFICATION OF VALIDITY AND RELIABILITY OF THE WHOQOL-BREF TAIWAN VERSION Grace Yao, 1 Chih-Wen Chung, 2 Cheng-Fen Yu, 2 and Jung-Der Wang 2,3 Background
University of Warwick institutional repository:
 University of Warwick institutional repository: http://go.warwick.ac.uk/wrap This paper is made available online in accordance with publisher policies. Please scroll down to view the document itself. Please
University of Warwick institutional repository: http://go.warwick.ac.uk/wrap This paper is made available online in accordance with publisher policies. Please scroll down to view the document itself. Please
Non-auditory: 9th International Congress on Noise as a Public Health Problem (ICBEN) 2008, Foxwoods, CT
 Relationship between subjective health and disturbances of daily life due to aircraft noise exposure Questionnaire study conducted around Narita International Airport Masamitsu Miyakawa 1*, Toshihito Matsui
Relationship between subjective health and disturbances of daily life due to aircraft noise exposure Questionnaire study conducted around Narita International Airport Masamitsu Miyakawa 1*, Toshihito Matsui
LOCUS OF CONTROL AND REACTION TO ILLNESS: A STUDY OF PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE
 Med. J. Malaysia VoI. 39 No. 4 December 1984 LOCUS OF CONTROL AND REACTION TO ILLNESS: A STUDY OF PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BOEY KAM WENG SUMMARY The relationship between locus of control and
Med. J. Malaysia VoI. 39 No. 4 December 1984 LOCUS OF CONTROL AND REACTION TO ILLNESS: A STUDY OF PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BOEY KAM WENG SUMMARY The relationship between locus of control and
Factorial Validity and Consistency of the MBI-GS Across Occupational Groups in Norway
 Brief Report Factorial Validity and Consistency of the MBI-GS Across Occupational Groups in Norway Astrid M. Richardsen Norwegian School of Management Monica Martinussen University of Tromsø The present
Brief Report Factorial Validity and Consistency of the MBI-GS Across Occupational Groups in Norway Astrid M. Richardsen Norwegian School of Management Monica Martinussen University of Tromsø The present
Brief report Normative data for the HADS from a large non-clinical sample
 British Journal of Clinical Psychology (2001), 40, 429 434 # 2001 The British Psychological Society Printed in Great Britain 429 Brief report Normative data for the HADS from a large non-clinical sample
British Journal of Clinical Psychology (2001), 40, 429 434 # 2001 The British Psychological Society Printed in Great Britain 429 Brief report Normative data for the HADS from a large non-clinical sample
GENERAL BEHAVIOR INVENTORY Self-Report Version Never or Sometimes Often Very Often
 GENERAL BEHAVIOR INVENTORY Self-Report Version Here are some questions about behaviors that occur in the general population. Think about how often they occur for you. Using the scale below, select the
GENERAL BEHAVIOR INVENTORY Self-Report Version Here are some questions about behaviors that occur in the general population. Think about how often they occur for you. Using the scale below, select the
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Cohen DJ, Van Hout B, Serruys PW, et al. Quality of life after
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Cohen DJ, Van Hout B, Serruys PW, et al. Quality of life after
Evaluating the Greek Version of Religious Commitment Inventory-10 on a Sample of Pomak Households
 (Volume 12, Issue 2/2016), pp. 5-11 Evaluating the Greek Version of Religious Commitment Inventory-10 on a Sample of Pomak Households Nikolaos Satsios 1+ 1 University of Nicosia, Cyprus Abstract. The aim
(Volume 12, Issue 2/2016), pp. 5-11 Evaluating the Greek Version of Religious Commitment Inventory-10 on a Sample of Pomak Households Nikolaos Satsios 1+ 1 University of Nicosia, Cyprus Abstract. The aim
THEORETICAL ASSUMPTIONS AND PSYCHOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SENSE OF PERSONAL CONTROL AT WORK QUESTIONNAIRE
 International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health, Vol. 5, No., 29 36, 2002 THEORETICAL ASSUMPTIONS AND PSYCHOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SENSE OF PERSONAL CONTROL AT WORK QUESTIONNAIRE
International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health, Vol. 5, No., 29 36, 2002 THEORETICAL ASSUMPTIONS AND PSYCHOMETRIC CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SENSE OF PERSONAL CONTROL AT WORK QUESTIONNAIRE
Title of measure: Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Brain (FACT-Br)
 Title of measure: Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Brain (FACT-Br) This summary was last revised 5 October 2010. Brief overview: The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Brain (FACT-Br) is a
Title of measure: Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Brain (FACT-Br) This summary was last revised 5 October 2010. Brief overview: The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Brain (FACT-Br) is a
6800$5< /,)(7,0( ',$*126(6 &+(&./,67 'DWH RI &XUUHQW BBBB BBBB BBBBBB
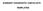 Criteria for Probable Diagnosis: 1. Meets criteria for core symptoms of the disorder. 2. Meets all but one, or a minimum of 75% of the remaining criteria required for the diagnosis 3. Evidence of functional
Criteria for Probable Diagnosis: 1. Meets criteria for core symptoms of the disorder. 2. Meets all but one, or a minimum of 75% of the remaining criteria required for the diagnosis 3. Evidence of functional
Study of the Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Self Efficacy among School Going Adolescents
 Study of the Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Self Efficacy among School Going Adolescents P.S FATHIMA SWAIN MAMTA SINHA V.K Department of Psychiatric Social Work, Central Institute of Psychiatry,
Study of the Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Self Efficacy among School Going Adolescents P.S FATHIMA SWAIN MAMTA SINHA V.K Department of Psychiatric Social Work, Central Institute of Psychiatry,
Factor structure of the Schalock and Keith Quality of Life Questionnaire (QOL-Q): validation on Mexican and Spanish samples
 773 Journal of Intellectual Disability Research volume 49 part 10 pp 773 776 october 2005 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKJIRJournal of Intellectual Disability Research0964-2633Blackwell Publishing Ltd,
773 Journal of Intellectual Disability Research volume 49 part 10 pp 773 776 october 2005 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKJIRJournal of Intellectual Disability Research0964-2633Blackwell Publishing Ltd,
Jun SHIGEMI, Yoshio MINO and Toshihide TSUDA. Journal of Occupational Health
 J Occup Health 2000; 42: 284 291 Journal of Occupational Health Stability of Factor Structure and Correlation with Perceived Job Stress in General Health Questionnaire: a Three-wave Survey over One Year
J Occup Health 2000; 42: 284 291 Journal of Occupational Health Stability of Factor Structure and Correlation with Perceived Job Stress in General Health Questionnaire: a Three-wave Survey over One Year
ISSN X Journal of Educational and Social Research Vol. 2 (8) October 2012
 The Investigation of Czech Lower Secondary School Pupils Toward Science Subjects Milan Kubiatko Doi:10.5901/jesr.2012.v2n8p11 Institute for Research in School Education, Masaryk University, Brno,Czech
The Investigation of Czech Lower Secondary School Pupils Toward Science Subjects Milan Kubiatko Doi:10.5901/jesr.2012.v2n8p11 Institute for Research in School Education, Masaryk University, Brno,Czech
Results of the Study Stage Fright, Well-being and Recovery in Performing Artists
 1 Results of the Study Stage Fright, Well-being and Recovery in Performing Artists Contents Demographics... 1 Part 1: Stage Fright, Health & Well-being, and Recovery... 5 Constructs... 5 Assumptions...
1 Results of the Study Stage Fright, Well-being and Recovery in Performing Artists Contents Demographics... 1 Part 1: Stage Fright, Health & Well-being, and Recovery... 5 Constructs... 5 Assumptions...
DISCUSSION: PHASE ONE THE RELIABILITY AND VALIDITY OF THE MODIFIED SCALES
 CHAPTER SIX DISCUSSION: PHASE ONE THE RELIABILITY AND VALIDITY OF THE MODIFIED SCALES This chapter discusses the main findings from the quantitative phase of the study. It covers the analysis of the five
CHAPTER SIX DISCUSSION: PHASE ONE THE RELIABILITY AND VALIDITY OF THE MODIFIED SCALES This chapter discusses the main findings from the quantitative phase of the study. It covers the analysis of the five
Reliability and Exploratory Factor Analysis of Psychological Well-being in a Persian Sample
 From the SelectedWorks of Seyed Mohammad Kalantarkousheh June, 2012 Reliability and Exploratory Factor Analysis of Psychological Well-being in a Persian Sample دکتر سید محمد کالنتر کوشه Kalantarkousheh,
From the SelectedWorks of Seyed Mohammad Kalantarkousheh June, 2012 Reliability and Exploratory Factor Analysis of Psychological Well-being in a Persian Sample دکتر سید محمد کالنتر کوشه Kalantarkousheh,
Journal of Occupational Health
 Advance Publication Journal of Occupational Health Accepted for Publication: May 8, 2015 J-STAGE Advance Published Date: Jun 17, 2015 Title Psychometric Properties of the Thai Version of the Work Ability
Advance Publication Journal of Occupational Health Accepted for Publication: May 8, 2015 J-STAGE Advance Published Date: Jun 17, 2015 Title Psychometric Properties of the Thai Version of the Work Ability
Quality of Life Assessment of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Adults (QoL-AGHDA)
 Quality of Life Assessment of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Adults (QoL-AGHDA) Guidelines for Users May 2016 B1 Chorlton Mill, 3 Cambridge Street, Manchester, M1 5BY, UK Tel: +44 (0)161 226 4446 Fax: +44
Quality of Life Assessment of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Adults (QoL-AGHDA) Guidelines for Users May 2016 B1 Chorlton Mill, 3 Cambridge Street, Manchester, M1 5BY, UK Tel: +44 (0)161 226 4446 Fax: +44
Internal structure evidence of validity
 Internal structure evidence of validity Dr Wan Nor Arifin Lecturer, Unit of Biostatistics and Research Methodology, Universiti Sains Malaysia. E-mail: wnarifin@usm.my Wan Nor Arifin, 2017. Internal structure
Internal structure evidence of validity Dr Wan Nor Arifin Lecturer, Unit of Biostatistics and Research Methodology, Universiti Sains Malaysia. E-mail: wnarifin@usm.my Wan Nor Arifin, 2017. Internal structure
Critical Evaluation of the Beach Center Family Quality of Life Scale (FQOL-Scale)
 Critical Evaluation of the Beach Center Family Quality of Life Scale (FQOL-Scale) Alyssa Van Beurden M.Cl.Sc (SLP) Candidate University of Western Ontario: School of Communication Sciences and Disorders
Critical Evaluation of the Beach Center Family Quality of Life Scale (FQOL-Scale) Alyssa Van Beurden M.Cl.Sc (SLP) Candidate University of Western Ontario: School of Communication Sciences and Disorders
Psychiatric Epidemiology
 Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol (1991) 26:252-258 Social Psychiatry an~ {3 Springer-Verlag 1991 Psychiatric Epidemiology Qualitative differences in psychiatric symptoms between high risk groups assessed
Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol (1991) 26:252-258 Social Psychiatry an~ {3 Springer-Verlag 1991 Psychiatric Epidemiology Qualitative differences in psychiatric symptoms between high risk groups assessed
The Short NART: Cross-validation, relationship to IQ and some practical considerations
 British journal of Clinical Psychology (1991), 30, 223-229 Printed in Great Britain 2 2 3 1991 The British Psychological Society The Short NART: Cross-validation, relationship to IQ and some practical
British journal of Clinical Psychology (1991), 30, 223-229 Printed in Great Britain 2 2 3 1991 The British Psychological Society The Short NART: Cross-validation, relationship to IQ and some practical
Is Happiness Different From Flourishing? Cross-Country Evidence from the ESS
 Is Happiness Different From Flourishing? Cross-Country Evidence from the ESS Andrew E. Clark (Paris School of Economics and IZA) http://www.pse.ens.fr/clark/ ESRI Tokyo. November 30 th 2012. Economics
Is Happiness Different From Flourishing? Cross-Country Evidence from the ESS Andrew E. Clark (Paris School of Economics and IZA) http://www.pse.ens.fr/clark/ ESRI Tokyo. November 30 th 2012. Economics
CHAPTER VI RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
 CHAPTER VI RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 6.1 Research Design Research is an organized, systematic, data based, critical, objective, scientific inquiry or investigation into a specific problem, undertaken with the
CHAPTER VI RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 6.1 Research Design Research is an organized, systematic, data based, critical, objective, scientific inquiry or investigation into a specific problem, undertaken with the
Sex Differences in Depression in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
 171 Sex Differences in Depression in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Andrae J. Laws, McNair Scholar, Penn State University Faculty Research Advisor Dr. Peter A. Arnett, Associate Professor of Psychology
171 Sex Differences in Depression in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Andrae J. Laws, McNair Scholar, Penn State University Faculty Research Advisor Dr. Peter A. Arnett, Associate Professor of Psychology
"I know what to do, but if s not possible to do it" general practitioners' perceptions of their ability to detect psychological distress
 Family Practice Oxford University Press 1996 VoL 13, No. 2 Printed in Great Britain "I know what to do, but if s not possible to do it" general practitioners' perceptions of their ability to detect psychological
Family Practice Oxford University Press 1996 VoL 13, No. 2 Printed in Great Britain "I know what to do, but if s not possible to do it" general practitioners' perceptions of their ability to detect psychological
Assessment of Mental Health Status of Middle-Aged Female School Teachers of Varanasi City
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 5 Number 1 Assessment of Mental Health Status of Middle-Aged Female School Teachers of Varanasi City M Singh, G Singh Citation M Singh, G Singh. Assessment
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Health Volume 5 Number 1 Assessment of Mental Health Status of Middle-Aged Female School Teachers of Varanasi City M Singh, G Singh Citation M Singh, G Singh. Assessment
Validation of the Patient Perception of Migraine Questionnaire
 Volume 5 Number 5 2002 VALUE IN HEALTH Validation of the Patient Perception of Migraine Questionnaire Kimberly Hunt Davis, MS, 1 Libby Black, PharmD, 1 Betsy Sleath, PhD 2 1 GlaxoSmithKline, Research Triangle
Volume 5 Number 5 2002 VALUE IN HEALTH Validation of the Patient Perception of Migraine Questionnaire Kimberly Hunt Davis, MS, 1 Libby Black, PharmD, 1 Betsy Sleath, PhD 2 1 GlaxoSmithKline, Research Triangle
Life style and health in men and women followed from age 21 to 27 - the Amsterdam Growth Study
 Life style and health in men and women followed from age 21 to 27 - the Amsterdam Growth Study Jan Snel*, Willem van Mechelen** & Pieter Kempe* *Faculty of Psychology Department of Psychonomics University
Life style and health in men and women followed from age 21 to 27 - the Amsterdam Growth Study Jan Snel*, Willem van Mechelen** & Pieter Kempe* *Faculty of Psychology Department of Psychonomics University
International Conference on Humanities and Social Science (HSS 2016)
 International Conference on Humanities and Social Science (HSS 2016) The Chinese Version of WOrk-reLated Flow Inventory (WOLF): An Examination of Reliability and Validity Yi-yu CHEN1, a, Xiao-tong YU2,
International Conference on Humanities and Social Science (HSS 2016) The Chinese Version of WOrk-reLated Flow Inventory (WOLF): An Examination of Reliability and Validity Yi-yu CHEN1, a, Xiao-tong YU2,
Affective Control Scale
 K. Elaine Williams and Dianne L. Chambless Bibliography Berg, C.Z., Shapiro, N., Chambless, D. L., Ahrens, A. H. (1998). Are emotions frightening? II: An analogue study of fear of emotion, interpersonal
K. Elaine Williams and Dianne L. Chambless Bibliography Berg, C.Z., Shapiro, N., Chambless, D. L., Ahrens, A. H. (1998). Are emotions frightening? II: An analogue study of fear of emotion, interpersonal
Psychological wellbeing in heart failure
 Patient information Struggling to cope? Can trelax? Psychological wellbeing in heart failure Stressedout? Trouble sleeping? Feelinglow? i Living with heart failure can be challenging mentally as well as
Patient information Struggling to cope? Can trelax? Psychological wellbeing in heart failure Stressedout? Trouble sleeping? Feelinglow? i Living with heart failure can be challenging mentally as well as
Pain Psychology: Disclosure Slide. Learning Objectives. Bio-psychosocial Model 8/12/2014. What we won t cover (today) What influences chronic pain?
 Disclosure Slide Pain Psychology: No commercial interests to disclose Screening for distress and maladaptive attitudes and beliefs Paul Taenzer PhD, CPsych Learning Objectives At the end of the session,
Disclosure Slide Pain Psychology: No commercial interests to disclose Screening for distress and maladaptive attitudes and beliefs Paul Taenzer PhD, CPsych Learning Objectives At the end of the session,
Measuring Perceived Social Support in Mexican American Youth: Psychometric Properties of the Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette College of Education Faculty Research and Publications Education, College of 5-1-2004 Measuring Perceived Social Support in Mexican American Youth: Psychometric
Marquette University e-publications@marquette College of Education Faculty Research and Publications Education, College of 5-1-2004 Measuring Perceived Social Support in Mexican American Youth: Psychometric
Dr. Catherine Mancini and Laura Mishko
 Dr. Catherine Mancini and Laura Mishko Interviewing Depression, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Anxiety, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Observation Asking questions
Dr. Catherine Mancini and Laura Mishko Interviewing Depression, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Anxiety, with case study Screening When it needs treatment Observation Asking questions
Tenovus Cancer Care Counselling Evaluation. September 2016
 Tenovus Cancer Care Counselling Evaluation September 2016 1 Contents Contents 1. Context... 2 2. Background... 2 3. General Findings... 2 4. Findings: Age... 2 5. Findings: Gender... 2 6. Findings: Client
Tenovus Cancer Care Counselling Evaluation September 2016 1 Contents Contents 1. Context... 2 2. Background... 2 3. General Findings... 2 4. Findings: Age... 2 5. Findings: Gender... 2 6. Findings: Client
European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR) A Registered Branch of the ESC
 Quality of life of cardiac patients in Europe: HeartQoL Project Stefan Höfer The HeartQol Questionnaire: methodological and analytical approaches Patients Treatment Is quality of life important in cardiovascular
Quality of life of cardiac patients in Europe: HeartQoL Project Stefan Höfer The HeartQol Questionnaire: methodological and analytical approaches Patients Treatment Is quality of life important in cardiovascular
Constructing Indices and Scales. Hsueh-Sheng Wu CFDR Workshop Series June 8, 2015
 Constructing Indices and Scales Hsueh-Sheng Wu CFDR Workshop Series June 8, 2015 1 Outline What are scales and indices? Graphical presentation of relations between items and constructs for scales and indices
Constructing Indices and Scales Hsueh-Sheng Wu CFDR Workshop Series June 8, 2015 1 Outline What are scales and indices? Graphical presentation of relations between items and constructs for scales and indices
INSTRUCTION MANUAL Instructions for Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) and GAD-7 Measures
 PHQ and GAD-7 Instructions P. 1/9 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Instructions for Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) and GAD-7 Measures TOPIC PAGES Background 1 Coding and Scoring 2, 4, 5 Versions 3 Use as Severity
PHQ and GAD-7 Instructions P. 1/9 INSTRUCTION MANUAL Instructions for Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) and GAD-7 Measures TOPIC PAGES Background 1 Coding and Scoring 2, 4, 5 Versions 3 Use as Severity
Onset and recurrence of depressive disorders: contributing factors
 SUMMARY People with depressive disorders frequently come to see their general practitioner (GP) as these conditions are highly prevalent. In the Netherlands, 19% of the general population experiences a
SUMMARY People with depressive disorders frequently come to see their general practitioner (GP) as these conditions are highly prevalent. In the Netherlands, 19% of the general population experiences a
Psychiatric morbidity in married females living away from their spouses attending the psychiatry clinic in a tertiary care, teaching hospital
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Baig MG et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Aug;3(8):2086-2092 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20150331
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Baig MG et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Aug;3(8):2086-2092 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20150331
A naturalistic observational study of Western herbal medicine practice in self-reported anxiety and depression
 INFORMATION SHEET (PATIENT PARTICIPANT) A naturalistic observational study of Western herbal medicine practice in self-reported anxiety and depression WHO IS DOING THE RESEARCH? Our names are Dr Jon Wardle,
INFORMATION SHEET (PATIENT PARTICIPANT) A naturalistic observational study of Western herbal medicine practice in self-reported anxiety and depression WHO IS DOING THE RESEARCH? Our names are Dr Jon Wardle,
Validity of the Perceived Health Competence Scale in a UK primary care setting.
 Validity of the Perceived Health Competence Scale in a UK primary care setting. Dempster, M., & Donnelly, M. (2008). Validity of the Perceived Health Competence Scale in a UK primary care setting. Psychology,
Validity of the Perceived Health Competence Scale in a UK primary care setting. Dempster, M., & Donnelly, M. (2008). Validity of the Perceived Health Competence Scale in a UK primary care setting. Psychology,
Work Personality Index Factorial Similarity Across 4 Countries
 Work Personality Index Factorial Similarity Across 4 Countries Donald Macnab Psychometrics Canada Copyright Psychometrics Canada 2011. All rights reserved. The Work Personality Index is a trademark of
Work Personality Index Factorial Similarity Across 4 Countries Donald Macnab Psychometrics Canada Copyright Psychometrics Canada 2011. All rights reserved. The Work Personality Index is a trademark of
KCP learning. factsheet 44: mapp validity. Face and content validity. Concurrent and predictive validity. Cabin staff
 mapp validity Face and content validity Careful design and qualitative screening of the questionnaire items in the development of MAPP has served to maximise both the face validity and the content validity
mapp validity Face and content validity Careful design and qualitative screening of the questionnaire items in the development of MAPP has served to maximise both the face validity and the content validity
Technical Specifications
 Technical Specifications In order to provide summary information across a set of exercises, all tests must employ some form of scoring models. The most familiar of these scoring models is the one typically
Technical Specifications In order to provide summary information across a set of exercises, all tests must employ some form of scoring models. The most familiar of these scoring models is the one typically
Initial assessment of patients without cognitive failure admitted to palliative care: a validation study
 Original Article Initial assessment of patients without cognitive failure admitted to palliative care: a validation study José António Ferraz Gonçalves 1, Clara Castro 2, Paula Silva 1, Rui Carneiro 1,
Original Article Initial assessment of patients without cognitive failure admitted to palliative care: a validation study José António Ferraz Gonçalves 1, Clara Castro 2, Paula Silva 1, Rui Carneiro 1,
Prevalence and Associated Factors of Depression among Elderly Population Living in Geriatric Homes in Kathmandu Valley
 39 Prevalence and Associated Factors of Depression among Elderly Population Living in Geriatric Homes in Kathmandu Valley Choulagai P S, Sharma C K, Choulagai B P Tribhuvan University, Institute of Medicine,
39 Prevalence and Associated Factors of Depression among Elderly Population Living in Geriatric Homes in Kathmandu Valley Choulagai P S, Sharma C K, Choulagai B P Tribhuvan University, Institute of Medicine,
THE SLEEP DIAGNOSIS LIST (SDL): A QUESTIONNAIRE FOR SCREENING GENERAL SLEEP DISORDERS
 THE SLEEP DIAGNOSIS LIST (SDL): A QUESTIONNAIRE FOR SCREENING GENERAL SLEEP DISORDERS Sweere Y 1, Kerkhof GA 2, De Weerd AW 1, Kamphuisen HAC 1, Kemp B 1 & Schimsheimer RJ 1 1 Centre for Sleep and Wake
THE SLEEP DIAGNOSIS LIST (SDL): A QUESTIONNAIRE FOR SCREENING GENERAL SLEEP DISORDERS Sweere Y 1, Kerkhof GA 2, De Weerd AW 1, Kamphuisen HAC 1, Kemp B 1 & Schimsheimer RJ 1 1 Centre for Sleep and Wake
Seattle Personality Inventory Kindergarten-Grade 1 / Years 1-2 Fast Track Project Technical Report Mark Greenberg & Lili Lengua November 10, 1995
 Seattle Personality Inventory Kindergarten-Grade 1 / Years 1-2 Fast Track Project Technical Report Mark Greenberg & Lili Lengua November 10, 1995 This technical report was written for both years one and
Seattle Personality Inventory Kindergarten-Grade 1 / Years 1-2 Fast Track Project Technical Report Mark Greenberg & Lili Lengua November 10, 1995 This technical report was written for both years one and
CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG. Psychosocial Factors and Depression: The Mediating Role of Sleep
 CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Psychosocial Factors and Depression: The Mediating Role of Sleep A Report Submitted to Department of Applied Social Studies in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the
CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Psychosocial Factors and Depression: The Mediating Role of Sleep A Report Submitted to Department of Applied Social Studies in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the
POST-STROKE DEPRESSION
 POST-STROKE DEPRESSION Stroke Annual Review March 7 th & 8 th, 2018 Justine Spencer, PhD, CPsych OVERVIEW What is Post-Stroke Depression (PSD)? Risk factors/predictors Impact of PSD Treatment and Management
POST-STROKE DEPRESSION Stroke Annual Review March 7 th & 8 th, 2018 Justine Spencer, PhD, CPsych OVERVIEW What is Post-Stroke Depression (PSD)? Risk factors/predictors Impact of PSD Treatment and Management
The study of relationship between optimism (positive thinking) and mental health (Case study: students of Islamic Azad University of Bandar Abbas)
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received 8 April. 2017 Accepted 24 Aguste. 2017 Vol. 6, Issue 4, 98-106, 2017 Academic Journal of Psychological Studies ISSN: 2333-0821 ajps.worldofresearches.com The study of relationship
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received 8 April. 2017 Accepted 24 Aguste. 2017 Vol. 6, Issue 4, 98-106, 2017 Academic Journal of Psychological Studies ISSN: 2333-0821 ajps.worldofresearches.com The study of relationship
A STUDY OF ADJUSTMENT PROBLEMS OF COLLEGE STUDENTS IN RELATION TO GENDER, SOCIO-ECONOMIC STATUS & ACADEMIC ACHIEVEMENT
 A STUDY OF ADJUSTMENT PROBLEMS OF COLLEGE STUDENTS IN RELATION TO GENDER, SOCIO-ECONOMIC STATUS & ACADEMIC ACHIEVEMENT 1 Sangeeta 2 Chirag 1 Senior Research Fellow, Department of Education, M.D University,
A STUDY OF ADJUSTMENT PROBLEMS OF COLLEGE STUDENTS IN RELATION TO GENDER, SOCIO-ECONOMIC STATUS & ACADEMIC ACHIEVEMENT 1 Sangeeta 2 Chirag 1 Senior Research Fellow, Department of Education, M.D University,
Psychometric properties of the PsychoSomatic Problems scale an examination using the Rasch model
 Psychometric properties of the PsychoSomatic Problems scale an examination using the Rasch model Curt Hagquist Karlstad University, Karlstad, Sweden Address: Karlstad University SE-651 88 Karlstad Sweden
Psychometric properties of the PsychoSomatic Problems scale an examination using the Rasch model Curt Hagquist Karlstad University, Karlstad, Sweden Address: Karlstad University SE-651 88 Karlstad Sweden
RESULTS. Chapter INTRODUCTION
 8.1 Chapter 8 RESULTS 8.1 INTRODUCTION The previous chapter provided a theoretical discussion of the research and statistical methodology. This chapter focuses on the interpretation and discussion of the
8.1 Chapter 8 RESULTS 8.1 INTRODUCTION The previous chapter provided a theoretical discussion of the research and statistical methodology. This chapter focuses on the interpretation and discussion of the
These questionnaires are used by psychology services to help us understand how people feel. One questionnaire measures how sad people feel.
 ADAPTED PHQ-9 & GAD-7 QUESTIONNAIRES How to fill in these questionnaires: These questionnaires are used by psychology services to help us understand how people feel. One questionnaire measures how sad
ADAPTED PHQ-9 & GAD-7 QUESTIONNAIRES How to fill in these questionnaires: These questionnaires are used by psychology services to help us understand how people feel. One questionnaire measures how sad
CHAPTER IV VALIDATION AND APPLICATION OF ABERRANT BEHAVIOUR ASSESSMENT CHECKLIST PREPARED IN TELUGU LANGUAGE
 CHAPTER IV VALIDATION AND APPLICATION OF ABERRANT BEHAVIOUR ASSESSMENT CHECKLIST PREPARED IN TELUGU LANGUAGE 4.1 Translation of Aberrant Behaviour Checklist and its Validation Until now, no translation
CHAPTER IV VALIDATION AND APPLICATION OF ABERRANT BEHAVIOUR ASSESSMENT CHECKLIST PREPARED IN TELUGU LANGUAGE 4.1 Translation of Aberrant Behaviour Checklist and its Validation Until now, no translation
ADULT QUESTIONNAIRE. Date of Birth: Briefly describe the history and development of this issue from onset to present.
 ADULT QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Address: Preferred phone number to reach you: Is it okay to leave a message? Yes No (Please check one) Date of Birth: Reason(s) for seeking treatment at this time? Briefly describe
ADULT QUESTIONNAIRE Name: Address: Preferred phone number to reach you: Is it okay to leave a message? Yes No (Please check one) Date of Birth: Reason(s) for seeking treatment at this time? Briefly describe
Measuring mathematics anxiety: Paper 2 - Constructing and validating the measure. Rob Cavanagh Len Sparrow Curtin University
 Measuring mathematics anxiety: Paper 2 - Constructing and validating the measure Rob Cavanagh Len Sparrow Curtin University R.Cavanagh@curtin.edu.au Abstract The study sought to measure mathematics anxiety
Measuring mathematics anxiety: Paper 2 - Constructing and validating the measure Rob Cavanagh Len Sparrow Curtin University R.Cavanagh@curtin.edu.au Abstract The study sought to measure mathematics anxiety
1. Evaluate the methodological quality of a study with the COSMIN checklist
 Answers 1. Evaluate the methodological quality of a study with the COSMIN checklist We follow the four steps as presented in Table 9.2. Step 1: The following measurement properties are evaluated in the
Answers 1. Evaluate the methodological quality of a study with the COSMIN checklist We follow the four steps as presented in Table 9.2. Step 1: The following measurement properties are evaluated in the
Description and Psychometrics
 APPENDIX 6.3: Revised Memory and Behavior Problem Checklist Description and Psychometrics Brief Descriptive Information The Revised Memory and Behavior Problems Checklist (RMBPC; Teri et al., 1992) is
APPENDIX 6.3: Revised Memory and Behavior Problem Checklist Description and Psychometrics Brief Descriptive Information The Revised Memory and Behavior Problems Checklist (RMBPC; Teri et al., 1992) is
CHAPTER - 6 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS. This chapter discusses inferential statistics, which use sample data to
 CHAPTER - 6 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS 6.1 Introduction This chapter discusses inferential statistics, which use sample data to make decisions or inferences about population. Populations are group of interest
CHAPTER - 6 STATISTICAL ANALYSIS 6.1 Introduction This chapter discusses inferential statistics, which use sample data to make decisions or inferences about population. Populations are group of interest
PATIENTS ILLNESS PERCEPTIONS Do they matter and can we change them
 PATIENTS ILLNESS PERCEPTIONS Do they matter and can we change them Rona Moss-Morris Professor of Psychology as Applied to Medicine Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience Section of Health
PATIENTS ILLNESS PERCEPTIONS Do they matter and can we change them Rona Moss-Morris Professor of Psychology as Applied to Medicine Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology and Neuroscience Section of Health
Other significant mental health complaints
 Other significant mental health complaints 2 Session outline Introduction to other significant mental health complaints Assessment of other significant mental health complaints Management of other significant
Other significant mental health complaints 2 Session outline Introduction to other significant mental health complaints Assessment of other significant mental health complaints Management of other significant
CHAPTER V. Summary and Recommendations. policies, including uniforms (Behling, 1994). The purpose of this study was to
 HAPTER V Summary and Recommendations The current belief that fashionable clothing worn to school by students influences their attitude and behavior is the major impetus behind the adoption of stricter
HAPTER V Summary and Recommendations The current belief that fashionable clothing worn to school by students influences their attitude and behavior is the major impetus behind the adoption of stricter
An International Study of the Reliability and Validity of Leadership/Impact (L/I)
 An International Study of the Reliability and Validity of Leadership/Impact (L/I) Janet L. Szumal, Ph.D. Human Synergistics/Center for Applied Research, Inc. Contents Introduction...3 Overview of L/I...5
An International Study of the Reliability and Validity of Leadership/Impact (L/I) Janet L. Szumal, Ph.D. Human Synergistics/Center for Applied Research, Inc. Contents Introduction...3 Overview of L/I...5
Problem Summary. * 1. Name
 Problem Summary This questionnaire is an important part of providing you with the best health care possible. Your answers will help in understanding problems that you may have. Please answer every question
Problem Summary This questionnaire is an important part of providing you with the best health care possible. Your answers will help in understanding problems that you may have. Please answer every question
Spiritual well-being and mental health in university students
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences 5 (2010) 1477 1481 WCPCG-2010 Spiritual well-being and mental health in university students Esa Jafari a, Gholam Reza Dehshiri
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences 5 (2010) 1477 1481 WCPCG-2010 Spiritual well-being and mental health in university students Esa Jafari a, Gholam Reza Dehshiri
Optimal Health Questionnaire
 Optimal Health Questionnaire This questionnaire is intended to help you assess how well you are balancing the various elements in your life. The basis of the process is that we have 5 dimensions which
Optimal Health Questionnaire This questionnaire is intended to help you assess how well you are balancing the various elements in your life. The basis of the process is that we have 5 dimensions which
