On the Role of Shape in the Detection of Melanomas
|
|
|
- Russell Lambert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
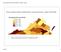
1 On the Role of Shape in the Detection of Melanomas Margarida Ruela ISR, IST, Lisbon, Portugal. Catarina Barata ISR, IST, Lisbon, Portugal. Teresa Mendonça FCUP, Porto, Portugal. Jorge S. Marques ISR, IST, Lisbon, Portugal. Abstract This paper presents a study on the role of shape in the detection of melanomas in dermoscopy images. The contribution of shape-related features was assessed by developing a Computer-Aided Diagnosis (CAD) system whose classification is solely based on this type of features. Four shape descriptors were used, first separately and then simultaneously, to describe the images. Image segmentation was performed both manually, by an expert, and automatically, by using an Adaptive Thresholding algorithm. The best performances were SE = 92% and SP = 74%, obtained for manually segmented images, and SE = 92% and SP = 78%, obtained for automatically segmented images. These results were achieved by combining the shape descriptors and show that shape information plays an important role in melanoma detection. Furthermore, no degradation was observed when automatic segmentation methods are used, instead of manual ones. A. Motivation I. INTRODUCTION Melanomas are one of the most aggressive types of cancer. They result from an abnormal proliferation of melanocytic cells, which are responsible for the production of melanin, the dark pigment responsible for skin color. Due to these increased growth rates, the early detection of melanomas is crucial for the treatment of these lesions. In fact, if a melanoma is detected in the beginning of its development, chances are that it can be easily treated by a simple excision. However, if a melanoma has already metastasize, survival rate drops drastically and, in most cases, it is considered incurable. In a study performed in the United States, the five year relative survival, from 2002 to 2008, dropped from 98.2% in the case of a localized melanoma to 15.1% in the case of a metastasized melanoma [2]. Melanomas can usually be distinguished from other lesions due to their larger dimensions, variegation, asymmetric shape and/or due to the presence of differential structures [1]. Furthermore, they usually present a darker coloration. Fig. 1 shows (a) an example of a melanoma and (b) an example of a benign lesion. As one can observe, these lesions are easily differentiated by the above mentioned features. Nevertheless, not all benign lesions are so easily differentiated from melanomas. Fig. 2 shows (a) another melanoma and (b) another a benign lesion, but now exhibiting similar features. Though they have different diagnosis, these lesions This work was supported by FCT in the scope of projects PTDC/SAUBEB/ /2008 and PEst-OE/EEI/LA0009/2011. look quite similar. Therefore, due to possible similarity between melanomas and other lesions, naked eye diagnosis leads to unreliable results and jeopardizes the early detection of melanomas. Fig. 1. Example of (a) a melanoma and (b) a benign lesion presenting different color and shape features. Fig. 2. Example of (a) a melanoma and (b) a benign lesion presenting similar color and shape features. B. State of the art In order to differentiate benign from malign lesions, sophisticated diagnosis techniques are required. Dermoscopy is a good example of such a technique and has been used by dermatologists to diagnose pigmented skin lesions[1]. Dermoscopy images are acquired by using a dermatoscope which magnifies the lesions by a factor of x, using special light and fluid. The acquisition process enhances the morphological structures present in the images and allows the visualization of structures not visible by naked eye [1]. Diagnostic methods such as the ABCD rule of dermoscopy [3] and the 7-point checklist [4] help dermatologists to make a more objective interpretation of the images. However, the interpretation of the images may still be subjective and time consuming. Computer-Aided Diagnosis Biomedical Imaging 268
2 (CAD) systems, which have been developed for the last two decades, intend to aid dermatologists in the classification task. CAD systems are usually divided into three main stages: image segmentation [5], [6], feature extraction and lesion classification [7], [8], [9], [10], [11]. Most CAD systems proposed in the literature combine several types of features extracted from the image, e.g., texture, color, shape and symmetry features [7], [8], [9], [14]. Regarding shape, simple features such as the area, perimeter, major and minor axis length, compactness index [8], [11], [12], rectangularity [7], [8], [9], ellipsoidality [14], eccentricity [8] and bulkiness [13], among others, have been used to describe the lesions. In addition to these features, some systems consider other features such as the symmetry about the minimum inertia axis [8], [11], [12], the fractal dimension [11], [13] and the irregularity index [15]. Shape features are never considered in isolation. They have always been considered together with other types of features and therefore it is not known how important is shape information in the automated detection of melanomas. In this work we focus on shape. We wish to determine the contribution of shape to the classification of melanomas, we also intend to evaluate the performance of several shape descriptors and to determine the best combination of shaperelated features. Fig. 3. Overall description of the system. Fig. 4. Example of a (a) Dermoscopy image and (b) its correspondent binary mask. The white area of the mask corresponds to the skin lesion, whereas the black one represents the healthy tissue. II. SYSTEM OVERVIEW The system developed in this work can be divided into three main stages: image segmentation, feature extraction and lesion classification. Fig. 3 shows an overall description of the proposed system. The system works as follows. Firstly, the system receives a dermoscopy image, I, which is submitted to the image segmentation block. This block computes a binary segmentation mask, B, whose active pixels define the lesion, see Fig. 4. Segmentation was performed both manually by an experienced dermatologist and automatically by using Adaptive Thresholding [5]. Examples of the segmentation contours generated by both methods are represented in Figs. 5, 8 and 9. We chose to use these two different segmentation strategies in order to assess the impact of different segmentation methods on the performance of the system. Secondly, the segmentation mask generated in the first block proceeds to the feature extraction stage. As this study aims to assess the role of shape in the diagnosis of skin lesions, only shape-related features were extracted from the images. Furthermore, all the features were extracted from the binary image B, neglecting important information (e.g., lesion color and texture). The extracted features can be divided into four groups: simple shape features, symmetry-related features, moment invariants and Fourier descriptors. In the last stage, the feature vector, x, generated in the second block is submitted to a classifier, which returns the decision of the system, y. In this work, we opted to use the AdaBoost classifier. AdaBoost is used with a Decision Stump (DS) as weak classifier [16]. III. SHAPE FEATURES As aforementioned, the shape features used in this work are organized in four groups: simple shape (SS) features, symmetry-related (SR) features, moment invariants (MI) and Fourier descriptors (FD). All these features were extracted solely from the binary segmentation masks. A. Simple Shape Features In this work, we consider to be simple shape (SS) features the most simple shape-related features which can be extracted from the images as well as some features which can be derived from them. This group includes the lesion s area (A) in pixels, compactness, major and minor axis length and rectangularity. The compactness (C = 4πA P ) corresponds to the ratio between 2 the area of the lesion and the area of a circle with the same perimeter (P) as the lesion. The lengths of the major and minor axis are the maximum and minimum diameters of the lesion (in pixels) and the rectangularity of the lesion corresponds to the ratio between the area of the lesion and the area of the smallest rectangle able to contain the whole lesion [8], [12]. B. Symmetry-related Features In this work, the symmetry of the lesion is measured by using two different methods: i) the symmetry with respect to the principal axis and ii) the symmetry between opposite slices of the lesion. In both cases, the principal axes were determined by performing a Principal Component Analysis. The symmetry about an axis is determined by overlapping one of the sides of the axis and the mirrored image of the other side. This measure of symmetry is computed by dividing Biomedical Imaging 269
3 However these coefficients are not invariant yet. Translation, rotation and scaling invariance is achieved after performing the following operations d k = c k c 1 + c 2 k = 1, 2,..., N 1, (2) note that the first coefficient (c 0 ) is not considered. Fig. 5. Examples of segmentation contours obtained by manual segmentation (blue line) and by using the Adaptive Thresholding algorithm (red line). twice the number of overlapping pixels by the total area of the lesion(in pixels). The symmetry of opposite slices is measured by dividing the image into an even number of slices with a common vertex: the lesion centroid. All the slices are defined by the intersection of the lesion with circular sectors with the same angle. The symmetry between two opposite slices is determined by overlapping the mirrored image of a slice with its opposite slice. The feature representing the symmetry between two slices is computed by dividing twice the number of overlapping pixels by the sum of the areas of the two slices (in pixels). C. Moment Invariants Moment invariants are classic shape features proposed by Hu. Seven central moments of the object of interest are computed from the binary image and modified, in order to make them invariant to translation, rotation and scaling (see [17] for details). D. Fourier Descriptors The Fourier Descriptors (FD) also provide shape information invariant to translation, rotation and scaling of the object of interest. They correspond to the coefficients, c k, of the Discrete Fourier Transform of a shape signature [18], which is a 1D function that represents the shape of the object contained in the image. The shape signature used in this work is defined as follows z(n) = x(n) + iy(n) n = 0, 1,..., N 1, (1) where i is the imaginary unit, i 2 = 1, N is the number points selected from the boundary of the object and (x(n), y(n)) are the coordinates of the n th point. The selected points are equally spaced and separated by 1 N of the lesion perimeter. Since the sequence z(n) is periodic with period N, it can be represented by a Fourier series and expressed as a function of complex Fourier coefficients c k, k Z. IV. EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS AND DISCUSSION A. Database The data-set used in this work contains images from the database PH 2 [20], collected in Hospital Pedro Hispano, in Matosinhos. This data-set comprises 167 lesions, from which 24 are melanomas ( 14%). All the lesions whose boundary is not contained inside the image were discarded. The dermoscopy images were acquired during routine clinical examinations using a dermatoscope with 20 magnification and were stored in JPEG format. Lesion diagnosis was performed by an experienced dermatologist and was, in some cases, confirmed by histological examination. The preprocessement of the images consisted in hair and reflection removal by using directional filters in the former and a thresholding algorithm in the latter. Afterwards, an inpaintig algorithm was used to fill the resulting gaps [21]. B. Evaluation Metrics For each configuration of the system parameters, training and test were performed through Leave-One-Out Cross Validation (LOOCV). Performance was measured in terms of sensitivity (SE) and specificity (SP). The best performance was determined with the aid of a cost function that combines SE and SP. The adopted cost function is given by C T = SE 2 SP, (3) 5 where SE has a greater weight because the misclassification of a melanoma has more severe consequences than the misdiagnosis of a non-melanoma lesion. C. Experimental Results and Discussion The system developed in this work was tested using both manual and automatic segmentation methods. For each type of segmentation we assessed the performance of the system by using four shape descriptors (SS, SR, MI, FD). These descriptors were firstly tested individually and were posteriorly combined. Both SR and FD were defined by more than one configuration. In the former we varied the number of points sampled from the boundary of the lesions (N {16, 32, 64}). In the latter we used the two axis of symmetry (A = 2) and varied the number of slices (S {4, 8, 16}). Classification was performed using AdaBoost [16] with a Decision Stump (DS) as weak classifier. DS is a simple classifier, with few parameters to tune, which selects a single feature. In this stage we tried to optimize the weight (α) given to melanoma patterns (α {1, 2}) and the number (T ) of weak classifiers (T {2, 3,..., 20}), see [16] for more details. A total of 684 system configurations were trained and evaluated by LOOCV. Biomedical Imaging 270
4 Manual Segmentation Automatic Segmentation Descriptor SE SP Cost α T A S N SE SP Cost α T A S N SS SR MI FD , SS+MI SS+SR+MI All ,64 TABLE I BEST PERFORMANCE OF THE SYSTEM FOR EACH OF THE SEGMENTATION METHODS AND FOR EACH DESCRIPTOR. THE PARAMETERS FILLED WITH - INDICATE THAT THE PARAMETER IS NOT APPLIED TO THAT DESCRIPTOR. Fig. 6. Scatter plots of the four most selected features selected by AdaBoost for manual segmentation (area, compactness, symmetry and 3 rd Hu invariant) and automatic segmentation (area, major axis length and 2 nd and 3 rd Hu invariants). Non-melanomas are represented in blue, melanomas are represented in red. Both area and major axis length were normalized by using MAXMIN normalization. Table I shows the best results achieved by each shape descriptor and by each segmentation method. As presented in the table, regardless of the segmentation method, SS was by far the individual descriptor which led to the best performance (minimum cost). For example, the manually segmented images achieved a performance of SE = 88% and SP = 67% by using this descriptor. This result was achieved by using α = 2 and four different values of T, T {2, 3, 4, 5}. The features which were more frequently selected by the weak classifiers were the area, the compactness and the length of the major axis. The performance achieved by using the automatically segmented images was slightly better with SE = 92% and SP = 69%. This result was obtained by using α = 1 and T = 2. In this case, the area of the lesion and the length of the minor axis were the most selected features. A best performance from the system using automatic segmentation is a rather unexpected result. However, by analyzing the segmentation masks generated by both methods, one observes that the automatic segmentation requires relatively sharp color transitions in order to identify the border of the lesion. Therefore, the lighter regions from the border of the lesion are sometimes neglected by the segmentation algorithm. However, these regions usually provide valuable information and are considered by dermatologists when performing manual segmentation, see Fig. 5. As a result, manual segmentation will most times originate larger lesion areas. Since the SS features are strongly correlated to the size of the lesion and since non-melanomas usually have smaller dimensions, the larger areas generated by manual segmentation may lead to the misdiagnosis of non-melanomas. Melanomas do not face this problem as often as non-melanomas because they usually present darker colors which facilitates the detection of the lesion s border. However, in a few cases, some of the lighter regions of melanomas that present high color variation may be neglected by the automatic segmentation algorithms generating even more asymmetric shapes, which when solely using shape descriptors may benefit this segmentation technique. The best performance of the system, SE = 92% and SP = 78%, was achieved by using automatic segmentation and resulted from the combination of two descriptors: SS and MI. This result was achieved by using α = 2 and T = 4. The most selected features, by the weak classifiers, were the area, the major axis length and the second and third Hu invariants. The combination of these descriptors with SR or both SR and FD leads to an increase of SP, but to a decrease in SE and an increase in cost and, thus, the performance of the system does not improve. An almost as good performance, SE = 92% and SP = 74%, was achieved by using the manual segmentation and resulted from the combination of three descriptors: SS, SR and MI. This result was achieved by using α = 2 and T = 4. The most selected features were the area, the length of the major axis, the symmetry about the first principal component and the third Hu invariant. The combination of all four sets of descriptors does not improve the performance. Biomedical Imaging 271
5 Fig. 7. System performance (cost) as a function of the number of weak classifiers (T) (α = 2) for the individual descriptors (top row) and for the combined descriptors (bottom row). On the left column are represented the results obtained by using manual segmentation whereas on the right column are represented the results obtained by using automatic segmentation. Fig. 8. Examples of images classified by the best configuration of the system using manual segmentation: (a) TN, (b) FP, (c) FN and (d) TP. The blue line represents the manual segmentation. Fig. 9. Examples of images classified by the best configuration of the system using automatic segmentation: (a) TN, (b) FP, (c) FN and (d) TP. The red line represents the automatic segmentation. Fig. 6 shows scatter plots of the four most selected features by using the best configuration of the system for both manual and automatic segmentation masks. Fig. 6 shows that this is a difficult problem, because there is a big overlap between the features of both classes. However, in both cases it is possible to see that the misdiagnosed melanomas were the ones which presented the smallest lesion area. Nevertheless, given the difficulty of the problem, the results presented in Table I are quite surprising. Since the best results were achieved using α = 2, let us analyze how the performances vary with T, see Fig. 7. On the top row we compare the performance of each shape descriptor type, for both segmentation methods, whereas on the bottom row we compare the performance of the combined descriptors. Figs. 8 and 9 show, for the best configuration of the system for each segmentation technique (manual and by using the Adaptive Thresholding algorithm), examples of true positives (TP), false positives (FP), true negatives (TN) and false negatives (FN). TP and TN are, respectively, melanomas and non-melanomas which were correctly classified whereas FN and FP are, respectively, misclassified melanomas and nonmelanomas. Biomedical Imaging 272
6 V. CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK This paper presents a study on the role of shape-related features in the detection of melanomas using dermoscopy images. This role was assessed by developing a CAD system in which classification is solely based on shape descriptors. Four sets of shape descriptors (SS, SR, MI and FD) were separately and jointly analyzed. Furthermore, the system was tested using both manually and automatically segmented images. The descriptors which achieved the best individual performance were simple shape (SS) features, regardless the applied segmentation method. The best performance, SE = 92% and SP = 78%, was achieved by using the automatically segmented images and the combination of SS and moment invariants (MI) descriptors. The results obtained with manually segmented images are similar, SE = 92% and SP = 74%, and were achieved by using a combination of SS, symmetryrelated (SR) and MI descriptors. According to these results, we conclude that shape-related features have an important role in the detection of melanomas. In addition, we may also conclude that classification by using shape descriptors is fairly robust to a change in the segmentation method. In a previous studies such as [10], [22], the role of color and texture descriptors were evaluated by also using subsets of the PH 2 database [20]. In [22], it is performed a study on the role of color features in the detection of melanomas. The best configuration of the system achieved a performance of SE=100% and SP=93%, using a subset of the dataset used in this paper comprising 14 of the melanomas and 134 of the non melanomas. In [23] color and texture features are studied individually and combined. The combination of these features lead to a performance of SE=96% and SP=82%. This result was obtained by using a dataset with 151 non-melanomas and 25 melanomas, most of which are also used in this paper. Since color and texture descriptors were able to achieve slightly better results, in the future, it would be interesting to enrich these shape descriptors with the best set of texture and color features, determined in previous studies. Furthermore, it would also be interesting to analyze the behavior of these shape descriptors when applied to larger databases. VI. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors would like to thank Dr. J. Rozeira from Hospital Pedro Hispano for kindly providing the dermoscopy images used in this work. Most of these images belong to PH 2 database which will soon be freely available [20]. REFERENCES [1] Dermoscopy. [2] Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou R, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Cho H, Mariotto A, Eisner MP, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA SEER Cancer Statistics Review, (Vintage 2009 Populations) National Cancer Institute Bethesda, MD. [3] Nachbar, F., Stolz, W., Merkle, T., Cognetta, A. B., Vogt, T., Landthaler, M., Bilek, P., Braun-Falco, O., Plewig, G.: The ABCD rule of dermatoscopy. High prospective value in the diagnosis of doubtful melanocytic skin lesions. J Am Acad Dermatol 30(4), (1994) [4] Argenziano, G., Fabbrocini, G., Carli, P., De Giorgi, V., Sammarco, E., Delfino, M.: Epiluminescence microscopy for the diagnosis of doubtful melanocytic skin lesions. Comparison of the ABCD rule of dermatoscopy and a new 7-point checklist based on pattern analysis. Arch Dermatol 134, (1998). [5] Barata, C., Ruela, M., Francisco, M., Mendonça, T. and Marques, J. S., Two Systems for the Detection of Melanomas in Dermoscopy Images using Texture and Color Features, IEEE System Journal, accepted, [6] Celebi, M E., Wen, Q., Hwang, S., Iyatomi, H., Schaefer, G.: Lesion Border Detection in Dermoscopy Images Using Ensembles of Thresholding Methods. Skin Research and Technology 19, (2013). [7] Iyatomi, H., Celebi, M. E., Oka, H., Tanaka, M.: An Improved Internet- Based Melanoma Screening System with Dermatologist-like Tumor Area Extraction Algorithm. Comp Medical Imaging and Graphics 32, (2008). [8] Celebi, M. E., Kingravi, H. A., Uddin, B.,Iyatomi, H., Aslandogan, Y. A., Stoecker, W. V., Moss, R. H.: A methodological approach to the classification of dermoscopy images. Comp Medical Imaging and Graphics 31(6), (2007). [9] Ganster, H., Pinz, A., Rohrer, R., Wildling, E., Blinder, M., Kittler H.: Automated Melanoma Recognition. IEEE Trans on Biom Eng 20(3), (2001). [10] Marques, J.S., Barata, C., Mendonça, T.: On the role of texture and color in the classification of dermoscopy images. Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE. [11] Andreassi, L., Perotti, R., Rubegni, P., Burroni, M., Cevenini, G., Biagioli, M., Taddeucci, P., Dell Eva, G., Barbini, P.: Digital Dermoscopy Analysis for the Differentiation of Atypical Nevi and Early Melanoma: a new quantitative semiology. Archives of Dermatological Research 135, (1999). [12] Ecral, F., Chawla, A., Stoecker, W. V., Lee, H.-C., Moss, R. H.: Neural network diagnosis of malignant melanoma from color images. IEEE Trans on Biom Eng 41(9), (1994). [13] Claridge, E., Hall, P. N., Keefe, M., Allen, J.P.: Shape analysis for classification of malignant melanoma. J. Biomed. Eng. 14, (1992). [14] Rubegni, P., Cevenini, G., Burroni, M., Perotti, R., Dell Eva, G., Sbano, P., Miracco, C., Luzi, P., Tosi, P., Barbini, P., Andreassi, L.: Automated diagnosis of pigmented skin lesions. Inter J. of Cancer 101, (2002). [15] Lee, T. K., McLean, D. I., Atkins, M. S.: Irregularity index: A new border irregularity measure for cutaneous melanocytic lesions. Medical Image Analysis 7, (2003). [16] Viola, P., Michael, J.: Robust real-time face detection. Inter J of Comp Vision 57, (2004). [17] Hu, M.-K.: Visual Pattern Recognition by Moment Invariants. IRE Transactions on Information Theory 49, (1962). [18] Zhang, D., Lu, G.: A Comparative Study on Shape Retrieval Using Fourier Descriptors with Different Shape Signatures. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation 14(1), (2003). [19] Jain, Anil K.: Fundamentals of digital image processing. Prentice-Hall, Inc. (1989). [20] Mendonça, T., Ferreira, P. M., Marques, J., Marçal, A. R. S., Rozeira, J.: Accepted for presentation in Proc. PH 2 - A Dermoscopic Image Database for Research and Benchmarking. IEEE EMBC, [21] Barata, C., Marques, J. S., Rozeira, J.: A System for the Detection of Pigment Network in Dermoscopy Images Using Directional Filters. IEEE Trans on Biom Eng 59(10), (2012) [22] Ruela, M.,Barata, C., Mendonça, T.,Marques, J.S.: What is the role of color in dermoscopy analysis?. Accepted for presentation in Proc. of IbPRIA th Iberian Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis, Madeira, Portugal, [23] Barata, C., Ruela, M., Marques, J S. and Mendonça, T.: A Bag-of- Features Approach for the Classification of Melanomas in Dermoscopy Images: The Role of Color and Texture Descriptors. Accepted for publication in Computer Vision Techniques for the Diagnosis of Skin Cancer Biomedical Imaging 273
Decision Support System for Skin Cancer Diagnosis
 The Ninth International Symposium on Operations Research and Its Applications (ISORA 10) Chengdu-Jiuzhaigou, China, August 19 23, 2010 Copyright 2010 ORSC & APORC, pp. 406 413 Decision Support System for
The Ninth International Symposium on Operations Research and Its Applications (ISORA 10) Chengdu-Jiuzhaigou, China, August 19 23, 2010 Copyright 2010 ORSC & APORC, pp. 406 413 Decision Support System for
THE American Cancer Society estimates that more than
 IEEE SYSTEMS JOURNAL 1 Two Systems for the Detection of Melanomas in Dermoscopy Images Using Texture and Color Features Catarina Barata, Margarida Ruela, Mariana Francisco, Teresa Mendonça, and Jorge S.
IEEE SYSTEMS JOURNAL 1 Two Systems for the Detection of Melanomas in Dermoscopy Images Using Texture and Color Features Catarina Barata, Margarida Ruela, Mariana Francisco, Teresa Mendonça, and Jorge S.
Algorithmic reproduction of asymmetry and border cut-off parameters according to the ABCD rule for dermoscopy
 JEADV ISSN 1468-3083 Blackwell Publishing Ltd ORIGINAL ARTICLE Algorithmic reproduction of asymmetry and border cut-off parameters according to the ABCD rule for dermoscopy G Pellacani,* C Grana, S Seidenari
JEADV ISSN 1468-3083 Blackwell Publishing Ltd ORIGINAL ARTICLE Algorithmic reproduction of asymmetry and border cut-off parameters according to the ABCD rule for dermoscopy G Pellacani,* C Grana, S Seidenari
INCREASE IN incidence and mortality rates for
 Skin Research and Technology 2005; 11: 236 241 Copyright & Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Skin Research and Technology Pigment distribution in melanocytic lesion images:
Skin Research and Technology 2005; 11: 236 241 Copyright & Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Skin Research and Technology Pigment distribution in melanocytic lesion images:
ANN BASED COMPUTER AIDED DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATION OF SKIN CANCERS
 ANN BASED COMPUTER AIDED DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATION OF SKIN CANCERS Sasirooba Thirumavalavann and Sasikala Jayaraman Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Annamalai University, Tamil Nadu,
ANN BASED COMPUTER AIDED DIAGNOSIS AND CLASSIFICATION OF SKIN CANCERS Sasirooba Thirumavalavann and Sasikala Jayaraman Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Annamalai University, Tamil Nadu,
Asymmetry in Dermoscopic Melanocytic Lesion Images: a Computer Description Based on Colour Distribution
 Acta Derm Venereol INVESTIGATIVE REPORT Asymmetry in Dermoscopic Melanocytic Lesion Images: a Computer Description Based on Colour Distribution Stefania Seidenari 1, Giovanni Pellacani 1 and Costantino
Acta Derm Venereol INVESTIGATIVE REPORT Asymmetry in Dermoscopic Melanocytic Lesion Images: a Computer Description Based on Colour Distribution Stefania Seidenari 1, Giovanni Pellacani 1 and Costantino
Improved Melanoma Diagnosis Support System Based on Fractal Analysis of Images
 The Tenth International Symposium on Operations Research and Its Applications (ISORA 2011) Dunhuang, China, August 28 31, 2011 Copyright 2011 ORSC & APORC, pp. 203 210 Improved Melanoma Diagnosis Support
The Tenth International Symposium on Operations Research and Its Applications (ISORA 2011) Dunhuang, China, August 28 31, 2011 Copyright 2011 ORSC & APORC, pp. 203 210 Improved Melanoma Diagnosis Support
AN INTELLIGENT SYSTEM TO DIAGNOSIS THE SKIN DISEASE
 AN INTELLIGENT SYSTEM TO DIAGNOSIS THE SKIN DISEASE Manish Kumar and Rajiv Kumar Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Sharda University Greater Noida, India E-Mail: manishkumar1310@gmail.com
AN INTELLIGENT SYSTEM TO DIAGNOSIS THE SKIN DISEASE Manish Kumar and Rajiv Kumar Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Sharda University Greater Noida, India E-Mail: manishkumar1310@gmail.com
Graph-based Pigment Network Detection in Skin Images
 Graph-based Pigment Network Detection in Skin Images M. Sadeghi a,b, M. Razmara a, M. Ester a, T. K. Lee a,b,c, M. S. Atkins a a Simon Fraser University, 8888 University Drive, Burnaby, BC, Canada, V5A1S6;
Graph-based Pigment Network Detection in Skin Images M. Sadeghi a,b, M. Razmara a, M. Ester a, T. K. Lee a,b,c, M. S. Atkins a a Simon Fraser University, 8888 University Drive, Burnaby, BC, Canada, V5A1S6;
A novel algorithm for the detection of melanoma border
 A novel algorithm for the detection of melanoma border A. HATZIGAIDAS, A. PAPASTERGIOU, P. TZEKIS Department of Electronics, Alexander Technological Educational Institute of Thessaloniki, Sindos, 57400
A novel algorithm for the detection of melanoma border A. HATZIGAIDAS, A. PAPASTERGIOU, P. TZEKIS Department of Electronics, Alexander Technological Educational Institute of Thessaloniki, Sindos, 57400
Lung and Bronchus Cancer Statistics in Virginia - Maps. July
 July 2011 4 July 2011 5 July 2011 6 July 2011 7 Lung and Bronchus Cancer Statistics in Virginia - Notes Sources: Incidence and percent local staging (VA Cancer Registry); mortality (VDH Division of Health
July 2011 4 July 2011 5 July 2011 6 July 2011 7 Lung and Bronchus Cancer Statistics in Virginia - Notes Sources: Incidence and percent local staging (VA Cancer Registry); mortality (VDH Division of Health
Novel ABCD Formula to Diagnose and Feature Ranking of Melanoma
 Novel ABCD Formula to Diagnose and Feature Ranking of Melanoma Reshma. M Research Scholar at Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology, Dept. of E & C UBDT College of Engineering Davangere, India
Novel ABCD Formula to Diagnose and Feature Ranking of Melanoma Reshma. M Research Scholar at Sathyabama Institute of Science and Technology, Dept. of E & C UBDT College of Engineering Davangere, India
South Asian Journal of Engineering and Technology Vol.3, No.9 (2017) 17 22
 South Asian Journal of Engineering and Technology Vol.3, No.9 (07) 7 Detection of malignant and benign Tumors by ANN Classification Method K. Gandhimathi, Abirami.K, Nandhini.B Idhaya Engineering College
South Asian Journal of Engineering and Technology Vol.3, No.9 (07) 7 Detection of malignant and benign Tumors by ANN Classification Method K. Gandhimathi, Abirami.K, Nandhini.B Idhaya Engineering College
ABCD Rules for Melanoma
 World Journal of Technology, Engineering and Research, Volume 2, Issue 1 (2017) 300-308 Contents available at WJTER World Journal of Technology, Engineering and Research Journal Homepage: www.wjter.com
World Journal of Technology, Engineering and Research, Volume 2, Issue 1 (2017) 300-308 Contents available at WJTER World Journal of Technology, Engineering and Research Journal Homepage: www.wjter.com
Colorectal Cancer Statistics in Virginia - Maps. July
 July 2011 5 July 2011 6 July 2011 7 July 2011 8 Colorectal Cancer Statistics in Virginia - Notes Sources: Incidence and percent local staging (VA Cancer Registry); mortality (VDH Division of Health Statistics);
July 2011 5 July 2011 6 July 2011 7 July 2011 8 Colorectal Cancer Statistics in Virginia - Notes Sources: Incidence and percent local staging (VA Cancer Registry); mortality (VDH Division of Health Statistics);
Segmentation and Lesion Detection in Dermoscopic Images
 Segmentation and Lesion Detection in Dermoscopic Images A thesis submitted as partial fulfillment of the requirement of Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) by Khalid Ahmad A Eltayef Computer Science Department
Segmentation and Lesion Detection in Dermoscopic Images A thesis submitted as partial fulfillment of the requirement of Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) by Khalid Ahmad A Eltayef Computer Science Department
AUTOMATIC QUANTIFICATION OF SKIN CANCER
 AUTOMATIC QUANTIFICATION OF SKIN CANCER Dr.R. Pon Periyasamy 1, V.Gayathiri 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Computer Science, Nehru Memorial College, Tamilnadu, India 2Assistant Professor, Department
AUTOMATIC QUANTIFICATION OF SKIN CANCER Dr.R. Pon Periyasamy 1, V.Gayathiri 2 1 Associate Professor, Department of Computer Science, Nehru Memorial College, Tamilnadu, India 2Assistant Professor, Department
Automated Detection and Analysis of Dermoscopic Structures on Dermoscopy Images
 Automated Detection and Analysis of Dermoscopic Structures on Dermoscopy Images Maryam Sadeghi Computing Science Simon Fraser University Burnaby, BC, Canada msa68@sfu.ca Tim K. Lee Cancer Control Research
Automated Detection and Analysis of Dermoscopic Structures on Dermoscopy Images Maryam Sadeghi Computing Science Simon Fraser University Burnaby, BC, Canada msa68@sfu.ca Tim K. Lee Cancer Control Research
Automatic Detection of Early-Stage Malignant Melanoma from Skin Lesion Images
 Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS) 7(4): 173-178 Scholarlink Research Institute Journals, 2016 (ISSN: 2141-7016) jeteas.scholarlinkresearch.com Journal of Emerging
Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences (JETEAS) 7(4): 173-178 Scholarlink Research Institute Journals, 2016 (ISSN: 2141-7016) jeteas.scholarlinkresearch.com Journal of Emerging
New Dermatological Asymmetry Measure of Skin Lesions
 New Dermatological Asymmetry Measure of Skin Lesions Piotr Milczarski, Zofia Stawska Faculty of Physics and Applied Informatics University of Lodz Pomorska str. 149/153, Lodz, Poland {piotr.milczarski,zofia.stawska}@uni.lodz.pl
New Dermatological Asymmetry Measure of Skin Lesions Piotr Milczarski, Zofia Stawska Faculty of Physics and Applied Informatics University of Lodz Pomorska str. 149/153, Lodz, Poland {piotr.milczarski,zofia.stawska}@uni.lodz.pl
Overview of All SEER-Medicare Publications
 Overview of All SEER-Medicare Publications Outcomes Insights, Inc. Mark D. Danese, MHS, PhD Claire Cangialose February 22, 2017 Overview Information was extracted from the National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Overview of All SEER-Medicare Publications Outcomes Insights, Inc. Mark D. Danese, MHS, PhD Claire Cangialose February 22, 2017 Overview Information was extracted from the National Cancer Institute (NCI)
A Novel Image Segmentation Method for Early Detection and Analysis of Melanoma
 A Novel Image Segmentation Method for Early Detection and Analysis of Melanoma L.Anjali Devi 1 & Dr.M.Roja Rani 2 1.M.Tech student,amara Institute of Engineering&Technology,JNTUK,NRT,AP. 2.Professor, Amara
A Novel Image Segmentation Method for Early Detection and Analysis of Melanoma L.Anjali Devi 1 & Dr.M.Roja Rani 2 1.M.Tech student,amara Institute of Engineering&Technology,JNTUK,NRT,AP. 2.Professor, Amara
International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering. Review Paper Volume-5, Issue-12 E-ISSN:
 International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Open Access Review Paper Volume-5, Issue-12 E-ISSN: 2347-2693 Different Techniques for Skin Cancer Detection Using Dermoscopy Images S.S. Mane
International Journal of Computer Sciences and Engineering Open Access Review Paper Volume-5, Issue-12 E-ISSN: 2347-2693 Different Techniques for Skin Cancer Detection Using Dermoscopy Images S.S. Mane
An effective hair removal algorithm for dermoscopy images
 Skin Research and Technology 2013; 0: 1 6 Printed in Singapore All rights reserved doi: 10.1111/srt.12015 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd Skin Research and Technology
Skin Research and Technology 2013; 0: 1 6 Printed in Singapore All rights reserved doi: 10.1111/srt.12015 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd Skin Research and Technology
Melanoma Computer-Aided Diagnosis: Reliability and Feasibility Study
 Vol. 10, 1881 1886, March 15, 2004 Clinical Cancer Research 1881 Featured Article Melanoma Computer-Aided Diagnosis: Reliability and Feasibility Study Marco Burroni, 1 Rosamaria Corona, 2 Giordana Dell
Vol. 10, 1881 1886, March 15, 2004 Clinical Cancer Research 1881 Featured Article Melanoma Computer-Aided Diagnosis: Reliability and Feasibility Study Marco Burroni, 1 Rosamaria Corona, 2 Giordana Dell
Diet, Physical Activity, Weight & Cancer Survivorship: Perspectives from the NCI
 Diet, Physical Activity, Weight & Cancer Survivorship: Perspectives from the NCI American Institute for Cancer Research Meeting October 21, 2010 Catherine M. Alfano, Ph.D. Program Director & Behavioral
Diet, Physical Activity, Weight & Cancer Survivorship: Perspectives from the NCI American Institute for Cancer Research Meeting October 21, 2010 Catherine M. Alfano, Ph.D. Program Director & Behavioral
A Novel Image Segmentation Method for Early Detection and Analysis of Melanoma
 A Novel Image Segmentation Method for Early Detection and Analysis of Melanoma 1 Sk.Mastan, PG Scholar, Department of ECE, Eswar College of engineering, Narasaraopet, Guntur (Dist), A.P, Email Id: sk.mastan1991@gmail.com
A Novel Image Segmentation Method for Early Detection and Analysis of Melanoma 1 Sk.Mastan, PG Scholar, Department of ECE, Eswar College of engineering, Narasaraopet, Guntur (Dist), A.P, Email Id: sk.mastan1991@gmail.com
DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL. Gabriel Salerni 1,2, Teresita Terán 3, Carlos Alonso 1,2, Ramón Fernández-Bussy 1 ABSTRACT
 DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL www.derm101.com The role of dermoscopy and digital dermoscopy follow-up in the clinical diagnosis of melanoma: clinical and dermoscopic features of 99 consecutive primary
DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL www.derm101.com The role of dermoscopy and digital dermoscopy follow-up in the clinical diagnosis of melanoma: clinical and dermoscopic features of 99 consecutive primary
Early Detection: Screening Guidelines
 Early Detection: Screening Guidelines National Cancer Statistics 2015 National Cancer Statistics 1. 6 Million Cases Expected 589,430 Cancer Deaths expected 2015 Virginia Cancer Statistics: Projected cases:
Early Detection: Screening Guidelines National Cancer Statistics 2015 National Cancer Statistics 1. 6 Million Cases Expected 589,430 Cancer Deaths expected 2015 Virginia Cancer Statistics: Projected cases:
INFOSCIENCE TECHNOLOGY: THE IMPACT OF INTERNET ACCESSIBLE MELANOID DATA ON HEALTH ISSUES
 INFOSCIENCE TECHNOLOGY: THE IMPACT OF INTERNET ACCESSIBLE MELANOID DATA ON HEALTH ISSUES JW Grzymała-Busse 1, ZS Hippe 2, M Knap 2 and W Paja 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science,
INFOSCIENCE TECHNOLOGY: THE IMPACT OF INTERNET ACCESSIBLE MELANOID DATA ON HEALTH ISSUES JW Grzymała-Busse 1, ZS Hippe 2, M Knap 2 and W Paja 2 1 Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science,
MELANOMA DETECTION FROM DIGITAL IMAGES USING TEXTURE DISTINCTIVENESS BASED SEGMENTATION Sinu S V 1,Dr.R.A Jaikumar 2, Abhilash S Vasu 3 1
 MELANOMA DETECTION FROM DIGITAL IMAGES USING TEXTURE DISTINCTIVENESS BASED SEGMENTATION Sinu S V 1,Dr.R.A Jaikumar 2, Abhilash S Vasu 3 1 PG Scholar, Dept. of ECE, SHM Engineering College, Kollam, Kerala,
MELANOMA DETECTION FROM DIGITAL IMAGES USING TEXTURE DISTINCTIVENESS BASED SEGMENTATION Sinu S V 1,Dr.R.A Jaikumar 2, Abhilash S Vasu 3 1 PG Scholar, Dept. of ECE, SHM Engineering College, Kollam, Kerala,
An Improved Automated Malignant Melanoma Detection using Image Classification System
 An Improved Automated Malignant Melanoma Detection using Image Classification System 1 Priyanka C Mohan Dept. of Electronics and Communication. KMCT College of Engineering Calicut, India 2 Ms. Nishida
An Improved Automated Malignant Melanoma Detection using Image Classification System 1 Priyanka C Mohan Dept. of Electronics and Communication. KMCT College of Engineering Calicut, India 2 Ms. Nishida
Cancer Cells Detection using OTSU Threshold Algorithm
 Cancer Cells Detection using OTSU Threshold Algorithm Nalluri Sunny 1 Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College Mithinti Srikanth 2 Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College Kodali
Cancer Cells Detection using OTSU Threshold Algorithm Nalluri Sunny 1 Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College Mithinti Srikanth 2 Velagapudi Ramakrishna Siddhartha Engineering College Kodali
Early Detection of Lung Cancer
 Early Detection of Lung Cancer Aswathy N Iyer Dept Of Electronics And Communication Engineering Lymie Jose Dept Of Electronics And Communication Engineering Anumol Thomas Dept Of Electronics And Communication
Early Detection of Lung Cancer Aswathy N Iyer Dept Of Electronics And Communication Engineering Lymie Jose Dept Of Electronics And Communication Engineering Anumol Thomas Dept Of Electronics And Communication
COMPUTERIZED SYSTEM DESIGN FOR THE DETECTION AND DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG NODULES IN CT IMAGES 1
 ISSN 258-8739 3 st August 28, Volume 3, Issue 2, JSEIS, CAOMEI Copyright 26-28 COMPUTERIZED SYSTEM DESIGN FOR THE DETECTION AND DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG NODULES IN CT IMAGES ALI ABDRHMAN UKASHA, 2 EMHMED SAAID
ISSN 258-8739 3 st August 28, Volume 3, Issue 2, JSEIS, CAOMEI Copyright 26-28 COMPUTERIZED SYSTEM DESIGN FOR THE DETECTION AND DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG NODULES IN CT IMAGES ALI ABDRHMAN UKASHA, 2 EMHMED SAAID
STUDY. Epiluminescence Microscopy for the Diagnosis of Doubtful Melanocytic Skin Lesions
 STUDY Epiluminescence Microscopy for the Diagnosis of Doubtful Melanocytic Skin Lesions Comparison of the ABCD Rule of Dermatoscopy and a New 7-Point Checklist Based on Pattern Analysis Giuseppe Argenziano,
STUDY Epiluminescence Microscopy for the Diagnosis of Doubtful Melanocytic Skin Lesions Comparison of the ABCD Rule of Dermatoscopy and a New 7-Point Checklist Based on Pattern Analysis Giuseppe Argenziano,
Skin Lesion Classification using Machine Learning Algorithms
 International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications in Engineering Advanced Technology and Science ISSN:2147-67992147-6799 www.atscience.org/ijisae Original Research Paper Skin Lesion Classification
International Journal of Intelligent Systems and Applications in Engineering Advanced Technology and Science ISSN:2147-67992147-6799 www.atscience.org/ijisae Original Research Paper Skin Lesion Classification
DERMATOSCOPY, ALSO. Inter- and intra-variability of pigmented skin lesions: could the ABCD rule be influenced by host characteristics?
 Skin Research and Technology 2004; 10: 193 199 Copyright & Blackwell Munksgaard 2004 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Skin Research and Technology Inter- and intra-variability of pigmented skin
Skin Research and Technology 2004; 10: 193 199 Copyright & Blackwell Munksgaard 2004 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Skin Research and Technology Inter- and intra-variability of pigmented skin
MODULE 1. LOCAL AND GENERAL CRITERIA IN PIGMENTED MELANOCYTIC LESIONS.
 DERMOSCOPY TEACHING PROGRAMME Dermoscopy Teaching Programme Module 1 MODULE 1. LOCAL AND GENERAL CRITERIA IN PIGMENTED MELANOCYTIC LESIONS. Dermoscopy is a non-invasive in vivo technique that provides
DERMOSCOPY TEACHING PROGRAMME Dermoscopy Teaching Programme Module 1 MODULE 1. LOCAL AND GENERAL CRITERIA IN PIGMENTED MELANOCYTIC LESIONS. Dermoscopy is a non-invasive in vivo technique that provides
An Optimized, Economical and Painless Artificial Intelligence Technique to Diagnose Melanoma
 An Optimized, Economical and Painless Artificial Intelligence Technique to Diagnose Melanoma J.Abdul Jaleel, Sibi Salim, Aswin.R.B Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, TKM College of Engineering,
An Optimized, Economical and Painless Artificial Intelligence Technique to Diagnose Melanoma J.Abdul Jaleel, Sibi Salim, Aswin.R.B Dept. of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, TKM College of Engineering,
Tree Structure for Modeling Skin Lesion Growth
 Chapter 10 Tree Structure for Modeling Skin Lesion Growth Tim K. Lee,,,, Sina Khakabi, Paul Wighton, # Harvey Lui,, David I. McLean and M. Stella Atkins, Departments of Cancer Control Research and Integrative
Chapter 10 Tree Structure for Modeling Skin Lesion Growth Tim K. Lee,,,, Sina Khakabi, Paul Wighton, # Harvey Lui,, David I. McLean and M. Stella Atkins, Departments of Cancer Control Research and Integrative
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/22172 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Rhee, Jasper Immanuel van der Title: Clinical characteristics and management of
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/22172 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Rhee, Jasper Immanuel van der Title: Clinical characteristics and management of
Improved Intelligent Classification Technique Based On Support Vector Machines
 Improved Intelligent Classification Technique Based On Support Vector Machines V.Vani Asst.Professor,Department of Computer Science,JJ College of Arts and Science,Pudukkottai. Abstract:An abnormal growth
Improved Intelligent Classification Technique Based On Support Vector Machines V.Vani Asst.Professor,Department of Computer Science,JJ College of Arts and Science,Pudukkottai. Abstract:An abnormal growth
ISSN: ISO 9001:2008 Certified International Journal of Engineering and Innovative Technology (IJEIT) Volume 3, Issue 2, August 2013
 Diagnosis and Detection of Skin Cancer Using Artificial Intelligence Dr. J. Abdul Jaleel 1, Sibi Salim 2, Aswin.R.B 3 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, TKM College of Engineering, Kerala,
Diagnosis and Detection of Skin Cancer Using Artificial Intelligence Dr. J. Abdul Jaleel 1, Sibi Salim 2, Aswin.R.B 3 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, TKM College of Engineering, Kerala,
An improved Internet-based melanoma screening system with dermatologist-like tumor area extraction algorithm
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 32 (2008) 566 579 An improved Internet-based melanoma screening system with dermatologist-like tumor area extraction
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics 32 (2008) 566 579 An improved Internet-based melanoma screening system with dermatologist-like tumor area extraction
Cancer of the Breast (Female) - Cancer Stat Facts
 Page 1 of 9 Home Statistical Summaries Cancer Stat Facts Cancer of the Breast (Female) Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer Statistics at a Glance At a Glance Estimated New Cases in 2016 % of All New
Page 1 of 9 Home Statistical Summaries Cancer Stat Facts Cancer of the Breast (Female) Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer Statistics at a Glance At a Glance Estimated New Cases in 2016 % of All New
Multispectral Digital Skin Lesion Analysis. Summary
 Subject: Multispectral Digital Skin Lesion Analysis Page: 1 of 8 Last Review Status/Date: March 2016 Multispectral Digital Skin Lesion Analysis Summary There is interest in noninvasive devices that will
Subject: Multispectral Digital Skin Lesion Analysis Page: 1 of 8 Last Review Status/Date: March 2016 Multispectral Digital Skin Lesion Analysis Summary There is interest in noninvasive devices that will
What is Dermoscopy? Early Dermoscopes. Deciphering Dermoscopy: Terminology, Features & Algorithms 6/17/2018
 Deciphering Dermoscopy: Terminology, Features & Algorithms Where did it come from and why do we use it? Jennie T. Clarke, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology University of Utah School of Medicine What
Deciphering Dermoscopy: Terminology, Features & Algorithms Where did it come from and why do we use it? Jennie T. Clarke, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology University of Utah School of Medicine What
EXTRACT THE BREAST CANCER IN MAMMOGRAM IMAGES
 International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 10, Issue 02, February 2019, pp. 96-105, Article ID: IJCIET_10_02_012 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=10&itype=02
International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) Volume 10, Issue 02, February 2019, pp. 96-105, Article ID: IJCIET_10_02_012 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijciet/issues.asp?jtype=ijciet&vtype=10&itype=02
Classification of benign and malignant masses in breast mammograms
 Classification of benign and malignant masses in breast mammograms A. Šerifović-Trbalić*, A. Trbalić**, D. Demirović*, N. Prljača* and P.C. Cattin*** * Faculty of Electrical Engineering, University of
Classification of benign and malignant masses in breast mammograms A. Šerifović-Trbalić*, A. Trbalić**, D. Demirović*, N. Prljača* and P.C. Cattin*** * Faculty of Electrical Engineering, University of
Skin cancer reorganization and classification with deep neural network
 Skin cancer reorganization and classification with deep neural network Hao Chang 1 1. Department of Genetics, Yale University School of Medicine 2. Email: changhao86@gmail.com Abstract As one kind of skin
Skin cancer reorganization and classification with deep neural network Hao Chang 1 1. Department of Genetics, Yale University School of Medicine 2. Email: changhao86@gmail.com Abstract As one kind of skin
ACCELERATING EMPHYSEMA DIAGNOSIS ON LUNG CT IMAGES USING EMPHYSEMA PRE-DETECTION METHOD
 ACCELERATING EMPHYSEMA DIAGNOSIS ON LUNG CT IMAGES USING EMPHYSEMA PRE-DETECTION METHOD 1 KHAIRUL MUZZAMMIL BIN SAIPULLAH, 2 DEOK-HWAN KIM, 3 NURUL ATIQAH ISMAIL 1 Lecturer, 3 Student, Faculty of Electronic
ACCELERATING EMPHYSEMA DIAGNOSIS ON LUNG CT IMAGES USING EMPHYSEMA PRE-DETECTION METHOD 1 KHAIRUL MUZZAMMIL BIN SAIPULLAH, 2 DEOK-HWAN KIM, 3 NURUL ATIQAH ISMAIL 1 Lecturer, 3 Student, Faculty of Electronic
Age-related prevalence of dermatoscopic patterns of acral melanocytic nevi
 DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL www.derm101.com Age-related prevalence of dermatoscopic patterns of acral melanocytic nevi Reiko Suzaki 1, Sumiko Ishizaki 1, Hitoshi Iyatomi 2, Masaru Tanaka 1 1 Department
DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL www.derm101.com Age-related prevalence of dermatoscopic patterns of acral melanocytic nevi Reiko Suzaki 1, Sumiko Ishizaki 1, Hitoshi Iyatomi 2, Masaru Tanaka 1 1 Department
BORDER IRREGULARITY is an important clinical. Predictive power of irregular border shapes for malignant melanomas
 Skin Research and Technology 2005; 11: 1 8 Copyright & Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Skin Research and Technology Predictive power of irregular border shapes for malignant
Skin Research and Technology 2005; 11: 1 8 Copyright & Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Skin Research and Technology Predictive power of irregular border shapes for malignant
ABCD Features Extraction for Malignant Melanoma Using Image Segmentation
 ABCD Features Extraction for Malignant Melanoma Using Image Segmentation Gorintla Mounika Manju, Kompella Venkata Ramana Andhra university college of engineering (A), Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh gorintlamounikamanju@gmail.com
ABCD Features Extraction for Malignant Melanoma Using Image Segmentation Gorintla Mounika Manju, Kompella Venkata Ramana Andhra university college of engineering (A), Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh gorintlamounikamanju@gmail.com
Malignant Melanoma Detection Based on Machine Learning Techniques: A Survey
 Malignant Melanoma Detection Based on Machine Learning Techniques: A Survey 1 Munya A. Arasi, 2 El-Sayed A. El-Dahshan, 3 El-Sayed M. El-Horbaty, 4 Abdel- Badeeh M. Salem 1,3,4 Dept. of Computer Science,
Malignant Melanoma Detection Based on Machine Learning Techniques: A Survey 1 Munya A. Arasi, 2 El-Sayed A. El-Dahshan, 3 El-Sayed M. El-Horbaty, 4 Abdel- Badeeh M. Salem 1,3,4 Dept. of Computer Science,
Detection of Glaucoma and Diabetic Retinopathy from Fundus Images by Bloodvessel Segmentation
 International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT) ISSN: 2249 8958, Volume-5, Issue-5, June 2016 Detection of Glaucoma and Diabetic Retinopathy from Fundus Images by Bloodvessel Segmentation
International Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology (IJEAT) ISSN: 2249 8958, Volume-5, Issue-5, June 2016 Detection of Glaucoma and Diabetic Retinopathy from Fundus Images by Bloodvessel Segmentation
NAÏVE BAYESIAN CLASSIFIER FOR ACUTE LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA DETECTION
 NAÏVE BAYESIAN CLASSIFIER FOR ACUTE LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA DETECTION Sriram Selvaraj 1 and Bommannaraja Kanakaraj 2 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, P.S.N.A College of Engineering and Technology,
NAÏVE BAYESIAN CLASSIFIER FOR ACUTE LYMPHOCYTIC LEUKEMIA DETECTION Sriram Selvaraj 1 and Bommannaraja Kanakaraj 2 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, P.S.N.A College of Engineering and Technology,
Case Report Micromelanomas: A Review of Melanomas 2mmand a Case Report
 Case Reports in Oncological Medicine, Article ID 206260, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/206260 Case Report Micromelanomas: A Review of Melanomas 2mmand a Case Report Sharad P. Paul 1,2,3 1 Skin
Case Reports in Oncological Medicine, Article ID 206260, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/206260 Case Report Micromelanomas: A Review of Melanomas 2mmand a Case Report Sharad P. Paul 1,2,3 1 Skin
Implementation of Automatic Retina Exudates Segmentation Algorithm for Early Detection with Low Computational Time
 www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN: 2319-7242 Volume 5 Issue 10 Oct. 2016, Page No. 18584-18588 Implementation of Automatic Retina Exudates Segmentation Algorithm
www.ijecs.in International Journal Of Engineering And Computer Science ISSN: 2319-7242 Volume 5 Issue 10 Oct. 2016, Page No. 18584-18588 Implementation of Automatic Retina Exudates Segmentation Algorithm
Primary Level Classification of Brain Tumor using PCA and PNN
 Primary Level Classification of Brain Tumor using PCA and PNN Dr. Mrs. K.V.Kulhalli Department of Information Technology, D.Y.Patil Coll. of Engg. And Tech. Kolhapur,Maharashtra,India kvkulhalli@gmail.com
Primary Level Classification of Brain Tumor using PCA and PNN Dr. Mrs. K.V.Kulhalli Department of Information Technology, D.Y.Patil Coll. of Engg. And Tech. Kolhapur,Maharashtra,India kvkulhalli@gmail.com
Copyright 2007 IEEE. Reprinted from 4th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, April 2007.
 Copyright 27 IEEE. Reprinted from 4th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, April 27. This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the
Copyright 27 IEEE. Reprinted from 4th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, April 27. This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the
Analysing the Performance of Classifiers for the Detection of Skin Cancer with Dermoscopic Images
 GRD Journals Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering International Conference on Innovations in Engineering and Technology (ICIET) - 2016 July 2016 e-issn: 2455-5703 Analysing the Performance
GRD Journals Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering International Conference on Innovations in Engineering and Technology (ICIET) - 2016 July 2016 e-issn: 2455-5703 Analysing the Performance
Investigating the performance of a CAD x scheme for mammography in specific BIRADS categories
 Investigating the performance of a CAD x scheme for mammography in specific BIRADS categories Andreadis I., Nikita K. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering National Technical University of
Investigating the performance of a CAD x scheme for mammography in specific BIRADS categories Andreadis I., Nikita K. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering National Technical University of
Introduction to Dermoscopy. Nicholas Compton, MD June 16, 2010
 Introduction to Dermoscopy Nicholas Compton, MD June 16, 2010 Overview What is dermoscopy Brief history Types of dermoscopy General approach to lesion of interest 2 step algorithm 3-point checklist Practice
Introduction to Dermoscopy Nicholas Compton, MD June 16, 2010 Overview What is dermoscopy Brief history Types of dermoscopy General approach to lesion of interest 2 step algorithm 3-point checklist Practice
A developed system for melanoma diagnosis
 International Journal of Computer Vision and Signal Processing, 3(1), 10-17(2013) ORIGINAL ARTICLE A developed system for melanoma diagnosis Nadia Smaoui Control and Energy Management laboratory National
International Journal of Computer Vision and Signal Processing, 3(1), 10-17(2013) ORIGINAL ARTICLE A developed system for melanoma diagnosis Nadia Smaoui Control and Energy Management laboratory National
Detection of melanoma from dermoscopic images of naevi acquired under uncontrolled conditions.
 Detection of melanoma from dermoscopic images of naevi acquired under uncontrolled conditions. Arthur Tenenhaus, Alex Nkengne, Jean-Francois Horn, Camille Serruys, Alain Giron, Bernard Fertil To cite this
Detection of melanoma from dermoscopic images of naevi acquired under uncontrolled conditions. Arthur Tenenhaus, Alex Nkengne, Jean-Francois Horn, Camille Serruys, Alain Giron, Bernard Fertil To cite this
IJREAS Volume 2, Issue 2 (February 2012) ISSN: LUNG CANCER DETECTION USING DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING ABSTRACT
 LUNG CANCER DETECTION USING DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING Anita Chaudhary* Sonit Sukhraj Singh* ABSTRACT In recent years the image processing mechanisms are used widely in several medical areas for improving
LUNG CANCER DETECTION USING DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING Anita Chaudhary* Sonit Sukhraj Singh* ABSTRACT In recent years the image processing mechanisms are used widely in several medical areas for improving
Multiple Convolutional Neural Network for Skin Dermoscopic Image Classification
 Multiple Convolutional Neural Network for Skin Dermoscopic Image Classification Yanhui Guo 1 and Amira S. Ashour 2 1Department of Computer Science, University of Illinois at Springfield, Springfield, Illinois,
Multiple Convolutional Neural Network for Skin Dermoscopic Image Classification Yanhui Guo 1 and Amira S. Ashour 2 1Department of Computer Science, University of Illinois at Springfield, Springfield, Illinois,
Trends in dermoscopy use in the UK: results from surveys in 2003 and 2012
 DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL www.derm101.com Trends in dermoscopy use in the UK: results from surveys in 2003 and 2012 Thomas D. Butler 1, Rubeta N. Matin 1, Andrew G. Affleck 2, Colin J. Fleming
DERMATOLOGY PRACTICAL & CONCEPTUAL www.derm101.com Trends in dermoscopy use in the UK: results from surveys in 2003 and 2012 Thomas D. Butler 1, Rubeta N. Matin 1, Andrew G. Affleck 2, Colin J. Fleming
Clinical evaluation of melanomas and common nevi by spectral imaging
 Clinical evaluation of melanomas and common nevi by spectral imaging Ilze Diebele, 1,* Ilona Kuzmina, 1 Alexey Lihachev, 1 Janis Kapostinsh, 2 Alexander Derjabo, 2 Lauma Valeine, 3 and Janis Spigulis 1
Clinical evaluation of melanomas and common nevi by spectral imaging Ilze Diebele, 1,* Ilona Kuzmina, 1 Alexey Lihachev, 1 Janis Kapostinsh, 2 Alexander Derjabo, 2 Lauma Valeine, 3 and Janis Spigulis 1
arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 15 Aug 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 15 Aug 2018 arxiv: v1 [cs.cv] 15 Aug 2018](/thumbs/83/87651811.jpg) Ensemble of Convolutional Neural Networks for Dermoscopic Images Classification Tomáš Majtner 1, Buda Bajić 2, Sule Yildirim 3, Jon Yngve Hardeberg 3, Joakim Lindblad 4,5 and Nataša Sladoje 4,5 arxiv:1808.05071v1
Ensemble of Convolutional Neural Networks for Dermoscopic Images Classification Tomáš Majtner 1, Buda Bajić 2, Sule Yildirim 3, Jon Yngve Hardeberg 3, Joakim Lindblad 4,5 and Nataša Sladoje 4,5 arxiv:1808.05071v1
Classification of Benign and Malignant Vertebral Compression Fractures in Magnetic Resonance Images
 Classification of Benign and Malignant Vertebral Compression Fractures in Magnetic Resonance Images Lucas Frighetto-Pereira, Guilherme Augusto Metzner, Paulo Mazzoncini de Azevedo-Marques, Rangaraj Mandayam
Classification of Benign and Malignant Vertebral Compression Fractures in Magnetic Resonance Images Lucas Frighetto-Pereira, Guilherme Augusto Metzner, Paulo Mazzoncini de Azevedo-Marques, Rangaraj Mandayam
Lesion Border Detection in Dermoscopy Images Using Ensembles of Thresholding Methods
 Skin Research and Technology 2013; 19: e252 e258 Printed in Singapore All rights reserved doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0846.2012.00636.x 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S Skin Research and Technology Lesion Border Detection
Skin Research and Technology 2013; 19: e252 e258 Printed in Singapore All rights reserved doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0846.2012.00636.x 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S Skin Research and Technology Lesion Border Detection
Enhanced Detection of Lung Cancer using Hybrid Method of Image Segmentation
 Enhanced Detection of Lung Cancer using Hybrid Method of Image Segmentation L Uma Maheshwari Department of ECE, Stanley College of Engineering and Technology for Women, Hyderabad - 500001, India. Udayini
Enhanced Detection of Lung Cancer using Hybrid Method of Image Segmentation L Uma Maheshwari Department of ECE, Stanley College of Engineering and Technology for Women, Hyderabad - 500001, India. Udayini
Automated Detection of Vascular Abnormalities in Diabetic Retinopathy using Morphological Entropic Thresholding with Preprocessing Median Fitter
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 3 September 2014 ISSN(online) : 2349-784X Automated Detection of Vascular Abnormalities in Diabetic Retinopathy using Morphological
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 1 Issue 3 September 2014 ISSN(online) : 2349-784X Automated Detection of Vascular Abnormalities in Diabetic Retinopathy using Morphological
Skin Cancer A Personal Approach. Dr Matthew Strack Dunedin New Zealand
 Skin Cancer A Personal Approach Dr Matthew Strack Dunedin New Zealand Outline Dermoscopy Instruments and setup Photochemosurgery Clinical Aim: Leave with 2-3 ideas JLE Benign Junctional Nevus Management
Skin Cancer A Personal Approach Dr Matthew Strack Dunedin New Zealand Outline Dermoscopy Instruments and setup Photochemosurgery Clinical Aim: Leave with 2-3 ideas JLE Benign Junctional Nevus Management
Vector Based Classification of Dermoscopic Images Using SURF
 Vector Based Classification of Dermoscopic Images Using SURF Felsia Thompson 1 and M.K. Jeyakumar 2 1 Research Scholar, Department of Computer Applications, Noorul Islam University, Kumaracoil (TN), India.
Vector Based Classification of Dermoscopic Images Using SURF Felsia Thompson 1 and M.K. Jeyakumar 2 1 Research Scholar, Department of Computer Applications, Noorul Islam University, Kumaracoil (TN), India.
Optical Diagnostic Devices for Evaluating Skin Lesions Suspected of Malignancy. Original Policy Date
 MP 2.01.29 Optical Diagnostic Devices for Evaluating Skin Lesions Suspected of Malignancy Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with
MP 2.01.29 Optical Diagnostic Devices for Evaluating Skin Lesions Suspected of Malignancy Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with
[Solunke, 5(12): December2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor
![[Solunke, 5(12): December2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor [Solunke, 5(12): December2018] ISSN DOI /zenodo Impact Factor](/thumbs/91/107370915.jpg) GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES SKIN CANCER DETECTION USING MATLAB AND IMAGE PROCESSING TOOLSBOX Solunke Ganesh S. Institute of Management Studies and Information Technology, Aurangabad,
GLOBAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND RESEARCHES SKIN CANCER DETECTION USING MATLAB AND IMAGE PROCESSING TOOLSBOX Solunke Ganesh S. Institute of Management Studies and Information Technology, Aurangabad,
Total body photography in high risk patients
 Total body photography in high risk patients Doug Grossman, MD, PhD Department of Dermatology Huntsman Cancer Institute University of Utah Summer AAD F032 Practical Considerations for Patients with Melanoma
Total body photography in high risk patients Doug Grossman, MD, PhD Department of Dermatology Huntsman Cancer Institute University of Utah Summer AAD F032 Practical Considerations for Patients with Melanoma
Facial expression recognition with spatiotemporal local descriptors
 Facial expression recognition with spatiotemporal local descriptors Guoying Zhao, Matti Pietikäinen Machine Vision Group, Infotech Oulu and Department of Electrical and Information Engineering, P. O. Box
Facial expression recognition with spatiotemporal local descriptors Guoying Zhao, Matti Pietikäinen Machine Vision Group, Infotech Oulu and Department of Electrical and Information Engineering, P. O. Box
Percent Surviving 5 Years 89.4%
 Page 1 of 8 Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program Turning Cancer Data Into Discovery Home Statistical Summaries Cancer Stat Fact Sheets Cancer of the Breast SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Breast
Page 1 of 8 Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program Turning Cancer Data Into Discovery Home Statistical Summaries Cancer Stat Fact Sheets Cancer of the Breast SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Breast
On Shape And the Computability of Emotions X. Lu, et al.
 On Shape And the Computability of Emotions X. Lu, et al. MICC Reading group 10.07.2013 1 On Shape and the Computability of Emotion X. Lu, P. Suryanarayan, R. B. Adams Jr., J. Li, M. G. Newman, J. Z. Wang
On Shape And the Computability of Emotions X. Lu, et al. MICC Reading group 10.07.2013 1 On Shape and the Computability of Emotion X. Lu, P. Suryanarayan, R. B. Adams Jr., J. Li, M. G. Newman, J. Z. Wang
Automated Assessment of Diabetic Retinal Image Quality Based on Blood Vessel Detection
 Y.-H. Wen, A. Bainbridge-Smith, A. B. Morris, Automated Assessment of Diabetic Retinal Image Quality Based on Blood Vessel Detection, Proceedings of Image and Vision Computing New Zealand 2007, pp. 132
Y.-H. Wen, A. Bainbridge-Smith, A. B. Morris, Automated Assessment of Diabetic Retinal Image Quality Based on Blood Vessel Detection, Proceedings of Image and Vision Computing New Zealand 2007, pp. 132
22/04/2015. Dermoscopy of Melanoma. Ilsphi Browne. Overview
 Dermoscopy of Melanoma Ilsphi Browne Overview The device Dermoscopic criteria (terminology) Colour Patterns Global features Local features Approach to diagnosing pigmented lesions Other uses in general
Dermoscopy of Melanoma Ilsphi Browne Overview The device Dermoscopic criteria (terminology) Colour Patterns Global features Local features Approach to diagnosing pigmented lesions Other uses in general
Melanoma Skin Cancer Detection by Segmentation and Feature Extraction using combination of OTSU and STOLZ Algorithm Technique
 Melanoma Skin Cancer Detection by Segmentation and Feature Extraction using combination of OTSU and STOLZ Algorithm Technique Nayana Banjan #1, Prajkta Dalvi #2, Neha Athavale #3 #1 Degree of Bachelor,
Melanoma Skin Cancer Detection by Segmentation and Feature Extraction using combination of OTSU and STOLZ Algorithm Technique Nayana Banjan #1, Prajkta Dalvi #2, Neha Athavale #3 #1 Degree of Bachelor,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 20, NO. 3, MARCH II. COMPUTER AIDED IMAGE ANALYSIS IN MELANOMA RESEARCH
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 20, NO. 3, MARCH 2001 233 Correspondence Automated Melanoma Recognition Harald Ganster*, Axel Pinz, Reinhard Röhrer, Ernst Wildling, Michael Binder, and Harald
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING, VOL. 20, NO. 3, MARCH 2001 233 Correspondence Automated Melanoma Recognition Harald Ganster*, Axel Pinz, Reinhard Röhrer, Ernst Wildling, Michael Binder, and Harald
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. 980 Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2006), Volume 126 & 2006 The Society for Investigative Dermatology
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Results from an Observational Trial: Digital Epiluminescence Microscopy Follow-Up of Atypical Nevi Increases the Sensitivity and the Chance of Success of Conventional Dermoscopy in Detecting
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Results from an Observational Trial: Digital Epiluminescence Microscopy Follow-Up of Atypical Nevi Increases the Sensitivity and the Chance of Success of Conventional Dermoscopy in Detecting
EARLY STAGE DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG CANCER USING CT-SCAN IMAGES BASED ON CELLULAR LEARNING AUTOMATE
 EARLY STAGE DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG CANCER USING CT-SCAN IMAGES BASED ON CELLULAR LEARNING AUTOMATE SAKTHI NEELA.P.K Department of M.E (Medical electronics) Sengunthar College of engineering Namakkal, Tamilnadu,
EARLY STAGE DIAGNOSIS OF LUNG CANCER USING CT-SCAN IMAGES BASED ON CELLULAR LEARNING AUTOMATE SAKTHI NEELA.P.K Department of M.E (Medical electronics) Sengunthar College of engineering Namakkal, Tamilnadu,
Lung Cancer Detection using CT Scan Images
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 125 (2018) 107 114 6th International Conference on Smart Computing and Communications, ICSCC 2017, 7-8 December 2017, Kurukshetra,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Computer Science 125 (2018) 107 114 6th International Conference on Smart Computing and Communications, ICSCC 2017, 7-8 December 2017, Kurukshetra,
A Software Approach for Border Detection using Pigmented Skin Lesions
 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.17 No.5, May 2017 231 A Software Approach for Border Detection using Pigmented Skin Lesions Qaisar Abbas College of Computer and
IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.17 No.5, May 2017 231 A Software Approach for Border Detection using Pigmented Skin Lesions Qaisar Abbas College of Computer and
Automatic analysis of skin lesions in dermoscopy images: feature extraction and classification
 Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto Automatic analysis of skin lesions in dermoscopy images: feature extraction and classification Ricardo Pereira Cunha de Sousa Lé MONOGRAFIA DE PREPARAÇÃO
Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto Automatic analysis of skin lesions in dermoscopy images: feature extraction and classification Ricardo Pereira Cunha de Sousa Lé MONOGRAFIA DE PREPARAÇÃO
Automatic Detection of Malaria Parasite from Blood Images
 Volume 1, No. 3, May 2012 ISSN 2278-1080 The International Journal of Computer Science & Applications (TIJCSA) RESEARCH PAPER Available Online at http://www.journalofcomputerscience.com/ Automatic Detection
Volume 1, No. 3, May 2012 ISSN 2278-1080 The International Journal of Computer Science & Applications (TIJCSA) RESEARCH PAPER Available Online at http://www.journalofcomputerscience.com/ Automatic Detection
Automatic Detection and Classification of Skin Cancer
 Received: March 1, 2017 444 Automatic Detection and Classification of Skin Cancer Akila Victor 1 * Muhammad Rukunuddin Ghalib 1 1 Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, Tamilnadu, India * Corresponding
Received: March 1, 2017 444 Automatic Detection and Classification of Skin Cancer Akila Victor 1 * Muhammad Rukunuddin Ghalib 1 1 Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, Tamilnadu, India * Corresponding
AUTOMATIC DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DETECTION USING GABOR FILTER WITH LOCAL ENTROPY THRESHOLDING
 AUTOMATIC DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DETECTION USING GABOR FILTER WITH LOCAL ENTROPY THRESHOLDING MAHABOOB.SHAIK, Research scholar, Dept of ECE, JJT University, Jhunjhunu, Rajasthan, India Abstract: The major
AUTOMATIC DIABETIC RETINOPATHY DETECTION USING GABOR FILTER WITH LOCAL ENTROPY THRESHOLDING MAHABOOB.SHAIK, Research scholar, Dept of ECE, JJT University, Jhunjhunu, Rajasthan, India Abstract: The major
1 Introduction. Abstract: Accurate optic disc (OD) segmentation and fovea. Keywords: optic disc segmentation, fovea detection.
 Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering 2017; 3(2): 533 537 Caterina Rust*, Stephanie Häger, Nadine Traulsen and Jan Modersitzki A robust algorithm for optic disc segmentation and fovea detection
Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering 2017; 3(2): 533 537 Caterina Rust*, Stephanie Häger, Nadine Traulsen and Jan Modersitzki A robust algorithm for optic disc segmentation and fovea detection
Basics in Dermoscopy
 Basics in Dermoscopy Manal Bosseila Professor of Dermatology, Cairo University Member of European Academy Dermatology & Venereology EADV Member of International Dermoscopy Society IDS Member of Aesthetic
Basics in Dermoscopy Manal Bosseila Professor of Dermatology, Cairo University Member of European Academy Dermatology & Venereology EADV Member of International Dermoscopy Society IDS Member of Aesthetic
Gabor Wavelet Approach for Automatic Brain Tumor Detection
 Gabor Wavelet Approach for Automatic Brain Tumor Detection Akshay M. Malviya 1, Prof. Atul S. Joshi 2 1 M.E. Student, 2 Associate Professor, Department of Electronics and Tele-communication, Sipna college
Gabor Wavelet Approach for Automatic Brain Tumor Detection Akshay M. Malviya 1, Prof. Atul S. Joshi 2 1 M.E. Student, 2 Associate Professor, Department of Electronics and Tele-communication, Sipna college
ECG Beat Recognition using Principal Components Analysis and Artificial Neural Network
 International Journal of Electronics Engineering, 3 (1), 2011, pp. 55 58 ECG Beat Recognition using Principal Components Analysis and Artificial Neural Network Amitabh Sharma 1, and Tanushree Sharma 2
International Journal of Electronics Engineering, 3 (1), 2011, pp. 55 58 ECG Beat Recognition using Principal Components Analysis and Artificial Neural Network Amitabh Sharma 1, and Tanushree Sharma 2
