Premature Stroke in a Family With Lupus Anticoagulant and Antiphospholipid Antibodies
|
|
|
- Donald Hines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 66 Premature Stroke in a amily With Lupus Anticoagulant and Antiphospholipid Antibodies Peter M. ord, MB, RCP(C), Donald Brunet, MD, RCP(C), David P. Lillicrap, MB, RCP(C), and SaUy E. ord, MB, RCP(C) Lupus anticoagulant and antiphospholipid antibodies are associated with thromboembolic phenomena in individuals both with and without systemic lupus erythematosus. A 32-year-old woman (the index case) with lupus anticoagulant, multiple cerebrovascular events, and a family history of premature stroke raised the possibility of a familial diathesis. Histories or interviews, examinations, and blood tests were obtained for 23 members of four generations of her family. our individuals had suffered strokes and three more had suffered neurologic symptoms. Two living individuals who had suffered strokes, two individuals with neurologic symptoms, and five asymptomatic individuals had antiphospholipid activity in their blood. In addition, a cousin of the index case was found to have systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid activity. Elevated concentrations of von Willebrand factor antigen were found associated with some positive lupus anticoagulant assays, the highest concentrations in the two individuals with stroke. The characteristic presentation of the index case and her good response to treatment suggests that further studies of families in whom antiphospholipid antibodies may represent a risk factor for stroke is worthwhile. (Stroke 1990;21:66-71) Since the original description of lupus anticoagulant (LAC) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), 1 it has become apparent that antiphospholipid antibodies are responsible for the in vitro abnormality 2 and that thrombosis is the associated clinical problem. 34 Numerous associations are described, including recurrent abortion, 5-6 vascular thrombosis, 7 ' 8 thrombocytopenia, 9-10 valvular heart disease, 1112 and cerebrovascular disease. 13 " 16 Antiphospholipid antibodies are also seen in patients without SLE, with similar clinical associations. These patients are increasingly described as having the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. 3 We describe a Caucasian family in which a few members have a history of premature stroke and in which there is a more widespread occurrence of antiphospholipid antibody activity. Recently there have been reports of an association between antiphospholipid antibody activity and strokes in young patients, sometimes against the background of migraine. 16 Since this syndrome may be detectable clinically before a rom the Departments of Medicine (P.M.., D.B., D.P.L.) and Pathology (P.M.., D.P.L., S.E..), Queen's University, Kingston, Canada. D.P.L. is a career scientist of the Ontario Ministry of Health. Address for reprints: Dr. P. M. ord, Room 2043, Etherington Hall, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada K7L 3N6. Received April 20, 1989; accepted August 8, major stroke occurs and since it seems possible to treat these patients effectively with aspirin or anticoagulants, it is important to define more clearly the patient profile and the clinical significance of the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies. Subjects and Methods A questionnaire was applied to all members of the pedigree who were studied, all of whom gave informed consent. In addition to a full medical history, all members were specifically questioned about a history of migraine-like episodes, possible transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), thrombosis, and any drug therapy. A smoking history was obtained, and all females were questioned as to their use of oral contraceptives and any history of miscarriages. or the coagulation assays, blood was collected into 3.2% trisodium citrate (nine parts blood to one part anticoagulant). Platelet-poor plasma was obtained by centrifuging the samples at 3,000g for 15 minutes at 4 C. Plasma was stored at -70 C until tested. Activated partial thromboplastin times (APTTs) were determined using a Coag-a-mate coagulometer (General Diagnostics, Morris Plains, New Jersey) with Actin-S (Dade-American Hospital Supply del Caribe, Inc., Aguada, Puerto Rico) as the first reagent. Testing was repeated using Automated APTT Reagent (Organon Technika Corp., Durham, North Caro-
2 ord et al amilial Lupus Anticoagulant and Stroke 67 (NT {NT 0 a. (JNT 0 tmt f\ Q QJ EMALE m. o 6 Q MALE 0 STROKE OR NEUROLOGIC SYMPTOMS ) POSITIVE LAC /APA t NT DEAD NOT TESTED IGURE 1. Pedigree for family with history of premature stroke. Arrow, index case (III 5); LAC/ APA, lupus anticoagulant and/ or antiphospholipid antibodies. lina) as the second reagent. The presence of LAC was tested using the kaolin clotting time (KCT) as described by Exner et al. 17 LAC was diagnosed as present when the mixing curve was convex in the region of the left axis. Positive samples were screened for the presence of a heparin-like inhibitor with a thrombin clotting time, and the presence of factor VIII antibodies were excluded by a lack of the time-dependency shown by these inhibitors. The concentration of von Willebrand factor antigen (vw Ag) was measured by an electroimmunoassay method as described. 18 Each assay was standardized by including a commercial reference standard (assayed reference plasma, Helena Laboratories, Beaumont, Texas). The range for vw.ag concentration in normal subjects in our laboratory is p.g/dl. Activity assays were also performed for antithrombin III and protein C. or the antiphospholipid antibody assays, antibodies to cardiolipin and phosphatidylserine were detected using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). orty-five microliters of a 50 jig/ml solution of either cardiolipin or phosphatidylserine (Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, Missouri) in ethanol was applied to each well and evaporated to dryness overnight at 4 C under N 2. Two hundred microliters of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 10% fetal calf serum (CS) was then added to each well, and the plate was incubated for 2 hours. The wells were then washed three times with PBS, and 50 /il of either test or control sera diluted l : 40 in PBS containing 10% CS were then added and incubated for 1 hour. All samples were run in duplicate. The wells were then washed and developed with alkaline phosphatase-conjugated goat antihuman IgG or IgM in a standard ELISA. The normal ranges for phospholipid concentrations were established using 50 normal controls. Any result >3 standard deviations (SDs) greater than the mean of the normal controls was regarded as positive. Results are expressed in arbitrary units (AUs); 1 AU is 1 SD greater than the mean of the normal controls, and therefore any value of >3 AU is positive. The range of reactivity for our anticardiolipin assay has been validated against the standards circulated as part of the Kingston Anti- Phospholipid (KAPS) international study group, 19 and their cutoff level for low positives (<20 units) is 2 SDs above the mean for our normal controls (2 AU). The presence of antinuclear antibodies was assayed using a standardfluorescencemethod employing rodent liver as the substrate. 20 luorescence at a dilution of 1:20 or greater was regarded as positive. The presence of double-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) antibodies were sought using the Crithidia luciliae fluorescence assay, 21 with a sample giving fluorescence at a dilution of 1 : 10 or greater being positive. Case Studies Index Case A 32-year-old woman (III 5 in igure 1) presented in the 32nd week of her first pregnancy with weakness and numbness in her left arm. Three and a half months previously she had noticed the onset of daily right-sided supraorbital headaches associated with nausea and photophobia, lasting a few hours at a time. One month before admission she suffered episodes of numbness and tingling in her left arm that had increased in frequency until a few days before admission, when the numbness and tingling became continuous. Shortly before presentation she had also noticed visual blurring in her right eye and periods of confusion and had suffered two amnesic spells. Her medical history was unremarkable. She had taken an oral contraceptive, which she had stopped 6 months before becoming pregnant because of migrainous-type headaches that had then resolved. She had no risk factors for cerebrovascular disease other than a positive family history of stroke occurring at an early age in three close relatives. On examination, the index case was mentally alert. She had mild weakness and subjective loss of pinprick sensation in her left arm. Deep tendon reflexes were increased on the left side; both plantar reflexes were downgoing. There was a right upper temporal
3 68 Stroke Vol 21, No 1, January 1990 TABLE 1. Pt 113 II II 9 III 3 III 5 III 6 HI 7 III 10 Clinical Status and Serologic Data for amily Members Who Tested Positive for Either LAC or Antiphosphollpid Antibodies Age (yr) Sex M M Clinical status Stroke, miscellaneous X2, neurologic symptoms deep-vein thrombosis (pregnant) Stroke Systemic lupus erythematosus on treatment Dizzy episodes on oral contraceptives Antibodies (arbitrary units) PhosphatidylserineIgM count Anticardiolipin vwrag Platelet LAC AN IgG IgM IgG * Pt, patient; LAC, lupus anticoagulant; AN, antinuclear factor, vw-ag, von Willebrand factor antigen (normal range fi/d\). 'May be secondary to pregnancy I quadrantic field defect associated with a small ischemic area in the right retina. Her blood pressure was 115/75 mm Hg, and there was a grade II/VI systolic murmur at the left sternal edge. Her uterus was compatible with a 32-week pregnancy. Hemoglobin concentration was 111 g/1, leukocyte count was 7.5xlO 9 /l, platelet count was 151x1071, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 49 mm/hr. Prothrombin time and partial thromboplastin time were within normal limits, but KCT revealed the presence of LAC. Tests for the presence of antinuclear antibody and anti-dna antibody were negative. Anticardiolipin antibody concentrations were elevated, IgG at 19.3 AU and IgM at 4.2 AU. A test for the presence of IgG phosphatidylserine antibody was also strongly positive at 16.6 AU. VDRL was positive, with a negative confirmatory test (biologic false-positive). Echocardiogram was normal, and carotid Doppler studies showed normal blood flow. Magnetic resonance imaging showed multiple small right-hemispheric white matter hyperintensities on T 2 -weighted images. In the absence of clinical evidence of vasculitis and in view of the presence of LAC and a high concentration of anticardiolipin antibodies, it was felt that her illness was thromboembolic in nature and she was started on 80 mg aspirin/day. Within 48 hours after the start of aspirin therapy, her neurologic episodes and headaches ceased and there was gradual resolution of the neurologic deficit in her left arm. Labor was induced at 38 weeks, resulting in the delivery of a healthy 3,050-g infant. The index case continued on aspirin and 10 months after presentation remains well. Case 2 The index case's mother, aged 64 years (II 3 in igure 1), had suffered episodes of numbness of her lips and left arm with occasional loss of consciousness at age 35 years, diagnosed as epilepsy and treated with antiepileptics without relief. At age 45 years, case 2 had suffered a right-sided hemiplegia with aphasia, and a computed tomogram of her head at that time showed a large left-sided frontoparietal infarction; the results of carotid Doppler blood flow studies were normal. Case 2 continues to have periods of "absence," unaffected by the administration of aspirin. In addition, she has had three first-trimester miscarriages, deep-vein thrombosis, and transient thrombocytopenia. Current investigations show a decreased platelet count of 153x1071, tests negative for antinuclear factor (AN) and antidna antibodies, and a normal KCT but strongly positive antiphospholipid antibody assays (Table 1). In view of the strong family history of stroke and the presence of antiphospholipid antibody activity in mother and daughter, a study of all other available family members was undertaken. The pedigree (igure 1) covers members of four generations, with detailed histories and results of laboratory studies on members of three generations. Results The maternal grandmother of the index case (11 in igure 1) died at age 60 years following several strokes that had occurred during 20 years. The mother of the index case (II 3, or case 2) has had a stroke, three miscarriages, deep-vein thrombosis, and an episode of thrombocytopenia. She had a negative KCT test for LAC but serology positive for anticardiolipin and antiphosphatidylserine antibodies. II 3, or case 2, had nine siblings, of whom one brother (II 2 in igure 1) died at age 52 years following several strokes. Of his four children, one (III 3 in igure 1) had a positive test for LAC and was pregnant at the
4 time of testing; the other three children had normal serology. Three of these four children were asymptomatic. One of the three seronegative children, a 38-year-old woman (III 2 in igure 1), has classical migraine and episodes suggestive of TIAs, which were exacerbated by oral contraceptives. Seven of case 2's other eight siblings are alive and well; one brother (II 5 in igure 1) died at age 49 years of carcinoma. Blood was obtained from six of case 2's remaining seven siblings. Three were negative for all tests. Two (II 8 and II 9 in igure 1) had positive results on the KCT assay for LAC but negative antiphospholipid antibody assays; the third (II 7 in igure 1) had positive results for LAC, AN, anticardiolipin antibodies, and antiphosphatidylserine antibodies. One of his two children, III 6 in igure 1, has SLE and is being treated with steroids and azathioprine. She had positive results for LAC and antiphosphatidylserine antibodies. Her sister, III 7 in igure 1, had had vertiginous episodes while taking oral contraceptives and had positive results for LAC, anticardiolipin antibodies, and antiphosphatidylserine antibodies and a low platelet count. A child of one of case 2's siblings (III 10 in igure 1) had negative results for LAC and AN but positive results for anticardiolipin antibodies. our members of the fourth generation, all grandchildren of case 2's brother who died of stroke (II 2 in igure 1), have been tested; all four are normal. No individual who tested positive had taken drugs recognized as causing antiphospholipid activity. It is of interest that in this pedigree, those individuals testing positive for LAC showed a paradoxical response to the two APTT reagents. In the presence of LAC, the second reagent usually exhibits increased sensitivity to antiphospholipid activity, resulting in a prolonged APTT. In the affected members of this family, APTT with this second reagent were shorter than APTT with the first reagent. In an attempt to identify an independent marker of endothelial cell damage in these subjects, plasma levels of vw.ag were assayed. Of the 19 family members studied, 10 had results above the normal range and eight of the 10 had other serologic abnormalities (either positive LAC or antiphospholipid antibody assays, Table 1). One of these eight (III 3) was pregnant, which could account for her elevated vw.ag concentration, but the greatest elevations (244 and 212 ^/dl) were seen in the index case and case 2, both of whom have had strokes but were not acutely ill at the time of testing. The APTT might be shortened, at least in part, by increased concentrations of coagulation factors such as vw.ag. Antithrombin III and protein C activities were normal in all members of this family, both symptomatic and asymptomatic. Discussion The index case, a young patient with migraine, multiple cerebrovascular events, and LAC, who fits a clinical profile described by this and other centers, 13 > ord et al amilial Lupus Anticoagulant and Stroke 69 and her similarly affected mother pointed to the possibility of a familial diathesis. This is borne out by the family investigation, which revealed other symptomatic members with a variety of laboratory abnormalities indicating antiphospholipid activity and asymptomatic members with similar serologic abnormalities, together with one family member with SLE and another positive for AN. Raised concentrations of vw.ag in some family members suggests the chronic release of von Willebrand factor from damaged endothelium. Alternatively, the elevated levels may represent an additional hereditary abnormality in this family. The clinical symptoms and the results of laboratory tests are, however, not in complete concordance (Table 1). All but one symptomatic family member had one or more laboratory abnormalities. A number of asymptomatic members had one or more positive tests; this may be explained by the propensity of serologic markers in autoimmune disease to occur in asymptomatic family members, 23 or it may indicate that the laboratory abnormalities are markers for some other as-yet undefined factor that promotes thromboembolic events. The presence of antiphospholipid antibodies and LAC in this family in both symptomatic and asymptomatic members argues for a causal association rather than their being the result of thromboembolic events. The raised concentrations of vw.ag in both symptomatic and asymptomatic family members, usually together with other laboratory abnormalities, argues for a perturbation of endothelial cells, perhaps mediated by the antiphospholipid antibodies as has been suggested This also supports a causal relation between antiphospholipid activity and the neurologic symptoms. It is notable that the highest levels of vw.ag were found in the two patients with the most severe symptoms. The lack of concordance between the various tests themselves is not unexpected, having been noted in a large phenothiazine-treated psychiatric population investigated by us, as well as in patients symptomatic for cerebrovascular disorders. 26 The observed discrepancy between the APTT results and those for KCT suggest that the latter is a more sensitive test for the presence of LAC. The patient with SLE (III 6) whose father (II 7) was positive for AN and antiphospholipid antibodies and whose sister (III 7) was also positive for antiphospholipid antibodies raises an additional point of interest. The original descriptions of LAC, as the name implies, and the associated thromboembolic phenomena were in patients with SLE. There have also been reports of the same clinical and serologic associations in patients who clearly do not have SLE, as well as in patients with illnesses bearing many of the features of SLE but who did not meet criteria sufficient for such a diagnosis to be made. This suggests a spectrum of diseases between the so-called antiphospholipid antibody syndrome and a subgroup of patients with SLE who have these antibodies. Additionally, observations that family members of
5 70 Stroke Vol 21, No 1, January 1990 SLE patients may have either LAC 27 or antiphospholipid antibodies 28 suggests that such antibody activity in the blood of patients without SLE may in some cases reflect a genetic susceptibility to SLE. Studies of family members are necessary to examine the possibility that these antibodies are a part of the wider lupus diathesis. Mackie et al 27 also noted LAC activity in the spouses of some SLE patients, suggesting the possibility of transmissible or environmental agents. Although we did not extensively study the spouses in this family, we tested the husbands of the index case and case 1; both men were negative for LAC and antiphospholipid activity. There have been a few reports of the familial occurrence of LAC-like activity in asymptomatic patients without SLE Jacobson et al 32 reported brothers who presented at 39 and 41 years of age with stroke and evidence of both LAC and antiphospholipid antibodies, but tests of the rest of the family were negative. This family is of interest for several reasons. irst, a high incidence of stroke occurring at a young age is associated with a familial incidence of LAC and/or antiphospholipid antibodies. Although the pattern of inheritance is unclear, the genetic susceptibility to the development of various autoimmune conditions has been associated with certain class II human lymphocyte antigen alleles, 33 and a similar association may underlie the familial pattern of disease seen in this family. Second, although it is too early to be certain in the younger members, the presence of such antiphospholipid activity does not appear to be invariably associated with manifestations of thromboembolic disease, suggesting either that such activity is not in itself harmful but merely acts as a marker for another process, or that an additional and as-yet unidentified cofactor is required for disease expression. It is notable that the index case and her cousin (III 7) both developed migraine while taking oral contraceptives, a combination recognized as a risk factor for cerebrovascular events, 34 and that the index case developed major problems while pregnant, as pregnancy itself can cause a hypercoagulable state. Third, the elevated concentrations of vw.ag in the two individuals who have had strokes as well as in several individuals with antiphospholipid activity suggests a chronic endothelial disturbance. Indeed, elevated vwag levels have been reported in SLE in association with thromboembolic phenomena. 35 Last, a cousin (III 2) of the index case has recurrent migraines and possible TIAs, yet she has neither LAC nor any serologic abnormalities. These observations are important because the clinical picture is that of multiple small events rather than a single catastrophic one, and the rapid and sustained response to aspirin in the index case, which is in accord with our experience in some other patients with antiphospholipid-related cerebrovascular syndromes, 16 suggests that early identification of such patients is well worthwhile. urthermore, the study of families with a high incidence of premature stroke may uncover more such groupings and help clarify the pathogenetic mechanisms involved. References 1. Conley CL, Hartmann RC: A hemorrhagic disorder caused by a circulating anticoagulant in patients with disseminated systemic lupus erythematosus (abstract). / Clin Invest 1952; 31: Pengo V, Thiagarajan P, Shapiro SS, Heine MJ: Immunological specificity and mechanism of action of IgG lupus anticoagulants. Blood 1987;70: Harris EN, Gharavi AE, Hughes GRV: Antiphospholipid antibodies. Clin Rheum Dis 1985;ll: Margolius A, Jackson DP, Ratnoff OD: Circulating anticoagulants: A study of 40 cases and a review of the literature. Medicine 1961 ;40: Lockshin MD, Qamar T, Druzin ML, Goei S: Antibody to cardiolipin, lupus anticoagulant and fetal death. / Rheumatol 1987;14: Lubbe W, Butler WS, Palmer SJ, Liggins GC: Lupus anticoagulant in pregnancy. BrJ Obstet Gynaecol 1984;91: Mueh JR, Herbst KD, Rappaport SL: Thrombosis in patients with the lupus anticoagulant. Ann Intern Med 1980;92: Harris EN, Gharavi AE, Boey ML, Patel BM, Mackworth- Young CG, Loizou S, Hughes GRV: Anticardiolipin antibodies: Detection by radioimmunoassay and association with thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 1983; 2: Harris EN, Asherson RA, Gharavi AE, Morgan SH, Derue G, Hughes GRV: Thrombocytopenia in SLE and related autoimmune disorders: Associations with anticardiolipin antibody. Br J Haematol 1985;59: Harris EN, Gharavi AE, Hedge V, Derue G, Morgan SH, Englert H, Chan JKH, Asherson RA, Hughes GRV: Anticardiolipin antibodies in autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura. BrJ Haematol 1985^9: ord PM, ord SE, Lillicrap DP: Association of lupus anticoagulant with severe valvular heart disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. / Rheumatol 1988;15: ord SE, Lillicrap D, Brunet D, ord PM: Thrombotic endocarditis and lupus anticoagulant, a pathogenetic possibility for idiopathic "rheumatic type" valvular heart disease. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1989;113: Coull MB, Bourdette DN, Goodnight SH, Briley DP, Hart R: Multiple cerebral infarctions and dementia associated with cardiolipin antibodies. Stroke 1987;18: Levine SR, Kim S, Deegan MJ, Welch KMA: Ischemic stroke associated with anticardiolipin antibodies. Stroke 1987; 18: Harris EN, Gharavi AE, Asherson RA, Boey ML, Hughes GRV: Cerebral infarction in systemic lupus: Association with anticardiolipin antibodies. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1984;2: Hogan MJ, Brunet DG, ord PM, Lillicrap D: Lupus anticoagulant, antiphospholipid antibodies and migraine. Can J Neurol Sci 1988;15: Exner T, Rickard KA, Kronenberg H: A sensitive test demonstrating lupus anticoagulant and its behavioural patterns. Br J Haematol 1978;4O: Giddings JC, Peake IR: The investigation of factor VIII deficiency, in Thomson JM (ed): Blood Coagulation and Hemostasis, a Practical Guide. Edinburgh, Churchill Livingstone, 1985, p Harris EN: Anticardiolipin versus lupus anticoagulant tests: No final judgment. Ann Rheum Dis 1989;48: ritzler MJ: Immunofluorescent antibody tests, in Rose NR, riedman H, ahey JL (eds): Manual of Clinical Laboratory Immunology. Washington, DC, American Society for Microbiology, 1986, p Ballou SP, Kushner I: Crithidia luciliae immunofluorescence test for antibodies to DNA, in Rose NR, riedman H, ahey JL (eds): Manual of Clinical Laboratory Immunology. Washington, DC, American Society for Microbiology, 1986, pp
6 ord et al amilial Lupus Anticoagulant and Stroke Levine SR, Welch KMA: The spectrum of neurologic disease associated with antiphospholipid antibodies. Arch Neurol 1987; 44: Arnett C: amilial SLE, the HLA system and the genetics of lupus erythematosus, in Wallace DJ, Dubois LE (eds): Lupus Erythematosus. Philadelphia, Lea & ebiger, 1987, pp Malia RG, Greaves M, Rowlands LM, Lawrence ACK, Hume A, Rowell NR, Moult CM, Lindsey M, Hughes P: Anticardiolipin antibodies in systemic sclerosis: Immunological and clinical associations. Clin Exp Immunol 1988;23: Byron MA, Allington MJ, Chapel HM, Mowat AG, Cederholm- Williams SA: Indications of vascular endothelial cell dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 1987; 46: Lockshin MD: Anticardiolipin antibody. Arthritis Rheum 1987; 30: Mackie IJ, Colaco CB, Machin SJ: amilial lupus anticoagulants. BrJ Haematol 1987;67: Shapiro SS, Thiagarajan P: Lupus anticoagulants. Prog Hemost Thromb 1982;6: Mackworth-Young C, Chan J, Harris N, Walport M, Bernstein R, Batchelor R, Hughes GRV, Gharavi A: High incidence of anticardiolipin antibodies in relatives of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. / Rheumatol 1987;14: Hermansky, Dejmal S: Anticoagulant familial a activite antithromboplastique. Nouv Rev r Hematol 1959;14: Exner T, Barber S, Kronenberg H, Rickard KA: amilial association of the lupus anticoagulant. Br J Haematol 1980; 45: Jacobson DM, Lewis JH, Bontempo A, Spero JA, Ragni MV, Reinmuth OM: Recurrent cerebral infarctions in two brothers with antiphospholipid antibodies that block coagulation reactions. Stroke 1986;17: Svejgaard A: HLA and disease, in Rose NR, riedman H, ahey JL (eds): Manual of Clinical Laboratory Immunology. Washington, DC, American Society for Microbiology, 1986, pp Collaborative Group for the Study of Stroke in Young Women: Oral contraception and increased risk of cerebral ischemia or thrombosis. N Engl J Med 1973;288: Angles-Caneto E, Sultan Y, Clauvel JP: Predisposing factors to thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: Possible relation to endothelial cell damage. / Lab Clin Med 1979; 94: KEY WORDS anticoagulants, lupus anticoagulants, antiphospholipid antibodies cerebrovascular disorders
å ORIGINAL ARTICLE å Distribution and Clinical Significance of Lupus Anticoagulant and Anticardiolipin Antibody in 349 Patients with
 å ORIGINAL ARTICLE å Distribution and Clinical Significance of Lupus Anticoagulant and Anticardiolipin Antibody in 349 Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Chiho Ninomiya, Osamu Taniguchi, Toshihiko
å ORIGINAL ARTICLE å Distribution and Clinical Significance of Lupus Anticoagulant and Anticardiolipin Antibody in 349 Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Chiho Ninomiya, Osamu Taniguchi, Toshihiko
Antiphospholipid Syndrome ( APS)
 Antiphospholipid Syndrome ( APS) Edward John Walter Bowie, MD Mayo Medical School the first to identify APS as an acquired thrombophilia Graham Robert Vivian Hughes MD FRCP Unit Rayne Institute St Thomas
Antiphospholipid Syndrome ( APS) Edward John Walter Bowie, MD Mayo Medical School the first to identify APS as an acquired thrombophilia Graham Robert Vivian Hughes MD FRCP Unit Rayne Institute St Thomas
Anti β 2. -Glycoprotein I and Antiphosphatidylserine Antibodies Are Predictors of Arterial Thrombosis in Patients With Antiphospholipid Syndrome
 Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / PREDICTIVE VALUE OF ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID ANTIBODIES Anti β -Glycoprotein I and Antiphosphatidylserine Antibodies Are Predictors of Arterial Thrombosis in Patients With
Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / PREDICTIVE VALUE OF ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID ANTIBODIES Anti β -Glycoprotein I and Antiphosphatidylserine Antibodies Are Predictors of Arterial Thrombosis in Patients With
Key words: antiphospholipid syndrome, trombosis, pathogenesis
 26. XI,. 4/2011,.,..,..,., -..,,. 2GPI. -,.,,., -,, -, -,,,,, IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-10, TNF, INF-. :,, N. Stoilov, R. Rashkov and R. Stoilov. ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME HISTORICAL DATA, ETI-
26. XI,. 4/2011,.,..,..,., -..,,. 2GPI. -,.,,., -,, -, -,,,,, IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-10, TNF, INF-. :,, N. Stoilov, R. Rashkov and R. Stoilov. ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME HISTORICAL DATA, ETI-
Mohammadreza Tabatabaei IBTO COAG LAB
 Tests for the Evaluation of Lupus Anticoagulants t Mohammadreza Tabatabaei MSc Hematology blood bank MSc Hematology blood bank IBTO COAG LAB Lupus Anticoagulants General Background Lupus anticoagulants
Tests for the Evaluation of Lupus Anticoagulants t Mohammadreza Tabatabaei MSc Hematology blood bank MSc Hematology blood bank IBTO COAG LAB Lupus Anticoagulants General Background Lupus anticoagulants
Lupus anticoagulant and anticardiolipin antibodies in SLE with secondary Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome
 Turk J Hematol 2007; 24:69-74 Turkish Society of Hematology RESEARCH ARTICLE Lupus anticoagulant and anticardiolipin antibodies in SLE with secondary Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome Shveta Garg, Annamma
Turk J Hematol 2007; 24:69-74 Turkish Society of Hematology RESEARCH ARTICLE Lupus anticoagulant and anticardiolipin antibodies in SLE with secondary Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome Shveta Garg, Annamma
Manifestation of Antiphospholipid Syndrome among Saudi patients :examining the applicability of sapporo Criteria
 Manifestation of Antiphospholipid Syndrome among Saudi patients :examining the applicability of sapporo Criteria Farjah H AlGahtani Associate professor,md,mph Leukemia,Lymphoma in adolescent,thromboembolic
Manifestation of Antiphospholipid Syndrome among Saudi patients :examining the applicability of sapporo Criteria Farjah H AlGahtani Associate professor,md,mph Leukemia,Lymphoma in adolescent,thromboembolic
Antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with venous thrombosis at Kenyatta National Hospital
 Research article Department of Human Pathology, School of Medicine, University of Nairobi, P. O. Box 19676 00202, Nairobi, Kenya Corresponding author: Dr KA Barasa, Department of Human Pathology, School
Research article Department of Human Pathology, School of Medicine, University of Nairobi, P. O. Box 19676 00202, Nairobi, Kenya Corresponding author: Dr KA Barasa, Department of Human Pathology, School
ANTICARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODIES IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATIC DISEASES
 752 ANTICARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODIES IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATIC DISEASES JOHN G FORT, F SUSAN COWCHOCK, JOHN L ABRUZZO, and J BRUCE SMITH Recent attention has focused on the presence of anticardiolipin (ACL)
752 ANTICARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODIES IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATIC DISEASES JOHN G FORT, F SUSAN COWCHOCK, JOHN L ABRUZZO, and J BRUCE SMITH Recent attention has focused on the presence of anticardiolipin (ACL)
Thrombophilia. Diagnosis and Management. Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI
 Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
LOUISVILLE APL DIAGNOSTICS, INC. APL ELISA IgM Kit
 LOUISVILLE APL DIAGNOSTICS, INC. APL ELISA IgM Kit REF LAPL-K-AP-M-0 For the Measurement of IgM Anticardiolipin Antibodies IVD For In Vitro Diagnostic Use Manufactured by: Louisville APL Diagnostics, Inc.
LOUISVILLE APL DIAGNOSTICS, INC. APL ELISA IgM Kit REF LAPL-K-AP-M-0 For the Measurement of IgM Anticardiolipin Antibodies IVD For In Vitro Diagnostic Use Manufactured by: Louisville APL Diagnostics, Inc.
Warfarin Does Not Interfere with Lupus Anticoagulant Detection by Dilute Russell s Viper Venom Time
 Clin. Lab. 2009;55:XXX-XXX Copyright ORIGINAL ARTICLE Warfarin Does Not Interfere with Lupus Anticoagulant Detection by Dilute Russell s Viper Venom Time HORATIU OLTEANU 2, KATHARINE. A. DOWNES 1, JIGAR
Clin. Lab. 2009;55:XXX-XXX Copyright ORIGINAL ARTICLE Warfarin Does Not Interfere with Lupus Anticoagulant Detection by Dilute Russell s Viper Venom Time HORATIU OLTEANU 2, KATHARINE. A. DOWNES 1, JIGAR
IMMUNOWELL CARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODY (IGM) TEST
 IMMUNOWELL CARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODY (IGM) TEST Product No. 3100 For In Vitro Diagnostic Use SEE CALIBRATION VALUES, TABLE 2, PAGE 3 INTENDED USE The ImmunoWELL Cardiolipin Antibody (IgM) Test is an enzyme
IMMUNOWELL CARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODY (IGM) TEST Product No. 3100 For In Vitro Diagnostic Use SEE CALIBRATION VALUES, TABLE 2, PAGE 3 INTENDED USE The ImmunoWELL Cardiolipin Antibody (IgM) Test is an enzyme
Lupus Anticoagulants (LA), Antiphospholipid (APL) Antibodies & APL Syndrome: Review & Update. Antiphospholipid. Antiphospholipid
 , Antiphospholipid (APL) Antibodies & APL Syndrome: Review & Update William L. Nichols, MD Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Rochester, Minnesota USA Disclosures & Objectives (Nichols) Disclosures Relevant
, Antiphospholipid (APL) Antibodies & APL Syndrome: Review & Update William L. Nichols, MD Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Rochester, Minnesota USA Disclosures & Objectives (Nichols) Disclosures Relevant
LOUISVILLE APL DIAGNOSTICS, INC. APhL ELISA IgG HRP Kit
 LOUISVILLE APL DIAGNOSTICS, INC APhL ELISA IgG HRP Kit REF LAPL-K-HRP-001G For the Measurement of IgG Antiphospholipid Antibodies IVD For In Vitro Diagnostic Use Manufactured by: Louisville APL Diagnostics,
LOUISVILLE APL DIAGNOSTICS, INC APhL ELISA IgG HRP Kit REF LAPL-K-HRP-001G For the Measurement of IgG Antiphospholipid Antibodies IVD For In Vitro Diagnostic Use Manufactured by: Louisville APL Diagnostics,
Anticardiolipin antibodies, livedo reticularis, and major cerebrovascular and renal disease in systemic
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 110-115 Anticardiolipin antibodies, livedo reticularis, and major cerebrovascular and renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus N J McHUGH,' 2 J MAYMO,'
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 110-115 Anticardiolipin antibodies, livedo reticularis, and major cerebrovascular and renal disease in systemic lupus erythematosus N J McHUGH,' 2 J MAYMO,'
Antiphospholipid Syndrome
 Antiphospholipid Syndrome EliA Cardiolipin and EliA β2-glycoprotein I Fully Automated Testing for Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) Testing for APS according to classification criteria determination of anti-β2-glycoprotein
Antiphospholipid Syndrome EliA Cardiolipin and EliA β2-glycoprotein I Fully Automated Testing for Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) Testing for APS according to classification criteria determination of anti-β2-glycoprotein
THE antiphospholipid-antibody syndrome is a
 Vol. 332. 15 MANAGEMENT OF THROMBOSIS IN THE ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID-ANTIBODY SYNDROME 993 THE MANAGEMENT OF THROMBOSIS IN THE ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID-ANTIBODY SYNDROME MUNTHER A. KHAMASHTA, M.D., MARIA JOSE CUADRADO,
Vol. 332. 15 MANAGEMENT OF THROMBOSIS IN THE ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID-ANTIBODY SYNDROME 993 THE MANAGEMENT OF THROMBOSIS IN THE ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID-ANTIBODY SYNDROME MUNTHER A. KHAMASHTA, M.D., MARIA JOSE CUADRADO,
Systemic lupus erythematosus in 50 year olds
 Postgrad Med J (1992) 68, 440-444 The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1992 Systemic lupus erythematosus in 50 year olds I. Domenech, 0. Aydintug, R. Cervera, M. Khamashta, A. Jedryka-Goral, J.L. Vianna
Postgrad Med J (1992) 68, 440-444 The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1992 Systemic lupus erythematosus in 50 year olds I. Domenech, 0. Aydintug, R. Cervera, M. Khamashta, A. Jedryka-Goral, J.L. Vianna
Arterial Ischemic Stroke with Protein S Deficiency in Pakistan
 Case Reports Arterial Ischemic Stroke with Protein S Deficiency in Pakistan Faika Usman, Ali Hassan, Arsalan Ahmad From Section of Neurology, Department of Medicine, Shifa International Hospitals and College
Case Reports Arterial Ischemic Stroke with Protein S Deficiency in Pakistan Faika Usman, Ali Hassan, Arsalan Ahmad From Section of Neurology, Department of Medicine, Shifa International Hospitals and College
TECHNICAL SERIES. Lupus Anticoagulants: Basic Concepts and Laboratory Diagnosiss. ...Setting trends TULIP DIAGNOSTICS (P) LTD.
 For the use of Registered Medical Practioners and Laboratories only TECHNICAL SERIES Lupus Anticoagulants: Basic Concepts and Laboratory Diagnosiss TULIP DIAGNOSTICS (P) LTD. Gitanjali, Tulip Block, Dr.
For the use of Registered Medical Practioners and Laboratories only TECHNICAL SERIES Lupus Anticoagulants: Basic Concepts and Laboratory Diagnosiss TULIP DIAGNOSTICS (P) LTD. Gitanjali, Tulip Block, Dr.
ANTICARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODIES IN PATIENTS WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS
 382 ANTICARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODIES IN PATIENTS WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS GUNNAR STURFELT, OLA NIVED, RENEE NORBERG, RIGMOR THORSTENSSON, and KATARINA KROOK We studied a group of 59 unselected patients
382 ANTICARDIOLIPIN ANTIBODIES IN PATIENTS WITH SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS GUNNAR STURFELT, OLA NIVED, RENEE NORBERG, RIGMOR THORSTENSSON, and KATARINA KROOK We studied a group of 59 unselected patients
patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
 332 Institute of Clinical Medicine I, University of Rome "La Sapienza," Rome, Italy D Ferro M Saliola C Quintarelli G Valesini S Basili A M Grandilli M S Bonavita F Violi Correspondence to: Dr Francesco
332 Institute of Clinical Medicine I, University of Rome "La Sapienza," Rome, Italy D Ferro M Saliola C Quintarelli G Valesini S Basili A M Grandilli M S Bonavita F Violi Correspondence to: Dr Francesco
DISCLOSURE. Presented by: Merav Sendowski, MD Oregon Health and Science University
 Thrombophilia! DISCLOSURE Presented by: Merav Sendowski, MD Oregon Health and Science University Created by: Thomas Deloughery, MD Oregon Health and Science University Current Relevant Financial Relationship(s)
Thrombophilia! DISCLOSURE Presented by: Merav Sendowski, MD Oregon Health and Science University Created by: Thomas Deloughery, MD Oregon Health and Science University Current Relevant Financial Relationship(s)
Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT?
 Carotid artery stenosis and risk of stroke Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT? Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS Faculty of Medicine of University of Porto Munich, 2016
Carotid artery stenosis and risk of stroke Are there still any valid indications for thrombophilia screening in DVT? Armando Mansilha MD, PhD, FEBVS Faculty of Medicine of University of Porto Munich, 2016
ACTICLOT dpt REF 824. IVD C i 2 l. Dilute Prothrombin Time Test for the Determination of Lupus Anticoagulants (LA) (CPT Code No.
 Sekisui Diagnostics, LLC 500 West Avenue, Stamford, CT 06902 M Tel. (203) 602-7777 Fax (203) 602-2221 INTENDED USE The ACTICLOT dpt is intended for the qualitative determination of Lupus Anticoagulants
Sekisui Diagnostics, LLC 500 West Avenue, Stamford, CT 06902 M Tel. (203) 602-7777 Fax (203) 602-2221 INTENDED USE The ACTICLOT dpt is intended for the qualitative determination of Lupus Anticoagulants
Thrombophilia. Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS
 Autoimmune Thrombophilia Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS Saraf@sina.tums.ac.ir Acquired Thrombophilia HIT PNH Cyckle cell Anemia Myeloproliferative lf Diseases Thrombocytosis
Autoimmune Thrombophilia Dr. A Sarrafnejad PhD Dep. Immunology School of public health TUMS Saraf@sina.tums.ac.ir Acquired Thrombophilia HIT PNH Cyckle cell Anemia Myeloproliferative lf Diseases Thrombocytosis
antiphospholipid antibody binding to platelet membranes*
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 849-854 Immune mediated mechanism for thrombosis: antiphospholipid antibody binding to platelet membranes* MUNTHER A KHAMASHTA,1 E NIGEL HARRIS,2 AZZUDIN E GHARAVI,3
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 849-854 Immune mediated mechanism for thrombosis: antiphospholipid antibody binding to platelet membranes* MUNTHER A KHAMASHTA,1 E NIGEL HARRIS,2 AZZUDIN E GHARAVI,3
Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome: Management Issues for the Hematologist
 Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome: Management Issues for the Hematologist Wisconsin Institute of Discovery Karen Rossi/Bristol-Myers Squibb Morey A. Blinder, MD Washington University, St. Louis, MO March
Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome: Management Issues for the Hematologist Wisconsin Institute of Discovery Karen Rossi/Bristol-Myers Squibb Morey A. Blinder, MD Washington University, St. Louis, MO March
Antiphospholipid syndrome: five year follow up
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1991; 50: 805-810 805 Lupus Arthritis Research Unit, The Rayne Institute, St Thomas's Hospital, London SEI 7EH R A Asherson E Baguley C Pal G R V Hughes Correspondence
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1991; 50: 805-810 805 Lupus Arthritis Research Unit, The Rayne Institute, St Thomas's Hospital, London SEI 7EH R A Asherson E Baguley C Pal G R V Hughes Correspondence
Inherited Thrombophilia Testing. George Rodgers, MD, PhD Kristi Smock MD
 Inherited Thrombophilia Testing George Rodgers, MD, PhD Kristi Smock MD Prevalence and risk associated with inherited thrombotic disorders Inherited Risk Factor % General Population % Patients w/ Thrombosis
Inherited Thrombophilia Testing George Rodgers, MD, PhD Kristi Smock MD Prevalence and risk associated with inherited thrombotic disorders Inherited Risk Factor % General Population % Patients w/ Thrombosis
Vague Neurological Conditions
 Vague Neurological Conditions Dr. John Lefebre, MD, FRCPC Chief Regional Medical Director Europe, India, South Africa, Middle East and Turkey Canada 2014 2 3 4 Agenda Dr. John Lefebre, M.D., FRCPC 1. TIA
Vague Neurological Conditions Dr. John Lefebre, MD, FRCPC Chief Regional Medical Director Europe, India, South Africa, Middle East and Turkey Canada 2014 2 3 4 Agenda Dr. John Lefebre, M.D., FRCPC 1. TIA
Thyroid disease and haemostasis: a relationship with clinical implications? Squizzato, A.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Thyroid disease and haemostasis: a relationship with clinical implications? Squizzato, A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Squizzato, A.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Thyroid disease and haemostasis: a relationship with clinical implications? Squizzato, A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Squizzato, A.
patients with fetal loss
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1991; 50: 553-557 553 Department of Internal Medicine (Division of Immunopathology), University Hospital Utrecht, H J Out M van Vliet R H W M Derksen Department of Obstetrics
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1991; 50: 553-557 553 Department of Internal Medicine (Division of Immunopathology), University Hospital Utrecht, H J Out M van Vliet R H W M Derksen Department of Obstetrics
Antiphospholipid antibodies
 CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE Antiphospholipid Antibodies Caron P. Misita, PharmD; Stephan Moll, MD Antiphospholipid antibodies (APLAs) are proteins that may be present in the blood and
CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE CARDIOLOGY PATIENT PAGE Antiphospholipid Antibodies Caron P. Misita, PharmD; Stephan Moll, MD Antiphospholipid antibodies (APLAs) are proteins that may be present in the blood and
Committee Approval Date: May 9, 2014 Next Review Date: May 2015
 Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru248 Topic: Benlysta, belimumab Date of Origin: May 13, 2011 Committee Approval Date: May 9, 2014 Next Review Date: May 2015 Effective Date: June 1, 2014 IMPORTANT
Medication Policy Manual Policy No: dru248 Topic: Benlysta, belimumab Date of Origin: May 13, 2011 Committee Approval Date: May 9, 2014 Next Review Date: May 2015 Effective Date: June 1, 2014 IMPORTANT
AN INTERESTING CASE OF RESPIRATORY DISTRESS. Dr.V.Akila Devi DNB PG Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital Chennai
 AN INTERESTING CASE OF RESPIRATORY DISTRESS Dr.V.Akila Devi DNB PG Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital Chennai 11 month old female infant 1 st born to parents of NC marriage referred from Kolkatta H/O:
AN INTERESTING CASE OF RESPIRATORY DISTRESS Dr.V.Akila Devi DNB PG Southern Railway Headquarters Hospital Chennai 11 month old female infant 1 st born to parents of NC marriage referred from Kolkatta H/O:
Plasma From Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients With Antiphospholipid Antibodies Promotes Platelet Aggregation. Studies in a Perfusion System
 196 Plasma rom Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients With Antiphospholipid Antibodies Promotes Platelet Aggregation Studies in a Perfusion System G. Escolar, J. ont, J.C. Reverter, A. Lopez-Soto, M. Garrido,
196 Plasma rom Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients With Antiphospholipid Antibodies Promotes Platelet Aggregation Studies in a Perfusion System G. Escolar, J. ont, J.C. Reverter, A. Lopez-Soto, M. Garrido,
Coagulation Disorders. Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU
 Coagulation Disorders Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU 1 Introduction Local Vs. General Hematoma & Joint bleed Coagulation Skin/Mucosal Petechiae & Purpura PLT wound / surgical bleeding Immediate
Coagulation Disorders Dr. Muhammad Shamim Assistant Professor, BMU 1 Introduction Local Vs. General Hematoma & Joint bleed Coagulation Skin/Mucosal Petechiae & Purpura PLT wound / surgical bleeding Immediate
L iter diagnostico di laboratorio nelle coagulopatie congenite emorragiche
 L iter diagnostico di laboratorio nelle coagulopatie congenite emorragiche Armando Tripodi Angelo Bianchi Bonomi Hemophilia and Thrombosis Center Dept. of Clinical Sciences and Community Health University
L iter diagnostico di laboratorio nelle coagulopatie congenite emorragiche Armando Tripodi Angelo Bianchi Bonomi Hemophilia and Thrombosis Center Dept. of Clinical Sciences and Community Health University
THROMBOPHILIA SCREENING
 THROMBOPHILIA SCREENING Introduction The regulation of haemostasis Normally, when a clot occurs, it exactly occurs where it has to be and does not grow more than necessary due to the action of the haemostasis
THROMBOPHILIA SCREENING Introduction The regulation of haemostasis Normally, when a clot occurs, it exactly occurs where it has to be and does not grow more than necessary due to the action of the haemostasis
Thrombophilia. Stephan Moll, MD Medicine, Heme-Coag UNC Chapel Hill, NC. GASCO Atlanta Sept 8 th, Disclosures. Conflicts of interest: NONE
 LA APLA 1 3 ACA Anti-ß2-GP I 2 45 Thrombophilia Stephan Moll, MD Medicine, Heme-Coag UNC Chapel Hill, NC GASCO Atlanta Sept 8 th, 2017 Disclosures Conflicts of interest: NONE Off-label product use discussion:
LA APLA 1 3 ACA Anti-ß2-GP I 2 45 Thrombophilia Stephan Moll, MD Medicine, Heme-Coag UNC Chapel Hill, NC GASCO Atlanta Sept 8 th, 2017 Disclosures Conflicts of interest: NONE Off-label product use discussion:
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13
 Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13 Mark Cunningham,MD Director, Hematology Laboratory Department of Pathology University of Kansas Medical Center College of American Pathologists
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura and the Role of ADAMTS-13 Mark Cunningham,MD Director, Hematology Laboratory Department of Pathology University of Kansas Medical Center College of American Pathologists
HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders
 HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders When injury occurs, three mechanisms occur Blood vessels Primary hemostasis Secondary hemostasis Diseases of the blood vessels Platelet disorders Thrombocytopenia Functional
HEME 10 Bleeding Disorders When injury occurs, three mechanisms occur Blood vessels Primary hemostasis Secondary hemostasis Diseases of the blood vessels Platelet disorders Thrombocytopenia Functional
T he antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is a thrombophilic
 1639 EXTENDED REPORT ntiphospholipid antibody tests: spreading the net M L ertolaccini, S Gomez, J F P Pareja, Theodoridou, G Sanna, G R V Hughes, M Khamashta... See end of article for authors affiliations...
1639 EXTENDED REPORT ntiphospholipid antibody tests: spreading the net M L ertolaccini, S Gomez, J F P Pareja, Theodoridou, G Sanna, G R V Hughes, M Khamashta... See end of article for authors affiliations...
Coagulation disorders (thrombophilias) are a rare but
 Physician Knowledge and Practices in the Evaluation of Coagulopathies in Stroke Patients Cheryl D. Bushnell, MD, MHS; Larry B. Goldstein, MD Background and Purpose Coagulopathies are a rare cause of ischemic
Physician Knowledge and Practices in the Evaluation of Coagulopathies in Stroke Patients Cheryl D. Bushnell, MD, MHS; Larry B. Goldstein, MD Background and Purpose Coagulopathies are a rare cause of ischemic
The Antiphospholipid Syndrome
 The Antiphospholipid Syndrome 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Antiphospholipid Syndrome Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (commonly called antiphospholipid syndrome or APS) is an autoimmune disease present mostly
The Antiphospholipid Syndrome 1 / 6 2 / 6 3 / 6 The Antiphospholipid Syndrome Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (commonly called antiphospholipid syndrome or APS) is an autoimmune disease present mostly
Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Kristine Krafts, M.D. Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Bleeding disorders von Willebrand disease Hemophilia A and B DIC TTP/HUS ITP Thrombotic disorders Factor V Leiden
Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Kristine Krafts, M.D. Bleeding and Thrombotic Disorders Bleeding disorders von Willebrand disease Hemophilia A and B DIC TTP/HUS ITP Thrombotic disorders Factor V Leiden
Prevalence of antiphospholipid auto antibodies in patients with thrombosis
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 6/ September 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Prevalence of antiphospholipid auto antibodies in patients
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 6/ September 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Prevalence of antiphospholipid auto antibodies in patients
Thursday, February 26, :00 am. Regulation of Coagulation/Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation HEMOSTASIS/THROMBOSIS III
 REGULATION OF COAGULATION Introduction HEMOSTASIS/THROMBOSIS III Regulation of Coagulation/Disseminated Coagulation necessary for maintenance of vascular integrity Enough fibrinogen to clot all vessels
REGULATION OF COAGULATION Introduction HEMOSTASIS/THROMBOSIS III Regulation of Coagulation/Disseminated Coagulation necessary for maintenance of vascular integrity Enough fibrinogen to clot all vessels
Neurological involvement in antiphospholipid antibodies syndrome (APS)
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Neurological involvement in antiphospholipid antibodies syndrome (APS) A. AMOROSO, A.P. MITTERHOFER, G.M. FERRI, S. GALLUZZO, M. VADACCA, A. AFELTRA
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Neurological involvement in antiphospholipid antibodies syndrome (APS) A. AMOROSO, A.P. MITTERHOFER, G.M. FERRI, S. GALLUZZO, M. VADACCA, A. AFELTRA
10/24/2013. Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy:
 Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy: Heparin-Induced (HIT) Michael H. Creer, MD Professor of Pathology Director, Clinical Laboratories, Medical Co- Director, Hematopathology and Chief, Division
Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy: Heparin-Induced (HIT) Michael H. Creer, MD Professor of Pathology Director, Clinical Laboratories, Medical Co- Director, Hematopathology and Chief, Division
Thrombophilia: To test or not to test
 Kenneth Bauer, MD Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Professor of Medicine VA Boston Healthcare System Chief, Hematology Section Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA Director, Thrombosis Clinical
Kenneth Bauer, MD Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Professor of Medicine VA Boston Healthcare System Chief, Hematology Section Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, MA Director, Thrombosis Clinical
CEREBRO VASCULAR ACCIDENTS
 CEREBRO VASCULAR S MICHAEL OPONG-KUSI, DO MBA MORTON CLINIC, TULSA, OK, USA 8/9/2012 1 Cerebrovascular Accident Third Leading cause of deaths (USA) 750,000 strokes in USA per year. 150,000 deaths in USA
CEREBRO VASCULAR S MICHAEL OPONG-KUSI, DO MBA MORTON CLINIC, TULSA, OK, USA 8/9/2012 1 Cerebrovascular Accident Third Leading cause of deaths (USA) 750,000 strokes in USA per year. 150,000 deaths in USA
Autoantibodies have been implicated in a variety of diseases.
 Antiphospholipid Antibodies Douglas A. Triplett, MD Objective. To review the role of lupus anticoagulants in the pathogenesis of both venous and arterial thromboembolic events, as well as in recurrent
Antiphospholipid Antibodies Douglas A. Triplett, MD Objective. To review the role of lupus anticoagulants in the pathogenesis of both venous and arterial thromboembolic events, as well as in recurrent
Laboratory Evaluation of Venous Thrombosis Risk
 Laboratory Evaluation of Venous Thrombosis Risk Dorothy M. Adcock, MD Volume 17, Number 12 December 2003 Objective: The reader will be able to discuss the concepts of risk factor, risk potential and thrombotic
Laboratory Evaluation of Venous Thrombosis Risk Dorothy M. Adcock, MD Volume 17, Number 12 December 2003 Objective: The reader will be able to discuss the concepts of risk factor, risk potential and thrombotic
Sindrome da anticorpi antifosfolipidi: clinica e terapia. Vittorio Pengo Clinical Cardiology, Padova, Italy
 Sindrome da anticorpi antifosfolipidi: clinica e terapia Vittorio Pengo Clinical Cardiology, Padova, Italy Revised Classification Criteria for the Antiphospholipid Syndrome J Thromb Haemost 2006;4:295-306
Sindrome da anticorpi antifosfolipidi: clinica e terapia Vittorio Pengo Clinical Cardiology, Padova, Italy Revised Classification Criteria for the Antiphospholipid Syndrome J Thromb Haemost 2006;4:295-306
Anticardiolipin Antibodies in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 CM&R Rapid Release. Published online ahead of print February 26, 2009 as doi:10.3121/cmr.2008.828 Original Research Anticardiolipin Antibodies in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus José María Calvo-Romero,
CM&R Rapid Release. Published online ahead of print February 26, 2009 as doi:10.3121/cmr.2008.828 Original Research Anticardiolipin Antibodies in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus José María Calvo-Romero,
Chapter. Absolute risk of venous and arterial thrombosis in HIV-infected patients and effects of combination antiretroviral therapy
 Chapter Absolute risk of venous and arterial thrombosis in HIV-infected patients and effects of combination antiretroviral therapy Willem M. Lijfering Min Ki ten Kate Herman G. Sprenger Jan van der Meer
Chapter Absolute risk of venous and arterial thrombosis in HIV-infected patients and effects of combination antiretroviral therapy Willem M. Lijfering Min Ki ten Kate Herman G. Sprenger Jan van der Meer
A Percent Correction Formula for Evaluation of Mixing Studies
 Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / A PERCENT CORRECTION FORMULA FOR EVALUATION OF MIXING STUDIES A Percent Correction Formula for Evaluation of Mixing Studies Sheng-hsiung Chang, MD, Veronica Tillema,
Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / A PERCENT CORRECTION FORMULA FOR EVALUATION OF MIXING STUDIES A Percent Correction Formula for Evaluation of Mixing Studies Sheng-hsiung Chang, MD, Veronica Tillema,
criterion (positive lupus anticoagulant or
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 66, No.4, October 1996 Copyright 1996 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Printed on acid~free paper in U. s. A. Antiphospholipid antibody panels and recurrent pregnancy
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 66, No.4, October 1996 Copyright 1996 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Printed on acid~free paper in U. s. A. Antiphospholipid antibody panels and recurrent pregnancy
Laboratory Diagnosis of Lupus Inhibitors: A Comparison of the Tissue Thromboplastin Inhibition Procedure with a New Platelet Neutralization Procedure
 Laboratory Diagnosis of Lupus Inhibitors: A Comparison of the Tissue Thromboplastin Inhibition Procedure with a New Platelet Neutralization Procedure DOUGLAS A. TRIPLETT, M.D., JOHN T. BRANDT, M.D. JANIS
Laboratory Diagnosis of Lupus Inhibitors: A Comparison of the Tissue Thromboplastin Inhibition Procedure with a New Platelet Neutralization Procedure DOUGLAS A. TRIPLETT, M.D., JOHN T. BRANDT, M.D. JANIS
Guidelines. 704 q 2000 Blackwell Science Ltd GUIDELINES ON THE INVESTIGATION AND MANAGEMENT OF THE ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME
 British Journal of Haematology 2000, 109, 704±715 Guidelines GUIDELINES ON THE INVESTIGATION AND MANAGEMENT OF THE ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME In 1991, the Haemostasis and Thrombosis Task Force of the British
British Journal of Haematology 2000, 109, 704±715 Guidelines GUIDELINES ON THE INVESTIGATION AND MANAGEMENT OF THE ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME In 1991, the Haemostasis and Thrombosis Task Force of the British
Cerebrovascular Disorders. Blood, Brain, and Energy. Blood Supply to the Brain 2/14/11
 Cerebrovascular Disorders Blood, Brain, and Energy 20% of body s oxygen usage No oxygen/glucose reserves Hypoxia - reduced oxygen Anoxia - Absence of oxygen supply Cell death can occur in as little as
Cerebrovascular Disorders Blood, Brain, and Energy 20% of body s oxygen usage No oxygen/glucose reserves Hypoxia - reduced oxygen Anoxia - Absence of oxygen supply Cell death can occur in as little as
Patient with Musculo-skeletal Complaints - Summary
 Patient with Musculo-skeletal Complaints - Summary 1. Soft Tissue Rheumatism or Arthritis 2. Arthritis Monoarticular Polyarticular - :- (Asymmetrical) (Symetrical) :- -Crystals, Gout - Infective acute
Patient with Musculo-skeletal Complaints - Summary 1. Soft Tissue Rheumatism or Arthritis 2. Arthritis Monoarticular Polyarticular - :- (Asymmetrical) (Symetrical) :- -Crystals, Gout - Infective acute
Hemostasis. PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures
 Hemostasis PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures Disorders of Hemostasis - Hemophilia - von Willebrand Disease HEMOPHILIA A defect in the thrombin propagation phase
Hemostasis PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures Disorders of Hemostasis - Hemophilia - von Willebrand Disease HEMOPHILIA A defect in the thrombin propagation phase
Systemic lupus erythematosus
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (1988) 64, 517-521 Systemic lupus erythematosus Graham R.V. Hughes Lupus Research Laboratory, St Thomas' Hospital, London SE] 7EH, UK. Summary: Systemic lupus erythematosus
Postgraduate Medical Journal (1988) 64, 517-521 Systemic lupus erythematosus Graham R.V. Hughes Lupus Research Laboratory, St Thomas' Hospital, London SE] 7EH, UK. Summary: Systemic lupus erythematosus
Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis
 Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis A Summary Sinus and cerebral vein clots are uncommon. They can lead to severe headaches, confusion, and stroke-like symptoms. They may lead to bleeding into the surrounding
Sinus and Cerebral Vein Thrombosis A Summary Sinus and cerebral vein clots are uncommon. They can lead to severe headaches, confusion, and stroke-like symptoms. They may lead to bleeding into the surrounding
DOWNLOAD OR READ : POSITIVE OPTIONS FOR ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME APS SELF HELP AND TREATMENT PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : POSITIVE OPTIONS FOR ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME APS SELF HELP AND TREATMENT PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 positive options for antiphospholipid syndrome aps self help and treatment
DOWNLOAD OR READ : POSITIVE OPTIONS FOR ANTIPHOSPHOLIPID SYNDROME APS SELF HELP AND TREATMENT PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 positive options for antiphospholipid syndrome aps self help and treatment
COAGULATION INHIBITORS LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF PROTHROMBOTIC STATES REGULATION OF. ANTICOAGULANT PROTEIN DEFICIENCY Disease entities COAGULATION
 LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF PROTHROMBOTIC COAGULATION INHIBITORS Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor (TFPI) Lipoprotein Associated Coagulation Inhibitor (LACI) Extrinsic Pathway Inhibitor (EPI) Complexes with
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF PROTHROMBOTIC COAGULATION INHIBITORS Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor (TFPI) Lipoprotein Associated Coagulation Inhibitor (LACI) Extrinsic Pathway Inhibitor (EPI) Complexes with
What is the appropriate evaluation of cryptogenic stroke, and when is a hypercoagulability work-up needed? David E. Thaler, MD, PhD, FAHA
 What is the appropriate evaluation of cryptogenic stroke, and when is a hypercoagulability work-up needed? David E. Thaler, MD, PhD, FAHA Neurologist in Chief, Tufts Medical Center Professor and Chair
What is the appropriate evaluation of cryptogenic stroke, and when is a hypercoagulability work-up needed? David E. Thaler, MD, PhD, FAHA Neurologist in Chief, Tufts Medical Center Professor and Chair
Antiphospholipid Antibody Testing: Which Are Most Useful for Diagnosis?
 Rheum Dis Clin N Am 32 (2006) 455 463 Antiphospholipid Antibody Testing: Which Are Most Useful for Diagnosis? Maria Laura Bertolaccini, MD, PhD*, Graham R.V. Hughes, MD, FRCP Lupus Research Unit, The Rayne
Rheum Dis Clin N Am 32 (2006) 455 463 Antiphospholipid Antibody Testing: Which Are Most Useful for Diagnosis? Maria Laura Bertolaccini, MD, PhD*, Graham R.V. Hughes, MD, FRCP Lupus Research Unit, The Rayne
Interactive Case Vignette: DOACs (Direct Oral Anti-Coagulants) vs. Warfarin for APLA (Anti-Phospholipid Antibody Syndrome)
 Interactive Case Vignette: DOACs (Direct Oral Anti-Coagulants) vs. Warfarin for APLA (Anti-Phospholipid Antibody Syndrome) Ara Metjian, MD Duke Debates Benign Hematologic Highlights April 22, 2017 Disclaimer
Interactive Case Vignette: DOACs (Direct Oral Anti-Coagulants) vs. Warfarin for APLA (Anti-Phospholipid Antibody Syndrome) Ara Metjian, MD Duke Debates Benign Hematologic Highlights April 22, 2017 Disclaimer
APPENDIX A NORTH AMERICAN SYMPTOMATIC CAROTID ENDARTERECTOMY TRIAL
 APPENDIX A Primary Findings From Selected Recent National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke-Sponsored Clinical Trials That Have shaped Modern Stroke Prevention Philip B. Gorelick 178 NORTH
APPENDIX A Primary Findings From Selected Recent National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke-Sponsored Clinical Trials That Have shaped Modern Stroke Prevention Philip B. Gorelick 178 NORTH
Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89
 Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89 Presented by Jennifer Kurkulonis 1 FOUR MAJOR TYPES OF BLOOD CELLS White blood cells
Chapter 3 Diseases of the Blood and Bloodforming Organs and Certain Disorders Involving the Immune Mechanism D50-D89 Presented by Jennifer Kurkulonis 1 FOUR MAJOR TYPES OF BLOOD CELLS White blood cells
Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook
 Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, Oier Ateka-Barrutia, and Munther A. Khamashta Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, MD, PhD Lupus Research Unit The Rayne
Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, Oier Ateka-Barrutia, and Munther A. Khamashta Antiphospholipid Syndrome Handbook Maria Laura Bertolaccini, MD, PhD Lupus Research Unit The Rayne
Guidelines for Shared Care Centres and Community Staff
 Reference: CG1410 Written by: Dr Jeanette Payne Peer reviewer Dr Jenny Welch Approved: February 2016 Approved by D&TC: 8th January 2016 Review Due: February 2019 Intended Audience This document contains
Reference: CG1410 Written by: Dr Jeanette Payne Peer reviewer Dr Jenny Welch Approved: February 2016 Approved by D&TC: 8th January 2016 Review Due: February 2019 Intended Audience This document contains
Haemostasis & Coagulation disorders Objectives:
 Haematology Lec. 1 د.ميسم مؤيد علوش Haemostasis & Coagulation disorders Objectives: - Define haemostasis and what are the major components involved in haemostasis? - How to assess the coagulation status?
Haematology Lec. 1 د.ميسم مؤيد علوش Haemostasis & Coagulation disorders Objectives: - Define haemostasis and what are the major components involved in haemostasis? - How to assess the coagulation status?
Lupus Erythematosus - Can Anti-SS-A Antibody Predict the Next Event?
 Original Article Thrombocytopenia Subsequently Develops Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - Can Anti-SS-A Antibody Predict the Next Event? Masanori ADACHI*, Seiji MlTA, Mitsuo OBANA, Yasuo MATSUOKA,Keiichi
Original Article Thrombocytopenia Subsequently Develops Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - Can Anti-SS-A Antibody Predict the Next Event? Masanori ADACHI*, Seiji MlTA, Mitsuo OBANA, Yasuo MATSUOKA,Keiichi
Current View of the Treatment of Antiphospholipid Syndrome
 GROUPE HOSPITALIER PITIE SALPETRIERE Current View of the Treatment of Antiphospholipid Syndrome Pr Zahir AMOURA Department of Internal Medicine French National Reference center for SLE and APS Hôpital
GROUPE HOSPITALIER PITIE SALPETRIERE Current View of the Treatment of Antiphospholipid Syndrome Pr Zahir AMOURA Department of Internal Medicine French National Reference center for SLE and APS Hôpital
Optimal Utilization of Thrombophilia Testing
 Optimal Utilization of Thrombophilia Testing Rajiv K. Pruthi, MBBS Special Coagulation Laboratory & Comprehensive Hemophilia Center Division of Hematology/Internal Medicine Dept of Laboratory Medicine
Optimal Utilization of Thrombophilia Testing Rajiv K. Pruthi, MBBS Special Coagulation Laboratory & Comprehensive Hemophilia Center Division of Hematology/Internal Medicine Dept of Laboratory Medicine
DRG Anti-Phospholipid Screen IgG/IgM ELISA (EIA-3591) USA: RUO Revised 1 Aug rm (Vers. 5.1)
 This kit is intended for Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Please use only the valid version of the package insert provided with the kit. 1. NAME AND INTENDED USE The Anti-Phospholipid
This kit is intended for Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Please use only the valid version of the package insert provided with the kit. 1. NAME AND INTENDED USE The Anti-Phospholipid
Disclosures. Sneddon Syndrome: Untangling the Web. Case Presentation. MRI head w/ and w/o contrast. Further Workup. Further Workup 10/26/2017
 Sneddon Syndrome: Untangling the Web Sadhana Murali, MD, PGY-4 University of Wisconsin-Madison WNS Conference October 27-28, 2017 Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with any commercial
Sneddon Syndrome: Untangling the Web Sadhana Murali, MD, PGY-4 University of Wisconsin-Madison WNS Conference October 27-28, 2017 Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with any commercial
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISSEMINATED INTRAVASCULAR COAGULATION
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISSEMINATED INTRAVASCULAR COAGULATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY DISSEMINATED INTRAVASCULAR COAGULATION Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Dr Kirsten Herbert. Dr Melita Kenealy. MBBS(Hons) FRCPA FRACP. Common Blood Tests
 Common Blood Tests Your Haematologist may order numerous blood and urine tests to help diagse or manage your condition. Listed below are some of the more common tests that can be ordered in a haematology
Common Blood Tests Your Haematologist may order numerous blood and urine tests to help diagse or manage your condition. Listed below are some of the more common tests that can be ordered in a haematology
Prekallikrein Inhibition Associated Anticoagulant
 Prekallikrein Inhibition Associated with the Lupus Anticoagulant A Mechanism of Thrombosis MICHAEL J. SANFELIPPO, M.S. AND CHRISTOPHER J. DRAYNA, M.D. Sanfelippo, Michael J., and Drayna, Christopher J.:
Prekallikrein Inhibition Associated with the Lupus Anticoagulant A Mechanism of Thrombosis MICHAEL J. SANFELIPPO, M.S. AND CHRISTOPHER J. DRAYNA, M.D. Sanfelippo, Michael J., and Drayna, Christopher J.:
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PLATELET DISORDERS
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PLATELET DISORDERS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY PLATELET DISORDERS Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn
There are two main causes of a low platelet count
 Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia is a condition in which a person's blood has an unusually low level of platelets Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are found in a person's blood along with red blood
Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia is a condition in which a person's blood has an unusually low level of platelets Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are found in a person's blood along with red blood
Comparison of Samples Obtained From 3.2% Sodium Citrate Glass and Two 3.2% Sodium Citrate Plastic Blood Collection Tubes Used in Coagulation Testing
 Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / GLASS VS PLASTIC IN HEMOSTASIS TESTING Comparison of Samples Obtained From 3.2% Sodium Citrate Glass and Two 3.2% Sodium Citrate Plastic Blood Collection Tubes Used
Coagulation and Transfusion Medicine / GLASS VS PLASTIC IN HEMOSTASIS TESTING Comparison of Samples Obtained From 3.2% Sodium Citrate Glass and Two 3.2% Sodium Citrate Plastic Blood Collection Tubes Used
Prevalence and heterogeneity of antiphosphatidylethanolamine antibodies in patients with recurrent early pregnancy losses
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 71, NO. 6, JUNE 1999 Copyright 1999 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Science Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. Prevalence and heterogeneity
FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 71, NO. 6, JUNE 1999 Copyright 1999 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Science Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. Prevalence and heterogeneity
Determination of APTT factor sensitivity the misguiding guideline
 International Journal of Laboratory Hematology ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Official journal of the International Society for Laboratory Hematology INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF LABORATORY HEMATOLOGY Determination
International Journal of Laboratory Hematology ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Official journal of the International Society for Laboratory Hematology INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF LABORATORY HEMATOLOGY Determination
Generate Knowledge Lupus Anticoagulant Testing Made Simple
 Generate Knowledge Lupus Anticoagulant Testing Made Simple Paul Riley, PhD, MBA Learning objectives Describe antiphospholipid syndrome (aps) and role of the lupus anticoagulant (LA) in thrombosis Present
Generate Knowledge Lupus Anticoagulant Testing Made Simple Paul Riley, PhD, MBA Learning objectives Describe antiphospholipid syndrome (aps) and role of the lupus anticoagulant (LA) in thrombosis Present
The Taipan snake venom time: a new test for lupus anticoagulant
 J Clin Pathol 1994;47:497-51 The Taipan snake venom time: a new test for lupus anticoagulant 497 Department of Haematology, University College London Medical School, London WClE 6HX M Rooney T McNally
J Clin Pathol 1994;47:497-51 The Taipan snake venom time: a new test for lupus anticoagulant 497 Department of Haematology, University College London Medical School, London WClE 6HX M Rooney T McNally
It s Always a Stroke; Except For When It s Not..
 It s Always a Stroke; Except For When It s Not.. TREVOR PHINNEY, D.O. Disclosures No Relevant Disclosures 1 Objectives Discuss variables of differential diagnosis for stroke Review when to TPA and when
It s Always a Stroke; Except For When It s Not.. TREVOR PHINNEY, D.O. Disclosures No Relevant Disclosures 1 Objectives Discuss variables of differential diagnosis for stroke Review when to TPA and when
Situaciones estresantes en el lupus
 Situaciones estresantes en el lupus Munther A Khamashta MD FRCP PhD Director: Lupus Research Unit Barcelona, Noviembre 2008 What is Lupus? Lupus is a neurological disease and sometimes affects other organs
Situaciones estresantes en el lupus Munther A Khamashta MD FRCP PhD Director: Lupus Research Unit Barcelona, Noviembre 2008 What is Lupus? Lupus is a neurological disease and sometimes affects other organs
Supplemental Figures and Legends
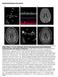 Supplemental Figures and Legends Online Figure 1. 18 year old female with SLE and acute homonymous hemianopsia, confusional state, and cognitive dysfunction. A. This TEE four chamber view demonstrates
Supplemental Figures and Legends Online Figure 1. 18 year old female with SLE and acute homonymous hemianopsia, confusional state, and cognitive dysfunction. A. This TEE four chamber view demonstrates
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Neonatal cerebral infarction
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal cerebral infarction May 2002 2 Mann C, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Landeskrankenhaus und Akademisches Lehrkrankenhaus Feldkirch, Austria Swiss Society
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Neonatal cerebral infarction May 2002 2 Mann C, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Landeskrankenhaus und Akademisches Lehrkrankenhaus Feldkirch, Austria Swiss Society
THROMBOPHILIA TESTING: PROS AND CONS SHANNON CARPENTER, MD MS CHILDREN S MERCY HOSPITAL KANSAS CITY, MO
 THROMBOPHILIA TESTING: PROS AND CONS SHANNON CARPENTER, MD MS CHILDREN S MERCY HOSPITAL KANSAS CITY, MO DISCLAIMER I m a pediatrician I will be discussing this issue primarily from a pediatric perspective
THROMBOPHILIA TESTING: PROS AND CONS SHANNON CARPENTER, MD MS CHILDREN S MERCY HOSPITAL KANSAS CITY, MO DISCLAIMER I m a pediatrician I will be discussing this issue primarily from a pediatric perspective
Cerebrovascular Disease
 Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Circulating autoimmune antibodies may be responsible for implantation failure in in vitro fertilization
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1994 The American Fertility Society Vol. 62, No.4, October 1994 Printed on acid-free paper in U. S. A Circulating autoimmune antibodies may be responsible for implantation
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1994 The American Fertility Society Vol. 62, No.4, October 1994 Printed on acid-free paper in U. S. A Circulating autoimmune antibodies may be responsible for implantation
