T he advent in the 1980s of meters for
|
|
|
- Susan Stewart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Epidemiology/Health Services Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Evidence of a Strong Association Between Frequency of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose and Hemoglobin A1C Levels in T1D Exchange Clinic Registry Participants KELLEE M. MILLER, MPH 1 ROY W. BECK, MD, PHD 1 RICHARD M. BERGENSTAL, MD 2 ROBIN S. GOLAND, MD 3 MICHAEL J. HALLER, MD 4 JANET B. MCGILL, MD 5 HENRY RODRIGUEZ, MD 6 JILL H. SIMMONS, MD 7 IRL B. HIRSCH, MD 8 FOR THE T1D EXCHANGE CLINIC NETWORK OBJECTIVEdDespite substantial evidence of the benefit of frequent self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) in type 1 diabetes, certain insurers limit the number of test strips that they will provide. The large database of the T1D Exchange Clinic Registry provided an opportunity to evaluate the relationship between the number of SMBG measurements per day and HbA 1c levels across a wide age range of children and adults. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODSdThe analysis included 20,555 participants in the T1D Exchange clinic registry with type 1 diabetes $1 year and not using a continuous glucose monitor (11,641 younger than age 18 years and 8, years old or older). General linear models were used to assess the association between the number of SMBG measurements and HbA 1c levels after adjusting for potential confounding variables. RESULTSdA higher number of SMBG measurements per day were associated with non- Hispanic white race, insurance coverage, higher household income, and use of an insulin pump for insulin delivery (P, for each factor). After adjusting for these factors, a higher number of SMBG measurements per day was strongly associated with a lower HbA 1c level (adjusted P, 0.001), with the association being present in all age groups and in both insulin pump and injection users. CONCLUSIONSdThere is a strong association between higher SMBG frequency and lower HbA 1c levels. It is important for insurers to consider that reducing restrictions on the number of test strips provided per month may lead to improved glycemic control for some patients with type 1 diabetes. T he advent in the 1980s of meters for self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) has had a substantial impact on the management of type 1 diabetes (1). Several studies have demonstrated a strong correlation between frequency of SMBG and glycemic control (2 5). However, acceptance of the value of frequent SMBG has not been universal and many insurers limit the number of test strips that they will provide to four to six strips per day. In the past year, the Washington ccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccc From the 1 Jaeb Center for Health Research, Tampa, Florida; the 2 International Diabetes Center/Park Nicollet, Minneapolis, Minnesota; the 3 Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center, Columbia University, New York City, New York; the 4 University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida; the 5 Washington University, St. Louis, Missouri; the 6 University of South Florida, Tampa, Florida; the 7 Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee; and the 8 University of Washington Medical Center, Seattle, Washington. Corresponding author: Kellee M. Miller, T1dstats@jaeb.org. Received 31 August 2012 and accepted 25 December DOI: /dc This article contains Supplementary Data online at by the American Diabetes Association. Readers may use this article as long as the work is properly cited, the use is educational and not for profit, and the work is not altered. See licenses/by-nc-nd/3.0/ for details. State Healthcare Authority questioned whether sufficient evidence is available to justify unlimited coverage of SMBG test strips for patients with type 1 diabetes (6). The large database of the T1D Exchange clinic registry provided an opportunity to evaluate the relationship between the number of SMBG measurements per day and HbA 1c across a wide age range of children and adults, and to evaluate factors associated with the number of SMBG measurements per day. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODSdThe T1D Exchange Clinic Network includes 67 pediatric and adult endocrinology practices based in the United States. A registry of individuals with type 1 diabetes commenced enrollment in September 2010 (7). Each clinic received approval from an Institutional Review Board. Informed consent was obtained according to Institutional Review Board requirements from adult participants and parents/guardians of minors; assent from minors was obtained as required. Data were collected for the registry s central database from the participant s medical record and by having the participant or parent complete a comprehensive questionnaire, as previously described (7). This report includes data of 20,555 participants enrolled through 1 August 2012 who met the following criteria: type 1 diabetes for at least 1 year; not pregnant; not using real-time continuous glucose monitoring; and availability of an HbA 1c measurement between 6 months before and 1 month after enrollment. Information on SMBG measurements per day was obtained on a questionnaire completed by participants 18 years old or older, parent or guardian of participants younger than 13 years old, and by either the participant or the parent/guardian for participants 13 years old to younger than 18 years old, with the following question: care.diabetesjournals.org DIABETES CARE 1 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online February 1, 2013
2 SMBG and HbA1c in T1D exchange clinic registry Approximately how many are you (is your child) checking your (his/ her) blood glucose with a blood glucose meter? For a subset of the participants, the number of SMBG measurements per day was available from a meter download located in the clinic chart. HbA 1c levels, mainly measured with point-of-care devices(74%dca,4%fromanother point-of-care device, 19% from a laboratory, 3% by an unrecorded method), were obtained from the clinic chart. When more than one HbA 1c value was available between 6 months before and 1 month after enrollment, the value obtained closest to the enrollment date was used. Statistical Methods Frequency of SMBG measurements per day was categorized for illustration purposes into five groupings: 0 2 times per day; 3 4timesperday;5 6 ; 7 9 ; and $10 times per day. Analyses stratified by age used the following age groups: 1 to younger than 6 years old; 6 to younger than 13 years old; 13 to younger than 18 years old; 18 to younger than 26 years old; 26 to younger than 50 years old; 50 to younger than 65 years old; and 65 years or older. Demographic and clinical factors associated with the number of SMBG measurements per day were assessed in linear regression models adjusted for age group. Factors with a significance level #0.05 from individual factor models adjusted for age were included in the initial multivariate linear regression model and were removed from the final model if adjusted P $ General linear models were used to assess the association between the number of SMBG measurements per day and HbA 1c in each age group after adjusting for potential confounding variables. Additional analyses assessing the association between frequency of SMBG per day and HbA 1c,7.0% were performed using logistic regression. Covariates adjusted for in the multivariate models included the following: gender; race/ethnicity; insulin delivery method; insurance status (private, other, none); and household income (participants who were living alone but still supported by parents were asked to estimate their family income). The effect of the interaction between SMBG and household income on HbA 1c levels was evaluated. Separate analyses for pump and injection users also were performed. The Van der Waerden normal scores of the frequency of SMBG per day were used in the models Table 1dDescriptive characteristics of the cohort Characteristics Total N = 20,555 Age (years) 1to,6 819 (4) 6to,13 5,445 (26) 13 to,18 5,377 (26) 18 to,26 3,307 (16) 26 to,50 3,351 (16) 50 to,65 1,646 (8) $ (3) Female* 10,266 (50) Race/ethnicity White non-hispanic 16,919 (82) Black non-hispanic 1,043 (5) Hispanic or Latino 1,673 (8) Asian 243 (1) More than one race 567 (3) Other 110 (,1) Diabetes duration (years) 1to,5 6,853 (33) 5to,10 5,553 (27) 10 to,20 4,614 (22) 20 to,30 1,632 (8) 30 to,40 1,060 (5) 40 to, (3) $ (1) Annual household income,$25,000 1,857 (12) $25,000 to,$35,000 1,278 (8) $35,000 to,$50,000 1,759 (12) $50,000 to,$75,000 2,674 (18) $75,000 to,$100,000 2,648 (17) $$100,000 4,988 (33) Education level Less than a high school diploma 867 (4) High school diploma/ged 7,278 (37) Associate degree 2,134 (11) Bachelor degree 5,426 (28) Master degree 2,826 (14) Professional or doctorate degree 1,147 (6) Insurance status Private 13,957 (74) Other 4,563 (24) No insurance 236 (1) Family history of type 1 diabetes x 3,294 (16) Pump use 10,783 (52) HbA 1c { (mean 6 SD) Group n (%),6.5% 1,383 (7) 6.5 to,7.5% 4,864 (24) 7.5 to,8.5% 6,661 (32) 8.5 to,9.5% 4,095 (20) 9.5 to,10.5% 1,821 (9) $10.5% 1,731 (8) Data are presented as N (%) unless otherwise stated. *Total of 3 transgender individuals in cohort; 877 participants are missing education level; 5,351 participants are missing household income; 1,799 participants are missing insurance status; For participants younger than 18 years of age, education reported is highest parent education; xindicates those with a first degree family member with T1D including parent, sibling, halfsibling, or child; {Most recent HbA 1c recorded, within six months prior or 30 days after enrollment visit. 2 DIABETES CARE care.diabetesjournals.org
3 as a result of the skewed distribution of the data. Self-reported SMBG measurements per day were used in the analyses. Analytic results were similar when data from clinic meter downloads were used from the subset of participants for whom downloaded data were available (data not shown). Analyses were conducted using SAS software version 9.3 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC). All P values are twosided. In view of the large sample size and multiple comparisons, only P, 0.01 was considered statistically significant. RESULTSdThe cohort included 20,555 participants: 11,641 younger than 18 years old and 8,914 who were 18 years old or older. Characteristics of the cohort are shown in Table 1. Mean number of SMBG measurements per day was lower among participants 13 to younger than 26 years old ( ) than among younger ( ) and older participants ( ; P, 0.001; Table 2). Among 10,384 participants for whom a meter download was available, selfreported SMBG measurements averaged per day compared with the clinic assessment from meter downloads of per day (Pearson correlation = 0.65). In a multivariate model adjusted for age group, participants who reported a higher number of SMBG measurements per day were more likely to be non- Hispanic white, have private insurance, have higher household income, and use an insulin pump for insulin delivery (Supplementary Table 1; P, for each factor). A higher number of SMBG measurements per day was strongly associated with a lower HbA 1c in all age groups (Fig. 1A adjusted means and Table 3 unadjusted means; P = for 1 to younger than 6 years and P, for all other age groups adjusted for potential demographic and socioeconomic confounders) despite the differences in HbA 1c between age groups. The association was present in both insulin pump and injection users (Fig. 1B and C adjusted means; P, 0.001) and across annual household income categories (Supplementary Table 2). There was no significant interaction between SMBG and household income on HbA 1c levels for any age group. The association between SMBG and HbA 1c levels appeared to level-off at approximately 10 SMBG measurements per day, with adjusted mean HbA 1c being similar in participants testing times as in those testing $13, 7.8% and 7.7%, respectively. Results were similar when evaluating the association between SMBG measurements per day and HbA 1c,7.0% (Table 3). CONCLUSIONSdSMBG is the cornerstone of modern-day therapy for people with type 1 diabetes. Early studies clearly demonstrated that capillary glucose information was valuable for making appropriate decisions regarding insulin dosing and therefore for improvement of diabetes control (1). The intensive therapy group in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) was asked, as part of their therapy, to perform SMBG before meals and at bedtime as well as overnight once per week (8). Whereas this was not a randomized trial for SMBG, it is, to our knowledge, the last study comparing a treatment regimen including glucose testing four times daily against little to no testing (9). Today, it would be impossible to perform Miller and Associates a randomized trial in type 1 diabetes comparing SMBG with no SMBG given our understanding of the importance of glucose control in preventing the complications of T1D (10). The best alternative is to use a large database, such as the T1D Exchange clinic registry, to analyze associations between frequency of SMBG and HbA 1c and to provide the evidence desired by payers, such as the State of Washington, to support the cost-effectiveness of providing coverage for test strips. Consistent with other smaller studies in the United States and the large Germany and Austria DPV registry (2 5), we clearly show that for all ages and with both major forms of insulin delivery (pump and multiple injections), increased frequency of SMBG is associated with lower mean HbA 1c. This is true even after adjusting for demographic and socioeconomic confounders. Our study observed a similar association between SMBG and HbA 1c across levels of household income, which has not been previously reported. Nevertheless, because diabetes management in those with more frequent SMBG likely differs from those with less frequent SMBG, frequent SMBG by itself is not the sole explanation for the association with lower HbA 1c,but it almost certainly is an important contributor. Of course, for frequent SMBG to influence HbA 1c,thebloodglucoseinformationmustbeusedeffectivelyindiabetes management including insulin dosing and meal and snack composition; the act of performing SMBG alone is not directly related to improvements in HbA 1c. Thus, frequent SMBG is a behavior associated with good glycemic control but in itself does not have a direct causal relationship with glycemic control. Table 2dSMBG by age group Total 1to,6 6 to,13 13 to,18 18 to,26 26 to,50 50 to,65 $65 yearsold yearsold yearsold yearsold yearsold yearsold yearsold Self-reported SMBG N = 20,555 N =819 N =5,445 N =5,377 N =3,307 N =3,351 N =1,646 N =610 Mean 6 SD Group (%) 0times/day*,1 0,1,1 2 1,1,1 1 2 times/day 6,1, times/day times/day times/day $10 times/day *A total of 127 (,1%) participants reported 0 SMBG checks per day. care.diabetesjournals.org DIABETES CARE 3
4 SMBG and HbA1c in T1D exchange clinic registry The 2012 American Diabetes Association clinical guidelines recommend SMBG at least three for patients using insulin pump therapy or multiple insulin injections (11). In this analysis of individuals with type 1 diabetes, participants testing 3 4 timesper day had a mean HbA 1c of 8.6% comparedwithanhba 1c of 7.6% among those testing $10. Because prospective trials testing how the frequency of SMBG impacting HbA 1c are not likely, we are hopeful that future guidelines better-reflect our current understanding of the relationship of SMBG and HbA 1c. Our data suggest a slight over-reporting of the frequency of SMBG compared with meter downloads, which could, in part, be explained by incomplete data for patients who use more than one meter and difficulty in interpreting downloaded meter data when the date of the meter is incorrect. However, these issues are not germane to our results, because the same association between frequency of SMBG and HbA 1c is seen when the meter download glucose values were used in the analyses (data not shown). In conclusion, there is a strong association between a higher SMBG frequency and lower HbA 1c across the entire age range in our large population of patients with type 1 diabetes, with similar findings in pump users and injection users. The observational nature of the study precludes a definitive statement regarding causality. Nevertheless, it is important for insurers to consider that reducing restrictions on the number of test strips provided per month may lead to improved glycemic control for some patients with type 1 diabetes, resulting in a potential cost-savings from both short-term and long-term complications. Figure 1dA: Association between frequency of SMBG per day and HbA 1c. Solid black line and diamonds represent those 1 to younger than 13 years old. Solid black line and squares represent those 13 to younger than 26 years old. Solid black line and triangle represent those 26 to younger than 50 years old. Dotted black line and squares represent those 50 years old and older. HbA 1c means with numbers,30 are not included here. Means are adjusted for insulin delivery method, gender, race/ethnicity, insurance status, and household income (treated as ordinal variables with AcknowledgmentsdFunding was provided by the Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust. The nonprofit employer of R.W.B. has received consultant payments on his behalf from Sanofi and Animas and a research grant from NovoNordisk, but R.W.B. received no personal compensation. The nonprofit employer of R.M.B. received consultant payments from Abbott Diabetes Care, Amylin, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Calibra, Eli Lilly, Halozyme, Helmsley Trust, Hygieia, Johnson and Johnson, Medtronic, Novo Nordisk, ResMed, Roche, Sanofi, Takeda, and Valeritas. I.H. received consultant payments from Roche Diagnostics, Johnson and Johnson, and Abbott Diabetes Care. The nonprofit employer 4 DIABETES CARE care.diabetesjournals.org
5 Miller and Associates Table 3dAssociation between frequency of SMBG per day and HbA 1c according to age Mean HbA 1c * SMBG 0 2 N SMBG 3 4 SMBG 5 6 SMBG 7 9 SMBG $10 HbA 1c Mean, % Mean, % Mean, % Mean, % Mean, % Age 1 to,6 years Age 6 to,13 years , , ,0.001 Age 13 to,18 years , , ,0.001 Age 18 to,26 years , ,0.001 Age 26 to,50 years , ,0.001 Age 50 to,65 years ,0.001 Age $65 years ,0.001 HbA 1c, 7.0% % with N HbA 1c,7.0%,7.0%,7.0%,7.0%,7.0% Age 1 to,6 years Age 6 to,13 years , , ,0.001 Age 13 to,18 years , , ,0.001 Age 18 to,26 years , ,0.001 Age 26 to, 50 years , ,0.001 Age 50 to,65 years ,0.001 Age $65 years *Means are unadjusted. P values are from general linear regression models adjusted for insulin delivery method, gender, race/ethnicity, insurance status, and household income (treated as ordinal variables with a missing indicator); Percentages are unadjusted. P values are from logistic regression models adjusted for insulin delivery method, gender, race-ethnicity, insurance status, and household income (treated as ordinal variables with a missing indicator); The median HbA 1c for the 127 participants who reported 0 SMBG checks per day was 9.6 P of I.H. received or will receive a grant from Sanofi. H.R. received consultant payments from Eli Lilly and Roche Diagnostics as well as lecture payments from Eli Lilly. The nonprofit employer of H.R. received or will receive grants from Bristol-Meyers-Squibb, Daichi Sankyo, and the National Institutes of Health National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported. K.M.M., R.W.B., R.M.B., R.S.G., M.J.H., J.B.M., H.R., J.H.S., and I.B.H. researched data. K.M.M., R.W.B., R.M.B., R.S.G., M.J.H., J.B.M., H.R., J.H. S., J.H.S., and I.B.H. contributed to discussion. K.M.M. wrote the manuscript. R.W.B., R.S.G., M.J.H., J.B.M., H.R., J.H.S., and I.B.H. reviewed and edited the manuscript. I.B.H. is the guarantor of this work and, as such, hadfullaccesstoallthedatainthestudyand takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. These data have been presented in part at the 71st Scientific Sessions of the American Diabetes Association, San Diego, California, June 2011 and at the 47th European Association for the Study of Diabetes Meeting, Lisbon, Portugal, September References 1. Schiffrin A, Belmonte M. Multiple daily self-glucose monitoring: its essential role in long-term glucose control in insulindependent diabetic patients treated with pump and multiple subcutaneous injections. Diabetes Care 1982;5: Sch uttm, KernW, KrauseU, etal; DPV Initiative. Is the frequency of self-monitoring of blood glucose related to long-term metabolic control? Multicenter analysis including 24,500 patients from 191 centers in Germany and Austria. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 2006;114: Ziegler R, Heidtmann B, Hilgard D, Hofer S, Rosenbauer J, Holl R; DPV-Wiss-Initiative. Frequency of SMBG correlates with HbA1c and acute complications in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes 2011;12: Haller MJ, Stalvey MS, Silverstein JH. Predictors of control of diabetes: monitoring may be the key. J Pediatr 2004;144: Levine BS, Anderson BJ, Butler DA, Antisdel JE, Brackett J, Laffel LM. Predictors of glycemic control and short-term a missing indicator). B: Association between frequency of SMBG per day and HbA 1c among insulin pump users. Solid black line and diamonds indicate those 1 to younger than 13 years old. Solid black line and squares indicate those 13 to younger than 26 years old. Solid black line and triangle indicate those 26 to younger than 50 years old. Dotted black line and squares indicate those 50 years old or older. HbA 1c means with numbers,30 are not included here. Means are adjusted for gender, race/ethnicity, insurance status, and household income (treated as ordinal variables with a missing indicator) C: Association between frequency of SMBG per day and HbA 1c among injection users. Solid black line and diamonds represent those 1 to younger than 13 years old. Solid black line and squares represent those 13 to younger than 26 years old. Solid black line and triangle represent those 26 to younger than 50 years old. Dotted black line and squares represent those 50 years old and older. HbA 1c means with numbers,30 are not included here. Means are adjusted for gender, race/ethnicity, insurance status, and household income (treated as ordinal variables with a missing indicator). care.diabetesjournals.org DIABETES CARE 5
6 SMBG and HbA1c in T1D exchange clinic registry adverse outcomes in youth with type 1 diabetes. J Pediatr 2001;139: Pollack A. A panel decides Washington State s healthcare costs. New York Times 2011 Mar 22;Sect. B:1 7. Beck RW, Tamborlane WV, Bergenstal RM, Miller KM, Dubose SN, Hall CA; for the T1D Exchange Clinic Network. The T1D Exchange Clinic Registry. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012;97: The DCCT Research Group. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT). Design and methodologic considerations for the feasibility phase. Diabetes 1986; 35: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Implementation of treatment protocols in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Care 1995;18: The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;329: American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetesd2012. Diabetes Care 2012;35(Suppl 1):S11 S63 6 DIABETES CARE care.diabetesjournals.org
The Diamond Study: Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Patients on Mulitple Daily Insulin Injections
 8/5/217 The Diamond Study: Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Patients on Mulitple Daily Insulin Injections Richard M. Bergenstal, MD Executive Director International Diabetes Center at Park Nicollet Minneapolis,
8/5/217 The Diamond Study: Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Patients on Mulitple Daily Insulin Injections Richard M. Bergenstal, MD Executive Director International Diabetes Center at Park Nicollet Minneapolis,
February 19, Dear Medical Director:
 141 Northwest Point Blvd Elk Grove Village, IL 60007-1019 Phone: 847/434-4000 Fax: 847/434-8000 E-mail: kidsdocs@aap.org www.aap.org Executive Committee President Sandra G. Hassink, MD, FAAP President-Elect
141 Northwest Point Blvd Elk Grove Village, IL 60007-1019 Phone: 847/434-4000 Fax: 847/434-8000 E-mail: kidsdocs@aap.org www.aap.org Executive Committee President Sandra G. Hassink, MD, FAAP President-Elect
See accompanying articles, pp. 968, 979, 989, 997, 1008, 1016, 1030, and 1036.
 Diabetes Care Volume 38, June 2015 971 CurrentStateofType1Diabetes Treatment in the U.S.: d Data From the T1D Exchange Clinic Registry Diabetes Care 2015;38:971 978 DOI: 10.2337/dc15-0078 Kellee M. Miller,
Diabetes Care Volume 38, June 2015 971 CurrentStateofType1Diabetes Treatment in the U.S.: d Data From the T1D Exchange Clinic Registry Diabetes Care 2015;38:971 978 DOI: 10.2337/dc15-0078 Kellee M. Miller,
Comparing the use of SMBG vs. CGM data to Optimize Glucose Control in T2DM
 Comparing the use of SMBG vs. CGM data to Optimize Glucose Control in T2DM For the first time using CGM to assess glucose control achieved in both groups Richard M. Bergenstal, MD International Diabetes
Comparing the use of SMBG vs. CGM data to Optimize Glucose Control in T2DM For the first time using CGM to assess glucose control achieved in both groups Richard M. Bergenstal, MD International Diabetes
T1D Exchange Clinic Registry: 25,000 strong! What is it and what have we learned to date? Georgeanna J Klingensmith, MD Barbara Davis Center
 T1D Exchange Clinic Registry: 25,000 strong! What is it and what have we learned to date? Georgeanna J Klingensmith, MD Barbara Davis Center T1D Exchange Mission and Goals Improve outcomes of people touched
T1D Exchange Clinic Registry: 25,000 strong! What is it and what have we learned to date? Georgeanna J Klingensmith, MD Barbara Davis Center T1D Exchange Mission and Goals Improve outcomes of people touched
Lessons From The Type 1 Diabetes Exchange
 Lessons From The Type 1 Diabetes Exchange Andrew Ahmann, MD Harold Schnitzer Diabetes Health Center at OHSU Presenter Disclosure Information In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American
Lessons From The Type 1 Diabetes Exchange Andrew Ahmann, MD Harold Schnitzer Diabetes Health Center at OHSU Presenter Disclosure Information In compliance with the accrediting board policies, the American
An Evaluation of the Barriers to Patient use of Glucometer Control Solutions: A Survey of Patients, Pharmacists, and Providers
 AADE14 ANNUAL MEETING & EXHIBITION AUGUST 6-9, 2014 ORLANDO, FL An Evaluation of the Barriers to Patient use of Glucometer s: A Survey of Patients, Pharmacists, and Providers Katherine S. O Neal, Pharm.D.,
AADE14 ANNUAL MEETING & EXHIBITION AUGUST 6-9, 2014 ORLANDO, FL An Evaluation of the Barriers to Patient use of Glucometer s: A Survey of Patients, Pharmacists, and Providers Katherine S. O Neal, Pharm.D.,
Depression in Adults in the T1D Exchange Clinic Registry Diabetes Care 2014;37: DOI: /dc
 Diabetes Care Volume 37, June 2014 1563 Depression in Adults in the T1D Exchange Clinic Registry Diabetes Care 2014;37:1563 1572 DOI: 10.2337/dc13-1867 OBJECTIVE Little is known about the frequency of
Diabetes Care Volume 37, June 2014 1563 Depression in Adults in the T1D Exchange Clinic Registry Diabetes Care 2014;37:1563 1572 DOI: 10.2337/dc13-1867 OBJECTIVE Little is known about the frequency of
Evaluation of Pump Discontinuation and Associated Factors in the T1D Exchange Clinic Registry
 663963DSTXXX10.1177/1932296816663963Journal of Diabetes Science and TechnologyWong et al research-article2016 Original Article Evaluation of Pump Discontinuation and Associated Factors in the T1D Exchange
663963DSTXXX10.1177/1932296816663963Journal of Diabetes Science and TechnologyWong et al research-article2016 Original Article Evaluation of Pump Discontinuation and Associated Factors in the T1D Exchange
Management and Family Burdens Endorsed by Parents of Youth <7 Years Old With Type 1 Diabetes
 721938DSTXXX10.1177/1932296817721938Journal of Diabetes Science and TechnologyHarrington et al research-article2017 Original Article Management and Family Burdens Endorsed by Parents of Youth
721938DSTXXX10.1177/1932296817721938Journal of Diabetes Science and TechnologyHarrington et al research-article2017 Original Article Management and Family Burdens Endorsed by Parents of Youth
Adherence to therapy. Kamlesh Khunti University of Leicester, UK. William Polonsky University of California San Diego, USA
 Adherence to therapy Kamlesh Khunti University of Leicester, UK William Polonsky University of California San Diego, USA 1 Dualities of interest Kamlesh Khunti: Honoraria for speaking, advising or research
Adherence to therapy Kamlesh Khunti University of Leicester, UK William Polonsky University of California San Diego, USA 1 Dualities of interest Kamlesh Khunti: Honoraria for speaking, advising or research
Original Article. Nicholas B. Argento, MD 1 ; Katherine Nakamura, PhD 2 ABSTRACT
 Original Article Nicholas B. Argento, MD 1 ; Katherine Nakamura, PhD 2 ABSTRACT Objective: Little information is available on personal real-time continuous glucose monitoring (PCGM) in patients 65 years
Original Article Nicholas B. Argento, MD 1 ; Katherine Nakamura, PhD 2 ABSTRACT Objective: Little information is available on personal real-time continuous glucose monitoring (PCGM) in patients 65 years
Florida Network Symposium
 Katrina J. Ruedy, MSPH John W. Lum, MS Jaeb Center for Health Research NE Florida Network Symposium In Conjunction with The 28th Annual Clinical Conference on Diabetes Jaeb Center for Health Research (JCHR)
Katrina J. Ruedy, MSPH John W. Lum, MS Jaeb Center for Health Research NE Florida Network Symposium In Conjunction with The 28th Annual Clinical Conference on Diabetes Jaeb Center for Health Research (JCHR)
When Will CGM Replace SMBG? Roy W. Beck, MD, PhD. JAEB Center for Health Research Tampa, Florida
 When Will CGM Replace SMBG? Roy W. Beck, MD, PhD JAEB Center for Health Research Tampa, Florida Financial Disclosures Dr. Beck does not have any personal conflicts of interest His employer, the JAEB Center
When Will CGM Replace SMBG? Roy W. Beck, MD, PhD JAEB Center for Health Research Tampa, Florida Financial Disclosures Dr. Beck does not have any personal conflicts of interest His employer, the JAEB Center
Diabetes Management: Current High Tech Innovations
 Diabetes Management: Current High Tech Innovations How Far We ve Come in the Last 40 Years William V. Tamborlane, MD Department of Pediatrics Yale School of Medicine Disclosures I am a consultant for:
Diabetes Management: Current High Tech Innovations How Far We ve Come in the Last 40 Years William V. Tamborlane, MD Department of Pediatrics Yale School of Medicine Disclosures I am a consultant for:
PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS)
 PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS) Pathways for Future Treatment and Management of Diabetes H. Peter Chase, MD Carousel of Hope Symposium Beverly Hilton, Beverly
PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS) Pathways for Future Treatment and Management of Diabetes H. Peter Chase, MD Carousel of Hope Symposium Beverly Hilton, Beverly
Research Article Measures of Adherence and Challenges in Using Glucometer Data in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes: Rethinking the Value of Self-Report
 Hindawi Diabetes Research Volume 2017, Article ID 1075428, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1075428 Research Article Measures of Adherence and Challenges in Using Glucometer Data in Youth with Type
Hindawi Diabetes Research Volume 2017, Article ID 1075428, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1075428 Research Article Measures of Adherence and Challenges in Using Glucometer Data in Youth with Type
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) changes over time among adolescent and young adult participants in the T1D exchange clinic registry
 Pediatric Diabetes 2016: 17: 327 336 doi: 10.1111/pedi.12295 All rights reserved 2015 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Pediatric Diabetes Original Article Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
Pediatric Diabetes 2016: 17: 327 336 doi: 10.1111/pedi.12295 All rights reserved 2015 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Pediatric Diabetes Original Article Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c)
Diabetes Care 34: , with an increased risk of SH. In a
 Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Factors Predictive of Severe Hypoglycemia in Type 1 Diabetes Analysis from the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation
Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Factors Predictive of Severe Hypoglycemia in Type 1 Diabetes Analysis from the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation
Insulin Pumps and Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management
 Diabetes Update+ 2014 Congress Whistler, British Columbia Friday March 21, 2014ǀ 8:15 8:45 am Insulin Pumps and Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management Bruce A Perkins MD MPH Division of Endocrinology Associate
Diabetes Update+ 2014 Congress Whistler, British Columbia Friday March 21, 2014ǀ 8:15 8:45 am Insulin Pumps and Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management Bruce A Perkins MD MPH Division of Endocrinology Associate
Efficacy and Safety of Flexible Versus Fixed Dosing Intervals of Insulin Glargine 300 U/mL in People with Type 2 Diabetes
 https://helda.helsinki.fi Efficacy and Safety of Flexible Versus Fixed Dosing Intervals of Insulin Glargine 300 U/mL in People with Type 2 Diabetes Riddle, Matthew C. 2016-04-01 Riddle, M C, Bolli, G B,
https://helda.helsinki.fi Efficacy and Safety of Flexible Versus Fixed Dosing Intervals of Insulin Glargine 300 U/mL in People with Type 2 Diabetes Riddle, Matthew C. 2016-04-01 Riddle, M C, Bolli, G B,
ACCORD, ADVANCE & VADT. Now what do I do in my practice?
 ACCORD, ADVANCE & VADT Now what do I do in my practice? Richard M. Bergenstal, MD International Diabetes Center Park Nicollet Health Services University of Minnesota Minneapolis, MN richard.bergenstal@parknicollet.com
ACCORD, ADVANCE & VADT Now what do I do in my practice? Richard M. Bergenstal, MD International Diabetes Center Park Nicollet Health Services University of Minnesota Minneapolis, MN richard.bergenstal@parknicollet.com
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. C-Reactive Protein Concentration and Incident Hypertension in Young Adults
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION C-Reactive Protein Concentration and Incident Hypertension in Young Adults The CARDIA Study Susan G. Lakoski, MD, MS; David M. Herrington, MD, MHS; David M. Siscovick, MD, MPH; Stephen
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION C-Reactive Protein Concentration and Incident Hypertension in Young Adults The CARDIA Study Susan G. Lakoski, MD, MS; David M. Herrington, MD, MHS; David M. Siscovick, MD, MPH; Stephen
Presented by Dr. Bruce Perkins, MD MPH Dr. Michael Riddell, PhD
 Type 1 Diabetes and Exercise: Optimizing the Medtronic MiniMed Veo Insulin Pump and Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) for Better Glucose Control 1,2 for Healthcare Professionals Presented by Dr. Bruce
Type 1 Diabetes and Exercise: Optimizing the Medtronic MiniMed Veo Insulin Pump and Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) for Better Glucose Control 1,2 for Healthcare Professionals Presented by Dr. Bruce
UTILIZING ACTIGRAPHY TO EXAMINE SLEEP IN YOUNG CHILDREN WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES
 UTILIZING ACTIGRAPHY TO EXAMINE SLEEP IN YOUNG CHILDREN WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES Jadienne Lord, B.A. Beth Malow, M.D. Sarah Jaser, Ph.D. Vanderbilt University Medical Center Ian M. Burr Division of Pediatric
UTILIZING ACTIGRAPHY TO EXAMINE SLEEP IN YOUNG CHILDREN WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES Jadienne Lord, B.A. Beth Malow, M.D. Sarah Jaser, Ph.D. Vanderbilt University Medical Center Ian M. Burr Division of Pediatric
Diabetes Care 32: , for achieving euglycemia in type 1 diabetes
 Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E The Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Well-Controlled Type 1 Diabetes JUVENILE DIABETES RESEARCH FOUNDATION
Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E The Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Well-Controlled Type 1 Diabetes JUVENILE DIABETES RESEARCH FOUNDATION
AACE/ACE Consensus Conference on Glucose Monitoring: An Update
 Can You Manage Diabetes Without Glucose Monitoring? Didn t Think So! George Grunberger, MD, FACP, FACE Chairman, Grunberger Diabetes Institute Clinical Professor, Internal Medicine and Molecular Medicine
Can You Manage Diabetes Without Glucose Monitoring? Didn t Think So! George Grunberger, MD, FACP, FACE Chairman, Grunberger Diabetes Institute Clinical Professor, Internal Medicine and Molecular Medicine
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the US FDA estimated
1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the US FDA estimated
Gli inibitori di SGLT-2 possono essere impiegati nel diabete di tipo 1?
 Impatto degli inibitori di SGLT-2 nei pazienti con diabete di tipo 2 Corso SID Hotel Michelangelo, Milano. 26 Giugno 2018 Gli inibitori di SGLT-2 possono essere impiegati nel diabete di tipo 1? Emanuele
Impatto degli inibitori di SGLT-2 nei pazienti con diabete di tipo 2 Corso SID Hotel Michelangelo, Milano. 26 Giugno 2018 Gli inibitori di SGLT-2 possono essere impiegati nel diabete di tipo 1? Emanuele
SCIENTIFIC STUDY REPORT
 PAGE 1 18-NOV-2016 SCIENTIFIC STUDY REPORT Study Title: Real-Life Effectiveness and Care Patterns of Diabetes Management The RECAP-DM Study 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction: Despite the well-established
PAGE 1 18-NOV-2016 SCIENTIFIC STUDY REPORT Study Title: Real-Life Effectiveness and Care Patterns of Diabetes Management The RECAP-DM Study 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Introduction: Despite the well-established
Presenter Disclosure
 Presenter Disclosure Linong Ji.M.D Consulting and lecture fee Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Bayer, Takeda, Sanofi-Aventis, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Johnson & Johnson, boehinger
Presenter Disclosure Linong Ji.M.D Consulting and lecture fee Eli Lilly, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Merck, Bayer, Takeda, Sanofi-Aventis, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche, Johnson & Johnson, boehinger
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Insulin pump use: ~ 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM < 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM 2007 FDA estimates ~375,000 insulin pumps for
1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Insulin pump use: ~ 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM < 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM 2007 FDA estimates ~375,000 insulin pumps for
Pediatric diabetes consortium T1D New Onset (NeOn) study: clinical outcomes during the first year following diagnosis
 Pediatric Diabetes 2014: 15: 287 293 doi: 10.1111/pedi.12068 All rights reserved 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Pediatric Diabetes Original Article Pediatric diabetes consortium
Pediatric Diabetes 2014: 15: 287 293 doi: 10.1111/pedi.12068 All rights reserved 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd. Pediatric Diabetes Original Article Pediatric diabetes consortium
Diabetes Management with Continuous Glucose Monitoring & Multiple Daily Injections. Aaron Michels MD
 Diabetes Management with Continuous Glucose Monitoring & Multiple Daily Injections Aaron Michels MD Outline SMBG & CGM by age group JDRF CGM Trial Sensor Augmented Insulin Pump Therapy for A1c Reduction
Diabetes Management with Continuous Glucose Monitoring & Multiple Daily Injections Aaron Michels MD Outline SMBG & CGM by age group JDRF CGM Trial Sensor Augmented Insulin Pump Therapy for A1c Reduction
A n aly tical m e t h o d s
 a A n aly tical m e t h o d s If I didn t go to the screening at Farmers Market I would not have known about my kidney problems. I am grateful to the whole staff. They were very professional. Thank you.
a A n aly tical m e t h o d s If I didn t go to the screening at Farmers Market I would not have known about my kidney problems. I am grateful to the whole staff. They were very professional. Thank you.
Factors Affecting Use of Insulin Pens by Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online November 26, 2007 Factors Affecting Use of Insulin Pens by Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Richard R. Rubin, PhD 1,2 Mark Peyrot, PhD 1,3 1= Department
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online November 26, 2007 Factors Affecting Use of Insulin Pens by Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Richard R. Rubin, PhD 1,2 Mark Peyrot, PhD 1,3 1= Department
Youth-Perceived Burden of Type 1 Diabetes: Problem Areas in Diabetes Survey Pediatric Version (PAID-Peds)
 583506DSTXXX10.1177/1932296815583506Journal of Diabetes Science and TechnologyMarkowitz et al research-article2015 Original Article Youth-Perceived Burden of Type 1 Diabetes: Problem Areas in Diabetes
583506DSTXXX10.1177/1932296815583506Journal of Diabetes Science and TechnologyMarkowitz et al research-article2015 Original Article Youth-Perceived Burden of Type 1 Diabetes: Problem Areas in Diabetes
European Perspective on Paediatric Diabetes Care
 Keystone, Colorado, July 2013 Practical Ways to Achieve Targets in Diabetes Care European Perspective on Paediatric Diabetes Care Professor David Dunger Department of Paediatrics Practical Ways to Achieve
Keystone, Colorado, July 2013 Practical Ways to Achieve Targets in Diabetes Care European Perspective on Paediatric Diabetes Care Professor David Dunger Department of Paediatrics Practical Ways to Achieve
Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond)
 Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond) 9501366-011 20110401 Objectives Understand the need for insulin pumps and CGMS in managing
Diabetes II Insulin pumps; Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) Ernest Asamoah, MD FACE FACP FRCP (Lond) 9501366-011 20110401 Objectives Understand the need for insulin pumps and CGMS in managing
Update on Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Technology in Diabetes. Elena Toschi, MD November 12, 2016
 Update on Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Technology in Diabetes Elena Toschi, MD November 12, 2016 Presenter Disclosure Information Elena Toschi, MD No financial disclosure Objectives: Use of CGM
Update on Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Technology in Diabetes Elena Toschi, MD November 12, 2016 Presenter Disclosure Information Elena Toschi, MD No financial disclosure Objectives: Use of CGM
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 1979 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% to 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the U.S. FDA
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 1979 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% to 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the U.S. FDA
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online April 7, 2017
 Diabetes Care 1 The Impact of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Markers of Quality of Life in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: Further Findings From the DIAMOND Randomized Clinical Trial DOI: 10.2337/dc17-0133
Diabetes Care 1 The Impact of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Markers of Quality of Life in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: Further Findings From the DIAMOND Randomized Clinical Trial DOI: 10.2337/dc17-0133
Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness
 Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) www.ahrq.gov Outline of Material Introduction
Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring Methods for Diabetes Mellitus: Comparative Effectiveness Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) www.ahrq.gov Outline of Material Introduction
Female- n (%) 494 (54) White Non-Hispanic 840 (91) Black Non-Hispanic 31 (3) Hispanic 27 (3) Other 21 (2) Age- mean±sd (range) 37.2±18.
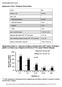 Supplementary Table 1. Participant Characteristics Total- n 919 Female- n (%) 494 (54) Race- n (%) White Non-Hispanic 840 (91) Black Non-Hispanic 31 (3) Hispanic 27 (3) Other 21 (2) Age- mean±sd (range)
Supplementary Table 1. Participant Characteristics Total- n 919 Female- n (%) 494 (54) Race- n (%) White Non-Hispanic 840 (91) Black Non-Hispanic 31 (3) Hispanic 27 (3) Other 21 (2) Age- mean±sd (range)
UNCOVERING THE BENEFITS OF THE ACCU- CHEK BOLUS ADVISOR MICHAEL PORTER CDE
 UNCOVERING THE BENEFITS OF THE ACCU- CHEK BOLUS ADVISOR MICHAEL PORTER CDE 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this session participants should be able to understand: The benefits of bolus advisors The
UNCOVERING THE BENEFITS OF THE ACCU- CHEK BOLUS ADVISOR MICHAEL PORTER CDE 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this session participants should be able to understand: The benefits of bolus advisors The
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Continuous Monitoring of Glucose in the Interstitial Fluid File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: continuous_monitoring_of_glucose_in_the_interstitial_fluid
Corporate Medical Policy Continuous Monitoring of Glucose in the Interstitial Fluid File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: continuous_monitoring_of_glucose_in_the_interstitial_fluid
As the number of new glucose monitoring devices
 DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 17, Number 9, 2015 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2014.0417 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Development of a New Measure for Assessing Glucose Monitoring Device-Related
DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 17, Number 9, 2015 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2014.0417 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Development of a New Measure for Assessing Glucose Monitoring Device-Related
Improving Type 2 Diabetes Patient Health Outcomes with Individualized Continuing Medical Education for Primary Care
 Diabetes Ther (2016) 7:473 481 DOI 10.1007/s13300-016-0176-9 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Improving Type 2 Diabetes Patient Health Outcomes with Individualized Continuing Medical Education for Primary Care Brian
Diabetes Ther (2016) 7:473 481 DOI 10.1007/s13300-016-0176-9 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Improving Type 2 Diabetes Patient Health Outcomes with Individualized Continuing Medical Education for Primary Care Brian
Association between serum IGF-1 and diabetes mellitus among US adults
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online July 16, 2010 Association between serum IGF-1 and diabetes mellitus among US adults Running title: Serum IGF-1 and diabetes mellitus Srinivas Teppala
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online July 16, 2010 Association between serum IGF-1 and diabetes mellitus among US adults Running title: Serum IGF-1 and diabetes mellitus Srinivas Teppala
Flash Glucose Monitoring & Implantable Sensors
 Flash Glucose Monitoring & Implantable Sensors Timothy Bailey, MD, FACE, CPI President & CEO, AMCR Institute Clinical Associate Professor, UCSD School of Medicine Disclosures Research Support: Abbott,
Flash Glucose Monitoring & Implantable Sensors Timothy Bailey, MD, FACE, CPI President & CEO, AMCR Institute Clinical Associate Professor, UCSD School of Medicine Disclosures Research Support: Abbott,
T he benefits of intensive treatment of
 Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Hypoglycemia in Type 1 Diabetes TADEJ BATTELINO, MD, PHD 1 MOSHE PHILLIP,
Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Hypoglycemia in Type 1 Diabetes TADEJ BATTELINO, MD, PHD 1 MOSHE PHILLIP,
Racial and Socioeconomic Disparities in Appendicitis
 Racial and Socioeconomic Disparities in Appendicitis Steven L. Lee, MD Chief of Pediatric Surgery, Harbor-UCLA Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics David Geffen School of Medicine at
Racial and Socioeconomic Disparities in Appendicitis Steven L. Lee, MD Chief of Pediatric Surgery, Harbor-UCLA Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics David Geffen School of Medicine at
Reduction in Hypoglycemia and No Increase in A1C with Threshold-Based Sensor-Augmented Pump (SAP) Insulin Suspension: ASPIRE In-Home
 Reduction in Hypoglycemia and No Increase in A1C with Threshold-Based Sensor-Augmented Pump (SAP) Insulin Suspension: ASPIRE In-Home Richard M. Bergenstal 1, David C. Klonoff 2, Bruce W. Bode 3, Satish
Reduction in Hypoglycemia and No Increase in A1C with Threshold-Based Sensor-Augmented Pump (SAP) Insulin Suspension: ASPIRE In-Home Richard M. Bergenstal 1, David C. Klonoff 2, Bruce W. Bode 3, Satish
Identifying Geographic & Socioeconomic Disparities in Access to Care for Pediatric Cancer Patients in Texas
 Identifying Geographic & Socioeconomic Disparities in Access to Care for Pediatric Cancer Patients in Texas Mary T. Austin, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatric Surgery University of Texas Health Science
Identifying Geographic & Socioeconomic Disparities in Access to Care for Pediatric Cancer Patients in Texas Mary T. Austin, MD, MPH Assistant Professor, Pediatric Surgery University of Texas Health Science
Clinical Impact of Prandial State, Exercise, and Site Preparation on the Equivalence of Alternative-Site Blood Glucose Testing
 Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Clinical Impact of Prandial State, Exercise, and Preparation on the Equivalence of Alternative- Blood Glucose Testing DAWN M. BINA, CMT ROBYN
Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Clinical Impact of Prandial State, Exercise, and Preparation on the Equivalence of Alternative- Blood Glucose Testing DAWN M. BINA, CMT ROBYN
8/8/2015. The Educational Needs of Fathers of Youth with Diabetes: A Mixed Methods Study. Diabetes Management
 Anastasia Albanese-O Neill PhD, ARNP, CDE Assistant Professor University of Florida, College of Nursing Gainesville, FL Disclosure to Participants Notice of Requirements For Successful Completion Please
Anastasia Albanese-O Neill PhD, ARNP, CDE Assistant Professor University of Florida, College of Nursing Gainesville, FL Disclosure to Participants Notice of Requirements For Successful Completion Please
THE INFLUENCE OF PSYCHOSOCIAL AND TREATMENT-RELATED VARIABLES ON ADHERENCE AND METABOLIC CONTROL IN ADOLESCENTS WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS
 THE INFLUENCE OF PSYCHOSOCIAL AND TREATMENT-RELATED VARIABLES ON ADHERENCE AND METABOLIC CONTROL IN ADOLESCENTS WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS Lene J. Kristensen, Niels H. Birkebaek, Anne H. Mose, Morten
THE INFLUENCE OF PSYCHOSOCIAL AND TREATMENT-RELATED VARIABLES ON ADHERENCE AND METABOLIC CONTROL IN ADOLESCENTS WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS Lene J. Kristensen, Niels H. Birkebaek, Anne H. Mose, Morten
Diabetes-related parameters and periodontal conditions in children
 J Periodont Res 2007; 42: 345 349 rights reserved Diabetes-related parameters and periodontal conditions in children Ó 2007 The Authors. Journal compilation Ó 2007 Blackwell Munksgaard JOURNAL OF PERIODONTAL
J Periodont Res 2007; 42: 345 349 rights reserved Diabetes-related parameters and periodontal conditions in children Ó 2007 The Authors. Journal compilation Ó 2007 Blackwell Munksgaard JOURNAL OF PERIODONTAL
Despite the availability of an effective treatment of Kawasaki
 ORIGINAL STUDIES Delayed Diagnosis by Physicians Contributes to the Development of Coronary Artery Aneurysms in Children With Matthew S. Wilder, MD,* Lawrence A. Palinkas, PhD,* Annie S. Kao, MPH, PhD,
ORIGINAL STUDIES Delayed Diagnosis by Physicians Contributes to the Development of Coronary Artery Aneurysms in Children With Matthew S. Wilder, MD,* Lawrence A. Palinkas, PhD,* Annie S. Kao, MPH, PhD,
DAZED AND CONFUSED: THE CHARACTERISTICS AND BEHAVIOROF TITLE CONFUSED READERS
 Worldwide Readership Research Symposium 2005 Session 5.6 DAZED AND CONFUSED: THE CHARACTERISTICS AND BEHAVIOROF TITLE CONFUSED READERS Martin Frankel, Risa Becker, Julian Baim and Michal Galin, Mediamark
Worldwide Readership Research Symposium 2005 Session 5.6 DAZED AND CONFUSED: THE CHARACTERISTICS AND BEHAVIOROF TITLE CONFUSED READERS Martin Frankel, Risa Becker, Julian Baim and Michal Galin, Mediamark
The Effect of Glycemic Exposure on the Risk of Microvascular Complications in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial -- Revisited
 Diabetes Publish Ahead of Print, published online January 25, 2008 The Effect of Glycemic Exposure on the Risk of Microvascular Complications in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial -- Revisited
Diabetes Publish Ahead of Print, published online January 25, 2008 The Effect of Glycemic Exposure on the Risk of Microvascular Complications in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial -- Revisited
ARTICLE. Prevalence of Diabetes and Impaired Fasting Glucose Levels Among US Adolescents. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey,
 ARTICLE Prevalence of Diabetes and Impaired Fasting Glucose Levels Among US Adolescents National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999-2002 Glen E. Duncan, PhD, RCEPSM Objective: To determine the
ARTICLE Prevalence of Diabetes and Impaired Fasting Glucose Levels Among US Adolescents National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999-2002 Glen E. Duncan, PhD, RCEPSM Objective: To determine the
8/5/2017. Disclosure to Participants. What is PCORI? Outline. To Test or Not To Test. What is PCORI? THE MONITOR TRIAL
 THE MONITOR TRIAL Effect of Glucose Monitoring on Patient and Provider Outcomes in Non-insulin Treated Diabetes Laura Young, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medicine University of North Carolina To Test
THE MONITOR TRIAL Effect of Glucose Monitoring on Patient and Provider Outcomes in Non-insulin Treated Diabetes Laura Young, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Medicine University of North Carolina To Test
What is a CGM? (Continuous Glucose Monitor) The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming
 The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming Montana Diabetes Professional Conference October 23, 2014 H. Peter Chase, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Colorado Barbara Davis Center Stanford: Bruce Buckingham,
The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming Montana Diabetes Professional Conference October 23, 2014 H. Peter Chase, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Colorado Barbara Davis Center Stanford: Bruce Buckingham,
Original Article Clinical Care/Education INTRODUCTION DIABETES & METABOLISM JOURNAL
 Original Article Clinical Care/Education Diabetes Metab J Published online Jun 29, 2018 https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0018 pissn 2233-6079 eissn 2233-6087 DIABETES & METABOLISM JOURNAL Frequency of
Original Article Clinical Care/Education Diabetes Metab J Published online Jun 29, 2018 https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0018 pissn 2233-6079 eissn 2233-6087 DIABETES & METABOLISM JOURNAL Frequency of
Assessing the value of the Ambulatory Glucose Profile in clinical practice
 Assessing the value of the Ambulatory Glucose Profile in clinical practice STEPHAN MATTHAEI Abstract Glycated haemoglobin (HbA 1c) is a measure of mean blood glucose levels over time. It is not a good
Assessing the value of the Ambulatory Glucose Profile in clinical practice STEPHAN MATTHAEI Abstract Glycated haemoglobin (HbA 1c) is a measure of mean blood glucose levels over time. It is not a good
ADAG Study Group Data Links A1C Levels with Empirically Measured Blood Glucose Values - New Treatment Guidelines Will Now be Needed
 529638DSTXXX10.1177/1932296814529638Journal of Diabetes Science and TechnologyKlonoff research-article2014 Editorial ADAG Study Group Data Links A1C Levels with Empirically Measured Blood Glucose Values
529638DSTXXX10.1177/1932296814529638Journal of Diabetes Science and TechnologyKlonoff research-article2014 Editorial ADAG Study Group Data Links A1C Levels with Empirically Measured Blood Glucose Values
Role of SMBG in Non-Insulin Treated Subjects with T2DM Richard M. Bergenstal, MD
 Role of SMBG in Non-Insulin Treated Subjects with T2DM Richard M. Bergenstal, MD International Diabetes Center and Health Services University of Minnesota Minneapolis, MN richard.bergenstal@parknicollet.com
Role of SMBG in Non-Insulin Treated Subjects with T2DM Richard M. Bergenstal, MD International Diabetes Center and Health Services University of Minnesota Minneapolis, MN richard.bergenstal@parknicollet.com
Role of Mobile Technology to Improve Diabetes Care in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: The Remote-T1D Study ibgstar Ò in Type 1 Diabetes Management
 Diabetes Ther (2017) 8:811 819 DOI 10.1007/s13300-017-0272-5 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Role of Mobile Technology to Improve Diabetes Care in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: The Remote-T1D Study ibgstar Ò in Type
Diabetes Ther (2017) 8:811 819 DOI 10.1007/s13300-017-0272-5 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Role of Mobile Technology to Improve Diabetes Care in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: The Remote-T1D Study ibgstar Ò in Type
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adolescents PHIL ZEITLER MD, PHD SECTION OF ENDOCRINOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO DENVER
 Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adolescents PHIL ZEITLER MD, PHD SECTION OF ENDOCRINOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO DENVER Yes! Is Type 2 diabetes the same in kids as in adults? And No!
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Adolescents PHIL ZEITLER MD, PHD SECTION OF ENDOCRINOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO DENVER Yes! Is Type 2 diabetes the same in kids as in adults? And No!
Caring for Adult Patients with Diabetes
 Internati ona l E D U C AT I O N Caring for Adult Patients with Diabetes for A llied Health Professionals 2016 page 1 of 5 Caring for Adult Patients with Diabetes for Allied Health Professionals Nursing
Internati ona l E D U C AT I O N Caring for Adult Patients with Diabetes for A llied Health Professionals 2016 page 1 of 5 Caring for Adult Patients with Diabetes for Allied Health Professionals Nursing
Racial Variation In Quality Of Care Among Medicare+Choice Enrollees
 Racial Variation In Quality Of Care Among Medicare+Choice Enrollees Black/white patterns of racial disparities in health care do not necessarily apply to Asians, Hispanics, and Native Americans. by Beth
Racial Variation In Quality Of Care Among Medicare+Choice Enrollees Black/white patterns of racial disparities in health care do not necessarily apply to Asians, Hispanics, and Native Americans. by Beth
Similar risk of malignancy with insulin glargine and neutral protamine Hagedorn
 Letter Similar risk of malignancy with insulin glargine and neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes: findings from a 5 year randomised, openlabel study J. Rosenstock 1,2,
Letter Similar risk of malignancy with insulin glargine and neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes: findings from a 5 year randomised, openlabel study J. Rosenstock 1,2,
06/13/17. A. Completed a comprehensive diabetes education program within the past two years; and
 Reference #: MC/L011 Page 1 of 4 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Community Health Plan (PCHP) PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) Non-ERISA
Reference #: MC/L011 Page 1 of 4 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Community Health Plan (PCHP) PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) Non-ERISA
Durable change in glycaemic control following intensive management of type 2 diabetes in the ACCORD clinical trial
 Diabetologia (2014) 57:2030 2037 DOI 10.1007/s00125-014-3318-5 ARTICLE Durable change in glycaemic control following intensive management of type 2 diabetes in the ACCORD clinical trial Zubin Punthakee
Diabetologia (2014) 57:2030 2037 DOI 10.1007/s00125-014-3318-5 ARTICLE Durable change in glycaemic control following intensive management of type 2 diabetes in the ACCORD clinical trial Zubin Punthakee
Quarterly Visits with Glycated Hemoglobin Monitoring: The Sweet Spot for Glycemic Control in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes
 Page 1 of 16 Diabetes Care 1 Quarterly Visits with Glycated Hemoglobin Monitoring: The Sweet Spot for Glycemic Control in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes Running title: Visit Frequency and Glycemic Control
Page 1 of 16 Diabetes Care 1 Quarterly Visits with Glycated Hemoglobin Monitoring: The Sweet Spot for Glycemic Control in Youth with Type 1 Diabetes Running title: Visit Frequency and Glycemic Control
Community Health Profile: Minnesota, Wisconsin, & Michigan Tribal Communities 2006
 Community Health Profile: Minnesota, Wisconsin, & Michigan Tribal Communities 26 This report is produced by: The Great Lakes EpiCenter If you would like to reproduce any of the information contained in
Community Health Profile: Minnesota, Wisconsin, & Michigan Tribal Communities 26 This report is produced by: The Great Lakes EpiCenter If you would like to reproduce any of the information contained in
22 Diabetes Care Volume 38, January 2015
 22 Diabetes Care Volume 38, January 2015 CLIN CARE/EDUCATION/NUTRITION/PSYCHOSOCIAL Predictors of Nonsevere and Severe Hypoglycemia During Glucose- Lowering Treatment With Insulin Glargine or Standard
22 Diabetes Care Volume 38, January 2015 CLIN CARE/EDUCATION/NUTRITION/PSYCHOSOCIAL Predictors of Nonsevere and Severe Hypoglycemia During Glucose- Lowering Treatment With Insulin Glargine or Standard
TABLE OF CONTENTS. HLC102A - Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Technologies and Global Markets
 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1 STUDY GOALS AND OBJECTIVES 1 REASONS FOR DOING THIS STUDY 1 CONTRIBUTIONS TO THE STUDY AND INTENDED AUDIENCE 1 SCOPE AND FORMAT 1 METHODOLOGY AND INFORMATION
TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1 STUDY GOALS AND OBJECTIVES 1 REASONS FOR DOING THIS STUDY 1 CONTRIBUTIONS TO THE STUDY AND INTENDED AUDIENCE 1 SCOPE AND FORMAT 1 METHODOLOGY AND INFORMATION
BRIAN MOSES, MD, FRCPC (INTERNAL MEDICINE) CHIEF OF MEDICINE, SOUTH WEST HEALTH
 Insulin Initiation BRIAN MOSES, MD, FRCPC (INTERNAL MEDICINE) CHIEF OF MEDICINE, SOUTH WEST HEALTH Disclosures In the past 12 months, I have received speakers honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim,
Insulin Initiation BRIAN MOSES, MD, FRCPC (INTERNAL MEDICINE) CHIEF OF MEDICINE, SOUTH WEST HEALTH Disclosures In the past 12 months, I have received speakers honoraria from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim,
Making Sense of Glucose Monitoring. My Journey with Glucose Monitoring Over the Last 37 Years 8/7/2017
 HSW1 Disclosure to Participants Making Sense of Glucose Monitoring Alison B. Evert, MS, RD, CDE UW Neighborhood Clinics UW Medicine Seattle, WA Conflict of Interest (COI) and Financial Relationship Disclosures:
HSW1 Disclosure to Participants Making Sense of Glucose Monitoring Alison B. Evert, MS, RD, CDE UW Neighborhood Clinics UW Medicine Seattle, WA Conflict of Interest (COI) and Financial Relationship Disclosures:
Ensuring Safe Physical Activity in Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes
 Ensuring Safe Physical Activity in Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes FACULTY ADVISOR Lori Laffel, MD, MPH Professor, Pediatrics Harvard Medical School Chief, Pediatric, Adolescent and Young
Ensuring Safe Physical Activity in Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes FACULTY ADVISOR Lori Laffel, MD, MPH Professor, Pediatrics Harvard Medical School Chief, Pediatric, Adolescent and Young
Safety and Effectiveness of Insulin Pump Therapy in Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes
 Emerging Treatments and Technologies O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Safety and Effectiveness of Insulin Pump Therapy in Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes LESLIE P. PLOTNICK, MD 1 LORETTA M.
Emerging Treatments and Technologies O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Safety and Effectiveness of Insulin Pump Therapy in Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes LESLIE P. PLOTNICK, MD 1 LORETTA M.
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Drury KE, Schaeffer M, Silverberg JI. Association between atopic disease and anemia in US children. JAMA Pediatr. Published online vember 30, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.3065.
Supplementary Online Content Drury KE, Schaeffer M, Silverberg JI. Association between atopic disease and anemia in US children. JAMA Pediatr. Published online vember 30, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2015.3065.
NEWS BRIEFING Advances in Technology. moderated by: Irl Hirsch, MD University of Washington Medical Center
 NEWS BRIEFING Advances in Technology moderated by: Irl Hirsch, MD University of Washington Medical Center 1 EMBARGO POLICY All recordings are for personal use only and not for rebroadcast online or in
NEWS BRIEFING Advances in Technology moderated by: Irl Hirsch, MD University of Washington Medical Center 1 EMBARGO POLICY All recordings are for personal use only and not for rebroadcast online or in
Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices Pharmacy Policy
 Line of Business: All Line of Business Effective date: August 16, 2017 Revision date: August 16, 2017 Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices Pharmacy Policy This policy has been developed through review
Line of Business: All Line of Business Effective date: August 16, 2017 Revision date: August 16, 2017 Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices Pharmacy Policy This policy has been developed through review
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
 Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Date of Origin: 02/2001 Last Review Date: 07/26/2017 Effective Date: 07/26/2017 Dates Reviewed: 04/2004, 04/2005, 03/2006, 11/2006, 12/2007, 03/2008, 09/2008, 04/2009,
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Date of Origin: 02/2001 Last Review Date: 07/26/2017 Effective Date: 07/26/2017 Dates Reviewed: 04/2004, 04/2005, 03/2006, 11/2006, 12/2007, 03/2008, 09/2008, 04/2009,
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online February 25, 2010
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online February 25, 2010 Undertreatment Of Mental Health Problems In Diabetes Undertreatment Of Mental Health Problems In Adults With Diagnosed Diabetes
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online February 25, 2010 Undertreatment Of Mental Health Problems In Diabetes Undertreatment Of Mental Health Problems In Adults With Diagnosed Diabetes
Paolo Di Bartolo U.O di Diabetologia Dip. Malattie Digestive & Metaboliche AULS Prov. di Ravenna. Ipoglicemie e Monitoraggio Glicemico
 Paolo Di Bartolo U.O di Diabetologia Dip. Malattie Digestive & Metaboliche AULS Prov. di Ravenna Ipoglicemie e Monitoraggio Glicemico Management of Hypoglycaemia.if hypoglycemia is a problem, the principles
Paolo Di Bartolo U.O di Diabetologia Dip. Malattie Digestive & Metaboliche AULS Prov. di Ravenna Ipoglicemie e Monitoraggio Glicemico Management of Hypoglycaemia.if hypoglycemia is a problem, the principles
Effectiveness Of A Diabetic Ketoacidosis Prevention Intervention In Children With Type 1 Diabetes
 Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Public Health Theses School of Public Health January 2015 Effectiveness Of A Diabetic Ketoacidosis Prevention Intervention
Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Public Health Theses School of Public Health January 2015 Effectiveness Of A Diabetic Ketoacidosis Prevention Intervention
Diabetes Care 34: , 2011
 Epidemiology/Health Services Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Temporal Trends in Recording of Diabetes on Death Certificates Results from Translating Research Into Action for Diabetes (TRIAD) LAURA
Epidemiology/Health Services Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Temporal Trends in Recording of Diabetes on Death Certificates Results from Translating Research Into Action for Diabetes (TRIAD) LAURA
HEALTH CARE EXPENDITURES ASSOCIATED WITH PERSISTENT EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT USE: A MULTI-STATE ANALYSIS OF MEDICAID BENEFICIARIES
 HEALTH CARE EXPENDITURES ASSOCIATED WITH PERSISTENT EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT USE: A MULTI-STATE ANALYSIS OF MEDICAID BENEFICIARIES Presented by Parul Agarwal, PhD MPH 1,2 Thomas K Bias, PhD 3 Usha Sambamoorthi,
HEALTH CARE EXPENDITURES ASSOCIATED WITH PERSISTENT EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT USE: A MULTI-STATE ANALYSIS OF MEDICAID BENEFICIARIES Presented by Parul Agarwal, PhD MPH 1,2 Thomas K Bias, PhD 3 Usha Sambamoorthi,
Asthma and Tobacco: Double Trouble for Wisconsin Adolescents
 Asthma and Tobacco: Double Trouble for Wisconsin Adolescents Livia Navon, MS, RD; Beth Fiore, MS; Henry Anderson, MD ABSTRACT Background: Environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) exposure has been identified
Asthma and Tobacco: Double Trouble for Wisconsin Adolescents Livia Navon, MS, RD; Beth Fiore, MS; Henry Anderson, MD ABSTRACT Background: Environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) exposure has been identified
PEER REVIEW HISTORY ARTICLE DETAILS TITLE (PROVISIONAL)
 PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form (see an example) and are provided with free text boxes to
PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form (see an example) and are provided with free text boxes to
How I use the latest technology to investigate and treat a person with Type 1 Diabetes. Dr Pratik Choudhary
 How I use the latest technology to investigate and treat a person with Type 1 Diabetes Dr Pratik Choudhary Disclosures Advisory board and speaker fees from Medtronic, Roche, Abbott and Johnson and Johnson,
How I use the latest technology to investigate and treat a person with Type 1 Diabetes Dr Pratik Choudhary Disclosures Advisory board and speaker fees from Medtronic, Roche, Abbott and Johnson and Johnson,
Con - SMBG Should be the Standard of Care in All Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
 JUNE 9 13, 2006 WASHINGTON, DC Con - SMBG Should be the Standard of Care in All Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Antonio Nicolucci, MD Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Epidemiology Consorzio Mario
JUNE 9 13, 2006 WASHINGTON, DC Con - SMBG Should be the Standard of Care in All Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Antonio Nicolucci, MD Department of Clinical Pharmacology and Epidemiology Consorzio Mario
Glimepiride Versus Metformin as Monotherapy in Pediatric Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
 Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Glimepiride Versus Metformin as Monotherapy in Pediatric Patients With Type 2 Diabetes A randomized, single-blind comparative study MICHAEL
Clinical Care/Education/Nutrition O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Glimepiride Versus Metformin as Monotherapy in Pediatric Patients With Type 2 Diabetes A randomized, single-blind comparative study MICHAEL
CAROLINAS CHAPTER/AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS Annual Meeting HILTON HEAD ISLAND FRIDAY PRESENTATION
 CAROLINAS CHAPTER/AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS 2016 Annual Meeting HILTON HEAD ISLAND FRIDAY PRESENTATION September 9-11, 2016 ~ Sonesta Resort ~ Hilton Head Island, SC This continuing
CAROLINAS CHAPTER/AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGISTS 2016 Annual Meeting HILTON HEAD ISLAND FRIDAY PRESENTATION September 9-11, 2016 ~ Sonesta Resort ~ Hilton Head Island, SC This continuing
High rate of non-adherence to insulin pump: over prescription, overuse or misuse? A population-based case-cohort study.
 High rate of non-adherence to insulin pump: over prescription, overuse or misuse? A population-based case-cohort study. Dr. Eugene Merzon MD; Ilia Merhasin, MBA; Dr. Avivit Golan-Cohen MD ; Dr. Shmuel
High rate of non-adherence to insulin pump: over prescription, overuse or misuse? A population-based case-cohort study. Dr. Eugene Merzon MD; Ilia Merhasin, MBA; Dr. Avivit Golan-Cohen MD ; Dr. Shmuel
Artificial Pancreas Device Systems. Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes. pump. pump
 Protocol Artificial Pancreas Device Systems (10130) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/19 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/15, 03/16, 03/17, 01/18 Preauthorization is required.
Protocol Artificial Pancreas Device Systems (10130) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 04/01/18 Next Review Date: 01/19 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/15, 03/16, 03/17, 01/18 Preauthorization is required.
