Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy
|
|
|
- James Porter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet. Please visit the intranet for the latest version. Purpose of Agreement Document Type Reference Number To ensure insulin syringes are pre-loaded appropriately by registered Community Nurses to allow patients to self-administer their insulin at home appropriately. Policy Solent NHST/Policy/MMT025 Version 1 Name of Approving Committees/Groups Medicines Committee Policy Steering Group Assurance Committee Operational Date September 2016 Document Review Date September 2019 Document Sponsor (Name & Job Title) Document Manager (Name & Job Title) Document developed in consultation with Intranet Location Website Location Keywords (for website/intranet uploading) Acting Chief Pharmacist Pharmacist Intermediate Care & Community Nursing Quality & Training Lead Adults Southampton Lead Nurse Diabetes, Specialist Diabetes Nurse, Lead Solent Community Nurses GP and Clinical Director Business Zone / Policies, SOPs and Clinical Guidelines Publication Scheme / Policies and Procedures Insulin Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 1 of 25 Version 1
2 Amendments Summary: Please fill the table below: Amend No Issued Page Subject Action Date Review Log: Include details of when the document was last reviewed: Version Number Review Date Lead Name Ratification Process Notes Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 2 of 25 Version 1
3 SUMMARY OF POLICY Any Community Nurses who are in a situation where they may be required to pre-load insulin syringes for patients must be aware of the contents of this policy. The policy details: The assessments that must be undertaken when a patient may require insulin to be pre-loaded (Section 3 - Process). The practicalities around pre-loading, labelling and storing pre-loaded insulin (Section 3 Process). The roles & responsibilities of staff pre-loading insulin (Section 4) Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 3 of 25 Version 1
4 Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Contents INTRODUCTION... 5 PURPOSE... 5 SCOPE... 5 DEFINITIONS PROCESS/REQUIREMENTS ROLES & RESPONSIBILITIES TRAINING EQUALITY IMPACT ASSESSMENT AND MENTAL CAPACITY SUCCESS CRITERIA / MONITORING EFFECTIVENESS REVIEW REFERENCES AND LINKS TO OTHER DOCUMENTS Appendix A: Process for Applying this Policy to Patients Appendix B: Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for the assessment of a patient to have insulin prepared in advance of administration Appendix C: Risk Assessment Form Advanced Preparation of Insulin into Syringes for a Patient to Administer at a Later Date Appendix D: Documentation Form for the Advanced Preparation of Insulin in Syringes Appendix E: Labels for Insulin Syringes and Insulin Syringe Containers Appendix G: Equality Impact Assessment Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 4 of 25 Version 1
5 1. INTRODUCTION & PURPOSE INTRODUCTION 1.1 This policy is supported by a risk assessment and Standard Operating Procedure (SOP; Appendices B & C) for the pre-loading of insulin for patients to self-administer later. It stresses the necessary principles of practice including patient assessment and review, ensures other methods of insulin administration have been considered, together with contra-indications, and details appropriate insulin storage requirements and record keeping. 1.2 Some patients with diabetes are unable or unwilling to use insulin pens and are only able to self-inject using a syringe. If they are unable to draw up insulin from a vial using the syringe, the patient s independence can be maintained by a Community Nurse pre-loading the syringes. The preparation of insulin injections by Community Nurses for patients to administer in their own homes at a later time has been the practice for many years. 1.3 The pre-loading of insulin into syringes is an unlicensed activity that falls outside of the Medicines Act, and adherence to this policy protects the patient, and provides legal protection for the Registered Nurse and this organisation under vicarious liability. The Royal College of Nursing (2015) advises that this activity must be seen as the final option, and only considered when all other options have been exhausted. PURPOSE 1.4 The purpose of this policy is: To promote patient safety. To ensure that Registered Nurses (RNs) employed by Solent NHS Trust are aware of the potential risks of pre-loading insulin syringes for later use by a patient. To provide a clear and consistent framework across Solent NHS Trust for the appropriate assessment and management of a person with diabetes who cannot safely prepare their own insulin dose. To support RNs to provide insulin therapy as detailed in this policy which is classified as secondary dispensing (and thus not covered in the Medicines Act 1968) however, takes note of RCN guidance Advance preparation of insulin syringes for adult patients to administer at home (RCN, 2015). 2. SCOPE & DEFINITIONS SCOPE 2.1 This document applies to all directly and indirectly employed staff within Solent NHS Trust and other persons working within the organisation in line with Solent NHS Trust s Equal Opportunities Document. This document is also recommended to Independent Contractors as good practice. Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 5 of 25 Version 1
6 2.2 Solent NHS Trust is committed to the principles of Equality and Diversity and will strive to eliminate unlawful discrimination in all its forms. We will strive towards demonstrating fairness and Equal Opportunities for users of services, carers, the wider community and our staff. DEFINITIONS 2.3 Within the context of this policy the definition of pre-loading an insulin syringe refers to insulin that has been withdrawn from a 10ml vial, using an insulin syringe that is marked in one or two unit graduations for self-administration by a patient at a later date. 3. PROCESS/REQUIREMENTS 3.1 Pre-loading of insulin must only be recommended when alternative methods of delivery are not possible and after appropriate risk assessment, as outlined in Appendix C. 3.2 RNs must be aware of the alternative injection devices available and discuss the patient s needs and preferred options with a Diabetes Specialist Nurse. The patient s General Practitioner must also be made aware; understand the unlicensed nature of pre-loaded insulin syringes and be in agreement with the need for the patient to have pre-loaded insulin syringes. After the GP has verbally agreed this, the letter template in Appendix G must be completed and sent to the GP with a copy of the completed Risk Assessment form (Appendix C). Pre-loading of insulin for injection must only begin following a full written risk assessment, involving a Diabetes Specialist Nurse, and the ruling out of alternative methods of administration. A thorough assessment of the patient s understanding of the insulin regimen, their ability to manage it and the support available between Community Nurse visits, must be undertaken using Appendix B (Standard Operating Procedure; SOP) for the assessment of a patient to have insulin prepared in advance of administration. This should be followed by completion of Appendix C (Risk Assessment Form Advanced Preparation of Insulin into Syringes for a Patient to Administer at a Later Date). 3.3 The Risk assessment form in Appendix C must be undertaken for new patients every three months, or sooner if the patient s condition changes. A copy must be sent to the patient s GP. After patients are stable, it may be appropriate to reduce this frequency to a 6-monthly review of their risk assessment. 3.4 The patient must always be consulted about their insulin administration and informed consent obtained regarding the care provided. 3.5 On completion of the risk assessment the RN must decide on the appropriate number of days that the insulin syringes can be prepared for and left with the patient. It is important that the RN considers all aspects of social and health care for their patient in this decision. This number and the reason for the decision must be recorded in Appendix C. The maximum period of time that insulin syringes can be left pre-loaded for is seven days. Each time a nurse pre-loads a syringe, Appendix D (Documentation Form for the Advanced Preparation of Insulin in Syringes) must be completed. Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 6 of 25 Version 1
7 3.6 Pre-loaded insulin syringes must be labelled individually and stored in a wipeable, labelled, sealable container (see Appendix B). If the patient is having a different type of insulin or dose at another time of the day another storage container must be used. To prevent any confusion the containers will ideally be either different colours and/or shapes. The size of the lid should be different to reduce the risk of the wrong lid with the wrong label being put on the incorrect container. 3.7 The patient s fridge should be visibly clean and free of debris; if there are concerns about the cleanliness of the fridge storage, the patient may not be appropriate for pre-loading insulin (see Appendix C). The insulin must be stored in the fridge door or top shelf to prevent cross-contamination from other food items. 3.8 It is recommended that insulin stored between a temperature of between 2 and 8 degrees Celsius. Never allow insulin to freeze; containers should not be stored next to the freezer section or at the back of the fridge to reduce the risk of this happening. 3.9 Unopened insulin can be kept in these conditions until the expiry date printed on the packaging. Once opened, a vial of insulin kept in these conditions must be discarded after 28 days. The date that the vial was opened must be written on the vial and in Appendix D Patients in residential care must have their pre-loaded insulin syringes stored as outlined in , but in a locked fridge Arrangements must be made to ensure that the monitoring of diabetes control is undertaken. Capillary blood glucose monitoring may be undertaken by the patient themselves, a family member or friend using their own glucometer. A full written assessment must be undertaken to check that they are confident and competent to undertake this procedure. The meter must also be checked weekly with the relevant quality control solution that is provided by the relevant meter company to ensure that it is accurate. Accuracy can also be checked by comparing a capillary blood glucose result with a venous glucose sample. An HbA1C every three to six months is also required to evaluate the level of diabetes control Liaise with a Diabetes Specialist Nurse as required for advice if circumstances change The Community Matron or Service Manager may wish to undertake an audit for the patients under their care in order to provide an element of Quality Assurance. A suggested method for such an audit is to review the Risk Assessments (Appendix C) that have been carried out for a selection of patients, check that the Registered Nurse has completed them correctly and that any actions resulting from the Risk Assessment were followed up appropriately. The number of records to review and the frequency of audit may be determined by the Service, since the Community Nursing Teams in Solent NHS Trust have varying numbers of patients who have insulin prepared in this manner It is recommended that needles of 8mm or less be used when using with an insulin syringe. Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 7 of 25 Version 1
8 3.15 An overview of the processes involved in points is outlined in Appendix A. Contra-Indications to Pre-Loading Insulin: 3.16 The use of a non-insulin syringe to pre-load insulin. No other type of syringe, other than an insulin syringe must ever be used for insulin administration/preloading Insulin glargine (e.g. Lantus, or an insulin glargine biosimilar) must not be preloaded into insulin syringes Very variable capillary blood glucose recordings Lack of satisfactory storage conditions in the patient s home, for example, lack of a fridge, or lack of adequate space in the fridge Pre-filled insulin cartridges and commercially available pre-loaded pens must not be used to withdraw insulin from in order to comply with this policy. Only 10ml vials are permissible to be used If any of the points are found, then this is to be reported to the patient s GP and the advanced preparation of insulin in syringes will be discontinued. Alternative arrangements must be made for the insulin to be administered. A clinical incident form must be completed. 4. ROLES & RESPONSIBILITIES 4.1 This policy covers all RNs (as defined in Section 2.1) employed by Solent NHS Trust who are required to treat patients with diabetes mellitus within their own home. 4.2 It relates specifically to patients who are able to safely administer the correct dose of insulin at the correct time, but are unable to draw up insulin or utilise standard commercially available insulin preparations. 4.3 It is the responsibility of every Trust-employed RN who is required to treat patients with diabetes mellitus to be familiar with this policy and procedure. 4.4 RN to positively identify the patient (obtaining confirmation of name and DOB) and establish allergy status. 4.5 RNs involved in the administration of insulin, as in all other areas of their practice, will be responsible for maintaining and updating their knowledge and practice. 4.6 RNs are responsible for the initial and continued assessment of patients who are self-administering and have continued responsibility for recognising and acting upon changes in a patient s condition with regards to safety of the patient and others. The Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) and Mental Capacity Act 2005 state that for a patient to be able to self-administer, the patient must be assessed as being at Level 3 which is defined: the patient accepts full responsibility for the storage and administration of the medicinal products. The level must be documented in the patient s records. Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 8 of 25 Version 1
9 4.7 Patients must be allowed to decide whether they will agree to treatment in this way and their consent must be documented in the patient case notes. Please refer to the Consent to Examination and Treatment Policy for further information about informed consent, including what action to take if the patient is unable to consent. 4.8 RNs are accountable to ensure that the patient is competent to carry out the task of injecting the insulin. 4.9 RNs are responsible for implementing this policy. Pre-loading insulin syringes must not be delegated to non-registered staff Pre-loaded syringes may not be prepared by one Registered Nurse for another health professional or skilled professional that is not registered to administer them Under no circumstances may RNs mix and pre-load different insulins in the same syringe for administration at a later time (there is no longer a need to mix insulins due to the availability of suitable manufacturer s preparations) Registered Nurses are responsible for recognising any limitations in their knowledge and competence and declining any duties they do not feel able to perform in a skilled and safe manner It is the responsibility of the Community Nursing Locality Leads to maintain a register of patients having insulin pre-loaded syringes in their areas. This must be made available on request to the Specialist Diabetes Nurses, the Medicines Committee, the Risk Team or Medicines Management Team upon request It is the responsibility of individual Community Nurses to ensure that they inform their Locality Lead Nurse of patients that they are pre-loading insulin for so that a register of patients can be maintained. 5. TRAINING Solent NHS Trust recognises the importance of appropriate training for staff. For training requirements and refresher frequencies in relation to this policy subject matter, please refer to the Training Needs Analysis (TNA) on the intranet. 5.1 All staff involved with the care of these patients will be required to access an online training session written by the Medicines Management Team. This session will cover a detailed presentation of the policy, the responsibilities of the RN, completing the risk assessment and practical aspects of dispensing insulin into syringes. Support and advice may also be sought from the Specialist Diabetes Nurses. 5.2 Nurses undertaking pre-loading of insulin syringes are required to view the online training session annually; this will be monitored at RNs annual appraisals. 5.3 All Community Nurses must be made aware of this policy at induction (new staff) by their Clinical Nurse Manager or Locality Manager and specific medicines management training where appropriate. Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 9 of 25 Version 1
10 5.4 Any observations from audits which Services have carried out (as discussed in 3.13) and any incidents associated with this practice will be fed back to the Medicines Committee and Clinical Governance Groups so learning can be shared across the Trust. 6. EQUALITY IMPACT ASSESSMENT AND MENTAL CAPACITY 6.1 An Equality Impact Assessment has been completed for this policy and no significant adverse effects have been noted. (See Appendix H) 7. SUCCESS CRITERIA / MONITORING EFFECTIVENESS 7.1 Incident Reports will be reviewed/monitored and this policy will be updated accordingly if any changes are necessary; any relevant incident reports or learning outcomes will be discussed at the Medicines Committee meeting. 7.2 Implementation of this policy will be reviewed within 1 year by the Medicines Management Team the results will be presented at the Medicines Committee. 7.3 Non-compliance with this policy must be reported via the Trust incident reporting system. 7.4 All patients receiving insulin by this methodology will be recorded and held on a register. This must be available to the Medicines Committee, the Risk Team or Medicines Management Team upon request. 8. REVIEW 8.1 This document may be reviewed at any time at the request of either staff side or management, but will automatically be reviewed 3 years from initial approval and thereafter on a triennial basis unless organisational changes, legislation, guidance or non-compliance prompt an earlier review. 9. REFERENCES AND LINKS TO OTHER DOCUMENTS Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) (2010a) Standards for medicines management; Nursing and Midwifery Council (2015) The Code. Professional standards of conduct, performance and ethics for nurses and midwives. National Patient Safety Agency (2010) Rapid response Report. Safer Administration of Insulin. NPSA/2010/RRR013. Parliament (1968) Medicines Act 1968, London: Stationery Office. Parliament (2005) Mental Capacity Act 2005, London: Stationery Office. Rosindale, S (2014) Pre-loading of insulin syringes for people with diabetes to administer at home: new solution to an old practice, Diabetes and Primary Care, 16 (3), pp Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 10 of 25 Version 1
11 Royal College of Nursing (2015) Advance preparation of insulin syringes for patients to administer at home; Solent NHS Trust Medicines Policy Solent NHS Trust Consent to Examination and Treatment Policy Solent NHS Trust Deprivation of Liberty Safeguards and Mental Capacity Act Policy Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 11 of 25 Version 1
12 Appendix A: Process for Applying this Policy to Patients 1. Process of syringes being pre-loaded for the patient on the first occasion: 2. Ongoing process of syringes being pre-loaded for the patient Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 12 of 25 Version 1
13 Appendix B: Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for the assessment of a patient to have insulin prepared in advance of administration 1. Mental capacity and physical capability Activity Rationale Responsibility Assess the mental capacity and physical capability of the patient to self-administer insulin. The patient must be at Level 3 which Reduce risk of medication error. NMC Standards for Clinical Lead/Registered Nurse is defined: the patient accepts full responsibility for the storage and administration of the medicinal products. The level must be documented in the patient s records. Registered Nurses must be aware that the Mental Capacity Act 2005 requires all those working with potentially incapacitated people to assess the individual s capacity at a particular moment about particular decision. Any change in the patient s condition would necessitate a review of their self-administration status; for example, risk of self-harm. Medicines Management (2010). Care plan must be updated as a minimum every three months to meet needs of patient. Reduce risk of medication error. 2. Consent Activity Rationale Responsibility Discuss risks and benefits of selfadministration with the patient. Support available between Community Nurse visits. Where patients consent to selfadministration of their medicines the following must be considered: Patients share the responsibility for their actions, relating to self-administration of their medicines. If children have access to the fridge that the patient ensures that the syringes are kept out of their reach and/or a childproof fridge lock is in situ. Patients can withdraw consent at any time. To gain informed consent and document in patient s record. Patients are empowered to make informed choices. Safeguarding of children. Patients retain right to withdraw consent. Clinical Lead/Registered Nurse 3. Ensure most appropriate product has been prescribed Activity Rationale Responsibility Discuss and assess potential alternative insulin preparation with diabetes nurse or prescriber. Clinical Lead/Registered Nurse Unable to pre-load/use pen devices due to manual dexterity/poor vision/ peripheral neuropathy/physical weakness to deliver insulin dose in insulin pen device/patient preference/ reluctance to change 4. Contra-indications Activity Rationale Responsibility Are there any contra indications for the preloading of insulin syringes? Risk of deterioration of insulin. Clinical Lead/Registered Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 13 of 25 Version 1
14 4.1 Insulin glargine (including biosimilar insulin glargine) must not be pre-loaded for later administration. 4.2 Only use 10ml vials to withdraw insulin into syringes. Do not withdraw from preloaded pens or 3ml cartridges. 4.3 Is the fridge in working order? 4.4 Is the fridge visibly clean? 4.5 Is the fridge free from debris? 4.6 Patient suffers from an unpredictable mental state or declining cognitive ability. 4.7 Very variable capillary blood glucose readings. 4.8 If any risks or contra-indications are identified from the list above, then this needs to be reported to the GP or Out Of Hours Doctors; the advanced preparation of insulin in syringes will be discontinued and arrangements made for the Community Nursing Team to visit at the required intervals. Complete incident form. 5. Education of patient To ensure appropriate storage conditions. Risk to patient safety. Nurse Activity Rationale Responsibility Information/education given and supervision should be tailored to meet individual patient need, to enable the patient to administer the right dose, at the right time using the correct technique. To ensure safe administration of insulin. Clinical Lead/ Registered Nurse The information below must be provided to the patient before commencing selfadministration. 5.1 The name of the medicine. 5.2 Why they are taking it; dose and frequency. 5.3 Re-suspending each pre-loaded syringe: holding between the hands to warm the insulin, rocking back and forth (do not shake) at least 20 times prior to injection if using a cloudy insulin. 5.4 Inject at a 90 angle into sub-cutaneous tissue using a pinch-up technique into abdomen, outer thigh or buttocks as decided in care plan. 5.5 Rotation within an injection site or between different injection sites. 5.6 Common side effects and what to do if they occur e.g. hypoglycaemia. 5.7 Any special instructions. 5.8 How to obtain further supplies. 5.9 How to store the medication Frequency of visits and contact number for between visits Recognition of error and procedure to To comply with NMC Standards for Medicines Management (2010). Injecting cold insulin can be painful and it is not absorbed so effectively. Clinical Lead/ Registered Nurse Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 14 of 25 Version 1
15 follow Correct disposal of sharps at the point of use. Plan of care documented and agreed with patient and nurse to ensure adequate support, monitoring of diabetes control and wellbeing. 6. Preparation of insulin To demonstrate partnership working. Clinical Lead/Registered Nurse Activity Rationale Responsibility Nurses must not mix different insulins in the same syringe for administration at a later time. (There is no longer a need to mix insulins due to the availability of suitable manufacturer s preparations). To reduce risk of administration errors and mixing of incompatible formulations. All Registered Nurses Pre loaded insulin must be left up to a maximum of seven days. Document the advanced preparation of insulin on the Nursing Record Sheets, ensuring full details are recorded. This should include batch number, type of insulin and expiry date, and required equipment. 6.1 Plan of care. 6.2 Sharps box (obtained from council). 6.3 Insulin syringes 30, 50 or 100 unit syringes (depending on which is most appropriate for the dose), needle length must be no more than 8mm. 6.4 Relevant insulin vial. 6.5 Wipeable, sealable, labelled container/s for storage of pre-filled syringes. 6.6 Alcohol swab. 6.7 Syringe labels. 6.8 Read and check plan of care. Check all previous pre-loaded syringes have been administered and safely disposed of. An adverse event form must be completed to investigate why the syringes had not been used. 6.9 Explain procedure to patient, ensuring consent obtained Prepare clean working surface and wipe with a Clinell wipe Collect equipment required; check insulin for expiry date and against instructions of care plan Wash hands Prepare equipment and re-suspend (by rocking back and forth between the hands) insulin at least 20 times if using a cloudy insulin. Do not shake as you will damage the insulin suspension. If using a clear insulin there is no need to re-suspend. RCN (2015) and Rosindale (2014). To comply with Trust documentation record keeping standards. To ensure adequate preparation of procedure. To reduce risk of administration errors. To reduce risk of crossinfection. To ensure safe administration of insulin. To comply with NMC Standards for Medicines Management (2010). All Registered Nurses All Registered Nurses Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 15 of 25 Version 1
16 6.14 Swab insulin vial with an alcohol wipe and allow to dry Draw up insulin in presence of patient as follows for each syringe using a clean procedure to prevent contamination Remove needle cover and pull back plunger to measure an amount of air equivalent to the amount of insulin prescribed With insulin vial standing upright, insert the needle through the centre of the rubber cap and push down plunger Invert the insulin vial Pull back plunger until slightly more than correct dose is drawn up Expel any air bubbles back into vial Re-check correct prescribed dose has been drawn up and remove needle from vial Carefully re-sheath needle (there is no risk of contaminated needle stick injury as needle is sterile in event of a needle stick injury the syringe must be safely discarded) Label each syringe with patient name, insulin name, date of preparation, initials of RN Label each container with patient name, insulin name, insulin dose, time of administration, number of syringes, date, name and signature of Registered Nurse Dispose of clinical waste and wash hands Complete nursing notes ensuring date, time, insulin type/dose, batch number and number of syringes pre-filled are recorded If any pre-loaded syringes have not been used within the designated period, they must be disposed of. A check must be made to ensure that no doses have been omitted. If any have been omitted the risk assessment must be repeated. 7. Safe storage of pre-drawn insulin To ensure best practice in the preparation of insulin prior to injection. All Registered Nurses Activity Rationale Responsibility 7.1 The syringe should be stored with the needle pointing up at an angle to prevent blockage by suspended substances in the insulin 7.2 Separate containers must be used for insulin to be delivered at different times of day, particularly if the syringe contains a different dosage or type of insulin (RCN, 2015). 7.3 When each new insulin vial is opened, the date and time must be recorded on the Needle blockage by suspended insulin. To promote safe storage of pre-loaded insulin. To ensure best practice in the administration of medicines. To reduce risk of medication errors. To reduce medication All Registered Nurses Patient/Carer Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 16 of 25 Version 1
17 vial and in the patient s notes. 7.4 Any insulin remaining in the vial after 28 days must be discarded. 7.5 Patients should have a vial in use and a backup vial at all times to ensure that vials are used methodically. 7.6 The patient must be advised of the correct storage (as above) and advised to notify the district nurse team ASAP if their fridge stops working or the fridge freezes. error To meet patients individual needs. To promote standardisation of labels used. To promote safe storage of insulin. Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 17 of 25 Version 1
18 Appendix C: Risk Assessment Form Advanced Preparation of Insulin into Syringes for a Patient to Administer at a Later Date To be completed every three months for new patients, or for continuing patients if risk assessment dictates that frequent review is required For stable patients, may be reduced to 6-monthly review thereafter Name of patient NHS number Date of Birth GP Community Nursing Team Type of diabetes How long has the patient been insulin treated? Range of blood glucose readings Last HbA1C result and date Date Risk Assessment completed Date of review for Risk Assessment Full name of nurse completing Risk Assessment form Signature 1. Assessment of patient s suitability for self-administration of insulin a) Have you assessed the mental and physical capability of the patient/carer to self-administer insulin? b) Is the patient at Level 1? = The Registered Nurse is responsible for the safe storage of the insulin and the supervision of the administration process ensuring that the patient understands the insulin product being administered. c) Is the patient at Level 2? = The Registered Nurse is responsible for the storage of the insulin. At administration time the patient will ask the nurse to open the cabinet/locker. The patient will then selfadminister the insulin under the supervision of the nurse. Yes No Potential risk Not known Seek advice Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 18 of 25 Version 1
19 d) Is the patient at Level 3? = The patient accepts full responsibility for the storage and administration of the medicinal products. Note: the patient must be at Level 3 for this assessment to continue further. e) Is the level documented in the patient s records? f) Risk associated with disability sensory and/or physical? g) Risk of self-harm? 2. Consent Yes No Potential risk a) Have you discussed the risks and benefits of self-administration with the patient? b) Do children have access the fridge? c) If yes, have you advised the patient to ensure that the syringes are kept out of the reach of children? d) Is a fridge lock in situ? e) Have you provided information about support available between Community Nurse visits? f) Is the patient happy to receive this service? 3. Ensure most appropriate product has been prescribed Yes No Potential risk Note: this discussion must have taken place before the assessment can continue further. 4. Contra-indications Yes No Potential risk a) Is the patient on insulin glargine (e.g. Lantus ) or an insulin glargine biosimilar? b) Is the fridge in working order? c) Is the fridge visibly clean? d) Is the fridge free from debris? e) Does the patient suffer from an unpredictable mental state or declining cognitive ability? f) Do blood glucose levels show wide variations? g) Is their current insulin in a pre-filled cartridge/pen? If any problems or potential risks are found from points a-g above, then this needs to be reported to the patient s GP or the Out Of Hours doctors (outside normal working hours) and the advanced preparation of insulin in syringes must cease and Not known Not known Not known Seek advice Seek advice Seek advice Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 19 of 25 Version 1
20 arrangements made for the Community Nursing Team to visit at the required intervals. 5. Education of patient Yes No Potential risk Has the patient received the following information before commencing selfadministration: a) The name of the insulin? b) Why they are taking it? c) Dose and frequency? d) How to re-suspend each pre-loaded syringe, holding between their hands to warm the insulin, rocking syringe back and forth at least 20 times prior to injection if using a cloudy insulin? e) How to inject at a 90 angle into subcutaneous tissue using a pinch-up technique into abdomen, outer thigh or buttocks as documented in the care plan? f) How to rotate within an injection site or between different injection sites? g) How to manage hypoglycaemia and what to do if it occurs? h) How to obtain further supplies? i) How to store the insulin? j) Frequency of visits and contact number for between visits? k) Recognition of error and procedure to follow? l) Correct disposal of sharps at the point of use? m) Is the plan of care documented and agreed with patient? n) Nurse to ensure adequate support, monitoring of diabetes and wellbeing. 6. Summary of risks identified Yes No Potential Summarise risks identified, including intuition and patient s awareness and experience of risk factors. 7. Would pre-loading of insulin promote independence and meet patient need? risk Yes No Potential risk Not known Not known Not known Seek advice Seek advice Seek advice 8. Is there a need for any further assessments? Yes No Potential risk Not known Seek advice Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 20 of 25 Version 1
21 Appendix D: Documentation Form for the Advanced Preparation of Insulin in Syringes Date of Preparation Name of Patient NHS Number Date of Birth GP Community Nursing Team Syringes prepared on this date Morning / Before breakfast Lunchtime / Before midday meal Evening / Before evening meal Name of insulin preparation and pre-loaded dose prepared No. prepared (max 7 days) Night Time / e.g. at Bedtime All syringes labelled using pre-printed labels with the following details added: Patient name, insulin name, date of preparation, initials of Registered Nurse Yes / No All containers in fridge labelled using pre-printed labels with the following details added: Patient name, insulin name, insulin dose, time of administration, number of Yes / No syringes, date and signature of Registered Nurse Number of containers in patient s fridge: Separate containers should be used for syringes to be administered at different times of day, particularly if they contain a different dose or type of insulin Syringes stored so that needles are pointing up at a slight angle: Yes / No Prevents needle blockage, especially if using isophane or cloudy insulins Containers are stored in the fridge door, or otherwise kept away from the Yes / No freezer section or the back of the fridge to prevent accidental freezing: Records of insulin vials used on this date: Batch Number of insulin vial(s) Expiry Date of insulin vial(s) Date vial(s) opened (discard 28 days after opening) Do any insulins/supplies need re-ordering? Patients should have a vial in use Yes / No and a backup vial at all times to ensure that vials are used methodically. Other: Instructions for administration: for example, just before or 30 minutes before food at times agreed with the patient? Does the fridge appear to be in good working order? Yes / No Today s visit documented in the nursing notes? Yes / No Registered Nurse to Sign and Print Date and time Date of next planned visit Completed forms should be stored in the patient s notes Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 21 of 25 Version 1
22 Appendix E: Labels for Insulin Syringes and Insulin Syringe Containers Sample Insulin Syringe Label: Name of insulin: Date syringes pre-loaded: Initials of nurse preloading syringe: Patient Name: Sample Insulin Container Label: Name of insulin: Preloaded dose: No. of syringes units Time and instructions of administration: Patient Name: Date syringes preloaded: Route: Initials of nurse preloading syringes: Pre-Prepared Sheets of Labels for Printing: These are available embedded in the electronic version of this policy on the Trust Intranet Sheet of Insulin Syringe Labels Sheet of Labels for Fridge Containers Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 22 of 25 Version 1
23 Appendix F: Letter to be completed and sent to GP after they have agreed to pre-loading of insulin syringes Community Nursing Team & Base Address: GP Surgery Address:.l.. Date.... Dear Dr.. As discussed on (date) following the completion of the accompanying Risk Assessment form, Solent NHS Trust Community Nurses will pre-load insulin syringes for your patient: Name:.. Date of Birth: NHS Number:.. Address: With the following type(s) of insulin: We would like to re-iterate that this practice is unlicensed, and as such the prescriber carriers responsibility for the use of the insulin in this way. We would advise that this information be made available to your colleagues so they are aware of this if they are asked prescribe insulin for pre-loading, for this patient. Insulin syringes are pre-loaded by our Community Nurses according to the Solent NHS Trust Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy, only when a Risk Assessment has been undertaken and this is the only option for the patient to self-administer their insulin independently. The policy is based on guidance issued from the Royal College of Nursing. A copy of the policy is available on request from the Solent NHS Trust Medicines Management Team. If you or any of your colleagues have any questions about this please contact the relevant Community Nursing Team or the Solent NHS Trust Medicines Management Team. Yours sincerely, Community Nurse Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 23 of 25 Version 1
24 Appendix G: Equality Impact Assessment Step 1 Scoping; identify the policies aims Answer 1. What are the main aims and objectives of the document? To ensure insulin syringes are pre-loaded appropriately by registered Community Nurses to allow patients to self-administer their insulin at home appropriately. 2. Who will be affected by it? Patients who require pre-loaded insulin syringes to self-administer insulin at home; Adult Community Nurses. 3. What are the existing performance indicators/measures No adverse events concerning patients selfadministering insulin using syringes pre- for this? What are the outcomes you want to achieve? loaded by Solent Nurses. Existence of this policy means nurses can fulfil this function and take advantage of vicarious liability protection offered by the Trust. 4. What information do you already have on the equality None impact of this document? 5. Are there demographic changes or trends locally to be None considered? 6. What other information do you need? None Step 2 - Assessing the Impact; consider the data and research 1. Could the document unlawfully against any group? 2. Can any group benefit or be excluded? 3. Can any group be denied fair & equal access to or treatment as a result of this document? 4. Can this actively promote good relations with and between different groups? 5. Have you carried out any consultation internally/externally with relevant individual groups? 6. Have you used a variety of different methods of consultation/involvement Mental Capacity Act implications 7. Will this document require a decision to be made by or about a service user? (Refer to the Mental Capacity Act document for further information) Yes No Answer (Evidence) X X X X X X X Patients who cannot administer the pre-loaded syringes due to disabilities None If there is no negative impact end the Impact Assessment here. Step 3 - Recommendations and Action Plans Answer 1. Is the impact low, medium or high? Low 2. What action/modification needs to be taken to minimise None or eliminate the negative impact? 3. Are there likely to be different outcomes with any N/A Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 24 of 25 Version 1
25 modifications? Explain these? Step 4- Implementation, Monitoring and Review 1. What are the implementation and monitoring arrangements, including timescales? 2. Who within the Department/Team will be responsible for monitoring and regular review of the document? Answer These will be reviewed when the policy is reviewed Medicines Management Step 5 - Publishing the Results Answer How will the results of this assessment be published and Trust intranet where? (It is essential that there is documented evidence of why decisions were made). **Retain a copy and also include as an appendix to the document** Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Page 25 of 25 Version 1
Pre-loading of insulin syringes for adult patients to administer at home
 Title: Directorate: Responsible for review: Ratified by: Diabetes - Pre-loading of insulin syringes for adult patients to administer at home Operations Samantha Rosindale, Diabetes Lead Champion Lynda
Title: Directorate: Responsible for review: Ratified by: Diabetes - Pre-loading of insulin syringes for adult patients to administer at home Operations Samantha Rosindale, Diabetes Lead Champion Lynda
ADVANCE PREPARATION OF INSULIN FOR PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ADVANCE PREPARATION OF INSULIN FOR PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME First Issued July 08 Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ADVANCE PREPARATION OF INSULIN FOR PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME First Issued July 08 Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote
Advanced Preparation of Insulin Syringes for Adult Patients to Administer at Home
 Advanced Preparation of Insulin Syringes for Adult Patients to Administer at Home Guidance for nurses Third edition CLINICAL PROFESSIONAL RESOURCE ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS
Advanced Preparation of Insulin Syringes for Adult Patients to Administer at Home Guidance for nurses Third edition CLINICAL PROFESSIONAL RESOURCE ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS
Creating a Smoke Free Workplace Policy
 Creating a Smoke Free Workplace Policy Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet. Please visit the intranet for the latest version. Purpose of
Creating a Smoke Free Workplace Policy Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet. Please visit the intranet for the latest version. Purpose of
ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN Issue History First issued April 2012 Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote the safe administration
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN Issue History First issued April 2012 Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote the safe administration
Assistant Practitioner and Health Care Assistants Administration of Insulin, via Pen device, by Delegation Training and competency Toolkit
 Assistant Practitioner and Health Care Assistants Administration of Insulin, via Pen device, by Delegation Training and competency Toolkit Document Summary The purpose of this policy is to guide and promote
Assistant Practitioner and Health Care Assistants Administration of Insulin, via Pen device, by Delegation Training and competency Toolkit Document Summary The purpose of this policy is to guide and promote
PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING
 PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING First Issued Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote safe and effective blood glucose monitoring using Trust equipment
PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING First Issued Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote safe and effective blood glucose monitoring using Trust equipment
Introduction. Guidelines for patient involvement in the administration of insulin under supervision in hospital (Adult patients)
 Guidelines for patient involvement in the administration of insulin under supervision in hospital (Adult patients) Introduction This guideline is designed to provide a framework for patients to administer
Guidelines for patient involvement in the administration of insulin under supervision in hospital (Adult patients) Introduction This guideline is designed to provide a framework for patients to administer
PATIENT INFORMATION. D iabetes. What You Need to Know About. Insulin
 PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: D iabetes What You Need to Know About Insulin INTRODUCTION The insulin preparations currently available in Singapore are mostly from human origin; pork or bovine
PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: D iabetes What You Need to Know About Insulin INTRODUCTION The insulin preparations currently available in Singapore are mostly from human origin; pork or bovine
Guidelines for managing the health care needs of children and young persons with diabetes in education
 Guidelines for managing the health care needs of children and young persons with diabetes in education Contents Page: Page Number 1.0 Introduction 1 2.0 The Care Management Plan 2 2.1 Blood Glucose monitoring
Guidelines for managing the health care needs of children and young persons with diabetes in education Contents Page: Page Number 1.0 Introduction 1 2.0 The Care Management Plan 2 2.1 Blood Glucose monitoring
Administration of Injectable Medication by Healthcare Assistants (Band 3) Standard Operating Procedure
 Administration of Injectable Medication by Healthcare Assistants (Band 3) Standard Operating Procedure DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 1 Ratified by: Quality Assurance Sub Committee Date ratified: 4 September
Administration of Injectable Medication by Healthcare Assistants (Band 3) Standard Operating Procedure DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 1 Ratified by: Quality Assurance Sub Committee Date ratified: 4 September
Case scenarios: Patient Group Directions
 Putting NICE guidance into practice Case scenarios: Patient Group Directions Implementing the NICE guidance on Patient Group Directions (MPG2) Published: March 2014 [updated March 2017] These case scenarios
Putting NICE guidance into practice Case scenarios: Patient Group Directions Implementing the NICE guidance on Patient Group Directions (MPG2) Published: March 2014 [updated March 2017] These case scenarios
Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy
 Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 4 Ratified by: Corporate Policy Panel Date ratified: 20 July 2017 Name of originator/author: HR Manager Name of responsible
Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 4 Ratified by: Corporate Policy Panel Date ratified: 20 July 2017 Name of originator/author: HR Manager Name of responsible
MS Society Safeguarding Adults Policy and Procedure (Scotland)
 MS Society Safeguarding Adults Policy and Procedure (Scotland) Safeguarding Adults Policy The phrase adult support and protection is used instead of safeguarding in Scotland. However for consistency across
MS Society Safeguarding Adults Policy and Procedure (Scotland) Safeguarding Adults Policy The phrase adult support and protection is used instead of safeguarding in Scotland. However for consistency across
To provide nursing staff with guidelines for the safe and appropriate administration of insulin.
 SUBJECT: ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN This cancels NP 513 dated 3/1/07 1. PURPOSE: COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Medications POLICY NUMBER: 513 Effective Date: June
SUBJECT: ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN This cancels NP 513 dated 3/1/07 1. PURPOSE: COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Medications POLICY NUMBER: 513 Effective Date: June
Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection
 Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 3 Ratified by: Risk Management Sub Group Date ratified: 17 July 2013 Name of originator/author: Health
Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 3 Ratified by: Risk Management Sub Group Date ratified: 17 July 2013 Name of originator/author: Health
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES. Insulin
 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES Insulin This medicine has been proven to be safe and effective, but it can cause serious injury if a mistake happens while taking it. This means
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES Insulin This medicine has been proven to be safe and effective, but it can cause serious injury if a mistake happens while taking it. This means
Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections. No Action Rationale
 Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections Preparation Overview No Action Rationale 1 Collect and check all equipment 2 Check that the packaging of all
Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections Preparation Overview No Action Rationale 1 Collect and check all equipment 2 Check that the packaging of all
SAFE HANDLING OF VACCINES
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE SAFE HANDLING OF VACCINES Issue History Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To ensure vaccines are stored in accordance with manufacturers
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE SAFE HANDLING OF VACCINES Issue History Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To ensure vaccines are stored in accordance with manufacturers
TRANSCRIPT for Lantus SoloSTAR pen injection for your patients
 TRANSCRIPT for Lantus SoloSTAR pen injection for your patients SUPER: Prescription Lantus is a long-acting insulin used to treat adults with type 2 diabetes and adults and pediatric patients (children
TRANSCRIPT for Lantus SoloSTAR pen injection for your patients SUPER: Prescription Lantus is a long-acting insulin used to treat adults with type 2 diabetes and adults and pediatric patients (children
KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY
 KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? Insulin treatment improves the quality of life in many people and saves the lives of others. It is used to lower blood glucose levels.
KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? Insulin treatment improves the quality of life in many people and saves the lives of others. It is used to lower blood glucose levels.
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION PROCEDURE
 PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION PROCEDURE Date approved 2 October 2015 Version 3 Approved by Yvette Oade, Chief Medical Officer Procedure Lead Clinical Governance Lead - Medicines Management Procedure Author Karen
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION PROCEDURE Date approved 2 October 2015 Version 3 Approved by Yvette Oade, Chief Medical Officer Procedure Lead Clinical Governance Lead - Medicines Management Procedure Author Karen
Policy for Supporting. Children and Young People with. Diabetes in Education
 Policy for Supporting Children and Young People with Diabetes in Education December 2011 POLICY FOR SUPPORTING CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE WITH DIABETES IN EDUCATION Contents 1. Introduction 2. Before a
Policy for Supporting Children and Young People with Diabetes in Education December 2011 POLICY FOR SUPPORTING CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE WITH DIABETES IN EDUCATION Contents 1. Introduction 2. Before a
Protocol (Clinical) Country Health SA Local Health Network. Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in Hospital and Aged Care
 Protocol (Clinical) Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in Hospital and Aged Care Protocol developed by: CHSALHN Diabetes Service Protocol Sponsor: CHSALHN, Executive Director, Medical Services
Protocol (Clinical) Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in Hospital and Aged Care Protocol developed by: CHSALHN Diabetes Service Protocol Sponsor: CHSALHN, Executive Director, Medical Services
OWNER MANUAL Diabetes in Cats
 www.mypetonline.co.uk/petdiabetes OWNER MANUAL Diabetes in Cats DIABETES IN CATS What is Diabetes? Glucose (blood sugar) is derived from the food your cat eats and provides the energy body cells need to
www.mypetonline.co.uk/petdiabetes OWNER MANUAL Diabetes in Cats DIABETES IN CATS What is Diabetes? Glucose (blood sugar) is derived from the food your cat eats and provides the energy body cells need to
Document Details Patient Group Direction Hepatitis A vaccine (Havrix Monodose ) Trust Ref No Local Ref (optional) Main points the
 Document Details Title Patient Group Direction Hepatitis A vaccine (Havrix Monodose ) Trust Ref No 1506-41174 Local Ref (optional) Main points the Active immunisation against infection caused by Hepatitis
Document Details Title Patient Group Direction Hepatitis A vaccine (Havrix Monodose ) Trust Ref No 1506-41174 Local Ref (optional) Main points the Active immunisation against infection caused by Hepatitis
Service Level Agreement for the Provision of Level 1 Substance Misuse Services from a Community Pharmacy under contract to NHS Grampian
 Service Level Agreement for the Provision of Level 1 Substance Misuse Services from a Community Pharmacy under contract to NHS Grampian 1. Introduction The provision of Substance Misuse (SM) services through
Service Level Agreement for the Provision of Level 1 Substance Misuse Services from a Community Pharmacy under contract to NHS Grampian 1. Introduction The provision of Substance Misuse (SM) services through
INSULIN MANAGEMENT POLICY
 INSULIN MANAGEMENT POLICY To be read in conjunction with the Hypoglycaemia Management Policy for adult Patients and the Countywide Standard Operating Procedure for Implementing the Insulin Passport/Safety
INSULIN MANAGEMENT POLICY To be read in conjunction with the Hypoglycaemia Management Policy for adult Patients and the Countywide Standard Operating Procedure for Implementing the Insulin Passport/Safety
Policy for the safe administration of Insulin
 Policy for the safe administration of Insulin This is a working document and any changes that become necessary to this policy must be Notified in writing to the Medicine Management Group via the Chief
Policy for the safe administration of Insulin This is a working document and any changes that become necessary to this policy must be Notified in writing to the Medicine Management Group via the Chief
Template Standard Operating Procedure For: Handling of Midazolam and other controlled drugs in Dental Practices
 Name of Dental Practice : Objectives To ensure implementation of the regulations and guidance on safe and secure handling of midazolam and other controlled drugs (CDs) Scope To cover all aspects of obtaining
Name of Dental Practice : Objectives To ensure implementation of the regulations and guidance on safe and secure handling of midazolam and other controlled drugs (CDs) Scope To cover all aspects of obtaining
Trust Policy 218 Ionising Radiation Safety Policy
 Trust Policy 218 Ionising Radiation Safety Policy Purpose Date Version August 2016 7 To ensure that Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust complies with all relevant legislation with regard to the use of ionising
Trust Policy 218 Ionising Radiation Safety Policy Purpose Date Version August 2016 7 To ensure that Plymouth Hospitals NHS Trust complies with all relevant legislation with regard to the use of ionising
Acknowledgement goes to WHO for use of their hand washing technique
 How to administer third party insulin injections safely with a pen device, safety pen needle and syringe 1 Hand washing It takes at least 15 seconds to wash your hands. This is about how long it takes
How to administer third party insulin injections safely with a pen device, safety pen needle and syringe 1 Hand washing It takes at least 15 seconds to wash your hands. This is about how long it takes
Procedure for Subcutaneous Injection of Insulin or GLP1 Analogue in Adults Using a Pen Device V2.0
 Procedure for Subcutaneous Injection of Insulin or GLP1 Analogue in Adults Using a Pen Device V2.0 11 October 2017 Table of Contents 1. Introduction.. 3 2. Purpose of this Policy/Procedure. 3 3. Scope
Procedure for Subcutaneous Injection of Insulin or GLP1 Analogue in Adults Using a Pen Device V2.0 11 October 2017 Table of Contents 1. Introduction.. 3 2. Purpose of this Policy/Procedure. 3 3. Scope
Procedure for the prescribing and administration of insulin
 Procedure for the prescribing and administration of insulin Author: Lilian Baxendale and Heather Beadle Designation: Clinical Governance Pharmacists Version: Version 3 Date: December 2016 Date Approved:
Procedure for the prescribing and administration of insulin Author: Lilian Baxendale and Heather Beadle Designation: Clinical Governance Pharmacists Version: Version 3 Date: December 2016 Date Approved:
PROCEDURE REF NO SABP/EXECUTIVE BOARD/0017
 PROCEDURE REF NO SABP/EXECUTIVE BOARD/0017 NAME OF PROCEDURE: Medicines Procedure: Patient Group Directions for the Administration of Hepatitis B Vaccine for SABP Drug and Alcohol Teams. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE:
PROCEDURE REF NO SABP/EXECUTIVE BOARD/0017 NAME OF PROCEDURE: Medicines Procedure: Patient Group Directions for the Administration of Hepatitis B Vaccine for SABP Drug and Alcohol Teams. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE:
CHEMOTHERAPY NETWORK GROUP POLICY FOR ADMINISTRATION OF CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY
 CHEMOTHERAPY NETWORK GROUP POLICY FOR ADMINISTRATION OF CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY Version 4.0 March 2016 Review date March 2018 Introduction It is the purpose of this policy to provide clear guidelines that
CHEMOTHERAPY NETWORK GROUP POLICY FOR ADMINISTRATION OF CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY Version 4.0 March 2016 Review date March 2018 Introduction It is the purpose of this policy to provide clear guidelines that
All Saints First School Administering of Medicines Policy
 All Saints First School Administering of Medicines Policy Success Indicators The following indicators will demonstrate the level of compliance with this policy and its procedures: a) Employees who are
All Saints First School Administering of Medicines Policy Success Indicators The following indicators will demonstrate the level of compliance with this policy and its procedures: a) Employees who are
Holme Valley Primary School Asthma Policy
 Date adopted: March 2015 Review date: March 2018 Date of next review : March 2021 Holme Valley Primary School Asthma Policy This policy has been written using guidance from the Department of Health (September
Date adopted: March 2015 Review date: March 2018 Date of next review : March 2021 Holme Valley Primary School Asthma Policy This policy has been written using guidance from the Department of Health (September
Brook Green Centre for Learning. Policy and Guidance for Supporting Pupils with Medical Needs
 Brook Green Centre for Learning Policy and Guidance for Supporting Pupils with Medical Needs This document was written in line with recommendations made in the DfE s information pack Supporting Pupils
Brook Green Centre for Learning Policy and Guidance for Supporting Pupils with Medical Needs This document was written in line with recommendations made in the DfE s information pack Supporting Pupils
Policy and Procedure for the Development, Approval and Implementation of Patient Group Directions in NHS Haringey Clinical Commissioning Group
 BEFORE USING THIS POLICY ALWAYS ENSURE YOU ARE USING THE MOST UP TO DATE VERSION Policy and Procedure for the Development, Approval and Implementation of Patient Group Directions in NHS Haringey Clinical
BEFORE USING THIS POLICY ALWAYS ENSURE YOU ARE USING THE MOST UP TO DATE VERSION Policy and Procedure for the Development, Approval and Implementation of Patient Group Directions in NHS Haringey Clinical
Consultation Group: Dr Amalia Mayo, Paediatric Consultant. Review Date: March Uncontrolled when printed. Version 2. Executive Sign-Off
 Policy For The Adjustment Of Insulin Injections By Paediatric Diabetes Specialist Nurses/Community Paediatric Nurses Diabetes Working With Children Within NHS Grampian Co-ordinators: Lead Paediatric Diabetes
Policy For The Adjustment Of Insulin Injections By Paediatric Diabetes Specialist Nurses/Community Paediatric Nurses Diabetes Working With Children Within NHS Grampian Co-ordinators: Lead Paediatric Diabetes
Things you need to know about injections
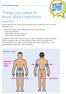 www.trend-uk.org Things you need to know about injections Injection sites: You can see from the picture below the best sites for injecting insulin or GLP-1 medications are: Back of the upper arms (difficult
www.trend-uk.org Things you need to know about injections Injection sites: You can see from the picture below the best sites for injecting insulin or GLP-1 medications are: Back of the upper arms (difficult
Patient Group Directions Policy
 Patient Group Directions Policy Category: Summary: Equality Analysis undertaken: Valid From: Date of Next Review: Approval Date/ Via: Distribution: Related Documents: Author(s): Further Information: This
Patient Group Directions Policy Category: Summary: Equality Analysis undertaken: Valid From: Date of Next Review: Approval Date/ Via: Distribution: Related Documents: Author(s): Further Information: This
Document Details. Patient Group Direction
 Document Details Title Patient Group Direction (PGD) Hepatitis B Vaccine (Engerix ) Trust Ref No 1505-41182 Local Ref (optional) Main points the Immunisation against Hepatitis B document covers Who is
Document Details Title Patient Group Direction (PGD) Hepatitis B Vaccine (Engerix ) Trust Ref No 1505-41182 Local Ref (optional) Main points the Immunisation against Hepatitis B document covers Who is
Guidance on Bulk Prescribing for Care Home Patients
 Guidance on Bulk Prescribing for Care Home Patients Introduction Many patients in care homes taking medicines when required (PRN) can inevitably present problems for the prescriber in determining the quantity
Guidance on Bulk Prescribing for Care Home Patients Introduction Many patients in care homes taking medicines when required (PRN) can inevitably present problems for the prescriber in determining the quantity
CABINET PROCURING A SUBSTANCE MISUSE & COMMUNITY TREATMENT SERVICE IN RUTLAND
 CABINET Report No: 105/2017 PUBLIC REPORT 16 May 2017 PROCURING A SUBSTANCE MISUSE & COMMUNITY TREATMENT SERVICE IN RUTLAND Report of the Director of Public Health Strategic Aim: Safeguarding Key Decision:
CABINET Report No: 105/2017 PUBLIC REPORT 16 May 2017 PROCURING A SUBSTANCE MISUSE & COMMUNITY TREATMENT SERVICE IN RUTLAND Report of the Director of Public Health Strategic Aim: Safeguarding Key Decision:
Medication Safety. Patient Safety. Setting Direction Julie Simmons, Medication Safety Pharmacist January 2016
 Medication Safety Patient Safety Setting Direction Julie Simmons, Medication Safety Pharmacist January 2016 1 The patient journey Admission Ward Transfer Ward stay Discharge Medication storage and supply
Medication Safety Patient Safety Setting Direction Julie Simmons, Medication Safety Pharmacist January 2016 1 The patient journey Admission Ward Transfer Ward stay Discharge Medication storage and supply
28 th September Author Jeremy Gilbert Bariatric Nurse Specialist
 POLICY FOR SELF ADMINISTRATION OF CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE BY COMPETENT PATIENTS COMING IN FOR METABOLIC AND OBESITY SURGERY (BARIATRIC SURGERY) TO PENDENNIS WARD 28 th September 2014 Author
POLICY FOR SELF ADMINISTRATION OF CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE BY COMPETENT PATIENTS COMING IN FOR METABOLIC AND OBESITY SURGERY (BARIATRIC SURGERY) TO PENDENNIS WARD 28 th September 2014 Author
Diabetes Competencies for Community Nurses
 Diabetes Competences for Community Nurses Lothian Health Board: August 2012 Lindsey Aniello, and Jill Little, Diabetes Specialist Nurses Judy Hamilton, District Nurse COMPETENCY DESCRIPTOR 1 Participates,
Diabetes Competences for Community Nurses Lothian Health Board: August 2012 Lindsey Aniello, and Jill Little, Diabetes Specialist Nurses Judy Hamilton, District Nurse COMPETENCY DESCRIPTOR 1 Participates,
Country Health SA Local Health Network. Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in the Community Setting
 Protocol (Clinical) Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in the Community Setting Protocol developed by: CHSALHN Diabetes Service Protocol Sponsor: CHSALHN, Executive Director, Medical Services Approved
Protocol (Clinical) Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in the Community Setting Protocol developed by: CHSALHN Diabetes Service Protocol Sponsor: CHSALHN, Executive Director, Medical Services Approved
EVER Pharma D-mine Pen Pen injector for Apomorphine 10 mg/ml
 EVER Pharma D-mine Pen Pen injector for Apomorphine 10 mg/ml Instructions for Use with Dacepton 3 ml Cartridges Apomorphine hydrochloride hemihydrate solution for injection Subcutaneous Use TABLE OF CONTENTS
EVER Pharma D-mine Pen Pen injector for Apomorphine 10 mg/ml Instructions for Use with Dacepton 3 ml Cartridges Apomorphine hydrochloride hemihydrate solution for injection Subcutaneous Use TABLE OF CONTENTS
BEECHFIELD SCHOOL. Asthma Policy
 BEECHFIELD SCHOOL Asthma Policy Author: James Roach Date: April 2017 Approved by: Governing Body Date: June 2017 To be reviewed by: Governing Body Date: June 2019 Beechfield School recognises that asthma
BEECHFIELD SCHOOL Asthma Policy Author: James Roach Date: April 2017 Approved by: Governing Body Date: June 2017 To be reviewed by: Governing Body Date: June 2019 Beechfield School recognises that asthma
Developed By Name Signature Date
 Patient Group Direction 2155 version 2.0 Administration / Supply of Inhaled Salbutamol in Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Trust Date of Introduction:
Patient Group Direction 2155 version 2.0 Administration / Supply of Inhaled Salbutamol in Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Trust Date of Introduction:
PLEASE READ THIS USER MANUAL BEFORE USE
 USER MANUAL Humalog 200 units/ml KwikPen, solution for injection in a pre-filled pen insulin lispro PLEASE READ THIS USER MANUAL BEFORE USE USE ONLY IN THIS PEN, OR SEVERE OVERDOSE CAN RESULT Read the
USER MANUAL Humalog 200 units/ml KwikPen, solution for injection in a pre-filled pen insulin lispro PLEASE READ THIS USER MANUAL BEFORE USE USE ONLY IN THIS PEN, OR SEVERE OVERDOSE CAN RESULT Read the
Insulin Basic facts. Patient Education Patient Care Services. What is insulin? What types of insulin are there? Basal Insulin
 Patient Education Insulin Basic facts Insulin is a protein made by the pancreas that allows your cells to use glucose for energy. There are different types of insulin: Basal long-acting insulin that controls
Patient Education Insulin Basic facts Insulin is a protein made by the pancreas that allows your cells to use glucose for energy. There are different types of insulin: Basal long-acting insulin that controls
The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust. Pre-filled Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA) syringes
 The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Pre-filled Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA) syringes Version.: 2.2 Effective From: 1 June 2016 Expiry Date: 1 June 2019 Date Ratified: 20 April
The Newcastle upon Tyne Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Pre-filled Patient Controlled Analgesia (PCA) syringes Version.: 2.2 Effective From: 1 June 2016 Expiry Date: 1 June 2019 Date Ratified: 20 April
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION. Oral (live attenuated) Typhoid Vaccine (Ty21a) (Vivotif )
 PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION Administration of: Oral (live attenuated) Typhoid Vaccine (Ty21a) (Vivotif ) By: Practice Nurses In: General Practice It is the responsibility of the professional working under
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION Administration of: Oral (live attenuated) Typhoid Vaccine (Ty21a) (Vivotif ) By: Practice Nurses In: General Practice It is the responsibility of the professional working under
Developed By Name Signature Date
 Patient Group Direction 2156 version 2.0 Administration of Ipratropium 250mcg/ml Nebuliser Solution in Acute Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Date of
Patient Group Direction 2156 version 2.0 Administration of Ipratropium 250mcg/ml Nebuliser Solution in Acute Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Date of
A patient guide to the use of insulin for diabetes
 A patient guide to the use of insulin for diabetes Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
A patient guide to the use of insulin for diabetes Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
THE RESPONSIBLE PHARMACIST REGULATIONS
 THE RESPONSIBLE PHARMACIST REGULATIONS A SUMMARY OF THE RESPONSES TO PUBLIC CONSULTATION ON PROPOSALS FOR THE CONTENT OF THE REGULATIONS DH INFORMATION READER BOX Policy HR / Workforce Management Planning
THE RESPONSIBLE PHARMACIST REGULATIONS A SUMMARY OF THE RESPONSES TO PUBLIC CONSULTATION ON PROPOSALS FOR THE CONTENT OF THE REGULATIONS DH INFORMATION READER BOX Policy HR / Workforce Management Planning
Care Homes - Homely Remedies Protocol
 Care Homes - Homely Remedies Protocol A homely remedy is a medicine for the short-term treatment of a minor ailment, such as indigestion, a cough, mild to moderate pain or constipation, and can be obtained
Care Homes - Homely Remedies Protocol A homely remedy is a medicine for the short-term treatment of a minor ailment, such as indigestion, a cough, mild to moderate pain or constipation, and can be obtained
SELF-INJECTION GUIDE
 SELF-INJECTION GUIDE (asfotase alfa) 40 mg/ml solution for injection 18 mg/0.45 ml 28 mg/0.7 ml 40 mg/1 ml 100 mg/ml solution for injection 80 mg/0.8 ml asfotase alfa Introduction Contents This Self-Injection
SELF-INJECTION GUIDE (asfotase alfa) 40 mg/ml solution for injection 18 mg/0.45 ml 28 mg/0.7 ml 40 mg/1 ml 100 mg/ml solution for injection 80 mg/0.8 ml asfotase alfa Introduction Contents This Self-Injection
GG&C PGD ref no: 2016/1408 YOU MUST BE AUTHORISED BY NAME, UNDER THE CURRENT VERSION OF THIS PGD BEFORE YOU ATTEMPT TO WORK ACCORDING TO IT
 GG&C PGD ref no: 2016/1408 YOU MUST BE AUTHORISED BY NAME, UNDER THE CURRENT VERSION OF THIS PGD BEFORE YOU ATTEMPT TO WORK ACCORDING TO IT Clinical Condition Indication: Active immunisation against disease
GG&C PGD ref no: 2016/1408 YOU MUST BE AUTHORISED BY NAME, UNDER THE CURRENT VERSION OF THIS PGD BEFORE YOU ATTEMPT TO WORK ACCORDING TO IT Clinical Condition Indication: Active immunisation against disease
Safeguarding Children and Young People Policy
 Safeguarding Children and Young People Policy Policy Summary This policy outlines our commitment to keeping the children and young people who engage with the Red Cross safe. It outlines the expectations
Safeguarding Children and Young People Policy Policy Summary This policy outlines our commitment to keeping the children and young people who engage with the Red Cross safe. It outlines the expectations
Lilly. Disposable Insulin Delivery Device User Manual
 1 PV 3734 AMP Lilly Disposable Insulin Delivery Device User Manual Instructions for Use Read and follow all of these instructions carefully. If you do not follow these instructions completely, you may
1 PV 3734 AMP Lilly Disposable Insulin Delivery Device User Manual Instructions for Use Read and follow all of these instructions carefully. If you do not follow these instructions completely, you may
AUDIT TOOL FOR SELF INSPECTION OF COMPLIANCE WITH QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM FOR PATIENT GROUP DIRECTIONS
 AUDIT TOOL FOR DISPENSING SERVICES COMPILED BY: Lynn Morrison ISSUE 1 CHECKED BY: Colette Byrne NUMBER: ISSUE DATE: 01.12.07 SUPERSEDES: NEW REVIEW DATE: 01.12.09 AUDIT TOOL FOR SELF INSPECTION OF COMPLIANCE
AUDIT TOOL FOR DISPENSING SERVICES COMPILED BY: Lynn Morrison ISSUE 1 CHECKED BY: Colette Byrne NUMBER: ISSUE DATE: 01.12.07 SUPERSEDES: NEW REVIEW DATE: 01.12.09 AUDIT TOOL FOR SELF INSPECTION OF COMPLIANCE
INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY AND PROCEDURES Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust (The Trust)
 A member of: Association of UK University Hospitals INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY AND PROCEDURES Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust (The Trust) IPC17 SINGLE USE AND SINGLE PATIENT USE MEDICAL
A member of: Association of UK University Hospitals INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY AND PROCEDURES Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust (The Trust) IPC17 SINGLE USE AND SINGLE PATIENT USE MEDICAL
making a referral for breast imaging Standard Operating Procedure
 Document Control Title Reporting Radiographer Author Directorate Surgery Date Version Issued 0.1 May 2016 Status Draft Author s job title Reporting Radiographer Department Breast Imaging Comment / Changes
Document Control Title Reporting Radiographer Author Directorate Surgery Date Version Issued 0.1 May 2016 Status Draft Author s job title Reporting Radiographer Department Breast Imaging Comment / Changes
HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen
 1 Instructions for Use HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen (70% human insulin isophane suspension 30% human insulin injection [rdna origin]) 100 units/ml, 3 ml pen Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking
1 Instructions for Use HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen (70% human insulin isophane suspension 30% human insulin injection [rdna origin]) 100 units/ml, 3 ml pen Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking
Patient/Carer instructions for the administration of Subcutaneous Cytarabine
 Patient/Carer instructions for the administration of Subcutaneous Cytarabine This document covers the following information: What cytarabine is What subcutaneous means What happens if you decide to inject
Patient/Carer instructions for the administration of Subcutaneous Cytarabine This document covers the following information: What cytarabine is What subcutaneous means What happens if you decide to inject
INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARING AND GIVING AN INJECTION OF ENBREL POWDER
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARING AND GIVING AN INJECTION OF ENBREL POWDER Introduction The following instructions explain how to prepare and inject Enbrel powder for injection. Please read the instructions carefully
INSTRUCTIONS FOR PREPARING AND GIVING AN INJECTION OF ENBREL POWDER Introduction The following instructions explain how to prepare and inject Enbrel powder for injection. Please read the instructions carefully
A patient guide to administration of subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement therapy - using manual push technique
 A patient guide to administration of subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement therapy - using manual push technique This piece of patient information is a step by step guide to administering your immunoglobulin
A patient guide to administration of subcutaneous immunoglobulin replacement therapy - using manual push technique This piece of patient information is a step by step guide to administering your immunoglobulin
The Accessible Information Standard - guidance for practices
 The Accessible Information Standard - guidance for practices The Accessible Information Standard guidance for practices The Accessible Information Standard (AIS) known officially as SCCI1605 Accessible
The Accessible Information Standard - guidance for practices The Accessible Information Standard guidance for practices The Accessible Information Standard (AIS) known officially as SCCI1605 Accessible
Patient Group Directions (PGDs)
 Patient Group Directions (PGDs) Document level: Trustwide (TW) Code: MP2 Issue number: 4 Lead executive Authors details Type of document Target audience Document purpose Medical Director Senior Clinical
Patient Group Directions (PGDs) Document level: Trustwide (TW) Code: MP2 Issue number: 4 Lead executive Authors details Type of document Target audience Document purpose Medical Director Senior Clinical
Draft Guidance for Pharmacists on Extemporaneous Dispensing. Version 1
 1. Introduction Draft Guidance for Pharmacists on Extemporaneous Dispensing Version 1 The purpose of this guidance is to assist pharmacists in discharging their legal and professional obligations to patients
1. Introduction Draft Guidance for Pharmacists on Extemporaneous Dispensing Version 1 The purpose of this guidance is to assist pharmacists in discharging their legal and professional obligations to patients
Safe Use of Latex Policy
 Safe Use of Latex Policy Lead Manager: Andy Crawford- Head of Clinical Governance Responsible Director: Jointly by: Director of Human Resources Medical Director Approved by: Jointly by: Health & Safety
Safe Use of Latex Policy Lead Manager: Andy Crawford- Head of Clinical Governance Responsible Director: Jointly by: Director of Human Resources Medical Director Approved by: Jointly by: Health & Safety
Procedure/ Care Plan for Domiciliary Care Workers/ Support Workers Instillation of Ear Drops (Adult)
 Procedure/ Care Plan for Domiciliary Care Workers/ Support Workers Instillation of Ear Drops (Adult) CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Medicines Management Specific Title: Procedure: Instillation of ear drops
Procedure/ Care Plan for Domiciliary Care Workers/ Support Workers Instillation of Ear Drops (Adult) CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Medicines Management Specific Title: Procedure: Instillation of ear drops
Patient Education Pharmacy Services
 Patient Education This handout details the types of insulin. It also covers how to store, mix and inject insulin. What is insulin? Insulin is made by the pancreas and acts as a key to move glucose (sugar)
Patient Education This handout details the types of insulin. It also covers how to store, mix and inject insulin. What is insulin? Insulin is made by the pancreas and acts as a key to move glucose (sugar)
Administration of Medication
 Administration of Medication Prescribed medications must arrive in a container with the original, unaltered prescription label attached. The label must display all legal information required for a pharmacist
Administration of Medication Prescribed medications must arrive in a container with the original, unaltered prescription label attached. The label must display all legal information required for a pharmacist
Instructions for Use HEMLIBRA (hem-lee-bruh) (emicizumab-kxwh) injection, for subcutaneous use
 Instructions for Use HEMLIBRA (hem-lee-bruh) (emicizumab-kxwh) injection, for subcutaneous use Be sure that you read, understand, and follow the Instructions for Use before injecting HEMLIBRA. Your healthcare
Instructions for Use HEMLIBRA (hem-lee-bruh) (emicizumab-kxwh) injection, for subcutaneous use Be sure that you read, understand, and follow the Instructions for Use before injecting HEMLIBRA. Your healthcare
School Hearing Screening Policy
 School Hearing Screening Policy V2.1 1st August 2017 Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Purpose of this Policy... 3 3. Scope... 3 4. Definitions / Glossary... 3 5. Ownership and Responsibilities...
School Hearing Screening Policy V2.1 1st August 2017 Page 1 of 13 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 2. Purpose of this Policy... 3 3. Scope... 3 4. Definitions / Glossary... 3 5. Ownership and Responsibilities...
Adminstration of Insulin to Patients at Home and in Community Hospitals
 1929 Version 2 The Administration of Insulin to patients at home and in Community Hospitals Date: 26 January 2017 Adminstration of Insulin to Patients at Home and in Community Hospitals Page 1 of 7 Partners
1929 Version 2 The Administration of Insulin to patients at home and in Community Hospitals Date: 26 January 2017 Adminstration of Insulin to Patients at Home and in Community Hospitals Page 1 of 7 Partners
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTIONS POLICY
 PATIENT GROUP DIRECTIONS POLICY To be read in conjunction with the Medicines Policy and the Controlled Drugs Policy Version: 5 Ratified by: Senior Managers Operations Group Date ratified: August 2015 October
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTIONS POLICY To be read in conjunction with the Medicines Policy and the Controlled Drugs Policy Version: 5 Ratified by: Senior Managers Operations Group Date ratified: August 2015 October
USER GUIDE. Melanotan must not be used if you are:
 USER GUIDE This document is for guidance purposes only and in no way replaces any official statements or other legal guidance documentation. This document does not claim to be correct or complete, no one
USER GUIDE This document is for guidance purposes only and in no way replaces any official statements or other legal guidance documentation. This document does not claim to be correct or complete, no one
Medicines Optimisation Team Standard Operating Procedure Insulin Quantities Audit
 Medicines Optimisation Team Standard Operating Procedure Insulin Quantities Audit Aim Review and rationalise the insulin quantities based on dosage instructions for diabetic patients in order to align
Medicines Optimisation Team Standard Operating Procedure Insulin Quantities Audit Aim Review and rationalise the insulin quantities based on dosage instructions for diabetic patients in order to align
USE OF UNLICENSED MEDICINES AND OFF-LABEL MEDICINES WHERE A LICENSED MEDICINE IS AVAILABLE
 NHS Scotland Directors of Pharmacy and Scottish Association of Medical Directors USE OF UNLICENSED MEDICINES AND OFF-LABEL MEDICINES WHERE A LICENSED MEDICINE IS AVAILABLE CONSENSUS STATEMENT This consensus
NHS Scotland Directors of Pharmacy and Scottish Association of Medical Directors USE OF UNLICENSED MEDICINES AND OFF-LABEL MEDICINES WHERE A LICENSED MEDICINE IS AVAILABLE CONSENSUS STATEMENT This consensus
Care homes - Homely remedies
 Bulletin 72 August 2014 Community Interest Company Care homes - Homely remedies Care home staff have a recognised duty of care to be able to respond to minor symptoms experienced by residents. A homely
Bulletin 72 August 2014 Community Interest Company Care homes - Homely remedies Care home staff have a recognised duty of care to be able to respond to minor symptoms experienced by residents. A homely
The Administration of Insulin to patients at home and in Community Hospitals
 The Administration of Insulin to patients at home and in Community Hospitals Partners in Care Document Ratification This is a controlled document and should not be altered in any way without the express
The Administration of Insulin to patients at home and in Community Hospitals Partners in Care Document Ratification This is a controlled document and should not be altered in any way without the express
Pharmacy Needle and Syringe Programme. Enhanced Contract
 Pharmacy Needle and Syringe Programme Enhanced Contract 1 st April 2012 31 st March 2013 Signed on behalf of LPC Signed on behalf of CRI Signed on behalf of Turning Point Signed on behalf of KCA Signed
Pharmacy Needle and Syringe Programme Enhanced Contract 1 st April 2012 31 st March 2013 Signed on behalf of LPC Signed on behalf of CRI Signed on behalf of Turning Point Signed on behalf of KCA Signed
INFORMATION FOR THE CONSUMER
 INFORMATION FOR THE CONSUMER This insert provides a summary of the information about CETROTIDE (cetrorelix for injection). If you have any questions or concerns, or want more information about CETROTIDE,
INFORMATION FOR THE CONSUMER This insert provides a summary of the information about CETROTIDE (cetrorelix for injection). If you have any questions or concerns, or want more information about CETROTIDE,
Instructions for Use. BASAGLAR KwikPen. insulin glargine injection (100 units/ml, 3 ml pen)
 Instructions for Use BASAGLAR KwikPen insulin glargine injection (100 units/ml, 3 ml pen) 1 Read the Instructions for Use before you start using BASAGLAR and each time you get another BASAGLAR KwikPen.
Instructions for Use BASAGLAR KwikPen insulin glargine injection (100 units/ml, 3 ml pen) 1 Read the Instructions for Use before you start using BASAGLAR and each time you get another BASAGLAR KwikPen.
SINGLE USE MEDICAL DEVICES POLICY
 SINGLE USE MEDICAL DEVICES POLICY First Issued by/date BWW /BKW March 2001 Issue Version Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date 2 Update May 2011 Named Responsible Officer:- Approved
SINGLE USE MEDICAL DEVICES POLICY First Issued by/date BWW /BKW March 2001 Issue Version Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date 2 Update May 2011 Named Responsible Officer:- Approved
PHARMACY SERVICE ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE SUPPLY OF PALLIATIVE CARE SYRINGES AND MEDICINES FOR COMMUNITY PATIENTS
 PHARMACY SERVICE ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE SUPPLY OF PALLIATIVE CARE SYRINGES AND MEDICINES FOR COMMUNITY PATIENTS The benefits of prefilled syringes for palliative care from the hospital pharmacy service In
PHARMACY SERVICE ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE SUPPLY OF PALLIATIVE CARE SYRINGES AND MEDICINES FOR COMMUNITY PATIENTS The benefits of prefilled syringes for palliative care from the hospital pharmacy service In
Guidance for Pharmacists on Safe Supply of Oral Methotrexate
 Guidance for Pharmacists on Safe Supply of Oral Methotrexate Pharmaceutical Society of Ireland Version 2 January 2015 Contents 1. Introduction 2 2. Methotrexate 2 3. Guidance 2 3.1 Patient Review 2 3.2
Guidance for Pharmacists on Safe Supply of Oral Methotrexate Pharmaceutical Society of Ireland Version 2 January 2015 Contents 1. Introduction 2 2. Methotrexate 2 3. Guidance 2 3.1 Patient Review 2 3.2
This document expires on Patient Group Direction No. VI 5
 Patient Group Direction (PGD) for The Administration of Combined Adsorbed Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, (Acellular Component) and Inactivated Poliomyelitis Vaccine (Infanrix-IPV ) to children aged between
Patient Group Direction (PGD) for The Administration of Combined Adsorbed Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, (Acellular Component) and Inactivated Poliomyelitis Vaccine (Infanrix-IPV ) to children aged between
GG&C PGD ref no: 2017/1427 YOU MUST BE AUTHORISED BY NAME, UNDER THE CURRENT VERSION OF THIS PGD BEFORE YOU ATTEMPT TO WORK ACCORDING TO IT
 GG&C PGD ref no: 2017/1427 YOU MUST BE AUTHORISED BY NAME, UNDER THE CURRENT VERSION OF THIS PGD BEFORE YOU ATTEMPT TO WORK ACCORDING TO IT Clinical Condition Indication: Active immunisation against rotavirus.
GG&C PGD ref no: 2017/1427 YOU MUST BE AUTHORISED BY NAME, UNDER THE CURRENT VERSION OF THIS PGD BEFORE YOU ATTEMPT TO WORK ACCORDING TO IT Clinical Condition Indication: Active immunisation against rotavirus.
Community Psychiatric Nurse. Consultant Psychiatrist, Substance Misuse Services
 PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION (PGD) FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF HEPATITIS A VACCINE (HAVRIX MONODOSE VACCINE) BY REGISTERED NURSES WORKING IN THE COMMUNITY SUBSTANCE MISUSE TEAMS Version Number : 2 Patient Group
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION (PGD) FOR THE ADMINISTRATION OF HEPATITIS A VACCINE (HAVRIX MONODOSE VACCINE) BY REGISTERED NURSES WORKING IN THE COMMUNITY SUBSTANCE MISUSE TEAMS Version Number : 2 Patient Group
Supporting Students with Medical Conditions
 1. Introduction Most students will at some time have a medical condition that may affect their participation in school activities. For many this will be short term. Other students have medical conditions
1. Introduction Most students will at some time have a medical condition that may affect their participation in school activities. For many this will be short term. Other students have medical conditions
Trust Protocol for the Administration of Intravenous Methylprednisolone for Thyroid Eye Disease A Protocol. The Clinical Investigation Unit (CIU)
 A Protocol For Use in: By: For: Division responsible for document: Key words: Name of document author: Job title of document author: Name and job title of document author s Line Manager: Supported by:
A Protocol For Use in: By: For: Division responsible for document: Key words: Name of document author: Job title of document author: Name and job title of document author s Line Manager: Supported by:
A three month project September December 2016
 Improving Insulin Safety in the Clinical Decision Unit A three month project September December 2016 Sarah Gregory - In-Patient DSN, QEQM Hospital Julie Gammon - Ward Manager, CDU, QEQM Hospital 1 The
Improving Insulin Safety in the Clinical Decision Unit A three month project September December 2016 Sarah Gregory - In-Patient DSN, QEQM Hospital Julie Gammon - Ward Manager, CDU, QEQM Hospital 1 The
