Advanced Preparation of Insulin Syringes for Adult Patients to Administer at Home
|
|
|
- Agatha Gwendoline Golden
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advanced Preparation of Insulin Syringes for Adult Patients to Administer at Home Guidance for nurses Third edition CLINICAL PROFESSIONAL RESOURCE
2 ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME Acknowledgements The RCN would like to thank everyone who contributed to the review and development of this third edition. Samantha Kelly (nee Rosindale), lead author, Merton Diabetes Service Lead, Central London Community Healthcare NHS Trust. Jo Reed, reviewer, Renal Diabetes Specialist Nurse, Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust Samantha and Jo are both committee members of the RCN Diabetes Forum. This publication is due for review in December To provide feedback on its contents or on your experience of using the publication, please Publication This is an RCN clinical professional resource. Publication date: December 2018 Review date: December The Nine Quality Standards This publication has met the nine quality standards of the quality framework for RCN professional publications. For more information, or to request further details on how the nine quality standards have been met in relation to this particular professional publication, please contact publications. Evaluation The authors would value any feedback you have about this publication. Please contact clearly stating which publication you are commenting on. RCN Legal Disclaimer This publication contains information, advice and guidance to help members of the RCN. It is intended for use within the UK but readers are advised that practices may vary in each country and outside the UK. The information in this booklet has been compiled from professional sources, but its accuracy is not guaranteed. Whilst every effort has been made to ensure the RCN provides accurate and expert information and guidance, it is impossible to predict all the circumstances in which it may be used. Accordingly, the RCN shall not be liable to any person or entity with respect to any loss or damage caused or alleged to be caused directly or indirectly by what is contained in or left out of this website information and guidance. Published by the Royal College of Nursing, 20 Cavendish Square, London, W1G 0RN 2018 Royal College of Nursing. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without prior permission of the Publishers. This publication may not be lent, resold, hired out or otherwise disposed of by ways of trade in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published, without the prior consent of the Publishers. 2
3 ROYAL COLLEGE OF NURSING Contents About the RCN Diabetes Nursing Forum 4 Preface 5 Part 1: Guidelines 6 Part 2: Example policy for the pre-loading of insulin syringes for patients to administer at home 11 Appendix: Consensus statement and methodology 29 References 30 3
4 ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME About the RCN Diabetes Nursing Forum The Royal College of Nursing Diabetes Nursing Forum is one of more than 30 RCN forums that support a range of nursing specialities. The forum offers RCN members the opportunity to network, increase knowledge, share expertise and keep up to date with the latest developments in diabetes nursing. The RCN Diabetes Nursing Forum also maintains the RCN online resource that signposts key sources of information and resources for diabetes care across the four UK countries. This can be found at: diabetes It is designed for people with diabetes and their families or carers, those new to diabetes care, as well as more experienced practitioners looking for information on a particular aspect of diabetes and its management. These resources include national standards and guidelines, evidence digests and guidance, and information on initiatives about specific aspects of diabetes care for specific contexts of care and populations. The resource supplements the Diabetes essentials learning area, published by the RCN Learning Zone in December This provides an overview of the key concepts of diabetes, diagnosis and current treatments, and roles and responsibilities in regard to treating patients with diabetes and is available at: uk/clinical-topics/diabetes/professionalresources RCN members can join the RCN Diabetes Nursing Forum online at or by calling RCN Direct on
5 ROYAL COLLEGE OF NURSING Preface The RCN views the practice of pre-loading insulin as necessary for the small minority of patients unable to use insulin pen devices, and should only be considered after all other options have been exhausted. There are potential legal and safety complexities associated with the practice of pre-loading insulin syringes in order to enable people to selfadminister in their own homes that health care practitioners must be aware of. Firstly, the preparation of pre-loaded syringes represents a form of secondary dispensing which, under the terms of the Medicines Act (1968), is classified as an unlicensed activity in all four UK countries. Consequently, health care organisations and practitioners must take full responsibility for the safety of this activity. Vicarious liability Employers are legally responsible for the actions you carry out in the course of your work. This is known as vicarious liability, and your employer will have insurance for this purpose. However, to remain covered by an employer s vicarious liability clause, an employee must only work within an area of assessed competence and within the responsibilities of their role and job description. A comprehensive review of the issues relating to the preparation of pre-loaded syringes and vicarious liability are provided in the summary of professional issues section of this publication on page 7. Secondly, the safety of individuals using preloaded insulin syringes, as well as the storage, stability and sterility of insulin once drawn up in the syringe, is of paramount importance (Rosindale, 2014). For this reason the RCN recommends that nurses should operate within the framework of a local pre-loaded insulin syringe clinical policy which details the responsibilities of every individual involved in the practice (employing organisation/ patient/gp/community nurse) and standardises how nurses perform the preparation of syringes (essential to assure vicarious liability protection for nurses undertaking this practice). Health care organisations and practitioners are also directed to review the Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) Standards for Medicines Management (NMC, 2018). An overview of the local framework requirement is outlined in Rosindale (2014) and an example insulin syringe clinical policy document can be found in the appendix on page 29 of this publication. The policy, which should be regularly updated by a local diabetes lead nurse and the medicines management team, should contain a clearly defined standard operating procedure to guide and support local health care practitioners. 5
6 ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME Part 1: Guidelines Introduction This guidance has been updated and replaces previous guidance in 2006 and Developed for nursing practitioners working in a variety of settings, this publication highlights the professional, organisational and safety issues that must be addressed when pre-loading insulin syringes for later use by a person with diabetes. Professional consensus statements Prior to updating these guidelines, the RCN working group undertook an exercise to evaluate the views of senior diabetes nurse specialists and draw on their professional expertise in the development of these recommendations. The findings of the consensus statement exercise revealed a significant variation of understanding in relation to the professional risks and legal issues surrounding the practice of pre-loading insulin syringes: just 20 per cent of respondents knew the practice of pre-filling an insulin syringe was outside the Medicines Act, and only 20 per cent were aware that pre-loading insulin syringes is not considered to be best practice. The consensus participants were, however, clearly in agreement on the imperatives relating to patient safety. They agreed strongly that: only registered nurses should be involved in pre-loading insulin syringes patients must have capacity for this practice to be considered full patient training and education must be provided nursing staff cannot undertake this practice if there is no organisational policy in place. The consensus statement exercise provided the group with an invaluable snapshot of the state of knowledge on this topic, highlighting why the re-issue of this updated guidance is both timely and necessary. The responses revealed how the practice of pre-filling insulin syringes has become so embedded in every day practice that it is often considered normal by many health care organisations and their employees. It is hoped that these guidelines will prompt a reevaluation and discussion of the issues involved while ensuring that appropriate steps are taken to protect all concerned: patients, nursing staff, and employers. Full details of the consensus statement submitted to the independent panel of experts can be found in the appendix on page 29. Context: a growing issue In recent years the arrival of innovative insulin delivery devices means more people with diabetes have been able to find an insulin pen that suits their needs, reducing the number of people requiring pre-loaded insulin syringes. However, there remains a small number of people who will not or cannot use an insulin pen for a variety of reasons: poor manual dexterity; visual impairment; an inability to find a pen device that suits their needs; or a reluctance to make the change from the standard insulin injection syringe they are familiar with (Rosindale, 2014). As a result, these patients will be unable to autonomously inject once or twice a day and, consequently, will require nursing support to pre-load the insulin syringes they use in order to maintain their independence. The RCN is aware that the potential number of people requiring such support in the community is likely to increase for two reasons: the number of people with Type 2 diabetes that require insulin treatment is growing: over the past two decades the number of people with diabetes in the UK has more than doubled, from 1.4 million in 1996 to 4.5 million in 2016 (Diabetes UK, 2016) Diabetes UK estimates that by 2025, 5.2 million people will have diabetes: most of these cases will be Type 2 diabetes because of the ageing population and the rapidly rising number of overweight people (Diabetes UK, 2016). The preparation of insulin injections by community nurses for patients to administer 6
7 ROYAL COLLEGE OF NURSING in their own homes at a later time has been the practice for many years. Preserving an individual s convenience and independence, the practice reduces the risk of hypoglycaemia and, by enabling people to administer their insulin at the correct time in relation to meal times, releases nursing time and resources. Anecdotally, the practice of pre-loading insulin syringes for people with diabetes to administer themselves has taken place satisfactorily for decades. However, there are no national guidelines currently in place to support this practice (Rosindale, 2014). The RCN believes the practice of pre-loading insulin syringes should only be considered when all other options to enable patients to self-manage have been exhausted such as the introduction and use of an insulin pen device. This guidance outlines the key considerations and essential elements that should be in place when the only alternative is to undertake the advanced preparation of insulin syringes for adult patients to administer at home. Issues relating to prescribing and medicines management are a leading cause of cases being referred to the NMC for consideration of fitness to practise proceedings against nurses and midwives. Following these guidelines should ensure that nurses avoid finding themselves in a position where they are referred to the NMC for inadvertent or deliberate breaches of medicines management standards. These guidelines therefore provide an essential tool for nurses who work in the treatment of adult diabetics. Summary of professional issues The act of pre-loading an insulin syringe is considered a form of secondary dispensing which is not covered by the terms of the Medicines Act (1968). In essence, the act of pre-loading an insulin syringe creates an unlicensed product. This is an important legal consideration that needs to be taken into account by health care professionals and employers. If something were to go wrong, it is the nurse who prepares a preloaded insulin syringe outside the bounds of the Medicines Act that would be liable (Rosindale, 2014). A second key consideration relates to the lapse of time between preparation of the syringe and its administration by an individual with diabetes. The Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC, 2010) advises registrants must not prepare substances in advance of their immediate use and that the dispensing of drugs should include: checking the validity of the prescription the appropriateness of the medicine for an individual patient the assembly of the product and labelling in accordance with legal requirements the provision of information leaflets for patients. These points have significant implications for community nurses. While the pre-loading of insulin syringes is considered to be common practice, ultimately, it is the nurse who is professionally accountable for this action. For this reason the RCN recommends that, for their own legal protection, nurses must operate within the requirements of a local policy/protocol for the pre-loading of insulin syringes for patients to administer at home. Therefore, a local policy must be in place to ensure that nurses benefit from vicarious liability, in which the employer takes full responsibility for the safety of this activity. The pre-loading of insulin syringes should only be undertaken by registered nurses; this activity cannot be devolved to health care assistants. Protecting the safety of an individual with diabetes is of paramount importance. In 2010, the National Patient Safety Agency (NPSA) issued two rapid response reports (NPSA, 2010a; NPSA 2010b) highlighting the potential errors that can occur in relation to insulin administration: omitted doses, delayed doses and inappropriate use of non-insulin syringes. However, no harm to patients was reported between 2005 and 2013 as a result of using this method (Rosindale, 2014). TREND-UK and Welsh Assembly for Nursing in Diabetes have released a diabetes nurse competency assessment tool (WAND) for diabetes specialist nurses, especially those new in post to support insulin administration (TREND-UK, 2018). 7
8 ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME Before preparing to pre-load insulin syringes for adults with diabetes to administer at home, the RCN therefore recommends the following. Ensuring that there is an organisation-wide policy in place covering the use of pre-loaded insulin syringes; this is essential for your protection and the protection of patients (see Appendix 1 for an example policy document). Patients must be assessed and have full capacity for this practice to be considered and patient capacity must be routinely and frequently re-assessed (as per local policy). A senior diabetes specialist nurse (SDSN) must be involved in the initial patient assessment; this risk assessment should be updated on a regular basis (as per local policy). Comprehensive training on pre-drawn insulin for self-administration must have been undertaken. A patient care plan must be in place. A quality assurance plan must be in place (as per local policy) which is overseen by your local SDSN. The patient s GP is aware, understands and is in agreement that prescribing pre-loaded insulin syringes has associated medical-legal issues, and that there is a policy in place to support this process. Patient requirements A number of essential elements need to be checked when assessing an individual with diabetes who requires pre-loaded insulin syringes. At a minimum the patient must: have Level 3 mental capacity, as defined by the Mental Capacity Act (2005) accept full responsibility for the storage and administration of the insulin-filled syringes be assessed to confirm they cannot use any other first-line licensed alternative (such as an insulin pen device) receive full training and education in their specific medication (dose, frequency of injections, time/action profile), resuspending the pre-loaded syringe, injection technique and rotation of relevant injection sites be able to describe the signs, symptoms and treatment of a hypoglycaemic event know who to contact should they encounter any problems between visits. Registered nurse requirements To benefit from vicarious liability protection, the registered nurse must adhere to the requirements of their local policy for the pre-loading of insulin syringes. At a minimum, the nurse must: always involve the senior diabetes specialist nurse (SDSN) in each patient case undertake an initial, and regularly update, a patient risk assessment (as per local policy) never delegate the pre-loading of insulin syringes to a health care assistant ensure syringes and storage boxes are clearly labelled with content (drug name, dose), time and date of preparation, and patient s name (as per local policy) ensure the patient is educated on their medication, what they are taking and why they are injecting insulin ensure patients understand that pre-loaded syringes are their responsibility and are not the responsibility of their carer ensure the patient is trained in the correct injection technique (and is still capable of self-injecting), the rotation of sites, the safe storage of insulation and the disposal of sharps ensure the patient has a contact number for any problems between visits. 8
9 ROYAL COLLEGE OF NURSING Storage conditions for pre-loaded insulin In relation to the storage, stability and sterility of pre-loaded insulin syringes in the home, studies have shown these can remain stable and sterile at refrigerator temperatures for up to 28 days (Rosindale, 2014). However, the RCN (2015) and Rosindale (2014) advise that the maximum number of days that insulin syringes can be left pre-loaded is seven days. Pre-loaded insulin syringes should be stored in the main part of the refrigerator at between 2ºC and 8ºC, and should not be placed in the freezer or at the back of the refrigerator. The needle should point upwards in mixtures containing isophane insulin to prevent blockage by suspended substances in the insulin (Rosindale, 2014). Lantus (Glargine) or Abasglar (biosimilar Glargine) are unsuitable for use in pre-loaded syringes as it will become turbid (cloudy). Tresiba and Toujeo are also not suitable and should not be drawn from the cartridge or the pre-filled pen into a syringe as it is available in different doses and can overdose the patient. Syringes should be stored in a sealable container, and both syringes and container should be clearly labelled. If the patient is required to administer insulin more than once per day (for example, prior to eating breakfast, and again, before the evening meal) there should be a separate container for each administration time even if the doses that are utilised are the same. Syringe label The syringe label should contain the following information: date and time of preparation patient s name name of insulin the dose (in number of units) the time the insulin injection should be administered initials of the registered nurse who prepared the syringe. Sealable container label The sealable container label should contain the following information: date and time of preparation patient s name and address the name of the insulin preparation the dose (in number of units) administration instructions; for example, just before or 30 minutes before food, at times agreed with the patient and documented in the nursing notes the number of syringes prepared and left in the container the signature of the registered nurse who prepared the syringes. Separate containers should be used for insulin that is to be delivered at different times of the day. Whether to re-suspend pre-loaded insulin before injection If the pre-loaded dose contains isophane insulin or is a cloudy insulin, the syringe should be gently rotated back and forth between the hands at least 20 times until the insulin is uniformly suspended before injection. This also warms the insulin, which is important because injecting cold insulin can be painful and is less effectively absorbed. Potential patient problems If morning and evening doses are different, it is possible that the two doses may become confused, particularly if the patient has poor vision. This should be addressed by the community nurse when assessing a patient s capabilities and circumstances. Ways of overcoming this risk include the use of different shaped boxes for storage, which should be clearly marked to differentiate each dose. 9
10 ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME A further potential problem is the accidental wastage of insulin through spillage or the dropping of a syringe, and community nurses should ensure that patients know who to contact if this happens. Finally, doses could be self-administered at too close or too long an interval. To minimise this risk, the community nurse should regularly assess the patient s understanding of their regimen and routine. Nursing professionals are responsible for overseeing every aspect of patient safety, which should include the provision of education, support and insulin safety awareness training (including infection control and how to test blood glucose levels). Disposing of syringes after use Patients should be provided with yellow sharps boxes to dispose of syringes. These are available on prescription or through the local council, and should be returned in accordance with local guideline on clinical waste management. Summary of key points Community nurses are under increased pressure to undertake the pre-loading of insulin syringes for people with diabetes to administer at home. The RCN advises that: the pre-loading of insulin into a syringe for use by the patient at a later date must be seen as the final option, and should only be considered when all other options have been exhausted pre-preparing insulin syringes is an unlicensed activity that falls outside the Medicines Act (1968): practitioners and health organisations must take responsibility for the safety of this activity an organisation-wide policy/protocol on the pre-loading of insulin syringes for patients must be in place; this is essential to ensure patient safety and provide nurses with legal protection through vicarious liability the policy/protocol must set out responsibilities for all parties concerned and set out an agreed standard operating framework for every aspect of the practice (patient education, storage, labelling, monitoring of diabetes control and wellbeing etc) the specialist diabetes service/a senior diabetes specialist nurse lead must be involved in the preparation of the organisational policy, the initial patient risk assessment, and ongoing quality assurance to ensure policy adherence. The rising numbers of people with Type 2 diabetes, combined with an ageing population demographic, means the number of people unable to utilise a pen device due to dexterity or other reasons, is growing. Furthermore, in the current economic climate, there is also a potential for the use of pre-loaded insulin syringes to be abused in an attempt to generate perceived efficiencies by reducing community nurse visits/time. The RCN considers the pre-loading of insulin syringes not to be best practice, and recommends that the use of licensed first-line injection devices (such as an insulin pen) should be promoted to enable patient self-management. 10
11 ROYAL COLLEGE OF NURSING Part 2: Example of a best practice policy for the pre-loading of insulin syringes for patients to administer at home Torbay and South Devon Health and Care NHS Trust This is a controlled document. It should not be altered in any way without the express permission of the author or their representative. On receipt of a new version, please destroy all previous versions. Document Information Date of issue: Version: 1.0 Authors: Directorate: Approval Route: Care and clinical policies sub group Approved By: Care and clinical policies sub group Links or overlaps with other strategies/policies: Medicines policy for registered professionals: Non-medical prescribing policy: Blood glucose monitoring policy: Long acting insulin analogues: Sharps disposal: Next review date: Last review date: Sam Rosindale, Diabetes Lead Champion for Torbay Paul Humphriss, Head of Medicines Management Jacquie Phare, Head of Nursing Professional Practice and Medical Directorates Date approved: Mental capacity: 11
12 ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME 1 Introduction 1.1 This policy is supported by a risk assessment and standard operating procedure (SOP) for the pre-loading of insulin for patients to self-administer later. It stresses the necessary principles of practice including patient assessment and review, ensures other methods of insulin administration have been considered, together with contra-indications, and details appropriate insulin storage requirements and record keeping. 1.2 Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition. Patients require long-term medication to control blood glucose levels and reduce the risk of associated complications. For some patients the prescribed treatment is regular insulin injections. 1.3 There are a number of patients with diabetes who cannot convert to using an insulin pen for independent selfadministration of insulin because of manual dexterity, lack of strength, personal preference or reluctance to change. As a result many patients are unable to draw up their own insulin and need community nurse support, although they are able to inject independently using a syringe once or twice a day. The preparation of insulin injections by community nurses for patients to administer in their own homes at a later time has been the practice for many years. In this way, each patient can administer their insulin at the correct time in relation to their meals. This preserves the individual s independence (Rosindale, 2014). 1.4 The pre-loading of insulin into syringes is an unlicensed activity that falls outside of the Medicines Act (Rosindale, 2014) and adherence to this policy protects the patient, and provides legal protection for the registered nurse and this organisation under vicarious liability. The Royal College of Nursing (RCN, 2015) advises that this activity must be seen as the final option, and only considered when all other options have been exhausted. 1.5 Within the context of this policy the definition of pre-loading an insulin syringe refers to insulin that has been withdrawn from a 10ml vial, using an insulin syringe that is marked in one or two unit graduations. It is recommended that 8mm needles be used when using an insulin syringe. 1.6 No other type of syringe should ever be used for insulin administration. 2 Statement/objective 2.1 To promote patient safety. 2.2 To ensure that registered nurses (RNs) are aware of the potential risks of pre-loading insulin syringes for later use by a patient. 2.3 To provide a clear and consistent framework across Torbay & Southern Devon Health and Care NHS Trust for the appropriate assessment and management of a person with diabetes who cannot safely prepare their own insulin dose. 2.4 The Nursing & Midwifery Council (NMC) Standards for medicines management 14 (2010a) state that registrants must not prepare substances for injection in advance of their immediate use. The Department of Health (DH)/Medicines & Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) advise against pre-loading medication for injection at a later time (Rosindale, 2014). 2.5 To support RNs to provide insulin therapy as detailed in this policy which is classified as secondary dispensing (and thus not covered in the Medicines Act 1968) however, takes note of RCN guidance Advance preparation of insulin syringes for adult patients to administer at home (RCN, 2015). 2.6 The National Patient Safety Agency (NPSA) are unaware of any reports where insulin syringes prepared in advance by nurses in the community and given expiry dates of greater than 24 hours have caused serious harm due to infection and contamination issues (Rosindale, 2014). However, a Rapid Response Report has been issued for the safer prescribing and administration of insulin (2010). 12
13 ROYAL COLLEGE OF NURSING 3 Roles and responsibilities 3.1 This policy covers all RNs employed by Torbay and Southern Devon Health & Care NHS Trust who are required to treat patients with diabetes mellitus within their own home. 3.2 It relates specifically to the patient who is able to safely administer the correct dose of insulin at the correct time, but is unable to draw up insulin or utilise standard commercially available insulin preparations. 3.3 It is the responsibility of every trust employed RN who is required to treat patients with diabetes mellitus to be familiar with this policy and procedure. 3.4 RN to positively identify the patient (obtaining confirmation of name and DOB) and establish allergy status. 3.5 RNs involved in the administration of insulin, as in all other areas of their practice, will be responsible for maintaining and updating their knowledge and practice. The e-learning module on the Safe use of insulin is a mandatory requirement every two years with a pass mark of 80 per cent. 3.6 RNs are responsible for the initial and continued assessment of patients who are self-administering and have continued responsibility for recognising and acting upon changes in a patient s condition with regards to safety of the patient and others. The Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) and Mental Capacity Act 2005 state that for a patient to be able to self-administer, the patient should be assessed as being at Level 3 which is defined: the patient accepts full responsibility for the storage and administration of the medicinal products. The level should be documented in the patient s records (Standard 9 NMC, 2010a). 3.7 Patients must be allowed to decide whether they will agree to treatment in this way and this should be documented in the patient case notes. 3.8 RNs in administering any medicines, in assisting with administration, or in overseeing any self-administration must assess the patient s suitability and understanding of how to use an appropriate compliance aid safely (Standard 16 NMC, 2010a). 3.9 RNs are accountable to ensure that the patient is competent to carry out the task (Standard 17 NMC, 2010a) RNs are responsible for implementing this policy. Pre-loading insulin syringes must not be delegated to non-registered staff Pre-loaded syringes may not be prepared by one registered nurse for another health professional or skilled professional that is not registered to administer them Under no circumstances may RNs mix and pre-load different insulins in the same syringe for administration at a later time (there is no longer a need to mix insulins due to the availability of suitable manufacturer s preparations) Registered nurses are responsible for recognising any limitations in their knowledge and competence and declining any duties they do not feel able to perform in a skilled and safe manner (NMC, 2015). 4 Principles of practice for the preloading of insulin in syringes 4.1 Pre-loading of insulin should only be recommended when alternative methods of delivery are not possible and after appropriate risk assessment, as outlined in Appendices RNs should be aware of the alternative injection devices available and discuss the patient s needs and preferred options with the senior diabetes specialist nurse (SDSN) and general practitioner. 4.3 Pre-loading of insulin for injection must only begin following a full written risk assessment, involving the SDSN, and the ruling out of alternative methods of administration. A thorough assessment of the patients understanding of the insulin regime, their ability to manage it and the support available between community nurse visits, must be undertaken using Appendix B (Standard operating procedure (SOP)) for the assessment of a patient to have insulin 13
14 ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME prepared in advance of administration. Followed by completion of Appendix C (Risk assessment form advanced preparation of insulin into syringes for a patient to administer at a later date). 4.4 The risk assessment form in Appendix C should be undertaken every three months, or sooner if the patient s condition changes. 4.5 The patient should always be consulted about their insulin administration and informed consent obtained regarding the care provided. 4.6 On completion of the risk assessment the RN should decide on the appropriate number of days that the insulin syringes can be prepared for and left with the patient. It is important that the RN considers all aspects of social and health care for their patient in this decision. This number and the reason for the decision should be recorded in Appendix C. The maximum number of days that insulin syringes can be left pre-loaded is seven (RCN, 2015; Rosindale, 2014). Advice may be sought from the SDSN. Each time a nurse pre-loads a syringe, Appendix D (Documentation form for the advanced preparation of insulin in syringes) should be completed. 4.7 Pre-loaded insulin syringes must be labelled individually and stored in a wipeable, labelled, sealable, hinge-lidded container (see Appendix B). If the patient is having a different type of insulin or dose at another time of the day a different storage container should be used. To prevent any confusion the containers should be either different colours or shapes. 4.8 The patient s fridge should be visibly clean and free of debris. The insulin should be stored in the fridge door or top shelf to prevent cross-contamination from other food items. 4.9 It is recommended that insulin is most stable when stored at a temperature of between 2 and 8 Celsius. Never allow insulin to freeze Unopened insulin can be kept in these conditions until the expiry date. An opened vial of insulin kept in these conditions should be discarded after 28 days. The date that the vial was opened must be written on the vial and in Appendix D Patients in residential care must have their pre-loaded insulin syringes stored as outlined in but in a locked fridge Arrangements must be made to ensure that the monitoring of diabetes control is undertaken. Capillary blood glucose monitoring may be undertaken by the patient themselves, a family member or friend using their own glucometer. A full written assessment should be undertaken to check that they are confident and competent to undertake this procedure. The meter should also be checked weekly with the relevant quality control solution that is provided by the relevant meter company to ensure that it is accurate. Accuracy can also be checked by comparing a capillary blood glucose result with a venous glucose sample on a weekly basis. An Hba1c every three months is also required to evaluate the level of diabetes control Liaise with SDSN as required for advice if circumstances change The SDSN will quality assure that the risk assessment and SOP are being completed as outlined in this policy in Appendices B, C and D, using Appendix E every six months to ensure that this type of care remains appropriate for the individual An overview of the processes involved in points is outlined in Appendix A. 5 Contra-indications 5.1 Lantus (Glargine), Abasglar (biosimilar Glargine), Tresiba & Toujeo must not be preloaded into a insulin syringe. 5.2 Very variable capillary blood sugar recordings. 5.3 Lack of satisfactory storage conditions in the patient s home. 5.4 Unpredictable mental state or declining cognitive ability. 5.5 Pre-filled insulin cartridges and 14
15 ROYAL COLLEGE OF NURSING commercially available pre-loaded pens must not be used to withdraw insulin in order to comply with this policy. Only 10ml vials are permissible to be used. 5.6 If any of the points are found, then this is to be reported to the GP or [INSERT NAME OF PRACTICE] Doctors (when out of hours) and the advanced preparation of insulin in syringes should cease and arrangements made for the community nursing team to visit at the required intervals. A clinical incident form should be completed. 6 Training 6.1 All staff involved with the care of these patients will receive a training session delivered through the SDSN. This session will cover a detailed presentation of the policy, the responsibilities of the RN, completing the risk assessment and practical aspects of dispensing insulin into syringes. Support and advice may also be sought from the medicines management team. 6.2 There will be annual training offered to the staff concerned by the SDSN to update staff and feed back any observations from the six monthly quality assurance assessments. 6.3 All clinical staff should be made aware of this policy at induction (new staff) by their zone leads and specific medicines management training where appropriate. 6.4 All community nurses involved in insulin administration will undertake the MERIT course helping people with diabetes to maintain insulin therapy. 7 Monitoring, auditing, reviewing and evaluation This policy will be reviewed in two years through the Torbay and Southern Devon Health and Care NHS Trust Care and Clinical Policies Sub Group. The assistant director of professional practice will report to the care and clinical policies and procedures sub-group any concerns over the implementation of this policy. All patients receiving insulin by this methodology will be recorded and held on a register by the SDSN. This should be available to the provider safety group at their request. 8 Contact details for any further Information Senior diabetes specialist nurse (SDSN): [INSERT CONTACT DETAILS] Medicines management: [INSERT CONTACT DETAILS OF LOCAL MEDICINES MANAGEMENT TEAM] Head of nursing: [INSERT CONTACT DETAILS] 15
16 ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME Appendices Appendix A: Process of syringes being pre-loaded for the patient on the first occasion 5. Pre-load syringes using appendix D documentation form at every visit 4. After risk assessment completed discuss with diabetes lead champion 1. Patient unable to administer insulin with a pen device 3. Undertake risk assessment in appendix C 2. Read appendix B to understand rationale for Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) and risk assessment 16
17 ROYAL COLLEGE OF NURSING Ongoing process of syringes being pre-loaded for the patient 4. Diabetes lead champion to quality assure risk assessment and SOP are completed in line with this policy every six months using appendix E 1. Patient unable to administer insulin with a pen device 3. Undertake risk assessment in appendix C every three months 2. Pre-load syringes using appendix D documentation form every time 17
18 ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME Appendix B: Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for the assessment of a patient to have insulin prepared in advance of administration 1. Mental capacity and physical capability Activity Rationale Responsibility Assess the mental capacity and physical capability of the patient/carers to selfadminister insulin. The patient should be at Level 3 which is defined: the patient accepts full responsibility for the storage and administration of the medicinal products. The level should be documented in the patient s records. Registered nurses should be aware that the Mental Capacity Act 2005 requires all those working with potentially incapacitated people to assess the individual s capacity at a particular moment about a particular decision. Any change in the patient s condition would necessitate a review of their self-administration status; for example, risk of self-harm. 2. Consent Discuss risks and benefits of self-administration with the patient. Support available between community nurse visits. Where patients consent to self-administration of their medicines the following must be considered: Patients share the responsibility for their actions, relating to self-administration of their medicines. If children have access to the fridge that the patient ensures that the syringes are kept out of their reach and/or a childproof fridge lock is in situ. Patients can withdraw consent at any time 3. Ensure most appropriate product has been prescribed Discuss and assess potential alternative insulin preparation with diabetes lead champion for Torbay or prescriber. Reduce risk of medication error. NMC Standards for Medicines Management (2010). Care plan must be updated as a minimum every three months to meet needs of patient. Reduce risk of medication error. To gain informed consent and document in patient s record. Patients are empowered to make informed choices. Safeguarding of children. Patients retain right to withdraw consent. Unable to pre-load/use pen devices due to manual dexterity/ poor vision/peripheral neuropathy/ physical weakness to deliver insulin dose in insulin pen device/patient preference/reluctance to change Zone lead/ registered nurse Zone lead/ registered nurse Zone lead/ registered nurse 18
19 ROYAL COLLEGE OF NURSING 4. Contra-indications Activity Rationale Responsibility Are there any contra-indications for the pre-loading of insulin syringes? 4.1 Lantus (Glargine), Abasglar (biosimilar Glargine), Tresiba & Toujeo must not be preloaded into a insulin syringe. 4.2 Only use 10ml vials to withdraw insulin into syringes. Do not withdraw from pre-loaded pens or 3ml cartridges. 4.3 Is the fridge in working order? 4.4 Is the fridge visibly clean? 4.5 Is the fridge free from debris? 4.6 Patient suffers from an unpredictable mental state or declining cognitive ability. 4.7 Very variable capillary blood glucose readings. 4.8 If any of the above points are found, then this needs to be reported to the GP or doctors (when out of hours) and the advanced preparation of insulin in syringes should cease and arrangements made for the community nursing team to visit at the required intervals. Complete incident form. 5. Education of patient Information/education given and supervision should be tailored to meet individual patient need, to enable the patient to administer the right dose, at the right time using the correct technique. The information below should be provided to the patient before commencing self-administration. 5.1 The name of the medicine. 5.2 Why they are taking it; dose and frequency. 5.3 Re-suspending each pre-loaded syringe, between the hands to warm the insulin, at least 20 times prior to injection, if using a cloudy insulin. 5.4 Inject at a 90 angle into sub-cutaneous tissue using a pinch-up technique into abdomen, outer thigh or buttocks as decided in care plan. 5.5 Rotation within an injection site or between different injection sites. 5.6 Common side effects and what to do if they occur eg hypoglycaemia. 5.7 Any special instructions. 5.8 How to obtain further supplies. 5.9 How to store the medication Frequency of visits and contact number for between visits Recognition of error and procedure to follow Correct disposal of sharps at the point of use. Risk of deterioration of insulin. To ensure appropriate storage conditions. Risk to patient safety. To ensure safe administration of insulin. To comply with NMC Standards for medicines management (2010). Injecting cold insulin can be painful and it is not absorbed so effectively. Zone lead/ registered nurse Zone lead/ registered nurse Zone lead/ registered nurse Plan of care documented and agreed with patient and nurse to ensure adequate support, monitoring of diabetes control and wellbeing. To demonstrate partnership working. Zone lead/ registered nurse 19
20 ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME 6. Preparation of insulin Activity Rationale Responsibility Nurses must not mix different insulins in the same syringe for administration at a later time. (There is no longer a need to mix insulins due to the availability of suitable manufacturer s preparations). Pre loaded insulin should be left up to a maximum of seven days. Document the advanced preparation of insulin on the PCT Community Nursing Record Sheets, ensuring full details are recorded, including batch number, type of insulin and expiry date are recorded. Required equipment. 6.1 Plan of care. 6.2 Sharps box (obtained from council). 6.3 Insulin syringes 30, 50 or 100 unit syringes (depending on which is most appropriate for the dose), needle length should be no more than 8mm. 6.4 Relevant insulin vial. 6.5 Wipeable, sealable, hinged, labelled container/s for storage of pre-filled syringes. 6.6 Alcohol swab. 6.7 Syringe labels. 6.8 Read and check plan of care. Check all previous pre-loaded syringes have been administered and safely disposed of. An adverse event form should be completed to investigate why the syringes had not been used. 6.9 Explain procedure to patient, ensuring consent obtained Prepare clean working surface and wipe with a Clinell wipe Collect equipment required; check insulin for expiry date and against instructions of care plan Wash hands Prepare equipment and re-suspend (by rocking back and forth) insulin at least 20 times if using a cloudy insulin. Do not shake as you will damage the insulin suspension. If using a clear insulin there is no need to re-suspend Swab insulin vial with an alcohol wipe and allow to dry Draw up insulin in presence of patient as follows for each syringe using a clean procedure to prevent contamination Remove needle cover and pull back plunger to measure an amount of air equivalent to the amount of insulin prescribed With insulin vial standing upright, insert the needle through the centre of the rubber cap and push down plunger Invert the insulin vial. To reduce risk of administration errors. RCN (2015) and Rosindale (2014). To comply with Torbay and Southern Devon Health and Care NHS Trust documentation record keeping. To ensure adequate preparation of procedure. To reduce risk of administration errors. To reduce risk of cross-infection. To ensure safe administration of insulin. To comply with NMC Standards for medicines management (2010). All registered nurses All registered nurses All registered nurses All registered nurses All registered nurses 20
21 ROYAL COLLEGE OF NURSING 6.19 Pull back plunger until slightly more than correct dose is drawn up Expel any air bubbles back into vial Re-check correct prescribed dose has been drawn up and remove needle from vial Carefully re-sheath needle (there is no risk of contaminated needle stick injury as needle is sterile in event of a needle stick injury the syringe must be safely discarded) Label each syringe with patient name, insulin name, date of preparation, initials of RN Label each container with patient name, insulin name, insulin dose, time of administration, number of syringes, date, mane and signature of registered nurse Store pre-filled syringes with needles slightly elevated, within a labelled container as described earlier in main body of the fridge (away from freezer section or the back of the fridge) Dispose of clinical waste and wash hands Complete nursing notes ensuring date, time, insulin type/dose, batch number and number of syringes pre-filled are recorded If any pre-loaded syringes have not been used within the designated period, they must be disposed of. To ensure best practice in the preparation of insulin prior to injection. All registered nurses 21
22 ADVANCED PREPARATION OF INSULIN SYRINGES FOR ADULT PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME 7. Safe storage of pre-drawn insulin Activity Rationale Responsibility 7.1 The needle should be stored approximately at 45 to prevent blockage by suspended substances in the insulin 7.2 Pre-filled syringes should be labelled and stored in a protective container. If there are different doses then use more than one container. Store in the main body of the fridge (away from the freezer section or the back of the fridge) between 2-8. The container should be clearly labelled with the following information: date name of patient pre-loaded dose number of syringes name of insulin preparation time of insulin administration eg before breakfast, before evening meal route (subcutaneous) instructions for administration eg just before or 30 minutes before food at times agreed with the patient and documented in the nursing notes who has prepared the syringes. 7.3 Separate containers should be used for insulin to be delivered at different times of day, particularly if the syringe contains a different dosage or type of insulin (RCN, 2015). 7.4 When each new insulin vial is opened, the date and time must be recorded on the vial and in the patient s notes. 7.5 Any insulin remaining in the vial after 28 days should be discarded. 7.6 Patients should have a vial in use and a backup vial at all times to ensure that vials are used methodically. 7.7 The patient should be advised of the correct storage (as above) and advised to notify the district nurse team ASAP if their fridge stops working or the fridge freezes. Needle blockage by suspended insulin. To promote safe storage of preloaded insulin. To ensure best practice in the administration of medicines. To reduce risk of medication errors. To reduce medication error. To meet patients individual needs. To promote standardisation of labels used. To promote safe storage of insulin. All registered nurses Patient/carer 22
Pre-loading of insulin syringes for adult patients to administer at home
 Title: Directorate: Responsible for review: Ratified by: Diabetes - Pre-loading of insulin syringes for adult patients to administer at home Operations Samantha Rosindale, Diabetes Lead Champion Lynda
Title: Directorate: Responsible for review: Ratified by: Diabetes - Pre-loading of insulin syringes for adult patients to administer at home Operations Samantha Rosindale, Diabetes Lead Champion Lynda
Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy
 Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet. Please visit the intranet for the latest version. Purpose of Agreement
Pre-Loaded Insulin Syringe Policy Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet. Please visit the intranet for the latest version. Purpose of Agreement
ADVANCE PREPARATION OF INSULIN FOR PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ADVANCE PREPARATION OF INSULIN FOR PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME First Issued July 08 Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ADVANCE PREPARATION OF INSULIN FOR PATIENTS TO ADMINISTER AT HOME First Issued July 08 Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote
ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN Issue History First issued April 2012 Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote the safe administration
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN Issue History First issued April 2012 Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote the safe administration
Assistant Practitioner and Health Care Assistants Administration of Insulin, via Pen device, by Delegation Training and competency Toolkit
 Assistant Practitioner and Health Care Assistants Administration of Insulin, via Pen device, by Delegation Training and competency Toolkit Document Summary The purpose of this policy is to guide and promote
Assistant Practitioner and Health Care Assistants Administration of Insulin, via Pen device, by Delegation Training and competency Toolkit Document Summary The purpose of this policy is to guide and promote
Guidelines for managing the health care needs of children and young persons with diabetes in education
 Guidelines for managing the health care needs of children and young persons with diabetes in education Contents Page: Page Number 1.0 Introduction 1 2.0 The Care Management Plan 2 2.1 Blood Glucose monitoring
Guidelines for managing the health care needs of children and young persons with diabetes in education Contents Page: Page Number 1.0 Introduction 1 2.0 The Care Management Plan 2 2.1 Blood Glucose monitoring
PATIENT INFORMATION. D iabetes. What You Need to Know About. Insulin
 PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: D iabetes What You Need to Know About Insulin INTRODUCTION The insulin preparations currently available in Singapore are mostly from human origin; pork or bovine
PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: D iabetes What You Need to Know About Insulin INTRODUCTION The insulin preparations currently available in Singapore are mostly from human origin; pork or bovine
Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy
 Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 4 Ratified by: Corporate Policy Panel Date ratified: 20 July 2017 Name of originator/author: HR Manager Name of responsible
Management of AIDS/HIV Infected Healthcare Workers Policy DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 4 Ratified by: Corporate Policy Panel Date ratified: 20 July 2017 Name of originator/author: HR Manager Name of responsible
Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections. No Action Rationale
 Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections Preparation Overview No Action Rationale 1 Collect and check all equipment 2 Check that the packaging of all
Standard operating procedures for preparation and administration of intramuscular injections Preparation Overview No Action Rationale 1 Collect and check all equipment 2 Check that the packaging of all
Administration of Injectable Medication by Healthcare Assistants (Band 3) Standard Operating Procedure
 Administration of Injectable Medication by Healthcare Assistants (Band 3) Standard Operating Procedure DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 1 Ratified by: Quality Assurance Sub Committee Date ratified: 4 September
Administration of Injectable Medication by Healthcare Assistants (Band 3) Standard Operating Procedure DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 1 Ratified by: Quality Assurance Sub Committee Date ratified: 4 September
PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING
 PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING First Issued Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote safe and effective blood glucose monitoring using Trust equipment
PROCEDURE FOR BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING First Issued Issue Version Two Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To promote safe and effective blood glucose monitoring using Trust equipment
To provide nursing staff with guidelines for the safe and appropriate administration of insulin.
 SUBJECT: ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN This cancels NP 513 dated 3/1/07 1. PURPOSE: COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Medications POLICY NUMBER: 513 Effective Date: June
SUBJECT: ADMINISTRATION OF INSULIN This cancels NP 513 dated 3/1/07 1. PURPOSE: COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Medications POLICY NUMBER: 513 Effective Date: June
Introduction. Guidelines for patient involvement in the administration of insulin under supervision in hospital (Adult patients)
 Guidelines for patient involvement in the administration of insulin under supervision in hospital (Adult patients) Introduction This guideline is designed to provide a framework for patients to administer
Guidelines for patient involvement in the administration of insulin under supervision in hospital (Adult patients) Introduction This guideline is designed to provide a framework for patients to administer
SAFE HANDLING OF VACCINES
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE SAFE HANDLING OF VACCINES Issue History Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To ensure vaccines are stored in accordance with manufacturers
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE SAFE HANDLING OF VACCINES Issue History Issue Version One Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date To ensure vaccines are stored in accordance with manufacturers
Policy for Supporting. Children and Young People with. Diabetes in Education
 Policy for Supporting Children and Young People with Diabetes in Education December 2011 POLICY FOR SUPPORTING CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE WITH DIABETES IN EDUCATION Contents 1. Introduction 2. Before a
Policy for Supporting Children and Young People with Diabetes in Education December 2011 POLICY FOR SUPPORTING CHILDREN AND YOUNG PEOPLE WITH DIABETES IN EDUCATION Contents 1. Introduction 2. Before a
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES. Insulin
 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES Insulin This medicine has been proven to be safe and effective, but it can cause serious injury if a mistake happens while taking it. This means
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET MEDICINE TO TREAT: DIABETES Insulin This medicine has been proven to be safe and effective, but it can cause serious injury if a mistake happens while taking it. This means
INSULIN MANAGEMENT POLICY
 INSULIN MANAGEMENT POLICY To be read in conjunction with the Hypoglycaemia Management Policy for adult Patients and the Countywide Standard Operating Procedure for Implementing the Insulin Passport/Safety
INSULIN MANAGEMENT POLICY To be read in conjunction with the Hypoglycaemia Management Policy for adult Patients and the Countywide Standard Operating Procedure for Implementing the Insulin Passport/Safety
TRANSCRIPT for Lantus SoloSTAR pen injection for your patients
 TRANSCRIPT for Lantus SoloSTAR pen injection for your patients SUPER: Prescription Lantus is a long-acting insulin used to treat adults with type 2 diabetes and adults and pediatric patients (children
TRANSCRIPT for Lantus SoloSTAR pen injection for your patients SUPER: Prescription Lantus is a long-acting insulin used to treat adults with type 2 diabetes and adults and pediatric patients (children
Template Standard Operating Procedure For: Handling of Midazolam and other controlled drugs in Dental Practices
 Name of Dental Practice : Objectives To ensure implementation of the regulations and guidance on safe and secure handling of midazolam and other controlled drugs (CDs) Scope To cover all aspects of obtaining
Name of Dental Practice : Objectives To ensure implementation of the regulations and guidance on safe and secure handling of midazolam and other controlled drugs (CDs) Scope To cover all aspects of obtaining
Protocol (Clinical) Country Health SA Local Health Network. Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in Hospital and Aged Care
 Protocol (Clinical) Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in Hospital and Aged Care Protocol developed by: CHSALHN Diabetes Service Protocol Sponsor: CHSALHN, Executive Director, Medical Services
Protocol (Clinical) Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in Hospital and Aged Care Protocol developed by: CHSALHN Diabetes Service Protocol Sponsor: CHSALHN, Executive Director, Medical Services
Diabetes is a lifelong, chronic. Survey on the quality of diabetes care in prison settings across the UK. Keith Booles
 Survey on the quality of diabetes care in prison settings across the UK Article points 1. The Royal College of Nursing Diabetes Forum conducted an audit of prisons within the UK to determine the level
Survey on the quality of diabetes care in prison settings across the UK Article points 1. The Royal College of Nursing Diabetes Forum conducted an audit of prisons within the UK to determine the level
Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection
 Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 3 Ratified by: Risk Management Sub Group Date ratified: 17 July 2013 Name of originator/author: Health
Latex and Occupational Dermatitis Policy Incorporating Glove Selection DOCUMENT CONTROL: Version: 3 Ratified by: Risk Management Sub Group Date ratified: 17 July 2013 Name of originator/author: Health
KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY
 KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? Insulin treatment improves the quality of life in many people and saves the lives of others. It is used to lower blood glucose levels.
KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? Insulin treatment improves the quality of life in many people and saves the lives of others. It is used to lower blood glucose levels.
INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY AND PROCEDURES Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust (The Trust)
 A member of: Association of UK University Hospitals INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY AND PROCEDURES Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust (The Trust) IPC17 SINGLE USE AND SINGLE PATIENT USE MEDICAL
A member of: Association of UK University Hospitals INFECTION PREVENTION AND CONTROL POLICY AND PROCEDURES Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust (The Trust) IPC17 SINGLE USE AND SINGLE PATIENT USE MEDICAL
Insulin Management. By Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse
 Insulin Management By Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse The Discovery of Insulin - 1921 - Banting & Best University Of Toronto Discovered hormone insulin in pancreatic extract of dog - Marjorie the
Insulin Management By Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse The Discovery of Insulin - 1921 - Banting & Best University Of Toronto Discovered hormone insulin in pancreatic extract of dog - Marjorie the
PLEASE READ THIS USER MANUAL BEFORE USE
 USER MANUAL Humalog 200 units/ml KwikPen, solution for injection in a pre-filled pen insulin lispro PLEASE READ THIS USER MANUAL BEFORE USE USE ONLY IN THIS PEN, OR SEVERE OVERDOSE CAN RESULT Read the
USER MANUAL Humalog 200 units/ml KwikPen, solution for injection in a pre-filled pen insulin lispro PLEASE READ THIS USER MANUAL BEFORE USE USE ONLY IN THIS PEN, OR SEVERE OVERDOSE CAN RESULT Read the
Case scenarios: Patient Group Directions
 Putting NICE guidance into practice Case scenarios: Patient Group Directions Implementing the NICE guidance on Patient Group Directions (MPG2) Published: March 2014 [updated March 2017] These case scenarios
Putting NICE guidance into practice Case scenarios: Patient Group Directions Implementing the NICE guidance on Patient Group Directions (MPG2) Published: March 2014 [updated March 2017] These case scenarios
Insulin Basic facts. Patient Education Patient Care Services. What is insulin? What types of insulin are there? Basal Insulin
 Patient Education Insulin Basic facts Insulin is a protein made by the pancreas that allows your cells to use glucose for energy. There are different types of insulin: Basal long-acting insulin that controls
Patient Education Insulin Basic facts Insulin is a protein made by the pancreas that allows your cells to use glucose for energy. There are different types of insulin: Basal long-acting insulin that controls
Acknowledgement goes to WHO for use of their hand washing technique
 How to administer third party insulin injections safely with a pen device, safety pen needle and syringe 1 Hand washing It takes at least 15 seconds to wash your hands. This is about how long it takes
How to administer third party insulin injections safely with a pen device, safety pen needle and syringe 1 Hand washing It takes at least 15 seconds to wash your hands. This is about how long it takes
Pre-Dialysis Insulin Information for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes receiving haemodialysis
 Pre-Dialysis Insulin Information for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes receiving haemodialysis Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered 2 This leaflet is for patients with Type 2 diabetes who require insulin
Pre-Dialysis Insulin Information for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes receiving haemodialysis Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered 2 This leaflet is for patients with Type 2 diabetes who require insulin
How to use your gonal-f pre-filled pen
 How to use your gonal-f pre-filled pen Information in this user guide is based on the European product information for Gonal-f. It is not country specific and may vary from country to country. Please always
How to use your gonal-f pre-filled pen Information in this user guide is based on the European product information for Gonal-f. It is not country specific and may vary from country to country. Please always
OWNER MANUAL Diabetes in Cats
 www.mypetonline.co.uk/petdiabetes OWNER MANUAL Diabetes in Cats DIABETES IN CATS What is Diabetes? Glucose (blood sugar) is derived from the food your cat eats and provides the energy body cells need to
www.mypetonline.co.uk/petdiabetes OWNER MANUAL Diabetes in Cats DIABETES IN CATS What is Diabetes? Glucose (blood sugar) is derived from the food your cat eats and provides the energy body cells need to
The Administration of Insulin to patients at home and in Community Hospitals
 The Administration of Insulin to patients at home and in Community Hospitals Partners in Care Document Ratification This is a controlled document and should not be altered in any way without the express
The Administration of Insulin to patients at home and in Community Hospitals Partners in Care Document Ratification This is a controlled document and should not be altered in any way without the express
Instructions for Use HEMLIBRA (hem-lee-bruh) (emicizumab-kxwh) injection, for subcutaneous use
 Instructions for Use HEMLIBRA (hem-lee-bruh) (emicizumab-kxwh) injection, for subcutaneous use Be sure that you read, understand, and follow the Instructions for Use before injecting HEMLIBRA. Your healthcare
Instructions for Use HEMLIBRA (hem-lee-bruh) (emicizumab-kxwh) injection, for subcutaneous use Be sure that you read, understand, and follow the Instructions for Use before injecting HEMLIBRA. Your healthcare
Patient Education Pharmacy Services
 Patient Education This handout details the types of insulin. It also covers how to store, mix and inject insulin. What is insulin? Insulin is made by the pancreas and acts as a key to move glucose (sugar)
Patient Education This handout details the types of insulin. It also covers how to store, mix and inject insulin. What is insulin? Insulin is made by the pancreas and acts as a key to move glucose (sugar)
The RPS is the professional body for pharmacists in Wales and across Great Britain. We are the only body that represents all sectors of pharmacy.
 Royal Pharmaceutical Society 2 Ash Tree Court Woodsy Close Cardiff Gate Business Park Pontprennau Cardiff CF23 8RW Mr Mark Drakeford AM, Chair, Health and Social Care Committee National Assembly for Wales
Royal Pharmaceutical Society 2 Ash Tree Court Woodsy Close Cardiff Gate Business Park Pontprennau Cardiff CF23 8RW Mr Mark Drakeford AM, Chair, Health and Social Care Committee National Assembly for Wales
Sunderland Diabetes Network - Recommendations for safe prescribing of insulin.
 Sunderland Diabetes Network - Recommendations for safe prescribing of insulin. Note: High strength insulins and biosimilar insulins are for specialist initiation only. They should not be initiated in primary
Sunderland Diabetes Network - Recommendations for safe prescribing of insulin. Note: High strength insulins and biosimilar insulins are for specialist initiation only. They should not be initiated in primary
Medication Safety. Patient Safety. Setting Direction Julie Simmons, Medication Safety Pharmacist January 2016
 Medication Safety Patient Safety Setting Direction Julie Simmons, Medication Safety Pharmacist January 2016 1 The patient journey Admission Ward Transfer Ward stay Discharge Medication storage and supply
Medication Safety Patient Safety Setting Direction Julie Simmons, Medication Safety Pharmacist January 2016 1 The patient journey Admission Ward Transfer Ward stay Discharge Medication storage and supply
Adminstration of Insulin to Patients at Home and in Community Hospitals
 1929 Version 2 The Administration of Insulin to patients at home and in Community Hospitals Date: 26 January 2017 Adminstration of Insulin to Patients at Home and in Community Hospitals Page 1 of 7 Partners
1929 Version 2 The Administration of Insulin to patients at home and in Community Hospitals Date: 26 January 2017 Adminstration of Insulin to Patients at Home and in Community Hospitals Page 1 of 7 Partners
USE OF UNLICENSED MEDICINES AND OFF-LABEL MEDICINES WHERE A LICENSED MEDICINE IS AVAILABLE
 NHS Scotland Directors of Pharmacy and Scottish Association of Medical Directors USE OF UNLICENSED MEDICINES AND OFF-LABEL MEDICINES WHERE A LICENSED MEDICINE IS AVAILABLE CONSENSUS STATEMENT This consensus
NHS Scotland Directors of Pharmacy and Scottish Association of Medical Directors USE OF UNLICENSED MEDICINES AND OFF-LABEL MEDICINES WHERE A LICENSED MEDICINE IS AVAILABLE CONSENSUS STATEMENT This consensus
Service Level Agreement for the Provision of Level 1 Substance Misuse Services from a Community Pharmacy under contract to NHS Grampian
 Service Level Agreement for the Provision of Level 1 Substance Misuse Services from a Community Pharmacy under contract to NHS Grampian 1. Introduction The provision of Substance Misuse (SM) services through
Service Level Agreement for the Provision of Level 1 Substance Misuse Services from a Community Pharmacy under contract to NHS Grampian 1. Introduction The provision of Substance Misuse (SM) services through
SFHDiabIPT01. Assess the suitability of insulin pump therapy for an individual with Type 1 diabetes. Overview
 Assess the suitability of insulin pump therapy for an individual with Type Overview This standard covers the activities associated with assessing the suitability of insulin pump therapy for individuals
Assess the suitability of insulin pump therapy for an individual with Type Overview This standard covers the activities associated with assessing the suitability of insulin pump therapy for individuals
Procedure for the prescribing and administration of insulin
 Procedure for the prescribing and administration of insulin Author: Lilian Baxendale and Heather Beadle Designation: Clinical Governance Pharmacists Version: Version 3 Date: December 2016 Date Approved:
Procedure for the prescribing and administration of insulin Author: Lilian Baxendale and Heather Beadle Designation: Clinical Governance Pharmacists Version: Version 3 Date: December 2016 Date Approved:
Hearing aid dispenser approval process review Introduction Hearing aid dispenser data transfer... 6
 Hearing aid dispenser approval process review 2010 11 Content 1.0 Introduction... 4 1.1 About this document... 4 1.2 Overview of the approval process... 4 2.0 Hearing aid dispenser data transfer... 6 2.1
Hearing aid dispenser approval process review 2010 11 Content 1.0 Introduction... 4 1.1 About this document... 4 1.2 Overview of the approval process... 4 2.0 Hearing aid dispenser data transfer... 6 2.1
Country Health SA Local Health Network. Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in the Community Setting
 Protocol (Clinical) Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in the Community Setting Protocol developed by: CHSALHN Diabetes Service Protocol Sponsor: CHSALHN, Executive Director, Medical Services Approved
Protocol (Clinical) Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in the Community Setting Protocol developed by: CHSALHN Diabetes Service Protocol Sponsor: CHSALHN, Executive Director, Medical Services Approved
Policy and Procedure for the Development, Approval and Implementation of Patient Group Directions in NHS Haringey Clinical Commissioning Group
 BEFORE USING THIS POLICY ALWAYS ENSURE YOU ARE USING THE MOST UP TO DATE VERSION Policy and Procedure for the Development, Approval and Implementation of Patient Group Directions in NHS Haringey Clinical
BEFORE USING THIS POLICY ALWAYS ENSURE YOU ARE USING THE MOST UP TO DATE VERSION Policy and Procedure for the Development, Approval and Implementation of Patient Group Directions in NHS Haringey Clinical
Things you need to know about injections
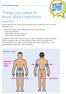 www.trend-uk.org Things you need to know about injections Injection sites: You can see from the picture below the best sites for injecting insulin or GLP-1 medications are: Back of the upper arms (difficult
www.trend-uk.org Things you need to know about injections Injection sites: You can see from the picture below the best sites for injecting insulin or GLP-1 medications are: Back of the upper arms (difficult
Policy for the safe administration of Insulin
 Policy for the safe administration of Insulin This is a working document and any changes that become necessary to this policy must be Notified in writing to the Medicine Management Group via the Chief
Policy for the safe administration of Insulin This is a working document and any changes that become necessary to this policy must be Notified in writing to the Medicine Management Group via the Chief
Sunderland Diabetes Network - Recommendations for safe prescribing of insulin.
 Sunderland Diabetes Network - Recommendations for safe prescribing of insulin. Note: High strength insulins and biosimilar insulins are for specialist initiation only. They should not be initiated in primary
Sunderland Diabetes Network - Recommendations for safe prescribing of insulin. Note: High strength insulins and biosimilar insulins are for specialist initiation only. They should not be initiated in primary
PHARMACY SERVICE ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE SUPPLY OF PALLIATIVE CARE SYRINGES AND MEDICINES FOR COMMUNITY PATIENTS
 PHARMACY SERVICE ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE SUPPLY OF PALLIATIVE CARE SYRINGES AND MEDICINES FOR COMMUNITY PATIENTS The benefits of prefilled syringes for palliative care from the hospital pharmacy service In
PHARMACY SERVICE ARRANGEMENTS FOR THE SUPPLY OF PALLIATIVE CARE SYRINGES AND MEDICINES FOR COMMUNITY PATIENTS The benefits of prefilled syringes for palliative care from the hospital pharmacy service In
A patient guide to the use of insulin for diabetes
 A patient guide to the use of insulin for diabetes Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
A patient guide to the use of insulin for diabetes Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
SELF-INJECTION GUIDE
 SELF-INJECTION GUIDE (asfotase alfa) 40 mg/ml solution for injection 18 mg/0.45 ml 28 mg/0.7 ml 40 mg/1 ml 100 mg/ml solution for injection 80 mg/0.8 ml asfotase alfa Introduction Contents This Self-Injection
SELF-INJECTION GUIDE (asfotase alfa) 40 mg/ml solution for injection 18 mg/0.45 ml 28 mg/0.7 ml 40 mg/1 ml 100 mg/ml solution for injection 80 mg/0.8 ml asfotase alfa Introduction Contents This Self-Injection
This Diabetes Policy should be read in conjunction with the Dealing with Medical Conditions Policy of Goulburn Region Preschool Association Inc.
 DIABETES POLICY Mandatory Quality Area 2 The content of this policy was developed for KPV by advocacy and diabetes educators at Diabetes Australia Vic and the Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne s manager
DIABETES POLICY Mandatory Quality Area 2 The content of this policy was developed for KPV by advocacy and diabetes educators at Diabetes Australia Vic and the Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne s manager
THE RESPONSIBLE PHARMACIST REGULATIONS
 THE RESPONSIBLE PHARMACIST REGULATIONS A SUMMARY OF THE RESPONSES TO PUBLIC CONSULTATION ON PROPOSALS FOR THE CONTENT OF THE REGULATIONS DH INFORMATION READER BOX Policy HR / Workforce Management Planning
THE RESPONSIBLE PHARMACIST REGULATIONS A SUMMARY OF THE RESPONSES TO PUBLIC CONSULTATION ON PROPOSALS FOR THE CONTENT OF THE REGULATIONS DH INFORMATION READER BOX Policy HR / Workforce Management Planning
Administering Rescue Medication into Children for Prolonged Seizures
 Standard Operating Procedure 10 (SOP 10) Administering Rescue Medication into Children for Prolonged Seizures Why we have a procedure? Black Country Partnership NHS Trust (hereafter referred to as the
Standard Operating Procedure 10 (SOP 10) Administering Rescue Medication into Children for Prolonged Seizures Why we have a procedure? Black Country Partnership NHS Trust (hereafter referred to as the
Care Homes - Homely Remedies Protocol
 Care Homes - Homely Remedies Protocol A homely remedy is a medicine for the short-term treatment of a minor ailment, such as indigestion, a cough, mild to moderate pain or constipation, and can be obtained
Care Homes - Homely Remedies Protocol A homely remedy is a medicine for the short-term treatment of a minor ailment, such as indigestion, a cough, mild to moderate pain or constipation, and can be obtained
SFHDiabPT03 Provide dietary education for an individual with Type 1 diabetes who is contemplating insulin pump therapy
 Provide dietary education for an individual with Type 1 diabetes who is contemplating insulin pump therapy Overview This standard concerns the activities of helping an individual with diabetes understand
Provide dietary education for an individual with Type 1 diabetes who is contemplating insulin pump therapy Overview This standard concerns the activities of helping an individual with diabetes understand
Patient/Carer instructions for the administration of Subcutaneous Cytarabine
 Patient/Carer instructions for the administration of Subcutaneous Cytarabine This document covers the following information: What cytarabine is What subcutaneous means What happens if you decide to inject
Patient/Carer instructions for the administration of Subcutaneous Cytarabine This document covers the following information: What cytarabine is What subcutaneous means What happens if you decide to inject
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION PROCEDURE
 PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION PROCEDURE Date approved 2 October 2015 Version 3 Approved by Yvette Oade, Chief Medical Officer Procedure Lead Clinical Governance Lead - Medicines Management Procedure Author Karen
PATIENT GROUP DIRECTION PROCEDURE Date approved 2 October 2015 Version 3 Approved by Yvette Oade, Chief Medical Officer Procedure Lead Clinical Governance Lead - Medicines Management Procedure Author Karen
Pharmacy Needle and Syringe Programme. Enhanced Contract
 Pharmacy Needle and Syringe Programme Enhanced Contract 1 st April 2012 31 st March 2013 Signed on behalf of LPC Signed on behalf of CRI Signed on behalf of Turning Point Signed on behalf of KCA Signed
Pharmacy Needle and Syringe Programme Enhanced Contract 1 st April 2012 31 st March 2013 Signed on behalf of LPC Signed on behalf of CRI Signed on behalf of Turning Point Signed on behalf of KCA Signed
How to use your Pergoveris pre-filled pen
 How to use your Pergoveris pre-filled pen Information in this user guide is based on the European product information for Pergoveris. It is not country specific and may vary from country to country. Please
How to use your Pergoveris pre-filled pen Information in this user guide is based on the European product information for Pergoveris. It is not country specific and may vary from country to country. Please
Education and Training Committee 15 November 2012
 Education and Training Committee 15 November 2012 Review of the process of approval of hearing aid dispenser pre-registration education and training programmes. Executive summary and recommendations Introduction
Education and Training Committee 15 November 2012 Review of the process of approval of hearing aid dispenser pre-registration education and training programmes. Executive summary and recommendations Introduction
EVER Pharma D-mine Pen Pen injector for Apomorphine 10 mg/ml
 EVER Pharma D-mine Pen Pen injector for Apomorphine 10 mg/ml Instructions for Use with Dacepton 3 ml Cartridges Apomorphine hydrochloride hemihydrate solution for injection Subcutaneous Use TABLE OF CONTENTS
EVER Pharma D-mine Pen Pen injector for Apomorphine 10 mg/ml Instructions for Use with Dacepton 3 ml Cartridges Apomorphine hydrochloride hemihydrate solution for injection Subcutaneous Use TABLE OF CONTENTS
USER GUIDE. Melanotan must not be used if you are:
 USER GUIDE This document is for guidance purposes only and in no way replaces any official statements or other legal guidance documentation. This document does not claim to be correct or complete, no one
USER GUIDE This document is for guidance purposes only and in no way replaces any official statements or other legal guidance documentation. This document does not claim to be correct or complete, no one
Community Pharmacy Enhanced Service. Just In Case 4 Core Drugs supply. Stock Holding of Palliative Care Medicines
 Community Pharmacy Enhanced Service Just In Case 4 Core Drugs supply Stock Holding of Palliative Care Medicines Parties to the Agreement Provider: Purchaser: NHS Blackpool 1. Service description 1.1 This
Community Pharmacy Enhanced Service Just In Case 4 Core Drugs supply Stock Holding of Palliative Care Medicines Parties to the Agreement Provider: Purchaser: NHS Blackpool 1. Service description 1.1 This
Instructions For Use PRALUENT (PRAHL-u-ent) (alirocumab) Injection, for Subcutaneous Injection Single-Dose Pre-Filled Syringe (75 mg/ml)
 Instructions For Use PRALUENT (PRAHL-u-ent) (alirocumab) Injection, for Subcutaneous Injection Single-Dose Pre-Filled Syringe (75 mg/ml) Important Information The device is a single-dose pre-filled syringe.
Instructions For Use PRALUENT (PRAHL-u-ent) (alirocumab) Injection, for Subcutaneous Injection Single-Dose Pre-Filled Syringe (75 mg/ml) Important Information The device is a single-dose pre-filled syringe.
PROCEDURE REF NO SABP/EXECUTIVE BOARD/0017
 PROCEDURE REF NO SABP/EXECUTIVE BOARD/0017 NAME OF PROCEDURE: Medicines Procedure: Patient Group Directions for the Administration of Hepatitis B Vaccine for SABP Drug and Alcohol Teams. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE:
PROCEDURE REF NO SABP/EXECUTIVE BOARD/0017 NAME OF PROCEDURE: Medicines Procedure: Patient Group Directions for the Administration of Hepatitis B Vaccine for SABP Drug and Alcohol Teams. PURPOSE OF PROCEDURE:
Types of insulin. Your blood glucose levels. Types of insulin
 Different types of insulin are available for people with diabetes. If you need insulin, you and your diabetes team will look at the options and decide which type fits best with your lifestyle and blood
Different types of insulin are available for people with diabetes. If you need insulin, you and your diabetes team will look at the options and decide which type fits best with your lifestyle and blood
Lilly. Disposable Insulin Delivery Device User Manual
 1 PV 3734 AMP Lilly Disposable Insulin Delivery Device User Manual Instructions for Use Read and follow all of these instructions carefully. If you do not follow these instructions completely, you may
1 PV 3734 AMP Lilly Disposable Insulin Delivery Device User Manual Instructions for Use Read and follow all of these instructions carefully. If you do not follow these instructions completely, you may
Appendix C. Aneurin Bevan Health Board. Smoke Free Environment Policy
 Appendix C Aneurin Bevan Health Board Smoke Free Environment Policy Content 1. Policy statement 2. Introduction 3. Smoking restrictions within the Health Board 4. Responsibilities 5. Staff working in patients
Appendix C Aneurin Bevan Health Board Smoke Free Environment Policy Content 1. Policy statement 2. Introduction 3. Smoking restrictions within the Health Board 4. Responsibilities 5. Staff working in patients
Administration of Hepatitis A and B Vaccine
 PRACTICE: Ref No: PGD/ONEL/2011/006 Valid from December 2011 Valid to December 2013 Supersedes PGD: Any previous PGD used to administer Twinrix Adult and Paediatric vaccine Professional groups covered
PRACTICE: Ref No: PGD/ONEL/2011/006 Valid from December 2011 Valid to December 2013 Supersedes PGD: Any previous PGD used to administer Twinrix Adult and Paediatric vaccine Professional groups covered
BEST 4 Diabetes. Optimisation of insulin module
 BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
MS Society Safeguarding Adults Policy and Procedure (Scotland)
 MS Society Safeguarding Adults Policy and Procedure (Scotland) Safeguarding Adults Policy The phrase adult support and protection is used instead of safeguarding in Scotland. However for consistency across
MS Society Safeguarding Adults Policy and Procedure (Scotland) Safeguarding Adults Policy The phrase adult support and protection is used instead of safeguarding in Scotland. However for consistency across
BEST 4 Diabetes. Optimisation of insulin module
 BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
Patient Group Directions (PGDs)
 Patient Group Directions (PGDs) Document level: Trustwide (TW) Code: MP2 Issue number: 4 Lead executive Authors details Type of document Target audience Document purpose Medical Director Senior Clinical
Patient Group Directions (PGDs) Document level: Trustwide (TW) Code: MP2 Issue number: 4 Lead executive Authors details Type of document Target audience Document purpose Medical Director Senior Clinical
Placename CCG. Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare
 Placename CCG Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for the funding of insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring devices for patients with diabetes 1 Introduction 1.1 This document
Placename CCG Policies for the Commissioning of Healthcare Policy for the funding of insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring devices for patients with diabetes 1 Introduction 1.1 This document
AUDIT TOOL FOR SELF INSPECTION OF COMPLIANCE WITH QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM FOR PATIENT GROUP DIRECTIONS
 AUDIT TOOL FOR DISPENSING SERVICES COMPILED BY: Lynn Morrison ISSUE 1 CHECKED BY: Colette Byrne NUMBER: ISSUE DATE: 01.12.07 SUPERSEDES: NEW REVIEW DATE: 01.12.09 AUDIT TOOL FOR SELF INSPECTION OF COMPLIANCE
AUDIT TOOL FOR DISPENSING SERVICES COMPILED BY: Lynn Morrison ISSUE 1 CHECKED BY: Colette Byrne NUMBER: ISSUE DATE: 01.12.07 SUPERSEDES: NEW REVIEW DATE: 01.12.09 AUDIT TOOL FOR SELF INSPECTION OF COMPLIANCE
Developed By Name Signature Date
 Patient Group Direction 2155 version 2.0 Administration / Supply of Inhaled Salbutamol in Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Trust Date of Introduction:
Patient Group Direction 2155 version 2.0 Administration / Supply of Inhaled Salbutamol in Asthma by Registered Practitioners employed by Torbay and South Devon NHS Foundation Trust Date of Introduction:
All Saints First School Administering of Medicines Policy
 All Saints First School Administering of Medicines Policy Success Indicators The following indicators will demonstrate the level of compliance with this policy and its procedures: a) Employees who are
All Saints First School Administering of Medicines Policy Success Indicators The following indicators will demonstrate the level of compliance with this policy and its procedures: a) Employees who are
CHEMOTHERAPY NETWORK GROUP POLICY FOR ADMINISTRATION OF CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY
 CHEMOTHERAPY NETWORK GROUP POLICY FOR ADMINISTRATION OF CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY Version 4.0 March 2016 Review date March 2018 Introduction It is the purpose of this policy to provide clear guidelines that
CHEMOTHERAPY NETWORK GROUP POLICY FOR ADMINISTRATION OF CYTOTOXIC CHEMOTHERAPY Version 4.0 March 2016 Review date March 2018 Introduction It is the purpose of this policy to provide clear guidelines that
Consultation Group: Dr Amalia Mayo, Paediatric Consultant. Review Date: March Uncontrolled when printed. Version 2. Executive Sign-Off
 Policy For The Adjustment Of Insulin Injections By Paediatric Diabetes Specialist Nurses/Community Paediatric Nurses Diabetes Working With Children Within NHS Grampian Co-ordinators: Lead Paediatric Diabetes
Policy For The Adjustment Of Insulin Injections By Paediatric Diabetes Specialist Nurses/Community Paediatric Nurses Diabetes Working With Children Within NHS Grampian Co-ordinators: Lead Paediatric Diabetes
Professional Development: proposals for assuring the continuing fitness to practise of osteopaths. draft Peer Discussion Review Guidelines
 5 Continuing Professional Development: proposals for assuring the continuing fitness to practise of osteopaths draft Peer Discussion Review Guidelines February January 2015 2 draft Peer Discussion Review
5 Continuing Professional Development: proposals for assuring the continuing fitness to practise of osteopaths draft Peer Discussion Review Guidelines February January 2015 2 draft Peer Discussion Review
Alcohol and Substance Policy
 Alcohol and Substance Policy Lead Manager Responsible Director Approved by Kenneth Fleming, Head of Health & Safety Anne MacPherson, Director of Human Resource and Organisational Development Health & Safety
Alcohol and Substance Policy Lead Manager Responsible Director Approved by Kenneth Fleming, Head of Health & Safety Anne MacPherson, Director of Human Resource and Organisational Development Health & Safety
Care homes - Homely remedies
 Bulletin 72 August 2014 Community Interest Company Care homes - Homely remedies Care home staff have a recognised duty of care to be able to respond to minor symptoms experienced by residents. A homely
Bulletin 72 August 2014 Community Interest Company Care homes - Homely remedies Care home staff have a recognised duty of care to be able to respond to minor symptoms experienced by residents. A homely
HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen
 1 Instructions for Use HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen (70% human insulin isophane suspension 30% human insulin injection [rdna origin]) 100 units/ml, 3 ml pen Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking
1 Instructions for Use HUMULIN 70/30 KwikPen (70% human insulin isophane suspension 30% human insulin injection [rdna origin]) 100 units/ml, 3 ml pen Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking
A Fact Sheet for Parents and Carers Insulin and Diabetes
 A Fact Sheet for Parents and Carers Insulin and Diabetes In type 1 diabetes the body stops producing insulin. Insulin therapy is essential in the treatment of type 1 diabetes, together with a healthy eating
A Fact Sheet for Parents and Carers Insulin and Diabetes In type 1 diabetes the body stops producing insulin. Insulin therapy is essential in the treatment of type 1 diabetes, together with a healthy eating
SINGLE USE MEDICAL DEVICES POLICY
 SINGLE USE MEDICAL DEVICES POLICY First Issued by/date BWW /BKW March 2001 Issue Version Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date 2 Update May 2011 Named Responsible Officer:- Approved
SINGLE USE MEDICAL DEVICES POLICY First Issued by/date BWW /BKW March 2001 Issue Version Purpose of Issue/Description of Change Planned Review Date 2 Update May 2011 Named Responsible Officer:- Approved
New York State Vaccine Program Vaccine Restitution Policy
 Purpose New York State (NYS) provides vaccine worth approximately $79 million to Vaccines for Children (VFC) providers in New York State (outside of New York City) each year at no cost to providers. As
Purpose New York State (NYS) provides vaccine worth approximately $79 million to Vaccines for Children (VFC) providers in New York State (outside of New York City) each year at no cost to providers. As
Safeguarding Children and Young People Policy
 Safeguarding Children and Young People Policy Policy Summary This policy outlines our commitment to keeping the children and young people who engage with the Red Cross safe. It outlines the expectations
Safeguarding Children and Young People Policy Policy Summary This policy outlines our commitment to keeping the children and young people who engage with the Red Cross safe. It outlines the expectations
North of England Cancer Network. Policies and Procedures. Standards for the Safe Use of Oral Anticancer Medicines
 \ North of England Cancer Network Policies and Procedures Standards for the Safe Use of Oral Anticancer Medicines NECN Oral Anticancer medicine Policy version 1.6 Page 1 of 17 Issue Date: Feb 2017 Contents
\ North of England Cancer Network Policies and Procedures Standards for the Safe Use of Oral Anticancer Medicines NECN Oral Anticancer medicine Policy version 1.6 Page 1 of 17 Issue Date: Feb 2017 Contents
GG&C PGD ref no: 2016/1408 YOU MUST BE AUTHORISED BY NAME, UNDER THE CURRENT VERSION OF THIS PGD BEFORE YOU ATTEMPT TO WORK ACCORDING TO IT
 GG&C PGD ref no: 2016/1408 YOU MUST BE AUTHORISED BY NAME, UNDER THE CURRENT VERSION OF THIS PGD BEFORE YOU ATTEMPT TO WORK ACCORDING TO IT Clinical Condition Indication: Active immunisation against disease
GG&C PGD ref no: 2016/1408 YOU MUST BE AUTHORISED BY NAME, UNDER THE CURRENT VERSION OF THIS PGD BEFORE YOU ATTEMPT TO WORK ACCORDING TO IT Clinical Condition Indication: Active immunisation against disease
Document Details Patient Group Direction Hepatitis A vaccine (Havrix Monodose ) Trust Ref No Local Ref (optional) Main points the
 Document Details Title Patient Group Direction Hepatitis A vaccine (Havrix Monodose ) Trust Ref No 1506-41174 Local Ref (optional) Main points the Active immunisation against infection caused by Hepatitis
Document Details Title Patient Group Direction Hepatitis A vaccine (Havrix Monodose ) Trust Ref No 1506-41174 Local Ref (optional) Main points the Active immunisation against infection caused by Hepatitis
A quick guide to diabetes for people changing from tablets to insulin (type 2 diabetes) Diabetes and Endocrinology Patient Information Leaflet
 A quick guide to diabetes for people changing from tablets to insulin (type 2 diabetes) Diabetes and Endocrinology Patient Information Leaflet What is diabetes? Diabetes is a condition where the amount
A quick guide to diabetes for people changing from tablets to insulin (type 2 diabetes) Diabetes and Endocrinology Patient Information Leaflet What is diabetes? Diabetes is a condition where the amount
GET TO KNOW YOUR PEN. Needle cap. Rubber seal. Insulin scale. Pen cap. Cartridge holder Plunger. Insulin name. Dose window Dose. pointer.
 GET TO KNOW YOUR PEN You ve taken an important step by adding Toujeo (insulin glargine injection) U-3 to your diabetes treatment plan. Toujeo is a long-acting insulin used to treat adults with type and
GET TO KNOW YOUR PEN You ve taken an important step by adding Toujeo (insulin glargine injection) U-3 to your diabetes treatment plan. Toujeo is a long-acting insulin used to treat adults with type and
HumaPen LUXURA HD INSULIN DELIVERY DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 1 HumaPen LUXURA HD INSULIN DELIVERY DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE For use only with Lilly 3 ml insulin cartridges (100 units/ml). Do not use other brands of insulin cartridges. The color of your HumaPen
1 HumaPen LUXURA HD INSULIN DELIVERY DEVICE INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE For use only with Lilly 3 ml insulin cartridges (100 units/ml). Do not use other brands of insulin cartridges. The color of your HumaPen
Information about cases being considered by the Case Examiners
 Information about cases being considered by the Case Examiners 13 October 2016 1 Contents Purpose... 3 What should I do next?... 3 Background... 4 Criteria that Case Examiners will consider... 5 Closing
Information about cases being considered by the Case Examiners 13 October 2016 1 Contents Purpose... 3 What should I do next?... 3 Background... 4 Criteria that Case Examiners will consider... 5 Closing
EVOGAM. Information for patients Evogam NZ Patient Brochure Update FA3
 EVOGAM Information for patients 11179 Evogam NZ Patient Brochure Update FA3 Information for patients and caregivers about EVOGAM This booklet is designed to help you follow the training you will have been
EVOGAM Information for patients 11179 Evogam NZ Patient Brochure Update FA3 Information for patients and caregivers about EVOGAM This booklet is designed to help you follow the training you will have been
Hounslow Safeguarding Children Board. Training Strategy Content.. Page. Introduction 2. Purpose 3
 Hounslow Safeguarding Children Board. Training Strategy 2018-2020. Content.. Page Introduction 2 Purpose 3 What does the Training Strategy hope to achieve?. 4 Review.. 4 Local context.. 4 Training sub
Hounslow Safeguarding Children Board. Training Strategy 2018-2020. Content.. Page Introduction 2 Purpose 3 What does the Training Strategy hope to achieve?. 4 Review.. 4 Local context.. 4 Training sub
This Diabetes Policy should be read in conjunction with the Dealing with Medical Conditions Policy of Auburn South Preschool.
 DIABETES POLICY Mandatory Quality Area 2 The content of this policy was developed for ELAA by advocacy and diabetes educators at Diabetes Australia Vic and the Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne s manager
DIABETES POLICY Mandatory Quality Area 2 The content of this policy was developed for ELAA by advocacy and diabetes educators at Diabetes Australia Vic and the Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne s manager
Policy for the Provision of Insulin Pumps for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
 Policy for the Provision of Insulin Pumps for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Version No. Changes Made Version of July 2018 V0.5 Changes made to the policy following patient engagement including: - the
Policy for the Provision of Insulin Pumps for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus Version No. Changes Made Version of July 2018 V0.5 Changes made to the policy following patient engagement including: - the
