Handgrip Strength in Individuals with Long- Standing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A preliminary report
|
|
|
- Oliver Owen
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Handgrip Strength in Individuals with Long- Standing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A preliminary report Ezema C.I., Iwelu E.V., Abaraogu U.O., Olawale O.A. 1 Department of Medical Rehabilitation, University of Nigeria, Enugu Campus, Enugu State 2 Department of Physiotherapy, University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Itiku-Ozall, Enugu State 3 Department of Physiotherapy,College of Medicine, University of Lagos, Idi-Araba, Lagos Correspondence: U.O. Abaraogu uabaraogu@yahoo.com SUMMARY Adequate muscle strength is required for optimum productivity and low muscle strength is a predictor of physical limitations. Individuals with long-standing type 2 diabetes mellitus have been found to have an increased risk of developing functional disabilities. Handgrip strength is a reliable measurement of the disability index. This study was designed to determine the effect of type 2 diabetes on handgrip strength in adults. Twenty adult patients with a clinical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (10 males, mean age: 52.9 ± 9.01 years and 10 females, mean age: 52.6 ± 5.71 years) and 20 apparently healthy adults (10 males, mean age: 53.1 ± 8.94 years and 10 females, mean age 54.5yrs±5.56 years) who met the inclusion criteria participated in the study. Handgrip strength was measured with an isometric hand dynamometer and comparisons were made between diabetic and non-diabetic males as well as between diabetic and non-diabetic females. Thev independent t-test were used to analyse the significance difference in hand grip strength between the diabetic and the non- diabetic subjects (p=0.05). Results showed significant differences in the mean handgrip strength between the male diabetic and nondiabetic subjects (p<0.004), as well as between the female diabetic and non-diabetic subjects (p<0.002). Long-standing type 2 diabetes mellitus seems to result in a decrease in handgrip strength in both male and female adults. This physical limitation may contribute to low productivity in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. KEY WORDS: Type 2 diabetes mellitus, handgrip, muscle strength, disability INTRODUCTION Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic condition characterized by persistent hyperglycaemia, with resultant morbidity and mortality (Cohen, 2007). Although there is a paucity of data on the prevalence of diabetes in Africa, available data suggest that diabetes is emerging as a major health problem (Jean et al, 1996). According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), the prevalence of type 2 diabetes exceeds 250 million worldwide, with Africa accounting for at least 10 percent of this number, with a minimum of six million sufferers in Nigeria (Chiejina, 2009). Muscle weakness has been associated with type 2 diabetes, even among subjects with high body mass indices (Balogun et al, 1991; Bohannon, 2001; Clerke and Clerke, 2001). Helmersson et al (2004) attribute this to insulin resistance and hyperglycaemia, which cause a reduction in the number of mitochondria in the muscle cells, a decrease AJPARS Vol. 4, Nos. 1 & 2, June 2012, pp doi: 67
2 Ezema, Iwelu, Abaraogu, Olawale in glycogen synthesis and an increase in the amount of circulating systemic inflammatory cytokines, all of which have a detrimental effect on the skeletal muscles. The relationship between muscle contractile functions and force generation on one side and hyperglycaemia had earlier been proposed by Helander et al (2002). Furthermore, Deal (1998) associated the duration of diabetes (>6 years) and poor glycaemic control with even poorer muscle quality and an increased incidence of musculoskeletal conditions like carpal-tunnel syndrome, muscle atrophy and Duputyren s contracture. However, little is known of the trend between long duration type 2 diabetes and handgrip strength in southeast Nigeria. This study was therefore designed to compare the handgrip strength of individuals with long standing type 2 diabetes with the handgrip strength of their apparently healthy age-matched counterparts. This is a preliminary report that precedes a longitudinal cohort study on this population. METHODOLOGY Subjects Forty subjects participated in the study, and were divided into two groups (four subgroups, numbering 10 each). Group A consisted of 20 (10 males and 10 females) apparently healthy adult staff of the University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital (UNTH), Ituku Ozalla and the University of Nigeria Enugu Campus (UNEC), all in Enugu State, southeast Nigeria. Group B consisted of 20 (10 males and 10 females) type 2 diabetes mellitus patients attending the diabetic clinic of UNTH, who had been clinically diagnosed as diabetics for at least 6 years before the commencement of this study. Information on the reported age at diagnosis was used to define diabetes duration. Plasma glucose for the control group was measured using an automated glucose oxidase reaction (Vitros 950 analyzer; Johnson & Johnson, Rochester, NY), to screen out those that were diabetic even without knowing it. Subjects were all right-handed, had no history of upper limb amputation and fell between the ages of 39 to 65 years. None of the participants was involved in an occupation that required manual handling or sports that may have conferred on them the advantage of a better handgrip. There was no difficulty performing basic activities of daily living and no reported use of walking aids. All the diabetic subjects were either on only hypoglycaemic agents, or hypoglycaemic agents and a diabetes diet formula. None of the subjects was on hospital admission at the time of the study. All participants gave written informed consent to participate in the study. Materials 1. Saehan hydraulic dynamometer: model SH5001 (Saehan Corporation, Mansan, South Korea) This was used to measure the hand grip strength. 2. Automated glucose oxidase reaction (Vitros 950 Analyzer; Johnson & Johnson, Rochester, NY) This was used to check the diabetic status of the control group. 3. Weighing scale (Hanson, Ireland) This was used to measure the weight of the participants to the nearest 1.0 kilogramme (kg). It has a range of 0-120kg. 4. Height Meter (Secca, England) This was used to measure the height of the participants to the nearest 0.1cm. It has a range of 0-200cm. 5. Time piece: A calibrated lugar, lug 2150 (made in Germany). This was used for timing the period of contractions and the period between contractions. Procedure Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the UNTH Health Research and Ethics Committee. Written consent was obtained from the participants prior to the commencement of the study. At the beginning of the study, demographic data (i.e., age, sex, weight, and height) were obtained and recorded. Height and body weight were measured on a height metre and a calibrated weighing scale, with the subjects not wearing shoes. The measurement of handgrip strength was done in the waiting room outside the consulting rooms of the diabetic clinic. The American Society of Hand Therapists standardized arm position for handgrip testing was utilized. Each subject was positioned in a straight back chair (about 46cm in height, without an arm rest) with both feet flat on the floor. The arm position was demonstrated to the subjects. Each subject was asked to place the right hand on their right thigh and assume a position of adducted and neutrally rotated shoulder, the elbow in approximately 90 degree flexion, with the forearm and wrist in neutral position, and the fingers flexed for the needed maximum contraction. They were instructed to breathe in through the nose and exhale through a pursed lip after a maximum grip effort was made. A demonstration of maximum handgrip strength was given to each subject before they were asked to do it themselves. Each subject was instructed to squeeze the handle of the dynamometer, which was placed vertically in their hands, as hard as possible. The period of the effort did not exceed 5 seconds. A period of 30 seconds rest was given between two trials 68 AJPARS Vol. 4, Nos. 1 & 2, June 2012, pp
3 Handgrip Strength in Individuals with Long-standing Type 2 Diabetes for the dominant (right) hand to be tested and the average of the two trials was taken. Data analysis Data collected were analysed using SPSS (Version 15). The results were presented using descriptive statistics: mean, standard deviation and range. The independent t-test (p=0.05) was used to assess the significance in the difference between handgrip strength among the different groups. RESULTS The demographic characteristics of the subjects are shown in table 1. The age ranges for the male groups were years for the diabetic group (MDG) and years for the male non-diabetic group (MNG). The mean ages of subjects in the MDG and the MNG were ± 9.01 years and ± 5.56 years respectively. The BMI values ranged from with a mean value of ± 1.50 in the MDG and with a mean value of ± 2.30 (table 1). Handgrip strength ranged between with a mean value of ± 3.39 for MDG and with a mean value of 48.77±3.86 for MNG. The independent t-test analysis showed that there was a significant difference between the mean handgrip strength of the male diabetic group and the non-diabetic group (p<0.004, table 2). Table 1. Demographic and anthropometric characteristics of the subjects (n = 40) Female (n = 20) M ale (n = 20) Diabetic (n = 10) Non-diabetic (n = 10) Diabetic (n = 10) Non-diabetic (n = 10) M ean±sd Range M ean±sd Range M ean±sd Range M ean±sd Range Age (yrs) ± ± ± ± Height (cm) ± ± ± ± 7.57 Weight (kg) 66 ± ± ± ± BM I (kg/m 2 ) ± ± ± ± 2.30 Table 2. Statistical analysis of handgrip strength of the subjects Diabetic M ean±sd Non-diabetic M ean±sd N df Independent t-test P-value M ale ± ± * Female ± ± * The age ranges for the female groups were 45-65years with a mean value of ± 5.71 for the diabetic group (FDG) and years with a mean value of ± 5.56 for the non-diabetic group (FNG) (table 1). The FDG had BMI values ranging from with a mean value of ± 3.50, while the FNG had BMI values falling between with a mean value of ± 2.96 (table 1). The handgrip strength for the female groups ranged from with a mean value of ± 1.39 for the FDG and with a mean value of ± 3.04 for FNG. There was a significant difference in the mean values of handgrip strength of the FDG and FNG (p < 0.05). DISCUSSION The age range of participants in this study, shows that type 2 diabetes mellitus occurs in adults at an earlier age. There 2 was an abnormally high BMI (>25kg/m ) among the male and female non-diabetic groups, suggesting a latent risk for development of type 2 diabetes even among the apparently healthy subjects. Our study clearly demonstrated that upper limb muscle quality was consistently lower in adults with a long duration (>6 years) of type 2 diabetes, regardless of sex. This finding plausibly explains the increased risk of upper limb functional limitations in older individuals with long-standing type diabetes. Although we were able to match the control subjects sex, age and physical activity, AJPARS Vol. 4, Nos. 1 & 2, June 2012, pp
4 Ezema, Iwelu, Abaraogu, Olawale we could not say whether muscle weakness in type 2 diabetics was due to reduced muscle mass or poor muscle quality because upper limb muscle mass was not assessed. This study particularly showed that type 2 diabetes may be occurring at an earlier age than previously thought. It is also possible that individuals (especially where routine medical checkup is not a common practice) may have subclinical type 2 diabetes for many years without knowing until hyperglycaemic and neuropathic symptoms manifest. This was the discovery during the screening for the control group. In this instance, age of diagnosis is usually delayed and may pose some difficulty in tracking the effect response trend between duration of diabetes and muscle quality. A backward extrapolation in a cohort study shortly after the clinical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes has strongly suggested that beta-cell dysfunction commences at least 10 years before hyperglycaemia develops (UK Prospective Diabetes Study, 1995; Temelkova, 2002). However, Boyle et al (2001) had earlier found that most of the diabetics in the developed countries are over 60 years. The mean BMI values of ± 1.50 in the diabetic males and ± 2.30 in their non-diabetic counterparts suggest abnormally high BMI values in the non-diabetic males compared to their diabetic counterparts. This could be due to the weight loss associated with long-standing diabetes; or some of the diabetic individuals were on a dietary formula and, therefore, may have had the benefit of weight control. The mean BMI values of ± 2.30 and ± 2.96 for the apparently healthy male and female groups could imply a latent risk for the development of type 2 diabetes among the apparently healthy subjects. One would expect that this would translate to a better handgrip in these individuals when compared to their non-diabetic counterparts. However, the reverse, surprisingly, was the case. Aponectin, an adipocytokine, which plays an important role in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, and also as a major modulator of insulin action, is characterized by lower circulating levels in the presence of obesity (Chandran et al, 2003). Also, subclinical neuropathic processes involving motor neurons might be another possible underlying mechanism for the poor muscle function in long-standing diabetes (Lesniewski et al, 2003). The mean handgrip strength of the non-diabetic males was higher than the value for their diabetic counterparts, which stood at There was also a higher mean handgrip strength in the female nondiabetics when compared to the value of the diabetic females. These differences in the mean handgrip strength were also found to be significant at p < Insulin resistance may have been responsible for the muscle weakness (Sayer et al, 2005) and, therefore, the decreased grip strength. Rantanen et al (1999) and Leveille et al (2004) have independently reported decreased handgrip strength in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. However, Andersen et al (1997) and Andersen et al (2004) opposed this view, insisting that grip strength is not compromised in long-standing diabetes type 2. These differences in the reports may be due to the lack of baseline record of grip strength in all the studies, thereby making it impossible for the change in grip strength after the onset of diabetes to be determined. The major limitation of this study was the sample size. Also, cross-sectional studies like this, at best, establish associations between variables but never a cause and effect relationship. Furthermore, no data exists on muscle quality at baseline, which may have an important mediating role in determining future muscle quality of individuals with type 2 diabetes. The study, however, has clinical implications for rehabilitation teams because individuals with longstanding diabetes are at increased risk of developing physical disability. If handgrip assessments are done for a diabetic at the time of diagnosis and routine monitoring incorporated during clinical visits, the development of disability can be detected and preventive modalities like resistive training exercise programme can be instituted to decelerate the rate of deterioration of muscle function before it is too late. Also, the fact that few of our control group subjects were excluded from this study on the basis that they showed evidence of diabetes goes to show that the prevalence of diabetes in our population may have been under-reported. CONCLUSION Type 2 diabetes is associated with poorer upper limb muscle strength and quality. These features may contribute to upper limb functional limitation and physical disability in individuals with long-standing type 2 diabetes. Cohort studies, with a larger sample size, which measure grip strength as well as muscle mass at the point of diagnosis are needed to determine if long-standing type 2 diabetes is associated with a longitudinal decline in upper limb strength and to evaluate the association between loss of muscle mass and muscle quality in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus. 70 AJPARS Vol. 4, No. 1, June 2012, pp
5 Handgrip Strength in Individuals with Long-standing Type 2 Diabetes ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The authors immensely appreciate the cooperation and help of the physicians at the diabetic clinic of UNTH. References Anderson, H., P.C. Gadeberg, B. Brock and J. Jakobsen Muscular atrophy in diabetic neuropathy: A stereological magnetic resonance imaging study. Diabetologia 40: Andersen, H., S. Nielsen, C.E. Mogensen and J. Jakobsen Muscle strength in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 53: Balogun, J.A., C.T. Akomolafe and L.O. Amusa Effect of testing posture and elbow position. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 72: Bohannon, R.W Dynamometer measurements of handgrip strength predict multiple outcomes. Percept Motor Skills 93(2): Boyle, J.P., A.A. Honeycutt, K.M. Narayan, T.J. Hoerger, L.S. Geiss, H. Chen and T.J. Thompson Projection of diabetes burden through 2050: Impact of changing demography and disease prevalence in the US. Diabetes Care 24: Chandran, M., S.A. Phillip, T. Ciaraldi and R.R. Henry Adiponectin: More than just another fat cell hormone? Diabetes Care 26: Chiejina, A Diabetes Mellitus: Fast Becoming An Epidemic. Summit on Changing Diabetes in Nigeria. Lagos, Nigeria. Clerke, A. and J. Clerke A literature review of the effects of handedness on isometric grip difference of the left and right hands. American Journal of Occupational Therapy 55(2): Cohen, Z Type 2 diabetes. Accessed on 8/6/2011. Deal, C The Endocrine System: Oxford Textbook of nd Rheumatology. 2 edition. London: Oxford University Press. Helander, I., H. Westerblad and A. Katz Effects of glucose + on contractile function, [Ca2 ]i, and glycogen in isolated mouse skeletal muscle. American Journal of Cell Physiology 282: Helmersson, J., B. Vessby, A. Larsson and S. Basu Association of type 2 diabetes with cyclooxygenase-mediated inflammation and oxidative stress in an elderly population. Circulation 109: Jean, M., F. Claude and B.K. Nagan Guidelines for the Management of NIDDM in Africa. A Consensus Document. Greece, Novo Nordisk. Lesniewski, L.A., T.A. Miller and R.B. Armstrong Mechanisms of force loss in diabetic mouse skeletal muscle. Muscle and Nerve 28: Leveille, S.G., L.P. Fried, W. McMullen and J.M. Guralnik Advancing the taxonomy of disability in the older adults. Journal of Gerontology 59: Rantanen, T., J.M. Guralnik, D. Foley, K.. Masaki, S. Leveille, J.D. Curb and L. White Midlife hand grip strength as a predictor of old age disability. JAMA 281: Sayer, A.A., E.M. Dennison,.H.E. Syddall, H.J. Gilbody, D.I. Phillips and C. Cooper Type 2 diabetes, muscle strength, and impaired physical function: The tip of the iceberg? Diabetes Care 28: Temelkova, K.T., E. Henkel, C. Koehler, K. Karrei and M. Hanefeld Subclinical inflammation in newly-detected type 2 diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetologia 45: 151. UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group UK Prospective Diabetes Study 16. Overview of six years therapy of type 2 diabetes: A progressive disease. Diabetes 44: AJPARS Vol. 4, Nos. 1 & 2, June 2012, pp
Effectiveness of strength training on hand function in patients with Diabetic neuropathy
 Original article Effectiveness of strength training on hand function in patients with Diabetic neuropathy Komal.D.Thorat 1, Dr Suvarna..Ganvir 2 1 Intern PDVVPFs College of Physiotherapy, Ahmednagar 2
Original article Effectiveness of strength training on hand function in patients with Diabetic neuropathy Komal.D.Thorat 1, Dr Suvarna..Ganvir 2 1 Intern PDVVPFs College of Physiotherapy, Ahmednagar 2
Effectiveness of strength training on hand function in patients with Diabetic neuropathy
 Original article Effectiveness of strength training on hand function in patients with Diabetic neuropathy Komal.D.Thorat 1, Dr Suvarna..Ganvir 2 1 Intern, PDVVPFs College of Physiotherapy, Ahmednagar,
Original article Effectiveness of strength training on hand function in patients with Diabetic neuropathy Komal.D.Thorat 1, Dr Suvarna..Ganvir 2 1 Intern, PDVVPFs College of Physiotherapy, Ahmednagar,
RELATIONSHIP OF PERIPHERAL MEDIAN MOTOR NERVE CONDUCTION VELOCITY TO GRIP STRENGTH
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE RELATIONSHIP OF PERIPHERAL MEDIAN MOTOR NERVE CONDUCTION VELOCITY TO GRIP STRENGTH Sumit Garg 1, Ramya CS, Vinutha Shankar 2, Karthiyanee Kutty 2, JL Agarwal 1 1. Saraswathi Institute
ORIGINAL ARTICLE RELATIONSHIP OF PERIPHERAL MEDIAN MOTOR NERVE CONDUCTION VELOCITY TO GRIP STRENGTH Sumit Garg 1, Ramya CS, Vinutha Shankar 2, Karthiyanee Kutty 2, JL Agarwal 1 1. Saraswathi Institute
School Visits Fitness Testing
 School Visits Fitness Testing 10m Sprint Test Purpose: To measure an athlete s ability to accelerate Equipment required: timing gates or stop watch, measuring tap - Participant ready s themselves on the
School Visits Fitness Testing 10m Sprint Test Purpose: To measure an athlete s ability to accelerate Equipment required: timing gates or stop watch, measuring tap - Participant ready s themselves on the
Effect of hand dominance and body mass index on maximal isometric hand grip strength in normal young adults
 Original article: Effect of hand dominance and body mass index on maximal isometric hand grip strength in normal young adults 1 Dr Sonali S. Pande, 2 Dr Nazish Shaikh, 3 Dr Arun Chutani 1Associate Prof,
Original article: Effect of hand dominance and body mass index on maximal isometric hand grip strength in normal young adults 1 Dr Sonali S. Pande, 2 Dr Nazish Shaikh, 3 Dr Arun Chutani 1Associate Prof,
Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects
 Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects Test protocol Muscle test procedures. Prior to each test participants
Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects Test protocol Muscle test procedures. Prior to each test participants
Hand grip strength is a measure of. Reliability and validity of an electronic dynamometer for measuring grip strength
 Research Reliability and validity of an electronic dynamometer for measuring grip strength Deborah Allen, Fiona Barnett Aims: This article describes a study aiming to establish the concurrent validity
Research Reliability and validity of an electronic dynamometer for measuring grip strength Deborah Allen, Fiona Barnett Aims: This article describes a study aiming to establish the concurrent validity
Osteoporosis Protocol
 PRODUCTS HELPING PEOPLE HELP THEMSELVES! Osteoporosis Protocol Rehabilitation using the Resistance Chair General Information Osteoporosis is a condition where bones gradually decrease in mass or density
PRODUCTS HELPING PEOPLE HELP THEMSELVES! Osteoporosis Protocol Rehabilitation using the Resistance Chair General Information Osteoporosis is a condition where bones gradually decrease in mass or density
Hands on Sports Therapy KNOWLEDGE REVIEW QUESTIONS 2004 Thomson Learning It can help to shape a basic fitness training programme
 Hands on Sports Therapy KNOWLEDGE REVIEW QUESTIONS 2004 Thomson Learning 1 CHAPTER 13 Knowledge Review Q1: Why is fitness testing useful? A1: Fitness testing is useful for various reasons: 1. It can help
Hands on Sports Therapy KNOWLEDGE REVIEW QUESTIONS 2004 Thomson Learning 1 CHAPTER 13 Knowledge Review Q1: Why is fitness testing useful? A1: Fitness testing is useful for various reasons: 1. It can help
This slide set provides an overview of the impact of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the United States, focusing on epidemiology, costs both
 This slide set provides an overview of the impact of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the United States, focusing on epidemiology, costs both direct and indirect and the projected burden of diabetes,
This slide set provides an overview of the impact of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the United States, focusing on epidemiology, costs both direct and indirect and the projected burden of diabetes,
Physical Capability Exam Testing Protocol
 Test Duration: ~ min Physical Capability Exam Testing Protocol Pinch Gauge Grip Dynamometer Inclinometer Stop Watch Lift Box Table Weight Plates (5 lbs., lbs., lbs., 50 lbs., 0 lbs.) Physical Capability
Test Duration: ~ min Physical Capability Exam Testing Protocol Pinch Gauge Grip Dynamometer Inclinometer Stop Watch Lift Box Table Weight Plates (5 lbs., lbs., lbs., 50 lbs., 0 lbs.) Physical Capability
Unit 1: Fitness for Sport and Exercise. Fitness Testing
 Unit 1: Fitness for Sport and Exercise Fitness Testing Importance of fitness testing Gives baseline data for monitoring/improving performance Can design training programmes based on test results and determine
Unit 1: Fitness for Sport and Exercise Fitness Testing Importance of fitness testing Gives baseline data for monitoring/improving performance Can design training programmes based on test results and determine
The Effects of Upper -Body and Lower -Body Fatigue on Standing Balance
 The Effects of Upper -Body and Lower -Body Fatigue on Standing Balance F. Cogswell 1, B. Dietze 1, F. Huang 1 1 School of Kinesiology, The University of Western Ontario No conflicts of interest declared.
The Effects of Upper -Body and Lower -Body Fatigue on Standing Balance F. Cogswell 1, B. Dietze 1, F. Huang 1 1 School of Kinesiology, The University of Western Ontario No conflicts of interest declared.
Exercises After a Mastectomy or Lymph Node Removal
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Exercises After a Mastectomy or Lymph Node Removal If you have had a mastectomy or lymph nodes removed, ask your doctor when you may start exercises. Do not
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Exercises After a Mastectomy or Lymph Node Removal If you have had a mastectomy or lymph nodes removed, ask your doctor when you may start exercises. Do not
Guidance on the Measurement and Estimation of Height and Weight
 APPENDIX 4: Guidance on the Measurement and Estimation of Height and Weight Guidance on the Measurement and Estimation of Height and Weight January 2013 Contents Measuring Weight Estimating weight in the
APPENDIX 4: Guidance on the Measurement and Estimation of Height and Weight Guidance on the Measurement and Estimation of Height and Weight January 2013 Contents Measuring Weight Estimating weight in the
Advanced Life Support (ALS) Paramedic. Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Pre-Employment Candidate Pack
 Advanced Life Support (ALS) Paramedic Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Pre-Employment Candidate Pack Developed by: Mark Jansz (Health & Fitness Advisor) AV Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Version
Advanced Life Support (ALS) Paramedic Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Pre-Employment Candidate Pack Developed by: Mark Jansz (Health & Fitness Advisor) AV Physical Capacity Testing Protocols Version
Spinal Biomechanics & Sitting Posture
 Spinal Biomechanics & Sitting Posture Sitting: weight of the body is transferred to a supporting area 1.Main Contact points (seat) Ischial tuberosities Soft tissues 2. Secondary contact points (other)
Spinal Biomechanics & Sitting Posture Sitting: weight of the body is transferred to a supporting area 1.Main Contact points (seat) Ischial tuberosities Soft tissues 2. Secondary contact points (other)
Overview of the FITNESSGRAM Body Composition Standards
 body composition Body composition refers to the division of total body weight (mass) into components, most commonly fat mass and fat-free mass. The proportion of total body weight that is fat (referred
body composition Body composition refers to the division of total body weight (mass) into components, most commonly fat mass and fat-free mass. The proportion of total body weight that is fat (referred
"INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
Physical Therapy for Your Oncologic Shoulder Replacement
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Physical Therapy for Your Oncologic Shoulder Replacement This handout has information about your oncologic shoulder replacement and the exercises you will need
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Physical Therapy for Your Oncologic Shoulder Replacement This handout has information about your oncologic shoulder replacement and the exercises you will need
Cardiovascular Risk Factors among Diabetic Patients Attending a Nigerian Teaching Hospital. O Alao, S Adebisi, G Jombo, D Joseph, O Damulak, F Puepet
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Endocrinology Volume 6 Number 1 Cardiovascular Risk Factors among Diabetic Patients Attending a Nigerian Teaching Hospital. O Alao, S Adebisi, G Jombo, D Joseph, O Damulak,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Endocrinology Volume 6 Number 1 Cardiovascular Risk Factors among Diabetic Patients Attending a Nigerian Teaching Hospital. O Alao, S Adebisi, G Jombo, D Joseph, O Damulak,
Good Working Positions
 Good Working Positions To understand the best way to set up a computer workstation, it is helpful to understand the concept of neutral body positioning. This is a comfortable working posture in which your
Good Working Positions To understand the best way to set up a computer workstation, it is helpful to understand the concept of neutral body positioning. This is a comfortable working posture in which your
ICU: Rehabilitation Programme
 Information and exercises ICU: Rehabilitation Programme Introduction During an ICU stay, maintaining a patient s stamina, muscle strength and general movement is very important to their prolonged recovery.
Information and exercises ICU: Rehabilitation Programme Introduction During an ICU stay, maintaining a patient s stamina, muscle strength and general movement is very important to their prolonged recovery.
Scapular Protraction in Sitting
 9 Pause and Practice: Scapular Protraction in Sitting This practice lab is an example of putting muscles on length in order to achieve proper alignment of shoulder structures in preparation for facilitating
9 Pause and Practice: Scapular Protraction in Sitting This practice lab is an example of putting muscles on length in order to achieve proper alignment of shoulder structures in preparation for facilitating
GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017
 GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only
GENERAL EXERCISES THUMB, WRIST, HAND BMW MANUFACTURING CO. PZ-AM-G-US I July 2017 Disclosure: The exercises, stretches, and mobilizations provided in this presentation are for educational purposes only
Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, 1
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2012; 36: 394-399 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.394 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Reliability of the Pinch Strength with
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2012; 36: 394-399 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2012.36.3.394 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Reliability of the Pinch Strength with
Session Objectives. Business & Legal Reports, Inc. 0903
 Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
Set Your World in Motion. Skeleton measurement
 Set Your World in Motion Skeleton measurement What is skeleton measurement? Use measurement tools, according to the definition of the size of the bones in various parts of the actor s body is measured
Set Your World in Motion Skeleton measurement What is skeleton measurement? Use measurement tools, according to the definition of the size of the bones in various parts of the actor s body is measured
The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection
 The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection SUPPORT Physiotherapy Intervention Training Manual Authors: Sue Jackson (SJ) Julie
The SUPPORT Trial: SUbacromial impingement syndrome and Pain: a randomised controlled trial Of exercise and injection SUPPORT Physiotherapy Intervention Training Manual Authors: Sue Jackson (SJ) Julie
Early Mobility in the Coronary Intensive Care Unit (CICU)
 Early Mobility in the Coronary Intensive Care Unit (CICU) Information for patients of the CICU and their caregivers This pamphlet has information about why early mobility in the CICU is important. Early
Early Mobility in the Coronary Intensive Care Unit (CICU) Information for patients of the CICU and their caregivers This pamphlet has information about why early mobility in the CICU is important. Early
Using crutches. Crutches after surgery. Safety first! Using and fitting crutches begins on page 2.
 Using and fitting crutches begins on page 2. Your doctor or physiotherapist has told you how much weight you are allowed to place on your leg. Partial weight bearing begins on page 4. Non-weight bearing
Using and fitting crutches begins on page 2. Your doctor or physiotherapist has told you how much weight you are allowed to place on your leg. Partial weight bearing begins on page 4. Non-weight bearing
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis
 Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference.
 Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference. Thank you for your urge to grow and willingness to learn.
Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference. Thank you for your urge to grow and willingness to learn.
Spinal cord injury (SCI) and lower-extremity amputation
 Using the BTE Primus to Measure Grip and Wrist Flexion Strength in Physically Active Wheelchair Users: An Exploratory Study Orit Shechtman, Leanne MacKinnon, Catherine Locklear Key Words: hand strength
Using the BTE Primus to Measure Grip and Wrist Flexion Strength in Physically Active Wheelchair Users: An Exploratory Study Orit Shechtman, Leanne MacKinnon, Catherine Locklear Key Words: hand strength
Older Adult Beginner
 Older Adult Beginner Older Adult - Beginners Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women over the age of 55. These individuals may have joint pain, muscular pain, new to a workout routine,
Older Adult Beginner Older Adult - Beginners Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women over the age of 55. These individuals may have joint pain, muscular pain, new to a workout routine,
On The Road. Training Manual
 On The Road Training Manual ST - 1 Standing External Rotation Strength Training Injury prevention Strengthening the rotator cuff Attach the tubing to a secure location like a fence or the net post. Start
On The Road Training Manual ST - 1 Standing External Rotation Strength Training Injury prevention Strengthening the rotator cuff Attach the tubing to a secure location like a fence or the net post. Start
Endpoints And Indications For The Older Population
 Endpoints And Indications For The Older Population William J. Evans, Head Muscle Metabolism Discovery Unit, Metabolic Pathways & Cardiovascular Therapy Area Outline Functional Endpoints and Geriatrics
Endpoints And Indications For The Older Population William J. Evans, Head Muscle Metabolism Discovery Unit, Metabolic Pathways & Cardiovascular Therapy Area Outline Functional Endpoints and Geriatrics
MOTOR EVALUATION SCALE FOR UPPER EXTREMITY IN STROKE PATIENTS (MESUPES-arm and MESUPES-hand)
 MOTOR EVALUATION SCALE FOR UPPER EXTREMITY IN STROKE PATIENTS (MESUPES-arm and MESUPES-hand) Name patient: Test date - hour: Name examiner: Duration of the test: min Handedness: right/left Support sitting
MOTOR EVALUATION SCALE FOR UPPER EXTREMITY IN STROKE PATIENTS (MESUPES-arm and MESUPES-hand) Name patient: Test date - hour: Name examiner: Duration of the test: min Handedness: right/left Support sitting
Version February 2016
 Version 3.1 29 February 2016 Health and Safety Unit 1 Table of Contents 1. Setting up your computer workstation... 3 Step 1: Adjusting yourself to the correct height... 3 Step 2 Adjusting your Chair...
Version 3.1 29 February 2016 Health and Safety Unit 1 Table of Contents 1. Setting up your computer workstation... 3 Step 1: Adjusting yourself to the correct height... 3 Step 2 Adjusting your Chair...
Humerus. Ulna. Radius. Carpals
 Posture Analysis Exercise T. Armstrong M. Ebersole 1.0 Objectives: 1. Improve skill for rating over all job and identifying specific force and posture problems 2. Learn how to characterize posture 3. Learn
Posture Analysis Exercise T. Armstrong M. Ebersole 1.0 Objectives: 1. Improve skill for rating over all job and identifying specific force and posture problems 2. Learn how to characterize posture 3. Learn
Exercises following Copeland Surface Replacement Arthroplasty (CSRA)
 Physiotherapy patient information Copeland Surface Replacement Arthroplasty Exercises following Copeland Surface Replacement Arthroplasty (CSRA) Introduction The Copeland Surface Replacement as it s name
Physiotherapy patient information Copeland Surface Replacement Arthroplasty Exercises following Copeland Surface Replacement Arthroplasty (CSRA) Introduction The Copeland Surface Replacement as it s name
Patients First. Upper Body Exercises: Back, Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, & Hands. To obtain the best results, please perform each exercise as shown.
 Patient Education ABOUT YOUR THERAPY Upper Body Exercises: Back, Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, & Hands To obtain the best results, please perform each exercise as shown. The goal of these exercises is to regain
Patient Education ABOUT YOUR THERAPY Upper Body Exercises: Back, Shoulders, Arms, Wrists, & Hands To obtain the best results, please perform each exercise as shown. The goal of these exercises is to regain
Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players.
 Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players. The programme consists of two parts, first the Therapeutic Exercise Programme to improve biomechanical function and secondly the Rehabilitation programme
Neck Rehabilitation programme for Rugby players. The programme consists of two parts, first the Therapeutic Exercise Programme to improve biomechanical function and secondly the Rehabilitation programme
TALLGRASS ORTHOPEDIC & SPORTS MEDICINE THROWING ATHLETE EXERCISE PROGRAM TALLGRASSORTHOPEDICS.COM
 TALLGRASS ORTHOPEDIC & SPORTS MEDICINE THROWING ATHLETE EXERCISE PROGRAM TALLGRASSORTHOPEDICS.COM Patient Name: Date of Surgery: General Principles: The Throwing Athlete Exercise Program is designed to
TALLGRASS ORTHOPEDIC & SPORTS MEDICINE THROWING ATHLETE EXERCISE PROGRAM TALLGRASSORTHOPEDICS.COM Patient Name: Date of Surgery: General Principles: The Throwing Athlete Exercise Program is designed to
Parental Overview Document of FITNESSGRAM Assessment in Georgia
 F I T N E S S G R A M R e f e r e n c e G u i d e P a g e 1 Parental Overview Document of FITNESSGRAM Assessment in Georgia The FITNESSGRAM Reference Guide is intended to provide answers to some common
F I T N E S S G R A M R e f e r e n c e G u i d e P a g e 1 Parental Overview Document of FITNESSGRAM Assessment in Georgia The FITNESSGRAM Reference Guide is intended to provide answers to some common
...let s move. Improve BIOSWING. Your professional exercise manual. The swinging rod with attenuation and frequency regulators.
 www.bioswing.de Your professional exercise manual BIOSWING Improve The swinging rod with attenuation and frequency regulators...let s move * Bioswing Improve 150 7 Schwingstäbe im Test HEFT 3 MÄRZ 2012
www.bioswing.de Your professional exercise manual BIOSWING Improve The swinging rod with attenuation and frequency regulators...let s move * Bioswing Improve 150 7 Schwingstäbe im Test HEFT 3 MÄRZ 2012
Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue
 Anatomy & Physiology Foothill High School Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers (see Figure 1) and has unique properties which allow it to
Anatomy & Physiology Foothill High School Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers (see Figure 1) and has unique properties which allow it to
Body Bar FLEX. Exercises for the Core and Abdominals. by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc.
 Body Bar FLEX Exercises for the Core and Abdominals by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc. 1 Exercises for the Core and Abdominals This presentation features stretching and strengthening exercises
Body Bar FLEX Exercises for the Core and Abdominals by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc. 1 Exercises for the Core and Abdominals This presentation features stretching and strengthening exercises
GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE
 GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE POSTERIOR CAPSULAR STRETCH Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your elbow.
GOLFERS TEN PROGRAM 1. SELF STRETCHING OF THE SHOULDER CAPSULE POSTERIOR CAPSULAR STRETCH Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your elbow.
EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow)
 EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow) Description Expected Outcome Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is the most common painful condition of the elbow. Inflammation and pain occur on the outer side
EPICONDYLITIS, LATERAL (Tennis Elbow) Description Expected Outcome Lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) is the most common painful condition of the elbow. Inflammation and pain occur on the outer side
The Golfers Ten Program. 1. Self Stretching of the Shoulder Capsule
 The Golfers Ten Program 1. Self Stretching of the Shoulder Capsule A. Posterior capsular stretch Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your
The Golfers Ten Program 1. Self Stretching of the Shoulder Capsule A. Posterior capsular stretch Bring your arm across your chest toward the opposite shoulder. With the opposite arm grasp your arm at your
WARM UP AND WARM DOWN ROUTINE: warm up and warm down routines should be performed before and after exercising.
 WARM UP AND WARM DOWN ROUTINE: warm up and warm down routines should be performed before and after exercising. 1. 1. Stand with your feet 30cm apart, hold the Bullworker inner grips with your arms extended
WARM UP AND WARM DOWN ROUTINE: warm up and warm down routines should be performed before and after exercising. 1. 1. Stand with your feet 30cm apart, hold the Bullworker inner grips with your arms extended
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH
 COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
Greater hand-grip strength predicts a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes over. 10 years in leaner Japanese Americans
 Greater hand-grip strength predicts a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes over 10 years in leaner Japanese Americans Running title: Hand-grip strength and risk of diabetes 1 Pandora L. Wander, M.D.
Greater hand-grip strength predicts a lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes over 10 years in leaner Japanese Americans Running title: Hand-grip strength and risk of diabetes 1 Pandora L. Wander, M.D.
Golfers elbow. Physiotherapy of Department
 Golfers elbow Physiotherapy of Department Image copied from http://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/arthritis-information/conditions/elbow-pain/ specific-conditions.aspx This document can be provided in different
Golfers elbow Physiotherapy of Department Image copied from http://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/arthritis-information/conditions/elbow-pain/ specific-conditions.aspx This document can be provided in different
Animal Services Officers Physical Fitness Assessment
 Animal Services Officers Physical Fitness Assessment Purpose of the Animal Services Officers Physical Fitness Assessment is to test the general level of fitness based on the general fitness standards.
Animal Services Officers Physical Fitness Assessment Purpose of the Animal Services Officers Physical Fitness Assessment is to test the general level of fitness based on the general fitness standards.
THROWERS TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM
 THROWERS TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM The Thrower s Ten Program is designed to exercise the major muscles necessary for throwing. The Program s goal is to be an organized and concise exercise program. In addition,
THROWERS TEN EXERCISE PROGRAM The Thrower s Ten Program is designed to exercise the major muscles necessary for throwing. The Program s goal is to be an organized and concise exercise program. In addition,
How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck
 OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
TO MAINTAIN THE INDEPENDENCE of older adults as
 1747 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Grip Strength in Older Adults: Test-Retest Reliability and Cutoff for Subjective Weakness of Using the Hands in Heavy Tasks Ching-Yi Wang, PhD, Li-Yuan Chen, MS ABSTRACT. Wang C-Y,
1747 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Grip Strength in Older Adults: Test-Retest Reliability and Cutoff for Subjective Weakness of Using the Hands in Heavy Tasks Ching-Yi Wang, PhD, Li-Yuan Chen, MS ABSTRACT. Wang C-Y,
IAIABC 2003 Upper Extremity Impairment Guides Part 3 of the Supplemental Impairment Rating Guides
 IAIABC 2003 Upper Extremity Impairment Guides Part 3 of the Supplemental Impairment Rating Guides Draft 11-03 IAIABC Executive Office 5610 Medical Circle, Suite 14 Madison, WI 53719 Phone: (608) 663-6355
IAIABC 2003 Upper Extremity Impairment Guides Part 3 of the Supplemental Impairment Rating Guides Draft 11-03 IAIABC Executive Office 5610 Medical Circle, Suite 14 Madison, WI 53719 Phone: (608) 663-6355
Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual
 Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual 2nd Edition Isabelle M. Bohman, M.S., P.T., NDT Coordinator Instructor TM Published by Clinician s View Albuquerque, NM 505-880-0058
Handling Skills Used in the Management of Adult Hemiplegia: A Lab Manual 2nd Edition Isabelle M. Bohman, M.S., P.T., NDT Coordinator Instructor TM Published by Clinician s View Albuquerque, NM 505-880-0058
DR. A. VIJAYA LAXMI M.P.T(Mumbai) HEAD OF DEPARTMENT PHYSIOTHERAPY HYDERABAD
 DR. A. VIJAYA LAXMI M.P.T(Mumbai) HEAD OF DEPARTMENT PHYSIOTHERAPY HYDERABAD ERGONOMICS Ergon - Means WORK Nomos - Means LAW Computer Ergonomics It is concerned with POSTURE of operator and his relationship
DR. A. VIJAYA LAXMI M.P.T(Mumbai) HEAD OF DEPARTMENT PHYSIOTHERAPY HYDERABAD ERGONOMICS Ergon - Means WORK Nomos - Means LAW Computer Ergonomics It is concerned with POSTURE of operator and his relationship
Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill. patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry
 Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry To proceed to voluntary muscle strength assessment, the neurologic en hemodynamic stability of the
Assessment protocol of limb muscle strength in critically ill patients admitted to the ICU: Dynamometry To proceed to voluntary muscle strength assessment, the neurologic en hemodynamic stability of the
Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important?
 Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important? No matter how well a workstation is designed, problems may arise if attention is not paid to the way the work is done. Working at a computer
Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important? No matter how well a workstation is designed, problems may arise if attention is not paid to the way the work is done. Working at a computer
Serum uric acid levels improve prediction of incident Type 2 Diabetes in individuals with impaired fasting glucose: The Rancho Bernardo Study
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 9, 2009 Serum uric acid and incident DM2 Serum uric acid levels improve prediction of incident Type 2 Diabetes in individuals with impaired fasting
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 9, 2009 Serum uric acid and incident DM2 Serum uric acid levels improve prediction of incident Type 2 Diabetes in individuals with impaired fasting
Mo-Bility 13. Station 1 Card: How Stable Am I? 1LESSON 3. PROBLEM STATEMENT: How does obesity affect your
 Station 1 Card: How Stable Am I? PROBLEM STATEMENT: How does obesity affect your balance? In this experiment you will test the relationship between the center of gravity of an object and the base of support.
Station 1 Card: How Stable Am I? PROBLEM STATEMENT: How does obesity affect your balance? In this experiment you will test the relationship between the center of gravity of an object and the base of support.
The purpose of this order is behind the belief that the MORE complex exercises should come before the LESS complex exercises.
 There will be 6 strength events taking place for the DECA Challenge. The events taking place will be (in order): 1. Power Clean 2. Push- Up 3. Pull- UP 4. Kneeling Power Ball Toss 5. Vertical Jump 6. Prone
There will be 6 strength events taking place for the DECA Challenge. The events taking place will be (in order): 1. Power Clean 2. Push- Up 3. Pull- UP 4. Kneeling Power Ball Toss 5. Vertical Jump 6. Prone
Latajet Rehabilitation Guidelines
 PH: 1300 746 853 Latajet Rehabilitation Guidelines The following is a detailed outline of the rehabilitation regime for patients who have had an Latajet Coracoid Process Transfer by Dr. Macgroarty. You
PH: 1300 746 853 Latajet Rehabilitation Guidelines The following is a detailed outline of the rehabilitation regime for patients who have had an Latajet Coracoid Process Transfer by Dr. Macgroarty. You
CS, IT Occupational Hazard
 CS, IT Occupational Hazard Ergonomics 1 485 patients average age of 38.5 years. 63% females. 70% computer users, 28% musicians, 2% were others engaged in repetitive work. A majority sought care within
CS, IT Occupational Hazard Ergonomics 1 485 patients average age of 38.5 years. 63% females. 70% computer users, 28% musicians, 2% were others engaged in repetitive work. A majority sought care within
Carpal tunnel syndrome
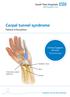 Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Adult grip strength norms for the Baseline digital dynamometer
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital epository Master s and Doctoral Projects Adult grip strength norms for the Baseline digital dynamometer Chelsey. Meek Follow this and additional
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital epository Master s and Doctoral Projects Adult grip strength norms for the Baseline digital dynamometer Chelsey. Meek Follow this and additional
Visual and Musculoskeletal Problems among Video Display Terminal (VDT) Operators and their Ergonomic and Working Conditions
 Research papers Visual and Musculoskeletal Problems among Video Display Terminal (VDT) Operators and their Ergonomic and Working Conditions D R De A Seneviratne, G K K Sewwandi, S Sharmilee AL 2001 batch
Research papers Visual and Musculoskeletal Problems among Video Display Terminal (VDT) Operators and their Ergonomic and Working Conditions D R De A Seneviratne, G K K Sewwandi, S Sharmilee AL 2001 batch
Throwers Ten Exercise Program
 The Thrower s Ten Program is designed to exercise the major muscles necessary for throwing. The Program s goal is to be an organized and concise exercise program. In addition, all exercises included are
The Thrower s Ten Program is designed to exercise the major muscles necessary for throwing. The Program s goal is to be an organized and concise exercise program. In addition, all exercises included are
PHYSICAL FUNCTION TESTS
 ?Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 15 minutes per response, including the time for reviewing instructions, searching existing data sources, gathering
?Public reporting burden for this collection of information is estimated to average 15 minutes per response, including the time for reviewing instructions, searching existing data sources, gathering
Introduction to Ergonomics Ergonomics (er'gõ nom'iks):
 March 10 th 2009 Construction Ergonomics Introduction to ergonomics Risk factors of MSDs Solutions to minimize risk factors Q & A Resources Yutonah Bowes, Oregon OSHA Mark Noll, SAIF Corp. Kim Rhodes,
March 10 th 2009 Construction Ergonomics Introduction to ergonomics Risk factors of MSDs Solutions to minimize risk factors Q & A Resources Yutonah Bowes, Oregon OSHA Mark Noll, SAIF Corp. Kim Rhodes,
Preventing Workplace Injuries with Ergonomics
 Preventing Workplace Injuries with Ergonomics Richard W. Bunch, PhD, PT, CBES ISR Institute / Dr. Bunch Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs) Low Back Injuries- #1 Disabling Orthopedic Injury Among
Preventing Workplace Injuries with Ergonomics Richard W. Bunch, PhD, PT, CBES ISR Institute / Dr. Bunch Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs) Low Back Injuries- #1 Disabling Orthopedic Injury Among
ACTIVE AGING.
 Shoulder Pain Rehabilitation Protocol Rotator Cuff Syndrome Shoulder impingement The Resistance Chair Solution Shoulder Impingement a. Shoulder impingement is one of the most common causes of shoulder
Shoulder Pain Rehabilitation Protocol Rotator Cuff Syndrome Shoulder impingement The Resistance Chair Solution Shoulder Impingement a. Shoulder impingement is one of the most common causes of shoulder
Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain
 Clinical Rehabilitation 2003; 17: 885 889 Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain CP van Wilgen Painexpertise Centre, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University
Clinical Rehabilitation 2003; 17: 885 889 Muscle strength in patients with chronic pain CP van Wilgen Painexpertise Centre, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery University
TPW 's Upper Back Menu
 TPW 's Upper Back Menu # Sets Reps Duration E-cise 1 1 1 00:10:00 Static Back 2 3 10 Static Back Reverse Presses 3 3 10 Static Back Pullovers 4 1 1 0:01:00 Floor Block 5 1 1 0:02:00 Static Extension Position
TPW 's Upper Back Menu # Sets Reps Duration E-cise 1 1 1 00:10:00 Static Back 2 3 10 Static Back Reverse Presses 3 3 10 Static Back Pullovers 4 1 1 0:01:00 Floor Block 5 1 1 0:02:00 Static Extension Position
Investigating Massage as a Complementary Therapy for Weight Loss By Morgan J Lawless, LMT
 Investigating Massage as a Complementary Therapy for Weight Loss By Morgan J Lawless, LMT Obesity and excess body fat in The United States is a growing health risk to many Americans. The Center for Disease
Investigating Massage as a Complementary Therapy for Weight Loss By Morgan J Lawless, LMT Obesity and excess body fat in The United States is a growing health risk to many Americans. The Center for Disease
Commonwealth Health Corporation NEXT
 Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Gender and Postural Differences in Cardiovascular Response to Hand Grip Exercise Among Elderly Normotensives
 Gender and Postural Differences in Cardiovascular Response to Hand Grip Exercise Among Elderly Normotensives 1 2 1 Kodzo, K.K., Mohammed, J., Kodzo, P. 1 Department of Physiotherapy, Aminu Kano Teaching
Gender and Postural Differences in Cardiovascular Response to Hand Grip Exercise Among Elderly Normotensives 1 2 1 Kodzo, K.K., Mohammed, J., Kodzo, P. 1 Department of Physiotherapy, Aminu Kano Teaching
Soteria Strains. Safe Patient Handling and Mobility Program Guide
 Soteria Strains Safe Patient Handling and Mobility Program Guide Section 4 Special Considerations Section 4.3 - Orthopedics V1.0 edited July 28, 2015 A provincial strategy for healthcare workplace musculoskeletal
Soteria Strains Safe Patient Handling and Mobility Program Guide Section 4 Special Considerations Section 4.3 - Orthopedics V1.0 edited July 28, 2015 A provincial strategy for healthcare workplace musculoskeletal
Lower Extremity Physical Performance Testing. Return to Function (Level I): Core Stability
 Physical performance testing is completed with patients in order to collect data and make observations regarding the overall function of the limb integrated into the entire functional unit of the body,
Physical performance testing is completed with patients in order to collect data and make observations regarding the overall function of the limb integrated into the entire functional unit of the body,
Sterile gauze used at incision site. Check brace for rubbing or irritation. Compression garment at elbow to be used with physician s authorization
 ULNAR COLLATERAL LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION GUIDELINE Functional Outcome Measure KJOC (Appendix 1) should be completed at initial evaluation and at all identified times through guideline, Phase 1 Immediate
ULNAR COLLATERAL LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION GUIDELINE Functional Outcome Measure KJOC (Appendix 1) should be completed at initial evaluation and at all identified times through guideline, Phase 1 Immediate
MUSCLE SIZE AND SPECIFIC FORCE ALONG THE LENGTH OF THE QUADRICEPS IN OLDER AND YOUNG INDIVIDUALS
 MUSCLE SIZE AND SPECIFIC FORCE ALONG THE LENGTH OF THE QUADRICEPS IN OLDER AND YOUNG INDIVIDUALS Hannah Barile Faculty Advisor: Dr. Summer Cook 2014 University of New Hampshire. All rights reserved. Introduction
MUSCLE SIZE AND SPECIFIC FORCE ALONG THE LENGTH OF THE QUADRICEPS IN OLDER AND YOUNG INDIVIDUALS Hannah Barile Faculty Advisor: Dr. Summer Cook 2014 University of New Hampshire. All rights reserved. Introduction
Physical Sense Activation Programme
 Flexion extension exercises for neck and upper back Sitting on stool Arms hanging by side Bend neck and upper back Breathe out Extend your neck and upper back Lift chest to ceiling Squeeze shoulder blades
Flexion extension exercises for neck and upper back Sitting on stool Arms hanging by side Bend neck and upper back Breathe out Extend your neck and upper back Lift chest to ceiling Squeeze shoulder blades
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Study on Prevalence of Pre-Diabetes in Urban Area of Mumbai and Its Association with Various
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Study on Prevalence of Pre-Diabetes in Urban Area of Mumbai and Its Association with Various
Low glycaemic index diet is effective in managing weight among obese postpartum women
 548 RESEARCH ARTICLE Low glycaemic index diet is effective in managing weight among obese postpartum women Shahnai Basharat, 1 Syed Amir Gilani, 2 Amjad Iqbal Burq, 3 Shahid Bashir 4 Abstract Objective:
548 RESEARCH ARTICLE Low glycaemic index diet is effective in managing weight among obese postpartum women Shahnai Basharat, 1 Syed Amir Gilani, 2 Amjad Iqbal Burq, 3 Shahid Bashir 4 Abstract Objective:
Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization
 Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization A Criteria-Based Reference Format for Observing & Analyzing Motor Behavior in Children with Learning Disabilities By W. Michael Magrun, MS, OTR 3 R D E D I T
Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization A Criteria-Based Reference Format for Observing & Analyzing Motor Behavior in Children with Learning Disabilities By W. Michael Magrun, MS, OTR 3 R D E D I T
Evaluation copy. EMG and Muscle Fatigue. Computer
 EMG and Muscle Fatigue Computer 18 Voluntary muscle contraction is the result of communication between the brain and individual muscle fibers of the musculoskeletal system. A thought is transformed into
EMG and Muscle Fatigue Computer 18 Voluntary muscle contraction is the result of communication between the brain and individual muscle fibers of the musculoskeletal system. A thought is transformed into
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Range of motion and positioning
 Range of motion and positioning Learning guide Why is motion important? Most people take free, comfortable movement for granted. Motion is meant to be smooth and painless. The ligaments, tendons, muscles,
Range of motion and positioning Learning guide Why is motion important? Most people take free, comfortable movement for granted. Motion is meant to be smooth and painless. The ligaments, tendons, muscles,
INTRODUCTION SUBJECTS AND METHODS
 J Korean Med Sci 23; 18: 2-8 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Normative Data and Developmental Characteristics of Hand Function for Elementary School Children in Suwon Area
J Korean Med Sci 23; 18: 2-8 ISSN 111-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Normative Data and Developmental Characteristics of Hand Function for Elementary School Children in Suwon Area
General Information - Exercise
 General Information - Exercise To maximize the potential for prevention and recovery, it is important to make a commitment to daily stretching and cardiovascular exercise and to perform strengthening exercises
General Information - Exercise To maximize the potential for prevention and recovery, it is important to make a commitment to daily stretching and cardiovascular exercise and to perform strengthening exercises
Reliability of Measuring Trunk Motions in Centimeters
 Reliability of Measuring Trunk Motions in Centimeters MARGARET ROST, SANDRA STUCKEY, LEE ANNE SMALLEY, and GLENDA DORMAN A method of measuring trunk motion and two related motions using a tape measure
Reliability of Measuring Trunk Motions in Centimeters MARGARET ROST, SANDRA STUCKEY, LEE ANNE SMALLEY, and GLENDA DORMAN A method of measuring trunk motion and two related motions using a tape measure
D: Doorway Stretch E: Towel Stretch for Pectoralis Minor Blackburn Exercises: 6 Positions A: Prone Horizontal Abduction (Neutral)
 D: Doorway Stretch Bring your shoulder into a horizontal position out to your side (abduction) and flex your elbow 90û Place your elbow against the edge of a doorway Lead forward and downwards with your
D: Doorway Stretch Bring your shoulder into a horizontal position out to your side (abduction) and flex your elbow 90û Place your elbow against the edge of a doorway Lead forward and downwards with your
How to Use Fellowes Sit-Stand Solutions
 How to Use Fellowes Sit-Stand Solutions Welcome to the sit-stand way of working We re delighted you ve chosen a Fellowes sit-stand solution to add movement to your working day. These guidelines will help
How to Use Fellowes Sit-Stand Solutions Welcome to the sit-stand way of working We re delighted you ve chosen a Fellowes sit-stand solution to add movement to your working day. These guidelines will help
Tips for Teaching the 3 Core Bulgarian Bag Movement Patterns
 Tips for Teaching the 3 Core Bulgarian Bag Movement Patterns The following tips will help you work with details and fine points of taking someone through the instruction process for the 3 core fundamental
Tips for Teaching the 3 Core Bulgarian Bag Movement Patterns The following tips will help you work with details and fine points of taking someone through the instruction process for the 3 core fundamental
Electronic Supplementary Materials
 Electronic Supplementary Materials Study 1 Body Measurements. To find proxies of lifting strength that could later be used in laboratory settings without cumbersome weight-lifting equipment, a variety
Electronic Supplementary Materials Study 1 Body Measurements. To find proxies of lifting strength that could later be used in laboratory settings without cumbersome weight-lifting equipment, a variety
