2015 PhD proposal. CIFRE Grant SANOFI Centre de Recherche en Myologie Altered calcium homeostasis and LMNA-cardiomyopathy
|
|
|
- Briana Stafford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2015 PhD proposal Project / Research program: Project Leader: Department/Unit: CIFRE Grant SANOFI Centre de Recherche en Myologie Altered calcium homeostasis and LMNA-cardiomyopathy Antoine Muchir, PhD, CR1 Inserm & Gisèle Bonne, PhD-HDR, DR2 Inserm. Centre de Recherche en Myologie / Institut de Myologie UPMC - Inserm UMRS 974 / CNRS FRE 3617 / AIM PhD scientific project title: Site: Exploration of altered calcium homeostasis in LMNAcardiomyopathy Institut de myologie, G.H. Pitié-Salpêtrière ; 47, boulevard de l'hôpital. F Paris Cedex 13 - France Proposed starting date Fall 2015 Contact Detail project Milestones & Objective Gisèle Bonne (g.bonne@institut-myologie.org) Antoine Muchir (a.muchir@institut-myologie.org) Background Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), one of the leading causes of heart failure in Europe, is characterized by an increase in both myocardial mass and volume resulting in poor left ventricular function. In 1999, we and other identified that LMNA mutations cause cardiomyopathy with ventricular arrhythmias and conduction defects (LMNA-cardiomyopathy), associated or not with striated muscle disease, the Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD) (Bonne et al. 1999; Fatkin et al. 1999). LMNA encodes nuclear A-type lamins, which are the main constituents of the nuclear lamina, a meshwork underlying the inner nuclear membrane of metazoan cells (Fisher et al. 1986; McKeon et al. 1986; Aebi et al. 1986). Lamins have been implicated in structural support to the nucleus and in processes such as chromatin organization, gene regulation, DNA replication and RNA splicing (Dechat et al. 2008). The inner nuclear membrane contains specific integral and associated proteins that connect the A-type lamins, which are proposed to form a mechanical link, called the LINC (LInker of Nucleoskeleton and Cytoskeleton) complex (Stewart et al. 2007), tethering the nucleo- and cyto-skeleton. Thus, the nucleus is considered as a mechanical sensor, which could partially explain the cardiac muscle disease, considering that heart is constantly subjected to mechanical forces (Lombardi et al. 2011). However, the mechanism through which mutated lamins cause cardiac dysfunction and arrhythmias remains obscure.
2 Our previous work has focused on investigation of the contractile dysfunction, and we demonstrated an early abnormal activation of the stress activated MAP kinases signaling pathways in the heart of Lmna H222P knock-in mice (Lmna H222P ), a mouse model of LMNA-cardiomyopathy we created (Arimura et al. 2005, Muchir et al. 2007). Pharmacological or genetic blockade of signaling in the MAPK cascade in Lmna H222P mice prevents left ventricular dilatation and deterioration in cardiac contractility, if administered prior or after the onset of detectable heart disease (Muchir et al. 2009; Wu et al. 2010, Wu et al. 2011; Muchir et al. 2011; Wu et al. 2014). Ca2+ is one of the major actors of the excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle. The release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum is triggered via the Ryanodin receptor type 2 (RYR2) and promotes cardiac contraction. A recent study demonstrated the relationship among increased S-nitrosylation of RyR2, diastolic sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ leak and the development of a cardiac phenotype (Fauconnier et al. 2010). We initiated quantification of RyR2 S-nitrosylation in the hearts of Lmna H222P knock-in mice, as well as patch-clamp analysis and calcium release experiments from Lmna H222P isolated cardiomyocytes (Collaboration with AM Gomez, Chatenay-Malabry). Our preliminary data on RYR2 S- nitrosylation, calcium sparks and NCX expression strongly underline a potential role of calcium homeostasis in the cardiomyopathy linked to mutations in LMNA. Objectives Aim 1. Assess the expression of the components of the excitationcontraction coupling in LMNA-cardiomyopathy. We have access to two mouse models of LMNA-cardiomyopathy (Lmna H222P and delk32 mouse models) (Arimura et al. 2005; Cattin et al. 2013). Heart muscle samples from patients will be collected from explanted hearts during cardiac transplantations. Through our network of clinicians and surgeons, we already collected cardiac biopsies (left ventricle) from 4 patients carrying different LMNA mutations. All tissue samples have been obtained with appropriate ethical approvals from the lnstitut de Myologie and provided without patient identifiers. We will i/ study the RyR2 S- nitrosylation and determine expression level of calstabin 2 (western blot, qpcr), and ii/ investigate the major actors of the Ca 2+ homeostasis: NCX, Calmodulin, CamKII and its targets phospholamban/ryr2 and phosphorylated phospholamban/ryr2, Serca2, Ip3, Ip3 receptor and DHPR (qpcr, western blot, immunohistochemistry). Aim 2. Develop ipsc-derived cardiomyocyte models that recapitulates the molecular and/or cellular abnormalities of LMNA-cardiomyopathy. We have access to one line of ipsc derived from fibroblasts of patients carrying LMNA mutations. We aim at generating additional lines as we currently have access to primary skin fibroblasts from 8 patients with LMNA-cardiomyopathy (if time and resources allow, in collaboration with I- Stem). Cardiomyocytes will be derived from these IPSC lines. We will assess the expression, post-translational modifications and localization of the main components involve in the calcium homeostasis, as described in Aim 1 (S-nitrosylation RyR2, NCX ). We will also study, in collaboration with AM Gomez, the ion channels activity (patch-clamp analysis, calcium
3 transient) on ipsc-derived cardiomyocytes. All this analysis will provide new insights on the pathophysiology and also define standard read-outs for drug screening. Aim 3. Analyze the role played by oxidative stress in the alteration of excitation-contraction in LMNA-cardiomyopathy. In the heart, mechanical stretch during diastolic filling activates mechanotransduction signaling pathways that have broad implications for cardiac health and disease. A small stretch of a ventricular myocyte causes a burst of Ca 2+ sparks, the elementary events corresponding to the release of free Ca 2+ from intracellular stores. The mechanism by which this occurs has remained elusive. Recent work from others showed that nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase 2 (NOX2) is overactive in a pathological model of cardiomyopathy, and this produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) in a process dependent on microtubules (X-ROS signaling), which triggers arrhythmogenic calcium waves in isolated cardiomyocytes (Proser et al. 2011). X-ROS signaling thus provides a mechanistic explanation for the mechanotransduction of Ca 2+ release in the heart and offers new therapeutic possibilities. We will assess the level of oxidative stress in the heart from Lmna H222P / delk32 mouse models and humans using the fluorescent ROS sensor 2,7 -dichlorofluorescein diacetate with or without application of the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine. We will also assess the impact of ROS on the activation of CaMKII (by quantification of oxidized CAMKII) (Luczak et al. 2014) and the phosphorylation of RYR2 on the CaMKII specific site (ser2814) whose excessive phosphorylation has been linked to atrial fibrillation, arrhythmias and sudden death trough alteration of Ca2+ handling. Additional functional readouts (contractility, Ca2+ transients, Ca2+ sparks ) will be used on ipsc-cm derived from patients and adult cardiomyocytes from LMNAcardiomyopathy mouse models with or without NAC, Nox2 inhibitors or CaMKII inhibitors to assess the causal role of oxidative stress in the alteration of excitation-contraction in LMNA-cardiomyopathy. Given the predominant role of oxidative stress (Terentyev et al. 2008; Murdoch et al. 2006) and cytoskeletal dysfunction (Heins et al. 2000) in the progression of cardiomyopathy, X-ROS signaling may have important pathophysiological effects in the context of LMNA-cardiomyopathy. Aim 4. Test molecules with potential therapeutic effect on IPSC-derived cardiomyocytes and on two mouse models of LMNA-cardiomyopathy. Anti-arrhythmic agents are a group of pharmaceuticals that are used to suppress abnormal rhythms of the heart. Among the different classes of anti-arrhythmic, we will focus on class II and IV. Class II, -adrenergic blockers are routinely used in cardiac laminopathic patients. Class IV which slow calcium channel blockers in particular the DHPR, are rarely used in laminopathy context. These two classes of anti-arrhythmic and new classes of molecules (in collaboration with partner, to be determined) will be tested on cardiomyocytes derived from patient ipsc, and will be further functionally validate (ECG, echocardiography) on mouse models (Lmna H222P and Lmna delk32 mice; Cattin et al, 2013).
4 Milestones Required skills: Cellular and molecular biology, biochemistry (expertise available in the team). Patch-clamp, calcium transient (expertise available in collaboration with Ana-Maria Gomez, Chatenay-Malabry). IPSC platform: not available in the team. Echocardiography, ECG (expertise available in the laboratory). Qualification and / or training desired: Student should have a strong background on cellular and molecular biology. An experience in the other skills will be an added value. Experience: Master 2 Additional information (if needed) Bibliography Aebi U, Cohn J, Buhle L, Gerace L. The nuclear lamina is a meshwork of intermediate-type filaments. Nature 1986, 323, Arimura T, Helbling-Leclerc A, Massart C, Varnous S, Niel F, Lacene E, Fromes Y, Toussaint M, Mura AM, Keller DI, Amthor H, Isnard R, Malissen M, Schwartz K, Bonne G. Mouse model carrying H222P-Lmna mutation develops muscular dystrophy and dilated cardiomyopathy similar to human striated muscle laminopathies. Hum Mol Genet 2005;14: Bonne G, Di Barletta MR, Varnous S, et al. Mutations in the gene encoding lamin A/C cause autosomal dominant Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Nat Genet. 1999, 21: Cattin ME, Bertrand AT, Schlossarek S, Le Bihan MC, Skov Jensen S, Neuber C, Crocini C, Maron S, Laine J, Mougenot N, Varnous S, Fromes Y, Hansen A, Eschenhagen T, Decostre V, Carrier L, Bonne G. Heterozygous LmnadelK32 mice develop dilated cardiomyopathy through a combined pathomechanism of haploinsufficiency and peptide toxicity. Hum Mol Genet 2013;22: Fatkin D, MacRae C, Sasaki T, et al. Missense mutations in the rod domain of the lamin A/C gene as causes of dilated cardiomyopathy and conduction-system disease. N Engl J Med. 1999, 341: Fauconnier J, Thireau J, Reiken S, Cassan C, Richard S, Matecki S, Marks AR, Lacampagne A. Leaky RyR2 trigger ventricular arrhythmias in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010;107: Fisher DZ, Chaudhary N, Blobel G. cdna sequencing of nuclear lamins A and C reveals primary and secondary structural homology to intermediate filament proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1986;83:
5 Hein S, Kostin S, Heling A, Maeno Y, Schaper J. The role of the cytoskeleton in heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 45, 273 (2000). Lombardi F, Gullotta F, Columbaro M, Filareto A, D'Adamo M, Vielle A, Guglielmi V, Nardone AM, Azzolini V, Grosso E, Lattanzi G, D'Apice MR, Masala S, Maraldi NM, Sbraccia P, Novelli G. Compound heterozygosity for mutations in LMNA in a patient with a myopathic and lipodystrophic mandibuloacral dysplasia type A phenotype. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007;92: Luczak ED, Anderson ME. CaMKII oxidative activation and the pathogenesis of cardiac disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2014; 73: McKeon FD, Tuffanelli DL, Kobayashi S, Kirschner MW. The redistribution of a conserved nuclear envelope protein during the cell cycle suggests a pathway for chromosome condensation. Cell 1984;36: Muchir A, Pavlidis P, Decostre V, Herron AJ, Arimura T, Bonne G, Worman HJ. Activation of MAPK Pathway Links LMNA Mutations to Cardiomyopathy in Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy. J Clin Invest 2007, 117: Muchir A, Reilly SA, Wu W, et al. Treatment with selumetinib preserves cardiac function and improves survival in cardiomyopathy caused by mutation in the lamin A/C gene. Cardiovasc Res. 2011, 93: Murdoch CE, Zhang M, Cave AC, Shah AM. NADPH oxidase-dependent redox signalling in cardiac hypertrophy, remodelling and failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 71, 208 (2006). Proser BL, Ward CW, Lederer WJ. X-ROS signaling: rapid mechano-cheno transduction in heart. Science 2011; 333: Stewart CL, Kozlov S, Fong LG, Young SG. Mouse models of the laminopathies. Exp Cell Res 2007;313: Terentyev D et al. Redox modification of ryanodine receptors contributes to sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ leak in chronic heart failure. Circ. Res. 103, 1466 (2008). Wu W, Muchir A, Shan J, Bonne G, Worman HJ. Mitogen activated protein kinase inhibitors improve heart function and prevent fibrosis in cardiomyopathy caused by lamin A/C gene mutation. Circulation 2011, 123: Wu W, Shan J, Bonne G, Worman HJ, Muchir A. Pharmacological inhibition of c- Jun N-terminal kinase signaling prevents cardiomyopathy caused by mutation in LMNA gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 2010, 1802: Wu W, Iwata S, Homma S, Worman HJ, Muchir A. Depletion of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 in mice with cardiomyopathy caused by lamin A/C gene mutation partially prevents pathology before isoenzyme activation. Hum Mol Genet 2014; 23:1-11.
HYBRID GENE THERAPY FOR AD-EDMD
 HYBRID GENE THERAPY FOR AD-EDMD Gene Therapy Prof. Isabella Saggio 2017/2018 Bertani Camilla Dezi Clara Difeo Giorgia di Palma Carmen AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT EMERY-DREIFUSS MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY Fig.1 Adapted
HYBRID GENE THERAPY FOR AD-EDMD Gene Therapy Prof. Isabella Saggio 2017/2018 Bertani Camilla Dezi Clara Difeo Giorgia di Palma Carmen AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT EMERY-DREIFUSS MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY Fig.1 Adapted
Nuclear Envelope and Muscular Dystrophy
 Nationwide Children s Hospital August 25, 2015 Nuclear Envelope and Muscular Dystrophy Howard J. Worman, M.D. Columbia University Columbia University Medical Center The Nuclear Envelope By D. W. Fawcett
Nationwide Children s Hospital August 25, 2015 Nuclear Envelope and Muscular Dystrophy Howard J. Worman, M.D. Columbia University Columbia University Medical Center The Nuclear Envelope By D. W. Fawcett
THURSDAY, JANUARY
 THURSDAY, JANUARY 15 2015 08.30-09.00 WELCOME COFFEE 09.00-09.15 Welcome and opening comments. A. De Sandre-Giovannoli, N. Lévy Presentation of the French Network on EDMD and other nucleopathies. G. Bonne,
THURSDAY, JANUARY 15 2015 08.30-09.00 WELCOME COFFEE 09.00-09.15 Welcome and opening comments. A. De Sandre-Giovannoli, N. Lévy Presentation of the French Network on EDMD and other nucleopathies. G. Bonne,
Familial DilatedCardiomyopathy Georgios K Efthimiadis, MD
 Familial DilatedCardiomyopathy Georgios K Efthimiadis, MD Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dilated LV/RV, reduced EF, in the absence of CAD valvulopathy pericardial disease Prevalence:40/100.000 persons Natural
Familial DilatedCardiomyopathy Georgios K Efthimiadis, MD Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dilated LV/RV, reduced EF, in the absence of CAD valvulopathy pericardial disease Prevalence:40/100.000 persons Natural
Declaration of conflict of interest. I have nothing to disclose.
 Declaration of conflict of interest I have nothing to disclose. Left Bundle branch block in HF: DO GENETICS MATTER? Silvia Giuliana Priori Cardiovascular Genetics, Langone Medical Center, New York University
Declaration of conflict of interest I have nothing to disclose. Left Bundle branch block in HF: DO GENETICS MATTER? Silvia Giuliana Priori Cardiovascular Genetics, Langone Medical Center, New York University
Inner Nuclear Membrane Protein MAN1 and Regulation of R-Smad Signaling
 4th International Melorheostosis Association Conference Inner Nuclear Membrane Protein MAN1 and Regulation of R-Smad Signaling Howard J. Worman Columbia University New York, NY The Nuclear Envelope By
4th International Melorheostosis Association Conference Inner Nuclear Membrane Protein MAN1 and Regulation of R-Smad Signaling Howard J. Worman Columbia University New York, NY The Nuclear Envelope By
Skeletal myopathy in a family with lamin A/C cardiac disease
 Original Article Skeletal myopathy in a family with lamin A/C cardiac disease Subha Ghosh 1, Rahul Renapurkar 1, Subha V. Raman 2 1 Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH, USA; 2 The Ohio State University
Original Article Skeletal myopathy in a family with lamin A/C cardiac disease Subha Ghosh 1, Rahul Renapurkar 1, Subha V. Raman 2 1 Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland, OH, USA; 2 The Ohio State University
Index. A Action potential duration, increased, by decreases in sodium current,
 Heart Failure Clin 1 (2005) 313 319 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Action potential duration, increased, by decreases in sodium current, 201 202 Adenylyl cyclase, overexpression
Heart Failure Clin 1 (2005) 313 319 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Action potential duration, increased, by decreases in sodium current, 201 202 Adenylyl cyclase, overexpression
Contribution of genetics for sudden death risk stratification in dilated cardiomyopathy
 Contribution of genetics for sudden death risk stratification in dilated cardiomyopathy Pr Philippe Charron Centre de Référence pour les maladies cardiaques héréditaires (1) Hôpital Ambroise Paré, Boulogne
Contribution of genetics for sudden death risk stratification in dilated cardiomyopathy Pr Philippe Charron Centre de Référence pour les maladies cardiaques héréditaires (1) Hôpital Ambroise Paré, Boulogne
ΜΥΟΚΑΡΔΙΟΠΑΘΕΙΕΣ. Ανεξήγητη βραδυκαρδία µε ή χωρίς διαταραχές κολποκοιλιακής αγωγής: τι µπορεί να κρύβει? ΕΦΗ Ι. ΠΡΑΠΠΑ Καρδιολόγος
 ΜΥΟΚΑΡΔΙΟΠΑΘΕΙΕΣ Ανεξήγητη βραδυκαρδία µε ή χωρίς διαταραχές κολποκοιλιακής αγωγής: τι µπορεί να κρύβει? ΕΦΗ Ι. ΠΡΑΠΠΑ Καρδιολόγος Β Καρδιολογική Κλινική, ΠΓΝΑ «Ο ΕΥΑΓΓΕΛΙΣΜΟΣ» CONFLICT of INTEREST : none
ΜΥΟΚΑΡΔΙΟΠΑΘΕΙΕΣ Ανεξήγητη βραδυκαρδία µε ή χωρίς διαταραχές κολποκοιλιακής αγωγής: τι µπορεί να κρύβει? ΕΦΗ Ι. ΠΡΑΠΠΑ Καρδιολόγος Β Καρδιολογική Κλινική, ΠΓΝΑ «Ο ΕΥΑΓΓΕΛΙΣΜΟΣ» CONFLICT of INTEREST : none
Evolving pharmacologic antiarrhythmic treatment targets Ready for clinical practice?
 Evolving pharmacologic antiarrhythmic treatment targets Ready for clinical practice? David O. Arnar MD PhD EMPH Landspitali The National University Hospital of Iceland, Reykjavik Disclosures Consultant
Evolving pharmacologic antiarrhythmic treatment targets Ready for clinical practice? David O. Arnar MD PhD EMPH Landspitali The National University Hospital of Iceland, Reykjavik Disclosures Consultant
Muscular Dystrophy. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49:
 Online publication October 6, 2009 48 2 20 J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 293 297 atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide, guanylyl cyclase-a receptor, cardiac remodeling, cardiac hypertrophy
Online publication October 6, 2009 48 2 20 J Jpn Coll Angiol, 2009, 49: 293 297 atrial natriuretic peptide, brain natriuretic peptide, guanylyl cyclase-a receptor, cardiac remodeling, cardiac hypertrophy
Inherited Arrhythmia Syndromes
 Inherited Arrhythmia Syndromes When to perform Genetic testing? Arthur AM Wilde February 4, 2017 Which pts should undergo genetic testing? SCD victims with a likely diagnosis Pts diagnosed with an inherited
Inherited Arrhythmia Syndromes When to perform Genetic testing? Arthur AM Wilde February 4, 2017 Which pts should undergo genetic testing? SCD victims with a likely diagnosis Pts diagnosed with an inherited
1. Cardiomyocytes and nonmyocyte. 2. Extracellular Matrix 3. Vessels שאלה 1. Pathobiology of Heart Failure Molecular and Cellular Mechanism
 Pathobiology of Heart Failure Molecular and Cellular Mechanism Jonathan Leor Neufeld Cardiac Research Institute Tel-Aviv University Sheba Medical Center, Tel-Hashomer שאלה 1 התא הנפוץ ביותר (75%~) בלב
Pathobiology of Heart Failure Molecular and Cellular Mechanism Jonathan Leor Neufeld Cardiac Research Institute Tel-Aviv University Sheba Medical Center, Tel-Hashomer שאלה 1 התא הנפוץ ביותר (75%~) בלב
Clinical Genetics in Cardiomyopathies
 Clinical Genetics in Cardiomyopathies Γεώργιος Κ Ευθυμιάδης Αναπληρωτής Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας ΑΠΘ No conflict of interest Genetic terms Proband: The first individual diagnosed in a family Mutation: A
Clinical Genetics in Cardiomyopathies Γεώργιος Κ Ευθυμιάδης Αναπληρωτής Καθηγητής Καρδιολογίας ΑΠΘ No conflict of interest Genetic terms Proband: The first individual diagnosed in a family Mutation: A
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca Homeostasis and Heart Failure
 Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca Homeostasis and Heart Failure Aleksey V. Zima and Dmitry Terentyev SR Ca Regulation in Heart Heart function vitally relies on precisely controlled intracellular Ca homeostasis
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca Homeostasis and Heart Failure Aleksey V. Zima and Dmitry Terentyev SR Ca Regulation in Heart Heart function vitally relies on precisely controlled intracellular Ca homeostasis
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders
 Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
Cardiac Considerations and Care in Children with Neuromuscular Disorders - importance of early and ongoing treatment, management and available able medications. Dr Bo Remenyi Department of Cardiology The
EHRA/EUROPACE 2011 Madrid, Spain June
 EHRA/EUROPACE 2011 Madrid, Spain June 26.-29.2011 Implementing modern management in atrial fibrillation patients Proceedings from the 3rd AFNet/EHRA consensus conference EHRA Special Session Different
EHRA/EUROPACE 2011 Madrid, Spain June 26.-29.2011 Implementing modern management in atrial fibrillation patients Proceedings from the 3rd AFNet/EHRA consensus conference EHRA Special Session Different
Mechanisms of Cell Injury: Loss of Calcium Homeostasis
 Mechanisms of Cell Injury: Loss of Calcium Homeostasis SCPA610: Cellular Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Leading questions Why is intracellular calcium important for the
Mechanisms of Cell Injury: Loss of Calcium Homeostasis SCPA610: Cellular Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Leading questions Why is intracellular calcium important for the
Εμφύτευση απινιδωτών για πρωτογενή πρόληψη σε ασθενείς που δεν περιλαμβάνονται στις κλινικές μελέτες
 Εμφύτευση απινιδωτών για πρωτογενή πρόληψη σε ασθενείς που δεν περιλαμβάνονται στις κλινικές μελέτες Δημήτριος M. Κωνσταντίνου Ειδικός Καρδιολόγος, MD, MSc, PhD, CCDS Πανεπιστημιακός Υπότροφος Dr. Konstantinou
Εμφύτευση απινιδωτών για πρωτογενή πρόληψη σε ασθενείς που δεν περιλαμβάνονται στις κλινικές μελέτες Δημήτριος M. Κωνσταντίνου Ειδικός Καρδιολόγος, MD, MSc, PhD, CCDS Πανεπιστημιακός Υπότροφος Dr. Konstantinou
Treatment with selumetinib preserves cardiac function and improves survival in cardiomyopathy caused by mutation in the lamin A/C gene
 Cardiovascular Research (2012) 93, 311 319 doi:10.1093/cvr/cvr301 Treatment with selumetinib preserves cardiac function and improves survival in cardiomyopathy caused by mutation in the lamin A/C gene
Cardiovascular Research (2012) 93, 311 319 doi:10.1093/cvr/cvr301 Treatment with selumetinib preserves cardiac function and improves survival in cardiomyopathy caused by mutation in the lamin A/C gene
In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease. Why Animal Models of Disease? Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison
 In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison Why Animal Models of Disease? Heart Failure (HF) Leading cause of morbidity and mortality
In Vivo Animal Models of Heart Disease Timothy A Hacker, PhD Department of Medicine University of Wisconsin-Madison Why Animal Models of Disease? Heart Failure (HF) Leading cause of morbidity and mortality
שינויים מולקולאריים ומבניים באי ספיקת לב אפשרויות לטיפול עתידני
 שינויים מולקולאריים ומבניים באי ספיקת לב אפשרויות לטיפול עתידני פרופ יהונתן ליאור 1 Braunwald s Heart Disease 8th Edition Chapter 21 Mechanisms of Cardiac Contraction and Relaxation Chapter 22 Pathophysiology
שינויים מולקולאריים ומבניים באי ספיקת לב אפשרויות לטיפול עתידני פרופ יהונתן ליאור 1 Braunwald s Heart Disease 8th Edition Chapter 21 Mechanisms of Cardiac Contraction and Relaxation Chapter 22 Pathophysiology
Ion channel dysfunction and diseases of the heart
 Basisvorlesung (BVO) Zelluläre Signaltransduktion- Krankheitsbilder Sommersemester 2015 902.384 PhD- Programm Molecular Signal Transduction Ion channel dysfunction and diseases of the heart H. Todt Dpt.
Basisvorlesung (BVO) Zelluläre Signaltransduktion- Krankheitsbilder Sommersemester 2015 902.384 PhD- Programm Molecular Signal Transduction Ion channel dysfunction and diseases of the heart H. Todt Dpt.
Risk prediction in inherited conditions Laminopathies
 Risk prediction in inherited conditions Laminopathies Karim Wahbi Cochin hospital, Paris karim.wahbi@aphp.fr Risk prediction in laminopathies Current approach for risk stratification A new score to predict
Risk prediction in inherited conditions Laminopathies Karim Wahbi Cochin hospital, Paris karim.wahbi@aphp.fr Risk prediction in laminopathies Current approach for risk stratification A new score to predict
Arrhythmogenic Mechanism of Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
 Review Article Arrhythmogenic Mechanism of Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Nian Liu MD 1, Barbara Colombi PhD 1, Silvia G. Priori MD PhD 1;2 1 Molecular Cardiology Fondazione Salvatore
Review Article Arrhythmogenic Mechanism of Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Nian Liu MD 1, Barbara Colombi PhD 1, Silvia G. Priori MD PhD 1;2 1 Molecular Cardiology Fondazione Salvatore
Cardiac follow-up in patients with hereditary muscular diseases
 Cardiac follow-up in patients with hereditary muscular diseases Tromsø 7. september 2018 Eystein Theodor Ek Skjølsvik, MD Professor Kristina H. Haugaa, MD, PhD Unit for genetic cardiac diseases, OUS Rikshospitalet
Cardiac follow-up in patients with hereditary muscular diseases Tromsø 7. september 2018 Eystein Theodor Ek Skjølsvik, MD Professor Kristina H. Haugaa, MD, PhD Unit for genetic cardiac diseases, OUS Rikshospitalet
Gene therapy and genome editing technologies for the study and potential treatment of :
 WORKSHOP ON GENOME EDITING Gene therapy and genome editing technologies for the study and potential treatment of : Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by Dr France Piétri-Rouxel, Institut de Myologie Centre de
WORKSHOP ON GENOME EDITING Gene therapy and genome editing technologies for the study and potential treatment of : Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by Dr France Piétri-Rouxel, Institut de Myologie Centre de
Basics of skeletal muscle electrophysiology. Tóth András, PhD
 Basics of skeletal muscle electrophysiology Tóth András, PhD Topics Structure Contraction and relaxation Activation Excitation-contraction coupling Action potential Ion channels* Calcium homeostasis Structure
Basics of skeletal muscle electrophysiology Tóth András, PhD Topics Structure Contraction and relaxation Activation Excitation-contraction coupling Action potential Ion channels* Calcium homeostasis Structure
Implications of the new diagnostic criteria for ARVC
 EUROECHO 2010 Echocardiographic assessment of cardiomyopathies Implications of the new diagnostic criteria for ARVC Barbara Bauce, MD, PhD Department of Cardiac, Thoracic and Vascular Sciences University
EUROECHO 2010 Echocardiographic assessment of cardiomyopathies Implications of the new diagnostic criteria for ARVC Barbara Bauce, MD, PhD Department of Cardiac, Thoracic and Vascular Sciences University
Nox-Dependent Mechanisms of Cardiomyocyte Dysfunction in a Model of Pressure Overload
 Nox-Dependent Mechanisms of Cardiomyocyte Dysfunction in a Model of Pressure Overload Giovanna Frazziano, PhD Vascular Medicine Institute Department of Pharmacology and Chemical Biology University of Pittsburgh
Nox-Dependent Mechanisms of Cardiomyocyte Dysfunction in a Model of Pressure Overload Giovanna Frazziano, PhD Vascular Medicine Institute Department of Pharmacology and Chemical Biology University of Pittsburgh
LMNA-related Dilated Cardiomyopathy therapy:
 LMNA-related Dilated Cardiomyopathy therapy: Silencing LMNA mrna and restoring wild type lamin proteins Gene Therapy Prof. I. Saggio 2018/2019 Adragna Cecilia, Anelli Valerio, D Avack Gloria, Rodríguez
LMNA-related Dilated Cardiomyopathy therapy: Silencing LMNA mrna and restoring wild type lamin proteins Gene Therapy Prof. I. Saggio 2018/2019 Adragna Cecilia, Anelli Valerio, D Avack Gloria, Rodríguez
Chapter 9 Muscle. Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle. Striated muscle
 Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
Genetics of Sudden Cardiac Death. Geoffrey Pitt Ion Channel Research Unit Duke University. Disclosures: Grant funding from Medtronic.
 Genetics of Sudden Cardiac Death Geoffrey Pitt Ion Channel Research Unit Duke University Disclosures: Grant funding from Medtronic Duke U N I V E R S I T Y Sudden Cardiac Death High incidence 50-100 per
Genetics of Sudden Cardiac Death Geoffrey Pitt Ion Channel Research Unit Duke University Disclosures: Grant funding from Medtronic Duke U N I V E R S I T Y Sudden Cardiac Death High incidence 50-100 per
SEMINAIRES IRIS. Sudden cardiac death in the adult. Gian Battista Chierchia. Heart Rhythm Management Center, UZ Brussel. 20% 25% Cancers !
 Sudden cardiac death in the adult Gian Battista Chierchia. Heart Rhythm Management Center, UZ Brussel.! " # $ % Cancers National Vital Statistics Report, Vol 49 (11), Oct. 12, 2001. 20% 25% State-specific
Sudden cardiac death in the adult Gian Battista Chierchia. Heart Rhythm Management Center, UZ Brussel.! " # $ % Cancers National Vital Statistics Report, Vol 49 (11), Oct. 12, 2001. 20% 25% State-specific
Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy
 orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy Disease name: Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy (EDMD) ICD 10: G71.0 Synonyms: Benign Scapuloperoneal
orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy Disease name: Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy (EDMD) ICD 10: G71.0 Synonyms: Benign Scapuloperoneal
Metrion Biosciences: the ion channel specialists
 Metrion Biosciences: the ion channel specialists In depth profiling of human ipsc cardiomyocytes: From electrophysiology to phenotypic assays Saïd El-Haou, PhD 30 November 2017 www.metrionbiosciences.com
Metrion Biosciences: the ion channel specialists In depth profiling of human ipsc cardiomyocytes: From electrophysiology to phenotypic assays Saïd El-Haou, PhD 30 November 2017 www.metrionbiosciences.com
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Genetic basis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Bos, J.M. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Genetic basis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Bos, J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Bos, J. M. (2010). Genetic basis of hypertrophic
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Genetic basis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Bos, J.M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Bos, J. M. (2010). Genetic basis of hypertrophic
International Graduate Research Programme in Cardiovascular Science
 1 International Graduate Research Programme in Cardiovascular Science This work has been supported by the European Community s Sixth Framework Programme under grant agreement n LSHM-CT-2005-01883 EUGeneHeart.
1 International Graduate Research Programme in Cardiovascular Science This work has been supported by the European Community s Sixth Framework Programme under grant agreement n LSHM-CT-2005-01883 EUGeneHeart.
Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA (
 Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA ( 夏强 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C518, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: xiaqiang@zju.edu.cn Course website: http://10.71.121.151/physiology
Skeletal Muscle Qiang XIA ( 夏强 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C518, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: xiaqiang@zju.edu.cn Course website: http://10.71.121.151/physiology
The Genes, Proteins, and the Cell Biological Processes Underlying Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy
 The Genes, Proteins, and the Cell Biological Processes Underlying Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy Megan E. Mastey a and Elise A. Kikis a Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy (EDMD) is a type of muscular
The Genes, Proteins, and the Cell Biological Processes Underlying Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy Megan E. Mastey a and Elise A. Kikis a Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy (EDMD) is a type of muscular
TABLE 1. Mutations in the Cardiac Ryanodine Receptor Gene (RyR2) Associated With CPVT and ARVD2* Amino acid Nucleotide Disease Families Familial? Doma
 EDITORIAL Sudden Unexplained Death Caused by Cardiac Ryanodine Receptor (RyR2) Mutations About 10% to 20% of postmortem examinations of young people who were apparently healthy but died suddenly and unexpectedly
EDITORIAL Sudden Unexplained Death Caused by Cardiac Ryanodine Receptor (RyR2) Mutations About 10% to 20% of postmortem examinations of young people who were apparently healthy but died suddenly and unexpectedly
Asaad Khoury 2,3 MD, Monther Boulos 1,3 MD, Mahmoud Suleiman 1,3 MD, Miry Blich 1,3 MD, Michael Eldar 4 MD, Ibrahim Marai 1,3 MD,
 Flecainide therapy suppresses exercise induced ventricular arrhythmias in patients with CASQ2 associated catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia Asaad Khoury 2,3 MD, Monther Boulos 1,3 MD,
Flecainide therapy suppresses exercise induced ventricular arrhythmias in patients with CASQ2 associated catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia Asaad Khoury 2,3 MD, Monther Boulos 1,3 MD,
New drugs on the horizon for heart failure: CaMK antagonists
 New drugs on the horizon for heart failure: CaMK antagonists (Lars S. Maier) Gerd Hasenfuss Disclosure Information: No relationship exists related to this presentation Dept. of Cardiology and Pneumology,
New drugs on the horizon for heart failure: CaMK antagonists (Lars S. Maier) Gerd Hasenfuss Disclosure Information: No relationship exists related to this presentation Dept. of Cardiology and Pneumology,
Introduction To Basic Cardiac Dysrhythmias, 4e By Sandra Atwood RN BA, Cheryl Stanton RN READ ONLINE
 Introduction To Basic Cardiac Dysrhythmias, 4e By Sandra Atwood RN BA, Cheryl Stanton RN READ ONLINE An important opening section Introduction to Cardiovascular Disorders provides a systems overview, beginning
Introduction To Basic Cardiac Dysrhythmias, 4e By Sandra Atwood RN BA, Cheryl Stanton RN READ ONLINE An important opening section Introduction to Cardiovascular Disorders provides a systems overview, beginning
Genetic Cardiomyopathies
 2017 HFCT Annual Scientific Meeting The Heart Failure Crosstalk Genetic Cardiomyopathies Teerapat Yingchoncharoen M.D. Ramathibodi Hospital Cardiomyopathy Group of diseases of the myocardium associated
2017 HFCT Annual Scientific Meeting The Heart Failure Crosstalk Genetic Cardiomyopathies Teerapat Yingchoncharoen M.D. Ramathibodi Hospital Cardiomyopathy Group of diseases of the myocardium associated
Basics of Signal Transduction. Ebaa M Alzayadneh, PhD
 Basics of Signal Transduction Ebaa M Alzayadneh, PhD What is signal transduction? Cell signaling The science of understanding how individual cells sense their environments and respond to stimuli... how
Basics of Signal Transduction Ebaa M Alzayadneh, PhD What is signal transduction? Cell signaling The science of understanding how individual cells sense their environments and respond to stimuli... how
Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department
 Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department Deffinition of cell The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all known living organisms The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 and also
Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department Deffinition of cell The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all known living organisms The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 and also
THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY
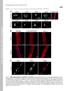 Supplemental Material Mejat et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200811035/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. SUN1, SUN2, and Nesprin-1 localization in muscle fibers. (A) SUN1 and SUN2
Supplemental Material Mejat et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.200811035/dc1 THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Figure S1. SUN1, SUN2, and Nesprin-1 localization in muscle fibers. (A) SUN1 and SUN2
Calcium Leak Through Ryanodine Receptors Leads To Atrial Fibrillation In Three Mouse Models of Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
 Calcium Leak Through Ryanodine Receptors Leads To Atrial Fibrillation In Three Mouse Models of Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Jian Shan 1, Wenjun Xie 1, Matthew Betzenhauser 1, Steven
Calcium Leak Through Ryanodine Receptors Leads To Atrial Fibrillation In Three Mouse Models of Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Jian Shan 1, Wenjun Xie 1, Matthew Betzenhauser 1, Steven
Clinical phenotypes associated with Desmosome gene mutations
 Clinical phenotypes associated with Desmosome gene mutations Serio A, Serafini E, Pilotto A, Pasotti M, Gambarin F, Grasso M, Disabella E, Diegoli M, Tagliani M, Arbustini E Centre for Inherited Cardiovascular
Clinical phenotypes associated with Desmosome gene mutations Serio A, Serafini E, Pilotto A, Pasotti M, Gambarin F, Grasso M, Disabella E, Diegoli M, Tagliani M, Arbustini E Centre for Inherited Cardiovascular
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common arrhythmia. Cellular Biology
 Cellular Biology Calcium Leak Through Ryanodine Receptors Leads to Atrial Fibrillation in 3 Mouse Models of Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Jian Shan, Wenjun Xie, Matthew Betzenhauser,
Cellular Biology Calcium Leak Through Ryanodine Receptors Leads to Atrial Fibrillation in 3 Mouse Models of Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia Jian Shan, Wenjun Xie, Matthew Betzenhauser,
Genotype Positive/ Phenotype Negative: Is It a Disease?
 Genotype Positive/ Phenotype Negative: Is It a Disease? Michelle Michels MD, PhD Center of Inherited Cardiovascular Diseases Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands No disclosures What is phenotype negative
Genotype Positive/ Phenotype Negative: Is It a Disease? Michelle Michels MD, PhD Center of Inherited Cardiovascular Diseases Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands No disclosures What is phenotype negative
InPulse: Development of an ipsc cardiomyocyte (ipsc-cm) platform to assess drug-induced contractility liabilities.
 InPulse: Development of an ipsc cardiomyocyte (ipsc-cm) platform to assess drug-induced contractility liabilities. Sponsors: Arun Sridhar, Peter J. Clements, Brian Berridge, Drug induced contractility
InPulse: Development of an ipsc cardiomyocyte (ipsc-cm) platform to assess drug-induced contractility liabilities. Sponsors: Arun Sridhar, Peter J. Clements, Brian Berridge, Drug induced contractility
Structure of the striated muscle general properties
 Structure of the striated muscle general properties Structure of the striated muscle membrane systems 1. Myofibrillum (contractile proteins) 2. Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) longitudinal tubule 3. SR terminal
Structure of the striated muscle general properties Structure of the striated muscle membrane systems 1. Myofibrillum (contractile proteins) 2. Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) longitudinal tubule 3. SR terminal
Physiology sheet #2. The heart composed of 3 layers that line its lumen and cover it from out side, these layers are :
 Physiology sheet #2 * We will talk in this lecture about cardiac muscle physiology, the mechanism and the energy sources of their contraction and intracellular calcium homeostasis. # Slide 4 : The heart
Physiology sheet #2 * We will talk in this lecture about cardiac muscle physiology, the mechanism and the energy sources of their contraction and intracellular calcium homeostasis. # Slide 4 : The heart
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL ADDITIONAL TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL ADDITIONAL TABLES Table S1. List of distinct rare variants detected by high-throughput sequencing in our cohort. The number of patients with each variant and the reference for the
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL ADDITIONAL TABLES Table S1. List of distinct rare variants detected by high-throughput sequencing in our cohort. The number of patients with each variant and the reference for the
What is New in CPVT? Diagnosis Genetics Arrhythmia Mechanism Treatment. Andreas Pflaumer
 What is New in CPVT? Diagnosis Genetics Arrhythmia Mechanism Treatment Andreas Pflaumer Diagnosis of CPVT Induction of different types of VES or VT by exercise or catecholamines AND exclusion of of other
What is New in CPVT? Diagnosis Genetics Arrhythmia Mechanism Treatment Andreas Pflaumer Diagnosis of CPVT Induction of different types of VES or VT by exercise or catecholamines AND exclusion of of other
When Lamins Go Bad: Nuclear Structure and Disease
 Leading Edge Review When Lamins Go Bad: Nuclear Structure and Disease Katherine H. Schreiber 1 and Brian K. Kennedy 1,2, * 1 Buck Institute for Research on Aging, 8001 Redwood Boulevard, Novato, CA 94945,
Leading Edge Review When Lamins Go Bad: Nuclear Structure and Disease Katherine H. Schreiber 1 and Brian K. Kennedy 1,2, * 1 Buck Institute for Research on Aging, 8001 Redwood Boulevard, Novato, CA 94945,
About This Chapter. Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Pearson Education, Inc.
 About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
Energetic state is a strong regulator of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ loss in cardiac muscle: different efficiencies of different energy sources
 Cardiovascular Research (2009) 83, 89 96 doi:10.1093/cvr/cvp125 Energetic state is a strong regulator of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ loss in cardiac muscle: different efficiencies of different energy
Cardiovascular Research (2009) 83, 89 96 doi:10.1093/cvr/cvp125 Energetic state is a strong regulator of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ loss in cardiac muscle: different efficiencies of different energy
4/11/2017. Cardiomyopathy. John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart. Disclosures. No Conflicts. Cardiomyopathy. WHO Classification
 Cardiomyopathy John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart Disclosures No Conflicts Cardiomyopathy WHO Classification Anatomy & physiology of the LV 1. Dilated Enlarged Systolic dysfunction 2. Hypertrophic Thickened
Cardiomyopathy John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart Disclosures No Conflicts Cardiomyopathy WHO Classification Anatomy & physiology of the LV 1. Dilated Enlarged Systolic dysfunction 2. Hypertrophic Thickened
Definition and classification of the cardiomyopathies. Georgios K Efthimiadis Ass Prof of Cardiology
 Definition and classification of the cardiomyopathies Georgios K Efthimiadis Ass Prof of Cardiology Historical Context WHO: 1980 classification "heart muscle diseases of unknown cause" WHO 1995 classification
Definition and classification of the cardiomyopathies Georgios K Efthimiadis Ass Prof of Cardiology Historical Context WHO: 1980 classification "heart muscle diseases of unknown cause" WHO 1995 classification
Reading Packet 2- Cells Unit. Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. What is resolving power?
 AP Biology Reading Packet 2- Cells Unit Name Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. What is resolving power? 2. How is an electron microscope different from a light microscope and what is the difference between
AP Biology Reading Packet 2- Cells Unit Name Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. What is resolving power? 2. How is an electron microscope different from a light microscope and what is the difference between
The Role of Defibrillator Therapy in Genetic Arrhythmia Syndromes
 The Role of Defibrillator Therapy in Genetic Arrhythmia Syndromes RHEA C. PIMENTEL, MD, FACC, FHRS UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS HOSPITAL MID AMERICA CARDIOLOGY AUGUST 19, 2012 Monogenic Arrhythmia Syndromes Mendelian
The Role of Defibrillator Therapy in Genetic Arrhythmia Syndromes RHEA C. PIMENTEL, MD, FACC, FHRS UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS HOSPITAL MID AMERICA CARDIOLOGY AUGUST 19, 2012 Monogenic Arrhythmia Syndromes Mendelian
PCB 3023 Exam 4 - Form A First and Last Name
 PCB 3023 Exam 4 - Form A First and Last Name Student ID # (U Number) A Before beginning this exam, please complete the following instructions: 1) Write your name and U number on the first page of this
PCB 3023 Exam 4 - Form A First and Last Name Student ID # (U Number) A Before beginning this exam, please complete the following instructions: 1) Write your name and U number on the first page of this
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
The ubiquitin proteasome system in cardiovascular disease Basic mechanisms
 ECS Congress 2010 Stockholm, Sweden 28 Aug 2010 01 Sep 2010 The ubiquitin proteasome system in cardiovascular disease Basic mechanisms Saskia Schlossarek Department of Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology
ECS Congress 2010 Stockholm, Sweden 28 Aug 2010 01 Sep 2010 The ubiquitin proteasome system in cardiovascular disease Basic mechanisms Saskia Schlossarek Department of Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology
Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy cases. Δέσποινα Παρχαρίδου Καρδιολόγος Επιστημονικός Συνεργάτης Α Καρδιολογική κλινική ΑΧΕΠΑ
 Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy cases Δέσποινα Παρχαρίδου Καρδιολόγος Επιστημονικός Συνεργάτης Α Καρδιολογική κλινική ΑΧΕΠΑ Definition ARVD (Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia) Progressive loss of
Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy cases Δέσποινα Παρχαρίδου Καρδιολόγος Επιστημονικός Συνεργάτης Α Καρδιολογική κλινική ΑΧΕΠΑ Definition ARVD (Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia) Progressive loss of
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Predisposition to Inherited Hypertrophic File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_predisposition_to_inherited_hypertrophic_cardiomyopathy
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Predisposition to Inherited Hypertrophic File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_predisposition_to_inherited_hypertrophic_cardiomyopathy
Risk Factors for Malignant Ventricular Arrhythmias in Lamin A/C Mutation Carriers
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 59, No. 5, 2012 2012 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/$36.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2011.08.078
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 59, No. 5, 2012 2012 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/$36.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2011.08.078
LMNA cardiomyopathy: cell biology and genetics meet clinical medicine
 Disease Models & Mechanisms 4, 562-568 (2011) doi:10.1242/dmm.006346 : cell biology and genetics meet clinical medicine Jonathan T. Lu 1, Antoine Muchir 1,2, Peter L. Nagy 2 and Howard J. Worman 1,2, *
Disease Models & Mechanisms 4, 562-568 (2011) doi:10.1242/dmm.006346 : cell biology and genetics meet clinical medicine Jonathan T. Lu 1, Antoine Muchir 1,2, Peter L. Nagy 2 and Howard J. Worman 1,2, *
SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1]
![SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1] SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1]](/thumbs/72/67086153.jpg) SMA OVERVIEW SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1] Autosomal recessive genetic inheritance 1 in 50 people (approximately 6 million Americans) are carriers [2] 1 in 6,000 to 1 in 10,000 children born
SMA OVERVIEW SMA IS A SEVERE NEUROLOGICAL DISORDER [1] Autosomal recessive genetic inheritance 1 in 50 people (approximately 6 million Americans) are carriers [2] 1 in 6,000 to 1 in 10,000 children born
Cardiac arrhythmias. Janusz Witowski. Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences. J. Witowski
 Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
Mechanistic Toxicology
 SECOND EDITION Mechanistic Toxicology The Molecular Basis of How Chemicals Disrupt Biological Targets URS A. BOELSTERLI CRC Press Tavlor & France Croup CRC Press is an imp^t o* :H Taylor H Francn C'r,,jpi
SECOND EDITION Mechanistic Toxicology The Molecular Basis of How Chemicals Disrupt Biological Targets URS A. BOELSTERLI CRC Press Tavlor & France Croup CRC Press is an imp^t o* :H Taylor H Francn C'r,,jpi
Differences in cardiac atrial and ventricular ion channels
 Differences in cardiac atrial and ventricular ion channels Norbert Jost, PhD Department of Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapy, University of Szeged Division for Cardiovascular Pharmacology, Hungarian Academy
Differences in cardiac atrial and ventricular ion channels Norbert Jost, PhD Department of Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapy, University of Szeged Division for Cardiovascular Pharmacology, Hungarian Academy
LES NOUVEAUX TROUBLES DE CONDUCTION HEREDITAIRES
 LES NOUVEAUX TROUBLES DE CONDUCTION HEREDITAIRES Alban Baruteau L institut du thorax, INSERM 1087 CNRS 6291 IRS Université de Nantes Centre Chirurgical Marie Lannelongue M3C Université Paris Sud Le Kremlin
LES NOUVEAUX TROUBLES DE CONDUCTION HEREDITAIRES Alban Baruteau L institut du thorax, INSERM 1087 CNRS 6291 IRS Université de Nantes Centre Chirurgical Marie Lannelongue M3C Université Paris Sud Le Kremlin
L aminopathies represent a heterogeneous group of genetic
 1of5 ONLINE MUTATION REPORT Mutation analysis of the lamin A/C gene (LMNA) among patients with different cardiomuscular phenotypes M Vytopil, S Benedetti, E Ricci, G Galluzzi, A Dello Russo, L Merlini,
1of5 ONLINE MUTATION REPORT Mutation analysis of the lamin A/C gene (LMNA) among patients with different cardiomuscular phenotypes M Vytopil, S Benedetti, E Ricci, G Galluzzi, A Dello Russo, L Merlini,
Sudden cardiac death: Primary and secondary prevention
 Sudden cardiac death: Primary and secondary prevention By Kai Chi Chan Penultimate Year Medical Student St George s University of London at UNic Sheba Medical Centre Definition Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA)
Sudden cardiac death: Primary and secondary prevention By Kai Chi Chan Penultimate Year Medical Student St George s University of London at UNic Sheba Medical Centre Definition Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA)
FIBER TYPES - oxidative metabolism is the main form here - ATPase activity is relatively low
 Cardiac Muscle Physiology Special characteristics of cardiac muscle - Branching and interdigitating cells - At their ends, they are connected by INTERCALATED DISCS - The discs are always at the Z-lines
Cardiac Muscle Physiology Special characteristics of cardiac muscle - Branching and interdigitating cells - At their ends, they are connected by INTERCALATED DISCS - The discs are always at the Z-lines
BIPN 100 F15 (Kristan) Human Physiology Lecture 10. Smooth muscle p. 1
 BIPN 100 F15 (Kristan) Human Physiology Lecture 10. Smooth muscle p. 1 Terms you should understand: smooth muscle, L-type Ca ++ channels, actin, myosin, sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), myosine phosphatase,
BIPN 100 F15 (Kristan) Human Physiology Lecture 10. Smooth muscle p. 1 Terms you should understand: smooth muscle, L-type Ca ++ channels, actin, myosin, sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), myosine phosphatase,
Aberrant sodium influx causes cardiomyopathy and atrial fibrillation in mice
 Aberrant sodium influx causes cardiomyopathy and atrial fibrillation in mice Elaine Wan, Jeffrey Adams, Richard L. Weinberg, Alexander N. Katchman, Joseph Bayne, Sergey I. Zakharov, Lin Yang, John P. Morrow,
Aberrant sodium influx causes cardiomyopathy and atrial fibrillation in mice Elaine Wan, Jeffrey Adams, Richard L. Weinberg, Alexander N. Katchman, Joseph Bayne, Sergey I. Zakharov, Lin Yang, John P. Morrow,
Breed specificities of Canine Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dr. Gerhard Wess
 Breed specificities of Canine Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dr. Gerhard Wess Diplomate ACVIM (Cardiology) Diplomate ECVIM-CA (Cardiology) Diplomate ECVIM-CA (Internal Medicine) INTRODUCTION Inherent disease of
Breed specificities of Canine Dilated Cardiomyopathy Dr. Gerhard Wess Diplomate ACVIM (Cardiology) Diplomate ECVIM-CA (Cardiology) Diplomate ECVIM-CA (Internal Medicine) INTRODUCTION Inherent disease of
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
The therapeutic potential of new insights into myocardial excitation contraction coupling
 371 REVIEW The therapeutic potential of new insights into myocardial excitation contraction coupling M Scoote, PA Poole-Wilson, A J Williams... The physiological mechanisms that link myocyte depolarisation
371 REVIEW The therapeutic potential of new insights into myocardial excitation contraction coupling M Scoote, PA Poole-Wilson, A J Williams... The physiological mechanisms that link myocyte depolarisation
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 18 Part A The Cardiovascular System 1/19/16 1 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Similarities of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle RMP Ion concentration Deploarization Action Potential Repolarization
Chapter 18 Part A The Cardiovascular System 1/19/16 1 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Similarities of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle RMP Ion concentration Deploarization Action Potential Repolarization
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Olivier CAZORLA. Effet délétère de l exercice sur la fonction cardiaque: modèles animaux
 Olivier CAZORLA Physiologie et Médecine Expérimentale du cœur et des muscles PHYMEDEXP INSERM U1046, CNRS UMR9214, Université de Montpellier CHU Arnaud de Villeneuve Stress physiologique et physiopathologique:
Olivier CAZORLA Physiologie et Médecine Expérimentale du cœur et des muscles PHYMEDEXP INSERM U1046, CNRS UMR9214, Université de Montpellier CHU Arnaud de Villeneuve Stress physiologique et physiopathologique:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature19102 Supplementary Discussion Benzothiazepine Binding in Ca V Ab Diltiazem and other benzothiazepines inhibit Ca V 1.2 channels in a frequency-dependent manner consistent with pore block
doi:10.1038/nature19102 Supplementary Discussion Benzothiazepine Binding in Ca V Ab Diltiazem and other benzothiazepines inhibit Ca V 1.2 channels in a frequency-dependent manner consistent with pore block
Laminopathies: many diseases, one gene. Report of the first Italian Meeting Course on Laminopathies
 Acta Myologica 2011; XXX: p. 138-143 workshop report Laminopathies: many diseases, one gene. Report of the first Italian Meeting Course on Laminopathies G. Lattanzi, S. Benedetti, E. Bertini, G. Boriani,
Acta Myologica 2011; XXX: p. 138-143 workshop report Laminopathies: many diseases, one gene. Report of the first Italian Meeting Course on Laminopathies G. Lattanzi, S. Benedetti, E. Bertini, G. Boriani,
The challenge of treating a stiff heart
 ResearchFeatures.com The challenge of treating a stiff heart Heart failure, when the heart fails to pump blood properly around the body, hospitalises more people in the Western world than any other condition.
ResearchFeatures.com The challenge of treating a stiff heart Heart failure, when the heart fails to pump blood properly around the body, hospitalises more people in the Western world than any other condition.
POSTDOCTORAL TRAINING
 2 Curriculum Vitae JULIAN E. STELZER, PhD CONTACT DETAILS Phone: 216-368-8636 julian.stelzer@case.edu EDUCATION 1992-96 McGill University, Montréal, Canada BS, Physiology. 1996-98 University of Saskatchewan,
2 Curriculum Vitae JULIAN E. STELZER, PhD CONTACT DETAILS Phone: 216-368-8636 julian.stelzer@case.edu EDUCATION 1992-96 McGill University, Montréal, Canada BS, Physiology. 1996-98 University of Saskatchewan,
Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure
 Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Francesco Paneni, MD, PhD, FESC Cardiology Unit Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Cardiology University Hospital Zurich Switzerland francesco.paneni@gmail.com
Pathophysiology and Diagnosis of Heart Failure Francesco Paneni, MD, PhD, FESC Cardiology Unit Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Cardiology University Hospital Zurich Switzerland francesco.paneni@gmail.com
1908 Biophysical Journal Volume 108 April
 1908 Biophysical Journal Volume 108 April 2015 1908 1921 Article Calcium-Voltage Coupling in the Genesis of Early and Delayed Afterdepolarizations in Cardiac Myocytes Zhen Song, 1,2 Christopher Y. Ko,
1908 Biophysical Journal Volume 108 April 2015 1908 1921 Article Calcium-Voltage Coupling in the Genesis of Early and Delayed Afterdepolarizations in Cardiac Myocytes Zhen Song, 1,2 Christopher Y. Ko,
Cell Signaling part 2
 15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY
 Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
Chapter 5 Control of Cells by Chemical Messengers
 Chapter 5 Control of Cells by Chemical Messengers = How hormones and other signals work Intercellular Communication = Intercellular Signal Transmission Chemical communication Electrical communication Intercellular
Chapter 5 Control of Cells by Chemical Messengers = How hormones and other signals work Intercellular Communication = Intercellular Signal Transmission Chemical communication Electrical communication Intercellular
Topic Page: congestive heart failure
 Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
