profiles Decision: Dalvance
|
|
|
- Beverly Cunningham
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Patient candidate profiles Decision: Dalvance
2 2 A series of patient candidate profiles The following patient candidate profiles are hypothetical examples of treatment decisions that could be seen in the treatment of adult patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI). In all cases, these hypothetical patient candidates were deemed to need IV antibiotics. Patient profiles do not represent actual patients. The profiles were developed with consultation from hospital and Emergency Department (ED) personnel. They are presented with and without the use of DALVANCE to illustrate how ABSSSI treatment regimens might vary before and after the introduction of DALVANCE. In the With DALVANCE scenario, patients are counseled that they have received the first IV infusion of DALVANCE 1000 mg and one week later should receive the second dose of DALVANCE 500 mg. In addition, they should follow up with their primary care physician 2-3 days after the first dose and again at the end of treatment to assess progress. Please note that these profiles are presented to illustrate the practical factors that may aid in the clinical decision-making process in dealing with these infections. The profiles do not represent medical advice or recommendations. Only the patient s own physician can determine the appropriate course of treatment for his or her patient. Indication DALVANCE (dalbavancin) for injection is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused by susceptible isolates of the following Gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant strains), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, and Streptococcus anginosus group (including S. anginosus, S. intermedius, S. constellatus). Important Safety Information Contraindications DALVANCE is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to dalbavancin. Warnings and Precautions Hypersensitivity Reactions Serious hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) and skin reactions have been reported with glycopeptide antibacterial agents, including DALVANCE. Exercise caution in patients with known hypersensitivity to glycopeptides due to the possibility of cross-sensitivity. If an allergic reaction occurs, treatment with DALVANCE should be discontinued. Infusion-Related Reactions Rapid intravenous infusion of DALVANCE can cause reactions, including flushing of the upper body, urticaria, pruritus, and rash. Hepatic Effects ALT elevations with DALVANCE treatment were reported in clinical trials. Clostridium difficile-associated Diarrhea Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with nearly all systemic antibacterial agents, including DALVANCE, with severity ranging from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Evaluate if diarrhea occurs. Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria Prescribing DALVANCE in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria. Adverse Reactions The most common adverse reactions in patients treated with DALVANCE were nausea (5.5%), headache (4.7%), and diarrhea (4.4%). Use in Specific Populations There have been no adequate and well-controlled studies with DALVANCE in pregnant or nursing women. DALVANCE should only be used if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk in these populations. In patients with renal impairment whose known creatinine clearance is less than 30 ml/min and who are not receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis, the recommended two-dose regimen for DALVANCE is 750 mg followed one week later by 375 mg. No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis, and DALVANCE can be administered without regard to the timing of hemodialysis. Caution should be exercised when prescribing DALVANCE to patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B or C) as no data are available to determine the appropriate dosing in these patients. Please see full Prescribing Information. 3
3 patient candidate #1 Middle-aged male Active Otherwise healthy, but with a spreading infection (cellulitis) of the skin on left thigh Admission Decision and Initial Antimicrobial Selection ED physician determines that the patient needs IV therapy with empiric treatment for S. pyogenes Given the patient s busy schedule and otherwise healthy constitution, and after consultation with his PCP, it is determined that the patient is a candidate for outpatient, IV antibiotic treatment Patient Profile Site of Presentation Assessment Otherwise-healthy 52-year-old male without serious comorbidities Has a full-time job Enjoys playing sports Has a wife and two young children No IV drug abuse, tobacco, or alcohol use Initially presents to general practitioner office with worsening infection on left thigh, sent to ED due to seriousness of infection Spreading infection of the skin on left thigh, which extends into subcutaneous tissues, developing over 24 hours Erythema of approximately 200 cm 2 Temperature of 101.5ºF Stable vital signs Lesion is swollen, warm, and tender to palpation CrCl of 119 ml/min WBC count of 13,000 cells/mm 3 With Other IV Antibiotics ED physician initiates an IV infusion of antibiotic and asks that the patient be monitored prior to release from the ED, with the option to admit if necessary Patient released to home after being treated as an outpatient in the ED; received discharge instructions of 7-14 days of daily IV antibiotic infusions to be initiated the next morning; option to switch to oral in 3 days Patient given number to call at any time if condition worsens Patient will be monitored in infusion center for improvement of condition over the next 2-3 days, including reports on status to primary care physician Patient schedules first 7 daily IV antibiotic infusion appointments at community s free-standing outpatient infusion clinic and goes to receive the first infusion the next day Initial Treatment Transition of Care With Dalvance ED physician initiates the first DALVANCE IV infusion of 1000 mg over 30 minutes, asks that the patient be monitored prior to release from the ED, with option to admit if necessary Patient released to home after being treated as an outpatient in the ED; given discharge instructions to receive second DALVANCE IV infusion one week later 500 mg given over 30 minutes Patient given number to call at any time if condition worsens Patient advised to see primary care physician in 2-3 days for follow-up exam Patient schedules appointment for one week later to receive second DALVANCE IV infusion of 500 mg infused over 30 minutes at community s free-standing outpatient infusion clinic; calls PCP for follow-up Diagnosis Cellulitis, treat for S. pyogenes Please see Important Safety Information. Please see full Prescribing Information. 4 5
4 patient candidate #2 Middle-aged female Previously scheduled commitments Soft tissue abscess surrounded by cellulitis Admission Decision and Initial Antimicrobial Selection Patient Profile Site of Presentation Assessment 40-year-old moderately overweight female (BMI = 28) with a history of Type 2 diabetes that is well-controlled Has two elementary school-aged children Husband works full-time Capable of performing activities of daily living and managing the household affairs Subcutaneous insulin Presents to the ED with a worsening infection that began a week ago and has been unresponsive to oral antibiotics Skin and soft tissue abscess/boil surrounded by significant cellulitis on back Erythema of approximately 150 cm 2 Temperature of 101 F BP 120/80; HR 100 Lesion is very warm and tender to palpation with likely formation of pus beneath WBC count of 14,000 cells/mm 3 CrCl of 68 ml/min Blood glucose is slightly elevated ED physician determines that the patient needs IV therapy for empiric treatment for S. aureus (MSSA) Given the patient s ability to manage her diabetes and the need to take care of her children, it is determined that the patient is a candidate for IV antibiotic treatment at a physician practice-based infusion center With Other IV Antibiotics ED physician performs incision and drainage (I & D); and then initiates an initial IV infusion of a daily antibiotic, and asks patient to stay for observation up to 24 hours Patient released to home after being treated as an outpatient for 24 hours under observation status; received discharge instructions to initiate daily IV antibiotic infusions for 10 days at a practice-based infusion center; option to switch to oral earlier Patient advised to see primary care physician in 2-3 days for follow-up exam and once again in a week Patient given number to call at any time if condition worsens Follow-up phone call from nursing staff 24 hours post-discharge to check on patient s fever Patient schedules appointments for first 7 days of daily IV infusions at physician practice-based infusion center and receives first infusion the next day Initial Treatment Transition of Care With Dalvance ED physician performs I & D and then orders first IV infusion of DALVANCE 1000 mg given over 30 minutes and asks patient to stay for observation up to 24 hours Patient released to home after being treated as an outpatient for 24 hours under observation status; received discharge instructions to receive second DALVANCE IV infusion one week later 500 mg infused over 30 minutes Patient advised to see primary care physician in 2-3 days for follow-up exam and again in one week Patient given number to call at any time if condition worsens Follow-up phone call from nursing staff 24 hours post-discharge to check on patient s fever Patient schedules appointment at physician practice-based infusion center and receives second DALVANCE IV infusion 500 mg given over 30 minutes one week after first dose Diagnosis Major cutaneous abscess, treat for S. aureus Please see Important Safety Information. Please see full Prescribing Information. 6 7
5 patient candidate #3 Elderly female, frail Needs assistance Recurrent cellulitis of lower extremities Admission Decision and Initial Antimicrobial Selection ED physician determines that patient needs IV therapy to treat empirically for Streptococci Given patient s age, comorbidities, and ongoing care in the SNF, ED physician admits patient to hospital Patient Profile Site of Presentation Assessment An 82-year-old woman with mild renal disease and well-controlled diabetes Lives in a skilled nursing facility (SNF) and is frequently visited by her daughter and other family members Has a history of coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, and chronic venous stasis Needs assistance performing most activities of daily living Presents to the ED with recurrent cellulitis of lower extremities Increased erythema and bullae of lower extremities, approximately 175 cm 2 Temperature of F BP 135/90; HR 90; 2+ peripheral edema WBC count of >15,000 cells/mm 3 CrCl of 44 ml/min With Other IV Antibiotics After hospital admission, PICC line is placed and patient receives twice-daily IV antibiotic infusions; requires careful therapeutic drug level monitoring given age and renal status Patient discharged back to SNF to continue treatment of infection with oral antibiotic therapy Patient to receive ongoing care and monitoring post-discharge in the skilled nursing facility Initial Treatment Transition of Care With Dalvance ED physician orders DALVANCE and first IV infusion is given in the ED 1000 mg given over 30 minutes; moves patient to observation unit to determine if patient needs to be admitted or released back to SNF Patient released to SNF after being treated as an outpatient for 36 hours in the observation unit; receives discharge orders for second dose of DALVANCE six days later at the HOPD Patient to receive ongoing care and monitoring post-discharge in the skilled nursing facility One week after first dose, patient brought to HOPD to receive second IV infusion of DALVANCE 500 mg given over 30 minutes Diagnosis Cellulitis, treat for Streptococci Please see Important Safety Information. Please see full Prescribing Information. 8 9
6 patient candidate #4 Middle-aged female Retired and active Wound infection Admission Decision and Initial Antimicrobial Selection ED physician determines that the patient needs IV therapy and should be treated empirically for MRSA Given patient independence and support at home, it is determined she is a candidate for outpatient IV antibiotic treatment at the hospital s infusion clinic Patient Profile A 67-year-old female, 170 lbs (BMI = 30) Recently retired, husband still works Spends a lot of time doing activities to maintain their home With Other IV Antibiotics Initial Treatment With Dalvance Site of Presentation Presents to ED with a supected spider bite on her hand received about a week ago that has gotten progressively worse ED physician orders placement of a PICC line and initiates IV antibiotic infusion over 2 hours due to renal insufficiency and asks for the patient to be watched prior to discharge Patient monitored under observation status in the ED for 20 hours ED physician orders first IV infusion of 1000 mg of DALVANCE over 30 minutes, and asks for the patient to be watched prior to discharge Patient monitored under observation status in the ED for 20 hours Assessment Diagnosis Infection characterized by purulent drainage from the wound with surrounding redness, edema, and induration Surface area of 150 cm 2 Lesion is warm and tender to palpation Lymph node enlargement Temperature of 101.5ºF HR 110; RR 16 WBC count of >12,000 cells/mm 3 CrCl of 55 ml/min Leukocytosis with left shift Wound infection, S. aureus considered, possibly MRSA Patient released to home following outpatient treatment for 20 hours under observation status in the ED Discharge planner helps arrange for continuation of care with second daily IV infusion the next day at the hospital outpatient infusion clinic and the additional daily IV infusions for a total of 10 days Patient advised to see primary care physician in 2-3 days for follow-up exam Patient to receive follow-up phone call from nursing staff 24 hours post-discharge Additional orders to follow from primary care physician for additional evaluations if necessary Transition of Care Patient released to home following outpatient treatment for 20 hours under observation status in the ED Discharge planner helps arrange for second DALVANCE IV infusion one week later 500 mg given over 30 minutes at hospital outpatient infusion clinic Patient advised to see primary care physician in 2-3 days for follow-up exam Patient to receive follow-up phone call from nursing staff 24 hours post-infusion Please see Important Safety Information. Please see full Prescribing Information
7 Decision: Dalvance Patient candidate profiles Actavis TM and its design are trademarks of Actavis, Inc. or its affiliates. Dalvance and its design are trademarks of Durata Therapeutics Holding C.V., an Actavis affiliate. Actavis All rights reserved. DAV /15
8 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DALVANCE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DALVANCE. DALVANCE (dalbavancin) for injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2014 INDICATIONS AND USAGE DALVANCE is indicated for acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused by designated susceptible strains of Gram-positive microorganisms. (1) To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of DALVANCE and other antibacterial drugs, DALVANCE should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Two-dose regimen: 1000 mg followed one week later by 500 mg (2.1) Dosage adjustment for patients with creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min and not receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis: 750 mg followed one week later by 375 mg (2.2) Administer by intravenous infusion over 30 minutes (2.3) DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS For injection: 500 mg of lyophilized powder in a single-use vial for reconstitution (3) CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity to dalbavancin (4) WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS Serious hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) and skin reactions have been reported with glycopeptide antibacterial agents, including DALVANCE; exercise caution in patients with known hypersensitivity to glycopeptides. (5.1) Rapid intravenous infusion of glycopeptide antibacterial agents can cause reactions. (5.2) ALT elevations with DALVANCE treatment were reported in clinical trials. (5.3) Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with nearly all systemic antibacterial agents, including DALVANCE. Evaluate if diarrhea occurs. (5.4) ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common adverse reactions in patients treated with DALVANCE were nausea (5.5%), headache (4.7%), and diarrhea (4.4%). To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Durata Therapeutics, Inc. at or FDA at FDA-1088 or USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Dosage adjustment is required in patients whose creatinine clearance is less than 30 ml/min and who are not receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis. (8.6) See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION Revised May 2014 FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS 1 INDICATION AND USAGE 1.1 Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections 1.2 Usage 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 2.1 Recommended Dose Regimen 2.2 Patients with Renal Impairment 2.3 Preparation and Administration 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS 5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions 5.2 Infusion-Related Reactions 5.3 Hepatic Effects 5.4 Clostridium diffi cile- Associated Diarrhea 5.5 Development of Drug- Resistant Bacteria 6 ADVERSE REACTIONS 6.1 Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS 7.1 Drug-Laboratory Test Interactions 7.2 Drug-Drug Interactions 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS 8.1 Pregnancy: Category C 8.3 Nursing Mothers 8.4 Pediatric Use 8.5 Geriatric Use 8.6 Renal Impairment 8.7 Hepatic Impairment 10 OVERDOSAGE 11 DESCRIPTION 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY 12.1 Mechanism of Action 12.2 Pharmacodynamics 12.3 Pharmacokinetics 12.4 Microbiology 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY 13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility 13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology 14 CLINICAL STUDIES 15 REFERENCES 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING 17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
9 FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION DALVANCE (dalbavancin) for injection 1 INDICATION AND USAGE 1.1 Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections DALVANCE (dalbavancin) for injection is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI) caused by susceptible isolates of the following Gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillinsusceptible and methicillin-resistant strains), Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae and Streptococcus anginosus group (including S. anginosus, S. intermedius, S. constellatus). 1.2 Usage To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of DALVANCE and other antibacterial agents, DALVANCE should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy. 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 2.1 Recommended Dosage Regimen For treatment of adults with ABSSSI, the recommended two-dose regimen of DALVANCE is 1000 mg followed one week later by 500 mg. DALVANCE should be administered over 30 minutes by intravenous infusion [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. 2.2 Patients with Renal Impairment In patients with renal impairment whose known creatinine clearance is less than 30 ml/min and who are not receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis, the recommended two-dose regimen of DALVANCE is 750 mg followed one week later by 375 mg. No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis, and DALVANCE can be administered without regard to the timing of hemodialysis [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. 2.3 Preparation and Administration DALVANCE (dalbavancin) for injection must be reconstituted with Sterile Water for Injection, USP, and subsequently diluted only with 5% Dextrose Injection, USP, to a final concentration of 1 mg/ml to 5 mg/ml. Reconstitution: DALVANCE must be reconstituted under aseptic conditions, using 25 ml of Sterile Water for Injection, USP, for each 500 mg vial. To avoid foaming, alternate between gentle swirling and inversion of the vial until its contents are completely dissolved. Do not shake. The reconstituted vial contains 20 mg/ml dalbavancin as a clear, colorless to yellow solution. Reconstituted vials may be stored either refrigerated at 2 to 8 C (36 to 46 F), or at controlled room temperature 20 to 25 C (68 to 77 F). Do not freeze. Dilution: Aseptically transfer the required dose of reconstituted dalbavancin solution from the vial(s) to an intravenous bag or bottle containing 5% Dextrose Injection, USP. The diluted solution must have a final dalbavancin concentration of 1 mg/ml to 5 mg/ml. Discard any unused portion of the reconstituted solution. Once diluted into an intravenous bag or bottle as described above, DALVANCE may be stored either refrigerated at 2 to 8 C (36 to 46 F) or at a controlled room temperature of 20 to 25 C (68 to 77 F). Do not freeze. The total time from reconstitution to dilution to administration should not exceed 48 hours. Like all parenteral drug products, diluted DALVANCE should be inspected visually for particulate matter prior to infusion. If particulate matter is identified, do not use. After reconstitution and dilution, DALVANCE is to be administered via intravenous infusion, using a total infusion time of 30 minutes. Do not co-infuse DALVANCE with other medications or electrolytes. Saline-based infusion solutions may cause precipitation and should not be used. The compatibility of reconstituted DALVANCE with intravenous medications, additives, or substances other than 5% Dextrose Injection, USP has not been established. If a common intravenous line is being used to administer other drugs in addition to DALVANCE, the line should be flushed before and after each DALVANCE infusion with 5% Dextrose Injection, USP. 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS DALVANCE is supplied in single-use, clear glass vials containing sterile powder (white/off-white to pale yellow) equivalent to 500 mg of anhydrous dalbavancin. 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS DALVANCE is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to dalbavancin. No data are available on cross-reactivity between dalbavancin and other glycopeptides, including vancomycin. 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS 5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions Serious hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) and skin reactions have been reported in patients treated with DALVANCE. If an allergic reaction occurs, treatment with DALVANCE should be discontinued. Before using DALVANCE, inquire carefully about previous hypersensitivity reactions to glycopeptides, and due to the possibility of cross-sensitivity, exercise caution in patients with a history of glycopeptide allergy [see Patient Counseling Information (17)]. 5.2 Infusion Related Reactions DALVANCE is administered via intravenous infusion, using a total infusion time of 30 minutes to minimize the risk of infusion-related reactions. Rapid intravenous infusions of DALVANCE can cause reactions that resemble Red-Man Syndrome, including flushing of the upper body, urticaria, pruritus, and/or rash. Stopping or slowing the infusion may result in cessation of these reactions. 5.3 Hepatic Effects In Phase 2 and 3 clinical trials, more DALVANCE- than comparator-treated subjects with normal baseline transaminase levels had post-baseline alanine aminotransferase (ALT) elevation greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN). Overall, abnormalities in liver tests (ALT, AST, bilirubin) were reported with similar frequency in the DALVANCE and comparator arms [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. 5.4 Clostridium difficile-associated Diarrhea Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported in users of nearly all systemic antibacterial drugs, including DALVANCE, with severity ranging from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents can alter the normal flora of the colon, and may permit overgrowth of C. difficile. C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin-producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antibacterial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibacterial use. Careful medical history is necessary because CDAD has been reported to occur more than 2 months after the administration of antibacterial agents. If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibacterial use not directed against C. difficile should be discontinued, if possible. Appropriate measures such as fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibacterial treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated. 5.5 Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria Prescribing DALVANCE in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria. 6 ADVERSE REACTIONS Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in clinical trials of DALVANCE cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect rates observed in practice.
10 FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION DALVANCE (dalbavancin) for injection 6.1 Adverse Reactions in Clinical Trials Adverse reactions were evaluated for 1778 patients treated with DALVANCE and 1224 patients treated with comparator antibacterial drugs in seven Phase 2 and Phase 3 clinical trials. A causal relationship between study drug and adverse reactions was not always established. The median age of patients treated with DALVANCE was 47 years, ranging between 16 and 93 years old. Patients treated with DALVANCE were predominantly male (60%) and Caucasian (78%). Serious Adverse Reactions and Adverse Reactions Leading to Discontinuation Serious adverse reactions occurred in 109/1778 (6.1%) of patients treated with DALVANCE and in 80/1224 (6.5%) of patients treated with comparator. DALVANCE was discontinued due to an adverse reaction in 53/1778 (3%) patients and the comparator was discontinued due to an adverse reaction in 35/1224 (2.8%) patients. Most Common Adverse Reactions The most common adverse reactions in patients treated with DALVANCE were nausea (5.5%), headache (4.7%), and diarrhea (4.4%). The median duration of adverse reactions was 4.0 days in both treatment groups. Table 1 lists selected adverse reactions occurring in more than 2% of patients treated with DALVANCE in clinical trials. Table 1. Selected Adverse Reactions in Phase 2/3 Trials (Number (%) of Patients) Dalbavancin (N = 1778) Comparator* (N = 1224) Nausea 98 (5.5) 78 (6.4) Vomiting 50 (2.8) 37 (3) Diarrhea 79 (4.4) 72 (5.9) Headache 83 (4.7) 59 (4.8) Rash 48 (2.7) 30 (2.4) Pruritus 38 (2.1) 41 (3.3) *Comparators included linezolid, cefazolin, cephalexin, and vancomycin. The following selected adverse reactions were reported in DALVANCE treated patients at a rate of less than 2% in these clinical trials: Blood and lymphatic system disorders: anemia, hemorrhagic anemia, leucopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, petechiae, eosinophilia, thrombocytosis Gastrointestinal disorders: gastrointestinal hemorrhage, melena, hematochezia, abdominal pain General disorders and administration site conditions: infusion related reactions Hepatobiliary disorders: hepatotoxicity Immune system disorders: anaphylactoid reaction Infections and infestations: Clostridium difficile colitis, oral candidiasis, vulvovaginal mycotic infection Investigations: hepatic transaminases increased, blood alkaline phosphatase increased, international normalized ratio increased Metabolism and nutrition disorders: hypoglycemia Nervous system disorders: dizziness Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: bronchospasm Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: urticaria Vascular disorders: flushing, phlebitis, wound hemorrhage, spontaneous hematoma Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) Elevations Among patients with normal baseline ALT levels, more DALVANCE- than comparator-treated patients had post-baseline ALT elevations greater than 3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), 12 (0.8%) vs. 2 (0.2%), respectively including three subjects with post-baseline ALT values greater than 10 times ULN. Eight of 12 patients treated with DALVANCE and one comparator patient had underlying conditions which could affect liver enzymes, including chronic viral hepatitis and a history of alcohol abuse. In addition, one DALVANCEtreated subject in a Phase 1 trial had post-baseline ALT elevations greater than 20 times ULN. ALT elevations were reversible in all subjects. No comparator-treated subject with normal baseline transaminases had post-baseline ALT elevation greater than 10 times ULN. 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS 7.1 Drug-Laboratory Test Interactions Drug-laboratory test interactions have not been reported. 7.2 Drug-Drug Interactions No clinical drug-drug interaction studies have been conducted with DALVANCE. There is minimal potential for drug-drug interactions between DALVANCE and cytochrome P450 (CYP450) substrates, inhibitors, or inducers [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. 8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS 8.1 Pregnancy: Category C There have been no adequate and well-controlled studies with dalbavancin in pregnant women. DALVANCE should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. No evidence of embryo or fetal toxicity was found in the rat or rabbit at a dose of 15 mg/kg/day (1.2 and 0.7 times the human dose on an exposure basis, respectively). Delayed fetal maturation was observed in the rat at a dose of 45 mg/kg/day (3.5 times the human dose on an exposure basis). In a rat prenatal and postnatal development study, increased embryo lethality and increased offspring deaths during the first week post-partum were observed at a dose of 45 mg/kg/day (3.5 times the human dose on an exposure basis). 8.3 Nursing Mothers Dalbavancin is excreted in the milk of lactating rats. It is not known whether dalbavancin or its metabolite is excreted in human milk; therefore, caution should be exercised when DALVANCE is administered to a nursing woman. 8.4 Pediatric Use Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients have not been established. 8.5 Geriatric Use Of the 1778 patients treated with DALVANCE in Phase 2 and 3 clinical trials, 313 patients (17.7%) were 65 years of age or older. The efficacy and tolerability of DALVANCE were similar to comparator regardless of age. The pharmacokinetics of dalbavancin were not significantly altered with age; therefore, no dosage adjustment is necessary based on age alone. DALVANCE is substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection in this age group. 8.6 Renal Impairment In patients with renal impairment whose known creatinine clearance is less than 30 ml/min and who are not receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis, the recommended two-dose regimen for DALVANCE is 750 mg followed one week later by 375 mg. No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis, and DALVANCE can be administered without regard to the timing of hemodialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. 8.7 Hepatic Impairment No dosage adjustment of DALVANCE is recommended for patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A). Caution should be exercised when prescribing dalbavancin to patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B or C) as no data are available to determine the appropriate dosing in these patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. 10 OVERDOSAGE Specific information is not available on the treatment of overdose with DALVANCE, as doselimiting toxicity has not been observed in clinical studies. In Phase 1 studies, healthy volunteers have been administered single doses of up to 1500 mg, and cumulative doses of up to 4500 mg over a period of up to 8 weeks, with no signs of toxicity nor laboratory results of clinical concern. Treatment of overdose with DALVANCE should consist of observation and general supportive measures. Although no information is available specifically regarding the use of hemodialysis to treat overdose, in a Phase 1 study in patients with renal impairment less than 6% of the recommended dalbavancin dose was removed [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
11 FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION DALVANCE (dalbavancin) for injection 11 DESCRIPTION DALVANCE (dalbavancin) for injection is a lipoglycopeptide synthesized from a fermentation product of Nonomuraea species. Dalbavancin is a mixture of five closely related active homologs (A 0, A 1, B 0, B 1, and B 2 ); the component B 0 is the major component of dalbavancin. The homologues share the same core structure and differ in the fatty acid side chain of the N-acylaminoglucuronic acid moiety (R 1 ) structure and/or the presence of an additional methyl group (R 2 ) on the terminal amino group (shown in the figure and table below). Figure 1. Dalbavancin Structural Formula Table 2. Substitution Patterns for Dalbavancin API Homologs Dalbavancin R 1 R 2 Molecular Formula Molecular Weight* A 0 CH(CH 3 ) 2 H C 87 H 98 N 10 O 28 Cl HCl A 1 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 H C 87 H 98 N 10 O 28 Cl HCl B 0 CH 2 CH(CH 3 ) 2 H C 88 H 100 N 10 O 28 Cl HCl B 1 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 H C 88 H 100 N 10 O 28 Cl HCl B 2 CH 2 CH(CH 3 ) 2 CH 3 C 89 H 102 N 10 O 28 Cl HCl *Anhydrous free base The B 0 INN chemical name is: 5,31-dichloro-38- de(methoxycarbonyl)-7-demethyl-19-deoxy-56- O-[2-deoxy-2-[(10-methylundecanoyl)amino]-ß-Dglucopyranuronosyl]-38-[[3-(dimethylamino)propyl] carbamoyl]-42-o-a-d-mannopyranosyl-15-nmethyl(ristomycin A aglycone) hydrochloride. DALVANCE is supplied in clear glass vials as a sterile, lyophilized, preservative-free, white to off-white to pale yellow solid. Each vial contains dalbavancin HCl equivalent to 500 mg of anhydrous dalbavancin as the free base, plus lactose monohydrate (129 mg) and mannitol (129 mg) as excipients. Sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid may be added to adjust the ph at the time of manufacture. The powder is to be reconstituted and further diluted for IV infusion [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]. 12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY 12.1 Mechanism of Action Dalbavancin is an antibacterial drug [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.4)] Pharmacodynamics The antibacterial activity of dalbavancin appears to best correlate with the ratio of area under the concentration-time curve to minimal inhibitory concentration (AUC/MIC) for Staphylococcus aureus based on animal models of infection. An exposure-response analysis of a single study in patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections supports the two-dose regimen [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Cardiac Electrophysiology: In a randomized, positive- and placebo-controlled, thorough QT/QTc study, 200 healthy subjects received dalbavancin 1000 mg IV, dalbavancin 1500 mg IV, oral moxifloxacin 400 mg, or placebo. Neither dalbavancin 1000 mg nor dalbavancin 1500 mg (supratherapeutic dose) had any clinically relevant adverse effect on cardiac repolarization Pharmacokinetics Dalbavancin pharmacokinetic parameters have been characterized in healthy subjects, patients, and specific populations. Pharmacokinetic parameters following administration of a single intravenous 1000 mg dose were as shown in Table 3. The pharmacokinetics of dalbavancin can be described using a three-compartment model. Table 3. Dalbavancin Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Healthy Subjects Parameter Single 1000 mg Dose C max (mg/l) 287 (13.9) 1 AUC 0-24 (mg h/l) 3185 (12.8) 1 AUC 0-Day7 (mg h/l) (41.1) 2 AUC 0-inf (mg h/l) (40.9) 2 Terminal t ½ (h) 346 (16.5) 2,3 CL (L/h) (46.8) 2 All values are presented as mean (% coeffi cient of variation) 1 Data from 50 healthy subjects. 2 Data from 12 healthy subjects. 3 Based upon population pharmacokinetic analyses of data from patients, the effective half-life is approximately 8.5 days (204 hours). In healthy subjects, dalbavancin AUC 0-24h and C max both increased proportionally to dose following single IV dalbavancin doses ranging from 140 mg to 1500 mg, indicating linear pharmacokinetics. The mean plasma concentration-time profile for dalbavancin at the recommended two-dose regimen of 1000 mg followed one week later by 500 mg is shown in Figure 2. Figure 2. Mean (± standard deviation) dalbavancin plasma concentrations versus time in healthy subjects (n=10) following IV administration over 30 minutes of 1000 mg dalbavancin (Day 1) and 500 mg dalbavancin (Day 8). Dalbavancin plasma concentration, (mg/l) (+ Standard Deviation) Time, days No apparent accumulation of dalbavancin was observed following multiple IV infusions administered once weekly for up to eight weeks, with 1000 mg on Day 1 followed by up to seven weekly 500 mg doses, in healthy adults with normal renal function. Distribution: Dalbavancin is reversibly bound to human plasma proteins, primarily to albumin. The plasma protein binding of dalbavancin is approximately 93% and is not altered as a function of drug concentration, renal impairment, or hepatic impairment. The mean concentrations of dalbavancin achieved in skin blister fluid remain above 30 mg/l up to 7 days (approximately 146 hours) post dose, following 1000 mg IV dalbavancin. The mean ratio of the AUC hrs in skin blister fluid/auc hrs in plasma is 0.60 (range 0.44 to 0.64). Metabolism: In vitro studies using human microsomal enzymes and hepatocytes indicate that dalbavancin is not a substrate, inhibitor, or inducer of CYP450 isoenzymes. A minor metabolite of dalbavancin (hydroxy-dalbavancin) has been observed in the urine of healthy subjects. Quantifiable concentrations of the hydroxydalbavancin metabolite have not been observed in human plasma (lower limit of quantitation = 0.4 µg/ml) [see Drug Interactions (7.2)]. Excretion: Following administration of a single 1000 mg dose in healthy subjects, 20% of the dose was excreted in feces through 70 days post dose. An average of 33% of the administered dalbavancin dose was excreted in urine as unchanged dalbavancin and approximately 12% of the administered dose was excreted in urine as the metabolite hydroxy-dalbavancin through 42 days post dose. Specific Populations Renal Impairment: The pharmacokinetics of dalbavancin were evaluated in 28 subjects with varying degrees of renal impairment and in 15 matched control subjects with normal renal function. Following a single dose of 500 mg or 1000 mg dalbavancin, the mean plasma clearance (CL T ) was reduced 11%, 35%, and 47% in subjects with mild (CL CR 50 to 79 ml/min), moderate (CL CR 30 to 49 ml/min), and severe (CL CR less than 30 ml/min), renal impairment, respectively, compared to subjects with normal renal function. The clinical significance of the decrease in mean plasma CL T, and the associated increase in AUC 0- noted in these pharmacokinetic studies of dalbavancin in subjects with severe renal impairment has not been established [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
12 FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION DALVANCE (dalbavancin) for injection No dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with CL CR greater than 30 ml/min or patients receiving hemodialysis. The recommended twodose regimen for dalbavancin in patients with severe renal impairment who are not receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis is 750 mg followed one week later by 375 mg. Dalbavancin pharmacokinetic parameters in subjects with end-stage renal disease receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis (three times/ week) are similar to those observed in subjects with mild to moderate renal impairment, and less than 6% of an administered dose is removed after three hours of hemodialysis. Therefore, no dosage adjustment is recommended for patients receiving regularly scheduled hemodialysis, and dalbavancin may be administered without regard to the timing of hemodialysis in such patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Overdosage (10)]. Hepatic Impairment: The pharmacokinetics of dalbavancin were evaluated in 17 subjects with mild, moderate, or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A, B or C) and compared to those in nine matched healthy subjects with normal hepatic function. The mean AUC hrs was unchanged in subjects with mild hepatic impairment compared to subjects with normal hepatic function; however, the mean AUC hrs decreased 28% and 31% in subjects with moderate and severe hepatic impairment respectively, compared to subjects with normal hepatic function. The clinical significance of the decreased AUC hrs in subjects with moderate and severe hepatic function is unknown. No dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with mild hepatic impairment. Caution should be exercised when prescribing dalbavancin to patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment as no data are available to determine the appropriate dosing. Gender: Clinically significant gender-related differences in dalbavancin pharmacokinetics have not been observed either in healthy subjects or in patients with infections. No dosage adjustment is recommended based on gender. Geriatric Patients: Clinically significant age-related differences in dalbavancin pharmacokinetics have not been observed in patients with infections. No dosage adjustment is recommended based solely on age. Pediatric Patients: The pharmacokinetics of dalbavancin in pediatric populations <12 years of age have not been established. Drug Interactions Nonclinical studies demonstrated that dalbavancin is not a substrate, inhibitor, or inducer of CYP450 isoenzymes. In a population pharmacokinetic analysis, dalbavancin pharmacokinetics were not affected by co-administration with known CYP450 substrates, inducers or inhibitors, nor by individual medications including acetaminophen, aztreonam, fentanyl, metronidazole, furosemide, proton pump inhibitors (omeprazole, esomeprazole, pantoprazole, lansoprazole), midazolam, and simvastatin Microbiology Mechanism of Action Dalbavancin, a semisynthetic lipoglycopeptide, interferes with cell wall synthesis by binding to the D-alanyl-D-alanine terminus of the stem pentapeptide in nascent cell wall peptidoglycan, thus preventing cross-linking. Dalbavancin is bactericidal in vitro against Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes at concentrations similar to those sustained throughout treatment in humans treated according to the recommended dosage regimen. Mechanism of Resistance The development of bacterial isolates resistant to dalbavancin has not been observed, either in vitro, in studies using serial passage, or in animal infection experiments. Interaction with Other Antimicrobials When tested in vitro, dalbavancin demonstrated synergistic interactions with oxacillin and did not demonstrate antagonistic or synergistic interactions with any of the following antibacterial agents of various classes: gentamicin, vancomycin, levofloxacin, clindamycin, quinupristin/dalfopristin, linezolid, aztreonam, rifampin or daptomycin. The clinical significance of these in vitro findings is unknown. Dalbavancin has been shown to be active against the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections [see Indications and Usage (1)]. Gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillinresistant isolates) Streptococcus pyogenes Streptococcus agalactiae Streptococcus anginosus group (including S. anginosus, S. intermedius, S. constellatus) The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. In addition, at least 90% of organisms in the following bacteria exhibit an in vitro minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) less than or equal to the dalbavancin susceptible breakpoint of 0.12 mcg/ml. However, the safety and efficacy of dalbavancin in treating clinical infections due to these bacteria have not been established in adequate well-controlled clinical trials. Gram-positive bacteria Enterococcus faecium (vancomycin-susceptible isolates only) Enterococcus faecalis (vancomycin-susceptible isolates only) Susceptibility Test Methods When available, the clinical microbiology laboratory should provide the results of in vitro susceptibility test results for antimicrobial drug products used in resident hospitals to the physician as periodic reports that describe the susceptibility profile of nosocomial and community-acquired pathogens. These reports should aid the physician in selecting an antibacterial drug for treatment. Dilution Techniques Quantitative methods are used to determine minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs). These MICs provide estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The MICs should be determined using a standardized test method. 1,2 When determining dalbavancin MICs, polysorbate-80 (P-80), should be added at a final concentration of 0.002% to freshly prepared or frozen microtiter trays. The MIC values should be interpreted according to the criteria provided in Table 4. Diffusion Techniques Dalbavancin disks for diffusion susceptibility testing are not available. Disk diffusion is not a reliable method for determining the in vitro activity of dalbavancin. Table 4. Susceptibility Test Interpretive Criteria for Dalbavancin Pathogen MIC (mcg/ml) a Zone Diameter (mm) S I R S I R Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillinresistant isolates) Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus agalactiae, and Streptococcus anginosus group a The current absence of data on resistant isolates precludes defi ning any category other than Susceptible. If isolates yield MIC results other than susceptible, they should be submitted to a reference laboratory for additional testing. A report of Susceptible indicates that the antibacterial agent is likely to inhibit growth of the pathogen if the antibacterial compound reaches the concentrations at the infection site necessary to inhibit growth of the pathogen. Quality Control Standardized susceptibility test procedures require the use of laboratory controls to monitor and ensure the accuracy and precision of supplies and reagents used in the assay, and the techniques of the individuals performing the test. 1,2 Standard dalbavancin powder should provide the following range of MIC values noted in Table 5. Table 5. Acceptable MIC Quality Control Ranges for Dalbavancin Quality Control Strain MIC Range (µg/ml) Staphylococcus aureus ATCC Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC a Enterococcus faecalis ATCC ATCC = American Type Culture Collection a This organism may be used for validation of susceptibility test results when testing Streptococcus species other than S. pneumoniae.
13 FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION DALVANCE (dalbavancin) for injection 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY 13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility Long-term studies in animals to determine the carcinogenic potential of dalbavancin have not been conducted. Dalbavancin was not genotoxic in a mammalian HGPRT gene mutation assay, an in vitro chromosome aberration assay in Chinese Hamster Ovary cells, or an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay. Impaired fertility in the rat was not observed at a dose of 15 mg/kg/day (1.2 times the human dose on an exposure basis). Reductions in male and female fertility and increased embryo resorptions occurred at a dose of 45 mg/kg/day (3.5 times the human dose on an exposure basis), at which signs of parental toxicity were also observed Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology Increases in serum levels of liver enzymes (ALT, AST), associated with microscopic findings in the liver were noted in toxicology studies in rats and dogs where dalbavancin was administered daily for 28 to 90 days. Hepatocellular necrosis was observed in dogs dosed at 10 mg/kg/day for longer than 2 months, i.e., at approximately 5 to 7 times the expected human dose on an exposure basis. Histiocytic vacuolation and hepatocyte necrosis were observed in rats dosed daily at 40 and 80 mg/kg/day, respectively, for 4 weeks, (approximately 3 and 6 times the expected human dose on an exposure basis, respectively). In addition, renal toxicity characterized by increases in serum BUN and creatinine and microscopic kidney findings was observed in rats and dogs at doses 5 to 7 times the expected human dose on an exposure basis. The relationship between these findings in the animal toxicology studies after 28 and 90 consecutive days of dosing to the indicated clinical dosing of 2 doses 7 days apart are unclear. 14 CLINICAL STUDIES Acute Bacterial Skin and Skin Structure Infections: Adult patients with ABSSSI were enrolled in two Phase 3, randomized, doubleblind, double-dummy clinical trials of similar design (Trial 1 and Trial 2). The Intent-to-Treat (ITT) population included 1,312 randomized patients. Patients were treated for two weeks with either a two-dose regimen of intravenous DALVANCE (1000 mg followed one week later by 500 mg) or intravenous vancomycin (1000 mg or 15 mg/kg every 12 hours, with the option to switch to oral linezolid after 3 days). DALVANCE-treated patients with creatinine clearance of less than 30 ml/min received 750 mg followed one week later by 375 mg. Approximately 5% of patients also received a protocol-specified empiric course of treatment with intravenous aztreonam for coverage of Gram-negative pathogens. The specific infections in these trials included cellulitis (approximately 50% of patients across treatment groups), major abscess (approximately 30%), and wound infection (approximately 20%). The median lesion area at baseline was 341 cm 2. In addition to local signs and symptoms of infection, patients were also required to have at least one systemic sign of disease at baseline, defined as temperature 38 C or higher (approximately 85% of patients), white blood cell count greater than 12,000 cells/mm 3 (approximately 40%), or 10% or more band forms on white blood cell differential (approximately 23%). Across both trials, 59% of patients were from Eastern Europe and 36% of patients were from North America. Approximately 89% of patients were Caucasian and 58% were males. The mean age was 50 years and the mean body mass index was 29.1 kg/m 2. The primary endpoint of these two ABSSSI trials was the clinical response rate where responders were defined as patients who had no increase from baseline in lesion area 48 to 72 hours after initiation of therapy, and had a temperature consistently at or below 37.6 C upon repeated measurement. Table 6 summarizes overall clinical response rates in these two ABSSSI trials using the pre-specified primary efficacy endpoint in the ITT population. Table 6. Clinical Response Rates in ABSSSI Trials at Hours after Initiation of Therapy DALVANCE Vancomycin/ Linezolid Difference (95% CI) 3 Trial 1 240/288 (83.3%) 233/285 (81.8%) 1.5% (-4.6, 7.9) Trial 2 285/371 (76.8%) 288/368 (78.3%) -1.5% (-7.4, 4.6) 1 There were 7 patients who did not receive treatment and were counted as non-responders: 6 dalbavancin patients (3 in each trial) and one vancomycin/linezolid patient in Trial 2. 2 Patients who died or used non-study antibacterial therapy or had missing measurements were classifi ed as non-responders. 3 The 95% Confi dence Interval (CI) is computed using the Miettinen and Nurminen approach, stratifi ed by baseline fever status. A key secondary endpoint in these two ABSSSI trials evaluated the percentage of ITT patients achieving a 20% or greater reduction in lesion area from baseline at hours after initiation of therapy. Table 7 summarizes the findings for this endpoint in these two ABSSSI trials. Table 7. Patients in ABSSSI Trials with Reduction in Lesion Area of 20% or Greater at Hours after Initiation of Therapy DALVANCE Vancomycin/ Linezolid Difference (95% CI) 3 Trial 1 259/288 (89.9%) 259/285 (90.9%) -1.0% (-5.7, 4.0) Trial 2 325/371 (87.6%) 316/368 (85.9%) 1.7% (-3.2, 6.7) 1 There were 7 patients (as described in Table 6) who did not receive treatment and were counted as non-responders. 2 Patients who died or used non-study antibacterial therapy or had missing measurements were classifi ed as non-responders. 3 The 95% CI is computed using the Miettinen and Nurminen approach, stratifi ed by baseline fever status. Another secondary endpoint in these two ABSSSI trials was the clinical success rate assessed at a follow-up visit occurring between Days 26 to 30. Clinical Success at this visit was defined as having a decrease in lesion size (both length and width measurements), a temperature of 37.6 C or lower, and meeting pre-specified criteria for local signs: purulent discharge and drainage absent or mild and improved from baseline, heat/warmth & fluctuance absent, swelling/ induration & tenderness to palpation absent or mild. Table 8 summarizes clinical success rates at a follow-up visit for the ITT and clinically evaluable population in these two ABSSSI trials. Note that there are insufficient historical data to establish the magnitude of drug effect for antibacterial drugs compared with placebo at the follow-up visits. Therefore, comparisons of DALVANCE to vancomycin/linezolid based on clinical success rates at these visits cannot be utilized to establish non-inferiority. Table 8. Clinical Success Rates in ABSSSI Trials at Follow-Up (Day 26 to 30) Trial 1 Trial 2 DALVANCE Vancomycin/ Linezolid ITT 241/288 (83.7%) 251/285 (88.1%) CE 212/226 (93.8%) 220/229 (96.1%) ITT 327/371 (88.1%) 311/368 (84.5%) CE 283/294 (96.3%) 257/272 (94.5%) Difference (95% CI) 3-4.4% (-10.1, 1.4) -2.3% (-6.6, 2.0) 3.6% (-1.3, 8.7) 1.8% (-1.8, 5.6) 1 There were 7 patients (as described in Table 6) who did not receive treatment and were counted as failures in the ITT analysis. 2 Patients who died, used non-study antibacterial therapy, or had an unplanned surgical intervention 72 hours after the start of therapy were classifi ed as Clinical Failures. 3 The 95% CI is computed using the Miettinen and Nurminen approach, stratifi ed by baseline fever status. Table 9 shows outcomes in patients with an identified baseline pathogen, using pooled data from Trials 1 and 2 in the microbiological ITT (microitt) population. The outcomes shown in the table are clinical response rates at 48 to 72 hours and clinical success rates at follow-up (Day 26 to 30), as defined above. Pathogen Staphylococcus aureus Methicillinsusceptible Methicillinresistant Streptococcus agalactiae Streptococcus pyogenes Streptococcus anginosus group Table 9. Outcomes by Baseline Pathogen (MicroITT) Early Clinical Response at hours Early Responder 2 DALVANCE 206/257 (80.2) 134/167 (80.2) 72/90 (80.0) 6/12 (50.0) 28/37 (75.7) 18/22 (81.8) Comparator 219/256 (85.5) 163/189 (86.2) 56/67 (83.6) 11/14 (78.6) 24/36 (66.7) 23/ 25 (92.0) 20% reduction in lesion size DALVANCE 239/257 (93.0) 156/167 (93.4) 83/90 (92.2) 10/12 (83.3) 32/37 (86.5) 21/22 (95.5) Comparator 232/256 (90.6) 173/189 (91.5) 59/67 (88.1) 10/14 (71.4) 27/36 (75.0) 25/25 (100.0) Clinical Success at Day 26 to 30 DALVANCE 217/257 (84.4) 142/167 (85.0) 75/90 (83.3) 10/12 (83.3) 33/37 (89.2) 21/22 (95.5) Comparator 229/256 (89.5) 171/189 (90.5) 57/67 (85.1) 11/14 (78.6) 32/36 (88.9) 23/25 (92.0) 1 There were 2 patients in the dalbavancin arm with methicillin-susceptible S. aureus at baseline who did not receive treatment and were counted as non-responders/failures. 2 Early Responders are patients who had no increase from baseline in lesion area 48 to 72 hours after initiation of therapy, and had a temperature consistently at or below 37.6 C upon repeated measurement. 3 All patients in the clinical trials had blood cultures obtained at baseline. A total of 16 ABSSSI patients receiving dalbavancin had positive cultures at baseline for one of the above pathogens. Isolates included eleven S. aureus, three S. agalactiae, one S. pyogenes, and one S anginosus. Eleven of these patients (69%) were clinical responders at hours and clinical successes at Day 26 to 30.
Flexible Outpatient. Opportunity. Decision: Dalvance
 Flexible Outpatient Opportunity Decision: Dalvance DALVANCE: an opportunity for use at various SITES OF CARE HOME HOME Outpatient Infusion Site ED One 30-minute infusion a week for two weeks provides a
Flexible Outpatient Opportunity Decision: Dalvance DALVANCE: an opportunity for use at various SITES OF CARE HOME HOME Outpatient Infusion Site ED One 30-minute infusion a week for two weeks provides a
Page CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity to dalbavancin (4)
 IGLIGTS F PRESCRIBING INFRMATIN These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DALVANCE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DALVANCE. DALVANCE (dalbavancin)
IGLIGTS F PRESCRIBING INFRMATIN These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DALVANCE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DALVANCE. DALVANCE (dalbavancin)
Dalvance (dalbavancin) for injection
 DALVANCE (dalbavancin) for injection Coding & Billing Reference guide For more information: Call the Durata CONNECTS SM program toll-free 1.855.DURATA4 (1.855.387.2824) TM Dalvance (dalbavancin) for injection
DALVANCE (dalbavancin) for injection Coding & Billing Reference guide For more information: Call the Durata CONNECTS SM program toll-free 1.855.DURATA4 (1.855.387.2824) TM Dalvance (dalbavancin) for injection
Reference ID:
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TRIFERIC safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TRIFERIC. TRIFERIC (ferric
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TRIFERIC safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TRIFERIC. TRIFERIC (ferric
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use OTIPRIO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for OTIPRIO. OTIPRIO (ciprofloxacin
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use OTIPRIO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for OTIPRIO. OTIPRIO (ciprofloxacin
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE. 1.1 Limitation of Use FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TRIFERIC safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TRIFERIC. TRIFERIC (ferric
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TRIFERIC safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TRIFERIC. TRIFERIC (ferric
ABSSSI Case Study days (clinical evaluation)
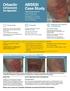 ABSSSI Case Study Cellulitis patient background 44-year-old single father Chronic renal insufficiency Hyperlipidemia, on rosuvastatin Has atrial fibrillation, on apixaban Fell and injured right leg At
ABSSSI Case Study Cellulitis patient background 44-year-old single father Chronic renal insufficiency Hyperlipidemia, on rosuvastatin Has atrial fibrillation, on apixaban Fell and injured right leg At
Reference ID:
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ZINPLAVA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ZINPLAVA. ZINPLAVA (bezlotoxumab)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ZINPLAVA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ZINPLAVA. ZINPLAVA (bezlotoxumab)
ICD-10 diagnostic codes consistent with ORBACTIV (oritavancin) indication
 ICD-10 diagnostic codes consistent with ORBACTIV (oritavancin) indication ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes Diagnosis INDICATION ORBACTIV (oritavancin) for injection is indicated for the treatment of adult patients
ICD-10 diagnostic codes consistent with ORBACTIV (oritavancin) indication ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes Diagnosis INDICATION ORBACTIV (oritavancin) for injection is indicated for the treatment of adult patients
Colistimethate FOR INJECTION, USP 10 DIGIT NDC STRENGTH SIZE WHOLESALE NUMBERS WEB LISTING. 150 mg*/vial 12
 Colistimethate FOR INJECTION, USP 10 DIGIT NDC STRENGTH SIZE WHOLESALE NUMBERS WEB LISTING 39822-0617-1 150 mg*/vial 1 ABC 10167618 Cardinal 5276001 11 DIGIT NDC Colistin base activity vial McKesson 3574043
Colistimethate FOR INJECTION, USP 10 DIGIT NDC STRENGTH SIZE WHOLESALE NUMBERS WEB LISTING 39822-0617-1 150 mg*/vial 1 ABC 10167618 Cardinal 5276001 11 DIGIT NDC Colistin base activity vial McKesson 3574043
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use epinastine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use epinastine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
Staphylococcal enterocolitis: Adult Patients (18 years of age and older): 500 mg to 2 g orally in 3 or 4 divided doses for 7 to 10 days. (2.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use FIRVANQ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for FIRVANQ. FIRVANQ (vancomycin
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use FIRVANQ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for FIRVANQ. FIRVANQ (vancomycin
ROSOBAC-1GM / ROSOBAC-FORT
 ROSOBAC-1GM / ROSOBAC-FORT ROSOBAC - 1GM. COMPOSITION : Each vial contains Sterile Cefoperazone Sodium IP Eq. to Anhydrous Cefoperazone - Sterile Sulbactam Sodium USP Eq. to Anhydrous Sulbactam - ROSOBAC
ROSOBAC-1GM / ROSOBAC-FORT ROSOBAC - 1GM. COMPOSITION : Each vial contains Sterile Cefoperazone Sodium IP Eq. to Anhydrous Cefoperazone - Sterile Sulbactam Sodium USP Eq. to Anhydrous Sulbactam - ROSOBAC
VORAXAZE (glucarpidase) For Injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2012
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VORAXAZE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VORAXAZE. VORAXAZE (glucarpidase)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VORAXAZE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VORAXAZE. VORAXAZE (glucarpidase)
KHAPZORY (levoleucovorin) for injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 1952 (d,l-leucovorin)
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use KHAPZORY safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for KHAPZORY. KHAPZORY (levoleucovorin)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use KHAPZORY safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for KHAPZORY. KHAPZORY (levoleucovorin)
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
 PATADAY- olopatadine hydrochloride solution/ drops Alcon Laboratories, Inc. ---------- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PATADAY safely
PATADAY- olopatadine hydrochloride solution/ drops Alcon Laboratories, Inc. ---------- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PATADAY safely
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 18 October 2006
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 18 October 2006 CUBICIN 350 mg (daptomycin), powder for perfusion solution Box of 1 bottle (CIP code: 567 219-3) CUBICIN
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 18 October 2006 CUBICIN 350 mg (daptomycin), powder for perfusion solution Box of 1 bottle (CIP code: 567 219-3) CUBICIN
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS Cream: Each gram contains 10 mg of ozenoxacin (1%) (3).
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use XEPI TM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for XEPI TM. XEPI TM (ozenoxacin)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use XEPI TM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for XEPI TM. XEPI TM (ozenoxacin)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION CONTRAINDICATIONS. None.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for. ONTAK (denileukin diftitox) Injection
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for. ONTAK (denileukin diftitox) Injection
WARNING: FETAL RISK See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VIBATIV safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VIBATIV. VIBATIV (telavancin)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VIBATIV safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VIBATIV. VIBATIV (telavancin)
WARNING: TENDON EFFECTS and EXACERBATION OF MYASTHENIA GRAVIS
 DECLESAU (dergrafloxacin) tablets, for oral use DECLESAU (dergrafloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use WARNING: TENDON EFFECTS and EXACERBATION OF MYASTHENIA GRAVIS Fluoroquinolones, including
DECLESAU (dergrafloxacin) tablets, for oral use DECLESAU (dergrafloxacin) injection, solution for intravenous use WARNING: TENDON EFFECTS and EXACERBATION OF MYASTHENIA GRAVIS Fluoroquinolones, including
VANLID Capsules (Vancomycin hydrochloride)
 Published on: 22 Sep 2014 VANLID Capsules (Vancomycin hydrochloride) Composition VANLID Capsules Each capsule contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride IP equivalent to Vancomycin.. 250 mg Approved colours used
Published on: 22 Sep 2014 VANLID Capsules (Vancomycin hydrochloride) Composition VANLID Capsules Each capsule contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride IP equivalent to Vancomycin.. 250 mg Approved colours used
ELSPAR (asparaginase) For injection, intravenous or intramuscular Initial U.S. Approval: 1978
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Elspar safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Elspar. ELSPAR (asparaginase)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Elspar safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Elspar. ELSPAR (asparaginase)
VIBATIV - telavancin hydrochlorideâ injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionâ Theravance, Inc
 VIBATIV - telavancin hydrochloride injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution Theravance, Inc. ---------- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed
VIBATIV - telavancin hydrochloride injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution Theravance, Inc. ---------- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed
Cefadroxil for Oral Suspension USP 250 mg/5 ml and 500 mg/5 ml
 Cefadroxil for Oral Suspension USP 250 mg/5 ml and 500 mg/5 ml Rx only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefadroxil for oral suspension and other antibacterial
Cefadroxil for Oral Suspension USP 250 mg/5 ml and 500 mg/5 ml Rx only To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefadroxil for oral suspension and other antibacterial
M0BCore Safety Profile
 M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Aztreonam Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: 500 mg, 1 g and 2 g powder for solution for injection and infusion NB! 75mg aztreonam for nebulisation to treat infections
M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Aztreonam Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: 500 mg, 1 g and 2 g powder for solution for injection and infusion NB! 75mg aztreonam for nebulisation to treat infections
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET
 MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE SUBSTANCE AND THE COMPANY Material Manufacturer Distributor Cefprozil For Oral Suspension USP 125 mg/5 ml and 250 mg/5 ml Lupin Limited Mumbai 400 098
MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE SUBSTANCE AND THE COMPANY Material Manufacturer Distributor Cefprozil For Oral Suspension USP 125 mg/5 ml and 250 mg/5 ml Lupin Limited Mumbai 400 098
ORBACTIV (oritavancin) for injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2014
 HIGHLIGHTS F PRESCRIBING INFRMATIN These highlights do not include all the information needed to use RBACTIV safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for RBACTIV. RBACTIV (oritavancin)
HIGHLIGHTS F PRESCRIBING INFRMATIN These highlights do not include all the information needed to use RBACTIV safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for RBACTIV. RBACTIV (oritavancin)
Immodium / loprarmide
 Immodium / loprarmide IMODIUM (loperamide hydrochloride) is indicated for the control and symptomatic relief of acute nonspecific diarrhea and of chronic diarrhea associated with inflammatory bowel disease.
Immodium / loprarmide IMODIUM (loperamide hydrochloride) is indicated for the control and symptomatic relief of acute nonspecific diarrhea and of chronic diarrhea associated with inflammatory bowel disease.
ALTARGO TM Retapamulin. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Retapamulin 10 mg per gram (1% w/w)
 ALTARGO TM Retapamulin QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Retapamulin 10 mg per gram (1% w/w) PHARMACEUTICAL FORM Ointment. CLINICAL PARTICULARS Indications ALTARGO (retapamulin) 1% ointment is indicated
ALTARGO TM Retapamulin QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Retapamulin 10 mg per gram (1% w/w) PHARMACEUTICAL FORM Ointment. CLINICAL PARTICULARS Indications ALTARGO (retapamulin) 1% ointment is indicated
DALVANCE (DALBAVANCIN) FOR INJECTION REIMBURSEMENT AT-A-GLANCE
 (DALBAVACI) FR IJECTI REIMBURSEMET AT-A-GLACE For more information: Call the CECTS SM program toll-free 1.855.387.2824 Program Coordinators are available 8:00 AM to 8:00 PM Eastern time, Monday through
(DALBAVACI) FR IJECTI REIMBURSEMET AT-A-GLACE For more information: Call the CECTS SM program toll-free 1.855.387.2824 Program Coordinators are available 8:00 AM to 8:00 PM Eastern time, Monday through
YONDELIS (trabectedin) DOSING & ADMINISTRATION GUIDE
 YONDELIS (trabectedin) DOSING & ADMINISTRATION GUIDE INDICATION YONDELIS (trabectedin) is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma who received
YONDELIS (trabectedin) DOSING & ADMINISTRATION GUIDE INDICATION YONDELIS (trabectedin) is indicated for the treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma who received
*Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GIAPREZA TM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GIAPREZA. GIAPREZA (angiotensin
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GIAPREZA TM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GIAPREZA. GIAPREZA (angiotensin
SIVEXTRO (tedizolid phosphate) for injection, for intravenous use SIVEXTRO (tedizolid phosphate) tablet, for oral use Initial U.S.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SIVEXTRO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SIVEXTRO. SIVEXTRO (tedizolid
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SIVEXTRO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SIVEXTRO. SIVEXTRO (tedizolid
DOSING GUIDE. Indications. Important Safety Information. Enable the immune system. RECOGNIZE. RESPOND.
 DOSING GUIDE For patients with unresectable Stage III NSCLC following concurrent CRT For patients with locally advanced or metastatic UC previously treated with platinum-based therapy Enable the immune
DOSING GUIDE For patients with unresectable Stage III NSCLC following concurrent CRT For patients with locally advanced or metastatic UC previously treated with platinum-based therapy Enable the immune
Core Safety Profile. Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Powder for solution for injection, 1 g LV/H/PSUR/0002/001 Date of FAR:
 Core Safety Profile Active substance: Ceftriaxone Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Powder for solution for injection, 1 g P-RMS: LV/H/PSUR/0002/001 Date of FAR: 14.10.2009 Section 4.2 (Posology and method
Core Safety Profile Active substance: Ceftriaxone Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Powder for solution for injection, 1 g P-RMS: LV/H/PSUR/0002/001 Date of FAR: 14.10.2009 Section 4.2 (Posology and method
CONTRAINDICATIONS None (4)
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Cystadane safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Cystadane. Cystadane (betaine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Cystadane safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Cystadane. Cystadane (betaine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use North American Coral Snake Antivenin (Equine) safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use North American Coral Snake Antivenin (Equine) safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
LUPIN LIMITED SAFETY DATA SHEET
 LUPIN LIMITED SAFETY DATA SHEET Section 1: Identification Section 1, Identification Material Manufacturer Distributor Cefprozil Tablets USP 250 mg and 500 mg Lupin Limited Mandideep 462 046 INDIA Lupin
LUPIN LIMITED SAFETY DATA SHEET Section 1: Identification Section 1, Identification Material Manufacturer Distributor Cefprozil Tablets USP 250 mg and 500 mg Lupin Limited Mandideep 462 046 INDIA Lupin
Initial U.S. Approval: 2010
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TEFLARO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TEFLARO. TEFLARO (ceftaroline
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TEFLARO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TEFLARO. TEFLARO (ceftaroline
Important Safety Information for Feraheme (ferumoxytol) Injection
 Dear Radiologist: (ferumoxytol) Injection for intravenous (IV) use is an IV iron replacement product indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in adult patients with chronic kidney disease
Dear Radiologist: (ferumoxytol) Injection for intravenous (IV) use is an IV iron replacement product indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in adult patients with chronic kidney disease
VANCOCIN CAPSULES (vancomycin hydrochloride)
 PRODUCT INFORMATION VANCOCIN CAPSULES (vancomycin hydrochloride) This preparation for the treatment of colitis is for oral use only. Vancocin must be given orally for treatment of staphylococcal enterocolitis
PRODUCT INFORMATION VANCOCIN CAPSULES (vancomycin hydrochloride) This preparation for the treatment of colitis is for oral use only. Vancocin must be given orally for treatment of staphylococcal enterocolitis
ERAXIS (anidulafungin) for injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2006
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ERAXIS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ERAXIS. ERAXIS (anidulafungin)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ERAXIS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ERAXIS. ERAXIS (anidulafungin)
ILUMYA (tildrakizumab-asmn) injection, for subcutaneous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ILUMYA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ILUMYA. ILUMYA (tildrakizumab-asmn)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ILUMYA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ILUMYA. ILUMYA (tildrakizumab-asmn)
Administer as an intravenous infusion over 35 to 60 minutes (2.1, 2.3) Dilution required prior to administration (2.2)
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EXONDYS 51 safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EXONDYS 51. EXONDYS 51 (eteplirsen)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EXONDYS 51 safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EXONDYS 51. EXONDYS 51 (eteplirsen)
400 mg IV (over 5 to 60 minutes) every 12 hours. > 30 to mg IV (over 5 to 60 minutes ) every 12 hours. 15 to 30
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TEFLARO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TEFLARO. TEFLARO (ceftaroline
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TEFLARO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TEFLARO. TEFLARO (ceftaroline
NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution Sterile (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and gramicidin ophthalmic solution, USP)
 NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution Sterile (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and gramicidin ophthalmic solution, USP) NEOSPORIN SOLUTION DESCRIPTION NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution (neomycin and polymyxin B
NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution Sterile (neomycin and polymyxin B sulfates and gramicidin ophthalmic solution, USP) NEOSPORIN SOLUTION DESCRIPTION NEOSPORIN Ophthalmic Solution (neomycin and polymyxin B
Reference ID:
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ETOPOPHOS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ETOPOPHOS. ETOPOPHOS (etoposide
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ETOPOPHOS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ETOPOPHOS. ETOPOPHOS (etoposide
AXITAB-CV TAB. COMPOSITION :
 AXITAB-CV TAB. COMPOSITION : Each film coated tablet contains: Cefuroxime Axetil I.P. Eq. to Anhydrous 500mg. Potassium Clavulanate Diluted I.P. Eq. to Clavulanic Acid 125mg DESCRIPTION : Cefuroxime Axetil
AXITAB-CV TAB. COMPOSITION : Each film coated tablet contains: Cefuroxime Axetil I.P. Eq. to Anhydrous 500mg. Potassium Clavulanate Diluted I.P. Eq. to Clavulanic Acid 125mg DESCRIPTION : Cefuroxime Axetil
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MOZOBIL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MOZOBIL. MOZOBIL (plerixafor
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MOZOBIL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MOZOBIL. MOZOBIL (plerixafor
The only biologic approved to treat SLE: now with multiple delivery options
 The only biologic approved to treat SLE: now with multiple delivery options BENLYSTA (belimumab) Autoinjector SC Prefilled syringe IV Intravenous infusion Consider the options: visit Belimumab.com INDICATION
The only biologic approved to treat SLE: now with multiple delivery options BENLYSTA (belimumab) Autoinjector SC Prefilled syringe IV Intravenous infusion Consider the options: visit Belimumab.com INDICATION
ACTEMRA IV Dosing & Administration Pocket Guide
 IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION BOXED WARNING Serious Infections Serious infections leading to hospitalization or death, including tuberculosis (TB), bacterial, invasive fungal, viral, and other opportunistic
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION BOXED WARNING Serious Infections Serious infections leading to hospitalization or death, including tuberculosis (TB), bacterial, invasive fungal, viral, and other opportunistic
Page 1 of 9. ERWINAZE (asparaginase Erwinia chrysanthemi) for injection, intramuscular (IM) or intravenous (IV) use Initial U.S.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ERWINAZE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ERWINAZE. ERWINAZE (asparaginase
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ERWINAZE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ERWINAZE. ERWINAZE (asparaginase
Rasburicase 1.5 mg/ml powder and solvent for concentrate for solution for infusion. FASTURTEC
 For the use only of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory This package insert is continually updated. Please read carefully before using a new pack. Rasburicase 1.5 mg/ml powder
For the use only of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory This package insert is continually updated. Please read carefully before using a new pack. Rasburicase 1.5 mg/ml powder
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION pdp-pyrazinamide Pyrazinamide Tablets, USP 500 mg Antimycobacterial / Antituberculosis Agent PENDOPHARM, Division of Pharmascience Inc.. 6111, Royalmount Ave, Suite 100 Montréal,
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION pdp-pyrazinamide Pyrazinamide Tablets, USP 500 mg Antimycobacterial / Antituberculosis Agent PENDOPHARM, Division of Pharmascience Inc.. 6111, Royalmount Ave, Suite 100 Montréal,
PACKAGE INSERT USP ANTIBIOTIC
 Pr AMPICILLIN for Injection USP ANTIBIOTIC ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Ampicillin has a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against many gram-positive and gramnegative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria.
Pr AMPICILLIN for Injection USP ANTIBIOTIC ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Ampicillin has a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against many gram-positive and gramnegative aerobic and anaerobic bacteria.
KEVEYIS (dichlorphenamide) tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1958
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use KEVEYIS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for KEVEYIS. KEVEYIS (dichlorphenamide)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use KEVEYIS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for KEVEYIS. KEVEYIS (dichlorphenamide)
PRODUCT INFORMATION. Colistin Link. Colistin 150 mg/2 ml (as colistimethate sodium) powder for injection vial
 PRODUCT INFORMATION Colistin Link Colistin 150 mg/2 ml (as colistimethate sodium) powder for injection vial For Intramuscular and Intravenous use. NAME OF THE MEDICINE Colistimethate sodium for injection,
PRODUCT INFORMATION Colistin Link Colistin 150 mg/2 ml (as colistimethate sodium) powder for injection vial For Intramuscular and Intravenous use. NAME OF THE MEDICINE Colistimethate sodium for injection,
Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Capsules, 200mg, 400mg, Oral suspensions, 90mg/5ml, 180mg/5ml, 36 mg/ml SI/H/PSUR/0002/002 Date of FAR:
 0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Ceftibuten Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Capsules, 200mg, 400mg, Oral suspensions, 90mg/5ml, 180mg/5ml, 36 mg/ml P-RMS: SI/H/PSUR/0002/002 Date of FAR: 14.02.2013
0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Ceftibuten Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Capsules, 200mg, 400mg, Oral suspensions, 90mg/5ml, 180mg/5ml, 36 mg/ml P-RMS: SI/H/PSUR/0002/002 Date of FAR: 14.02.2013
CONTRAINDICATIONS None.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PAZEO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PAZEO. PAZEO (olopatadine hydrochloride
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PAZEO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PAZEO. PAZEO (olopatadine hydrochloride
Reference ID:
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ENDARI TM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ENDARI. ENDARI (L-glutamine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ENDARI TM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ENDARI. ENDARI (L-glutamine
ALTARGO. Retapamulin. Retapamulin 10 mg per gram (1% w/w)
 ALTARGO Retapamulin 1. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Retapamulin 10 mg per gram (1% w/w) 2. PHARMACEUTICAL FORM Ointment 3. CLINICAL PARTICULARS 3.1 Indications Retapamulin is indicated for
ALTARGO Retapamulin 1. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Retapamulin 10 mg per gram (1% w/w) 2. PHARMACEUTICAL FORM Ointment 3. CLINICAL PARTICULARS 3.1 Indications Retapamulin is indicated for
AROMASIN 25mg (Tablets)
 APPROVED PACKAGE INSERT AROMASIN SCHEDULING STATUS: S4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM: AROMASIN 25mg (Tablets) COMPOSITION: Each sugar-coated tablet contains 25 mg exemestane. Preservative: methyl p-hydroxybenzoate
APPROVED PACKAGE INSERT AROMASIN SCHEDULING STATUS: S4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM: AROMASIN 25mg (Tablets) COMPOSITION: Each sugar-coated tablet contains 25 mg exemestane. Preservative: methyl p-hydroxybenzoate
Daptomycin (CUBICIN) 500 mg Lyophilized Powder for IV Infusion. CUBICIN contains daptomycin, a cyclic lipopeptide antibacterial agent.
 DAPTOMYCIN 0500778/2 CUBICIN TM 500 mg Lyophilized Powder for IV Infusion Antibacterial/Cyclic Lipopeptide Antibiotic 1. Product Description 1.1. Name of Pharmaceutical Product Daptomycin (CUBICIN) 500
DAPTOMYCIN 0500778/2 CUBICIN TM 500 mg Lyophilized Powder for IV Infusion Antibacterial/Cyclic Lipopeptide Antibiotic 1. Product Description 1.1. Name of Pharmaceutical Product Daptomycin (CUBICIN) 500
ADVERSE REACTIONS The most common (>10%) adverse reactions are hypercalcemia, nausea, and diarrhea. (6.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PHOSLYRA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PHOSLYRA. PHOSLYRA (calcium
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PHOSLYRA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PHOSLYRA. PHOSLYRA (calcium
ERAXIS (anidulafungin) for injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2006
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ERAXIS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ERAXIS. ERAXIS (anidulafungin)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ERAXIS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ERAXIS. ERAXIS (anidulafungin)
Farmadol. Paracetamol 10 mg/ml INFUSION SOLUTION
 Farmadol Paracetamol 10 mg/ml INFUSION SOLUTION Composition Each ml contains: Paracetamol 10 mg Pharmacology Pharmacodynamic properties The precise mechanism of the analgesic and antipyretic properties
Farmadol Paracetamol 10 mg/ml INFUSION SOLUTION Composition Each ml contains: Paracetamol 10 mg Pharmacology Pharmacodynamic properties The precise mechanism of the analgesic and antipyretic properties
Annex I: Proposed Core Safety Profile (CSP) 4.3 Contraindications
 Annex I: Proposed Core Safety Profile (CSP) 4.3 Contraindications Hypersensitivity to cefuroxime or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1. Patients with known hypersensitivity to cephalosporin
Annex I: Proposed Core Safety Profile (CSP) 4.3 Contraindications Hypersensitivity to cefuroxime or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1. Patients with known hypersensitivity to cephalosporin
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS mg or 500 mg single dose vials as sterile, pyrogen-free lyophilizates.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ZINECARD safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ZINECARD. ZINECARD (dexrazoxane)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ZINECARD safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ZINECARD. ZINECARD (dexrazoxane)
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author
 Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena, Seville New drugs against MRSA and VRE L. Eduardo López Cortés Seville, 8th July Tedizolid Oxazolidinone Ceftaroline // Ceftobiprole 5 th gen cephalosporin Overview
Hospital Universitario Virgen Macarena, Seville New drugs against MRSA and VRE L. Eduardo López Cortés Seville, 8th July Tedizolid Oxazolidinone Ceftaroline // Ceftobiprole 5 th gen cephalosporin Overview
2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION One sachet contains 5.631g fosfomycin trometamol equivalent to 3.0 g fosfomycin.
 Doctor leaflet 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MONUROL 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION One sachet contains 5.631g fosfomycin trometamol equivalent to 3.0 g fosfomycin. Excipients: One sachet
Doctor leaflet 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MONUROL 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION One sachet contains 5.631g fosfomycin trometamol equivalent to 3.0 g fosfomycin. Excipients: One sachet
12 to 17 years. 7 to 11 years
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CUBICIN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CUBICIN. CUBICIN (daptomycin
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CUBICIN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CUBICIN. CUBICIN (daptomycin
Referral Form. Referring physician s phone: Referring physician s fax:
 (ferumoxytol) Injection for intravenous (IV) use Referral Form Referring gphysician s name: Referring physician s phone: Referring physician s fax: Dear Dr or Infusion Center : I am referring my patient
(ferumoxytol) Injection for intravenous (IV) use Referral Form Referring gphysician s name: Referring physician s phone: Referring physician s fax: Dear Dr or Infusion Center : I am referring my patient
Feraheme (ferumoxytol) Injection Coding Tool
 AMAG Assist Patient Assistance and Reimbursement Support (ferumoxytol) Injection Coding Tool (ferumoxytol) Injection for intravenous (IV) use is indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in
AMAG Assist Patient Assistance and Reimbursement Support (ferumoxytol) Injection Coding Tool (ferumoxytol) Injection for intravenous (IV) use is indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in
M0BCore Safety Profile
 M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Aciclovir Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Tablets 200, 400 or 800 mg Dispersible tablets 200, 400 or 800 mg Oral suspensions 200 mg or 400 mg per 5 ml. Freeze
M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Aciclovir Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Tablets 200, 400 or 800 mg Dispersible tablets 200, 400 or 800 mg Oral suspensions 200 mg or 400 mg per 5 ml. Freeze
OTIPRIO an antibiotic medicine given to your child at the time of ear tube surgery
 Bring this Conversation Starter with you to your child s next doctor appointment an antibiotic medicine given to your child at the time of ear tube surgery Use this questionnaire to start a conversation
Bring this Conversation Starter with you to your child s next doctor appointment an antibiotic medicine given to your child at the time of ear tube surgery Use this questionnaire to start a conversation
INFUSING. ORENCIA (abatacept) IV INDICATION/USAGE. Your go-to guide for preparing and administering an ORENCIA intravenous (IV) infusion
 INFUSING ORENCIA (abatacept) IV Your go-to guide for preparing and administering an ORENCIA intravenous (IV) infusion INDICATION/USAGE Adult Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): ORENCIA is indicated for reducing
INFUSING ORENCIA (abatacept) IV Your go-to guide for preparing and administering an ORENCIA intravenous (IV) infusion INDICATION/USAGE Adult Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): ORENCIA is indicated for reducing
CSL Behring LLC Albuminar -25 US Package Insert Albumin (Human) USP, 25% Revised: 01/2008 Page 1
 Page 1 CSL Behring Albuminar -25 Albumin (Human) USP, 25% R x only DESCRIPTION Albuminar -25, Albumin (Human) 25%, is a sterile aqueous solution of albumin obtained from large pools of adult human venous
Page 1 CSL Behring Albuminar -25 Albumin (Human) USP, 25% R x only DESCRIPTION Albuminar -25, Albumin (Human) 25%, is a sterile aqueous solution of albumin obtained from large pools of adult human venous
(angiotensin II) injection for intravenous infusion
 ADMINISTERING GIAPREZA TM (angiotensin II) injection for intravenous infusion Visit www.giapreza.com INITIATE Recommended starting dose of GIAPREZA is 20 ng/kg/min, which is equivalent to 0.02 mcg/kg/min
ADMINISTERING GIAPREZA TM (angiotensin II) injection for intravenous infusion Visit www.giapreza.com INITIATE Recommended starting dose of GIAPREZA is 20 ng/kg/min, which is equivalent to 0.02 mcg/kg/min
Cetirizine Proposed Core Safety Profile
 Cetirizine Proposed Core Safety Profile Posology and method of administration Elderly subjects: data do not suggest that the dose needs to be reduced in elderly subjects provided that the renal function
Cetirizine Proposed Core Safety Profile Posology and method of administration Elderly subjects: data do not suggest that the dose needs to be reduced in elderly subjects provided that the renal function
AEMCOLO (rifamycin) delayed-release tablets, for oral use. Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use AEMCOLO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for AEMCOLO. AEMCOLO (rifamycin)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use AEMCOLO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for AEMCOLO. AEMCOLO (rifamycin)
PRODUCT INFORMATION 1 ABOUT THIS GUIDE DOSAGE FORM AND STRENGTH STORAGE AND HANDLING
 DOSING GUIDE INDICATION ONIVYDE (irinotecan liposome injection) is indicated, in combination with fluorouracil (5-FU) and leucovorin (LV), for the treatment of patients with metastatic adenocarcinoma of
DOSING GUIDE INDICATION ONIVYDE (irinotecan liposome injection) is indicated, in combination with fluorouracil (5-FU) and leucovorin (LV), for the treatment of patients with metastatic adenocarcinoma of
DOSING & ADMINISTRATION GUIDE
 DOSING & ADMINISTRATION GUIDE EXONDYS51.com INDICATION 1 EXONDYS 51 is indicated for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in patients who have a confirmed mutation of the DMD gene that is
DOSING & ADMINISTRATION GUIDE EXONDYS51.com INDICATION 1 EXONDYS 51 is indicated for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) in patients who have a confirmed mutation of the DMD gene that is
CEREZYME Genzyme. 70 mg (52 mg) (18 mg)
 CEREZYME Genzyme Imiglucerase for injection 400 UNITS 200 UNITS DESCRIPTION Cerezyme (imiglucerase for injection) is an analogue of the human enzyme ß-Glucocerebrosidase, produced by recombinant DNA technology.
CEREZYME Genzyme Imiglucerase for injection 400 UNITS 200 UNITS DESCRIPTION Cerezyme (imiglucerase for injection) is an analogue of the human enzyme ß-Glucocerebrosidase, produced by recombinant DNA technology.
Reference ID:
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CEFAZOLIN injection safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CEFAZOLIN injection.
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CEFAZOLIN injection safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CEFAZOLIN injection.
Dosing and Administration Guide for ARZERRA
 Dosing and Administration Guide for ARZERRA INDICATIONS for ARZERRA (ofatumumab) In combination with chlorambucil, for the treatment of previously untreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
Dosing and Administration Guide for ARZERRA INDICATIONS for ARZERRA (ofatumumab) In combination with chlorambucil, for the treatment of previously untreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
New Zealand Data Sheet COLISTIN-LINK
 New Zealand Data Sheet COLISTIN-LINK Colistimethate sodium equivalent to colistin 150mg powder for injection For intramuscular and intravenous use. Description Colistimethate sodium for injection, USP
New Zealand Data Sheet COLISTIN-LINK Colistimethate sodium equivalent to colistin 150mg powder for injection For intramuscular and intravenous use. Description Colistimethate sodium for injection, USP
GlucaGen (glucagon [rdna origin] for injection) Initial U.S. Approval: 1998
![GlucaGen (glucagon [rdna origin] for injection) Initial U.S. Approval: 1998 GlucaGen (glucagon [rdna origin] for injection) Initial U.S. Approval: 1998](/thumbs/77/74979541.jpg) HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GlucaGen safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GlucaGen. GlucaGen (glucagon
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GlucaGen safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GlucaGen. GlucaGen (glucagon
M0BCore Safety Profile
 M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Clindamycin Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: 300mg/2 ml Ampulle, 600 mg/4 ml Ampulle, 900 mg/6 ml Ampulle, 75 mg/5 ml Granulat für orale Lösung, 150 mg Kapselnn,
M0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Clindamycin Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: 300mg/2 ml Ampulle, 600 mg/4 ml Ampulle, 900 mg/6 ml Ampulle, 75 mg/5 ml Granulat für orale Lösung, 150 mg Kapselnn,
DBL NALOXONE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION USP
 Name of medicine Naloxone hydrochloride Data Sheet New Zealand DBL NALXNE HYDRCHLRIDE INJECTIN USP Presentation DBL Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection USP is a sterile, clear, colourless solution, free from
Name of medicine Naloxone hydrochloride Data Sheet New Zealand DBL NALXNE HYDRCHLRIDE INJECTIN USP Presentation DBL Naloxone Hydrochloride Injection USP is a sterile, clear, colourless solution, free from
Reference ID:
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LYSODREN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LYSODREN. LYSODREN (mitotane)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LYSODREN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LYSODREN. LYSODREN (mitotane)
PRODUCT INFORMATION TARGOCID
 NAME OF THE MEDICINE Non-proprietary Name teicoplanin PRODUCT INFORMATION TARGOCID DESCRIPTION Teicoplanin is a glycopeptide-antibiotic produced by Actinoplanes teichomyceticus. It is presented as a sterile,
NAME OF THE MEDICINE Non-proprietary Name teicoplanin PRODUCT INFORMATION TARGOCID DESCRIPTION Teicoplanin is a glycopeptide-antibiotic produced by Actinoplanes teichomyceticus. It is presented as a sterile,
Dear Dr or Infusion Center : Patient name: SS #: Patient address: Patient phone: Date of birth: / /
 Referral Form Referring physician s name: Referring physician s phone: Referring physician s fax: Dear Dr or Infusion Center : I am referring my patient to you to receive FERAHEME (ferumoxytol injection).
Referral Form Referring physician s name: Referring physician s phone: Referring physician s fax: Dear Dr or Infusion Center : I am referring my patient to you to receive FERAHEME (ferumoxytol injection).
CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity to any component of this product (4)
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use OMIDRIA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for OMIDRIA. OMIDRIA (phenylephrine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use OMIDRIA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for OMIDRIA. OMIDRIA (phenylephrine
Clodronate BE/H/PSUR/001/001 October 2011 Agreed CSP
 Clodronate BE/H/PSUR/001/001 October 2011 Agreed CSP 4. CLINICAL PARTICULARS 4.1 Therapeutic indications Intravenous use Treatment of hypercalcemia due to malignancy. Oral use Treatment of hypercalcemia
Clodronate BE/H/PSUR/001/001 October 2011 Agreed CSP 4. CLINICAL PARTICULARS 4.1 Therapeutic indications Intravenous use Treatment of hypercalcemia due to malignancy. Oral use Treatment of hypercalcemia
ENTEREG (alvimopan) Capsules Initial U.S. Approval: 2008
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ENTEREG safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ENTEREG. ENTEREG (alvimopan)
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ENTEREG safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ENTEREG. ENTEREG (alvimopan)
ZOMAX IV HIKMA PHARMACEUTICALS
 09-15 ZOMAX IV HIKMA PHARMACEUTICALS azithromycin for injection For IV infusion only DESCRIPTION Zomax (azithromycin for injection) contains the active ingredient azithromycin, an azalide, a subclass of
09-15 ZOMAX IV HIKMA PHARMACEUTICALS azithromycin for injection For IV infusion only DESCRIPTION Zomax (azithromycin for injection) contains the active ingredient azithromycin, an azalide, a subclass of
CRIFOS 4 GM Injection (Fosfomycin sodium)
 Published on: 30 Sep 2016 CRIFOS 4 GM Injection (Fosfomycin sodium) Composition CRIFOS 4 GM Each vial contains: Fosfomycin Sodium BP equivalent to Fosfomycin..4 g Excipients q.s. Dosage Form Powder for
Published on: 30 Sep 2016 CRIFOS 4 GM Injection (Fosfomycin sodium) Composition CRIFOS 4 GM Each vial contains: Fosfomycin Sodium BP equivalent to Fosfomycin..4 g Excipients q.s. Dosage Form Powder for
