A Review of Renal Diseases
|
|
|
- Ruth Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Review of Renal Diseases NDFS 356 Amber McArthur April 3,
2 INTRODUCITON Tom Harkin stated, America s health care system is in crisis precisely because we systematically neglect wellness and prevention. The main causes of death in the US include heart disease diabetes, nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, and nephrosis. Diabetes and hypertension are major contributors of kidney disease. 1 in 3 American adults are currently at risk for developing kidney disease and 1 in 9 currently have kidney disease (1). Consequently, an increased poor management of health will result in an increase of renal failure. Because of the high occurrence of this disease and the long term need for treatment and counseling during each stage, it is pertinent to have a general knowledge of the disease as a registered dietitian. This paper will discuss the general description of the disease, the etiology, pathophysiology, medical diagnosis, therapies, tool for nutritional assessment, medical nutritional therapy, and long term prognosis of kidney disease. DISEASE DESCRPITON The kidneys are responsible for multiple tasks and in short, when those processes are no long able to be performed by the kidneys it is called renal failure. It is a progressive disease with multiple stages and is determined by a decrease in GFR. Chronic kidney disease is a worldwide public health problem (2). As stated before there are many people that currently have kidney disease and there are even more at risk of getting it (1). A study analyzing the prevalence of CKD had results stating that 11% of the US population was at some state of the disease; that is 19.2 million individuals (3). This is a very ubiquitous disease that is only getting more common as diseases such as diabetes and hypertension increase. 1
3 ETIOLOGY AND RISK FACTORS The leading causes of kidney failure is chronic diabetes mellitus (4). Diabetes is followed behind by chronic hypertension. Secondary causes included but are not limited to kidney stones, glomerulonephritis, nephrotic and nephritic syndrome, and exposure to drugs and toxins (5). All of these dysfunctions cause some kind of stress or damage to the kidney, decreasing its ability to perform to its maximal capacity. For example, nephritic syndrome is a disease that causes inflammation of the capillary loops of the glomerulus. The inflammation damages the barrier to blood cells and causes blood to be excreted in the urine. Nephrotic syndrome hypoalbuminemia, edema, hypercholesterolemia, hypercoagulability, and abnormal bone metabolism because of a large loss of protein in the urine (4). Complications such as these can lead to the stages of chronic kidney disease. PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Some of the normal physiological responsibilities of the kidney include: water balance, fluid osmolarity maintenance, ion concentration regulation, plasma volume maintenance, acid base balance, excretion of waste products, and production of erythropoietin, rennin, and converting vitamin D to its active form (6). When there is stress on the kidney and function is decreased, these processes to do not function as well as they originally would. But their loss of function takes time. Chronic renal failure happens over a period of years and because of the kidney s adaptive capabilities, the problem might not be noticed until less than 25% kidney function is achieved (7). There are five states of CKD each progressing to a decrease renal function. In stage one the renal function slowly diminishes to an egfr of less than 90ml/min with little to now clinical symptoms and an 2
4 elevated blood BUN and creatinine levels. Stage two is called renal insufficiency and the egfr is from 89-60ml/min and clinical symptoms may start to appear. During this stage nephrons will start to compensate for the deficiency causing death of nephrons. Stage three is classified as renal failure with an egfr of 59-30ml/min and symptoms are more established. Stage four is a more severe form of stage three with an egfr ranging from 15-29ml/min. The last stage, end-stage kidney disease, has little to no GFR with it being less than 15ml/min. This will lead to uremia, elevated urea and creatinine in the blood, causing fatigue, vomiting, anorexia, nausea, and neurological problems (4). Stage five also contributes to bone and mineral disorders because of a decreased phosphorus excretion leading to bone breakdown and vascular calcification. Other major complications that occur at this stage are sodium and water imbalance, phosphate and calcium imbalance, and potassium and acid base imbalance (5). Stage five results in death unless transplantation or dialysis is administered (4). Chart 1.0 is a great visual of the progression of kidney disease. This disease does not progress quickly overnight but it takes time and poor management to evolve to the end-stage symptoms. But because there are treatments to help slow progression and sustain life of individuals with CKD it is important to know how to diagnosis a patient. 3
5 DIAGNOSIS As mentioned before kidney failure does not have many signs and symptoms until it has progressed further along to the more end-stage. Thus, lab values are important in diagnosing patients with kidney disease. Some important labs include: sodium, potassium, calcium, BUN, creatinine, protein, albumin, and hct. Because of the high prevalence of renal failure it is important that individuals that have primary and secondary risk factors regularly have blood work drawn to assure proper kidney function (4). MEDICAL THERAPIES There are multiple treatment options for patients and physicians to choose from when deciding what kind of medical therapy is best. There is not an overall best treatment for renal failure because each individual is a new, different and unique case. Medical therapies available for kidney disease patients include drugs, hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, transplants, and alternative therapy. Drugs The decreased function of the kidneys causes an imbalance of many vitamins and minerals in the body. Drugs are prescribed to help fix these abnormalities. Phosphate binders are needed for some patients who have low control which could lead to poor bone health (8). With therapies like dialysis, a lot of vitamins can be lost via diffusion. It is important to supplement those water soluble vitamins that will be low. Iron can be administered orally or through IV. Iron is important to maintain bone health and avoid anima. As stated before the kidney is no longer able to activate vitamin D and thus a oral or IV supplement should be taken by those that are at risk for bone disease. 4
6 Biphosphates inhibit bone resorption by blocking osteoclast activity. This can be taken by IV or orally. Potassium is linked to the function of the heart. Hyperkalemia can cause arrhythmia and to fix this imbalance cation exchange resin can per prescribed (4). Keeping blood levels normal will make dialysis and transplant treatments more effective because of better compliance. Hemodialysis Hemodialysis is a blood filtration treatment that uses needles, a fistula, purified water, a dialyzer, and a dialysate to remove waste products and electrolytes from the blood. To prepare a patient for hemodialysis an artery and vein must be surgically connected to make a fistula (4). The fistula will be the permanent access site for the large needles that will connect a patient to the dialysis machine. If the blood vessels of an individual are too weak or fragile a graft can be implanted, creating an artificial vessel. In order to do hemodialysis there must be an availability of purified water. In clinics there is a purification room that softens hard water, takes out any minerals in the water to create simple pure H2O. The purified water is then mixed into different baths according to the patients needs (8). The purified water mineral baths that have similar electrolyte contet of normal plasma, is called dialysate and is filtered through a dialyzer moving waste products (4). The waste moves from the blood into the filter, dialyzer, and out of the filter to be discarded. The waste and electrolytes move by diffusion, ultrafiltration, and osmosis. Diffusion is the passage of particles through a semipermeable membrane. Osmosis is the movement of fluid across a semipermeable membrane. Diffusion and osmosis can occur at the same time. Filtration is the passage of fluids through a membrane. Ultrafiltration provides additional pressure to squeeze extra fluid through the 5
7 membrane (4). All of these processes help do what the kidney cannot do by itself. There are three main types of hemodialysis. Outpatient treatment is 3-5 hours long 3 times a week. Home dialysis is hours 5-6 times a week. Nocturnal dialysis is 8 hours while sleeping 3-6 times a week. Newer therapies can shorten duration of treatment by increasing frequency. This type of therapy has lower mortality rates similar to that of a transplant (4). All these options allow a patient to choose what works best for them. Peritoneal Dialysis Peritoneal dialysis is a form of dialysis that uses the body s semi permeable membrane, the peritoneum, to diffuse waste products (4). In this treatment a catheter is implanted in the abdomen and into the peritoneal cavity. A high dextrose concentration solution called dialysate is instilled into the peritoneum. Diffusion carries waste products from the blood through the semi permeable walls of the peritoneum into the peritoneal cavity into the dialysate. Water also moves through osmosis in this process. When the exchange is completed, the fluid is removed by gravity or machine and a new solution is added (4). The two main types of peritoneal dialysis are continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) and continuous cyclic peritoneal dialysis (CCPD). In CAPD the dialysate is placed in the peritoneum and then exchanged manually by gravity 4 to 5 times daily making it a 24 hour treatment. CCPD on the other hand uses one Dialysate for the day and the main treatment id done at night by a machine that does the exchange (4). A Cochrane review examines the 6
8 difference between CAPD vs. APD. APD was seen beneficial over CAPD because of a reduced incidence of peritonitis and mechanical complications. Results also showed that APD is more beneficial in younger PD populations due to the psychological advantages (9). Out of the two dialysis treatments PD is a better treatment because of the increased residual renal function, lower fluctuation in blood chemistry, and ability to live a more normal lifestyle. The three main complications associated with PD are peritonitis, hypotension, and weight gain because of the dextrose absorption from the dialysate (4). But the extended renal function outweighs the other risk factors for most. Transplants Kidney transplants are the most common solid organ transplants as seen in Table 1. Most transplant surgeries include the process of the surgeon placing the new kidney inside the lower abdomen and connecting it with a vein and artery through which blood can flow and urine can be created (10). Renal transplant is the preferred method of treatment for many end-stage renal disease patients. However, insufficient organ donation accounts for the discrepancy between the number of recipients and candidates(11). There are two types of donors: deceased and living. Patient survival rates are increased with a living donor kidney transplant (12). Though transplants are highly successful, it is important that proper care is given during the three phases of the organ transplant. Pretrasnplant treatment is evaluation of candidates. The most important issue with receiving a transplant is proper weight. A 7
9 healthy weight must be attained before transplant. Acute posttransplant treatment is immunosuppressive therapy. The goal in this stage is to provide adequate calories and protein for would healing, to prevent acute and chronic rejection, and minimize toxicity of the agents and rates of infection while achieving high patient and graft survival. Induction therapy is short term and provides antilymphocyte antibody medication. Anti rejection therapy is long term to prevent rejection of the transplant. Chronic posttransplant therapy starts 6 weeks post surgery. It includes monitoring of obesity, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, and osteoporosis. The new nutritional goals are similar to that of a healthy individual (11). Alternative therapy There are only a few complimentary therapies known for kidney disease. One alternative therapy is flaxseed oil. Researchers observed a decrease in c-reactive protein levels in chronic hemodialysis patients. However there was a possible correlation between their BMI and lipoprotein cholesterol levels (13). There is also experimentation with herbs and spices as complementary therapy in kidney disease but much more research must be performed before any claims of success can be made. As for know, it is important that renal failure patients to not consume herbs and spices that are known for worsening kidney state. TOOLS FOR NUTRITIONAL ASSESSMENT Nutritional assessment for individuals with kidney disease would start with medical and dietary history, anthropometric data and labs (11). From this information a further assessment for proper nutritional therapy can be attained by some kind of clinician. 8
10 MEDICAL NUTRITIONAL THERAPY The main nutrients of concern for dialysis are protein, calories, sodium, potassium, iron, phosphorus, and calcium. Depending on what the lab values are for the patient they will be recommended to restrict their diet of a certain nutrient or they will be recommended to have some kind of supplement. For example, PD patients are losing a lot protein in the peritoneum. This means that they must increase their protein intake to g/kg/day. It is also recommended that dialysis patients eat high biological protein such as animal sources. Calorie recommendations range between kcal/kg with lower amounts for late stage transplant and pd patients and high amounts for nutritionally depleted patients. For some treatments there will be a fluid, sodium, potassium, phosphorus, iron, and calcium restriction or supplementation but it depends greatly upon the patient s blood values. LONG TERM PROGNOSIS Kidney disease often leads to death either by renal failure alone or because of other medical complications compliance to medical and nutritional therapy will help increase the quality and quantity of life for individuals with this disease. Poor compliance to the therapies will increase the rate of renal failure leading to death. SUMMARY In summary, renal failure is the progressive loss of kidney functions. The main risk factors for loss of renal function are diabetes and hypertension. If these and other risk factors were taken care of in their early stages renal failure would not be developed. The main treatments for it include peritoneal and hemodialysis and transplants with medications. However, the best treatment for this disease is prevention. Good health is 9
11 the best guard against developing any health problem and dieticians are available to help in that area. Deepak Hiwale was quoted saying, preventing disease rather than curing them makes more sense Doctors of the future will be clinicians, dieticians and personal trainers rolled into one. If only people would understand that a healthy life was the answer to their health problems. 10
12 REFERENCES 1. National Kidney Foundation. Kidney disease facts. Available at Accessed March 30, UpToDate. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease. Available at Accessed March 30, Coresh J, Astor BC, Greene T, Eknoyan G, Levey AS. Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and decreased kidney function in the adult US population: Third national health and nutrition examination survey. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2003;41(1): Wilkens K. Medical nutrition therapy for renal disease. In: Mahan LK, Escott- Stump S, ed. Krause s Food, Nutrition, & Diet Theraphy. 13 th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2012: McCance KL, Huether SE. Pathophysiology the Biologic Basis for Disease in Adults and Children. 5 th ed. Mosby Elsevier Sherwood L. Human physiology from cells to systems. 6 th ed. Belmont, CA: Thomson Brooks; DaVita. Stages of chronic kidney disease. Available at Accessed March 30, Thompson C. Personal communication. DaVita Utah Valley Dialysis Clinic, Provo, UT, March 27, Rabindranth KS, Adams J, Ali T, Macleod AM, Vale L, Cody JD, Wallace SA, Daly C. Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis versus automated peritoneal dialysis for end-stage renal disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007, Issue 2. Art. No.: CD DOI: / CD National Kidney Center. Chronic kidney disease. Available at Accessed March 30, Byham-Gray L, Stover J, Wiesen K. A clinical guide to nutrition care in kidney disease. 2 nd ed. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Ochsner. Kidney transplant statistics. Available at Accessed March 30,
13 13. Lemos J, Gascue de Alencastro M, Konrath AV, Cargnin M, Manfro RC. Flaxseed oil supplementation decreases C-reactive protein levels in chronic hemodialysis patients. J. Nutres. 2012;32:
CHRONIC KIDNEY FAILURE
 CHRONIC KIDNEY FAILURE Overview Chronic kidney disease, also called chronic kidney failure, describes the gradual loss of kidney function. Your kidneys filter wastes and excess fluids from your blood,
CHRONIC KIDNEY FAILURE Overview Chronic kidney disease, also called chronic kidney failure, describes the gradual loss of kidney function. Your kidneys filter wastes and excess fluids from your blood,
KIDNEY FAILURE TREATMENT OPTIONS Choosing What s Best For You
 KIDNEY FAILURE TREATMENT OPTIONS Choosing What s Best For You What Kidneys Do The kidneys are a pair of bean shaped organs located below your ribcage near the middle of your back. Kidneys play a vital
KIDNEY FAILURE TREATMENT OPTIONS Choosing What s Best For You What Kidneys Do The kidneys are a pair of bean shaped organs located below your ribcage near the middle of your back. Kidneys play a vital
Patient Education Programme. Kidney Options Guiding you when kidneys fail
 Patient Education Programme Kidney Options Guiding you when kidneys fail About the kidneys What do healthy kidneys do? Your two kidneys work more than you realise. The kidneys remove excess body water
Patient Education Programme Kidney Options Guiding you when kidneys fail About the kidneys What do healthy kidneys do? Your two kidneys work more than you realise. The kidneys remove excess body water
HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL. Living well with Kidney Disease
 HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL Living well with Kidney Disease KIDNEY DISEASE CAN AFFECT ANYONE! 1 HEALTHYSTART PROGRAMME HEALTHYSTART is a lifestyle management programme to assist you to remain healthy
HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL Living well with Kidney Disease KIDNEY DISEASE CAN AFFECT ANYONE! 1 HEALTHYSTART PROGRAMME HEALTHYSTART is a lifestyle management programme to assist you to remain healthy
Drug Use in Dialysis
 (Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Drug Use in Dialysis Drambarean, B. (2017). Drug Use in Dialysis. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. DIALYSIS
(Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Drug Use in Dialysis Drambarean, B. (2017). Drug Use in Dialysis. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. DIALYSIS
Choices. Patient Education. Making the treatment decision. Overview. How do you define quality of life?
 Patient Education (KEEP) Chapter 6 Making the treatment decision Objectives: 1. List the 3 main options to supplement or replace failing kidney function. 2. Review steps for each of the main kidney replacement
Patient Education (KEEP) Chapter 6 Making the treatment decision Objectives: 1. List the 3 main options to supplement or replace failing kidney function. 2. Review steps for each of the main kidney replacement
Understanding. Your Kidneys. Laurie Biel, RN,BSN, CNN The MGH Center For Renal Education March 28, 2016
 Understanding Your Kidneys Laurie Biel, RN,BSN, CNN The MGH Center For Renal Education March 28, 2016 Today s Discussion - The Role of your kidneys Common causes of kidney disease Treatment for kidney
Understanding Your Kidneys Laurie Biel, RN,BSN, CNN The MGH Center For Renal Education March 28, 2016 Today s Discussion - The Role of your kidneys Common causes of kidney disease Treatment for kidney
Chronic Kidney Disease. Dr Mohan B. Biyani A. Professor of Medicine University of Ottawa/Ottawa Hospital
 Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Mohan B. Biyani A. Professor of Medicine University of Ottawa/Ottawa Hospital Health Seminar Series Date 12 May 2013 Objectives Normal functioning of Kidneys. Risk factors to
Chronic Kidney Disease Dr Mohan B. Biyani A. Professor of Medicine University of Ottawa/Ottawa Hospital Health Seminar Series Date 12 May 2013 Objectives Normal functioning of Kidneys. Risk factors to
Filters 1600 L of blood/day Makes 180 L of ultrafiltrate Kidney contains 600,000 to 1.4 million nephrons
 Filters 1600 L of blood/day Makes 180 L of ultrafiltrate Kidney contains 600,000 to 1.4 million nephrons Filtered: Ammonia Protein Amino acids Creatinine Uric acid Electrolytes Some are then reabsorbed
Filters 1600 L of blood/day Makes 180 L of ultrafiltrate Kidney contains 600,000 to 1.4 million nephrons Filtered: Ammonia Protein Amino acids Creatinine Uric acid Electrolytes Some are then reabsorbed
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Making your treatment decision. How do you define quality of life?
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Choices Making your treatment decision Class Goals 1. List the 3 main options to supplement or replace kidney function. 2. Review steps for each of the main kidney replacement
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Choices Making your treatment decision Class Goals 1. List the 3 main options to supplement or replace kidney function. 2. Review steps for each of the main kidney replacement
Patient Description and Diagnosis: Sarah Jones is a 50-year-old female, 5 4, 131
 Julia Kaesberg Counseling Session KNH 413 February 27 th, 2014 Patient Description and Diagnosis: Sarah Jones is a 50-year-old female, 5 4, 131 pounds and her usual body weight is 125 pounds. Her %UBW
Julia Kaesberg Counseling Session KNH 413 February 27 th, 2014 Patient Description and Diagnosis: Sarah Jones is a 50-year-old female, 5 4, 131 pounds and her usual body weight is 125 pounds. Her %UBW
What is renal failure?
 What is renal failure? The kidney is a very important organ, and cannot be restored to health once it fails. However, it is possible to avoid or retard the deterioration of its functionality if therapy
What is renal failure? The kidney is a very important organ, and cannot be restored to health once it fails. However, it is possible to avoid or retard the deterioration of its functionality if therapy
ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1
 ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1 This document is a supplement to the Online Training. Do not reproduce. Copyright Dialysis4Career. All Rights Reserved. The Renal System - A highly sophisticated
ONLINE HEMODIALYSIS TRAINING SESSION 1 This document is a supplement to the Online Training. Do not reproduce. Copyright Dialysis4Career. All Rights Reserved. The Renal System - A highly sophisticated
Taking Care of Your Kidneys
 Taking Care of Your Kidneys Part A Roseville & Sacramento Medical Centers Health Promotion Department Nutritional Services Agenda Slide How your kidneys work Explaining chronic kidney disease Protecting
Taking Care of Your Kidneys Part A Roseville & Sacramento Medical Centers Health Promotion Department Nutritional Services Agenda Slide How your kidneys work Explaining chronic kidney disease Protecting
HIV AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE. Understanding GFR
 HIV AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Understanding GFR in PEOPLE WITH HIV contents Introduction... 4 Chronic Kidney Disease... 5 What are kidneys and what do they do?... 5 What is glomerular filtration rate
HIV AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Understanding GFR in PEOPLE WITH HIV contents Introduction... 4 Chronic Kidney Disease... 5 What are kidneys and what do they do?... 5 What is glomerular filtration rate
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Peritoneal Dialysis. A treatment option for kidney disease. There are 2 types of PD: continuous ambulatory
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peritoneal Dialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and basic principles of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). 2.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peritoneal Dialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and basic principles of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). 2.
Case Study: Chronic Kidney Disease
 Taylor Zwimpfer Joan Rupp Nutrition 409 23 September 2014 Case Study: Chronic Kidney Disease 1. Kidneys act to maintain the balance of fluids, electrolytes and organic solutes in the body through filtration
Taylor Zwimpfer Joan Rupp Nutrition 409 23 September 2014 Case Study: Chronic Kidney Disease 1. Kidneys act to maintain the balance of fluids, electrolytes and organic solutes in the body through filtration
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stages. CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Treatment Options. Incident counts & adjusted rates, by primary diagnosis Figure 2.
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stages Stage 1 GFR > 90 (evidence of renal disease) Stage 2 GFR 60-89 Stage 3 GFR 30-59 Stage 4 GFR 15-29 Stage 5 GFR
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stages Stage 1 GFR > 90 (evidence of renal disease) Stage 2 GFR 60-89 Stage 3 GFR 30-59 Stage 4 GFR 15-29 Stage 5 GFR
End-Stage Renal Disease. Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology
 End-Stage Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology ESRD : Life with renal replacement therapy CASE: 18 month old male with HUS develops ESRD PD complicated
End-Stage Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology ESRD : Life with renal replacement therapy CASE: 18 month old male with HUS develops ESRD PD complicated
A PATIENT S GUIDE. Author: Dr. A. Patel. Editor: Dr. A. Kadri
 A PATIENT S GUIDE Author: Dr. A. Patel Editor: Dr. A. Kadri 1 ACKNOWLEDGMENT I would like to thank all of those individuals involved in producing this educational book for patients. The printing of this
A PATIENT S GUIDE Author: Dr. A. Patel Editor: Dr. A. Kadri 1 ACKNOWLEDGMENT I would like to thank all of those individuals involved in producing this educational book for patients. The printing of this
Know The Facts About Home Dialysis Choices
 Know The Facts About Home Dialysis Choices Fact Sheet www.esrdncc.org Table of Contents What are my choices for dialysis at home?...3 Why consider home hemodialysis?...4 What are the different types of
Know The Facts About Home Dialysis Choices Fact Sheet www.esrdncc.org Table of Contents What are my choices for dialysis at home?...3 Why consider home hemodialysis?...4 What are the different types of
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
Chronic Kidney Disease. Basics of CKD Terms Diagnosis Management
 Chronic Kidney Disease Basics of CKD Terms Diagnosis Management Review the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) Review how CKD develops Review populations at risk for CKD Review CKD diagnosis Objectives
Chronic Kidney Disease Basics of CKD Terms Diagnosis Management Review the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) Review how CKD develops Review populations at risk for CKD Review CKD diagnosis Objectives
Kidney Decisions Aid
 Kidney Decisions Aid A G U I D E F O R P E O P L E W H O H A V E, O R K N O W S O M E O N E, W I T H C H R O N I C K I D N E Y D I S E A S E, A N D T O A I D I N T H E D E C I S I O N A B O U T W H I C
Kidney Decisions Aid A G U I D E F O R P E O P L E W H O H A V E, O R K N O W S O M E O N E, W I T H C H R O N I C K I D N E Y D I S E A S E, A N D T O A I D I N T H E D E C I S I O N A B O U T W H I C
What Your Kidneys Do
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What Your Kidneys Do And what happens with kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia. 3. Know the common causes of kidney
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What Your Kidneys Do And what happens with kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia. 3. Know the common causes of kidney
Excretory System Workbook
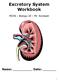 Excretory System Workbook MCHS Biology 20 Mr. Korotash Name: Date: 1 Study the diagram above. Name the structures and indicate their functions by completing the following table: Structure 1. Function 2.
Excretory System Workbook MCHS Biology 20 Mr. Korotash Name: Date: 1 Study the diagram above. Name the structures and indicate their functions by completing the following table: Structure 1. Function 2.
YOUR KIDNEYS AREN T WORKING PROPERLY.
 When you re born, everything works perfectly. Then something goes wrong and you ask: YOUR KIDNEYS AREN T WORKING PROPERLY. What does this mean? How can you stay healthy? HOW DO I DEAL WITH THIS? WHAT ROLE
When you re born, everything works perfectly. Then something goes wrong and you ask: YOUR KIDNEYS AREN T WORKING PROPERLY. What does this mean? How can you stay healthy? HOW DO I DEAL WITH THIS? WHAT ROLE
Chapter 12. Excretion and the Interaction of Systems
 Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Stage 5 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Stage 5 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
Patient Education Kidney Early Education Program (KEEP) Chapter 2 bjectives: Overview 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms
 Patient Education (KEEP) Chapter 2 What Your Kidneys Do And what happens when they fail Objectives: 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some ways to treat it. 3. Know the
Patient Education (KEEP) Chapter 2 What Your Kidneys Do And what happens when they fail Objectives: 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some ways to treat it. 3. Know the
Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Guideline (2010) Chronic Kidney Disease CKD: Executive Summary of Recommendations (2010) Executive Summary of Recommendations Below are the major recommendations
Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Guideline (2010) Chronic Kidney Disease CKD: Executive Summary of Recommendations (2010) Executive Summary of Recommendations Below are the major recommendations
Your Kidney Health. Your Choices. Chronic Kidney Disease
 Your Kidney Health Your Choices Your doctor may have told you that you have chronic kidney disease (CKD or advanced kidney disease; or, you may be in kidney failure, and may have to make a decision about
Your Kidney Health Your Choices Your doctor may have told you that you have chronic kidney disease (CKD or advanced kidney disease; or, you may be in kidney failure, and may have to make a decision about
Kidney Failure. Haemodialysis
 Kidneys & Kidney Failure 2 Haemodialysis This booklet will help you to know the process of Haemodialysis in detail. It will also tell you about the disposables of Haemodialysis. In the end the advantages
Kidneys & Kidney Failure 2 Haemodialysis This booklet will help you to know the process of Haemodialysis in detail. It will also tell you about the disposables of Haemodialysis. In the end the advantages
Kidney Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
 Cheshire and Merseyside Kidney Care Services Renal Replacement Therapy Options for Kidney Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5 Renal Replacement Therapy Options for Kidney Patients with Chronic
Cheshire and Merseyside Kidney Care Services Renal Replacement Therapy Options for Kidney Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5 Renal Replacement Therapy Options for Kidney Patients with Chronic
What Your Kidneys Do and What Happens When They Fail
 Patient Education Chapter 2 Page 1 What Your Kidneys Do and What Happens When They Fail Objectives: 1. Understand basic kidney functions. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some treatments used for it.
Patient Education Chapter 2 Page 1 What Your Kidneys Do and What Happens When They Fail Objectives: 1. Understand basic kidney functions. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia and some treatments used for it.
Kidney Disease Treatment Options
 Page 1 Fact sheet The kidneys play a number of important roles in your body such as: extracting excess water to make urine (wee) controlling your blood pressure filtering waste products and toxins from
Page 1 Fact sheet The kidneys play a number of important roles in your body such as: extracting excess water to make urine (wee) controlling your blood pressure filtering waste products and toxins from
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have any signs or symptoms of acute kidney failure.
 Acute Kidney Failure Acute kidney failure occurs when your kidneys suddenly become unable to filter waste products from your blood. When your kidneys lose their filtering ability, dangerous levels of wastes
Acute Kidney Failure Acute kidney failure occurs when your kidneys suddenly become unable to filter waste products from your blood. When your kidneys lose their filtering ability, dangerous levels of wastes
It is important upfront to realize and believe that, like many adults,
 Kids With Kidney Disease Can Realize Their Dreams and Live Long, Normal, Productive Lives By Gordon Lore It is important upfront to realize and believe that, like many adults, children with kidney failure
Kids With Kidney Disease Can Realize Their Dreams and Live Long, Normal, Productive Lives By Gordon Lore It is important upfront to realize and believe that, like many adults, children with kidney failure
Renal Disease and PK/PD. Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology
 Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
Renal Disease and PK/PD Anjay Rastogi MD PhD Division of Nephrology Drugs and Kidneys Kidney is one of the major organ of drug elimination from the human body Renal disease and dialysis alters the pharmacokinetics
ARE YOU AT INCREASED RISK FOR CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE?
 ARE YOU AT INCREASED RISK FOR CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE? www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease
ARE YOU AT INCREASED RISK FOR CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE? www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease
Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
 Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS St George Hospital Renal Department, reviewed 2017 St George Hospital Renal Department RENAL SELF LEARNING PACKAGE INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL
Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS St George Hospital Renal Department, reviewed 2017 St George Hospital Renal Department RENAL SELF LEARNING PACKAGE INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL
Kidney Failure: Choosing a treatment that is RIGHT FOR YOU
 Kidney Failure: Choosing a treatment that is RIGHT FOR YOU Your kidneys filter wastes from your blood and regulate other functions of your body. When your kidneys fail, you need treatment to replace the
Kidney Failure: Choosing a treatment that is RIGHT FOR YOU Your kidneys filter wastes from your blood and regulate other functions of your body. When your kidneys fail, you need treatment to replace the
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Hemodialysis. A treatment option for kidney disease. Treatment Options for Kidney Disease
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
Exer Ex cise Pa P tien tien with End End stag sta e g renal Disease
 Exercise in Patients with End stage Exercise in Patients with End stage renal Disease Chronic renal failure : gradual and progressive loss of the ability of the kidneys to function Structural kidney damage
Exercise in Patients with End stage Exercise in Patients with End stage renal Disease Chronic renal failure : gradual and progressive loss of the ability of the kidneys to function Structural kidney damage
Treatment choices for someone with Stage 5 kidney disease are:
 Information for patients about advanced kidney disease Dialysis and non-dialysis treatments DOCUMENT PREPARED FOR This information is to help you understand some key issues about dialysis; it is designed
Information for patients about advanced kidney disease Dialysis and non-dialysis treatments DOCUMENT PREPARED FOR This information is to help you understand some key issues about dialysis; it is designed
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
Objectives. Peritoneal Dialysis vs. Hemodialysis 02/27/2018. Peritoneal Dialysis Prescription and Adequacy Monitoring
 Peritoneal Dialysis Prescription and Adequacy Monitoring Christine B. Sethna, MD, EdM Division Director, Pediatric Nephrology Cohen Children s Medical Center Associate Professor Hofstra Northwell School
Peritoneal Dialysis Prescription and Adequacy Monitoring Christine B. Sethna, MD, EdM Division Director, Pediatric Nephrology Cohen Children s Medical Center Associate Professor Hofstra Northwell School
Home Dialysis. Peritoneal Dialysis. Home Hemodialysis
 Home Dialysis The information provided is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. A licensed healthcare professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and
Home Dialysis The information provided is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. A licensed healthcare professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
The Kidneys. The kidneys are vital organs. Two bean-shaped organs, about the size of a fist
 Kidney Health Coach The Kidneys The kidneys are vital organs Two bean-shaped organs, about the size of a fist Each kidney connects to the bladder by a thin tube called a ureter What do the kidneys do?
Kidney Health Coach The Kidneys The kidneys are vital organs Two bean-shaped organs, about the size of a fist Each kidney connects to the bladder by a thin tube called a ureter What do the kidneys do?
DIALYSIS. Ellie Stanger, Tessie Atwater, Summer White, McKenzie Driscoll
 DIALYSIS Ellie Stanger, Tessie Atwater, Summer White, McKenzie Driscoll PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Chronic Kidney Disease A wide range of kidney lesions characterized by a slow, steady decline in renal function A
DIALYSIS Ellie Stanger, Tessie Atwater, Summer White, McKenzie Driscoll PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Chronic Kidney Disease A wide range of kidney lesions characterized by a slow, steady decline in renal function A
Case Study: Renal Disease
 Case Study: Renal Disease Laboratory Values: Lab Units Patient Normal Source Interpretation GFR ml/min 46 above 90 Renal Lecture 2 BUN mg/dl 40 10-20 NTP A-90 Serum creatinine mg/dl 2.5 0.6-1.2 NTP A-90
Case Study: Renal Disease Laboratory Values: Lab Units Patient Normal Source Interpretation GFR ml/min 46 above 90 Renal Lecture 2 BUN mg/dl 40 10-20 NTP A-90 Serum creatinine mg/dl 2.5 0.6-1.2 NTP A-90
Select the dialysis treatment option that is best for you and your family.
 PEP CONNECT PEP Talk Outline P a t i e n t E d u c a t i o n P r o g r a m Your Treatment Options Part 1 Peritoneal Dialysis Select the dialysis treatment option that is best for you and your family. This
PEP CONNECT PEP Talk Outline P a t i e n t E d u c a t i o n P r o g r a m Your Treatment Options Part 1 Peritoneal Dialysis Select the dialysis treatment option that is best for you and your family. This
Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD
 Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD Develop patient treatment plan according to level of severity. Source: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012
Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD Develop patient treatment plan according to level of severity. Source: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012
Urinary System. Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system
 Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Treatment Options Not Not access
 Treatment Options Treatment options for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) CKD is a permanent condition. Treatment will: Help the patient feel better Not cure the disease Not make the kidneys start working again
Treatment Options Treatment options for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) CKD is a permanent condition. Treatment will: Help the patient feel better Not cure the disease Not make the kidneys start working again
Blood pressure and kidney disease
 Blood pressure and High blood pressure is the second most common cause of. Your heart pumps your blood through tubes (blood vessels) called arteries and veins. When your blood moves through the blood vessels,
Blood pressure and High blood pressure is the second most common cause of. Your heart pumps your blood through tubes (blood vessels) called arteries and veins. When your blood moves through the blood vessels,
Oxford Kidney Unit. Treatment options for chronic kidney disease A brief overview
 Oxford Kidney Unit Treatment options for chronic kidney disease A brief overview You may feel well at the moment and may not have any symptoms from your kidney disease, but it is important that you understand
Oxford Kidney Unit Treatment options for chronic kidney disease A brief overview You may feel well at the moment and may not have any symptoms from your kidney disease, but it is important that you understand
Treatment Options for Kidney Failure Living with End-Stage Renal Disease
 Treatment Options for Kidney Failure Dialysis Center Living with End-Stage Renal Disease 1887_FMech_1601.indd 25 12/29/15 10:56 AM Facing Kidney Failure Your doctor has told you that you have kidney failure,
Treatment Options for Kidney Failure Dialysis Center Living with End-Stage Renal Disease 1887_FMech_1601.indd 25 12/29/15 10:56 AM Facing Kidney Failure Your doctor has told you that you have kidney failure,
Fundamentals of DIALYSIS
 Fundamentals of DIALYSIS Knowing Your Kidneys Healthy Kidneys are the body s cleaning crew These are twin bean shaped organs, of the size of fist They make up a filter system for the blood & reabsorb almost
Fundamentals of DIALYSIS Knowing Your Kidneys Healthy Kidneys are the body s cleaning crew These are twin bean shaped organs, of the size of fist They make up a filter system for the blood & reabsorb almost
The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion. What are the functions of the urinary system? Maintenance of water-salt and acidbase
 10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
CREATININE: is another nitrogenous waste. Creatinine comes from creatinine phosphate in muscle metabolism (a Phosphate-storage molecule)
 BIOLOGY 12 - EXCRETION: CHAPTER NOTES Your cells are constantly carrying out chemical reactions to maintain homeostasis. Many of these chemical reactions produce wastes that must be removed from cells
BIOLOGY 12 - EXCRETION: CHAPTER NOTES Your cells are constantly carrying out chemical reactions to maintain homeostasis. Many of these chemical reactions produce wastes that must be removed from cells
PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST. AR. Merrikhi. MD. Isfahan University of Medical Sciences
 PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST AR. Merrikhi. MD. Isfahan University of Medical Sciences INTRODUCTION The peritoneal equilibration test (PET) is a semiquantitative assessment of peritoneal membrane transport
PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST AR. Merrikhi. MD. Isfahan University of Medical Sciences INTRODUCTION The peritoneal equilibration test (PET) is a semiquantitative assessment of peritoneal membrane transport
INTRODUCTION TO HAEMODIALYSIS
 INTRODUCTION TO HAEMODIALYSIS Why do I need dialysis? What is dialysis? How does haemodialysis work? Where will I have my treatment? Will dialysis cure my kidney failure? Will dialysis keep me well? I
INTRODUCTION TO HAEMODIALYSIS Why do I need dialysis? What is dialysis? How does haemodialysis work? Where will I have my treatment? Will dialysis cure my kidney failure? Will dialysis keep me well? I
Presented by UIC College of Nursing
 Presented by UIC College of Nursing Renal Disease Purpose and Objectives Background Renal disease Causes Statistics Renal disease and Hypertension Renal disease and Diabetes Types Acute renal failure Chronic
Presented by UIC College of Nursing Renal Disease Purpose and Objectives Background Renal disease Causes Statistics Renal disease and Hypertension Renal disease and Diabetes Types Acute renal failure Chronic
Understanding Your Hemodialysis Access Options UNDERSTANDING WHAT IT MEANS TO HAVE PROTEIN IN YOUR URINE
 Understanding Your Hemodialysis Access Options UNDERSTANDING WHAT IT MEANS TO HAVE PROTEIN IN YOUR URINE 2 AAKP: Understanding What It Means to Have Protein in Your Urine Understanding What It Means to
Understanding Your Hemodialysis Access Options UNDERSTANDING WHAT IT MEANS TO HAVE PROTEIN IN YOUR URINE 2 AAKP: Understanding What It Means to Have Protein in Your Urine Understanding What It Means to
* It is proportionate to body size and the reference value is usually expressed after correction for body surface area as 120 ± 25 ml/min/1.
 Ahmad Al-zoubi Glomerular filtration rate : is the sum of the ultrafiltration rates from plasma into the Bowman s space in each nephron and is a measure of renal excretory function *co : 6L *renal blood
Ahmad Al-zoubi Glomerular filtration rate : is the sum of the ultrafiltration rates from plasma into the Bowman s space in each nephron and is a measure of renal excretory function *co : 6L *renal blood
Kidney Disease and Failure. March 2018
 Kidney Disease and Failure March 2018 Objectives l State the function of the kidney l Define kidney disease l Identify tests and abnormal test results for kidney function l Recognize prevention and treatment
Kidney Disease and Failure March 2018 Objectives l State the function of the kidney l Define kidney disease l Identify tests and abnormal test results for kidney function l Recognize prevention and treatment
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion
 Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Peritoneal Dialysis. Choosing your logo. V2.0 logos. information. you can trust. Certified Member. The Information Standard
 Use of The Information Standard s Member Logos Peritoneal Dialysis Patient Information Choosing your logo The Information Standard has four logo versions for its members. They are designed to fit neatly
Use of The Information Standard s Member Logos Peritoneal Dialysis Patient Information Choosing your logo The Information Standard has four logo versions for its members. They are designed to fit neatly
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS
 THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
THE KIDNEY AND SLE LUPUS NEPHRITIS JACK WATERMAN DO FACOI 2013 NEPHROLOGY SIR RICHARD BRIGHT TERMINOLOGY RENAL INSUFFICIENCY CKD (CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE) ESRD (ENDSTAGE RENAL DISEASE) GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
Diseases of the Renal System
 Diseases of the Renal System Chapter 20 1 2 Kidneys - Anatomy Regulatory and metabolic functions Nephron - functional unit; approx. 1.2 million in each kidney Glomerulus within Bowman s capsule Afferent
Diseases of the Renal System Chapter 20 1 2 Kidneys - Anatomy Regulatory and metabolic functions Nephron - functional unit; approx. 1.2 million in each kidney Glomerulus within Bowman s capsule Afferent
Utopia Health Career Center
 Utopia Health Career Center Magda Castaneda RN, BSN, CNN, HTC Coordinator / Instructor BONENT Approved Program Florida Board of Nursing CE Provider # 50-16333 Property of Utopia Health Career Center, LLC.
Utopia Health Career Center Magda Castaneda RN, BSN, CNN, HTC Coordinator / Instructor BONENT Approved Program Florida Board of Nursing CE Provider # 50-16333 Property of Utopia Health Career Center, LLC.
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
 Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
LIVING WITH KIDNEY DISEASE: A PATIENT MANUAL
 LIVING WITH KIDNEY DISEASE: A PATIENT MANUAL Fifth Edition, September, 2002 i Presented by The Renal Network, Inc., this manual was published under CMS contact numbers 500-00-NW09 & 500-00-NW10. Living
LIVING WITH KIDNEY DISEASE: A PATIENT MANUAL Fifth Edition, September, 2002 i Presented by The Renal Network, Inc., this manual was published under CMS contact numbers 500-00-NW09 & 500-00-NW10. Living
NATIONAL QUALITY FORUM Renal EM Submitted Measures
 NATIONAL QUALITY FORUM Renal EM Submitted Measures Measure ID/ Title Measure Description Measure Steward Topic Area #1662 Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of CKD ACE/ARB
NATIONAL QUALITY FORUM Renal EM Submitted Measures Measure ID/ Title Measure Description Measure Steward Topic Area #1662 Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of CKD ACE/ARB
TABLE OF CONTENTS T-1. A-1 Acronyms and Abbreviations. S-1 Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
 A-1 Acronyms and Abbreviations TABLE OF CONTENTS S-1 Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Chapter 1: Nutrition Assessment Charts, Tables and Formulas 1-2 Practical Steps to Nutrition Assessment Adult
A-1 Acronyms and Abbreviations TABLE OF CONTENTS S-1 Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Chapter 1: Nutrition Assessment Charts, Tables and Formulas 1-2 Practical Steps to Nutrition Assessment Adult
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University
 RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
Getting Knowledge About Kidney Disease
 Last Reviewed Getting Knowledge About Kidney Disease Have you been told that you have late stage kidney disease? Choose Your Lifestyle On Dialysis There are two kinds of dialysis. Dialysis can be done
Last Reviewed Getting Knowledge About Kidney Disease Have you been told that you have late stage kidney disease? Choose Your Lifestyle On Dialysis There are two kinds of dialysis. Dialysis can be done
Starting Peritoneal Dialysis
 PD Education Booklet 1 Starting Peritoneal Dialysis What you will learn: What your kidneys do Uremia (kidney disease) and its symptoms How Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) helps The two types of PD: Automated
PD Education Booklet 1 Starting Peritoneal Dialysis What you will learn: What your kidneys do Uremia (kidney disease) and its symptoms How Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) helps The two types of PD: Automated
Peritoneal Dialysis Prescriptions: A Primer for Nurses
 Peritoneal Dialysis Prescriptions: A Primer for Nurses A Primer ABCs of PD R x Betty Kelman RN-EC MEd CNeph (C) Toronto General Hospital University Health Network Toronto, Ontario, Canada A moment to remember
Peritoneal Dialysis Prescriptions: A Primer for Nurses A Primer ABCs of PD R x Betty Kelman RN-EC MEd CNeph (C) Toronto General Hospital University Health Network Toronto, Ontario, Canada A moment to remember
SAMPLE. Chronic Kidney Disease, Evidence-Based Practice, and the Nutrition Care Process. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Chronic Kidney Disease, Evidence-Based Practice, and the Nutrition Care Process This guide follows the steps of the Nutrition Care Process (NCP) nutrition assessment, nutrition diagnosis, nutrition
Chapter 1 Chronic Kidney Disease, Evidence-Based Practice, and the Nutrition Care Process This guide follows the steps of the Nutrition Care Process (NCP) nutrition assessment, nutrition diagnosis, nutrition
HIHIM 409 7/26/2009. Kidney and Nephron. Fermamdo Vega, M.D. 1
 Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
The UK Renal Registry collects national data about the causes and treatment of kidney failure.
 1 Kidney failure is a serious condition. Many kidney patients receive some form of renal replacement therapy (RRT) such as dialysis. The UK Renal Registry collects national data about the causes and treatment
1 Kidney failure is a serious condition. Many kidney patients receive some form of renal replacement therapy (RRT) such as dialysis. The UK Renal Registry collects national data about the causes and treatment
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
STARTING PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
 STARTING PERITONEAL DIALYSIS What you will learn: What your kidneys do What uremia (kidney disease) is and what the symptoms are How Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) helps What the two types of PD are: automated
STARTING PERITONEAL DIALYSIS What you will learn: What your kidneys do What uremia (kidney disease) is and what the symptoms are How Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) helps What the two types of PD are: automated
About Your Dialysis Treatment
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Your Dialysis Treatment This information explains dialysis at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK). Your Kidneys and Their Functions Your kidneys are 2 bean-shaped organs
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION About Your Dialysis Treatment This information explains dialysis at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK). Your Kidneys and Their Functions Your kidneys are 2 bean-shaped organs
Managing Fluid, Diet and Medications
 Managing Fluid, Diet and Medications This lesson covers: Fluid and body weight Managing your diet Understanding your medications It is important that you feel comfortable with the information and procedures
Managing Fluid, Diet and Medications This lesson covers: Fluid and body weight Managing your diet Understanding your medications It is important that you feel comfortable with the information and procedures
The Urinary System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
network of thin-walled capillaries closely surrounded by a pear-shaped epithelial membrane called the Bowman s capsule
 Renal Terminology Renal-Root Words & Combining Forms calyx cortex glomerul/o medulla nephr/o pyel/o py/o ur/o ren/o cuplike division of the kidney outer layer of kidney glomerula inner or central portion
Renal Terminology Renal-Root Words & Combining Forms calyx cortex glomerul/o medulla nephr/o pyel/o py/o ur/o ren/o cuplike division of the kidney outer layer of kidney glomerula inner or central portion
FND 431 Clinical Experience Case Study! Introduction!
 FND 431 Clinical Experience Case Study Jennifer Millard Introduction Ms. B is a Type II diabetic with ESRD who has been receiving dialysis since April of 2013. Previously, she has shown excellent compliance
FND 431 Clinical Experience Case Study Jennifer Millard Introduction Ms. B is a Type II diabetic with ESRD who has been receiving dialysis since April of 2013. Previously, she has shown excellent compliance
A VIDEO SERIES. living WELL. with kidney failure WHAT IS KIDNEY FAILURE?
 A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure WHAT IS KIDNEY FAILURE? Contents 2 Introduction 11 What is a kidney transplant? 3 What will I learn? 12 What role do diet and medi- 5 Who is on my 7 healthcare
A VIDEO SERIES living WELL with kidney failure WHAT IS KIDNEY FAILURE? Contents 2 Introduction 11 What is a kidney transplant? 3 What will I learn? 12 What role do diet and medi- 5 Who is on my 7 healthcare
AV Fistula for Dialysis
 AV Fistula for Dialysis Introduction Before starting regular hemodialysis sessions, you must first prepare a vascular access. A vascular access is the site on your body where blood is removed and returned
AV Fistula for Dialysis Introduction Before starting regular hemodialysis sessions, you must first prepare a vascular access. A vascular access is the site on your body where blood is removed and returned
NATIONAL KIDNEY MONTH
 NATIONAL KIDNEY MONTH According to the WebMD website, kidneys have several specific roles: Maintain your body s balance of water and concentration of minerals, such as sodium, potassium, magnesium and
NATIONAL KIDNEY MONTH According to the WebMD website, kidneys have several specific roles: Maintain your body s balance of water and concentration of minerals, such as sodium, potassium, magnesium and
Chronic Kidney Disease - An Overview
 REVIEW ARTICLE KERALA MEDICAL JOURNAL Chronic Kidney Disease - An Overview Rajesh R Nair Department of Nephrology, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, Kerala* ABSTRACT Published on 28 th December
REVIEW ARTICLE KERALA MEDICAL JOURNAL Chronic Kidney Disease - An Overview Rajesh R Nair Department of Nephrology, Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Kochi, Kerala* ABSTRACT Published on 28 th December
Management of the patient with established AKI. Kelly Wright Lead Nurse for AKI King s College Hospital
 Management of the patient with established AKI Kelly Wright Lead Nurse for AKI King s College Hospital Medical management Medical management Respiratory- pulmonary oedema, repositioning- upright, oxygen
Management of the patient with established AKI Kelly Wright Lead Nurse for AKI King s College Hospital Medical management Medical management Respiratory- pulmonary oedema, repositioning- upright, oxygen
UNDERSTANDING PROCESS OF DIALYSIS
 UNDERSTANDING PROCESS OF DIALYSIS Introduction: End-stage renal disease (ESRD), the final stage of chronic kidney disease (CKD), occurs when the kidneys have deteriorated to the point that they are no
UNDERSTANDING PROCESS OF DIALYSIS Introduction: End-stage renal disease (ESRD), the final stage of chronic kidney disease (CKD), occurs when the kidneys have deteriorated to the point that they are no
Ana Paula Bernardo. CHP Hospital de Santo António ICBAS/ Universidade do Porto
 Ana Paula Bernardo CHP Hospital de Santo António ICBAS/ Universidade do Porto Clinical relevance of hyperphosphatemia Phosphate handling in dialysis patients Phosphate kinetics in PD peritoneal phosphate
Ana Paula Bernardo CHP Hospital de Santo António ICBAS/ Universidade do Porto Clinical relevance of hyperphosphatemia Phosphate handling in dialysis patients Phosphate kinetics in PD peritoneal phosphate
