EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
|
|
|
- Ezra Fields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area labeled\ A. W B. X C. Y D. Z 3. If the urine of a healthy person were analyzed. there would he only trace amounts of A. litre a B. water C. glucose D. mineral salts 4. Plasma moves into the Bowman's capsule because of A. osmosis B. diffusion C. force filtration D. active transport
2 5. The inability of a pituitary gland to release an antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) would inhibit the reabsorption of A. water B. glucose C. amino acids D. sodium ions 6. If a person drinks a large amount of water, his blood becomes diluted. The body immediately reacts by A. increasing salt retention in the kidney B. decreasing salt retention in the kidney C. secreting vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) D. inhibiting the secretion of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) 7. The filtering process in the kidney depends MAINLY on A. osmosis B. reabsorption C. blood pressure D. active transport 8. Dialysis machines purity blood by passing it through semi-permeable cellophane tubing immersed in a tank of dialysing fluid. Wastes are transferred through the tubing into the fluid. A system of this type can perform all the functions of a normal kidney except the A. diffusion of salts into the blood B. osmosis of water into the collecting duct C. filtration of smaller particles into the nephron D. active transport of substances out of the blood 9. The presence of antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) in the wall of the collecting duct of the nephron ensures that A. the blood pressure will be lowered B. more water will appear in the urine C. sodium will be reabsorbed into the bloodstream D. more water will be reabsorbed into the bloodstream 10. Urea is formed from A. sugars in the liver B. sugars in the kidney C. excess amino acids in the liver D. excess amino acids in the kidney 11. Under normal conditions proteins are found in the fluid of the A. glomerulus B. loop of Henle C. proximal tubule D. Bowman's capsule
3 12. One function of the kidney is to A. form urea B. regulate body temperature C. regulate the acid-base balance D. secrete antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) 13. Which is the correct sequence of structures through which a molecule of water passes before it is eliminated from the body? A. Tubule urethra bladder ureter B. Bowman's capsule tubule ureter urethra C. Bowman's capsule glomerulus tubule ureter D. Collecting tubule distal tubule ureter bladder 14. Amino acids move from the glomerulus to Bowman's capsule because of A. diffusion B. endocytosis C. blood pressure D. active transport 15. Blood enters the kidney through the A. aorta B. vena cava C. renal vein D. renal artery 16. Production of urea results primarily from the metabolism of A. fats B. amino acids C. nucleic acids D. carbohydrates 17. Between the proximal tubule and the loop of Henle the change in glucose concentration is due to A. osmosis B. filtration C. exocytosis D. reabsorption 18. Aldosterone acts on kidney tubules causing an increase in the reabsorption of A. urea B. glucose C. sodium ions D. amino acids
4 19. The correct sequence of structures through which a molecule of urea would pass is A. Bowman's capsule glomerulus tubules and loop of Henle ureter collecting duct bladder urethra B. glomerulus Bowman's capsule tubules and loop of Henle collecting duct urethra bladder ureter C. Bowman's capsule glomerulus tubules and loop of Henle collecting duct ureter bladder urethra D. glomerulus Bowman's capsule tubules and loop of Henle collecting duct ureter bladder urethra 20. Which statement best expresses the relationship between ADH levels in the blood and the formation of concentrated or dilute urine? A. Low levels of ADH result in the production of concentrated urine. B. High levels of ADH result in the production of concentrated urine. C. Low levels of ADH result in greater reabsorption of water by the blood. D. High levels of ADH result in greater reabsorption of salt by distal tubules. 21. Diabetes insipidus is a disease that results in an excessive volume of highly dilute urine. This is probably due to A. low TSH levels B. low ADH levels C. high TSH levels D. high ADH levels Use the following information to answer the next question. 22. If the concentration of a substance is 0.01 g / L in the structure labelled W and 0.10 g / L in the structure labelled X, then the substance is probably A. retained in the blood B. reabsorbed by tubule cells C. not reabsorbed by tubule cells D. returned to the circulatory system
5 Use the following information to answer question If the concentration of a substance is 0.01 g/l at X and g/l at Y, then that substance is MOST LIKELY A. not required by the tubules B. secreted by the tubule cells C. reabsorbed from the tubules D. metabolized by the tubule cells 24. Most reabsorption of glucose in the nephron occurs in the A. distal tubule B. loop of Henle C. proximal tubule D. collecting ducts 25. A function of aldosterone in the body is to A. help regulate urea formation B. help regulate the body fluid volume C. stimulate the oxidation of amino acids D. stimulate the adrenal glands to produce adrenalin
6 26. Most of the glomerular filtrate that enters a nephron is A. converted to urea B. retained in the glomerulus C. excreted through the bladder D. reabsorbed into the capillaries 27. In an insulin-deficient human, there is excretion of glucose in the urine even though the diet is carbohydratefree. This observation is explained by the fact that A. urea is either manufactured or stored in the liver B. amino acids are converted by the liver into glucose C. amino acids are synthesized in the liver from glucose D. glucose is continually manufactured in the liver from carbon dioxide and water 28. If a person has a damaged pituitary gland and has lost the ability to secrete ADH the urine would have a high concentration of A. protein B. glucose C. water D. urea 29. After an individual drinks large quantities of water, the blood becomes slightly diluted. The body immediately reacts by A. increasing the secretion of ADH B. decreasing the secretion of ADH C. increasing the secretion of aldosterone from the adrenal glands D. reabsorbing more sodium ions from the filtrate of the nephron into the blood 30. In the kidney, active transport occurs when A. glucose molecules move from the glomerulus to Bowman's capsule B. amino acids are rcabsorbed into the blood from the proximal tubule C. small particles are separated from large particles by the capsule of the nephron D. water moves from a region of lower solute concentration to one of a higher solute concentration through a selectively permeable membrane 31. Filtration of blood plasma by the nephron occurs between the A. arteries and the loop of Henle B. glomerulus and Bowman's capsule C. capillaries and the distal tubule D. capillaries and the proximal tubule 32. The normal sequence of processes in urine formation is A. filtration, reabsorption, tubular secretion B. reabsorption, filtration, tubular secretion C. tubular secretion, filtration, reabsorption D. tubular secretion, reabsorption, filtration
7 Use the following information to answer the next question. 33. Removal of chloride ions and sodium ions from the filtrate in structure Y allows for A. the secretion of glucose into the distal tubule B. further reabsorption of all filtrate components C. further reabsorption of water in the distal tubule D. the secretion of nitrogenous wastes into the distal tubule 34. The factor that exerts negative feedback control over the release of ADH is the amount of A. ADH in the blood B. ADH in the urine C. water in the blood D. water in the urine 35. A human blood sample contains a greater concentration of urea than normal. This may have been caused by the person having eaten excessive amounts of A. fat B. sugar C. starch D. protein
8 Use the following information to answer the next question. 36. The most likely occurrence at W is A. a decrease in urine output and a decrease in blood pressure B. a decrease in urine output and an increase in blood pressure C. an increase in urine output and a decrease in blood pressure D. an increase in urine output and an increase in blood pressure 37. Blood leaving a kidney has lost much of its A. urea B. plasma C. glucose D. vitamins 38. Glomerulonephritis is an inflammatory condition that causes the walls of the glomeruli to become swollen and ruptured. The BEST indication of this condition would be the presence of A. glucose in the urine B. urea and amino acids in the urine C. red blood cells and plasma proteins in the urine D. glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids in the urine
9 Use the following data to answer the next question. Samples Taken from a Human Kidney Component Composition of Samples (g/100 ml of fluid) Sample 1 Sample 2 Sample 3 Urea Glucose Protein Sample 2 was most likely taken from the A. glomerulus B. loop of Henle C. distal tubule D. collecting tubule 40. The correct sequence depicting flow of materials through the nephron is A. proximal tubule Bowman's capsule distal tubule loop of Henle collecting tubule B. Bowman's capsule distal tubule loop of Henle proximal tubule collecting tubule C. proximal tubule distal tubule collecting tubule Bowman's capsule loop of Henle D. Bowman's capsule proximal tubule loop of Henle distal tubule collecting tubule 41. A MAJOR function of the kidney is the A. deamination of amino acids B. chemical breakdown of urea C. removal of glucose from the blood D. removal of nitrogenous wastes from the blood 42. A patient is diagnosed as suffering from high blood pressure. The physician chooses to treat the patient with a drug that is OPPOSITE in function to antidiuretic hormone (ADH) because the drug will A. increase the reabsorption of water, which will lower the blood volume B. decrease the reabsorption of water, which will lower the blood volume C. decrease the reabsorption of water, which will raise the blood volume D. increase the reabsorption of water, which will raise the blood volume 43. Through which sequence of structures does a molecule of urea pass as it is eliminated from the body? A. Renal artery proximal tubule urethra ureter B. Renal vein Bowman's capsule urethra ureter C. Bowman's capsule distal tubule bladder urethra D. Glomerulus loop of Henle bladder collecting duct 44. Fluid is delivered to the urinary bladder by the A. ureters B. urethra C. renal veins D. collecting ducts
10 Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 45. The HIGHEST concentration of mitochondria would be expected in the cells of the area labelled A. Q B. R C. S D. T 46. In urine, the absence of large protein molecules is due to their inability to pass into A. collecting ducts B. Bowman's capsules C. the urinary bladder D. proximal convoluted tubules 47. Two important sources of the nitrogenous compounds excreted in urine are A. fats and sugars B. sugars and proteins C. nucleic acids and proteins D. nucleic acids and phospholipids EXCRETION SYSTEM QUESTIONS FROM JUNE DIPLOMA EXAMS Page 10 of 22
11 Use the following diagrams to answer the next question. 48. The processes shown in the three diagrams from left to right are A. filtration, reabsorption, and secretion B. filtration, secretion, and reabsorption C. secretion, reabsorption, and filtration D. secretion, filtration, and reabsorption Use the following information to answer the next question. Possible Responses to Dehydration of the Human Body I. Increased water in the blood II. Decreased water in the blood III. Increased release of ADH IV. Decreased release of ADH V. Increased water reabsorption by the kidneys VI. Decreased water reabsorption by the kidneys 49. In order to restore homeostasis in an individual, which sequence of responses occurs when the individual becomes dehydrated through prolonged perspiration? A. I, III, and V B. I, IV, and VI C. II, III, and V D. II, IV, and VI 50. Which function is not carried out by human kidneys? A. The regulation of the ph of the blood B. The formation of urea from excess amino acids C. The removal of metabolic wastes from the blood D. The regulation of the amount of water in the blood EXCRETION SYSTEM QUESTIONS FROM JUNE DIPLOMA EXAMS Page 11 of 22
12 Use the following diagram to answer the next two questions. 51. An increase in blood pressure would most directly affect the function of the structure labeled A. H B. K C. M D. P 52. The concentration of urea is greatest in the structure labeled A. M B. N C. P D. Q 53. A molecule of urea passes through which sequence of structures in the excretory system? A. Glomerulus, Bowman's capsule, loop of Henle, collecting duct, ureter, bladder, urethra B. Bowman's capsule, glornerulus, loop of Henle, collecting duct, ureter, bladder, urethra C. Bowman's capsule, glomerulus, loop of Henle, ureter, collecting duct, bladder, urethra D. Glomerulus, Bowman's capsule, loop of Henle, collecting duct, urethra, bladder, ureter 54. A dialysis machine has a membrane that is permeable to water, urea, uric acid, ammonia, salts, and glucose. The membrane is impermeable to protein molecules. In relation to the blood flowing through the dialysis machine, the dialyzing solution must have A. the same concentrations of urea and salts B. lower concentrations of glucose and protein C. lower concentrations of urea, uric acid, and ammonia, and higher or equal concentrations of glucose D. higher concentrations of urea, uric acid, and ammonia, and lower or equal concentrations of glucose EXCRETION SYSTEM QUESTIONS FROM JUNE DIPLOMA EXAMS Page 12 of 22
13 Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 55. The concentration of glucose is lower in the structure labeled A. 1 than in the structure labeled 2 B. 3 than in the structure labeled 1 C. 4 than in the structure labeled 2 D. 4 than in the structure labeled 3 Use the following table to answer the next question. Aldosterone Secretion Plasma Electrolytes (meq/l) Na + K + Cl - HCO 3 - Normal Below normal Above normal Aldosterone affects kidney function and therefore affects plasma composition. It is evident from the table that above normal secretion of aldosterone causes an increase in the A. excretion of Cl - and HCO 3 - B. reabsorption of K + and the excretion of Na + C. reabsorption of Na + and the excretion of K + D. excretion of Na + and the reabsorption of Cl + EXCRETION SYSTEM QUESTIONS FROM JUNE DIPLOMA EXAMS Page 13 of 22
14 Use the following table to answer the next question. Dialyzing Fluid from an Artificial Kidney Compared with Uremic Plasma and Normal Plasma Constituent Dialyzing Fluid Uremic Plasma Normal Plasma Electrolytes (units/l) Na K Ca Cl HCO HPO Nonelectrolytes (mg/dl) Glucose Urea Note: Assume that the dialysis membrane of the artificial kidney is permeable to all the plasma constituents listed in the table. Uremic plasma refers to the plasma of a person suffering from kidney failure. 57. Which three substances will undergo a net movement into dialyzing fluid from uremic plasma? A. Ca 2+, Na +, and Cl - B. Ca 2+, HCO 3 -, and glucose C. K +, HPO4 2-, and urea D. Na +, glucose, and urea 58. Specialized cells in the hypothalamus called osmoreceptors monitor the concentration of water in the blood and control the release of ADH. The event most likely to cause osmoreceptors to initiate the release of ADH is A. depletion of blood glucose B. dehydration of the tissues C. storage of urine in the bladder D. accumulation of water in the tissues 59. Which structure transports urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder? A. Ureter B. Urethra C. Loop of Henle D. Collecting duct 60. Which metabolic wastes are removed from the blood by nephrons? A. Urea, glucose, and water B. Urea, hydrogen ions, and water C. Amino acids, glucose, and carbon dioxide D. Amino acids, hydrogen ions, and carbon dioxide EXCRETION SYSTEM QUESTIONS FROM JUNE DIPLOMA EXAMS Page 14 of 22
15 Use the following information to answer the next question. Acute Glomerulonephritis In acute glomerulonephritis, many of the glomeruli of the kidneys become blocked by inflammation. Other glomeruli become permeable to erythrocytes and large molecules. Characteristics and Test Results of Urine Samples from Two Individuals Urine Sample Color of Urine Biuret Test Test for Iron Test for Urea From a healthy individual yellow negative negative positive From a person suffering from acute glomerulonephritis W X Y Z 61. Which words for W, X, Y, and Z describe the test results for a person suffering from acute glomerulonephritis? A. W-red, X-negative, Y-positive, and Z-negative B. W-red, X-positive, Y-positive, and Z-positive C. W-yellow, X-negative, Y-negative, and Z-positive D. W-yellow, X-positive, Y-negative, and Z-negative Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 62. In a healthy person, the sequence of structures through which a molecule of glucose passes is A. F, J, G, and H B. G, J, F, and K C. H, G, J, and F D. H, J, G, and K EXCRETION SYSTEM QUESTIONS FROM JUNE DIPLOMA EXAMS Page 15 of 22
16 63. Which graph best represents the relationship between arterial blood pressure in the kidney and urinary volume output in litres per 24 hours? 64. In humans, renal veins carry blood from the kidneys to the A. superior vena cava B. inferior vena cava C. pulmonary vein D. aorta 65. Blood leaving the liver has a high concentration of urea, which is formed by the A. digestion of protein B. denaturation of protein C. deamination of amino acids D. detoxification of fatty acids 66. The movement of fluid from blood in the glomerulus to Bowman's capsule is called A. filtration B. diffusion C. reabsorption D. active transport EXCRETION SYSTEM QUESTIONS FROM JUNE DIPLOMA EXAMS Page 16 of 22
17 Use the following diagram to answer the next three questions. 67. Water is reabsorbed from the three structures labelled A. 1, 3, and 9 B. 1, 6, and 8 C. 3, 5, and 8 D. 5, 6, and The concentration of urea is greatest in the blood vessel labelled A. 2 B. 4 C. 7 D An increase in blood levels of both aldosterone and ADH would most directly affect the structure labelled A. 1 B. 5 C. 6 D. 8 EXCRETION SYSTEM QUESTIONS FROM JUNE DIPLOMA EXAMS Page 17 of 22
18 Use the following information to answer the next question. 70. Which statement is a correct conclusion based on these test results? A. The tubules of the kidney reabsorb all available glucose. B. The tubules of the kidney have a maximum potential for reabsorbing glucose. C. The permeability of the collecting ducts to glucose decreases, slowing reabsorption. D. The extra glucose triggers a decrease in cellular respiration; therefore, glucose is excreted. 71. In the human kidney, increased blood pressure directly affects the function of the A. glomerulus B. distal tubule C. loop of Henle D. A collecting duct 72. As filtrate is processed in the kidney to form urine, there is a change in the concentration of solutes present in the fluid within nephric tubules. Which substance in this fluid undergoes the greatest increase in concentration? A. Urea B. Glucose C. Amino acids D. Sodium ions EXCRETION SYSTEM QUESTIONS FROM JUNE DIPLOMA EXAMS Page 18 of 22
19 Use the following information to answer the next question. 73. Peritoneal (abdominal) dialysis and the artificial kidney machine function in similar ways. Which steps are similar in both procedures? A. 1 and 5, 2 and 4, 3 and 6 B. 1 and 5, 2 and 6, 3 and 4 C. 1 and 6, 2 and 4, 3 and 5 D. 1 and 6, 2 and 5, 3 and 4 EXCRETION SYSTEM QUESTIONS FROM JUNE DIPLOMA EXAMS Page 19 of 22
20 Use the following information to answer the next question. 74. Which row correctly identifies the symbols used in the diagram? Symbol Row A protein glucose urea B glucose protein urea C glucose urea protein D protein urea glucose 75. In the liver, urea is produced as a result of the breakdown of A. fats B. glucose C. glycogen D. amino acids EXCRETION SYSTEM QUESTIONS FROM JUNE DIPLOMA EXAMS Page 20 of 22
21 76. Which is the best illustration of the transport of Na+ and H2O between the distal tubule of a nephron and its surrounding interstitial fluid in a dehydrated person? Use the diagram at the right to answer the next two questions. 77. The fluid that is most similar in composition to plasma is found in the structure labelled A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 EXCRETION SYSTEM QUESTIONS FROM JUNE DIPLOMA EXAMS Page 21 of 22
22 78. If the structure labelled 3 were reduced in length, what would happen in the kidney, even if ADH and aldosterone were present? A. Urine volume would increase. B. Blood volume would increase. C. More Na + ions would be reabsorbed. D. Osmotic pressure in the blood would decrease. 79. When a person drinks alcohol, the amount of urine produced increases. The physiological reason for this is that alcohol A. stimulates ADH secretion and more water is reabsorbed B. stimulates ADH secretion and less water is reabsorbed C. inhibits ADH secretion and more water is reabsorbed D. inhibits ADH secretion and less water is reabsorbed Use the following information to answer the next question. Some Characteristics and Components of Normal Urine Characteristic/Component Description/Amount Volume Colour Cloudiness 1-2 litres/24 h yellow or amber transparent when fresh but becomes cloudy upon standing ph Specific gravity (density) Urea Creatinine Uric Acid NaCl Potassium ions Sulfate ions Phosphate ions Other substances 80. Why are some values in the table given as ranges of numbers? A. Waste production occurs only after meals or exercise. B. Some substances are continually filtered by the kidneys. C. Excretion of substances is determined by activity and diet. D. A Many substances are retained in the blood and not excreted g/24 h 1.5 g/24 h g/24 h 15.0 g/24 h 3.3 g/24 h 2.5 g/24 h 2.5 g/24 h 4.8 g/24 h EXCRETION SYSTEM QUESTIONS FROM JUNE DIPLOMA EXAMS Page 22 of 22
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
EXCRETORY SYSTEM WHY DO WE NEED AN EXCRETORY SYSTEM? Function: To eliminate waste To maintain water and salt balance To maintain blood pressure These wastes include: Carbon dioxide Mostly through breathing
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Excretory System. Biology 2201
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations ORGANS
Excretory System. Excretory System
 Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
Excretory System Biology 2201 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates: Body heat Water-salt concentrations Acid-base concentrations Metabolite concentrations 1
November 30, 2016 & URINE FORMATION
 & URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
& URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
Structures of the Excretory System include: ü Skin ü Lung ü Liver ü Kidneys ü Ureter ü Urinary Bladder ü Urethra
 Excretory System Structures of the Excretory System include: ü Skin ü Lung ü Liver ü Kidneys ü Ureter ü Urinary Bladder ü Urethra Function of the Excretory System The function of the excretory system is
Excretory System Structures of the Excretory System include: ü Skin ü Lung ü Liver ü Kidneys ü Ureter ü Urinary Bladder ü Urethra Function of the Excretory System The function of the excretory system is
Chapter 12. Excretion and the Interaction of Systems
 Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Chapter 12 Excretion and the Interaction of Systems 1 2 Goals for This Chapter 1. Identify the main structures and functions of the human excretory system 2. Explain the function of the nephron 3. Describe
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste:
 I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
I. Metabolic Wastes Metabolic Waste: a) Carbon Dioxide: by-product of cellular respiration. b) Water: by-product of cellular respiration & dehydration synthesis reactions. c) Inorganic Salts: by-product
Excretion and Waste Management. Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski
 Excretion and Waste Management Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski Lesson 1 Waste Products and Organs 2 3 Excretion Excretion: Process by which dissolved metabolic wastes are separated from body fluids and removed
Excretion and Waste Management Biology 30S - Miss Paslawski Lesson 1 Waste Products and Organs 2 3 Excretion Excretion: Process by which dissolved metabolic wastes are separated from body fluids and removed
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013
 EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
EXCRETION IN HUMANS 31 JULY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Discuss organs of excretion Look at the structure of the urinary system Look at the structure and functioning of the kidney Discuss
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
EXCRETORY SYSTEM E. F. G. H.
 XRTORY SYSTM 1. Label the following parts of the nephron in the diagram below:..... F. G. H. I. J. K. L. 2. Identify the following as either True or False: There is a greater osmotic concentration in the
XRTORY SYSTM 1. Label the following parts of the nephron in the diagram below:..... F. G. H. I. J. K. L. 2. Identify the following as either True or False: There is a greater osmotic concentration in the
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance 1. Osmoregulation (water balance) a. Most marine invertebrates are osmoconformers in which the concentration of solutes in their body fluid is equal to that of their environment.
Excretion and Water Balance 1. Osmoregulation (water balance) a. Most marine invertebrates are osmoconformers in which the concentration of solutes in their body fluid is equal to that of their environment.
Homeostatic Regulation
 Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
Homeostatic Regulation A hormone is :a Water-soluble hormones: Composed of amino acids and bind a receptor protein on the of the target cell. This starts a signal cascade inside the cell and the signal
Lesson Overview. The Excretory System. Lesson Overview The Excretory System
 Lesson Overview 30.4 THINK ABOUT IT It s a hot day and you gulp down water. As you drink, you begin to wonder. Where s all that water going? Will it just dilute your blood, or is something in your body
Lesson Overview 30.4 THINK ABOUT IT It s a hot day and you gulp down water. As you drink, you begin to wonder. Where s all that water going? Will it just dilute your blood, or is something in your body
Chapter 16. Urinary System and Thermoregulation THERMOREGULATION. Homeostasis
 Homeostasis Chapter 16 Urinary System and Thermoregulation! Homeostasis Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite fluctuations in the external environment! Examples of homeostasis Thermoregulation
Homeostasis Chapter 16 Urinary System and Thermoregulation! Homeostasis Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite fluctuations in the external environment! Examples of homeostasis Thermoregulation
Regulating the Internal Environment. AP Biology
 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external
Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to external
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
Excretion: is the removal of waste products formed by metabolism, out of the body
 Excretion in Humans Excretion: is the removal of waste products formed by metabolism, out of the body Accumulation of wastes in the cells would affect the normal functioning of the cells By getting rid
Excretion in Humans Excretion: is the removal of waste products formed by metabolism, out of the body Accumulation of wastes in the cells would affect the normal functioning of the cells By getting rid
Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment
 Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform
Ch. 44 Regulating the Internal Environment 2006-2007 Conformers vs. Regulators Two evolutionary paths for organisms regulate internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT. 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys.
 Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
Fifth Year Biology. Excretion. Miss Rochford
 Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
CREATININE: is another nitrogenous waste. Creatinine comes from creatinine phosphate in muscle metabolism (a Phosphate-storage molecule)
 BIOLOGY 12 - EXCRETION: CHAPTER NOTES Your cells are constantly carrying out chemical reactions to maintain homeostasis. Many of these chemical reactions produce wastes that must be removed from cells
BIOLOGY 12 - EXCRETION: CHAPTER NOTES Your cells are constantly carrying out chemical reactions to maintain homeostasis. Many of these chemical reactions produce wastes that must be removed from cells
What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body.
 Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
The Urinary System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Chapter 10 EXCRETION
 Chapter 10 EXCRETION Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance as a part of homeostasis Homeostasis means Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite
Chapter 10 EXCRETION Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance as a part of homeostasis Homeostasis means Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
Osmoregulation and the Excretory System
 Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Honors Biology Study Guide Chapter 25.4 25.10 Name Osmoregulation and the Excretory System FUNCTIONS OF THE EXCRETORY SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION Freshwater: Marine: Land Animals: Sources of Nitrogenous Wastes?
Ch17-18 Urinary System
 Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Salt and Water Balance and Nitrogen Excretion
 Announcements Exam is in class on WEDNESDAY. Bring a #2 pencil and your UFID. You must come to your registered class section (except those with DRC accommodations). Office hours Mon 1-3 pm. Teaching evals:
Announcements Exam is in class on WEDNESDAY. Bring a #2 pencil and your UFID. You must come to your registered class section (except those with DRC accommodations). Office hours Mon 1-3 pm. Teaching evals:
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Biology Slide 1 of 36
 Biology 1 of 36 38 3 The Excretory System 2 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System 1.Function: process which eliminates metabolic wastes 3 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System (The skin excretes excess
Biology 1 of 36 38 3 The Excretory System 2 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System 1.Function: process which eliminates metabolic wastes 3 of 36 Functions of the Excretory System (The skin excretes excess
1.&Glomerular/Pressure&Filtration&
 Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Chapter 13 The Urinary System
 Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Biology 12 Name: Urinary System Per: Date: Chapter 13 The Urinary System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 408-435 13.1 The Urinary System pages 412-413 1. As the kidneys produce urine, they carry out
Chapter 32 Excretion
 Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
A. Correct! Flushing acids from the system will assist in re-establishing the acid-base equilibrium in the blood.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
UNIT 3 Conditions supporting life
 Biology Form 4 Page 32 Ms. R. Buttigieg UNIT 3 Conditions supporting life In this unit we shall be seeing how an important condition that supports life is the ability of the organism to maintain a constant
Biology Form 4 Page 32 Ms. R. Buttigieg UNIT 3 Conditions supporting life In this unit we shall be seeing how an important condition that supports life is the ability of the organism to maintain a constant
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Osmoregulation and Renal Function
 1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion
 Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Chapter 10: Urinary System & Excretion Organs of Urinary System Kidneys (2) form urine Ureters (2) Carry urine from kidneys to bladder Bladder Stores urine Urethra Carries urine from bladder to outside
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment. AP Biology
 Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment Homeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment Homeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
The Urinary System 15PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART A Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 11 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Animal Life and Excretion Harder for multicellular organisms Internal circulation Coordination, information transfer Structural maintenance Movement Maintenance of homeostatic internal environment 15 July
Animal Life and Excretion Harder for multicellular organisms Internal circulation Coordination, information transfer Structural maintenance Movement Maintenance of homeostatic internal environment 15 July
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Question 1: Solution 1: Question 2: Question 3: Question 4: Class X The Excretory System Biology
 A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
The Excretory System
 The Excretory System The excretory system The excretory system includes the skin, lungs and kidneys which all release metabolic wastes from the body. The kidneys, skin and the lungs are the principle organs
The Excretory System The excretory system The excretory system includes the skin, lungs and kidneys which all release metabolic wastes from the body. The kidneys, skin and the lungs are the principle organs
Kidney Lab. Name: By the end of this lab, you should:
 Kidney Lab Name: Kidneys do a grand job removing the toxic waste products of metabolism. This process is called excretion. Our kidneys produce urine which contains urea, excess salts and excess water.
Kidney Lab Name: Kidneys do a grand job removing the toxic waste products of metabolism. This process is called excretion. Our kidneys produce urine which contains urea, excess salts and excess water.
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System
 Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
Anatomy/Physiology Study Guide: Unit 9 Excretory System 1) In the space below, list the primary structures (organs) and their corresponding functions. Structures: Functions: KIDNEY 1) URETER BLADDER URETHRA
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
Homeostasis. Thermoregulation. Osmoregulation. Excretion. how organisms regulate their body temperature
 Homeostasis the steady-state physiological condition of the body Ability to regulate the internal environment important for proper functioning of cells Thermoregulation Homeostasis how organisms regulate
Homeostasis the steady-state physiological condition of the body Ability to regulate the internal environment important for proper functioning of cells Thermoregulation Homeostasis how organisms regulate
WJEC. BY4 Kidney Questions
 NAME: OPTION GROUP WJEC BY4 Kidney Questions Question Book 2 (Legacy Qs from Jan 2000 to June 2014) Question Number(s) Due Date & Pass Mark Homework Mark Resist Question number(s) Resist Due Date & Pass
NAME: OPTION GROUP WJEC BY4 Kidney Questions Question Book 2 (Legacy Qs from Jan 2000 to June 2014) Question Number(s) Due Date & Pass Mark Homework Mark Resist Question number(s) Resist Due Date & Pass
Body Fluid Regulation and Excretion. Chapter 36
 Body Fluid Regulation and Excretion Chapter 36 Excretion The excretory system monitors the concentration of body fluids and removes harmful or waste substances from the body Water, nutrients and minerals
Body Fluid Regulation and Excretion Chapter 36 Excretion The excretory system monitors the concentration of body fluids and removes harmful or waste substances from the body Water, nutrients and minerals
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion. What are the functions of the urinary system? Maintenance of water-salt and acidbase
 10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
10.1 Urinary system The Urinary S. (Chp. 10) & Excretion 10.1 Urinary system What are the functions of the urinary system? 1. Excretion of metabolic wastes (urea, uric acid & creatinine) 1. Maintenance
5. Maintaining the internal environment. Homeostasis
 5. Maintaining the internal environment Homeostasis Blood and tissue fluid derived from blood, flow around or close to all cells in the body. Blood and tissue fluid form the internal environment of the
5. Maintaining the internal environment Homeostasis Blood and tissue fluid derived from blood, flow around or close to all cells in the body. Blood and tissue fluid form the internal environment of the
Excretion Chapter 29. The Mammalian Excretory System consists of. The Kidney. The Nephron: the basic unit of the kidney.
 Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
The Urinary System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
9.1. Metabolic processes produce waste products that can be harmful to the body.
 Excretion in Humans Notes 1 9.1 The Process of Excretion Metabolic processes produce waste products that can be harmful to the body. 2 These waste products are constantly removed through the process of
Excretion in Humans Notes 1 9.1 The Process of Excretion Metabolic processes produce waste products that can be harmful to the body. 2 These waste products are constantly removed through the process of
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Chapter 44. Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Chapter 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Overview: A Balancing Act Physiological systems of animals operate in a fluid environment Relative concentrations of water and solutes must be maintained within
Chapter 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Overview: A Balancing Act Physiological systems of animals operate in a fluid environment Relative concentrations of water and solutes must be maintained within
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Structure of the Kidney Excretion is the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Structure of the Kidney Excretion is the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water
 Ch 44 Osmoregulation & Excretion Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water uptake and conserve solutes
Ch 44 Osmoregulation & Excretion Osmoregulation regulates solute concentrations and balances the gain and loss of water Freshwater animals show adaptations that reduce water uptake and conserve solutes
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
AP Biology. Homeostasis. Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment. Homeostasis
 Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment omeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Chapter 44. Regulating the Internal Environment omeostasis Living in the world organisms had a choice: regulate their internal environment maintain relatively constant internal conditions conform to the
Title: Oct 12 3:37 PM (1 of 39) Ch 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Title: Oct 12 3:37 PM (1 of 39) Ch 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Water Balance and Waste Disposal osmoregulation managing water content and solute composition based on movements of solutes excretion
Title: Oct 12 3:37 PM (1 of 39) Ch 44 Osmoregulation and Excretion Water Balance and Waste Disposal osmoregulation managing water content and solute composition based on movements of solutes excretion
1 Regulation of water content
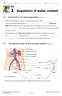 Class: Name: ( ) Date: E1 1 Regulation of water content 1.1 Importance of osmoregulation (Book E1, p. 3) If there is an imbalance between water intake and water loss, the (1) content of the blood and hence
Class: Name: ( ) Date: E1 1 Regulation of water content 1.1 Importance of osmoregulation (Book E1, p. 3) If there is an imbalance between water intake and water loss, the (1) content of the blood and hence
1. remove: waste products: urea, creatinine, and uric acid foreign chemicals: drugs, water soluble vitamins, and food additives, etc.
 Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
QUESTIONSHEET 1. Read through the following passage on homeostasis and then answer the questions.
 QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage on homeostasis and then answer the questions. Homeostasis is the regulation of the internal environment within narrow limits. This gives the organism
QUESTIONSHEET 1 Read through the following passage on homeostasis and then answer the questions. Homeostasis is the regulation of the internal environment within narrow limits. This gives the organism
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
