Cutoff value of HbA1c for predicting diabetes and prediabetes in a Chinese high risk population aged over 45
|
|
|
- Brice Newman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 360 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2015;24(3): Original Article Cutoff value of HbA1c for predicting diabetes and prediabetes in a Chinese high risk population aged over 45 Ruyi Zhang MD 1, Jiao Wang PhD 2, Jinhua Luo PhD 3, Xiaoyan Yang PhD 3, Rui Yang MD 3, Dehong Cai PhD 3, Hua Zhang PhD 3 1 Department of Endocrinology, Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital, Medical College of Jinan University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China 2 Division of Endocrinology, Department of Internal Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China 3 Department of Endocrinology, Southern Medical University, Zhujiang Hospital, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China Objective: To evaluate the cutoff value of HbA1c for predicting diabetes and prediabetes in a Chinese high risk population aged over 45. Methods: A total of 619 people aged over 45 without diabetes were randomly recruited to complete the Finnish Diabetes Risk Score (FINDRISC) questionnaire. 208 high-risk individuals (defined by Diabetes Risk Score 9) had OGTT and HbA1c determined at the same time. Results: In a Chinese population aged over 45, the best cutoff values of HbA1c for detecting diabetes and prediabetes were 5.8% and 5.4% respectively. The area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve of HbA1c for detecting diabetes was 0.85 (95% CI: ) and prediabetes was 0.62 (95% CI: ). The combined use of HbA1c and fasting blood glucose (FPG) had a larger AUROC than HbA1c alone (0.88, 95%CI: in detecting diabetes vs 0.75, 95% CI: in prediabetes), and had a higher sensitivity in predicting diabetes and higher specificity and positive predictive value (PPV) in predicting prediabetes. However, the AUROC between HbA1c alone and combined use in predicting diabetes was not significantly different (p=0.173). Conclusions: FINDRISC is a feasible tool to screen people who are at high risk of diabetes. The cutoff values of HbA1c to diagnose diabetes and prediabetes in a Chinese high risk population aged over 45 were 5.8% and 5.4%, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of HbA1c for detecting diabetes and prediabetes were relatively low, so that the combined use of HbA1c and FPG may be more effective in prediction. Key Words: cutoff, HbA1c, diabetes, prediabetes, risk INTRODUCTION As the lifestyle factors are changing in China, the latest survey of Chinese Diabetes Association showed that the prevalence of diabetes in adults increased from 2.6% to 9.7% over the past decade. 1 Considerable evidence has shown that middle aged people were prone to suffer from hypertension, obesity dyslipidemia and etc, 2,3 which are risk factors of diabetes. Moreover, in China, the prevalence of prediabetes is 15.5%, accounting for million adults with prediabetes. 4 However, two-thirds of individuals with diabetes remained undiagnosed in Mainland China. 5 Therefore, to identify diabetes and prediabetes in high-risk subjects is most important for the health care system. In 2010, an HbA1c value of 6.5% was adopted to diagnose diabetes 6 and the data to decide the criteria of HbA1c were from three cross sectional epidemiological studies, 7 not including the data of Chinese population. However, HbA1c may vary by ethnic group, 8-11 and results from studies on the effect of age and HbA1c have been conflicting Several investigations have studied the cutoff values of HbA1c for detecting diabetes in Chi- nese people, but to date there is no data on cutoff point of HbA1c for a Chinese high risk population aged over 45. In this study, we used FINDRISC questionnaire to screen people with high risk of diabetes and then identified the best cutoff value of HbA1c for predicting diabetes and prediabetes in high-risk individuals who were over 45 years old. SUBJECTS This was a cross sectional epidemiological survey in Haizhu District in Guangzhou between May 2009 and June Residents in five communities were randomly chosen in the study. Exclusion criteria were known diabe- Corresponding Author: Dr Hua Zhang, Department of Endocrinology, Southern Medical University, Zhujiang Hospital, NO.253 industry road, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China. Tel: ; Fax: dehongcaizj@163.com Manuscript received 25 June Initial review completed 05 August Revision accepted 09 October doi: /apjcn
2 Cutoff value of HbA1c in high risk population 361 tes, cancer, hepatic failure, renal failure, psychiatric disturbance, and other systemic medical conditions. Excluding the missing data, a total of 619 Chinese people aged over 45 without previously diagnosed diabetes participated in the survey. All participants were firstly expected to complete FINDRISC questionnaire which is a one-page questionnaire containing eight questions, with categorized answers, about age, BMI and waist circumstance (WC), family history of diabetes, history of antihypertensive drug treatment and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT), physical activity, and daily consumption of fruits or vegetables. 18 Subjects with a FINDRISC Score 9 were defined as people who were at high risk of diabetes. 19 Furthermore, 208 high-risk subjects were allocated to receive a standard oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), a physical examination including body height, weight, WC, hip circumstance (HC) and blood pressure, a collection of blood samples to determine the levels of fasting plasma glucose (FPG), two-hour postprandial plasma glucose (2h PG), glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c), total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL- C). Each participant gave written informed consent. The study had been approved by the local ethics committee (Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Ethics Approval Number: 2007-NFMK-001). MATERIALS AND METHODS Measurements Participants had a physical examination including measurement of body height, weight, WC, HC, and blood pressure. Body height and weight were measured with the participants minimally clothed, without shoes, in a standing position and BMI (kg/m 2 ) was calculated. WC was measured at midpoint between lower border of the rib cage and iliac crest at the end of a normal expiration. HC was measured at the horizontal of pubic symphysis. Blood pressure was measured twice by a doctor with a standard mercury sphygmomanometer on the non-dominant arm, with subjects seated after rest for at least 15 minutes. FPG was tested after 10 hours overnight fast and the blood sample was obtained 120 minutes after OGTT. Plasma glucose concentrations were determined by glucose oxidase method. TG, TC, HDL-C and LDL-C were determined enzymatically by an Abbott Aeroset biochemical analyzer. HbA1c was measured by high-performance liquid chromatography (HLC-723GHbG7; Tosoh Inc, Japan). Definitions The diagnosis of diabetes and impaired glucose regulation (IGR) were previously defined based on the 1999 World Health Organization (WHO) diagnostic criteria. 20 IGR included impaired fasting glucose (6.1 mmol/l FPG<7.0 mmol/l) as well as impaired glucose tolerance (7.8 mmol/l FPG<11.1 mmol/l). Individuals with IGR have been referred to as having prediabetes. 6 Diabetes and IGR were determined based on an OGTT. Statistical analysis The test of characteristics of the subjects were analyzed using SPSS software version 13.0 and the cutoff points of the indicators and area under receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve were calculated using MedCalc software version Quantitative variables were expressed as means±standard deviation (SD). Categorical variables were expressed as percentages. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare continuous variables. Bonferroni s correction was used for multiple comparisons. The combined use of HbA1c and FPG to detect diabetes and prediabetes was obtained by logistic models. Performance of HbA1c and the composite indicators were tested using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. Usefulness of a test was assessed by sensitivity, specificity, likelihood ratios (LRs), AUROC and predictive value (PV). The best cutoff point was determined as the value closest to the upper left-hand corner of the ROC curve, and was determined where the test characteristics were maximized. In a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, sensitivity was prioritized over specificity as much as possible for the purpose of screening. Positive/negative PV (PPV/NPV) is defined as the proportion of those with a positive/negative test result who actually has/does not have disease. According to Hosmer and Lemeshow, 21 an AUROC value between 0.7 and 0.8 is considered acceptable, and one between 0.8 and 0.9 excellent discrimination. A value of p<0.05 was considered statistically significant in all analyses. RESULTS Of the total 619 participants who were aged more than 45, 208 (33.6%) were at high risk of diabetes (86 men and 122 women). Of the 208 subjects, 69 (33.2%) had NGT (normal glucose tolerance), 84 (40.4%) had prediabetes, 55 (26.4%) had diabetes. Table 1 shows the clinical characteristics of the participants. Subjects were divided into three groups on the basis of the results of OGTT. We found no differences in age, BMI, WC, HC, TG, HDL-C, systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) among subjects with NGT, prediabetes and diabetes. Compared with subjects with diabetes, those with prediabetes had lower values of TC (p=0.009), LDL-C (p=0.027) and HbA1c (p<0.001). Compared with subjects with NGT, those with diabetes and prediabetes had higher value of HbA1c (p<0.001). The AUROC curve shown in Figure 1-a and Figure 1-b represented the diagnostic accuracy of HbA1c, FPG, the combined use of HbA1c and FPG for diabetes and prediabetes. The best cutoff point of HbA1c for detecting diabetes and prediabetes in these high-risk subjects was 5.8% and 5.4%, respectively. The AUROC of HbA1c for detecting diabetes was 0.85 (95% CI: ) with a sensitivity of 0.73 (95% CI: ), a specificity of 0.88 (95% CI: ) and for prediabetes was 0.62 (95% CI: ) with a sensitivity of 0.61 (95% CI: ), and a specificity of 0.58 (95% CI: ). The combined use of HbA1c and FPG had larger AUROC than HbA1c alone (0.88, 95% CI: in detecting diabetes vs 0.75, 95% CI: in prediabetes), and had higher sensitivity in predicting diabetes and higher specificity and PPV in prediabetes. However, the AU- ROC between HbA1c alone and combined use in predicting diabetes were not statistically different (p=0.173). The sensitivity of FPG alone was lowest among the three
3 362 RY Zhang, J Wang, JH Luo, XY Yang, R Yang, DH Cai and H Zhang methods, both in predicting diabetes and prediabetes (Table 2). DISCUSSION In the past 20 years, China has undergone rapid social and economic changes. The lifestyle and dietary habits of its people have also been changing, and the rates of diabetes, obesity, and other chronic conditions have increased dramatically over the past decades. 22 A national survey conducted in 1994 showed that the prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance were 2.5% and 3.2%, respectively. 23 However, according to a study from June 2007 through May 2008, Yang et al found that 92.4 million adults 20 years of age or older (9.7% of adult population) have diabetes; million adults (15.5%) have prediabetes. Further, the prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes increased with increasing age. 24 As society has aged, the proportion of the population in China aged 60 or above has exceeded 10% since 2000 and it is estimated that the population will reach 18% by As a result, the prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes in older persons might increase dramatically. Nevertheless, it was still found that more than two in five cases with diabetes were undiagnosed. 26 Therefore, effective measurements should be taken for screening individuals who are at high risk of diabetes especially in middle aged and elderly persons. FINDRISC is a widely used, simple tool for identification of those at risk for diabetes and prediabetes. There were several projects already ongoing in different countries, using risk scores for identification of diabetic high-risk subjects With optimal cutoff level, the FINDRISC identified 66% men and 70% women of previously undiagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes. 18 Tankova et al found that, depending on the cutoff point chosen, the FINDRISC recognized undetected diabetes and prediabetes fairly well. 33 In our study, the high-risk subjects were based on Diabetes Risk Score Besides, HbA1c, which does not require patients to be fasting and reflects longer-term glycemia than does plasma glucose, 34 is more convenient for screening diabetes than plasma glucose. The aim of our study was to identify the optimal thresholds of HbA1c for detecting diabetes and prediabetes in middle aged and elderly individuals who may be at higher risk and to assess the performance of HbA1c in evaluating glucose tolerance. Our results showed that with scoring 9 and above, the FINDRISC identified 40% subjects with prediabetes, and 26% with diabetes. The level of HbA1c increased significantly in the process of progression from NGT to prediabetes and diabetes. We found that compared with those with NGT, the value of HbA1c was higher in subjects with diabetes and prediabetes (p<0.001). Furthermore, compared with those with diabetes, the value of HbA1c in subjects with prediabetes was lower (p<0.001). The AU- ROC values of HbA1c for detecting diabetes and prediabetes were 0.85 (95% CI: ) and 0.62 (95% CI: ), respectively. The cutoff point of HbA1c for predicting diabetes was 5.8%, with a sensitivity of 0.73, and a specificity of The optimal threshold of HbA1c for prediabetes was 5.4% with a sensitivity of 0.61, and a specificity of However, the AUROC of HbA1c for detecting prediabetes was smaller than the acceptable discrimination and the sensitivity and the specificity of HbA1c for predicting diabetes and prediabetes were relatively low. As a result, the combined use of HbA1c and FPG was calculated in this study. The combined indicator had larger AUROC values than HbA1c alone (0.88, 95% CI: in detecting diabetes vs 0.75, 95% CI: in prediabetes). Furthermore, the combined use had higher sensitivity in predicting diabetes and higher specificity and PPV in prediabetes. Nevertheless, the AUROC between HbA1c alone and combined use in predicting diabetes were not statistically different (p=0.173), and the sensitivity of FPG alone was lowest among the three methods both in predicting diabetes and prediabetes. Other investigations had reported similar results about Table 1. Clinical characteristics of participants Characteristics NGT Diabetes Prediabetes Total number (n) Men/women (n) 30/39 26/29 30/54 Age (years) 67.0 (8.2) 69.8 (9.1) 70.1 (7.9) FPG (mmol/l) 5.2 (0.5) 7.1 (1.9) 5.7 (0.6) 2h-PPG (mmol/l) 6.3 (1.0) 15.0 (4.0) 9.0 (1.0) HbA1c (%) 5.4 (0.4) 6.5 (1.2) 5.5 (0.4) BMI (kg/m 2 ) 26.5 (2.75) 26.5 (3.17) 26.8 (3.47) WC (cm) 89.5 (7.0) 90.0 (7.4) 89.7 (8.9) HC (cm) 100 (6.4) 99.1 (6.1) 99.7 (7.0) TC (mmol/l) 5.31 (1.51) 5.76 (1.21) 5.03 (1.43) TG (mmol/l) 1.96 (1.41) 2.39 (2.01) 2.36 (1.84) LDL-C (mmol/l) 3.62 (1.01) 3.70 (1.00) 3.26 (0.89) HDL-C (mmol/l) 1.43 (0.33) 1.37 (0.34) 1.40 (0.33) SBP (mmhg) 139 (19.2) 140 (19.8) 140 (19.1) DBP (mmhg) 80.2 (10.6) 78.4 (10.2) 81.8 (9.8) Patients with a family history of diabetes-no (%) 3 (4.8) 4 (7.3) 4 (4.8) Patients had anti-hypertensive drugs-no (%) 31 (49.2) 33 (60.0) 52 (61.9) Patients participated in physical activities-no (%) 33 (52.4) 50 (54.5) 53 (63.1) Patients had vegetables-no (%) 42 (66.7) 41 (74.5) 68 (81.0) Values are mean(sd) unless stated otherwise. p=0.009 versus diabetes, p=0.027 versus diabetes, p<0.001 versus NGT, p<0.001 versus diabetes.
4 Cutoff value of HbA1c in high risk population 363 Table 2. Test characteristics (95% CIs) maximized under the best cut-off point in the entire population for predicting diabetes and prediabetes Sen Spec PPV NPV LR+ LR- AUROC Cut-off points for predicting diabetes: HbA1c 5.8%, FPG 6.4 mmol/l HbA1c 0.73 (0.59, 0.84) 0.88 (0.81, 0.93) 0.69 (0.56, 0.81) 0.89 (0.83, 0.94) 5.86 (4.9, 7.0) 0.31 (0.2, 0.6) 0.85 (0.80, 0.90) FPG 0.58 (0.44, 0.71) 0.95 (0.89, 0.98) 0.80 (0.64, 0.91) 0.86 (0.79, 0.91) 10.6 (8.4, 13.2) 0.44 (0.2, 0.9) 0.84 (0.78, 0.88) HbA1c plus FPG 0.84 (0.71, 0.92) 0.82 (0.75, 0.88) 0.64 (0.52, 0.75) 0.93 (0.87, 0.97) 4.66 (4.1, 5.4) 0.20 (0.1, 0.4) 0.88 (0.83, 0.92) Cut-off points for predicting prediabetes: HbA1c 5.4%, FPG 5.6 mmol/l HbA1c 0.61 (0.49, 0.72) 0.58 (0.46, 0.70) 0.61 (0.49, 0.72) 0.57 (0.45, 0.69) 1.44 (1.1, 1.9) 0.68 (0.5, 1.0) 0.62 (0.54, 0.70) FPG 0.47 (0.36, 0.59) 0.86 (0.75, 0.93) 0.78 (0.64, 0.89) 0.60 (0.49, 0.69) 3.27 (2.5, 4.2) 0.62 (0.3, 1.1) 0.73 (0.65, 0.80) HbA1c plus FPG 0.61 (0.49, 0.72) 0.77 (0.65, 0.86) 0.74 (0.62, 0.85) 0.64 (0.53, 0.74) 2.61 (2.1, 3.3) 0.51 (0.3, 0.9) 0.75 (0.67, 0.82) CI: confidence interval; FPG: fasting plasma glucose; LR+; positive likelihood ratio; LR-: negative likelihood ratio; NPV: negative predictive value; PPV: positive predictive value; Sen: sensitivity; Spec: specificity. FPG vs HbA1c: p=0.681; HbA1c plus FPG vs HbA1c: p= FPG vs HbA1c: p=0.061; HbA1c plus FPG vs HbA1c: p=0.01.
5 364 RY Zhang, J Wang, JH Luo, XY Yang, R Yang, DH Cai and H Zhang HbA1c for detecting diabetes. The optimal threshold for HbA1c of 5.9% was found in a Canadian multiethnic population. 35 The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that an HbA1c value of 6.5% was an optimal threshold for identifying diabetes in the US population. 36 A study from Japanese population showed that the HbA1c threshold of 6.1% was suitable for detecting undiagnosed diabetes. 11 Bao YQ et al concluded that an HbA1c threshold of 6.3% was highly specific for detecting undiagnosed diabetes in Chinese adults. 15 On the other hand, similar results of HbA1c for detecting prediabetes had been reported. The International Expert Committee noted that those with HbA1c levels ranging from 6.0% to 6.4% were at very high risk of developing diabetes. 37 American Diabetes Association in 2010 considered an HbA1c range of 5.7% to 6.4% as identifying individuals who were prediabetes. 38 Tankova et al demonstrated that the cutoff level of HbA1c for diagnosing prediabetes was 5.5% with a sensitivity of 86% and a specificity of 92%. 39 Data from Japan found that baseline HbA1c of 5.8% or greater imposed a 10-fold increase in diagnosed diabetes over next 7 years. 40 Yang et al found that the measurement of HbA1c may be efficient to diagnose prediabetes with the cutoff point of 5.9% in Chinese high risk people. 17 Concerning the results, it should be considered that there were differences between the present study and previous investigations. Firstly, we focused on the highrisk Chinese individuals (determined by FINDRISC 9), but most previous studies, while finding the threshold of HbA1c for predicting diabetes and/or prediabetes in total population, had failed to focus on the people with high risk for diabetes. Secondly, compared with previous studies, the subjects in the study were above 45 years of age. Thirdly, the environment and lifestyle of people in Guangzhou is different from other populations, which may contribute to the distinctions. People in Guangzhou are thinner than those in Chinese northern cities and populations in other countries, which might result in lower value of HbA1c. In addition, the high-risk individuals were based on Diabetes Risk Score 9 in present study, which was different from some other studies. 28,30,32 Limitations of the current study cannot be ignored. Inadequate sample size may have an effect on the outcome. The high-risk subjects in five communities is unlikely represent the Chinese population with high risk of diabetes, and the sensitivity and specificity of HbA1c to predict diabetes and prediabetes in this sample of subjects was relatively low and the combined use of HbA1c and FPG may be more effective for prediction to some extent. Moreover, it was a cross sectional study, so that similar epidemiological and clinical studies are needed to confirm and modify the results we found. In conclusion, FINDRISC is a feasible, inexpensive, non-invasive tool to find asymptomatic high-risk subjects of diabetes. In a Chinese high risk population aged over 45, the optimal cutoff value of HbA1c for detecting diabetes was 5.8% with a sensitivity of 0.73, and a specificity of 0.88 and for prediabetes was 5.4% with a sensitivity of 0.61, and a specificity of However, the sensitivity and specificity of HbA1c for detecting diabetes and prediabetes was relatively low, so that confirmation of the diagnosis by an additional plasma glucose measurement should be considered. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The study was supported by the Science and Technology Project of Haizhu District, Guangzhou, Guangdong Province (2007-Z-055). AUTHOR DISCLOSURES There are no conflicts of interests. REFERENCES 1. Li H, Oldenburg B, Chamberlain C, O'Neil A, Xue B, Jolley D et al. Diabetes prevalence and determinants in adults in China mainland from 2000 to 2010: a systematic review. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012;98: doi: /j. diabres Feng RN, Zhao C, Wang C, Niu YC, Li K, Guo FC et al. BMI is strongly associated with hypertension, and waist circumference is strongly associated with type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia, in northern Chinese adults. J Epidemiol. 2012;22: doi: /jea.JE Nsakashalo-Senkwe M, Siziya S, Goma FM, Songolo P, Mukonka V, Babaniyi O. Combined prevalence of impaired glucose level or diabetes and its correlates in Lusaka urban district, Zambia: a population based survey. Int Arch Med. 2011;4:2. doi: / Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, Kadowaki T, Yajnik CS, Yoon KH et al. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA. 2009;301: doi: / jama Wong KC, Wang Z. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus of Chinese populations in Mainland China, Hong Kong, and Taiwan. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2006;73: doi: /j.diabres American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes Diabetes Care. 2010;33(Suppl):11S-61S. doi: /dc10-S International Expert Committee report on the role of the A1C assay in the diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32: doi: /dc Bennett CM, Guo M, Dharmage SC. HbA(1c) as a screening tool for detection of Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Diabet Med. 2007;24: doi: /j x. 9. Rohlfing CL, Little RR, Wiedmeyer HM, England JD, Madsen R, Harris MI et al. Use of GHb (HbA1c) in screening for undiagnosed diabetes in the U.S. population. Diabetes Care. 2000;23: doi: /diacare Christensen DL, Witte DR, Kaduka L, Jorgensen ME, Borch-Johnsen K, Mohan V et al. Moving to an A1C-based diagnosis of diabetes has a different impact on prevalence in different ethnic groups. Diabetes Care. 2010;33: doi: /dc Nakagami T, Tominaga M, Nishimura R, Yoshiike N, Daimon M, Oizumi T et al. Is the measurement of glycated hemoglobin A1c alone an efficient screening test for undiagnosed diabetes? Japan National Diabetes Survey. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;76: doi: /j.diabres Simon D, Senan C, Garnier P, Saint-Paul M, Papoz L. Epidemiological features of glycated haemoglobin A1cdistribution in a healthy population. The Telecom Study. Diabetologia. 1989;32: doi: /BF Hashimoto Y, Futamura A, Ikushima M. Effect of aging on HbA1c in a working male Japanese population. Diabetes Care. 1995;18: doi: /diacare
6 Cutoff value of HbA1c in high risk population Mulkerrin EC, Arnold JD, Dewar R, Sykes D, Rees A, Pathy MS. Glycosylated haemoglobin in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus in elderly people. Age Ageing. 1992;21: doi: /ageing/ Bao Y, Ma X, Li H, Zhou M, Hu C, Wu H et al. Glycated haemoglobin A1c for diagnosing diabetes in Chinese population: cross sectional epidemiological survey. BMJ. 2010; 340:c2249. doi: /bmj.c Hu Y, Zhang M, She Y, Gao J, Yuan GP, Xiong ZY et al. The optimal cut-points of HbA1c for detecting newly diagnosed diabetes and pre-diabetes in the Chinese population living in Sichuan. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011;49: doi: /CCLM Yang C, Liu Y, Li X, Liang H, Jiang X. Utility of hemoglobin A1c for the identification of individuals with diabetes and prediabetes in a Chinese high risk population. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2012;72: doi: / Saaristo T, Peltonen M, Lindstrom J, Saarikoski L, Sundvall J, Eriksson JG et al. Cross-sectional evaluation of the Finnish Diabetes Risk Score: a tool to identify undetected type 2 diabetes, abnormal glucose tolerance and metabolic syndrome. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2005;2: doi: / dvdr Lindstrom J, Tuomilehto J. The diabetes risk score: a practical tool to predict type 2 diabetes risk. Diabetes Care. 2003;26: doi: /diacare Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ. Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med. 1998;15: doi: /(SICI) (199807)15:7<539::AID-DI A668>3.0.CO;2-S. 21. Hosmer D, Lemeshow S. Applied logistic regression. 2 Edition. New York: John Wiley & Sons; Wang Y, Mi J, Shan XY, Wang QJ, Ge KY. Is China facing an obesity epidemic and the consequences? The trends in obesity and chronic disease in China. Int J Obes (Lond). 2007;31: doi: /sj.ijo Pan XR, Yang WY, Li GW, Liu J. Prevalence of diabetes and its risk factors in China, National Diabetes Prevention and Control Cooperative Group. Diabetes Care. 1997;20: doi: /diacare Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 2010;362: doi: /NEJMoa Li C, Wu W, Jin H, Zhang X, Xue H, He Y et al. Successful aging in Shanghai, China: definition, distribution and related factors. Int Psychogeriatr. 2006;18: doi: /S Jia WP, Pang C, Chen L, Bao YQ, Lu JX, Lu HJ et al. Epidemiological characteristics of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose regulation in a Chinese adult population: the Shanghai Diabetes Studies, a cross-sectional 3-year followup study in Shanghai urban communities. Diabetologia. 2007;50: doi: /s Ackermann RT, Marrero DG. Adapting the Diabetes Prevention Program lifestyle intervention for delivery in the community: the YMCA model. Diabetes Educ. 2007;33:69, 74-5,77-8. doi: / Kilkkinen A, Heistaro S, Laatikainen T, Janus E, Chapman A, Absetz P et al. Prevention of type 2 diabetes in a primary health care setting. Interim results from the Greater Green Triangle (GGT) Diabetes Prevention Project. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;76: doi: /j.diabres Saaristo T, Peltonen M, Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi S, Vanhala M, Saltevo J, Niskanen L et al. National type 2 diabetes prevention programme in Finland: FIN-D2D. Int J Circumpolar Health. 2007;66: doi: /ijch.v66i Saaristo T, Moilanen L, Korpi-Hyovalti E, Vanhala M, Saltevo J, Niskanen L et al. Lifestyle intervention for prevention of type 2 diabetes in primary health care: one-year follow-up of the Finnish National Diabetes Prevention Program (FIN-D2D). Diabetes Care. 2010;33: doi: /dc Schwarz PE, Schwarz J, Schuppenies A, Bornstein SR, Schulze J. Development of a diabetes prevention management program for clinical practice. Public Health Rep. 2007; 122: Makrilakis K, Liatis S, Grammatikou S, Perrea D, Katsilambros N. Implementation and effectiveness of the first community lifestyle intervention programme to prevent Type 2 diabetes in Greece. The DE-PLAN study. Diabet Med. 2010;27: doi: /j x. 33. Tankova T, Chakarova N, Atanassova I, Dakovska L. Evaluation of the Finnish Diabetes Risk Score as a screening tool for impaired fasting glucose, impaired glucose tolerance and undetected diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;92: doi: /j.diabres Saudek CD, Herman WH, Sacks DB, Bergenstal RM, Edelman D, Davidson MB. A new look at screening and diagnosing diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93: doi: /jc Anand SS, Razak F, Vuksan V, Gerstein HC, Malmberg K, Yi Q et al. Diagnostic strategies to detect glucose intolerance in a multiethnic population. Diabetes Care. 2003;26: doi: /diacare Buell C, Kermah D, Davidson MB. Utility of A1C for diabetes screening in the NHANES population. Diabetes Care. 2007;30: doi: /dc Gillett MJ. International Expert Committee report on the role of the A1c assay in the diagnosis of diabetes: Diabetes Care. 2009;32: doi: /dc Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(Suppl):62S-9S. doi: /dc10-S Tankova T, Chakarova N, Dakovska L, Atanassova I. Assessment of HbA1c as a diagnostic tool in diabetes and prediabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2012;49: doi: /s Inoue K, Matsumoto M, Kobayashi Y. The combination of fasting plasma glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin predicts type 2 diabetes in Japanese workers. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;77: doi: /j.diabres
7 366 RY Zhang, J Wang, JH Luo, XY Yang, R Yang, DH Cai and H Zhang Original Article Cutoff value of HbA1c for predicting diabetes and prediabetes in a Chinese high risk population aged over 45 Ruyi Zhang MD 1, Jiao Wang PhD 2, Jinhua Luo PhD 3, Xiaoyan Yang PhD 3, Rui Yang MD 3, Dehong Cai PhD 3, Hua Zhang PhD 3 1 Department of Endocrinology, Guangzhou Red Cross Hospital, Medical College of Jinan University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China 2 Division of Endocrinology, Department of Internal Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China 3 Department of Endocrinology, Southern Medical University, Zhujiang Hospital, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China 糖化血红蛋白在中国 45 岁以上糖尿病高危人群糖尿病及糖尿病前期诊断的界点 目的 : 探讨糖化血红蛋白 (HbA1c) 在中国中老年糖尿病高危人群中是否存在诊断糖尿病及糖尿病前期的界点 方法 : 随机抽取广州市 5 个社区 619 名 45 岁或以上的中老年人填写芬兰糖尿病风险积分表 (FINDRSC), 积分 9 分定义为糖尿病高危人群 随后对筛查出的糖尿病高危人群 ( 共 208 例 ) 进行生化指标的检测, 同时使用口服葡萄糖耐量试验 (OGTT) 及 HbA1c 诊断糖尿病及糖尿病前期, 使用受试者工作特征 (ROC) 曲线下面积判断 HbA1c 或 HbA1c 联合空腹血浆血糖 (FPG) 在诊断糖尿病及糖尿病前期的诊断效能 结果 : 在这组糖尿病高危人群中,HbA1c 诊断糖尿病及糖尿病前期的界值分别为 5.8% 及 5.4%, 其 ROC 曲线下面积分别为 0.85(95% CI: ) 及 0.62 (95% CI: ); 而 HbA1c 联合 FPG 诊断糖尿病及糖尿病前期的 ROC 曲线下面积均比前者大, 且在诊断糖尿病中具有更高的灵敏度, 而在诊断糖尿病前期中具有更高的特异度及阳性预测值 但是单用 HbA1c 或联合 FPG 诊断糖尿病的 ROC 曲线下面积之间差异无统计学意义 (p=0.173) 结论 : FINDRSC 是筛查糖尿病高危人群的有效量表 在中国 45 岁或以上的中老年糖尿病高危人群中 HbA1c 诊断糖尿病及糖尿病前期的界值分别为 5.8% 及 5.6%, 但是其特异度及敏感度相对较低, 因此需要联合 FPG 增加其预测疾病的可靠性 关键词 : 诊断界值 糖化血红蛋白 糖尿病 糖尿病前期 风险
宫颈上皮内瘤变 ; IgG1 IgG2 亚类 ; 酶联免疫吸附试验 R A (2009)
 2009 年第 19 卷第 11 期 CHINA ONCOLOGY 2009 Vol.19 No.11 831 免疫球蛋白 G(immunoglobulin G,IgG) 是血清和细胞外液中含量最高的免疫球蛋白, 其某个亚类的升高, 可能与宫颈上皮内瘤变 (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, CIN) 的发生 发展及转归有密切相关 然而对于 CIN 患者血清人乳头瘤病毒样颗粒
2009 年第 19 卷第 11 期 CHINA ONCOLOGY 2009 Vol.19 No.11 831 免疫球蛋白 G(immunoglobulin G,IgG) 是血清和细胞外液中含量最高的免疫球蛋白, 其某个亚类的升高, 可能与宫颈上皮内瘤变 (cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, CIN) 的发生 发展及转归有密切相关 然而对于 CIN 患者血清人乳头瘤病毒样颗粒
500 中国肺癌杂志2010年5月第13卷第5期 C h i n J L u n g C a n c e r, M ay , Vo l. 1 3, No. 5 临床研究 血清TPS CEA Pro-GRP和CYFRA21-1 水平在肺癌患者中的临床意义 王敬慧 时广利 张树才 王群慧
 5 临床研究 血清 和CYFRA- 水平在肺癌患者中的临床意义 王敬慧 时广利 张树才 王群慧 杨新杰 李曦 王海永 张卉 宋长兴 摘要 背景与目的 血清肿瘤标志物在肺癌的诊断 疗效 预后判断中起着重要作用 本研究探讨血清组 织多肽特异性抗原 tissue polypeptide specific antigen, 与癌胚抗原 carcinoembryonic antigen, 胃泌素释放 肽前体
5 临床研究 血清 和CYFRA- 水平在肺癌患者中的临床意义 王敬慧 时广利 张树才 王群慧 杨新杰 李曦 王海永 张卉 宋长兴 摘要 背景与目的 血清肿瘤标志物在肺癌的诊断 疗效 预后判断中起着重要作用 本研究探讨血清组 织多肽特异性抗原 tissue polypeptide specific antigen, 与癌胚抗原 carcinoembryonic antigen, 胃泌素释放 肽前体
The clinical value of HbA1c in combination with FPG in the early screening of the elderly with type 2 diabetes
 The clinical value of HbA1c in combination with FPG in the early screening of the elderly with type 2 diabetes Lihua Liu 1,#, Wenqing Chen 2, Minghua Dong 3,#, Lixia Jiang 4, Wei Qiu 3, Jian Li 5, Xiaoting
The clinical value of HbA1c in combination with FPG in the early screening of the elderly with type 2 diabetes Lihua Liu 1,#, Wenqing Chen 2, Minghua Dong 3,#, Lixia Jiang 4, Wei Qiu 3, Jian Li 5, Xiaoting
ARTICLE. W. P. Jia & C. Pang & L. Chen & Y. Q. Bao & J. X. Lu & H. J. Lu & J. L. Tang & Y. M. Wu & Y. H. Zuo & S. Y. Jiang & K. S.
 Diabetologia (2007) 50:286 292 DOI 10.1007/s00125-006-0503-1 ARTICLE Epidemiological characteristics of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose regulation in a Chinese adult population: the Shanghai Diabetes
Diabetologia (2007) 50:286 292 DOI 10.1007/s00125-006-0503-1 ARTICLE Epidemiological characteristics of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose regulation in a Chinese adult population: the Shanghai Diabetes
中国 HIV 新发感染检测发展及未来 Development and Future of HIV-1 Incidence Assay in China
 中国 HIV 新发感染检测发展及未来 Development and Future of HIV-1 Incidence Assay in China Yan Jiang MD, PhD. National HIV Reference Laboratory, China CDC 中国 HIV 检测体系 HIV Testing in China Screening Confirmatory Recent
中国 HIV 新发感染检测发展及未来 Development and Future of HIV-1 Incidence Assay in China Yan Jiang MD, PhD. National HIV Reference Laboratory, China CDC 中国 HIV 检测体系 HIV Testing in China Screening Confirmatory Recent
290 Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(4):
 290 Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(4): 290-294 Letter to the Editor Prevalence and Predictors of Hypertension in the Labor Force Population in China: Results from a Cross-sectional Survey in Xinjiang Uygur
290 Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(4): 290-294 Letter to the Editor Prevalence and Predictors of Hypertension in the Labor Force Population in China: Results from a Cross-sectional Survey in Xinjiang Uygur
间歇性低氧运动对大鼠骨骼肌线粒体自由基代谢的影响
 第 14 卷第 7 期 2007 年 10 月 体育学刊 Journal of Physical Education Vol.14 No.7 Oct.2007 间歇性低氧运动对大鼠骨骼肌线粒体自由基代谢的影响 1 1 弢 2, 2 13 (1. 华南师范大学体育科学学院, 广东广州 510631; 广州体育学院运动人体科学系, 广东广州 510500) 摘要 : 100 SD (40 )(60 )
第 14 卷第 7 期 2007 年 10 月 体育学刊 Journal of Physical Education Vol.14 No.7 Oct.2007 间歇性低氧运动对大鼠骨骼肌线粒体自由基代谢的影响 1 1 弢 2, 2 13 (1. 华南师范大学体育科学学院, 广东广州 510631; 广州体育学院运动人体科学系, 广东广州 510500) 摘要 : 100 SD (40 )(60 )
Update on AIDS in China
 Update on AIDS in China Kong-Lai Zhang, MD Professor, Department of Epidemiology, Peking Union Medical College Beijing, CHINA March, 2013 1 HIV epidemic in Asia General Population Family Bridge Population
Update on AIDS in China Kong-Lai Zhang, MD Professor, Department of Epidemiology, Peking Union Medical College Beijing, CHINA March, 2013 1 HIV epidemic in Asia General Population Family Bridge Population
Uric acid status and its correlates in Hangzhou urban population
 102 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2006;15 (1):102-106 Original Article Uric acid status and its correlates in Hangzhou urban population Duo Li PhD 1, Xiaomei Yu MB 2, Xiaoqun Zhou MB 2, Sirithon Siriamornpun PhD
102 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2006;15 (1):102-106 Original Article Uric acid status and its correlates in Hangzhou urban population Duo Li PhD 1, Xiaomei Yu MB 2, Xiaoqun Zhou MB 2, Sirithon Siriamornpun PhD
读书报告 2015 年 月 唐之韵
 读书报告 2015 年 03-04 月 唐之韵 Mar. Apr. NEJM VOL.372 Kaukonen KM1, Bailey M, Pilcher D, et al. N Engl J Med. 2015 Apr 23;372(17):1629-38. Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Criteria in Defining Severe Sepsis.
读书报告 2015 年 03-04 月 唐之韵 Mar. Apr. NEJM VOL.372 Kaukonen KM1, Bailey M, Pilcher D, et al. N Engl J Med. 2015 Apr 23;372(17):1629-38. Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Criteria in Defining Severe Sepsis.
Study on current situation and development trends of domestic and foreign lead maximum level standards in food
 5 1 Vol. 5 No. 1 2014 1 Journal of Food Safety and Quality Jan., 2014 邵 1, 懿 2, 王君 1, 吴永宁 1* (1., 100022; 2., 100021) 摘要 : 目的, 方法 结果,, 结论,, 关键词 : ; ; ; Study on current situation and development trends
5 1 Vol. 5 No. 1 2014 1 Journal of Food Safety and Quality Jan., 2014 邵 1, 懿 2, 王君 1, 吴永宁 1* (1., 100022; 2., 100021) 摘要 : 目的, 方法 结果,, 结论,, 关键词 : ; ; ; Study on current situation and development trends
Cross-sectional survey of prevalence and personality characteristics of college students with internet addiction in Wenzhou, China
 99 Cross-sectional survey of prevalence and personality characteristics of college students with internet addiction in Wenzhou, China Deguo JIANG 1, Sheng ZHU 2, Minjie YE 1*, Chongguang LIN 1 Original
99 Cross-sectional survey of prevalence and personality characteristics of college students with internet addiction in Wenzhou, China Deguo JIANG 1, Sheng ZHU 2, Minjie YE 1*, Chongguang LIN 1 Original
Prevalence and risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in a high-risk Chinese population
 Wang et al. BMC Public Health 2013, 13:633 RESEARCH ARTICLE Prevalence and risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in a high-risk Chinese population Open Access Jiao Wang 1, Ru-Yi Zhang 1, Rong-Ping Chen
Wang et al. BMC Public Health 2013, 13:633 RESEARCH ARTICLE Prevalence and risk factors for diabetic retinopathy in a high-risk Chinese population Open Access Jiao Wang 1, Ru-Yi Zhang 1, Rong-Ping Chen
Implementing Type 2 Diabetes Prevention Programmes
 Implementing Type 2 Diabetes Prevention Programmes Jaakko Tuomilehto Department of Public Health University of Helsinki Helsinki, Finland FIN-D2D Survey 2004 Prevalence of previously diagnosed and screen-detected
Implementing Type 2 Diabetes Prevention Programmes Jaakko Tuomilehto Department of Public Health University of Helsinki Helsinki, Finland FIN-D2D Survey 2004 Prevalence of previously diagnosed and screen-detected
Liver Enzymes Concentrations Are Closely Related to Pre diabetes: Findings of the Shanghai Diabetes Study II (SHDS II) *
 30 Biomed Environ Sci, 2012; 25(1): 30 37 Original Article Liver Enzymes Concentrations Are Closely Related to Pre diabetes: Findings of the Shanghai Diabetes Study II (SHDS II) * GAO Fei 1, PAN Jie Min
30 Biomed Environ Sci, 2012; 25(1): 30 37 Original Article Liver Enzymes Concentrations Are Closely Related to Pre diabetes: Findings of the Shanghai Diabetes Study II (SHDS II) * GAO Fei 1, PAN Jie Min
Doing Business in China
 Doing Business in China 1 Doing Business in China 在中国经商 How to Win in Business in China 怎么在中国赢取商机 Read the text below and do the activity that follows. 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习 China has changed enormously over
Doing Business in China 1 Doing Business in China 在中国经商 How to Win in Business in China 怎么在中国赢取商机 Read the text below and do the activity that follows. 阅读下面的短文, 然后完成练习 China has changed enormously over
Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology 2015, 52(6): DOI: /j.issn 红火蚁不同品级个体的药剂敏感性研究 刘家莉崔儒坤曾鑫年
 Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology 2015, 52(6): 1392 1396. DOI: 10.7679/j.issn.2095 1353.2015.166 * 红火蚁不同品级个体的药剂敏感性研究 ** 郭文举 *** 刘家莉崔儒坤曾鑫年, 510642 摘要 目的 Solenopsis invicta Buren 方法 结果 3 4 3 428.77 mg/kg
Chinese Journal of Applied Entomology 2015, 52(6): 1392 1396. DOI: 10.7679/j.issn.2095 1353.2015.166 * 红火蚁不同品级个体的药剂敏感性研究 ** 郭文举 *** 刘家莉崔儒坤曾鑫年, 510642 摘要 目的 Solenopsis invicta Buren 方法 结果 3 4 3 428.77 mg/kg
老年与中青年急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者的特点及预后相关危险因素分析
 794 中华危重病急救医学 2014 年 11 月第 26 卷第 11 期 Chin Crit Care Med,November 2014,Vol.26,No.11 论著 老年与中青年急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者的特点及预后相关危险因素分析 摘要 目的比较重症监护病房 (ICU) 内老年及中青年急性呼吸窘迫综合征 (ARDS) 患者的临床特点及预后相关危险因素 方法回顾性分析 2011 年 8 月至 2013
794 中华危重病急救医学 2014 年 11 月第 26 卷第 11 期 Chin Crit Care Med,November 2014,Vol.26,No.11 论著 老年与中青年急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者的特点及预后相关危险因素分析 摘要 目的比较重症监护病房 (ICU) 内老年及中青年急性呼吸窘迫综合征 (ARDS) 患者的临床特点及预后相关危险因素 方法回顾性分析 2011 年 8 月至 2013
Research Article Reanalysis and External Validation of a Decision Tree Model for Detecting Unrecognized Diabetes in Rural Chinese Individuals
 Hindawi International Endocrinology Volume 2017, Article ID 3894870, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3894870 Research Article Reanalysis and External Validation of a Decision Tree Model for Detecting
Hindawi International Endocrinology Volume 2017, Article ID 3894870, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3894870 Research Article Reanalysis and External Validation of a Decision Tree Model for Detecting
programme. The DE-PLAN follow up.
 What are the long term results and determinants of outcomes in primary health care diabetes prevention programme. The DE-PLAN follow up. Aleksandra Gilis-Januszewska, Noël C Barengo, Jaana Lindström, Ewa
What are the long term results and determinants of outcomes in primary health care diabetes prevention programme. The DE-PLAN follow up. Aleksandra Gilis-Januszewska, Noël C Barengo, Jaana Lindström, Ewa
1) 有哪些方法, 为什么需要采用这些方法? 2) 有哪些参数, 这些参数的生理学意义是什么? 3) 功能的研究如何提示机制的改变?
 心脏泵功能的 测量方法 1 1) 有哪些方法, 为什么需要采用这些方法? 2) 有哪些参数, 这些参数的生理学意义是什么? 3) 功能的研究如何提示机制的改变? 2 心功能测量方法 In vivo 1. 超声法 2. 超声 + 导管法 In vitro 1. Langendorff mode 2. Working heart mode 3. Papillary muscle 4. Skinned fibers
心脏泵功能的 测量方法 1 1) 有哪些方法, 为什么需要采用这些方法? 2) 有哪些参数, 这些参数的生理学意义是什么? 3) 功能的研究如何提示机制的改变? 2 心功能测量方法 In vivo 1. 超声法 2. 超声 + 导管法 In vitro 1. Langendorff mode 2. Working heart mode 3. Papillary muscle 4. Skinned fibers
Community Based Diabetes Prevention
 Community Based Diabetes Prevention Melanie Davies Professor of Diabetes Medicine Outline NIHR Programme Grant proposal and update to progress The Vascular Check programme HbA1c debate Algorithm to detect
Community Based Diabetes Prevention Melanie Davies Professor of Diabetes Medicine Outline NIHR Programme Grant proposal and update to progress The Vascular Check programme HbA1c debate Algorithm to detect
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online August 19, 2010
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online August 19, 2010 Neck circumference positively related with central obesity, overweight and metabolic syndrome in Chinese people with type 2 diabetes:
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online August 19, 2010 Neck circumference positively related with central obesity, overweight and metabolic syndrome in Chinese people with type 2 diabetes:
300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4):
 300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4): 300-305 Letter to the Editor Combined Influence of Insulin Resistance and Inflammatory Biomarkers on Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-based Prospective Cohort Study of
300 Biomed Environ Sci, 2018; 31(4): 300-305 Letter to the Editor Combined Influence of Insulin Resistance and Inflammatory Biomarkers on Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-based Prospective Cohort Study of
Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes
 Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes L. Yang*, S.J. Chen*, G.Y. Yuan, D. Wang and J.J. Chen Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu
Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes L. Yang*, S.J. Chen*, G.Y. Yuan, D. Wang and J.J. Chen Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu
CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION
 CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION 3.1 BACKGROUND Diabetes mellitus (DM) and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) have reached epidemic proportions
CHAPTER 3 DIABETES MELLITUS, OBESITY, HYPERTENSION AND DYSLIPIDEMIA IN ADULT CENTRAL KERALA POPULATION 3.1 BACKGROUND Diabetes mellitus (DM) and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) have reached epidemic proportions
Association between perceived stress, alcohol consumption levels and obesity in Koreans
 316 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2016;25(2):316-325 Original Article Association between perceived stress, alcohol consumption levels and obesity in Koreans Seung-Jin Yoon MS 1,2, Hae-Joon Kim MD, PhD 1, Miae
316 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2016;25(2):316-325 Original Article Association between perceived stress, alcohol consumption levels and obesity in Koreans Seung-Jin Yoon MS 1,2, Hae-Joon Kim MD, PhD 1, Miae
Global Mental Health Challenges Facing China and the World
 Global Mental Health Challenges Facing China and the World 世界与中国面对的精神卫生挑战 Arthur Kleinman, M.D. Rabb Professor of, University and Professor of Medical and Psychiatry, Medical School; Fung Director, Asia
Global Mental Health Challenges Facing China and the World 世界与中国面对的精神卫生挑战 Arthur Kleinman, M.D. Rabb Professor of, University and Professor of Medical and Psychiatry, Medical School; Fung Director, Asia
Fasting Glucose, Obesity, and Metabolic Syndrome as Predictors of Type 2 Diabetes: The Cooper Center Longitudinal Study
 Fasting Glucose, Obesity, and Metabolic Syndrome as Predictors of Type 2 Diabetes: The Cooper Center Longitudinal Study Laura F. DeFina, MD,* Gloria Lena Vega, PhD,Þ David Leonard, PhD,Þ and Scott M. Grundy,
Fasting Glucose, Obesity, and Metabolic Syndrome as Predictors of Type 2 Diabetes: The Cooper Center Longitudinal Study Laura F. DeFina, MD,* Gloria Lena Vega, PhD,Þ David Leonard, PhD,Þ and Scott M. Grundy,
Impact of Physical Activity on Metabolic Change in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
 2012 International Conference on Life Science and Engineering IPCBEE vol.45 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2012. V45. 14 Impact of Physical Activity on Metabolic Change in Type
2012 International Conference on Life Science and Engineering IPCBEE vol.45 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore DOI: 10.7763/IPCBEE. 2012. V45. 14 Impact of Physical Activity on Metabolic Change in Type
乙型肝炎疫苗初次免疫成年正常应答和高应答者 3 年抗体持久性观察
 478 中华预防医学杂志 216 年 6 月第 5 卷第 6 期 Chin J Prev Med,June 216, Vol. 5, No. 6 乙型肝炎疫苗初次免疫成年正常应答和高应答者 3 年抗体持久性观察 吕静静 张丽 颜丙玉 刘甲野 冯艺 宋立志 陈士玉 周立波 梁晓峰 崔富强 王富珍 徐爱强 摘要 目的探讨乙型肝炎疫苗 (HepB) 初次免疫成年正常应答和高应答者 3 年的抗体持久性及其影响因素
478 中华预防医学杂志 216 年 6 月第 5 卷第 6 期 Chin J Prev Med,June 216, Vol. 5, No. 6 乙型肝炎疫苗初次免疫成年正常应答和高应答者 3 年抗体持久性观察 吕静静 张丽 颜丙玉 刘甲野 冯艺 宋立志 陈士玉 周立波 梁晓峰 崔富强 王富珍 徐爱强 摘要 目的探讨乙型肝炎疫苗 (HepB) 初次免疫成年正常应答和高应答者 3 年的抗体持久性及其影响因素
Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Uygur children of Xinjiang, China
 Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Uygur children of Xinjiang, China J. Zhang 1, Y.T. Ma 1, X. Xie 1, Y.N. Yang 1, F. Liu 2, X.M. Li 1, Z.Y. Fu 1, X. Ma 1, B.D. Chen 2, Y.Y. Zheng 1,
Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in Uygur children of Xinjiang, China J. Zhang 1, Y.T. Ma 1, X. Xie 1, Y.N. Yang 1, F. Liu 2, X.M. Li 1, Z.Y. Fu 1, X. Ma 1, B.D. Chen 2, Y.Y. Zheng 1,
Ling Zhao Huazhong Agricultural University Sep. 21, 2015
 Rabies vaccine development Ling Zhao Huazhong Agricultural University Sep. 21, 2015 Outlines 1. Rabies 2. Rabies virus 3. Rabies epidemiology 4. Rabies vaccine development 5. Perspective Rabies-one of
Rabies vaccine development Ling Zhao Huazhong Agricultural University Sep. 21, 2015 Outlines 1. Rabies 2. Rabies virus 3. Rabies epidemiology 4. Rabies vaccine development 5. Perspective Rabies-one of
Relationships Between Indices of Obesity and Its Cardiovascular Comorbidities in a Chinese Population
 Circ J 2008; 72: 973 978 Relationships Between Indices of Obesity and Its Cardiovascular Comorbidities in a Chinese Population Rui Li, MD ; Wei Lu, MD, PhD ; Jian Jia, MD, MPH*; Shengnian Zhang, MD; Liang
Circ J 2008; 72: 973 978 Relationships Between Indices of Obesity and Its Cardiovascular Comorbidities in a Chinese Population Rui Li, MD ; Wei Lu, MD, PhD ; Jian Jia, MD, MPH*; Shengnian Zhang, MD; Liang
MACC1 upregulation promotes gastric cancer tumor cell metastasis and predicts a poor prognosis *
 Xie et al. / J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol) 2016 17(5):361-366 361 Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B (Biomedicine & Biotechnology) ISSN 1673-1581 (Print); ISSN 1862-1783 (Online) www.zju.edu.cn/jzus;
Xie et al. / J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B (Biomed & Biotechnol) 2016 17(5):361-366 361 Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B (Biomedicine & Biotechnology) ISSN 1673-1581 (Print); ISSN 1862-1783 (Online) www.zju.edu.cn/jzus;
Unraveling the concealed and calculated cardiovascular risks in diabetes
 15 P B Fernando Memorial Oration 2015 Unraveling the concealed and calculated cardiovascular risks in diabetes Weerarathna T P 1 Journal of the Ceylon College of Physicians, 2016, 47, 15-19 Abstract Cardiovascular
15 P B Fernando Memorial Oration 2015 Unraveling the concealed and calculated cardiovascular risks in diabetes Weerarathna T P 1 Journal of the Ceylon College of Physicians, 2016, 47, 15-19 Abstract Cardiovascular
A Case Report on Primary Ovarian Leiomyo-Sarcoma and Some Related Documents Review
 Asian Case Reports in Oncology 亚洲肿瘤科病例研究, 2013, 2, 11-15 http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/acrpo.2013.23004 Published Online July 2013 (http://www.hanspub.org/journal/acrpo.html) A Case Report on Primary Ovarian
Asian Case Reports in Oncology 亚洲肿瘤科病例研究, 2013, 2, 11-15 http://dx.doi.org/10.12677/acrpo.2013.23004 Published Online July 2013 (http://www.hanspub.org/journal/acrpo.html) A Case Report on Primary Ovarian
PREVALENCE OF METABOLİC SYNDROME İN CHİLDREN AND ADOLESCENTS
 PREVALENCE OF METABOLİC SYNDROME İN CHİLDREN AND ADOLESCENTS Mehmet Emre Atabek,MD,PhD Necmettin Erbakan University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology and
PREVALENCE OF METABOLİC SYNDROME İN CHİLDREN AND ADOLESCENTS Mehmet Emre Atabek,MD,PhD Necmettin Erbakan University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Pediatrics, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology and
Uncertainty of Measurement Application to Laboratory Medicine 鏡檢組 蔡雅雯 2014/09/09
 Uncertainty of Measurement Application to Laboratory Medicine 鏡檢組 蔡雅雯 2014/09/09 Objectives Definitions Methodology Equation of Measurement Uncertainty Measurement Uncertainty Goal Examples Uncertainty
Uncertainty of Measurement Application to Laboratory Medicine 鏡檢組 蔡雅雯 2014/09/09 Objectives Definitions Methodology Equation of Measurement Uncertainty Measurement Uncertainty Goal Examples Uncertainty
The investigation of serum lipids and prevalence of dyslipidemia in urban adult population of Warangal district, Andhra Pradesh, India
 eissn: 09748369, www.biolmedonline.com The investigation of serum lipids and prevalence of dyslipidemia in urban adult population of Warangal district, Andhra Pradesh, India M Estari, AS Reddy, T Bikshapathi,
eissn: 09748369, www.biolmedonline.com The investigation of serum lipids and prevalence of dyslipidemia in urban adult population of Warangal district, Andhra Pradesh, India M Estari, AS Reddy, T Bikshapathi,
Metabolically obese but normal weight (MONW) and metabolically healthy but obese (MHO) phenotypes in Koreans: characteristics and health behaviors
 280 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2009;18 (2): 280-284 Short Communication Metabolically obese but normal weight (MONW) and metabolically healthy but obese (MHO) phenotypes in Koreans: characteristics and health
280 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2009;18 (2): 280-284 Short Communication Metabolically obese but normal weight (MONW) and metabolically healthy but obese (MHO) phenotypes in Koreans: characteristics and health
The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea
 Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2016;31:349-33 http://dx.doi.org/.3803/enm.2016.31.3.349 pissn 2093-96X eissn 2093-978 The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea Junghyun Noh Department of Internal Medicine, Inje
Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2016;31:349-33 http://dx.doi.org/.3803/enm.2016.31.3.349 pissn 2093-96X eissn 2093-978 The Diabetes Epidemic in Korea Junghyun Noh Department of Internal Medicine, Inje
Waist circumference as an indicator of high blood pressure in preschool obese children
 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2011;20 (4):557-562 557 Short Communication Waist circumference as an indicator of high blood pressure in preschool obese children Bin Chen MD, Hai-fei Li MD Department of Children
Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2011;20 (4):557-562 557 Short Communication Waist circumference as an indicator of high blood pressure in preschool obese children Bin Chen MD, Hai-fei Li MD Department of Children
Cross-sectional study on the relationship between life events and mental health of secondary school students in Shanghai, China
 162 Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 2012, Vol.24, No.3 Cross-sectional study on the relationship between life events and mental health of secondary school students in Shanghai, China Linlin ZHOU, Juan
162 Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 2012, Vol.24, No.3 Cross-sectional study on the relationship between life events and mental health of secondary school students in Shanghai, China Linlin ZHOU, Juan
Association of serum adipose triglyceride lipase levels with obesity and diabetes
 Association of serum adipose triglyceride lipase levels with obesity and diabetes L. Yang 1 *, S.J. Chen 1 *, G.Y. Yuan 1, L.B. Zhou 2, D. Wang 1, X.Z. Wang 1 and J.J. Chen 1 1 Department of Endocrinology,
Association of serum adipose triglyceride lipase levels with obesity and diabetes L. Yang 1 *, S.J. Chen 1 *, G.Y. Yuan 1, L.B. Zhou 2, D. Wang 1, X.Z. Wang 1 and J.J. Chen 1 1 Department of Endocrinology,
Role of HbA1c in the Screening of Diabetes Mellitus in a Korean Rural Community
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.1.37 pissn 2233-6079 eissn 2233-6087 D I A B E T E S & M E T A B O L I S M J O U R N A L Role of HbA1c in the Screening of Diabetes Mellitus in a
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.1.37 pissn 2233-6079 eissn 2233-6087 D I A B E T E S & M E T A B O L I S M J O U R N A L Role of HbA1c in the Screening of Diabetes Mellitus in a
Serum Retinol-binding Protein 4 Levels in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy
 The Journal of International Medical Research 2010; 38: 95 99 Serum Retinol-binding Protein 4 Levels in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy Z-Z LI 1, X-Z LU 2, J-B LIU 1 AND L CHEN 1 1 Department of Endocrinology,
The Journal of International Medical Research 2010; 38: 95 99 Serum Retinol-binding Protein 4 Levels in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy Z-Z LI 1, X-Z LU 2, J-B LIU 1 AND L CHEN 1 1 Department of Endocrinology,
Different worlds, different tasks for health promotion: comparisons of health risk profiles in Chinese and Finnish rural people
 HEALTH PROMOTION INTERNATIONAL Vol. 16, No. 4 Oxford University Press 2001. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain Different worlds, different tasks for health promotion: comparisons of health risk
HEALTH PROMOTION INTERNATIONAL Vol. 16, No. 4 Oxford University Press 2001. All rights reserved Printed in Great Britain Different worlds, different tasks for health promotion: comparisons of health risk
Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden
 Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Cardiovascular Disease Prevention (CVD) Three Strategies for CVD
Optimizing risk assessment of total cardiovascular risk What are the tools? Lars Rydén Professor Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Cardiovascular Disease Prevention (CVD) Three Strategies for CVD
A Novel Testing Model for Opportunistic Screening of Pre-Diabetes and Diabetes among U.S. Adults
 RESEARCH ARTICLE A Novel Testing Model for Opportunistic Screening of Pre-Diabetes and Diabetes among U.S. Adults Yurong Zhang 1, Gang Hu 2, Lu Zhang 3, Rachel Mayo 4, Liwei Chen 4 * 1 The First Affiliated
RESEARCH ARTICLE A Novel Testing Model for Opportunistic Screening of Pre-Diabetes and Diabetes among U.S. Adults Yurong Zhang 1, Gang Hu 2, Lu Zhang 3, Rachel Mayo 4, Liwei Chen 4 * 1 The First Affiliated
Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(3): LI Jian Hong, WANG Li Min, LI Yi Chong, ZHANG Mei, and WANG Lin Hong #
 Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(3): 205-211 205 Letter to the Editor Prevalence of Major Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Cardiovascular Disease in Women in China: Surveillance Efforts LI Jian Hong, WANG Li
Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(3): 205-211 205 Letter to the Editor Prevalence of Major Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Cardiovascular Disease in Women in China: Surveillance Efforts LI Jian Hong, WANG Li
Anthropometric, metabolic and dietary fatty acids profiles in lean and obese diabetic Asian Indian subjects
 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2006;5 (2):89-95 89 Original Article Anthropometric, metabolic and dietary fatty acids profiles in lean and obese diabetic Asian Indian subjects Arnab Ghosh PhD Palli Charcha Kendra,
Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2006;5 (2):89-95 89 Original Article Anthropometric, metabolic and dietary fatty acids profiles in lean and obese diabetic Asian Indian subjects Arnab Ghosh PhD Palli Charcha Kendra,
Trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes and prediabetes in community-dwelling Japanese subjects: The Hisayama Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes and prediabetes in community-dwelling Japanese subjects: The Hisayama Study Naoko Mukai 1,2 *, Yasufumi Doi 1,2, Toshiharu Ninomiya 1,2, Yoichiro
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Trends in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes and prediabetes in community-dwelling Japanese subjects: The Hisayama Study Naoko Mukai 1,2 *, Yasufumi Doi 1,2, Toshiharu Ninomiya 1,2, Yoichiro
Isolated Post-challenge Hyperglycemia: Concept and Clinical Significance
 CLINICAL PRACTICE Isolated Post-challenge Hyperglycemia: Concept and Clinical Significance John MF. Adam*, Daniel Josten** ABSTRACT The American Diabetes Association has strongly recommended that fasting
CLINICAL PRACTICE Isolated Post-challenge Hyperglycemia: Concept and Clinical Significance John MF. Adam*, Daniel Josten** ABSTRACT The American Diabetes Association has strongly recommended that fasting
Health: Acupuncture in the UK 健康 : 针灸在英国
 Health: Acupuncture in the UK 健康 : 针灸在英国 1 Health: Acupuncture in the UK 健康 : 针灸在英国 A Better Way to Beat Back Pain? 腰疼有救吗? What is the single largest cause of sick leave in the UK? The answer is not the
Health: Acupuncture in the UK 健康 : 针灸在英国 1 Health: Acupuncture in the UK 健康 : 针灸在英国 A Better Way to Beat Back Pain? 腰疼有救吗? What is the single largest cause of sick leave in the UK? The answer is not the
A Simplified Indian Diabetes Risk Score for Screening for Undiagnosed Diabetic Subjects
 Original Article# A Simplified Indian Diabetes Risk Score for Screening for Undiagnosed Diabetic Subjects V Mohan*, R Deepa*, M Deepa*, S Somannavar*, M Datta** Abstract Aim : The aim of this study was
Original Article# A Simplified Indian Diabetes Risk Score for Screening for Undiagnosed Diabetic Subjects V Mohan*, R Deepa*, M Deepa*, S Somannavar*, M Datta** Abstract Aim : The aim of this study was
G. W. Katulanda 1, P. Katulanda 2,3,4, C. Dematapitiya 2, H. A. Dissanayake 2*, S. Wijeratne 5, M. H. R. Sheriff 2 and D. R.
 Katulanda et al. BMC Endocrine Disorders (2019) 19:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-019-0343-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Plasma glucose in screening for diabetes and pre-diabetes: how much is too much?
Katulanda et al. BMC Endocrine Disorders (2019) 19:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12902-019-0343-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Plasma glucose in screening for diabetes and pre-diabetes: how much is too much?
Relationship of Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Chinese Adult 1
 BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 23, 92-101 (2010) www.besjournal.com Relationship of Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Chinese Adult 1 SONG-MING DU *, #, GUAN-SHENG
BIOMEDICAL AND ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES 23, 92-101 (2010) www.besjournal.com Relationship of Body Mass Index, Waist Circumference and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Chinese Adult 1 SONG-MING DU *, #, GUAN-SHENG
利用 PEN 项目网络教育 Making use of PEN project web-based education 发展聋人高等特殊教育 to develop higher education for the deaf
 利用 PEN 项目网络教育 Making use of PEN project web-based education 发展聋人高等特殊教育 to develop higher education for the deaf 长春大学副校长庄树范 Vice-president of Changchun University Zhuang Shufan 一 PEN 项目与我校的机缘 内容提要 Informative
利用 PEN 项目网络教育 Making use of PEN project web-based education 发展聋人高等特殊教育 to develop higher education for the deaf 长春大学副校长庄树范 Vice-president of Changchun University Zhuang Shufan 一 PEN 项目与我校的机缘 内容提要 Informative
Serum levels of galectin-1, galectin-3, and galectin-9 are associated with large artery atherosclerotic
 Supplementary Information The title of the manuscript Serum levels of galectin-1, galectin-3, and galectin-9 are associated with large artery atherosclerotic stroke Xin-Wei He 1, Wei-Ling Li 1, Cai Li
Supplementary Information The title of the manuscript Serum levels of galectin-1, galectin-3, and galectin-9 are associated with large artery atherosclerotic stroke Xin-Wei He 1, Wei-Ling Li 1, Cai Li
Thyroid gland & Root of the neck OUTLINE. Thyroid gland
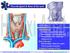 Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Thyroid gland & Root of the neck OUTLINE Thyroid gland Location & superficial feature Blood supply & Venous drainage Relationship
Dept. of Human Anatomy, Si Chuan University Zhou hongying eaglezhyxzy@163.com Thyroid gland & Root of the neck OUTLINE Thyroid gland Location & superficial feature Blood supply & Venous drainage Relationship
Thyroid gland & Root of neck. L o g o
 Thyroid gland & Root of neck Dept. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying L o g o Thyroid gland Outline Location & superficial feature Blood supply & Venous drainage Relationship of its vessels and related nerves
Thyroid gland & Root of neck Dept. of Human Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying L o g o Thyroid gland Outline Location & superficial feature Blood supply & Venous drainage Relationship of its vessels and related nerves
Iodine excess or not: analysis on the necessity of reducing the iodine content in edible salt based on the national monitoring results
 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2011;20 (4):501-506 501 Review Iodine excess or not: analysis on the necessity of reducing the iodine content in edible salt based on the national monitoring results Sumei Li 1, Qingsi
Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2011;20 (4):501-506 501 Review Iodine excess or not: analysis on the necessity of reducing the iodine content in edible salt based on the national monitoring results Sumei Li 1, Qingsi
Waist circumference percentile criteria for the pediatric metabolic syndrome in Korean adolescents
 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 8;17 (3):422-428 422 Original Article Waist circumference percentile criteria for the pediatric metabolic syndrome in Korean adolescents Kayoung Lee MD PhD Department of Family Medicine,
Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 8;17 (3):422-428 422 Original Article Waist circumference percentile criteria for the pediatric metabolic syndrome in Korean adolescents Kayoung Lee MD PhD Department of Family Medicine,
Effects of a summer program for weight management in obese children and adolescents in Shanghai
 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2014;23(3):459-464 459 Short Communication Effects of a summer program for weight management in obese children and adolescents in Shanghai Qingya Tang MD 1,2, Huijuan Ruan MD 1, Yexuan
Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2014;23(3):459-464 459 Short Communication Effects of a summer program for weight management in obese children and adolescents in Shanghai Qingya Tang MD 1,2, Huijuan Ruan MD 1, Yexuan
Assessment of muscle mass and its association with protein intake in a multi-ethnic Asian population: relevance in chronic kidney disease
 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2014;23(4):619-625 619 Original Article Assessment of muscle mass and its association with protein intake in a multi-ethnic Asian population: relevance in chronic kidney disease Boon
Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2014;23(4):619-625 619 Original Article Assessment of muscle mass and its association with protein intake in a multi-ethnic Asian population: relevance in chronic kidney disease Boon
Association between Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia in Hong Kong Chinese
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 12, 2008 Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia Association between Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia in Hong Kong Chinese Bernard My Cheung,
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 12, 2008 Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia Association between Raised Blood Pressure and Dysglycemia in Hong Kong Chinese Bernard My Cheung,
Diabetes Care 34: , 2011
 Epidemiology/Health Services Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Hemoglobin A 1c as a Diagnostic Tool for Diabetes Screening and New-Onset Diabetes Prediction A 6-year community-based prospective study
Epidemiology/Health Services Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Hemoglobin A 1c as a Diagnostic Tool for Diabetes Screening and New-Onset Diabetes Prediction A 6-year community-based prospective study
Maternal high-fat diet inversely affects insulin sensitivity in dams and young adult male rat offspring *#
 728 Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B (Biomedicine & Biotechnology) ISSN 1673-1581 (Print); ISSN 1862-1783 (Online) www.zju.edu.cn/jzus; www.springerlink.com E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn Correspondence:
728 Journal of Zhejiang University-SCIENCE B (Biomedicine & Biotechnology) ISSN 1673-1581 (Print); ISSN 1862-1783 (Online) www.zju.edu.cn/jzus; www.springerlink.com E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.cn Correspondence:
The Diseases of Lymphoid & Hematopoietic system ( 淋巴和造血系统疾病 )
 The Diseases of Lymphoid & Hematopoietic system ( 淋巴和造血系统疾病 ) Wei Zhang ( 张伟 ) Ph.D Associate Professor Department of Pathology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine zwei72@zju.edu.cn Tel: 13819103401
The Diseases of Lymphoid & Hematopoietic system ( 淋巴和造血系统疾病 ) Wei Zhang ( 张伟 ) Ph.D Associate Professor Department of Pathology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine zwei72@zju.edu.cn Tel: 13819103401
Definition of Stroke ( 中风 )
 Definition of Stroke ( 中风 ) Sudden brain damage Lack of blood flow to the brain caused by a clot or rupture of a blood vessel Ischemia = Clot 缺血 (makes up approximately 87% of all strokes) Embolic Thrombotic
Definition of Stroke ( 中风 ) Sudden brain damage Lack of blood flow to the brain caused by a clot or rupture of a blood vessel Ischemia = Clot 缺血 (makes up approximately 87% of all strokes) Embolic Thrombotic
Identification of subjects at high risk for cardiovascular disease
 Master Class in Preventive Cardiology Focus on Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Geneva April 14 2011 Identification of subjects at high risk for cardiovascular disease Lars Rydén Karolinska Institutet
Master Class in Preventive Cardiology Focus on Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease Geneva April 14 2011 Identification of subjects at high risk for cardiovascular disease Lars Rydén Karolinska Institutet
Epidemiology of NAFLD in China Jian-Gao Fan MD, PhD.
 Epidemiology of NAFLD in China Jian-Gao Fan MD, PhD. Professor and Director Department of Gastroenterology Xinhua Hospital Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine Shanghai 200092, China Epidemiological
Epidemiology of NAFLD in China Jian-Gao Fan MD, PhD. Professor and Director Department of Gastroenterology Xinhua Hospital Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine Shanghai 200092, China Epidemiological
Letter to the Editor. Association of TCF7L2 and GCG Gene Variants with Insulin Secretion, Insulin Resistance, and Obesity in New-onset Diabetes *
 814 Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(11): 814-817 Letter to the Editor Association of TCF7L2 and GCG Gene Variants with Insulin Secretion, Insulin Resistance, and Obesity in New-onset Diabetes * ZHANG Lu 1,^,
814 Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(11): 814-817 Letter to the Editor Association of TCF7L2 and GCG Gene Variants with Insulin Secretion, Insulin Resistance, and Obesity in New-onset Diabetes * ZHANG Lu 1,^,
Metabolic Syndrome among Type-2 Diabetic Patients in Benghazi- Libya: A pilot study. Arab Medical University. Benghazi, Libya
 Original Article Metabolic Syndrome among Type-2 Diabetic Patients in Benghazi- Libya: A pilot study Alshkri MM 1, Elmehdawi RR 2 1 Benghazi Diabetes Center. 2 Medical Department, Faculty of Medicine,
Original Article Metabolic Syndrome among Type-2 Diabetic Patients in Benghazi- Libya: A pilot study Alshkri MM 1, Elmehdawi RR 2 1 Benghazi Diabetes Center. 2 Medical Department, Faculty of Medicine,
Combining glycosylated hemoglobin A 1c and fasting plasma glucose for diagnosis of type 2 diabetes in Chinese adults
 Mo et al. BMC Endocrine Disorders 2013, 13:44 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Combining glycosylated hemoglobin A 1c and fasting plasma glucose for diagnosis of type 2 diabetes in Chinese adults Miao Mo 1,
Mo et al. BMC Endocrine Disorders 2013, 13:44 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Combining glycosylated hemoglobin A 1c and fasting plasma glucose for diagnosis of type 2 diabetes in Chinese adults Miao Mo 1,
Kidney Failure- Are you at risk?? ( 腎功能衰竭 - 你是在高危險群嗎?)
 Kidney Failure- Are you at risk?? ( 腎功能衰竭 - 你是在高危險群嗎?) Dr Goh Heong Keong, Penang www.passpaces.com/kidney.htm Outline of Lecture Introduction( 介紹 ) Definition of Chronic kidney disease( 慢性肾脏病的定义 ) Stages
Kidney Failure- Are you at risk?? ( 腎功能衰竭 - 你是在高危險群嗎?) Dr Goh Heong Keong, Penang www.passpaces.com/kidney.htm Outline of Lecture Introduction( 介紹 ) Definition of Chronic kidney disease( 慢性肾脏病的定义 ) Stages
25-Hydroxyvitamin D is closely related with the function of the pancreatic islet β cells
 Original Article 25-Hydroxyvitamin D is closely related with the function of the pancreatic islet β cells Jingjing Guo 1, Zhengda Xiao 2, Xia Xue 3, Xin Liu 4, Yong Lu 5, Xiao Yin 6, Kun Ma 7 Open Access
Original Article 25-Hydroxyvitamin D is closely related with the function of the pancreatic islet β cells Jingjing Guo 1, Zhengda Xiao 2, Xia Xue 3, Xin Liu 4, Yong Lu 5, Xiao Yin 6, Kun Ma 7 Open Access
博士后学位论文. Importin 13: 一个新的角膜上皮前体细胞标志物. Importin 13:a Novel Potential Marker for Corneal Epithelial Progenitor Cells 指导教师 : 刘祖国 专业名称 : 眼科学
 学校编码 :10384 学号 :BH17000206 博士后学位论文 Importin 13: 一个新的角膜上皮前体细胞标志物 Importin 13:a Novel Potential Marker for Corneal Epithelial Progenitor Cells 王华 指导教师 : 刘祖国 专业名称 : 眼科学 答辩日期 :2009 年 9 月 厦门大学学位论文原创性声明 本人呈交的学位论文是本人在导师指导下,
学校编码 :10384 学号 :BH17000206 博士后学位论文 Importin 13: 一个新的角膜上皮前体细胞标志物 Importin 13:a Novel Potential Marker for Corneal Epithelial Progenitor Cells 王华 指导教师 : 刘祖国 专业名称 : 眼科学 答辩日期 :2009 年 9 月 厦门大学学位论文原创性声明 本人呈交的学位论文是本人在导师指导下,
Research Article Increased Serum ANGPTL8 Concentrations in Patients with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes
 Hindawi Diabetes Research Volume 2017, Article ID 8293207, 7 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8293207 Research Article Increased Serum Concentrations in Patients with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes
Hindawi Diabetes Research Volume 2017, Article ID 8293207, 7 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8293207 Research Article Increased Serum Concentrations in Patients with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes
Interferon-gamma and interleukin-10 levels in serum and saliva are related to different types of oral lichen planus
 中国组织工程研究第 19 卷第 2 期 2015 01 08 出版 Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research January 8, 2015 Vol.19, No.2 Interferon-gamma and interleukin-10 levels in serum and saliva are related to different types
中国组织工程研究第 19 卷第 2 期 2015 01 08 出版 Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research January 8, 2015 Vol.19, No.2 Interferon-gamma and interleukin-10 levels in serum and saliva are related to different types
Relations of body weight status in early adulthood and weight changes until middle age with metabolic syndrome in the Chinese population
 International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Zhao L et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Nov;4(11):4011-4017 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original Research
International Journal of Community Medicine and Public Health Zhao L et al. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017 Nov;4(11):4011-4017 http://www.ijcmph.com pissn 2394-6032 eissn 2394-6040 Original Research
Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Registered in Primary Health Care in Bahrain
 Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Page 1 of 10 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.25, No.1, March 2003 Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Registered in Primary
Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Page 1 of 10 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.25, No.1, March 2003 Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus among Non-Bahraini Workers Registered in Primary
Contribution of hypoalbuminemia and decreased renal function to the increased mortality after newly diagnosed vertebral fracture in Japanese subjects
 472 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2016;25(3):472-477 Original Article Contribution of hypoalbuminemia and decreased renal function to the increased mortality after newly diagnosed vertebral fracture in Japanese
472 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2016;25(3):472-477 Original Article Contribution of hypoalbuminemia and decreased renal function to the increased mortality after newly diagnosed vertebral fracture in Japanese
Ginkgo biloba extract for dementia: a systematic review
 10 Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 2013, Vol.25, No.1 Meta-analysis Ginkgo biloba extract for dementia: a systematic review Lijuan JIANG 1, Lijie SU 2, Huiru CUI 1, Juanjuan REN 1, Chunbo LI 1 * Background:
10 Shanghai Archives of Psychiatry, 2013, Vol.25, No.1 Meta-analysis Ginkgo biloba extract for dementia: a systematic review Lijuan JIANG 1, Lijie SU 2, Huiru CUI 1, Juanjuan REN 1, Chunbo LI 1 * Background:
British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research 19(5): XX-XX, 2017; Article no.bjmmr ISSN: , NLM ID:
 British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research 19(5): XX-XX, 2017; Article no.bjmmr.31022 ISSN: 2231-0614, NLM ID: 101570965 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org The Performance of the Finnish
British Journal of Medicine & Medical Research 19(5): XX-XX, 2017; Article no.bjmmr.31022 ISSN: 2231-0614, NLM ID: 101570965 SCIENCEDOMAIN international www.sciencedomain.org The Performance of the Finnish
DIABETES. A growing problem
 DIABETES A growing problem Countries still grappling with infectious diseases such as tuberculosis, HIV/AIDS and malaria now face a double burden of disease Major social and economic change has brought
DIABETES A growing problem Countries still grappling with infectious diseases such as tuberculosis, HIV/AIDS and malaria now face a double burden of disease Major social and economic change has brought
Optimal Cutoff Points of Waist Circumference for the Criteria of Abdominal Obesity
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epidemiology Circ J 2009; 73: 2068 2075 Optimal Cutoff Points of Waist Circumference for the Criteria of Abdominal Obesity Comparison With the Criteria of the International Diabetes Federation
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epidemiology Circ J 2009; 73: 2068 2075 Optimal Cutoff Points of Waist Circumference for the Criteria of Abdominal Obesity Comparison With the Criteria of the International Diabetes Federation
Relationship between cardiovascular risk factors and traditional Chinese constitution in subjects with high-normal blood pressure
 World Journal of Cardiovascular Diseases, 2013, 3, 234-238 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wjcd.2013.32036 Published Online April 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjcd/) WJCD Relationship between cardiovascular
World Journal of Cardiovascular Diseases, 2013, 3, 234-238 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wjcd.2013.32036 Published Online April 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjcd/) WJCD Relationship between cardiovascular
Research Article The Association of Retinopathy and Plasma Glucose and HbA1c: A Validation of Diabetes Diagnostic Criteria in a Chinese Population
 Diabetes Research Volume 216, Article ID 434129, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/434129 Research Article The Association of Retinopathy and Plasma Glucose and HbA1c: A Validation of Diabetes Diagnostic
Diabetes Research Volume 216, Article ID 434129, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/434129 Research Article The Association of Retinopathy and Plasma Glucose and HbA1c: A Validation of Diabetes Diagnostic
兒童及青少年肥胖評估工具 黃秀玫張碧真 * Cole & Rolland-Cachera, body mass index, BMI Mei et al., 2002 BMI. body mass index, BMI BMI
 78 兒童及青少年肥胖評估工具 黃秀玫張碧真 * 身體組成的測量可以觀察身體的相關生長與疾病的狀態, 臨床與研究上常運用各種測量方式以定 義兒童及青少年肥胖 本文主要回顧實地測量方 式, 探討各種工具的運用與信 效度, 並以臺 灣實施現況加以討論, 以期在未來可以正確地評 估兒童及青少年肥胖 測量身體組成的方式包括 實驗室檢查法與實地測量法, 其中實地測量法包 括重高指標與脂肪分佈的測量, 而實地測量方式
78 兒童及青少年肥胖評估工具 黃秀玫張碧真 * 身體組成的測量可以觀察身體的相關生長與疾病的狀態, 臨床與研究上常運用各種測量方式以定 義兒童及青少年肥胖 本文主要回顧實地測量方 式, 探討各種工具的運用與信 效度, 並以臺 灣實施現況加以討論, 以期在未來可以正確地評 估兒童及青少年肥胖 測量身體組成的方式包括 實驗室檢查法與實地測量法, 其中實地測量法包 括重高指標與脂肪分佈的測量, 而實地測量方式
Trends In CVD, Related Risk Factors, Prevention and Control In China
 Trends In CVD, Related Risk Factors, Prevention and Control In China Youfa Wang, MD, MS, PhD Associate Professor Center for Human Nutrition Department of International Health Department of Epidemiology
Trends In CVD, Related Risk Factors, Prevention and Control In China Youfa Wang, MD, MS, PhD Associate Professor Center for Human Nutrition Department of International Health Department of Epidemiology
Why Do We Treat Obesity? Epidemiology
 Why Do We Treat Obesity? Epidemiology Epidemiology of Obesity U.S. Epidemic 2 More than Two Thirds of US Adults Are Overweight or Obese 87.5 NHANES Data US Adults Age 2 Years (Crude Estimate) Population
Why Do We Treat Obesity? Epidemiology Epidemiology of Obesity U.S. Epidemic 2 More than Two Thirds of US Adults Are Overweight or Obese 87.5 NHANES Data US Adults Age 2 Years (Crude Estimate) Population
Abdominal volume index and conicity index in predicting metabolic abnormalities in young women of different socioeconomic class
 Research Article Abdominal volume index and conicity index in predicting metabolic abnormalities in young women of different socioeconomic class Vikram Gowda, Kripa Mariyam Philip Department of Physiology,
Research Article Abdominal volume index and conicity index in predicting metabolic abnormalities in young women of different socioeconomic class Vikram Gowda, Kripa Mariyam Philip Department of Physiology,
Background. Background. Acupuncture Protocol
 Background The Achilles tendon is a problematic structure in the general population and in competitive and recreational athletes Specifically affecting middle aged runners (Paavola et al, 2002; Woo et
Background The Achilles tendon is a problematic structure in the general population and in competitive and recreational athletes Specifically affecting middle aged runners (Paavola et al, 2002; Woo et
Risk of development of diabetes mellitus in Chinese women with persistently impaired glucose tolerance after gestational diabetes
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Risk of development of diabetes mellitus in Chinese women with persistently impaired glucose tolerance after gestational diabetes KF Lee Maria WH Mak KO Lau Harriet HY Chung
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Risk of development of diabetes mellitus in Chinese women with persistently impaired glucose tolerance after gestational diabetes KF Lee Maria WH Mak KO Lau Harriet HY Chung
Rare Diseases Research in China:
 Rare Diseases Research in China: Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow Shuyang Zhang, M.D. Peking Union Medical College Hospital Rare Diseases: Global Challenges Difficulties Low frequency of single disease,
Rare Diseases Research in China: Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow Shuyang Zhang, M.D. Peking Union Medical College Hospital Rare Diseases: Global Challenges Difficulties Low frequency of single disease,
Single vegetable meal content equivalence as an alternative to fat for satiety: a randomised trial in Japanese women
 478 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2016;25(3):478-486 Original Article Single vegetable meal content equivalence as an alternative to fat for satiety: a randomised trial in Japanese women Chisaki Adachi MS 1, Hisami
478 Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2016;25(3):478-486 Original Article Single vegetable meal content equivalence as an alternative to fat for satiety: a randomised trial in Japanese women Chisaki Adachi MS 1, Hisami
Trend analysis of diabetic prevalence and incidence in a rural area of South Korea between
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Trend analysis of diabetic prevalence and incidence in a rural area of South Korea between 2003 2008 Ji Yun Jeong 1, Jung-Guk Kim 1,Bo-WanKim 1, Seong Su Moon 1, Hye-Soon Kim 2, Keun-Gyu
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Trend analysis of diabetic prevalence and incidence in a rural area of South Korea between 2003 2008 Ji Yun Jeong 1, Jung-Guk Kim 1,Bo-WanKim 1, Seong Su Moon 1, Hye-Soon Kim 2, Keun-Gyu
Research Article Associated Factors with Biochemical Hypoglycemia during an Oral Glucose Tolerance Test in a Chinese Population
 Hindawi Diabetes Research Volume 2017, Article ID 3212814, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3212814 Research Article Associated Factors with Biochemical Hypoglycemia during an Oral Glucose Tolerance
Hindawi Diabetes Research Volume 2017, Article ID 3212814, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3212814 Research Article Associated Factors with Biochemical Hypoglycemia during an Oral Glucose Tolerance
