Neurocysticercosis in sub-saharan Africa. Dr. Andrea-Sylvia Winkler, PhD Department of Neurology Technical University Munich
|
|
|
- Janice Karin Phillips
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neurocysticercosis in sub-saharan Africa Dr. Andrea-Sylvia Winkler, PhD Department of Neurology Technical University Munich
2 (Sero-)prevalence of cysticercosis (worldwide) Worldwide 50 million people with cysticercosis (WHO 2005) = most frequent cerebral helminthosis Seroprevalences are highest in Mexico (44%) and India (24%). Community-based study (DANIDA) shows high seroprevalences of about 45% in Tanzania (rt-24h Ab-detecting ELISA). Antigen-ELISA was positive in about 17% of people. Seroprevalence in California 1.8% - more than 1000 NCC cases/year in USA. Reports from within Europe, mainly Eastern Europe, indicate 10 NCC cases/year (many cases not reported no seroprevalence studies)
3 Prevalence of neurocysticercosis (worldwide) Ecuador: 14% of normal population (CT confirmed) Peru: 52% of all children with partial epilepsy South Africa: 50% of incident epilpesy cases Tansania: 20% of prevalent epilepsy cases 30% of people with epilepsy in endemic areas have got NCC (Ndimubanzi et al. 2010).
4 Prevalence of NCC
5 Prevalence of neurocysticercosis (sub-saharan Africa) Median prevalence of epilepsy in SSA is 15/1000 (Preux and Druet-Cabanac 2005). Real prevalence between 4 and 10/1000 (Edwards et al. 2008, Winkler et al. 2009).
6 Äthiopien Nigeria Nigeria Elfenbeink. Senegal Tansania Tansania Burkina F: Tansania Mali Togo Zambia Uganda Togo Tansania Benin Mali Togo Kenya Togo Madagaskar Senegal Benin Liberia Benin Nigeria Kamerun Elfenbeink. Kamerun Elfenbeink. Prävalenz pro Prevalences of epilepsy from rural Africa (n=30) 74, ,2 11,2 13,2 0
7 Prevalence of neurocysticercosis (sub-saharan Africa) Median prevalence of epilepsy in SSA is 15/1000 (Preux and Druet-Cabanac 2005). Real prevalence between 4 and 10/1000 (Edwards et al. 2008, Winkler et al. 2009). Assume that 850 million people live in SSA (World bank 2011). Assume a global prevalence of NCC in PWE of almost 30% of PWE (Ndimubanzi et al. 2010).
8 Prevalence of neurocysticercosis (sub-saharan Africa) Median prevalence of epilepsy in SSA is 15/1000 (Preux and Druet-Cabanac 2005). Real prevalence between 4 and 10/1000 (Edwards et al. 2008, Winkler et al. 2009). Assume that 850 million people live in SSA (World bank 2011). Assume a global prevalence of NCC in PWE of almost 30% of PWE (Ndimubanzi et al. 2010) million people with epilepsy in SSA million people with NCC based on epilepsy
9 Prevalence of neurocysticercosis (sub-saharan Africa) Median prevalence of epilepsy in SSA is 15/1000 (Preux and Druet-Cabanac 2005). Real prevalence between 4 and 10/1000 (Edwards et al. 2008, Winkler et al. 2009). Assume that 850 million people live in SSA (World bank 2011). Assume a global prevalence of NCC in PWE of almost 30% of PWE (Ndimubanzi et al. 2010) million people with epilepsy in SSA million people with NCC based on epilepsy 3 million people with NCC based on all neurological symptoms In addition, 2.4 million people with latent NCC
10 Focal lesions (with and without inflammation) Encephalitis (rarely Meningitis < 10% of all cases) Infarcts Vasculitis Hydrocephalus Myelopathy Pathology of NCC
11 Classification of NCC Active (cysts) Transitional (granuloma and ring enhancing lesions) Inactive (calcifications) Parenchymal NCC Extraparenchymal NCC (ventricle, subarachnoid space)
12 Symptoms of NCC Symptomatic seizures Epilepsy Headache Increased i.c. pressure Focal neurological signs Psychiatric problems Learning difficulties Very sick patient with encephalitis!
13 Locally adapted classification for epilepsy Causes are different (e.g. infection, perinatal brain damage) Limited diagnostic possibilities (no EEG, MRT) Few specialized clinics Few trained personnel Limited medication
14 Epilepsy study in northern Tanzania Haydom Lutheran Hospital, northern Tanzania Recruitment of 346 people with epilepsy Recruitment phase 25 months (August September 2004) Screening of all patients with standardized questionnaires
15 ILAE classification of epileptic seizures (ICES) I. Partial seizures (Seizures with a focal origin) 1. Simple partial seizures (consciousness not impaired) 2. Complex partial seizures (consciousness not impaired) 3. Secondary generalized seizures II. Generalized seizures 1. Absences 2. Myoclonic seizures 3. Clonic seizures 4. Tonic seizures 5. Tonic-clonic seizures (Grand-mal) 6. Atonic seizures III. Unclassified epileptic seizures
16 focal signs or diffuse brain damage obvious yes no onset outside 6-25 years onset between 6-25 years
17 focal signs or diffuse brain damage obvious yes no diffuse brain damage (nonprogressive) focal signs/ focal neurology (progressive) onset outside 6-25 years onset between 6-25 years
18 focal signs or diffuse brain damage obvious yes no diffuse brain damage (nonprogressive) focal signs/ focal neurology (progressive) onset outside 6-25 years onset between 6-25 years further clinical work-up only in selected cases further clinical work-up EEG/CT necessary further clinical work-up only in selected cases
19 focal signs or diffuse brain damage obvious yes no diffuse brain damage (nonprogressive) focal signs/ focal neurology (progressive) onset outside 6-25 years onset between 6-25 years further clinical work-up only in selected cases close follow-up necessary further clinical work-up EEG/CT necessary close follow-up necessary further clinical work-up only in selected cases close follow-up not necessary
20 focal signs or diffuse brain damage obvious yes no diffuse brain damage (nonprogressive) focal signs/ focal neurology (progressive) onset outside 6-25 years onset between 6-25 years further clinical work-up only in selected cases close follow-up necessary further clinical work-up EEG/CT necessary close follow-up necessary further clinical work-up only in selected cases close follow-up not necessary drug of choice: 1.CBZ 2.PHT drug of choice: 1.CBZ 2.PHT or PHB drug of choice: children: PHT adults: PHB
21 Advantages of the SSA classification Easy to use also for untrained personnel No need of EEG and imaging Transferrable to the ILAE classification Quick therapeutic triage Choice of right antiepileptic medication Approximate prognostic estimation
22 Diagnostic algorithm for suspected NCC in SSA? Epileptic seizures and epilepsy most likely due to NCC CT scan Negative CT scan refer back to the system CT suggestive of NCC Antigen ELISA Positive Confirmed as NCC
23 Diagnostic algorithm for suspected NCC in SSA? Epileptic seizures and epilepsy most likely due to NCC CT scan Negative CT scan refer back to the system CT suggestive of NCC Antigen ELISA Positive Negative Confirmed as NCC Immunoblot Positive Negative
24 CT scan in SSA - why so important? Within a few weeks or months the situation in the brain can change for better or for worse. HIV status of the patients may play a role. If the number of cysts has increased, antihelminthic treatment may harm the patient seriously. If the number of cysts has decreased, antihelminthic treatment may be unnecessary altogether. Triaging of patients suitable for neurosurgery or those that would require special treatment regimes (subarachnoid/ventricular forms)
25 Therapy when? Factors that determine therapeutic approach in general: Localisation of cysts (intra- extraparenchymal) Stage of cysts (active, transitional, inactive) Number and size of cysts (single lesion many lesions) Inflammatory response (contained widespread) Severity of clinical symptoms Potential risk of future complications
26 Sentences to be retained when it comes to therapy? Do not treat asymptomatic cysts. Do not treat inactive lesions with antihelminthic drugs. Do not treat transitional lesion with antihelminthic drugs. Never use antihelminthic drugs in widespread inflammation. Never use antihelminthic drugs if cysts are scattered throughout the brain (encephalitis!). Subarachnoid and ventricular forms need special treatment considerations.
27 Symptomatic treatment Analgesics Steroids Antiepileptic drugs
28 Steroids Prednisolone: 1mg/kg/day p.o. or Dexamethasone mg/d Length of treatment variable, according to symptoms At once and without antihelminthics in cases with cerebral oedema, signs of increased intracranial pressure, vasculitis, compression of the brainstem, spine or optic nerve. Antihelminthics may be given at a later point. In most parenchymal NCC together with antihelminthics; pretreatment may be required; in subarachnoid forms high doses of both drugs and long treatment. Increased metabolism by antiepileptic medication
29 Antiepileptic medication Phenytoin, Phenobarbitone, Carbamazepine (usually well controlled with monotherapy on standard dosage) Therapy may be lifelong if calcifications are present. In active NCC after successful treatment for at least one year (no calcifications!) trial of tapering Additional antihelminthic medication reduces severity but not frequency of epileptic seizures (Garcia et al. 2004).
30 Antihelminthics (active NCC) Albendazole: 15 mg/kg per day x 8-15 days Praziquantel: 50 mg/kg per day x 8-15 days; short course: 100 mg/kg for one day! Albendazole is more effective than Praziquantel (better penetration into CNS) Increased metabolism by steroids and antiepileptic drugs (Praziquantel > Albendazole) Only in active NCC; be aware of sudden increased intracranial pressure with sudden death ; Combination with steroids and control-cts are essential! Contraindicated in encephalitis, increased intracranial pressure and ophthalmological cysticercosis
31 Surgery Ventricular form (endoscopically) Hydrocephalus shunting (mainly ventricular and subarachnoid form prognosis in SSA poor) Accessible cysts with mass effect (e.g. Sylvian fissure) Potential danger of dissemination of cyst material Potential danger of hydrocephalus post-op Perioperative risks (high in SSA)
32 Treatment algorithm for NCC Parenchymal neurocysticercosis Active Transitional Inactive Antihelminthics Steroids AED Steroids AED (Steroids) AED
33 Treatment algorithm for NCC Parenchymal neurocysticercosis Extraparenchymal neurocysticercosis Active Transitional Inactive Subarachnoid* Ventricular Antihelminthics Steroids AED Steroids AED (Steroids) AED Antihelminthics Steroids (AED) Neurosurgery Neurosurgery Steroids Antihelminthics * The racemose NCC form is a malignant version of the subarachnoid form.
34 Treatment algorithm for epileptic seizures Active or transitional stage Initiate AED treatment CT control in 3-6 months Cysts not resolved with or without seizure recurrence Cysts resolved but seizure recurrence Cysts resolved an no seizure recurrence Maintain AED and perform control CT as above Maintain AED at least for another year Withdraw AED
35 Treatment algorithm for epileptic seizures Active or transitional stage Inactive (calcification) stage Initiate AED treatment CT control in 3-6 months Initiate AED treatment Cysts not resolved with or without seizure recurrence Cysts resolved but seizure recurrence Cysts resolved an no seizure recurrence No seizure recurrence for one year Seizure recurrence Maintain AED and perform control CT as above Maintain AED at least for another year Withdraw AED Withdraw AED Maintain on AED until no seizure recurrence for one year Carpio and Ross
36 Treatment algorithm for SSA according to availability of CT scans Epileptic seizures and epilepsy most likely due to NCC (narrow window between first seizure and first CT scan) Performance of CT scan (not older than a couple of months) CT scan possible active NCC confirmed
37 Treatment algorithm for SSA according to availability of CT scans Epileptic seizures and epilepsy most likely due to NCC (narrow window between first seizure and first CT scan) Performance of CT scan (not older than a couple of months) CT scan possible active NCC confirmed Praziquantel and steroids (encephalitis steroids only)
38 Treatment algorithm for SSA according to availability of CT scans Epileptic seizures and epilepsy most likely due to NCC (narrow window between first seizure and first CT scan) Performance of CT scan (not older than a couple of months) CT scan possible active NCC confirmed Praziquantel and steroids (encephalitis steroids only) Follow up with CT? Follow up with serology? Treatment for how long? What to do with defaulters? What to do with treatment failure?
39 Treatment algorithm for SSA according to availability of CT scans Epileptic seizures and epilepsy most likely due to NCC (narrow window between first seizure and first CT scan) Performance of CT scan (not older than a couple of months) CT scan not possible a) none available b) financial constraints CT scan possible active NCC confirmed Praziquantel and steroids (encephalitis steroids only) Treatment with steroids (without antihelminthics) based on serology under very close observation by a specialist?? Follow up with CT? Follow up with serology? Treatment for how long? Or Symptomatic treatment, i.e. AED only, and follow wait and see policy??? What to do with defaulters? What to do with treatment failure?
40 Future?
41 Five important 80:20 rules Most people with NCC are asymptomatic: Symptomatic cases account for between 10% and 40% of all NCC cases (Carpio & Ross 2012 (medscape)). 20% of symptomatic cases will be due to active NCC (cysts etc); 80% due to calcifications. If symptomatic, seizures present in approx 80% (78%; Carabin et al. 2011). 30% of people with epilepsy in endemic areas have got NCC (Ndimubanzi et al. 2010) % have intraparenchymal forms and 20-10% have extraparenchymal forms.
Neurocysticercosis an uncommon intra-cerebral infection in Malaysia-
 Neurocysticercosis an uncommon intra-cerebral infection in Malaysia- A review of 3 cases. Kalai Arasu M. M.S (Malaya), Khairul Anuar FACTM *, Waran V. FRCS(SN). Division of Neurosurgery, Department of
Neurocysticercosis an uncommon intra-cerebral infection in Malaysia- A review of 3 cases. Kalai Arasu M. M.S (Malaya), Khairul Anuar FACTM *, Waran V. FRCS(SN). Division of Neurosurgery, Department of
THE TREATMENT GAP AND POSSIBLE THERAPIES OF EPILEPSY IN SUB- SAHARAN AFRICA
 THE TREATMENT GAP AND POSSIBLE THERAPIES OF EPILEPSY IN SUB- SAHARAN AFRICA DR A.O. CHARWAY-FELLI, MD, PhD NEUROLOGIST 37 MILITARY HOSPITAL, ACCRA, GHANA SECRETARY-GENERAL AFRICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY
THE TREATMENT GAP AND POSSIBLE THERAPIES OF EPILEPSY IN SUB- SAHARAN AFRICA DR A.O. CHARWAY-FELLI, MD, PhD NEUROLOGIST 37 MILITARY HOSPITAL, ACCRA, GHANA SECRETARY-GENERAL AFRICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY
There are several types of epilepsy. Each of them have different causes, symptoms and treatment.
 1 EPILEPSY Epilepsy is a group of neurological diseases where the nerve cell activity in the brain is disrupted, causing seizures of unusual sensations, behavior and sometimes loss of consciousness. Epileptic
1 EPILEPSY Epilepsy is a group of neurological diseases where the nerve cell activity in the brain is disrupted, causing seizures of unusual sensations, behavior and sometimes loss of consciousness. Epileptic
Epilepsy. Epilepsy can be defined as:
 Epilepsy Epilepsy can be defined as: A neurological condition causing the tendency for repeated seizures of primary cerebral origin Epilepsy is currently defined as a tendency to have recurrent seizures
Epilepsy Epilepsy can be defined as: A neurological condition causing the tendency for repeated seizures of primary cerebral origin Epilepsy is currently defined as a tendency to have recurrent seizures
Landscape analysis: management of neurocysticercosis with an emphasis on low- and middle-income countries
 Landscape analysis: management of neurocysticercosis with an emphasis on low- and middle-income countries Commissioned by the World Health Organization Corresponding author: PD Dr Dr Andrea Sylvia Winkler
Landscape analysis: management of neurocysticercosis with an emphasis on low- and middle-income countries Commissioned by the World Health Organization Corresponding author: PD Dr Dr Andrea Sylvia Winkler
Review Article. Neurocysticercosis: Management Issues
 Review Article Neurocysticercosis: Management Issues Tarun Dua S. Aneja* Neurocysticercosis (NCC) is infestation of human central nervous system with tissue cysts of pork tapeworm Taenia solium. Human
Review Article Neurocysticercosis: Management Issues Tarun Dua S. Aneja* Neurocysticercosis (NCC) is infestation of human central nervous system with tissue cysts of pork tapeworm Taenia solium. Human
Clinical Infectious Diseases IDSA GUIDELINE. Keywords. Taenia solium; cysticercosis; neurocysticersosis; taeniasis.
 Clinical Infectious Diseases IDSA GUIDELINE Diagnosis and Treatment of Neurocysticercosis: 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society
Clinical Infectious Diseases IDSA GUIDELINE Diagnosis and Treatment of Neurocysticercosis: 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society
Clinical Infectious Diseases IDSA GUIDELINE. Keywords. Taenia solium; cysticercosis; neurocysticersosis; taeniasis.
 Clinical Infectious Diseases IDSA GUIDELINE Diagnosis and Treatment of Neurocysticercosis: 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society
Clinical Infectious Diseases IDSA GUIDELINE Diagnosis and Treatment of Neurocysticercosis: 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society
A Study on Clinical and Etiological Factors of New-Onset Seizures in Adults
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X A Study on Clinical and Etiological Factors of New-Onset Seizures in Adults P. S. V. Ramana Murthy Associate Professor, Department of General
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X A Study on Clinical and Etiological Factors of New-Onset Seizures in Adults P. S. V. Ramana Murthy Associate Professor, Department of General
Introduction. 1 person in 20 will have an epileptic seizure at some time in their life
 Introduction 1 person in 20 will have an epileptic seizure at some time in their life Epilepsy is diagnosed on the basis of two or more epileptic seizures. Around 450,000 people in the UK have epilepsy
Introduction 1 person in 20 will have an epileptic seizure at some time in their life Epilepsy is diagnosed on the basis of two or more epileptic seizures. Around 450,000 people in the UK have epilepsy
Outline. What is a seizure? What is epilepsy? Updates in Seizure Management Terminology, Triage & Treatment
 Outline Updates in Seizure Management Terminology, Triage & Treatment Joseph Sullivan, MD! Terminology! Videos of different types of seizures! Diagnostic evaluation! Treatment options! Acute! Maintenance
Outline Updates in Seizure Management Terminology, Triage & Treatment Joseph Sullivan, MD! Terminology! Videos of different types of seizures! Diagnostic evaluation! Treatment options! Acute! Maintenance
Epilepsy and Epileptic Seizures
 Epilepsy and Epileptic Seizures Petr Marusič Dpt. of Neurology Charles University, Second Faculty of Medicine Motol University Hospital Diagnosis Steps Differentiation of nonepileptic events Seizure classification
Epilepsy and Epileptic Seizures Petr Marusič Dpt. of Neurology Charles University, Second Faculty of Medicine Motol University Hospital Diagnosis Steps Differentiation of nonepileptic events Seizure classification
Late Onset Shake-Etiology At Stake - A Prospective Study
 Original Article Late Onset Shake-Etiology At Stake - A Prospective Study G Sendil 1, Arun N Kumar 1, Mohan V Kumar 2 1 Senior Resident, ESIC PGIMSR & MH, Bangalore, 2 Consultant Physician Columbia Asia
Original Article Late Onset Shake-Etiology At Stake - A Prospective Study G Sendil 1, Arun N Kumar 1, Mohan V Kumar 2 1 Senior Resident, ESIC PGIMSR & MH, Bangalore, 2 Consultant Physician Columbia Asia
ICD-9 to ICD-10 Conversion of Epilepsy
 ICD-9-CM 345.00 Generalized nonconvulsive epilepsy, without mention of ICD-10-CM G40.A01 Absence epileptic syndrome, not intractable, with status G40.A09 Absence epileptic syndrome, not intractable, without
ICD-9-CM 345.00 Generalized nonconvulsive epilepsy, without mention of ICD-10-CM G40.A01 Absence epileptic syndrome, not intractable, with status G40.A09 Absence epileptic syndrome, not intractable, without
Neuromuscular Disease(2) Epilepsy. Department of Pediatrics Soochow University Affiliated Children s Hospital
 Neuromuscular Disease(2) Epilepsy Department of Pediatrics Soochow University Affiliated Children s Hospital Seizures (p130) Main contents: 1) Emphasize the clinical features of epileptic seizure and epilepsy.
Neuromuscular Disease(2) Epilepsy Department of Pediatrics Soochow University Affiliated Children s Hospital Seizures (p130) Main contents: 1) Emphasize the clinical features of epileptic seizure and epilepsy.
AIDS in Africa. An Update. Basil Reekie
 AIDS in Africa An Update Basil Reekie Contents General Statistics The trend of HIV in Africa Ugandan experience UNAIDS 2006 Latest African Statistics by Country HIV Intervention Light at the end of the
AIDS in Africa An Update Basil Reekie Contents General Statistics The trend of HIV in Africa Ugandan experience UNAIDS 2006 Latest African Statistics by Country HIV Intervention Light at the end of the
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 5 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
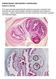 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 5 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 47 year-old male presented with symptoms that were consistent with possible late adult-onset epilepsy (frequent headaches and occasional seizures).
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 5 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 47 year-old male presented with symptoms that were consistent with possible late adult-onset epilepsy (frequent headaches and occasional seizures).
Neurocysticercosis A Journey from Pre-independence to Modern India
 Ann Natl Acad Med Sci (India), 52(2): 76-99, 2016 Neurocysticercosis A Journey from Pre-independence to Modern India Gagandeep Singh, Monika Singla Department of Neurology, Dayanand Medical College and
Ann Natl Acad Med Sci (India), 52(2): 76-99, 2016 Neurocysticercosis A Journey from Pre-independence to Modern India Gagandeep Singh, Monika Singla Department of Neurology, Dayanand Medical College and
Cryptococcal Meningitis
 Cryptococcal Meningitis Dr N Thumbiran Infectious Diseases Department UKZN Index patient 27 year old female Presented to King Edward Hospital on 17/07/2005 with: Severe headaches Vomiting Photophobia X
Cryptococcal Meningitis Dr N Thumbiran Infectious Diseases Department UKZN Index patient 27 year old female Presented to King Edward Hospital on 17/07/2005 with: Severe headaches Vomiting Photophobia X
Management of Epilepsy in Primary Care and the Community. Carrie Burke, Epilepsy Specialist Nurse
 Management of Epilepsy in Primary Care and the Community Carrie Burke, Epilepsy Specialist Nurse Epilepsy & Seizures Epilepsy is a common neurological disorder characterised by recurring seizures (NICE,
Management of Epilepsy in Primary Care and the Community Carrie Burke, Epilepsy Specialist Nurse Epilepsy & Seizures Epilepsy is a common neurological disorder characterised by recurring seizures (NICE,
FORM ID. Patient's Personal Details. SECTION A : Medical Record of the Patient. Name. Policy Number. NRIC/Old IC/Passport/Birth Cert/Others
 CRITICAL ILLNESS CLAIM - DOCTOR'S STATEMENT Brain and Nerve Related Conditions Note: This form is to be completed at the Patient s expense by the Attending Physician/ Surgeon who treated the patient. Patient's
CRITICAL ILLNESS CLAIM - DOCTOR'S STATEMENT Brain and Nerve Related Conditions Note: This form is to be completed at the Patient s expense by the Attending Physician/ Surgeon who treated the patient. Patient's
In our patients the cause of seizures can be broadly divided into structural and systemic causes.
 Guidelines for the management of Seizures Amalgamation and update of previous policies 7 (Seizure guidelines, ND, 2015) and 9 (Status epilepticus, KJ, 2011) Seizures can occur in up to 15% of the Palliative
Guidelines for the management of Seizures Amalgamation and update of previous policies 7 (Seizure guidelines, ND, 2015) and 9 (Status epilepticus, KJ, 2011) Seizures can occur in up to 15% of the Palliative
Ashton Lehmann, Harvard Medical School Year III. Gillian Lieberman, MD
 May, 2012 Ashton Lehmann, Harvard Medical School Year III Our patient presents to ED with acute onset, worsening headache: worst headache of my life Evaluation for subarachnoid hemorrhage with noncontrast
May, 2012 Ashton Lehmann, Harvard Medical School Year III Our patient presents to ED with acute onset, worsening headache: worst headache of my life Evaluation for subarachnoid hemorrhage with noncontrast
Antiepileptics Audit
 Antiepileptics Audit Dr Kate Marley Dr Lucy Potter Dr Melanie Brooks Dr Averil Fountain CNS Sue Croft External Reviewer: Dr A Nicolson Consultant Neurologist c CURRENT GUIDANCE 4.1 GENERAL PRINCIPLES Anti-epileptic
Antiepileptics Audit Dr Kate Marley Dr Lucy Potter Dr Melanie Brooks Dr Averil Fountain CNS Sue Croft External Reviewer: Dr A Nicolson Consultant Neurologist c CURRENT GUIDANCE 4.1 GENERAL PRINCIPLES Anti-epileptic
AIDS at 25. Epidemiology and Clinical Management MID 37
 AIDS at 25 Epidemiology and Clinical Management Blood HIV Transmission transfusion injection drug use Sexual Intercourse heterosexual male to male Perinatal intrapartum breast feeding Regional HIV and
AIDS at 25 Epidemiology and Clinical Management Blood HIV Transmission transfusion injection drug use Sexual Intercourse heterosexual male to male Perinatal intrapartum breast feeding Regional HIV and
Epilepsy: diagnosis and treatment. Sergiusz Jóźwiak Klinika Neurologii Dziecięcej WUM
 Epilepsy: diagnosis and treatment Sergiusz Jóźwiak Klinika Neurologii Dziecięcej WUM Definition: the clinical manifestation of an excessive excitation of a population of cortical neurons Neurotransmitters:
Epilepsy: diagnosis and treatment Sergiusz Jóźwiak Klinika Neurologii Dziecięcej WUM Definition: the clinical manifestation of an excessive excitation of a population of cortical neurons Neurotransmitters:
Antiepileptic agents
 Antiepileptic agents Excessive excitability of neurons in the CNS Abnormal function of ion channels Spread through neural networks Abnormal neural activity leads to abnormal motor activity Suppression
Antiepileptic agents Excessive excitability of neurons in the CNS Abnormal function of ion channels Spread through neural networks Abnormal neural activity leads to abnormal motor activity Suppression
CHILDHOOD OCCIPITAL EPILEPSY OF GASTAUT: A LONG-TERM PROSPECTIVE STUDY
 Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2017, 33: 1175 CHILDHOOD OCCIPITAL EPILEPSY OF GASTAUT: A LONG-TERM PROSPECTIVE STUDY MURAT GÖNEN ¹, EMRAH AYTAǹ, BÜLENT MÜNGEN¹ University of Fırat, Faculty of medicine, Neurology
Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2017, 33: 1175 CHILDHOOD OCCIPITAL EPILEPSY OF GASTAUT: A LONG-TERM PROSPECTIVE STUDY MURAT GÖNEN ¹, EMRAH AYTAǹ, BÜLENT MÜNGEN¹ University of Fırat, Faculty of medicine, Neurology
WHOLE LOTTA SHAKIN GOIN ON
 WHOLE LOTTA SHAKIN GOIN ON ADAM M. YATES, MD FACEP ASSOCIATE CHIEF OF EMERGENCY SERVICES UPMC MERCY SEIZURE DEFINITIONS Partial(focal) only involves part of the brain General Involves entire brain Simple
WHOLE LOTTA SHAKIN GOIN ON ADAM M. YATES, MD FACEP ASSOCIATE CHIEF OF EMERGENCY SERVICES UPMC MERCY SEIZURE DEFINITIONS Partial(focal) only involves part of the brain General Involves entire brain Simple
Pediatrics. Convulsive Disorders in Childhood
 Pediatrics Convulsive Disorders in Childhood Definition Convulsion o A sudden, violent, irregular movement of a limb or of the body o Caused by involuntary contraction of muscles and associated especially
Pediatrics Convulsive Disorders in Childhood Definition Convulsion o A sudden, violent, irregular movement of a limb or of the body o Caused by involuntary contraction of muscles and associated especially
Management of the Fitting Child. Dr Mergan Naidoo
 Management of the Fitting Child Dr Mergan Naidoo Seizures A seizure is a change in movement, attention or level of awareness that is sustained or repetitive and occurs as a result of abnormal neuronal
Management of the Fitting Child Dr Mergan Naidoo Seizures A seizure is a change in movement, attention or level of awareness that is sustained or repetitive and occurs as a result of abnormal neuronal
Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors
 Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors David I. Sandberg, M.D. Director of Pediatric Neurosurgery & Associate Professor Dr. Marnie Rose Professorship in Pediatric Neurosurgery Pre-talk Questions for Audience
Update on Pediatric Brain Tumors David I. Sandberg, M.D. Director of Pediatric Neurosurgery & Associate Professor Dr. Marnie Rose Professorship in Pediatric Neurosurgery Pre-talk Questions for Audience
Research Article Prevalence, Response to Cysticidal Therapy, and Risk Factors for Persistent Seizure in Indian Children with Neurocysticercosis
 Hindawi International Pediatrics Volume 2017, Article ID 8983958, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8983958 Research Article Prevalence, Response to Cysticidal Therapy, and Risk Factors for Persistent
Hindawi International Pediatrics Volume 2017, Article ID 8983958, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8983958 Research Article Prevalence, Response to Cysticidal Therapy, and Risk Factors for Persistent
Single Seizure of Unknown Cause
 S1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Seizures of Unknown Cause 1. Seizure or Epilepsy of Unknown Cause are the classifications used in these medical standards for a probable seizure(s),
S1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Seizures of Unknown Cause 1. Seizure or Epilepsy of Unknown Cause are the classifications used in these medical standards for a probable seizure(s),
Progress Towards the Child Mortality MDG in Urban Sub-Saharan Africa. Nyovani Janet Madise University of Southampton
 Progress Towards the Child Mortality MDG in Urban Sub-Saharan Africa Nyovani Janet Madise University of Southampton United Nations Expert group Meeting on Population Distribution, Urbanization, Internal
Progress Towards the Child Mortality MDG in Urban Sub-Saharan Africa Nyovani Janet Madise University of Southampton United Nations Expert group Meeting on Population Distribution, Urbanization, Internal
David Dredge, MD MGH Child Neurology CME Course September 9, 2017
 David Dredge, MD MGH Child Neurology CME Course September 9, 2017 } 25-40,000 children experience their first nonfebrile seizure each year } AAN/CNS guidelines developed in early 2000s and subsequently
David Dredge, MD MGH Child Neurology CME Course September 9, 2017 } 25-40,000 children experience their first nonfebrile seizure each year } AAN/CNS guidelines developed in early 2000s and subsequently
Clinical characteristics, seizure spread patterns and prognosis of seizures associated with a single small cerebral calcific CT lesion
 Seizure 1998; 7:153-157 Clinical characteristics, seizure spread patterns and prognosis of seizures associated with a single small cerebral calcific CT lesion J. M. K. MURTHY & V. SREENIVAS REDDY Department
Seizure 1998; 7:153-157 Clinical characteristics, seizure spread patterns and prognosis of seizures associated with a single small cerebral calcific CT lesion J. M. K. MURTHY & V. SREENIVAS REDDY Department
CNS Infections in the Pediatric Age Group
 CNS Infections in the Pediatric Age Group Introduction CNS infections are frequently life-threatening In the Philippines, bacterial meningitis is one of the top leading causes of mortality in children
CNS Infections in the Pediatric Age Group Introduction CNS infections are frequently life-threatening In the Philippines, bacterial meningitis is one of the top leading causes of mortality in children
Global Perspective on Epilepsy: Improving Access to Epilepsy Care. Tarun Dua
 Global Perspective on Epilepsy: Improving Access to Epilepsy Care Tarun Dua Why Epilepsy is a Priority? 2 Fight Against Epilepsy 9 Dec 2011 I. Epilepsy: The Burden More than 50 million people with epilepsy
Global Perspective on Epilepsy: Improving Access to Epilepsy Care Tarun Dua Why Epilepsy is a Priority? 2 Fight Against Epilepsy 9 Dec 2011 I. Epilepsy: The Burden More than 50 million people with epilepsy
NEONATAL SEIZURES-PGPYREXIA REVIEW
 NEONATAL SEIZURES-PGPYREXIA REVIEW This is a very important Postgraduate topics will few Q asked in undergraduation also. Lets see them in detail. References: 1.Volpe s Neurology of newborn 2.Nelson s
NEONATAL SEIZURES-PGPYREXIA REVIEW This is a very important Postgraduate topics will few Q asked in undergraduation also. Lets see them in detail. References: 1.Volpe s Neurology of newborn 2.Nelson s
Toxoplasma gondii. Jarmila Kliescikova, MD 1. LF UK
 Toxoplasma gondii Jarmila Kliescikova, MD 1. LF UK Toxoplasma gondii Apicomplexa, Koccidia Obligate intracellular parasite Distribution: cosmopolite Transmission: alimentary transplacentary (transfusions,
Toxoplasma gondii Jarmila Kliescikova, MD 1. LF UK Toxoplasma gondii Apicomplexa, Koccidia Obligate intracellular parasite Distribution: cosmopolite Transmission: alimentary transplacentary (transfusions,
Epilepsy. Presented By: Stan Andrisse
 Epilepsy Presented By: Stan Andrisse What Is Epilepsy Chronic Neurological Disorder Characterized by seizures Young children or elderly Developing countries Famous Cases Socrates Muhammad Aristotle Joan
Epilepsy Presented By: Stan Andrisse What Is Epilepsy Chronic Neurological Disorder Characterized by seizures Young children or elderly Developing countries Famous Cases Socrates Muhammad Aristotle Joan
PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A STRATEGY FOR THE AFRICAN REGION. Information Document CONTENTS
 29 June 2009 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, 31 August 4 September 2009 Provisional agenda item 9.2 PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A
29 June 2009 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, 31 August 4 September 2009 Provisional agenda item 9.2 PROGRESS REPORT ON CHILD SURVIVAL: A
Refractory Seizures. Dr James Edwards EMCORE May 30th 2014
 Refractory Seizures Dr James Edwards EMCORE May 30th 2014 Refractory Seizures Seizures are a common presentation to the ED and some patients will have multiple seizures or have a reduced level of consciousness
Refractory Seizures Dr James Edwards EMCORE May 30th 2014 Refractory Seizures Seizures are a common presentation to the ED and some patients will have multiple seizures or have a reduced level of consciousness
Epilepsy T.I.A. Cataplexy. Nonepileptic seizure. syncope. Dystonia. Epilepsy & other attack disorders Overview
 : Clinical presentation and management Markus Reuber Professor of Clinical Neurology Academic Neurology Unit University of Sheffield, Royal Hallamshire Hospital. Is it epilepsy? Overview Common attack
: Clinical presentation and management Markus Reuber Professor of Clinical Neurology Academic Neurology Unit University of Sheffield, Royal Hallamshire Hospital. Is it epilepsy? Overview Common attack
Spectrum. Quick Start Tutorial
 Spectrum Quick Start Tutorial March 2005 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 What you will learn... 4 Basic Steps in Using Spectrum... 4 Step 1. Installing Spectrum... 4 Step 2. Changing the language in
Spectrum Quick Start Tutorial March 2005 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 What you will learn... 4 Basic Steps in Using Spectrum... 4 Step 1. Installing Spectrum... 4 Step 2. Changing the language in
Anticonvulsants Antiseizure
 Anticonvulsants Antiseizure Seizure disorders Head trauma Stroke Drugs (overdose, withdrawal) Brain tumor Encephalitis/ Meningitis High fever Hypoglycemia Hypocalcemia Hypoxia genetic factors Epileptic
Anticonvulsants Antiseizure Seizure disorders Head trauma Stroke Drugs (overdose, withdrawal) Brain tumor Encephalitis/ Meningitis High fever Hypoglycemia Hypocalcemia Hypoxia genetic factors Epileptic
Talk outline. Some definitions. Emergency epilepsy now what? Recognising seizure types. Dr Richard Perry. Management of status epilepticus
 Emergency epilepsy now what? Dr Richard Perry Imperial College NHS Trust Imperial College Talk outline Recognising seizure types Management of status epilepticus Some definitions Epileptic seizure A clinical
Emergency epilepsy now what? Dr Richard Perry Imperial College NHS Trust Imperial College Talk outline Recognising seizure types Management of status epilepticus Some definitions Epileptic seizure A clinical
2018 American Academy of Neurology
 Practice Guideline Update Efficacy and Tolerability of the New Antiepileptic Drugs I: Treatment of New-Onset Epilepsy Report by: Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of
Practice Guideline Update Efficacy and Tolerability of the New Antiepileptic Drugs I: Treatment of New-Onset Epilepsy Report by: Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of
Review of Anticonvulsant Medications: Traditional and Alternative Uses. Andrea Michel, PharmD, CACP
 Review of Anticonvulsant Medications: Traditional and Alternative Uses Andrea Michel, PharmD, CACP Objectives Review epidemiology of epilepsy Classify types of seizures Discuss non-pharmacologic and pharmacologic
Review of Anticonvulsant Medications: Traditional and Alternative Uses Andrea Michel, PharmD, CACP Objectives Review epidemiology of epilepsy Classify types of seizures Discuss non-pharmacologic and pharmacologic
S E C T I O N. Neurology
 S E C T I O N V Neurology 208 CME 2004 C h a p t e r 2 6 Neurocysticercosis - An Update Prasanta Kumar Gangopadhyay 1, Debasish Guha 2, Tufan Kanti Dolui 3, Sujan Kumar Biswas 3 1 Professor, Department
S E C T I O N V Neurology 208 CME 2004 C h a p t e r 2 6 Neurocysticercosis - An Update Prasanta Kumar Gangopadhyay 1, Debasish Guha 2, Tufan Kanti Dolui 3, Sujan Kumar Biswas 3 1 Professor, Department
AIDS at 30 Epidemiology and Clinical Epidemiology and Management MID 37
 AIDS at 30 Epidemiology and Clinical Management Blood HIV Transmission transfusion injection drug use Sexual Intercourse heterosexual male to male Perinatal intrapartum breast feeding Adults and children
AIDS at 30 Epidemiology and Clinical Management Blood HIV Transmission transfusion injection drug use Sexual Intercourse heterosexual male to male Perinatal intrapartum breast feeding Adults and children
Fertility and Family Planning in Africa: Call for Greater Equity Consciousness
 Fertility and Family Planning in Africa: Call for Greater Equity Consciousness Eliya Msiyaphazi Zulu President, Union for African Population Studies Director of Research, African Population & Health Research
Fertility and Family Planning in Africa: Call for Greater Equity Consciousness Eliya Msiyaphazi Zulu President, Union for African Population Studies Director of Research, African Population & Health Research
Family Planning: Succeeding in Meeting Needs To Make a Better World. Amy Tsui April 12, 2011
 Family Planning: Succeeding in Meeting Needs To Make a Better World Amy Tsui April 12, 2011 Family Planning, One of the Ten Best Public Health Achievements of the 20 th Century and Now Remarkable health
Family Planning: Succeeding in Meeting Needs To Make a Better World Amy Tsui April 12, 2011 Family Planning, One of the Ten Best Public Health Achievements of the 20 th Century and Now Remarkable health
Fungal Meningitis. Stefan Zimmerli Institute for infectious diseases University of Bern Friedbühlstrasse Bern
 Fungal Meningitis Stefan Zimmerli Institute for infectious diseases University of Bern Friedbühlstrasse 51 3010 Bern Death due to infectious diseases in sub-saharan Africa Park BJ. Et al AIDS 2009;23:525
Fungal Meningitis Stefan Zimmerli Institute for infectious diseases University of Bern Friedbühlstrasse 51 3010 Bern Death due to infectious diseases in sub-saharan Africa Park BJ. Et al AIDS 2009;23:525
A Child with Cross Eye. Nia Kurniati
 A Child with Cross Eye Nia Kurniati Background When dealing with new case with potential social problem, complication related to ARV treatment may pose difficulties Restricted resource to address potential
A Child with Cross Eye Nia Kurniati Background When dealing with new case with potential social problem, complication related to ARV treatment may pose difficulties Restricted resource to address potential
When to start, which drugs and when to stop
 When to start, which drugs and when to stop Dr. Suthida Yenjun, MD. PMK Epilepsy Annual Meeting 2016 The main factors to consider in making the decision The risk for recurrent seizures, which varies based
When to start, which drugs and when to stop Dr. Suthida Yenjun, MD. PMK Epilepsy Annual Meeting 2016 The main factors to consider in making the decision The risk for recurrent seizures, which varies based
The causal relationship between neurocysticercosis infection and the development of epilepsy - a systematic review
 Gripper and Welburn Infectious Diseases of Poverty (2017) 6:31 DOI 10.1186/s40249-017-0245-y SCOPING REVIEW Open Access The causal relationship between neurocysticercosis infection and the development
Gripper and Welburn Infectious Diseases of Poverty (2017) 6:31 DOI 10.1186/s40249-017-0245-y SCOPING REVIEW Open Access The causal relationship between neurocysticercosis infection and the development
Epilepsy is the tendency to have repeated seizures that originate in the brain.
 Epilepsy Epilepsy - G40.9 (Clinical term: Epilepsy F25) Presenting complaints Usual presentation is sudden collapse associated with loss of consciousness and a convulsion. A range of phenomena may also
Epilepsy Epilepsy - G40.9 (Clinical term: Epilepsy F25) Presenting complaints Usual presentation is sudden collapse associated with loss of consciousness and a convulsion. A range of phenomena may also
NON MALIGNANT BRAIN TUMOURS Facilitator. Ros Taylor Advanced Neurosurgical Nurse Practitioner Southmead Hospital Bristol
 NON MALIGNANT BRAIN TUMOURS Facilitator Ros Taylor Advanced Neurosurgical Nurse Practitioner Southmead Hospital Bristol Neurosurgery What will be covered? Meningioma Vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma)
NON MALIGNANT BRAIN TUMOURS Facilitator Ros Taylor Advanced Neurosurgical Nurse Practitioner Southmead Hospital Bristol Neurosurgery What will be covered? Meningioma Vestibular schwannoma (acoustic neuroma)
Pure sleep seizures: risk of seizures while awake
 Original article Epileptic Disord 2007; 9 (1): 65-70 Pure sleep seizures: risk of seizures while awake Lorena Benavente Fernández, Javier Salas-Puig Department of Neurology, Hospital Universitario Central
Original article Epileptic Disord 2007; 9 (1): 65-70 Pure sleep seizures: risk of seizures while awake Lorena Benavente Fernández, Javier Salas-Puig Department of Neurology, Hospital Universitario Central
Pre- Travel Case Studies (*with Key Pads)
 Pre- Travel Case Studies (*with Key Pads) Judi Piasecki, RN, BN Dana Male, RN, BN Pam White RN, BN Certificate in Travel Health A. Which year was the first Manitoba Travel Health Conference? 1. 1999 2.
Pre- Travel Case Studies (*with Key Pads) Judi Piasecki, RN, BN Dana Male, RN, BN Pam White RN, BN Certificate in Travel Health A. Which year was the first Manitoba Travel Health Conference? 1. 1999 2.
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION. Control of neurocysticercosis
 WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION FIFTY-SIXTH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A56/10 Provisional agenda item 14.2 6 March 2003 Control of neurocysticercosis Report by the Secretariat BACKGROUND 1. Cysticercosis of the central
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION FIFTY-SIXTH WORLD HEALTH ASSEMBLY A56/10 Provisional agenda item 14.2 6 March 2003 Control of neurocysticercosis Report by the Secretariat BACKGROUND 1. Cysticercosis of the central
Epilepsy. Annual Incidence. Adult Epilepsy Update
 Adult Epilepsy Update Annual Incidence J. Layne Moore, MD, MPH Associate Professor Department of Neurology and Pharmacy Director, Division of Epilepsy The Ohio State University Used by permission Health
Adult Epilepsy Update Annual Incidence J. Layne Moore, MD, MPH Associate Professor Department of Neurology and Pharmacy Director, Division of Epilepsy The Ohio State University Used by permission Health
Parasitic Nervous System Infections Last updated: September 5, 2017
 PARASITIC NERVOUS SYSTEM INFECTIONS Inf11 (1) Parasitic Nervous System Infections Last updated: September 5, 2017 CYSTICERCOSIS... 1 NEUROCYSTICERCOSIS (NCC)... 2 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY, CLINICAL FEATURES...
PARASITIC NERVOUS SYSTEM INFECTIONS Inf11 (1) Parasitic Nervous System Infections Last updated: September 5, 2017 CYSTICERCOSIS... 1 NEUROCYSTICERCOSIS (NCC)... 2 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY, CLINICAL FEATURES...
Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration
 Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration François DABIS with the contribution of Didier Koumavi EKOUEVI INSERM U-897, Bordeaux, France, Programme PACCI, ANRS site, Abidjan, Côte d Ivoire
Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration François DABIS with the contribution of Didier Koumavi EKOUEVI INSERM U-897, Bordeaux, France, Programme PACCI, ANRS site, Abidjan, Côte d Ivoire
ACTH therapy for generalized seizures other than spasms
 Seizure (2006) 15, 469 475 www.elsevier.com/locate/yseiz ACTH therapy for generalized seizures other than spasms Akihisa Okumura a,b, *, Takeshi Tsuji b, Toru Kato b, Jun Natsume b, Tamiko Negoro b, Kazuyoshi
Seizure (2006) 15, 469 475 www.elsevier.com/locate/yseiz ACTH therapy for generalized seizures other than spasms Akihisa Okumura a,b, *, Takeshi Tsuji b, Toru Kato b, Jun Natsume b, Tamiko Negoro b, Kazuyoshi
Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa
 Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa 355 million people at risk for malaria in 215 297 million at high risk A. Parasite prevalence, 215 Funding for malaria increased from US$ 233 million to US$ 262
Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa 355 million people at risk for malaria in 215 297 million at high risk A. Parasite prevalence, 215 Funding for malaria increased from US$ 233 million to US$ 262
Neurology: The pilot, the AME, the FAA. John Hastings CAMA, Greensboro NC September 2017
 Neurology: The pilot, the AME, the FAA John Hastings CAMA, Greensboro NC September 2017 Aviation Safety As AME s and regulators, we have a primary obligation to aviation safety Arguably, we also have an
Neurology: The pilot, the AME, the FAA John Hastings CAMA, Greensboro NC September 2017 Aviation Safety As AME s and regulators, we have a primary obligation to aviation safety Arguably, we also have an
Surgical Neurology International
 Surgical Neurology International OPEN ACCESS For entire Editorial Board visit : http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com Editor: James I. Ausman, MD, PhD University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA Case
Surgical Neurology International OPEN ACCESS For entire Editorial Board visit : http://www.surgicalneurologyint.com Editor: James I. Ausman, MD, PhD University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA Case
of Eectroencephalograms in Paediatrics
 Uti~ity ~An of Eectroencephalograms in Paediatrics iatrics Analysis of 66 Records I H M I Hussain, MRCp, A It Mazidah, MD, Neurology Unit, Paediatric Institute, Hospital Kuala Lumpur Discovered by Hans
Uti~ity ~An of Eectroencephalograms in Paediatrics iatrics Analysis of 66 Records I H M I Hussain, MRCp, A It Mazidah, MD, Neurology Unit, Paediatric Institute, Hospital Kuala Lumpur Discovered by Hans
Defining refractory epilepsy
 Defining refractory epilepsy Pasiri S, PMK Hospital @ 8.30 9.00, 23/7/2015 Nomenclature Drug resistant epilepsy Medically refractory epilepsy Medical intractable epilepsy Pharmacoresistant epilepsy 1 Definition
Defining refractory epilepsy Pasiri S, PMK Hospital @ 8.30 9.00, 23/7/2015 Nomenclature Drug resistant epilepsy Medically refractory epilepsy Medical intractable epilepsy Pharmacoresistant epilepsy 1 Definition
Classification of Seizures. Generalized Epilepsies. Classification of Seizures. Classification of Seizures. Bassel F. Shneker
 Classification of Seizures Generalized Epilepsies Bassel F. Shneker Traditionally divided into grand mal and petit mal seizures ILAE classification of epileptic seizures in 1981 based on clinical observation
Classification of Seizures Generalized Epilepsies Bassel F. Shneker Traditionally divided into grand mal and petit mal seizures ILAE classification of epileptic seizures in 1981 based on clinical observation
Prescribing and Monitoring Anti-Epileptic Drugs
 Prescribing and Monitoring Anti-Epileptic Drugs Mark Granner, MD Clinical Professor and Vice Chair for Clinical Programs Director, Iowa Comprehensive Epilepsy Program Department of Neurology University
Prescribing and Monitoring Anti-Epileptic Drugs Mark Granner, MD Clinical Professor and Vice Chair for Clinical Programs Director, Iowa Comprehensive Epilepsy Program Department of Neurology University
Overview: Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsies
 Epilepsia, 44(Suppl. 2):2 6, 2003 Blackwell Publishing, Inc. 2003 International League Against Epilepsy Overview: Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsies Richard H. Mattson Department of Neurology, Yale University
Epilepsia, 44(Suppl. 2):2 6, 2003 Blackwell Publishing, Inc. 2003 International League Against Epilepsy Overview: Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsies Richard H. Mattson Department of Neurology, Yale University
Review of neurocysticercosis
 Neurosurg Focus 12 (6):Article 1, 2002, Click here to return to Table of Contents Review of neurocysticercosis JULIO SOTELO, M.D., AND OSCAR H. DEL BRUTTO, M.D. National Institute of Neurology and Neurosurgery,
Neurosurg Focus 12 (6):Article 1, 2002, Click here to return to Table of Contents Review of neurocysticercosis JULIO SOTELO, M.D., AND OSCAR H. DEL BRUTTO, M.D. National Institute of Neurology and Neurosurgery,
Journal of Pediatric Sciences
 Journal of Pediatric Sciences Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy for the Diagnosis of Unusual Case of Cystecercal Meningoencephalitis Anita Kumari, Gaurav Mukhija, Ajeet Pratap Singh Journal of Pediatric
Journal of Pediatric Sciences Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy for the Diagnosis of Unusual Case of Cystecercal Meningoencephalitis Anita Kumari, Gaurav Mukhija, Ajeet Pratap Singh Journal of Pediatric
3/16/2018. Disclosures. Learning objectives. Neurosyphilis CNS INFECTIONS: PEARLS AND PERILS. I have no disclosures.
 Disclosures CNS INFECTIONS: PEARLS AND PERILS Felicia Chow, MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Neurology March 16, 2018 I have no disclosures. https://www.intechopen.com/books/novel-aspects-on-cysticercosis-andneurocysticercosis/epilepsy-and-neurocysticercosis-in-sub-saharan-africa
Disclosures CNS INFECTIONS: PEARLS AND PERILS Felicia Chow, MD, MAS Assistant Professor of Neurology March 16, 2018 I have no disclosures. https://www.intechopen.com/books/novel-aspects-on-cysticercosis-andneurocysticercosis/epilepsy-and-neurocysticercosis-in-sub-saharan-africa
Cerebral malaria in children
 Cerebral malaria in children M. Chiara Stefanini Catholic University - Rome Malaria: epidemiology Global distribution of malaria transmission risk,, 2003 World malaria report, WHO, 2005 Estimated incidence
Cerebral malaria in children M. Chiara Stefanini Catholic University - Rome Malaria: epidemiology Global distribution of malaria transmission risk,, 2003 World malaria report, WHO, 2005 Estimated incidence
Prospective Study of Adult Onset Seizure
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. V (April. 2017), PP 46-50 www.iosrjournals.org Prospective Study of Adult Onset Seizure
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 4 Ver. V (April. 2017), PP 46-50 www.iosrjournals.org Prospective Study of Adult Onset Seizure
The Schistosomiasis Control Initiative (SCI) Professor Alan Fenwick
 The Schistosomiasis Control Initiative (SCI) Professor Alan Fenwick Department of Infectious Disease Epidemiology School of Public Health Imperial College (St Mary s campus) Established in 2002 SCI assists
The Schistosomiasis Control Initiative (SCI) Professor Alan Fenwick Department of Infectious Disease Epidemiology School of Public Health Imperial College (St Mary s campus) Established in 2002 SCI assists
Seizure Disorders. Guidelines for assessment of fitness to work as Cabin Crew
 Seizure Disorders Guidelines for assessment of fitness to work as Cabin Crew General Considerations As with all medical guidelines, it is important that each individual case is assessed on its own merits.
Seizure Disorders Guidelines for assessment of fitness to work as Cabin Crew General Considerations As with all medical guidelines, it is important that each individual case is assessed on its own merits.
Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level
 Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level Prerequisites: Any prior pediatric rotations and experience Primary Goals for this
Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level Prerequisites: Any prior pediatric rotations and experience Primary Goals for this
Ernie Somerville Prince of Wales Hospital EPILEPSY
 Ernie Somerville Prince of Wales Hospital EPILEPSY Overview Classification New and old anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) Neuropsychiatric side-effects Limbic encephalitis Non-drug therapies Therapeutic wishlist
Ernie Somerville Prince of Wales Hospital EPILEPSY Overview Classification New and old anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) Neuropsychiatric side-effects Limbic encephalitis Non-drug therapies Therapeutic wishlist
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Neurology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Neurology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing neurological diseases, and in counseling and screening
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Neurology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing neurological diseases, and in counseling and screening
Hepatitis B and C Basics
 Hepatitis B and C Basics What is the liver? The liver is the largest internal organ that performs many important functions. Stores nutrients and vitamins Fights infection Stores energy Removes harmful
Hepatitis B and C Basics What is the liver? The liver is the largest internal organ that performs many important functions. Stores nutrients and vitamins Fights infection Stores energy Removes harmful
Introduction. A difficult dilemma. Historical note. Magnitude of the burden. Overview
 Epilepsy: treatment in developing countries Manjari Tripathi MD ( Dr. Tripathi of All India Institute of Medical Sciences in New Delhi, India, has no relevant financial relationships to disclose. ) John
Epilepsy: treatment in developing countries Manjari Tripathi MD ( Dr. Tripathi of All India Institute of Medical Sciences in New Delhi, India, has no relevant financial relationships to disclose. ) John
Seizures explained. What is a seizure? Triggers for seizures
 Seizures explained What is a seizure? A seizure is a sign of a temporary disruption in the brain s electrical activity. Billions of brain cells pass messages to each other and these affect what we say
Seizures explained What is a seizure? A seizure is a sign of a temporary disruption in the brain s electrical activity. Billions of brain cells pass messages to each other and these affect what we say
Prevalence of Infertility
 Prevalence of Infertility Dr S. Van der Poel focal point for Infertility on behalf of WHO/RHR and HRP Infertility: Primary versus Secondary Primary infertility: inability to become pregnant (or have a
Prevalence of Infertility Dr S. Van der Poel focal point for Infertility on behalf of WHO/RHR and HRP Infertility: Primary versus Secondary Primary infertility: inability to become pregnant (or have a
Is it epilepsy? Does the patient need long-term therapy?
 Is it a seizure? Definition Transient occurrence of signs and/or symptoms due to abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain Is it provoked or unprovoked? Is it epilepsy? Does the
Is it a seizure? Definition Transient occurrence of signs and/or symptoms due to abnormal excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain Is it provoked or unprovoked? Is it epilepsy? Does the
Antiepileptics Audit
 Antiepileptics Audit Dr Kate Marley Dr Lucy Potter Dr Melanie Brooks Dr Averil Fountain CNS Sue Croft External Reviewer: Dr A Nicolson Consultant Neurologist c CURRENT GUIDANCE 4.1 GENERAL PRINCIPLES Anti-epileptic
Antiepileptics Audit Dr Kate Marley Dr Lucy Potter Dr Melanie Brooks Dr Averil Fountain CNS Sue Croft External Reviewer: Dr A Nicolson Consultant Neurologist c CURRENT GUIDANCE 4.1 GENERAL PRINCIPLES Anti-epileptic
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT. G. Tamburrini, Rome
 INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
Epilepsy 7/28/09! Definitions. Classification of epilepsy. Epidemiology of Seizures and Epilepsy. International classification of epilepsies
 Definitions Epilepsy Dr.Yotin Chinvarun M.D., Ph.D. Seizure: the clinical manifestation of an abnormal and excessive excitation of a population of cortical neurons Epilepsy: a tendency toward recurrent
Definitions Epilepsy Dr.Yotin Chinvarun M.D., Ph.D. Seizure: the clinical manifestation of an abnormal and excessive excitation of a population of cortical neurons Epilepsy: a tendency toward recurrent
Epilepsy Syndromes: Where does Dravet Syndrome fit in?
 Epilepsy Syndromes: Where does Dravet Syndrome fit in? Scott Demarest MD Assistant Professor, Departments of Pediatrics and Neurology University of Colorado School of Medicine Children's Hospital Colorado
Epilepsy Syndromes: Where does Dravet Syndrome fit in? Scott Demarest MD Assistant Professor, Departments of Pediatrics and Neurology University of Colorado School of Medicine Children's Hospital Colorado
Epilepsy in a children's hospital: an out-patient survey
 Seizure 1995; 4:279-285 Epilepsy in a children's hospital: an out-patient survey A.P. HUGHES & R.E. APPLETON Roald Dahl E.E.G. Unit, Royal Liverpool Children's NHS Trust Address for correspondence: Dr
Seizure 1995; 4:279-285 Epilepsy in a children's hospital: an out-patient survey A.P. HUGHES & R.E. APPLETON Roald Dahl E.E.G. Unit, Royal Liverpool Children's NHS Trust Address for correspondence: Dr
Stroke in the ED. Dr. William Whiteley. Scottish Senior Clinical Fellow University of Edinburgh Consultant Neurologist NHS Lothian
 Stroke in the ED Dr. William Whiteley Scottish Senior Clinical Fellow University of Edinburgh Consultant Neurologist NHS Lothian 2016 RCP Guideline for Stroke RCP guidelines for acute ischaemic stroke
Stroke in the ED Dr. William Whiteley Scottish Senior Clinical Fellow University of Edinburgh Consultant Neurologist NHS Lothian 2016 RCP Guideline for Stroke RCP guidelines for acute ischaemic stroke
Dr. Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University
 Dr. Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University change in motor activity and/or behaviour due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. seizures in children either - provoked by somatic disorders originating
Dr. Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University change in motor activity and/or behaviour due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. seizures in children either - provoked by somatic disorders originating
CEREBRO VASCULAR ACCIDENTS
 CEREBRO VASCULAR S MICHAEL OPONG-KUSI, DO MBA MORTON CLINIC, TULSA, OK, USA 8/9/2012 1 Cerebrovascular Accident Third Leading cause of deaths (USA) 750,000 strokes in USA per year. 150,000 deaths in USA
CEREBRO VASCULAR S MICHAEL OPONG-KUSI, DO MBA MORTON CLINIC, TULSA, OK, USA 8/9/2012 1 Cerebrovascular Accident Third Leading cause of deaths (USA) 750,000 strokes in USA per year. 150,000 deaths in USA
Keywords. neurocysticercosis, epilepsy, seizures, computed tomography, albendazole, India
 TRANSACTIONS OF THE ROYAL SOCIETY OF TROPICAL MEDICINE AND HYGIENE (2003) 97, 416-421 Neurocysticercosis in children: clinical findings and response to albendazole therapy in a randomized, double-blind,
TRANSACTIONS OF THE ROYAL SOCIETY OF TROPICAL MEDICINE AND HYGIENE (2003) 97, 416-421 Neurocysticercosis in children: clinical findings and response to albendazole therapy in a randomized, double-blind,
Lieven Lagae Department of Paediatric Neurology Leuven University Leuven, Belgium. Management of acute seizure settings from infancy to adolescence
 Lieven Lagae Department of Paediatric Neurology Leuven University Leuven, Belgium Management of acute seizure settings from infancy to adolescence Consequences of prolonged seizures Acute morbidity and
Lieven Lagae Department of Paediatric Neurology Leuven University Leuven, Belgium Management of acute seizure settings from infancy to adolescence Consequences of prolonged seizures Acute morbidity and
