To educate employees that they share in the responsibility for their comfort and prevention of injury.
|
|
|
- Cory Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 It is the County of Fresno's policy to provide its employees with a safe and healthy workplace. This handbook reflects General Industry Safety guidelines for safe workstation arrangements for employees who work at computer workstations. The purpose of this guide is: To educate employees that they share in the responsibility for their comfort and prevention of injury. To increase awareness of how poor work habits and improper posture contribute to muscular discomfort and potential injury. To provide employees with guides and checklist to enable them to arrange and adjust their workstation equipment safely, comfortably and according to established guidelines. To provide employees with exercises that addresses common computer workstation complaints and should help to reduce workstation related injuries. The legal/regulatory authority for these guidelines is based on: Labor Codes 142.3, 6357, 6400, 6401, Management Directive Department Safety Programs Management Directive Ergonomics Title 8, California Code of Regulations, Section 3203, Injury and Illness Prevention Program Section 5110, Repetitive Motion Injuries American National Standards for Human Factors Engineering of Visual Display Work Terminal Workstations (ANSI/HFES ) 2
3 With the increase in the number of injuries that have resulted from work at computer workstations, the County of Fresno has developed this handbook to help enable employees to work more comfortably and to reduce the potential for injury. Ergonomics considers the physical capacities and limits of the employee as he or she interacts with tools, equipment, work methods, job functions and the physical-working environment. By applying ergonomic principles, we can arrive at the best possible fit between our employees, the equipment they use and the work they are required to perform. Proper workstation use, including proper posture and reasonable equipment adjustments, with attention to muscle and eye fatigue, will help prevent musculoskeletal and visual problems. It is every supervisor's responsibility to ensure all employees understand and follow these guidelines. Employees are responsible for adjusting their workstations and their work habits to prevent injury by using this handbook. If employees feel that their workstations are still not set up appropriately, they should contact their immediate supervisor to express their concerns. Department Safety Coordinator: Human Resources - Risk Management Division Stop 188 3
4 STEP 1- Lumbar Support Sit firmly back in the chair. Adjust the lumbar (lower back) support by moving the backrest up or down to match the inward curve of your spine. Adjust the height of the chair so the thighs are parallel to the floor and the feet are flat on the floor TOO LOW BETTER STEP 2- Back Tilt Adjust the tilt of the backrest and/or seat to keep your body supported in an upright position. If this position is not comfortable Caution: Do NOT recline too far back as this will cause lower back discomfort. 4 Adjust the backrest back slightly
5 STEP 3- Arm Adjustment Adjust armrests so that they are slightly below your elbows when your shoulders are relaxed. Too High Shoulder Relaxed STEP 4- Seat Adjustment Try to maintain 2 to 4 inches of clearance between the front edge of your seat pan and the back of your knees. Pull out to make seat pan deeper Push back to make seat pan shallower 5
6 STEP 5- Keyboard Adjustment and Use The keyboard should be positioned at elbow level and your arms should be at a 90 degree angle. Keyboard too high Keyboard too low Good The keyboard tray (if used) should be either in a negative tilt, flat or neutral. NEVER in a positive tilt position. Use a light touch on the keys with fingers straight. Negative Tilt Flat or Neutral Positive Tilt Avoid using the wrist rest on the keyboard or mouse while typing and do not compress the wrists or arms on the edge of the desk or mouse platform on the keyboard tray. Pull the wrist rest and keyboard to the edge of the desk. Wrists should be free floating while typing or mousing. YES! 6
7 STEP 6- Use of Pointing Devices Pointing devices should be used as close as possible to the keyboard and at the same level. Avoid gripping the device with your thumb and pinky fingers. Use small circular motions with the mouse by making arm movements from the shoulder. Use the mid-section of the finger to click versus the fingertip. Wrist position is CRUCIAL! Periodically check your posture. 7
8 STEP 7- Monitor Placement and Adjustment Adjust the monitor so the top of the screen is at or just below eye level with a viewing distance generally between inches. Comfort level may also dictate the distance. Adjust the monitor lower if wearing bifocals, trifocals or progressive lenses. The height of the monitor will be determined once the head and neck are straight. Dual Monitors Good position for non bi/tri focal and progressive glasses use Good position for bi/tri focal and progressive glasses use When using dual monitors and the use of the monitors is equal, the split between the two screens should be centered in front of you. If one monitor is used significantly more than the other, you may position the one that is used more frequently in front of you. 8
9 STEP 8- Document Holder Placement If frequent data entry is performed, use a document holder that places documents at the same height and distance as the monitor or just below in front of the screen to avoid repeated head turning and frequent refocusing. 9
10 Keep your head in line with your shoulders and hips. Keep your elbows close to your body. Keep your wrists in a neutral position, bent no more than 10 degrees up or down. Keep your knees at the same level as your hips or slightly higher. Keep your feet flat on the floor or supported by a footrest if necessary. Keep fingers in a relaxed position when working. Avoid extreme finger extensions. Proper work surface height for reading/writing may be one to two inches higher than that for keyboard typing. DO NOT reach for and remove large binders or files from shelving while seated. Turn to face work materials. DO NOT TWIST YOUR TORSO OR TRUNK while reaching for items. 10
11 Employees are generally most comfortable when they work toward their dominant side. For example, if you are right handed, the right side of your body is going to be the dominant side. Left- Handed Workstation Right- Handed Workstation NO! YES! 11
12 A well-organized and properly arranged workstation can help prevent muscle strain while improving efficiency. Place the telephone on the desktop closest to where you work the most frequently. If it is necessary to write or type while talking, place the phone on your non- dominant side. If you frequently use a telephone while at your computer, consider using a headset or telephone s intercom feature if appropriate. Cradling a receiver on your shoulder contributes to muscle strain and nerve damage. Keep frequently used materials within easy reach. No more than 12 inches for items used several times throughout the day. Occasionally used items should be no more than 20 inches away. Clear the floor under your workstation so you can move your feet and avoid trip hazards. Simple lighting adjustments can help minimize glare and reduce or eliminate eye strain and headaches. Position the screen so it is at a right angle to the window producing the glare. Close shades, curtains, or blinds if necessary, as light changes during the day. If you use a task lamp, position it to aim the light at your document instead of your screen. To improve your viewing comfort, you may also need to adjust your display's contrast and brightness controls. Periodically clean your screen to maximize clarity. Characters on the screen should be clear, stable, and free from perceptible flicker. 12
13 Viewing a computer monitor for long periods can cause visual fatigue and eye strain. Symptoms of visual fatigue are eye irritation, burning or pain, blurring of vision, and double images. Preventive measures should be taken to ensure correct vision for this type of work. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recommends employees have periodic eye examinations. Eye exams are covered under the County of Fresno health plans. Contact lens wearers should blink often to prevent their eyes from becoming dry. Frequent eye breaks are necessary during the workday. Periodically focusing on an object at least twenty feet away will give your eyes a rest. Repetitive Motion Injuries (RMIs) are caused by repeated motions and exertions. The arms and hands are especially vulnerable. The disorders can involve nerves, blood vessels or tendons, which connect muscles to bones. RMI SYMPTOMS Swollen feeling of the fingers, yet no physical evidence of swelling Numbness in the thumb or hand Tingling in the thumb or hand Pain in the fingers or hand Weakness in hand or arm Burning sensation in the hand or arm Weakening of the muscle at the base of the thumb Dry, shiny palms and clumsiness of the affected hand Changes in sensation and power to squeeze things Your workstation should be re-evaluated by you and your supervisor for proper work habits, workstation adjustments, and body posture if you are experiencing any of these symptoms. Your Department Safety Coordinator or Risk Management is also available to provide assistance if the problems persist. 13
14 If you suffer from any of the symptoms of an RMI that you think may be work related, report it to your supervisor. Even the best posture and the most ergonomically correct workstation won't prevent muscular stress and fatigue if you sit for several hours in one position. Breaks from computer work can help keep your eyes, mind, and body refreshed and energized. NIOSH recommends taking a short break every couple of hours of uninterrupted computer work. Check with your supervisor for your break schedule. Experts also suggest brief, frequent "micro-breaks." These breaks are defined as time spent doing something other than work on a computer. They don't involve leaving your workstation. Suggestions include moving around, stretching, doing non-computer tasks, refocusing your eyes, etc. Note: The timing of such micro-breaks is more important than the duration. To be most effective, a break should be taken prior to the onset of fatigue, rather than a means of recuperating from it. Minimizing the use of the mouse whenever possible should be considered. For example, while working with software requiring data to be entered into different fields, can the Tab key be used? Or could the function keys be used to eliminate the extra clicks of the mouse? Having to grasp tightly filed documents frequently can also lead to injury. You may need to consider thinning out files. While grasping thicker files, consider grasping and lifting with both hands. Increased circulation Increased alertness and concentration Improved posture by increasing body awareness Improved potential to prevent and/or eliminate muscle and joint pain Improved potential to prevent RMIs 14
15 Cup Them Lean your elbows on your desk. Cup your hands and place them lightly over your closed eyes. Hold for a minute, while simultaneously breathing deeply in and out. Slowly uncover your eyes. Roll Them Close your eyes and slowly roll your eyeballs clockwise all the way around. Repeat this three times. Slowly roll them all the way around counter-clockwise. Repeat this step three times. Slowly open your eyes away from a direct source of light. Look Away Every 1/2-hour, look away from the computer screen. Focus on an object at least twenty feet away. Look back at the screen, then look away and focus again. Repeat this three times. 15
16 HAND STRETCH Make a fist then extend your fingers as far apart as possible. Hold for about 10 seconds. Relax. Repeat the entire sequence 5-10 times until the hands and fingers feel relaxed. WRIST ROTATION Make a fist and rotate your entire hand (from the wrist) in one direction. Repeat 15 times. Switch directions and repeat 15 times. Then release your hands and with fingers extended, do the same rotations. 16
17 Gently press against table stretching fingers and wrist for five seconds. A. PRONE FLEXOR STRETCH With elbow straight, grasp the middle of the hand and pull back as far as possible. Hold for a 10 count. Release and proceed to B and then back to A, etc. B. PRONE EXTENSOR STRETCH With elbow straight, grasp the back of the hand and pull down as far as possible. Hold for a 10 count. 17
18 Allowing yourself time to do regular stretches can help relieve stiffness and discomfort from desk and computer work and make you feel better in general. Keep in mind key points for the greatest benefit. STOP the specific stretch IMMEDIATELY IF YOU FEEL PAIN; continue stretches that don t cause pain- always stretch only within your comfort zone/limits. IT S BEST TO HAVE YOUR DOCTOR OKAY ANY EXERCISE PROGRAM BEFORE YOU START. Lift the shoulders towards the ears. Hold for 10 seconds then rotate them back and down. Repeat several times. Starting with the head upright, lean it toward a shoulder, hold for seconds. Repeat on the other side. Keep the opposite shoulder down. Rotate the head to one side, then the other. Keep the head upright. Clasp the hands behind the head and push the shoulder blades together. Hold for 20 seconds. Interweave the fingers and push forward. Hold 20 seconds. Lace the fingers and push the palms up. Hold for 20 seconds then slowly release and lower the arms. 18
19 Raise one arm in the air and place the head behind the head. With the other hand, lift elbow slightly and pull the arm back. Keep the head upright. Lace your fingers together behind you. Lift your hands while keeping the upper body upright. Hold for seconds. You can also rotate the hands to the right and left. With your feet about shoulder width apart and your knees bent, place your hands on your lower back. Push to lift your back up and extended it creating length in the entire back. Hold 20 seconds. With a wide stance, face forward with the body upright and the hips squared. Pull toward the front foot. Hold 30 to 45 seconds. Slowly rotate the foot, using support if necessary. Grasp a foot with a hand on the same side. Pull back while keeping upper body erect. Use support if needed. Hold 20 seconds. 19
20 Q: What other activities, in addition to computer work, can cause RMIs? A: Any activity that requires the body to remain in the same position and repeat the same mechanical motion many times. For example: work, such as removing large numbers of staples, chopping, and mechanical work; hobbies, such as gardening, needle work, and making jewelry; and sports, such as tennis, racquetball, golf, baseball. Q: How can I prevent RMIs? A: RMIs can be prevented and/or minimized by taking rest breaks and using proper stretching exercises. Good workspace design can also minimize RMI s. By using this handbook, you should set up your work area and develop habits that create the least amount of resistance to your muscles, nerves and tendons. Report any workstation issues that you cannot correct on your own to your supervisor ASAP! Q: What ergonomic equipment can an employer provide? A: Within financial constraints, an employer can provide: - Adjustable workstations or modular furniture with separate components, such as: keyboard trays, and document holders - Ergonomically designed chairs Q: Who can perform workstation evaluations? A: Your Department Safety Coordinator and/or your functional area/immediate supervisor using these guidelines and the checklists in this handbook. Q: What should I do if I have tried everything in these guidelines and I still have RMI symptoms? A: Discuss the specific problems with your supervisor and your Department Safety Coordinator. If the problems persist, contact the Risk Management Division at for assistance. Q: What non-occupational factors contribute to RMIs? A: The following non-occupational factors contribute to RMIs: - Systemic diseases - Congenital defects - Acute trauma - Pregnancy, oral contraceptives, menopause, and gynecological surgery 20
21 - Vitamin B-6 deficiency - Wrist size, shape, and strength Q: Can carpal tunnel syndrome recur? A: Yes, if you return to unsafe workstations, unsafe work practices, and/or Engage in activities outside of work that may increase your exposure such as various sport activities or hobbies such as needle work or making jewelry. 21
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis
 Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
Courtesy of your source for the best ergonomic office furniture.
 Enjoy this free ergonomic evaluation form courtesy of Get Up Stand Up Desk Co., your online source for the best ergonomic office furniture at the best prices. We hope that this evaluation will help you
Enjoy this free ergonomic evaluation form courtesy of Get Up Stand Up Desk Co., your online source for the best ergonomic office furniture at the best prices. We hope that this evaluation will help you
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every
 According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
Office Ergonomics. Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer
 Office Ergonomics Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer Objectives Define Ergonomics & MSDs Identify Ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up workstations to minimize
Office Ergonomics Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer Objectives Define Ergonomics & MSDs Identify Ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up workstations to minimize
PERSONAL COMPUTER WORKSTATION CHECKLIST
 PERSONAL COMPUTER WORKSTATION CHECKLIST Last Revised: 6/26/17 A. Summary Use the following checklists to assess your own computer workstation. If you say No to any items within the lists, it may indicate
PERSONAL COMPUTER WORKSTATION CHECKLIST Last Revised: 6/26/17 A. Summary Use the following checklists to assess your own computer workstation. If you say No to any items within the lists, it may indicate
OFFICE ERGONOMICS. Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh Ergonomics What is it? Why should I be interested? What do I need to know to help myself? Where can I get help?
OFFICE ERGONOMICS Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh Ergonomics What is it? Why should I be interested? What do I need to know to help myself? Where can I get help?
OFFICE ERGONOMICS SELF-ASSESSMENT
 This self-assessment is designed to assist Coast Community College District employees achieve an ergonomically correct work posture. Through a progressive series of questions and solutions, this program
This self-assessment is designed to assist Coast Community College District employees achieve an ergonomically correct work posture. Through a progressive series of questions and solutions, this program
Ergonomics. Julie W. Burnett, COTA/L, ATP
 Ergonomics Julie W. Burnett, COTA/L, ATP What is Ergonomics? Definition: the Science of designing a person s environment so that it facilitates the highest level of function Good Ergonomics: Prevent Injury
Ergonomics Julie W. Burnett, COTA/L, ATP What is Ergonomics? Definition: the Science of designing a person s environment so that it facilitates the highest level of function Good Ergonomics: Prevent Injury
Setting up Your Home Office
 Setting up Your Home Office The home office is becoming more and more prevalent. Even those who do not work from home on a regular basis have computer workstations set up in the home for personal activities.
Setting up Your Home Office The home office is becoming more and more prevalent. Even those who do not work from home on a regular basis have computer workstations set up in the home for personal activities.
Ergonomics 101. Presented by: Macomb Benefits
 Ergonomics 101 Presented by: Macomb Benefits Today s agenda Learn what ergonomics is and why it s important at Be able to detect early symptoms of problems Have a list of comfort tips and quick fixes to
Ergonomics 101 Presented by: Macomb Benefits Today s agenda Learn what ergonomics is and why it s important at Be able to detect early symptoms of problems Have a list of comfort tips and quick fixes to
Reference Material Searched and Brought to you
 Reference Material Searched and Brought to you by While requesting for additional reference material, always mention Title and Reference of the document. Please ensure you provide your name, company email
Reference Material Searched and Brought to you by While requesting for additional reference material, always mention Title and Reference of the document. Please ensure you provide your name, company email
ERGONOMIC ASSESSMENT TOOL. Eyes
 This tool was designed to provide guidance to perform ergonomic workstation evaluations for computer users. This form will determine how computer users interact with their workstations. Person/Workstation
This tool was designed to provide guidance to perform ergonomic workstation evaluations for computer users. This form will determine how computer users interact with their workstations. Person/Workstation
260- OFFICE ERGONOMICS
 260.1 PURPOSE A. To provide some universally applicable suggestions and procedures that may be helpful when setting up an ergonomically correct work station in an office setting. 260.2 SCOPE A. This procedure
260.1 PURPOSE A. To provide some universally applicable suggestions and procedures that may be helpful when setting up an ergonomically correct work station in an office setting. 260.2 SCOPE A. This procedure
Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design
 PPT Presentation page 1 Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design Presented by the NYS Public Employees Federation Paige Engelhardt PEF Health & Safety Trainer www.pef.org
PPT Presentation page 1 Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design Presented by the NYS Public Employees Federation Paige Engelhardt PEF Health & Safety Trainer www.pef.org
Ergonomics. For additional assistance, contact the Occupational Safety office to schedule an evaluation.
 Ergonomics 1. Purpose: Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Safety and Risk and Risk Management (SRM) developed this program to improve the health and happiness of it s employees by assisting
Ergonomics 1. Purpose: Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Safety and Risk and Risk Management (SRM) developed this program to improve the health and happiness of it s employees by assisting
Beginning of Process: Development of the Office Ergonomics program.
 CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Office Ergonomics Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Office Ergonomics Program Purpose: To provide applicable suggestions and procedures that may be help reduce
CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Office Ergonomics Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Office Ergonomics Program Purpose: To provide applicable suggestions and procedures that may be help reduce
Environmental Health & Safety
 Environmental Health & Safety Roene Fuller Occupational Therapist This guy needs more than a new chair! Socorro General Hospital Objectives What is ergonomics? Occupational risk factors How to sit properly
Environmental Health & Safety Roene Fuller Occupational Therapist This guy needs more than a new chair! Socorro General Hospital Objectives What is ergonomics? Occupational risk factors How to sit properly
OPNAVINST G 30 Dec 05
 Appendix 23-B Computer Workstation Checklist The computer workstation checklist is one method available for performing computer workstation assessments. The checklist is designed to be printed as two double-sided
Appendix 23-B Computer Workstation Checklist The computer workstation checklist is one method available for performing computer workstation assessments. The checklist is designed to be printed as two double-sided
Corporate Safety Manual. Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics
 Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
PURPOSE To provide the tools to set up and maintain a healthy office workspace & environment
 Office Ergonomics PURPOSE To provide the tools to set up and maintain a healthy office workspace & environment WHAT IS A GOOD POSTURE? OFFICE SETUP CHAIR WORK SURFACE INPUT DEVICES MONITOR ACCESSORIES
Office Ergonomics PURPOSE To provide the tools to set up and maintain a healthy office workspace & environment WHAT IS A GOOD POSTURE? OFFICE SETUP CHAIR WORK SURFACE INPUT DEVICES MONITOR ACCESSORIES
Ergonomics Seminar. Presented by Stephanie Materazzi & Christine Miller
 Ergonomics Seminar Presented by Stephanie Materazzi & Christine Miller The muscles in the back are unlike many other muscles in your body. They are almost always in use. They hold your torso in an upright
Ergonomics Seminar Presented by Stephanie Materazzi & Christine Miller The muscles in the back are unlike many other muscles in your body. They are almost always in use. They hold your torso in an upright
Risk Management Department. Office Ergonomics
 Risk Management Department Office 1 Introduction In order to prevent injuries, reduce stress and improve work productivity, APS has developed this training to provide you the knowledge to help yourself
Risk Management Department Office 1 Introduction In order to prevent injuries, reduce stress and improve work productivity, APS has developed this training to provide you the knowledge to help yourself
Work Efficiently and Safely
 Work Efficiently and Safely Workstation Ergonomics 12 July 2017 Working Safely and Efficiently What is Covered? Apply Ergonomic Principles to 3 Develop Good Postures 4 Screen Positioning Guidelines 7 Focusing
Work Efficiently and Safely Workstation Ergonomics 12 July 2017 Working Safely and Efficiently What is Covered? Apply Ergonomic Principles to 3 Develop Good Postures 4 Screen Positioning Guidelines 7 Focusing
Ergonomics Checklist - Computer and General Workstations 1
 Ergonomics Checklist - Computer and General Workstations 1 Information to collect before conducting the Ergonomics Assessment 1. Evaluation Completed by 2. Date 3. Employee Name(s) observed 4. Department
Ergonomics Checklist - Computer and General Workstations 1 Information to collect before conducting the Ergonomics Assessment 1. Evaluation Completed by 2. Date 3. Employee Name(s) observed 4. Department
Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03
 Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03 Working from home is becoming more of an option for employees today. The type of work usually entails working from the home computer work station.
Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03 Working from home is becoming more of an option for employees today. The type of work usually entails working from the home computer work station.
OFFICE WORKSTATION DESIGN
 No matter what industry you work in, computers are commonly used. Extended work with computers can lead to muscular fatigue and discomfort, usually in the back, arms, shoulders and neck. The risk of a
No matter what industry you work in, computers are commonly used. Extended work with computers can lead to muscular fatigue and discomfort, usually in the back, arms, shoulders and neck. The risk of a
Ergonomics. Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques (EOHSS)
 Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents
 Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents Introduction What is Office Ergonomics? 1 Goal of Office Ergonomics 1 What are Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)? 2 MSD Risk Factors 2 Office Ergonomics Guidelines
Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents Introduction What is Office Ergonomics? 1 Goal of Office Ergonomics 1 What are Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)? 2 MSD Risk Factors 2 Office Ergonomics Guidelines
The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
Version February 2016
 Version 3.1 29 February 2016 Health and Safety Unit 1 Table of Contents 1. Setting up your computer workstation... 3 Step 1: Adjusting yourself to the correct height... 3 Step 2 Adjusting your Chair...
Version 3.1 29 February 2016 Health and Safety Unit 1 Table of Contents 1. Setting up your computer workstation... 3 Step 1: Adjusting yourself to the correct height... 3 Step 2 Adjusting your Chair...
Feel Better. Stanford University ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE. USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better.
 Feel Better. PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better. Stanford University Your workspace should respond to your changing needs, helping you eliminate uncomfortable
Feel Better. PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better. Stanford University Your workspace should respond to your changing needs, helping you eliminate uncomfortable
How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck
 OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
Proper Workstation Setup
 Proper Workstation Setup A Step by Step Guide to help you organize your workstation and reduce the risk of injury Step 1 Review Work Habits Working in a stationary position for long periods will increase
Proper Workstation Setup A Step by Step Guide to help you organize your workstation and reduce the risk of injury Step 1 Review Work Habits Working in a stationary position for long periods will increase
Session Objectives. Business & Legal Reports, Inc. 0903
 Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
WORKSTATION ERGONOMICS GUIDE
 Seat Height Office Chair Sit well back into chair with both feet (heels and toes) firmly on the floor Find lever to elevate seat height adjust seat height Lift bottom slightly off chair to elevate - place
Seat Height Office Chair Sit well back into chair with both feet (heels and toes) firmly on the floor Find lever to elevate seat height adjust seat height Lift bottom slightly off chair to elevate - place
Employee Musculoskeletal Discomfort Report (Office) yorku.ca/ergo Revised 2013-Dec-2
 Employee Musculoskeletal Discomfort Report (Office) yorku.ca/ergo Revised 2013-Dec-2 Name: Employee Group/Union: Date: Month/year you started working at York? Month/year you started working at your current
Employee Musculoskeletal Discomfort Report (Office) yorku.ca/ergo Revised 2013-Dec-2 Name: Employee Group/Union: Date: Month/year you started working at York? Month/year you started working at your current
ERGONOMICS. Risk Management
 ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important?
 Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important? No matter how well a workstation is designed, problems may arise if attention is not paid to the way the work is done. Working at a computer
Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important? No matter how well a workstation is designed, problems may arise if attention is not paid to the way the work is done. Working at a computer
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings. ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders. Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
Maine. Video Display Terminal Law. Training Program SAFE345
 Maine Video Display Terminal Law Training Program By the end of this presentation you will be able to: Identify the elements of the law Identify the training requirements Define ergonomics and its benefits
Maine Video Display Terminal Law Training Program By the end of this presentation you will be able to: Identify the elements of the law Identify the training requirements Define ergonomics and its benefits
Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd.
 1523 OFFICE ERGONOMICS TRAINING Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. Structure and Organization Information in this program is presented in a definite order so that employees will see the relationships between
1523 OFFICE ERGONOMICS TRAINING Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. Structure and Organization Information in this program is presented in a definite order so that employees will see the relationships between
Commonwealth Health Corporation NEXT
 Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Choosing the right Office Chair
 Choosing the right Office Chair Choosing the Right Ergonomic Office Chair Working in an office typically involves spending a great deal of time sitting in an office chair a position that adds stress to
Choosing the right Office Chair Choosing the Right Ergonomic Office Chair Working in an office typically involves spending a great deal of time sitting in an office chair a position that adds stress to
HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT CHAIR
 HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT CHAIR ADJ SEAT HEIGHT & BACK: A GOOD SIZED SEAT: GOOD SEAT PADDING: Easy to adjust seat height. Provide a good range of approximately 40-53cm from the floor to the height of the
HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT CHAIR ADJ SEAT HEIGHT & BACK: A GOOD SIZED SEAT: GOOD SEAT PADDING: Easy to adjust seat height. Provide a good range of approximately 40-53cm from the floor to the height of the
OFFICE ERGONOMICS TODAY FACILITATOR S GUIDE
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS TODAY FACILITATOR S GUIDE What s Inside 1 Facilitator s Guidelines 1-a Overview 1-b Getting Started 1-c Presentation Guidelines 1-d Lesson Plan 1-e Frequently Asked Questions 2 Why these
OFFICE ERGONOMICS TODAY FACILITATOR S GUIDE What s Inside 1 Facilitator s Guidelines 1-a Overview 1-b Getting Started 1-c Presentation Guidelines 1-d Lesson Plan 1-e Frequently Asked Questions 2 Why these
Ergonomic Education For Computer Workstations
 Ergonomic Education For Computer Workstations The University of Maryland Baltimore County s (UMBC) on-line ergonomic workstation tutorial is intended to provide you with the knowledge, skills, and educational
Ergonomic Education For Computer Workstations The University of Maryland Baltimore County s (UMBC) on-line ergonomic workstation tutorial is intended to provide you with the knowledge, skills, and educational
The Evolution of Human s? Objectives. Agenda. Defining Ergonomics. History of Ergonomics. Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer.
 Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer The Evolution of Human s? Presented By: Steve Grimmett Ergonomic Consultant Agenda Introduction to Ergonomics Form and Function of the Human Body Ergonomic Issues in
Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer The Evolution of Human s? Presented By: Steve Grimmett Ergonomic Consultant Agenda Introduction to Ergonomics Form and Function of the Human Body Ergonomic Issues in
DSE3 - HINTS AND TIPS: PREVENTING HEALTH PROBLEMS
 DSE3 - HINTS AND TIPS: PREVENTING HEALTH PROBLEMS This Information Sheet provides guidance on how to prevent health problems which may arise as a result of having your display screen equipment set up incorrectly.
DSE3 - HINTS AND TIPS: PREVENTING HEALTH PROBLEMS This Information Sheet provides guidance on how to prevent health problems which may arise as a result of having your display screen equipment set up incorrectly.
CS, IT Occupational Hazard
 CS, IT Occupational Hazard Ergonomics 1 485 patients average age of 38.5 years. 63% females. 70% computer users, 28% musicians, 2% were others engaged in repetitive work. A majority sought care within
CS, IT Occupational Hazard Ergonomics 1 485 patients average age of 38.5 years. 63% females. 70% computer users, 28% musicians, 2% were others engaged in repetitive work. A majority sought care within
Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference.
 Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference. Thank you for your urge to grow and willingness to learn.
Congratulations to the American Association of Electronic Reporters and Transcribers for celebrating the 25th year of their professional conference. Thank you for your urge to grow and willingness to learn.
Your Computer Workstation and Your Office Environment
 WORKPLACE ERGONOMICS Your Computer Workstation and Your Office Environment Your guide to health and comfort at work Can You Answer These Self-Help Questions? How do you adjust your chair for good posture
WORKPLACE ERGONOMICS Your Computer Workstation and Your Office Environment Your guide to health and comfort at work Can You Answer These Self-Help Questions? How do you adjust your chair for good posture
The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person What is Ergonomics? By the end of this chapter, You will be able to: Demonstrate a general knowledge of office ergonomics Identify
OFFICE ERGONOMICS The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person What is Ergonomics? By the end of this chapter, You will be able to: Demonstrate a general knowledge of office ergonomics Identify
Good Working Positions
 Good Working Positions To understand the best way to set up a computer workstation, it is helpful to understand the concept of neutral body positioning. This is a comfortable working posture in which your
Good Working Positions To understand the best way to set up a computer workstation, it is helpful to understand the concept of neutral body positioning. This is a comfortable working posture in which your
The School District of Philadelphia. Ergonomics Program. Ergonomics Program
 The School District of Philadelphia Table of Contents I. Policy II. III. IV. Definitions Procedures a. Accident and Related Data Analysis b. Worksite Analysis c. Hazard Prevention and Control d. Medical
The School District of Philadelphia Table of Contents I. Policy II. III. IV. Definitions Procedures a. Accident and Related Data Analysis b. Worksite Analysis c. Hazard Prevention and Control d. Medical
Workstation Ergonomics Self Assessment
 A well designed workstation can help to reduce the risk of discomfort, pain and injury. Setting up your workstation properly encourages good posture and minimises risk of discomfort and injury. The following
A well designed workstation can help to reduce the risk of discomfort, pain and injury. Setting up your workstation properly encourages good posture and minimises risk of discomfort and injury. The following
Department of Defense Ergonomics Working Group
 Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
15 Minute Desk Workout
 15 Minute Desk Workout Wall Squats Lean your back against a sturdy wall, with your feet planted 1-2 feet in front of you. Bend the knees to squat down and straighten them to push back up. Keep the abs
15 Minute Desk Workout Wall Squats Lean your back against a sturdy wall, with your feet planted 1-2 feet in front of you. Bend the knees to squat down and straighten them to push back up. Keep the abs
Ergonomics: How to set-up your office equipment BAYLOR UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH & SAFETY KEN O CONNOR
 Ergonomics: How to set-up your office equipment BAYLOR UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH & SAFETY KEN O CONNOR KENNETH_OCONNOR@BAYLOR.EDU What is office ergonomics? Ergonomics addresses the
Ergonomics: How to set-up your office equipment BAYLOR UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH & SAFETY KEN O CONNOR KENNETH_OCONNOR@BAYLOR.EDU What is office ergonomics? Ergonomics addresses the
Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc
 Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc Every job or task has unique physical and cognitive demands. Each person has unique physical attributes and abilities. www.prbembodychair.co.uk www.youandyourself.com
Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc Every job or task has unique physical and cognitive demands. Each person has unique physical attributes and abilities. www.prbembodychair.co.uk www.youandyourself.com
Appendix A: Repetitive Motion Injuries (Cal/OSHA Standard)
 20.16.1 Appendix A: Repetitive Motion Injuries (Cal/OSHA Standard) 5110. Repetitive Motion Injuries. (a) Scope and application. This section shall apply to a job, process, operation where a repetitive
20.16.1 Appendix A: Repetitive Motion Injuries (Cal/OSHA Standard) 5110. Repetitive Motion Injuries. (a) Scope and application. This section shall apply to a job, process, operation where a repetitive
ESI Wellness Program The BioSynchronistics Design. Industrial Stretching Guide
 ESI Wellness Program The BioSynchronistics Design Industrial Stretching Guide ESI Wellness The BioSynchronistics Design Industrial Stretching Basics Stretch 2-4 times/day Hold each Stretch for 5 seconds
ESI Wellness Program The BioSynchronistics Design Industrial Stretching Guide ESI Wellness The BioSynchronistics Design Industrial Stretching Basics Stretch 2-4 times/day Hold each Stretch for 5 seconds
WORKPLACE ERGONOMICS
 WORKPLACE ERGONOMICS This handout has the aim of preventing workplace injuries and covers: 1. Workstation tips and design 2. Exercises for rest breaks 3. Work station Set Up Checklists Sit with your bo
WORKPLACE ERGONOMICS This handout has the aim of preventing workplace injuries and covers: 1. Workstation tips and design 2. Exercises for rest breaks 3. Work station Set Up Checklists Sit with your bo
Safety Manual: Ergonomics. February 8, 2017
 Safety Manual: Ergonomics February 8, 2017 Overview 2.0 Ergonomics Introduction This Chapter provides a general overview of issues in the workplace and recommendations for reducing ergonomic injuries.
Safety Manual: Ergonomics February 8, 2017 Overview 2.0 Ergonomics Introduction This Chapter provides a general overview of issues in the workplace and recommendations for reducing ergonomic injuries.
CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY
 CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY POLICY An ergonomics program is a systematic process that communicates information so that adequate and feasible solutions to ergonomic risks can be implemented to improve
CITY OF TURLOCK ERGONOMICS POLICY POLICY An ergonomics program is a systematic process that communicates information so that adequate and feasible solutions to ergonomic risks can be implemented to improve
"LABORATORY ERGONOMICS"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "LABORATORY ERGONOMICS" Part of the "LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES" Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow Outline of Major Points Covered in the "Laboratory Ergonomics"
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "LABORATORY ERGONOMICS" Part of the "LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES" Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow Outline of Major Points Covered in the "Laboratory Ergonomics"
Ergonomic Guidelines for Computer Users Frank Gonzales, CEES, CEAS
 Office Ergonomics Ergonomic Guidelines for Computer Users Frank Gonzales, CEES, CEAS Ergonomics Program Services What other services are provided? Training sessions Office, Industrial (can be specific
Office Ergonomics Ergonomic Guidelines for Computer Users Frank Gonzales, CEES, CEAS Ergonomics Program Services What other services are provided? Training sessions Office, Industrial (can be specific
LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2955 LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2955 LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in
TRAINING PACKAGE DISPLAY SCREEN EQUIPMENT (DSE) Any alphanumeric or graphic display screen, regardless of the display process involved
 TRAINING PACKAGE DISPLAY SCREEN EQUIPMENT (DSE) Any alphanumeric or graphic display screen, regardless of the display process involved Why? To Avoid ACHES AND PAINS - NECK, ARMS, WRISTS, LEGS & BACK (there
TRAINING PACKAGE DISPLAY SCREEN EQUIPMENT (DSE) Any alphanumeric or graphic display screen, regardless of the display process involved Why? To Avoid ACHES AND PAINS - NECK, ARMS, WRISTS, LEGS & BACK (there
The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person What is Ergonomics? By the end of this training program learners will be able to: Demonstrate a general knowledge of office ergonomics
OFFICE ERGONOMICS The Art & Science of Fitting the Work to the Person What is Ergonomics? By the end of this training program learners will be able to: Demonstrate a general knowledge of office ergonomics
A guide to microbreaks with practical exercises
 A guide to microbreaks with practical exercises Why microbreak? To avoid prolonged static postures Ensures a healthy musculoskeletal system Allows stressed body tissues to rest/recover Prolonged sitting,
A guide to microbreaks with practical exercises Why microbreak? To avoid prolonged static postures Ensures a healthy musculoskeletal system Allows stressed body tissues to rest/recover Prolonged sitting,
Regulatory Requirements
 Safe Use of Display Screen Equipment The wide application of display screen equipment (DSE) to improve the quality of work and efficiency are commonly recognized in our daily life such as paper work, data
Safe Use of Display Screen Equipment The wide application of display screen equipment (DSE) to improve the quality of work and efficiency are commonly recognized in our daily life such as paper work, data
COMPUTER WORKSTATION ERGONOMIC SELF-ASSESSMENT
 COMPUTER WORKSTATION ERGONOMIC SELF-ASSESSMENT Name Reason for conducting self- Date Assessed New Starter Injury/Discomfort Relocation New Equipment Other Please detail below: Should a staff member have
COMPUTER WORKSTATION ERGONOMIC SELF-ASSESSMENT Name Reason for conducting self- Date Assessed New Starter Injury/Discomfort Relocation New Equipment Other Please detail below: Should a staff member have
Low Back Pain Home Exercises
 Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Cognitive and Physical Ergonomics of Translation What can we do to make a computer workplace more ergonomic?
 Cognitive and Physical Ergonomics of Translation What can we do to make a computer workplace more ergonomic? Michèle Gasser Ursula Meidert 1 Objectives of the workshop You are able to set up an ergonomic
Cognitive and Physical Ergonomics of Translation What can we do to make a computer workplace more ergonomic? Michèle Gasser Ursula Meidert 1 Objectives of the workshop You are able to set up an ergonomic
"INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
UPPER BODY STANDING 12. March in place (hand to opposite knee) For more intensity raise arms above head if your balance is GOOD. 13.
 LOW IMPACT EXERCISES SITTING 1. Breathe 2. Half circles with head 3. Neck movements (Chin to chest, ear to shoulder) 4. Neck Stretch Sitting in your chair, reach down and grab the side of the chair with
LOW IMPACT EXERCISES SITTING 1. Breathe 2. Half circles with head 3. Neck movements (Chin to chest, ear to shoulder) 4. Neck Stretch Sitting in your chair, reach down and grab the side of the chair with
Practicing Office Ergonomics: or..my Arms Are Too Short!?
 Practicing Office Ergonomics: or..my Arms Are Too Short!? Presented By: Tom Mayfield, CPE Director Ergonomics Programs Evans Incorporated Presentation Background Ergonomic Risk Factors Practicing Office
Practicing Office Ergonomics: or..my Arms Are Too Short!? Presented By: Tom Mayfield, CPE Director Ergonomics Programs Evans Incorporated Presentation Background Ergonomic Risk Factors Practicing Office
THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG LIBRARIES. This book was a gift from. Cheng Kar-Foo, Andrew
 THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG LIBRARIES This book was a gift from Cheng Kar-Foo, Andrew HEALTH HINTS ON COMPUTER WORK This guide is prepared by the Occupational Safety and Health Branch Labour Department
THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG LIBRARIES This book was a gift from Cheng Kar-Foo, Andrew HEALTH HINTS ON COMPUTER WORK This guide is prepared by the Occupational Safety and Health Branch Labour Department
2002 Physioball Supplement
 2002 Physioball Supplement These exercises are not detailed on the 2002 Off-Ice Training video but will be taught in detail during the 2002 Reach for the Stars Seminar. CORE STRENGTH Physioball/ Sport
2002 Physioball Supplement These exercises are not detailed on the 2002 Off-Ice Training video but will be taught in detail during the 2002 Reach for the Stars Seminar. CORE STRENGTH Physioball/ Sport
Carpal tunnel syndrome
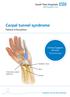 Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Good display screen equipment (DSE) practice
 Health & Safety Services Good display screen equipment (DSE) practice If you normally use a computer for an hour or more a day, then the following guidance is for you Potential health problems Poor DSE
Health & Safety Services Good display screen equipment (DSE) practice If you normally use a computer for an hour or more a day, then the following guidance is for you Potential health problems Poor DSE
Body Bar FLEX. Exercises for the Core and Abdominals. by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc.
 Body Bar FLEX Exercises for the Core and Abdominals by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc. 1 Exercises for the Core and Abdominals This presentation features stretching and strengthening exercises
Body Bar FLEX Exercises for the Core and Abdominals by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc. 1 Exercises for the Core and Abdominals This presentation features stretching and strengthening exercises
Office and Laboratory Ergonomics. WSU-TFREC Safety Training
 Office and Laboratory Ergonomics WSU-TFREC Safety Training What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the scientific study of human work Ergonomic principals adapt work to a specific person by designing tasks &
Office and Laboratory Ergonomics WSU-TFREC Safety Training What is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the scientific study of human work Ergonomic principals adapt work to a specific person by designing tasks &
Computer Workstation Safety Overview. Mike Papakyriakou Occupational Health & Safety (OHS) yorku.ca/ergo
 Computer Workstation Safety Overview Mike Papakyriakou Occupational Health & Safety (OHS) yorku.ca/ergo Phone: 416-736-5491 E-mail: mikepapa@yorku.ca Revised Sep 05, 2013 Musculoskeletal Overuse Injuries
Computer Workstation Safety Overview Mike Papakyriakou Occupational Health & Safety (OHS) yorku.ca/ergo Phone: 416-736-5491 E-mail: mikepapa@yorku.ca Revised Sep 05, 2013 Musculoskeletal Overuse Injuries
Office Ergonomics OSHA Resources. Risk Factors for Developing MSDs taken from OSHA voluntary guidelines. Mary Loughlin, OTR/L,CHT, CEAS
 Office Ergonomics Mary Loughlin, OTR/L,CHT, CEAS OSHA Occupational Safety and Health Administration November 2000 Federal OSHA published the Final Ergonomics Program Standard in the Federal Register. Effective
Office Ergonomics Mary Loughlin, OTR/L,CHT, CEAS OSHA Occupational Safety and Health Administration November 2000 Federal OSHA published the Final Ergonomics Program Standard in the Federal Register. Effective
Office Ergonomics. A Healthy Workstation Guide. Safety Resources
 Office Ergonomics A Healthy Workstation Guide 2017 Safety Resources How to Use this Document: This document provides basic guidelines that will allow you to proactively set up and /or adjust your office
Office Ergonomics A Healthy Workstation Guide 2017 Safety Resources How to Use this Document: This document provides basic guidelines that will allow you to proactively set up and /or adjust your office
It is recommended that a person break for 5-10 minutes for every hour spent at a workstation.
 Office Stretches Why is stretching important? No matter how well a workstation is designed, problems may arise if attention is not paid to the way the work is done. Working at a computer often involves
Office Stretches Why is stretching important? No matter how well a workstation is designed, problems may arise if attention is not paid to the way the work is done. Working at a computer often involves
CBIA Ergonomic Conference Office Environments December 8 th, 2016
 Loss Control & Risk Management Approach to Control Ergonomic Risks CBIA Ergonomic Conference Office Environments December 8 th, 2016 Course Outline Controlling Ergonomics In Office Environments 1. Experience
Loss Control & Risk Management Approach to Control Ergonomic Risks CBIA Ergonomic Conference Office Environments December 8 th, 2016 Course Outline Controlling Ergonomics In Office Environments 1. Experience
BOHS-Series. Series. Ergonomics Training Module
 BOHS-Series Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the
BOHS-Series Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the
Shoulder Exercises. Instructions. Codmans. Do all exercises slowly and gently. Work hard, but stay within your level of comfort.
 Page 1 of 7 Shoulder Exercises Instructions Do all exercises slowly and gently. Work hard, but stay within your level of comfort. Exercises should not cause sharp pain. If you have pain, ease up on the
Page 1 of 7 Shoulder Exercises Instructions Do all exercises slowly and gently. Work hard, but stay within your level of comfort. Exercises should not cause sharp pain. If you have pain, ease up on the
Display Screen Equipment Risk Assessment Workshop
 Display Screen Equipment Risk Assessment Workshop Objectives Hazard Identification Use of HSE checklist Provision of information Drawing conclusions from assessments Risk reduction and control. What is
Display Screen Equipment Risk Assessment Workshop Objectives Hazard Identification Use of HSE checklist Provision of information Drawing conclusions from assessments Risk reduction and control. What is
Low Back Program Exercises
 Low Back Program Exercises Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite
Low Back Program Exercises Exercise 1: Knee to Chest Starting Position: Lie on your back on a table or firm surface. Action: Clasp your hands behind the thigh and pull it towards your chest. Keep the opposite
AMG Transfer Training and Ergonomics
 AMG Transfer Training and Ergonomics Musculoskeletal Disorders Healthcare workers often experience musculoskeletal disorders at a rate exceeding that of workers in construction, mining, and manufacturing.
AMG Transfer Training and Ergonomics Musculoskeletal Disorders Healthcare workers often experience musculoskeletal disorders at a rate exceeding that of workers in construction, mining, and manufacturing.
Ergonomics in the Laboratory
 instrumentation [management/administration and training generalist] Ergonomics in the Laboratory Terry Jo Gile, MT(ASCP)MA Ed From Gile and Associates, St Louis, MO Ergonomic disorders Work-site analysis
instrumentation [management/administration and training generalist] Ergonomics in the Laboratory Terry Jo Gile, MT(ASCP)MA Ed From Gile and Associates, St Louis, MO Ergonomic disorders Work-site analysis
BF X Furniture. Ergonomic Assessment Checklist
 BF X Furniture Ergonomic Assessment Checklist Ergonomic Assessment Checklist We ve put together this ergonomic assessment just for you! Your own comfort and health should be your number one priority. Working
BF X Furniture Ergonomic Assessment Checklist Ergonomic Assessment Checklist We ve put together this ergonomic assessment just for you! Your own comfort and health should be your number one priority. Working
9. Making Changes to Reduce Discomfort & Workstation Settings Revised: October 21, 2013
 9. Making Changes to Reduce Discomfort & Workstation Settings Revised: October 21, 2013 The checklist referred to in this section is the Computer User MSD Prevention Checklist available at the link below
9. Making Changes to Reduce Discomfort & Workstation Settings Revised: October 21, 2013 The checklist referred to in this section is the Computer User MSD Prevention Checklist available at the link below
A Free Tool Box Talk From Safetyphoto
 A Free Tool Box Talk From Safetyphoto The presentation is intentionally in base colour for easy adaptation into your company design but please credit safetyphoto. 1 Display Screen Equipment (DSE) Tool
A Free Tool Box Talk From Safetyphoto The presentation is intentionally in base colour for easy adaptation into your company design but please credit safetyphoto. 1 Display Screen Equipment (DSE) Tool
BOHS-Series. Ergonomics Training Module
 BOHS-Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the science
BOHS-Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the science
It s a fact... Your computer workstation should include a chair that s right for you.
 MARCH 2002 DoD Ergonomics Working Group It s a fact... Your computer workstation should include a chair that s right for you. Most chairs are designed for people weighing no more than 275 pounds. If you
MARCH 2002 DoD Ergonomics Working Group It s a fact... Your computer workstation should include a chair that s right for you. Most chairs are designed for people weighing no more than 275 pounds. If you
BODY MECHANICS CMHA-CEI
 BODY MECHANICS CMHA-CEI Basics about backs Facts about Back Disorders Maintaining a Healthy Back Common activities Lifting Techniques Stretching Techniques Topics Your back Spine & Vertebrae Discs Nerves
BODY MECHANICS CMHA-CEI Basics about backs Facts about Back Disorders Maintaining a Healthy Back Common activities Lifting Techniques Stretching Techniques Topics Your back Spine & Vertebrae Discs Nerves
