R041 Reducing the risk of sports injuries
|
|
|
- Willa Franklin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 R041 Reducing the risk of sports injuries
2 Learning outcome 1 Learners must be taught: extrinsic factors which can influence the risk of injury, i.e. type of activity (e.g. contact sports present different injury risks from gymnastic activities) coaching/supervision, i.e. poor/incorrect coaching techniques ineffective communication skills importance of adhering to rules and regulations environmental factors, i.e. weather playing surface/performance area and surrounding area other participants equipment, i.e.
3 protective equipment (e.g. shin pads in football, gum shield in boxing, helmet in cycling, goggles in skiing) performance equipment (e.g. hockey stick, cricket ball, rock climbing harness) clothing/footwear suitable for playing surface/weather conditions/specific sport or activity safety hazards, i.e. risk assessments safety checks emergency action plans intrinsic factors which can influence the risk of injury, i.e. physical preparation, i.e. training warm up cool down fitness levels overuse muscle imbalances individual variables, i.e. gender age flexibility nutrition sleep previous/recurring injuries
4 psychological factors, i.e. motivation aggression arousal/anxiety levels posture and causes of poor posture, i.e. poor stance/gait (e.g. bending your knees or hunching your shoulders when standing) sitting positions (e.g. slumping/slouching on the sofa rather than sitting upright) physical defects (e.g. muscles weaken around an injured area) lack of exercise (e.g. lack of core muscle strength means less support, being overweight puts strain on posture) fatigue (e.g. tired muscles will be unable to support the skeleton properly) emotional factors (e.g. having low self-esteem/lack of confidence can influence posture) clothing/footwear (e.g. wearing shoes with high heels can affect posture) sports injuries related to poor posture, i.e. pelvic tilt lordosis kyphosis round shoulder scoliosis.
5 Intrinsic injury- can cause injury over something you have control over Extrinsic injury-one which results from factors external to the body Task-for each of the following, decide whether it is intrinsic or extrinsic Type of activity (e.g. contact sports present different injury risks from gymnastic activity). Individual variables, i.e. gender, age, nutrition, flexibility, sleep, previous injury Environmental factors weather, playing surfaces, other participants Safety hazards, i.e. risk assessments (size of group, age), safety checks (equipment, playing surface) Sports injuries caused by poor posture: Round shoulder, scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis, pelvic tilt.
6 Emergency action plans where to go in an emergency. Physical preparation, i.e. Training, warm-up, cool down, fitness levels, overuse of particular muscles Equipment protective equipment, i.e. shin pads in football, gum shield in boxing, helmet in cycling, goggles in skiing). Psychological factors, i.e. motivation, aggression, arousal/anxiety levels. Coaching/supervision (e.g. poor/incorrect coaching techniques, ineffective communication skills, importance of following the rules and regulations). Posture and causes, i.e. poor stance (e.g. bending knees, hunching shoulders when standing), sitting positions (e.g. slumping/slouching on the sofa rather than sitting upright), lack of exercise (e.g. lack of core strength or being overweight which puts a strain on your muscles), clothing and footwear (e.g. high heels)
7 Extrinsic factors Type of activity (e.g. contact sports present different injury risks from gymnastic activity). Coaching/supervision (e.g. poor/incorrect coaching techniques, ineffective communication skills, importance of following the rules and regulations). Environmental factors weather, playing surfaces, other participants Equipment protective equipment, i.e. shin pads in football, gum shield in boxing, helmet in cycling, goggles in skiing). Safety hazards, i.e. risk assessments (size of group, age), safety checks (equipment, playing surface) Emergency action plans where to go in an emergency.
8 Practice Exam Question
9 Practice Exam Question
10 Intrinsic Factors Physical preparation, i.e. Training, warm-up, cool down, fitness levels, overuse of particular muscles Individual variables, i.e. gender, age, nutrition, flexibility, sleep, previous injury Psychological factors, i.e. motivation, aggression, arousal/anxiety levels. Posture and causes, i.e. poor stance (e.g. bending knees, hunching shoulders when standing), sitting positions (e.g. slumping/slouching on the sofa rather than sitting upright), lack of exercise (e.g. lack of core strength or being overweight which puts a strain on your muscles), clothing and footwear (e.g. high heels) Sports injuries caused by poor posture: Round shoulder, scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis, pelvic tilt.
11 Practice Exam Question
12 Practice Exam Question
13
14
15
16 Causes of poor posture poor stance/gait (e.g. bending your knees or hunching your shoulders when standing) sitting positions (e.g. slumping/slouching on the sofa rather than sitting upright) physical defects (e.g. muscles weaken around an injured area) lack of exercise (e.g. lack of core muscle strength means less support, being overweight puts strain on posture) fatigue (e.g. tired muscles will be unable to support the skeleton properly) emotional factors (e.g. having low self-esteem/lack of confidence can influence posture) clothing/footwear (e.g. wearing shoes with high heels can affect posture)
17 Round shoulder-one way to tell if you've got rounded shoulders is to stand in front of a mirror and let your arms hang naturally by your sides. If your knuckles face forward, it may indicate that you have a tight chest and a weak upper back, giving the appearance of rounded shoulders. Scoliosis-sideways curvature of the spine Kyphosis-excessive outward curvature of the spine, causing hunching of the back. Lordosis-excessive inward curvature of the spine. Pelvic tilt is the orientation of the pelvis in respect to the thighbones and the rest of the body. The pelvis can tilt towards the front, back, or either side of the body
18 Learning outcome 2-Understand how appropriate warm up and cool down routines can help to prevent injury Learners must be taught: the physical benefits of a warm up, i.e. warming up muscles/preparing the body for physical activity increase in body temperature increase in heart rate increase in flexibility of muscles and joints increase in pliability of ligaments and tendons increase in blood flow and oxygen to muscles increase in the speed of muscle contraction
19 the psychological benefits of a warm up, i.e. heighten or control arousal levels (e.g. get in the zone or settle nerves) improve concentration/focus increase motivation mental rehearsal key components of a warm up, i.e. pulse raising, i.e. exercises that slowly increase heart rate and body temperature (e.g. jogging, cycling, skipping) mobility, i.e. exercises that take the joints through their full range of movement (ROM) (e.g. arm swings, hip circles) dynamic movements (e.g. change of speed and direction) stretching (e.g. developmental stretches, dynamic stretches linked to sport open and close the gate groin walk) skill rehearsal phase, i.e. rehearsing common movement patterns and skills which will be used in the activity (e.g. dribbling drills for football, passing drills for netball) physical benefits of a cool down, i.e. helps the body s transition back to a resting state gradually lowers heart rate gradually lowers temperature circulates blood and oxygen reduces breathing rate removes waste products such as lactic acid
20 reduces the risk of muscle soreness and stiffness aids recovery by stretching muscles, i.e. lengthening and strengthening muscles for next work-out/use key components of a cool down, i.e. pulse lowering, i.e. exercises which gradually lower heart rate and reduce temperature (e.g. easy movements, light running, stretching) stretching, i.e. maintenance stretches, static stretches (e.g. hamstring stretches) specific needs which a warm up and cool down must consider, i.e. characteristics of the individual/group, i.e. size of group age of participants experience of participants individual fitness levels any medical conditions participants may have suitability as preparation for a particular activity/sport environmental factors (e.g. weather/temperature if outdoors, available facilities).
21 Learning outcome 2 Task 2 Why warm up? Note down all of the different jobs that a warm up should do/the reasons why we warm up. Then transfer it into Column 1 of the table below depending on whether it is a physical benefit or a psychological benefit. Now in Column 2 suggest reasons why/how/in what way each of the reasons listed might reduce the risk of injury and in Column 3 record the possible negative consequences if a warm up does not include any of the aspects highlighted
22 . Reason to/benefit of a warm up How this element could help to reduce the risk of injury Possible negative consequences of not including this element Physical -Body Temp -Heart rate -Sweating -Nerve impulses -Prepare muscles -Blood flow Psychological -Arousal -Mental rehearsal -Motivation -Concentration
23 Understand how appropriate warm up and cool down routines can help to prevent injury. Physical benefits of a warm up: Warming up muscles/preparing the body for physical activity Increase in body temperature Increase in heart rate Increase in flexibility of muscles and joints Increase in pliability of ligaments and tendons Increase in blood flow and oxygen to muscles Increase in the speed of muscle contraction
24 Psychological benefits of a warm up: Heighten or control arousal levels (e.g. get in the zone or settle nerves) Improve concentration/focus Increase motivation Mental rehearsal
25 Key components of a warm up: Pulse raising, i.e. exercises that slowly increase heart rate and body temperature (e.g. jogging, cycling, skipping) Mobility, i.e. exercises that take the joints through their full range of movement (ROM) (e.g. arm swings, hip circles) Dynamic movements (e.g. change of speed and direction) Stretching (e.g. developmental stretches, dynamic stretches linked to sport open and close the gate groin walk) Skill rehearsal phase, i.e. rehearsing common movement patterns and skills which will be used in the activity (e.g. dribbling drills for football, passing drills for netball)
26 Physical benefits of a cool down: Helps the body s transition back to a resting state Gradually lowers heart rate Gradually lowers temperature Circulates blood and oxygen Reduces breathing rate Removes waste products such as lactic acid Reduces the risk of muscle soreness and stiffness Aids recovery by stretching muscles, i.e. lengthening and strengthening muscles for next work-out/use
27 Key components of a cool down: Pulse lowering, i.e. exercises which gradually lower heart rate and reduce temperature (e.g. easy movements, light running, stretching) Stretching, i.e. maintenance stretches, static stretches (e.g. hamstring stretches)
28 Specific needs which a warm up and cool down must consider: Characteristics of the individual/group, i.e. Size of group Age of participants Experience of participants Individual fitness levels Any medical conditions participants may have Suitability as preparation for a particular activity/sport Environmental factors (e.g. weather/temperature if outdoors, available facilities).
29
30 8 mark question Jan 2013
31 Practice Exam Question
32 Practice Exam Question
33 Group leaders-act as scribe and presenter Zak, Callum, Joel, Liam H, James, Tom 1.Physical benefits of a cool down (8) 2.Specific needs which a warm up and cool down must consider (8) 3.Key components of a cool down (2) 4.Key components of a warm up (5) 5.Psychological benefits of a warm up (4) 6.Physical benefits of a warm up (7)
34
35 Learning Outcome 3-Know how to respond to injuries within a sporting context Learners must be taught about: acute and chronic injuries acute injuries, i.e. caused as a result of a sudden trauma to the body (e.g. hard rugby tackle, being hit by a ball) result in immediate pain, and usually swelling with a loss of function chronic injuries, i.e. also known as overuse injuries and are a result of continuous stress on an area (e.g. Achilles tendonitis, shin splints or tennis elbow) these injuries tend to develop gradually over a period of time
36 types, causes and treatment of common sports injuries, i.e. soft tissue injuries, i.e. sprains, strains overuse injuries, i.e. tendonitis, tennis elbow, golfers elbow, shin splints fractures, i.e. open, closed concussion, i.e. signs and symptoms of concussion abrasions, i.e. grazes and cuts contusions, i.e. bruises blisters (e.g. blisters on the foot due to poorly fitting footwear) cramp, i.e. painful sensations caused by muscle contractions or over shortening injuries related to children (e.g. severs diseases, Osgood Schlatter s disease)
37 how to respond to injuries and medical conditions in a sporting context, i.e. SALTAPS on-field assessment routine (See, Ask, Look, Touch, Active, Passive, Strength) R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compress, Elevate) stretching and massage taping, bandaging, splints, slings hot and cold treatments (e.g. heat pack, freeze spray) action plan to respond to injuries and medical conditions in a sporting context i.e. emergency procedures Emergency Action Plans (EAP) in a sporting context: emergency personnel, i.e. first responder, first aider, coach emergency communication, i.e. telephone, emergency numbers, emergency services emergency equipment, i.e. first aid kits, evacuation chair.
38 Know how to respond to injuries within a sporting context Acute and Chronic injuries Acute injuries, i.e. Caused as a result of a sudden trauma to the body (e.g. hard rugby tackle, being hit by a ball) Result in immediate pain, and usually swelling with a loss of function Chronic injuries, i.e. Also known as overuse injuries and are a result of continuous stress on an area (e.g. Achilles tendonitis, shin splints or tennis elbow) These injuries tend to develop gradually over a period of time
39 Demba Ba-Chronic or acute?
40 Liam s blister injury- Chronic or acute?
41 Title Types, causes and treatment of common sports injuries: Acute or Chronic-Two examples of howthey happen in sport Soft tissue injuries, i.e. sprains, strains Overuse injuries, i.e. tendonitis, tennis elbow, golfers elbow, shin splints Fractures, i.e. open, closed Concussion, i.e. signs and symptoms of concussion Abrasions, i.e. grazes and cuts Contusions, i.e. bruises Blisters (e.g. blisters on the foot due to poorly fitting footwear) Cramp, i.e. painful sensations caused by muscle contractions or over shortening Injuries related to children (e.g. severs diseases, Osgood Schlatter s disease)
42
43 How to respond to injuries and medical conditions in a sporting context: SALTAPS on-field assessment routine (See, Ask, Look, Touch, Active, Passive, Strength) R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compress, Elevate) Stretching and massage Taping, bandaging, splints, slings Hot and cold treatments (e.g. heat pack, freeze spray) Action plan to respond to injuries and medical conditions in a sporting context i.e. emergency procedures
44 FIFA Guidance S A L T A P S S is for Stop play if a player goes down. S A L T A P S A is for Ask the player what happened and how they feel. Check facial expressions, and posture (position either standing or lying down). S A L T A P S L is for Look at injured limbs for obvious signs of injury: bleeding, bruising, swelling, deformity. Take the player off if there are significant signs of injury. S A L T A P S T is for Touch the injured site if the player will let you. Gently palpate to find source of pain. If you are unsure, don t touch or move the limb until a qualified person can assess the player. S A L T A P S A is for Active movement: Can the player move the limb, with or without pain? If unable to move take the player off. S A L T A P S P is for Passive movement: If A applies, move the limb/joint to full extent and note reaction. S A L T A P S S is for Strength testing (and play on): Is the player up and running or rather trying to run-it-off? Whatever the case, keep a close eye and take the player off if in doubt.
45 Emergency Action Plans (EAP) in a sporting context: Emergency personnel, i.e. first responder, first aider, coach Emergency communication, i.e. telephone, emergency numbers, emergency services Emergency equipment, i.e. first aid kits, evacuation chair. A good way for learners to appreciate the importance of an Emergency Action Plan is to create their own. You may have a template that they can use or you could follow an example from the internet. Key information that should be on the plan includes: Name and contact details for relevant roles such as first aider etc. Location of fire exits, fire extinguishers etc. Overview of evacuation procedure and muster stations Procedure to follow if the emergency services are required Any other relevant information
46 Practice Exam Questions
47 Practice Exam Questions
48 Practice Exam Questions
49 Learners must be taught: Learning outcome 4-Know how to respond to common medical conditions the symptoms of common medical conditions, i.e. Asthma, i.e. coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, tightness in the chest. Diabetes, i.e. increased thirst, going to the toilet lots, extreme tiredness, and weight loss, differences between Type 1 (insulin-dependent) and Type 2 (non-insulin dependent) Epilepsy, i.e. seizures how to respond to these common medical conditions, i.e. ensure awareness of any participants medical conditions prior to commencing physical activity Asthma, i.e. reassurance, inhaler, emergency services (if needed) Diabetes, i.e. insulin (or glucose) hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar), give the individual sugar (e.g. fruit juice, sugary sweets) Epilepsy, i.e. emergency care plans in place for the individual when to refer the performer on to a professional and how to do so.
50 Fact Condition you think is being described 10 points 5 points 2 points Actual answer (Condition) Points scored
51 Condition: 1 10 point fact 34.1 million Americans have this condition and it kills between 3,500 and 5000 Americans each year 5 point fact Although it can be fatal this condition is easily treated with a range of drugs including Salbutamol 2 point fact This disease makes the sufferers airways swell and narrow making it difficult to breathe ANSWER- ASTHMA Condition: 2 10 point fact This condition develops most often in young people 5 point fact It occurs when the body s immune system attacks cells in the pancreas 2 point fact It is characterised by high blood glucose levels and a complete lack of insulin ANSWER- TYPE 1 DIABETES
52 Condition: 3 10 point fact Develops gradually, most often in middle aged and older adults 5 point fact Obesity is thought to be the primary cause 2 point fact It is characterised by high blood glucose levels due to the body s inability to use insulin efficiently ANSWER-TYPE 2 DIABETES Condition: 4 10 point fact This is actually the catch all name for a group of syndromes 5 point fact The different types include absence, focal, generalised, grand mal and petit mal amongst others 2 point fact Symptoms are due to the disturbance of electrical activity in the brain ANSWER-EPILEPSY
53 Condition: 5 10 point fact Causes are diverse but include atherosclerosis and/or hypertension 5 point fact It is the leading cause of deaths worldwide and poor diet, inactivity and smoking are key risk factors 2 point fact This is a disease that affects the heart, blood vessels or both ANSWER-CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE
54 The symptoms of common medical conditions: Asthma, i.e. coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, tightness in the chest. Diabetes, i.e. increased thirst, going to the toilet lots, extreme tiredness, and weight loss, differences between Type 1 (insulin-dependent) and Type 2 (non-insulin dependent) Epilepsy, i.e. seizures Cardiovascular Disease-This is a disease that affects the heart, blood vessels or both. Causes are diverse but include atherosclerosis and/or hypertension
55 How to respond to these common medical conditions: Ensure awareness of any participants medical conditions prior to commencing physical activity Asthma, i.e. reassurance, inhaler, emergency services (if needed) Diabetes, i.e. insulin (or glucose) hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar), give the individual sugar (e.g. fruit juice, sugary sweets) Epilepsy, i.e. emergency care plans in place for the individual SEIZURE FIRST AID Keep calm, provide reassurance, remove bystanders Keep airway clear, turn on side if possible, nothing in mouth Keep safe, remove objects, do not restrain Time, observe, record what happens Stay with person until recovered from seizure Other care needed:
56 Cardiovascular disease-high blood pressure, overweight, possible heart attack. Call ambulance When to refer the performer on to a professional and how to do so.
57 Practice Exam Questions
58 Practice Exam Questions
R041 Reducing the risk of sports injuries
 R041 Reducing the risk of sports injuries Learning outcome 1 Learners must be taught: extrinsic factors which can influence the risk of injury, i.e. type of activity (e.g. contact sports present different
R041 Reducing the risk of sports injuries Learning outcome 1 Learners must be taught: extrinsic factors which can influence the risk of injury, i.e. type of activity (e.g. contact sports present different
Cambridge National Sport Science. Unit 1: Reducing the Risk of Sports Injuries
 Cambridge National Sport Science Unit 1: Reducing the Risk of Sports Injuries YEAR 10 FINAL EXAM: 11 th January 2019 YEAR 10 FINAL EXAM: 11th January 2019 Written paper 1 hour 60 marks Learners answer
Cambridge National Sport Science Unit 1: Reducing the Risk of Sports Injuries YEAR 10 FINAL EXAM: 11 th January 2019 YEAR 10 FINAL EXAM: 11th January 2019 Written paper 1 hour 60 marks Learners answer
Extrinsic factors which can influence the risk of injury
 Sports Studies Unit RO41 Reducing the risk of Injury Learning Outcome 1: Understand the different Factors that influence the risk of Injury objectives Content Complete and TCEES Type of activity (e.g.
Sports Studies Unit RO41 Reducing the risk of Injury Learning Outcome 1: Understand the different Factors that influence the risk of Injury objectives Content Complete and TCEES Type of activity (e.g.
OCR Sports Science Revision Booklet R041 Name: Teacher:
 OCR Sports Science Revision Booklet R041 Name: Teacher: Environmental Factors Surface/performance area or surrounding area Holes in ground/glass in area/electrical equipment /slippy Temperature / weather
OCR Sports Science Revision Booklet R041 Name: Teacher: Environmental Factors Surface/performance area or surrounding area Holes in ground/glass in area/electrical equipment /slippy Temperature / weather
Sports Science Revision Pack. Overview of the whole exam paper. Please use this as a tick list to follow.
 Sports Science Revision Pack Overview of the whole exam paper. Please use this as a tick list to follow. Learning Outcome 1: Understand different factors which influence the risk of injury 2 Risk of Injury
Sports Science Revision Pack Overview of the whole exam paper. Please use this as a tick list to follow. Learning Outcome 1: Understand different factors which influence the risk of injury 2 Risk of Injury
Injuries in sport UV30578 Y/601/4998 VRQ. Learner name: Learner number:
 Injuries in sport Y/601/4998 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy and Sport and Active Leisure sectors, with
Injuries in sport Y/601/4998 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy and Sport and Active Leisure sectors, with
Injuries in sport UV21534 M/601/4330 VRQ. Learner name: Learner number:
 Injuries in sport UV21534 M/601/4330 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality and Catering and Sport
Injuries in sport UV21534 M/601/4330 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality and Catering and Sport
Cambridge National Sport Science. Mark Scheme for January Unit R041: Reducing the risk of sports injuries. Level 1/Level 2
 Cambridge National Sport Science Unit R04: Reducing the risk of sports injuries Level /Level 2 Mark Scheme for January 204 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading
Cambridge National Sport Science Unit R04: Reducing the risk of sports injuries Level /Level 2 Mark Scheme for January 204 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading
Friday 13 January 2017 Afternoon
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Friday 13 January 2017 Afternoon LEVEL 1/2 CAMBRIDGE NATIONAL IN SPORT SCIENCE R041/01 Reducing the risk of sports injuries *5197485478* Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Friday 13 January 2017 Afternoon LEVEL 1/2 CAMBRIDGE NATIONAL IN SPORT SCIENCE R041/01 Reducing the risk of sports injuries *5197485478* Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT
 UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT Every year, millions of teenagers participate in high school sports. An injury to a high school athlete can be a significant disappointment for the teen,
UNIT 2.- SPORT INJURIES: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT Every year, millions of teenagers participate in high school sports. An injury to a high school athlete can be a significant disappointment for the teen,
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 2 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 2 Physical preparation and readiness for sport and physical activity T/615/2385 Guided learning hours: 30 Version 1 September 2016
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 2 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 2 Physical preparation and readiness for sport and physical activity T/615/2385 Guided learning hours: 30 Version 1 September 2016
AMERICAN RED CROSS FIRST AID RESPONDING TO EMERGENCIES FOURTH EDITION Copyright 2006 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved.
 Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash)
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 17 Sports injuries and rehabilitation T/507/4468 Guided learning hours: 60 Version 4 - revised September 2018 *changes indicated
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 17 Sports injuries and rehabilitation T/507/4468 Guided learning hours: 60 Version 4 - revised September 2018 *changes indicated
Unit 1 The Human Body in Motion AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM WORK TO PRODUCE MOVEMENT?
 Unit 1 The Human Body in Motion AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM WORK TO PRODUCE MOVEMENT? Acute and Chronic Injuries of the Musculoskeletal System AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
Unit 1 The Human Body in Motion AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM WORK TO PRODUCE MOVEMENT? Acute and Chronic Injuries of the Musculoskeletal System AREA OF STUDY 1 - HOW DOES THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
UNIT 2. THE IMPORTANCE OF CORRECT POSTURE
 UNIT 2. THE IMPORTANCE OF CORRECT POSTURE 1. WHY IS POSTURE IMPORTANT? The term posture is used to describe how your body is positioned when you're sitting, standing and lying down. Proper posture is important
UNIT 2. THE IMPORTANCE OF CORRECT POSTURE 1. WHY IS POSTURE IMPORTANT? The term posture is used to describe how your body is positioned when you're sitting, standing and lying down. Proper posture is important
Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life.
 Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life. You can find the time to be active. Set aside one block of time every day to be active. When can you set aside 20 to 30 minutes to do an activity you like?
Session 3 or 6: Being Active: A Way of Life. You can find the time to be active. Set aside one block of time every day to be active. When can you set aside 20 to 30 minutes to do an activity you like?
Musculoskeletal Injuries
 Musculoskeletal Injuries KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the four main structures of the musculoskeletal system. 2. List five common signs or symptoms of musculoskeletal injuries. 3. List seven signs
Musculoskeletal Injuries KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the four main structures of the musculoskeletal system. 2. List five common signs or symptoms of musculoskeletal injuries. 3. List seven signs
Hip Strains. Anyone can experience a hip strain just doing everyday tasks, but strains most often occur during sports activities.
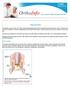 Hip Strains A hip strain occurs when one of the muscles supporting the hip joint is stretched beyond its limit or torn. Strains may be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of the injury.
Hip Strains A hip strain occurs when one of the muscles supporting the hip joint is stretched beyond its limit or torn. Strains may be mild, moderate, or severe, depending on the extent of the injury.
Everything. You Should Know. About Your Ankles
 Everything You Should Know About Your Ankles How Your Ankle Works The ankle joint is a hinge type joint that participates in movement and is involved in lower limb stability. There are 2 types of motions
Everything You Should Know About Your Ankles How Your Ankle Works The ankle joint is a hinge type joint that participates in movement and is involved in lower limb stability. There are 2 types of motions
ACTIVITY TYPE. Stretching COACHING RESOURCE
 ACTIVITY TYPE Stretching 161 Stretching, Warm-up and Cool-down A regular stretching, warm-up and cool-down routine is an essential component of any athlete s program no matter what their age or competition
ACTIVITY TYPE Stretching 161 Stretching, Warm-up and Cool-down A regular stretching, warm-up and cool-down routine is an essential component of any athlete s program no matter what their age or competition
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 17 Sports injuries and rehabilitation T/507/4468 Guided learning hours: 60 Version 3 - revised September 2016 *changes indicated
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 17 Sports injuries and rehabilitation T/507/4468 Guided learning hours: 60 Version 3 - revised September 2016 *changes indicated
Injury Recovery and Prevention. ~Joshua Bowen
 Injury Recovery and Prevention ~Joshua Bowen Injury and Warming up Playing sports as an athlete competitively or just for fun can often lend itself to injuries, sometimes minor and sometimes serious. Like
Injury Recovery and Prevention ~Joshua Bowen Injury and Warming up Playing sports as an athlete competitively or just for fun can often lend itself to injuries, sometimes minor and sometimes serious. Like
Hamstring Strain. 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) Website: philip-bayliss.com.
 43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Hamstring Strain The hamstring muscles are very susceptible to tears, strains and other common sporting
43 Thames Street, St Albans, Christchurch 8013 Phone: (03) 356 1353. Website: philip-bayliss.com Hamstring Strain The hamstring muscles are very susceptible to tears, strains and other common sporting
Warm Up. What do you think the difference is between exercise and physical fitness?
 Warm Up What do you think the difference is between exercise and physical fitness? Physical Fitness Chapter 4 Lesson 1: The Parts of Fitness Physical Fitness vs. Exercise Physical Fitness is the ability
Warm Up What do you think the difference is between exercise and physical fitness? Physical Fitness Chapter 4 Lesson 1: The Parts of Fitness Physical Fitness vs. Exercise Physical Fitness is the ability
Cambridge National Sport Science. Mark Scheme for January Unit R041: Reducing the risk of sports injuries. Level 1/Level 2
 Cambridge National Sport Science Unit R041: Reducing the risk of sports injuries Level 1/Level 2 Mark Scheme for January 2018 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading
Cambridge National Sport Science Unit R041: Reducing the risk of sports injuries Level 1/Level 2 Mark Scheme for January 2018 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading
PE Assessment Point 2 Revision booklet
 PE Assessment Point 2 Revision booklet Assessment point 2 PE assessment Theory Practical Theory Topics Locations of major bones Functions of the skeletal system Aerobic and anaerobic Warm ups and cool
PE Assessment Point 2 Revision booklet Assessment point 2 PE assessment Theory Practical Theory Topics Locations of major bones Functions of the skeletal system Aerobic and anaerobic Warm ups and cool
Injury Prevention: Quadriceps Contusion (cork thigh)
 Injury Prevention: Quadriceps Contusion (cork thigh) Quadriceps contusion or a cork thigh, as it is commonly known, is the result of a severe impact to the thigh which consequently compresses against the
Injury Prevention: Quadriceps Contusion (cork thigh) Quadriceps contusion or a cork thigh, as it is commonly known, is the result of a severe impact to the thigh which consequently compresses against the
Physiotherapist's Guide to Elbow Fracture
 Physiotherapist's Guide to Elbow Fracture An elbow fracture is a bone break that occurs in the middle of the arm, in the area of the elbow joint. Its main cause is trauma, such as falling on the elbow,
Physiotherapist's Guide to Elbow Fracture An elbow fracture is a bone break that occurs in the middle of the arm, in the area of the elbow joint. Its main cause is trauma, such as falling on the elbow,
Part A: Running. Max 5 mins. Slow run forwards 5m and return x 2. Hip out x 2. Hip in x 2. Heel Flicks x 2
 Part A: Running. Max 5 mins. Slow run forwards 5m and return x 2 Jog straight to the 20m line. Make sure you keep your upper body straight. Your hip, knee and foot are aligned. Do not let your knee buckle
Part A: Running. Max 5 mins. Slow run forwards 5m and return x 2 Jog straight to the 20m line. Make sure you keep your upper body straight. Your hip, knee and foot are aligned. Do not let your knee buckle
Hockey Canada. 8.0 Injury Prevention Techniques. 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning
 8.0 Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they are physically fit. In addition, well conditioned athletes
8.0 Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they are physically fit. In addition, well conditioned athletes
Common Sports Injuries 1. Ankle Sprain Prevention:
 Common Sports Injuries This guide is intended to help coaches treat, prevent, and speed recovery in their athletes. The most common 10 injuries are covered below. They include ankle sprain, groin pull,
Common Sports Injuries This guide is intended to help coaches treat, prevent, and speed recovery in their athletes. The most common 10 injuries are covered below. They include ankle sprain, groin pull,
Wellness 360 Online Nutrition Counseling* Session 6: Being Active A Way of Life
 Wellness 360 Online Nutrition Counseling* Session 6: Being Active A Way of Life. powered by WELLSTAR 360 Session 6: Overview Be Active It s Your Choice! This session focuses on how to become more physically
Wellness 360 Online Nutrition Counseling* Session 6: Being Active A Way of Life. powered by WELLSTAR 360 Session 6: Overview Be Active It s Your Choice! This session focuses on how to become more physically
INJURY PREVENTION TECHNIQUES
 Hockey Canada Safety Program Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning INJURY PREVENTION TECHNIQUES It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they
Hockey Canada Safety Program Injury Prevention Techniques 8.1 General Principles of Conditioning INJURY PREVENTION TECHNIQUES It is a well known fact that athletes are less likely to be injured when they
Heat Injuries caoches should be aware of...4
 Coaches Handbook 2018 Part D Items that don't relate directly to coaching but are things a coach needs to know - Injuries/first aid - Table of Contents Overview...2 Care and prevention of injuries...2
Coaches Handbook 2018 Part D Items that don't relate directly to coaching but are things a coach needs to know - Injuries/first aid - Table of Contents Overview...2 Care and prevention of injuries...2
Hey Coach! I m Injured! Top 10 Injuries To Recognize Brent George, MPT CEO G4 Athlete
 Hey Coach! I m Injured! Top 10 Injuries To Recognize Brent George, MPT CEO G4 Athlete WIAA, Yakima July 27, 2013 Contents 3.The front lines 12...The reality 14...The sports we play 18...The epidemic 29...It
Hey Coach! I m Injured! Top 10 Injuries To Recognize Brent George, MPT CEO G4 Athlete WIAA, Yakima July 27, 2013 Contents 3.The front lines 12...The reality 14...The sports we play 18...The epidemic 29...It
First Aid Policy. One member of every coaching staff (competitive) is "required" to be first aid certified.
 First Aid Policy When you accept the role of coach with LSSC, regardless of what level, you accept a major responsibility for the care and safety of your players. Although the athletes share in the responsibility
First Aid Policy When you accept the role of coach with LSSC, regardless of what level, you accept a major responsibility for the care and safety of your players. Although the athletes share in the responsibility
Stretching. Knees: Rotate your knees in a circle, keeping them together and bending down slightly.
 Stretching Stretching the Major Muscle Groups Static Stretches Hamstrings: Hang down and try to reach your toes; don t push it. Keep legs and back straight. Just go down to a comfortable level for your
Stretching Stretching the Major Muscle Groups Static Stretches Hamstrings: Hang down and try to reach your toes; don t push it. Keep legs and back straight. Just go down to a comfortable level for your
Acute Lower Back Pain. Physiotherapy department
 Acute Lower Back Pain Physiotherapy department Back pain is a common condition and in the UK it affects 7 out of 10 people at some point in their lives. Back pain can be very uncomfortable but it is not
Acute Lower Back Pain Physiotherapy department Back pain is a common condition and in the UK it affects 7 out of 10 people at some point in their lives. Back pain can be very uncomfortable but it is not
Hidden Injuries. by Shari Feu. Prevent joint and muscle damage
 Hidden Injuries Prevent joint and muscle damage by Shari Feu A few simple preventive strategies can prevent exercise-related injury and promote joint and muscle health. Exercise-related injuries are sneaky
Hidden Injuries Prevent joint and muscle damage by Shari Feu A few simple preventive strategies can prevent exercise-related injury and promote joint and muscle health. Exercise-related injuries are sneaky
An overview of posture
 An overview of posture What is posture? Posture is the description of an overall body position. This can be intentional or unintentional how we are hold our bodies, but it is the way each individual will
An overview of posture What is posture? Posture is the description of an overall body position. This can be intentional or unintentional how we are hold our bodies, but it is the way each individual will
SPORTS INJURIES IN CYCLING. dr. Luthfi Hidayat, Sp. OT (K)
 SPORTS INJURIES IN CYCLING dr. Luthfi Hidayat, Sp. OT (K) But, injury can happen Acute traumatic injuries due to fall Overuse injuries develop gradually overtime (due to repeated movement patterns or
SPORTS INJURIES IN CYCLING dr. Luthfi Hidayat, Sp. OT (K) But, injury can happen Acute traumatic injuries due to fall Overuse injuries develop gradually overtime (due to repeated movement patterns or
INDEX DR. NICK MARTICHENKO BIO NOTES INTRODUCTION APPLICATIONS AND SOLUTIONS THAT WILL ALLOW YOU TO PLAY BETTER, LONGER AND MORE OFTEN
 01 03 03 05 07 09 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 28 29 INTRODUCTION NOTES INDEX APPLICATIONS AND SOLUTIONS THAT WILL ALLOW YOU TO PLAY BETTER, LONGER AND MORE OFTEN Elbow - Improve wrist range of motion and decreased
01 03 03 05 07 09 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25 28 29 INTRODUCTION NOTES INDEX APPLICATIONS AND SOLUTIONS THAT WILL ALLOW YOU TO PLAY BETTER, LONGER AND MORE OFTEN Elbow - Improve wrist range of motion and decreased
Cambridge National Sport Science. Mark Scheme for June Unit R041: Reducing the risk of sports injuries. Level 1/Level 2
 Cambridge National Sport Science Unit R041: Reducing the risk of sports injuries Level 1/Level 2 Mark Scheme for June 2016 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading
Cambridge National Sport Science Unit R041: Reducing the risk of sports injuries Level 1/Level 2 Mark Scheme for June 2016 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Examinations OCR (Oxford Cambridge and RSA) is a leading
STAYING FIT & ON THE PITCH
 STAYING FIT & ON THE PITCH For Hockey Players The nature of field hockey puts extraordinary amounts of strain on the body and as a result injury is common, particularly when you fatigue during a game or
STAYING FIT & ON THE PITCH For Hockey Players The nature of field hockey puts extraordinary amounts of strain on the body and as a result injury is common, particularly when you fatigue during a game or
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education Prevention of Injury These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
KS4 Physical Education Prevention of Injury These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
MEDICAL CONDITIONS INFORMATION + QUIZ
 MEDICAL CONDITIONS INFORMATION + QUIZ Information to help answer questions Medical conditions include such pre-existing conditions as asthma, epilepsy and diabetes, severe allergic reactions. For an outdoor
MEDICAL CONDITIONS INFORMATION + QUIZ Information to help answer questions Medical conditions include such pre-existing conditions as asthma, epilepsy and diabetes, severe allergic reactions. For an outdoor
BASIC MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND TREND CONCEPTS IN SPORTS INJURIES
 BASIC MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND TREND CONCEPTS IN SPORTS INJURIES 1 RUCHIKA SHARMA 2 DR. MANDEEP SINGH 1 Physical Education Teacher, Department of Youth Services And Sports, J&K, India 2 Department of Higher
BASIC MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND TREND CONCEPTS IN SPORTS INJURIES 1 RUCHIKA SHARMA 2 DR. MANDEEP SINGH 1 Physical Education Teacher, Department of Youth Services And Sports, J&K, India 2 Department of Higher
OV United Soccer Club
 Preventing disease transmission Place an effective barrier between you and the victim s blood when you give first aid. Examples of such barriers are: the victim s hand, a piece of plastic, clean folded
Preventing disease transmission Place an effective barrier between you and the victim s blood when you give first aid. Examples of such barriers are: the victim s hand, a piece of plastic, clean folded
Hip Pain. Anatomy of the hip
 Hip Pain Anatomy of the hip The hip is a ball and socket joint, the ball is on the head of femur (the top of the thigh bone) and the socket (acetabulum) is a part of the pelvis. It s surrounded by tendons
Hip Pain Anatomy of the hip The hip is a ball and socket joint, the ball is on the head of femur (the top of the thigh bone) and the socket (acetabulum) is a part of the pelvis. It s surrounded by tendons
Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries. Emergency Reference Guide p
 Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries Emergency Reference Guide p. 33-43 Objectives Define strain, sprain, fracture and dislocation List Signs & Symptoms of strain, sprain, fracture & dislocation Demonstrate
Lesson 9: Bone & Joint Injuries Emergency Reference Guide p. 33-43 Objectives Define strain, sprain, fracture and dislocation List Signs & Symptoms of strain, sprain, fracture & dislocation Demonstrate
Strength, any two: curl-ups/crunches, push-ups, step-ups; heart and lung endurance, any two:
 Chapter 3 Study Guide Study Tips Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
Chapter 3 Study Guide Study Tips Read the chapter objectives. Look up any unfamiliar words. Read the questions below before you read the chapter. As you read the chapter, answer the following questions.
First Aid in Agriculture
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health First Aid in Agriculture Mario works at Orange Peel Farm. His job is to bend over, pick up boxes of oranges, and place the boxes on a truck. A
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health First Aid in Agriculture Mario works at Orange Peel Farm. His job is to bend over, pick up boxes of oranges, and place the boxes on a truck. A
 SPORTS MEDICINE CONCEPT Sports medicinespecializes in preventing, diagnosing and treating injuries related to participation in sports and/or exercise, specifically the rotation or deformation of joints
SPORTS MEDICINE CONCEPT Sports medicinespecializes in preventing, diagnosing and treating injuries related to participation in sports and/or exercise, specifically the rotation or deformation of joints
SSA Player Injury Prevention and Care Guide
 SSA Player Injury Prevention and Care Guide Prevention of Injuries The first line of defense in the treatment of athletic injuries is to prevent them. There are a variety of ways to accomplish this: 1.
SSA Player Injury Prevention and Care Guide Prevention of Injuries The first line of defense in the treatment of athletic injuries is to prevent them. There are a variety of ways to accomplish this: 1.
Falls Prevention Strength & Balance Programme Exercise Booklet
 Falls Prevention Strength & Balance Programme Exercise Booklet Working together to prevent falls This booklet describes the exercises which form the strength and balance component of the Trust falls prevention
Falls Prevention Strength & Balance Programme Exercise Booklet Working together to prevent falls This booklet describes the exercises which form the strength and balance component of the Trust falls prevention
Module Summaries: The emergency plan is a crucial part of the total sports program.
 Module Summaries: Summary - The Emergency Plan The emergency plan is a crucial part of the total sports program. Prior to each season and game, those individuals responsible for the program and athletes
Module Summaries: Summary - The Emergency Plan The emergency plan is a crucial part of the total sports program. Prior to each season and game, those individuals responsible for the program and athletes
Static Flexibility/Stretching
 Static Flexibility/Stretching Points of Emphasis Always stretch before and after workouts. Stretching post-exercise will prevent soreness and accelerate recovery. Always perform a general warm-up prior
Static Flexibility/Stretching Points of Emphasis Always stretch before and after workouts. Stretching post-exercise will prevent soreness and accelerate recovery. Always perform a general warm-up prior
Football First Aid: An Overview. Steven Richmond 95# Commissioner --BRYC Firefighter II, EMT-B, HTR & HZMT Tech City of Alexandria Fire and EMS
 Football First Aid: An Overview Steven Richmond 95# Commissioner --BRYC Firefighter II, EMT-B, HTR & HZMT Tech City of Alexandria Fire and EMS Overview Hyperthermia (Heat Related Injuries) Concussions
Football First Aid: An Overview Steven Richmond 95# Commissioner --BRYC Firefighter II, EMT-B, HTR & HZMT Tech City of Alexandria Fire and EMS Overview Hyperthermia (Heat Related Injuries) Concussions
RETURN TO SPORT PROTOCOL CO.RE
 RETURN TO SPORT PROTOCOL CO.RE WHO CAN USE THIS PROGRAM This protocol is designed as a return to sport program following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction but applies equally well to rehabilitation
RETURN TO SPORT PROTOCOL CO.RE WHO CAN USE THIS PROGRAM This protocol is designed as a return to sport program following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction but applies equally well to rehabilitation
Lesson 7.2. Benefits of Flexibility
 Lesson 7.2 Benefits of Flexibility Student Learning Objectives After completing this lesson you will be able to explain how good flexibility improves your health, wellness, and fitness; name some good
Lesson 7.2 Benefits of Flexibility Student Learning Objectives After completing this lesson you will be able to explain how good flexibility improves your health, wellness, and fitness; name some good
SAMPLE. Fitness What You Need To Know. 2. Benefits of Fitness. Permafold Topics. Fitness has four parts:
 1. What Is Fitness? When you are fit, you are at a healthy body weight. You have energy. Exercise and a healthy diet are a regular part of your life. Fitness What You Need To Know Permafold Topics 1. What
1. What Is Fitness? When you are fit, you are at a healthy body weight. You have energy. Exercise and a healthy diet are a regular part of your life. Fitness What You Need To Know Permafold Topics 1. What
Pre and Post pool sessions. County Camps
 Pre and Post pool sessions County Camps Key themes of the session PREPOOL Health and safety Environmental factors Swimmers clothing Why warm up? RMAP Which exercises? POST POOL Why do it? Good technique
Pre and Post pool sessions County Camps Key themes of the session PREPOOL Health and safety Environmental factors Swimmers clothing Why warm up? RMAP Which exercises? POST POOL Why do it? Good technique
Injuries to the Extremities
 Injuries to the Extremities KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. List seven signs and symptoms that suggest a serious extremity injury. 2. Describe how to care for injuries to the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. 3.
Injuries to the Extremities KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. List seven signs and symptoms that suggest a serious extremity injury. 2. Describe how to care for injuries to the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. 3.
Great Valley Little League First Aid Manual For Managers and Coaches 2017 Play Hard - Play Safe
 Great Valley Little League First Aid Manual For Managers and Coaches 2017 Play Hard - Play Safe HISTORY/STATS: At the start in 1939, Little League Baseball had just 45 players. Today, Little League Baseball
Great Valley Little League First Aid Manual For Managers and Coaches 2017 Play Hard - Play Safe HISTORY/STATS: At the start in 1939, Little League Baseball had just 45 players. Today, Little League Baseball
WRIST SPRAIN. Description
 WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
ESSENTIAL STRETCHES FOR SWIMMERS
 ESSENTIAL STRETCHES FOR SWIMMERS Clare Kersley BSc (Hons) Ost Osteopath & Sports Massage Therapist Notes 1. Stretches should form the 4th part of all your swimming training sessions: Page 1 of 13 Warm
ESSENTIAL STRETCHES FOR SWIMMERS Clare Kersley BSc (Hons) Ost Osteopath & Sports Massage Therapist Notes 1. Stretches should form the 4th part of all your swimming training sessions: Page 1 of 13 Warm
The Footballers 7 Deadly Sins
 The Footballers 7 Deadly Sins CONTENTS 1. Not enough core strength 2. Not enough balance retraining 3. Not enough hamstring strength 4. Too many ACL Injuries 5. Not enough flexibility/warming up 6. Not
The Footballers 7 Deadly Sins CONTENTS 1. Not enough core strength 2. Not enough balance retraining 3. Not enough hamstring strength 4. Too many ACL Injuries 5. Not enough flexibility/warming up 6. Not
BODY MECHANICS CMHA-CEI
 BODY MECHANICS CMHA-CEI Basics about backs Facts about Back Disorders Maintaining a Healthy Back Common activities Lifting Techniques Stretching Techniques Topics Your back Spine & Vertebrae Discs Nerves
BODY MECHANICS CMHA-CEI Basics about backs Facts about Back Disorders Maintaining a Healthy Back Common activities Lifting Techniques Stretching Techniques Topics Your back Spine & Vertebrae Discs Nerves
ANKLE SPRAINS. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
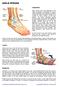 ANKLE SPRAINS Explanation Ankle sprains occur when ligaments in the ankle are partially or completely torn due to sudden stretching, either laterally or medially, or when the ankle is suddenly twisted
ANKLE SPRAINS Explanation Ankle sprains occur when ligaments in the ankle are partially or completely torn due to sudden stretching, either laterally or medially, or when the ankle is suddenly twisted
REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY
 The Athlete s Guide to REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY THE ATHLETE S GUIDE TO REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY Table of Contents Introduction...3 Common Sports
The Athlete s Guide to REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY THE ATHLETE S GUIDE TO REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY Table of Contents Introduction...3 Common Sports
12-WEEK, MARATHON WALK (26.2 MILES) TRAINING SCHEDULE
 ABOUT THE WALK 12-WEEK, MARATHON WALK (26.2 MILES) TRAINING SCHEDULE The Boston Marathon Jimmy Fund Walk presented by Hyundai raises the most money of any singleday walk in the nation and has raised more
ABOUT THE WALK 12-WEEK, MARATHON WALK (26.2 MILES) TRAINING SCHEDULE The Boston Marathon Jimmy Fund Walk presented by Hyundai raises the most money of any singleday walk in the nation and has raised more
August 2015 Newsletter
 1 August 2015 Newsletter www.coretherapy.co.uk CONTENTS: Stretch of the month Exercise of the month Education Section: Where have I been? STRETCH OF THE MONTH Overdeveloped and tight hip flexors can contribute
1 August 2015 Newsletter www.coretherapy.co.uk CONTENTS: Stretch of the month Exercise of the month Education Section: Where have I been? STRETCH OF THE MONTH Overdeveloped and tight hip flexors can contribute
Exercise Warm Ups and Cool Downs
 Exercise Warm Ups and Cool Downs How to Warm-up and Cool-down Appropriate warm-ups and cool-downs are important parts of any physical activity. The greater the speed of the movements required during the
Exercise Warm Ups and Cool Downs How to Warm-up and Cool-down Appropriate warm-ups and cool-downs are important parts of any physical activity. The greater the speed of the movements required during the
Injury Prevention and Treatment in Sport and Exercise
 Unit 26: Injury Prevention and Treatment in Sport and Exercise Unit code: F/601/1870 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit examines the causes of common injuries in sport and exercise and how they
Unit 26: Injury Prevention and Treatment in Sport and Exercise Unit code: F/601/1870 QCF level: 4 Credit value: 15 Aim This unit examines the causes of common injuries in sport and exercise and how they
Range of motion and positioning
 Range of motion and positioning Learning guide Why is motion important? Most people take free, comfortable movement for granted. Motion is meant to be smooth and painless. The ligaments, tendons, muscles,
Range of motion and positioning Learning guide Why is motion important? Most people take free, comfortable movement for granted. Motion is meant to be smooth and painless. The ligaments, tendons, muscles,
Back Safety In The Workplace
 Back Safety In The Workplace Greg Hogan Oklahoma State University Environmental Health and Safety (405) 744-7241 Current as of June 2017 Objectives Common Causes of Back Injuries Back Injury Prevention
Back Safety In The Workplace Greg Hogan Oklahoma State University Environmental Health and Safety (405) 744-7241 Current as of June 2017 Objectives Common Causes of Back Injuries Back Injury Prevention
Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment
 Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment Suprascapular nerve entrapment is an uncommon nerve condition in the shoulder, causing pain and weakness. It involves compression of the suprascapular nerve at the top or
Suprascapular Nerve Entrapment Suprascapular nerve entrapment is an uncommon nerve condition in the shoulder, causing pain and weakness. It involves compression of the suprascapular nerve at the top or
RIB FRACTURE. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms. Diagnosis
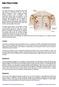 RIB FRACTURE Explanation The heart and lungs are encased by the chest wall, which is composed of the ribs. The ribs must be flexible in order to allow movement during expansion and contraction. This movement
RIB FRACTURE Explanation The heart and lungs are encased by the chest wall, which is composed of the ribs. The ribs must be flexible in order to allow movement during expansion and contraction. This movement
NECK OWNER S MANUAL. A Guide to the Care of the Neck
 NECK OWNER S MANUAL A Guide to the Care of the Neck A Real Pain in the Neck If you suffer from neck pain, you re not alone. Many people have this pain at some point in their lives. Things such as poor
NECK OWNER S MANUAL A Guide to the Care of the Neck A Real Pain in the Neck If you suffer from neck pain, you re not alone. Many people have this pain at some point in their lives. Things such as poor
Information Following Ankle Injury
 Patient & Family Guide Information Following Ankle Injury 2016 www.nshealth.ca Information Following Ankle Injury Physiotherapy Department Date Physiotherapist What to expect after cast/bandage removal:
Patient & Family Guide Information Following Ankle Injury 2016 www.nshealth.ca Information Following Ankle Injury Physiotherapy Department Date Physiotherapist What to expect after cast/bandage removal:
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
LESSON 2.1 Minor Wound Management Process
 LESSON 2.1 Minor Wound Management Process How do we make use of the four different kinds of first aid items such as gauze, melolin, padding (triangular bandage), and plaster to cover up the wounds? Cleaning
LESSON 2.1 Minor Wound Management Process How do we make use of the four different kinds of first aid items such as gauze, melolin, padding (triangular bandage), and plaster to cover up the wounds? Cleaning
Vermeulen, Liebenberg, Dippenaar en Louw Fisioterapeute
 Vermeulen, Liebenberg, Dippenaar en Louw Fisioterapeute In the Office Relaxation? Relaxation at work? Why doesn t my pain go away? Acute pain = Short term pain (Sprained ankle) Persistent/ Chronic
Vermeulen, Liebenberg, Dippenaar en Louw Fisioterapeute In the Office Relaxation? Relaxation at work? Why doesn t my pain go away? Acute pain = Short term pain (Sprained ankle) Persistent/ Chronic
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg)
 MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
MEDIAL HEAD GASTROCNEMIUS TEAR (Tennis Leg) Description Expected Outcome Medial head gastrocnemius tear is a strain of the inner part (medial head) of the major calf muscle (gastrocnemius muscle). Muscle
Flexibility and Stretching
 Flexibility and Stretching Stretching before exercise prepares the joints for motion, helps avoid injury and increases the range of motion of the area being stretched. After exercise stretching reduces
Flexibility and Stretching Stretching before exercise prepares the joints for motion, helps avoid injury and increases the range of motion of the area being stretched. After exercise stretching reduces
Spondylolisthesis DESCRIPTION EXPECTED OUTCOME POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS COMMON SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS GENERAL TREATMENT CONSIDERATIONS CAUSES
 DESCRIPTION is the slippage of one or more vertebrae, the bones of the spine. Many causes of slippage of the vertebra are possible; these include stress fracture (spondylolysis), which is often seen in
DESCRIPTION is the slippage of one or more vertebrae, the bones of the spine. Many causes of slippage of the vertebra are possible; these include stress fracture (spondylolysis), which is often seen in
Key Words. clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma. Linked Core Abilities
 Lesson 4 Treating for Shock and Immobilizing Fractures Key Words clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma What You Will Learn to Do Determine first
Lesson 4 Treating for Shock and Immobilizing Fractures Key Words clammy closed fracture dislocation fainting ligament open fracture splint sprain strain trauma What You Will Learn to Do Determine first
KS3 - PE THEORY REVISION GUIDE Y9
 KS3 - PE THEORY REVISION GUIDE Y9 Theory Knowledge Checklist Topic Tick off I can explain why physical activity is essential to a healthy lifestyle I can identify different types of movement using the
KS3 - PE THEORY REVISION GUIDE Y9 Theory Knowledge Checklist Topic Tick off I can explain why physical activity is essential to a healthy lifestyle I can identify different types of movement using the
Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021
 Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis 0496 October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021 This advice and exercise booklet has been produced by senior physiotherapists working for DynamicHealth.
Advice and exercises for managing knee and hip osteoarthritis 0496 October 2018 V1.2 April 2018 April 2021 This advice and exercise booklet has been produced by senior physiotherapists working for DynamicHealth.
Walking Program Sequence
 Walking Program Sequence 1. Warm up - Warming up is exercising at a lower intensity in order to get the blood circulating and let your body know that you are preparing for exercise. For many of your walks
Walking Program Sequence 1. Warm up - Warming up is exercising at a lower intensity in order to get the blood circulating and let your body know that you are preparing for exercise. For many of your walks
How To Achieve Your Best Plumb Line
 How To Achieve Your Best Plumb Line Created by Allison Oswald DPT, WCS, CPT Doctor of Physical Therapy Women s Certified Specialist Certified Pilates Teacher & Owner of Plumb Line Pilates and Physical
How To Achieve Your Best Plumb Line Created by Allison Oswald DPT, WCS, CPT Doctor of Physical Therapy Women s Certified Specialist Certified Pilates Teacher & Owner of Plumb Line Pilates and Physical
temperature, increase heart rate and breathing rate raising the athlete to their optimal level of preparedness for physical activity.
 Warm-Up & Cool-Down The warm-up and cool-down are both integral components of the ROAR session and must be completed before and after physical activity. The warmup is designed to prepare the body for the
Warm-Up & Cool-Down The warm-up and cool-down are both integral components of the ROAR session and must be completed before and after physical activity. The warmup is designed to prepare the body for the
What causes it? Sports experts believe that groin strains can be caused by a variety of different factors, including:
 Groin Strains A strain is often a bruise, stretching, or tearing of muscle fibres, which run from the front of the hip bone to the inside of the thigh. These 'hip-adductor' muscles, namely the adductor
Groin Strains A strain is often a bruise, stretching, or tearing of muscle fibres, which run from the front of the hip bone to the inside of the thigh. These 'hip-adductor' muscles, namely the adductor
ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE. Description
 Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
Description ANKLE SPRAIN, ACUTE An acute ankle sprain involves the stretching and tearing of one or more ligaments in the ankle. A two-ligament sprain causes more disability than a single-ligament sprain.
Spondylolysis DESCRIPTION EXPECTED OUTCOME POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS COMMON SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS GENERAL TREATMENT CONSIDERATIONS CAUSES
 DESCRIPTION is a stress or fatigue fracture of the bones of the spine (vertebrae) that does not involve the main weight-bearing part of those bones, the body of the vertebra. Instead, it involves an area
DESCRIPTION is a stress or fatigue fracture of the bones of the spine (vertebrae) that does not involve the main weight-bearing part of those bones, the body of the vertebra. Instead, it involves an area
