THE ROLE OF THE MID-TORSO IN SPEED DEVELOPMENT
|
|
|
- Timothy Allison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE ROLE OF THE MID-TORSO IN SPEED DEVELOPMENT The mid-torso is made up of 4 major muscle groups: 1. Rectus Abdominus Origin Base of sternum and bottom ribs Insertion Pubis bone (as part of the pelvis) 2. External Oblique Origin Last 3 ribs Insertion Linea alba, pubic crest. Lateral Flexion Opposite side Rotation Increased intra-abdominal pressure Lumbosacral stabilization 3. Internal Oblique Origin lliac crest and inguinal ligament. Insertion Linea alba, pubic crest and last 3 ribs. Lateral Flexion Same side Rotation Increased intra-abdominal pressure Lumbosacral stabilization 4. Transverse Abdominus Origin Insertion Inguinal ligament, cartilages of last 6 ribs, iliac crest. Linea alba, pubic crest. Compresses abdominal contents Increases intra-abdominal pressure THE FUNCTION OF THE MID TORSO IN SPORT ACTIVITIES. Most sports encompass relatively large movements of the trunk. Since the trunk segment has a large mass, great demands are exerted on the trunk musculature, particularly if the trunk movements are to be performed with high accelerations. Also the trunk has a critical role in the maintenance of stability and balance when performing movements with the extremities. Sporting activities requiring running or jumping place pressure on the lumbo-pelvic region (that includes the 4th and 5th lumbar vertebra), the pelvis and the hips as this region becomes the hub of weight bearing. The superior forces (from torso, head and arms) meet the inferior forces transmitted from the ground through the lower extremity. No part of the body is more vulnerable to tissue strains and sprains. This point is the centre of all body movements and efficient movements (as required in sprinting) can only occur through the maintaining of an anatomically correct body position, (Which occurs through appropriate tension being produced by the Abdominal muscle groups, erector spinae (making up the mid-torso region) and the gluteus maximus. (Porterfield 1985)
2 A study bycomerford et al (1991) analysed the mid-torso muscle groups to see which group had the greatest impact on lumbo-pelvic stabilisation. Results indicated that Oblique muscle groups were the most important for this stabilisation (especially from pelvic rotation forces) as found in high speed sprint movements. To assist in sprint acceleration, powerful arm drive will allow for a more rapid and powerful leg extension. The limitation with this technique is that large rotational forces can be placed upon the midtorso musculature. If there is inadequate stability in this region, rotation of the pelvis will occur to counteract shoulder rotation resulting in poor technique and inefficient force application, therefore a slower athlete will be the result. At an elite level, upper body strength is emphasised in sprint athletes but with a concurrent development of the mid-torso strength to allow efficient usage of this additional strength during high-speed sprinting movements. The naturally occurring wide pelvis of the mature female also leads to the above problem and midtorso strength is absolutely vital if the coach wishes to maximise efficient technique at maximal speed in his/her female sprint athletes. Hip rotation is required to maximise stride length, but if excessive then poor technique will result and if combined with a poor pelvic tilt, then major inefficiencies will result leading to either poor performance, injuries or both. Apart from resistance to rotational forces, there must be support of the pelvis to minimise excessive anterior pelvic tilt. An excessive anterior tilt indicates poorly toned mid-torso musculature and this can increase the lordotic curve (lower back arch) in the lumbar region. This can increase the strain on the facet joints in the vertebral column and can result in the Ilio-psoas going into spasm to protect the lower core from injury. Also increased pressure on the neural plexus from the lumbar region can result in nerve irritation (Eg. Sciatic nerve) which can then affect the optimal functioning of lower limb musculature that can have deleterious effects if maximal effort work (Eg. 100% sprinting) is performed (Such as Hamstring strains). Excessive anterior tilt of the pelvis can limit hip range of motion leading to excessive hip extension and limited hip flexion. This technical position limits stride length and increases ground contact time (which is undesirable for increases in speed performance) due to the athlete's centre of gravity being lower than required for maximal sprinting speed. The demands of sprinting require the abdominals to function in away that leads to optimal torsional stabilisation during explosive contractile sequences matching the needs of performing up to 5 strides per seconds (such as that which occurs in an elite sprint race). During sprinting at this rate, the lower limb velocity can reach 80km/h, therefore the stresses placed upon the pelvic stabilisers are extreme and can only be accommodated for with extremely well developed abdominal (including oblique) musculature. (Francis 1992) 3. WAYS OF DEVELOPING THE MID-TORSO REGION. The development of a strong mid-torso should be the goal of all speed/ power athletes and the preferred procedures for maximising strength in this region is by the common situp. Kinesiologically the situp and its many variations are the ideal exercises to develop the vertebral flexor and rotational muscles (namely the rectus abdominus RA, external oblique EO and internal oblique IO). The mid-torso musculature consists of postural muscles with a high percentage of slow twitch muscle fibres. Their function is to be able to hold contractions for long periods to maximise trunk stability. (Nordel and Frankel 1989, p104) To best condition this region, variations on the situp can be used. To maximise abdominal development and minimise stress placed upon the lower back, exercises should be performed slowly (1-4 seconds per repetition) whilst working on all muscle groups in the mid-torso region. These exercises should also be performed through a range of motion that minimises lower back strain, and maximal control is required. When compared to the stress placed upon the lumbar region when standing (assume this is measured as 100%), the full situp (even with knees bent and feet flat on the floor) creates a stress equal to 200%. This load can be decreased if the situp is only partial (first 30 0 from floor) and lessened even more if a reverse situp is performed (pelvis lifted off the floor). The reverse curl has been shown to increase the activation on the EO and I0 as well as the RA. (Nordin & Frankel 1989, p202) A modification to maximise load and minimise stress upon the lumbar region is to perform a partial crunch as well as a reverse situp concurrently and hold each
3 maximal contraction for 4 seconds. This minimises the use of assistant muscle groups and quickly fatigues the musculature targeted in only 5-15 repetitions. Situps performed fast and or with the feet supported have; 1. The relative contribution of the hip flexors increasing while the relative contribution of the abdominal muscles decreasing. (Sevier 1969) 2. Increased stress placed upon the lumbar region of the spine. 3. Decreased load on the abdominal musculature due to increased momentum from the upper body. The major limitation of the situp is the functional application of mid-torso strength transferable from a situp routine to the pelvic stabilisation required under the stresses of a sprint or any high speed movement performance. Personal observation of a variety of athletes has highlighted that even the development of very strong mid-torso regions from situps and squat type activities do not automatically transfer to the pelvic and mid-torso positions required to maximise sprinting performance. Many athletes are strong enough through their mid-torso region but have not developed correct motor patterns to be able to stabilise the body whilst having rapid upper and lower limb movements. (Eg. arm and leg movements in sprinting). To develop the specific strength qualities or transfer mid-torso strength to the required strength positions can be achieved both in a weight room and on the field/court/track situation. 4. WEIGHT ROOM MID-TORSO TRAINING. The best adaptation in the mid-torso musculature results from slow isotonic training in combination with isometric training in a range of non-specific and sprinting specific body positions. Once the athlete can perform acceptable slow isotonic (with movement) mid-torso exercises, more sprint specific positioning can be introduced that requires the athlete to place their hips in the correct pelvic position (posterior pelvic tilt) and have them perform rapid limb movements whilst minimising pelvic movement. Some of the abdominal exercises that have been useful in development of a stable mid-torso are as follows: 1. Abdominal hollowing To perform abdominal hollowing the athlete can be either in a supine position or standing. The technique is to contract the abdominals "INWARDS" as hard as possible whilst maintaining normal rib cage positioning. This can be assisted by placing a finger into the belly button and try to push the abdominal wall inwards whilst maximally contracting. The athlete should continue to breath as normally as possible throughout the exercise, each contraction can be held for up to 60 seconds. 2. Isometric prone To perform an Isometric Prone exercise the athlete begins on elbows and knees and then takes the knees off the ground whilst trying to maximally contract the abdominal musculature upwards. If any stress is felt on the lower back, this is an indication that the abdominal wall is not being totally contracted allowing the psoas musculature to help in the stability process (which in turn places great stress upon the lower back as the psoas attaches from the 12 th Thoracic vertebra to the 5 th Lumbar vertebra. 3. Single leg raise with lumbar support To perform a single leg raise with lumbar support, the athlete places his/ her tips of their fingers under the lower back and maximally contracts the back against the fingers. Then one leg at a time is
4 slowly lowered (up to 10 seconds per leg) whilst maintaining a constant pressure on the fingers. As soon as the pressure decreases, this indicates that the abdominal musculature is beginning to fail and the hip flexors have been activated. At this point if the pressure can not be regained, the athlete either finishes that repetition or brings the leg slowly back to the starting position until lower back pressure can be regained and then continues the repetition. These are still "PASSIVE" isometric exercises (done slowly) that once a high competency is reached can be followed by "ACTIVE" isometric exercises that are highly sprint specific. Examples of these exercises are; 1. Rapid hip Extension/ hip Flexion The athlete places themselves in a correct sprint position and with either a cable, theraband or specific flexion/extension machine (eg Keiser air pressured), they can perform repeated flexion/extension movements at speed with resistance whilst attempting to maintain a correct pelvic position Modified Russian Twist with/ without arm swing The athlete lays supine on a back extension machine and leans back until they attain the correct body position. From here they can then perform dynamic arm actions whilst again trying to hold their pelvis stable. ON TRACK/FIELD/COURT MID-TORSO TRAINING. The weight room training is purely a precursor to what must be achieved in the "on field" situation. This is where true application of the strength gain can be both assessed and true transfer can be completed. This goal can be achieved in 2 ways; 1. The correct body positioning can be further applied by several "running drills" that are aimed at correct running form (which usually means correct body posture through the mid-torso). The "A", modified single leg "A", "B", Heel flick and High knee drills are all aimed at increasing the tilting and rotational stresses that are placed upon the mid-torso musculature. These drills can be done slowly at first and progressively sped up as the athlete's ability to hold the correct position improves. The modified single leg 'A' places high levels of stress upon the mid-torso region to hold the pelvis in place whilst the athletes perform very explosive hip flexion and extension movements in a single leg form. The most specific transfer to sprinting is to have the athlete sprint whilst concentrating on the positioning drilled previously. Sprints should be less than maximal at first progressing only as the athlete is able to maintain the correct running position. As soon as pelvic stability decreases, the drill should be stopped. External resistance to increase learning can be in the form of a towing device that the athletes place around their mid-torso and the pressure on this region through each repetition reinforces the control required and increases the level of control as the athlete is having to work harder to maintain good body position under this increased resistance. In summary, the mid-torso is the link between the upper and lower body and must allow the transfer of strength movements and allow powerful movements of both the upper and lower body to complement each other. The way to achieve this is to develop torso strength through traditional (situps) but ensure functional strength (by more specific mid-torso training methods) is being attained throughout the athlete's training year. REFERENCES Comerford, M., Richardson, C., jull, & G., Toppenhurg, R Techniques for active lumbar stabilisation for spinal protection: A pilot study. Australian Physiotherapy. 38: Francis, C & Patterson, P The Charlle Francis training system. TBLI Publications Inc
5 Nordin, M. & Frankel, V Basic blomechanies of the musculoskeletal system. 2nd Ed. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphlap 104, 202. Porterfleld, J.A Dynamic stabilisation of the trunk. J. Orth. & Spts. Phy. Therapy. 6: Sevier, B.A Comparative electromyo. graphic analysis of three abdominal muscle (rectus abdominis, internal oblique and external oblique), while running an performing sit-ups. University of 0 Eugene, Ore, 1971,3 fisches.
Connecting the Core. Rationale. Physiology. Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS. Athletes have been inundated with terminology
 Connecting the Core Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS Athletes have been inundated with terminology and references to core development in recent years. However, little has been conveyed to these athletes on what
Connecting the Core Paul J. Goodman, MS, CSCS Athletes have been inundated with terminology and references to core development in recent years. However, little has been conveyed to these athletes on what
PHYSICAL TRAINING INSTRUCTORS MANUAL TABLE OF CONTENT PART 5. Exercise No 31: Reverse Crunch 1. Exercise No 32: Single Hip Flexion 3
 TABLE OF CONTENT PART 5 Exercise No 31: Reverse Crunch 1 Exercise No 32: Single Hip Flexion 3 Exercise No 33: Bicycle Crunch 4 Exercise No 34: Straight Leg U Crunches 5 Exercise No 35: Bent Knee U Crunch
TABLE OF CONTENT PART 5 Exercise No 31: Reverse Crunch 1 Exercise No 32: Single Hip Flexion 3 Exercise No 33: Bicycle Crunch 4 Exercise No 34: Straight Leg U Crunches 5 Exercise No 35: Bent Knee U Crunch
Guidelines for the Trunk test for Paracanoe Athletes. Trunk test guidelines for Paracanoe
 Guidelines for the Trunk test for Paracanoe Athletes Information Please note that the purpose of the pictures is to show the position of the athlete and classifier. The classifier s job is to assess function
Guidelines for the Trunk test for Paracanoe Athletes Information Please note that the purpose of the pictures is to show the position of the athlete and classifier. The classifier s job is to assess function
# Work your Abs when you re not working your abs: See above When you do all of your other exercises all exercise is an abdominal exercise!!
 #178 Tools for Training Torso Presented by: Alex McMillan President of Northwest Personal Training & Fitness Education 2006 IDEA Program Director of the Year NASM and ACE Certified Personal Trainer Nike,
#178 Tools for Training Torso Presented by: Alex McMillan President of Northwest Personal Training & Fitness Education 2006 IDEA Program Director of the Year NASM and ACE Certified Personal Trainer Nike,
ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK
 ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK Posture and Balance Posture refers to the biomechanical alignment of the individual body parts and the orientation of the body to the
ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK Posture and Balance Posture refers to the biomechanical alignment of the individual body parts and the orientation of the body to the
3 Movements of the Trunk. Flexion Rotation Extension
 3 Movements of the Trunk Flexion Rotation Extension 1 TRUNK FLEXION 2 TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis. I: By «3 portions into cartilages
3 Movements of the Trunk Flexion Rotation Extension 1 TRUNK FLEXION 2 TRUNK FLEXION: Rectus Abdominalis O: Crest of Pubis & ligaments covering front of symphysis pubis. I: By «3 portions into cartilages
Core Stability Exercises
 Core Stability Exercises Static Floor Exercises The plank Hold a straight body position, supported on elbows and toes. Brace the abdominals and set the low back in the neutral position. Hold this position
Core Stability Exercises Static Floor Exercises The plank Hold a straight body position, supported on elbows and toes. Brace the abdominals and set the low back in the neutral position. Hold this position
Rehabilitation 2. The Exercises
 Rehabilitation 2 This is the next level from rehabilitation 1. You should have spent time mastering the previous exercises and be ready to move on. If you are unsure about any of the previous exercises
Rehabilitation 2 This is the next level from rehabilitation 1. You should have spent time mastering the previous exercises and be ready to move on. If you are unsure about any of the previous exercises
Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises
 Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises Most athletes (swimmers included) use a combination of controlled movement exercises and specific joint/muscle stretching to improve performance potential. The proposed
Warm-Up and Stretching Exercises Most athletes (swimmers included) use a combination of controlled movement exercises and specific joint/muscle stretching to improve performance potential. The proposed
MODULE 4: Stability Training for Riders
 MODULE 4: Stability Training for Riders The most common answer you will get from almost any rider when you ask them what they need more of, in terms of their fitness, is core strength. Indeed, core strength
MODULE 4: Stability Training for Riders The most common answer you will get from almost any rider when you ask them what they need more of, in terms of their fitness, is core strength. Indeed, core strength
The Role of the Rectus Abdominis in Predicting and Preventing Low Back Pain
 The Role of the Rectus Abdominis in Predicting and Preventing Low Back Pain What causes low back pain? The causes of low back pain and complicated and varied, but the pain we feel is in most cases the
The Role of the Rectus Abdominis in Predicting and Preventing Low Back Pain What causes low back pain? The causes of low back pain and complicated and varied, but the pain we feel is in most cases the
Lumbar Stenosis Rehabilitation Using the Resistance Chair
 PRODUCTS HELPING PEOPLE HELP THEMSELVES! Lumbar Stenosis Rehabilitation Using the Resistance Chair a. Description Lumbar spinal stenosis is a term used to describe a narrowing of the spinal canal. The
PRODUCTS HELPING PEOPLE HELP THEMSELVES! Lumbar Stenosis Rehabilitation Using the Resistance Chair a. Description Lumbar spinal stenosis is a term used to describe a narrowing of the spinal canal. The
TRAINING THE CORE BEGIN WITH ONE SET OF ALL 17 EXERCISES FOR A TOTAL OF 250 REPS. NEXT, MOVE TO TWO SETS FOR A TOTAL OF 500 REPS.
 TRAINING THE CORE 1. LATERAL SIT UPS.X 20 (10 EACH SIDE) 2. HYPEREXTENSIONS.X 10 3. LEG HUGS...X 15 4. RUSSIAN TWIST X 20 (10 EACH SIDE) 5. HIP CURLS..X 14 (7 EACH LEG) 6. JACK KNIFES..X 10 7. REVERSE
TRAINING THE CORE 1. LATERAL SIT UPS.X 20 (10 EACH SIDE) 2. HYPEREXTENSIONS.X 10 3. LEG HUGS...X 15 4. RUSSIAN TWIST X 20 (10 EACH SIDE) 5. HIP CURLS..X 14 (7 EACH LEG) 6. JACK KNIFES..X 10 7. REVERSE
Exercise Techniques For
 EBook Exercise Techniques For The Core The Health Doctor 2009 Contents 1) Ab Crunch Machine...3 2) Crunches Beginner...4 3) Crunches Intermediate...5 4) Crunches Advanced...6 5) Oblique Crunches...7 6)
EBook Exercise Techniques For The Core The Health Doctor 2009 Contents 1) Ab Crunch Machine...3 2) Crunches Beginner...4 3) Crunches Intermediate...5 4) Crunches Advanced...6 5) Oblique Crunches...7 6)
Dynamic slings and optimal 3D function
 Dynamic slings and optimal 3D function Abstract Trish Wisbey-Roth Olympic/Specialist Sports Physiotherapist (FACP), Masters of Sport Physiotherapy (AIS/UC) Active Rehabilitation Consultant Layered over
Dynamic slings and optimal 3D function Abstract Trish Wisbey-Roth Olympic/Specialist Sports Physiotherapist (FACP), Masters of Sport Physiotherapy (AIS/UC) Active Rehabilitation Consultant Layered over
Training Philosophy. There are numerous views on core conditioning.
 Abs Lab Presented by Helen Vanderburg BKin, ACE, CanFitPro, Yoga and Pilates 2005 IDEA Instructor of the Year 2006/ 1996 CanFitPro Presenter of the Year Nautilus and BOSU Fitness Education Team Introduction
Abs Lab Presented by Helen Vanderburg BKin, ACE, CanFitPro, Yoga and Pilates 2005 IDEA Instructor of the Year 2006/ 1996 CanFitPro Presenter of the Year Nautilus and BOSU Fitness Education Team Introduction
Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation
 Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation Assistant professor of Sports Medicine Department of Sports Medicine Tehran university of Medical Sciences Introduction To develop a comprehensive functional
Core Stabilization Training in Rehabilitation Assistant professor of Sports Medicine Department of Sports Medicine Tehran university of Medical Sciences Introduction To develop a comprehensive functional
Mobility sequencing!
 Mobility sequencing When practicing joint mobility drills we have the opportunity to improve our movement. The muscles associated with the joint being mobilised as well as the joint itself will improve
Mobility sequencing When practicing joint mobility drills we have the opportunity to improve our movement. The muscles associated with the joint being mobilised as well as the joint itself will improve
Lumbar/Core Strength and Stability Exercises
 Athletic Medicine Lumbar/Core Strength and Stability Exercises Introduction Low back pain can be the result of many different things. Pain can be triggered by some combination of overuse, muscle strain,
Athletic Medicine Lumbar/Core Strength and Stability Exercises Introduction Low back pain can be the result of many different things. Pain can be triggered by some combination of overuse, muscle strain,
Home Workout with Household Items
 Home Workout Home Workout with Household Items Introduction This home routine is created for women and men to workout while they are at home. It incorporates the use of household items to imitate weights
Home Workout Home Workout with Household Items Introduction This home routine is created for women and men to workout while they are at home. It incorporates the use of household items to imitate weights
External Obliques Abdominal muscles that attaches at the lower ribs, pelvis, and abdominal fascia.
 The Core The core is where most of the body s power is derived. It provides the foundation for all movements of the arms and legs. The core must be strong, have dynamic flexibility, and function synergistically
The Core The core is where most of the body s power is derived. It provides the foundation for all movements of the arms and legs. The core must be strong, have dynamic flexibility, and function synergistically
PART ONE. Belly Dance Fitness Technique
 PART ONE Belly Dance Fitness Technique OVERVIEW Understanding belly dance movement The gentle, symmetrical, rhythmic undulations that we practice in Belly dance can help to revitalize almost every part
PART ONE Belly Dance Fitness Technique OVERVIEW Understanding belly dance movement The gentle, symmetrical, rhythmic undulations that we practice in Belly dance can help to revitalize almost every part
The Muscles of the Core
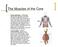 The Muscles of the Core Rectus abdominis - abdominal muscle that attaches at the fifth through seventh ribs, the lower sternum and the front of the pubic bone. This muscle flexes the spine, compresses
The Muscles of the Core Rectus abdominis - abdominal muscle that attaches at the fifth through seventh ribs, the lower sternum and the front of the pubic bone. This muscle flexes the spine, compresses
Pilates instructor final mat exam - ANSWERS
 Balanced Body - Mat EXAM Pilates instructor final mat exam - ANSWERS Name Date Training Location Examiner Total Points - 60 Passing Grade - 42 1) Which of the following are considered Balanced Body Pilates
Balanced Body - Mat EXAM Pilates instructor final mat exam - ANSWERS Name Date Training Location Examiner Total Points - 60 Passing Grade - 42 1) Which of the following are considered Balanced Body Pilates
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE. CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement?
 PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
EXERCISE CLASSIFICATION
 EXERCISE CLASSIFICATION To assist in the safe, effective prescription and execution of exercise, each exercise in this guide is classified as follows: Skill Classification exercises suitable for different
EXERCISE CLASSIFICATION To assist in the safe, effective prescription and execution of exercise, each exercise in this guide is classified as follows: Skill Classification exercises suitable for different
Provide movement Maintain posture/stability Generate heat
 How we move.. What do muscles do for us? Provide movement Maintain posture/stability Generate heat (skeletal muscle accounts for 40% body mass) So looking at skeletal muscles.. What do skeletal muscles
How we move.. What do muscles do for us? Provide movement Maintain posture/stability Generate heat (skeletal muscle accounts for 40% body mass) So looking at skeletal muscles.. What do skeletal muscles
Rotational Forces. : Their impact; our treatments
 Rotational Forces : Their impact; our treatments Lee Stang, LMT, LMBT, BCTMB NCBTMB Provider: 450217-06 bridgestohealthseminars.com bthseminars@gmail.com 860.985.5834 Facebook.com/BridgesToHealthSeminars
Rotational Forces : Their impact; our treatments Lee Stang, LMT, LMBT, BCTMB NCBTMB Provider: 450217-06 bridgestohealthseminars.com bthseminars@gmail.com 860.985.5834 Facebook.com/BridgesToHealthSeminars
Rehabilitation, Core Stability & Personal Training using the Swiss Ball
 s EDUCATION WORKSHOPS Rehabilitation, Core Stability & Personal Training using the Swiss Ball with B.App.Sc (Physio), Dip.Ed (P.E.) CONTENTS Topic Page 1. Introduction 2. Core Stability Basics 3 3. Core
s EDUCATION WORKSHOPS Rehabilitation, Core Stability & Personal Training using the Swiss Ball with B.App.Sc (Physio), Dip.Ed (P.E.) CONTENTS Topic Page 1. Introduction 2. Core Stability Basics 3 3. Core
The theory and practice of getting fitter and stronger
 The theory and practice of getting fitter and stronger David Docherty, PhD, Professor Emeritus School of Exercise Science, Physical and Health Education University of Victoria All the presentations are
The theory and practice of getting fitter and stronger David Docherty, PhD, Professor Emeritus School of Exercise Science, Physical and Health Education University of Victoria All the presentations are
2002 Physioball Supplement
 2002 Physioball Supplement These exercises are not detailed on the 2002 Off-Ice Training video but will be taught in detail during the 2002 Reach for the Stars Seminar. CORE STRENGTH Physioball/ Sport
2002 Physioball Supplement These exercises are not detailed on the 2002 Off-Ice Training video but will be taught in detail during the 2002 Reach for the Stars Seminar. CORE STRENGTH Physioball/ Sport
Side Split Squat. The exercises you need to hit with more power and accuracy every time
 GOLF FITNESS The exercises you need to hit with more power and accuracy every time POWER Training for more power on the course doesn t necessarily involve heavy weights and explosive ballistic workouts
GOLF FITNESS The exercises you need to hit with more power and accuracy every time POWER Training for more power on the course doesn t necessarily involve heavy weights and explosive ballistic workouts
Core #1 - Atlas. Outline. Goals
 Outline Core #1 - Atlas 1. Prone or planks - 60 seconds 2. Side/lateral holds - 60 seconds 3. Supine - 60 seconds 4. Prone knee bent - 60 seconds 5. Donkey kicks - 15-25 repetitions each leg 6. Fire hydrant
Outline Core #1 - Atlas 1. Prone or planks - 60 seconds 2. Side/lateral holds - 60 seconds 3. Supine - 60 seconds 4. Prone knee bent - 60 seconds 5. Donkey kicks - 15-25 repetitions each leg 6. Fire hydrant
Corrective activities for Postural Assessment test:
 Corrective activities for Postural Assessment test: An exercise for improvement of all postures. Wall Drill This exercise can be performed to help practice good standing posture. Stand with head, shoulders,
Corrective activities for Postural Assessment test: An exercise for improvement of all postures. Wall Drill This exercise can be performed to help practice good standing posture. Stand with head, shoulders,
Beginner and advanced exercises. utilizing a stability ball. Professionally managed by:
 Beginner and advanced exercises utilizing a stability ball Professionally managed by: Mission: The National Institute for Fitness and Sport is committed to enhancing human health, physical fitness and
Beginner and advanced exercises utilizing a stability ball Professionally managed by: Mission: The National Institute for Fitness and Sport is committed to enhancing human health, physical fitness and
Physical Sense Activation Programme
 Flexion extension exercises for neck and upper back Sitting on stool Arms hanging by side Bend neck and upper back Breathe out Extend your neck and upper back Lift chest to ceiling Squeeze shoulder blades
Flexion extension exercises for neck and upper back Sitting on stool Arms hanging by side Bend neck and upper back Breathe out Extend your neck and upper back Lift chest to ceiling Squeeze shoulder blades
2017 COS ANNUAL MEETING AND EXHIBITION HOME EXERCISES
 UPPER BODY Push Up From a push up position. Lower whole body down to floor. Press up to return to start position. Maintain abdominal hollow and neutral spinal alignment throughout movement. Note: Perform
UPPER BODY Push Up From a push up position. Lower whole body down to floor. Press up to return to start position. Maintain abdominal hollow and neutral spinal alignment throughout movement. Note: Perform
Muscles of the Core. PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS
 Muscles of the Core PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Intercostal Muscles Run between the ribs Provide shape and movement for chest wall External intercostals: aid in both quiet (passive) and forced
Muscles of the Core PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Intercostal Muscles Run between the ribs Provide shape and movement for chest wall External intercostals: aid in both quiet (passive) and forced
Exercise Program WARNING: DO NOT USE THIS OR ANY OTHER EXERCISE PROGRAM WITHOUT FIRST BEING CLEARED BY YOUR DOCTOR.
 Exercise Program WARNING: DO NOT USE THIS OR ANY OTHER EXERCISE PROGRAM WITHOUT FIRST BEING CLEARED BY YOUR DOCTOR. Things you MUST know before you begin Posture It is absolutely critical to maintain proper
Exercise Program WARNING: DO NOT USE THIS OR ANY OTHER EXERCISE PROGRAM WITHOUT FIRST BEING CLEARED BY YOUR DOCTOR. Things you MUST know before you begin Posture It is absolutely critical to maintain proper
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual
 Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Torso Training and Core Stability. Torso and Core Training ~ Gary Fillery Personal Training
 Torso Training and Core Stability Mobile personal training. Let the trainer come to you! No gym fees, 100% you, and what you want. I understand that in today s busy lifestyle, time can be an issue and
Torso Training and Core Stability Mobile personal training. Let the trainer come to you! No gym fees, 100% you, and what you want. I understand that in today s busy lifestyle, time can be an issue and
Do the same as above, but turn your head TOWARDS the side that you re holding on to the chair.
 Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Stability Ball Band & Free Weight Work-out
 Stability Ball Band & Free Weight Work-out High Mountain Personal Training Michael Martin Cell Phone: 970-946-6398 1. Chest Do 2 sets of 1 exercise Or Do 1 set of 2 different exercises Start position End
Stability Ball Band & Free Weight Work-out High Mountain Personal Training Michael Martin Cell Phone: 970-946-6398 1. Chest Do 2 sets of 1 exercise Or Do 1 set of 2 different exercises Start position End
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001)
 Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Foundation Upper Body B (60 min)
 Foundation Upper Body B (60 min) Protection (5 min) Exercise Reps Duration (s) Ys on an Exercise Ball 8 30 Ws on an Exercise Ball 8 30 Hip Flexion (Hands and Knees) 10 60 Hip Internal Rotation (Side Lying)
Foundation Upper Body B (60 min) Protection (5 min) Exercise Reps Duration (s) Ys on an Exercise Ball 8 30 Ws on an Exercise Ball 8 30 Hip Flexion (Hands and Knees) 10 60 Hip Internal Rotation (Side Lying)
Full Body (medicine ball) Saggital Front Reach
 Saggital Front Reach Saggital Front Reach 1) Start position: Stand with feet hip width apart. Hold medicine ball or dumbbell at waist. 2) Step forward 2-3 feet with the heel striking first and lean torso
Saggital Front Reach Saggital Front Reach 1) Start position: Stand with feet hip width apart. Hold medicine ball or dumbbell at waist. 2) Step forward 2-3 feet with the heel striking first and lean torso
Foundation Upper Body A (60 min)
 Foundation Upper Body A (60 min) Protection (5 min) Exercise Reps Duration (s) Ys on an Exercise Ball 8 30 Ws on an Exercise Ball 8 30 Hip Flexion (Hands and Knees) 10 60 Hip Internal Rotation (Side Lying)
Foundation Upper Body A (60 min) Protection (5 min) Exercise Reps Duration (s) Ys on an Exercise Ball 8 30 Ws on an Exercise Ball 8 30 Hip Flexion (Hands and Knees) 10 60 Hip Internal Rotation (Side Lying)
Core Stability for Sailing
 Core Stability for Sailing What is it? The core is essentially the mid-section of the body. It comprises the deep and superficial muscles of the trunk, such as the abdominals, obliques, spinae erector,
Core Stability for Sailing What is it? The core is essentially the mid-section of the body. It comprises the deep and superficial muscles of the trunk, such as the abdominals, obliques, spinae erector,
BACK SPASM. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
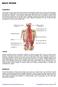 BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
April 1, 2018 Team Telemark Core Strength Training V2.0
 April 1, 2018 Team Telemark Core Strength Training V2.0 Courtesy Ross McKinnon, PT, FCAMPT, CGIMS, CMT, FMSC Kelowna Manual Therapy Centre Team Telemark Physiotherapist Key Points - Highly recommended
April 1, 2018 Team Telemark Core Strength Training V2.0 Courtesy Ross McKinnon, PT, FCAMPT, CGIMS, CMT, FMSC Kelowna Manual Therapy Centre Team Telemark Physiotherapist Key Points - Highly recommended
WOW Workout on Weights Repeat this entire sequence twice. Squat with front deltoid raise with bands Incline Pushups: 12 repetitions
 WOW Workout on Weights Repeat this entire sequence twice. Squat with front deltoid raise with bands: 12 repetitions 1. Stand on the center of your band. 2. Feet are just wider than hip width apart, toes
WOW Workout on Weights Repeat this entire sequence twice. Squat with front deltoid raise with bands: 12 repetitions 1. Stand on the center of your band. 2. Feet are just wider than hip width apart, toes
CLARE ETP PROGRAMME. Sets - This is the completion of the prescribed number of reps without rest
 Programme Objective: Strength Development & Core Development Glossary Reps - Also written as repetition. This refers to the completion of one single lift/exercise Sets - This is the completion of the prescribed
Programme Objective: Strength Development & Core Development Glossary Reps - Also written as repetition. This refers to the completion of one single lift/exercise Sets - This is the completion of the prescribed
CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system. Practice questions - text book pages QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system Practice questions - text book pages 64-66 1) A prime mover of hip flexion is the: a. rectus femoris. b. Iliopsoas. c. vastus muscles. d. gluteus maximus. b. Key
CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system Practice questions - text book pages 64-66 1) A prime mover of hip flexion is the: a. rectus femoris. b. Iliopsoas. c. vastus muscles. d. gluteus maximus. b. Key
Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives
 1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
1 2 Thoracolumbar Anatomy Eric Shamus Catherine Patla Objectives List the muscular and ligamentous attachments of the thoracic and lumbar spine Describe how the muscles affect the spine and upper extremity
Introduction. The Inner Core Muscles. Why Train The Inner Core? How Do You Train The Inner Core?
 Introduction Pilates focuses on the deep postural muscles, including the pelvic floor, the transversus abdominis (TA) and the multifidus. These deep postural muscles are also referred to as the core. Improving
Introduction Pilates focuses on the deep postural muscles, including the pelvic floor, the transversus abdominis (TA) and the multifidus. These deep postural muscles are also referred to as the core. Improving
 1 of 8 9/21/2006 1:02 PM Smith College Dept. of Athletics Program for The Average Division III Female Athlete Trainer : Timothy Bacon Introduction Core, functional and complementary exercises. Warm Up
1 of 8 9/21/2006 1:02 PM Smith College Dept. of Athletics Program for The Average Division III Female Athlete Trainer : Timothy Bacon Introduction Core, functional and complementary exercises. Warm Up
Warm Up Always start by foam rolling the key areas, follow with static stretching at the end of the session. Perform cardio activity or 6-7 R.P.E.
 VISIT FULL SITE PROGRAM FOR VIC SKI TEAM SKI TEAM CORE STABILISATION #2 Trainer : Jean-Claude Legras PRINT Introduction The goal of core stabilization training should be to increase postural control, improve
VISIT FULL SITE PROGRAM FOR VIC SKI TEAM SKI TEAM CORE STABILISATION #2 Trainer : Jean-Claude Legras PRINT Introduction The goal of core stabilization training should be to increase postural control, improve
RESISTANCE STRENGTH TRAINING EXERCISE
 RESISTANCE STRENGTH TRAINING EXERCISE Alternating Dumbbell Chest Press Lie supine on a flat bench with dumbbells in each hand with a pronated grip. Extend your arms, holding the dumbbells in line with
RESISTANCE STRENGTH TRAINING EXERCISE Alternating Dumbbell Chest Press Lie supine on a flat bench with dumbbells in each hand with a pronated grip. Extend your arms, holding the dumbbells in line with
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME:
 VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME:
 VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
Abdominal Hollow In Neutral
 Abdominal Hollow In Neutral This hollowing technique ensures that you pre-activate your abdominals which helps you isolate them better. This exercise helps you derive the most benefit from other abdominal
Abdominal Hollow In Neutral This hollowing technique ensures that you pre-activate your abdominals which helps you isolate them better. This exercise helps you derive the most benefit from other abdominal
Strength Exercises for Improved Running Biomechanics
 2 CHAPTER Strength Exercises for Improved Running Biomechanics ssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssdd s Many gait abnormalities seen
2 CHAPTER Strength Exercises for Improved Running Biomechanics ssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssssdd s Many gait abnormalities seen
Intermediate: Lift the elbows off the floor for added difficulty.
 Core Stability Please Note: The postures, techniques, and exercises contained on this web site are solely for the use of patients of our clinic who have been given a prescription to do them. Unauthorized
Core Stability Please Note: The postures, techniques, and exercises contained on this web site are solely for the use of patients of our clinic who have been given a prescription to do them. Unauthorized
CORE STABILITY. Contents Understanding your Back... 3
 Contents Understanding your Back........................................................... 3 What is core stability?............................................................... 5 YOUR GUIDE TO CORE
Contents Understanding your Back........................................................... 3 What is core stability?............................................................... 5 YOUR GUIDE TO CORE
Perform ten 30 second intervals alternating 5 at a slow speed with 5 at a moderate speed.
 Session 1 Details Cardio - Choose one of the following Elliptical Slow to Moderate Cardio Intervals (1) Perform ten 30 second intervals alternating 5 at a slow speed with 5 at a moderate speed. Treadmill
Session 1 Details Cardio - Choose one of the following Elliptical Slow to Moderate Cardio Intervals (1) Perform ten 30 second intervals alternating 5 at a slow speed with 5 at a moderate speed. Treadmill
Posture. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Posture Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Posture = body alignment = the relative arrangement of parts of the body Changes with the positions and movements of the body throughout the day
Posture Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Posture = body alignment = the relative arrangement of parts of the body Changes with the positions and movements of the body throughout the day
Part A: Running. Max 5 mins. Slow run forwards 5m and return x 2. Hip out x 2. Hip in x 2. Heel Flicks x 2
 Part A: Running. Max 5 mins. Slow run forwards 5m and return x 2 Jog straight to the 20m line. Make sure you keep your upper body straight. Your hip, knee and foot are aligned. Do not let your knee buckle
Part A: Running. Max 5 mins. Slow run forwards 5m and return x 2 Jog straight to the 20m line. Make sure you keep your upper body straight. Your hip, knee and foot are aligned. Do not let your knee buckle
FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT
 THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) A 12 part assessment tool to screen your athletic performance in 4 key components: Flexibility, Balance, Strength & Core
THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) A 12 part assessment tool to screen your athletic performance in 4 key components: Flexibility, Balance, Strength & Core
MODULE 10: Breaking down the Exercises - Stability Exercises
 MODULE 10: Breaking down the Exercises - Stability Exercises Stability is a core component of the Ridefit program, because so much of riding is dependent on the stability of the rider s body in the saddle.
MODULE 10: Breaking down the Exercises - Stability Exercises Stability is a core component of the Ridefit program, because so much of riding is dependent on the stability of the rider s body in the saddle.
Ares Power core. Outline. Goals. 1. V-ups with med ball x Lumber jack x Rotations x Alternate toe touches x 30
 Outline Ares Power core 1. V-ups with med ball x 15 2. Lumber jack x 15 3. Rotations x 15 4. Alternate toe touches x 30 5. Big Turns x 15 each direction 6. Seated swing x 15 each direction 7. Two leg lift
Outline Ares Power core 1. V-ups with med ball x 15 2. Lumber jack x 15 3. Rotations x 15 4. Alternate toe touches x 30 5. Big Turns x 15 each direction 6. Seated swing x 15 each direction 7. Two leg lift
Daily. Workout Workout Focus: Bodyweight strength, power, speed, mobility MOBILITY WARM UP. Exercise Descriptions.
 Workout 5.18.18 Workout Focus: Bodyweight strength, power, speed, mobility Pelvic Tilt Lateral Pelvic Tilt Hip Circles Lateral Spine Glide Spinal Flexion and Extension Lateral Spinal Flexion Neck Juts
Workout 5.18.18 Workout Focus: Bodyweight strength, power, speed, mobility Pelvic Tilt Lateral Pelvic Tilt Hip Circles Lateral Spine Glide Spinal Flexion and Extension Lateral Spinal Flexion Neck Juts
Biceps Curl. Muscle Focus: Biceps. You do < 12 Reps = 500 Body Building Points You do > 12 Reps = 1000 Body Building Points
 Biceps Curl Muscle Focus: Biceps Stand tall with feet shoulder-width apart, invisible dumbbells at hips Curl both invisible dumbbells up toward shoulders Lower arms and repeat You do < 12 Reps = 500 Body
Biceps Curl Muscle Focus: Biceps Stand tall with feet shoulder-width apart, invisible dumbbells at hips Curl both invisible dumbbells up toward shoulders Lower arms and repeat You do < 12 Reps = 500 Body
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS
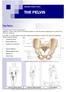 NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS The Pelvis The pelvis has 3 joints connecting it together 2 sacro-iliac joints at the back (posterior) and the pubic symphysis joint which is at the front (anterior). A
NETWORK FITNESS FACTS THE PELVIS The Pelvis The pelvis has 3 joints connecting it together 2 sacro-iliac joints at the back (posterior) and the pubic symphysis joint which is at the front (anterior). A
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises. Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
An overview of posture
 An overview of posture What is posture? Posture is the description of an overall body position. This can be intentional or unintentional how we are hold our bodies, but it is the way each individual will
An overview of posture What is posture? Posture is the description of an overall body position. This can be intentional or unintentional how we are hold our bodies, but it is the way each individual will
Low Back Pain Home Exercises
 Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
PHYSICAL TRAINING INSTRUCTORS MANUAL TABLE OF CONTENT PART 3
 TABLE OF CONTENT PART 3 Exercise No 11: Chest Press... 2 Exercise No 12: Shoulder Press... 3 Exercise No 13: Pull-overs... 5 Exercise No 14: Tricep Extension... 6 informal exercises to develop upper body
TABLE OF CONTENT PART 3 Exercise No 11: Chest Press... 2 Exercise No 12: Shoulder Press... 3 Exercise No 13: Pull-overs... 5 Exercise No 14: Tricep Extension... 6 informal exercises to develop upper body
Stable Lower Body A (60 min)
 Stable Lower Body A (60 min) Protection (5 min) Exercise Reps Duration (s) Ts on an Exercise Ball 8 30 Ls on an Exercise Ball 8 30 Scapular Push-Up (1 Arm, Kneeling) 10 ea 60 Lateral Band Walk (Straight,
Stable Lower Body A (60 min) Protection (5 min) Exercise Reps Duration (s) Ts on an Exercise Ball 8 30 Ls on an Exercise Ball 8 30 Scapular Push-Up (1 Arm, Kneeling) 10 ea 60 Lateral Band Walk (Straight,
An athlete s ability to handle their own
 Training Force Couples for Optimized Sports Performance An athlete s ability to handle their own body weight is foundational to competition-based actions. Thus, strength to weight ratio is a key correlate
Training Force Couples for Optimized Sports Performance An athlete s ability to handle their own body weight is foundational to competition-based actions. Thus, strength to weight ratio is a key correlate
Calisthenic Guidelines
 8 Calisthenics In this chapter you will learn about: Proper form and guidelines for performing calisthenics. Designing a calisthenic exercise program. Abdominal exercise techniques. Calisthenics require
8 Calisthenics In this chapter you will learn about: Proper form and guidelines for performing calisthenics. Designing a calisthenic exercise program. Abdominal exercise techniques. Calisthenics require
EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS
 Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
Page 1 of 21 EXERCISE PHOTOS, TIPS AND INSTRUCTIONS Page 2. Squat Page 12. Crab Walks Page 3. Single Leg Squat Page 13. Bench Press Page 4. Split Squat Page 14. Bench Pull Page 5. Deadlift Page 15. Shoulder
ETS EXERCISE SHEETS EXPLAINED
 ETS EXERCISE SHEETS EXPLAINED Exercises 4pt kneeling Supermans Extend opposite arm/leg whilst maintaining neutral spine. Hips are to remain parallel to the floor during movement. Core. Also assists in
ETS EXERCISE SHEETS EXPLAINED Exercises 4pt kneeling Supermans Extend opposite arm/leg whilst maintaining neutral spine. Hips are to remain parallel to the floor during movement. Core. Also assists in
Walking/Running Stretch Routine
 Walking/Running Stretch Routine Quadriceps Stretch With left hand grasp your right ankle, gently pull heel toward buttocks until stretch is felt. Repeat on opposite side. Walking/Running Stretch Routine
Walking/Running Stretch Routine Quadriceps Stretch With left hand grasp your right ankle, gently pull heel toward buttocks until stretch is felt. Repeat on opposite side. Walking/Running Stretch Routine
Warm Up Start by foam rolling the key areas, and follow with static stretching and at end of session. Perform cardio activity or 6-7 R.P.E.
 VISIT FULL SITE PROGRAM FOR VIC SKI TEAM SKI TEAM CORE STABILISATION #3 Trainer : Jean-Claude Legras PRINT Introduction The goal of every core stabilization training should be to increase postural control,
VISIT FULL SITE PROGRAM FOR VIC SKI TEAM SKI TEAM CORE STABILISATION #3 Trainer : Jean-Claude Legras PRINT Introduction The goal of every core stabilization training should be to increase postural control,
Home Exercise Program
 YOUR HOME PROGRAM Home Exercise Program Created by Dr. Furr MD Nov 30th, 1999 Total 21 LOWER TRUNK ROTATIONS - LTR Lying on your back with your knees bent, gently move your knees side-to-side. PRAYER STRETCH
YOUR HOME PROGRAM Home Exercise Program Created by Dr. Furr MD Nov 30th, 1999 Total 21 LOWER TRUNK ROTATIONS - LTR Lying on your back with your knees bent, gently move your knees side-to-side. PRAYER STRETCH
Core Stabilization for a Pain- Free Posture
 PAIN-FREE POSTURE PROGRAM Core Stabilization for a Pain- Free Posture with Mary Ann Foster ABOUT MARY ANN FOSTER Massage therapist since 1981 Somatic educator and movement teacher Author of Somatic Patterning
PAIN-FREE POSTURE PROGRAM Core Stabilization for a Pain- Free Posture with Mary Ann Foster ABOUT MARY ANN FOSTER Massage therapist since 1981 Somatic educator and movement teacher Author of Somatic Patterning
Strength Challenge Week #4
 Strength Challenge Week # DAY / PULL & BALANCE WORLDS GREATEST WARM UP DUMBBELL UNILATERAL DEADLIFT Set - 0 light weight Set - moderate weight- slow eccentric lowering the weight for seconds Set - 0 moderate
Strength Challenge Week # DAY / PULL & BALANCE WORLDS GREATEST WARM UP DUMBBELL UNILATERAL DEADLIFT Set - 0 light weight Set - moderate weight- slow eccentric lowering the weight for seconds Set - 0 moderate
Beginner and advanced exercises for the abdominal and lower back muscles
 Beginner and advanced exercises for the abdominal and lower back muscles Professionally managed by: Mission: The National Institute for Fitness and Sport is committed to enhancing human health, physical
Beginner and advanced exercises for the abdominal and lower back muscles Professionally managed by: Mission: The National Institute for Fitness and Sport is committed to enhancing human health, physical
Lift it, Shift it, Twist it
 Lift it, Shift it, Twist it Optimizing Movement to Avoid Workplace Injury Dr. Amanda Williamson, PT, DPT, CSCS Dr. Constanza Aranda, PT, DPT, MSPH Disclosures We present on behalf of the Florida Physical
Lift it, Shift it, Twist it Optimizing Movement to Avoid Workplace Injury Dr. Amanda Williamson, PT, DPT, CSCS Dr. Constanza Aranda, PT, DPT, MSPH Disclosures We present on behalf of the Florida Physical
Stand Tall with Osteoporosis thru Pilates
 Stand Tall with Osteoporosis thru Pilates C A S S I T E R P E N I N G P T, D P T, C S C S, C P I C H R I S R I E G E R P T U P S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L J U N E 1 9, 2 0 1 7 Content
Stand Tall with Osteoporosis thru Pilates C A S S I T E R P E N I N G P T, D P T, C S C S, C P I C H R I S R I E G E R P T U P S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L J U N E 1 9, 2 0 1 7 Content
BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER. Planes of Lumbar Pelvic Femoral (Back, Pelvic, Hip) Muscle Function
 BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER Functional performance of the soccer player reflects functional capability of certain specific muscle and muscle groups of the back, pelvis and hip to work
BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER Functional performance of the soccer player reflects functional capability of certain specific muscle and muscle groups of the back, pelvis and hip to work
Improving swimming through Pilates
 Improving swimming through Pilates Cleia Ramsey 10 Mar 2017 2016 BASI Training Class Herndon, VA Introduction As a mother of two swimmers, I spend many hours at the pool deck and have learned a lot about
Improving swimming through Pilates Cleia Ramsey 10 Mar 2017 2016 BASI Training Class Herndon, VA Introduction As a mother of two swimmers, I spend many hours at the pool deck and have learned a lot about
Static Flexibility/Stretching
 Static Flexibility/Stretching Points of Emphasis Always stretch before and after workouts. Stretching post-exercise will prevent soreness and accelerate recovery. Always perform a general warm-up prior
Static Flexibility/Stretching Points of Emphasis Always stretch before and after workouts. Stretching post-exercise will prevent soreness and accelerate recovery. Always perform a general warm-up prior
PGYVC Volleyball Circuit Athletic Plan
 PGYVC Volleyball Circuit Athletic Plan Workout Plan: This workout plan is to introduce and promote off court training for PGYVC athletes as well as to build confidence for athletes who have not done physical
PGYVC Volleyball Circuit Athletic Plan Workout Plan: This workout plan is to introduce and promote off court training for PGYVC athletes as well as to build confidence for athletes who have not done physical
Foundation Mobility (50 min)
 Foundation Mobility (50 min) Protection (10 min) Exercise Reps Duration (s) Wrist Abduction 12 ea 60 Wrist Adduction 12 ea 60 Wrist Pronation and Supination 10 ea 60 Wrist Pronation and Supination (Reverse
Foundation Mobility (50 min) Protection (10 min) Exercise Reps Duration (s) Wrist Abduction 12 ea 60 Wrist Adduction 12 ea 60 Wrist Pronation and Supination 10 ea 60 Wrist Pronation and Supination (Reverse
Dynamic Flexibility All exercises should be done smoothly while taking care to maintain good posture and good technique.
 Dynamic Flexibility All exercises should be done smoothly while taking care to maintain good posture and good technique. Lying on back: Hip Crossover: Arms out in T position, feet flat on the floor, knees
Dynamic Flexibility All exercises should be done smoothly while taking care to maintain good posture and good technique. Lying on back: Hip Crossover: Arms out in T position, feet flat on the floor, knees
Masters Swimming Dryland Training Program. November-December
 Masters Swimming Dryland Training Program November-December Staggered Stance High Kneeling Chop with Theraband (1 minute each side) Engage core. Pull Theraband down toward knee that is on the ground keeping
Masters Swimming Dryland Training Program November-December Staggered Stance High Kneeling Chop with Theraband (1 minute each side) Engage core. Pull Theraband down toward knee that is on the ground keeping
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
PILATES CONDITIONING FOR SURFERS
 PILATES CONDITIONING FOR SURFERS Michelle Hopper January 11, 2018 Body Arts and Science International Comprehensive Teacher Training Program 2013 Jen Pearlstein Oceanside CA ABSTRACT Modern surfing is
PILATES CONDITIONING FOR SURFERS Michelle Hopper January 11, 2018 Body Arts and Science International Comprehensive Teacher Training Program 2013 Jen Pearlstein Oceanside CA ABSTRACT Modern surfing is
