Work Pain & MSD Prevention in the Office. from. SmartCare Physical Therapy
|
|
|
- Toby Peters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 from. SmartCare Physical Therapy Work Pain & MSD Prevention in the Office Dr. Lauren A. Hebert, DPT, OCS Doctor of Physical Therapy Orthopedic PT Specialist Ergonomics Specialist Copyright 2017 Lauren Hebert, DPT, OCS prexar.com www. smartcarept.co www. impacc.com ** This is prevention information. If you already have a problem, have your PT approve these for you
2 M.S.D. PROBLEMS (low back and neck-arm MSD) : Musculo-Skeletal Disorders (MSD) of the neck, low back, and upper extremity are epidemic in today s workplace, AT 55% of Worker Comp claims and 65% of costs. But they are highly preventable! There is a high risk of these MSD s in office-computer work. RE-DEFINING THE PROBLEM: Some call these problems Repetitive motion injuries. This is not quite correct. Most MSD problems in the office-computer workplace are more the result of SUSTAINED POSTURES at the neck, back, and upper extremities (especially prolonged SITTING) SUSTAINED POSTURE DISORDERS.. Sustained sitting, rounded-shoulders, hands postured on mouse and keyboard all day: create sustained work posture for long periods, prolonged joint loading, muscle contraction, tendon tension. These cause pressures that block blood supply to these structures, causing irritation that leads to MSD s. It is a BLOOD SUPPLY issue. Sitting leads to roundedshoulders slouching, tightening muscles on sides of neck, squeezing nerves and blood vessels to arms-hands risking MSD in arms. Round-shoulders slouching squeeze blood vessels-nerves Rounded-shoulders forward-head slouching stresses neck and upper back; squeezes nerves & blood supply to arms and hands. PREVENTING MSD requires attention to workstation ergonomics, improving worker posture habits, using a VARIETY of postures and activity, frequent micro-stretches to restore blood supply, and worker self-care education. SITTING the top priority issue Sitting is very damaging to the body. Sitting doubles weight-bearing on spinal discs in the lower back, in a stressed position, bulging and compressing discs, while weakening back muscles. It encourages slouched forward head posture, stressing upper back and neck structures. Overall lack of movement activity ages heart-lungs-blood vessels. Is there a proper fit of the chair? Actually NO. Finding perfect posture and staying there all day is not good. There is still weightbearing loads to key structures. Even proper posture is bad for you IF YOU SUSTAIN that position too long. What is far BETTER is POSTURE VARIETY! What is the correct chair? We cannot point one out because chairs are like shows what feels good to one, feels terrible to another. What is key is to be able to change the adjustment every hour. The best advice on chair adjustment is to CHANGE the fit every half hour, simply changing seat height and inch or two, or changing seat tilt if that is an available adjustment. Even more important: stand and STRETCH backward 10 seconds every hour to reverse low back disc pressure and bulging that comes with sitting. WALK around a short distance often also helps this. Many offices now offer STAND-SIT workstations: tall desks where workers can switch between sitting (tall chair) and standing. This has been very effective at reducing fatigue, pain, and other effects of too much sitting. This rotates compression loads among more tissues, for less time exposure of weight-bearing to each structure. It helps restore circulation to working tissues. sit-stand unit 10 second back-bend every hour!! copyright L Hebert 2017
3 NECK AND LOW BACK (spine function) : The spine is a stack of bones (vertebrae) balanced upright. The spine must be MOBILE for movements and STABLE for posture. This is a difficult set of demands on the spine, causing many potential problems, and vulnerable to early aging changes. The bones are connected at facet joints, forming a pivot point for movement and posture. These joints run up the back of the spine, on left and right sides. They have very sensitive nerves to control balance, posture, and motion. But that sensitivity can create lots of pain with even minor injury. These small joints can become arthritic over time, growing bone spurs that can pinch nerves. Facet joints are stressed by prolonged postures, overhead work, and twisting. Degenerated discs can also stress these joints. Rear view; facet joints Front view; discs The Discs: Lots of problems come from the discs, directly and indirectly. The discs are cushion pads between vertebrae, at the front ¾ of the vertebrae. They are shock absorbers. They also act as ball bearings for vertebrae to pivot on during bending. When we are young, the discs are 80% water, to allow shock absorption and easy pivoting during bending. But as we get older (even by age 35) discs lose water and elasticity. They cannot absorb loads or bend as well as before. They get thin from water loss, shifting more load to nearby joints, causing strains and arthritis. As discs thin, bones sit closer together. This can squeeze nerves passing nearby. This is degenerative disc disease. This is VERY common with years of SITTING at a desk or in a vehicle. SITTING squeezes water out of discs and encourages bulging. Sitting is a major risk for degenerated discs in low back and neck. In the center of the disc is a wet gel contained in tough fibrous outer rings. Bending forward (or sitting) squeezes the front of the disc, pushing that gel back against the back wall of the disc. This wall is weak and tends to balloon out, causing a bulging disc. It can eventually burst, tear or leak, causing a ruptured disc. But this is very reversible. Bending backward tends to reverse this, pulling the gel back to the center of the disc. Frequent standing back-bend stretches tend to reverse disc damage from sitting. Normal posture has slight swayback Forward-bend or sit bulges & degenerates discs Back-bend stretch corrects disc mechanics Ligaments; Ligaments are elastic straps that allow reasonable movement while tying all the bones and joints together. Sitting with a slouched posture causes an all-day stretch to upper back ligaments, weakening this part of the spine. Muscles Muscles have two jobs: move the spine, and hold the spine upright (posture). Pain develops from either of these. Repeated motions, heavy loading, sustaining a posture too long can all overwork muscle, causing buildup of waste products and tissue damage. BUT the primary problem on office jobs is prolonged sitting causing posture muscles to become very weak setting you up for a back strain outside of office work, such as lifting something at home. This is overstretch weakness-instability. Ligament bind together bones & joints Low back muscles protect other tissues Neck vertebrae, discs, joints
4 NECK & BACK MSD PROBLEMS: X-RAYs & MRI: are usually not accurate!! MOST adults with NO PAIN show bulging discs, ruptured discs, degenerated discs, significant arthritis on an MRI but NO pain. Don t decide you are disabled by what is on your MRI It is often WRONG! MOST adults with NO BACK or NECK PAIN have degenerated discs, bulging discs, arthritis on x-ray or MRI but NO pain. So, x-rays and MRI findings for these are not considered valid unless the patient has worsening neurological symptoms down their legs or arms. Most back-neck pain is mechanical and can be corrected with simple exercises and habit changes. Pain goes away, while the x-ray and MRI still shows disc and arthritis findings but no pain. Do NOT let the x-ray and MRI falsely disable you!! Most problems are mechanical weakness, stiffness, instability, posture strain. Degenerated Discs Discs are 80% water when you are 25, but can drop to 40% water by age 50. The discs get much thinner. This increases loads on facet joints and lead to arthritis and sprains. This is reversible with certain stretches, described later. Caused by aging, inactivity, years of prolonged sitting, years of repeated or sustained bending. Bulging or Ruptured Discs Caused by repeated or sustained bending, lifting loads, and EXCESSIVE SITTING. Gel in center of disc pushes out back wall of disc, or leaks through back wall. This can press on nearby nerves, causing pain down arm or leg. These sometimes require surgery, but that is rare. Most will resolve with stretches, discussed later. Soft Tissue Sprain (ligament or muscle) Torn tissues caused by loading in an awkward or extreme or prolonged position. Heals with rest, followed by stretches, then strengthening. Also caused by prolonged posture loading (sitting, holding mouse, keyboard use) Stress Stress may (sometimes) show up as pain. It may not cause your pain, but it can make it LOTS worse. Pain and lost work causes stress, which causing spasm, causing more pain, causing more stress. Being aware of this can help recovery. NECK-SHOULDER PAIN Many shoulder strains are actually coming from the neck. Pain in shoulder blade, upper shoulder between neck and shoulder joint are usually neck issues. Shoulder and neck easily irritate each other. Many arm-hand pain problems also have inputs from neck due to pinched nerves and postures that can reduce blood supply down the arm. OVERUSE, TENDINITIS: important new definition! Nerves & blood vessels to arm pass through neck muscles. Can be squeezed by poor posture. WORK: Muscle contract, pulling on tendons, pulling on bones, to move joints, or hold a sustained position (such as gripping). This is work to produce motion or to sustain a posture. Damage may come with too much motion, or prolonged posture. These actions produce pressures in muscles, tendons, and joints pressure that often exceeds blood pressure.., this pressure blocks blood supply-oxygen to these tissues. Reduced oxygen causes increased waste products that build up in tissues. These wastes irritate tissues: inflammation: tendinitis, and other damage. IT IS A BLOOD SUPPLY_OXYGEN PROBLEM. We prevent MSD by boosting blood supply to these working tissues. It is easy. It is effective, with everal tactics available. ROUND-SHOULDERS, SLOUCHING, FORWARD HEAD POSTURE: Very common posture habit, placing head well ahead of spine. This compresses joints in upper neck, discs in middle neck, weakens muscles and ligaments in upper back. Muscles on side of neck tighten, compressing nerves and blood vessels passing through to arm structures. All this greatly adds to stress down the arm. Forward head slouching Chin-tuck: be an inch taller! Lateral neck stretch hourly micro-stretches at neck CORRECTIONS: Position work higher. Switch between sitting-standing. Job task rotation. Neck micro-stretches (described later)
5 ROTATOR CUFF: Overuse tendinitis at shoulder tendons located between bones of shoulder in tightly-confined space. Irritation causes swelling, blocking blood supply. Very painful, disabling, costly, often difficult to treat! Caused by reaching (too high, too far, too often, too prolonged, or with load in hand. In the office, it is usually reaching for calculator or a mouse or other materials placed too far. cuff tendons pinched between bones Reaching high, far or often CORRECTIONS: Make reach lower, closer, less often, less prolonged, lighter. Job task rotation. Shoulder micro-stretches. TENNIS ELBOW: This is actually a tendinitis of WRIST muscles where they originate on outside of elbow. Caused by loading the wrist-hand, where wrist muscles-tendons are supporting the load, hurting up at elbow where wrist muscles start. Causes may be heavy loads lifted or light loads held for hours (such computer mouse work). CORRECTIONS: Reduce load or holding time; change work postures (switch between mouse and trackball hourly); task rotation; wrist-arm micro-stretches. GOLFER S ELBOW: Similar to tennis elbow except on inside of elbow. Actually problem at muscle of grip-pinch, or pronator muscle (turns forearm over): prolonged, repeated, forceful grip; turning or prolonged holding palm-up position. Lots of mouse work may risk this Tennis elbow wrist load Golfer s elbow grip & twist WRIST-HAND-CARPAL TUNNEL: Wrist and thumb overuse comes from grip, pinch, wrist bent, vibration, thumb actions. These are sensitive structures easily irritated. Swelling at wrist or base of thumb can compress nerves entering hand (carpal tunnel) causing pinched nerve that (sometimes) requires surgery. Several medical issues add to this risk (pregnancy, diabetes, smoking, thyroid problems, obesity, wrist or thumb arthritis). CORRECTIONS: Reduce time spent in grip-pinch, padded pen-pencil; change keyboard legs in-out often for variety, improve neck posture, rotate job tasks, switch between mouse & trackball often; micro-stretches at wrist. elbow straight, palm-up, stretch wrist back palm down, fist closed, curl wrist down
6 ERGONOMICS Risks for C.T.S. Work risks are pinch or grip that is too forceful, too often, or too prolonged. bent wrist positioning during grip or pinch makes this worse. Vibration is also a strong risk (power tools, for example). Forward head posture adds to CTS risks. One may need to improve the ergonomics of their job (see upcoming page on Computer Ergonomics, as an example). Minimize grip force or duration. Grip diameter should be about 2 inches. Try to increasing the variety of work tasks, because doing the same task all day increases risks. Frequently switch between sitting and standing, if appropriate. Resting arms on work surface reduces neck loading, reducing arm stress. Frequently stretch during workday (see our page of workplace stretches). Self-care for the wrist includes reasonable rest periods, maybe with a splint (especially worn at night), frequent stretching at wrist and neck, plus maintaining more upright and tall neck posture. grip, pinch, wrist bent Grip size too small Switch between mouse vs trackball for work variety Resting arms on work surface reduces neck load micro-stretching Grip size good Night splint Good neck posture and flexibility helps maintain good blood supply and healthy nerves to arm-hand (be an inch taller!). Correct slouching: be an inch taller Lateral neck side stretch Switch between sitting and standing, easing neck strain, reducing arm stress
7 THE COMPUTER WORKSTATION : YOU NEED Symmetrical posture Head centered Eyes slightly down Arms rest on surface posture variety motion variety. MONITOR Position squarely in front (NOT off to one side). Height places top of screen at eye level so eyes track from zero to about 30 degrees down. BUT all this changes if you wear BIFOCALS or PROGRESSIVE lenses. These are made for reading a book (lower & closer than a computer monitor). These cause you to lean forward and tip head backward to look through reader part of eyeglasses. This is very damaging to upper neck, a common source of headache and neck arthritis. It is best to get separate singlevision medium focus-distance reading glasses that allow you to better posture your head-neck more upright, less awkward. bifocals: NO Upright, arm-supported posture KEYBOARD Pushed in enough to provide some surface to rest forearms (NEW TACTIC). Place gel pad in front of these to cushion forearms resting. (Old rules said to do not rest arms, but new research suggests this is wrong.) One of the best setups for this is to place keyboard and monitor in CORNER of a right-angle desk so arms have lots of rest surface on either side. Keyboard trays tend to position arms too low, causing slouching. But the best use of these is to use tray for an hour, then move keyboard to desk for an hour, switching back and forth to create good posture VARIETY. KEYBOARD LEGS Work with rear legs flipped out for slight wrist extension for an hour, then fold legs in for slight wrist flexion for an hour. The key is to give wrists some variety of posture and movement patterns. Variety reduces MSD risks. MOUSE OR TRACKBALL? Mouse risks golfer s elbow, but trackball risks tennis elbow. Answer? Use BOTH, switching between them hourly. This rotates work between two sets of muscles, reducing exposure to each muscle. Work task variety is key. TELEPHONE Do NOT jam phone between neck and shoulder. Very damaging! Use a headset or speaker-phone. Corner desk setup great to rest arms NO! Use headset! PREVENT MSD with WORK VARIETY Change seat fit-height every hour. Switch between sitting and standing often. Switch between mouse and track-ball often. Switch keyboard between tray and desktop. Flip keyboard legs in, then out often. Change tasks often (filing, etc.) for work VARIETY.
8 MICRO-STRETCHING? We used to say workplace stretching is not effective. But newer studies and our experience at several hundred workplaces show this can work very well IF it is done CORRECTLY! We also see some workplaces doing incorrect stretches. Micro-stretches are set of 6-8 stretches done only 10 seconds each, several time per day specifically designed by a physical therapist to fit risks, professionally taught by a physical therapist and adequately enforced by management. IT WORKS if done RIGHT! Workplace Micro-stretching for the office see handout WORKER EDUCATION: Workers respond well to properly presented motivational training on how to take care of the aches and pains they of daily life. Physical therapists are trained to present these programs on personal ergonomics skills, workplace micro-stretching, after-work recovery stretches. Workers hunger for this information because they do Not want to hurt. And they want to tolerate life after work. Ergonomics does not work without workplace education teaching works not what to do, but WHY to do it. Once they understand WHY they hurt and WHY to do certain prevention tactics then they willing follow our advice. After-work low back recovery exercises THE AGING WORKER One cannot separate work-related MSD from the effects of AGING. Age changes start to show up around age 30. Older workers are often your most skilled essential people with good work ethic: too valuable to lose. AGING changes to the musculo-skeletal system are REVERSIBLE! This is especially true for office jobs where days of sitting speeds and worsens aging. Off-work activity, walking, specific gentle stretches can restore lost function, reduce pain, reverse age changes. Not difficult!
9 COMPUTER WORK-STATION Set-up one-page summary New ergonomics tactics Bifocal eyeglasses cause neck posture strain-headache Place MONITOR squarely in front, NOT off to one side top edge of screen at eye-level. NOTE Wearing BIFOCAL-progressive eyeglasses for computer work risks serious neck-headache problems because you lean forward and tip head back to see screen. Use single-vision reading glasses here! Push KEYBOARD in 4-6 inches from edge of desk, then place gel pad here for arm support. Rest arms to type. NOTE Best: place computer in CORNER to allow full surface support for forearms. See pic below KEYBOARD TRAY is often too low but switching every hour between keyboard in tray versus placed on desk does provide work posture VARIETY, which can be good for posture work relief. MOUSE should also be pushed in to allow forearm support, with gel pad placed in front for hand-wrist rest. Also, switch between using MOUSE versus TRACKBALL every 1-2 hours for wrist posture VARIETY. Use a DOCUMENT HOLDER to hold papers upright, and move this setup often for posture work variety. TELEPHONE do NOT EVER hold telephone handset between head and shoulder. Use HEAD SET!! PEN-PENCIL place padded SLEEVE over pinch surface to reduce pinch risks. CHAIR Most important to be height-adjustable. The KEY is to CHANGE height often, 2 inches up or down every hour for posture variety, PLUS do a standing back-bend stretch every hour. STANDUP OPTION Many offices employ STANDING DESKS with tall chairs to allow switch between sitting work and standing work. This has been very well received by workers, for improved work comfort. Another option is the VARI-DESK platform placed on conventional desk, which allows worker to raise computer to standing height, for work posture VARIETY much cheaper-easier option than standing desk-chair. Do our MICRO-STRETCHES hourly to keep circulation to working tissues!! Vari-Desk allows switching between sit vs stand Corner desk setup allows best arm support copyright L Hebert 2017
10 Workplace Micro-Stretches We set up have set up microstretcing program for more than 500 workplaces, customized to the types of jobs and work risks for each workplace. This is the typical program we recommend for the office setting or other sitting jobs (such as driving jobs). It is very important that employees be educated by the Physical Therapist on how and why to do each of these, to make sure people are trainined motivated expert at these. Without that training, employees will not comply, or be safe with these. Do NOT start these until you have received professional instruction If you already have a problem, have your Physical Therapist approve-modify these for you Copyright L Hebert, DPT 1982 to at prexar.com
M.S.D. Prevention & Ergonomics
 Musculo-Skeletal Disorders M.S.D. Prevention & Ergonomics Dr. Lauren A. Hebert, DPT, OCS Doctor of Physical Therapy Orthopedic PT Specialist Ergonomics Specialist Copyright L Hebert 2017 Lhebertpt @ prexar.com
Musculo-Skeletal Disorders M.S.D. Prevention & Ergonomics Dr. Lauren A. Hebert, DPT, OCS Doctor of Physical Therapy Orthopedic PT Specialist Ergonomics Specialist Copyright L Hebert 2017 Lhebertpt @ prexar.com
Musculo-Skeletal Disorders
 Musculo-Skeletal Disorders Identifying Ergonomics Risks & Prevention Tactics Dr. Lauren A. Hebert, DPT, OCS Orthopedic PT Specialist Ergonomics Specialist Copyright L Hebert 2017 LHebertpt @ prexar.com
Musculo-Skeletal Disorders Identifying Ergonomics Risks & Prevention Tactics Dr. Lauren A. Hebert, DPT, OCS Orthopedic PT Specialist Ergonomics Specialist Copyright L Hebert 2017 LHebertpt @ prexar.com
PERSONAL COMPUTER WORKSTATION CHECKLIST
 PERSONAL COMPUTER WORKSTATION CHECKLIST Last Revised: 6/26/17 A. Summary Use the following checklists to assess your own computer workstation. If you say No to any items within the lists, it may indicate
PERSONAL COMPUTER WORKSTATION CHECKLIST Last Revised: 6/26/17 A. Summary Use the following checklists to assess your own computer workstation. If you say No to any items within the lists, it may indicate
"INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS"
 PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
PRESENTER'S GUIDE "INDUSTRIAL ERGONOMICS" Part of the General Safety Series Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS OUTLINE OF MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every
 According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA many office workers report work-related musculoskeletal disorders or MSDs every year. For some, the problem becomes so severe that they
the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back
 the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back anatomy Your spine s job is to: Support your upper body and neck Increase flexibility of your spine Protect your spinal cord There are 6 primary components of
the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back anatomy Your spine s job is to: Support your upper body and neck Increase flexibility of your spine Protect your spinal cord There are 6 primary components of
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings. ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders. Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2120 ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal Disorders Leader s Guide 2001, ERI PRODUCTIONS ERGONOMICS EMPLOYEE TRAINING: Preventing Musculoskeletal
Ergonomics Glossary. Force The amount of physical effort a person uses to do a task.
 Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
Ergonomics Glossary Administrative controls Procedures used to reduce the duration, frequency, or severity of exposure to a hazard. They may include training, job rotation, and gradual introduction to
Ergonomics. Julie W. Burnett, COTA/L, ATP
 Ergonomics Julie W. Burnett, COTA/L, ATP What is Ergonomics? Definition: the Science of designing a person s environment so that it facilitates the highest level of function Good Ergonomics: Prevent Injury
Ergonomics Julie W. Burnett, COTA/L, ATP What is Ergonomics? Definition: the Science of designing a person s environment so that it facilitates the highest level of function Good Ergonomics: Prevent Injury
NECK OWNER S MANUAL. A Guide to the Care of the Neck
 NECK OWNER S MANUAL A Guide to the Care of the Neck A Real Pain in the Neck If you suffer from neck pain, you re not alone. Many people have this pain at some point in their lives. Things such as poor
NECK OWNER S MANUAL A Guide to the Care of the Neck A Real Pain in the Neck If you suffer from neck pain, you re not alone. Many people have this pain at some point in their lives. Things such as poor
Physiology of Injuries
 Presented By: Du-All Safety, 2019 Physiology of Injuries Strains: the muscles and tendons that support the spine are twisted, pulled or torn. Ex. Overstretching when carrying extra weight. Over flexion:
Presented By: Du-All Safety, 2019 Physiology of Injuries Strains: the muscles and tendons that support the spine are twisted, pulled or torn. Ex. Overstretching when carrying extra weight. Over flexion:
Risk Management Department. Office Ergonomics
 Risk Management Department Office 1 Introduction In order to prevent injuries, reduce stress and improve work productivity, APS has developed this training to provide you the knowledge to help yourself
Risk Management Department Office 1 Introduction In order to prevent injuries, reduce stress and improve work productivity, APS has developed this training to provide you the knowledge to help yourself
Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design
 PPT Presentation page 1 Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design Presented by the NYS Public Employees Federation Paige Engelhardt PEF Health & Safety Trainer www.pef.org
PPT Presentation page 1 Reducing Computer Workstation Hazards Through Proper Set-up and Design Presented by the NYS Public Employees Federation Paige Engelhardt PEF Health & Safety Trainer www.pef.org
Beginning of Process: Development of the Office Ergonomics program.
 CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Office Ergonomics Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Office Ergonomics Program Purpose: To provide applicable suggestions and procedures that may be help reduce
CNM WAY PROCESS CNM Process Name Office Ergonomics Program (05/15/2018 Revision) Overview of Office Ergonomics Program Purpose: To provide applicable suggestions and procedures that may be help reduce
Office Ergonomics. Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer
 Office Ergonomics Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer Objectives Define Ergonomics & MSDs Identify Ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up workstations to minimize
Office Ergonomics Presented by: Samar Khalil, Environmental & Chemical Safety Officer Objectives Define Ergonomics & MSDs Identify Ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up workstations to minimize
Version February 2016
 Version 3.1 29 February 2016 Health and Safety Unit 1 Table of Contents 1. Setting up your computer workstation... 3 Step 1: Adjusting yourself to the correct height... 3 Step 2 Adjusting your Chair...
Version 3.1 29 February 2016 Health and Safety Unit 1 Table of Contents 1. Setting up your computer workstation... 3 Step 1: Adjusting yourself to the correct height... 3 Step 2 Adjusting your Chair...
260- OFFICE ERGONOMICS
 260.1 PURPOSE A. To provide some universally applicable suggestions and procedures that may be helpful when setting up an ergonomically correct work station in an office setting. 260.2 SCOPE A. This procedure
260.1 PURPOSE A. To provide some universally applicable suggestions and procedures that may be helpful when setting up an ergonomically correct work station in an office setting. 260.2 SCOPE A. This procedure
ERGONOMICS. Risk Management
 ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
ERGONOMICS Risk Management ERGONOMICS-What is it? Derived from two Greek words: Nomoi meaning natural laws Ergon meaning work Hence, ergonomists study human capabilities in relationship to work demands
Feel Better. Stanford University ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE. USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better.
 Feel Better. PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better. Stanford University Your workspace should respond to your changing needs, helping you eliminate uncomfortable
Feel Better. PROPER ERGONOMIC POSTURE ADJUSTING YOUR WORKSTATION USEFUL ERGONOMIC TIPS Work Better. Stanford University Your workspace should respond to your changing needs, helping you eliminate uncomfortable
Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03
 Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03 Working from home is becoming more of an option for employees today. The type of work usually entails working from the home computer work station.
Home Office Solutions By: Laura Cervantes QAS 515 3/26/03 Working from home is becoming more of an option for employees today. The type of work usually entails working from the home computer work station.
Back Safety Healthcare #09-066
 Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
neck pain WHAT YOU CAN DO
 neck pain WHAT YOU CAN DO Neck pain Neck pain is a common problem. Nearly 25 percent of adults will experience neck pain at some time in their lives. Even though neck problems can be painful and frustrating,
neck pain WHAT YOU CAN DO Neck pain Neck pain is a common problem. Nearly 25 percent of adults will experience neck pain at some time in their lives. Even though neck problems can be painful and frustrating,
Ergonomics Seminar. Presented by Stephanie Materazzi & Christine Miller
 Ergonomics Seminar Presented by Stephanie Materazzi & Christine Miller The muscles in the back are unlike many other muscles in your body. They are almost always in use. They hold your torso in an upright
Ergonomics Seminar Presented by Stephanie Materazzi & Christine Miller The muscles in the back are unlike many other muscles in your body. They are almost always in use. They hold your torso in an upright
BODY MECHANICS CMHA-CEI
 BODY MECHANICS CMHA-CEI Basics about backs Facts about Back Disorders Maintaining a Healthy Back Common activities Lifting Techniques Stretching Techniques Topics Your back Spine & Vertebrae Discs Nerves
BODY MECHANICS CMHA-CEI Basics about backs Facts about Back Disorders Maintaining a Healthy Back Common activities Lifting Techniques Stretching Techniques Topics Your back Spine & Vertebrae Discs Nerves
"LABORATORY ERGONOMICS"
 MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "LABORATORY ERGONOMICS" Part of the "LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES" Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow Outline of Major Points Covered in the "Laboratory Ergonomics"
MAJOR PROGRAM POINTS "LABORATORY ERGONOMICS" Part of the "LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES" Quality Safety and Health Products, for Today... and Tomorrow Outline of Major Points Covered in the "Laboratory Ergonomics"
LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics
 ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2955 LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in
ERI Safety Videos Videos for Safety Meetings 2955 LABORATORY SAFETY SERIES: Laboratory Ergonomics Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in
Ergonomics. Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques (EOHSS)
 Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Ergonomics Best Practices Lifting Tips and Techniques Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services Environmental and Occupational Health Support Services (EOHSS) Ergonomics: Agenda Ergonomics
Ergonomics. For additional assistance, contact the Occupational Safety office to schedule an evaluation.
 Ergonomics 1. Purpose: Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Safety and Risk and Risk Management (SRM) developed this program to improve the health and happiness of it s employees by assisting
Ergonomics 1. Purpose: Virginia Commonwealth University Department of Safety and Risk and Risk Management (SRM) developed this program to improve the health and happiness of it s employees by assisting
Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important?
 Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important? No matter how well a workstation is designed, problems may arise if attention is not paid to the way the work is done. Working at a computer
Stretching - At the Workstation Why is stretching important? No matter how well a workstation is designed, problems may arise if attention is not paid to the way the work is done. Working at a computer
How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck
 OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
OR How to Avoid a Pain in the Neck COURSE INTRODUCTION Computers are found in almost every workplace. Unfortunately, many employees suffer work related injuries from prolonged use of a computer. This CE
Reference Material Searched and Brought to you
 Reference Material Searched and Brought to you by While requesting for additional reference material, always mention Title and Reference of the document. Please ensure you provide your name, company email
Reference Material Searched and Brought to you by While requesting for additional reference material, always mention Title and Reference of the document. Please ensure you provide your name, company email
BACK SAFETY. How to prevent a lifetime of back problems! Source: https://www.summitholdings.com
 BACK SAFETY How to prevent a lifetime of back problems! Source: https://www.summitholdings.com Volunteer Annual Review 2017 BACK INJURIES More than 1 million workers suffer back injuries each year, accounting
BACK SAFETY How to prevent a lifetime of back problems! Source: https://www.summitholdings.com Volunteer Annual Review 2017 BACK INJURIES More than 1 million workers suffer back injuries each year, accounting
Posture. recreational activities.
 Posture Why maintain correct posture? When maintaining correct posture, the joints, ligaments and muscles of the neck and back are positioned optimally so they are under minimal stress. Maintaining this
Posture Why maintain correct posture? When maintaining correct posture, the joints, ligaments and muscles of the neck and back are positioned optimally so they are under minimal stress. Maintaining this
Ergonomics 101. Presented by: Macomb Benefits
 Ergonomics 101 Presented by: Macomb Benefits Today s agenda Learn what ergonomics is and why it s important at Be able to detect early symptoms of problems Have a list of comfort tips and quick fixes to
Ergonomics 101 Presented by: Macomb Benefits Today s agenda Learn what ergonomics is and why it s important at Be able to detect early symptoms of problems Have a list of comfort tips and quick fixes to
Spine Conditions and Treatments. Your Guide to Common
 Your Guide to Common Spine Conditions and Treatments The spine is made up of your neck and backbone. It allows your body to bend and move freely. As you get older, it is normal to have aches and pains.
Your Guide to Common Spine Conditions and Treatments The spine is made up of your neck and backbone. It allows your body to bend and move freely. As you get older, it is normal to have aches and pains.
CBIA Ergonomic Conference Office Environments December 8 th, 2016
 Loss Control & Risk Management Approach to Control Ergonomic Risks CBIA Ergonomic Conference Office Environments December 8 th, 2016 Course Outline Controlling Ergonomics In Office Environments 1. Experience
Loss Control & Risk Management Approach to Control Ergonomic Risks CBIA Ergonomic Conference Office Environments December 8 th, 2016 Course Outline Controlling Ergonomics In Office Environments 1. Experience
The Chiropractic Neck Book
 The Chiropractic Neck Book A Painful Neck Problem Many people have neck pain at some point in their lives. Pain is often the result of injuries or other problems that cause the spine to be misaligned.
The Chiropractic Neck Book A Painful Neck Problem Many people have neck pain at some point in their lives. Pain is often the result of injuries or other problems that cause the spine to be misaligned.
TOP RYDE CHIROPRACTIC
 1. Ankle Pain Conditions Helped by Chiropractic The ankle joint is made up of ligaments, tendons, nerves, and a disc to cushion motion. Distortions of motion of the ankle can strain the ligaments and muscles
1. Ankle Pain Conditions Helped by Chiropractic The ankle joint is made up of ligaments, tendons, nerves, and a disc to cushion motion. Distortions of motion of the ankle can strain the ligaments and muscles
Commonwealth Health Corporation NEXT
 Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Commonwealth Health Corporation This computer-based learning (CBL) module details important aspects of musculoskeletal disorders, body mechanics and ergonomics in the workplace. It examines: what causes
Corporate Safety Manual. Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics
 Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
Corporate Safety Manual Chapter 8 Office Ergonomics Last updated: April 2015 Office Ergonomics Chapter 8: Office Ergonomics Index Page Introduction to Ergonomics...8-3 Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders
Carpal tunnel syndrome
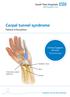 Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Carpal tunnel syndrome Patient Information Clinical Support Services Physiotherapy Median nerve Transverse carpal ligament Ulna Radius What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition
Session Objectives. Business & Legal Reports, Inc. 0903
 Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
Ofis Ergonomisi Session Objectives Define ergonomics and MSDs Identify ergonomic risk factors Recognize MSD symptoms Set up your workstation to minimize stress and strain Perform tasks safely and avoid
OFFICE ERGONOMICS. Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh
 OFFICE ERGONOMICS Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh Ergonomics What is it? Why should I be interested? What do I need to know to help myself? Where can I get help?
OFFICE ERGONOMICS Department of Environmental Health and Safety University of Pittsburgh Ergonomics What is it? Why should I be interested? What do I need to know to help myself? Where can I get help?
ACTIVE AGING.
 Shoulder Pain Rehabilitation Protocol Rotator Cuff Syndrome Shoulder impingement The Resistance Chair Solution Shoulder Impingement a. Shoulder impingement is one of the most common causes of shoulder
Shoulder Pain Rehabilitation Protocol Rotator Cuff Syndrome Shoulder impingement The Resistance Chair Solution Shoulder Impingement a. Shoulder impingement is one of the most common causes of shoulder
DSE3 - HINTS AND TIPS: PREVENTING HEALTH PROBLEMS
 DSE3 - HINTS AND TIPS: PREVENTING HEALTH PROBLEMS This Information Sheet provides guidance on how to prevent health problems which may arise as a result of having your display screen equipment set up incorrectly.
DSE3 - HINTS AND TIPS: PREVENTING HEALTH PROBLEMS This Information Sheet provides guidance on how to prevent health problems which may arise as a result of having your display screen equipment set up incorrectly.
When Technology Strikes Back!
 When Technology Strikes Back! Suffering from thumb or wrist pain from chronic texting? Many tech-savvy individuals have felt the side-effects of texting, typing, or web browsing. This is the pain you get
When Technology Strikes Back! Suffering from thumb or wrist pain from chronic texting? Many tech-savvy individuals have felt the side-effects of texting, typing, or web browsing. This is the pain you get
Straight Spine Safe Spine Newsletter May Is National Correct Posture Month, but Every Day Should Be Perfect Posture Day
 Straight Spine Safe Spine Newsletter May Is National Correct Posture Month, but Every Day Should Be Perfect Posture Day May is Correct Posture Month, but every day should be Perfect Posture Day. This may
Straight Spine Safe Spine Newsletter May Is National Correct Posture Month, but Every Day Should Be Perfect Posture Day May is Correct Posture Month, but every day should be Perfect Posture Day. This may
What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis?
 Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Shoulder Tendinitis, Bursitis, and Impingement Syndrome What Are Bursitis and Tendinitis? Two types of tendinitis can affect the shoulder. Biceps tendinitis causes pain in the front or side of the shoulder.
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis
 Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
Office Ergonomics and Workstation Analysis Ergonomics is the study of the relationship between people and their environment. In the workplace, ergonomics is the science of designing or redesigning the
BOHS-Series. Series. Ergonomics Training Module
 BOHS-Series Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the
BOHS-Series Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the
OPNAVINST G 30 Dec 05
 Appendix 23-B Computer Workstation Checklist The computer workstation checklist is one method available for performing computer workstation assessments. The checklist is designed to be printed as two double-sided
Appendix 23-B Computer Workstation Checklist The computer workstation checklist is one method available for performing computer workstation assessments. The checklist is designed to be printed as two double-sided
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH
 COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
COMPOSITE WRIST FLEXOR STRETCH Purpose: To reduce fatigue of the elbow, forearm, wrist and fingers. Workers who perform forceful or repetitive grasping may benefit by performing this stretch every 2 hours.
Stay Fit While You Sit: 10 Simple Exercises for Sewers
 Published on Sew4Home Stay Fit While You Sit: 10 Simple Exercises for Sewers Editor: Liz Johnson Friday, 05 May 2017 1:00 There is a lot of sitting involved in sewing, which can lead to aches and pains
Published on Sew4Home Stay Fit While You Sit: 10 Simple Exercises for Sewers Editor: Liz Johnson Friday, 05 May 2017 1:00 There is a lot of sitting involved in sewing, which can lead to aches and pains
The Evolution of Human s? Objectives. Agenda. Defining Ergonomics. History of Ergonomics. Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer.
 Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer The Evolution of Human s? Presented By: Steve Grimmett Ergonomic Consultant Agenda Introduction to Ergonomics Form and Function of the Human Body Ergonomic Issues in
Office Ergonomics Train the Trainer The Evolution of Human s? Presented By: Steve Grimmett Ergonomic Consultant Agenda Introduction to Ergonomics Form and Function of the Human Body Ergonomic Issues in
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM. What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders
 MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
MUSCULOSKELETAL DISORDERS: THE BIGGEST JOB SAFETY PROBLEM What Are Musculoskeletal Disorders Every year more than 1.8 million workers in the United States suffer painful back and repetitive strain injuries,
Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents
 Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents Introduction What is Office Ergonomics? 1 Goal of Office Ergonomics 1 What are Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)? 2 MSD Risk Factors 2 Office Ergonomics Guidelines
Office Ergonomics Handbook Table of Contents Introduction What is Office Ergonomics? 1 Goal of Office Ergonomics 1 What are Musculoskeletal Disorders (MSDs)? 2 MSD Risk Factors 2 Office Ergonomics Guidelines
NECK PAIN HEADACHE T.M.J.
 Taking Care of Yourself Be Your Own Physical Therapist NECK PAIN HEADACHE T.M.J. Dr. Lauren A. Hebert, DPT, OCS Orthopedic Physical Therapist www. smartcarept.com Lhebertpt @ prexar.com Copyright L Hebert
Taking Care of Yourself Be Your Own Physical Therapist NECK PAIN HEADACHE T.M.J. Dr. Lauren A. Hebert, DPT, OCS Orthopedic Physical Therapist www. smartcarept.com Lhebertpt @ prexar.com Copyright L Hebert
PURPOSE To provide the tools to set up and maintain a healthy office workspace & environment
 Office Ergonomics PURPOSE To provide the tools to set up and maintain a healthy office workspace & environment WHAT IS A GOOD POSTURE? OFFICE SETUP CHAIR WORK SURFACE INPUT DEVICES MONITOR ACCESSORIES
Office Ergonomics PURPOSE To provide the tools to set up and maintain a healthy office workspace & environment WHAT IS A GOOD POSTURE? OFFICE SETUP CHAIR WORK SURFACE INPUT DEVICES MONITOR ACCESSORIES
BOHS-Series. Ergonomics Training Module
 BOHS-Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the science
BOHS-Series Ergonomics Training Module IAOH - 2013 2 INTRODUCTION IAOH - 2013 3 What is Ergonomics? Ergo = nomics = work laws or rules Ergonomics = the laws of work OSHA defines ergonomics as: the science
The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
 STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURES (SOP) FOR COMPUTER WORK, DESK TOP General Guidelines-Best Practices: The following guidelines are applicable to office workers who sit at a desk and/or work on computers.
HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT CHAIR
 HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT CHAIR ADJ SEAT HEIGHT & BACK: A GOOD SIZED SEAT: GOOD SEAT PADDING: Easy to adjust seat height. Provide a good range of approximately 40-53cm from the floor to the height of the
HOW TO CHOOSE THE RIGHT CHAIR ADJ SEAT HEIGHT & BACK: A GOOD SIZED SEAT: GOOD SEAT PADDING: Easy to adjust seat height. Provide a good range of approximately 40-53cm from the floor to the height of the
Part 1: Overview. Upper Crossed Syndrome
 Part 1: Overview A common misconception circulating social media, the workplace, and healthcare is the idea that bad posture causes pain. Sit up straight!, Stop slouching!, you look like a slob!, Your
Part 1: Overview A common misconception circulating social media, the workplace, and healthcare is the idea that bad posture causes pain. Sit up straight!, Stop slouching!, you look like a slob!, Your
CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 WHAT IS CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME? SYMPTOMS Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most commonly occurring nerve compression in the upper body It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow The
WHAT IS CUBITAL TUNNEL SYNDROME? SYMPTOMS Cubital tunnel syndrome is the second most commonly occurring nerve compression in the upper body It is caused by compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow The
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises. Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
 The spine is made of a column of bones. Each bone, or vertebra, is formed by a round block of bone, called a vertebral body. A bony ring attaches to the back of the vertebral body. When the vertebra bones
The spine is made of a column of bones. Each bone, or vertebra, is formed by a round block of bone, called a vertebral body. A bony ring attaches to the back of the vertebral body. When the vertebra bones
White Sands Guide for a Healthy Back
 White Sands Guide for a Healthy Back 7157 Curtiss Ave. Sarasota, FL 34231 Phone: (941) 924-9525 www.aquaticsphysicaltherapy.com Home of the Spinal Solutions Program 1 What Causes Back Pain? Since the lower
White Sands Guide for a Healthy Back 7157 Curtiss Ave. Sarasota, FL 34231 Phone: (941) 924-9525 www.aquaticsphysicaltherapy.com Home of the Spinal Solutions Program 1 What Causes Back Pain? Since the lower
INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM
 INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in this program is presented in a definite order so that employees will see the relationships between the various groups of information
INTRODUCTION TO THE PROGRAM Structure and Organization Information in this program is presented in a definite order so that employees will see the relationships between the various groups of information
LOW BACK PAIN. what you can do
 LOW BACK PAIN what you can do Back pain Nearly 80 percent of adults will experience back pain at some point in their life. The good news is that back pain will normally go away within four to six weeks
LOW BACK PAIN what you can do Back pain Nearly 80 percent of adults will experience back pain at some point in their life. The good news is that back pain will normally go away within four to six weeks
Ergonomic Guidelines for Computer Users Frank Gonzales, CEES, CEAS
 Office Ergonomics Ergonomic Guidelines for Computer Users Frank Gonzales, CEES, CEAS Ergonomics Program Services What other services are provided? Training sessions Office, Industrial (can be specific
Office Ergonomics Ergonomic Guidelines for Computer Users Frank Gonzales, CEES, CEAS Ergonomics Program Services What other services are provided? Training sessions Office, Industrial (can be specific
ERGONOMIC ASSESSMENT TOOL. Eyes
 This tool was designed to provide guidance to perform ergonomic workstation evaluations for computer users. This form will determine how computer users interact with their workstations. Person/Workstation
This tool was designed to provide guidance to perform ergonomic workstation evaluations for computer users. This form will determine how computer users interact with their workstations. Person/Workstation
Department of Defense Ergonomics Working Group
 Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
Welcome to the module. The purpose of the module is to explain the importance of ergonomics and the risks that can result when ergonomics principles are not applied to work activities. Upon completion
Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc
 Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc Every job or task has unique physical and cognitive demands. Each person has unique physical attributes and abilities. www.prbembodychair.co.uk www.youandyourself.com
Darrell Skinner MScPT, CAFCI, CMedAc Every job or task has unique physical and cognitive demands. Each person has unique physical attributes and abilities. www.prbembodychair.co.uk www.youandyourself.com
General Information - Exercise
 General Information - Exercise To maximize the potential for prevention and recovery, it is important to make a commitment to daily stretching and cardiovascular exercise and to perform strengthening exercises
General Information - Exercise To maximize the potential for prevention and recovery, it is important to make a commitment to daily stretching and cardiovascular exercise and to perform strengthening exercises
It is recommended that a person break for 5-10 minutes for every hour spent at a workstation.
 Office Stretches Why is stretching important? No matter how well a workstation is designed, problems may arise if attention is not paid to the way the work is done. Working at a computer often involves
Office Stretches Why is stretching important? No matter how well a workstation is designed, problems may arise if attention is not paid to the way the work is done. Working at a computer often involves
Posture. In this article
 Posture Posture is the way we hold our bodies against gravity and maintaining a good posture involves training yourself to become aware of how you hold yourself in all activities as your posture is constantly
Posture Posture is the way we hold our bodies against gravity and maintaining a good posture involves training yourself to become aware of how you hold yourself in all activities as your posture is constantly
Safety Meeting. Meeting Leader Instructions. Safety, Teamwork & Our Customer s 1 st Choice
 Meeting Leader Instructions These meetings are more than safety meetings. While they address safety as a top priority, these meetings are also an opportunity for you to interact with your team; a chance
Meeting Leader Instructions These meetings are more than safety meetings. While they address safety as a top priority, these meetings are also an opportunity for you to interact with your team; a chance
Ergonomics and Back Safety PPT-SM-BACKSFTY V.A.0.0
 Ergonomics and Back Safety 1 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomics Scientific study of equipment design for the purpose of improving efficiency, comfort and safety 2 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomic
Ergonomics and Back Safety 1 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomics Scientific study of equipment design for the purpose of improving efficiency, comfort and safety 2 Ergonomics and Back Safety Ergonomic
BACK OWNER S MANUAL. A Guide to the Care of the Low Back
 BACK OWNER S MANUAL A Guide to the Care of the Low Back When You Have Back Pain Low back pain affects many of us. That s because we tend to neglect our backs. But your back is what keeps you in motion.
BACK OWNER S MANUAL A Guide to the Care of the Low Back When You Have Back Pain Low back pain affects many of us. That s because we tend to neglect our backs. But your back is what keeps you in motion.
AMG Transfer Training and Ergonomics
 AMG Transfer Training and Ergonomics Musculoskeletal Disorders Healthcare workers often experience musculoskeletal disorders at a rate exceeding that of workers in construction, mining, and manufacturing.
AMG Transfer Training and Ergonomics Musculoskeletal Disorders Healthcare workers often experience musculoskeletal disorders at a rate exceeding that of workers in construction, mining, and manufacturing.
Courtesy of your source for the best ergonomic office furniture.
 Enjoy this free ergonomic evaluation form courtesy of Get Up Stand Up Desk Co., your online source for the best ergonomic office furniture at the best prices. We hope that this evaluation will help you
Enjoy this free ergonomic evaluation form courtesy of Get Up Stand Up Desk Co., your online source for the best ergonomic office furniture at the best prices. We hope that this evaluation will help you
 www.fitnessfirst-usa.com Chest Fly Shoulders, elbows and wrists aligned in same plane with elbows at 90 degrees Feet should be staggered, and body leaning slightly forward for leverage Step far enough
www.fitnessfirst-usa.com Chest Fly Shoulders, elbows and wrists aligned in same plane with elbows at 90 degrees Feet should be staggered, and body leaning slightly forward for leverage Step far enough
Osteoporosis Exercise:
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Balance, Posture and Functional Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction You can help improve and maintain your balance, posture
Osteoporosis Exercise: Balance, Posture and Functional Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction You can help improve and maintain your balance, posture
Back Safety. Version 1.0
 This document is intended to provide basic safety guidelines for the Physical Plant Department at Community College of Allegheny County. The information provided in this guide may vary by site. Version
This document is intended to provide basic safety guidelines for the Physical Plant Department at Community College of Allegheny County. The information provided in this guide may vary by site. Version
Lowe Plastic Surgery (LPS)
 Lowe Plastic Surgery (LPS) PATIENT EDUCATION FOR: CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDER THE PROBLEM: There has been a remarkable increase in what is termed cumulative trauma disorder (CTD) in the last 20 years. Other
Lowe Plastic Surgery (LPS) PATIENT EDUCATION FOR: CUMULATIVE TRAUMA DISORDER THE PROBLEM: There has been a remarkable increase in what is termed cumulative trauma disorder (CTD) in the last 20 years. Other
Taking Care of Your Back
 Taking Care of Your Back Most people will feel back pain at some point in their lives, but not all back pain is the same for everyone. The good news is, most low back pain improves without any treatment
Taking Care of Your Back Most people will feel back pain at some point in their lives, but not all back pain is the same for everyone. The good news is, most low back pain improves without any treatment
Low Res SAMPLE SPINAL CURVES THE SPINE
 THE SPINE The normal healthy spine has a naturally curved shape. Like a coiled spring, these curves help to absorb some of the forces that are placed on your spine while standing erect. When looking at
THE SPINE The normal healthy spine has a naturally curved shape. Like a coiled spring, these curves help to absorb some of the forces that are placed on your spine while standing erect. When looking at
Computer Ergonomics. Static Efforts
 Welcome to Essential WorkWellness online continuing education activities. Please be aware that this activity does not include a post test or certificate of completion. Simply read the article below to
Welcome to Essential WorkWellness online continuing education activities. Please be aware that this activity does not include a post test or certificate of completion. Simply read the article below to
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Q: What is carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)? A: Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the name for a group of problems that includes swelling, pain, tingling, and loss of strength in your
Good Working Positions
 Good Working Positions To understand the best way to set up a computer workstation, it is helpful to understand the concept of neutral body positioning. This is a comfortable working posture in which your
Good Working Positions To understand the best way to set up a computer workstation, it is helpful to understand the concept of neutral body positioning. This is a comfortable working posture in which your
Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd.
 1523 OFFICE ERGONOMICS TRAINING Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. Structure and Organization Information in this program is presented in a definite order so that employees will see the relationships between
1523 OFFICE ERGONOMICS TRAINING Leader s Guide Marcom Group Ltd. Structure and Organization Information in this program is presented in a definite order so that employees will see the relationships between
Vibration (i.e., driving a Lack of exercise
 What is low back pain? Almost everyone has back pain at one time or another. The pain may be in the center of the back or to one side, or may move down the leg. Besides pain in the back, the symptoms may
What is low back pain? Almost everyone has back pain at one time or another. The pain may be in the center of the back or to one side, or may move down the leg. Besides pain in the back, the symptoms may
Choosing the right Office Chair
 Choosing the right Office Chair Choosing the Right Ergonomic Office Chair Working in an office typically involves spending a great deal of time sitting in an office chair a position that adds stress to
Choosing the right Office Chair Choosing the Right Ergonomic Office Chair Working in an office typically involves spending a great deal of time sitting in an office chair a position that adds stress to
Thoracic Home Exercise Program
 Home Exercise Program 1. Bridging Laying on your back, knees bent with feet flat on the floor, arms along side resting on the floor, tighten your abdominals to stabilize your low back. Raise your buttocks
Home Exercise Program 1. Bridging Laying on your back, knees bent with feet flat on the floor, arms along side resting on the floor, tighten your abdominals to stabilize your low back. Raise your buttocks
OFFICE ERGONOMICS SELF-ASSESSMENT
 This self-assessment is designed to assist Coast Community College District employees achieve an ergonomically correct work posture. Through a progressive series of questions and solutions, this program
This self-assessment is designed to assist Coast Community College District employees achieve an ergonomically correct work posture. Through a progressive series of questions and solutions, this program
Safety Manual: Ergonomics. February 8, 2017
 Safety Manual: Ergonomics February 8, 2017 Overview 2.0 Ergonomics Introduction This Chapter provides a general overview of issues in the workplace and recommendations for reducing ergonomic injuries.
Safety Manual: Ergonomics February 8, 2017 Overview 2.0 Ergonomics Introduction This Chapter provides a general overview of issues in the workplace and recommendations for reducing ergonomic injuries.
October 2015 Statins and Exercise: Maintain a Balance A
 Statins and Exercise: Maintain a Balance A high cholesterol level puts you at an increased risk for a heart attack or stroke. Perhaps your physician has recommended that you take a statin, a drug that
Statins and Exercise: Maintain a Balance A high cholesterol level puts you at an increased risk for a heart attack or stroke. Perhaps your physician has recommended that you take a statin, a drug that
Low Back Pain Home Exercises
 Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN Description Cervical strain/sprain is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or forward. The structures involved are the muscles, ligaments,
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash)
 CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
CERVICAL STRAIN AND SPRAIN (Whiplash) Description time and using proper technique decrease the frequency of Whiplash is an injury to the neck caused when it is forcefully whipped or forced backward or
SAFE LIFTING Protecting Your Back. Dwayne Fuchs Reg. Kinesiologist Ergonomist
 SAFE LIFTING Protecting Your Back Dwayne Fuchs Reg. Kinesiologist Ergonomist Back Injury 60 % of all adults experience back pain Most frequent cause of activity limitation in individuals under 45 years
SAFE LIFTING Protecting Your Back Dwayne Fuchs Reg. Kinesiologist Ergonomist Back Injury 60 % of all adults experience back pain Most frequent cause of activity limitation in individuals under 45 years
