GERD. See Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) (GERD)
|
|
|
- Harvey Hutchinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Abnormal GERD, LTX recipients description, 208 gastric motility, 211 postoperative oropharyngeal dysphagia, 212 prevalence, Acid aromatic amino, 26 BA, 27 fatty, 27 gastric, hydrochloric, 25 reflux, 32 stomach, 27 taurocholic, 27 Acid-suppressing agents adverse effects, H2-RA therapy, 236 adverse events, 240 CDI, 242 description, 233 drug-drug interactions, 243 H2-RAs, nocturnal, 109 parietal cell, ph, 234 PPI (see Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)) Aerodigestive tract reflexes, 10, 11, 26, 36 Airway protection and closure, 2 and deglutition, 10, 19 function, 9 motor actions, and pharynx, 12 reflex, 7, 8, Alginic acid, 233 Antacids, 232 Anti-reflex surgery defined, 168 evaluation, 131 fundoplication, 35 recreation, anatomical barrier, 219 Arousals causes, 145 omeprazole, 141 OSA events, 143 response, 138, 146 and sleep architecture, 138, 146 Aspiration. See also Children, GERD and aspiration acidic secretions, 180 bronchiolitis, 188 chronic, 180 elderly age-related changes, pulmonary immunity, 88, 89 modifications, oropharyngeal flora, 88 morbidity and mortality, 87 pneumonia, 87, 88 prevention and treatment, food particles, 188 gastric fluid, 180 intradeglutitive, 18 laryngopharyngeal sensory thresholds, 17 and pneumonia, 18 pneumonitis, 178 postoperative, 192 puree, 12, 13 refluxate, 190 repetitive, 182 residue, 12 silent, 5 6 K.C. Meyer and G. Raghu (eds.), Gastroesophageal Refl ux and the Lung, Respiratory Medicine 2, DOI / , Springer Science+Business Media New York
2 268 Aspiration of gastric content, CF and NCFB, Asthma aspiration, gastric contents, description, 121 diagnosis (see Gastroesophageal reflux embryonic origins, increased bronchial reactivity, 126 medical therapy, nervous system, prevalence, and reflux, Autoimmune diseases, 2, 98 B BA. See Bile acids (BA) BALF. See Bronchoalveolar lavage fl uid (BALF) Barrett s esophagus, 15, 24, 32, 77, 84 Bethanechol, 244 Bile acids (BA) administration, agents, 220 defined, 26 27, 207 detection, BALF, 211, 213 GER and aspiration, 213 BO. See Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) BPD. See Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) Bronchiectasis, 206 Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS) biopsy specimens, 212 chronic allograft rejection, 201 ColV sensitization, 215 defined, 62 HRCT imaging, 214 OB, 212 stages, 214 Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), 101, 256 Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) aspirated material, 58 babies, 66 pepsin levels, 63 symptoms, 62 C CA. See Carbonic anhydrase (CA) Carbonic anhydrase (CA), 28, 31 CDI. See Clostridium dif fi cile infection (CDI) Central pattern generator (CPG), 8, 9, 11 Chest physiotherapy (CPT), 61, 166 Children, GERD and aspiration apnea and reflux, 63 asthma and reflux, BO and reflux, 59 bronchiectasis and reflux, 61 chronic lung disease, infancy and re fl ux, diagnosis antisecretory agents, 64 esophageal ph monitoring, 65 MII, 65 nuclear scintiscan/milk scan test, 65 salivagram and LLMI, 66 symptoms, reflux, 64 medical management, medical treatment, recurrent croup and reflux, recurrent pneumonia and reflux, and reflux, lung disease, surgical treatment, syndromes, reflux, 59 Chronic cough hypersensitivity syndrome, 102 Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD) description, 121 diagnosis (see Gastroesophageal reflux medical therapy, pathophysiology, 127 prevalence, Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) broad-spectrum antibiotics, 242 and pneumonia, 240 PPIs (see Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)) Collagen V (ColV), 215 ColV. See Collagen V (ColV) Computed tomogram (CT), 104, 190, 216 Connective tissue disorders (CTD) CTD-ILD, , 220 dilated esophagus, 185, 187 HRCT, 185 MCTD, 185 non-scleroderma, 206 scleroderma, 188, 202 Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) defined, 144 nasal, 144, 145, 148 OSA treatment, 145 COPD. See Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD) Cough asthma-related symptoms, 122 capsaicin, 126
3 chronic, 123 humans, 126 CPAP. See Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) CPG. See Central pattern generator (CPG) CPT. See Chest physiotherapy (CPT) CT. See Computed tomogram (CT) CTD. See Connective tissue disorders (CTD) Cystic fibrosis (CF) children, bronchiectasis, 61 and NCFB, GERD anamnesis, 159 aspiration, gastric content, CPT, 166 defined, DGER, 161 esophageal factors, 165 gastric factors, 163 gold standard method, 157 NERD and ERD, 161 prevalence study, re fl ux and aspiration effects, lung disease, reflux characteristics, children and adults, 160, 161 sphincteric factors, D Defense mechanisms, esophageal mucosa epithelial CA, 31 EGF, 30 heat shock proteins, 32 Na +-dependent Cl- /HCO -exchanger, 32 3 Na + + /H exchanger, 31 structural, TGF, post-epithelial, 32 pre-epithelial LES, 28 peristalsis, 28 saliva, Deglutition CPG, 8 defined, 1 dysfunctional, esophageal phase, 7 8 oral preparatory phase, 2 4 oral propulsive phase, 4 5 pharyngeal phase, 5 7 swallows, neural pathway, 8 9 Dermatomyositis, 79 DES. See Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES) DGER. See Duodenogastroesophageal reflux (DGER) Diabetes mellitus, 79, 88 Diagnosing GERD and IPF, 257 and therapy selection, Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES), 78, 81 Dorsal vagal complex, 15 Duodenogastroesophageal reflux (DGER), 161, 163 Dysphagia causes, bolus transfer, 16 esophageal GERD, 77 medications, 78 strictures, 77 oropharyngeal Parkinson s disease, 76 stroke, structural lesions, Zenker s diverticulum, 76 and pneumonia, E ECLs. See Enterochromaffin-like cells (ECLs) EEG. See Electroencephalogram (EEG) EER. See Extra-esophageal reflux (EER) Elderly patients aspiration, GERD (see Gastroesophageal reflux swallowing disorders (see Swallowing disorders, elderly) Electroencephalogram (EEG), 138 Endoluminal therapy description, EsophyX system, 265 GE junction and LES, 264 LES pressure, PPI therapy and symptoms, 264 radiofrequency technique, 265 TIF, 264 Endoscopic approaches. See Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Endoscopy, 45, 46 Enterochromaffin-like cells (ECLs), Epidermal growth factor (EGF) defined, 30 production, 29 and TGF-a, ERD. See Erosive re fl ux disease (ERD) Erosive reflux disease (ERD), 159, 161 Esophago-bronchial reflex,
4 270 Esophagus adenocarcinoma, 77 CA, 31 distal, 33 gastric contents, 23 intermittent exposure, 33 pepsin, 26 peristalsis, 28 reflux, gastric acid, 25 saliva, 29 Exhaled breath condensate (EBC), Extra-esophageal reflux (EER), 24, 36 F FEESST. See Functional endoscopic evaluation of swallowing with sensory testing (FEESST) Functional endoscopic evaluation of swallowing with sensory testing (FEESST), 14, 17, 65, 66, 101 G GABA. See Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), Gastroesophageal pressure gradient (GEPG), 165, 169 Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). See also Children, GERD and aspiration; Cystic fi brosis (CF); Sleep-related GERDacid suppression, algorithm, diagnosis, ambulatory ph monitoring, and aspiration diagnosis biomarkers, 216 description, 215 distal and proximal esophagus, 215 EBC, pyloroplasty, 217 radiologic techniques, 216 suppression pharmacologic therapies, 216 aspirators, 251 asthma (see Asthma) and autoimmunity, 215 bile, causes, 104, 105 chronic cough, complexities, 14, vs. control subjects, normal ph-metry, 17 COPD (see Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD)) cough reflex hypersensitivity, 102 CTD-ILD, 188 defense mechanisms (see Defense mechanisms, esophageal mucosa) defined, 23, 43, 229, 251 detection, elderly altered esophageal pain perception, 84 barium swallow, 84 heartburn, 83 prevention and treatment, symptoms, endoluminal therapy (see Endoluminal therapy) endoscopy, 45, 46 end-stage lung disease, 251 esophago-bronchial reflex, and extraesophageal reflux, 231 gastric acid, ILD (see Interstitial lung disease (ILD)) indications, surgical management, and LPR (see Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR)) lung allograft dysfunction ( see Lung allograft dysfunction) lung disease, manometry, measurements, laryngopharyngeal sensitivity, 14 microaspiration, 101 non-acidic stimulation, cough, nonacid reflux, laryngeal inflammation disease, non-invasive biomarkers, 113 operative technique (see Operative technique, GERD) pathophysiology, 33 pepsin, pharmacologic treatment (see Pharmacologic treatment, GERD) pneumonia, 188 pulmonary symptoms, 252 reflux and cough, reflux and symptoms, 44 severity and frequency, symptoms, 179 step-up strategy, 231 surgical management, 254 treatment (see Surgical management) symptoms, 122, 231 testing modalities, reflux, 51 53
5 therapy selection and diagnosing, treatment and prevention, trypsin, UGI esophagram, VCD (see Vocal cord dysfunction (VCD)) GEPG. See Gastroesophageal pressure gradient (GEPG) GER. See Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) GERD. See Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) H HH. See Hiatal hernias (HH) Hiatal hernias (HH) CT scanning, 190, 216 defined, diffuse pulmonary fibrosis, 182 EGD, 45, 46 high-resolution manometry tracing, 48 and mediastinal esophageal dissection, 261 multi-detector computed tomography, 185 prevalence, 83 sliding, 45 symptoms, dysphagia, 192 UGI esophagram, 46, 47 High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) changes, UIP, 182 fibrosis degree, 193 radiologic, 185 scores, 191, 256 imaging, 188 Histamine type 2 receptor antagonists (H2-RAs) acid-suppressant medications, 235 adverse effects, 236 clinical studies, 236 description, 235 on-demand therapy, 236 oral absorption, 235 H2-RAs. See Histamine type 2 receptor antagonists (H2-RAs) HRCT. See High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) I Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) abnormal GER, 182 abnormal proximal/distal esophageal acid, 256 description, diagnosis, 255 distal esophagus, 184 GER and pulmonary fibrosis, HH, 185 HRCT, 182 mutations, 181 NSIP, 182 parenchymal lung diseases, 255 PPIs, proximal and distal esophageal acid, UIP, ILD. See Interstitial lung disease (ILD) Impedance-pH monitoring detection, acid and non-acid re fl ux, 105, 106 detection, pharyngeal reflux, 113 esophageal, 107, 108 Insomnia predictors, sleep-related heartburn, 139, 140 sleep-related GER, 141, 146 Interstitial lung disease (ILD) animal and in vitro studies, aspiration (see Aspiration) CTD (see Connective tissue disorders (CTD)) DeMeester score, 188 description, 177 diagnosis, , 255 GER and microaspiration, IPF (see Idiopathic pulmonary fi brosis (IPF)) nodular granulomatous inflammatory process, 188 progressive type, 255 treatment, UIP, 178 IPF. See Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) 271 L Laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery (LARS) BOS and BAL, 256 esophageal dysfunction and aspiration, 255 GERD symptoms, 256 HRCT and UIP, 255 ILD and IPF, 255 pharmacologic treatment, IPF, 256 prevention, LARS. See Laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery (LARS) Laryngeal inflammation disease, 34 36
6 272 Laryngeal protection aerodigestive tract protective reflexes, 10, 11 bolus transfer, 16 changes, sleep, 15 esophagoglottal reflex, 14 esophago-ues contractile reflex, 13 functions, 9 laryngeal reflexes, 14 LES (see Lower esophageal sphincter (LES)) molecular vehicles and receptors, 19 motor disorders, pharyngoglottal reflex, pharyngo-ues contractile reflex, 12 PRS/secondary pharyngeal swallow, 12 sensory disorders, timing disorders, UES (see Upper esophageal sphincter (UES)) Laryngeal reflexes, 14 Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) defined, 24 esophagitis and laryngitis, 34 hoarseness, 33 and microaspiration, 103 oropharynx, 231 pathophysiology, 33 prevention, 265 Larynx aditus, 5 aspiration pneumonia, 87, 178 functions, 9 removal, 5 LES. See Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) Lipid-laden macrophage index (LLMI), 52 53, 66, 167 LLMI. See Lipid-laden macrophage index (LLMI) Lower esophageal sphincter (LES) body dysmotility, 206 COPD, 127 hypotonia, 206 intrinsic esophageal muscle thickening, 14 pressure, , swallow-induced relaxation, 15 and UES function, 212 LPR. See Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) Lung allograft dysfunction BOS, 212 cough reflex, 213 description, 212 esophageal motility, 212 esophageal ph probe, 213 histopathology, OB, 212, 214 HRCT imaging of BOS, 212, 214 microaspiration, 213 PPI therapy, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Aspergillus, 212 Lung disease CF and NCFB acid suppression, 168 antireflux surgery, 168 diagnostic tools, 169 end-stage bronchiectasis, 169 LLMI, 167 Pa, 167 chronic, infancy and reflux/aspiration, CTD, 202 esophageal abnormalities, HRCT, 202, 206 esophageal dysmotility and gastroparesis, 206 LES and ESLD, 206 LPR, 206 LTX, MCTD, microaspiration, 207 reflux and aspiration mechanisms, children, symptoms, 202 Lung transplantation (LTX) abnormal GERD (see Abnormal GERD, LTX recipients) bronchiolar injury, description, 201 diagnosis, aspiration, gastric juice, GERD (see Gastroesophageal reflux lung allograft dysfunction ( see Lung allograft dysfunction) treatment and prevention, M Manometry high-resolution tracing, 48 LES, peristaltic waveform, 47 MCTD. See Mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) Mechanisms for re fl ux and aspiration, lung disease antegrade, 58 defined, gastric contents, 58 TEF, 59
7 Metoclopramide, 244 Microaspiration abnormal GER, 178 allograft dysfunction, 213 biomarkers, 193 chronic, 131 gastric juice, 191 ILD, 207 IPF vs. GER, 191 lung disease exacerbation, 193 lung resistance, 126 pathogenesis, 193 PEF, 126 Pepsin and BA, 213 proximal gastrointestinal tract, 201 pulmonary parenchymal changes, 216 silent, 178 transverse HRCT, prone positioning, 179 MII. See Multichannel intraluminal impedance (MII) Mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD) and esophageal motility, 185 lung parenchymal abnormalities, 188 non-scleroderma CTD, 185 Motor disorders, Multichannel intraluminal impedance (MII), 34, 35, 65 N Nasal CPAP, 144, 145, 148 NERD. See Nonerosive re fl ux disease (NERD) Neurodegenerative diseases, 18, 88 Neuromuscular/motility disorders achalasia, 78 amyloidosis, 79 causes, dysphagia, 79 dermatomyositis, 79 DES, 78 prevention and treatment, rheumatoid arthritis, therapeutic modes, dysphagia, thyrotoxicosis, 79 Nissen fundoplication antireflux operation, 258 endoluminal plication, 264 GERD and respiratory symptoms, 253 laparoscopic approach, 254 Nonacid reflux, laryngeal inflammation disease anti-reflux fundoplication surgery, 35 multichannel intraluminal impedance, phmonitoring, 34 pepsin, Non-CF bronchiectasis (NCFB). See Cystic fibrosis (CF) Nonerosive reflux disease (NERD), 159, 161 Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), 182 NSIP. See Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) O OB. See Obliterative bronchiolitis (OB) Obliterative bronchiolitis (OB) CLAD, 201 histopathology, 212, 213 Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). See OSA and sleep-related GERD Operative technique, GERD completed 2-cm fl oppy Nissen, 261, 262 descritpion, dietary guidance, 262 gastrohepatic ligament, 260 GE junction, 261 Nissen fundoplication, 260 penrose drain, 261 phrenogastric ligament, 260 pneumoperitoneum, 260 toupet fundoplication, 262 OSA and sleep-related GERD abnormal esophageal acid, 143 CPAP, 144 defined, 142 surgical treatment, UES, 144 OTC. See Over-the-counter (OTC) Over-the-counter (OTC) acid-neutralizing medications, meta-analysis, randomized controlled trials, 233 P Pa. See Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pa) Paradoxical vocal fold motion (PVFM), 60, 97. See also Vocal cord dysfunction (VCD) Parkinson s disease, 76 Peak expiratory flow (PEF), 126 PEF. See Peak expiratory fl ow (PEF) Penetration and aspiration, 5 6, 13 laryngeal, 18 nonsmokers, pharyngeal anesthesia, 17 pharyngeal reflexive swallows, 12 testing, aryngopharyngeal sensory thresholds, 17
8 274 Pepsin and BA, 35 defined, nonacid reflux, 35 saliva measurement, 113 sputum analysis, 51 PES. See Pharyngoesophageal segment (PES) PF. See Pulmonary fibrosis (PF) ph ambulatory monitoring catheter and Bravoprobe, 49 parameters, measurements, 49 tracing, 50 impedance testing, Pharmacologic treatment, GERD acid-suppressing agents (see Acidsuppressing agents) cholinergic prokinetic agents, 244 combination therapy, 246 description, 229 dopaminergic antagonist prokinetic agents, 244 GABA receptor prokinetic agents, GERD (see Gastroesophageal reflux maintenance therapy, OTC, reflux-moderating agents (see Refluxmoderating agents) serotonin receptor prokinetic agents, Pharyngeal phmetry technique, 106 Pharyngeal reflexive swallow (PRS), 12, 17 Pharyngoesophageal segment (PES) bolus, 5 closure, 8 opening, 5, 8 9, outlet obstruction, 6 residue, 12 Postnasal drip, 98 Postprandial acid pocket, 162, 165 Power spectral analysis, sleep EEG, 138 PPIs. See Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) Proteolysis, 25 Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) adverse events, 240 benzimidazole derivatives, 237 CDI (see Clostridium dif fi cile infection (CDI)) dose, 113, 147 double-dose treatment, 231 drug-drug interactions, 243 esophageal acid exposure, 256 formulations, 147, and GER symptoms, 264 healing-time curves, 237 H + /K + ATPase, 238 H2-RAs, 230 and LARS, 254 metabolism, 239 oral, 102, 104, 109 and osteoporosis-related fractures, pharmacodynamic profiles, 238 pharmacokinetic properties, 238, 239 PPI + nocturnal H2-RA, 236 prodrug accumulation, 237 work productivity, 141 PRS. See Pharyngeal re fl exive swallow (PRS) Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pa), 167, 212, 215, 256 Pulmonary fibrosis (PF), 202, PVFM. See Paradoxical vocal fold motion (PVFM) R Reflexive pharyngeal swallow (RPS), 7, 17 Reflux LLMI, sputum pepsin analysis, 51 and symptoms, 44 Reflux induced cough, 102, 109, 110 Reflux-moderating agents adverse effects, alginic acid, 233 antacids, 232 Rheumatoid arthritis, RPS. See Reflexive pharyngeal swallow (RPS) S Scleroderma CTD-ILD, 188 and IPF, 192 surgical lung biopsies, 188 visceral organs, 185 Selecting the best therapy, Sensory disorders esophagus, 17 nonsmokers, 17 Zenker diverticulum, 16, 17 Sleep quality, 141, 142, 145 Sleep-related GERD distribution, acid-reflux events, 137, 138 EEG, 138 esophageal ph monitoring, 138 esophageal ph testing, 145
9 laryngospasm, 142 omeprazole, 141 and OSA (see OSA and sleep-related GERD) prevalence, prevention, 140, 141, surgical fundoplication, treatment, 147 Stroke, Surgical approaches. See Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Surgical management, GERD contraindications, 254 symptoms, 253 treatment description, 254 LARS (see Laparoscopic antireflux surgery (LARS)) partial vs. fundoplication, PPI therapy, 254 Swallowing disorders, elderly changes, 74 esophageal dysphagia, malnutrition, 75 medications, dysphagia and GERD risk, 75 neuromuscular/motility disorders, oropharyngeal dysphagia, T TEF. See Tracheoesophageal fistulas (TEF) TGF-a. See Transforming growth factor alpha (TGF- a ) Thyrotoxicosis, 79 TIF. See Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF) Timing disorders, Tracheoesophageal fistulas (TEF), 59, 61, 69 Transforming growth factor alpha (TGF- a ), Transient LES relaxations defined, 136, 142, 145 frequency, 147 OSA events, 143 tors, 137 Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF), Treatment strategies, reflux disease double-dose PPI treatment, 231 H2-RA-based therapy, 231 LPR, PPI acid, 231 pyramidal protocol, 231 step-up therapy, Trypsin, U UES. See Upper esophageal sphincter (UES) UGI series. See Upper gastrointestinal (UGI) series UIP. See Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) Upper esophageal sphincter (UES) anatomic components, 10 dermatomyositis, 79 esophago-ues contractile reflex, 13 factors, pressures, 11 function, 33 hypotonia, 164 laryngo-ues contractile reflex, 14 PES, 12 pharyngeal phase, 74 pharyngo-ues contractile reflex, 12 pressure, 136, 144, 178 relaxation, 5 Upper gastrointestinal (UGI) series, Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) clinical diagnosis, histopathologic pattern, 178 HRCT, 182 V VCD. See Vocal cord dysfunction (VCD) Vocal cord dysfunction (VCD) autonomic balance and laryngeal hyperresponsiveness, defined, diagnosis, 99 dyspnea, 100 microaspiration and LPR, 103 organic and non-organic precipitants, 103 treatment, 111 W Wake time sleepiness, 135 Z Zenker sdiverticulum, 76 Zollinger Ellison syndrome, 25
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, barium esophagography for, 57 58 Acid pocket, 18 19 Acid-sensing ion, 20 Acupuncture, 128 Adiponectin, in obesity, 166 ADX10059 metabotropic
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, barium esophagography for, 57 58 Acid pocket, 18 19 Acid-sensing ion, 20 Acupuncture, 128 Adiponectin, in obesity, 166 ADX10059 metabotropic
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc 2 and Marcelo F. Vela MD, MSCR 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Einstein
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc 2 and Marcelo F. Vela MD, MSCR 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Einstein
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT DISCLOSURES 4/18/2018
 GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
GERD: A linical Clinical Clinical Update Objectives
 GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Afferent nerves, interactions of, in cough, 20 21 Airway, eosinophilic inflammation of, 124 narrowing of, in asthma, 126 protection of, terms
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Afferent nerves, interactions of, in cough, 20 21 Airway, eosinophilic inflammation of, 124 narrowing of, in asthma, 126 protection of, terms
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Paraesophageal Hernias &
 530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University
 Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University Asthma-related Comorbidities Comorbid conditions of the upper airways Rhinitis and Sinusitis
Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University Asthma-related Comorbidities Comorbid conditions of the upper airways Rhinitis and Sinusitis
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice
 Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications
 GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications Esophageal Syndromes Extra - esophageal Syndromes Symptomatic Syndromes Typical reflux
GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications Esophageal Syndromes Extra - esophageal Syndromes Symptomatic Syndromes Typical reflux
Speaker disclosure. Objectives. GERD: Who and When to Treat 7/21/2015
 GERD: Who and When to Treat Eugenio J Hernandez, MD Gastrohealth, PL Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine, FIU Herbert Wertheim School of Medicine Speaker disclosure I do not have any relevant commercial
GERD: Who and When to Treat Eugenio J Hernandez, MD Gastrohealth, PL Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine, FIU Herbert Wertheim School of Medicine Speaker disclosure I do not have any relevant commercial
Myogenic Control. Esophageal Motility. Enteric Nervous System. Alimentary Tract Motility. Determinants of GI Tract Motility.
 Myogenic Control Esophageal Motility David Markowitz, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons Basic Electrical Rythym: intrinsic rhythmic fluctuation of smooth muscle membrane potential
Myogenic Control Esophageal Motility David Markowitz, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons Basic Electrical Rythym: intrinsic rhythmic fluctuation of smooth muscle membrane potential
Esophageal Motility. Alimentary Tract Motility
 Esophageal Motility David Markowitz, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons Alimentary Tract Motility Propulsion Movement of food and endogenous secretions Mixing Allows for greater
Esophageal Motility David Markowitz, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons Alimentary Tract Motility Propulsion Movement of food and endogenous secretions Mixing Allows for greater
A Multidisciplinary Approach to Esophageal Dysphagia: Role of the SLP. Darlene Graner, M.A., CCC-SLP, BRS-S Sharon Burton, M.D.
 A Multidisciplinary Approach to Esophageal Dysphagia: Role of the SLP Darlene Graner, M.A., CCC-SLP, BRS-S Sharon Burton, M.D. What is the role of the SLP? Historically SLPs the preferred providers for
A Multidisciplinary Approach to Esophageal Dysphagia: Role of the SLP Darlene Graner, M.A., CCC-SLP, BRS-S Sharon Burton, M.D. What is the role of the SLP? Historically SLPs the preferred providers for
David Markowitz, MD. Physicians and Surgeons
 Esophageal Motility David Markowitz, MD Columbia University, College of Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons Alimentary Tract Motility Propulsion Movement of food and endogenous secretions
Esophageal Motility David Markowitz, MD Columbia University, College of Columbia University, College of Physicians and Surgeons Alimentary Tract Motility Propulsion Movement of food and endogenous secretions
Surgical Evaluation for Benign Esophageal Disease. Kimberly Howard, PA-C, MHS Duke University Medical Center April 7, 2018
 Surgical Evaluation for Benign Esophageal Disease Kimberly Howard, PA-C, MHS Duke University Medical Center April 7, 2018 Disclosures No disclosures relevant to this presentation. Objectives (for CME purposes)
Surgical Evaluation for Benign Esophageal Disease Kimberly Howard, PA-C, MHS Duke University Medical Center April 7, 2018 Disclosures No disclosures relevant to this presentation. Objectives (for CME purposes)
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX
 DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (404) 270-7479 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DEFINITION: *MONTREAL CONSENSUS DEFINED GERD AS A CONDITION WHICH
DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (404) 270-7479 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DEFINITION: *MONTREAL CONSENSUS DEFINED GERD AS A CONDITION WHICH
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion
 Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
9/18/2015. Disclosures. Objectives. Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C. I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest
 Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C Disclosures I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest Objectives Define what dysphagia is Define types of dysphagia Define studies
Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C Disclosures I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest Objectives Define what dysphagia is Define types of dysphagia Define studies
127 Chapter 1 Chapter 2 Chapter 3
 CHAPTER 8 Summary Summary 127 In Chapter 1, a general introduction on the principles and applications of intraluminal impedance monitoring in esophageal disorders is provided. Intra-esophageal impedance
CHAPTER 8 Summary Summary 127 In Chapter 1, a general introduction on the principles and applications of intraluminal impedance monitoring in esophageal disorders is provided. Intra-esophageal impedance
Fecal incontinence causes 196 epidemiology 8 treatment 196
 Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia. Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone. Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital
 THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital Objectives Definitions Common causes Investigations Treatment options Anatomy
THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital Objectives Definitions Common causes Investigations Treatment options Anatomy
PeriOperative Concerns for Anti Reflux Procedure Patients
 PeriOperative Concerns for Anti Reflux Procedure Patients Kevin Gillian, M.D., F.A.C.S. VHC Heartburn Center Director GERD word association Heartburn Chest pain Spicy food Tums Purple pills How big a problem
PeriOperative Concerns for Anti Reflux Procedure Patients Kevin Gillian, M.D., F.A.C.S. VHC Heartburn Center Director GERD word association Heartburn Chest pain Spicy food Tums Purple pills How big a problem
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE. William M. Brady
 Drugs of Today 1998, 34(1): 25-30 Copyright PROUS SCIENCE GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE William M. Brady Section of General Internal Medicine, Temple University School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania,
Drugs of Today 1998, 34(1): 25-30 Copyright PROUS SCIENCE GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE William M. Brady Section of General Internal Medicine, Temple University School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania,
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD. Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd
 ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
Falk Symposium, , , Portorož. Physiology of Swallowing and Anti-Gastroesophageal. Reflux-Mechanisms. Mechanisms: C.
 Falk Symposium, 15.-16.6.07, 16.6.07, Portorož Physiology of Swallowing and Anti-Gastroesophageal Reflux-Mechanisms Mechanisms: Anything new from a radiologist s view? C.Kulinna-Cosentini Cosentini Medical
Falk Symposium, 15.-16.6.07, 16.6.07, Portorož Physiology of Swallowing and Anti-Gastroesophageal Reflux-Mechanisms Mechanisms: Anything new from a radiologist s view? C.Kulinna-Cosentini Cosentini Medical
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease:
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Introduction Gastroesophageal reflux is the involuntary movement of gastric contents to the esophagus. It is a common disease, occurring in one third of the population
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Introduction Gastroesophageal reflux is the involuntary movement of gastric contents to the esophagus. It is a common disease, occurring in one third of the population
4/24/2015. History of Reflux Surgery. Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux
 Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux Scott Carpenter, DO, FACOS, FACS Mercy Hospital Ardmore Ardmore, OK History of Reflux Surgery - 18 th century- first use of term heartburn - 1934-
Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux Scott Carpenter, DO, FACOS, FACS Mercy Hospital Ardmore Ardmore, OK History of Reflux Surgery - 18 th century- first use of term heartburn - 1934-
Surgical aspects of dysphagia
 Dysphagia Why is dysphagia important? Surgery Surgical aspects of dysphagia Adrian P. Ireland aireland@eircom.net Academic RCSI Department of Surgery, Beaumont Hospital Why important Definitons Swallowing
Dysphagia Why is dysphagia important? Surgery Surgical aspects of dysphagia Adrian P. Ireland aireland@eircom.net Academic RCSI Department of Surgery, Beaumont Hospital Why important Definitons Swallowing
Gastro esophageal reflux disease DR. AMMAR I. ABDUL-LATIF
 Gastro esophageal reflux disease )GERD( DR. AMMAR I. ABDUL-LATIF GERD DEFINITION EPIDEMIOLOGY CAUSES PATHOGENESIS SIGNS &SYMPTOMS COMPLICATIONS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT Definition Montreal consensus defined
Gastro esophageal reflux disease )GERD( DR. AMMAR I. ABDUL-LATIF GERD DEFINITION EPIDEMIOLOGY CAUSES PATHOGENESIS SIGNS &SYMPTOMS COMPLICATIONS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT Definition Montreal consensus defined
Esophageal Disorders. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T.
 Esophageal Disorders Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T. Massey, MD, FACP Learning Objectives AFTER COMPLETING THIS CHAPTER, THE LEARNER SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Recognize the typical and atypical presentations
Esophageal Disorders Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T. Massey, MD, FACP Learning Objectives AFTER COMPLETING THIS CHAPTER, THE LEARNER SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Recognize the typical and atypical presentations
Dysphagia. Conflicts of Interest
 Dysphagia Bob Kizer MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Creighton University School of Medicine August 25, 2018 Conflicts of Interest None 1 Which patient does not need an EGD as the first test? 1. 50 year
Dysphagia Bob Kizer MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Creighton University School of Medicine August 25, 2018 Conflicts of Interest None 1 Which patient does not need an EGD as the first test? 1. 50 year
Catherine Kerschen DO, FACOI Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine
 Catherine Kerschen DO, FACOI Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine none 32 yo male presents with a burning sensation in chest following most large meals for 2-3 months. He denies dysphagia,
Catherine Kerschen DO, FACOI Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine none 32 yo male presents with a burning sensation in chest following most large meals for 2-3 months. He denies dysphagia,
Anatomy: From cricoid cartilage to diaphragm 25 Cms. 4 portions: Cervical 5 cms. Thoracic 25 cms. Abdominal 2 cms. Blood supply Lymphatic spread
 Esophagus Anatomy: From cricoid cartilage to diaphragm 25 Cms. 4 portions: Cervical 5 cms. Thoracic 25 cms. Abdominal 2 cms. Blood supply Lymphatic spread Upper 2/3 Cephalad Lower 1/3 Caudad Physiology:
Esophagus Anatomy: From cricoid cartilage to diaphragm 25 Cms. 4 portions: Cervical 5 cms. Thoracic 25 cms. Abdominal 2 cms. Blood supply Lymphatic spread Upper 2/3 Cephalad Lower 1/3 Caudad Physiology:
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that
 Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that may occur daily in healthy infants, children and adults.
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that may occur daily in healthy infants, children and adults.
GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DR RONALDA DELACY
 GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DR RONALDA DELACY DEFINITIONS GERD -Involuntary, effortless passage of gastric contents into the oesophagus +/-ejected from the mouth resulting in troublesome symptoms or complications
GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DR RONALDA DELACY DEFINITIONS GERD -Involuntary, effortless passage of gastric contents into the oesophagus +/-ejected from the mouth resulting in troublesome symptoms or complications
Burning Issues in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 3:45 4:45pm Burning Issues in GERD SPEAKER Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP,
3:45 4:45pm Burning Issues in GERD SPEAKER Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP,
Understanding GERD. & Stretta Therapy. GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Understanding GERD & Stretta Therapy GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease What is GERD? When the muscle between your stomach and esophagus is weak, stomach contents like acid or bile can reflux
Understanding GERD & Stretta Therapy GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease What is GERD? When the muscle between your stomach and esophagus is weak, stomach contents like acid or bile can reflux
Guiding Principles. Trans-oral Incisionless Fundoplication (TIF) for GERD: When, Why & How 4/6/18
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Shaping the Future of GERD Management Treating patients with the TIF procedure using the EsophyX device (EndoGastric Solutions) Gonzalo Pandolfi, MD Trans-oral Incisionless
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Shaping the Future of GERD Management Treating patients with the TIF procedure using the EsophyX device (EndoGastric Solutions) Gonzalo Pandolfi, MD Trans-oral Incisionless
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina
 Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
Back to Basics: What Imaging Test should I order? Jeanne G. Hill, M.D. Pediatric Radiology Medical University of South Carolina Disclosure Neither I nor any member of my immediate family has a relevant
Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children
 Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children Prof. A. K. Patwari MD, DCH, MNAMS, FIAP, FAMS Department of Paediatrics HIMSR & HAHC Hospital, New Delhi GER in Children GER : Merely a descriptive term Regurgitation
Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children Prof. A. K. Patwari MD, DCH, MNAMS, FIAP, FAMS Department of Paediatrics HIMSR & HAHC Hospital, New Delhi GER in Children GER : Merely a descriptive term Regurgitation
Novel Approaches for Managing Reflux. Marcus Reddy Consultant General and Upper GI surgeon
 Novel Approaches for Managing Reflux Marcus Reddy Consultant General and Upper GI surgeon Medigus SRS Endoscope (TIFS) EsophyX STRETTA LINX Persistent GORD RF delivery for GORD RF fits in the
Novel Approaches for Managing Reflux Marcus Reddy Consultant General and Upper GI surgeon Medigus SRS Endoscope (TIFS) EsophyX STRETTA LINX Persistent GORD RF delivery for GORD RF fits in the
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease. (GERD) is often accompanied
 ...PRESENTATIONS... Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Based on a presentation by Peter J. Kahrilas, MD Presentation Summary Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) accompanied by regurgitation
...PRESENTATIONS... Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Based on a presentation by Peter J. Kahrilas, MD Presentation Summary Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) accompanied by regurgitation
Oesophageal Disorders
 Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Gastroesophageal reflux disease Principles of GERD treatment Treatment of reflux diseases GERD
 Esophagus Anatomy/Physiology Gastroesophageal reflux disease Principles of GERD treatment Treatment of reflux diseases GERD Manometry Question 50 years old female with chest pain and dysphagia. Manometry
Esophagus Anatomy/Physiology Gastroesophageal reflux disease Principles of GERD treatment Treatment of reflux diseases GERD Manometry Question 50 years old female with chest pain and dysphagia. Manometry
Aerodigestive Disorders in the NICU. Dawn Simon, M.D Associate Professor in Pediatrics Attending in Pediatric Pulmonary Medicine
 Aerodigestive Disorders in the NICU Dawn Simon, M.D. 2016 Associate Professor in Pediatrics Attending in Pediatric Pulmonary Medicine Dawn M. Simon, M.D. Personal/Professional Financial Relationships with
Aerodigestive Disorders in the NICU Dawn Simon, M.D. 2016 Associate Professor in Pediatrics Attending in Pediatric Pulmonary Medicine Dawn M. Simon, M.D. Personal/Professional Financial Relationships with
Disclosures. Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus. Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus. GERD is common in the U.S. None
 Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus None Disclosures Christian Mathy, MD University of California, San Francisco 2015 Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus Heartburn and GERD GERD therapy Extraesophageal GERD
Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus None Disclosures Christian Mathy, MD University of California, San Francisco 2015 Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus Heartburn and GERD GERD therapy Extraesophageal GERD
Treating Achalasia. When to consider surgery and New options for therapy
 Treating Achalasia When to consider surgery and New options for therapy James B. Wooldridge,Jr., MD Ochsner Medical Center Senior Staff Surgeon General, Laparoscopic, and Bariatric Surgery Disclosures
Treating Achalasia When to consider surgery and New options for therapy James B. Wooldridge,Jr., MD Ochsner Medical Center Senior Staff Surgeon General, Laparoscopic, and Bariatric Surgery Disclosures
Achalasia is a rare disease with an annual incidence estimated REVIEWS. Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:1020 1024 REVIEWS Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia BOUDEWIJN F. KESSING, ALBERT J. BREDENOORD, and ANDRÉ J. P. M. SMOUT
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:1020 1024 REVIEWS Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia BOUDEWIJN F. KESSING, ALBERT J. BREDENOORD, and ANDRÉ J. P. M. SMOUT
EGD. John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008
 EGD John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008 Different Ways to do an EGD Which scope? Pediatric, regular, jumbo EGD endoscope or pediatric colonoscope Transnasal vs. transoral insertion Sedation
EGD John M. Wo, M.D. University of Louisville July 3, 2008 Different Ways to do an EGD Which scope? Pediatric, regular, jumbo EGD endoscope or pediatric colonoscope Transnasal vs. transoral insertion Sedation
A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES. Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus
 A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus CASE DESCRIPTION 63yo, F, single, attending nurse. PMH includes T2DM (Sitagliptin/Metformin), Hyperlipidemia
A CURIOUS CASE OF HYPERTENSIVE LES Erez Hasnis Department of Gastroenterology Rambam Health Care Campus CASE DESCRIPTION 63yo, F, single, attending nurse. PMH includes T2DM (Sitagliptin/Metformin), Hyperlipidemia
Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia Difficulty
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Endoscopic carbon dioxide laser cricopharyngeal myotomy for relief of oropharyngeal dysphagia Difficulty
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus
 Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
INFECTIOUS AND INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS
 Chapter 52 INFECTIOUS AND INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS Allen M. Seiden Infection or inflammation of the esophagus typically produces dysphagia and odynophagia, so these patients may frequently present to the
Chapter 52 INFECTIOUS AND INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS Allen M. Seiden Infection or inflammation of the esophagus typically produces dysphagia and odynophagia, so these patients may frequently present to the
GERD. Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the. stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the
 GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
Oro-pharyngeal and Esophageal Motility and Dysmotility John E. Pandolfino, MD, MSci
 Oro-pharyngeal and Esophageal Department of Medicine Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University 1 Oro-pharyngeal and Esophageal Motility Function: Oropharynx Transfer food Prevent aspiration Breathing
Oro-pharyngeal and Esophageal Department of Medicine Feinberg School of Medicine Northwestern University 1 Oro-pharyngeal and Esophageal Motility Function: Oropharynx Transfer food Prevent aspiration Breathing
Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus. Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery
 Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery Objectives Identify the use of different diagnostic modalities for hiatal hernias List the different types of hiatal hernias
Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery Objectives Identify the use of different diagnostic modalities for hiatal hernias List the different types of hiatal hernias
Refractory GERD. Kenneth R. DeVault, MD, FACG President American College of Gastroenterology Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida
 Refractory GERD Kenneth R. DeVault, MD, FACG President American College of Gastroenterology Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida Objectives Define the terminology associated with refractory
Refractory GERD Kenneth R. DeVault, MD, FACG President American College of Gastroenterology Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida Objectives Define the terminology associated with refractory
34th Annual Toronto Thoracic Surgery Refresher Course
 34th Annual Toronto Thoracic Surgery Refresher Course TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR ACHALASIA Dr. Carmine Simone Director, Intensive Care Unit Head, Division of Critical Care Departments of Medicine and Surgery
34th Annual Toronto Thoracic Surgery Refresher Course TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR ACHALASIA Dr. Carmine Simone Director, Intensive Care Unit Head, Division of Critical Care Departments of Medicine and Surgery
HEARTBURN (GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX)
 DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (403) 270-7479 HEARTBURN (GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX) DOCTOR, I HAVE HAD PROBLEMS WITH A BURNING FIRE SENSATION
DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (403) 270-7479 HEARTBURN (GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX) DOCTOR, I HAVE HAD PROBLEMS WITH A BURNING FIRE SENSATION
Caffeine, drug interaction profile, 152t Calcium absorption, PPIs and, 156 Calcium carbonate, 130 Campylobacter infection, 155
 INDEX Note: Page numbers in italics indicate figures. Page numbers followed by a t indicate tables. Gastroesophageal reflux disease is abbreviated as GERD. Abdominal pain, as side effect of PPIs, 149,
INDEX Note: Page numbers in italics indicate figures. Page numbers followed by a t indicate tables. Gastroesophageal reflux disease is abbreviated as GERD. Abdominal pain, as side effect of PPIs, 149,
Epidemiology Classic Symptoms of GERD
 Definitions LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX AND ITS ROLE IN PEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGY Wendy Mackey, APRN, CORLN SOHN Congress Meeting Washington, DC September 2012 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Retrograde movement
Definitions LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX AND ITS ROLE IN PEDIATRIC OTOLARYNGOLOGY Wendy Mackey, APRN, CORLN SOHN Congress Meeting Washington, DC September 2012 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Retrograde movement
Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation. Introduction. Predisposing factor. Introduction.
 Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) JUSTIN CHE-YUEN WU, et. al. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Gastroenterology,
Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) JUSTIN CHE-YUEN WU, et. al. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Gastroenterology,
Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children
 Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children Jose Luis Martinez, M.D. Associate Professor University of California San Francisco Director Endoscopy Unit Children s Hospital Central California Overview
Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children Jose Luis Martinez, M.D. Associate Professor University of California San Francisco Director Endoscopy Unit Children s Hospital Central California Overview
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
There is considerable discussion regarding. The Center for Videoendoscopic Surgery The Center for Esophageal and Gastric Surgery
 LEFT TO RIGHT: Oelschlager, Pellegrini, Tatum, Wright, Khandelwal Brant K. Oelschlager, M.D.; Professor of Surgery; Byers Endowed Professor in Esophageal Research Carlos A. Pellegrini, M.D.; The Henry
LEFT TO RIGHT: Oelschlager, Pellegrini, Tatum, Wright, Khandelwal Brant K. Oelschlager, M.D.; Professor of Surgery; Byers Endowed Professor in Esophageal Research Carlos A. Pellegrini, M.D.; The Henry
The STRETTA Procedure
 THE HEARTBURN AND REFLUX STUDY CENTER The STRETTA Procedure Introduction The STRETTA procedure is an advanced state-of-the-art endoscopic technique for the correction of all forms of reflux disease including:
THE HEARTBURN AND REFLUX STUDY CENTER The STRETTA Procedure Introduction The STRETTA procedure is an advanced state-of-the-art endoscopic technique for the correction of all forms of reflux disease including:
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Information for patients UHN Read this handout to learn about: What gastroesohageal reflux (GERD) is Signs and symptoms How your doctor will know if you have it Tests
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Information for patients UHN Read this handout to learn about: What gastroesohageal reflux (GERD) is Signs and symptoms How your doctor will know if you have it Tests
MBSImP. Case example 3/6/2018. Esophageal Dysphagia and the role of the SLP Management of Lung Transplant Patients
 Esophageal Dysphagia and the role of the SLP Management of Lung Transplant Patients March 10, 2018 Regina Carr MS CCC-SLP Why address the esophagus? ASHA: A basic understanding of oropharyngeal and esophageal
Esophageal Dysphagia and the role of the SLP Management of Lung Transplant Patients March 10, 2018 Regina Carr MS CCC-SLP Why address the esophagus? ASHA: A basic understanding of oropharyngeal and esophageal
The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.4, December 2000 The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality Saleh Mohsen
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.4, December 2000 The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality Saleh Mohsen
Duke Masters of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Orlando, FL. September 17, Session VI: Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery: Miscellaneous
 Duke Masters of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Orlando, FL September 17, 2016 Session VI: Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery: Miscellaneous NOTES and POEM James D. Luketich MD, FACS Henry T. Bahnson
Duke Masters of Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery Orlando, FL September 17, 2016 Session VI: Minimally Invasive Thoracic Surgery: Miscellaneous NOTES and POEM James D. Luketich MD, FACS Henry T. Bahnson
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
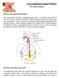 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
Radiology. Gastrointestinal. Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact. Farooq P. Agha
 Gastrointest Radiol 9:9%103 (1984) Gastrointestinal Radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1984 Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact Farooq P. Agha Department of Radiology,
Gastrointest Radiol 9:9%103 (1984) Gastrointestinal Radiology 9 Springer-Verlag 1984 Transient Intraluminal Diverticulum of the Esophagus: A Significant Flow Artifact Farooq P. Agha Department of Radiology,
Medical Policy Manual. Topic: Gastric Reflux Surgery Date of Origin: November Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: March 2014
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Gastric Reflux Surgery Date of Origin: November 2012 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: March 2014 Policy No: 186 Effective Date: May 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Gastric Reflux Surgery Date of Origin: November 2012 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: March 2014 Policy No: 186 Effective Date: May 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies
Options for Gastroesophageal Reflux: Endoluminal. W. Scott Melvin, M.D. Montefiore Medical System and the Albert Einstein School of Medicine
 Options for Gastroesophageal Reflux: Endoluminal W. Scott Melvin, M.D. Montefiore Medical System and the Albert Einstein School of Medicine The patient with GERD The Therapy Gap Effectively Treated with
Options for Gastroesophageal Reflux: Endoluminal W. Scott Melvin, M.D. Montefiore Medical System and the Albert Einstein School of Medicine The patient with GERD The Therapy Gap Effectively Treated with
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
ESOPHAGEAL MOTOR DISORDERS
 Medicine Dr. Taha Alkarbuli Lecture 1 (Esophageal & GIT Disorders) ESOPHAGEAL DISORDERS: - ESOPHAGEAL MOTOR DISORDERS. - GERD - ESOPHAGEAL TUMORS. ESOPHAGEAL MOTOR DISORDERS Present with chest pain, dysphagia,
Medicine Dr. Taha Alkarbuli Lecture 1 (Esophageal & GIT Disorders) ESOPHAGEAL DISORDERS: - ESOPHAGEAL MOTOR DISORDERS. - GERD - ESOPHAGEAL TUMORS. ESOPHAGEAL MOTOR DISORDERS Present with chest pain, dysphagia,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Factors Affecting Esophageal Motility in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors Affecting Esophageal Motility in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Emmanuel Chrysos, MD; George Prokopakis, MD; Elias Athanasakis, MD; George Pechlivanides, MD; John Tsiaoussis,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Factors Affecting Esophageal Motility in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Emmanuel Chrysos, MD; George Prokopakis, MD; Elias Athanasakis, MD; George Pechlivanides, MD; John Tsiaoussis,
GERD: Pitfalls and Pearls
 GERD: Pitfalls and Pearls Gary W. Falk, M.D., M.S. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Perelman School of Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania Conflicts of Interest Nothing to disclose
GERD: Pitfalls and Pearls Gary W. Falk, M.D., M.S. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology Perelman School of Medicine of the University of Pennsylvania Conflicts of Interest Nothing to disclose
Gastroesophageal Reflux in Infants
 Gastroesophageal Reflux in Infants Lindsey Albenberg, DO Andrew Grossman, MD The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia 2013 Resident Education Series Reviewed by Jyoti Ramakrishna, MD of the Professional
Gastroesophageal Reflux in Infants Lindsey Albenberg, DO Andrew Grossman, MD The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia 2013 Resident Education Series Reviewed by Jyoti Ramakrishna, MD of the Professional
Acidic and Non-Acidic Reflux During Sleep Under Conditions of Powerful Acid Suppression*
 Original Research SLEEP MEDICINE Acidic and Non-Acidic Reflux During Sleep Under Conditions of Powerful Acid Suppression* William C. Orr, PhD; Andrea Craddock, PhD; and Suanne Goodrich, PhD Background:
Original Research SLEEP MEDICINE Acidic and Non-Acidic Reflux During Sleep Under Conditions of Powerful Acid Suppression* William C. Orr, PhD; Andrea Craddock, PhD; and Suanne Goodrich, PhD Background:
11/10/2014. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
AGA SECTION. Gastroenterology 2016;150:
 Gastroenterology 2016;150:1026 1030 April 2016 AGA Section 1027 Procedural intervention (3) Upper endoscopy indications 3 6 Non-response of symptoms to a 4 8 week empiric trial of twice-daily PPI Troublesome
Gastroenterology 2016;150:1026 1030 April 2016 AGA Section 1027 Procedural intervention (3) Upper endoscopy indications 3 6 Non-response of symptoms to a 4 8 week empiric trial of twice-daily PPI Troublesome
Esophageal Disease. Objectives:
 Esophageal Disease Objectives: Basic function of esophagus Definition of dysphagia Mechanism of dysphagia Types of dysphagia Common causes Algorithm to approach dysphagia Doctor: prof. Saleh Alamri Team
Esophageal Disease Objectives: Basic function of esophagus Definition of dysphagia Mechanism of dysphagia Types of dysphagia Common causes Algorithm to approach dysphagia Doctor: prof. Saleh Alamri Team
There are four general types of congenital lung disorders:
 Pediatric Pulmonology Conditions Evaluated and Treated As a parent, watching a child suffer from a respiratory disorder can be frightening and worrisome. Our respiratory specialists provide compassionate
Pediatric Pulmonology Conditions Evaluated and Treated As a parent, watching a child suffer from a respiratory disorder can be frightening and worrisome. Our respiratory specialists provide compassionate
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)?
 WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
In the Name of God. Refractory GERD
 In the Name of God Refractory GERD S Nasseri-Moghaddam MD, MPH, AGAF Associate Professor of Medicine Digestive Disease Research Institute Shariati Hospital, TUMS sianasseri@yahoo.com IAGH meeting, Ordibehesht
In the Name of God Refractory GERD S Nasseri-Moghaddam MD, MPH, AGAF Associate Professor of Medicine Digestive Disease Research Institute Shariati Hospital, TUMS sianasseri@yahoo.com IAGH meeting, Ordibehesht
Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of the Literature
 International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 291472, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/291472 Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of
International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 291472, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/291472 Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of
What can you expect from the lab?
 Role of the GI Motility Lab in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Esophageal Disorders Kenneth R. DeVault MD, FACG, FACP Professor and Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida What can you expect from
Role of the GI Motility Lab in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Esophageal Disorders Kenneth R. DeVault MD, FACG, FACP Professor and Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida What can you expect from
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Acid Reflux Acid reflux occurs when acid from the stomach moves backwards into the esophagus. Heartburn Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux and GERD. It may feel
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Acid Reflux Acid reflux occurs when acid from the stomach moves backwards into the esophagus. Heartburn Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux and GERD. It may feel
There are many different symptoms of GER. Your child may only have a few of these symptoms. The most common symptoms include:
 This document is a short Overview of Pediatric Acid Reflux and GERD from www.reflux.org web site. Dozens of other documents about Pediatric GERD can be found in the Reading Room section of this web site.
This document is a short Overview of Pediatric Acid Reflux and GERD from www.reflux.org web site. Dozens of other documents about Pediatric GERD can be found in the Reading Room section of this web site.
What s New in the Management of Esophageal Disease
 What s New in the Management of Esophageal Disease Philip O. Katz, MD Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College
What s New in the Management of Esophageal Disease Philip O. Katz, MD Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College
Case Presentations in ILD. Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco
 Case Presentations in ILD Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Definition/Classification High-resolution CT scan Multidisciplinary
Case Presentations in ILD Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Definition/Classification High-resolution CT scan Multidisciplinary
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
LINX Reflux Management System. Patient Information. Caution: Federal (USA) Law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician.
 LINX Reflux Management System Patient Information Caution: Federal (USA) Law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. 2 Table of Contents What is the LINX System? 3 Why doctors
LINX Reflux Management System Patient Information Caution: Federal (USA) Law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. 2 Table of Contents What is the LINX System? 3 Why doctors
GUIDELINES FOR CLINICIANS. Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults. Reflux Disease. 4th Edition Digestive Health Foundation
 GUIDELINES FOR CLINICIANS Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults Reflux Disease 4th Edition 2008 Digestive Health Foundation Digestive Health Foundation Table of contents Page 4 Gastro-oesophageal
GUIDELINES FOR CLINICIANS Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults Reflux Disease 4th Edition 2008 Digestive Health Foundation Digestive Health Foundation Table of contents Page 4 Gastro-oesophageal
Chapter 14: Training in Radiology. DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12
 DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
DDSEP Chapter 1: Question 12 A 52-year-old white male presents for evaluation of sudden onset of abdominal pain and shoulder pain. His past medical history is notable for a history of coronary artery disease,
Successful resolution of refractory chronic cough induced by gastroesophageal reflux with treatment of baclofen
 Xu et al. Cough, 8:8 Cough CASE REPORT Open Access Successful resolution of refractory chronic cough induced by gastroesophageal reflux with treatment of baclofen Xianghuai Xu, Qiang Chen, Siwei Liang,
Xu et al. Cough, 8:8 Cough CASE REPORT Open Access Successful resolution of refractory chronic cough induced by gastroesophageal reflux with treatment of baclofen Xianghuai Xu, Qiang Chen, Siwei Liang,
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/acid-reflux-gastroesophageal-reflux-disease-in-adults-...
 Page 1 of 10 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Page 1 of 10 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
