Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease. (GERD) is often accompanied
|
|
|
- Alexandrina Powers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ...PRESENTATIONS... Maximizing Outcome of Extraesophageal Reflux Disease Based on a presentation by Peter J. Kahrilas, MD Presentation Summary Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) accompanied by regurgitation and aspiration has been suggested as the cause of many conditions, but the strongest evidence exists for a relationship between asthma and GERD and posterior laryngitis and GERD. The exact mechanism of the tracheopulmonary damage has not been determined, but studies show that proton pump inhibitor therapy can ameliorate to some extent the laryngeal symptoms in laryngitis as well as asthma symptoms, asthma medication use, and lung function. Antireflux surgery appears to be more effective than antireflux medication in asthma patients with GERD symptoms. The role of tracheopulmonary damage in patients with chest pain is less clear, and the difficulty lies in determining which patients have gastroesophageal etiology. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is often accompanied by regurgitation and aspiration. Given the acidic nature of the refluxate, it is not surprising to find damage to the trachea and pulmonary system. Although it has taken time to convince the medical community that these tracheopulmonary complications exist (extraesophageal reflux disease), they are now well established, and the challenge is to determine their cause and to identify their mechanism. In theory, 2 possible ways exist to cause tracheopulmonary manifestations of reflux disease. First, a gastroesophageal reflexive mechanism stimulates chemoreceptors in the distal esophagus and activates a vagovagal reflex. Most often, this reflex causes bronchospasm. The other potential and more direct pathway occurs when the microaspirate of the refluxate contacts the pharynx directly. Evidence most strongly supports the latter event as the most common etiology of laryngopulmonary changes. Gastroesophageal reflux accompanied by regurgitation and aspiration has been suggested as the cause of many conditions, including asthma, posterior laryngitis, chronic coughing, recurrent pneumonitis or nocturnal choking, chronic hoarseness, pharyngitis, and dental disease. However, establishing unequivocal causality is difficult. The most compelling evidence exists for laryngitis and asthma. Posterior Laryngitis Pharyngeal injury caused by acid S876 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MANAGED CARE OCTOBER 2000
2 ... MAXIMIZING OUTCOME OF EXTRAESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE... reflux was first described in Before that time, the injury was considered a manifestation of voice abuse. 1,2 The initial presentation is subtle and is usually caused by erythema spilling onto the vocal folds. When a patient is referred with such a presentation, it is often because he or she complains of persistent hoarseness. Only some of those cases are the result of acid, so the challenge is to determine which ones, particularly if the squamocolumnar junction is intact and no good evidence of reflux disease exists. There are several possible causes for this type of lesion. First, during sleep the upper esophageal sphincter tone is practically absent. GERD appears to be mainly a nocturnal injury to the larynx. Eating late at night causes reflux and directly exposes the larynx to the refluxate. Second, there is no reflex contraction of the upper esophageal sphincter as it responds to acidification, so it does not protect itself in any way. Third, the esophagus responds to abrupt distension by relaxing and facilitating the flow of whatever material is in the proximal esophagus. Because it does not contract, as might be expected, it is not a protective sphincter but may be considered to act as a respiratory muscle. 3-5 Given these findings, a clinician would expect that if these were acidrelated injuries, acid exposure would be observed proximal to or close to the larynx. However, dual-channel ph studies (of the distal esophagus and the very proximal esophagus) in individuals who had reflux disease without laryngitis, reflux disease with laryngeal symptoms, or reflux disease with both laryngeal symptoms and laryngoscopic findings that were believed consistent with reflux laryngitis show that most reflux events are limited to the distal esophagus. 6 Whereas there was no difference among the groups in the distal ph values, the proximal ph values showed a significant increase in acid exposure among those with laryngoscopic findings and laryngoscopic symptoms. When these measurements were done only at night (when the patients were supine), the differences became even more profound. In fact, individuals with laryngeal symptoms and findings had significantly more nocturnal acid exposure. However, these data do not support using ph monitoring as a diagnostic modality, because several participants with laryngeal symptoms and laryngitis had no acid exposure in the proximal esophagus. As a result, this test can provide supportive data for this diagnosis, but all treatment decisions cannot be based on these findings because the results for many individuals will be false negatives. Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy would be expected to improve reflux laryngitis symptoms, and studies support this theory. In a study of 16 patients with persistent posterior laryngitis, PPI therapy (40 mg/day of omeprazole) was given for 6 to 24 weeks. Omeprazole significantly reduced laryngeal symptoms after 6 weeks of therapy, but the symptoms recurred after discontinuation, suggesting that reflux is the underlying etiology (Figure 1). 7 Similarly, 182 patients with chronic laryngitis symptoms (edema or erythema only) were treated with nocturnal antireflux precautions (eg, not eating late). The study results showed that simple lifestyle modifications cured most of the mild cases. Pharmacotherapy was progressively introduced to patients who did not respond to antireflux precautions alone: first famotidine 20 mg at bedtime, then omeprazole 20 mg at bedtime, and finally omeprazole 40 to 80 mg or antireflux surgery. The final results showed that 96% of the patients responded to lifestyle changes and/or PPI therapy. Those with refractory symptoms had a partial response or chose fundoplication. 8 VOL. 6, NO. 16, SUP. THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MANAGED CARE S877
3 ... PRESENTATIONS... The data suggest that the pathophysiology of reflux laryngitis is caused by intermittent contact of the laryngeal mucosa by gastric refluxate. Exposure appears to be more common at night, probably because of the physiologic properties of the upper sphincter (diminished upper esophageal sphincter pressure and poor esophageal clearance). Although PPI therapy appears to be beneficial, its benefits are not complete so other cofactors are probably involved (eg, excessive voice use, viral laryngitis, or smoking). Therefore, the recommended treatment is PPI therapy in addition to identifying and modifying the cofactors when possible. Atypical GERD Symptoms The data for treating atypical GERD symptoms are limited. In a recent study of 150 patients who were referred for laparoscopic antireflux surgery, 35 of whom had atypical symptoms, 16 had pulmonary symptoms (eg, asthma or chronic cough), 12 had atypical chest or epigastric pain (excluding cardiovascular etiology of pain), and 9 had pharyngeal or laryngeal symptoms (eg, hoarseness, halitosis, or sore throat). The outcomes were measured by independent observers. 9 The results show a significant improvement in the symptom score for those with atypical symptoms: 48% of the patients with pulmonary symptoms, 58% of atypical chest pain patients, and 78% of patients with pharyngo/laryngeal symptoms improved. Those with typical symptoms showed substantially greater improvement after the surgery: heartburn was relieved in 93% of patients with typical symptoms. However, improvement is less satisfactory and more difficult to predict in patients with atypical symptoms. In fact, the response to acid suppression was the only predictor of outcome for those with atypical symptoms. Therefore, Figure 1. Effect of PPI Therapy on Symptoms of Reflux Laryngitis Laryngeal Symptom Score Baseline Completion of Study 6 Weeks After Discontinuation of Treatment Laryngeal symptom scores were based on 2 scales: severity parameters were graded from 0 to 3, and the frequency was graded from 0 to 4. The symptom score was the sum of the severity x frequency for the worst 2 symptoms. PPI = proton pump inhibitor. Source: Adapted from reference 7. S878 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MANAGED CARE OCTOBER 2000
4 ... MAXIMIZING OUTCOME OF EXTRAESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE... the authors conclude that because laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication can have undesirable side effects, realistic expectations are important in optimizing patient satisfaction. 9 Cough is also a poor predictor of outcome after surgery, even though it is recognized as a reflux-related symptom. In a study of 195 consecutive patients treated with laparoscopic antireflux procedures, 133 were treated for inadequate control of reflux and 62 were treated primarily for refractory respiratory symptoms. With independent observer assessment, the results showed improvement in cough score in those with respiratory symptoms (but with a large confidence interval) and a significant improvement in cough score in those with esophageal symptoms who had a complete resolution of cough. The evidence indicates that antireflux surgery, with or without esophageal symptoms, has an impact on cough as a symptom of reflux disease, however, the result was better for those with esophageal symptoms as well. 10 Asthma and GERD The data for patients with asthma and its relationship to GERD are not clear cut. In a study of patients with adult-onset wheezing who had no history of allergy, 90% had GERD with mild or absent symptoms. Patients were randomized to receive either placebo or antireflux surgery. At the 6-month and 7-year endpoints, there was no significant change in the asthma medication score (an indicator of the severity of bronchospasm) for those who took placebo, and the range of medication scores in this group was broad. Those who received antireflux surgery had a fairly similar spectrum of asthma medication scores at baseline compared with the placebo group. At 6 months, 30% to 40% of the patients in this group had complete resolution of asthma, which was maintained for 7 years. 11 Although encouraging, the data have not been replicated. A survey of 8 randomized, controlled trials shows significant improvement in the asthma response (ie, asthma symptoms and asthma medication use) to medical reflux treatment (Figure 2). However, there was less significant improvement in asthma medication use, and the peak expiratory flow rate indicated that fewer patients were improved than not improved. Similarly, spirometric measurements (the most objective measure of asthma) indicated no improvement. 12 Looking at the asthma response to antireflux surgery (summarized from controlled trials in the literature), asthma symptoms, medication use, and pulmonary function improved in the majority of patients (Figure 3). 13 Together, these data reveal that whereas medical GERD treatment can produce some symptomatic improvement, it does not produce functional improvement. With surgical GERD treatment, a large subset of patients experienced functional improvement as well. Unfortunately, no way to select these patients currently exists. Patients With Chest Pain In analyzing the symptom of chest pain, the history taking is most important. Patients with chest pain are divided into 3 groups: 1) those with concomitant esophageal symptoms, 2) those with isolated chest pain without any concomitant symptoms, and 3) those with anxiety and somatization neurosis. The last group is often easy to identify, although there may be some overlap with the other 2 groups. As expected, the approach to treatment for each group is different. If patients have chest pain with esophageal symptoms (eg, heartburn, regurgitation, dysphasia, water VOL. 6, NO. 16, SUP. THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MANAGED CARE S879
5 ... PRESENTATIONS... Figure 2. Asthma Response to Medical GERD Treatment: Summary Data from 8 Randomized Controlled Trials Patients Improved Patients Not Improved 120 Number of 100 Subjects Asthma Symptoms Asthma Medication Use Peak Expiratory Flow Rate Spirometry GERD = gastroesophageal reflux disease. Source: Field SK, Sutherland LR. Does medical antireflux therapy improve asthma in asthmatics with gastroesophageal reflux? A critical review of the literature. Chest 1998;114: Reprinted with permission. Figure 3. Asthma Response to Antireflux Surgery: Literature Review Patients Improved Patients Not Improved Number of Subjects GERD Symptoms Asthma Symptoms Asthma Medication Pulmonary Function GERD = gastroesophageal reflux disease. Source: Field SK, Gelfand GA, McFadden SD. The effects of antireflux surgery on asthmatics with gastroesophageal reflux. Chest 1999;116: Reprinted with permission. S880 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MANAGED CARE OCTOBER 2000
6 ... MAXIMIZING OUTCOME OF EXTRAESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE... brash, nausea, or vomiting), they should be treated as if they have only GERD, and their chest pain will invariably improve. It is very rare to have an esophageal etiology in those who experience isolated chest pain. Evaluating other noncardiac causes is just as valid as considering an esophageal cause of pain. A useful approach is to scrutinize the cardiologic evaluation and monitor and reassure the patient. It is not prudent to extensively pursue esophageal etiologies in the absence of any evidence. Those with anxiety and neuroses may best be referred to a psychiatrist. Evaluating Esophageal Disorders in Patients With Chest Pain Endoscopy or a barium swallow and manometry will detect an esophageal etiology most of the time. The quagmire exists in endoscopy-negative reflux disease that may lead to chest pain, which has led to some support for a PPI test for noncardiac chest pain. A recent study evaluated the ability of a short course of omeprazole to identify the cause of noncardiac chest pain in 37 patients who had daily chest pain and a negative cardiovascular evaluation. They were randomized to receive either omeprazole 40 mg every morning and 20 mg for every hour of sleep or placebo for 7 days. A positive response was defined as a 50% decrease in symptoms. Of the 37 patients, 23 were GERD positive, as documented by ph monitoring or endoscopy, and 14 were GERD negative. Seventy-eight percent of the GERD-positive group had a response to the PPI trial; 14% of the GERD-negative group responded. This omeprazole test did identify GERD in noncardiac chest pain patients, but its value is questionable, because the patients were already identified as having GERD. The real challenge is to identify a GERD etiology in patients who have no available evidence of reflux disease. 14 Summary Extraesophageal reflux disease presents unique clinical challenges, primarily because the treatment regimens are not formally outlined. They are determined empirically, and a review of the etiology of this disease can explain why. In the 1990s, the greatest challenge regarding extraesophageal manifestations of reflux disease was convincing the medical community that they really existed. In 2000, we accept that they exist and are now trying to define the disease and its diagnosis. In the future, physicians will be faced with the difficult issue of how and when to treat the disease when the response to standard treatment is not obvious or immediate.... REFERENCES Jackson C. Contact ulcer of larynx. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1928;37: Cherry J, Margulies SI. Contact ulcer of larynx. Laryngoscope 1968;78: Kahrilas PJ, Dodds WJ, Dent J, Haeberle B, Hogan WJ, Arndorfer RC. Effect of sleep, spontaneous gastroesophageal reflux, and a meal on upper esophageal sphincter pressure in normal human volunteers. Gastroenterology 1987;92: Vakil NB, Kahrilas PJ, Dodds WJ, Vanagunas A. Absence of an upper esophageal sphincter response to acid reflux. Am J Gastroenterol 1989;84: Karhilas PJ, Dodds WJ, Dent J, Wyman JB, Hogan WJ, Arndorfer RC. Upper esophageal sphincter function during belching. Gastroenterology 1986;91: Jacob P, Kahrilas PJ, Herzon G. Proximal esophageal ph-metry in patients with reflux laryngitis. Gastroenterology 1991;100: Kamel PL, Hanson D, Kahrilas PJ. Omeprazole for the treatment of posterior laryngitis. Am J Med 1994;96: Hanson DG, Kamel PL, Kahrilas PJ. Outcomes of antireflux therapy for the treatment of chronic laryngitis. Ann Otol Rhinol VOL. 6, NO. 16, SUP. THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MANAGED CARE S881
7 ... PRESENTATIONS... Laryngol 1995;104: So JB, Zeitels SM, Rattner DW. Outcomes of atypical symptoms attributed to gastroesophageal reflux treated by laparoscopic fundoplication. Surgery 1998;124: Allen CJ, Anvari M. Gastro-oesophageal reflux related cough and its response to laparoscopic fundoplication. Thorax 1998;53: Larrain A, Carrasco E, Galleguillos F, Sepulveda R, Pope CE II. Medical and surgical treatment of nonallergic asthma associated with gastroesophageal reflux. Chest 1991;99: Field SK, Sutherland LR. Does medical antireflux therapy improve asthma in asthmatics with gastroesophageal reflux? A critical review of the literature. Chest 1998;114: Field SK, Gelfand GA, McFadden SD. The effects of antireflux surgery on asthmatics with gastroesophageal reflux. Chest 1999;116: Fass R, Fennerty MB, Ofman JJ, et al. The clinical and economic value of a short course of omeprazole in patients with noncardiac chest pain. Gastroenterology 1998;115: S882 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MANAGED CARE OCTOBER 2000
GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications
 GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications Esophageal Syndromes Extra - esophageal Syndromes Symptomatic Syndromes Typical reflux
GERD is a condition which develops when the reflux of stomach contents causes troublesome symptoms and/or complications Esophageal Syndromes Extra - esophageal Syndromes Symptomatic Syndromes Typical reflux
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc 2 and Marcelo F. Vela MD, MSCR 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Einstein
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Philip O. Katz MD 1, Lauren B. Gerson MD, MSc 2 and Marcelo F. Vela MD, MSCR 3 1 Division of Gastroenterology, Einstein
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: esophageal_ph_monitoring 4/2011 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Acid reflux is the
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: esophageal_ph_monitoring 4/2011 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Acid reflux is the
Lansoprazole Treatment of Patients With Chronic Idiopathic Laryngitis: A Placebo-Controlled Trial
 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 4, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02244-4 Lansoprazole Treatment
THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF GASTROENTEROLOGY Vol. 96, No. 4, 2001 2001 by Am. Coll. of Gastroenterology ISSN 0002-9270/01/$20.00 Published by Elsevier Science Inc. PII S0002-9270(01)02244-4 Lansoprazole Treatment
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Paraesophageal Hernias &
 530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
530.81 553.3 & 530.00 43289, 43659 1043432842, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Surgery, UH JABSOM Associate General Surgery Program Director Director of Minimally Invasive & Bariatric Surgery Programs
Extraesophageal presentations of gastroesophageal reflux disease: the case for aggressive diagnosis and treatment
 JOEL E. RICHTER, MD Dr. Richter is chairman of the Department of Gastroenterology at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, specializing in esophageal diseases with particular interest in GERD, achalasia, and
JOEL E. RICHTER, MD Dr. Richter is chairman of the Department of Gastroenterology at the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, specializing in esophageal diseases with particular interest in GERD, achalasia, and
GERD: A linical Clinical Clinical Update Objectives
 GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
GERD: A Clinical Update Jeff Gilbert, M.D. University i of Kentucky Gastroenterology 11/6/08 Objectives To review the basic pathophysiology underlying gastroesophageal reflux disease To highlight current
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
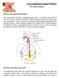 Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
Laryngopharyngeal Reflux The Silent Reflux What is Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Also called Reflux laryngitis, laryngopharyngeal reflux is a condition where the acid from the stomach reaches the voicebox
SASKATCHEWAN REGISTERED NURSES ASSOCIATION
 DEFINITION Reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus, which results in esophageal irritation or inflammation. IMMEDIATE CONSULTATION REQUIRED IN THE FOLLOWING SITUATIONS Dysphagia (solid food, progressive)
DEFINITION Reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus, which results in esophageal irritation or inflammation. IMMEDIATE CONSULTATION REQUIRED IN THE FOLLOWING SITUATIONS Dysphagia (solid food, progressive)
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Extraesophageal symptoms of GERD
 Extraesophageal symptoms of GERD KENNETH R. DEVAULT, MD ABSTRACT Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can be the primary cause of, or an aggravating contributor to, a wide variety of conditions affecting
Extraesophageal symptoms of GERD KENNETH R. DEVAULT, MD ABSTRACT Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can be the primary cause of, or an aggravating contributor to, a wide variety of conditions affecting
Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do?
 Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do? Philip O. Katz, MD, FACG Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia,
Refractory GERD: What s a Gastroenterologist To Do? Philip O. Katz, MD, FACG Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology Einstein Medical Center Clinical Professor of Medicine Jefferson Medical College Philadelphia,
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice
 Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
Putting Chronic Heartburn On Ice Over the years, gastroesophageal reflux disease has proven to be one of the most common complaints facing family physicians. With quicker diagnosis, this pesky ailment
A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Idiopathic Laryngitis ABSTRACT
 THAI J 28 GASTROENTEROL Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Original Idiopathic Laryngitis Article A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic
THAI J 28 GASTROENTEROL Rabeprazole for Therapeutic Trial in Chronic Original Idiopathic Laryngitis Article A Prospective, Randomized, Placebo-controlled, Double-Blind Study of Rabeprazole for Therapeutic
Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ronnie Fass MD Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Esophageal
Unmet Needs in the Management of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Ronnie Fass MD Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University Chairman, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Director, Esophageal
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Infants and Children 4 Marzo 2017 Drssa Chiara Leoni Drssa Valentina Giorgio pediatriagastro@gmail.com valentinagiorgio1@gmail.com Definitions: GER GER is the passage
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that
 Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that may occur daily in healthy infants, children and adults.
Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) Gastroesophageal reflux (GER), the passage of gastric contents into the esophagus, is a normal physiologic process that may occur daily in healthy infants, children and adults.
Speaker disclosure. Objectives. GERD: Who and When to Treat 7/21/2015
 GERD: Who and When to Treat Eugenio J Hernandez, MD Gastrohealth, PL Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine, FIU Herbert Wertheim School of Medicine Speaker disclosure I do not have any relevant commercial
GERD: Who and When to Treat Eugenio J Hernandez, MD Gastrohealth, PL Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine, FIU Herbert Wertheim School of Medicine Speaker disclosure I do not have any relevant commercial
GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DR RONALDA DELACY
 GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DR RONALDA DELACY DEFINITIONS GERD -Involuntary, effortless passage of gastric contents into the oesophagus +/-ejected from the mouth resulting in troublesome symptoms or complications
GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DR RONALDA DELACY DEFINITIONS GERD -Involuntary, effortless passage of gastric contents into the oesophagus +/-ejected from the mouth resulting in troublesome symptoms or complications
Effects of anti-reflux surgery on chronic cough and asthma in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
 RESPIRATORY MEDICINE (2000) 94, 1166 1170 doi:10.1053/rmed.2000.0944, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Effects of anti-reflux surgery on chronic cough and asthma in patients with gastro-oesophageal
RESPIRATORY MEDICINE (2000) 94, 1166 1170 doi:10.1053/rmed.2000.0944, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Effects of anti-reflux surgery on chronic cough and asthma in patients with gastro-oesophageal
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Acid Reflux Acid reflux occurs when acid from the stomach moves backwards into the esophagus. Heartburn Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux and GERD. It may feel
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Acid Reflux Acid reflux occurs when acid from the stomach moves backwards into the esophagus. Heartburn Heartburn is a symptom of acid reflux and GERD. It may feel
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Extraesophageal Manifestations Karen B. Zur, MD Director, Pediatric Voice Program Associate Director, Center for Pediatric Airway Disorders The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia
Understanding GERD. & Stretta Therapy. GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
 Understanding GERD & Stretta Therapy GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease What is GERD? When the muscle between your stomach and esophagus is weak, stomach contents like acid or bile can reflux
Understanding GERD & Stretta Therapy GERD (gĕrd): Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease What is GERD? When the muscle between your stomach and esophagus is weak, stomach contents like acid or bile can reflux
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE. William M. Brady
 Drugs of Today 1998, 34(1): 25-30 Copyright PROUS SCIENCE GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE William M. Brady Section of General Internal Medicine, Temple University School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania,
Drugs of Today 1998, 34(1): 25-30 Copyright PROUS SCIENCE GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE William M. Brady Section of General Internal Medicine, Temple University School of Medicine, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania,
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion
 Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
Refractory GERD : case presentation and discussion Ping-Huei Tseng National Taiwan University Hospital May 19, 2018 How effective is PPI based on EGD? With GERD symptom 75% erosive 25% NERD Endoscopy 81%
Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of the Literature
 International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 291472, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/291472 Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of
International Otolaryngology Volume 2012, Article ID 291472, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/291472 Review Article Impact of Laparoscopic Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Review of
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.6.EN2 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease. Santhana Krishna Kumar. B 1, Sivasankari. L 1 1 Assistant
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.6.EN2 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 ENT Manifestations in Gastro - Esophageal Reflux Disease. Santhana Krishna Kumar. B 1, Sivasankari. L 1 1 Assistant
Extraesophageal GERD: Fact or Fiction?
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/gi-insights/extraesophageal-gerd-fact-or-fiction/4157/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/gi-insights/extraesophageal-gerd-fact-or-fiction/4157/
GERD. Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the. stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the
 GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
GERD What is GERD? Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, occurs when acid from the stomach backs up into the esophagus. Normally, food travels from the mouth, down through the esophagus and into the
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Information for patients UHN Read this handout to learn about: What gastroesohageal reflux (GERD) is Signs and symptoms How your doctor will know if you have it Tests
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Information for patients UHN Read this handout to learn about: What gastroesohageal reflux (GERD) is Signs and symptoms How your doctor will know if you have it Tests
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT DISCLOSURES 4/18/2018
 GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
GERD DIAGNOSIS & TREATMENT Subhash Chandra MBBS Assistant Professor CHI Health Clinic Gastroenterology Creighton University, School of Medicine April 28, 2018 DISCLOSURES None 1 OBJECTIVES Review update
Burning Issues in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
 3:45 4:45pm Burning Issues in GERD SPEAKER Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP,
3:45 4:45pm Burning Issues in GERD SPEAKER Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Prateek Sharma, MD, FACG, FACP,
Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children
 Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children Jose Luis Martinez, M.D. Associate Professor University of California San Francisco Director Endoscopy Unit Children s Hospital Central California Overview
Extraesophageal Manifestations of GERD in Children Jose Luis Martinez, M.D. Associate Professor University of California San Francisco Director Endoscopy Unit Children s Hospital Central California Overview
Gastro-oesophageal reflux related cough and its response to laparoscopic fundoplication
 Thorax 1998;53:963 968 963 Departments of Medicine and Surgery, McMaster University, St Joseph s Hospital, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada L8N 4A6 C J Allen M Anvari Correspondence to: Dr C Allen. Received 10
Thorax 1998;53:963 968 963 Departments of Medicine and Surgery, McMaster University, St Joseph s Hospital, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada L8N 4A6 C J Allen M Anvari Correspondence to: Dr C Allen. Received 10
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)?
 WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
WHAT IS GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GERD)? The term gastroesophageal reflux describes the movement (or reflux) of stomach contents back up into the esophagus, the muscular tube that extends from the
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Correlation of Findings at Direct Laryngoscopy and Bronchoscopy With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Children
 Correlation of Findings at Direct Laryngoscopy and Bronchoscopy With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Children A Prospective Study ORIGINAL ARTICLE Michele M. Carr, DDS, MD, MEd, FRCSC; Mark L. Nagy,
Correlation of Findings at Direct Laryngoscopy and Bronchoscopy With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Children A Prospective Study ORIGINAL ARTICLE Michele M. Carr, DDS, MD, MEd, FRCSC; Mark L. Nagy,
GERD: 2014 Dilemmas and Solutions. Ronnie Fass MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University
 GERD: 2014 Dilemmas and Solutions Ronnie Fass MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University How to Maximize Your PPI Treatment? Improve compliance and adherance Fass R. Am J Gastroenterol.
GERD: 2014 Dilemmas and Solutions Ronnie Fass MD, FACP Professor of Medicine Case Western Reserve University How to Maximize Your PPI Treatment? Improve compliance and adherance Fass R. Am J Gastroenterol.
Achalasia is a rare disease with an annual incidence estimated REVIEWS. Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:1020 1024 REVIEWS Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia BOUDEWIJN F. KESSING, ALBERT J. BREDENOORD, and ANDRÉ J. P. M. SMOUT
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2011;9:1020 1024 REVIEWS Erroneous Diagnosis of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Achalasia BOUDEWIJN F. KESSING, ALBERT J. BREDENOORD, and ANDRÉ J. P. M. SMOUT
Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 2.01.17 Esophageal ph Monitoring Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Subsection Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
MP 2.01.17 Esophageal ph Monitoring Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Subsection Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.4, December 2000 The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality Saleh Mohsen
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.22, No.4, December 2000 The Frequency of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Nutcracker Esophagus and the Effect of Acid-Reduction Therapy on the Motor Abnormality Saleh Mohsen
Gastro esophageal reflux disease DR. AMMAR I. ABDUL-LATIF
 Gastro esophageal reflux disease )GERD( DR. AMMAR I. ABDUL-LATIF GERD DEFINITION EPIDEMIOLOGY CAUSES PATHOGENESIS SIGNS &SYMPTOMS COMPLICATIONS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT Definition Montreal consensus defined
Gastro esophageal reflux disease )GERD( DR. AMMAR I. ABDUL-LATIF GERD DEFINITION EPIDEMIOLOGY CAUSES PATHOGENESIS SIGNS &SYMPTOMS COMPLICATIONS DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT Definition Montreal consensus defined
4/24/2015. History of Reflux Surgery. Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux
 Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux Scott Carpenter, DO, FACOS, FACS Mercy Hospital Ardmore Ardmore, OK History of Reflux Surgery - 18 th century- first use of term heartburn - 1934-
Recent Innovations in the Surgical Treatment of Reflux Scott Carpenter, DO, FACOS, FACS Mercy Hospital Ardmore Ardmore, OK History of Reflux Surgery - 18 th century- first use of term heartburn - 1934-
The Prevalence of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Asthma Patients without Reflux Symptoms
 The Prevalence of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Asthma Patients without Reflux Symptoms SUSAN M. HARDING, MELANY R. GUZZO, and JOEL E. RICHTER Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care Medicine, Department
The Prevalence of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Asthma Patients without Reflux Symptoms SUSAN M. HARDING, MELANY R. GUZZO, and JOEL E. RICHTER Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care Medicine, Department
Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia
 Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Objectives Understand the means of diagnosing functional heartburn
Functional Heartburn and Dyspepsia Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina Objectives Understand the means of diagnosing functional heartburn
Four-Day Bravo ph Capsule Monitoring With and Without Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:1083 1088 Four-Day Bravo ph Capsule Monitoring With and Without Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy IKUO HIRANO, QING ZHANG, JOHN E. PANDOLFINO, and PETER J. KAHRILAS
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2005;3:1083 1088 Four-Day Bravo ph Capsule Monitoring With and Without Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy IKUO HIRANO, QING ZHANG, JOHN E. PANDOLFINO, and PETER J. KAHRILAS
Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University
 Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University Asthma-related Comorbidities Comorbid conditions of the upper airways Rhinitis and Sinusitis
Somkiat Wongtim Professor of Medicine Division of Respiratory Disease and Critical Care Chulalongkorn University Asthma-related Comorbidities Comorbid conditions of the upper airways Rhinitis and Sinusitis
The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. The Validity and Reliability of the Reflux Finding Score (RFS)
https://www.uptodate.com/contents/acid-reflux-gastroesophageal-reflux-disease-in-adults-...
 Page 1 of 10 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Page 1 of 10 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate The content on the UpToDate website is not intended nor recommended as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
GUIDELINES FOR CLINICIANS. Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults. Reflux Disease. 4th Edition Digestive Health Foundation
 GUIDELINES FOR CLINICIANS Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults Reflux Disease 4th Edition 2008 Digestive Health Foundation Digestive Health Foundation Table of contents Page 4 Gastro-oesophageal
GUIDELINES FOR CLINICIANS Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux Disease in Adults Reflux Disease 4th Edition 2008 Digestive Health Foundation Digestive Health Foundation Table of contents Page 4 Gastro-oesophageal
Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus. Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery
 Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery Objectives Identify the use of different diagnostic modalities for hiatal hernias List the different types of hiatal hernias
Hiatal Hernias and Barrett s esophagus Dr Sajida Ahad Mercy General Surgery Objectives Identify the use of different diagnostic modalities for hiatal hernias List the different types of hiatal hernias
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association.
 Esophageal ph Monitoring Page 1 of 13 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Title: Esophageal ph Monitoring Professional Institutional Original Effective Date:
Esophageal ph Monitoring Page 1 of 13 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Title: Esophageal ph Monitoring Professional Institutional Original Effective Date:
Outline. Outline. Definition. Asthma, GERD and Laryngeal Pharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Definitions
 Asthma, GERD and Laryngeal Pharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Richard F. Lockey, M.D. Division of Allergy and Immunology Department of Internal Medicine University of South Florida College of Medicine and James A.
Asthma, GERD and Laryngeal Pharyngeal Reflux (LPR) Richard F. Lockey, M.D. Division of Allergy and Immunology Department of Internal Medicine University of South Florida College of Medicine and James A.
Esophageal Disorders. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T.
 Esophageal Disorders Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T. Massey, MD, FACP Learning Objectives AFTER COMPLETING THIS CHAPTER, THE LEARNER SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Recognize the typical and atypical presentations
Esophageal Disorders Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T. Massey, MD, FACP Learning Objectives AFTER COMPLETING THIS CHAPTER, THE LEARNER SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Recognize the typical and atypical presentations
Disclosures. Proton Pump Inhibitors Deprescribing? Deprescribing PPI Objectives. Deprescribing. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPI) 5/28/2018.
 Proton Pump Inhibitors Deprescribing? None Disclosures Chad Burski, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine UAB Gastroenterology Deprescribing PPI Objectives AR Why? Who? How? The mechanism of action of Proton
Proton Pump Inhibitors Deprescribing? None Disclosures Chad Burski, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine UAB Gastroenterology Deprescribing PPI Objectives AR Why? Who? How? The mechanism of action of Proton
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus
 Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons:
 Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons: http://dspace.flinders.edu.au/dspace/ This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: Fox M, Omari T, Rommel N. Supraesophageal Reflux Disease: Solving
Archived at the Flinders Academic Commons: http://dspace.flinders.edu.au/dspace/ This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: Fox M, Omari T, Rommel N. Supraesophageal Reflux Disease: Solving
In the Name of God. Refractory GERD
 In the Name of God Refractory GERD S Nasseri-Moghaddam MD, MPH, AGAF Associate Professor of Medicine Digestive Disease Research Institute Shariati Hospital, TUMS sianasseri@yahoo.com IAGH meeting, Ordibehesht
In the Name of God Refractory GERD S Nasseri-Moghaddam MD, MPH, AGAF Associate Professor of Medicine Digestive Disease Research Institute Shariati Hospital, TUMS sianasseri@yahoo.com IAGH meeting, Ordibehesht
Policy #: 138 Latest Review Date: November 2016
 Name of Policy: Ambulatory Esophageal ph Monitoring Policy #: 138 Latest Review Date: November 2016 Category: Medical Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under
Name of Policy: Ambulatory Esophageal ph Monitoring Policy #: 138 Latest Review Date: November 2016 Category: Medical Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, barium esophagography for, 57 58 Acid pocket, 18 19 Acid-sensing ion, 20 Acupuncture, 128 Adiponectin, in obesity, 166 ADX10059 metabotropic
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achalasia, barium esophagography for, 57 58 Acid pocket, 18 19 Acid-sensing ion, 20 Acupuncture, 128 Adiponectin, in obesity, 166 ADX10059 metabotropic
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD. Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd
 ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
ESOPHAGEAL CANCER AND GERD Prof Salman Guraya FRCS, Masters MedEd Learning objectives Esophagus anatomy and physiology Esophageal cancer Causes, presentations of esophageal cancer Diagnosis and management
Dysphagia. Conflicts of Interest
 Dysphagia Bob Kizer MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Creighton University School of Medicine August 25, 2018 Conflicts of Interest None 1 Which patient does not need an EGD as the first test? 1. 50 year
Dysphagia Bob Kizer MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Creighton University School of Medicine August 25, 2018 Conflicts of Interest None 1 Which patient does not need an EGD as the first test? 1. 50 year
Oesophageal Disorders
 Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Medical Policy Manual. Topic: Gastric Reflux Surgery Date of Origin: November Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: March 2014
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Gastric Reflux Surgery Date of Origin: November 2012 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: March 2014 Policy No: 186 Effective Date: May 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Gastric Reflux Surgery Date of Origin: November 2012 Section: Surgery Last Reviewed Date: March 2014 Policy No: 186 Effective Date: May 1, 2014 IMPORTANT REMINDER Medical Policies
Nexium 24HR Pharmacy Training
 Nexium 24HR Pharmacy Training Your pharmacist's advice is required. Always read the label. Use only as directed. If symptoms persist, consult your doctor/ healthcare professional. Pfizer Consumer Healthcare
Nexium 24HR Pharmacy Training Your pharmacist's advice is required. Always read the label. Use only as directed. If symptoms persist, consult your doctor/ healthcare professional. Pfizer Consumer Healthcare
9/18/2015. Disclosures. Objectives. Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C. I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest
 Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C Disclosures I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest Objectives Define what dysphagia is Define types of dysphagia Define studies
Dysphagia Sherri Ekobena PA-C Disclosures I have no relevant financial interests to disclose I have no conflicts of interest Objectives Define what dysphagia is Define types of dysphagia Define studies
Definition: gas tro e soph a ge al re f lux dis ease (GERD) from Stedman's Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing
 Topic Page: Gastroesophageal reflux Definition: gas tro e soph a ge al re f lux dis ease (GERD) from Stedman's Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing (gas trō-ĕ-sof ă-jē ăl rē flŭks
Topic Page: Gastroesophageal reflux Definition: gas tro e soph a ge al re f lux dis ease (GERD) from Stedman's Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing (gas trō-ĕ-sof ă-jē ăl rē flŭks
Reflux of gastric contents, particularly acid, into the esophagus
 Heartburn Reflux of gastric contents, particularly acid, into the esophagus Patient assessment with GERD 1-signs and symptoms The hallmark of typical symptom of GERD is heartburn (restrosternal),acid regurgitation,
Heartburn Reflux of gastric contents, particularly acid, into the esophagus Patient assessment with GERD 1-signs and symptoms The hallmark of typical symptom of GERD is heartburn (restrosternal),acid regurgitation,
ACID REFLUX & GERD: The Unsettling Reality in Canada
 ACID REFLUX & GERD: The Unsettling Reality in Canada gerd fact 1 see page 8 Canadian Society of Intestinal Research On average, ARD patients wait over two years before seeking care 1. 1 gerd fact 2 see
ACID REFLUX & GERD: The Unsettling Reality in Canada gerd fact 1 see page 8 Canadian Society of Intestinal Research On average, ARD patients wait over two years before seeking care 1. 1 gerd fact 2 see
Refractory GERD. Kenneth R. DeVault, MD, FACG President American College of Gastroenterology Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida
 Refractory GERD Kenneth R. DeVault, MD, FACG President American College of Gastroenterology Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida Objectives Define the terminology associated with refractory
Refractory GERD Kenneth R. DeVault, MD, FACG President American College of Gastroenterology Chair Department of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida Objectives Define the terminology associated with refractory
LINX. A new, FDA approved treatment for GERD
 LINX A new, FDA approved treatment for GERD What Causes Reflux? Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), also called reflux, is a chronic, often progressive disease caused by a weak lower esophageal sphincter
LINX A new, FDA approved treatment for GERD What Causes Reflux? Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), also called reflux, is a chronic, often progressive disease caused by a weak lower esophageal sphincter
The role of 24 h ph-recording in pediatric otolaryngologic gastro-esophageal reflux disease
 International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology (2003) 67S1, S95 S100 The role of 24 h ph-recording in pediatric otolaryngologic gastro-esophageal reflux disease Thierry van Den Abbeele a, *, Vincent
International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology (2003) 67S1, S95 S100 The role of 24 h ph-recording in pediatric otolaryngologic gastro-esophageal reflux disease Thierry van Den Abbeele a, *, Vincent
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association.
 Esophageal ph Monitoring Page 1 of 13 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Title: Esophageal ph Monitoring Professional Institutional Original Effective Date:
Esophageal ph Monitoring Page 1 of 13 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Title: Esophageal ph Monitoring Professional Institutional Original Effective Date:
Effective Health Care
 Effective Health Care Comparative Effectiveness of Management Strategies for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Executive Summary Background Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), defined as weekly heartburn
Effective Health Care Comparative Effectiveness of Management Strategies for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Executive Summary Background Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), defined as weekly heartburn
Increased Prevalence of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
 Increased Prevalence of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis RICHARD W. TOBIN, CHARLES E. POPE II, CARLOS A. PELLEGRINI, MARY J. EMOND, JIM SILLERY, and GANESH RAGHU Department
Increased Prevalence of Gastroesophageal Reflux in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis RICHARD W. TOBIN, CHARLES E. POPE II, CARLOS A. PELLEGRINI, MARY J. EMOND, JIM SILLERY, and GANESH RAGHU Department
TBURN TBURN BURN ARTBURN EARTBURN EART HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST
 TBURN BURN TBURN ARTBURN. EARTBURN EART N EARTBURN HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST Do you sometimes wake up at night with a sharp, burning sensation in your chest? Does this sometimes happen during
TBURN BURN TBURN ARTBURN. EARTBURN EART N EARTBURN HEARTBURN: HOW TO GET IT OFF YOUR CHEST Do you sometimes wake up at night with a sharp, burning sensation in your chest? Does this sometimes happen during
EXTRAESOPHAGEAL MANIFESTATIONS OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR ORAL CAVITY
 EXTRAESOPHAGEAL MANIFESTATIONS OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR ORAL CAVITY Crînguţa Paraschiv*, Cristina Gavrilescu, Irina Cotea, Manea Paloma, Rodica Ghiuru Gr. T. Popa" U.M.Ph.
EXTRAESOPHAGEAL MANIFESTATIONS OF GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE WITH IMPLICATIONS FOR ORAL CAVITY Crînguţa Paraschiv*, Cristina Gavrilescu, Irina Cotea, Manea Paloma, Rodica Ghiuru Gr. T. Popa" U.M.Ph.
GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX
 DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (404) 270-7479 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DEFINITION: *MONTREAL CONSENSUS DEFINED GERD AS A CONDITION WHICH
DR. PHILIP K. BLUSTEIN M.D. F.R.C.P.(C) 415 14 TH ST. NW. CALGARY AB T2N2A1 PHONE (403) 270-9555 FAX (404) 270-7479 GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DEFINITION: *MONTREAL CONSENSUS DEFINED GERD AS A CONDITION WHICH
Motility - Difficult Issues in Practice and How to Investigate
 Motility - Difficult Issues in Practice and How to Investigate Geoff Hebbard The Issues (Upper GI) Difficult Dysphagia Non-Cardiac Chest pain Reflux Symptoms Regurgitation Belching 1 The Tools Oesophageal
Motility - Difficult Issues in Practice and How to Investigate Geoff Hebbard The Issues (Upper GI) Difficult Dysphagia Non-Cardiac Chest pain Reflux Symptoms Regurgitation Belching 1 The Tools Oesophageal
GERD solo patologia gastro-esofagea?
 GERD solo patologia gastro-esofagea? Prof. Giancarlo D Ambrosio UNIVERSITÀ DI ROMA LA SAPIENZA Resp. UO Chirurgia Generale ad Indirizzo Colo-Rettale Az. Policlinico Umberto I, Roma Gastroesophageal reflux
GERD solo patologia gastro-esofagea? Prof. Giancarlo D Ambrosio UNIVERSITÀ DI ROMA LA SAPIENZA Resp. UO Chirurgia Generale ad Indirizzo Colo-Rettale Az. Policlinico Umberto I, Roma Gastroesophageal reflux
The prevalence of upper respiratory symptoms in a cohort of adults presenting with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
 The prevalence of upper respiratory symptoms in a cohort of adults presenting with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease D L Amarasiri 1, A Pathmeswaran 2, A S Dassanayake 3, A P de Silva 4, M
The prevalence of upper respiratory symptoms in a cohort of adults presenting with symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease D L Amarasiri 1, A Pathmeswaran 2, A S Dassanayake 3, A P de Silva 4, M
Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation. Introduction. Predisposing factor. Introduction.
 Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) JUSTIN CHE-YUEN WU, et. al. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Gastroenterology,
Obesity Is Associated With Increased Transient Lower Esophageal Sphincter Relaxation Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) JUSTIN CHE-YUEN WU, et. al. The Chinese University of Hong Kong Gastroenterology,
Disclosures. Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus. Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus. GERD is common in the U.S. None
 Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus None Disclosures Christian Mathy, MD University of California, San Francisco 2015 Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus Heartburn and GERD GERD therapy Extraesophageal GERD
Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus None Disclosures Christian Mathy, MD University of California, San Francisco 2015 Heartburn and Barrett s Esophagus Heartburn and GERD GERD therapy Extraesophageal GERD
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540
 Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
Nonerosive reflux disease as a presentation of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease
 Nonerosive reflux disease as a presentation of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Abstract Simmonds WM, MMed (Internal Medicine) Gastroenterology Fellow, Department of Internal Medicine, Free State University
Nonerosive reflux disease as a presentation of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Abstract Simmonds WM, MMed (Internal Medicine) Gastroenterology Fellow, Department of Internal Medicine, Free State University
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease:
 Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Introduction Gastroesophageal reflux is the involuntary movement of gastric contents to the esophagus. It is a common disease, occurring in one third of the population
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Introduction Gastroesophageal reflux is the involuntary movement of gastric contents to the esophagus. It is a common disease, occurring in one third of the population
Review article: gastric acidity ) comparison of esomeprazole with other proton pump inhibitors
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17 (Suppl. 1): 10 15. Review article: gastric acidity ) comparison of esomeprazole with other proton pump inhibitors J. G. HATLEBAKK Department of Medicine, Haukeland Sykehus,
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17 (Suppl. 1): 10 15. Review article: gastric acidity ) comparison of esomeprazole with other proton pump inhibitors J. G. HATLEBAKK Department of Medicine, Haukeland Sykehus,
The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation
 The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation James P. Dworkin, Ph.D. Jayme Dowdall, M.D. Adam Folbe, M.D. Tom Willis, M.S. Richard Culatta, Ph.D. Wayne
The role of the modified barium swallow study & esophagram in patients with GERD/Globus sensation James P. Dworkin, Ph.D. Jayme Dowdall, M.D. Adam Folbe, M.D. Tom Willis, M.S. Richard Culatta, Ph.D. Wayne
Esophageal ph Monitoring
 Esophageal ph Monitoring Policy Number: 2.01.20 Last Review: 11/2017 Origination: 11/2003 Next Review: 11/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for esophageal
Esophageal ph Monitoring Policy Number: 2.01.20 Last Review: 11/2017 Origination: 11/2003 Next Review: 11/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will provide coverage for esophageal
Symptoms such as heartburn, pyrosis, and acid regurgitation
 CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS 99m Tc-Sulfur Colloid Gastroesophageal Scintigraphy with Late Lung Imaging to Evaluate Patients with Posterior Laryngitis Alberto Bestetti, Federica Carola, PierMarziano Carnevali-Ricci,
CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS 99m Tc-Sulfur Colloid Gastroesophageal Scintigraphy with Late Lung Imaging to Evaluate Patients with Posterior Laryngitis Alberto Bestetti, Federica Carola, PierMarziano Carnevali-Ricci,
THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia. Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone. Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital
 THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital Objectives Definitions Common causes Investigations Treatment options Anatomy
THORACIC SURGERY: Dysphagia Dr. Robert Zeldin Dr. John Dickie Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgery Toronto East General Hospital Objectives Definitions Common causes Investigations Treatment options Anatomy
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association.
 Esophageal ph Monitoring Page 1 of 17 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Title: Esophageal ph Monitoring Professional Institutional Original Effective Date:
Esophageal ph Monitoring Page 1 of 17 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association. Title: Esophageal ph Monitoring Professional Institutional Original Effective Date:
Related Policies None
 Medical Policy MP 2.01.20 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.20 Last Review: 11/30/2017 Effective Date: 11/30/2017 Section: Medicine Related Policies None DISCLAIMER Our medical policies are designed for informational
Medical Policy MP 2.01.20 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.20 Last Review: 11/30/2017 Effective Date: 11/30/2017 Section: Medicine Related Policies None DISCLAIMER Our medical policies are designed for informational
The STRETTA Procedure
 THE HEARTBURN AND REFLUX STUDY CENTER The STRETTA Procedure Introduction The STRETTA procedure is an advanced state-of-the-art endoscopic technique for the correction of all forms of reflux disease including:
THE HEARTBURN AND REFLUX STUDY CENTER The STRETTA Procedure Introduction The STRETTA procedure is an advanced state-of-the-art endoscopic technique for the correction of all forms of reflux disease including:
THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE AND EPITHELIUM
 THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE AND EPITHELIUM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of connective tissue and epithelium. The lab will introduce you to the four basic tissue types: epithelium, connective
THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE AND EPITHELIUM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of connective tissue and epithelium. The lab will introduce you to the four basic tissue types: epithelium, connective
There are many different symptoms of GER. Your child may only have a few of these symptoms. The most common symptoms include:
 This document is a short Overview of Pediatric Acid Reflux and GERD from www.reflux.org web site. Dozens of other documents about Pediatric GERD can be found in the Reading Room section of this web site.
This document is a short Overview of Pediatric Acid Reflux and GERD from www.reflux.org web site. Dozens of other documents about Pediatric GERD can be found in the Reading Room section of this web site.
INFECTIOUS AND INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS
 Chapter 52 INFECTIOUS AND INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS Allen M. Seiden Infection or inflammation of the esophagus typically produces dysphagia and odynophagia, so these patients may frequently present to the
Chapter 52 INFECTIOUS AND INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS Allen M. Seiden Infection or inflammation of the esophagus typically produces dysphagia and odynophagia, so these patients may frequently present to the
Review article: pharmacology of esomeprazole and comparisons with omeprazole
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17 (Suppl. 1): 5 9. Review article: pharmacology of esomeprazole and comparisons with omeprazole J. DENT Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and General Medicine, Royal
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003; 17 (Suppl. 1): 5 9. Review article: pharmacology of esomeprazole and comparisons with omeprazole J. DENT Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and General Medicine, Royal
GERD. More Than Just Heartburn. written by Harvard Medical School
 GERD More Than Just Heartburn written by Harvard Medical School www.patientedu.org Doctors call it gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD. Millions of Americans call it heartburn. Many more also have
GERD More Than Just Heartburn written by Harvard Medical School www.patientedu.org Doctors call it gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD. Millions of Americans call it heartburn. Many more also have
James Paget University Hospitals. NHS Foundation Trust. Hiatus hernia. Patient Information
 James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Hiatus hernia Patient Information What is a hiatus hernia? A hiatus hernia can cause highly irritating stomach contents, such as acid, to move up into
James Paget University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Hiatus hernia Patient Information What is a hiatus hernia? A hiatus hernia can cause highly irritating stomach contents, such as acid, to move up into
Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease. Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 3, September 2011 Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)* Objective: To evaluate the efficacy
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 3, September 2011 Management of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Disease Abdul Aziz J Ashoor, Facharzt fuer Hals Nasen Ohren (H.N.O.)* Objective: To evaluate the efficacy
