The Relationship of Concha Bullosa with Nasal Septal Deviation and Paranasal Sinus Disease
|
|
|
- Joanna West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Advances in Health Sciences (IJHS) ISSN Vol2, Issue6, 2015, pp Research Article The Relationship of Concha Bullosa with Nasal Septal Deviation and Paranasal Sinus Disease 1 *Smrity Rupa Borah Dutta, 1 Sanchita Kalita and 2 Rohit Tigga 1 Department of ENT, 2 Department of Pharmacology, Silchar Medical College and Hospital, Corresponding Author Smritylana@gmail.com [Received-05/12/2015, Accepted-15/12/2015, Published- 31/12/2015] ABSTRACT Aims: (1) To find out the incidence of contralateral DNS in relation to concha bullosa. (2) To find out the incidence of PNS disease in relation to concha bullosa.(3)to determine whether there is any statistical correlation of concha bullosa with DNS and chronic sinusitis. Materials and Methods: A prospective study was carried out in the Department of ENT, Silchar Medical College and Hospital. Study group comprised of 286 patients, from age group of 5 to 65 yrs, with Computed tomography scan of PNS showing one or more of the following findings - concha bullosa, nasal septal deviation, chronic sinusitis. Exclusion criteria included acute Sinusitis, any other anatomical aberration of the nose, prior surgery of nose and/or PNS, faciomaxillary trauma, any growth in the nasal cavity or PNS, patients who could not afford CT scan of PNS. Chi square test and Correlation Coefficient was used to evaluate statistical relevance. Results: In our study, we found the incidence of contralateral DNS in relation to concha bullosa to be 69.41%, correlation coefficient +1 and p value <0.05. The incidence of ipsilateral PNS disease in relation to concha bullosa was 47.93%, correlation coefficient -1 and p value >0.05. Conclusion: A positive statistical correlation was found between concha bullosa and contralateral DNS. However the relationship of concha bullosa and ipsilateral PNS disease was not found to be statistically relevant. A review of available literature has shown studies that support our results, however few studies negate it. Further large scale studies are warranted for reaching a uniform conclusion. Key words: Concha bullosa, Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS), Paranasal Sinus (PNS) disease, Computed Tomography(CT) INTRODUCTION Concha bullosa(cb) is the pneumatisation of middle turbinate. It is one of the common anatomical variants of the lateral wall of nose. The interior of the CB is lined with ciliated respiratory epithelium and its ostium may drain into the frontal recess, lateral sinus or hiatus semilunaris. [8] CB can be classified into three groups [11] 1. Lamellar type: Pneumatisation is localized to the vertical lamella of the middle turbinate. 2. Bulbous type: Pneumatisation of the inferior bulbous part of the middle turbinate. 3. True or Extensive type: Pneumatisation of both the vertical lamella and the inferior part of the middle turbinate.
2 The presence of CB might be unilateral or bilateral; bilateral CB might be equal, right dominant or left dominant depending on the size. Again, based on the amount of aeration of vertical height of the middle turbinate, CB can be: -Small: upto 50% pneumatisation - Moderate: 51-75% - Large : >75% Occasionally, the presence of CB may lead to DNS and/or obstruct the opening of an adjacent PNS, possibly leading to recurrent sinusitis. A number of studies have been aimed to study the relationship of CB with nasal septal deviation and paranasal sinus disease. A Review of some available literature - Jamie et al. (2004) concluded that when a unilateral or dominant CB is present, there is no statistical relationship with any sinus diease (on either side). There is, however, a strong relationship between the presence of a unilateral or dominant CB and contralateral nasal septal deviation. [5] Y.K. Maru et al. (2000), concluded that that CB is is frequently associated with diseases of adjacent osteomeatal complex. However relationship between overall incidence of inflammatory disease in osteomeatal complex in the symptomatic patients included in the study were found to be statistically insignificant. [19] Stammberger et al. (1991) stated that after the formation of septum deviation, the air flow pattern of nasal cavity on the opposite side of the deviation, provoking the development of CB. [14] According to Uygur et al. (2003), CB incidence doesn t increase with nasal septal deviation. [17] Kyle D. Smith et al. (2010) found no definitive relationship between the presence of CB or nasal septal deviation and the development of maxillary sinusitis. [6] Ozdemir Sevine et al. (2013) found that the incidence of CB was higher in individuals with septal deviation. [9] The aim of our study is to evaluate this association as there have been varied observations from different studies. Aims and Objectives 1. To evaluate the CT scan of PNS of patients with clinical features suggestive of DNS and/or chronic sinusitis. 2. To identify CB, DNS, chronic sinusitis from the CT scan of PNS. 3. To find out the incidence of CB in relation to nasal septal deviation. 4. To find out the incidence of CB in relation to chronic sinusitis. 5. To determine whether there is any statistical correlation of CB with DNS and chronic sinusitis. MATERIALS AND METHODS Type of study: A prospective observational case series study. Place of study: Department of ENT, Silchar Medical College and Hospital. Study period: One year, from August 2014 to July 2015 Inclusion Criteria: All the patients who attended the OPD with clinical features suggestive of DNS and/or Chronic Sinusitis. Coronal sections of the CT Scan of PNS were reviewed. Any deviation of the nasal septum from the midline was considered as DNS in the study. Paranasal Sinus Disease was considered as any amount of mucosal thickening in the paranasal sinus. Any type of pneumatisation of the middle turbinate (Concha Bullosa), Lamellar; Bulbous or Extensive, of any size, were included in the study. Exclusion Criteria: Patients below 13 years, Acute Sinusitis, any other anatomical variation or aberration of the Smrity Rupa Borah Dutta, et al. 763
3 nose, prior surgery of nose and/or PNS, faciomaxillary trauma, any growth in the nasal cavity or PNS, pregnant women. Study group: Comprised of 286 patients, ranging from age group of 13 to 65 years, with CT scan of PNS report showing one or more of the following findings - concha bullosa, nasal septal deviation, chronic sinusitis. Statistics: All data were evaluated in Microsoft Excel The results were analyzed by applying Chi-Square test and Pearson's Correlation Coefficient using Graph Pad and Social Science Statistics software. P value less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. RESULTS Of the 447 patients who were advised CT scan of PNS, 286 patients, with CT scan of PNS report who met the inclusion criteria, comprised the study group. 121 out of 286 CT scan of PNS showed presence of CB. Of the 121, 58 showed unilateral CB, 63 showed bilateral CB; of the 63, 27 showed one sided dominance. 182 CT scan of PNS of patients showed presence of DNS and 168 showed presence of PNS disease. Small=28(23%), Moderate=50(41%) and Large=44(36%). (Fig 4). The incidence of contralateral DNS and ipsilateral PNS disease was observed to be highest in bulbous type of CB(64.44%), followed by extensive type(60%), then lamellar type(33.43%); P>0.05. (Table VI). Likewise, the incidence of ipsilateral PNS disease was the highest in bulbous type of CB (68.89%), followed by extensive type(33.33%), then lamellar type(30.07%); P>0.05.(Table VII). In the study group, the incidence of CB was more in females (68%), P< 0.05.( Fig 1) % of the patients with CB was in the age group of 26 to 35 yrs, followed by 16 to 25 yrs (27.27%), then 36 to 45 yrs(17.35%), then 46 to 55 yrs(9.09%), then 5 to 15 yrs(7.44%), then 56 to 65 yrs(4.96%); P > 0.5. (Table I)(Fig 2). Incidence of DNS in the study group was 67.77% and PNS disease was 63.64%. In the study group, Unilateral or Dominant CB was present in 85 cases and absent in 201 cases, which included absence of CB and bilateral equal CB. Incidence of DNS in cases having Unilateral and Dominant CB is 69.41%, incidence of DNS in cases without CB is 61.19%, incidence of absence of DNS in cases with CB is 37.64%, incidence of DNS absence in cases without concha bullosa is 5.97%; In the study group of 286 cases, there were 160 (56%) females and 126 (44%) males. Distribution of CB found in the study were- Lamellar type=61(50%), Bulbous type=45(37%), Extensive type=15(13%). (Fig 3). Incidences of different sizes of CB were; P<0.05 and Correlation coefficient was found out to be +1, which implies that the relationship of contralateral DNS in cases with Unilateral or Dominant CB is statistically relevant. The incidence of this relation was higher in females (62.71%); P<0.05(Table II). From our study, it Smrity Rupa Borah Dutta, et al. 764
4 was evident that the incidence of DNS in the presence of Unilateral or Dominant CB was more in the contralateral side; P< In relation to left unilateral/dominant CB, right contralateral DNS was 63.88% in comparison to left ipsilateral DNS (13.89%). Likewise in relation to right unilateral/dominant CB, left contralateral DNS was 67.34% in comparison to right ipsilateral DNS(16.32%). (Table III) Incidence of PNS disease from our study was 58.74%. Incidence of adjacent PNS disease in cases with CB is 47.93%, and without CB is 60.00%, incidence of absence of ipsilateral PNS disease with CB is 51.23% and without CB is 45.45%. P>0.05 and Correlation coefficient was found out to be -1, which implied that the relationship of PNS disease in presence of ipsilateral concha is statistically irrelevant. From the study, we also found a slight higher incidence of this relationship in females (53.45%); P>0.05(Table IV). It is observed that there is increased incidence of ipsilateral PNS disease in unilateral/dominant CB(23.53%) in comparison to contralateral PNS disease(4.70%). In bilateral equal CB however, there was found to be increased incidence of bilateral PNS disease(58.33%) in comparison to unilateral PNS disease(11.11%); P< (Table V). DISCUSSION In our study, the incidence of CB is found to be 42.3%. There is, however, a wide reported incidence (14-66%) of CB as assessed by CT scan of PNS findings in available literatures.[2] This wide range is attributed to the difference in defining CB. Some authors have considered only aeration of the bulbous part of middle turbinate, some have also included the upper non-bulbous part of middle turbinate, while there are studies which considered aeration of at least 50% of vertical height of middle turbinate for defining CB. [1] In our study, the presence of CB was significantly more in females (67.77%), which is slightly higher than Kyle D Smith et al s 58.9%. [2] Most of the patients with CB were scattered in the age group of 26 to 35 years (61.16%). The incidence of DNS from our study was 63.64%, which meets Stallman s 65% and Sazgar s 62.9% prevalences. [6] [12] The incidence of PNS disease from our study is 58.74%, in comparison to Bolger s study (83.2%). [18] The incidence of contralateral DNS in presence of CB is 69.41%, and it was found out to be statistically relevant as supported by Jamie et al, Stammberger et al, Ozdemir Sevine et al. [1] [17] [12] [7] However Uygur et al, Kyle D. Smith et al found no positive statistical relationship. [3] [8] In our study, this relationship between CB and DNS showed a statistically significant female preponderance (62.71%). (Table II) Moreover contralateral DNS and ipsilateral PNS disease was predominant in bulbous type of CB (64.44%,68,89%), and in large sized CB(86%,72%), but both showed no statistical significance.(table VI&VII) The incidence of ipsilateral paranasal sinus disease in presence of CB was 54.89%, seen slightly higher in females(53.45%), but the relation was not found to be statistically relevant. (Table IV). This negative statistical relationship is supported by Jamie et al and Kyle D. Smith et al. [2] [12] A positive correlation was however found in Y.K Maru et al s study. [15] CONCLUSION There exists a statistically positive relationship between unilateral or dominant CB and contralateral DNS, indicating that the presence of CB increases the possibility of the development of contralateral DNS or vice versa. However ipsilateral PNS disease in relation to concha bullosa has shown statistically insignificant results. There were certain limitations during our study such that many patients belonged to the lower socioeconomic strata and could not afford the CT scan of the PNS; some patients being lost to follow up and hence could not be advised the CT scan of PNS despite having significant clinical features. This limited the sample size of our study. Moreover, our statistical inference is attributable only to the symptomatic population who presented in our institution. No final Smrity Rupa Borah Dutta, et al. 765
5 conclusion about the general population can be made from our study results. Although there are literatures which support our findings, there are certain studies which negate our study results. Such non-uniformity of results warrants further studies in this respect, probably with a larger study group and with definitive criteria of selection of the study group. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT We acknowledge the support of the Department of Radiodiagnostics, Silchar Medical College and Hospital for timely assistance in conduction and evaluation of the CT scan of PNS of the patients. Age (yrs) Female Male Total /121 (7.44%) /121 (27.27%) /121 (33.88%) /121 (17.35%) /121 (9.09%) /121 (4.96%) 82/121 (67.77%) 39/121 (32.23%) 121 Table I: Age and Sex Distribution of patients with Concha Bullosa No DNS DNS Females Males U/L or Dominant Concha bullosa absent 12/201 (5.97%) 72/123(58.54%) 51/123(41.46%) 123/201(61.19%) Females Males U/L or Dominant Concha bullosa present 37/59(62.71%) 22/59(37.29%) 32/85 (37.64%) 59/85 (69.41%) Table II: Relationship of Contralateral DNS with Unilateral or Dominant Concha bullosa and the sex distribution No septal Rightward septal Leftward septal deviation deviation deviation No concha or equal bilateral concha bullosa 81/201 (40.29%) 62/201 (30.84%) 47/201(23.38%) Right unilateral or dominant concha bullosa 10/49 (20.40%) 8/49 (16.32%) 33/49 (67.34%) Left unilateral or dominant dominant concha bullosa 8/36 (22.22%) 23/36 (63.88%) 5/36 (13.89%) Table III: Incidence of nasal septal deviation broken down by convexity compared to the presence and location of unilateral concha bullosa or bilateral dominant concha bullosa No ipsilateral PNS disease Ipsilateral PNS disease No PNS disease Contralateral PNS disease Female Male No concha bullosa 75/165 (45.45%) Concha bullosa 51/121 (42.15%) 11/121 (9.09%) 54/99(54.54%) 45/99(45.45%) Female 99/165 (60.00%) Male 31/58(53.45%) 28/58(48.28%) 62/121(51.24%) 58/121 (47.93%) Table IV: Relationship of ipsilateral Paranasal Sinus Disease with concha bullosa and the sex distribution Smrity Rupa Borah Dutta, et al. 766
6 Unilateral PNS disease Bilateral PNS Ipsilateral Contralateral disease Concha bullosa Unilateral and Bilateral 20/85 (23.53%) 4/85 (4.70%) 5/85 (5.88%) Dominant Bilateral equal 4/36 (11.11%) 21/36 (58.33%) No concha bullosa 99/165 (60%) 16/165 (9.69%) Table V: Incidence of unilateral and bilateral PNS disease in unilateral/dominant concha bullosa, bilateral equal concha bullosa and no concha bullosa Contralateral DNS Ipsilateral PNS disease Lamellar Concha(61) 21 (34.43%) 22 (30.07%) Bulbous Concha(45) 29 (64.44%) 31 (68.89%) Extensive Concha(15) 9 (60%) 5 (33.33%) Table VI: Incidence of contralateral DNS and ipsilateral PNS disease in different types of conchae Contralateral DNS Ipsilateral PNS disease Small 6 (23%) 18 (11%) Moderate 35 (71%) 97 (58%) Large 37 (86%) 121 (72%) Table VII: Incidences of contralateral DNS and ipsilateral PNS disease in different sizes of conchae Figure 1: Pie chart showing sex distribution of Concha bullosa in the study group Figure 2: Bar diagram showing age distribution of concha bullosa Smrity Rupa Borah Dutta, et al. 767
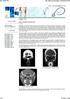
7 Figure 3: Bar diagram showing incidences of different types of CB Figure 4: Showing incidences of different sizes of CB Figure 5: A coronal section of CT scan of PNS showing right unilateral concha, with left sided DNS, and right sided maxillary and ethmoidal sinusitis. Smrity Rupa Borah Dutta, et al. 768
8 Figure 6: Coronal section of CT scan of PNS showing a right dominant concha with mucosal thickening in the right maxillary sinus. Figure 7: Coronal section of CT scan of PNS showing bilateral equal conchae, with no DNS or paranasal sinus disease. ABBREVIATIONS: DNS- Deviated Nasal Septum PNS- Paranasal Sinus CT- Computed Tomography CB- Concha Bullosa BIBLIOGRAPHY 1. A. A. Sazgar, J. Massah, M. Sadeghi, A. Bagheri, and F. Rasool The incidence of concha bullosa and the correlation with nasal septal deviation. B- ENT, vol. 4, no. 2, pp Al-Qudah, M The relationship between anatomical variations of the sinonasal region and chronic sinusitis extension in children. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology. 72(6): H. G. Hatipoglu, M. A. Cetin, and E. Yuksel Nasal septal deviation and concha bullosa coexistence: CT evaluation. BENT, vol. 4, no. 4, pp J. S. Lee, J. Ko, H. D. Kang, and H. S. Lee Massive concha bullosa with secondary maxillary sinusitis. Clinical and Experimental Otorhinolaryngology, vol. 1, no. 4, pp J. S. Stallman, J. N. Lobo, and P. M. Som The incidence of concha bullosa and its relationship to nasal septal deviation and paranasal sinus disease. American Smrity Rupa Borah Dutta, et al. 769
9 Journal of Neuroradiology, vol. 25, no. 9, pp Kyle D. Smith,Paul C. Edwards,Tarnjit S. Saini, and Neil S. Norton The Prevalence of Concha Bullosa and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship to Maxillary Sinusitis by Volumetric Tomography. International Journal of Dentistry Volume Article ID , 5 pages doi: /2010/ Paksoy M, Sanlı A., Evren, C., Kayhan, F. T.; Bozkurt, Z.; Aydin, S., Hardal The role of concha bullosa in nasal pathologies. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis. Derg., 18: S. A. R. Nouraei, A. R. Elisay, A. DiMarco et al Variations in paranasal sinus anatomy: implications for the pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis and safety of endoscopic sinus surgery. Journal of Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery. vol. 38, no. 1. pp Sevinc Ozdemir; Barut C.; Kacar, D. & IS, M Evaluation of the lateral wall of the nasal cavity in relation to septal deviation. Int. J. Morphol. 31(2): S. J. Zinreich, D. E. Mattox, D. W. Kennedy, H. L. Chisholm, D. M. Diffley, and A. E. Rosenbaum Concha bullosa: CT evaluation. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography, vol. 12, no. 5, pp Smith, K. D., Edwards, P. C., Saini, T. S. & Norton, N. S The Prevalence of Concha Bullosa and Nasal Septal deviation and Their Relationship to Maxillary Sinusitis by Volumetric Tomography. International Journal of Dentistry pii: S. Collet, B. Bertrand, S. Cornu, P. Eloy, and P. Rombaux Is septal deviation a risk factor for chronic sinusitis? Review of literature. Acta Oto-Rhino- Laryngologica Belgica, vol. 55, no. 4, pp S. Subramanian, G. R. L. Rampal, E. F. M. Wong, S. Mastura, and A. Razi Concha bullosa in chronic sinusitis. Medical Journal of Malaysia. vol. 60, no. 5, pp Stammberger, H 'Endoscopic and Radiologic Diagnosis,' In: Stammberger H, editor. Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: The Messerklinger Technique. 1 st ed. Philadelphia: BC Decker; p Unlu, H. H., Akyar, S., Caylan, R. & Nalca, Y Concha Bullosa. The Journal of Otolaryngology 23 (1) Ural, A., Kanmaz, A., Inançli, H. M. & Imamoglu, M Association of Inferior Turbinate Enlargement, Concha Bullosa and Nasal Valve Collapse with the Convexity of Septal Deviation. Acta Otolaryngologica. 130 (2) Uygur, K., Tuz, M. & Dogru, H The Correlation between Septal Deviation and Concha Bullosa. Otolaryngology-- Head and Neck Surgery 129 (1) W. E. Bolger, C. A. Butzin, and D. S. Parsons Paranasal sinus bony anatomic variations and mucosal abnormalities: CT analysis for endoscopic sinus surgery. Laryngoscope, vol. 101, no. 1 I, pp Y.K. Maru, Yamini Gupta Concha Bullosa Frequency and Appearances on Sinonasal CT Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery. Vol 52, No.1. Smrity Rupa Borah Dutta, et al. 770
Review Article The Prevalence of Concha Bullosa and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship to Maxillary Sinusitis by Volumetric Tomography
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 404982, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/404982 Review Article The Prevalence of and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 404982, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/404982 Review Article The Prevalence of and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship
Review Article The Prevalence of Concha Bullosa and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship to Maxillary Sinusitis by Volumetric Tomography
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 404982, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/404982 Review Article The Prevalence of and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 2010, Article ID 404982, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/404982 Review Article The Prevalence of and Nasal Septal Deviation and Their Relationship
ORIGINAL ARTICLE RELATIONSHIP OF CONCHA BULLOSA WITH OSTEOMEATAL UNIT BLOCKAGE. TOMOGRAPHIC STUDY IN 200 PATIENTS.
 RELATIONSHIP OF CONCHA BULLOSA WITH OSTEOMEATAL UNIT BLOCKAGE. TOMOGRAPHIC STUDY IN 200 PATIENTS. Shrikrishna B H 1, Jyothi A C 2, Sanjay G 3, Sandeep Samson G 4. 1. Associate Professor, Department of
RELATIONSHIP OF CONCHA BULLOSA WITH OSTEOMEATAL UNIT BLOCKAGE. TOMOGRAPHIC STUDY IN 200 PATIENTS. Shrikrishna B H 1, Jyothi A C 2, Sanjay G 3, Sandeep Samson G 4. 1. Associate Professor, Department of
The Incidence of Concha Bullosa and Its Association with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Deviated Nasal Septum and Osteomeatal Complex Obstruction
 1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 The Incidence of Concha Bullosa and Its Association with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Deviated Nasal Septum and Osteomeatal Complex Obstruction Fatma
1 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 33, No. 4, December 2011 The Incidence of Concha Bullosa and Its Association with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Deviated Nasal Septum and Osteomeatal Complex Obstruction Fatma
The frequency of nasal septal deviation and concha bullosa and their relationship with maxillary sinusitis based on CBCT finding
 Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 11:152-156 The frequency of nasal septal deviation and concha bullosa and their
Available online at www.ijmrhs.com ISSN No: 2319-5886 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 11:152-156 The frequency of nasal septal deviation and concha bullosa and their
An epidemiologic study of factors associated with nasal septum deviation by computed tomography scan: a cross sectional study
 Mohebbi et al. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders 2012, 12:15 RESEARCH ARTICLE An epidemiologic study of factors associated with nasal septum deviation by computed tomography scan: a cross sectional study
Mohebbi et al. BMC Ear, Nose and Throat Disorders 2012, 12:15 RESEARCH ARTICLE An epidemiologic study of factors associated with nasal septum deviation by computed tomography scan: a cross sectional study
ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS
 From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan July 1, 2012 ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/51/
From the SelectedWorks of Balasubramanian Thiagarajan July 1, 2012 ROLE OF ANATOMICAL OBSTRUCTION IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CHRONIC SINUSITIS Balasubramanian Thiagarajan Available at: https://works.bepress.com/drtbalu/51/
Anatomical Variations of the Middle Turbinate Concha Bullosa and its Relationship with Chronic Sinusitis: A Prospective Radiologic Study
 THIEME Original Research 297 Anatomical Variations of the Middle Turbinate Concha Bullosa and its Relationship with Chronic Sinusitis: A Prospective Radiologic Study Raja Kalaiarasi 1 Venkataramanan Ramakrishnan
THIEME Original Research 297 Anatomical Variations of the Middle Turbinate Concha Bullosa and its Relationship with Chronic Sinusitis: A Prospective Radiologic Study Raja Kalaiarasi 1 Venkataramanan Ramakrishnan
Prevalence of Anatomical Variations of the Sinonasal Region and their Relationship with Chronic Rhinosinusitis
 Prevalence of Anatomical Variations of the Sinonasal Region and their Relationship with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Karki S, 1 Pokharel M, 2 Suwal S, 1 Poudel R 1 ABSTRACT Background 1 Department of Radiology
Prevalence of Anatomical Variations of the Sinonasal Region and their Relationship with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Karki S, 1 Pokharel M, 2 Suwal S, 1 Poudel R 1 ABSTRACT Background 1 Department of Radiology
International Journal of Biological & Medical Research
 Int J Biol Med Res.2015;6(1):4775-4781 Contents lists available at BioMedSciDirect Publications International Journal of Biological & Medical Research Journal homepage: www.biomedscidirect.com BioMedSciDirect
Int J Biol Med Res.2015;6(1):4775-4781 Contents lists available at BioMedSciDirect Publications International Journal of Biological & Medical Research Journal homepage: www.biomedscidirect.com BioMedSciDirect
Anatomical Variations in Osteomeatal Complex among Patients undergoing Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 V Narendrakumar, V Subramanian Original article 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1259 Anatomical Variations in Osteomeatal Complex among Patients undergoing Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery 1 V Narendrakumar,
V Narendrakumar, V Subramanian Original article 10.5005/jp-journals-10013-1259 Anatomical Variations in Osteomeatal Complex among Patients undergoing Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery 1 V Narendrakumar,
A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis.
 DOI: 10.2127/aimdr.201..2.EN1 Original Article ISSN (O):239-222; ISSN (P):239-21 A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Smruti Swain 1 1 Associate Professor, Department
DOI: 10.2127/aimdr.201..2.EN1 Original Article ISSN (O):239-222; ISSN (P):239-21 A Study of Anatomical Variations in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Smruti Swain 1 1 Associate Professor, Department
Spheno-Ethmoidectomy
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 1-8 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1998 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 5, pp. 1-8 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1998 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published
A radiological study of anatomical variations in ostiomeatal complex in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Rajneesh et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):528-533 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Rajneesh et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):528-533 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
The Relation between Anatomical Variations of Osteomeatal Complex & Nasal Structures and Chronic Sinusitis by Computed Tomography
 International Journal of Medical Imaging 2015; 3(2): 16-20 Published online March 6, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi) doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20150302.12 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN:
International Journal of Medical Imaging 2015; 3(2): 16-20 Published online March 6, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijmi) doi: 10.11648/j.ijmi.20150302.12 ISSN: 2330-8303 (Print); ISSN:
Correlation of anatomical variations of Paranasal sinuses and Chronic Rhinosinusitis
 Original Research Article Correlation of anatomical variations of Paranasal sinuses and Chronic Rhinosinusitis Neeraj Suri 1, Toshi Janardan 2, Hiren Parmar 3* 1 Associate Professor, ENT Department, GMERS
Original Research Article Correlation of anatomical variations of Paranasal sinuses and Chronic Rhinosinusitis Neeraj Suri 1, Toshi Janardan 2, Hiren Parmar 3* 1 Associate Professor, ENT Department, GMERS
Variation in frontal cells in relation to chronic frontal sinusitis
 International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 244-71 P-ISJN: A472-04, E -ISJN: A472-01 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume, Issue 1-2019 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2019.0.01.00
International Journal of Current Research in Medical Sciences ISSN: 244-71 P-ISJN: A472-04, E -ISJN: A472-01 www.ijcrims.com Original Research Article Volume, Issue 1-2019 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijcrms.2019.0.01.00
Computed tomographic evaluation of anatomical variations of paranasal sinus region
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gupta S et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Jul;4(7):2909-2913 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161975
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Gupta S et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Jul;4(7):2909-2913 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20161975
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ANATOMICAL VARIATIONS OF THE OSTEOMEATAL COMPLEX TOMOGRAPHIC FINDINGS IN 100 PATIENTS
 ANATOMICAL VARIATIONS OF THE OSTEOMEATAL COMPLEX TOMOGRAPHIC FINDINGS IN 100 PATIENTS Jyothi A. C 1, Shrikrishna B. H 2, Sanjay G 3, Sandeep Samson G 4. 1. Associate Professor, Department of ENT and head
ANATOMICAL VARIATIONS OF THE OSTEOMEATAL COMPLEX TOMOGRAPHIC FINDINGS IN 100 PATIENTS Jyothi A. C 1, Shrikrishna B. H 2, Sanjay G 3, Sandeep Samson G 4. 1. Associate Professor, Department of ENT and head
Boundaries Septum Turbinates & Meati Lamellae Drainage Pathways Variants
 The Fastest 20 Minutes in Michelle A. Michel, MD Professor of Radiology and Otolaryngology Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee Overview Nasal cavity Anterior skull base Ostiomeatal complex Frontal
The Fastest 20 Minutes in Michelle A. Michel, MD Professor of Radiology and Otolaryngology Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee Overview Nasal cavity Anterior skull base Ostiomeatal complex Frontal
Evaluation of the Lateral Wall of the Nasal Cavity in Relation to Septal Deviation
 Int. J. Morphol., 31(2):438-443, 2013. Evaluation of the Lateral Wall of the Nasal Cavity in Relation to Septal Deviation Evaluación de la Pared Lateral de la Cavidad Nasal en Relación con la Desviación
Int. J. Morphol., 31(2):438-443, 2013. Evaluation of the Lateral Wall of the Nasal Cavity in Relation to Septal Deviation Evaluación de la Pared Lateral de la Cavidad Nasal en Relación con la Desviación
Unique Journal of Medical and Dental Sciences Available online: Research Article
 ISSN 2347-5579 Unique Journal of Medical and Dental Sciences Available online: www.ujconline.net Research Article STUDY OF ANATOMICAL VARIATIONS OF LATERAL WALL OF NOSE BY ENDOSCOPE Kolvekar VD 1*, Kazi
ISSN 2347-5579 Unique Journal of Medical and Dental Sciences Available online: www.ujconline.net Research Article STUDY OF ANATOMICAL VARIATIONS OF LATERAL WALL OF NOSE BY ENDOSCOPE Kolvekar VD 1*, Kazi
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 05 Page May 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i5.25 Radiologic Variations of Nose and Paranasal
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i5.25 Radiologic Variations of Nose and Paranasal
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 09 Page September 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i9.52 Relationship of Agger Nasi Cell and Uncinate
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i9.52 Relationship of Agger Nasi Cell and Uncinate
Chapter Five. 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM.
 1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
1 of 8 11/3/2008 2:52 PM Email : myousefmian@hotmail.com Chapter Five FRONT COVER Introduction Acknowledgement CHAPTERS Chapter One Chapter Two Chapter Three Chapter Four Chapter Five Chapter Six Chapter
Katya A. Shpilberg 1 Simon C. Daniel 1 Amish H. Doshi 1 William Lawson 2 Peter M. Som 1. Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Shpilberg et al. CT of Paranasal Sinuses and Nasal Cavity Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Katya A. Shpilberg 1 Simon C. Daniel
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Shpilberg et al. CT of Paranasal Sinuses and Nasal Cavity Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Katya A. Shpilberg 1 Simon C. Daniel
A COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHIC STUDY OF UNCINATE PROCESS OF ETHMOID BONE
 Original Article A COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHIC STUDY OF UNCINATE PROCESS OF ETHMOID BONE N. Vinay Kumar * 1, E. Kamala 2, T. S. Guga Priya 3, S. D. NalinaKumari 4. *1,2 Assistant professor, Department of
Original Article A COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHIC STUDY OF UNCINATE PROCESS OF ETHMOID BONE N. Vinay Kumar * 1, E. Kamala 2, T. S. Guga Priya 3, S. D. NalinaKumari 4. *1,2 Assistant professor, Department of
Incidence of accessory ostia in patients with chronic maxillary sinusitis
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Ghosh P et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Mar;4(2):443-447 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Ghosh P et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Mar;4(2):443-447 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu
 2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
CT OF THE PARANASAL SINUSES : NORMAL ANATOMY, VARIANTS AND PATHOLOGY
 Journal of Optoelectronics and Biomedical Materials Vol.2 Issue 4, October-December 2010, p. 281 289 CT OF THE PARANASAL SINUSES : NORMAL ANATOMY, VARIANTS AND PATHOLOGY AMIT N D DWIVEDI *, KAPIL KUMAR
Journal of Optoelectronics and Biomedical Materials Vol.2 Issue 4, October-December 2010, p. 281 289 CT OF THE PARANASAL SINUSES : NORMAL ANATOMY, VARIANTS AND PATHOLOGY AMIT N D DWIVEDI *, KAPIL KUMAR
A CORRELATION STUDY OF PARANASAL SINUSES BETWEEN OPERATIVE ENDOSCOPIC FINDINGS IN FESS AND PREOPERATIVE CT SCAN
 A CORRELATION STUDY OF PARANASAL SINUSES BETWEEN OPERATIVE ENDOSCOPIC FINDINGS IN FESS AND PREOPERATIVE CT SCAN Polisetti Ravi Babu 1, Bhennur Durga Prasad 2, Lanke Sowmya 3, K.S.B.S. Krishna Sasanka 4
A CORRELATION STUDY OF PARANASAL SINUSES BETWEEN OPERATIVE ENDOSCOPIC FINDINGS IN FESS AND PREOPERATIVE CT SCAN Polisetti Ravi Babu 1, Bhennur Durga Prasad 2, Lanke Sowmya 3, K.S.B.S. Krishna Sasanka 4
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Anatomical Study of the Middle Meatus with Emphasis to the Maxillary Ostium and Their Clinical
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Anatomical Study of the Middle Meatus with Emphasis to the Maxillary Ostium and Their Clinical
Volume 2 issue 4 ISSN A STUDY ON CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA ACTIVE MUCOSAL TYPE WITH SINUSITIS AS FOCAL SEPSIS
 Volume 2 issue 4 ISSN 2250-0359 A STUDY ON CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA ACTIVE MUCOSAL TYPE WITH SINUSITIS AS FOCAL SEPSIS * Sankaranaryanan Gopalakrishnan, * Satheesh kumar * Kilpaulk Medical College, Royepettah
Volume 2 issue 4 ISSN 2250-0359 A STUDY ON CHRONIC OTITIS MEDIA ACTIVE MUCOSAL TYPE WITH SINUSITIS AS FOCAL SEPSIS * Sankaranaryanan Gopalakrishnan, * Satheesh kumar * Kilpaulk Medical College, Royepettah
Osteomeatal unit OMU
 20074724752 CT Osteomeatal unitomu Assessment of the Relationship between Odontogenic Maxillary Sinusitis and Findings in the Ostiomeatal Unit on Coronal CT Images Miya Kato, Takashi Kaneda, Masataka Kato,
20074724752 CT Osteomeatal unitomu Assessment of the Relationship between Odontogenic Maxillary Sinusitis and Findings in the Ostiomeatal Unit on Coronal CT Images Miya Kato, Takashi Kaneda, Masataka Kato,
Evaluation of ostiomeatal complex pathology related to endoscopic sinus surgery a retrospective analysis
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 5, No. 18, April-June 2015 Original study Evaluation of ostiomeatal complex pathology related to endoscopic sinus surgery a retrospective analysis Vlad Budu 1, Alexandra
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 5, No. 18, April-June 2015 Original study Evaluation of ostiomeatal complex pathology related to endoscopic sinus surgery a retrospective analysis Vlad Budu 1, Alexandra
Anatomical variants of the uncinate process CT scan imaging study
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 2, No. 7, July - September 2012 original Study Anatomical variants of the uncinate process CT scan imaging study Vasilica Baldea 1, Mihail Dan Cobzeanu 2, Florina Mihalcea
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 2, No. 7, July - September 2012 original Study Anatomical variants of the uncinate process CT scan imaging study Vasilica Baldea 1, Mihail Dan Cobzeanu 2, Florina Mihalcea
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (3), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (3), Page 1390-1394 Anatomical Variations of Nasal Structures in Chronic Rhinosinusitis as Detected by Computed Tomography Scan Omar Adnan Hasan,
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (3), Page 1390-1394 Anatomical Variations of Nasal Structures in Chronic Rhinosinusitis as Detected by Computed Tomography Scan Omar Adnan Hasan,
Towards the Understanding of Sinonasal Anatomical Variations A Cadaveric Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Towards the Understanding of Sinonasal Anatomical Variations A Cadaveric Study Towards the Understanding of Sinonasal Anatomical Variations A Cadaveric Study 1 Daisy Sahni, 2 Rupa Mehta,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Towards the Understanding of Sinonasal Anatomical Variations A Cadaveric Study Towards the Understanding of Sinonasal Anatomical Variations A Cadaveric Study 1 Daisy Sahni, 2 Rupa Mehta,
Three-Dimensional Volumetric Display of the Nasal Ostiomeatal Channels and Paranasal Sinuses
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.192 on 12/22/17 from IP address 37.44.202.192. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Three-Dimensional Volumetric Display of the Nasal
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.202.192 on 12/22/17 from IP address 37.44.202.192. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Three-Dimensional Volumetric Display of the Nasal
Open Access Effect of Septal Deviation, Concha Bullosa and Haller s Cell on Maxillary Sinus s Inferior Pneumatization; a Retrospective Study
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 282 The Open Dentistry Journal, 2015, 9, (Suppl 2: M5) 282-286 Open Access Effect of Septal Deviation, Concha Bullosa and Haller s Cell on Maxillary
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 282 The Open Dentistry Journal, 2015, 9, (Suppl 2: M5) 282-286 Open Access Effect of Septal Deviation, Concha Bullosa and Haller s Cell on Maxillary
Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 44-51 www.iosrjournals.org Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess *
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. III (July. 2017), PP 44-51 www.iosrjournals.org Conventional Sinus Surgery Vs Fess *
Endoscopic Management Of A Giant Ethmoid Mucocele
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 S Ceylan, F Bora Citation S Ceylan, F Bora.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract We present
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 6 Number 1 S Ceylan, F Bora Citation S Ceylan, F Bora.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract We present
A comparative analysis of CT scan versus diagnostic nasal endoscopy in chronic rhino sinusitis
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Pullarat AN et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Jul;4(4):930-934 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Pullarat AN et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Jul;4(4):930-934 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
Radiological significance of the sinonasal anatomical variants in recurrent acute rhinosinusitis patients
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Sahu N et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 Jun;5(6):2379-2384 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20172121
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Sahu N et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 Jun;5(6):2379-2384 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20172121
The advent of high-resolution computerized tomography
 An anatomic classification of the ethmoidal bulla REUBEN C. SETLIFF, III, MD, PETER J. CATALANO, MD, FACS, LISA A. CATALANO, MPH, and CHAD FRANCIS, BA, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, and Burlington, Massachusetts
An anatomic classification of the ethmoidal bulla REUBEN C. SETLIFF, III, MD, PETER J. CATALANO, MD, FACS, LISA A. CATALANO, MPH, and CHAD FRANCIS, BA, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, and Burlington, Massachusetts
Diagnostic Performance of Multidetector Computed Tomography (MDCT) in Diagnosis of Sinus Variations
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 713-725 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.903684 ORIGINL RTICLE Received: 2017.02.08 ccepted: 2017.02.23 Published: 2017.11.17 uthors Contribution: Study Design Data Collection C Statistical
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 713-725 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.903684 ORIGINL RTICLE Received: 2017.02.08 ccepted: 2017.02.23 Published: 2017.11.17 uthors Contribution: Study Design Data Collection C Statistical
Nasal Septal Deviation and Concha Bullosa Do They Have an Impact on Maxillary Sinus Volumes and Prevalence of Maxillary Sinusitis?
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 126-133 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.900634 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.07.16 Accepted: 2016.09.02 Published: 2017.03.04 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 126-133 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.900634 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.07.16 Accepted: 2016.09.02 Published: 2017.03.04 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Correlations between anatomic variations of maxillary sinus ostium and postoperative complication after sinus lifting
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms..42.5.278 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Correlations between anatomic variations of maxillary sinus ostium and postoperative complication after sinus lifting
ORIGINAL ARTICLE https://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms..42.5.278 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Correlations between anatomic variations of maxillary sinus ostium and postoperative complication after sinus lifting
Frontal sinus disease continues to be one of the great
 Unilateral transnasal endoscopic approach to frontal sinuses: Draf IIc Mohammed K. Al Komser, M.D., M.A.S. and Andrew N. Goldberg, M.D., M.S.C.E. ABSTRACT For chronic sinusitis surgery, the Draf III approach
Unilateral transnasal endoscopic approach to frontal sinuses: Draf IIc Mohammed K. Al Komser, M.D., M.A.S. and Andrew N. Goldberg, M.D., M.S.C.E. ABSTRACT For chronic sinusitis surgery, the Draf III approach
Computed tomography road map of the paranasal sinuses for treatment planning
 Computed tomography road map of the paranasal sinuses for treatment planning Poster No.: C-2607 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Schembri, A. S. Gatt, D. Ellul, J. Brunton; Dundee/UK
Computed tomography road map of the paranasal sinuses for treatment planning Poster No.: C-2607 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Schembri, A. S. Gatt, D. Ellul, J. Brunton; Dundee/UK
Anatomical Analysis of the Frontal Recess Cells in Endoscopic Sinus Surgery An Indian Perspective
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anatomical Analysis of the Frontal Recess Cells in Endoscopic Sinus Surgery An Indian Perspective 1 Dhingra Shruti, 2 Agarwal AK, 3 Passey JC, 4 Kaul JM 1 Resident, Department of Otolaryngology
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anatomical Analysis of the Frontal Recess Cells in Endoscopic Sinus Surgery An Indian Perspective 1 Dhingra Shruti, 2 Agarwal AK, 3 Passey JC, 4 Kaul JM 1 Resident, Department of Otolaryngology
SINUSITIS. HAVAS ENT CLINICS Excellence in otolaryngology
 JULY 2015 SINUSITIS WHAT IS IT? WHAT SHOULD YOU DO? WHAT WORKS? THOMAS E HAVAS MBBS (SYD) MD (UNSW) FRCSE, FRACS, FACS CONJOINT ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR UNSW OTOLARNGOLOGY HEAD AND NECK SURGERY HAVAS ENT CLINICS
JULY 2015 SINUSITIS WHAT IS IT? WHAT SHOULD YOU DO? WHAT WORKS? THOMAS E HAVAS MBBS (SYD) MD (UNSW) FRCSE, FRACS, FACS CONJOINT ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR UNSW OTOLARNGOLOGY HEAD AND NECK SURGERY HAVAS ENT CLINICS
Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision
 THIEME Original Research 73 Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision Jan Alessandro Socher 1 Jonas Mello 2 Barbara Batista Baltha 2 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
THIEME Original Research 73 Tomographical Findings in Adult Patients Undergoing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery Revision Jan Alessandro Socher 1 Jonas Mello 2 Barbara Batista Baltha 2 1 Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488 Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP - SINUS CT 76380 Guideline
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines/considerations SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT 70486, 70487, 70488 Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP - SINUS CT 76380 Guideline
Communication issue - What should the radiologist report before functional endoscopic sinus surgery
 Communication issue - What should the radiologist report before functional endoscopic sinus surgery Poster No.: C-0509 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. M. Dobra 1, C. A. Badiu 1,
Communication issue - What should the radiologist report before functional endoscopic sinus surgery Poster No.: C-0509 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. M. Dobra 1, C. A. Badiu 1,
STUDY OF CORRELATION BETWEEN NASAL ENDOSCOPY AND RHINOGENIC HEADACHE Santhosha Kumar B 1, Manjunath Rao S. V 2
 STUDY OF CORRELATION BETWEEN NASAL ENDOSCOPY AND RHINOGENIC HEADACHE Santhosha Kumar B 1, Manjunath Rao S. V 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Santhosha Kumar B, Manjunath Rao S. V. Study of Correlation between
STUDY OF CORRELATION BETWEEN NASAL ENDOSCOPY AND RHINOGENIC HEADACHE Santhosha Kumar B 1, Manjunath Rao S. V 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Santhosha Kumar B, Manjunath Rao S. V. Study of Correlation between
Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
A Computer-Assisted Anatomical Study of the Nasofrontal Region
 The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. A Computer-Assisted Anatomical Study of the Nasofrontal Region
The Laryngoscope Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia 2001 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. A Computer-Assisted Anatomical Study of the Nasofrontal Region
The Frontal Sinus Drainage Pathway and Related Structures
 Pictorial Essay The Frontal Sinus Drainage Pathway and Related Structures David L. Daniels, Mahmood F. Mafee, Michelle M. Smith, Timothy L. Smith, Thomas P. Naidich, W. Douglas Brown, William E. Bolger,
Pictorial Essay The Frontal Sinus Drainage Pathway and Related Structures David L. Daniels, Mahmood F. Mafee, Michelle M. Smith, Timothy L. Smith, Thomas P. Naidich, W. Douglas Brown, William E. Bolger,
IJCMR 606. ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation of Computed Tomography And Nasal Endoscopic Findings In Chronic Rhinosinusitis A Clinical Study
 IJCMR 606 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation of Computed Tomography And Nasal Endoscopic Findings In Chronic Rhinosinusitis A Clinical Study Umeek Jeelani 1, Ulfat Ara Wani 2, Shabir Khanday 3, Shahi Jahan
IJCMR 606 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation of Computed Tomography And Nasal Endoscopic Findings In Chronic Rhinosinusitis A Clinical Study Umeek Jeelani 1, Ulfat Ara Wani 2, Shabir Khanday 3, Shahi Jahan
Skull Base Danger Zones in FESS
 Skull Base Danger Zones in FESS Poster No.: C-2278 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Renza Lozada, R. Carreño Gonzalez, G. Quintana Sanchez, 1 2 1 1 1 2 R. E. Figueroa ; Malaga/ES,
Skull Base Danger Zones in FESS Poster No.: C-2278 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Renza Lozada, R. Carreño Gonzalez, G. Quintana Sanchez, 1 2 1 1 1 2 R. E. Figueroa ; Malaga/ES,
Variations in Paranasal Sinus Anatomy: Implications for the Pathophysiology of Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Safety of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 ARTICLE Variations in Paranasal Sinus Anatomy: Implications for the Pathophysiology of Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Safety of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery S.A.R. Nouraei, MBBChir, MRCS, A.R. Elisay, MD, A. DiMarco,
ARTICLE Variations in Paranasal Sinus Anatomy: Implications for the Pathophysiology of Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Safety of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery S.A.R. Nouraei, MBBChir, MRCS, A.R. Elisay, MD, A. DiMarco,
A study of causes of nasal obstruction in Garhwal region of Uttarakhand
 Original Research Article Amit Arya 1, R S Bisht 2,*, Venkatashivareddy B 3, Richa Mina 4 1,4 Senior Resident, 2 Professor, Dept. of ENT, 3 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Community Medicine, VCSGGMS & RI
Original Research Article Amit Arya 1, R S Bisht 2,*, Venkatashivareddy B 3, Richa Mina 4 1,4 Senior Resident, 2 Professor, Dept. of ENT, 3 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Community Medicine, VCSGGMS & RI
Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma Nasal Type: Detection by Computed Tomography Features
 The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma Nasal Type: Detection by Computed Tomography Features Yin-Ping
The Laryngoscope VC 2014 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma Nasal Type: Detection by Computed Tomography Features Yin-Ping
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr.V. Krishna Chaitanya
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(1G):508-513 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(1G):508-513 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Bonifacius Hariyanto and 2 Andi Nilawati Usman
 Research Paper JMS (ISSN 1682-4474) is an International, peer-reviewed scientific journal that publishes original article in experimental & clinical medicine and related disciplines such as molecular biology,
Research Paper JMS (ISSN 1682-4474) is an International, peer-reviewed scientific journal that publishes original article in experimental & clinical medicine and related disciplines such as molecular biology,
THE ROLE OF OSTEOMEATAL COMPLEX ANATOMICAL VARIANTS IN CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS*
 1 Review Article THE ROLE OF OSTEOMEATAL COMPLEX ANATOMICAL VARIANTS IN CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS* Severino Aires de Araújo Neto 1, Paulo de Sá Leite Martins 2, Antônio Soares de Souza 3, Emílio Carlos Elias
1 Review Article THE ROLE OF OSTEOMEATAL COMPLEX ANATOMICAL VARIANTS IN CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS* Severino Aires de Araújo Neto 1, Paulo de Sá Leite Martins 2, Antônio Soares de Souza 3, Emílio Carlos Elias
Computed Tomography Scan Correlation between Anatomic Variations of Paranasal Sinuses and Chronic Rhinosinusitis
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/389 Computed Tomography Scan Correlation between Anatomic Variations of Paranasal Sinuses and Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/389 Computed Tomography Scan Correlation between Anatomic Variations of Paranasal Sinuses and Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Spontaneous Silent Sinus Syndrome (Imploding Antrum Syndrome): Case Series of 11 Patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Spontaneous Silent Sinus Syndrome (Imploding Antrum Syndrome): Case Series of 11 Patients Ahmed Adly a, Gamal Abdel -attah b, ohamed Shehata a, Sameh Amin b, Hatem Badran c Otolaryngology
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Spontaneous Silent Sinus Syndrome (Imploding Antrum Syndrome): Case Series of 11 Patients Ahmed Adly a, Gamal Abdel -attah b, ohamed Shehata a, Sameh Amin b, Hatem Badran c Otolaryngology
A Targeted Endoscopic Approach to Chronic Isolated Frontal Sinusitis
 Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2006) 134, 28-32 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A Targeted Endoscopic Approach to Chronic Isolated Frontal Sinusitis Roee Landsberg, MD, Yoram Segev, MD, Michael Friedman, MD,
Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2006) 134, 28-32 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A Targeted Endoscopic Approach to Chronic Isolated Frontal Sinusitis Roee Landsberg, MD, Yoram Segev, MD, Michael Friedman, MD,
Intranasal location of lacrimal sac in Thai cadavers
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 2 April 2010; 323-327 Clinical report Napas Tanamai a, Teeraporn Ratanaanekchai a, Sanguansak Thanaviratananich a, Kowit Chaisiwamongkol b, Thanarat Chantaumpalee b a Department
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 4 No. 2 April 2010; 323-327 Clinical report Napas Tanamai a, Teeraporn Ratanaanekchai a, Sanguansak Thanaviratananich a, Kowit Chaisiwamongkol b, Thanarat Chantaumpalee b a Department
A comprehensive study on complications of endoscopic sinus surgery
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Shyras JAD et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):472-477 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Shyras JAD et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):472-477 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE XXXX Patient information Patient Name: - Referring Doctor: - Patient DOB: - Scan Date: [Start date] Reason for Exam: Maxillary facial pain Doctor Notes:
MATERIALS AND METHODS
 sinus surgery as described by Messerklinger, wherein infundibulotomy forms an integral step by removal of the uncinate process [Stammberger and Posawetz, 1990; Kennedy et al, 1985; Rice, 1989]. Even though
sinus surgery as described by Messerklinger, wherein infundibulotomy forms an integral step by removal of the uncinate process [Stammberger and Posawetz, 1990; Kennedy et al, 1985; Rice, 1989]. Even though
Presenter: dr. Labeb Sailan Obad F1
 Presenter: dr. Labeb Sailan Obad F1 the correlation between currently existing objective tests for nasal airway patency and the patient s symptoms remains controversial Different measurement tools for
Presenter: dr. Labeb Sailan Obad F1 the correlation between currently existing objective tests for nasal airway patency and the patient s symptoms remains controversial Different measurement tools for
Endoscopic surgery in the treatment of crista galli pneumatization evolving with localizated frontal headaches
 Original Article Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;17(3):246-250. DOI: 10.7162/S1809-97772013000300003 Endoscopic surgery in the treatment of crista galli pneumatization evolving with localizated frontal
Original Article Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013;17(3):246-250. DOI: 10.7162/S1809-97772013000300003 Endoscopic surgery in the treatment of crista galli pneumatization evolving with localizated frontal
Anatomical Variants in Frontal Recess Region and their Impact on Frontal Sinus Surgery in Chronic Sinusitis
 American Journal of Health Research 2015; 3(3): 140-145 Published online April 23, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajhr) doi: 10.11648/j.ajhr.20150303.15 ISSN: 2330-8788 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8796
American Journal of Health Research 2015; 3(3): 140-145 Published online April 23, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajhr) doi: 10.11648/j.ajhr.20150303.15 ISSN: 2330-8788 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8796
Evaluation With Acoustic Rhinometry of Patients Undergoing Sinonasal Surgery
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation With Acoustic Rhinometry of Patients Undergoing Sinonasal Surgery R L A Raja Ahmad, MS (ORL)*, B S Gendeh, MS (ORL)** Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, Kulliyyah
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation With Acoustic Rhinometry of Patients Undergoing Sinonasal Surgery R L A Raja Ahmad, MS (ORL)*, B S Gendeh, MS (ORL)** Department of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery, Kulliyyah
Morphological Changes of the Ethmoid and Maxillary Cavities after Endoscopic Sinus Surgery, A Quantitative Digital Analysis.
 Morphological Changes of the Ethmoid and Maxillary Cavities after Endoscopic Sinus Surgery, A Quantitative Digital Analysis Thesis Submitted for fulfillment of M.D. degree in Otorhinolaryngology By: Hisham
Morphological Changes of the Ethmoid and Maxillary Cavities after Endoscopic Sinus Surgery, A Quantitative Digital Analysis Thesis Submitted for fulfillment of M.D. degree in Otorhinolaryngology By: Hisham
EVALUATION OF PATIENT'S OUTCOME AFTER ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY
 Basrah Journal Of Surgery Bas J Surg, September, 16, 2010 EVALUATION OF PATIENT'S OUTCOME AFTER ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY Hiwa A Abdulkareem MB.ChB, FICMS, CABS(ENT); Teaching Hospital; University of Sulaimania.
Basrah Journal Of Surgery Bas J Surg, September, 16, 2010 EVALUATION OF PATIENT'S OUTCOME AFTER ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY Hiwa A Abdulkareem MB.ChB, FICMS, CABS(ENT); Teaching Hospital; University of Sulaimania.
Relationship between Severity of Nasal Septum Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Cells and Chronic Otitis Media
 Original Article J Babol Univ Med Sci Vol 20, Issu 2; Feb 2018. P:27-32 Relationship between Severity of Nasal Septum Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Cells and Chronic Otitis Media E. Shobeiri
Original Article J Babol Univ Med Sci Vol 20, Issu 2; Feb 2018. P:27-32 Relationship between Severity of Nasal Septum Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Cells and Chronic Otitis Media E. Shobeiri
Major inflammatory patterns of chronic sinonasal diseases and their. accompanied anatomical variations; CT scan review
 Major inflammatory patterns of chronic sinonasal diseases and their accompanied anatomical variations; CT scan review Dr. Qays Ahmed Hassan AL-Timimy ABSTRACT Background: Because of wide use of Functional
Major inflammatory patterns of chronic sinonasal diseases and their accompanied anatomical variations; CT scan review Dr. Qays Ahmed Hassan AL-Timimy ABSTRACT Background: Because of wide use of Functional
Incidence of sinonasal anatomical variations associated with chronic sinusitis by CT scan in Karaikal, South India
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Gouripur K et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):576-580 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Gouripur K et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jul;3(3):576-580 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP SINUS CT Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70486, 70487, 70488, 76380
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS & MAXILLOFACIAL AREA CT LIMITED OR LOCALIZED FOLLOW UP SINUS CT Original Date: September 1997 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70486, 70487, 70488, 76380
DIFFICULT-TO-TREAT CHRONIC
 MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES FOR DIFFICULT-TO-TREAT CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS DR ZULKEFLI HUSSEIN CONSULTANT EAR NOSE & THROAT SURGEON PANTAI HOSPITAL PENANG DISCLAIMER Nothing to disclose PENANG ISLAND, MALAYSIA
MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES FOR DIFFICULT-TO-TREAT CHRONIC RHINOSINUSITIS DR ZULKEFLI HUSSEIN CONSULTANT EAR NOSE & THROAT SURGEON PANTAI HOSPITAL PENANG DISCLAIMER Nothing to disclose PENANG ISLAND, MALAYSIA
Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, UKGM, Marburg, Germany 2. Department of Neuroradiology, UKGM, Marburg, Germany 3
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Rhinology 49: 248-252, 2011 Radiological examinations of the anatomy of the inferior turbinate using Digital Volume Tomography (DVT) L. Balbach 1, V. Trinkel 1, C. Güldner 1, S. Bien
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Rhinology 49: 248-252, 2011 Radiological examinations of the anatomy of the inferior turbinate using Digital Volume Tomography (DVT) L. Balbach 1, V. Trinkel 1, C. Güldner 1, S. Bien
Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017
 Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017 Fungal Rhinosinusitis (FRS) Rhinosinusitis, is a common disorder affecting approximately 20% of the population at some time
Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017 Fungal Rhinosinusitis (FRS) Rhinosinusitis, is a common disorder affecting approximately 20% of the population at some time
FESS imaging - the role of MDCT
 FESS imaging - the role of MDCT Poster No.: C-0179 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Plascak, K. Makaruha, B. Klasic, L. Kavur, V. Vidjak; Zagreb/HR Keywords: Image verification,
FESS imaging - the role of MDCT Poster No.: C-0179 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Plascak, K. Makaruha, B. Klasic, L. Kavur, V. Vidjak; Zagreb/HR Keywords: Image verification,
Functional endoscopic sinus surgery for the management of sinonasal diseases
 46 Bangladesh J of Otorhinolaryngology 2008; 14(2) : 46-50 Functional endoscopic sinus surgery for the management of sinonasal diseases Kanu Lal Saha 1, Ahmmad Taous 2, Md. Zillur Rahman 3 Abstract This
46 Bangladesh J of Otorhinolaryngology 2008; 14(2) : 46-50 Functional endoscopic sinus surgery for the management of sinonasal diseases Kanu Lal Saha 1, Ahmmad Taous 2, Md. Zillur Rahman 3 Abstract This
Association between Septal Deviation and Sinonasal Papilloma
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2013, 231, 315-319 Septal Deviation and Papilloma 315 Association between Septal Deviation and Sinonasal Papilloma Kazuhiro Nomura, 1,2 Takenori Ogawa, 1 Mitsuru Sugawara, 2 Yohei
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2013, 231, 315-319 Septal Deviation and Papilloma 315 Association between Septal Deviation and Sinonasal Papilloma Kazuhiro Nomura, 1,2 Takenori Ogawa, 1 Mitsuru Sugawara, 2 Yohei
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Rhinologic Computed Tomographic Evaluation in Patients With Cleft Lip and Palate
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Rhinologic Computed Tomographic Evaluation in Patients With Cleft Lip and Palate Hideaki Suzuki, MD, PhD; Tai Yamaguchi, DDS, PhD; Masayuki Furukawa, MD, PhD Objective: To investigate
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Rhinologic Computed Tomographic Evaluation in Patients With Cleft Lip and Palate Hideaki Suzuki, MD, PhD; Tai Yamaguchi, DDS, PhD; Masayuki Furukawa, MD, PhD Objective: To investigate
Relation between Nasal Septal Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells A Computerised Tomographic Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relation between Nasal Septal Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells A Computerised Tomographic Study N. Vinay Kumar 1, T. S. Gugapriya 2 ISSN (0): 2455-5274; ISSN (P): 2617-5207
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relation between Nasal Septal Deviation and Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells A Computerised Tomographic Study N. Vinay Kumar 1, T. S. Gugapriya 2 ISSN (0): 2455-5274; ISSN (P): 2617-5207
Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem
 Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Rhinology Chair Introduction: It is important to classify and stage nasal polyposis. ( decide
Rhinology Chair Weekly Activity Dr.Adel A. Al Ibraheem www.rhinologychair.org conference@rhinologychair.org Rhinology Chair Introduction: It is important to classify and stage nasal polyposis. ( decide
Crista galli sinusitis a radiological impression or a real clinical entity
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 6, No. 23, July - September 2016 ORIGINAL STUDY Crista galli sinusitis a radiological impression or a real clinical entity Claudiu Manea 1,2, Ranko Mladina 3 1 CESITO
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Vol. 6, No. 23, July - September 2016 ORIGINAL STUDY Crista galli sinusitis a radiological impression or a real clinical entity Claudiu Manea 1,2, Ranko Mladina 3 1 CESITO
Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells, Temporal Bone, Ethmoid and Sphenoid Sinuses. Any Correlation?
 DOI 10.1007/s12070-014-0745-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells, Temporal Bone, Ethmoid and Sphenoid Sinuses. Any Correlation? Khalid Hindi Sarmad Alazzawi Rajagopalan Raman Narayanan
DOI 10.1007/s12070-014-0745-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pneumatization of Mastoid Air Cells, Temporal Bone, Ethmoid and Sphenoid Sinuses. Any Correlation? Khalid Hindi Sarmad Alazzawi Rajagopalan Raman Narayanan
Rhinolithiasis and value of nasal endoscopy: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 7 Number 2 Rhinolithiasis and value of nasal endoscopy: A Case Report R Singh, S Varshney, S Bist, N Gupta, R Bhatia, S Kishore Citation R Singh,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 7 Number 2 Rhinolithiasis and value of nasal endoscopy: A Case Report R Singh, S Varshney, S Bist, N Gupta, R Bhatia, S Kishore Citation R Singh,
Anatomy and Physiology of the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses
 Anatomy and Physiology of the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses PD Dr. med. Basile N. Landis Unité de Rhinologie-Olfactologie Service d Oto-Rhino-Laryngologie et de Chirurgie cervicofaciale, Hôpitaux Universitaires
Anatomy and Physiology of the Nose and Paranasal Sinuses PD Dr. med. Basile N. Landis Unité de Rhinologie-Olfactologie Service d Oto-Rhino-Laryngologie et de Chirurgie cervicofaciale, Hôpitaux Universitaires
1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING
 RHINOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING Exposure to clinical rhinology is provided in each of the four ORL years over the course of several rotations in a graduated approach. MEE General Otolaryngology
RHINOLOGY 1. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF TRAINING Exposure to clinical rhinology is provided in each of the four ORL years over the course of several rotations in a graduated approach. MEE General Otolaryngology
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2018) Vol. 73 (8), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2018) Vol. 73 (8), Page 7329-7333 Subjective Evaluation of Smell Dysfunctions before and after Different Nasal Surgeries Wafaie Abd El-Rasoul M. Mourad
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2018) Vol. 73 (8), Page 7329-7333 Subjective Evaluation of Smell Dysfunctions before and after Different Nasal Surgeries Wafaie Abd El-Rasoul M. Mourad
