Study of the additive effect of timolol and epinephrine in lowering intraocular pressure
|
|
|
- Barnard Malone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1981, 65, Study of the additive effect of timolol and epinephrine in lowering intraocular pressure JOHN V. THOMAS AND DAVID L. EPSTEIN From the Glaucoma Clinical Research Center, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA SUMMARY A randomised, double-masked clinical study was conducted in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma to determine if timolol and epinephrine have an additive effect in lowering intraocular pressure. Sixteen patients were randomly assigned to one of 2 treatment sequences (timolol alone, supplemented after 2 weeks with epinephrine, and vice versa). An initial additive effect in lowering intraocular pressure was found in both sequences. However, after several weeks of combined therapy complete loss of additive effect was found. Patients who were treated first with epinephrine for 2 weeks and then supplemented with timolol had significantly lower intraocular pressures for at least 2 weeks than patients in the reverse treatment sequence. Epinephrine treatment alone caused a significant increase in facility of outflow, but this effect did not occur with simultaneous t molol treatment. The results are discussed in terms of possible fundamental beta and alpha adrenergic influences on aqueous dynamics and their potential clinical relevance. Timolol is a beta adrenergic blocking agent which together, have an additive effect in lowering intraocular pressure. competes with catecholamines for adrenergic beta receptor sites. It has been shown to lower intraocular Radius et al. 6 have reported in a single-drop study pressure in normal and glaucomatous animal eyes,` that epinephrine given to rabbits pretreated with in normal volunteers,4 and in patients with timolol has a small additive effect in lowering glaucoma.5'- The reduction in intraocular pressure intraocular pressure which lasts for approximately 9 produced by timolol is probably due to specific hours. However, albuterol (a beta agonist) when blockade of beta adrenergic receptors. " It is obvious used in animals pretreated with timolol did not that if timolol were found to be additive to other produce any further lowering of intraocular pressure. intraocular pressure-reducing drugs it would A few investigators'7"1 have noted their clinical represent an important advance in the treatment of impression that there is an enhanced reduction of glaucoma. intraocular pressure when epinephrine is used in A few studies"2-4 have indicated that timolol has a patients already on timolol, and Nielson'9 has statistically significant additive effect when used in recorded an additional reduction of intraocular patients receiving maximum-tolerated antiglaucoma pressure by epinephrine in eyes treated with timolol. therapy. However, it has also been reported that this However, Boger et al.7 did not find any such additive additive effect in lowering intraocular pressure is not effect. clinically significant. 5 It is important to note that the We decided therefore to conduct a randomised, results of the above studies do not imply that timolol double-masked clinical study to determine with has an additive effect with each of the several drugs greater certainty whether timolol and epinephrine that constitutes maximal medical therapy. have an additive effect in lowering intraocular Timolol acts as an antagonist at adrenergic beta pressure in patients with primary open-angle receptor sites, while epinephrine is an agonist at glaucoma. adrenergic alpha and beta receptor sites. It is therefore of both practical and theoretical significance to determine if these 2 drugs, when used Patients and methods The criteria for inclusion of patients and for their Correspondence to John V. Thomas MD. 100 Charles River Plaza. continuance in this study were the presence of optic Cambridge Street. Boston. Mass USA. nerves healthy enough to be safe without treatment 596
2 Study of the additive effect of timolol and epinephrine in lowering intraocular pressure for a month, applanation tensions greater than or equal to 23 mmhg without treatment, open angles by gonioscopy, and stable visual fields. Patients were excluded if they had a history of recent ocular infection, cataract extraction and/or other surgical procedures, severe ocular trauma within 3 months, current contact lens usage or use within 3 weeks, corneal foreign body within I month, dendritic keratitis or active corneal ulcer within 3 months, corneal abnormalities preventing reliable applanation tonometry, allergy to epinephrine, uveitis, angle closure, and bronchial asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Further, patients receiving propranolol or other systemic,8-adrenergic blocking drugs, pregnant or nursing women, patients with heart rates of less than 56 beats per minute after 4 minutes of rest, and children were excluded. A total of 31 eyes of 16 patients were selected for the study. The patients, 9 men and 7 women, ranged in age from 31 to 78 years with an average age of 62 years. Fourteen patients were white and 2 were black. All subjects were informed precisely of the nature of the study before they gave their consent. The treatment protocol is presented in Fig. 1. After 2 weeks without any medication the patients returned for a complete baseline examination including Goldmann applanation tension measurements every hour for 4 consecutive hours, followed by tonography. rimo 9 REPLAr.1X EXAMfNAr r o ft TMOLOL r - REPEAr EXAMWN4rr REPEAT rnj EXAMINArlow Aur ATiENTS MSELff 'S EYES EXAMINATION (2 WEE ) DAY) (la DAYS) 7 PATEns 073 EYES) ERE I 1I EA IREPEAr hiexawati"on TION rexa irm ne ErAr if- VOLOL rtmxot.. 6 WEEKS (AVERAGE) SOLO rn REAT EXAMIWATION EXAAriO Fig. 1 Flow diagram oftreatment protocol. 597 The patients were then assigned to 1 of 2 treatment groups according to a table of random numbers. Eighteen eyes in 9 patients were treated with timolol maleate 1/2% (Timoptic) twice a day for 2 weeks. Thirteen eyes in 7 patients were treated with epinephrine borate 1% (Eppy) twice a day for 2 weeks. Coded, identical-appearing bottles were used to dispense both medications. Physicians examining the patients, technicians performing tonography, and the patients themselves were unaware of the drugs being used. At the end of 2 weeks all patients returned for repeat 4-hourly intraocular pressure measurements and tonography. The regular moming dose of the medication was administered by the nurse prior to the measurements of intraocular pressure. Then epinephrine was added to the regimen of patients who had been treated with timolol alone, and timolol was added to the regimen of patients who had been treated with epinephrine alone. The medications were administered 1 minute apart by the patients at home and by the nurse on the morning of the clinic visit. All patients returned after I day and after 2 weeks of combined therapy with timolol and epinephrine. Measurements of intraocular pressure and tonography were similarly repeated at both visits. Combined therapy was then continued. Pressure measurements were repeated at the last visit, which took place at periods of time varying from 4 to 15 weeks (average 6 weeks) after the previous visit. We used a straight-line extrapolation to calculate intraocular pressure data points 10 weeks after the start of the experiment so that we could compare results from all patients. Measurements of intraocular pressure were performed at approximately the same time of day on each visit in order to minimise the influence of diurnal variation. The changes in intraocular pressure were expressed in terms of mean percentage reduction in outflow pressure consistently using 10 mmhg as episcleral venous pressure, as determined previously for similar patients with primary open-angle glaucoma in our clinic.20 The calculations reported in this paper for intraocular pressure are based on the mean of 5 applanation measurements per subject per test day. We determined the significance of differences between the 2 groups with a standard t-test and differences within treatment series with a t-test for paired samples. To ensure independence the tests were done on left eyes (i.e., left and right eyes were not pooled). Tests of both absolute and relative (percentage change) differences were consistent. As a further check we also computed t values for individual applanation measurements (e.g., first measurement on day x with first measurement on day y, second with
3 H~~1 P p.1.o5~ E E * Epin.Ptwine /0 WEEKS Fig. 2 Intraocular pressure measurements in the 2 treatment sequences. (T=timolol; E=epinephrine; T+E=timolol supplemented with epinephrine; E+ T=epinephrine supplemented with timolol). second, etc.), and repeated the entire series of calculations on right-eye measurements. Tonography data are based on a single measurement per eye per visit. Calculations were done on left and right eyes separately and were consistent. Pressure measurement and tonography data from left eyes are presented in the tables. Results After treatment with timolol alone for 2 weeks a significant reduction of oufflow pressure was found. (Fig. 2, Table 1). One day after epinephrine was added to timolol there was a significant additive reduction in outflow pressure (Table 1). This additive effect of epinephrine was still present, but diminished, after 2 weeks of combined therapy (Table 1). However, after an average of 8 weeks of combined therapy there was no significant additive reduction in outflow attributable to epinephrine (Table 1). In patients treated with epinephrine alone for 2 weeks there occurred a significant reduction in outflow pressure (Fig. 2, Table 2). One day after timolol was added to the epinephrine regimen there was a significant additive reduction in outflow pressure (Table 2). Two weeks after combined John V. Thomas and David L. Epstein therapy in this sequence an additive reduction in outflow pressure attributable to timolol was still present, but the net additive effect was significantly less (Table 2). After an average of 8 weeks of combined therapy no significant additive effect was attributable to timolol (Table 2). The data expressed in terms of absolute mmhg showed the same levels of statistical significance. A significant difference in the intraocular pressure reduction was found between the 2 treatment sequences (Fig. 2). Pretreatment pressures of the 2 groups were not significantly different. The drop in intraocular pressure when timolol was added to Table 1 Mean percentage reduction of outflow pressure in timolol-epinephrine treatment sequence Mean % reduction of outflow pressure Significance After timolol for 2 weeks-compared with pretherapy level -34 5%±6 4 p<0001 timolol and I day of timolol and epinephrine -compared with timolol after 2 weeks -21 1% +5-4 p<001 timolol and 2 weeks of timolol and epinephrine -compared with timolol after 2 weeks -144% +4-6 p<005 timolol and 8 weeks of timolol and epinephrine -compared with timolol after 2 weeks -10-2%+7-9 p>0 I Table 2 Mean percentage reduction ofoutflow pressure in epinephrine-timolol treatment sequence Mean % reduction of outflow pressure Significance After epinephrine for 2 weeks-compared with pretherapy level -37-6%±+8-2 p<0.01 epinephrine and I day of epinephrine and timolol-compared with epinephrine after 2 weeks -58-7%+9 4 p<0001 epinephrine and 2 weeks of epinephrine and timolol-compared with epinephrine after 2 weeks -36-2%+12-3 p<0-05 epinephrine and 8 weeks of epinephrine and timolol-compared with epinephrine after 2 weeks -15 5%+17t1 p>0 2
4 Study of the additive effect of timolol and epinephrine in lowering intraocular pressure epinephrine was significantly greater than when epinephrine was added to timolol both after 1 day (p<0-01) and after 2 weeks (p<005) of combined therapy. However, after an average of 8 weeks of combined therapy we could find no significant difference in pressure reduction between the 2 treatment sequences. Tonography measurements revealed that after 2 weeks of treatment with epinephrine alone there was a significant increase in facility of outflow (Table 3). One day after timolol was added no significant change in facility of outflow occurred. However, after 2 weeks of combined therapy a significant decrease in outflow facility was observed. Tonography measurements in the other treatment sequence revealed that after two weeks of treatment with timolol alone there was a significant increase in facility of outflow (Table 4). However, adding Table 3 Tonography data in epinephrine-timolol treatment sequence Facility ofoutflow (pl/minlmmhlg) Pretreatment 0-09±0-01 epinephrine 0 17±0-03 epinephrine and I day of epinephrine and timolol 0-18±0-02 epinephrine and 2 weeks of epinephrine and timolol 0-13±0-02 Change Increase (p<0o02) No change (p>02) Decrease (p<0-00) Table 4 Tonography data in timolol-epinephrine treatment Facility ofoutflow (,ul/min/mmhg) Pretreatment 0-11±0 02 timolol 0 16±0-02 timolol and I day of timolol and epinephrine 0 14±0-02 timolol and 2 weeks of timolol and epinephrine 0-16±0-02 Change Increase (p<0*02) No change (p>0-09) No change (p>04) epinephrine to those patients pretreated with timolol, did not increase outflow facility (Table 4). Discussion 599 An initial additive effect in intraocular pressure reduction is observed when epinephrine is given to patients already on timolol, and vice versa (Fig. 2). However, a statistically significant complete loss of this additive effect occurs when patients are maintained on both drugs for an average of 8 weeks (Tables 1, 2). After treatment with epinephrine alone for 2 weeks a significant increase in facility of outflow was found (Table 3). This is consistent with previous clinical studies.2"26 One day after timolol was added to epinephrine no significant change in facility of outflow was found. However, after 2 weeks of combined therapy a significant decrease in facility occurred (Table 3). In the reverse sequence, when epinephrine was added to patients already treated with timolol (Table 4), no increase in facility of outflow was observed. From these data it may be postulated that timolol can block the effect of epinephrine on facility of outflow. This is consistent with Neufeld's experimental finding27 that timolol blocks catecholamine-stimulated increase in cyclic adenosine monophosphate (AMP) in the isolated rabbit iris-ciliary body preparation. Thus, epinephrine probably causes an increase in facility of outflow by a beta receptor mechanism. This finding is of interest because it casts doubt on the validity of the traditional concept of adrenergic receptor sites in the eye. According to this traditional concept, stimulation of alpha receptors in the outflow tract is supposed to increase facility of outflow, whereas stimulation of beta receptors is supposed to affect only the inflow mechanism, resulting in a decrease in aqueous production Although such a concept may offer a logical explanation for the mechanism of action of epinephrine, it does not explain the action of timolol, a drug which selectively blocks beta receptors yet causes a reduction in intraocular pressure. In addition to our clinical study there are experimental data from studies in primate eyes that contradict this traditional concept.3"33 For example, it has been shown that isoproterenol, when injected into the anterior chamber, causes both an increase in facility of outflow33 and an increase in the rate of aqueous humour formation.3' It has also been observed that alpha-adrenergic stimulation produces no change in facility of outflow.32 Based on the clinical data in our study and on experimental data reported by others3"33 a model of ocular adrenergic receptor sites is proposed which
5 600 Fig. 3 Proposed model of ocular adrenergic receptor sites and effects on aqueous dynamics. OUTFLOW p (notone) appears to explain, at least partially, the mechanisms of action of timolol and epinephrine in human glaucomatous eyes (Fig. 3). This model is not intended to serve as the 'final mechanism' but rather as a framework for understanding current primate and human glaucoma data and as a basis for further hypothesis and study. According to this model beta receptors play a role in both the outflow and inflow systems. The beta receptors mediating outflow are possibly located in the trabecular meshwork and stimulating them (e.g., with epinephrine) produces an increase in the facility of aqueous outflow. The assumption is made that these receptors maintain no tone in the outflow system.27 Therefore blocking them (e.g., with timolol) has no substantial effect on facility of outflow. The beta receptors mediating inflow are possibly located in the ciliary processes, and stimulating them (e.g., with epinephrine) produces an increase in aqueous humour formation. The assumption is made that these receptors provide a certain tone to the inflow mechanisms.27 Therefore blocking them (e.g., with timolol) causes a decrease in aqueous humour production. Alpha receptors may also play a role in the inflow mechanism. They are possibly located in the walls of blood vessels supplying the ciliary processes, and stimulating them (e.g., with epinephrine) may cause constriction of these vessels leading to decreased blood flow and consequently decreased aqueous production. The data from our clinical study are interpreted then as follows. It is postulated that the initial stimulation of beta receptors in the outflow tract by epinephrine alone produced an increased facility of outflow. The addition of timolol blocked this effect of John V. Thomas and David L. Epstein INFLOW P+ren l(tone present) STMLATING 19 (OUTFLOW) CAUSES t OUTFLOW BLOCKING p (OUTFLOW) HAS NO EFFECT ON OUTFLOW STIMULATING P (INFLOW) CAUSES tinflcw BLOCKING P (INFLOW) C S IFLOW STIMULATING CX (INFLOW) CAUS IfFLOW epinephrine on outflow, but produced a reduction of intraocular pressure by reducing the rate of aqueous inflow. This is consistent with previously reported fluorophotometric34" and electro-oculogram36 studies which indicate that timolol causes a decrease in intraocular pressure by reducing the rate of aqueous production. Timolol reduces the rate of aqueous production by blocking beta receptors involved with inflow. Stimulating these beta receptors, then, should theoretically cause an increase in aqueous production. Townsend and Brubaker37 have recently presented evidence that supports this hypothesis. In a fluorophotometric study of normal human eyes, they found that topical epinephrine did cause an increase in aqueous production (and also an increase in facilitv of outflow). When timolol is added to epinephrine therapy we propose that there is a gradual lessening of the additive effect on intraocular pressure because the timolol interferes with the beta agonist effect of epinephrine on outflow (Table 3). Timolol has greater affinity for beta receptors than does epinephrine When epinephrine is added to timolol therapy a temporary reduction in intraocular pressure may be produced (Table 1) by a non-beta (hence, alpha) mechanism (since the timolol would block the epinephrine-beta agonist effect on inflow and outflow). Radius et al. have similarly concluded that the additive effect of epinephrine to timolol is via an alpha mechanism.'6 This possible alpha effect on inflow apparently diminishes with time (Table 1). The net effect of epinephrine in reducing intraocular pressure in most patients reflects the resultant of beta and alpha effects respectively increasing and reducing inflow, and of the beta effect increasing facility of outflow.
6 Study of the additive effect of timolol and epinephrine in lowering intraocular pressure The small increase in facility of outflow seen in patients treated with timolol alone for 2 weeks is difficult to explain within the context of this model. Investigators disagree about the effect of timolol on facility of outflow. Some conclude that timolol has no effect on outflow facility,1332 while others7' 843 believe that a small increase in facility occurs after a period of continued use. Perhaps there are differing effects involving 8, and 32 receptors that are not addressed in the above model. It is evident from our data that patients who were treated first with epinephrine for 2 weeks and then supplemented with timolol had significantly lower intraocular pressures for at least 2 weeks than patients in the reverse treatment sequence (Fig. 2). Neufeld's studies of the effects of timolol and epinephrine on the density of beta receptors in ocular tissues is pertinent to this clinical observation.2745 Neufeld has shown experimentally that application of epinephrine causes a reduction, and timolol a proliferation, of beta receptors.45 It may be postulated that when a patient is treated with epinephrine alone the number of beta receptors is reduced. Then, when timolol is added, relatively few receptors remain for it to act on, and it therefore produces more effective beta blockade and reduction of aqueous production. From our interpretation of our results we believe there is a reasonable manner in which patients who need both drugs for reduction of intraocular pressure might be more effectively managed. Such patients logically should be treated with epinephrine, first for several weeks and then intermittently with addition of timolol. Such pulsed administration of timolol to patients on epinephrine we expect should provide better overall control of pressure than the continuous administration of both timolol and epinephrine, but the efficacy of this projected regimen is yet to be clinically evaluated. Lawrence Rand, MD, provided consultation in the design of the study, and Mr Aaron Seidman provided statistical analysis of the data. This study was supported in part hy grants P50EY R(IEY01894, and ROIEYOO(X)2 from the National Eye Institute. and hy the American Health Assistance Foundation. References I Merck Sharp and Dohme Research Lahoratories. Preclinical Brochure on Timolol, LeDouarec JC, Vareiller P, Plazonnet B, et al: The effect of timolol, a beta-adrenergic blocking agent, on intraocular pressure in rabbits. Pharmacology 1976; 18: Vareiller P, Silverstone D, Plazonnet D, et al. Comparison of the effects of timolol and other adrenergic agents on initraocular pressure in the rabbit. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci 1977; 16: Katz IM, Hubbard WA, Getson A.l, et al. Intraocular pressure decrease in normal volunteers following timolol ophthalmic solution. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci 1976; 15: Zimmerman TJ, Kaufman HE. Timolol: A B-adrenergic blocking agent for the treatment of glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol 1977; 95: Zimmerman TJ, Kaufman HE. Timolol-dose response and duration of action. Arch Ophthalmol 1977; 95: Boger WP, Puliafito CA, Steinert RF, et al. Long-term experience with timolol ophthalmic solution in patients with open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmology 1978; 85: Ritch R, Harzett NA, Podos SM. The effect of 1 5% timolol maleate on intraocular pressure. Acta Ophthalmol (Kbh) 1978; 56: Goethals M, Missotten L. Long-term trial of timolol in different forms of glaucoma. Bull Soc Belge Ophthalmol 1977; 79: Kerty E, Hirven I. Glaucoma treatment with timolol. Acta Ophthalmol (Kbh) 1978; 56: Vale J, Phillips Cl. Effect of dl- and d-propranolol on ocular tension in rabbits and patients. Exp Eye Res 1970; 9: Zimmerman TJ, Gillespie JE, Kass MA, et al. Timolol plus maximum-tolerated antiglaucoma therapy. Arch Ophthalmol 1979; 97: Sonty S, Schwartz B. The additive effect of timolol on open angle glaucoma patients on maximal medical therapy. Surv Ophthalmol 1979; 23: Ashburn FS, Gillespie JE, Kass MA, et al. Timolol plus maximum tolerated antiglaucoma therapy: a one-vear follow-up study. Surv Ophthalmol 1979; 23: Diamond GR, Werblin TP, Richter R, et al. Extended clinical studies using timolol in patients with ocular hypertension and chronic open angle glaucoma. Glaucoma 1979; 1: Radius RL, Diamond GR, Pollack IP, etal. Timolol-a new drug for management of chronic simple glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol 1978; 96: 10() Katz IM. Beta-blockers and the eve: an overview. Ann Ophthalmol 1978; 10: Obstbaum SA, Galin MA, Katz IM. Timolol: effect on intraocular pressure in chronic open-angle glaucoma. Ann Ophthalmol 1978; 10: Nielsen NV. Timolol: Hypotensive effect. used alone and in combination for treatment of increased intraocular pressure. Acta Ophthalmol (Kbh) 1978; 56: Bellows AR, Epstein DL, Grant WM. Episcleral venous pressure in eyes with glaucoma and prominent episcleral vessels. Presented at the 1977 Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Meeting, Sarasota, Fla.. 25 April Submitted for publication. 21 Becker B, Petitt TH, Gay AJ. Topical epinephrine therapy on open angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol 1961; 66: Ballantine EJ, Gamer L. Improvement of the coefficient of outflow in glaucomatous eyes. Arch Ophthalmol 1961; 66: Krill AE, Newell FW, Novak M. Early and long-term effects of levo-epinephrine. Am J Ophthalmol 1965; 59: Sonntag JR, Brindly GO, Shields MB, et al. Timolol and epinephrine-comparison of efficacy and side effects. Arch Ophthalmol 1979; 97: Obstbaum SA, Kolker AE, Phelps CD. Low-dose epinephrine: effect on intraocular pressure. Arch Ophthalmol 1974; 92: 18-20). 26 Richards JSF, Drance SM. The effect of 2% epinephrine on aqueous humor dynamics in the human eve. Can J Ophthalmol 1967; 2: Neufeld AH. Experimental studies on the mechanism of action of timolol. Surv Ophthalmol 1979; 23: Richardson KT. Sympathetic physiology and pharmacology. Surv Ophthalmol 1972; 17: 12() Havener WH. Ocliar Pharmacology. 4th ed. St Louis: Mosby, 1978; ) Bill A. Early effects of epinephrine on aqueous humor dynamics in vervet monkeys (Cercopithecuis ethiops). Exp Eve Res 1969; 8:
7 Bill A. Effects of norephinephrine, isoproterenol and sympathetic stimulation on aqueous humor dynamics in the vervet monkeys. Exp Eye Res 1970; 10: Bill A, Heilmann K. Ocular effects of clonidine in cats and monkeys (Macaca irus). Exp Eye Res 1975; 21: Neufeld AH. Influences of cyclic nucleotides on outflow facility in the vervet monkey. Exp Eye Res 1978; 27: Coakes RL, Brubaker RF. The mechanism of timolol in lowering intraocular pressure in the normal eyes. Arch Ophthalmol 1978; 96: Yablonski ME, Zimmerman TJ, Waltman SR, et al. A fluorophotometric study of the effect of topical timolol on aqueous humor dynamics. Exp Eye Res 1978; 27: Missoten L, Goethals M. Timolol reduces the standing potential of the eye. Ophthalmol Res 1977; 9: Townsend DJ, Brubaker RF. Acute effect of epinephrine on aqueous formation in the normal human eye. ARVO, Sarasota, Fla., April Neufeld AH, Page ED. In vitro determination of the ability of drugs to bind to adrenergic receptors. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci 1978; 16: John V. Thomas and David L. Epstein 39 Dausch D, Honegger H. The effect of timolol on intraocular pressure: a year-long study. Presentation at the 23rd International Congress of Ophthalmology, Kyoto, Japan. May Moss AP, Ritch R, Hargett NA, et al. A comparison of the effects of timolol and epinephrine on intraocular pressure. Am J Ophthalmol 1978; 86: Zimmerman TJ, Harbin R. Pett M. et al. Timolol and facility of outflow. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci 1977; 16: Sonntag JR, Brindley GO, Shields MB. Effect of timolol therapy on outflow facility. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci 1978; 17: Boger WP, Steinert R, Puliafito C. et al. A double-masked clinical trial comparing timolol ophthalmic solution and pilocarpine in the therapy of open-angle glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 1978; 86: Lin LL. Galin MA, Obstbaum SA, et al. Longterm timolol therapy. Surv Ophthalmol 1979; 23: Neufeld AH, Zawistowski KA. Page ED. et al. Influences on the density of beta adrenergic receptors in the cornea and iris-ciliarv body of the rabbit. Invest Ophthalmol Visual Sci 1978; 17: Br J Ophthalmol: first published as /bjo on 1 September Downloaded from on 3 May 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Dose response of oral timolol combined with
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1982, 66, 242-246 Dose response of oral timolol combined with adrenaline ARNE OHRSTROM From the University Eye Clinic of Malmo and the Hospital of Koping, Sweden SUMMARY
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1982, 66, 242-246 Dose response of oral timolol combined with adrenaline ARNE OHRSTROM From the University Eye Clinic of Malmo and the Hospital of Koping, Sweden SUMMARY
Restoring Sensitivity to Timolol After Long-Term Drift in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol., No. 2, February 90 Copyright Association for esearch in Vision and Ophthalmology estoring Sensitivity to Timolol After ong-term Drift in Primary Open-Angle
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol., No. 2, February 90 Copyright Association for esearch in Vision and Ophthalmology estoring Sensitivity to Timolol After ong-term Drift in Primary Open-Angle
evaluation of these two combined
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1978, 62, 296-31 Atenolol versus adrenaline eye drops and an evaluation of these two combined CALBERT I. PHILLIPS, SHEILA M. GORE,* AND PATRICIA M. GUNN From the Department
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1978, 62, 296-31 Atenolol versus adrenaline eye drops and an evaluation of these two combined CALBERT I. PHILLIPS, SHEILA M. GORE,* AND PATRICIA M. GUNN From the Department
Effect of brimonidine on intraocular pressure in normal tension glaucoma: A short term clinical trial
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 7, 2003 / pp. 611-615 Effect of brimonidine on intraocular pressure in normal tension glaucoma: A short term clinical trial S.A. GANDOLFI, L. CIMINO, P.
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 7, 2003 / pp. 611-615 Effect of brimonidine on intraocular pressure in normal tension glaucoma: A short term clinical trial S.A. GANDOLFI, L. CIMINO, P.
M Diestelhorst, L-I Larsson,* for The European Latanoprost Fixed Combination Study Group...
 199 SCIENTIFIC REPORT A 12 week study comparing the fixed combination of latanoprost and timolol with the concomitant use of the individual components in patients with open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension
199 SCIENTIFIC REPORT A 12 week study comparing the fixed combination of latanoprost and timolol with the concomitant use of the individual components in patients with open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension
A. Incorrect! Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor given orally or by intravenous injection.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 20: Drugs that Treat Glaucoma Question No. 1 of 10 1. is a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Question #01 (A) Acetazolamide (B) Clonidine (C) Dorzolamide (D) Apraclonidine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 20: Drugs that Treat Glaucoma Question No. 1 of 10 1. is a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Question #01 (A) Acetazolamide (B) Clonidine (C) Dorzolamide (D) Apraclonidine
Effects of selective beta!- and beta 2 -adrenoreceptor agonists and antagonists on intraocular pressure in the cat
 Effects of selective beta!- and beta 2 -adrenoreceptor agonists and antagonists on intraocular pressure in the cat Brenda K. Colasanti and Robert R. Trotter Ocular tension of cats was measured after topical
Effects of selective beta!- and beta 2 -adrenoreceptor agonists and antagonists on intraocular pressure in the cat Brenda K. Colasanti and Robert R. Trotter Ocular tension of cats was measured after topical
VI.2.2 Summary of treatment benefits
 EU-Risk Management Plan for Bimatoprost V01 aetiology), both OAG and ACG can be secondary conditions. Secondary glaucoma refers to any case in which another disorder (e.g. injury, inflammation, vascular
EU-Risk Management Plan for Bimatoprost V01 aetiology), both OAG and ACG can be secondary conditions. Secondary glaucoma refers to any case in which another disorder (e.g. injury, inflammation, vascular
non-perforating injury
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 418 Anterior chamber angle tears after non-perforating injury DAVID MOONEY Croydon Eye Unit, Croydon, Surrey Recession of the anterior chamber angle is a common finding after
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 418 Anterior chamber angle tears after non-perforating injury DAVID MOONEY Croydon Eye Unit, Croydon, Surrey Recession of the anterior chamber angle is a common finding after
Glaucoma. Glaucoma. Optic Disc Cupping
 Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Bruce James A group of diseases in which damage to the optic nerve occurs as a result of intraocualar pressure being above the physiological norm for that eye Stoke Mandeville
Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Bruce James A group of diseases in which damage to the optic nerve occurs as a result of intraocualar pressure being above the physiological norm for that eye Stoke Mandeville
GLAUCOMA. An Overview
 GLAUCOMA An Overview Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com --()-- IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your
GLAUCOMA An Overview Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com --()-- IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your
Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma. Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4. Abstract
 Original article Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 4 Professor, Department of
Original article Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 4 Professor, Department of
effect of previous argon laser trabeculoplasty
 Graefe s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (2006) 244: 1073 1076 CLINICAL INVESTIGATION DOI 10.1007/s00417-005-0198-x Esther Arranz-Marquez Miguel A. Teus Effect of previous argon laser trabeculoplasty on the ocular
Graefe s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (2006) 244: 1073 1076 CLINICAL INVESTIGATION DOI 10.1007/s00417-005-0198-x Esther Arranz-Marquez Miguel A. Teus Effect of previous argon laser trabeculoplasty on the ocular
Isoproferenol Stimulates Aqueous Flow in Humans With Horner's Syndrome
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 29, No. 4, April 1988 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Isoproferenol Stimulates Aqueous Flow in Humans With Horner's Syndrome
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 29, No. 4, April 1988 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Isoproferenol Stimulates Aqueous Flow in Humans With Horner's Syndrome
The biphasic intraocular pressure response of rabbits to epinephrine
 The biphasic intraocular pressure response of rabbits to epinephrine Maurice E. Langham and Gunter K. Krieglstein A study has been made of the pupillary and intraocular pressure responses of conscious
The biphasic intraocular pressure response of rabbits to epinephrine Maurice E. Langham and Gunter K. Krieglstein A study has been made of the pupillary and intraocular pressure responses of conscious
EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED-RELEASE ACETAZOLAMIDE*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 31. From the EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED-RELEASE ACETAZOLAMIDE*t BY CARLOS MESTRE, MILES A. GALIN, AND JOHN M. McLEANt Department of Surgery (Ophthalmology) of The New York Hospital-Cornell
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 31. From the EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED-RELEASE ACETAZOLAMIDE*t BY CARLOS MESTRE, MILES A. GALIN, AND JOHN M. McLEANt Department of Surgery (Ophthalmology) of The New York Hospital-Cornell
Chronicity. Narrow Minded. Course Outline. Acute angle closure. Subacute angle closure. Classification of Angle Closure 5/19/2014
 Chronicity Narrow Minded The management of narrow angles in the optometric practice Acute Subacute Chronic Aaron McNulty, OD, FAAO Course Outline Classification of Angle Closure Evaluation of narrow angles
Chronicity Narrow Minded The management of narrow angles in the optometric practice Acute Subacute Chronic Aaron McNulty, OD, FAAO Course Outline Classification of Angle Closure Evaluation of narrow angles
BETAGAN Allergan Levobunolol HCl Glaucoma Therapy
 BETAGAN Allergan Levobunolol HCl Glaucoma Therapy Action And Clinical Pharmacology: Levobunolol is a noncardioselective beta- adrenoceptor antagonist, equipotent at both beta1 and beta2 receptors. Levobunolol
BETAGAN Allergan Levobunolol HCl Glaucoma Therapy Action And Clinical Pharmacology: Levobunolol is a noncardioselective beta- adrenoceptor antagonist, equipotent at both beta1 and beta2 receptors. Levobunolol
Patients with ocular hypertension or
 ... REPORTS... An Economic Analysis of Switching to Latanoprost from a β-blocker or Adding Brimonidine or Latanoprost to a β-blocker in Open-Angle Glaucoma or Ocular Hypertension William C. Stewart, MD;
... REPORTS... An Economic Analysis of Switching to Latanoprost from a β-blocker or Adding Brimonidine or Latanoprost to a β-blocker in Open-Angle Glaucoma or Ocular Hypertension William C. Stewart, MD;
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Comparison of the Early Effects of Brimonidine and Apraclonidine as Topical Ocular Hypotensive Agents
 Comparison of the Early Effects of Brimonidine and Apraclonidine as Topical Ocular Hypotensive Agents Todd L. Maus, MD; Cherie Nau; Richard F. Brubaker, MD CLINICAL SCIENCES Objective: To compare the mechanism
Comparison of the Early Effects of Brimonidine and Apraclonidine as Topical Ocular Hypotensive Agents Todd L. Maus, MD; Cherie Nau; Richard F. Brubaker, MD CLINICAL SCIENCES Objective: To compare the mechanism
The Systemic Effect Of Topical Timolol On Some Cardiovascular Parameters In Owerri Municipality
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 The Systemic Effect Of Topical Timolol On Some Cardiovascular Parameters In Owerri Municipality G Oze, M Emegwamuo, P Eleanya, H
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 The Systemic Effect Of Topical Timolol On Some Cardiovascular Parameters In Owerri Municipality G Oze, M Emegwamuo, P Eleanya, H
Precipitation of angle closure
 Brit. Y. Ophthal. (1974) 58, 46 Precipitation of angle closure R. MAPSTON St. Paul's ve Hospital, Old Hall Street, Liverpool, L3 9PF Previous papers (Mapstone, I974a, b) have shown that angle closure (AC)
Brit. Y. Ophthal. (1974) 58, 46 Precipitation of angle closure R. MAPSTON St. Paul's ve Hospital, Old Hall Street, Liverpool, L3 9PF Previous papers (Mapstone, I974a, b) have shown that angle closure (AC)
Goals. Glaucoma PARA PEARL TO DO. Vision Loss with Glaucoma
 Glaucoma Janet R. Fett, OD Drs. Kincaid, Fett and Tharp So Sioux City, NE eyewear21@hotmail.com Goals Understand Glaucoma Disease process Understand how your data (objective and subjective) assists in
Glaucoma Janet R. Fett, OD Drs. Kincaid, Fett and Tharp So Sioux City, NE eyewear21@hotmail.com Goals Understand Glaucoma Disease process Understand how your data (objective and subjective) assists in
Role of Initial Preoperative Medical Management in Controlling Post-Operative Anterior Uveitis in Patients of Phacomorphic Glaucoma
 Original Article Role of Initial Preoperative Medical Management in Controlling Post-Operative Anterior Uveitis in Patients of Phacomorphic Glaucoma Irfan Qayyum Malik, M. Moin, A. Rehman, Mumtaz Hussain
Original Article Role of Initial Preoperative Medical Management in Controlling Post-Operative Anterior Uveitis in Patients of Phacomorphic Glaucoma Irfan Qayyum Malik, M. Moin, A. Rehman, Mumtaz Hussain
Influences on the density of /3-adrenergic receptors in the cornea and iris-ciliary body of the rabbit
 Influences on the density of /3-adrenergic receptors in the cornea and iris-ciliary body of the rabbit Arthur H. Neufeld, Kathleen A. Zatvistowski, Ellen D. Page, and B. Britt Bromberg By measurement of
Influences on the density of /3-adrenergic receptors in the cornea and iris-ciliary body of the rabbit Arthur H. Neufeld, Kathleen A. Zatvistowski, Ellen D. Page, and B. Britt Bromberg By measurement of
Family studies in glaucoma
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (I 974) 58, 529 Family studies in glaucoma E. S. PERKINS Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London There is now strong evidence for a genetic basis to glaucoma. Numerous family
Brit. j. Ophthal. (I 974) 58, 529 Family studies in glaucoma E. S. PERKINS Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London There is now strong evidence for a genetic basis to glaucoma. Numerous family
CORNEO-SCLERAL TONOGRAPHY* t BY T. H. HODGSON AND R. K. MACDONALD From the Department of Ophthalmology, University of Toronto, Canada
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1957) 41, 301. CORNEO-SCLERAL TONOGRAPHY* t BY T. H. HODGSON AND R. K. MACDONALD From the Department of Ophthalmology, University of Toronto, Canada THAT pressure exerted on the eyeball
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1957) 41, 301. CORNEO-SCLERAL TONOGRAPHY* t BY T. H. HODGSON AND R. K. MACDONALD From the Department of Ophthalmology, University of Toronto, Canada THAT pressure exerted on the eyeball
Latanoprost 0.005% v/s Timolol Maleate 0.5% Pressure Lowering Effect in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
 Original Article Latanoprost 0.005% v/s Timolol Maleate 0.5% Pressure Lowering Effect in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Arshad Ali Lodhi, Khalid Iqbal Talpur, Mahtab Alam Khanzada Pak J Ophthalmol 2008, Vol.
Original Article Latanoprost 0.005% v/s Timolol Maleate 0.5% Pressure Lowering Effect in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Arshad Ali Lodhi, Khalid Iqbal Talpur, Mahtab Alam Khanzada Pak J Ophthalmol 2008, Vol.
The Uniocular Drug Trial and Second-Eye Response to Glaucoma Medications
 The Uniocular Drug Trial and Second-Eye Response to Glaucoma Medications Tony Realini, MD, 1 Robert D. Fechtner, MD, 2 Sean-Paul Atreides, MD, 3 Stephen Gollance, MD 2 Purpose: To determine if the intraocular
The Uniocular Drug Trial and Second-Eye Response to Glaucoma Medications Tony Realini, MD, 1 Robert D. Fechtner, MD, 2 Sean-Paul Atreides, MD, 3 Stephen Gollance, MD 2 Purpose: To determine if the intraocular
Prostaglandin F2,-isopropylester eye drops:
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1989, 73, 419-426 Prostaglandin F2,-isopropylester eye drops: effects in normal human eyes* JORGEN VILLUMSEN AND ALBERT ALM From the Department of Ophthalmology, University
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1989, 73, 419-426 Prostaglandin F2,-isopropylester eye drops: effects in normal human eyes* JORGEN VILLUMSEN AND ALBERT ALM From the Department of Ophthalmology, University
Building a Major Ophthalmic Pharmaceutical Company. Aerie Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Company Overview June 2-3, 2015
 Building a Major Ophthalmic Pharmaceutical Company Aerie Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Company Overview June 2-3, 2015 1 Important Information Any discussion of the potential use or expected success of our product
Building a Major Ophthalmic Pharmaceutical Company Aerie Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Company Overview June 2-3, 2015 1 Important Information Any discussion of the potential use or expected success of our product
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH. ratio-levobunolol. Levobunolol Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution 0.25% and 0.5% Glaucoma Therapy
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH ratio-levobunolol Levobunolol Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution 0.25% and 0.5% Glaucoma Therapy Noncardioselective beta-adrenoceptor blocking agent Teva Canada Limited DATE OF PREPARATION:
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH ratio-levobunolol Levobunolol Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution 0.25% and 0.5% Glaucoma Therapy Noncardioselective beta-adrenoceptor blocking agent Teva Canada Limited DATE OF PREPARATION:
Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma
 www.eyesurgeonlondon.co.uk Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Glaucoma is a condition in which there is damage to the optic nerve. This nerve carries visual signals from the eye to the brain.
www.eyesurgeonlondon.co.uk Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Glaucoma is a condition in which there is damage to the optic nerve. This nerve carries visual signals from the eye to the brain.
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Pachymetry Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Pachymetry Professional Institutional Original Effective Date: March 11, 2004 Original Effective
Pachymetry Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Pachymetry Professional Institutional Original Effective Date: March 11, 2004 Original Effective
Atenolol eye drops in glaucoma:
 Atenolol eye drops in glaucoma: a double-masked, controlled study British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1977, 61, 349-353 CALBERT. PHLLPS,' SHELA M. GORE,2 MARGARET J. MACDONALD, AND PATRCA M. CULLEN' 'From
Atenolol eye drops in glaucoma: a double-masked, controlled study British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1977, 61, 349-353 CALBERT. PHLLPS,' SHELA M. GORE,2 MARGARET J. MACDONALD, AND PATRCA M. CULLEN' 'From
Original Article. Abstract. Introduction. C Olali, G Malietzis, S Ahmed, E Samaila 1, M Gupta
 Original Article Real-life experience study of the safety and efficacy of travoprost 0.004% / timoptol 0.50% fixed combination ophthalmic solution in intraocular pressure control C Olali, G Malietzis,
Original Article Real-life experience study of the safety and efficacy of travoprost 0.004% / timoptol 0.50% fixed combination ophthalmic solution in intraocular pressure control C Olali, G Malietzis,
Intro to Glaucoma/2006
 Intro to Glaucoma/2006 Managing Patients with Glaucoma is Exciting Interesting Challenging But can often be frustrating! Clinical Challenges To identify patients with risk factors for possible glaucoma.
Intro to Glaucoma/2006 Managing Patients with Glaucoma is Exciting Interesting Challenging But can often be frustrating! Clinical Challenges To identify patients with risk factors for possible glaucoma.
A genetic basis has been postulated for
 Intraocular pressure response to topical corticosteroids Bernard Becker The intraocular pressure response to topical betamethasone appears to be genetically determined. A study of patients with primary
Intraocular pressure response to topical corticosteroids Bernard Becker The intraocular pressure response to topical betamethasone appears to be genetically determined. A study of patients with primary
Effects of Pilocarpine, Salbutamol, and Timolol on Aqueous Humor Formation in Cynomolgus Monkeys
 Effects of Pilocarpine, Salbutamol, and Timolol on Humor Formation in Cynomolgus Monkeys Hiroaki Miichi ond Shigefoshi Nagaraki The of aqueous was determined in the cynomolgus monkey eyes by a tracer dilution
Effects of Pilocarpine, Salbutamol, and Timolol on Humor Formation in Cynomolgus Monkeys Hiroaki Miichi ond Shigefoshi Nagaraki The of aqueous was determined in the cynomolgus monkey eyes by a tracer dilution
Effect of Dexomethasone on Corneol Endotheliol Function in Fuchs' Dystrophy
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 29, No. 3, March 1988 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Effect of Dexomethasone on Corneol Endotheliol Function in Fuchs'
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 29, No. 3, March 1988 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Effect of Dexomethasone on Corneol Endotheliol Function in Fuchs'
Glaucoma. Glaucoma. Glaucoma. Trevor Arnold, MS, DVM, DACVO
 Glaucoma Trevor Arnold, MS, DVM, DACVO Glaucoma Physiology of Aqueous Humor Produced in the ciliary body Flows out the iridocorneal angle and ciliary cleft High intraocular pressures are caused by a decreased
Glaucoma Trevor Arnold, MS, DVM, DACVO Glaucoma Physiology of Aqueous Humor Produced in the ciliary body Flows out the iridocorneal angle and ciliary cleft High intraocular pressures are caused by a decreased
Treatments on the Horizon
 Latanoprostene bunod (Vesneo) Treatments on the Horizon Dominick L Opitz, OD, FAAO Associate Professor Illinois College of Optometry Valeant (B+L) Nitrous oxide-donating prostaglandin F2-alpha analogue
Latanoprostene bunod (Vesneo) Treatments on the Horizon Dominick L Opitz, OD, FAAO Associate Professor Illinois College of Optometry Valeant (B+L) Nitrous oxide-donating prostaglandin F2-alpha analogue
BRIMOPRESS-T EYE DROPS. COMPOSITION Each ml of BRIMOPRESS-T EYE DROPS contains. Brimonidine Tartarate 0.2% Timolol Maleate 0.5%
 BRIMOPRESS-T EYE DROPS COMPOSITION Each ml of BRIMOPRESS-T EYE DROPS contains Brimonidine Tartarate 0.2% Timolol Maleate 0.5% BRIMOPRESS-T ophthalmic solution is a combination of Brimonidine Tartrate,
BRIMOPRESS-T EYE DROPS COMPOSITION Each ml of BRIMOPRESS-T EYE DROPS contains Brimonidine Tartarate 0.2% Timolol Maleate 0.5% BRIMOPRESS-T ophthalmic solution is a combination of Brimonidine Tartrate,
Elements for a public summary. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology The term ocular hypertension usually refers to any situation in which the pressure inside the eye, called intraocular pressure,
VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology The term ocular hypertension usually refers to any situation in which the pressure inside the eye, called intraocular pressure,
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CORNEAL ULTRASOUND PACHYMETRY. POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Technology Assessment
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CORNEAL ULTRASOUND,, PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CORNEAL ULTRASOUND,, PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
A LITTLE ANATOMY. three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera. 2. middle - uvea. anterior - iris,ciliary body. posterior - choroid
 GLAUCOMA A LITTLE ANATOMY three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera 2. middle - uvea anterior - iris,ciliary body posterior - choroid connection at the pars plana between post and ant uvea 3. retina
GLAUCOMA A LITTLE ANATOMY three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera 2. middle - uvea anterior - iris,ciliary body posterior - choroid connection at the pars plana between post and ant uvea 3. retina
KEY MESSAGES. Details of the evidence supporting these recommendations can be found in the above CPG, available on the following websites:
 QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS KEY MESSAGES 1. Glaucoma is a chronic eye disease that damages the optic nerve, & can result in serious vision loss and irreversible blindness. 2. Glaucoma diagnosis
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS KEY MESSAGES 1. Glaucoma is a chronic eye disease that damages the optic nerve, & can result in serious vision loss and irreversible blindness. 2. Glaucoma diagnosis
The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3%
 The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3% of our population age > 40 have glaucoma In the past:
The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3% of our population age > 40 have glaucoma In the past:
EFFECTS OF PREDNISOLONE EYE DROPS*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 51, 398 EFFECTS OF PREDNISOLONE EYE DROPS*t A TRIAL OF THE EFFECTS OF PREDNISOLONE PHOSPHATE EYE DROPS ON THE INTRA-OCULAR PRESSURE OF NORMAL VOLUNTEERS BY T. G. RAMSELL, W. TRILLWOOD,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1967) 51, 398 EFFECTS OF PREDNISOLONE EYE DROPS*t A TRIAL OF THE EFFECTS OF PREDNISOLONE PHOSPHATE EYE DROPS ON THE INTRA-OCULAR PRESSURE OF NORMAL VOLUNTEERS BY T. G. RAMSELL, W. TRILLWOOD,
Aqueous Flow in Humans After Adrenalectomy
 Aqueous Flow in Humans After Adrenalectomy Todd L. Maus,* William F. Young, Jr.,"\ and Richard F. Brubaker* Purpose. This study was performed to determine if the circadian rhythm of aqueous humor formation
Aqueous Flow in Humans After Adrenalectomy Todd L. Maus,* William F. Young, Jr.,"\ and Richard F. Brubaker* Purpose. This study was performed to determine if the circadian rhythm of aqueous humor formation
Provocative testing for primary open-angle glaucoma in "senior citizens" Norman Ballin* and Bernard Becker
 Provocative testing for primary open-angle glaucoma in "senior citizens" Norman Ballin* and Bernard Becker A group of "senior citizens" was studied with respect to applanation pressures, water-provocative
Provocative testing for primary open-angle glaucoma in "senior citizens" Norman Ballin* and Bernard Becker A group of "senior citizens" was studied with respect to applanation pressures, water-provocative
The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
 A Study of the Safety and Efficacy of Travoprost 0.004%/Timolol 0.5% Ophthalmic Solution Compared to Latanoprost 0.005% and Timolol 0.5% Dosed Concomitantly in Patients with Open-Angle Glaucoma or Ocular
A Study of the Safety and Efficacy of Travoprost 0.004%/Timolol 0.5% Ophthalmic Solution Compared to Latanoprost 0.005% and Timolol 0.5% Dosed Concomitantly in Patients with Open-Angle Glaucoma or Ocular
A Short-term Study of the Additive Effect of Latanoprost 0.005% and Brimonidine 0.2%
 A Short-term Study of the Additive Effect of Latanoprost 0.005% and Brimonidine 0.2% Haydar Erdoğan, İlker Toker, Mustafa Kemal Arıcı, Ahmet Aygen and Ayşen Topalkara Department of Ophthalmology, School
A Short-term Study of the Additive Effect of Latanoprost 0.005% and Brimonidine 0.2% Haydar Erdoğan, İlker Toker, Mustafa Kemal Arıcı, Ahmet Aygen and Ayşen Topalkara Department of Ophthalmology, School
Author s Affiliation. Original Article
 Original Article Comparison Between 0.5 Timolol Maleate And 0.2 Brimonidine Tartrate In Controlling Increase In Intraocular Pressure After Neodymium: Yttrium-Aluminium-Garnet Laser Iridotomy Author s Affiliation
Original Article Comparison Between 0.5 Timolol Maleate And 0.2 Brimonidine Tartrate In Controlling Increase In Intraocular Pressure After Neodymium: Yttrium-Aluminium-Garnet Laser Iridotomy Author s Affiliation
LEUKAEMIA*t INFILTRATION OF THE IRIS IN CHRONIC LYMPHATIC. pattemn * Received for pubiication November io, i967.
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 781 INFILTRATION OF THE IRIS IN CHRONIC LYMPHATIC LEUKAEMIA*t BY BRIAN MARTIN The General Infirmary, Leeds OCULAR involvement is common in the leukaemias though the anterior
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 781 INFILTRATION OF THE IRIS IN CHRONIC LYMPHATIC LEUKAEMIA*t BY BRIAN MARTIN The General Infirmary, Leeds OCULAR involvement is common in the leukaemias though the anterior
Inadequate diagnostic value of the
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (1974) 58, 55 Inadequate diagnostic value of the water-drinking test J. A. ROTH Department of Experimental Ophthalmology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London There is a large
Brit. j. Ophthal. (1974) 58, 55 Inadequate diagnostic value of the water-drinking test J. A. ROTH Department of Experimental Ophthalmology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London There is a large
Aqueous Humor Messengers in the Transient Decrease of Intraocular Pressure After Ganglionectomy
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 33, No. 11, October 1992 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Aqueous Humor Messengers in the Transient Decrease of Intraocular
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 33, No. 11, October 1992 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Aqueous Humor Messengers in the Transient Decrease of Intraocular
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Patients with Open-Angle Glaucoma or Ocular Hypertension
 3 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Isopto Carpine safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Isopto Carpine. Isopto
3 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Isopto Carpine safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Isopto Carpine. Isopto
Written by Administrator Wednesday, 13 January :27 - Last Updated Thursday, 21 January :34
 angle closure glaucoma A type of glaucoma caused by a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure. Occurs when the pupil enlarges too much or too quickly, and the outer edge of the iris blocks the eye s drainage
angle closure glaucoma A type of glaucoma caused by a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure. Occurs when the pupil enlarges too much or too quickly, and the outer edge of the iris blocks the eye s drainage
Original Article Intraocular Pressure Lowering Effect Pak Armed Forces Med J 2015; 65(1): 94-8
 Original Article Intraocular Pressure Lowering Effect Pak Armed Forces Med J 2015; 65(1): 94-8 COMPARISON OF INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE LOWERING EFFECT OF LATANOPROST AND TIMOLOL COMBINATION VERSUS LATANOPROST
Original Article Intraocular Pressure Lowering Effect Pak Armed Forces Med J 2015; 65(1): 94-8 COMPARISON OF INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE LOWERING EFFECT OF LATANOPROST AND TIMOLOL COMBINATION VERSUS LATANOPROST
T O Normal male 0 Normal female II U* Affected male % t7 8 t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I974) 58, 536 Familial glaucoma In nine generations of a South Hampshire family J. P. MARTIN AND E. C. ZORAB Southampton Eye Hospital A. Zorab (1932) reported a family suffering from
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I974) 58, 536 Familial glaucoma In nine generations of a South Hampshire family J. P. MARTIN AND E. C. ZORAB Southampton Eye Hospital A. Zorab (1932) reported a family suffering from
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 28 May 2008
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 28 May 2008 COSOPT 20 mg/5 mg/ml, eye drops, solution in single dose container Box of 60 0.2 ml single dose containers
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 28 May 2008 COSOPT 20 mg/5 mg/ml, eye drops, solution in single dose container Box of 60 0.2 ml single dose containers
Effect of Timolol Maleate on the Retinal Circulation of Human Eyes with Ocular Hypertension
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 31, No. 3, March 1990 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Effect of Maleate on the Retinal Circulation of Human Eyes with Ocular
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 31, No. 3, March 1990 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Effect of Maleate on the Retinal Circulation of Human Eyes with Ocular
Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015
 Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015 Jimmy Lai Clinical Professor Department of Ophthalmology The University of Hong Kong 1 Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma PACG
Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015 Jimmy Lai Clinical Professor Department of Ophthalmology The University of Hong Kong 1 Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma PACG
Provocative tests in closed-angle glaucoma
 Brit. 7. Ophthal. (I976) 6o, I 5 Provocative tests in closed-angle glaucoma R. MAPSTONE From St Paul's Eye Hospital, Liverpool The absence of a provocative test with proved predictive value, in s at risk
Brit. 7. Ophthal. (I976) 6o, I 5 Provocative tests in closed-angle glaucoma R. MAPSTONE From St Paul's Eye Hospital, Liverpool The absence of a provocative test with proved predictive value, in s at risk
T.opically applied corticoids were shown to produce in man an increase in intraocular pressure, a reduction in outflow facility,
 Aqueous outflow facility in monkeys and the effect of topical corticoids Mansour F. Armaly The ocular effects of topically applied dexamethasone 21-phosphate and subconjunctivally administered methylprednisolone
Aqueous outflow facility in monkeys and the effect of topical corticoids Mansour F. Armaly The ocular effects of topically applied dexamethasone 21-phosphate and subconjunctivally administered methylprednisolone
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
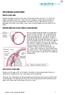 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
LENS INDUCED GLAUCOMA
 LENS INDUCED GLAUCOMA PRESENTER P SHILPA RAVI 2 ND YEAR PG DEPT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY LENS INDUCED GLAUCOMA It is a form of secondary glaucoma where intraocular pressure is raised due to disorder in crystalline
LENS INDUCED GLAUCOMA PRESENTER P SHILPA RAVI 2 ND YEAR PG DEPT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY LENS INDUCED GLAUCOMA It is a form of secondary glaucoma where intraocular pressure is raised due to disorder in crystalline
Efficacy and Safety of Latanoprost Eye Drops for Glaucoma Treatment: A 1-Year Study in Japan
 Efficacy and Safety of Latanoprost Eye Drops for Glaucoma Treatment: A 1-Year Study in Japan Masanobu Suzuki,* Hiromu K. Mishima,* Kanjiro Masuda, Makoto Araie, Yoshiaki Kitazawa and Ikuo Azuma *Department
Efficacy and Safety of Latanoprost Eye Drops for Glaucoma Treatment: A 1-Year Study in Japan Masanobu Suzuki,* Hiromu K. Mishima,* Kanjiro Masuda, Makoto Araie, Yoshiaki Kitazawa and Ikuo Azuma *Department
Abnormal intraocular pressure control
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1980, 64, 845-851 Abnormal intraocular pressure control in systemic hypertension and diabetic mellitus BILLIE I. WILLIAMS,' W. S. PEART,1 AND E. LETLEY2 From the 'Medical
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1980, 64, 845-851 Abnormal intraocular pressure control in systemic hypertension and diabetic mellitus BILLIE I. WILLIAMS,' W. S. PEART,1 AND E. LETLEY2 From the 'Medical
A,kCetazolamide lowers intraocular pressure
 Ocular and systemic effects of acetazolamide in nephrectomized rabbits Zvi Friedman,* Theodore Krupin, and Bernard Becker The effects of acetazolamide on intraocular pressure (IOP) were studied on rabbits
Ocular and systemic effects of acetazolamide in nephrectomized rabbits Zvi Friedman,* Theodore Krupin, and Bernard Becker The effects of acetazolamide on intraocular pressure (IOP) were studied on rabbits
Department of Ophthalmology
 Department of Ophthalmology Period : 02/July/18 to 30/August/18 Semester : 7 th Semester Lecture Lesson Plan Sr. Date Topic Lesson plan Name of Faculty No. 1 02.07.18 Lens- Lens-Anatomy, Classification
Department of Ophthalmology Period : 02/July/18 to 30/August/18 Semester : 7 th Semester Lecture Lesson Plan Sr. Date Topic Lesson plan Name of Faculty No. 1 02.07.18 Lens- Lens-Anatomy, Classification
Dr Taha Abdel Monein Labib Professor of Eye Surgery Cairo University.
 Dr Taha Abdel Monein Labib Professor of Eye Surgery Cairo University. Although the clinical picture of glaucoma is well described, the exact mechanism leading to this specific type of damage to the optic
Dr Taha Abdel Monein Labib Professor of Eye Surgery Cairo University. Although the clinical picture of glaucoma is well described, the exact mechanism leading to this specific type of damage to the optic
Closed Angle Glaucoma Or Narrow Angle Glaucoma. What s is a closed angle type of glaucoma,
 Closed Angle Glaucoma Or Narrow Angle Glaucoma What s is a closed angle type of glaucoma, This is where the iris is found to be blocking the drainage of the eye through the trabecular meshwork. The eye
Closed Angle Glaucoma Or Narrow Angle Glaucoma What s is a closed angle type of glaucoma, This is where the iris is found to be blocking the drainage of the eye through the trabecular meshwork. The eye
53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note.
 Case 1 Normal Tension Glaucoma 53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note. Table 1. Right Eye Left Eye Visual acuity 6/6 6/6 Ishihara
Case 1 Normal Tension Glaucoma 53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note. Table 1. Right Eye Left Eye Visual acuity 6/6 6/6 Ishihara
Human ciliary process adrenergic receptor: pharmacological characterization. James A. Nathanson
 Human ciliary process adrenergic receptor: pharmacological characterization James A. Nathanson To better understand the nature of interaction of various amines with adrenergic receptors in the human ciliary
Human ciliary process adrenergic receptor: pharmacological characterization James A. Nathanson To better understand the nature of interaction of various amines with adrenergic receptors in the human ciliary
Spontaneous Intraocular Pressure Reduction in Normal-Tension Glaucoma and Associated Clinical Factors
 CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Spontaneous Intraocular Pressure Reduction in Normal-Tension Glaucoma and Associated Clinical Factors Akihiro Oguri, Tetsuya Yamamoto and Yoshiaki Kitazawa Department of Ophthalmology,
CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Spontaneous Intraocular Pressure Reduction in Normal-Tension Glaucoma and Associated Clinical Factors Akihiro Oguri, Tetsuya Yamamoto and Yoshiaki Kitazawa Department of Ophthalmology,
Haemorrhagic glaucoma
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (I97I) 55, 444 Haemorrhagic glaucoma Comparative study in diabetic and nondiabetic patients P. H. MADSEN From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Internal Medicine, the University Hospital,
Brit. j. Ophthal. (I97I) 55, 444 Haemorrhagic glaucoma Comparative study in diabetic and nondiabetic patients P. H. MADSEN From the Departments of Ophthalmology and Internal Medicine, the University Hospital,
Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation
 Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation Masaru Inatani*, Hidenobu Tanihara, Takahito Muto*, Megumi Honjo*,
Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation Masaru Inatani*, Hidenobu Tanihara, Takahito Muto*, Megumi Honjo*,
Cases CFEH. CFEH Facebook Case #4
 CFEH Cases CFEH Facebook Case #4 A 42 year old female has noticed a floater in her left eye for many years but no flashes. She also reports hazy vision in this eye that has been present all her life. She
CFEH Cases CFEH Facebook Case #4 A 42 year old female has noticed a floater in her left eye for many years but no flashes. She also reports hazy vision in this eye that has been present all her life. She
Is Posner Schlossman Syndrome Benign?
 Is Posner Schlossman Syndrome Benign? Aliza Jap, FRCS (G), 1 Meenakshi Sivakumar, FRCS (Ed), M Med (Ophth), 2, Soon-Phaik Chee, FRCS (Ed), FRCOphth 2 Purpose: To determine the clinical course of patients
Is Posner Schlossman Syndrome Benign? Aliza Jap, FRCS (G), 1 Meenakshi Sivakumar, FRCS (Ed), M Med (Ophth), 2, Soon-Phaik Chee, FRCS (Ed), FRCOphth 2 Purpose: To determine the clinical course of patients
Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) is a major risk factor for
 Glaucoma Twenty-Four Hour Pattern of Intraocular Pressure in Untreated Patients with Ocular Hypertension Tomas M. Grippo, 1,2 John H. K. Liu, 1 Nazlee Zebardast, 2 Taylor B. Arnold, 3 Grant H. Moore, 1
Glaucoma Twenty-Four Hour Pattern of Intraocular Pressure in Untreated Patients with Ocular Hypertension Tomas M. Grippo, 1,2 John H. K. Liu, 1 Nazlee Zebardast, 2 Taylor B. Arnold, 3 Grant H. Moore, 1
APPROVED PACKAGE INSERT FOR XALATAN EYE DROPS. Each millilitre contains latanoprost 50 µg and benzalkonium chloride 0,02 % m/v as preservative.
 SCHEDULING STATUS: S4 APPROVED PACKAGE INSERT FOR XALATAN EYE DROPS PROPRIETARY NAME (and dosage form): XALATAN Eye Drops COMPOSITION: Each millilitre contains latanoprost 50 µg and benzalkonium chloride
SCHEDULING STATUS: S4 APPROVED PACKAGE INSERT FOR XALATAN EYE DROPS PROPRIETARY NAME (and dosage form): XALATAN Eye Drops COMPOSITION: Each millilitre contains latanoprost 50 µg and benzalkonium chloride
Serotonin-stimulated cyclic AMP synthesis in the rabbit corneal epithelium
 Serotonin-stimulated cyclic AMP synthesis in the rabbit corneal epithelium Arthur H. Neufeld, Sally. Ledgard, Marcia M. Jumblatt, and Stephen D. Klyce* Serotonin increases the level of cyclic AMP in incubated
Serotonin-stimulated cyclic AMP synthesis in the rabbit corneal epithelium Arthur H. Neufeld, Sally. Ledgard, Marcia M. Jumblatt, and Stephen D. Klyce* Serotonin increases the level of cyclic AMP in incubated
Glaucoma Disease Progression Role of Intra Ocular Pressure. Is Good Enough, Low Enough?
 Glaucoma Disease Progression Role of Intra Ocular Pressure Is Good Enough, Low Enough? Glaucoma Diseases Progression Key Considerations Good number of patients may be diagnosed only after some damage the
Glaucoma Disease Progression Role of Intra Ocular Pressure Is Good Enough, Low Enough? Glaucoma Diseases Progression Key Considerations Good number of patients may be diagnosed only after some damage the
Divakar Gupta Glaucoma Fellow, Duke Eye Center 5/14/16
 Divakar Gupta Glaucoma Fellow, Duke Eye Center 5/14/16 Pathophysiology of glaucoma Consider risk factors of glaucoma Understand the side effects of glaucoma medications Diagnostic testing Leading cause
Divakar Gupta Glaucoma Fellow, Duke Eye Center 5/14/16 Pathophysiology of glaucoma Consider risk factors of glaucoma Understand the side effects of glaucoma medications Diagnostic testing Leading cause
Occulohypotensive Effect Of Torasamide In Experimental Glaucoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pharmacology Volume 5 Number 2 Occulohypotensive Effect Of Torasamide In Experimental Glaucoma S Panchal, A Mehta, D Santani Citation S Panchal, A Mehta, D Santani.. The
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pharmacology Volume 5 Number 2 Occulohypotensive Effect Of Torasamide In Experimental Glaucoma S Panchal, A Mehta, D Santani Citation S Panchal, A Mehta, D Santani.. The
In vitro determination of the ability of drugs to bind to adrenergic receptors. Arthur H. Neufeld and Ellen D. Page
 In vitro determination of the ability of drugs to bind to adrenergic receptors Arthur H. Neufeld and Ellen D. Page Alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors were studied by measuring the binding of s H-dihydroergocryptine
In vitro determination of the ability of drugs to bind to adrenergic receptors Arthur H. Neufeld and Ellen D. Page Alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors were studied by measuring the binding of s H-dihydroergocryptine
Glaucoma: target intraocular pressures and current treatments James McAllister FRCS, FRCOphth
 Glaucoma: target intraocular pressures and current treatments James McAllister FRCS, FRCOphth Skyline Imaging Ltd Our Drug review of glaucoma management describes the use of target intraocular pressures
Glaucoma: target intraocular pressures and current treatments James McAllister FRCS, FRCOphth Skyline Imaging Ltd Our Drug review of glaucoma management describes the use of target intraocular pressures
THE TRABECTOME IS A NOVEL SURGICAL DEVICE USED
 Delayed-Onset Symptomatic Hyphema After Ab Interno Trabeculotomy Surgery YACHNA AHUJA, MEHRDAD MALIHI, AND ARTHUR J. SIT PURPOSE: To describe patients who have experienced delayed-onset hyphema after ab
Delayed-Onset Symptomatic Hyphema After Ab Interno Trabeculotomy Surgery YACHNA AHUJA, MEHRDAD MALIHI, AND ARTHUR J. SIT PURPOSE: To describe patients who have experienced delayed-onset hyphema after ab
N W KNOW. What You Need to Know. What You Know About Glaucoma Could Save Your Sight
 What You Need to Know is the second leading cause of blindness around the world, so it is important to understand its significance and treatment options. While glaucoma is not curable, there are several
What You Need to Know is the second leading cause of blindness around the world, so it is important to understand its significance and treatment options. While glaucoma is not curable, there are several
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
ROLE OF ORAL GLYCEROL IN GLAUCOMA*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 660 ROLE OF ORAL GLYCEROL IN GLAUCOMA* BY P. AWASTHI AND S. N. SRIVASTAVA Department of Ophthalmology,_Sarojni Naidu Medical College, Agra, India IN cases of acute glaucoma
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 660 ROLE OF ORAL GLYCEROL IN GLAUCOMA* BY P. AWASTHI AND S. N. SRIVASTAVA Department of Ophthalmology,_Sarojni Naidu Medical College, Agra, India IN cases of acute glaucoma
Selective laser trabeculoplasty v argon laser trabeculoplasty: a prospective randomised clinical trial
 718 University Of Ottawa Eye Institute, Ottawa Hospital, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada K F Damji K C Shah W J Rock H S Bains W G Hodge Correspondence to: Dr Karim F Damji, University Of Ottawa Eye Institute,
718 University Of Ottawa Eye Institute, Ottawa Hospital, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada K F Damji K C Shah W J Rock H S Bains W G Hodge Correspondence to: Dr Karim F Damji, University Of Ottawa Eye Institute,
chamber pigment in the anterior L beration of iris phenylephrine hydrochloride solution. After instillation of io per cent.
 Brit.. Ophthal. (I 97 I) 55, 544 L beration of iris chamber After instillation of io per cent. hydrochloride solution J. L. AGGARWAL AND B. BEVERIDGE Wolverhampton and Midland Counties Eye Infirmary pigment
Brit.. Ophthal. (I 97 I) 55, 544 L beration of iris chamber After instillation of io per cent. hydrochloride solution J. L. AGGARWAL AND B. BEVERIDGE Wolverhampton and Midland Counties Eye Infirmary pigment
Dr. D. Y. Patil Medical College, Pimpri, Pune
 Dr. D. Y. Patil Medical College, Pimpri, Pune - 411 018 Period : 04/July/16 to 22/September/16 Semester : 7 th Semester Department : Ophthalmology Lecture Lesson Plan Sr No Date Topic Learning objectives
Dr. D. Y. Patil Medical College, Pimpri, Pune - 411 018 Period : 04/July/16 to 22/September/16 Semester : 7 th Semester Department : Ophthalmology Lecture Lesson Plan Sr No Date Topic Learning objectives
Drug therapy of glaucoma
 288 GILLIAN D. PATERSON AND GAVIN PATERSON From the Glaucoma Unit, Moorfields Eye Hospital, High Holborn Branch, London, and the Department of Pharmacology, King's College, University of London Of the
288 GILLIAN D. PATERSON AND GAVIN PATERSON From the Glaucoma Unit, Moorfields Eye Hospital, High Holborn Branch, London, and the Department of Pharmacology, King's College, University of London Of the
Classification and management of primary angle closure disease
 Classification and management of primary angle closure disease B. Shantha and Rathini Lilian David Major Review Correspondence: B. Shantha, Director, Smt Jadhavbai Nathmal Singhvee Glaucoma Service, Sankara
Classification and management of primary angle closure disease B. Shantha and Rathini Lilian David Major Review Correspondence: B. Shantha, Director, Smt Jadhavbai Nathmal Singhvee Glaucoma Service, Sankara
Training Checking Vision Tonometry
 Training 101-2 Checking Vision Tonometry Checking Vision The classic example of an eye chart is the Snellen eye chart, in general they show 11 rows of capital letters. The top row contains one letter (usually
Training 101-2 Checking Vision Tonometry Checking Vision The classic example of an eye chart is the Snellen eye chart, in general they show 11 rows of capital letters. The top row contains one letter (usually
Effects of Adrenergic Agents and Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors on Outflow Facility and Cell Shape of Bovine Trabecular Meshwork
 ELSEVIER Effects of Adrenergic Agents and Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors on Outflow Facility and Cell Shape of Bovine Trabecular Meshwork Ryo Suzuki, *+ Levon N. Karageuzian, t Edmund V. Creant and P. John
ELSEVIER Effects of Adrenergic Agents and Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors on Outflow Facility and Cell Shape of Bovine Trabecular Meshwork Ryo Suzuki, *+ Levon N. Karageuzian, t Edmund V. Creant and P. John
