Catherine Otten MD. September 27 th, Pediatric Headache. Department of Pediatric Neurology
|
|
|
- Clarence Townsend
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Catherine Otten MD September 27 th, 2016 Pediatric Headache Department of Pediatric Neurology
2 Pediatric Headache Prevalence and Population History and physical Types of headache Primary Secondary Cranial neuralgias Red flags When to obtain imaging Treatment Abortive Preventative Non-pharmacologic New York Times, 2/28/2008
3 Headaches Are A Common in Pediatrics Age Headache prevalence Recurring headache 7 years old 37-51% 2.5% 15 years old 57-82% 15% Migraines more more prevalent prevalent earlier in earlier boys, but in girls boys, surpass girls by surpass puberty by - puberty Mean age of onset is 7.2 years in boys, 10.9 years in girls - Mean age of onset is 7.2 years in boys, 10.9 years in Prevalence of chronic daily headache is 1-2% in adolescents girls Tension-type headaches have a prevalence of 10-23% in ages 7-19 Prevalence of chronic daily headache is 1-2% in Headache precursors are also common in pediatrics adolescents - Abdominal migraine - Benign paroxysmal vertigo - Cyclic vomiting syndrome Tension-type headaches have a prevalence of 10-23% between ages 7-19 Laurell et al, Cephalalgia 2004; Bille et al, Med Pregl 1962; Stewart et al, JAMA 1992; Wang et al, Headache 2009)
4 Detailed Headache History Is Necessary Pattern of headache Triggers Timing Location Associated symptoms Severity How much school and activities are missed? Past medical history Previous medication trials Sleep patterns Insomnia Nighttime awakenings Exercise Diet Caffeine Food triggers Skipped meals Social history Activities Stressors School environment 504 Plan Mood/Depression screen Family history Migraine Motion sickness
5 Types of headache Primary Headache Migraine Tension-type Secondary Headache Post-traumatic headache Medication or substance-induced headache Infectious headache Headache secondary to dental disease Vascular headache Idiopathic intracranial hypertension Structural malformations and masses Cranial Neuralgias Ophthalmoplegic migraine Cluster headache Paroxysmal Hemicrania
6 Types of headache Primary Headache Migraine Tension-type Secondary Headache Post-traumatic headache Medication or substance-induced headache Infectious headache Headache secondary to dental disease Vascular headache Idiopathic intracranial hypertension Structural malformations and masses Cranial Neuralgias Ophthalmoplegic migraine Cluster headache Paroxysmal Hemicrania
7 Types of headache Migraine without aura Diagnostic criteria* 5+ attacks Attacks lasting 1 72 hours Headache has 2: Unilateral location - Children may have bitemporal or frontotemporal pain Pulsating quality Moderate or severe pain intensity Worsened by routine physical activity During headache, at least 1: Nausea and/or vomiting Photophobia and phonophobia - May have to infer based on child s behavior Not due to another disorder *per the International Headache Society 2015
8 Types of headache Migraine with aura Aura = reversible focal neurological symptoms Lasts 5 60 minutes Appears over 5 minutes Pathophysiology theory Polygenic ion channelopathy Cortical spreading depression Activation of the trigeminal system Central and peripheral sensitization
9 Types of headache Migraine Aura Visual Scotoma Binocular Field deficit Teichopsia Metamorphopsia Alice-In-Wonderland syndrome May arise from parietal or posterior temporal cortex Objects change size or shatter Micropsia or macropsia Cognitive Aphasia Confusion Vertigo Sensory Paresthesia Dysesthesia Perioral and hand numbness Motor Hemiparesis or monoparesis
10 Migraine Triggers Are Often Environmental Poor sleep Dehydration Exercise Concurrent illness Stressors Foods - Chocolate - Citrus - Cheese - MSG - Caffeine - Processed meats - Aspartamine - Alcoholic beverages
11 Migraine Variants Basilar migraine More frequent in younger children Case report of decreased PCA perfusion on SPECT (La Spina, Headache 1997) Symptoms attributable to posterior fossa Pallor Emesis Vertigo Ataxia Nystagmus Diplopia Familial hemiplegic migraine CACNA1A, ATP1A2, or SCN1A mutation Headaches are associated with prolonged hemiplegia, numbness, aphasia, encephalopathy May be acetazolamide-responsive
12 Diagnostic Testing in Pediatric Migraine Complete neurologic exam Fundoscopic exam with visual acuity and fields Ophthalmologic exam if visual concerns Routine neuro-imaging is not indicated Obtain if concerns for increased intracranial pressure or abnormal neurologic exam
13 Red Flags Indicate Neuroimaging Age < 7 years New daily persistent headache Occipital location Morning headaches Progressive worsening Worsened pain with cough or sneeze Papilledema Neurologic exam abnormalities Sleep-associated headache History of chronic disease - Immunosuppression - Neurofibromatosis I - Tuberous sclerosis - Chiari I malformation - Hypercoagulable disorder - Seizures - VP shunt
14 13 year-old with headache CASE Sporadic headaches for 2-3 years Worsening, now QOD Occipital pain is 8/10 Worse with bright lights or loud sounds Tylenol provides some relief Sumatriptan limited benefit Missing school 2-3 days/week Worse with exercise Is this migraine? Is neuroimaging needed?
15 13 year-old with headache CASE Sporadic headaches for 2-3 years Worsening, now QOD Occipital pain is 8/10 Worse with bright lights or loud sounds Tylenol provides some relief Sumatriptan limited benefit Missing school 2-3 days/week Worse with exercise Is this migraine? Is any neuroimaging needed?
16 13 year-old with headache CASE Mental status normal: Using ageappropriate language, makes good eye contact. Cranial nerves intact, specifically full visual fields and normal visual acuity, but is unable to tolerate funduscopic exam. Motor exam reveals full and symmetric strength, patellar reflexes symmetric with crossed adductors. Sensation intact to multiple modalities. Coordination and Gait normal. Is this migraine? Is neuroimaging needed?
17 13 year-old with headache CASE Mental status normal: Using ageappropriate language, makes good eye contact. Cranial nerves intact, specifically full visual fields and normal visual acuity, but is unable to tolerate funduscopic exam. Motor exam reveals full and symmetric strength, patellar reflexes symmetric with crossed adductors. Sensation intact to multiple modalities. Coordination and Gait normal. Is this migraine? Is any other testing needed?
18 13 year-old with headache CASE MRI and MRV
19 Types of headache Primary Headache Migraine Tension-type Secondary Headache Post-traumatic headache Medication or substance-induced headache Infectious headache Headache secondary to dental disease Vascular headache Idiopathic intracranial hypertension Structural malformations and masses Cranial Neuralgias Ophthalmoplegic migraine Cluster headache Paroxysmal Hemicrania
20 Primary Headache Tension-type headache Pain Band-like Bilateral Mild to moderate intensity May radiate down neck Similar triggers to migraine May be chronic or episodic No photophobia, phonophobia Not worsened by activity Often afternoon in children, midday or morning in teens Differentiating from migraine helps guide preventative strategies that address cervicogenic onset
21 Types of headache Primary Headache Migraine Tension-type Secondary Headache Post-traumatic headache Medication or substance-induced headache Infectious headache Headache secondary to dental disease Vascular headache Idiopathic intracranial hypertension Structural malformations and masses Cranial Neuralgias Ophthalmoplegic migraine Cluster headache Paroxysmal Hemicrania
22 Cranial Neuralgias Ophthalmoplegic migraine Differentiated from retinal migraine Characterized by ophthalmoparesis and headache Ptosis, adduction deficits, skew deviations Retro-orbital pain Signs may persist after pain resolves Inconsistent pupillary involvement Imaging often indicated Must be distinguished from aneurysm or mass lesion Image from J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus 2014;51:e58
23 Cranial Neuralgias Cluster Headache Unilateral painful headache Autonomic features Ipsilateral eye redness Tearing Congestion Rhinorrhea Sweating Ptosis or miosis Low prevalence of 0.1% in pediatrics Oxygen may abort attack Lampl et al, Pediatric Neurology 2009.
24 Types of headache Primary Headache Migraine Tension-type Secondary Headache Post-traumatic headache Medication or substance-induced headache Infectious headache Headache secondary to dental disease Vascular headache Idiopathic intracranial hypertension Structural malformations and masses Cranial Neuralgias Ophthalmoplegic migraine Cluster headache Paroxysmal Hemicrania
25 Types of headache Secondary headaches CASE 15 year-old adolescent teenager Acute viral gastroenteritis dehydration Severe holocephalic headache Worse with emesis and supine position Bilateral CN 6 palsies Papilledema on exam *CN 6 palsy is a falsely-localizing sign that can indicate elevated ICP
26 Types of headache Secondary headaches CASE MRI/MRV: Multi-sinus central venous sinus thrombosis
27 Types of headache Secondary headaches Idiopathic intracranial hypertension Pseudotumor cerebri Daily headache with diplopia and vision changes Positional headache: worse when supine Associations OCPs Obesity or rapid weight gain Hypervitaminosis A Steroids Retinoids Sarcoidosis Sleep apnea Systemic lupus erythematosus Cyclosporine Thyroid replacement CSVT
28 Types of headache Secondary headaches CASE 8 year-old boy with increasing headaches Daily occipital headaches Unresponsive to OTC medications Worse with coughing and defecation Relieved by hanging upside down at the playground Associated with burning arm pain
29 Types of headache Secondary headaches CASE 8 year-old boy with increasing occipital headaches induced by straining
30 Types of headache Secondary headaches CASE Chiari I malformation Cerebellar tonsillar ectopia > 5mm below the foramen magnum Can be associated with syrinx Headaches induced by straining or Valsalva Occipital headaches Nystagmus, ataxia, cranial nerve findings Can also be seen incidentally Posterior fossa decompression can be considered for severe cases
31 Types of headache Secondary headaches Primary Headache Migraine Tension-type Secondary Headache Post-traumatic headache Medication or substance-induced headache Infectious headache Headache secondary to dental disease Vascular headache Idiopathic intracranial hypertension Structural malformations and masses Cranial Neuralgias Ophthalmoplegic migraine Cluster headache Paroxysmal Hemicrania
32 Pediatric Headache Prevalence and Population History and physical Types of headache Primary Secondary Cranial neuralgias Red flags When to obtain imaging Treatment Abortive Preventative Pharmacologic Non-pharmacologic
33 Treatment Abortive Principles of abortive therapy Useful in episodic headaches Dosage often inadequate if OTC Limit use to prevent medication overuse headache < 2-3x/week for NSAIDS < 2x/week for triptans < 9 days/month for caffiene Avoid narcotics Avoid barbituates (Fioricet) Preventative therapy should be considered if abortives are required > 2x/week
34 Treatment Abortive Outpatient Options NSAIDs Acetaminophen Triptans NSAIDS = triptan > acetaminophen (Systemic reviews by Damen et al, Pediatrics 2005 and Evers et al, Neurology 2006)
35 Treatment Abortive Outpatient Options Triptans Rizatriptan (Maxalt) Longitudinal study by Hewitt et al, Headache % were pain-free in 2 hours Safe in ages Common side effects: nausea, dizziness, headache, chest pain and fatigue Most common adverse event was intentional overdose Zolmitriptan (Zomig) Sumatriptan (Imitrex) RTC of 738 teens showed adequate tolerance, but limited benefit due to high placebo response (Winner et al, Headache 2006). Almotriptan Avoid with cardiac disease or hypertension Intranasal, subcutaneous, and oral forms Not all triptans are equal, switching agents can be helpful *approved in pediatric/adolescent age range
36 Treatment Abortive ER Options NSAIDs IV fluid bolus Caffeine Oral or IV Valproic acid Open-label retrospective study showed 78% patients pain-free after 1000 mg valproate (Rieter et al, Headache 2005). Magnesium Anti-emetics Prochlorperazine Zofran Ben-Reg Steroid pulse
37 Treatment Abortive ER Options Pediatric evidence for anti-emetics Prochlorperazine resulted in 50% pain reduction Prospective small pediatric study (Trottier et al, Am J Emerg Med 2012). Benadryl co-administration still resulted in 5% akisthesia Prochlorperazine > ketorolac RTC in ER of 62 pediatric patients (Brousseau et al, Ann Emerg Med 2004).
38 Treatment Abortive
39 Pediatric Headache Prevalence and Population History and physical Types of headache Primary Secondary Cranial neuralgias Red flags When to obtain imaging Treatment Abortive Preventative Pharmacologic Non-pharmacologic
40 Treatment Preventative Principles of preventative therapy Expectations: Prophylactic medications take weeks to reduce symptoms Headache diary tracks symptoms and triggers Stress non-pharmacologic strategies in combination with medicine.
41 Treatment Non-pharmacologic SMART headache management Sleep: Sleep hygiene often poor Meals: Regular, healthy, and includes breakfast Activity: Regular exercise Relaxation Trigger reduction And appropriate oral hydration fluids!
42 Treatment Non-pharmacologic Biofeedback CBT/Relaxation techniques May be equivalent to propranolol (Olness et al, Pediatrics 1987) Massage Therapy Accupressure/Accupuncture Counseling Physical Therapy Most helpful in tension headaches
43 Treatment Preventative Tricyclic anti-depressants Amitriptyline or nortriptyline Dangerous in overdose Anti-hypertensives Propranolol Verapamil Anti-epileptics Topiramate : Low dose Carbamazepine Gabapentin Valproic acid Other Melatonin Cyproheptadine Causes sedation, weight gain Limited evidence
44 Treatment Preventative Tricyclic anti-depressants Amitriptyline Open-label study of low-dose in 192 pediatric patients showed 80% responded with headache frequency reduction (Hershey et al, Headache 2000) Dangerous in overdose Sedation Anti-hypertensives Propranolol Three trials with conflicting results, two showed no benefit (Forsythe et al, Dev Med Child Neurol 1984 and Olness et al, Pediatrics 1987). Randomized trial with mg daily showed 71% had complete reduction (Ludvigsson Acta Neurol 1974). Verapamil Multiple trials for flunarizine and nimodipine, but no quality pediatric trials with verapamil.
45 Treatment Preventative Anti-epileptics Topiramate mg daily div BID Retrospective study with limited follow-up showed reduction in headache, but 12% cognitive symptoms and 5% with weight loss, 3% paresthesias (Hershey et al, Headache 2002). CHAMPS study is a placebo-controlled RTC comparing amitriptyline and topiramate, results pending. Valproic acid 10 mg/kg 1000 mg daily div BID Retrospective study showed 50% reduction in headaches at 4 months in 79% of pediatric patients (Caruso et al, Headache 2000) Side effects often limit therapy Avoid in post-pubertal women
46 Treatment Preventative Melatonin RTC shows 3 mg was superior to placebo and amitriptyline 25 mg (Goncalves et al, J Neurol Neurosurg Psych 2016) Smaller trial with lower dosing found no benefit (Alstadhaug et al, Neurology 2010). Cyproheptadine Common expert recommendation: 2 mg QHS 4 mg BID Single retrospective trial showed 83% response rate at 6 months (Hershey et al, Headache 2004). Sedation, weight gain
47 Treatment Preventative Riboflavin (vitamin B2) 25 to 400 mg daily Small adult RTC (55 pts) showed riboflavin reduced headaches in 60% compared to 15% in the placebo group (Schoenen et al, Neurology 1998). No adequate pediatric trials. Coenzyme Q mg Qday - TID Small adult RTC (42 pts) showed CoQ10 reduced headaches in 50% compared to 14% in the placebo group (Sandor et al, Neurology 2005) Magnesium Magnesium oxide 9 mg/kg/day div TID Side effects: gastritis (5%) and diarrhea (19%) Avoid with kidney dysfunction Small RTC showed 45% reduction with magnesium at 3 months compared to 15% in placebo group (Piekert et al, Cephalalgia 1996) Migralief Pediatric Riboflavin, feverfew, magnesium
48 Thank you!
49 How to add your department name to this presentation 1. To add your department name, click on View > Master > Slide Master from the menu bar, then edit all of the Master slides. 2. Click on the Close Master View button
Outpatient Headache Care Guideline
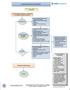 1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation.
 I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
A case of a patient with chronic headache. Focus on Migraine. None related to the presentation Grants to conduct clinical trials from: Speaker bureau:
 Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Migraine in Children. Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014
 Migraine in Children Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014 Headaches in Children One of the most common concerns reported by children 3% for children age 3-7 years 4-11% for children age 7-11
Migraine in Children Germano Falcao, MD Pediatric Neurology 03/07/2014 Headaches in Children One of the most common concerns reported by children 3% for children age 3-7 years 4-11% for children age 7-11
Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept
 Headaches in Children February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neuromuscular Center Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH 1 Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept Burton Gutierrez Kan
Headaches in Children February 23, 2011 Jinny Tavee, MD Associate Professor Neuromuscular Center Cleveland Clinic Foundation Cleveland, OH 1 Headaches in the Pediatric Emergency Dept Burton Gutierrez Kan
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care
 Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Headache Assessment In Primary Eye Care Spencer Johnson, O.D., F.A.A.O. Northeastern State University Oklahoma College of Optometry johns137@nsuok.edu Course Objectives Review headache classification Understand
Disclosures. Objectives 6/2/2017
 Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
Classification: Migraine and Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Assistant Professor, Child Neurology Assistant Director, Child Neurology Residency @StraussHeadache No disclosures
Index. Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Prim Care Clin Office Pract 31 (2004) 441 447 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, brain, headache in, 388 Acetaminophen for migraine, 406 407 headache from, 369
Can I send this headache patient home? Dr Nicola Giffin Consultant Neurologist Bath, Nov 2017
 Can I send this headache patient home? Dr Nicola Giffin Consultant Neurologist Bath, Nov 2017 SAH v benign thunderclap headaches Other pathologies not apparent on CT Severe primary headaches: management
Can I send this headache patient home? Dr Nicola Giffin Consultant Neurologist Bath, Nov 2017 SAH v benign thunderclap headaches Other pathologies not apparent on CT Severe primary headaches: management
Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert
 Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert Childhood headache: Is it really difficult to manage? It shouldn t be... But it can be...
Ishaq Abu Arafeh Consultant Paediatrician Royal Hospital for Children, Glasgow Forth Valley Royal Hospital, Larbert Childhood headache: Is it really difficult to manage? It shouldn t be... But it can be...
Lynne Kerr, MD May 2014
 Lynne Kerr, MD May 2014 Headache is one of top 5 health problems in children 2 nd most common diagnosis in the peds neurology outpatient clinic 14 year old girl severe headache Headaches 1-2 times/month
Lynne Kerr, MD May 2014 Headache is one of top 5 health problems in children 2 nd most common diagnosis in the peds neurology outpatient clinic 14 year old girl severe headache Headaches 1-2 times/month
CHRONIC HEADACHES IN CHILDHOOD
 CHRONIC HEADACHES IN CHILDHOOD EDWIN LIU, MD PEDIATRIC NEUROLOGISTS OF PALM BEACH PEDIATRIC SLEEP CENTERS OF FLORIDA ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR FSU ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR NOVA SOUTHEASTERN PEDIATRIC
CHRONIC HEADACHES IN CHILDHOOD EDWIN LIU, MD PEDIATRIC NEUROLOGISTS OF PALM BEACH PEDIATRIC SLEEP CENTERS OF FLORIDA ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR FSU ASSISTANT CLINICAL PROFESSOR NOVA SOUTHEASTERN PEDIATRIC
Chronic Daily Headaches
 Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
Chronic Daily Headaches ANWARUL HAQ, MD, MRCP(UK), FAHS DIRECTOR BAYLOR HEADACHE CENTER, DALLAS, TEXAS DISCLOSURES: None OBJECTIVES AT THE CONCLUSION OF THIS ACTIVITY, PARTICIPANTS WILL BE ABLE TO: define
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy
 HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
Neurological Dilemmas in Primary Care
 Neurological Dilemmas in Primary Care David Clark, DO dclark@oregonneurology.com When to test? How to test? Pitfalls in testing? When to treat? How to treat? How long to treat? Neurological Dilemmas Seizure
Neurological Dilemmas in Primary Care David Clark, DO dclark@oregonneurology.com When to test? How to test? Pitfalls in testing? When to treat? How to treat? How long to treat? Neurological Dilemmas Seizure
Headaches in Children
 How common are headaches? What is the impact? Very common! 20% of kids from preschool through teenage report frequent or severe headaches in any given year 2 Headaches are more common in children who have
How common are headaches? What is the impact? Very common! 20% of kids from preschool through teenage report frequent or severe headaches in any given year 2 Headaches are more common in children who have
MIGRAINE UPDATE. Objectives & Disclosures. Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment.
 MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
MIGRAINE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 16, 2018 Objectives & Disclosures Learn techniques used to diagnose headaches. Become familiar with medications used for headache treatment. Disclosure: I am
Headache and Facial Pain. Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology
 Headache and Facial Pain Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology Introduction It is the most common neurologic complain The diagnosis usually
Headache and Facial Pain Mohammed ALEssa MBBS, FRCSC Assistant Professor Consultant Otolaryngology,Head & Neck Surgical Oncology Introduction It is the most common neurologic complain The diagnosis usually
Pediatric Grand Rounds UT Health San Antonio 2/10/2017
 Jose Luis Aceves, M.D. has no relationships with commercial companies to disclose. Jose Luis Aceves, M.D. Clinical Associate Professor Department of Pediatrics at UTHSCSA At the end of this presentation
Jose Luis Aceves, M.D. has no relationships with commercial companies to disclose. Jose Luis Aceves, M.D. Clinical Associate Professor Department of Pediatrics at UTHSCSA At the end of this presentation
Strategies in Migraine Care
 Strategies in Migraine Care Julie L. Roth, MD Rhode Island Hospital Assistant Professor, Neurology The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University March 28, 2015 Financial Disclosures None. Objectives
Strategies in Migraine Care Julie L. Roth, MD Rhode Island Hospital Assistant Professor, Neurology The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University March 28, 2015 Financial Disclosures None. Objectives
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE
 MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in
 HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
HMFP Comprehensive Headache Center Department of Anesthesia, Critical Care and Pain Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Instructor in Anesthesia and Neurology Harvard Medical School Limited time
Headaches in Children: Clinical Pearls and Recent Advances. Paras M Bhattarai MD, MBA McLane Children s Hospital December 7, 2018
 Headaches in Children: Clinical Pearls and Recent Advances Paras M Bhattarai MD, MBA McLane Children s Hospital December 7, 2018 Conflict of Interest : None Question: How many patients with headaches have
Headaches in Children: Clinical Pearls and Recent Advances Paras M Bhattarai MD, MBA McLane Children s Hospital December 7, 2018 Conflict of Interest : None Question: How many patients with headaches have
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา
 ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
The Pediatric Headache Handbook
 The Pediatric Headache Handbook For the Primary Care Physician Brought to you by the Division of Pediatric Neurology cardinalglennon.com Classification of headache patterns in children Acute onset of worst
The Pediatric Headache Handbook For the Primary Care Physician Brought to you by the Division of Pediatric Neurology cardinalglennon.com Classification of headache patterns in children Acute onset of worst
A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline. Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN
 A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November 2008. PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS)
A synopsis of: Diagnosis and Management of Headaches in Adults: A national clinical guideline Scottish intercollegiate Guidelines Network SIGN November 2008. PETER FRAMPTON MSc MCOptom BAppSc (Optom)(AUS)
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis
 Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis Noboru Imai(Department of Neurology, Japanese Red Cross
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 II. Management of refractory headaches Case Presentation 2. SUNCT/SUNA: concept, management and prognosis Noboru Imai(Department of Neurology, Japanese Red Cross
MIGRAINE CLASSIFICATION
 MIGRAINE CLASSIFICATION Nada Šternić At most, only 30% of migraineurs have classic aura The same patient may have migraine headache without aura, migraine headache with aura as well as migraine aura without
MIGRAINE CLASSIFICATION Nada Šternić At most, only 30% of migraineurs have classic aura The same patient may have migraine headache without aura, migraine headache with aura as well as migraine aura without
Disclosures. Triptans for Kids 5/16/13
 5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Truths about Headaches (2017) Most headaches were muscle-tension headaches
 Agenda Case presentation Migraine Morphology Primary and Premonitory Phase Secondary Headache Aura Headache Primer on Pain Medication Overuse Headache Case Presentation RT is a 25 year old woman with daily
Agenda Case presentation Migraine Morphology Primary and Premonitory Phase Secondary Headache Aura Headache Primer on Pain Medication Overuse Headache Case Presentation RT is a 25 year old woman with daily
Headache. Headache Case. Migraine Headache. Eric Kraus, MD. Types» Without aura (common)» With aura (classic)
 Headache Eric Kraus, MD Headache Case This 23 year-old female has headaches behind the right eye that cause her to lay down in a quiet room. They have a throbbing quality and she may vomit. Migraine Headache
Headache Eric Kraus, MD Headache Case This 23 year-old female has headaches behind the right eye that cause her to lay down in a quiet room. They have a throbbing quality and she may vomit. Migraine Headache
Headache. Section 1. Migraine headache. Clinical presentation
 Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Section 1 Headache Migraine headache 1 Clinical presentation It is important to recognize just how significant a problem migraine headache is. It has been estimated that migraine affects 11% of the United
Current Migraine Treatment Therapy. Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN
 Current Migraine Treatment Therapy Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN Migraine a Disease Process Migraines are a chronic disease process similar to many other chronic medical conditions Migraine has a low mortality
Current Migraine Treatment Therapy Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN Migraine a Disease Process Migraines are a chronic disease process similar to many other chronic medical conditions Migraine has a low mortality
Faculty Disclosure. Karen L. Bremer, MD. Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest.
 Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
Faculty Disclosure Karen L. Bremer, MD Dr. Bremer has listed no financial interest/arrangement that would be considered a conflict of interest. HEADACHE UPDATE Karen L. Bremer, MD November 10, 2017 karen.bremer@creighton.edu
Farjam Farzam, M.D. Pediatric Neurology
 Headaches in Children Farjam Farzam, M.D. Pediatric Neurology University of Kentucky Headaches in Children Common complaint in pediatric population. All age groups. 2-3 years old. Teenagers/Adolescents.
Headaches in Children Farjam Farzam, M.D. Pediatric Neurology University of Kentucky Headaches in Children Common complaint in pediatric population. All age groups. 2-3 years old. Teenagers/Adolescents.
OH, MY ACHING HEAD! I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING SECONDARY HEADACHES
 1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
1 JUSTIN A. OSSMAN, MD CHATTANOOGA FAMILY MEDICINE UPDATE OH, MY ACHING HEAD! MANAGING HEADACHE IN THE OUTPATIENT SETTING 2 I HAVE NO DISCLOSURES OR CONFLICTS OF INTERESTS TO DECLARE OBJECTIVES International
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines
 How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
1. On how many days in the last 3 months did you miss work or school because of your headaches?
 The Migraine Disability Assessment Test The MIDAS (Migraine Disability Assessment) questionnaire was put together to help you measure the impact your headaches have on your life. The information on this
The Migraine Disability Assessment Test The MIDAS (Migraine Disability Assessment) questionnaire was put together to help you measure the impact your headaches have on your life. The information on this
Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE
 Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE IHS Classification 1989 (updated 2004) Primary Headaches 4 categories Migraine Tension-type Cluster and other trigeminal
Tears of Pain SUNCT and SUNA A/PROFESSOR ARUN AGGARWAL RPAH PAIN MANAGEMENT CENTRE IHS Classification 1989 (updated 2004) Primary Headaches 4 categories Migraine Tension-type Cluster and other trigeminal
Headaches in Children and Adolescents. Paul Shillito
 Headaches in Children and Adolescents Paul Shillito Topics For Discussion What s different about childhood migraine Chronic daily headache (CDH) Tumours and other things to worry about Management of childhood
Headaches in Children and Adolescents Paul Shillito Topics For Discussion What s different about childhood migraine Chronic daily headache (CDH) Tumours and other things to worry about Management of childhood
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates
 Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
Headache Pain Generators
 Objectives 1. Define the major categories of headache. 2. Take a history directed at characterizing a headache pattern in an individual patient and identify the cause or triggers of the headache. 3. Understand
Objectives 1. Define the major categories of headache. 2. Take a history directed at characterizing a headache pattern in an individual patient and identify the cause or triggers of the headache. 3. Understand
Headache Syndrome. Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL
 Headache Syndrome Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL What is a headache? A headache or cephalgia is defined as pain anywhere in the region of head or neck Where does
Headache Syndrome Karen Alvarez, D.O Nemours Children s Specialty Care Jacksonville, FL What is a headache? A headache or cephalgia is defined as pain anywhere in the region of head or neck Where does
Paediatric headaches. Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services. Brevity, levity, repetition
 Paediatric headaches Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services Brevity, levity, repetition Paediatric)headache?)! Headache!in!children!is!not!that!common.!The!question!is!which!headaches!do!I!
Paediatric headaches Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services Brevity, levity, repetition Paediatric)headache?)! Headache!in!children!is!not!that!common.!The!question!is!which!headaches!do!I!
Adult with headache. Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention
 Adult with headache Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention London Strategic Clinical Networks London Neuroscience Strategic Clinical Network
Adult with headache Problem-specific video guides to diagnosing patients and helping them with management and prevention London Strategic Clinical Networks London Neuroscience Strategic Clinical Network
Migraine Management. Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital
 Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
6/2/2017. Objectives. Statement of Problem: Migraine Headaches Are Common. Chronic Headache In Pediatrics, Botox and Beyond
 Chronic Headache In Pediatrics, Botox and Beyond Ken Mack MD PhD Mayo Clinic 2015 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Understand pediatric chronic headache presentations Review evidence for the treatment of chronic
Chronic Headache In Pediatrics, Botox and Beyond Ken Mack MD PhD Mayo Clinic 2015 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Understand pediatric chronic headache presentations Review evidence for the treatment of chronic
Headache A Practical Approach
 Headache A Practical Approach Integrated Pain Symposium December 1, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache and Pain Development Teams Disclosures:
Headache A Practical Approach Integrated Pain Symposium December 1, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache and Pain Development Teams Disclosures:
11/10/2017. THE BRIDGE Course Objectives. THE BRIDGE Course Objectives
 THE BRIDGE Course Objectives Describe clinical characteristics associated with migraine diagnosis in adult and pediatric populations. Identify barriers and risk factors impacting the clinical course of
THE BRIDGE Course Objectives Describe clinical characteristics associated with migraine diagnosis in adult and pediatric populations. Identify barriers and risk factors impacting the clinical course of
UCNS Course A Review of ICHD-3b
 UCNS Course A Review of ICHD-3b Andrew D. Hershey, M.D., Ph.D., FAHS Endowed Chair and Director of Neurology Director, Cincinnati Children s Headache Center Professor of Neurology and Pediatrics University
UCNS Course A Review of ICHD-3b Andrew D. Hershey, M.D., Ph.D., FAHS Endowed Chair and Director of Neurology Director, Cincinnati Children s Headache Center Professor of Neurology and Pediatrics University
Back Pain. John W. Engstrom, MD December 15, Disclosures. A Primary Care Approach to Headache. Headache Goals
 Disclosures Nothing to declare --- or --- Significant ownership interests Consulting, speaker bureaus, honorarium, grants Link to Harrison s Chapter on Headache: http://ucsfneuroresidency.com/public_html/educati
Disclosures Nothing to declare --- or --- Significant ownership interests Consulting, speaker bureaus, honorarium, grants Link to Harrison s Chapter on Headache: http://ucsfneuroresidency.com/public_html/educati
Headache Questionnaire
 Date: All Headache Patients We would appreciate your cooperation in filling out this form. In our evaluation of headache, your history is typically our most valuable tool for diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
Date: All Headache Patients We would appreciate your cooperation in filling out this form. In our evaluation of headache, your history is typically our most valuable tool for diagnosis and subsequent treatment.
Diagnosis of Primary Headache Syndromes. Gerald W. Smetana, M.D. Division of General Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
 Diagnosis of Primary Headache Syndromes Gerald W. Smetana, M.D. Division of General Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Goals Distinguish primary from secondary headaches Recognize typical histories
Diagnosis of Primary Headache Syndromes Gerald W. Smetana, M.D. Division of General Medicine Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Goals Distinguish primary from secondary headaches Recognize typical histories
9/9/13. Objectives. Is it real? Is it their eyes? Evaluating children with headaches. Types of pediatric headache Tension headache. Pediatric migraine
 Is it real? Is it their eyes? Evaluating children with headaches Rachel A. Stacey Coulter, OD, MS Dipl, Binocular Vision, Perception, and Pediatric Optometry Nova Southeastern University Objectives Describe
Is it real? Is it their eyes? Evaluating children with headaches Rachel A. Stacey Coulter, OD, MS Dipl, Binocular Vision, Perception, and Pediatric Optometry Nova Southeastern University Objectives Describe
Headache. Luke Bennetto Consultant Neurologist Engineers House 13 th September 2016
 Headache Luke Bennetto Consultant Neurologist Engineers House 13 th September 2016 Contents General thoughts Primary headache Secondary headache I want to curl up in a cave and die I want to drill a
Headache Luke Bennetto Consultant Neurologist Engineers House 13 th September 2016 Contents General thoughts Primary headache Secondary headache I want to curl up in a cave and die I want to drill a
Lynda J. Krasenbaum, MSN, ANP BC. Associate Director New York Headache Center
 Diagnosing Headache in Adults and Adolescents Lynda J. Krasenbaum, MSN, ANP BC Associate Director New York Headache Center New York, New York Learning Objectives Understand the diagnostic challenges of
Diagnosing Headache in Adults and Adolescents Lynda J. Krasenbaum, MSN, ANP BC Associate Director New York Headache Center New York, New York Learning Objectives Understand the diagnostic challenges of
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT
 ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
Disclosures. Objectives 6/20/2018. No disclosures. Tools & Tips for Headache Management in Special Populations: The Young & Old, Pregnant & Lactating
 Tools & Tips for Headache Management in Special Populations: The Young & Old, Pregnant & Lactating Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Child Neurology Residency Director @StraussHeadache No disclosures Disclosures
Tools & Tips for Headache Management in Special Populations: The Young & Old, Pregnant & Lactating Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO, FAHS Child Neurology Residency Director @StraussHeadache No disclosures Disclosures
Do you suffer from Headaches? - November/Dec 2011
 Do you suffer from Headaches? - November/Dec 2011 Inside this month's issue Headaches Acute single headaches Recurring Headaches: Migraine What causes Migraine? Treatments for migraine & prevention Headaches
Do you suffer from Headaches? - November/Dec 2011 Inside this month's issue Headaches Acute single headaches Recurring Headaches: Migraine What causes Migraine? Treatments for migraine & prevention Headaches
Primary Care Adult Headache Management Pathway (formerly North West Headache Management Guideline for Adults) Version 1.0
 Primary Care Adult Headache Management Pathway (formerly rth West Headache Management Guideline for Adults) Version 1.0 1 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1.0 October 2018 Reformatted
Primary Care Adult Headache Management Pathway (formerly rth West Headache Management Guideline for Adults) Version 1.0 1 VERSION CONTROL Version Date Amendments made Version 1.0 October 2018 Reformatted
FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE. No relevant financial relationships
 Sleep and Headache Paul Mathew, MD, FAHS Director of Continuing Medical Education John R. Graham Headache Center Brigham & Women s Hospital Director of Headache Medicine Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard
Sleep and Headache Paul Mathew, MD, FAHS Director of Continuing Medical Education John R. Graham Headache Center Brigham & Women s Hospital Director of Headache Medicine Cambridge Health Alliance Harvard
Controlling Migraine Pain
 Migraine Stats Controlling Migraine Pain Alan Zacharias, M.D. Associated Neurologists, Boulder Community Health 303-622-3365 Women 15% Men 5% Usually starts in 2 nd and 3 rd Decade Major Impact on days
Migraine Stats Controlling Migraine Pain Alan Zacharias, M.D. Associated Neurologists, Boulder Community Health 303-622-3365 Women 15% Men 5% Usually starts in 2 nd and 3 rd Decade Major Impact on days
General Patient Information Dr. David A. Branch, M.D.
 General Patient Information Dr. David A. Branch, M.D. **Please Print** Patient Name: Date of Birth: Social Security # Email Address: Patient Address: _ City: State: Zip Code: Phone : Marital Status: S
General Patient Information Dr. David A. Branch, M.D. **Please Print** Patient Name: Date of Birth: Social Security # Email Address: Patient Address: _ City: State: Zip Code: Phone : Marital Status: S
PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE. Headache. This document should be read in conjunction with this DISCLAIMER
 Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Princess Margaret Hospital for Children PAEDIATRIC ACUTE CARE GUIDELINE Scope (Staff): Scope (Area): All Emergency Department Clinicians Emergency Department This document should be read in conjunction
Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017
 Migraine Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache Disclosures: none Learning Objectives: At the conclusion
Migraine Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache Disclosures: none Learning Objectives: At the conclusion
Headache evaluation and management after concussion. Assistant Professor
 Headache evaluation and management after concussion Juliette Preston, M.D. Assistant Professor OHSU Headache Center OVERVIEW Introduction Definition Acute post-traumatic headache Red flags Persistent post-traumatic
Headache evaluation and management after concussion Juliette Preston, M.D. Assistant Professor OHSU Headache Center OVERVIEW Introduction Definition Acute post-traumatic headache Red flags Persistent post-traumatic
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias. Disclosures. Objectives 6/20/2018. Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018
 Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018 Disclosures Honoraria from Allergan and Amgen for advisory board, Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports
Trigeminal Autonomic Cephalalgias Rashmi Halker Singh, MD FAHS UCNS Review Course June 2018 Disclosures Honoraria from Allergan and Amgen for advisory board, Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports
Headache. Karen Thaxter
 Headache Karen Thaxter An eight year old girl is taken to her paediatrician because she has been complaining of almost daily pain at the back of her head for the past 4 months. She states that each headache
Headache Karen Thaxter An eight year old girl is taken to her paediatrician because she has been complaining of almost daily pain at the back of her head for the past 4 months. She states that each headache
WHY IS MIGRAINE IMPORTANT
 WHY IS MIGRAINE IMPORTANT Migraine is a complex disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of headache, most often unilateral and in some cases associated with visual or sensory symptoms collectively
WHY IS MIGRAINE IMPORTANT Migraine is a complex disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of headache, most often unilateral and in some cases associated with visual or sensory symptoms collectively
Pediatric Headache Diary
 Patient Name Age Pediatric Headache Diary Day of week Date Time of onset Duration (hours/minutes/days) Location (forehead, temples, back of head, generalized, etc.) Type of pain (throbbing, piercing, tight
Patient Name Age Pediatric Headache Diary Day of week Date Time of onset Duration (hours/minutes/days) Location (forehead, temples, back of head, generalized, etc.) Type of pain (throbbing, piercing, tight
Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE
 Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Headache in children and adolescents Çiçek Wöber-Bingöl HEADACHE UNIT FOR CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENCE Dept. of Psychiatry of Childhood and Adolescence Medical University of Vienna, Vienna, Austria Impact
Goals. Primary Headache Syndromes. One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders
 Goals One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders Impact of primary headache syndromes Non pharmacologic Rx of migraine individualized to patient triggers Complementary and alternative Rx of migraine
Goals One-Year Prevalence of Common Headache Disorders Impact of primary headache syndromes Non pharmacologic Rx of migraine individualized to patient triggers Complementary and alternative Rx of migraine
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines
 Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
6/4/2018. Headache. Headaches. Headache. Migraine Headaches. Headache. Red Flag signs and symptoms. Imaging CT without contrast.
 Presented by M.D. Shepherd, M.D. OH MY ACHING HEAD! Estimated that one half of the adult population is affected by a headache disorder International Society Classification Primary : Tension s 40% of the
Presented by M.D. Shepherd, M.D. OH MY ACHING HEAD! Estimated that one half of the adult population is affected by a headache disorder International Society Classification Primary : Tension s 40% of the
Headache Dr. Asghari Neurologist
 In the name of God Management of the Headache Dr. Asghari Neurologist Overall Approach Chief Complaint of Headache Headache Alarms Evidence of serious headache disorder by history or physical exam no Diagnosis
In the name of God Management of the Headache Dr. Asghari Neurologist Overall Approach Chief Complaint of Headache Headache Alarms Evidence of serious headache disorder by history or physical exam no Diagnosis
How could I be having migraine when I don't have a headache?
 Migraine Your doctor thinks you may have migraine. Classic migraine attacks start with visual symptoms (often zig-zag colored lights or flashes of light expanding to one side over 10-30 minutes) followed
Migraine Your doctor thinks you may have migraine. Classic migraine attacks start with visual symptoms (often zig-zag colored lights or flashes of light expanding to one side over 10-30 minutes) followed
I. Migraine management in the Emergency Department
 Comer Children s Hospital Pediatric Guidelines Guideline: Migraine management in the ED Guideline #: PED-06 Section: Neurology Page: 1 of 10 Developed date: 11/17/2016 Revision date: none Review date:
Comer Children s Hospital Pediatric Guidelines Guideline: Migraine management in the ED Guideline #: PED-06 Section: Neurology Page: 1 of 10 Developed date: 11/17/2016 Revision date: none Review date:
HEADACHE Transient discomfort, chronic nuisance, or looming disaster?
 HEADACHE Transient discomfort, chronic nuisance, or looming disaster? Hussien H. Rizk, MD Cairo University Medical School ١ Headache Second most common o symptom (after pain) Migraine alone afflicts 12
HEADACHE Transient discomfort, chronic nuisance, or looming disaster? Hussien H. Rizk, MD Cairo University Medical School ١ Headache Second most common o symptom (after pain) Migraine alone afflicts 12
10/31/2017 PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE DISCLOSURES WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Primary Care 67%
 PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Regional Headache Specialist Kaiser LAMC 1 WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Column1 Primary Care 67% Primary Care Headache Specialty Other
PRIMARY CARE AND HEADACHE Sonja Potrebic MD PhD Regional Headache Specialist Kaiser LAMC 1 WHERE DO THOSE WITH HEADACHE SEEK MEDICAL CARE? Column1 Primary Care 67% Primary Care Headache Specialty Other
Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes
 Presenter Disclosure Information 2:45 3:45pm Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes SPEAKER Gerald W. Smetana, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Gerald W.Smetana, MD,
Presenter Disclosure Information 2:45 3:45pm Treatment of Primary Headache Syndromes SPEAKER Gerald W. Smetana, MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Gerald W.Smetana, MD,
Migraine Migraine Age Specific Prevalence in the United States. Headache International Headache Society Classification
 28 Primary Care Medicine Principles and Practice 29 October 28 Professor Peter J. Goadsby Peter.Goadsby@headache.ucsf.edu Department of Neurology Headache International Headache Society Classification
28 Primary Care Medicine Principles and Practice 29 October 28 Professor Peter J. Goadsby Peter.Goadsby@headache.ucsf.edu Department of Neurology Headache International Headache Society Classification
Tools & Tips for Headache Management in Special populations: The Young & Old, Pregnant & Lactating, and those with Heart or Kidney Disease
 Tools & Tips for Headache Management in Special populations: The Young & Old, Pregnant & Lactating, and those with Heart or Kidney Disease Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center lstrauss@wakehealth.edu
Tools & Tips for Headache Management in Special populations: The Young & Old, Pregnant & Lactating, and those with Heart or Kidney Disease Lauren Doyle Strauss, DO Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center lstrauss@wakehealth.edu
Overview INTRODUCTION 3/15/2018. Headache Emergencies. Other way to differentiate between them? Is there an easy way to differentiate between them?
 Overview Headache Emergencies Primary versus Secondary headache disorder Red flags 4 cases of unusual headache emergencies Disclaimer: we will not talk about brain bleed as patients usually go the ED.
Overview Headache Emergencies Primary versus Secondary headache disorder Red flags 4 cases of unusual headache emergencies Disclaimer: we will not talk about brain bleed as patients usually go the ED.
Migraine Clinical Guideline
 Migraine Clinical Guideline Definition: Migraine refers to a chronic neurological disorder characterized by episodic attacks often in association with enhanced sensitivity of the nervous system and activation
Migraine Clinical Guideline Definition: Migraine refers to a chronic neurological disorder characterized by episodic attacks often in association with enhanced sensitivity of the nervous system and activation
Pearls in Child Neurology. Edgard Andrade, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor University of Florida
 Pearls in Child Neurology Edgard Andrade, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor University of Florida Outline 1. Autism 2. Bell s Palsy 3. First unprovoked seizure in children 4. Migraine headache Objectives 1.
Pearls in Child Neurology Edgard Andrade, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor University of Florida Outline 1. Autism 2. Bell s Palsy 3. First unprovoked seizure in children 4. Migraine headache Objectives 1.
June National Migraine and Headache Awareness Month
 June 2018- National Migraine and Headache Awareness Month A note from the author Hello NCP friends! This month, I wanted to feature a topic that has been much discussed amongst several of my friends and
June 2018- National Migraine and Headache Awareness Month A note from the author Hello NCP friends! This month, I wanted to feature a topic that has been much discussed amongst several of my friends and
Migraine Types and Triggering Factors in Children
 original ARTICLE Migraine Types and Triggering Factors in Children How to Cite this Article: Nejad Biglari H, Karimzadeh P, Mohammadi Kord-kheyli M, Hashemi SM. Migraine Types and Triggering Factors in
original ARTICLE Migraine Types and Triggering Factors in Children How to Cite this Article: Nejad Biglari H, Karimzadeh P, Mohammadi Kord-kheyli M, Hashemi SM. Migraine Types and Triggering Factors in
HEADACHE. Dr Nick Pendleton. September Headache
 HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2017 Headache Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache Raised ICP
HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2017 Headache Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache Raised ICP
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: occipital_nerve_stimulation 8/2010 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Occipital nerve
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: occipital_nerve_stimulation 8/2010 5/2017 5/2018 5/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Occipital nerve
Beyond the Basics, Bringing Concussion Out of the Dark
 Beyond the Basics, Bringing Concussion Out of the Dark Objectives Recognize different types of concussion based on symptomatology Identify risk factors for prolonged recovery after a concussion Predict
Beyond the Basics, Bringing Concussion Out of the Dark Objectives Recognize different types of concussion based on symptomatology Identify risk factors for prolonged recovery after a concussion Predict
Why does my child hurt? How can we reduce the burden of headache? What is the burden of headache?
 How can we reduce the burden of headache? Disclosure: Independent learning grant from Pfizer Jennifer Bickel, MD FAAN Chief, Headache Section Associate Professor of Pediatrics Division of Neurology The
How can we reduce the burden of headache? Disclosure: Independent learning grant from Pfizer Jennifer Bickel, MD FAAN Chief, Headache Section Associate Professor of Pediatrics Division of Neurology The
Clinical case. Clinical case 3/15/2018 OVERVIEW. Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment. Refractory headache.
 OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
ISSN doi: /head VC 2015 American Headache Society Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
 ISSN 0017-8748 Headache doi: 10.1111/head.12746 VC 2015 American Headache Society Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Article Acute Treatment Therapies for Pediatric Migraine: A Qualitative Systematic
ISSN 0017-8748 Headache doi: 10.1111/head.12746 VC 2015 American Headache Society Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Review Article Acute Treatment Therapies for Pediatric Migraine: A Qualitative Systematic
Chief Complaint. History. History of Similar Episodes. A 10 Year-Old Boy With Headache
 A 10 Year-Old Boy With Headache Chief Complaint Recent Advances in Neurology 2013 10 year-old boy presented with his fifth lifetime bout of left-sided head pain followed by diplopia. Amy A. Gelfand, MD
A 10 Year-Old Boy With Headache Chief Complaint Recent Advances in Neurology 2013 10 year-old boy presented with his fifth lifetime bout of left-sided head pain followed by diplopia. Amy A. Gelfand, MD
The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension
 The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension Michael Wall CEPHALALGIA Wall M. The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cephalalgia 1990;10:331-5. Oslo. ISSN 0333-1024
The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension Michael Wall CEPHALALGIA Wall M. The headache profile of idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Cephalalgia 1990;10:331-5. Oslo. ISSN 0333-1024
25/09/2018 HEADACHE. Dr Nick Pendleton
 HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2018 1 Small Group Work Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache
HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2018 1 Small Group Work Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache
HEADACHE HISTORY & PROFILE QUESTIONNAIRE
 1 HEADACHE HISTORY & PROFILE QUESTIONNAIRE Patient Name: On what part of the head do your headaches start? R Side L Side Either Side Both Sides Back On Top Temples Behind/AroundEyes Forehead Face Neck
1 HEADACHE HISTORY & PROFILE QUESTIONNAIRE Patient Name: On what part of the head do your headaches start? R Side L Side Either Side Both Sides Back On Top Temples Behind/AroundEyes Forehead Face Neck
Atypical presentations of cluster headache
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 200222Original ArticleAtypical presentations in cluster headachetd Rozen Atypical presentations of cluster headache TD Rozen Department
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKCHACephalalgia0333-1024Blackwell Science, 200222Original ArticleAtypical presentations in cluster headachetd Rozen Atypical presentations of cluster headache TD Rozen Department
By Nathan Hall Associate Editor
 By Nathan Hall Associate Editor 34 Practical Neurology March 2005 These new rules may change the definition of head pain, but some practitioners may find the new guidelines themselves to be a source of
By Nathan Hall Associate Editor 34 Practical Neurology March 2005 These new rules may change the definition of head pain, but some practitioners may find the new guidelines themselves to be a source of
July 2012 Target Population. Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings.
 Guideline for Primary Care Management of Headache in Adults July 2012 Target Population Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings. Exclusions: This guideline does not provide recommendations
Guideline for Primary Care Management of Headache in Adults July 2012 Target Population Adult patients 18 years or older in primary care settings. Exclusions: This guideline does not provide recommendations
