trial of celecoxib in the treatment of
|
|
|
- Marjorie Ferguson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Singapore Med , 48 (9) : 834 Randomised, open label, controlled trial of celecoxib in the treatment of acute migraine Loo C Y, Tan H J, Teh H S, Raymond A A Neurology Unit, Department of Medicine, Hospital Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Jalan Yaacob Latif, Bandar Tun Razak, Cheras 56000, Kuala Lumpur Malaysia Loo CY, MBBS, MMed Clinical Specialist Tan HJ, MD, MMed, MRCP Consultant Teh HS, MD, MMed Clinical Specialist Raymond AA, MD, MMed, FRCP Senior Consultant and Professor Correspondence to: Dr Loo Chee Yean Tel: (60) Fax: (60) cyloo7@ gmail.com ABSTRACT Introduction: Migraine is a common disabling condition that results in considerable socioeconomic loss. The role of non -steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in acute migraine has been well - established. We compared the efficacy of the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib with the NSAID, naproxen sodium, in the treatment of acute migraine. Methods: This was a randomised, open label, controlled trial. We selected patients with a diagnosis of migraine, based on the International Headache Society revised criteria. 60 patients were randomised to either celecoxib 400 mg (30 patients) or naproxen sodium 550 mg (30 patients). Patients took the study medicine for the first acute migraine episode that occurred during the study period and reported the headache reduction based on a visual analogue score (VAS). Patients were reviewed after a month to check on VAS at one and two hours, compared to the baseline. Any side effects of the medication were also recorded. Results: Of the 52 patients who completed the study, eight did not experience any headaches. The mean VAS in the celecoxib group improved significantly from baseline ( ) to one hour ( ) and two hours ( ) (p -value is less than ). The mean VAS in the naproxen sodium group also improved significantly from baseline ( ) to one hour ( ) and two hours ( ) (p -value is less than ). However, there was no significant difference between the magnitudes of improvement between the treatment groups. The incidence of gastric pain was significantly higher in the naproxen sodium group (p -value is equal to 0.029). Conclusion: In comparison with naproxen sodium, celecoxib was equally effective in relieving pain in acute migraine and caused significantly less gastric pain. Keywords: acute migraine, celecoxib, drug side -effects, gastric pain, migraine, naproxen sodium, visual analogue score Singapore Med J 2007; 48(9): INTRODUCTION Migraine is a common, disabling condition that results in considerable social and economic losses.(') The pathophysiological process of the attack is presumed to occur via the trigemino -vascular pathway and other systems that interact with intra- and extracranial vasculature and perivascular spaces.a3) Centrally -mediated prostaglandins are involved in the pathological amplification and exaggeration of the pain pathway, hence its pivotal role in causing acute migraine. The central role of prostaglandins (PGs) may provide a common denominator in several hormonal, neural and various other influences on the blood vessels for the pathophysiology of acute migraine attacks. The possible role of PG -associated inflammation may be countered with non -steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), as well as selective enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX -2) inhibitors.45) The up -regulation of COX -2 in the central nervous system in response to inflammation is not associated with an increase in COX -1. Selective inhibition of COX -2 within the brain is thus a rational strategy to counteract this process. The use of naproxen sodium in acute migraine has been well established. It abolishes the PG -associated inflammation centrally. It is a commonly -prescribed first line treatment for acute migraine because of its low cost and proven efficacy's) Pradalier et al reported its usefulness in acute migraine treatment. (6) They compared naproxen sodium with ergotamine in 114 patients. Naproxen sodium has been more effective in reducing headache severity, nausea, vomiting and light-headedness. In that trial, a relatively high dose of naproxen sodium (750-1,250 mg) was used. It can be easily absorbed and achieve therapeutic concentrations after minutes and maximum
2 Singapore Med J 2007; 48 (9) : 835 Table I. International Headache Society revised criteria for migraine.('n Diagnostic criteria A. At least five attacks fulfilling the criteria B-D. B. Headache lasting 4-72 hours and occurring < 15 days/month (untreated or unsuccessfully treated). C. Headache has at least two of the following characteristics: Unilateral localisation. Pulsating quality. Moderate or severe intensity (inhibits or prohibits daily activity). Aggravation by or causing avoidance of routine physical activity (i.e., walking or climbing stairs). D. During headache, at least one of the following: Nausea and/or vomiting. Photophobia and phonophobia. E. Not attributed to another disorder. Table II. International Headache Society revised criteria for typical aura with migraine headache. (17) A. At least two attacks fulfilling criteria B-D. B. Aura consisting of at least one of the following, but no motor weakness: I. Fully reversible visual symptoms including positive features (e.g., flickering lights, spots, or lines) and/or negative features (i.e., loss of vision). 2. Fully reversible sensory symptoms including positive features (i.e., pins and needles) and/or negative features (i.e., numbness). 3. Fully reversible dysphasic speech disturbance. C. At least two of the following: I. Homonymous visual symptoms and/or unilateral sensory symptoms. 2. At least one aura symptom develops gradually over >_ 5 minutes and/or different aura symptoms occur in succession over >_ 5 minutes. 3. Each symptom lasts >_ 5 and <_ 60 minutes. D. Headache fulfilling criteria B-D (Table I) begins during the aura or follows aura within 60 minutes E. Not attributed to another disorder concentration two hours after ingestion. Its biological half-life is hours. Our usual practice is to prescribe naproxen sodium at a dose of 550 mg; this appears to be the effective tolerable dose, although there is no conclusive evidence to support this in our local population. Ergotamine, a specific migraine treatment, causes nausea, vomiting and dependence. Sumatriptan, a 5- hydroxytryptamine agonist is effective against acute attacks but is costly. Prophylactic medication usually leads to weight gain and sedation. These side effects lead to poor compliance, especially in young patients and the working class. (7'8) Prescribed at therapeutic doses, the selective COX - 2 inhibitors are expected to offer the same anti-inflammatory benefits as the NSAIDs, with a lower risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse reactions.(9'10) Rofecoxib has been shown to be effective in acute migraine." However, celecoxib has been reported to be effective in non-migrainous headaches.(12) The aim of the study was to compare the efficacy of the COX -2 inhibitor, celecoxib, with the NSAID, naproxen sodium, in the treatment of acute migraine. METHODS This was a prospective, randomised, open label, com- parative study. 60 patients with migraine were recruited from the neurology outpatient clinic in Hospital Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Cheras, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, from December 2004 to March The patients were not naproxen sodium or celecoxib naive, this factor was considered if there was drug tolerance and or unresponsiveness to the trial medication in acute migrainous headache. The patient selection criteria included those who were older than 18 years, had disease duration of at least six months, and had an attack frequency of at least twice per month over the past six months. We excluded those who had underlying organic causes for headaches, previous adverse reaction to NSAIDs, pregnant and lactating women, and patients with known contraindications to the use of NSAIDs. The diagnosis of migraine was based on International the Headache Society revised criteria for migraine 2004 (Tables I and II). We used a visual analogue
3 1 (37) 1 (40.7) Singapore Med J 2007; 48 (9) : 836 Table Ill. Baseline demographical and clinical characteristics of migraine patients taking celecoxib or naproxen sodium. Celecoxib 400 mg (%) n = 25 Naproxen sodium 550 mg (%) n = 27 Chi-square value p_value* Age (years) Mean SD Gender Female 18 (72.0) 21 (77.8) Male 7 (28.0) 6 (22.2) Ethnicity Malay 20 (80.0) 18 (66.7) Chinese 3 (12.0) 7 (25.9) Indian 2 (8) 2 (7.4) Education Non -tertiary 10 (40) 16 (59.3) Tertiary 15 (60) 1 Migraine With aura 14 (63.0) 17 (63.3) Without aura 1 Duration of migraine since onset (years) 10 (36.7) Mean SD Frequency of attacks (76) 25 (92.6) (20.0) >10 1 Prophylactic medication 2 (7.4) Pizotifen 7 (28) 6 (22.0) Amitriptyline 2 (8) 3 (11.7) Propranolol 4 (16) 2 (7.4) Flunarizine 1 Others None 10 (40) 16 (59.3) * Significant at p < 0.05 scale (VAS) to assess pain severity, and considered VAS with a standard deviation of 17 mm and the minimal clinical difference of 13 mm. This allowed the detection of a statistically significant 25% difference in headache relief between celecoxib and naproxen sodium with a power of 80%, an alpha risk of 5% and a drop out rate of 20%. A sample size of 55 patients was required based on Altman's normogram. There were 60 envelopes, each concealed a piece of paper with a code number, out of which 30 were numbered Cl to C30 and the remaining, 51 to S30. The patients were then instructed to pick an envelope at random. The patients who selected the envelope containing the code C was given Celebrex (Celecoxib 400 mg) and S were given Synflex (Naproxen sodium 550 mg) accordingly. The patients were instructed to take the study medications at the onset of their migraine attacks and to score the severity of the attack at baseline, one hour and two hours after ingestion of the medication. The scores were documented on the VAS sheet Any side - effects and rescue medication needed were also entered on the same sheet The patients were then reassessed four weeks later. Rescue medication consisted of the patient's usual migraine medication. Once the rescue medication was used, these patients were disqualified from further analysis, because the pain scoring would be affected and the results would then not be representative of the therapeutic effect of the trial drugs. The use of prophylactic medication on a constant dosing regimen was allowed. The prophylactic medications used included amitriptyline, propranolol,
4 (3.7) (3.7) (3.7) Singapore Med J 2007; 48 (9) : 837 Table IV. Comparison of visual analogue scores between the celecoxib and naproxen sodium groups. Celecoxib 400 mg n = 25 Naproxen sodium 550 mg n = 27 Independence t -test p -value Baseline 6.48 ± ± First hour 4.28 ± ± Second hour 2.24 ± ± Table V. Adverse events reported by patients. Celecoxib (%) n=25 Naproxen sodium (%) n=27 Pearson chi-square value p_value* Epigastric pain 1 Nausea 1 7 (26.0) Numbness Drowsiness 0 1 Insomnia 0 1 * Significant at p < pizotifen, flunarizine, other calcium channels blockers, and oral contraceptive pills. We measured the breakthrough headache pains and selected those with at least two attacks in a month despite prophylactic medication. Those who had no or very mild migrainous headache were excluded. The data was analysed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences, version 11.0 (SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL, USA), and a p -value of less than 0.05 were deemed to be statistically significant. Parametric analysis was used. Numerical data was expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Student paired t -test was used to compare the means within each group. The independent t -test was used to compare the mean between two groups. The study was approved by the Medical Research and Ethics Committee of the Medical Faculty, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia. (Ethics Committee Approval Code: FF ). RESULTS 60 patients with migraine, with and without aura, were recruited. The mean age was 33 ± 10.2 years for the celecoxib group, and 32 ± 10.8 years for the naproxen sodium group. The distributions of the patients and their clinical characteristics are shown in Table III. Of the 60 subjects enrolled in the study, half were randomly assigned to receive celecoxib 400 mg (Celebrex) and the remaining half naproxen sodium 550 mg (Synflex). Eight patients (15%) did not take the study medication, because either they did not experience any attacks or the attacks were mild. The remaining 52 subjects who took the study medication were included in the intent -to -treat analysis, with 25 in the celecoxib group and 27 in the naproxen sodium group. Out of the 60 patients, 31 (52%) had migraine with aura. The mean duration of migraine since onset in the celecoxib group was longer (10 years versus 5.5 years) and frequency of migraine attacks was lower (less than five times per month) compared to the naproxen sodium group (19 [76%] versus 25 [92.6%]). 15 patients in the celecoxib group were on prophylactic medication for migraine compared to 11 in the naproxen sodium group, but those agents did not significantly alter the outcome on the VAS. In the celecoxib group, the VAS were 6.48 ± 1.53 at baseline, 4.28 ± 2.11 at one hour, and 2.24 ± 2.57 at two hours. In the naproxen sodium group, the VAS at baseline, one hour and two hours were 7.30 ± 1.66, 4.81 ± 2.50, and 2.63 ± 2.65, respectively (Table IV). In the celecoxib group, two patients (8.0%) achieved pain freedom at one hour and ten patients (40.0%) at two hours. This was comparable to the naproxen sodium group where two patients (7.7%) achieved total headache relief at one hour, and eight patients (30.8%) were symptom - free at two hours. In the intergroup analysis, there was no significant difference between both groups in VAS at baseline to one hour (p = 0.410) and at baseline to two hours (p = 0.407) (Table IV). The results were adjusted for differences in baseline characteristics between the two groups. The side -effects that were reported by the patients included epigastric pain, drowsiness, nausea, numbness and insomnia. Among all the reported side effects, only the incidence of epigastric pain was significantly higher in the naproxen sodium group (p = 0.029) (Table V). DISCUSSION 52 patients completed the study; the remaining eight did not experience any headaches during the study period. The mean VAS in the celecoxib group improved well from baseline (6.48 ± 1.53) to one hour (4.28 ± 2.11) and two hours (2.24 ± 2.57) (p < ). The mean VAS in
5 Singapore Med J 2007; 48 (9) : 838 the naproxen sodium group also improved from baseline (7.30 ± 1.66) to one hour (4.81 ± 2.50) and two hours (2.63 ± 2.65) (p < ). There was no significant difference between the magnitudes of improvement between the treatment groups. The incidence of gastric pain was significantly higher in the naproxen sodium group (p = 0.029). Migraine patients are of ten young adults who are active in life, either studying or working. In our study, the majority of the patients belonged to the years age group. The majority of patients were young women (75%). The female -to-male ratio for migraine has been previously reported to be in the order of 3: 1.(1) Abortive treatment, whether migraine specific and non-specific, is generally required to treat the acute migraine attack. The migraine -specific agents include ergotamine, dihydroergotamine and the triptans.(7'8) The cheaper and more easily available form of abortive non - migraine specific agent is a NSAID. The rationale for using NSAIDs in the treatment of migraine is based on the possible involvement of PG in the pathophysiology of migraine. NSAIDs exert their action by inhibiting the COX enzyme, and thereby decreasing the synthesis of PGs and leukotrienes from arachidonic acid. They prevent neurologically -mediated inflammation in the trigeminovascular system.(5) We now know that COX consists of two isoenzymes. COX -1 is constitutively expressed and generates PGs believed to be involved in GI mucosal protection, while COX -2 is induced at sites of inflammation throughout the body. The risk of gastric mucosa erosion is high with NSAIDs that are nonselective -COX inhibitors. (11,12) The efficacy of NSAIDs in acute migraine treatment has been proven in a few clinical trials. Based on the class effect of NSAIDs, selective COX -2 inhibitors could exert its pain -relieving properties in migraine and yet produce a lower incidence of GI disturbances. In Malaysia, celecoxib is the only approved COX -2 inhibitor. It is relatively safe for short-term use on a "when needed only" basis. There have been no trials so far using celecoxib in the treatment of acute migraine, but there were a few case reports on the use of celecoxib for other forms of headaches. ' In the present study, we have shown that celecoxib, at a dose of 400 mg taken during acute migrainous headaches, is as effective as naproxen sodium in pain relief. The majority of the study patients did not wait to take the medication after a meal as advised, as most of the attacks occurred acutely and quick pain relief was required. The complaint of numbness of the limbs, nausea and drowsiness did not differ significantly between the groups. One patient reported having insomnia after naproxen sodium, which did not occur when he was on mefenamic acid previously. The occurrence of epigastric pain was significantly less in the celecoxib group. Only one patient who took celecoxib on an empty stomach reported a brief episode of epigastric discomfort. In September 2004, Merck withdrew rofecoxib from the market because of unexpected increased cardiovascular toxicity in a trial, designed to test the hypothesis that COX -2 inhibitors could prevent recurrent colonic polyps.' '3' The increase in cardiovascular risk began after 18 months of treatment with rofecoxib. The Colorectal Adenoma Prevention with Celecoxib Study showed that celecoxib at either 200 mg or 400 mg twice a day, 2.8 to 3.1 years after treatment, had a relative risk of 2.8 for cardiovascular events.'14' Another COX -2 inhibitor, valdecoxib, and its intravenous form parecoxib, has increased incidence of cardiovascular events, in patients who have undergone coronary artery bypass surgery. These high -risk patients were given intravenous parecoxib for three days, before switching to valdecoxib for the next ten days.' 15 It has been recommended that COX -2 inhibitors should be avoided in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft. Thromboxane A2, a major COX -1 - mediated product of metabolised arachidonic acid causes irreversible platelet aggression, vasoconstriction, and smooth muscle proliferation, whereas prostacyclin, an inhibitor of platelet aggregation and a vasodilator, causes inhibition of smooth -muscle proliferation. COX -2 is the chief source of systemic prostacyclin synthesis, and COX -2 inhibitors may increase the cardiovascular risk by shifting the functional balance of these vasoactive eicosanoids.'10161 However, in our study, celecoxib was used in a relatively small dose and for a short duration. Our target population was relatively young with low cardiovascular risk. It is safe if used according to FDA recommendations. So far, all the previous acute migraine treatment trials compared NSAIDs with a placebo or other migraine -specific agents, such as triptans or ergotamines. Silberstein et al reported the effects of different doses of rofecoxib with a placebo.' They found that rofecoxib was beneficial for acute migraine pain relief within two hours. In our study, we compared celecoxib and naproxen sodium, which to the best of our knowledge, has never been reported before for acute migraine treatment. The study limitations were that there was no placebo arm, and the follow-up period was limited. We were not able to blind the study because of ethical issues relating to the use of placebo in migraine. The substantial evidence that celecoxib is a useful migraine drug has been considerably weakened by the withdrawal of some COX - 2 inhibitors from most markets. As such, celecoxib is seldom used by most neurologists to treat acute migraine. However, in some circumstances where the likelihood of patients developing NSAID-induced gastritis is high, celecoxib may be a useful alternative. We conclude from our study that celecoxib in a dose of 400 mg during an acute migraine attack can achieve the same efficacy as
6 Singapore Med J 2007; 48 (9) : 839 naproxen sodium 550 mg. Celecoxib is an alterative mode 7. of therapy in acute migraine treatment, and compared to naproxen sodium, is less likely to cause epigastric pain. The limitations of the present study call for a larger, randomised, double-blind trial. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT We would like to thank the Dean of the Medical Faculty at the Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia for allowing us to publish this paper. REFERENCES 1. Lipton RB, Stewart WF, von Korff M. Burden of migraine: societal costs 12. and therapeutic opportunities. Neurology 1997; 48(3 suppl 3): S The Headache Classification Committee. Diagnostic criteria: migraine. In: International Headache Society Members' Handbook. Oxford: 13. Scandinavian University Press, 2000: May A, Goadsby PJ. The trigeminovascular system in humans: pathophysiologic implications for primary headache syndromes of the 14. neural influences on the cerebral circulation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1999; 19: Many J, Michael B. Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the 15. treatment of migraine. Curr Med Res Opin 2001; 17: Pfaffenrath V, Scherzer S. Analgesics and NSAIDs in the treatment of the acute migraine attack. Cephalalgia 1995; 15 Suppl 15: Pradalier A, Rancurel G, Dordain G, et al. Acute migraine attack therapy: comparison of naproxen sodium and an ergotamine tartrate 17. compound. Cephalalgia 1985; 5: Silberstein SD, Young WB. Safety and efficacy of ergotamine tartrate and dihydroergotamine in the treatment of migraine and status migrainous. Working Panel of the Headache and Facial Pain Section of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 1995; 45: Dodick DW, Martin V. Triptans and CNS side -effects: pharmacokinetic and metabolic mechanisms. Cephalalgia 2004; 24: Talley H. Selective inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX -2). Prog Med Chem 1999; 36: McAdam BF, Catella-Lawson F, Mardini IA, et al. Systemic biosynthesis of prostacyclin by cyclooxygenase (COX) -2: the human pharmacology of a selective inhibitor of COX -2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: Silberstein S, Tepper S, Brandes J, et al. Randomized, placebo - controlled trial of rofecoxib in the acute treatment of migraine. Neurology 2004; 62: Piovesan EJ, Zukerman E, Kowacs PA, Werneck LC. COX -2 inhibitor for the treatment of idiopathic stabbing headache secondary to cerebrovascular diseases. Celphalalgia 2002; 22: Bresalier RS, Sandler RS, Quan H, et al. Cardiovascular events associated with rofecoxib in a colorectal adenoma chemoprevention trial. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: Solomon SD, McMurray JJ, Pfeffer MA, et al. Cardiovascular risk associated with celecoxib in a clinical trial for colorectal adenoma prevention. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: Nussmeier NA, Whelton AA, Brown MT, et al. Complications of the COX -2 inhibitors parecoxib and valdecoxib after cardiac surgery. N Engl J Med 2005; 352: Mukherjee D, Nissen SE, Topol EJ. Risk of cardiovascular events associated with selective COX -2 inhibitors. JAMA 2001; 286: Lipton RB, Bigal ME, Steiner TJ, Silberstein SD, Olesen J. Classification of primary headaches. Neurology 2004; 63:
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care. December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary
 Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
Chronic Migraine in Primary Care December 11 th, 2017 Werner J. Becker University of Calgary Disclosures Faculty: Werner J. Becker Relationships with commercial interests: Grants/Research Support: Clinical
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT
 ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
ADVANCES IN MIGRAINE MANAGEMENT Joanna Girard Katzman, M.D.MSPH Assistant Professor, Dept. of Neurology Project ECHO, Chronic Pain Program University of New Mexico Outline Migraine throughout the decades
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation.
 I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache
 MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
MEASURE #3: PREVENTIVE MIGRAINE MEDICATION PRESCRIBED Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older diagnosed with migraine headache whose migraine frequency is 4 migraine
Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital
 Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital Honorarium from Current Pain and Headache Reports; Section Editor Unusual
Jessica Ailani MD FAHS Director, Georgetown Headache Center Associate Professor Neurology Medstar Georgetown University Hospital Honorarium from Current Pain and Headache Reports; Section Editor Unusual
ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder
 ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
ONZETRA XSAIL (sumatriptan) nasal powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
Migraine much more than just a headache
 Migraine much more than just a headache Session hosted by Teva UK Limited PUU4 11:15 12:15 UK/NHSS/18/0021b Date of Preparation: August 2018 The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker
Migraine much more than just a headache Session hosted by Teva UK Limited PUU4 11:15 12:15 UK/NHSS/18/0021b Date of Preparation: August 2018 The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker
Rizatriptan vs. ibuprofen in migraine: a randomised placebo-controlled trial
 J Headache Pain (2007) 8:175 179 DOI 10.1007/s10194-007-0386-7 ORIGINAL Usha Kant Misra Jayantee Kalita Rama Kant Yadav Rizatriptan vs. ibuprofen in migraine: a randomised placebo-controlled trial Received:
J Headache Pain (2007) 8:175 179 DOI 10.1007/s10194-007-0386-7 ORIGINAL Usha Kant Misra Jayantee Kalita Rama Kant Yadav Rizatriptan vs. ibuprofen in migraine: a randomised placebo-controlled trial Received:
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines
 How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
How do we treat migraine? New SIGN Guidelines Managing your migraine Migraine Trust, Edinburgh 2018 Callum Duncan Consultant Neurologist Aberdeen Royal Infirmary Chair SIGN Guideline 155 Premonitory Mood
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, II. Management of Refractory Headaches
 Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, 2016 II. Management of Refractory Headaches Case presentation 1: A case of intractable daily-persistent headache Keio University School
Headache Master School Japan-Osaka 2016 (HMSJ-Osaka2016) October 23, 2016 II. Management of Refractory Headaches Case presentation 1: A case of intractable daily-persistent headache Keio University School
British Medical Journal. June 3, 2006;332: Patricia M Kearney, Colin Baigent, Jon Godwin, Heather Halls, Jonathan R Emberson, Carlo Patrono
 Do selective cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors and traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs increase the risk of atherothrombosis? Metaanalysis of randomised trials 1 British Medical Journal June 3,
Do selective cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitors and traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs increase the risk of atherothrombosis? Metaanalysis of randomised trials 1 British Medical Journal June 3,
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE
 MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
MIGRAINE A MYSTERY HEADACHE The migraine is a chronic neurological disease that is characterized by moderate to severe episodes of headache that is mostly associated with other central nervous system (CNS)
Disclosure. Learning Objectives 1/17/2018. Pumping the Breaks in Pain Management: An Update on Cardiovascular Risk with NSAID Use
 Disclosure Pumping the Breaks in Pain Management: An Update on Cardiovascular Risk with Liz Van Dril, PharmD, BCPS PGY2 Ambulatory Care Resident January 17 th, 2018 Dr. Liz Van Dril has no actual or potential
Disclosure Pumping the Breaks in Pain Management: An Update on Cardiovascular Risk with Liz Van Dril, PharmD, BCPS PGY2 Ambulatory Care Resident January 17 th, 2018 Dr. Liz Van Dril has no actual or potential
What is the Effectiveness of OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox ) in Reducing the Number of Chronic Migraines (CM) in Patients Years Old?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2013 What is the Effectiveness of OnabotulinumtoxinA
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2013 What is the Effectiveness of OnabotulinumtoxinA
Migraine Management. Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital
 Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Migraine Management Jane Melling Headache nurse Mater Misericordiae Hospital Migraine facts Among the most common disorders of the nervous system 3 rd most prevalent medical disorder on the planet (lancet
Migranal Nasal Spray. Migranal Nasal Spray (dihydroergotamine) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: June 22, 2017 Migranal Nasal Spray
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: June 22, 2017 Migranal Nasal Spray
10/17/2017 CHRONIC MIGRAINES BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES PATIENT CASE EPIDEMIOLOGY EPIDEMIOLOGY
 BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES JENNIFER SHIN, PHARMD PGY2 AMBULATORY CARE PHARMACY RESIDENT COMMUNITYCARE HEALTH CENTERS PHARMACOTHERAPY ROUNDS OCTOBER 20, 2017
BOTOX: TO INJECT OR NOT INJECT? IN CHRONIC MIGRAINE PROPHYLAXIS OBJECTIVES JENNIFER SHIN, PHARMD PGY2 AMBULATORY CARE PHARMACY RESIDENT COMMUNITYCARE HEALTH CENTERS PHARMACOTHERAPY ROUNDS OCTOBER 20, 2017
COX-2 inhibitors: A cautionary tale. October 2, 2006
 COX-2 inhibitors: A cautionary tale October 2, 2006 Molecular interventions in human disease... An approach as old as human civilization. With whom the herbs have come together Like kingly chiefs unto
COX-2 inhibitors: A cautionary tale October 2, 2006 Molecular interventions in human disease... An approach as old as human civilization. With whom the herbs have come together Like kingly chiefs unto
Regulatory Status FDA approved indication: Migranal Nasal Spray is indicated for the acute treatment of migraine headaches with or without aura (1).
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Migranal Nasal Spray
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.60 Subject: Migranal Nasal Spray Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Migranal Nasal Spray
Migraine: Developing Drugs for Acute Treatment Guidance for Industry
 Migraine: Developing Drugs for Acute Treatment Guidance for Industry U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) February 2018
Migraine: Developing Drugs for Acute Treatment Guidance for Industry U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) February 2018
MEASURE #1: MEDICATION PRESCRIBED FOR ACUTE MIGRAINE ATTACK Headache
 MEASURE #1: MEDICATION PRESCRIBED FOR ACUTE MIGRAINE ATTACK Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of migraine who were prescribed a guideline recommended
MEASURE #1: MEDICATION PRESCRIBED FOR ACUTE MIGRAINE ATTACK Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of migraine who were prescribed a guideline recommended
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centers: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 CGRP Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
CGRP Page 1 of 8 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
Headache Classifica-on
 Headache Classifica-on 2 Tension-Type Headache Criteria -Infrequent episodic tension-type headache- A. At least 10 episodes occurring on < 1 day per month on average (< 12 days per year) and fulfilling
Headache Classifica-on 2 Tension-Type Headache Criteria -Infrequent episodic tension-type headache- A. At least 10 episodes occurring on < 1 day per month on average (< 12 days per year) and fulfilling
LOW DOSE ASPIRIN CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE FOR PROPHYLAXIS OF FOR BACKGROUND USE ONLY NOT TO BE USED IN DETAILING
 LOW DOSE ASPIRIN FOR PROPHYLAXIS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE FOR BACKGROUND USE ONLY NOT TO BE USED IN DETAILING Use of Low Dose Aspirin to Treat and Prevent Cardiovascular Disease In recent decades, aspirin
LOW DOSE ASPIRIN FOR PROPHYLAXIS OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE FOR BACKGROUND USE ONLY NOT TO BE USED IN DETAILING Use of Low Dose Aspirin to Treat and Prevent Cardiovascular Disease In recent decades, aspirin
Zonisamide for migraine prophylaxis in refractory patients
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Neurology Faculty Papers Department of Neurology March 2006 Zonisamide for migraine prophylaxis in refractory patients Avi Ashkenazi
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Neurology Faculty Papers Department of Neurology March 2006 Zonisamide for migraine prophylaxis in refractory patients Avi Ashkenazi
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 CGRP Page 1 of 13 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
CGRP Page 1 of 13 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
Despite the widespread use of triptans ... REPORTS... Almotriptan: A Review of Pharmacology, Clinical Efficacy, and Tolerability
 ... REPORTS... Almotriptan: A Review of Pharmacology, Clinical Efficacy, and Tolerability Randal L. Von Seggern, PharmD, BCPS Abstract Objective: This article summarizes preclinical and clinical data for
... REPORTS... Almotriptan: A Review of Pharmacology, Clinical Efficacy, and Tolerability Randal L. Von Seggern, PharmD, BCPS Abstract Objective: This article summarizes preclinical and clinical data for
SUMAVEL DOSEPRO (sumatriptan succinate) solution for injection
 SUMAVEL DOSEPRO (sumatriptan succinate) solution for injection Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit
SUMAVEL DOSEPRO (sumatriptan succinate) solution for injection Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates
 Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
Headache Mary D. Hughes, MD Neuroscience Associates Case 1 22 year old female presents with recurrent headaches. She has had headaches for the past 3 years. They start on the right side of her head and
ACUTE TREATMENT FOR MIGRAINE. Cristina Tassorelli
 The European Headache School 2012 ACUTE TREATMENT FOR MIGRAINE Cristina Tassorelli Headache Science Centre, IRCCS Neurological Institute C. Mondino Foundation - Pavia University Centre for Adaptive Disorders
The European Headache School 2012 ACUTE TREATMENT FOR MIGRAINE Cristina Tassorelli Headache Science Centre, IRCCS Neurological Institute C. Mondino Foundation - Pavia University Centre for Adaptive Disorders
Inpatient Treatment of Status Migraine With Dihydroergotamine in Children and Adolescents
 Headache 2008 the Authors Journal compilation 2008 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01293.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Brief Communication Inpatient Treatment
Headache 2008 the Authors Journal compilation 2008 American Headache Society ISSN 0017-8748 doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2008.01293.x Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. Brief Communication Inpatient Treatment
MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache
 MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older with a diagnosis of primary headache
MEASURE #4: Overuse of Barbiturate Containing Medications for Primary Headache Disorders Headache Measure Description Percentage of patients age 18 years old and older with a diagnosis of primary headache
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
Headache A Practical Approach
 Headache A Practical Approach Integrated Pain Symposium December 1, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache and Pain Development Teams Disclosures:
Headache A Practical Approach Integrated Pain Symposium December 1, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache and Pain Development Teams Disclosures:
MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND
 MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND HEADACHE IN MEN: THE FACTS This leaflet was composed by Paolo Rossi M.D., Ph.D. of the European Headache Alliance to mark European Migraine Day of Action 2014. Why a leaflet
MIGRAINE ASSOCIATION OF IRELAND HEADACHE IN MEN: THE FACTS This leaflet was composed by Paolo Rossi M.D., Ph.D. of the European Headache Alliance to mark European Migraine Day of Action 2014. Why a leaflet
Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017
 Migraine Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache Disclosures: none Learning Objectives: At the conclusion
Migraine Clinical Learning Days November 10, 2017 Alyssa Lettich. MD Neurosciences Institute/Neurosciences Clinical Program Medical Director Headache Disclosures: none Learning Objectives: At the conclusion
Disclosures. Triptans for Kids 5/16/13
 5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
5/16/13 Disclosures Triptans for Kids Amy A. Gelfand, MD GelfandA@neuropeds.ucsf.edu Departments of Neurology and Pediatrics UCSF Child Neurology and Headache Center I receive grant funding from: NIH/NINDS
10/13/17. Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD
 Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD } Depomed Consultant 2014 to present } Avanir Consultant 2014 to present } Amgen
Christy M. Jackson, MD Director, Dalessio Headache Center Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Clinical Professor, Neurosciences UCSD } Depomed Consultant 2014 to present } Avanir Consultant 2014 to present } Amgen
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description
 Measure Title Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description Percentage of s age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of primary headache who were prescribed
Measure Title Overuse of barbiturate and opioid containing medications for primary headache disorders Description Percentage of s age 12 years and older with a diagnosis of primary headache who were prescribed
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines
 Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
Update on Diagnosis and Management of Migraines Joel J. Heidelbaugh, MD, FAAFP, FACG Clinical Professor Departments of Family Medicine and Urology University of Michigan Learning Objectives To distinguish
A case of a patient with chronic headache. Focus on Migraine. None related to the presentation Grants to conduct clinical trials from: Speaker bureau:
 Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Chronic Daily Headache Bassel F. Shneker, MD, MBA Associate Professor Vice Chair, OSU Neurology The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Financial Disclosures None related to the presentation Grants
Balanced Analgesia With NSAIDS and Coxibs. Raymond S. Sinatra MD, Ph.D
 Balanced Analgesia With NSAIDS and Coxibs Raymond S. Sinatra MD, Ph.D Prostaglandins and Pain The primary noxious mediator released from damaged tissue is prostaglandin (PG) PG is responsible for nociceptor
Balanced Analgesia With NSAIDS and Coxibs Raymond S. Sinatra MD, Ph.D Prostaglandins and Pain The primary noxious mediator released from damaged tissue is prostaglandin (PG) PG is responsible for nociceptor
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Pain therapeutics. Acetaminophen/NSAIDs Acute pain Osteoarthritis Migraine Acute Gout Neuropathic pain
 Pain therapeutics Acetaminophen/NSAIDs Acute pain Osteoarthritis Migraine Acute Gout Neuropathic pain James McCormack, Pharm.D. Professor Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, UBC Common types of pain killers
Pain therapeutics Acetaminophen/NSAIDs Acute pain Osteoarthritis Migraine Acute Gout Neuropathic pain James McCormack, Pharm.D. Professor Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, UBC Common types of pain killers
Adult & Pediatric Patients. Stanford Health Care, Division Pain Medicine
 Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients Theresa Mallick Searle, MS, RN BC, ANP BC Disclosures Speakers Bureau: Allergan, Depomed Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients
Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients Theresa Mallick Searle, MS, RN BC, ANP BC Disclosures Speakers Bureau: Allergan, Depomed Acute Treatment Strategies in Adult & Pediatric Patients
Guidance for Industry Migraine: Developing Drugs for Acute Treatment
 Guidance for Industry Migraine: Developing Drugs for Acute Treatment DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only. Comments and suggestions regarding this draft
Guidance for Industry Migraine: Developing Drugs for Acute Treatment DRAFT GUIDANCE This guidance document is being distributed for comment purposes only. Comments and suggestions regarding this draft
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 0 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 0 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention
 Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention Amanda Janisch, PharmD PGY2 Ambulatory Care Pharmacy Resident MCHS SWMN, Mankato, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures No financial interest
Get ahead of the ACHE: Monoclonal Antibodies in Migraine Prevention Amanda Janisch, PharmD PGY2 Ambulatory Care Pharmacy Resident MCHS SWMN, Mankato, MN 2018 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures No financial interest
Migraine Management. Roger Cady, MD Headache Care Center Springfield, MO
 Migraine Management Roger Cady, MD Headache Care Center Springfield, MO Disclosures Objectives The evolution of migraine From benign episodic (benign) headache to potentially a devastating chronic disease
Migraine Management Roger Cady, MD Headache Care Center Springfield, MO Disclosures Objectives The evolution of migraine From benign episodic (benign) headache to potentially a devastating chronic disease
A new questionnaire for assessment of adverse events associated with triptans: methods of assessment influence the results. Preliminary results
 J Headache Pain (2004) 5:S112 S116 DOI 10.1007/s10194-004-0123-4 Michele Feleppa Fred D. Sheftell Luciana Ciannella Amedeo D Alessio Giancarlo Apice Nino N. Capobianco Donato M.T. Saracino Walter Di Iorio
J Headache Pain (2004) 5:S112 S116 DOI 10.1007/s10194-004-0123-4 Michele Feleppa Fred D. Sheftell Luciana Ciannella Amedeo D Alessio Giancarlo Apice Nino N. Capobianco Donato M.T. Saracino Walter Di Iorio
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา
 ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
ปวดศ รษะมา 5 ป ก นยาแก ปวดก ย งไม ข น นพ.พาว ฒ เมฆว ช ย โรงพยาบาลนครราชส มา 1 CONTENT 1 2 3 Chronic Daily Headache Medical Overused Headache Management Headaches are one of the most common symptoms List
Gastrointestinal Safety of Coxibs and Outcomes Studies: What s the Verdict?
 Vol. 23 No. 4S April 2002 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S5 Proceedings from the Symposium The Evolution of Anti-Inflammatory Treatments in Arthritis: Current and Future Perspectives Gastrointestinal
Vol. 23 No. 4S April 2002 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S5 Proceedings from the Symposium The Evolution of Anti-Inflammatory Treatments in Arthritis: Current and Future Perspectives Gastrointestinal
What is new in the migraine world! Modar Khalil Consultant neurologist Hull Royal Infirmary
 What is new in the migraine world! Modar Khalil Consultant neurologist Hull Royal Infirmary Overview Understanding the burden Commonly used terms Acute therapy What we currently have What we are going
What is new in the migraine world! Modar Khalil Consultant neurologist Hull Royal Infirmary Overview Understanding the burden Commonly used terms Acute therapy What we currently have What we are going
Characteristics of selective and non-selective NSAID use in Scotland
 Characteristics of selective and non-selective NSAID use in Scotland Alford KMG 1, Simpson C 1, Williams D 2 1 Department of General Practice & Primary Care, The University of Aberdeen. 2 Department of
Characteristics of selective and non-selective NSAID use in Scotland Alford KMG 1, Simpson C 1, Williams D 2 1 Department of General Practice & Primary Care, The University of Aberdeen. 2 Department of
Statement from the Steering Committee of the Alzheimer s Disease Anti inflammatory Prevention Trial (ADAPT)
 Statement for FDA Joint Advisory Committee page 1 Statement from the Steering Committee of the Alzheimer s Disease Anti inflammatory Prevention Trial (ADAPT) for communication to the FDA Arthritis Advisory
Statement for FDA Joint Advisory Committee page 1 Statement from the Steering Committee of the Alzheimer s Disease Anti inflammatory Prevention Trial (ADAPT) for communication to the FDA Arthritis Advisory
...SELECTED ABSTRACTS...
 The following abstracts, from medical journals containing literature on migraine management, were selected for their relevance to this Special Report supplement. Two Sumatriptan Studies Two double-blind
The following abstracts, from medical journals containing literature on migraine management, were selected for their relevance to this Special Report supplement. Two Sumatriptan Studies Two double-blind
Sumatriptan Tablets, Nasal Spray (Imitrex), Nasal Powder (Onzetra Xsail), sumatriptan and naproxen sodium (Treximet tablets)
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: December 2, 2016 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 05.70.10 Subject: Sumatriptan Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: December 2, 2016 Sumatriptan Description Sumatriptan
Caspian Journal of Neurological Sciences "Caspian J Neurol Sci" Journal Homepage:
 Caspian Journal of Neurological Sciences "Caspian J Neurol Sci" Journal Homepage: http://cjns.gums.ac.ir Research aper: or for Treatment of Medication Overuse Headache: A Randomized, Double- Blind Clinical
Caspian Journal of Neurological Sciences "Caspian J Neurol Sci" Journal Homepage: http://cjns.gums.ac.ir Research aper: or for Treatment of Medication Overuse Headache: A Randomized, Double- Blind Clinical
The use of combination therapies in the acute management of migraine
 REVIEW The use of combination therapies in the acute management of migraine Abouch Valenty Krymchantowski Headache Center of Rio, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; Outpatient Headache Unit of the Instituto de Neurologia
REVIEW The use of combination therapies in the acute management of migraine Abouch Valenty Krymchantowski Headache Center of Rio, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil; Outpatient Headache Unit of the Instituto de Neurologia
Migraine and hormonal contraceptives
 Migraine and hormonal contraceptives Department of Community Medicine, Systems Epidemiology University of Tromsø, November 2017 Nora Stensland Bugge Medical research student Presentation outline What is
Migraine and hormonal contraceptives Department of Community Medicine, Systems Epidemiology University of Tromsø, November 2017 Nora Stensland Bugge Medical research student Presentation outline What is
What A Headache! Theresa Biesiada March 8, 2012
 What A Headache! Theresa Biesiada March 8, 2012 Objectives Describe the EM relevance of headaches and migraines Discuss the rationale for steroid therapy Review the evidence Conclusions My inspiration
What A Headache! Theresa Biesiada March 8, 2012 Objectives Describe the EM relevance of headaches and migraines Discuss the rationale for steroid therapy Review the evidence Conclusions My inspiration
ARxCH. Annual Review of Changes in Healthcare. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptors and the Prevention of Migraines. Abstract
 Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptors and the Prevention of Migraines Brian Schuler, PharmD Candidate 2018 1 1 University of Findlay College of Pharmacy Abstract Migraines are the third most prevalent
Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Receptors and the Prevention of Migraines Brian Schuler, PharmD Candidate 2018 1 1 University of Findlay College of Pharmacy Abstract Migraines are the third most prevalent
Preventive Effect of Greater Occipital Nerve Block on Severity and Frequency of Migraine Headache
 Proceeding S.Z.P.G.M.I. Vol: 31(2): pp. 75-79, 2017. Preventive effect of Greater Occipital Nerve Block on Severity and Frequency of Migraine Headache Dr. Syed Mehmood Ali, Dr. Mudassar Aslam, Dr. Dawood
Proceeding S.Z.P.G.M.I. Vol: 31(2): pp. 75-79, 2017. Preventive effect of Greater Occipital Nerve Block on Severity and Frequency of Migraine Headache Dr. Syed Mehmood Ali, Dr. Mudassar Aslam, Dr. Dawood
Recurrent Headaches in Children -- An Analysis of 47 Cases
 ---------------------------------------------- Recurrent Headaches in Children -- An Analysis of Cases I H M I Hussain, MRCP Neurology Unit Paediatric Institute, Kuala Lumpur Hospital, )aian Pahang, 50586
---------------------------------------------- Recurrent Headaches in Children -- An Analysis of Cases I H M I Hussain, MRCP Neurology Unit Paediatric Institute, Kuala Lumpur Hospital, )aian Pahang, 50586
Paediatric headaches. Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services. Brevity, levity, repetition
 Paediatric headaches Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services Brevity, levity, repetition Paediatric)headache?)! Headache!in!children!is!not!that!common.!The!question!is!which!headaches!do!I!
Paediatric headaches Dr Jaycen Cruickshank Director of Clinical Training Ballarat Health Services Brevity, levity, repetition Paediatric)headache?)! Headache!in!children!is!not!that!common.!The!question!is!which!headaches!do!I!
Zomig. Zomig / Zomig-ZMT (zolmitriptan) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
Is the Migraid device an asset in the non-pharmacologic treatment of migraine?
 Acta neurol. belg., 2007, 107, 40-46 Is the Migraid device an asset in the non-pharmacologic treatment of migraine? Herman PIETERSE 1,3, Joop A. M. KUSTER 2 and Luc M. VAN BORTEL 1 1 Heymans Institute
Acta neurol. belg., 2007, 107, 40-46 Is the Migraid device an asset in the non-pharmacologic treatment of migraine? Herman PIETERSE 1,3, Joop A. M. KUSTER 2 and Luc M. VAN BORTEL 1 1 Heymans Institute
MIGRAINE A CAUSE OF INTENSE THROBBING; A MINI REVIEW
 IJBPAS, January, 2016, 5(1): 87-92 ISSN: 2277 4998 MIGRAINE A CAUSE OF INTENSE THROBBING; A MINI REVIEW MUHAMMAD ZAMAN 1*, RABIA HASSAN 1, MUHAMMAD SHAFEEQ UR RAHMAN 2, MUHAMMAD HAFIZ ARSHAD 3, SYED ATIF
IJBPAS, January, 2016, 5(1): 87-92 ISSN: 2277 4998 MIGRAINE A CAUSE OF INTENSE THROBBING; A MINI REVIEW MUHAMMAD ZAMAN 1*, RABIA HASSAN 1, MUHAMMAD SHAFEEQ UR RAHMAN 2, MUHAMMAD HAFIZ ARSHAD 3, SYED ATIF
Clinical case. Clinical case 3/15/2018 OVERVIEW. Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment. Refractory headache.
 OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
OVERVIEW Refractory headaches and update on novel treatment Definition of refractory headache Treatment approach Medications Neuromodulation In the pipeline Juliette Preston, MD OHSU Headache Center Refractory
COMBINATION THERAPIES PREVENTATIVE THERAPIES BETA BLOCKERS
 ACUTE THEAPIES TIPTANS TICYCLIC ANTIDEPESSANTS When starting acute treatment, healthcare professionals should warn patients about the risk of developing medication-overuse headache. ASPIIN Aspirin (900
ACUTE THEAPIES TIPTANS TICYCLIC ANTIDEPESSANTS When starting acute treatment, healthcare professionals should warn patients about the risk of developing medication-overuse headache. ASPIIN Aspirin (900
A one-year prospective costing study of botulinum toxin type A treatment of chronic tension headache
 J Headache Pain (2004) 5:192 196 DOI 10.1007/s10194-004-0100-3 ORIGINAL Fabio Palazzo Francesco S. Mennini Laura Fioravanti Laura Piasini Gabriella Coloprisco Paolo Martelletti A one-year prospective costing
J Headache Pain (2004) 5:192 196 DOI 10.1007/s10194-004-0100-3 ORIGINAL Fabio Palazzo Francesco S. Mennini Laura Fioravanti Laura Piasini Gabriella Coloprisco Paolo Martelletti A one-year prospective costing
CARDIOVASCULAR RISK and NSAIDs
 CARDIOVASCULAR RISK and NSAIDs Dr. Syed Ghulam Mogni Mowla Assistant Professor of Medicine Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College, Dhaka INTRODUCTION NSAIDs are most commonly prescribed drugs Recent evidence
CARDIOVASCULAR RISK and NSAIDs Dr. Syed Ghulam Mogni Mowla Assistant Professor of Medicine Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College, Dhaka INTRODUCTION NSAIDs are most commonly prescribed drugs Recent evidence
Maternity. Migraine in pregnancy Information for women
 Maternity Migraine in pregnancy Information for women You have been given this leaflet as you have a diagnosis of migraines. It contains advice to help you manage your migraines safely during your pregnancy.
Maternity Migraine in pregnancy Information for women You have been given this leaflet as you have a diagnosis of migraines. It contains advice to help you manage your migraines safely during your pregnancy.
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Current Migraine Treatment Therapy. Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN
 Current Migraine Treatment Therapy Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN Migraine a Disease Process Migraines are a chronic disease process similar to many other chronic medical conditions Migraine has a low mortality
Current Migraine Treatment Therapy Daniel Kassicieh, DO, FAAN Migraine a Disease Process Migraines are a chronic disease process similar to many other chronic medical conditions Migraine has a low mortality
Advances in the Treatment of Migraine
 Advances in the Treatment of Migraine C. Philip O Carroll, M.D. Director Neurobehavioral Medicine Hoag Neurosciences Institute Guyuron B Headache, 2015;55:1464-1473 I m sorry your head hurts, sweetie.is
Advances in the Treatment of Migraine C. Philip O Carroll, M.D. Director Neurobehavioral Medicine Hoag Neurosciences Institute Guyuron B Headache, 2015;55:1464-1473 I m sorry your head hurts, sweetie.is
Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache
 doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01488.x Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache L Pageler 1,2, Z Katsarava 2, HC Diener 2 & V Limmroth 1,2 1 Department of Neurology,
doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01488.x Prednisone vs. placebo in withdrawal therapy following medication overuse headache L Pageler 1,2, Z Katsarava 2, HC Diener 2 & V Limmroth 1,2 1 Department of Neurology,
COX-2 inhibitors: A cautionary tale
 COX-2 inhibitors: A cautionary tale October 1, 2007 Molecular interventions in human disease... An approach as old as human civilization. With whom the herbs have come together Like kingly chiefs unto
COX-2 inhibitors: A cautionary tale October 1, 2007 Molecular interventions in human disease... An approach as old as human civilization. With whom the herbs have come together Like kingly chiefs unto
TABLE 1. Current Diagnostic Criteria for Migraine Without Aura 2 A. At least 5 attacks fulfilling criteria B-D B. Headache attacks lasting 4-72 hours
 ANSWERS CONCISE TO FREQUENTLY REVIEW ASKED QUESTIONS FOR CLINICIANS ABOUT MIGRAINE Answers to Frequently Asked Questions About Migraine IVAN GARZA, MD, AND JERRY W. SWANSON, MD Migraine is a common primary
ANSWERS CONCISE TO FREQUENTLY REVIEW ASKED QUESTIONS FOR CLINICIANS ABOUT MIGRAINE Answers to Frequently Asked Questions About Migraine IVAN GARZA, MD, AND JERRY W. SWANSON, MD Migraine is a common primary
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy
 HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
HEADACHE: Benign or Severe Dr Gobinda Chandra Roy Associate Professor, Department of Medicine, Shaheed Suhrawardy Medical College and Hospital Outlines 1. Introduction 2. Classification of headache 3.
This document has not been circulated to either the industry or Consultants within the Suffolk system.
 New Medicine Report Document Status COX II Inhibitors In Acute Analgesia For Suffolk Drug & Therapeutics Committee Date of Last Revision 15 th February 2002 Reviewer s Comments There seems to be a growing
New Medicine Report Document Status COX II Inhibitors In Acute Analgesia For Suffolk Drug & Therapeutics Committee Date of Last Revision 15 th February 2002 Reviewer s Comments There seems to be a growing
Management of headache
 Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Management of headache TJ Steiner Imperial College London Based on European principles of management of common headache disorders TJ Steiner, K Paemeleire, R Jensen, D Valade, L Savi, MJA Lainez, H-C Diener,
Migraine: Past, Present and Future Edward O Sullivan September 12 th 2015 Dublin 12/09/2015
 1 Migraine: Past, Present and Future Edward O Sullivan September 12 th 2015 Dublin Tour de France 2015: Mark Renshaw Yesterday at the end of the stage 17 I came down with a migraine before the final climb
1 Migraine: Past, Present and Future Edward O Sullivan September 12 th 2015 Dublin Tour de France 2015: Mark Renshaw Yesterday at the end of the stage 17 I came down with a migraine before the final climb
Zomig. Zomig / Zomig-ZMT (zolmitriptan) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.70.22 Subject: Zomig Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: November 30, 2018 Zomig Description Zomig / Zomig-ZMT
A New Era of Migraine Management: The Challenging Landscape in Prevention
 Provided by MediCom Worldwide, Inc. Supported by an educational grant from Teva Pharmaceuticals What is a Neuropeptide? Small chains of amino acids released by neural cells (neurons or glial cells) to
Provided by MediCom Worldwide, Inc. Supported by an educational grant from Teva Pharmaceuticals What is a Neuropeptide? Small chains of amino acids released by neural cells (neurons or glial cells) to
NSAIDs: Side Effects and Guidelines
 NSAIDs: Side Effects and James J Hale FY1 Department of Anaesthetics Introduction The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a diverse group of drugs that have analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory
NSAIDs: Side Effects and James J Hale FY1 Department of Anaesthetics Introduction The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a diverse group of drugs that have analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory
This policy addresses only the type B formulation rimabotulinumtoxinb marketed as Myobloc.
 RimabotulinumtoxinB NDC CODE(S) 10454-0710-XX Myobloc 2500 UNIT/0.5ML SOLN (SOLSTICE NEUROSCIENCES) 10454-0711-XX Myobloc 5000 UNIT/ML SOLN (SOLSTICE NEUROSCIENCES) 10454-0712-XX Myobloc 10000 UNIT/2ML
RimabotulinumtoxinB NDC CODE(S) 10454-0710-XX Myobloc 2500 UNIT/0.5ML SOLN (SOLSTICE NEUROSCIENCES) 10454-0711-XX Myobloc 5000 UNIT/ML SOLN (SOLSTICE NEUROSCIENCES) 10454-0712-XX Myobloc 10000 UNIT/2ML
Ana Podgorac Belgrade, May 2012
 Headache and reproductive life Ana Podgorac Belgrade, May 2012 52 years old woman, English teacher in primary school, married, mother of two, with a history of migraine without aura. Over the last 6 months
Headache and reproductive life Ana Podgorac Belgrade, May 2012 52 years old woman, English teacher in primary school, married, mother of two, with a history of migraine without aura. Over the last 6 months
medications. This was an openlabel study consisting of patients with migraines who historically failed to respond to oral triptan
 J Headache Pain (2007) 8:13 18 DOI 10.1007/s10194-007-0354-7 ORIGINAL Seymour Diamond Fred G. Freitag Alexander Feoktistov George Nissan Sumatriptan 6 mg subcutaneous as an effective migraine treatment
J Headache Pain (2007) 8:13 18 DOI 10.1007/s10194-007-0354-7 ORIGINAL Seymour Diamond Fred G. Freitag Alexander Feoktistov George Nissan Sumatriptan 6 mg subcutaneous as an effective migraine treatment
New Zealand Data Sheet
 Arrow - Sumatriptan Sumatriptan Injection 6mg/0.5mL Presentation New Zealand Data Sheet ARROW SUMATRIPTAN Injection 6mg/0.5mL is a clear, colourless to pale yellow solution in a prefilled syringe. Uses
Arrow - Sumatriptan Sumatriptan Injection 6mg/0.5mL Presentation New Zealand Data Sheet ARROW SUMATRIPTAN Injection 6mg/0.5mL is a clear, colourless to pale yellow solution in a prefilled syringe. Uses
Migraine Diagnosis and Treatment: Results From the American Migraine Study II
 Migraine Diagnosis and Treatment: Results From the American Migraine Study II Richard B. Lipton, MD; Seymour Diamond, MD; Michael Reed, PhD; Merle L. Diamond, MD; Walter F. Stewart, MPH, PhD Objective.
Migraine Diagnosis and Treatment: Results From the American Migraine Study II Richard B. Lipton, MD; Seymour Diamond, MD; Michael Reed, PhD; Merle L. Diamond, MD; Walter F. Stewart, MPH, PhD Objective.
Atenolol in the prophylaxis of chronic migraine: a 3-month open-label study
 Edvardsson SpringerPlus 2013, 2:479 a SpringerOpen Journal RESEARCH Open Access Atenolol in the prophylaxis of chronic migraine: a 3-month open-label study Bengt Edvardsson Abstract Background: Chronic
Edvardsson SpringerPlus 2013, 2:479 a SpringerOpen Journal RESEARCH Open Access Atenolol in the prophylaxis of chronic migraine: a 3-month open-label study Bengt Edvardsson Abstract Background: Chronic
Medication For Migraine Chart: Table 1: Acute Treatment when the attack begins
 Medication For Migraine Chart: Table 1: Acute Treatment when the attack begins Page a Analgesics (painkillers) Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Prescription required Brand Name Formulation
Medication For Migraine Chart: Table 1: Acute Treatment when the attack begins Page a Analgesics (painkillers) Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Prescription required Brand Name Formulation
25/09/2018 HEADACHE. Dr Nick Pendleton
 HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2018 1 Small Group Work Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache
HEADACHE Dr Nick Pendleton September 2018 1 Small Group Work Tension Type Headache Cranial Nerve Examination Migraine Migraine Treatment Medication Overuse Headache Headache Red Flags Sinusitis Headache
Triptans: Nonresponse, Recurrence, and Serious AEs for Many Patients
 Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Rimegepant 75 mg, an Oral CGRP Receptor Antagonist, for the Acute Treatment of Migraine: Results from a Phase 3, Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial,
Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Rimegepant 75 mg, an Oral CGRP Receptor Antagonist, for the Acute Treatment of Migraine: Results from a Phase 3, Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial,
Rimoxen. Rimoxen! "The Gastro and Cardio friendly anti-inflammatory ingredient"
 Rimoxen A Botanical Anti-Inflammatory COX-2 Selective Ingredient Question: How doses Rimoxen compare to the prescription COX-2 inhibitors (Vioxx and Celebrex) and the OTC NSAID pain relievers such as aspirin
Rimoxen A Botanical Anti-Inflammatory COX-2 Selective Ingredient Question: How doses Rimoxen compare to the prescription COX-2 inhibitors (Vioxx and Celebrex) and the OTC NSAID pain relievers such as aspirin
Outpatient Headache Care Guideline
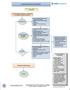 1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
1 Outpatient Care Guideline Inclusion criteria: children > 3 yrs with headaches Is urgent emergency department, neuroimaging, or Neurology consultation indicated? Referral to ED if: New severe headache
