Corneal hysteresis in patients with glaucoma-like optic discs, ocular hypertension and glaucoma
|
|
|
- Marianna Charlene Benson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Murphy et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:1 DOI /s RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Corneal hysteresis in patients with glaucoma-like optic discs, ocular hypertension and glaucoma Melissa L. Murphy *, Olya Pokrovskaya, Marie Galligan and Colm O Brien Abstract Background: To compare corneal hysteresis (CH) measurements between patients with glaucoma, ocular hypertension (OHT) and glaucoma-like optic discs (GLD)- defined as a cup to disc ratio greater than or equal to 0.6 with normal intraocular pressure (IOP) and visual fields. The secondary aim was to investigate whether corneal resistance factor (CRF) and central corneal thickness (CCT) differ between patient groups. Methods: In this cross sectional study a total of 123 patients (one eye each) were recruited from a glaucoma outpatient department to undergo ocular response analyser (ORA) testing and ultrasound pachymetry as well as clinical examination. A One-way Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA) was conducted to evaluate the mean difference in CH between the three diagnostic groups (glaucoma, OHT and GLD) correcting for potential confounding factors, IOP and age. Analysis was repeated for CRF and CCT. Results: There was a significant difference in mean CH across the three diagnosis groups; F(2, 115) = 96.95; p < Mean CH significantly higher for GLD compared to glaucoma (mean difference 1.83, p < 0.001), and significantly higher for OHT compared to glaucoma (mean difference 2.35, p < 0.001). Mean CH was slightly lower in patients with GLD than those with OHT but this difference was not statistically significant. A similar pattern was seen when the analysis was repeated for CRF and CCT. Conclusions: Higher CH in GLD and OHT compared to glaucoma suggests increased viscoelasticity of ocular tissues may have a protective role against glaucoma. Keywords: Corneal hysteresis, Corneal resistance factor, Glaucoma-like optic discs, Central corneal thickness, Ocular response analyser Background Glaucoma is a leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide. A recent meta-analysis estimated a significant increase in the incidence of glaucoma over the next three decades worldwide from 64.3 million affected in 2013, rising to 76 million in 2020, and to million in 2040 [1]. Glaucoma is defined as a multifactorial optic neuropathy characterised by the accelerated loss of retinal ganglion cells resulting in peripheral visual field loss. Age and raised intraocular pressure (IOP) are considered the main risk factors for glaucoma. Reduction in IOP, either by medical or surgical intervention, is currently the * Correspondence: murphm24@tcd.ie School of Medicine and Medical Sciences, Mater Misericordiae University Hospital, Eccles Street Dublin 7, Dublin, Ireland only proven treatment option [2]. It is estimated that 30 50% of glaucoma patients have normal IOP [3, 4] suggesting that other factors, including tissue biomechanics, may have a role in glaucoma risk and optic nerve damage progression. Recent studies have investigated the relationship between corneal structural properties and glaucoma. Corneal biomechanics offer us an insight into how the cornea behaves in certain situations and may thus be used to extrapolate optic nerve susceptibility to certain stressors. The physical composition of the cornea gives it viscoelastic properties, meaning it demonstrates elements of both viscosity and elasticity. Corneal hysteresis (CH) is defined as the viscous dampening of the cornea and reflects the ability of the cornea to absorb and The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Murphy et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:1 Page 2 of 8 dissipate energy [5, 6]. CH has a potential role as an IOP correction factor and as a proxy marker of an individual s susceptibility to glaucomatous optic neuropathy [5]. In addition, corneal resistance factor (CRF) reflects the elastic properties of the cornea i.e. its ability to deform reversibly under stress and appears to be an indicator of corneal resistance. Both can be measured using the Ocular Response Analyser (ORA) (Reichert, Corp.; NY, USA) which involves applying an air pulse of a defined magnitude to the surface of the cornea and measuring the difference between the two applantation measurements during corneal deformity and return to its original configuration [6]. The principal aim of our study was to determine if CH differs between patients with glaucoma, ocular hypertension (OHT) and glaucoma-like optic discs (GLD). The secondary aim was to investigate whether CRF and central corneal thickness (CCT) differ between these patient groups. We had a particular interest in GLD. To our knowledge, there have been no studies to date looking at the relationship between CH and GLD. Methods Subjects In this cross-sectional single-centre observational study a total of 123 patients were recruited at the glaucoma clinic in the Mater Misericordiae Hospital, Dublin, Ireland between July 2014 and July Both eyes from each patient were analysed using the ORA and one eye was chosen by random selection from each patient generating 123 eyes for inclusion in the study. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Patients with a diagnosis of high tension glaucoma (HTG) (n =37), pseudoexfoliative glaucoma (PXFG) (n =12), OHT (n =28), NTG (n =24) and GLD (n = 22) were recruited. The diagnosis was determined by a glaucoma specialist at a previous visit. Exclusion criteria were unreliable visual fields or previous glaucoma surgeries. The protocol of the study adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Examination techniques Diagnosis, IOP, CCT, CH and CRF was recorded for each patient. POAG referred to high or low pressure open angle glaucoma of unknown aetiology. High tension open angle glaucoma (HTG) was defined as a raised IOP of greater than 21 mmhg measured using Goldmann applanation tonometry (GAT), glaucomatous optic disc changes, an open drainage angle, and characteristic visual field defects on a Humphrey perimeter central 24-2 threshold test. Normal tension open angle glaucoma (NTG) was defined as glaucomatous disc changes and visual field loss without an IOP measurement exceeding 21 mmhg at any clinic visit. PXFG was defined as exfoliation material visualised within the anterior segment of the eye resulting in secondary open angle glaucoma. OHT was diagnosed on the basis of repeated IOP measurements of over 21 mmhg without evidence of glaucomatous nerve damage or visual field loss. For the purpose of this study GLD was defined similarly to the Tomita et al. study as an increased cup-to-disc ratio ( 0.6) and pallor, asymmetry of cupping between eyes in a patient with normal IOP, normal visual fields, and open angles [7]. The primary aim of this study was to determine whether CH differs between patients with glaucoma, OHT, and GLD. Therefore, CH is the primary outcome measure in this study. The secondary aim was to investigate whether CRF and CCT differ between these patient groups. For the purposes of statistical analysis NTG, HTG and PXFG patients were grouped together as glaucoma. Each of these subgroups demonstrate evidence of a glaucomatous optic neuropathy with corresponding visual field changes. The CH and CRF were measured using the Reichert ORA. Four measurements were taken for each selected eye and the average value was used in the analysis. CCT was measured in the same eye using a Pachmate 55 handheld ultrasonic pachymeter (DGH, Exton.; PA, USA) after instillation of one drop of topical proxymethacaine 0.5%. Statistical analysis Data including patient age, gender, diagnosis, CH, CRF and CCT was collated using Microsoft Excel and analysed using the statistical package IBM SPSS (version 20). Clinical information on patients was summarised by diagnosis group. Normality of each outcome variable was assessed using histograms and Shapiro-Wilk normality tests. One-way Analysis of Covariance (ANCOVA) was conducted to test for a difference in mean CH between the three diagnosis groups (glaucoma, OHT and GLD), whilst controlling for possible confounding factors IOP and age. IOP and age are both potential confounding factors for CH analysis, as lower CH is associated with higher IOP and older age, and these were corrected for in our analysis. All assumptions of ANCOVA including homogeneity of variance, homogeneity of regression slopes and homoscedasticity were tested before analysis. Bonferroni post hoc testing was used for conducting pairwise comparisons of CH between diagnosis groups. Similar analysis was carried out for CRF and CCT. Scatter plots and Pearson correlation coefficients were used to assess the relationships between CH and age, and between CH and CCT. In this study, a p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Murphy et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:1 Page 3 of 8 Results Subjects The study included one eye from each of 123 patients. Table 1 summarises the basic clinical information for the patients evaluated in this study in the three different diagnosis groups. There is a higher percentage of females (67.9%) in the GLD group compared to the OHT (53.4%) and glaucoma (45.5%) groups, and the GLD patients were a little younger on average than patients in the other two groups. Mean Goldmann-corrected IOP measured with ORA was higher in the GLD group (19.9 mmhg) than in the OHT and glaucoma groups (17.4 and 17.6 mmhg respectively). Differences in CH, CRF and CCT between patient subgroups Boxplots were used to compare the distribution of CH (Fig. 1, Top), CRF (Fig. 1, Middle) and CCT (Fig. 1, Bottom) across the three diagnostic groups. Table 2 shows the results of ANCOVA with CH as the dependent variable. It reveals a significant difference in mean CH across the three diagnosis groups; F(2, 115) = 96.95; p < Age and IOP were controlled for in this analysis but were not found to be significant. Post hoc pairwise comparisons of CH between diagnosis groups were conducted, using the Bonferroni method to correct for multiple testing error (Table 3). Mean CH was found to be significantly higher for GLD compared to glaucoma (mean difference 1.83, p < 0.001). Mean CH was also found to be significantly higher for OHT compared to glaucoma (mean difference 2.35, p < 0.001). Mean CH was slightly lower in patients with GLD than those with OHT but this difference was not statistically significant. These results are also reflected in the boxplots of CH by diagnosis group (Fig. 1a), showing lower CH values in general for patients with glaucoma, compared to the OHT and GLD diagnosis groups. A similar pattern was seen when the analysis was repeated for CRF and CCT. Mean CRF was significantly higher in GLD compared to glaucoma (mean difference 1.47, p < 0.01), and Table 1 Demographics and characteristics of the three diagnosis groups included in the study (Glaucoma, GLD and OHT) Glaucoma (n = 73) GLD (n = 22) OHT (n = 28) Total (n = 123) Female 10 (45.5%) 39 (53.4%) 19 (67.9%) 68 (55.3%) Male 12 (54.5%) 34 (46.6%) 9 (32.1%) 55 (44.7%) Age (years) 67 ± ± ± ± 13 IOPg (mm Hg) 17.6 ± ± ± ± 4.3 CH (mm Hg) 9.9 ± ± ± ± 2.1 Gender is summarised by frequency and percentage; other variables by mean ± SD GLD glaucoma-like optic discs, OHT ocular hypertension, IOPg Goldmann-corrected IOP, CH corneal hysteresis, SD standard deviation significantly higher in OHT compared to glaucoma (mean difference 2.17, p < 0.01). We also demonstrated that CCT is significantly thicker in GLD compared to glaucoma (mean difference 27.5 μm, p < 0.01) and CCT is also significantly thicker in OHT compared to glaucoma (mean difference 20.0 μm, p = 0.03). Correlations between CH and CCT and patient age Finally, the scatter plots (Fig. 2) illustrate the relationship between CH and age, and the relationship between CH and CCT across all groups pooled together. These plots demonstrate a negative correlation between CH and age (r = 0.22, p = 0.005) and a strong positive correlation between CH and CCT (r = 0.40, p = <0.001). Discussion and conclusions This work provides novel insight into the interplay of corneal biomechanical properties and glaucoma. Our results are consistent with previous research in demonstrating higher CH in patients with a diagnosis of OHT as compared to patients with glaucoma [8]. In a prospective observational study Shah et al. compared CH and CRF between patients with OHT, NTG and POAG and found CH to be highest in the OHT group in keeping with our findings [8]. This suggests that higher CH may have a protective role in patients with raised IOP. Furthermore, our study found a significantly higher CH in patients with GLD compared to glaucoma patients. A similar pattern was also seen in the CRF values between the groups, suggesting greater viscoelasticity of ocular tissue in GLD and OHT patients than in glaucoma patients. This adds to the body of evidence surrounding the diagnostic promise of corneal hysteresis, and the hypothesis that increased viscoelasticity of ocular tissues may be protective against glaucomatous nerve damage. Our work also demonstrated that CCT was significantly thicker in both the OHT and GLD groups compared to glaucoma patients. This may reflect an inherent resilience against glaucomatous tissue damage in the GLD and OHT subgroup. CCT has been shown to be a protective factor in patients against glaucoma in numerous previous studies [9 11]. We demonstrated a weak negative correlation between CH and age, as well as a strong positive correlation between both CH and CRF with CCT. This would suggest thicker corneas may be more compliant and reflect a reduced susceptibility to high IOP within the eye, as well as the established fact that thicker corneas may result in falsely elevated IOP measurements. A number of studies have been published in the area of corneal biomechanics in glaucoma patients. These findings are strongly suggestive that corneal viscoelasticity is altered in the disease progress. Kotecha et al. described an IOP-independent corneal factor (corneal
4 Murphy et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:1 Page 4 of 8 Fig. 1 Differences in CH, CRF and CCT between patient subgroups. Box and whiskers plots illustrating the difference in mean and interquartile range of corneal hysteresis (CH) (Top), corneal resistance factor (CRF) (Middle), and central corneal thickness (CCT) (Bottom) between the three diagnosis subgroups (glaucoma-like discs [GLD], glaucoma, ocular hypertension [OHT]). CH and CRF is higher in both OHT and GLD compared to glaucoma. A similar pattern was demonstrated in CCT across patient subgroups
5 Murphy et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:1 Page 5 of 8 Table 2 ANCOVA showing significantly different CH in diagnosis groups correcting for IOP and age Test of between-subject effects Source Type III sum of squares df Mean square F Sig. Partial Eta Squared Corrected Model a Intercept Diagnosis Age IOPg Error Total Corrected Total ANCOVA one-way analysis of covariance, CH corneal hysteresis, IOPg Goldmann-correlated IOP, df degrees of freedom, Sig. significance level a R Squared =.268 (Adjusted R Squared =.243) constant factor; mm Hg) and demonstrated that this parameter increased with thicker CCT and decreased with age [12]. Other studies have also found an association between greater CH, greater CCT, and lower IOP [6, 13, 14]. One such study looking at 207 normal eyes demonstrated only a moderate correlation between CH and increasing CCT suggesting CH measurements may reflect different aspects of biomechanical rigidity [6]. In contrast, a study on patients with unilateral POAG found that CH but not CRF was significantly correlated with IOP concluding that once CH is corrected for IOP, there is no difference in corneal biomechanical properties between eyes with and without POAG [13]. Due to these findings it is important to take both CH and CRF into consideration. Interestingly, a number of recent publications suggest faster rates of glaucomatous progression in patients with a lower CH. This is evidenced by accelerated progression of visual field defects [9, 15, 16]. Regarding GLD, a study conducted by Tomita et al. in 1989 first described this subgroup as a variant of glaucoma with increased cupping and pallor, superior or inferior extension of cupping with pallor and asymmetry of cupping, and pallor between eyes without associated increased IOP or visual field loss [7]. The study compared 48 GLD patients to 48 primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) patients in relation to optic disc fluoroscein angiography, family history of glaucoma and retinal nerve fiber layer defects with no statistically significant difference between groups concluding that GLD may be a variant of POAG. Furthermore, another study of GLD patients comparing glaucoma-like discs to optic discs in normal controls using stereophotogrammetry revealed a significant reduction in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in GLD compared to healthy controls, again suggesting GLD may be a variant of glaucoma [17]. The results of our study support the growing body of evidence for the importance of the biomechanical properties of ocular tissues in the pathophysiological glaucomatous process. This means structural changes, such as altered tissue compliance, especially at the optic nerve, may reflect altered susceptibility in individual patients to both disease emergence and progression. This may have particular significance in patients who have disease despite normal IOP (i.e. NTG) and in the required follow-up of patients with suspect discs who are yet to demonstrate visual field loss. It is also known that CH and CRF are affected by age such that age-associated tissue remodelling is reflected in a reduction of CH. This has been demonstrated in studies on corneal biomechanics in older healthy volunteers compared to younger counterparts in which a significantly reduced CH was seen with ageing [18, 19]. Ageing is associated with reduced elasticity and therefore reduced compliance in tissues throughout the body [20 23]. This process is believed to be a combination of Table 3 Bonferroni post-hoc analysis of CH across diagnosis groups Comparison Mean difference Std. error Sig. b 95% confidence interval for difference b Lower bound Upper bound GLD vs Glaucoma a OHT vs GLD OHT vs Glaucoma a Based on estimated marginal means CH corneal hysteresis, GLD glaucoma-like discs, OHT ocular hypertension, Sig. significance level a The mean difference is significant at the b Adjustment for multiple comparisons: Bonferroni
6 Murphy et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:1 Page 6 of 8 Fig. 2 Correlations between CH and age and also between CH and CCT. The relationships between corneal hysteresis (CH) and age (Top), and CH and central corneal thickness (CCT) (Bottom). There is a weak negative correlation between CH and age (r = 0.22, p = 0.01) and a strong positive correlation between CH and CCT (r = 0.40, p = <0.001) both oxidative stress caused by reactive oxygen species and the formation of advanced glycosylation end products caused by the non-enzymatic glycation of proteins [24]. These, in combination, result in haphazard crosslinking of proteins, altering tissue architecture and resulting in reduced elasticity. A reduction in mechanical compliance with age has been demonstrated in the cornea [22], the lamina cribrosa [20], the sclera [21], the ciliary muscle, and lens [23]. In 2014, the EPIC-Norfolk Eye Study found CH to be negatively correlated with both linear cup-to-disc ratio and increasing age [18]. In addition, hormonal factors may impact on the biomechanical properties of the cornea, with oestrogen believed to have a protective role [25, 26]. Due to the substantial evidence that ocular biomechanical response to increased IOP affects the degree of glaucoma damage this is becoming an exciting new target for the development of glaucoma therapies [27]. The significance of our results are that CH may provide further information on the reason why some individuals with a high cup:disc ratio and normal IOP develop NTG whereas others do not. To our knowledge
7 Murphy et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:1 Page 7 of 8 we are the first group to look at CH in patients with GLD compared to patients with demonstrable glaucoma and we find it to be significantly higher in this patient cohort. IOP measurements as well as CCT, optic disc characteristics and visual field defects are routinely reported in patients at risk of this disease. However, altered tissue biomechanics may have an important role to play in both the diagnosis and the monitoring of disease progression, and are not adequately accounted for in the aforementioned parameters. The inclusion of CH and CRF measurements as part of a routine follow-up examination or even as part of an initial assessment may help to individualise patient therapy resulting in improved and tailored management. A direct measurement of optic head tissue compliance may be more relevant in glaucoma patients. A recent paper by Li et al. in 2016 suggested lamina cribrosa depth analysis using enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography can help differentiate HTG from normal eyes as it is more posteriorly located in HTG [28]. Limitations of our study include that patients were not followed up over a period of time to assess CH as an independent risk factor in the emergence of disease in glaucoma suspects and OHT patients, as well as a potential risk factor in the disease progression of known glaucoma patients. Also HTG, PXFG and NTG were grouped together as glaucoma patients for the purpose of analysis whereas separate analysis of each of these groups could yield more accurate results. Future research in the area of CH should focus on its role in other diseases characterised by altered tissue compliance such as diabetes and hypertension. These areas may reflect a further advantage for the addition of CH measurements into routine ophthalmological examinations. Abbreviations ANCOVA: One-way analysis of covariance; CCT: Central corneal thickness; CH: Corneal hysteresis; CRF: Corneal resistance factor; GLD: Glaucoma-like optic discs; HTG: High tension glaucoma; IOP: Intraocular pressure; NTG: Normal tension glaucoma; OHT: Ocular hypertension; ORA: Ocular response analyser; POAG: Primary open angle glaucoma; PXFG: Pseudoexfoliation glaucoma Acknowledgements Not applicable. Funding There was no funding body involved in this research. Availability of data and materials All data generated or analysed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Authors contributions All authors contributed significantly to this work. COB conceived the study. MM and COB contributed to study design and data collection. OP and MG performed statistical analysis. MM and OP and COB contributed to writing up the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interest. Consent for publication Not applicable. Ethics approval and consent to participate All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the guidelines set out by the Irish Council for Bioethics on observational studies and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments. Informed consent was obtained from all the individual participants included in this non-interventional study. Received: 12 August 2016 Accepted: 16 December 2016 References 1. Tham YC, Li X, Quigley HA, Aung T, Cheng CY. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology. 2014;121: Kashiwagi K, Tsukahara S. Impact of Patient Access to Internet Health Records on Glaucoma Medication: Randomized Controlled Trial. J Med Internet Res. 2014;16: Klein B, Klein R, Sponsel WE, Franke T, Cantor LB, Martone J, et al. Prevalence of glaucoma. The Beaver Dam Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 1992;99: Sommer A. Epidemiology as it relates to screening for glaucoma. Surv Ophthalmol. 1989;33: Luce DA. Determining in vivo biomechanical properties of the cornea with an ocular response analyzer. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31: Shah S, Laiquzzaman M, Cunliffe, Mantry S. The use of the Reichert ocular response analyser to establish the relationship between ocular hysteresis, corneal resistance factor and central corneal thickness in normal eyes. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2006;29: Tomita G, Takamoto T, Schwartz B. Glaucoma-like disks without increased intraocular pressure or visual field loss. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989;108: Shah S, Laiquzzaman M, Mantry S, Cunliffe I. Ocular response analyser to assess hysteresis and corneal resistance factor in low tension, open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2008;36: Congdon NG, Broman AT, Bandeen-Roche K, Grover D, Quigley HA. Central corneal thickness and corneal hysteresis associated with glaucoma damage. Am J Ophthalmol. 2006;141: Insull E, Nicholas S, Ang GS, Poostchi A, Chan K, Wells A. Optic disc area and correlation with central corneal thickness, corneal hysteresis and ocular pulse amplitude in glaucoma patients and controls. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2010;38: Viswanathan D, Goldberg I, Graham SL. Relationship of change in central corneal thickness to visual field progression in eyes with glaucoma. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2013;251: Kotecha A, Elsheikh A, Roberts CR, Zhu H, Garway-Heath DF. Corneal thickness and age-related biomechanical properties of the cornea measured with the ocular response analyzer. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006;47: Hirneiß C, Neubauer AS, Yu A, Kampik A, Kernt M. Corneal biomechanics measured with the ocular response analyser in patients with unilateral open-angle glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol. 2011;89: Touboul D, Roberts C, Kérautret J, Garra C, Maurice-Tison S, Saubusse E, et al. Correlations between corneal hysteresis, intraocular pressure, and corneal central pachymetry. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34: Medeiros FA, Meira-Freitas D, Lisboa R, Kuang T-M, Zangwill LM, Weinreb RN. Corneal hysteresis as a risk factor for glaucoma progression: a prospective longitudinal study. Ophthalmology. 2013;120: De Moraes CVG, Hill V, Tello C, Liebmann JM, Ritch R. Lower corneal hysteresis is associated with more rapid glaucomatous visual field progression. J Glaucoma. 2012;21: Peigne G, Schwartz B, Takamoto T. Differences of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness between normal and glaucoma like optic disks (physiological cups) matched by optic disk area. Acta Ophthalmol. 1993;71: Khawaja AP, Chan MP, Broadway DC, Garway-Heath DF, Luben R, Yip JL, et al. Corneal biomechanical properties and glaucoma-related quantitative traits in the EPIC-Norfolk Eye Study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55:
8 Murphy et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:1 Page 8 of Kida T, Liu JH, Weinreb RN. Effects of aging on corneal biomechanical properties and their impact on 24-hour measurement of intraocular pressure. Am J Ophthalmol. 2008;146: Albon J, Purslow PP, Karwatowski WS, Easty DL. Age related compliance of the lamina cribrosa in human eyes. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000;84: Coudrillier B, Tian J, Alexander S, Myers KM, Quigley HA, Nguyen TD. Biomechanics of the human posterior sclera: age-and glaucoma-related changes measured using inflation testing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53: Cartwright NEK, Tyrer JR, Marshall J. Age-related differences in the elasticity of the human cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52: Strenk SA, Semmlow JL, Strenk LM, Munoz P, Gronlund-Jacob J, DeMarco JK. Age-related changes in human ciliary muscle and lens: a magnetic resonance imaging study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999;40: Bailey AJ. Molecular mechanisms of ageing in connective tissues. Mech Ageing Dev. 2001;122: Spoerl E, Zubaty V, Raiskup-Wolf F, Pillunat LE. Oestrogen-induced changes in biomechanics in the cornea as a possible reason for keratectasia. Br J Ophthalmol. 2007;91: Wei X, Cai S-P, Zhang X, Li X, Chen X, Liu X. Is low dose of estrogen beneficial for prevention of glaucoma? Med Hypotheses. 2012;79: Quigley HA, Cone FE. Development of diagnostic and treatment strategies for glaucoma through understanding and modification of scleral and lamina cribrosa connective tissue. Cell Tissue Res. 2013;353: Li L, Bian A, Cheng G, Zhou Q. Posterior displacement of the lamina cribrosa in normal-tension and high-tension glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol. 2016; doi: /aos Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and we will help you at every step: We accept pre-submission inquiries Our selector tool helps you to find the most relevant journal We provide round the clock customer support Convenient online submission Thorough peer review Inclusion in PubMed and all major indexing services Maximum visibility for your research Submit your manuscript at
Evaluation of the Effect of Diabetes Mellitus on Corneal Biomechanics
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2019) Vol. 74 (4), Page 782-788 Abd Elmagid Mohamed Tag Eldin, Abdulmoez Haddad Ahmed, Amr Khalil Abdelmonem* Ophthalmology department, Faculty of Medicine,
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2019) Vol. 74 (4), Page 782-788 Abd Elmagid Mohamed Tag Eldin, Abdulmoez Haddad Ahmed, Amr Khalil Abdelmonem* Ophthalmology department, Faculty of Medicine,
Make a more confident glaucoma risk assessment with Corneal Hysteresis, a superior predictor of glaucoma progression.
 Make a more confident glaucoma risk assessment with Corneal Hysteresis, a superior predictor of glaucoma progression. Advancing Eye Care. American Innovation. Reichert Ocular Response Analyzer G3. Make
Make a more confident glaucoma risk assessment with Corneal Hysteresis, a superior predictor of glaucoma progression. Advancing Eye Care. American Innovation. Reichert Ocular Response Analyzer G3. Make
The Ocular Response Analyzer (ORA; Reichert Ophthalmic
 Glaucoma Lack of Association Between Corneal Hysteresis and Corneal Resistance Factor With Glaucoma Severity in Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma Monisha E. Nongpiur, 1,2 Owen Png, 2 Jestin W. Chiew, 3 Kenric
Glaucoma Lack of Association Between Corneal Hysteresis and Corneal Resistance Factor With Glaucoma Severity in Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma Monisha E. Nongpiur, 1,2 Owen Png, 2 Jestin W. Chiew, 3 Kenric
Intro to Glaucoma/2006
 Intro to Glaucoma/2006 Managing Patients with Glaucoma is Exciting Interesting Challenging But can often be frustrating! Clinical Challenges To identify patients with risk factors for possible glaucoma.
Intro to Glaucoma/2006 Managing Patients with Glaucoma is Exciting Interesting Challenging But can often be frustrating! Clinical Challenges To identify patients with risk factors for possible glaucoma.
Role of Central Corneal Thickness in Circadian Intraocular Pressure Fluctuations among Patients with Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
 Role of Central Corneal Thickness in Circadian Intraocular Pressure Fluctuations among Patients with Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Mohannad Albdour MD*, Karanjit Kooner MD, PHD** ABSTRACT Objectives: To
Role of Central Corneal Thickness in Circadian Intraocular Pressure Fluctuations among Patients with Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Mohannad Albdour MD*, Karanjit Kooner MD, PHD** ABSTRACT Objectives: To
Policy #: 354 Latest Review Date: July 2011
 Name of Policy: Corneal Hysteresis Policy #: 354 Latest Review Date: July 2011 Category: Medicine Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and updates. Background/Definitions:
Name of Policy: Corneal Hysteresis Policy #: 354 Latest Review Date: July 2011 Category: Medicine Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and updates. Background/Definitions:
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Comparison of Ocular Response Analyzer Parameters in Chinese Subjects With Primary Angle-Closure and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Comparison of Ocular Response Analyzer Parameters in Chinese Subjects With Primary Angle-Closure and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Arun Narayanaswamy, DNB; Daniel H. Su, FRCS(Edin); Mani
CLINICAL SCIENCES Comparison of Ocular Response Analyzer Parameters in Chinese Subjects With Primary Angle-Closure and Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Arun Narayanaswamy, DNB; Daniel H. Su, FRCS(Edin); Mani
The innovative aspects are that ORA G3 is currently the only device capable of measuring corneal hysteresis.
 pat hways ORA G3 to measure corneal hysteresis Medtech innovation briefing Published: 18 June 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib150 Summary The technology described in this briefing is Ocular Response Analyzer
pat hways ORA G3 to measure corneal hysteresis Medtech innovation briefing Published: 18 June 2018 nice.org.uk/guidance/mib150 Summary The technology described in this briefing is Ocular Response Analyzer
Correlating central corneal thickness and intraocular pressure in ocular hypertension and glaucoma
 VOL. 3 NO. 1 PHILIPPINE JOURNAL OF Ophthalmology JANUARY ORIGINAL ARTICLE JUNE 07 Jonathan G. Soriano, MD 1 Ma. Margarita L. Lat-Luna, MD 1, 3 Patricia M. Khu, MD 1, 1 Department of Ophthalmology and Visual
VOL. 3 NO. 1 PHILIPPINE JOURNAL OF Ophthalmology JANUARY ORIGINAL ARTICLE JUNE 07 Jonathan G. Soriano, MD 1 Ma. Margarita L. Lat-Luna, MD 1, 3 Patricia M. Khu, MD 1, 1 Department of Ophthalmology and Visual
Corneal Hysteresis and Visual Field Asymmetry in Open Angle Glaucoma SUBJECTS AND METHODS
 Glaucoma Corneal Hysteresis and Visual Field Asymmetry in Open Angle Glaucoma Aashish Anand, 1 Carlos Gustavo V. De Moraes, 1,2 Christopher C. Teng, 1,2,3 Celso Tello, 1,3 Jeffrey M. Liebmann, 1,2 and
Glaucoma Corneal Hysteresis and Visual Field Asymmetry in Open Angle Glaucoma Aashish Anand, 1 Carlos Gustavo V. De Moraes, 1,2 Christopher C. Teng, 1,2,3 Celso Tello, 1,3 Jeffrey M. Liebmann, 1,2 and
Central Corneal Thickness-An important variable for prognostication in Primary Open Angle glaucoma; A Kolkata based study in Eastern India
 Original article: Central Corneal Thickness-An important variable for prognostication in Primary Open Angle glaucoma; A Kolkata based study in Eastern India 1Dr. Apala Bhattacharya, 2 Dr Gautam Bhaduri,
Original article: Central Corneal Thickness-An important variable for prognostication in Primary Open Angle glaucoma; A Kolkata based study in Eastern India 1Dr. Apala Bhattacharya, 2 Dr Gautam Bhaduri,
Effect of diabetes mellitus on biomechanical parameters of the cornea
 ARTICLE Effect of diabetes mellitus on biomechanical parameters of the cornea Yakov Goldich, MD, Yaniv Barkana, MD, Yariv Gerber, PhD, Adi Rasko, MD, Yair Morad, MD, Morris Harstein, MD, Isaac Avni, MD,
ARTICLE Effect of diabetes mellitus on biomechanical parameters of the cornea Yakov Goldich, MD, Yaniv Barkana, MD, Yariv Gerber, PhD, Adi Rasko, MD, Yair Morad, MD, Morris Harstein, MD, Isaac Avni, MD,
Targeting Intraocular Pressure in Glaucoma: a Teaching Case Report 1
 Targeting Intraocular Pressure in Glaucoma: a Teaching Case Report 1 By: Andrew Kemp, OD, Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO, Joe DeLoach, OD, FAAO, and Zanna Kruoch, OD FAAO Background Glaucoma is a range of conditions
Targeting Intraocular Pressure in Glaucoma: a Teaching Case Report 1 By: Andrew Kemp, OD, Marcus Gonzales, OD, FAAO, Joe DeLoach, OD, FAAO, and Zanna Kruoch, OD FAAO Background Glaucoma is a range of conditions
Study of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Within Normal Hemivisual Field in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma and Normal-Tension Glaucoma
 Study of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Within Normal Hemivisual Field in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma and Normal-Tension Glaucoma Chiharu Matsumoto, Shiroaki Shirato, Mai Haneda, Hiroko Yamashiro
Study of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Within Normal Hemivisual Field in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma and Normal-Tension Glaucoma Chiharu Matsumoto, Shiroaki Shirato, Mai Haneda, Hiroko Yamashiro
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CORNEAL ULTRASOUND PACHYMETRY. POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Technology Assessment
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CORNEAL ULTRASOUND,, PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: CORNEAL ULTRASOUND,, PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
Macular Ganglion Cell Complex Measurement Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, September: 67-72, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Macular Ganglion Cell Complex Measurement Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, September: 67-72, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Macular Ganglion Cell Complex Measurement Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma
Clinical Profile of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Suspects.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.2.OT3 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Clinical Profile of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Suspects. Pradnya Abhinav Mohan 1 1 Fellow Phaco-surgery, Department
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.2.OT3 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Clinical Profile of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Suspects. Pradnya Abhinav Mohan 1 1 Fellow Phaco-surgery, Department
Central corneal thickness and vascular risk factors in normal tension glaucoma
 Central corneal thickness and vascular risk factors in normal tension glaucoma Aoife Doyle, Ahmed Bensaid and Yves Lachkar L Institut du Glaucome, Fondation Hoˆpital St. Joseph, Paris, France ABSTRACT.
Central corneal thickness and vascular risk factors in normal tension glaucoma Aoife Doyle, Ahmed Bensaid and Yves Lachkar L Institut du Glaucome, Fondation Hoˆpital St. Joseph, Paris, France ABSTRACT.
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Conversion of Ocular Hypertensives into Glaucoma: A Retrospective Study Aditi Singh 1, Shibi
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Conversion of Ocular Hypertensives into Glaucoma: A Retrospective Study Aditi Singh 1, Shibi
Pre-operative intraocular pressure does not influence outcome of trabeculectomy surgery: a retrospective cohort study
 Nesaratnam et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2015) 15:17 DOI 10.1186/s12886-015-0007-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Pre-operative intraocular pressure does not influence outcome of trabeculectomy surgery: a retrospective
Nesaratnam et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2015) 15:17 DOI 10.1186/s12886-015-0007-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Pre-operative intraocular pressure does not influence outcome of trabeculectomy surgery: a retrospective
Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Measurements in Myopia Using Optical Coherence Tomography
 Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Measurements in Myopia Using Optical Coherence Tomography Dennis L. del Rosario, MD and Mario M. Yatco, MD University of Santo
Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Measurements in Myopia Using Optical Coherence Tomography Dennis L. del Rosario, MD and Mario M. Yatco, MD University of Santo
Jose M. Martinez-de-la-Casa, Julian Garcia-Feijoo, Ana Fernandez-Vidal, Carmen Mendez-Hernandez, and Julian Garcia-Sanchez METHODS
 Ocular Response Analyzer versus Goldmann Applanation Tonometry for Intraocular Pressure Measurements Jose M. Martinez-de-la-Casa, Julian Garcia-Feijoo, Ana Fernandez-Vidal, Carmen Mendez-Hernandez, and
Ocular Response Analyzer versus Goldmann Applanation Tonometry for Intraocular Pressure Measurements Jose M. Martinez-de-la-Casa, Julian Garcia-Feijoo, Ana Fernandez-Vidal, Carmen Mendez-Hernandez, and
Clinical Guidance and Monitoring for Change. Cecilia Fenerty MD FRCOphth Manchester Royal Eye Hospital
 Clinical Guidance and Monitoring for Change Cecilia Fenerty MD FRCOphth Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Glaucoma Referral Criteria 2000 Original referral scheme Simple criteria based on IOP/Disc/Field Solitary
Clinical Guidance and Monitoring for Change Cecilia Fenerty MD FRCOphth Manchester Royal Eye Hospital Glaucoma Referral Criteria 2000 Original referral scheme Simple criteria based on IOP/Disc/Field Solitary
The changes in corneal biomechanical parameters after phototherapeutic keratectomy in eyes with granular corneal dystrophy
 (2009) 23, 1790 179 & 2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 090-222X/09 $32.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY The changes in corneal biomechanical parameters after phototherapeutic keratectomy
(2009) 23, 1790 179 & 2009 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 090-222X/09 $32.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY The changes in corneal biomechanical parameters after phototherapeutic keratectomy
PRESCRIBING IN GLAUCOMA: GUIDELINES FOR NZ OPTOMETRISTS
 PRESCRIBING IN GLAUCOMA: GUIDELINES FOR NZ OPTOMETRISTS Introduction Independent prescribing relates to the capacity to use clinical judgement in respect of diagnosis and treatment. It does not mean working
PRESCRIBING IN GLAUCOMA: GUIDELINES FOR NZ OPTOMETRISTS Introduction Independent prescribing relates to the capacity to use clinical judgement in respect of diagnosis and treatment. It does not mean working
The Heritability of Corneal Hysteresis and Ocular Pulse Amplitude: A Twin Study
 The Heritability of Corneal Hysteresis and Ocular Pulse Amplitude: A Twin Study Francis Carbonaro 1, Toby Andrew 2, David A Mackey 3, Tim D Spector 1, Chris J Hammond 1,4 1. Twin Research and Genetic Epidemiology
The Heritability of Corneal Hysteresis and Ocular Pulse Amplitude: A Twin Study Francis Carbonaro 1, Toby Andrew 2, David A Mackey 3, Tim D Spector 1, Chris J Hammond 1,4 1. Twin Research and Genetic Epidemiology
Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) is a major risk factor for
 Glaucoma Twenty-Four Hour Pattern of Intraocular Pressure in Untreated Patients with Ocular Hypertension Tomas M. Grippo, 1,2 John H. K. Liu, 1 Nazlee Zebardast, 2 Taylor B. Arnold, 3 Grant H. Moore, 1
Glaucoma Twenty-Four Hour Pattern of Intraocular Pressure in Untreated Patients with Ocular Hypertension Tomas M. Grippo, 1,2 John H. K. Liu, 1 Nazlee Zebardast, 2 Taylor B. Arnold, 3 Grant H. Moore, 1
CORNEAL HYSTERESIS AND INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE MEASUREMENT
 CORNEAL HYSTERESIS AND INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE MEASUREMENT Protocol: OPT018 Effective Date: August 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page COMMERCIAL, MEDICARE & MEDICAID COVERAGE RATIONALE... 1 DESCRIPTION OF SERVICES...
CORNEAL HYSTERESIS AND INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE MEASUREMENT Protocol: OPT018 Effective Date: August 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page COMMERCIAL, MEDICARE & MEDICAID COVERAGE RATIONALE... 1 DESCRIPTION OF SERVICES...
Glaucoma. Glaucoma. Optic Disc Cupping
 Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Bruce James A group of diseases in which damage to the optic nerve occurs as a result of intraocualar pressure being above the physiological norm for that eye Stoke Mandeville
Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Bruce James A group of diseases in which damage to the optic nerve occurs as a result of intraocualar pressure being above the physiological norm for that eye Stoke Mandeville
53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note.
 Case 1 Normal Tension Glaucoma 53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note. Table 1. Right Eye Left Eye Visual acuity 6/6 6/6 Ishihara
Case 1 Normal Tension Glaucoma 53 year old woman attends your practice for routine exam. She has no past medical history or family history of note. Table 1. Right Eye Left Eye Visual acuity 6/6 6/6 Ishihara
Peretyagin O.A., Cand. Med. Sc., Ass. Prof.; Dmitriev S.K., Dr. Med. Sc., Prof.; Lazar Yu.M., Cand. Med. Sc.; Tatarina Yu.A., Junior Research Fellow
 Changes in corneoscleral rigidity and corneal thickness at various target intraocular pressures in patients with stabilized primary open-angle glaucoma Peretyagin O.A., Cand. Med. Sc., Ass. Prof.; Dmitriev
Changes in corneoscleral rigidity and corneal thickness at various target intraocular pressures in patients with stabilized primary open-angle glaucoma Peretyagin O.A., Cand. Med. Sc., Ass. Prof.; Dmitriev
Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in Indian eyes with optical coherence tomography
 Original articles in Indian eyes with optical coherence tomography Malik A, Singh M, Arya SK, Sood S, Ichhpujani P Department of Ophthalmology Government Medical College and Hospital, Sector 32, Chandigarh,
Original articles in Indian eyes with optical coherence tomography Malik A, Singh M, Arya SK, Sood S, Ichhpujani P Department of Ophthalmology Government Medical College and Hospital, Sector 32, Chandigarh,
Role of central corneal thickness measurement in management of open angle glaucoma and glaucoma suspects in Calabar, Nigeria
 Original Research Article Role of central corneal thickness measurement in management of open angle glaucoma and glaucoma suspects in Calabar, Nigeria Nkanga DG 1,2, Ibanga AA 1,2, Nkanga ED 2, Etim BA
Original Research Article Role of central corneal thickness measurement in management of open angle glaucoma and glaucoma suspects in Calabar, Nigeria Nkanga DG 1,2, Ibanga AA 1,2, Nkanga ED 2, Etim BA
Effect of corneal parameters on measurements using the pulsatile ocular blood flow tonograph and Goldmann applanation tonometer
 518 EXTENDED REPORT Effect of corneal parameters on measurements using the pulsatile ocular blood flow tonograph and Goldmann applanation tonometer P Gunvant, M Baskaran, L Vijaya, I S Joseph, R J Watkins,
518 EXTENDED REPORT Effect of corneal parameters on measurements using the pulsatile ocular blood flow tonograph and Goldmann applanation tonometer P Gunvant, M Baskaran, L Vijaya, I S Joseph, R J Watkins,
Prevalence Of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma in Diabetic Patients
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. III (June. 2017), PP 147-151 www.iosrjournals.org Prevalence Of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 6 Ver. III (June. 2017), PP 147-151 www.iosrjournals.org Prevalence Of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma
CLASS-y Laser Treats Glaucoma
 Article # 404 Comments About the Author Released: Author: Category: March 12th, 2014 Issue #0314 Ehud Assia Feature S S S S S CLASS-y Laser Treats Glaucoma Transforming complex, invasive and risky glaucoma
Article # 404 Comments About the Author Released: Author: Category: March 12th, 2014 Issue #0314 Ehud Assia Feature S S S S S CLASS-y Laser Treats Glaucoma Transforming complex, invasive and risky glaucoma
Based on new understanding that central corneal thickness. Corneal Biomechanical Properties and Retinal Vascular Caliber in Children
 Corneal Biomechanical Properties and Retinal Vascular Caliber in Children Laurence Lim, 1,2 Ning Cheung, 3 Gus Gazzard, 4 Yiong-Huak Chan, 5 Tien-Yin Wong, 1,2,3 and Seang-Mei Saw 6 PURPOSE. To examine
Corneal Biomechanical Properties and Retinal Vascular Caliber in Children Laurence Lim, 1,2 Ning Cheung, 3 Gus Gazzard, 4 Yiong-Huak Chan, 5 Tien-Yin Wong, 1,2,3 and Seang-Mei Saw 6 PURPOSE. To examine
Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma. Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4. Abstract
 Original article Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 4 Professor, Department of
Original article Efficacy of latanoprost in management of chronic angle closure glaucoma Kumar S 1, Malik A 2 Singh M 3, Sood S 4 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, 4 Professor, Department of
Comparative evaluation of time domain and spectral domain optical coherence tomography in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements
 Original article Comparative evaluation of time domain and spectral domain optical coherence tomography in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements Dewang Angmo, 1 Shibal Bhartiya, 1 Sanjay K Mishra,
Original article Comparative evaluation of time domain and spectral domain optical coherence tomography in retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements Dewang Angmo, 1 Shibal Bhartiya, 1 Sanjay K Mishra,
Relationship between central corneal thickness and parameters of optic nerve head topography in healthy subjects
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 18 no. 1, 2008 / pp. 32-38 Relationship between central corneal thickness and parameters of optic nerve head topography in healthy subjects A.B. CANKAYA, U. ELGIN,
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 18 no. 1, 2008 / pp. 32-38 Relationship between central corneal thickness and parameters of optic nerve head topography in healthy subjects A.B. CANKAYA, U. ELGIN,
CORNEAL HYSTERESIS AND INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE MEASUREMENT
 CORNEAL HYSTERESIS AND INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE MEASUREMENT UnitedHealthcare Oxford Clinical Policy Policy Number: DIAGNOSTIC 048.12 T2 Effective Date: July 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR
CORNEAL HYSTERESIS AND INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE MEASUREMENT UnitedHealthcare Oxford Clinical Policy Policy Number: DIAGNOSTIC 048.12 T2 Effective Date: July 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR
Relationship between corneal biomechanical properties and structural biomarkers in patients with normal-tension glaucoma: a retrospective study
 Park et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:7 DOI 10.1186/s12886-018-0673-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Relationship between corneal biomechanical properties and structural biomarkers in patients with normal-tension
Park et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:7 DOI 10.1186/s12886-018-0673-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Relationship between corneal biomechanical properties and structural biomarkers in patients with normal-tension
A Formula to Predict Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Measurements Based on Time Domain OCT Measurements
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(5):369-377 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.5.369 Original Article A Formula to Predict Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(5):369-377 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.5.369 Original Article A Formula to Predict Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Investigation of the relationship between central corneal thickness and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in ocular hypertension
 Acta Medica Anatolia Volume 2 Issue 1 2014 Investigation of the relationship between central corneal thickness and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in ocular hypertension Remzi Mısır 1, Sinan Sarıcaoğlu
Acta Medica Anatolia Volume 2 Issue 1 2014 Investigation of the relationship between central corneal thickness and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in ocular hypertension Remzi Mısır 1, Sinan Sarıcaoğlu
Scanning Laser Polarimetry in Patients with Acute Attack of Primary Angle Closure
 Scanning Laser Polarimetry in Patients with Acute Attack of Primary Angle Closure Jimmy S. M. Lai*, Clement C. Y. Tham, Jonathan C. H. Chan*, Nelson K. F. Yip, Wilson W. T. Tang, Patrick S. H. Li*, Jane
Scanning Laser Polarimetry in Patients with Acute Attack of Primary Angle Closure Jimmy S. M. Lai*, Clement C. Y. Tham, Jonathan C. H. Chan*, Nelson K. F. Yip, Wilson W. T. Tang, Patrick S. H. Li*, Jane
An Ultra-High-Speed Scheimpflug Camera for Evaluation of Corneal Deformation Response and Its Impact on IOP Measurement
 Glaucoma An Ultra-High-Speed Scheimpflug Camera for Evaluation of Corneal Deformation Response and Its Impact on IOP Measurement Christopher Kai-Shun Leung, 1 Cong Ye, 1 and Robert N. Weinreb 2 1 Department
Glaucoma An Ultra-High-Speed Scheimpflug Camera for Evaluation of Corneal Deformation Response and Its Impact on IOP Measurement Christopher Kai-Shun Leung, 1 Cong Ye, 1 and Robert N. Weinreb 2 1 Department
Research Article Optic Disc Hemorrhage after Phacoemulsification in Patients with Glaucoma
 ISRN Ophthalmology, Article ID 574054, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/574054 Research Article Optic Disc Hemorrhage after Phacoemulsification in Patients with Glaucoma Karine D. Bojikian, Daniel
ISRN Ophthalmology, Article ID 574054, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/574054 Research Article Optic Disc Hemorrhage after Phacoemulsification in Patients with Glaucoma Karine D. Bojikian, Daniel
True IOP No Doubt Facts and Figures Figures. Ziemer Ophthalmic Systems AG a Ziemer Group Company Allmendstrasse 11 CH-2562 Port, Switzerland
 True IOP No Doubt Facts and Figures Figures and Facts Ziemer Ophthalmic Systems AG a Ziemer Group Company Allmendstrasse 11 CH-2562 Port, Switzerland There is increasing evidence that DCT measures IOP
True IOP No Doubt Facts and Figures Figures and Facts Ziemer Ophthalmic Systems AG a Ziemer Group Company Allmendstrasse 11 CH-2562 Port, Switzerland There is increasing evidence that DCT measures IOP
LARGE DISCS WITH LARGE CUPS A DIAGNOSTIC CHALLENGE IN AFRICAN PATIENTS. Darshana Soma
 LARGE DISCS WITH LARGE CUPS A DIAGNOSTIC CHALLENGE IN AFRICAN PATIENTS Darshana Soma A research report submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, in partial
LARGE DISCS WITH LARGE CUPS A DIAGNOSTIC CHALLENGE IN AFRICAN PATIENTS Darshana Soma A research report submitted to the Faculty of Health Sciences, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, in partial
Early Detection Of Glaucoma Clinical Clues. Points To Live By. Glaucoma Risk Factors 10/3/2014
 Early Detection Of Glaucoma Clinical Clues Eric E. Schmidt, O.D. Omni Eye Specialists Wilmington, NC schmidtyvision@msn.com Points To Live By 25% of G pxs NEVER have IOP >21mm 50% of G pxs have trough
Early Detection Of Glaucoma Clinical Clues Eric E. Schmidt, O.D. Omni Eye Specialists Wilmington, NC schmidtyvision@msn.com Points To Live By 25% of G pxs NEVER have IOP >21mm 50% of G pxs have trough
Translating data and measurements from stratus to cirrus OCT in glaucoma patients and healthy subjects
 Romanian Journal of Ophthalmology, Volume 60, Issue 3, July-September 2016. pp:158-164 GENERAL ARTICLE Translating data and measurements from stratus to cirrus OCT in glaucoma patients and healthy subjects
Romanian Journal of Ophthalmology, Volume 60, Issue 3, July-September 2016. pp:158-164 GENERAL ARTICLE Translating data and measurements from stratus to cirrus OCT in glaucoma patients and healthy subjects
Spontaneous Intraocular Pressure Reduction in Normal-Tension Glaucoma and Associated Clinical Factors
 CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Spontaneous Intraocular Pressure Reduction in Normal-Tension Glaucoma and Associated Clinical Factors Akihiro Oguri, Tetsuya Yamamoto and Yoshiaki Kitazawa Department of Ophthalmology,
CLINICAL INVESTIGATIONS Spontaneous Intraocular Pressure Reduction in Normal-Tension Glaucoma and Associated Clinical Factors Akihiro Oguri, Tetsuya Yamamoto and Yoshiaki Kitazawa Department of Ophthalmology,
T he retinal ganglion cells of different sizes have distinct
 604 CLINICAL SCIENCE Agreement between frequency doubling perimetry and static perimetry in eyes with high tension glaucoma and normal tension glaucoma S Kogure, Y Toda, D Crabb, K Kashiwagi, F W Fitzke,
604 CLINICAL SCIENCE Agreement between frequency doubling perimetry and static perimetry in eyes with high tension glaucoma and normal tension glaucoma S Kogure, Y Toda, D Crabb, K Kashiwagi, F W Fitzke,
The Role of the RNFL in the Diagnosis of Glaucoma
 Chapter 1. The Role of the RNFL in the Diagnosis of Glaucoma Introduction Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy characterized by a loss of of retinal ganglion cells and their axons, the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer
Chapter 1. The Role of the RNFL in the Diagnosis of Glaucoma Introduction Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy characterized by a loss of of retinal ganglion cells and their axons, the Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer
Glaucoma Clinical Update. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012
 Glaucoma Clinical Update Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Objectives Understand the different categories of glaucoma Recognize the symptoms and signs of open angle and angle-closure
Glaucoma Clinical Update Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Objectives Understand the different categories of glaucoma Recognize the symptoms and signs of open angle and angle-closure
Present relevant clinical findings of four landmark glaucoma trials OHTS, EMGT, CNTGS and CIGTS.
 Course title: The Glaucoma Compass Course length: 1 hour +/- 31 slides Corse Description: Even with the technology and available information, glaucoma decision making can still be confusing. How should
Course title: The Glaucoma Compass Course length: 1 hour +/- 31 slides Corse Description: Even with the technology and available information, glaucoma decision making can still be confusing. How should
Glaucoma: Diagnostic Modalities
 Glaucoma: Diagnostic Modalities - Dr. Barun Kumar Nayak, Dr. Sarika Ramugade Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness in the world, especially in older people. Early detection and treatment by ophthalmologist
Glaucoma: Diagnostic Modalities - Dr. Barun Kumar Nayak, Dr. Sarika Ramugade Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness in the world, especially in older people. Early detection and treatment by ophthalmologist
The Effect of Pupil Dilation on Scanning Laser Polarimetry With Variable Corneal Compensation
 C L I N I C A L S C I E N C E The Effect of Pupil Dilation on Scanning Laser Polarimetry With Variable Corneal Compensation Amjad Horani, MD; Shahar Frenkel, MD, PhD; Eytan Z. Blumenthal, MD BACKGROUND
C L I N I C A L S C I E N C E The Effect of Pupil Dilation on Scanning Laser Polarimetry With Variable Corneal Compensation Amjad Horani, MD; Shahar Frenkel, MD, PhD; Eytan Z. Blumenthal, MD BACKGROUND
Citation BMC Ophthalmology, 2016, v. 16, article no. 64
 Title Recurrent acute angle-closure attack due to plateau iris syndrome after cataract extraction with or without argon laser peripheral iridoplasty: a case report Author(s) Choy, NKB; Chan, JCH; Chien,
Title Recurrent acute angle-closure attack due to plateau iris syndrome after cataract extraction with or without argon laser peripheral iridoplasty: a case report Author(s) Choy, NKB; Chan, JCH; Chien,
Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness parameters in myopic population using scanning laser polarimetry (GDxVCC)
 Dada T et al Original article Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness parameters in myopic population using scanning laser polarimetry (GDxVCC) Dada T1, Aggarwal A1, Bali SJ2, Sharma A1, Shah
Dada T et al Original article Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness parameters in myopic population using scanning laser polarimetry (GDxVCC) Dada T1, Aggarwal A1, Bali SJ2, Sharma A1, Shah
Ganglion cell complex scan in the early prediction of glaucoma
 Original article in the early prediction of glaucoma Ganekal S Nayana Super Specialty Eye Hospital and Research Center, Davangere, Karnataka, India Abstract Objective: To compare the macular ganglion cell
Original article in the early prediction of glaucoma Ganekal S Nayana Super Specialty Eye Hospital and Research Center, Davangere, Karnataka, India Abstract Objective: To compare the macular ganglion cell
RETINAL NERVE FIBER LAYER
 CLINICAL SCIENCES The Effect of Scan Diameter on Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measurement Using Stratus Optic Coherence Tomography Giacomo Savini, MD; Piero Barboni, MD; Michele Carbonelli, MD;
CLINICAL SCIENCES The Effect of Scan Diameter on Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measurement Using Stratus Optic Coherence Tomography Giacomo Savini, MD; Piero Barboni, MD; Michele Carbonelli, MD;
Comparison of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness between Stratus and Spectralis OCT
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2011;25(3):166-173 DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2011.25.3.166 Original Article Comparison of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness between Stratus and Spectralis
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2011;25(3):166-173 DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2011.25.3.166 Original Article Comparison of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness between Stratus and Spectralis
GLAUCOMA REPEAT READINGS PATHWAY
 GLAUCOMA REPEAT READINGS PATHWAY Level 1a: Goldmann style applanation tonometry repeat readings A first level community service for IOP refinement where other signs of glaucoma are not present will reduce
GLAUCOMA REPEAT READINGS PATHWAY Level 1a: Goldmann style applanation tonometry repeat readings A first level community service for IOP refinement where other signs of glaucoma are not present will reduce
Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015
 Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015 Jimmy Lai Clinical Professor Department of Ophthalmology The University of Hong Kong 1 Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma PACG
Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015 Jimmy Lai Clinical Professor Department of Ophthalmology The University of Hong Kong 1 Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma PACG
PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY Sanjay Upadhyay 1, Jayantilal Shah 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY Sanjay Upadhyay 1, Jayantilal Shah 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor,
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
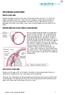 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
Effect of Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty in Glaucoma Patients with High or Low Central Corneal Thickness
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Effect of Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty in Glaucoma Patients with High or Low Central Corneal Thickness Abstract Purpose: Comparison of the effect
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Effect of Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty in Glaucoma Patients with High or Low Central Corneal Thickness Abstract Purpose: Comparison of the effect
Structural changes of the anterior chamber following cataract surgery during infancy
 Structural changes of the anterior chamber following cataract surgery during infancy Matthew Nguyen, Emory University Marla Shainberg, Emory University Allen Beck, Emory University Scott Lambert, Emory
Structural changes of the anterior chamber following cataract surgery during infancy Matthew Nguyen, Emory University Marla Shainberg, Emory University Allen Beck, Emory University Scott Lambert, Emory
1/25/2019 OCT & OCTA RETINAL IMAGING: HOW TO PREVENT RAGING GLAUCOMA! THE ORIGINAL RAGING GLAUCOMA OCT RETINAL IMAGING OPTIC NERVE HEAD EXAMINATION
 OCT & OCTA RETINAL IMAGING: HOW TO PREVENT RAGING GLAUCOMA! Craig Thomas, O.D. 3900 West Wheatland Road Dallas, Texas 75237 972-780-7199 thpckc@yahoo.com THE ORIGINAL RAGING GLAUCOMA 47-year-old Black
OCT & OCTA RETINAL IMAGING: HOW TO PREVENT RAGING GLAUCOMA! Craig Thomas, O.D. 3900 West Wheatland Road Dallas, Texas 75237 972-780-7199 thpckc@yahoo.com THE ORIGINAL RAGING GLAUCOMA 47-year-old Black
Effect of brimonidine on intraocular pressure in normal tension glaucoma: A short term clinical trial
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 7, 2003 / pp. 611-615 Effect of brimonidine on intraocular pressure in normal tension glaucoma: A short term clinical trial S.A. GANDOLFI, L. CIMINO, P.
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 7, 2003 / pp. 611-615 Effect of brimonidine on intraocular pressure in normal tension glaucoma: A short term clinical trial S.A. GANDOLFI, L. CIMINO, P.
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Effect of Central Corneal Thickness, Corneal Curvature, and Axial Length on Applanation Tonometry
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Effect of Central Corneal Thickness, Corneal Curvature, and Axial Length on Applanation Tonometry Markus Kohlhaas, MD; Andreas G. Boehm, MD; Eberhard Spoerl, PhD; Antje Pürsten, Dipl-Ing
CLINICAL SCIENCES Effect of Central Corneal Thickness, Corneal Curvature, and Axial Length on Applanation Tonometry Markus Kohlhaas, MD; Andreas G. Boehm, MD; Eberhard Spoerl, PhD; Antje Pürsten, Dipl-Ing
Noel de Jesus Atienza, MD, MSc and Joseph Anthony Tumbocon, MD
 Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Diagnostic Accuracy of the Optical Coherence Tomography in Assessing Glaucoma Among Filipinos. Part 1: Categorical Outcomes Based on a Normative Database
Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Diagnostic Accuracy of the Optical Coherence Tomography in Assessing Glaucoma Among Filipinos. Part 1: Categorical Outcomes Based on a Normative Database
A Review Of Risk Factors. Early Detection Of Glaucoma Clinical Clues. A risk factor analysis is critical. Points To Live By
 A Review Of Risk Factors Early Detection Of Glaucoma Clinical Clues Eric E. Schmidt, O.D. Omni Eye Specialists Wilmington, NC schmidtyvision@msn.com FINDACAR Family history IOP Nearsightedness Diabetes/Vascular
A Review Of Risk Factors Early Detection Of Glaucoma Clinical Clues Eric E. Schmidt, O.D. Omni Eye Specialists Wilmington, NC schmidtyvision@msn.com FINDACAR Family history IOP Nearsightedness Diabetes/Vascular
The evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer in pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma using scanning laser polarimetry
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 4, 2003 / pp. 377-382 The evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer in pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma using scanning laser polarimetry
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 4, 2003 / pp. 377-382 The evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer in pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma using scanning laser polarimetry
Effects of Intracorneal Ring Segment on Corneal Biomechanics in Keratoconic Eyes. Abstract
 Effects of Intracorneal Ring Segment on Corneal Biomechanics in Keratoconic Eyes Javad Amoozadeh, MD 1 Nima Mirzaee Rad, MD 2 Amir Houshang Beheshtnejad, MD 3 Ahmad Kheirkhah, MD 1 Hassan Hashemi, MD 4,5
Effects of Intracorneal Ring Segment on Corneal Biomechanics in Keratoconic Eyes Javad Amoozadeh, MD 1 Nima Mirzaee Rad, MD 2 Amir Houshang Beheshtnejad, MD 3 Ahmad Kheirkhah, MD 1 Hassan Hashemi, MD 4,5
The overall rate of decrease in visual field sensitivity in
 Glaucoma Estimating the True Distribution of Visual Field Progression Rates in Glaucoma Andrew J. Anderson Department of Optometry and Vision Sciences, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia
Glaucoma Estimating the True Distribution of Visual Field Progression Rates in Glaucoma Andrew J. Anderson Department of Optometry and Vision Sciences, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Steven L. Mansberger, MD; Pamela A. Sample, PhD; Linda Zangwill, PhD; Robert N. Weinreb, MD
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Achromatic and Short-Wavelength Automated Perimetry in Patients With Glaucomatous Large Cups Steven L. Mansberger, MD; Pamela A. Sample, PhD; Linda Zangwill, PhD; Robert N. Weinreb, MD
CLINICAL SCIENCES Achromatic and Short-Wavelength Automated Perimetry in Patients With Glaucomatous Large Cups Steven L. Mansberger, MD; Pamela A. Sample, PhD; Linda Zangwill, PhD; Robert N. Weinreb, MD
Research Article The Pattern of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer and Macular Ganglion Cell-Inner Plexiform Layer Thickness Changes in Glaucoma
 Hindawi Ophthalmology Volume 2017, Article ID 78365, 8 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/78365 Research Article The Pattern of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer and Macular Ganglion Cell-Inner Plexiform Layer
Hindawi Ophthalmology Volume 2017, Article ID 78365, 8 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/78365 Research Article The Pattern of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer and Macular Ganglion Cell-Inner Plexiform Layer
CHARTING THE NEW COURSE FOR MIGS
 CHARTING THE NEW COURSE FOR MIGS SEE WHAT S ON THE HORIZON CyPass Micro-Stent the next wave in micro-invasive glaucoma surgery. MICRO-INVASIVE GLAUCOMA SURGERY (MIGS) OFFERS A REVOLUTIONARY APPROACH TO
CHARTING THE NEW COURSE FOR MIGS SEE WHAT S ON THE HORIZON CyPass Micro-Stent the next wave in micro-invasive glaucoma surgery. MICRO-INVASIVE GLAUCOMA SURGERY (MIGS) OFFERS A REVOLUTIONARY APPROACH TO
The evaluation of the optic nerve and retinal nerve
 Five rules to evaluate the optic disc and retinal nerve fiber layer for glaucoma Murray Fingeret, O.D., a,b Felipe A. Medeiros, M.D., c Remo Susanna, Jr, M.D., d and Robert N. Weinreb, M.D. c a Department
Five rules to evaluate the optic disc and retinal nerve fiber layer for glaucoma Murray Fingeret, O.D., a,b Felipe A. Medeiros, M.D., c Remo Susanna, Jr, M.D., d and Robert N. Weinreb, M.D. c a Department
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: , 2013
 268 Comparison of optic nerve morphology in eyes with glaucoma and eyes with non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy by Fourier domain optical coherence tomography YUXIN YANG 1, HAITAO ZHANG 1,
268 Comparison of optic nerve morphology in eyes with glaucoma and eyes with non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy by Fourier domain optical coherence tomography YUXIN YANG 1, HAITAO ZHANG 1,
Is NTG different from POAG?
 Is NTG different from POAG? Sunita Radhakrishnan, M.D Glaucoma Center of San Francisco Glaucoma Research and Education Group Subset of POAG 1 Connective tissue structure within ONH Ganglion cell susceptibility
Is NTG different from POAG? Sunita Radhakrishnan, M.D Glaucoma Center of San Francisco Glaucoma Research and Education Group Subset of POAG 1 Connective tissue structure within ONH Ganglion cell susceptibility
Goldmann applanation tonometry compared with corneal-compensated intraocular pressure in the evaluation of primary open-angle Glaucoma
 Ehrlich et al. BMC Ophthalmology 2012, 12:52 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Goldmann applanation tonometry compared with corneal-compensated intraocular pressure in the evaluation of primary open-angle Glaucoma
Ehrlich et al. BMC Ophthalmology 2012, 12:52 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Goldmann applanation tonometry compared with corneal-compensated intraocular pressure in the evaluation of primary open-angle Glaucoma
1 Birmingham and Midland Eye Centre, City Hospital, Birmingham, 2 Ophthalmic Research Group, Life and Health Sciences, Aston
 Accuracy of Goldmann, Ocular Response Analyser, Pascal and TonoPen XL Tonometry in Keratoconic and Normal Eyes Susan P Mollan MB CHB MRCOphth 1, James S Wolffsohn BSc PhD PgDip MCOptom 2, Maged Nessim
Accuracy of Goldmann, Ocular Response Analyser, Pascal and TonoPen XL Tonometry in Keratoconic and Normal Eyes Susan P Mollan MB CHB MRCOphth 1, James S Wolffsohn BSc PhD PgDip MCOptom 2, Maged Nessim
Access to the published version may require journal subscription. Published with permission from: Elsevier
 This is an author produced version of a paper published in Ophthalmology. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proof-corrections or journal pagination. Citation for
This is an author produced version of a paper published in Ophthalmology. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final publisher proof-corrections or journal pagination. Citation for
NIIOS. Cornea Specialist, Melles Cornea Clinic, NIIOS, Rotterdam, the Netherlands Naval Hospital, Athens, Greece VASILIS S.
 Cornea Specialist, Melles Cornea Clinic, NIIOS, Rotterdam, the Netherlands Naval Hospital, Athens, Greece Goldman applanation tonometry is still the gold standard for measuring IOP, but its accuracy is
Cornea Specialist, Melles Cornea Clinic, NIIOS, Rotterdam, the Netherlands Naval Hospital, Athens, Greece Goldman applanation tonometry is still the gold standard for measuring IOP, but its accuracy is
Clinical Study Visual Field Loss Morphology in High- and Normal-Tension Glaucoma
 Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 2012, Article ID 327326, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2012/327326 Clinical Study Visual Field Loss Morphology in High- and Normal-Tension Glaucoma Michele Iester, 1, 2 Fabio De Feo,
Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 2012, Article ID 327326, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2012/327326 Clinical Study Visual Field Loss Morphology in High- and Normal-Tension Glaucoma Michele Iester, 1, 2 Fabio De Feo,
Il contributo dell'angio-oct: valutazione integrata della componente nervosa e vascolare della malattia glaucomatosa
 SIMPOSIO G.O.A.L. - LE NUOVE FRONTIERE DIAGNOSTICHE E LE LINEE DI INDIRIZZO AMBULATORIALI DEL GLAUCOMA Coordinatore e moderatore: D. Mazzacane Presidente: L. Rossetti Il contributo dell'angio-oct: valutazione
SIMPOSIO G.O.A.L. - LE NUOVE FRONTIERE DIAGNOSTICHE E LE LINEE DI INDIRIZZO AMBULATORIALI DEL GLAUCOMA Coordinatore e moderatore: D. Mazzacane Presidente: L. Rossetti Il contributo dell'angio-oct: valutazione
The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3%
 The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3% of our population age > 40 have glaucoma In the past:
The second most common causes of blindness worldwide. ( after cataract) The commonest cause of irreversible blindness in the world Estimated that 3% of our population age > 40 have glaucoma In the past:
Central corneal thickness determined with optical coherence tomography in various types of glaucoma
 Br J Ophthalmol 2000;84:1233 1237 1233 Department of Ophthalmology, Ludwig-Maximilians- University, Munich, Germany M Bechmann M J Thiel B Roesen S Ullrich M W Ulbig K Ludwig Correspondence to: Martin
Br J Ophthalmol 2000;84:1233 1237 1233 Department of Ophthalmology, Ludwig-Maximilians- University, Munich, Germany M Bechmann M J Thiel B Roesen S Ullrich M W Ulbig K Ludwig Correspondence to: Martin
The Common Clinical Competency Framework for Non-medical Ophthalmic Healthcare Professionals in Secondary Care
 The Common Clinical Competency Framework for Non-medical Ophthalmic Healthcare Professionals in Secondary Care Glaucoma November 2016 Association of Health Professions in Ophthalmology General basic competences
The Common Clinical Competency Framework for Non-medical Ophthalmic Healthcare Professionals in Secondary Care Glaucoma November 2016 Association of Health Professions in Ophthalmology General basic competences
Impact of Myopia on Corneal Biomechanics in Glaucoma and Nonglaucoma Patients
 Glaucoma Impact of Myopia on Corneal Biomechanics in Glaucoma and Nonglaucoma Patients Sunee Chansangpetch, 1,2 Rawiphan Panpruk, 1 Anita Manassakorn, 1 Visanee Tantisevi, 1 Prin Rojanapongpun, 1 Cameron
Glaucoma Impact of Myopia on Corneal Biomechanics in Glaucoma and Nonglaucoma Patients Sunee Chansangpetch, 1,2 Rawiphan Panpruk, 1 Anita Manassakorn, 1 Visanee Tantisevi, 1 Prin Rojanapongpun, 1 Cameron
THE BASIC PATHOLOGIC CHANGE IN GLAUCOMA IS
 Quantitative Assessment of Atypical Birefringence Images Using Scanning Laser Polarimetry With Variable Corneal Compensation HARMOHINA BAGGA, MD, DAVID S. GREENFIELD, MD, AND WILLIAM J. FEUER, MS PURPOSE:
Quantitative Assessment of Atypical Birefringence Images Using Scanning Laser Polarimetry With Variable Corneal Compensation HARMOHINA BAGGA, MD, DAVID S. GREENFIELD, MD, AND WILLIAM J. FEUER, MS PURPOSE:
Interest in central corneal thickness (CCT) and glaucoma was. Central Corneal Thickness and Glaucoma in East Asian People.
 Glaucoma Central Corneal Thickness and Glaucoma in East Asian People Alexander C. Day, 1,2 David Machin, 3 Tin Aung, 4 Gus Gazzard, 2 Rahat Husain, 4 Paul T. K. Chew, 5 Peng T. Khaw, 1,2,6 Steve K. L.
Glaucoma Central Corneal Thickness and Glaucoma in East Asian People Alexander C. Day, 1,2 David Machin, 3 Tin Aung, 4 Gus Gazzard, 2 Rahat Husain, 4 Paul T. K. Chew, 5 Peng T. Khaw, 1,2,6 Steve K. L.
Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature of
 1.2.4 OPHTHALMOLOGICAL ABNORMALITIES Ocular abnormalities are well documented in patients with NPS 6 62 81 95. 1.2.4.1 Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature
1.2.4 OPHTHALMOLOGICAL ABNORMALITIES Ocular abnormalities are well documented in patients with NPS 6 62 81 95. 1.2.4.1 Glaucoma Glaucoma is a complication which has only recently been confirmed as a feature
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is of fundamental importance in
 Glaucoma Effect of Corneal Stiffening on Goldmann Applanation Tonometry and Tono-Pen Measurements in Canine Eyes Junhua Tang, 1 Xueliang Pan, 2 Paul A. Weber, 3 and Jun Liu 1,3 PURPOSE. To experimentally
Glaucoma Effect of Corneal Stiffening on Goldmann Applanation Tonometry and Tono-Pen Measurements in Canine Eyes Junhua Tang, 1 Xueliang Pan, 2 Paul A. Weber, 3 and Jun Liu 1,3 PURPOSE. To experimentally
4/06/2013. Medication Observation POAG. Proportion. Native American 0.1% 0.4%
 Clinical Research in Glaucoma: Putting Science into Practice J. James Thimons, O.D., FAAO Chairman, National Glaucoma Society www.nationalglaucomasociety.org Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS)
Clinical Research in Glaucoma: Putting Science into Practice J. James Thimons, O.D., FAAO Chairman, National Glaucoma Society www.nationalglaucomasociety.org Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS)
Scanning laser polarimetry (SLP) provides real-time, objective
 The Effect of Atypical Birefringence Patterns on Glaucoma Detection Using Scanning Laser Polarimetry with Variable Corneal Compensation Christopher Bowd, Felipe A. Medeiros, Robert N. Weinreb, and Linda
The Effect of Atypical Birefringence Patterns on Glaucoma Detection Using Scanning Laser Polarimetry with Variable Corneal Compensation Christopher Bowd, Felipe A. Medeiros, Robert N. Weinreb, and Linda
To assess the glaucoma diagnostic ability of Fourier Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-11, pp-104-110 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access To assess the glaucoma diagnostic ability of
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn : 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-02, Issue-11, pp-104-110 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access To assess the glaucoma diagnostic ability of
