Management of Benign tracheal stenosis 25/7/2014
|
|
|
- Tamsin Reynolds
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Management of Benign tracheal stenosis 25/7/2014
2 Anatomy Begins at inferior border of cricoid at C6 till T4-T5 11 cm in length cartilages Tracheal rings receive blood supply from submucosal plexus and hence at risk of necrosis from ET/TT cuffs Diameter in males > females Coronal and sagittal: male 25 and 27 mm, female 21 and 23 mm Stridor at rest would indicate <30% normal lumen or 5mm diameter or less Salassa JR et al. Ann thoracic surg 24: , 1997 Wain JC et al. Sem in Thorac cardiovasc Surg. 21:
3 Etiology Post intubation tracheal stenosis Post tracheostomy tracheal stenosis suprastomal Stomal strictures Stricture at the level of the cuff Granulomatosis with polyangitis, relapsing polychondritis Sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, amyoidosis Stenosis at surgical anastamotic sites Idiopathic
4 ET/TT cuff related 3-4 cm from cricoid Respond well to radial dilatation (transient) LTS due to a tracheostomy too high in trachea Might respond to dilatation, but risk of airway edema and worsening
5 Type of stenosis Structural and benign Degree of stenosis: Myer-cotton grading I up to 50% stenosis, II 50% - 70%. III 70-99%, IV complete (100%) Location of stenosis upper, mid and lower trachea. Right and left main bronchus Complex stenosis stenosis along with cartilage fracture or tracheomalacia, tortuous strictures, those with contractions In complex stenosis endoscopic management is difficult Barros Casas D, et al. Arch Bronconeumol. 2014;50(8): Freitag L et al. Eur Resp J 2007; 30: 7-12
6 Classification of stenosis Freitag L et al. Eur Resp J 2007; 30: 7-12
7 Freitag L et al. Eur Resp J 2007; 30: 7-12
8
9 Zias N et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine2008, 8:18
10 Post tracheostomy stenosis Zias N et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine2008, 8:18
11 Post tracheostomy stenosis Percutaneous (PCT) vs. surgical (SGT) PCT group SGT group Stenosis closer to vocal cord 1.6 cm Mean time to onset of symptoms 5 weeks Subglottic location makes surgery a difficult option Distance from vocal cord 3.4 cm Time of presentation, mean of 28.5 weeks Surgical correction possible Raghuraman G et al. Chest 2005 Mar;127(3):879-85
12 How to assess? PFT: not evident till tracheal lumen <10 mm. Flattening of expiratory and inspiratory limbs may be noted 1 CT and virtual bronchoscopy 2 Flexible bronchoscopy Myer-Cotton system Stenotic Index (SI) = CSA normal -CSA abnormal /CSA normal 100 CSA cross sectional area 1 Acres JC, et al. Chest. 1981;80: Taha MS et al. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2009;266:863 6
13 Surgery for PITS Surgery has been considered treatment of choice, whenever feasible Reported success rate >90%, failure ranging from 5 to 15% Mortality up to 5% Data from India are limited, 92.85% success at the anastomotic site at 2 years follow up has been reported* Grillo HC, et al. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1995;109(3): Rea F, et al. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2002;22: Ciccone AM, et al. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2004;26: *Nandakumar R. J Laryngol Otol. 2011Sep;125(9):958-61
14 Inoperable cases Excessive length of damaged airway Comorbid illness precludes surgery Some complex injuries involving larynx as well as trachea Reasons for delaying surgery active inflammation, use of high dose steroids etc.
15 Bronchoscopic management Contraindications to surgery Temporary measure prior to surgery As a complement to surgery and in post operative stenosis As a primary therapy
16 Non surgical management of stenosis Dilatation with balloons, bougies, an dilators Laser resection (Nd:YAG) CO 2 Laser resection Covered and uncovered metal stents insertion Self-expandable silicone stents Silicone stents Montgomery T tube insertion
17 Balloon bronchoplasty Silicone balloons High pressure syringe required to carry out the procedure Determine the length of the stenosis prior to dilatation Can be done with flouroscopic guidance with a skin marker to know the site of stenosis Catheter is positioned in such a way that 0.5 cm of balloon is visible proximally Usually 2 to 3 inflations 30 seconds each John R Mc Ardle et al. J Bronchol 2005;12:
18 John R Mc Ardle et al. J Bronchol 2005;12:
19 Reference Population Methods Outcome Comments Shitrit D, et al. Eur J Cardiothoraci c Surg Aug;38(2): Mayse ML et al. Chest 2004 Aug;126(2): Retrospectiv e study 35 patients, 92 balloon dilatations (14 transplant recipients, 14 other benign, rest were malignant) Retrospectiv e 24 patients (benign diseases) Flouroscopy guided, done with flexible bronchoscop y Guidewire passed through stenotic segment, f/b dilatation* No flouroscopy Rigid (RB) 61% FB 39% Desired pressure Immediate improvement and maintained up to 1 month 25 of 35 (71%) required stent Mechanical debridement 68% Stent 47% Laser 19% Long term follow up 33+/- 4 months 6 atm pressure for 10 s 26% only balloon bronchoplast y No follow up
20 Balloon dilatation has been done with flexible 1 as well as rigid bronchoscopies 4/7 required repeated procedures including deployment of stent in one patient 1 (30 to 120 s inflation time) Has been used in post lung transplant patients with stenosis. 2 Immediately effective in a study of 10 patients, 5 of them subsequently required stent 1 Sheski FD et al. Chest Sep;114(3): De gracia J et al. Respir Med Jan;101(1): Epub 2006 Jun 13.
21 Flexible bronchoscopy alone For patients with comorbid illness, where surgery or few other interventions requiring GA can be avoided Majority were subglottic stenosis (81 of 115) and were web like (97 of 115). 56 had >50% stenosis Balloon bronchoplasty, NdYAG laser for granulation tissue When 3 or more intervention in 6 months, high dose rate (HDR) brachytherapy with 10 Gy was given Cumulative survival rates at 1, 2, and 5 years : 80%, 73%, and 62% respectively Rahman NA. J Cardiothorac Surg Jan 17;5:2
22 NdYAG laser 1994 Study from India 1 Population Intervention Outcome Complication s 35 benign tracheal stenosis 1.Stomal 80% (n-28) 2. Subglottic 14.3% (n-5) 3.Laryngeal stenosis 5.7% (n-2) Laser photocoagula tion of scar tissue (Nd:YAG) Mean 2.8 procedures per patient Adequate lumen in 29 patients (83%) All 5 subglottic stenosis patients had unsuccessful procedure Total 3 cases (8.5%) Bleeding in 2, Cervical emphysema in 1 1 Rau BK et al. Ann Acad Med Singapore May;23(3): Mean 23 month follow up, only one patient required surgery
23 NdYAG laser Mehta AC, et al. Chest 1993; 104: Population Intervention Outcome Complication s 18 patients Laser applied twice and if fails, more definitive therapy Laser photocoagula tion of scar tissue (Nd:YAG) And GD (gentle dilatation) 12 successful 8 of which required only 1 session > 1cm scar and tracheomalaci a in those who failed (difficulty in surgery) 1 Rau BK et al. Ann Acad Med Singapore May;23(3):333-4.
24 Other lasers CO 2 lasers can be used to give precise radial incisions, used in ENT Nd-YAG laser is preferred for airway resection because of its predictable effects on living tissue (i.e. photocoagulation or vapourization), depending on the amount of energy applied FiO 2 to be kept <40% Not to be used in extrinsic compression ERS/ATS statement on interventional pulmonology. ERJ 2002
25 Other LASER CT Bolliger et al. Eur Respir J 2006; 27:
26 Electrocautery Electrical current for tissue heating is called diathermy/electrocautery Various probes can be used: biopsy forceps, knives, cutting loops, blunt probes etc. to deliver Mainly used for palliative therapy in malignant tracheal obstruction. Can be used in benign as well Similar effectiveness as compared to NdYAG laser CT Bolliger et al. Eur Respir J 2006; 27:
27 Electrocautery As compared to Nd YAG, electrocautery and Argon Plasma Coagulation (APC) act superficially When deep coagulation is preferred LASER; for superficial APC and electrocautery Deep anticoagulation not preferred: when blood vessels are nearby, surgically treated patients with altered anatomy
28 Advantages Cost effective (compared to LASERs). Both APC and electrocautery are much cheaper Less electrical energy Can be done with flexible bronchoscopy van Boxem TJ, et al. Chest 2000; 117: Hooper RG, et al.chest1985; 87:
29 Argon Plasma Coagulation(APC) Ionized Argon gas jet flow is used instead of alternating current (electrocautery) to cause flow of electrons Shares the same indications and advantages of electrocautery It causes homogenous and diffuse tissue coagulation, by spraying larger surface areas Apart from treating early stage cancers, useful in management of granulation tissue and web like stenosis CT Bolliger et al. Eur Respir J 2006; 27: Grund KE, et al.endosc Surg Allied Technol1994; 2:
30 Mitomycin C Anthracycline antibiotic. Alkylating agent which inhibits DNA synthesis. Usually used along with CO 2 laser and rigid bronchoscopic dilatation 0.4 to 1 mg/ml has been used in various studies Not much useful, but can delay restenosis to a certain extent Madan K et al.j Bronchol Int Pulmonol. 2012
31 Intralesional steroid Intralesional steroid along with balloon bronchoplasty in 10 patients, found effective at 7 months follow up No long term data available Nouraea SA et al. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg Oct;145(4):623-7
32 Airway stents Named after C.R. Stent who invented a compound to cast dental splints
33 Classification of airway stents Based on the material used : polymers and metals (hybrid stents are an exception, metal stents covered with silicone and metal-enforced polymer stents) Based on method of deployment : by rigid or flexible instruments Based on positioning : T-tubes (require tracheostomy), straight stents (held in place by the contact pressure), bifurcated stents (placed over the carina) Freitag L. Airway stents. Eur Resp Monograph 2010
34 T-Tubes Different diameters and lengths of the three limbs available Can be used in tracheal stenosis even up to vocal cords level Voice and humidification can be preserved Migration unlikely to occur One of the safest stents for very high tracheal/subglottic stenosis Carretta A,et al.eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2009; 36:
35 Straight stents Montgomery Dumon Polyflex Noppe n Hanar o Taewoon g Ultraflex Aero Eco Nanjing Freitag L. Airway stents. Eur Resp Monograph 2010
36 Natural stents: Silicone straight stents (Samsung Medical Center) Has C circular studs on its outer surface mimics the posterior membrane of the trachea increase stent-to-wall contact Ryu RJ et al,eur Respir J 2006; 28: maintain physiological airway constriction and dilation.
37 Freitag L. Airway stents. Eur Resp Monograph 2010 Bifurcated stents Westaby Stent Orlawski Stent Hood stent Dynamic Y Stent Dumon Y Stent Nanjing covered Y
38 Biodegradable stents Post lung transplant, 7 anastomotic complications in 6 patients over 6 years (stenosis 5, malacia 2) Biodegradable polydiaxanone stents deployed over guide wire Stents dissolved by an average of five months 4 of 6 patients developed restenosis requiring restenting 50% patient stent free at one year and doing well Lischke R, et al. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 4: , 2011
39 Expandable stents poor outcomes Reference Population Intervention Complications Follow up Nashef SA et al. Ann Thorac Surg Nov;54(5): Eller RL. Ann oto Rhino; Laryngol Apr; 115(4): Charokopos et al. Eur J of Cardiothorac surg. 2011oct patients total Pure stenosis - 6 Fibroinflammat ory stenosis 4 Malacia 5 16 benign stenoses (81% were PITS) Total of 26 stents 11 PITS (all were tracheostomise d) Expanding wire stents Selfexpandable metal stents Dilatation f/b covered nitinol stent insertion Granulation tissue in 12 (removal of stent in 3) Granulation 81% Complication requiring surgical Rx 87% Obstructive granulation tissue in four patients Stent migration 2/11 13 months follow up 9 had stents in situ, doing well 14 stents removed Mean duration 12.4 months Late results: 3 died of unrelated Tracheitis & halitosis recurrent 4
40 Piece-meal removal of SEMS Charokopos et al. Eur J of Cardiothorac surg. 2011oct 40
41 When not to stent? Non viable lung beyond the obstruction Expandable metallic stents are to be avoided if planned for surgery. Known to increase the length of stenosis
42 Problems with stents Metallic piecemeal removal (up to 73%) an resultant problems mucosal tearing, rebleeding, tension pneumothorax and post op ventilation 1 Silicone stents migration 2, granulation tissue and mucus plugging 1 Lunn W et al. Endoscopic removal of metallic airway stents. Chest 2005; 127: Dumon J.P.et al. Seven-year experience with the Dumon prosthesis. J Bronchology 1996; 31: 6-10
43 Problems with stents Martinez- Jeong BH 2 Dumon JF 3 Ballarin JI 1 Benign (malignant) Migration 17.5% 32% 18.6% (6.0%) Granulation tissue 6.3% 33% 17.2% (1.4%) Mucostasis 6.3% 30% 5.7% (1.4%) Malacia NR 16% NR 1 Martinez-Ballarin JI 1 et al. Chest Mar;109(3): Jeong BH et al. J Cardiovasc Thorac Surg Jul;144(1): Dumon JF et al. J bronchology. 1996: 3; 6-10
44 Granulation tissue management Medical therapy Neodymium doped-yttrium aluminum garnet laser Argon-plasma coagulation 2 Photodynamic therapy Cryotherapy Brachytherapy Colt HG et al. J Bronchol 1998; 5:
45 Granulation tissue problems with APC Colt H, Murgu S. Saunders 2012.Bronchoscopy and central airway disorders,
46 Primary bronchoscopic Rx G. Galluccio et al. Eur J of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 35 (2009)
47 G. Galluccio et al. Eur J of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 35 (2009)
48 Primary bronchoscopic therapy Reference Study design Patients conclusions Noureai et al. Laryngoscop e 2007 Jun; 117(6): Prospective patients, average length 18 mm 82% Myer cotton III or IV Tracheal resection done for long segment or near complete collapse of tracheal cartilage support 96% success with <30 mm Only 20% success with >30 mm 14 pts (23%) surgery
49 Noureai et al. Laryngoscope 2007 Jun; 117(6):1073-9
50 KTP laser potassium titanyl phosphate laser f/b balloon dilatation Stent deployed in grade IV and grade III >15 mm length 1 treatment mortality stent related Overall Rx mortality 1.6% increased to 2.9% when stent was used Noureai et al. Laryngoscope 2007 Jun; 117(6):1073-9
51 Recently reported success in endoscopic therapies is due to advances in technology and therapeutic options available Early detection of lesions: only granulation tissue formation Late lesions have destruction of cartilage and a mature circumferential scar
52 Preoperative endoscopy 54 out of 65 benign tracheal stenosis required therapy prior to surgery Two to eight rings were resected and 54 patients had remarkable improvement on follow up Laser (37), tracheostomy (38), endoluminal prosthesis (16) were the preoperative therpies Rea F et al.eur J Cardiothorac Surg Sep;22(3):352-6
53 Endoscopic treatment in severe stenosis 22 patients over two years 3/6 of complete stenosis and 8/10 of circumferential stenosis with cartilage involvement improved 15% (3 patients) required surgery May be an alternative to surgery even in severe stenosis Schweinfurth JM. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Jan;115(1):30-4
54 Central airway complications following transplant Incidence ranges from 1.6% to 33% % of anastomosis would require some form of therapy 2,3 Six type of complications known,including early and late complications: bronchial stenosis, dehiscence, bronchomalacia, fistula, obstructive granulomas, endobronchial infections 1 Santacruz JF, et al. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2009;6: Shennib H, et al. Ann Thorac Surg 1994;57: Ruttmann E, et al.j Heart Lung Transplant 2005;24:275 81
55 Post lung transplant patients 41 of 312 (13.1%), had tracheobronchial stenosis, malacia, granulation tissue and dehiscence 26 patients underwent balloon dilatation, of which except seven rest required stent/additional intervention Mortality associated with interventional bronchoscopy was 2.4% (1 of 41) Chaajed PN et al.chest Dec;120(6):1894-9
56 Post lung transplant patients Can be managed similar to other benign tracheal stenosis Balloon bronchoplasty alone may help in many of the patients A recently proposed objective classification of airway complications following lung transplant may be helpful in deciding the type of management 1 Stents and biodegradable stents have been used successfully 2 1 Dutau et al. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (2013) Lischke R, et al. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 4: , 2011
57 Endoscopic grading of post lung transplant airway complication Both immediate and late complications are known post lung transplant, at the anastomotic sites Various classifications have been proposed for classifying airway complication following lung transplant 1-4 Recently proposed MDS classification ( M macroscopic appearance, D diameter of bronchial lumen, S suture) (next slide) 1 Shennib H, et al. Ann Thorac Surg 1994;57: Couraud L, et al. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 1992;6: Chhajed PN, et al. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2004;25: Thistlethwaite PA, et al. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2008;136:
58 Dutau et al. European Journal of Cardio- Thoracic Surgery (2013) 1 6
59 Perotin JM et al. Ann thorac Med Jul;92(1): Idiopathic tracheal stenosis(its) Endoscopic management of 23 patients with ITS Web like stenosis in 61% and complex in 39% Mechanical dilatation alone 52%, along with LASER 30% and stenting in 18% High recurrence rate: 30% at 6 months, 87% at 5 years
60 Stenosis due to tuberculosis Common and under recognized Wrongly labeled as asthma Stricture at multiple site and bilateral involvement make surgery technically difficult
61 Stenosis due to tuberculosis 22/34 7/11 7/10 Hee soon chung et al. CHEST 2000; 117:
62 Jaiswal P et al. J R Soc Med 2005;98:26 28
63 Reference Intervention Patients Outcome Comments Iwamoto et al. CHEST 2004; 126: dilatation alone 6 dilatation & Dumon stent 11 patients with tracheobronchial TB 8 out of 11 improved (all 6 stented improved) * 1 lobectomy for complete occlusion Migration and granulation tissue in stented patients SY Low ERJ September 1, 2004 vol. 24 no Balloon dilatation, Nd:YAG, Dumon stent 21 symptomatic tracheobronchial stenoses due to TB Ryu YJ et al. Respirology Nov;11(6): patients 100 stents (43 Dumon 57 Natural ) 74% were post TB Successful stent removal. 54% Dumon 49% Natural Complication rates similar in both stents at 42 months Duan HF. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi, 2007 May;30(5): Balloon dilatation alone 2 to 7 sittings required 25 patients with bronchial stenosis as a result of TB No complications A 2 to 36 months f/u no restenosis 16 patients followed > 1 year average of 5.5+/- 2 mm diameter maintained
64 Reference Patients Intervention Outcome Comments Ding WM. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi, 2010 Jul;33(7): (Chinese) Abstract in English So Yeon Lim et al. Respirology Aug; 16(6): patients 25 patients with bronchial stenosis as a result of TB 71 patients of Post TB tracheobronch ial stenosis Silicone stenting, and in f/u bronchial toileting Complications 3.4% At 12 months f/u restenosis 3.4% (?criteria ) 40 patients had successful stent removal (median 12.5 months) 27 had stent re-insertion 4 had surgery No difference in general outcome and airway diameter at 3, 12 months. It was similar to the values obtained immediately after dilatation Successful stent removal independently associated with atelectasis <1 month before stent and absence of complete lobar atelectasis.
65 Ryu RJ et al,eur Respir J 2006; 28:
66 Long term tolerance of stents in TB Some benign disease groups (tuberculosis, sarcoidosis, war gas exposure, and inhalation burns) have multiplicity of involvement or long length of stenosed segment. This precludes surgery and may require stenting for long duration 17 patients with Natural silicone stent followed up Tolerated for a median period of 7.9 years (range 3-11) Late complications included granulation tissue (76%), migration(70%), mucostasis (17%) Verma A et al. ASAIO J Sep- Oct;58(5):530-4.
67 When to remove the stent? Permeation of air in the space between the outer surface of the stent and the airway wall occurs Suggests regression and healing of the stenosis Hence an optimal indicator of stent removal Verma A, et al. Radiology. 2012;263(2):562-8.
68 Verma A, et al. Radiology. 2012;263(2):562-8.
69 Tissue engineered airway transplant First patient followed up to five years now At end of one year cicatrical stenosis required endoluminal stenting However the tissue was well vascularized, epithelialized, normal mucosal clearance Doing well, except for intermittent bronchoscopic interventions Gonfiotti A et al. Lancet Jan 18;383(9913):238-44
70 Barros Casas D, et al. Arch Bronconeumol. 2014;50(8):
71 Magnitude of problem in PGI Benign tracheal stenosis accounted 55.26% of the therapeutic rigid procedures (21 out of 38) Median of two procedures per patient Rigid bronchoscope alone was used in 57.9% procedures, rest used flexible as well Madan K et al. Lung India Jan- Mar;31(1):9-15
72 Department of pulmonary medicine, PGIMER. Unpublished data Magnitude of problem in PGI From July 2012 till July 2014 a total of 80 rigid bronchoscopies 26 out of the 80 (32.5%) were procedures related to benign tracheal stenosis A total of 15 patients were treated, with mean 1.73 procedure per patient( 2 procedures in 3 and 3 procedures in 4 patients)
73 Etiology of benign tracheal stenosis Indication Number of patients (%) PGI 1 Rome 2 Post intubation tracheal stenosis 12 (80) 167 (79.9) Post tracheostomy tracheal stenosis 2 (13.3) 34 (16.3) Post TB tracheobronchial stenosis 1 (6.7) Others 8 (3.8%) 1 Department of pulmonary medicine, PGIMER. Unpublished data 2 Gallucio G et al. Eur J of cardiothorac Surg Mar;35(3):429-33
74 Summary Post intubation tracheal stenosis is generally simple and web like Simple balloon dilatation or preferably Laser assisted mechanical dilatation (LAMD) may be used as first choice Failure of balloon bronchoplasty at least twice, can be managed with stents
75 Summary Complex stenosis (involving cartilage) may be subjected to either surgery or stenting followed by surgery Stenosis higher up in the trachea are better managed by T-Tubes In inoperable patients endoscopic interventions are the only options
76 Summary A stenosis of 3 cm or more associated with failure, hence surgical resection is to be considered Long standing stenosis > 6 months are also better managed surgically Multisite involvement and complex stenosis makes Post-TB tracheal stenosis difficult to manage, simple dilatation with or without stenting is helpful
4/24/2017. Tracheal Stenosis. Tracheal Stenosis. Tracheal Stenosis. Tracheal Stenosis. Tracheal Stenosis Endoscopic & Surgical Management
 Endoscopic & Surgical Management Pressure ulceration Healing: granulation cicatrization contraction Ann Surg 1969;169:334-348 Gary Schwartz, MD Department of Thoracic Surgery and Lung Transplantation Baylor
Endoscopic & Surgical Management Pressure ulceration Healing: granulation cicatrization contraction Ann Surg 1969;169:334-348 Gary Schwartz, MD Department of Thoracic Surgery and Lung Transplantation Baylor
Therapeutic Bronchoscopy Etiology - Benign Stenosis Post - intubation Trauma Post - operative Inflammatory Idiopathic
 Endobronchial Palliation of Airway Disease Douglas E. Wood, MD Professor and Chief Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery Vice-Chair, Department of Surgery Endowed Chair in Lung Cancer Research University
Endobronchial Palliation of Airway Disease Douglas E. Wood, MD Professor and Chief Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery Vice-Chair, Department of Surgery Endowed Chair in Lung Cancer Research University
ENDOBRONCHIAL ABLATIVE THERAPIES. Christopher Cortes, MD, FPCCP
 ENDOBRONCHIAL ABLATIVE THERAPIES Christopher Cortes, MD, FPCCP Choice of Ablative Therapy Size of the lesion Location of the lesion Characteristics of the lesion Availability of the different therapies
ENDOBRONCHIAL ABLATIVE THERAPIES Christopher Cortes, MD, FPCCP Choice of Ablative Therapy Size of the lesion Location of the lesion Characteristics of the lesion Availability of the different therapies
Double Y-stenting for tracheobronchial stenosis
 ERJ Express. Published on April 10, 2012 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00015012 Double Y-stenting for tracheobronchial stenosis M. Oki and H. Saka AFFILIATIONS Dept of Respiratory Medicine, Nagoya Medical Center,
ERJ Express. Published on April 10, 2012 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00015012 Double Y-stenting for tracheobronchial stenosis M. Oki and H. Saka AFFILIATIONS Dept of Respiratory Medicine, Nagoya Medical Center,
Audra Fuller MD, Mark Sigler MD, Shrinivas Kambali MD, Raed Alalawi MD
 Clinical Series Successful treatment of post-intubation tracheal stenosis with balloon dilation, argon plasma coagulation, electrocautery and application of mitomycin C Audra Fuller MD, Mark Sigler MD,
Clinical Series Successful treatment of post-intubation tracheal stenosis with balloon dilation, argon plasma coagulation, electrocautery and application of mitomycin C Audra Fuller MD, Mark Sigler MD,
Since central airway stenosis is often a lifethreatening. Double Y-stenting for tracheobronchial stenosis. Masahide Oki and Hideo Saka
 Eur Respir J 2012; 40: 1483 1488 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00015012 CopyrightßERS 2012 Double Y-stenting for tracheobronchial stenosis Masahide Oki and Hideo Saka ABSTRACT: The purpose of the present study
Eur Respir J 2012; 40: 1483 1488 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00015012 CopyrightßERS 2012 Double Y-stenting for tracheobronchial stenosis Masahide Oki and Hideo Saka ABSTRACT: The purpose of the present study
The use of metallic expandable tracheal stents in the management of inoperable malignant tracheal obstruction
 The use of metallic expandable tracheal stents in the management of inoperable malignant tracheal obstruction Alaa Gaafar-MD, Ahmed Youssef-MD, Mohamed Elhadidi-MD A l e x a n d r i a F a c u l t y o f
The use of metallic expandable tracheal stents in the management of inoperable malignant tracheal obstruction Alaa Gaafar-MD, Ahmed Youssef-MD, Mohamed Elhadidi-MD A l e x a n d r i a F a c u l t y o f
Use of the Silicone T-tube to Treat Tracheal Stenosis or Tracheal Injury
 Use of the Silicone T-tube to Treat Stenosis or Injury Chang-Jer Huang MD Backgound: stenosis or tracheal is a troublesome disease. Traditional temporary tracheostomy and reconstruction can resolve some
Use of the Silicone T-tube to Treat Stenosis or Injury Chang-Jer Huang MD Backgound: stenosis or tracheal is a troublesome disease. Traditional temporary tracheostomy and reconstruction can resolve some
External trauma (MVA, surf board, assault, etc.) Internal trauma (Endotracheal intubation, tracheostomy) Other
 Etiology External trauma (MVA, surf board, assault, etc.) Internal trauma (Endotracheal intubation, tracheostomy) Other Systemic diseases (vasculitis, etc.) Chemo/XRT Idiopathic Trans nasal Esophagoscope
Etiology External trauma (MVA, surf board, assault, etc.) Internal trauma (Endotracheal intubation, tracheostomy) Other Systemic diseases (vasculitis, etc.) Chemo/XRT Idiopathic Trans nasal Esophagoscope
Balloon Bronchoplasty: Case Series
 Original Article 2012 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran ISSN: 1735-0344 TANAFFOS Balloon Bronchoplasty: Case Series Hamid Reza Jabbardarjani 1, Arda Kiani 1, Negar
Original Article 2012 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran ISSN: 1735-0344 TANAFFOS Balloon Bronchoplasty: Case Series Hamid Reza Jabbardarjani 1, Arda Kiani 1, Negar
Stents for airway strictures: selection and results
 Review Article Stents for airway strictures: selection and results Adil Ayub, Adnan M. Al-Ayoubi, Faiz Y. Bhora Department of Thoracic Surgery, Icahn School of Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New
Review Article Stents for airway strictures: selection and results Adil Ayub, Adnan M. Al-Ayoubi, Faiz Y. Bhora Department of Thoracic Surgery, Icahn School of Medicine, Mount Sinai Health System, New
Montgomery T-tube placement in the treatment of benign tracheal lesions
 European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 36 (2009) 352 356 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejcts Montgomery T-tube placement in the treatment of benign tracheal lesions Angelo Carretta *, Monica Casiraghi,
European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 36 (2009) 352 356 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejcts Montgomery T-tube placement in the treatment of benign tracheal lesions Angelo Carretta *, Monica Casiraghi,
Interventional Pulmonology
 Interventional Pulmonology The Division of Thoracic Surgery Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery New York Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical College p: 212-746-6275 f: 212-746-8223 https://weillcornell.org/eshostak
Interventional Pulmonology The Division of Thoracic Surgery Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery New York Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical College p: 212-746-6275 f: 212-746-8223 https://weillcornell.org/eshostak
DUMON-NOVATECH Y-STENTS: A FOUR-YEAR EXPERIENCE WITH 50 TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TUMORS INVOLVING THE CARINA
 Solunum 3, Özel Sayı 2: 260-264, 2001 DUMON-NOVATECH Y-STENTS: A FOUR-YEAR EXPERIENCE WITH 50 TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TUMORS INVOLVING THE CARINA Jean F DUMON* M C DUMON* SUMMARY This article reports a 4-year
Solunum 3, Özel Sayı 2: 260-264, 2001 DUMON-NOVATECH Y-STENTS: A FOUR-YEAR EXPERIENCE WITH 50 TRACHEOBRONCHIAL TUMORS INVOLVING THE CARINA Jean F DUMON* M C DUMON* SUMMARY This article reports a 4-year
Therapeutic bronchoscopy for malignant airway stenoses: Choice of modality and survival
 Original Article Free full text available from www.cancerjournal.net Therapeutic bronchoscopy for malignant airway stenoses: Choice of modality and survival ABSTRACT Background: There are no data regarding
Original Article Free full text available from www.cancerjournal.net Therapeutic bronchoscopy for malignant airway stenoses: Choice of modality and survival ABSTRACT Background: There are no data regarding
Temporary placement of metallic stent could lead to long-term benefits for benign tracheobronchial stenosis
 Original Article on Airway Obstruction Temporary placement of metallic stent could lead to long-term benefits for benign tracheobronchial stenosis Guo-Wu Zhou*, Hai-Dong Huang*, Qin-Ying Sun*, Ye Xiong*,
Original Article on Airway Obstruction Temporary placement of metallic stent could lead to long-term benefits for benign tracheobronchial stenosis Guo-Wu Zhou*, Hai-Dong Huang*, Qin-Ying Sun*, Ye Xiong*,
Complex Airway problems - Paediatric Perspective
 Complex Airway problems - Paediatric Perspective Dave Albert BACO Liverpool 2009 www.albert.uk.com Complex Ξ not simple, multiple parts Multiple problems with airway Combined Web/stenosis/multiple levels
Complex Airway problems - Paediatric Perspective Dave Albert BACO Liverpool 2009 www.albert.uk.com Complex Ξ not simple, multiple parts Multiple problems with airway Combined Web/stenosis/multiple levels
Tracheobronchial stents are useful in the management
 Do Expandable Metallic Airway Stents Have a Role in the Management of Patients With Benign Tracheobronchial Disease? Brendan P. Madden, MD, FRCP, Tuck-Kay Loke, MRCP, and Abhijat C. Sheth, FRCS Department
Do Expandable Metallic Airway Stents Have a Role in the Management of Patients With Benign Tracheobronchial Disease? Brendan P. Madden, MD, FRCP, Tuck-Kay Loke, MRCP, and Abhijat C. Sheth, FRCS Department
Endobronchial Management of Benign, Malignant, and Lung Transplantation Airway Stenoses
 Endobronchial Management of Benign, Malignant, and Lung Transplantation Airway Stenoses Joshua R. Sonett, MD, Robert J. Keenan, MD, Peter F. Ferson, MD, Bartley P. Griffith, MD, and Rodney J. Landreneau,
Endobronchial Management of Benign, Malignant, and Lung Transplantation Airway Stenoses Joshua R. Sonett, MD, Robert J. Keenan, MD, Peter F. Ferson, MD, Bartley P. Griffith, MD, and Rodney J. Landreneau,
Central airway obstruction (CAO) : laser, APC, stents and other techniques.
 Thank you for viewing this presentation. We would like to remind you that this material is the property of the author. It is provided to you by the ERS for your personal use only, as submitted by the author.
Thank you for viewing this presentation. We would like to remind you that this material is the property of the author. It is provided to you by the ERS for your personal use only, as submitted by the author.
Introduction to Interventional Pulmonology
 Introduction to Interventional Pulmonology Alexander Chen, M.D. Director, Interventional Pulmonology Assistant Professor of Medicine and Surgery Divisions of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine and Cardiothoracic
Introduction to Interventional Pulmonology Alexander Chen, M.D. Director, Interventional Pulmonology Assistant Professor of Medicine and Surgery Divisions of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine and Cardiothoracic
Clinical implications of differentiating between types of posttracheostomy
 Original Article Clinical implications of differentiating between types of posttracheostomy tracheal stenosis Beomsu Shin 1 *, Kang Kim 1 *, Byeong-Ho Jeong 1, Jung Seop Eom 2, Won Jun Song 3, Hojoong
Original Article Clinical implications of differentiating between types of posttracheostomy tracheal stenosis Beomsu Shin 1 *, Kang Kim 1 *, Byeong-Ho Jeong 1, Jung Seop Eom 2, Won Jun Song 3, Hojoong
Airway stenting in excessive central airway collapse
 Review Article on Aerodigestive Endoscopy Airway stenting in excessive central airway collapse Mihir Parikh, Jennifer Wilson, Adnan Majid, Sidhu Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II)
Review Article on Aerodigestive Endoscopy Airway stenting in excessive central airway collapse Mihir Parikh, Jennifer Wilson, Adnan Majid, Sidhu Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II)
Vanishing Bronchus After Lung Transplantation: The Role of Sequential Airway Dilatations
 CASE REPORT Ochsner Journal 17:71 75, 2017 Ó Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Vanishing Bronchus After Lung Transplantation: The Role of Sequential Airway Dilatations Abdul Hamid Alraiyes,
CASE REPORT Ochsner Journal 17:71 75, 2017 Ó Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Vanishing Bronchus After Lung Transplantation: The Role of Sequential Airway Dilatations Abdul Hamid Alraiyes,
Novatech Products for Interventional Pulmonology
 Novatech Products for Novatech and Boston Medical Products Bringing you the finest products for Novatech is a manufacturer of top-quality medical products used successfully worldwide in the growing specialty
Novatech Products for Novatech and Boston Medical Products Bringing you the finest products for Novatech is a manufacturer of top-quality medical products used successfully worldwide in the growing specialty
Clinical Study Fully Covered Metallic Stents for the Treatment of Benign Airway Stenosis
 Canadian Respiratory Journal Volume 2016, Article ID 8085216, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8085216 Clinical Study Fully Covered Metallic Stents for the Treatment of Benign Airway Stenosis Caroline
Canadian Respiratory Journal Volume 2016, Article ID 8085216, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8085216 Clinical Study Fully Covered Metallic Stents for the Treatment of Benign Airway Stenosis Caroline
Self-expanding metallic stents (SEMS) have gained widespread
 Bronchoscopic Extraction of Incorporated Self-Expanding Metallic Stents Sudish C. Murthy, MD, PhD, FACS, FCCP Self-expanding metallic stents (SEMS) have gained widespread acceptance as a treatment for
Bronchoscopic Extraction of Incorporated Self-Expanding Metallic Stents Sudish C. Murthy, MD, PhD, FACS, FCCP Self-expanding metallic stents (SEMS) have gained widespread acceptance as a treatment for
Idiopathic laryngotracheal stenosis
 Surgical Technique Idiopathic laryngotracheal stenosis Christina L. Costantino, Douglas J. Mathisen Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA 02114, USA Correspondence to: Douglas J. Mathisen, MD. Massachusetts
Surgical Technique Idiopathic laryngotracheal stenosis Christina L. Costantino, Douglas J. Mathisen Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA 02114, USA Correspondence to: Douglas J. Mathisen, MD. Massachusetts
Endoscopic Removal of Metallic Airway Stents*
 bronchoscopy Endoscopic Removal of Metallic Airway Stents* William Lunn, MD, FCCP; David Feller-Kopman, MD, FCCP; Momen Wahidi, MD; Simon Ashiku, MD; Robert Thurer, MD, FCCP; and Armin Ernst, MD, FCCP
bronchoscopy Endoscopic Removal of Metallic Airway Stents* William Lunn, MD, FCCP; David Feller-Kopman, MD, FCCP; Momen Wahidi, MD; Simon Ashiku, MD; Robert Thurer, MD, FCCP; and Armin Ernst, MD, FCCP
Subject Index. Bacterial infection, see Suppurative lung disease, Tuberculosis
 Subject Index Abscess, virtual 107 Adenoidal hypertrophy, features 123 Airway bleeding, technique 49, 50 Airway stenosis, see Stenosis, airway Anaesthesia biopsy 47 complications 27, 28 flexible 23 26
Subject Index Abscess, virtual 107 Adenoidal hypertrophy, features 123 Airway bleeding, technique 49, 50 Airway stenosis, see Stenosis, airway Anaesthesia biopsy 47 complications 27, 28 flexible 23 26
Pediatric partial cricotracheal resection: A new technique for the posterior cricoid anastomosis
 Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2006) 135, 318-322 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Pediatric partial cricotracheal resection: A new technique for the posterior cricoid anastomosis Mark E. Boseley, MD, and Christopher
Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery (2006) 135, 318-322 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Pediatric partial cricotracheal resection: A new technique for the posterior cricoid anastomosis Mark E. Boseley, MD, and Christopher
Aetiology. Poor tube management. Small cricoid (acquired on congenital) Reflux Poor general status. Size of tube (leak) Duration of intubation
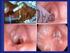 Aetiology Poor tube management Size of tube (leak) Duration of intubation Small cricoid (acquired on congenital) Reflux Poor general status Prevention Laryngeal Rest Medical Tubes Cricoid split Developing
Aetiology Poor tube management Size of tube (leak) Duration of intubation Small cricoid (acquired on congenital) Reflux Poor general status Prevention Laryngeal Rest Medical Tubes Cricoid split Developing
Metallic stent and flexible bronchoscopy without fluoroscopy for acute respiratory failure
 Eur Respir J 2008; 31: 1019 1023 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00099507 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2008 Metallic stent and flexible bronchoscopy without fluoroscopy for acute respiratory failure S-M. Lin*,#, T-Y.
Eur Respir J 2008; 31: 1019 1023 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00099507 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2008 Metallic stent and flexible bronchoscopy without fluoroscopy for acute respiratory failure S-M. Lin*,#, T-Y.
Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes. Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center
 Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Neonatal and Pediatric Tracheostomy Tracheostomy
Neonatal Airway Disorders, Treatments, and Outcomes Steven Goudy, MD Pediatric Otolaryngology Emory University Medical Center Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Neonatal and Pediatric Tracheostomy Tracheostomy
Surgical Treatment of Benign Subglottic Stenosis. JLKasperbauer MD Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN USA
 Surgical Treatment of Benign Subglottic Stenosis JLKasperbauer MD Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN USA Goals Review Subglottic Stenosis Anatomy, Airway Dynamics, Etiology Idiopathic Subglottic Stenosis Definition,
Surgical Treatment of Benign Subglottic Stenosis JLKasperbauer MD Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN USA Goals Review Subglottic Stenosis Anatomy, Airway Dynamics, Etiology Idiopathic Subglottic Stenosis Definition,
Advanced Bronchoscopy
 Advanced Bronchoscopy Radial Jaw 4 Pulmonary Forceps Ultraflex Tracheobronchial Stent System CRE Pulmonary Balloon Alair Bronchial Thermoplasty Catheter CRE Pulmonary Balloon Radial Jaw 4 Pulmonary Forceps
Advanced Bronchoscopy Radial Jaw 4 Pulmonary Forceps Ultraflex Tracheobronchial Stent System CRE Pulmonary Balloon Alair Bronchial Thermoplasty Catheter CRE Pulmonary Balloon Radial Jaw 4 Pulmonary Forceps
Tracheal Stenosis Following Cuffed Tube Tracheostomy
 Tracheal Stenosis Following Cuffed Tube Tracheostomy Anatomical Variation and Selected Treatment Armand A. Lefemine, M.D., Kenneth MacDonnell, M.D., and Hyung S. Moon, M.D. ABSTRACT Tracheal stenosis resulting
Tracheal Stenosis Following Cuffed Tube Tracheostomy Anatomical Variation and Selected Treatment Armand A. Lefemine, M.D., Kenneth MacDonnell, M.D., and Hyung S. Moon, M.D. ABSTRACT Tracheal stenosis resulting
Day 2 Pulmonary Breakout Interventional Pulmonology
 Day 2 Pulmonary Breakout Interventional Pulmonology R. Paul Boesch, DO, MS Assistant Professor, Pulmonary Medicine Mayo Clinic Children s Center Interventional Pediatric Pulmonology or Pulm/ENT airway
Day 2 Pulmonary Breakout Interventional Pulmonology R. Paul Boesch, DO, MS Assistant Professor, Pulmonary Medicine Mayo Clinic Children s Center Interventional Pediatric Pulmonology or Pulm/ENT airway
Large airway obstruction occurs secondary to a variety
 Medium-Term Follow-Up After Deployment of Ultraflex Expandable Metallic Stents to Manage Endobronchial Pathology Brendan P. Madden, MD, FRCP, John E. S. Park, MA, MRCP, and Abhijat Sheth, FRCS Department
Medium-Term Follow-Up After Deployment of Ultraflex Expandable Metallic Stents to Manage Endobronchial Pathology Brendan P. Madden, MD, FRCP, John E. S. Park, MA, MRCP, and Abhijat Sheth, FRCS Department
Respiratory distress in patients with central airway obstruction
 Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg (2010) 26:151 156 DOI 10.1007/s12055-010-0021-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Respiratory distress in patients with central airway obstruction Mohamed Abdel Hamied Regal & Yasser Ahmed
Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg (2010) 26:151 156 DOI 10.1007/s12055-010-0021-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Respiratory distress in patients with central airway obstruction Mohamed Abdel Hamied Regal & Yasser Ahmed
A Proposed Grading System for Post-Intubation Tracheal Stenosis
 Original Article 2012 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran ISSN: 1735-0344 TANAFFOS A Proposed Grading System for Post-Intubation Tracheal Stenosis Ali Ghorbani 1,
Original Article 2012 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran ISSN: 1735-0344 TANAFFOS A Proposed Grading System for Post-Intubation Tracheal Stenosis Ali Ghorbani 1,
Laryngo-tracheal stenosis is a congenital or. A Multi-Modality Surgical Management in Laryngeal Stenosis. Case Series
 Case Series A Multi-Modality Surgical Management in Laryngeal Stenosis Ashfaque Ansari, 1 Annju Thomas 1 ABSTRACT Introduction Postintubation laryngo-tracheal stenosis requires a precise diagnosis and
Case Series A Multi-Modality Surgical Management in Laryngeal Stenosis Ashfaque Ansari, 1 Annju Thomas 1 ABSTRACT Introduction Postintubation laryngo-tracheal stenosis requires a precise diagnosis and
Anaesthesia for surgery of the trachea and main bronchi
 Anaesthesia for surgery of the trachea and main bronchi Alistair Macfie Christopher Hawthorne Abstract Major surgery on the trachea and airway is an anaesthetic challenge, which necessitates the simultaneous
Anaesthesia for surgery of the trachea and main bronchi Alistair Macfie Christopher Hawthorne Abstract Major surgery on the trachea and airway is an anaesthetic challenge, which necessitates the simultaneous
Case Report. Management of recurrent distal tracheal stenosis using an endoprosthesis: a case report* Abstract. Introduction.
 121 Case Report Management of recurrent distal tracheal stenosis using an endoprosthesis: a case report* André Germano Leite 1, Douglas Kussler 2 Abstract The authors report the case of a patient with
121 Case Report Management of recurrent distal tracheal stenosis using an endoprosthesis: a case report* André Germano Leite 1, Douglas Kussler 2 Abstract The authors report the case of a patient with
Factors leading to tracheobronchial self-expandable metallic stent fracture
 GENERAL THORACIC SURGERY Factors leading to tracheobronchial self-expandable metallic stent fracture Fu-Tsai Chung, MD,* Shu-Min Lin, MD,* Hao-Cheng Chen, MD, Chun-Liang Chou, MD, Chih-Teng Yu, MD, Chien-
GENERAL THORACIC SURGERY Factors leading to tracheobronchial self-expandable metallic stent fracture Fu-Tsai Chung, MD,* Shu-Min Lin, MD,* Hao-Cheng Chen, MD, Chun-Liang Chou, MD, Chih-Teng Yu, MD, Chien-
Airway Remodeling: Preliminary Experience with Bio-Absorbable Airway Stents in Adults Jaus MO, Gonfiotti A, Barale D, Macchiarini P
 Airway Remodeling: Preliminary Experience with Bio-Absorbable Airway Stents in Adults Jaus MO, Gonfiotti A, Barale D, Macchiarini P University Hospital Careggi Florence, Italy Disclosure Statement THE
Airway Remodeling: Preliminary Experience with Bio-Absorbable Airway Stents in Adults Jaus MO, Gonfiotti A, Barale D, Macchiarini P University Hospital Careggi Florence, Italy Disclosure Statement THE
Operative and non-operative treatment of benign subglottic laryngotracheal stenosis *
 European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 26 (2004) 818 822 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejcts Operative and non-operative treatment of benign subglottic laryngotracheal stenosis * Abstract Anna Maria Ciccone
European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 26 (2004) 818 822 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejcts Operative and non-operative treatment of benign subglottic laryngotracheal stenosis * Abstract Anna Maria Ciccone
Metallic Stent and Flexible Bronchoscopy without Fluoroscopy for
 ERJ Express. Published on January 9, 2008 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00099507 Metallic Stent and Flexible Bronchoscopy without Fluoroscopy for Acute Respiratory Failure Shu-Min Lin, MD*,Ting-Yu Lin, MD*,
ERJ Express. Published on January 9, 2008 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00099507 Metallic Stent and Flexible Bronchoscopy without Fluoroscopy for Acute Respiratory Failure Shu-Min Lin, MD*,Ting-Yu Lin, MD*,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. The Use of Balloon-Expandable Metallic Stents in the Treatment of Pediatric Tracheomalacia and Bronchomalacia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Use of Balloon-Expandable Metallic Stents in the Treatment of Pediatric Tracheomalacia and Bronchomalacia Robert H. Furman, MD; Carl L. Backer, MD; Michael E. Dunham, MD; James Donaldson,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Use of Balloon-Expandable Metallic Stents in the Treatment of Pediatric Tracheomalacia and Bronchomalacia Robert H. Furman, MD; Carl L. Backer, MD; Michael E. Dunham, MD; James Donaldson,
Rigid Bronchoscopic Intervention in Patients with Respiratory Failure Caused by Malignant Central Airway Obstruction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Rigid Bronchoscopic Intervention in Patients with Respiratory Failure Caused by Malignant Central Airway Obstruction Kyeongman Jeon, MD, Hojoong Kim, MD, Chang-Min Yu, MD, Won-Jung Koh,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Rigid Bronchoscopic Intervention in Patients with Respiratory Failure Caused by Malignant Central Airway Obstruction Kyeongman Jeon, MD, Hojoong Kim, MD, Chang-Min Yu, MD, Won-Jung Koh,
Surgical treatment for patients with tracheal and subgllotic stenosis
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 3, November, 2009. pp. 132-138 Surgical treatment for patients with tracheal and subgllotic stenosis Mohammad Naeimi, MD.
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 23, No. 3, November, 2009. pp. 132-138 Surgical treatment for patients with tracheal and subgllotic stenosis Mohammad Naeimi, MD.
Metallic small y stent placement at primary right carina for bronchial disease
 Bi et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2018) 18:182 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-018-0742-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Metallic small y stent placement at primary right carina for bronchial disease Yonghua
Bi et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2018) 18:182 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-018-0742-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Metallic small y stent placement at primary right carina for bronchial disease Yonghua
Clinical Presentation and Outcome Laryngotracheal Stenosis: A Retrospective Analysis
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/369 Clinical Presentation and Outcome Laryngotracheal Stenosis: A Retrospective Analysis L Somu 1, Prasanna Kumar Saravanam 1, A Ravikumar 2, Raadhika Shree 3 1
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2015/369 Clinical Presentation and Outcome Laryngotracheal Stenosis: A Retrospective Analysis L Somu 1, Prasanna Kumar Saravanam 1, A Ravikumar 2, Raadhika Shree 3 1
Marc Noppen, MD, PhD, FCCP; Grigoris Stratakos, MD; Jan D Haese, MD; Marc Meysman, MD, FCCP; and Walter Vinken, MD, PhD
 Removal of Covered Self-Expandable Metallic Airway Stents in Benign Disorders* Indications, Technique, and Outcomes Marc Noppen, MD, PhD, FCCP; Grigoris Stratakos, MD; Jan D Haese, MD; Marc Meysman, MD,
Removal of Covered Self-Expandable Metallic Airway Stents in Benign Disorders* Indications, Technique, and Outcomes Marc Noppen, MD, PhD, FCCP; Grigoris Stratakos, MD; Jan D Haese, MD; Marc Meysman, MD,
Tracheal Trauma: Management and Treatment. Kosmas Iliadis, MD, PhD, FECTS
 Tracheal Trauma: Management and Treatment Kosmas Iliadis, MD, PhD, FECTS Thoracic Surgeon Director of Thoracic Surgery Department Hygeia Hospital, Athens INTRODUCTION Heterogeneous group of injuries mechanism
Tracheal Trauma: Management and Treatment Kosmas Iliadis, MD, PhD, FECTS Thoracic Surgeon Director of Thoracic Surgery Department Hygeia Hospital, Athens INTRODUCTION Heterogeneous group of injuries mechanism
Management of Pediatric Tracheostomy
 Management of Pediatric Tracheostomy Deepak Mehta Associate Professor Of Otolaryngology Director Pediatric Aerodigestive Center Definitions Tracheotomy: The making of an incision in the trachea The name
Management of Pediatric Tracheostomy Deepak Mehta Associate Professor Of Otolaryngology Director Pediatric Aerodigestive Center Definitions Tracheotomy: The making of an incision in the trachea The name
Application of the Montgomery T-tube in subglottic tracheal benign stenosis
 Surgical Technique pplication of the Montgomery T-tube in subglottic tracheal benign stenosis Huihui Hu, Jisong Zhang, Fengjie Wu, Enguo Chen Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Sir Run
Surgical Technique pplication of the Montgomery T-tube in subglottic tracheal benign stenosis Huihui Hu, Jisong Zhang, Fengjie Wu, Enguo Chen Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Sir Run
Temporary and permanent restoration of airway continuity with the tracheal T-tube
 Temporary and permanent restoration of airway continuity with the tracheal T-tube The advantages of the tracheal T -tube compared with a regular tracheostomy tube are a physiologic direction of air flow,
Temporary and permanent restoration of airway continuity with the tracheal T-tube The advantages of the tracheal T -tube compared with a regular tracheostomy tube are a physiologic direction of air flow,
Preliminary Experience with Bronchotherapeutic Procedures in Central Airway Obstruction
 Original Article 240 Preliminary Experience with Bronchotherapeutic Procedures in Central Airway Obstruction Ming-Shian Lu, MD; Yun-Hen Liu, MD; Po Jen Ko, MD; Yi-Chen Wu, MD; Ming-Ju Hsieh, MD; Hui-Ping
Original Article 240 Preliminary Experience with Bronchotherapeutic Procedures in Central Airway Obstruction Ming-Shian Lu, MD; Yun-Hen Liu, MD; Po Jen Ko, MD; Yi-Chen Wu, MD; Ming-Ju Hsieh, MD; Hui-Ping
Subglottic stenosis, with involvement of the lower larynx
 Laryngotracheal Resection and Reconstruction John D. Mitchell, MD n, Subglottic stenosis is being recognized with increasing frequency in adults, and may be the most frequent indication for airway intervention
Laryngotracheal Resection and Reconstruction John D. Mitchell, MD n, Subglottic stenosis is being recognized with increasing frequency in adults, and may be the most frequent indication for airway intervention
Original article Bronchoscopic profile of various diseases in a rural care hospital
 J M e d A l l i e d S c i 2 0 1 7 ; 7 ( 2 ) : 87-91 w w w. j m a s. i n P r i n t I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 6 9 6 O n l i n e I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 7 0 X Journal of M e d i cal & Allied Sciences Original article
J M e d A l l i e d S c i 2 0 1 7 ; 7 ( 2 ) : 87-91 w w w. j m a s. i n P r i n t I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 6 9 6 O n l i n e I S S N : 2 2 3 1 1 7 0 X Journal of M e d i cal & Allied Sciences Original article
Department of Thoracic Medicine, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Lin-Kuo Branch, Chang Gung Medical Foundation; Abstract
 DOI 10.6314/JIMT.2017.28(4).07 2017 28 243-251 Impacts of Airway Self-expandable Metallic Stent on Ventilator Weaning and Survival of Mechanically Ventilated Patients with Esophageal Cancer and Cental
DOI 10.6314/JIMT.2017.28(4).07 2017 28 243-251 Impacts of Airway Self-expandable Metallic Stent on Ventilator Weaning and Survival of Mechanically Ventilated Patients with Esophageal Cancer and Cental
in the Treatment of Re g actory Airway Strictures
 Endotracheal Cryothera y in the Treatment of Re g actory Airway Strictures Bradley M. Rodgers, M.D., Farhat Moazam, M.D., and James L. Talbert, M.D. ABSTRACT In 1977 we reported the successful use of endotracheal
Endotracheal Cryothera y in the Treatment of Re g actory Airway Strictures Bradley M. Rodgers, M.D., Farhat Moazam, M.D., and James L. Talbert, M.D. ABSTRACT In 1977 we reported the successful use of endotracheal
Flexible Bronchoscopy: More Than Just a Diagnostic Tool
 Flexible Bronchoscopy: More Than Just a Diagnostic Tool Kimberly M Baker-El Abiad, MD Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, & Occupational Medicine 10/19/2018 Objectives Brief historical background on
Flexible Bronchoscopy: More Than Just a Diagnostic Tool Kimberly M Baker-El Abiad, MD Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, & Occupational Medicine 10/19/2018 Objectives Brief historical background on
Airway stent placement for malignant tracheobronchial strictures in patients with an endotracheal tube
 Airway stent placement for malignant tracheobronchial strictures in patients with an endotracheal tube Poster No.: C-1121 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. J. Kim,
Airway stent placement for malignant tracheobronchial strictures in patients with an endotracheal tube Poster No.: C-1121 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. J. Kim,
Discussing feline tracheal disease
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Discussing feline tracheal disease Author : ANDREW SPARKES Categories : Vets Date : March 24, 2008 ANDREW SPARKES aims to
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Discussing feline tracheal disease Author : ANDREW SPARKES Categories : Vets Date : March 24, 2008 ANDREW SPARKES aims to
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005
 Close this window to return to IVIS Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005 Hosted by: Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the WSAVA Surgery
Close this window to return to IVIS Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Mexico City, Mexico 2005 Hosted by: Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the WSAVA Surgery
The Hitch Stitch : An Effective Method of Preventing Migration in High Tracheal Stenosis
 Interventional Pulmonology Respiration 2017;93:106 111 Received: July 6, 2016 Accepted after revision: November 3, 2016 Published online: December 17, 2016 The Hitch Stitch : An Effective Method of Preventing
Interventional Pulmonology Respiration 2017;93:106 111 Received: July 6, 2016 Accepted after revision: November 3, 2016 Published online: December 17, 2016 The Hitch Stitch : An Effective Method of Preventing
The treatment strategy for tracheoesophageal fistula
 Review Article on Airway Obstruction The treatment strategy for tracheoesophageal fistula Mingyao Ke, Xuemei Wu, Junli Zeng Department of Respiratory Centre, No. 2 Hospital Xiamen, Xiamen 361000, China
Review Article on Airway Obstruction The treatment strategy for tracheoesophageal fistula Mingyao Ke, Xuemei Wu, Junli Zeng Department of Respiratory Centre, No. 2 Hospital Xiamen, Xiamen 361000, China
Preliminary Results of Intraoperative Mitomycin-C in the Treatment and Prevention of Glottic and Subglottic Stenosis
 Journal of Voice Vol. 14, No. 2, pp. 282-286 2000 Singular Publishing Group Preliminary Results of Intraoperative Mitomycin-C in the Treatment and Prevention of Glottic and Subglottic Stenosis *Reza Rahbar,
Journal of Voice Vol. 14, No. 2, pp. 282-286 2000 Singular Publishing Group Preliminary Results of Intraoperative Mitomycin-C in the Treatment and Prevention of Glottic and Subglottic Stenosis *Reza Rahbar,
TRACHEOSTOMY. Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion
 TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
TRACHEOSTOMY Definition Tracheostomy means creation an artificial opening in the trachea with tracheostomy tube insertion Indications for tracheostomy 1-upper airway obstruction with stridor, air hunger,
Translaryngeal Tracheostomy - TLT Fantoni Method
 Translaryngeal Tracheostomy - TLT Fantoni Method Fantoni A., Ripamonti D., Lesmo A. About the Authors Fantoni Antonio Chief Emeritus of Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care - San Carlo Borromeo
Translaryngeal Tracheostomy - TLT Fantoni Method Fantoni A., Ripamonti D., Lesmo A. About the Authors Fantoni Antonio Chief Emeritus of Department of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care - San Carlo Borromeo
Sreeni Jonnalagadda, MD., FASGE Professor of Medicine, UMKC Director of Interventional Endoscopy Saint Luke s Hospital, Kansas City
 Sreeni Jonnalagadda, MD., FASGE Professor of Medicine, UMKC Director of Interventional Endoscopy Saint Luke s Hospital, Kansas City Peptic stricture Shtki Schatzki s ring Esophageal cancer Radiation therapy
Sreeni Jonnalagadda, MD., FASGE Professor of Medicine, UMKC Director of Interventional Endoscopy Saint Luke s Hospital, Kansas City Peptic stricture Shtki Schatzki s ring Esophageal cancer Radiation therapy
CHAPTER 7 Procedures on Respiratory System
 CHAPTER 7 Propunere noua clasificare proceduri folosind codificarea ICD-10-AM versiunea 3, 30 martie 2004 Procedures on Respiratory System BLOCK 520 Examination procedures on larynx 41764-03 Fibreoptic
CHAPTER 7 Propunere noua clasificare proceduri folosind codificarea ICD-10-AM versiunea 3, 30 martie 2004 Procedures on Respiratory System BLOCK 520 Examination procedures on larynx 41764-03 Fibreoptic
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION ISSN: OPEN ACCESS ARTICLE.
 ISSN: 0976-3104 Hashemi et al. ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS PROGNOSIS AND COMPLICATIONS OF TRACHEAL STENOSIS AND TRACHEAL RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY IN PATIENTS REFERRED TO AL- ZAHRA HOSPITAL IN ISFAHAN PROVINCE DURING
ISSN: 0976-3104 Hashemi et al. ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS PROGNOSIS AND COMPLICATIONS OF TRACHEAL STENOSIS AND TRACHEAL RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY IN PATIENTS REFERRED TO AL- ZAHRA HOSPITAL IN ISFAHAN PROVINCE DURING
Airway stenting 1. Douglas E. Wood, MD
 Chest Surg Clin N Am 13 (2003) 211 229 Airway stenting 1 Douglas E. Wood, MD Section of General Thoracic Surgery, Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery, University of Washington, Box 356310, 1959 NE Pacific,
Chest Surg Clin N Am 13 (2003) 211 229 Airway stenting 1 Douglas E. Wood, MD Section of General Thoracic Surgery, Division of Cardiothoracic Surgery, University of Washington, Box 356310, 1959 NE Pacific,
Stenting for Esophageal Cancer Technical Issues and Outcomes
 Stenting for Esophageal Cancer Technical Issues and Outcomes Moishe Liberman Director C.E.T.O.C. Division of Thoracic Surgery Centre Hospitalier de l Université de Montréal Disclosures Research and Educational
Stenting for Esophageal Cancer Technical Issues and Outcomes Moishe Liberman Director C.E.T.O.C. Division of Thoracic Surgery Centre Hospitalier de l Université de Montréal Disclosures Research and Educational
Review of Posttracheostomy And Postintubation Tracheal Stenosis With Special Regard to Etiology and Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Review of Posttracheostomy And Postintubation Tracheal Stenosis With Special Regard to Etiology and A Sarper, A Ayten,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Review of Posttracheostomy And Postintubation Tracheal Stenosis With Special Regard to Etiology and A Sarper, A Ayten,
Surgical Repair of Iatrogenic Cervical Tracheal Stenosis
 Surgical Repair of Iatrogenic Cervical Tracheal Stenosis Nirmal K. Veeramachaneni, MD, and Bryan F. Meyers, MD, MPH he advent of intensive care unit management has increased the potential opportunities
Surgical Repair of Iatrogenic Cervical Tracheal Stenosis Nirmal K. Veeramachaneni, MD, and Bryan F. Meyers, MD, MPH he advent of intensive care unit management has increased the potential opportunities
Silicone stents, the rigid bronchoscope, and the standard of care in central airway stenosis
 Curr Respir Care Rep (2012) 1:46 53 DOI 10.1007/s13665-011-0003-8 INTERVENTIONAL PULMONOLOGY (LM SEIJO, SECTION EDITOR) Silicone stents, the rigid bronchoscope, and the standard of care in central airway
Curr Respir Care Rep (2012) 1:46 53 DOI 10.1007/s13665-011-0003-8 INTERVENTIONAL PULMONOLOGY (LM SEIJO, SECTION EDITOR) Silicone stents, the rigid bronchoscope, and the standard of care in central airway
Section 4.1 Paediatric Tracheostomy Introduction
 Bite- sized training from the GTC Section 4.1 Paediatric Tracheostomy Introduction This is one of a series of bite- sized chunks of educational material developed by the Global Tracheostomy Collaborative.
Bite- sized training from the GTC Section 4.1 Paediatric Tracheostomy Introduction This is one of a series of bite- sized chunks of educational material developed by the Global Tracheostomy Collaborative.
Division of Pulmonology, Department of Medicine, Hat Yai Medical Education
 Obstructive Fibrinous Tracheal Pseudomembrane: A Rare condition in post-extubation stridor Narongwit Nakwan, M.D. Division of Pulmonology, Department of Medicine, Hat Yai Medical Education Center, Hat
Obstructive Fibrinous Tracheal Pseudomembrane: A Rare condition in post-extubation stridor Narongwit Nakwan, M.D. Division of Pulmonology, Department of Medicine, Hat Yai Medical Education Center, Hat
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 03 Page March 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-4 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/.18535/jmscr/v6i3.63 Diagnostic Role of FOB in Radiological
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-4 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/.18535/jmscr/v6i3.63 Diagnostic Role of FOB in Radiological
The role of T-tubes in the management of airway stenosis
 European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 43 (2013) 934 939 doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezs514 Advance Access publication 18 September 2012 ORIGINAL ARTICLE a b The role of T-tubes in the management of airway
European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 43 (2013) 934 939 doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezs514 Advance Access publication 18 September 2012 ORIGINAL ARTICLE a b The role of T-tubes in the management of airway
Owen Dickinson. Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology. Upper GI Stenting. Rotherham Foundation Trust
 Owen Dickinson Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology Upper GI Stenting Rotherham Foundation Trust Owen Dickinson Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology Rotherham Foundation Trust
Owen Dickinson Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology Upper GI Stenting Rotherham Foundation Trust Owen Dickinson Consultant in Endoscopy & Interventional Radiology Rotherham Foundation Trust
W hen tracheal stenosis results from trauma, inflammatory
 External Fixation of Subglottic Tracheal Stents* Henri G. Colt, M.D., F.C.C.P.; James Harrell, M.D., F.C.C.P.; Thomas R. Neuman, M.D.; and Thomas Robbins, M.D. Bronchoscopically placed silicone stents
External Fixation of Subglottic Tracheal Stents* Henri G. Colt, M.D., F.C.C.P.; James Harrell, M.D., F.C.C.P.; Thomas R. Neuman, M.D.; and Thomas Robbins, M.D. Bronchoscopically placed silicone stents
Are metallic stents really safe? A long-term analysis in lung transplant recipients
 Eur Respir J 2009; 34: 1417 1422 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00041909 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2009 Are metallic stents really safe? A long-term analysis in lung transplant recipients J. Gottlieb*, T. Fuehner*,
Eur Respir J 2009; 34: 1417 1422 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00041909 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2009 Are metallic stents really safe? A long-term analysis in lung transplant recipients J. Gottlieb*, T. Fuehner*,
Management Of Acquired Laryngotracheal Stenosis Our Experience.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. XII (Feb. 2016), PP 32-36 www.iosrjournals.org Management Of Acquired Laryngotracheal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. XII (Feb. 2016), PP 32-36 www.iosrjournals.org Management Of Acquired Laryngotracheal
Role of Montgomery T-tube in laryngotracheal stenosis
 International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Rakesh BS et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jan;3(1):61-65 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
International Journal of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery Rakesh BS et al. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017 Jan;3(1):61-65 http://www.ijorl.com pissn 2454-5929 eissn 2454-5937 Original
Steroid Therapy for Tracheal Stenosis in Children
 Steroid Therapy for Tracheal Stenosis in Children Clinical Experience in 4 Children with Severe Strictures H. Biemann Othersen, Jr., M.D. ABSTRACT Recently a refinement in the treatment of tracheal stenosis
Steroid Therapy for Tracheal Stenosis in Children Clinical Experience in 4 Children with Severe Strictures H. Biemann Othersen, Jr., M.D. ABSTRACT Recently a refinement in the treatment of tracheal stenosis
Coated expandable metal stents are effective irrespective of airway pathology
 Original Article Coated expandable metal stents are effective irrespective of airway pathology Cecilia Menna 1, Camilla Poggi 1, Mohsen Ibrahim 1, Antonio D Andrilli 1, Anna Maria Ciccone 1, Giulio Maurizi
Original Article Coated expandable metal stents are effective irrespective of airway pathology Cecilia Menna 1, Camilla Poggi 1, Mohsen Ibrahim 1, Antonio D Andrilli 1, Anna Maria Ciccone 1, Giulio Maurizi
ST-513-S ST-514-S 15ST-515-S
 Urmee Healthcare G-1, sho Plalav, (Jwala Estate), Opp. Flyover ridge, S. V. Road, orivali (W), Mumbai - 0 02. INDI +1 22 2 1, 4 5 Telefax : +1 22 2053 Email : deena@vsnl.com LRYNGOLOGY Hood Tracheal T-Tube
Urmee Healthcare G-1, sho Plalav, (Jwala Estate), Opp. Flyover ridge, S. V. Road, orivali (W), Mumbai - 0 02. INDI +1 22 2 1, 4 5 Telefax : +1 22 2053 Email : deena@vsnl.com LRYNGOLOGY Hood Tracheal T-Tube
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases. Punnarerk Thongcharoen
 Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children. Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital
 FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital How common is choking? About 3,000 people die/year from choking Figure remained unchanged
FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital How common is choking? About 3,000 people die/year from choking Figure remained unchanged
Tracheal stenosis is a frequent complication of tracheostomy
 Endotracheal Balloon Dilatation and Stent Implantation in Benign Stenoses Bernd Schmidt, MD, Heidi Olze, MD, Adrian C. Borges, MD, Matthias John, MD, Uta Liebers, MD, Oliver Kaschke, MD, Konrad Haake,
Endotracheal Balloon Dilatation and Stent Implantation in Benign Stenoses Bernd Schmidt, MD, Heidi Olze, MD, Adrian C. Borges, MD, Matthias John, MD, Uta Liebers, MD, Oliver Kaschke, MD, Konrad Haake,
Long-term follow-up of self-expandable metallic stents in benign tracheobronchial stenosis: a retrospective study
 Xiong et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2019) 19:33 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-019-0793-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Long-term follow-up of self-expandable metallic stents in benign tracheobronchial
Xiong et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2019) 19:33 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-019-0793-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Long-term follow-up of self-expandable metallic stents in benign tracheobronchial
Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon
 Technique for Managing Tracheo-Innominate Artery Fistula Gorav Ailawadi, MD Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon complication (0.1-1%) following both open and percutaneous tracheostomy.
Technique for Managing Tracheo-Innominate Artery Fistula Gorav Ailawadi, MD Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon complication (0.1-1%) following both open and percutaneous tracheostomy.
Central airway obstruction (CAO) refers to the obstruction of air flow in the trachea and main stem bronchi
 10-11-17 Central airway obstruction (CAO) refers to the obstruction of air flow in the trachea and main stem bronchi Syndrome of CAO: Occlusion of > 50 % lumen 1 Exact incidence and epidemiology is unknown
10-11-17 Central airway obstruction (CAO) refers to the obstruction of air flow in the trachea and main stem bronchi Syndrome of CAO: Occlusion of > 50 % lumen 1 Exact incidence and epidemiology is unknown
Surgical Management of Subglottic Stenosis
 Surgical Management of Subglottic Stenosis Cameron D. Wright, MD ubglottic stenosis is usually due to either endotracheal S tube ischemic necrosis or idiopathic larygotracheal stenosis. The ischemic area
Surgical Management of Subglottic Stenosis Cameron D. Wright, MD ubglottic stenosis is usually due to either endotracheal S tube ischemic necrosis or idiopathic larygotracheal stenosis. The ischemic area
Case Report Reoperation for complicated tracheoesophageal fistula after surgery of a tracheal lymphoma
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(6):9659-9663 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0051182 Case Report Reoperation for complicated tracheoesophageal fistula after surgery of a tracheal lymphoma Wei Dai 1, Qiang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(6):9659-9663 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0051182 Case Report Reoperation for complicated tracheoesophageal fistula after surgery of a tracheal lymphoma Wei Dai 1, Qiang
