Is thromboprophylaxis effective in reducing the pulmonary thromboembolism?
|
|
|
- Bethany Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Is thromboprophylaxis effective in reducing the pulmonary thromboembolism? Fereshteh Rajabi (1), Masoumeh Sadeghi (2), Fereshteh Karbasian (3), Ali Torkan (4) Abstract BACKGROUND: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a relatively prevalent disease which causes high costs due to the required diagnostic tests, specialized treatments, and hospital admission. In recent decades, implementation of thromboprophylaxis protocols has significantly reduced the incidence of thromboembolism in hospitals. The present study aimed to compare the incidence of venous thromboembolism before and after implementation of the mentioned protocol in hospital with identified risk factors and underlying diseases. METHODS: In this case-control group, 385 patients at the risk of DVT, some before and some after implementation of the protocol were studied. Therefore, the level of thromboprophylaxis and the incidence of venous thromboembolism were compared before and after the protocol. Data was entered into SPSS 15 and analyzed by chi-square and t tests. RESULTS: Out of 385 patients, 34 patients (8.8%) had venous thromboembolism while 351 (91.2%) were not affected. The incidence of venous thromboembolism was significantly different before and after the implementation of the protocol (17.7% vs. 5.9%; P < 0.001). The incidence of venous thromboembolism in patients not receiving thromboprophylaxis was almost 5 times higher than those who received it (20.7% vs. 5.1%). The frequency distribution of thromboembolism had a significant difference in the two above mentioned groups (P < 0.001). CONCLUSION: Thromboprophylaxis protocol reduced venous thromboembolism incidence in patients with underlying diseases which increase the risk of the complication. Keywords: Deep vein thrombosis, Thromboprophylaxis. ARYA Atherosclerosis Journal 2012, 8(1): Date of submission: 5 Dec 2011, Date of acceptance: 12 Mar 2012 Introduction Venous thromboembolism is one of the most common causes of emergency hospitalization. It is also a life-threatening complication in high risk patients admitted in internal and cardiac wards and patients undergoing surgery. 1 In most cases, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) either has no symptoms and or has nonspecific symptoms. Therefore, appropriate and timely usage of prophylactic anticoagulation is necessary to reduce the incidence of DVT and its related complications. 2 Pulmonary embolism is the third leading cause of cardiovascular diseases after acute coronary syndromes and brain stroke. It is also the first cause of mortality in admitted patients older than 65 years of age. 3 Different figures in previous research indicate that the actual incidence of pulmonary embolism is 10 times greater than those determined based on clinical symptoms, autopsy studies, and diagnostic tests. 3 Diagnostic tests for patients with suspected venous thromboembolism are highly expensive. On the other hand, in cases confirmed through diagnostic tests, anticoagulation, which is potentially associated with risk of serious bleedings, would be required. 4 Some studies have reported recurrent venous thromboses and their associated embolism to be caused by familial fibrinogen or plasminogen deficiency or reduced tissue plasminogen activator production. 5 Examining another group of patients showed that fibrinolytic activity is low in materials extracted from venous samples. 5 DVT is a relatively prevalent disease which causes high costs due to the required diagnostic tests, specialized treatments, and admission in hospital. 6 In recent decades, implementation of thromboprophylaxis protocols has significantly reduced the incidence of thromboembolism in related hospitals. Therefore, the present study aimed to compare the incidence of venous thromboembolism before and after implementation of a thromboprophylaxis protocol in patients with identified risk factors and underlying diseases. 1- Assistant Researcher, Cardiovascular Research Center, Isfahan Cardiovascular Research Institute, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. 2- Associate Professor, Cardiac Rehabilitation Research Center, Isfahan Cardiovascular Research Institute, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. 3- General Practitioner, Cardiovascular Department, Najafabad Branch, Islamic Azad University, Isfahan, Iran. 4- Assistant Professor, Department of Cardiovascular, Najafabad Branch, Islamic Azad University, Isfahan, Iran. Correspondence To: Masoumeh Sadeghi, sadeghimasoumeh@gmail.com 16 ARYA Atherosclerosis Journal 2012 (Spring); Volume 8, Issue 1
2 F. Rajabi, M. Sadeghi, F. Karbasian, A. Torkan Materials and Methods This case-control study included 125 patients at risk of vein thrombosis and pulmonary thromboembolism admitted to Shariati Hospital (Isfahan, Iran) during Convenient sampling method was used during which some patients with full and available records were evaluated. The inclusion criteria were a diagnosis of venous thromboembolism following congestive heart failure, severe respiratory disease, or limited physical activity, active cancer, acute neurologic illness, and previous venous thromboembolism, as well as having underlying risk factors of this complication such as obesity and old age. Patients classified as low-risk according to Wells criteria 7 were excluded. After obtaining informed consents from all subjects, patients who were admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of venous thromboembolism, had venous thromboembolism risk factors, and had received thromboprophylaxis according to the standard protocol were selected as the case group. The control group consisted of patients who had the abovementioned criteria but had not received thromboprophylaxis. The required data was collected and recorded in related forms. After editing and correcting, the collected data was analyzed in SPSS 17 using chi-square and student-t statistical tests. Results In this study, 385 patients, including 228 (59.2%) males and 157 (40.8%) females, at risk of DVT were studied. The mean age of patients was 48.3 ± 19.2 years and 23 subjects (6%) were under 20 years of age. The age group of years and over 70 years possessed the highest frequency distribution. The prevalence of DVT and pulmonary thromboembolism risk factors are presented in table 1. According to this table, old age and immobility had the highest frequencies (59.2% and 26.5%, respectively) among the studied patients. As indicated in table 2, predisposition to pulmonary thromboembolism and DVT in older ages was more in individuals with sedentary jobs. In fact, while the risk of thromboembolism was 8.3% among patients with more active jobs, it was 15% and 14.2% in patients with sedentary and semi-sedentary jobs, respectively. The correlation between the type of job and predisposition to pulmonary thromboembolism and DVT was significant (P = 0.009). The obtained results showed that 293 patients (76.1%) received thromboprophylaxis while 92 (23.9%) did not. On the other hand, before implementation of thromboprophylaxis protocol, thromboembolism was detected in 60.4% of the highrisk patients while 81.3% of the cases were prevented after the protocol. Therefore, prescription of thromboprophylaxis had a fully significant difference before and after the implementation of the standard thromboprophylaxis protocol (P < 0.001). Table 1. Frequency distribution of the risk factors for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary thromboembolism in the studied patients Risk factors Frequency Old age 228 (59.2%) Previous history of DVT and pulmonary thromboembolism 48 (12.5%) Family history 5 (1.3%) Blood problems 12 (3.1%) Immobility 102 (26.5%) Smoking 99 (25.7%) Surgery 46 (11.9%) Obesity 7 (1.8%) Pregnancy 8 (2.1%) Delivery 9 (2.3%) Cancer 20 (5.2%) Medications 38 (9.9) Hormone replacement therapy 3 (0.8) Table 2. Frequency distribution of level of mobility and risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary thromboembolism (P = 0.009) High mobility Sedentary Moderate mobility Total Low risk 24 (15.3%) 3 (3.8%) 9 (6.1%) 36 (9.4%) Moderate risk 120 (76.4%) 65 (81.3%) 118 (79.7%) 303 (78.7%) High risk 13 (8.3%) 12 (15%) 21 (14.2%) 46 (11.9%) Total 157 (100%) 80 (100%) 148 (100%) 385 (100%) ARYA Atherosclerosis Journal 2012 (Spring); Volume 8, Issue 1 17
3 Thromboembolism prophylaxis Before the implementation of thromboprophylaxis protocol, 96 patients were examined among whom 1 had a low risk, 73 had medium risk and 22 had high risk. Thromboprophylaxis had been prescribed for 40 patients (54.8%) with medium risk and 18 patients (81.8%) with high risk before the implementation of the protocol. Among the 289 patients who were examined after the implementation of the protocol, 35 had low risk, 230 had medium risk, and 24 had high risk. After the implementation of the protocol, thromboprophylaxis was prescribed for 11 patients with low risk, 200 patients with medium risk, and 24 patients with high risk. Figure 1 illustrates the frequency of thromboprophylaxis prescription before and after the implementation of the protocol according to Wells criteria. The results showed that out of the 385 studied patients, 34 patients (8.8%) suffered from venous thromboembolism and 351 patients (91.2%) did not. The prevalence of venous thromboembolism before and after the implementation of the protocol was 17.7% and 5.9%, respectively. The incidence of this complication had a significant difference before and after the implementation of the protocol (P < 0.001) (Table 3). Thromboembolism occurred in 5.1% of patients who received prophylaxis and 20.7% of those who did not. The results showed that 2 low risk patients (5.6%), 27 medium risk patients (8.9%), and 5 high risk patients (10.9%) suffered from venous thromboembolism (Table 4). high risk 11.9% low risk 9.4% moderate risk 78.7% Figure 1. Frequency percentage of patients classified according to Wells criteria Table 3. Frequency distribution of thromboprophylaxis and thromboembolism before and after the implementation of the protocol (P < 0.001) Thromboprophylaxis Before protocol After protocol Total Prescribed 58 (60.4%) 235 (81.3%) 293 (76.1%) Not prescribed 38 (39.6%) 54 (18.7%) 92 (23.9%) Total 96 (100%) 289 (100%) 385 (100%) Thromboembolism No 79 (82.3%) 272 (94.1%) 351 (91.2%) Yes 17 (17.7%) 17 (5.9%) 34 (8.8%) Total 96 (100%) 289 (100%) 385 (100%) Table 4. Frequency distribution of the incidence of venous thromboembolism according to thromboprophylaxis (P < 0.001) Thromboprophylaxis Yes No Total Thromboembolism Yes 278 (94.9%) 73 (79.3%) 351 (91.2%) No 15 (5.1%) 19 (20.7%) 34 (8.8%) Total 293 (100%) 92 (100%) 385 (100%) 18 ARYA Atherosclerosis Journal 2012 (Spring); Volume 8, Issue 1
4 F. Rajabi, M. Sadeghi, F. Karbasian, A. Torkan Discussion The results of this study showed that implementation of thromboprophylaxis protocols can reduce the incidence of venous thromboembolism. The mean age of patients was almost 48 years which was within the age range of people prone to venous thromboembolism (over 40 years of age). 8 In addition, consistent with previous studies which have shown DVT to be more common among men, 9,10 approximately 60% of our patients were male. On the other hand, although previous studied have reported DVT to be more prevalent among more sedentary jobs, 9 the present study resulted in different findings. The job combination of our studied patients might have been affected by the type of patients who usually refer to Alzahra Hospital who are mostly of working and middle-class people. Other variables could have also affected job combination in our population. Old age is one of the risk factors in patients with DVT. 10 Some studies have indicated that if the pathophysiology of thromboembolism was fully understood, higher age could have also been an important factor in pulmonary thromboembolism. 11 In addition to age, immobility and smoking were the most prevalent factors and were observed in 25% of patients. Venous thromboembolism is of high importance among hospitalized patients, surgery candidates, individuals with a sedentary lifestyle, and patients who use several anticoagulant drugs. Considering necessary cautions and preventive protocols would thus lower the incidence of the disease and its complications. 12 Many studies have suggested the effects of a previous history of thromboembolism as one of the risk factors. It is thus one of the complications which is given high attention almost in all medical centers. 13,14 In this study, almost half of the patients had more than one of the risk factors of venous thromboembolism. Therefore, determining the independent role of each factor is problematic and requires further comparative studies. However, the results indicated that there are many factors involved in the incidence of thromboembolism in Iranian society and there is usually more than one factor involved in this complication. We also examined the incidence of venous thromboembolism before and after implementation of thromboprophylaxis. Out of 96 studied patients, 1 patient had low risk, 73 had medium risk, and 22 patients had high risk before the implementation of thromboprophylaxis. Out of 289 patients who were studied after the implementation of thromboprophylaxis, 35 patients had low risk, 230 had medium risk, and 24 had high risk. After implementation of the protocol, thromboprophylaxis had been prescribed for 11 patients with low risk, 200 patients with medium risk and 24 patients with high risk which indicates large attempt to reduce the incidence of venous thromboembolism after implementation of the protocol. Conclusion Our results showed that implementation of thromboprophylaxis protocol affected reduced venous thromboembolism. Therefore, conducting an analytical study is recommended to compare the incidence of venous thromboembolism and determine the effects of thrombolytic medications on the incidence of venous thromboembolism. The effects of common heparin thromboprophylaxis and low molecular weight heparin in the incidence of venous thromboembolism should be evaluated in hospitals throughout the province of Isfahan. Conflict of Interests Authors have no conflict of interests. References 1. Carter CJ. The natural history and epidemiology of venous thrombosis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 1994; 36(6): Parker C, Coupland C, Hippisley-Cox J. Antipsychotic drugs and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control study. BMJ 2010; 341: c Cushman M, Tsai AW, White RH, Heckbert SR, Rosamond WD, Enright P, et al. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in two cohorts: the longitudinal investigation of thromboembolism etiology. Am J Med 2004; 117(1): Goldman L, Ausiello DA. Cecil textbook of medicine. 22 nd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; p Lechner D, Wiener C, Weltermann A, Eischer L, Eichinger S, Kyrle PA. Comparison between idiopathic deep vein thrombosis of the upper and lower extremity regarding risk factors and recurrence. J Thromb Haemost 2008; 6(8): Kasper DL. Principles of internal medicine. 16 th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; p Wells PS, Anderson DR, Bormanis J, Guy F, Mitchell M, Gray L, et al. Value of assessment of pretest probability of deep-vein thrombosis in clinical management. Lancet 1997; 350(9094): Goodacre S, Sutton AJ, Sampson FC. Meta-analysis: The value of clinical assessment in the diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis. Ann Intern Med 2005; 143(2): Tamariz LJ, Eng J, Segal JB, Krishnan JA, Bolger DT, Streiff MB, et al. Usefulness of clinical ARYA Atherosclerosis Journal 2012 (Spring); Volume 8, Issue 1 19
5 Thromboembolism prophylaxis prediction rules for the diagnosis of venous thromboembolism: a systematic review. Am J Med 2004; 117(9): Mohajer H, Khosravi A, Saadat Nia M, Abdar M, Azarm T. Genetic thromboembolic risk factors associated with deep vein thrombosis in Iranian population. Journal of Isfahan Medical School 2011; 28(114): Lee AY, Levine MN. Venous thromboembolism and cancer: risks and outcomes. Circulation 2003; 107(23 Suppl 1): I17-I Craig F. Pulmonary Embolism. emedicine [Online]; Available from: URL: Birdwell BG, Raskob GE, Whitsett TL, Durica SS, Comp PC, George JN, et al. The clinical validity of normal compression ultrasonography in outpatients suspected of having deep venous thrombosis. Ann Intern Med 1998; 128(1): Heit JA. The epidemiology of venous thromboembolism in the community: implications for prevention and management. J Thromb Thrombolysis 2006; 21(1): Blann AD, Lip GY. Venous thromboembolism. BMJ 2006; 332(7535): How to cite this article: Rajabi F, Sadeghi M, Karbasian F, Torkan A. Is thromboprophylaxis effective in reducing the pulmonary thromboembolism?. ARYA Atherosclerosis Journal 2012; 8(1): ARYA Atherosclerosis Journal 2012 (Spring); Volume 8, Issue 1
Deep Vein Thrombosis: Can a Second Sonographic Examination Be Avoided?
 Alfonsa Friera 1 Nuria R. Giménez 2 Paloma Caballero 1 Pilar S. Moliní 2 Carmen Suárez 2 Received August 15, 2001; accepted after revision October 16, 2001. 1 Radiology Department, Hospital de la Princesa,
Alfonsa Friera 1 Nuria R. Giménez 2 Paloma Caballero 1 Pilar S. Moliní 2 Carmen Suárez 2 Received August 15, 2001; accepted after revision October 16, 2001. 1 Radiology Department, Hospital de la Princesa,
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21764 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mos, Inge Christina Maria Title: A more granular view on pulmonary embolism Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/21764 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Mos, Inge Christina Maria Title: A more granular view on pulmonary embolism Issue
ACR Appropriateness Criteria Suspected Lower Extremity Deep Vein Thrombosis EVIDENCE TABLE
 . Fowkes FJ, Price JF, Fowkes FG. Incidence of diagnosed deep vein thrombosis in the general population: systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 003; 5():-5.. Hamper UM, DeJong MR, Scoutt LM. Ultrasound
. Fowkes FJ, Price JF, Fowkes FG. Incidence of diagnosed deep vein thrombosis in the general population: systematic review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 003; 5():-5.. Hamper UM, DeJong MR, Scoutt LM. Ultrasound
CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevalence Patho-physiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Management of DVT/PE Prevention VTE Patho-physiology
CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevalence Patho-physiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Management of DVT/PE Prevention VTE Patho-physiology
NICE Guidance: Venous thromboembolism (deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) in patients admitted to hospital 1
 The College of Emergency Medicine Patron: HRH The Princess Royal Churchill House Tel +44 (0)207 404 1999 35 Red Lion Square Fax +44 (0)207 067 1267 London WC1R 4SG www.collemergencymed.ac.uk CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS
The College of Emergency Medicine Patron: HRH The Princess Royal Churchill House Tel +44 (0)207 404 1999 35 Red Lion Square Fax +44 (0)207 067 1267 London WC1R 4SG www.collemergencymed.ac.uk CLINICAL EFFECTIVENESS
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT?
 How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
BACKGROUND METHODS RESULTS CONCLUSIONS
 CHAPTER 5 The combination of a normal D-dimer concentration and a non-high pretest clinical probability score is a safe strategy to exclude deep venous thrombosis R.E.G. Schutgens 1, P. Ackermark 2, F.J.L.M.
CHAPTER 5 The combination of a normal D-dimer concentration and a non-high pretest clinical probability score is a safe strategy to exclude deep venous thrombosis R.E.G. Schutgens 1, P. Ackermark 2, F.J.L.M.
Combined oral contraceptives and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case control studies using the QResearch and the CPRD databases
 Combined oral contraceptives and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case control studies using the QResearch and the CPRD databases Yana Vinogradova, Carol Coupland, Julia Hippisley-Cox Web appendix:
Combined oral contraceptives and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case control studies using the QResearch and the CPRD databases Yana Vinogradova, Carol Coupland, Julia Hippisley-Cox Web appendix:
What You Should Know
 1 New 2018 ASH Clinical Practice Guidelines on Venous Thromboembolism: What You Should Know New 2018 ASH Clinical Practice Guidelines on Venous Thromboembolism: What You Should Know The American Society
1 New 2018 ASH Clinical Practice Guidelines on Venous Thromboembolism: What You Should Know New 2018 ASH Clinical Practice Guidelines on Venous Thromboembolism: What You Should Know The American Society
DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE)
 DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE) Introduction VTE (DVT/PE) is an important complication in hospitalized patients Hospitalization for acute medical illness
DVT PROPHYLAXIS IN HOSPITALIZED MEDICAL PATIENTS SAURABH MAJI SR (PULMONARY,MEDICINE) Introduction VTE (DVT/PE) is an important complication in hospitalized patients Hospitalization for acute medical illness
Duration of Therapy for Venous Thromboembolism
 Duration of Therapy for Venous Thromboembolism Michael B Streiff, MD FACP Associate Professor of Medicine and Pathology Medical Director, Johns Hopkins Anticoagulation Service Chairman, VTE Guideline Committee
Duration of Therapy for Venous Thromboembolism Michael B Streiff, MD FACP Associate Professor of Medicine and Pathology Medical Director, Johns Hopkins Anticoagulation Service Chairman, VTE Guideline Committee
Patients with suspected DVT of the lower limb how to exam the patient
 Patients with suspected DVT of the lower limb how to exam the patient Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2015, Oslo Content Anatomy and pathophysiology
Patients with suspected DVT of the lower limb how to exam the patient Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2015, Oslo Content Anatomy and pathophysiology
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM. Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow
 CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
SCORES FOR 4 TH QUARTER, RD QUARTER, 2014
 SCORES FOR 4 TH QUARTER, 2013 3 RD QUARTER, 2014 PATIENT SATISFACTION SCORES (HCAHPS): 4 STARS OUT OF 5 (ONLY 4 AREA ACUTE CARE HOSPITALS RECEIVED A 4-STAR RATING. NONE ACHIEVED 5-STARS). STRUCTURAL MEASURES:
SCORES FOR 4 TH QUARTER, 2013 3 RD QUARTER, 2014 PATIENT SATISFACTION SCORES (HCAHPS): 4 STARS OUT OF 5 (ONLY 4 AREA ACUTE CARE HOSPITALS RECEIVED A 4-STAR RATING. NONE ACHIEVED 5-STARS). STRUCTURAL MEASURES:
EXTENDING VTE PROPHYLAXIS IN ACUTELY ILL MEDICAL PATIENTS
 EXTENDING VTE PROPHYLAXIS IN ACUTELY ILL MEDICAL PATIENTS Samuel Z. Goldhaber, MD Director, VTE Research Group Cardiovascular Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical
EXTENDING VTE PROPHYLAXIS IN ACUTELY ILL MEDICAL PATIENTS Samuel Z. Goldhaber, MD Director, VTE Research Group Cardiovascular Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical
Venous Thromboembolism. Prevention
 Venous Thromboembolism Prevention August 2010 Venous Thromboembloism Prevention 1 1 Expected Practice Assess all patients upon admission to the ICU for risk factors of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and
Venous Thromboembolism Prevention August 2010 Venous Thromboembloism Prevention 1 1 Expected Practice Assess all patients upon admission to the ICU for risk factors of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and
Results from RE-COVER RE-COVER II RE-MEDY RE-SONATE EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
 Assessment of the safety and efficacy of dabigatran etexilate (Pradaxa ) in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) and the prevention of recurrent DVT and PE Results from
Assessment of the safety and efficacy of dabigatran etexilate (Pradaxa ) in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) and the prevention of recurrent DVT and PE Results from
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Approved by: Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Vice President and Chief Medical Officer; and Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: Date Approved January
Approved by: Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Vice President and Chief Medical Officer; and Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: Date Approved January
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK?
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK? Ayman El-Menyar (1), MD, Hassan Al-Thani (2),MD (1)Clinical Research Consultant, (2) Head of Vascular Surgery, Hamad General Hospital
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK? Ayman El-Menyar (1), MD, Hassan Al-Thani (2),MD (1)Clinical Research Consultant, (2) Head of Vascular Surgery, Hamad General Hospital
Bath, Philip M.W. and England, Timothy J. (2009) Thighlength compression stockings and DVT after stroke. Lancet. ISSN (In Press)
 Bath, Philip M.W. and England, Timothy J. (2009) Thighlength compression stockings and DVT after stroke. Lancet. ISSN 0140-6736 (In Press) Access from the University of Nottingham repository: http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/1087/1/lancet_clots_1_20090522_4.pdf
Bath, Philip M.W. and England, Timothy J. (2009) Thighlength compression stockings and DVT after stroke. Lancet. ISSN 0140-6736 (In Press) Access from the University of Nottingham repository: http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/1087/1/lancet_clots_1_20090522_4.pdf
Understanding thrombosis in venous thromboembolism. João Morais Head of Cardiology Division and Research Centre Leiria Hospital Centre Portugal
 Understanding thrombosis in venous thromboembolism João Morais Head of Cardiology Division and Research Centre Leiria Hospital Centre Portugal Disclosures João Morais On the last year JM received honoraria
Understanding thrombosis in venous thromboembolism João Morais Head of Cardiology Division and Research Centre Leiria Hospital Centre Portugal Disclosures João Morais On the last year JM received honoraria
Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge
 Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge What is a venous thromboembolism (VTE)? This is a medical term that describes a blood clot that develops in a deep vein
Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge What is a venous thromboembolism (VTE)? This is a medical term that describes a blood clot that develops in a deep vein
Menopausal Hormone Therapy & Haemostasis
 Menopausal Hormone Therapy & Haemostasis The Haematologist Perspective Dr. Batia Roth-Yelinek Coagulation unit Hadassah MC Menopausal Hormone Therapy & Hemostasis Hemostatic mechanism Mechanism of estrogen
Menopausal Hormone Therapy & Haemostasis The Haematologist Perspective Dr. Batia Roth-Yelinek Coagulation unit Hadassah MC Menopausal Hormone Therapy & Hemostasis Hemostatic mechanism Mechanism of estrogen
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center
 Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Comparison of Venothromboembolism Prophylaxis Practices in a Winnipeg Tertiary Care Hospital to Chest Guidelines: A Quality Improvement Project
 Comparison of Venothromboembolism Prophylaxis Practices in a Winnipeg Tertiary Care Hospital to Chest Guidelines: A Quality Improvement Project Dr. Jonathan Laxton, FRCPC, R5 GIM University of Manitoba
Comparison of Venothromboembolism Prophylaxis Practices in a Winnipeg Tertiary Care Hospital to Chest Guidelines: A Quality Improvement Project Dr. Jonathan Laxton, FRCPC, R5 GIM University of Manitoba
Incidence of Diagnosed Deep Vein Thrombosis in the General Population: Systematic Review
 Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 25, 1±5 (2003) doi:10.1053/ejvs.2002.1778, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com on REVIEW Incidence of Diagnosed Deep Vein Thrombosis in the General Population: Systematic
Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 25, 1±5 (2003) doi:10.1053/ejvs.2002.1778, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com on REVIEW Incidence of Diagnosed Deep Vein Thrombosis in the General Population: Systematic
Dr Fahad Al-Hameed MD, FCCP, FRCPC Consultant Intensivist & Pulmonologist Professor Asst. of Medicine/Critical Care KSAU-HS Deputy chairman,
 Dr Fahad Al-Hameed MD, FCCP, FRCPC Consultant Intensivist & Pulmonologist Professor Asst. of Medicine/Critical Care KSAU-HS Deputy chairman, Intensive Care Department, Director, Ambulatory Care Center
Dr Fahad Al-Hameed MD, FCCP, FRCPC Consultant Intensivist & Pulmonologist Professor Asst. of Medicine/Critical Care KSAU-HS Deputy chairman, Intensive Care Department, Director, Ambulatory Care Center
Early Ambulation Reduces the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism After Total Knee Replacement. Marilyn Szekendi, PhD, RN
 Early Ambulation Reduces the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism After Total Knee Replacement Marilyn Szekendi, PhD, RN ANA 7 th Annual Nursing Quality Conference, February 2013 Research Team Banafsheh Sadeghi,
Early Ambulation Reduces the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism After Total Knee Replacement Marilyn Szekendi, PhD, RN ANA 7 th Annual Nursing Quality Conference, February 2013 Research Team Banafsheh Sadeghi,
Medical Patients: A Population at Risk
 Case Vignette A 68-year-old woman with obesity was admitted to the Medical Service with COPD and pneumonia and was treated with oral corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and antibiotics. She responded well
Case Vignette A 68-year-old woman with obesity was admitted to the Medical Service with COPD and pneumonia and was treated with oral corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and antibiotics. She responded well
Effectiveness and Safety of Direct Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin Among Patients with Sickle Cell Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study
 Effectiveness and Safety of Direct Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin Among Patients with Sickle Cell Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study Megan Roberts, PharmD, BCPS MUSC Medical Center and South Carolina
Effectiveness and Safety of Direct Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin Among Patients with Sickle Cell Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study Megan Roberts, PharmD, BCPS MUSC Medical Center and South Carolina
General. Recommendations. Guideline Title. Bibliographic Source(s) Guideline Status. Major Recommendations
 General Guideline Title Prevention of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Bibliographic Source(s) American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). Prevention of deep vein thrombosis
General Guideline Title Prevention of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Bibliographic Source(s) American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). Prevention of deep vein thrombosis
Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism after Total Hip/Knee Replacement: A Population-based Taiwan Study
 IMPROVING PATIENT SAFETY Preventing & Managing Venous Thromboembolism Session 8 Data Driving Strategies for VTE Prevention and Management 3/30/2012; 15.35-15.55 Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism after
IMPROVING PATIENT SAFETY Preventing & Managing Venous Thromboembolism Session 8 Data Driving Strategies for VTE Prevention and Management 3/30/2012; 15.35-15.55 Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism after
Cost-effectiveness of screening for deep vein thrombosis by ultrasound at admission to stroke rehabilitation Wilson R D, Murray P K
 Cost-effectiveness of screening for deep vein thrombosis by ultrasound at admission to stroke rehabilitation Wilson R D, Murray P K Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that
Cost-effectiveness of screening for deep vein thrombosis by ultrasound at admission to stroke rehabilitation Wilson R D, Murray P K Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
Chapter 1 Introduction Introduction 9 Even though the first reports on venous thromboembolism date back to the 13 th century and the mechanism of acute pulmonary embolism (PE) was unraveled almost 150
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
Prevalence of pulmonary embolism at autopsy among elderly patients in a Chinese general hospital
 Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2016) 13: 894 898 2016 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Research Article Open Access Prevalence of pulmonary embolism at autopsy among elderly patients in a Chinese
Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2016) 13: 894 898 2016 JGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Research Article Open Access Prevalence of pulmonary embolism at autopsy among elderly patients in a Chinese
Chapter 3. Simplification of the revised Geneva score for assessing clinical probability of pulmonary embolism
 Chapter 3 Simplification of the revised Geneva score for assessing clinical probability of pulmonary embolism F.A. Klok, I.C.M. Mos, M. Nijkeuter, M. Righini, A. Perrier, G. Le Gal and M.V. Huisman Arch
Chapter 3 Simplification of the revised Geneva score for assessing clinical probability of pulmonary embolism F.A. Klok, I.C.M. Mos, M. Nijkeuter, M. Righini, A. Perrier, G. Le Gal and M.V. Huisman Arch
AN AUDIT: THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PATIENTS AT NORTHWICK PARK AND CENTRAL MIDDLESEX HOSPITALS
 The West London Medical Journal 2010 Vol 2 No 4 pp 19-24 AN AUDIT: THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PATIENTS AT NORTHWICK PARK AND CENTRAL MIDDLESEX HOSPITALS Soneji ND Agni NR Acharya MN Anjari
The West London Medical Journal 2010 Vol 2 No 4 pp 19-24 AN AUDIT: THROMBOPROPHYLAXIS FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT PATIENTS AT NORTHWICK PARK AND CENTRAL MIDDLESEX HOSPITALS Soneji ND Agni NR Acharya MN Anjari
How to prevent blood clots whilst in hospital and after your return home
 How to prevent blood clots whilst in hospital and after your return home Patient information WHAT What IS is DEEP deep VEIN vein THROMBOSIS? thrombosis? Deep Vein Thrombosis DVT is a blood clot within
How to prevent blood clots whilst in hospital and after your return home Patient information WHAT What IS is DEEP deep VEIN vein THROMBOSIS? thrombosis? Deep Vein Thrombosis DVT is a blood clot within
Implementation and outcomes of point-ofcare testing in the emergency department of a large urban academic medical center
 Implementation and outcomes of point-ofcare testing in the emergency department of a large urban academic medical center Kent Lewandrowski, MD Associate Chief Of Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital
Implementation and outcomes of point-ofcare testing in the emergency department of a large urban academic medical center Kent Lewandrowski, MD Associate Chief Of Pathology, Massachusetts General Hospital
Anticoagulation for prevention of venous thromboembolism
 Anticoagulation for prevention of venous thromboembolism Original article by: Michael Tam Note: updated in June 2009 with the eighth edition (from the seventh) evidence-based clinical practice guidelines
Anticoagulation for prevention of venous thromboembolism Original article by: Michael Tam Note: updated in June 2009 with the eighth edition (from the seventh) evidence-based clinical practice guidelines
PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL Since French internist Armand Trousseau reported the occurrence of mysterious thrombotic disorders in cancer patients in the mid-19th century, the link
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS PROGNOSIS AND SURVIVAL Since French internist Armand Trousseau reported the occurrence of mysterious thrombotic disorders in cancer patients in the mid-19th century, the link
VTE in Children: Practical Issues
 VTE in Children: Practical Issues Wasil Jastaniah MBBS,FAAP,FRCPC Consultant Pediatric Hem/Onc/BMT May 2012 Top 10 Reasons Why Pediatric VTE is Different 1. Social, ethical, and legal implications. 2.
VTE in Children: Practical Issues Wasil Jastaniah MBBS,FAAP,FRCPC Consultant Pediatric Hem/Onc/BMT May 2012 Top 10 Reasons Why Pediatric VTE is Different 1. Social, ethical, and legal implications. 2.
Disclosures. DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Questions To Ask. Dr. Susanna Shin - DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) None
 Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Objectives. Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis. Case VTE WHY DO IT? Question: Who Is At Risk?
 Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis Rishi Garg, MD Department of Medicine Identify patients at risk for VTE Options for VTE prophylaxis Current Recommendations (based on The Seventh ACCP
Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis Rishi Garg, MD Department of Medicine Identify patients at risk for VTE Options for VTE prophylaxis Current Recommendations (based on The Seventh ACCP
Thrombolysis in PE. Outline. Disclosure. Overview on Pulmonary Embolism. Hot Topics in Emergency Medicine 2012 Midyear Clinical Meeting
 Disclosure Thrombolysis in PE Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP reports no relevant financial relationships. Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP Outline 55 YOF presents to ED with SOB PMH of DVT + noncompliance
Disclosure Thrombolysis in PE Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP reports no relevant financial relationships. Daniel P. Hays, PharmD, BCPS, FASHP Outline 55 YOF presents to ED with SOB PMH of DVT + noncompliance
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin
 Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.019 10/15/2007 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 10/28/2011 Section: Prescription Drugs Place(s) of Service:
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.019 10/15/2007 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO 10/28/2011 Section: Prescription Drugs Place(s) of Service:
GLIOMA - VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM. Miguel Navarro. Hospital Universitario de Salamanca-IBSAL
 GLIOMA - VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Miguel Navarro. Hospital Universitario de Salamanca-IBSAL GLIOMA - VTE GLIOMA - VTE The two string problem Substantial risk for developing VTE Concern antithrombotic agents
GLIOMA - VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Miguel Navarro. Hospital Universitario de Salamanca-IBSAL GLIOMA - VTE GLIOMA - VTE The two string problem Substantial risk for developing VTE Concern antithrombotic agents
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/40114 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Exter, Paul L. den Title: Diagnosis, management and prognosis of symptomatic and
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/40114 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Exter, Paul L. den Title: Diagnosis, management and prognosis of symptomatic and
Title: Low Molecular Weight Heparins (LMWH), fondaparinux (Arixtra)
 Origination: 03/29/05 Revised: 09/01/10 Annual Review: 11/20/13 Purpose: To provide guidelines and criteria for the review and decision determination of requests for medications that requires prior authorization.
Origination: 03/29/05 Revised: 09/01/10 Annual Review: 11/20/13 Purpose: To provide guidelines and criteria for the review and decision determination of requests for medications that requires prior authorization.
VTE Management in Surgical Patients: Optimizing Prophylaxis Strategies
 VTE Management in Surgical Patients: Optimizing Prophylaxis Strategies VTE in Surgical Patients: Recognizing the Patients at Risk Pathogenesis of thrombosis: Virchow s triad and VTE Risk Hypercoagulability
VTE Management in Surgical Patients: Optimizing Prophylaxis Strategies VTE in Surgical Patients: Recognizing the Patients at Risk Pathogenesis of thrombosis: Virchow s triad and VTE Risk Hypercoagulability
Venous Thromboembolism National Hospital Inpatient Quality Measures
 Venous Thromboembolism National Hospital Inpatient Quality Measures Presentation Overview Review venous thromboembolism as a new mandatory measure set Outline measures with exclusions and documentation
Venous Thromboembolism National Hospital Inpatient Quality Measures Presentation Overview Review venous thromboembolism as a new mandatory measure set Outline measures with exclusions and documentation
Annals of RSCB Vol. XVII, Issue 1/2012
 CORRELATIONS BETWEEN ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION AND GLYCEMIA IN VENOUS THROMBOSIS PATHOGENESIS Codruţa Bădescu 1, Oana Bădulescu 2, Manuela Ciocoiu 2, Magda Bădescu 2, M. Costuleanu 2 1 DEPARTMENT OF INTERNAL
CORRELATIONS BETWEEN ENDOTHELIAL DYSFUNCTION AND GLYCEMIA IN VENOUS THROMBOSIS PATHOGENESIS Codruţa Bădescu 1, Oana Bădulescu 2, Manuela Ciocoiu 2, Magda Bădescu 2, M. Costuleanu 2 1 DEPARTMENT OF INTERNAL
Deep vein thrombosis and its prevention in critically ill adults Attia J, Ray J G, Cook D J, Douketis J, Ginsberg J S, Geerts W H
 Deep vein thrombosis and its prevention in critically ill adults Attia J, Ray J G, Cook D J, Douketis J, Ginsberg J S, Geerts W H Authors' objectives To systematically review the incidence of deep vein
Deep vein thrombosis and its prevention in critically ill adults Attia J, Ray J G, Cook D J, Douketis J, Ginsberg J S, Geerts W H Authors' objectives To systematically review the incidence of deep vein
The management of venous thromboembolism has improved. Article
 Comparison of 10-mg and 5-mg Warfarin Initiation Nomograms Together with Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin for Outpatient Treatment of Acute Venous Thromboembolism A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial
Comparison of 10-mg and 5-mg Warfarin Initiation Nomograms Together with Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin for Outpatient Treatment of Acute Venous Thromboembolism A Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial
Venous Thrombosis in Asia
 Venous Thrombosis in Asia Pantep Angchaisuksiri, M.D. Professor of Medicine, Mahidol University, Thailand Adjunct Associate Professor, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, USA Venous Thromboembolism
Venous Thrombosis in Asia Pantep Angchaisuksiri, M.D. Professor of Medicine, Mahidol University, Thailand Adjunct Associate Professor, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, USA Venous Thromboembolism
IRB protocol Yair Lev, MD 11/25/08
 IRB protocol Yair Lev, MD 11/25/08 Abdominal and Pelvic CT as a screening modality for occult malignant disease in unprovoked Venous Thromboembolism: A randomized, controlled prospective study. A. Study
IRB protocol Yair Lev, MD 11/25/08 Abdominal and Pelvic CT as a screening modality for occult malignant disease in unprovoked Venous Thromboembolism: A randomized, controlled prospective study. A. Study
1. SCOPE of GUIDELINE:
 Page 1 of 35 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention Guideline: Thromboprophylaxis AUTHORIZATION: VP, Medicine Date Approved: May 17, 2012 Date Revised: Vancouver Coastal Health
Page 1 of 35 CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINE: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention Guideline: Thromboprophylaxis AUTHORIZATION: VP, Medicine Date Approved: May 17, 2012 Date Revised: Vancouver Coastal Health
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION. predictive value for compression ultrasonography. for Deep Vein Thrombosis in Symptomatic Outpatients
 ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Predictive Value of Compression Ultrasonography for Deep Vein Thrombosis in Symptomatic Outpatients Clinical Implications of the Site of Vein Noncompressibility Brian G. Birdwell,
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Predictive Value of Compression Ultrasonography for Deep Vein Thrombosis in Symptomatic Outpatients Clinical Implications of the Site of Vein Noncompressibility Brian G. Birdwell,
External validity of placebo-controlled trials of thromboprophylaxis for medical patients cited in clinical practice guidelines
 External validity of placebo-controlled trials of thromboprophylaxis for medical patients cited in clinical practice guidelines S. Morin-Ben Abdallah MD, A. Dutilleul MD, V. Nadon MD, X. Marchand-Sénécal
External validity of placebo-controlled trials of thromboprophylaxis for medical patients cited in clinical practice guidelines S. Morin-Ben Abdallah MD, A. Dutilleul MD, V. Nadon MD, X. Marchand-Sénécal
Clinical relevance of distal deep vein thrombosis Marc Righini and Henri Bounameaux
 Clinical relevance of distal deep vein thrombosis Marc Righini and Henri Bounameaux Division of Angiology and Hemostasis, Geneva University Hospital, Geneva, Switzerland Correspondence to Marc Righini,
Clinical relevance of distal deep vein thrombosis Marc Righini and Henri Bounameaux Division of Angiology and Hemostasis, Geneva University Hospital, Geneva, Switzerland Correspondence to Marc Righini,
*Corresponding Author:
 Audit of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis administered to general surgical patients undergoing elective and emergency operations at National Hospital, Sri Lanka *Migara Seneviratne 1, Asanka Hemachandra
Audit of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis administered to general surgical patients undergoing elective and emergency operations at National Hospital, Sri Lanka *Migara Seneviratne 1, Asanka Hemachandra
Antithrombotic therapy in patients with transient ischemic attack / stroke (acute phase <48h)
 Antithrombotic therapy in patients with transient ischemic attack / stroke (acute phase
Antithrombotic therapy in patients with transient ischemic attack / stroke (acute phase
Inferior Venacaval Filters Valuable vs. Dangerous Valuable Annie Kulungowski. Department of Surgery Grand Rounds March 24, 2008
 Inferior Venacaval Filters Valuable vs. Dangerous Valuable Annie Kulungowski Department of Surgery Grand Rounds March 24, 2008 History of Vena Cava Filters Virchow-1846-Proposes PE originate from veins
Inferior Venacaval Filters Valuable vs. Dangerous Valuable Annie Kulungowski Department of Surgery Grand Rounds March 24, 2008 History of Vena Cava Filters Virchow-1846-Proposes PE originate from veins
NQF-ENDORSED VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANDARDS FOR HOSPITAL CARE. Measure Information Form
 Last Updated: Version 4.3 NQF-ENORSE VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANARS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Information Form Measure Set: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Set Measure Set I #: Performance Measure Name: Intensive
Last Updated: Version 4.3 NQF-ENORSE VOLUNTARY CONSENSUS STANARS FOR HOSPITAL CARE Measure Information Form Measure Set: Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Set Measure Set I #: Performance Measure Name: Intensive
Primary Care practice clinics within the Edmonton Southside Primary Care Network.
 INR Monitoring and Warfarin Dose Adjustment Last Review: November 2016 Intervention(s) and/or Procedure: Registered Nurses (RNs) adjust warfarin dosage according to individual patient International Normalized
INR Monitoring and Warfarin Dose Adjustment Last Review: November 2016 Intervention(s) and/or Procedure: Registered Nurses (RNs) adjust warfarin dosage according to individual patient International Normalized
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM International Consensus Statement 2013 Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence Developed under the auspices of the: Cardiovascular Disease Educational
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM International Consensus Statement 2013 Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence Developed under the auspices of the: Cardiovascular Disease Educational
8,9,10. Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) is clotting of blood in a deep vein of Pulmonary embolism
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS DIAGNOSIS OF VTE In patients with cancer-associated thrombosis, landmark studies have demonstrated that effective prophylaxis and treatment of thrombosis reduces morbidity
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS DIAGNOSIS OF VTE In patients with cancer-associated thrombosis, landmark studies have demonstrated that effective prophylaxis and treatment of thrombosis reduces morbidity
Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Causative factors of deep vein thrombosis of lower limb in Indian population
 International Surgery Jthisnal Khadilkar R et al. Int Surg J. 18 Jan;(1):3-3 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 39-33 eissn 39-9 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.183/39-9.isj17919 Causative
International Surgery Jthisnal Khadilkar R et al. Int Surg J. 18 Jan;(1):3-3 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 39-33 eissn 39-9 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.183/39-9.isj17919 Causative
2.5 Other Hematology Consult:
 The Warfarin Order Sheet has been approved by the P & T committee to be implemented by pharmacists. These orders are not used to treat patients with serious hemorrhagic complications. WARFARIN TARGET INR
The Warfarin Order Sheet has been approved by the P & T committee to be implemented by pharmacists. These orders are not used to treat patients with serious hemorrhagic complications. WARFARIN TARGET INR
Venous Thrombo-Embolism (VTE)
 Venous Thrombo-Embolism (VTE) Information for service users and carers RDaSH leading the way with care Older People s Mental Health Services Reducing risk of unwanted blood clots whilst in hospital About
Venous Thrombo-Embolism (VTE) Information for service users and carers RDaSH leading the way with care Older People s Mental Health Services Reducing risk of unwanted blood clots whilst in hospital About
How to prevent thrombotic diseases? Sergio Fusco, MD
 How to prevent thrombotic diseases? Sergio Fusco, MD Geriatric Division - Department of Internal Medicine Ospedale Dell'Angelo - Venice, Italy CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURE I have no potential conflict
How to prevent thrombotic diseases? Sergio Fusco, MD Geriatric Division - Department of Internal Medicine Ospedale Dell'Angelo - Venice, Italy CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURE I have no potential conflict
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis - Why Should We Care? Harry Gibbs FRACP FCSANZ Vascular Physician The Alfred Hospital
 Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis - Why Should We Care? Harry Gibbs FRACP FCSANZ Vascular Physician The Alfred Hospital VTE is common and dangerous 5 VTE is Common VTE Incidence: 1.5 / 1000 per year
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis - Why Should We Care? Harry Gibbs FRACP FCSANZ Vascular Physician The Alfred Hospital VTE is common and dangerous 5 VTE is Common VTE Incidence: 1.5 / 1000 per year
Prevalence of Symptomatic Venous Thrombo-Embolism in Patients with Total Contact Cast for Diabetic foot Complications A Retrospective Case Series.
 Prevalence of Symptomatic Venous Thrombo-Embolism in Patients with Total Contact Cast for Diabetic foot Complications A Retrospective Case Series. Dr R King, Miss GE Jackson, Mr SR Platt Wirral University
Prevalence of Symptomatic Venous Thrombo-Embolism in Patients with Total Contact Cast for Diabetic foot Complications A Retrospective Case Series. Dr R King, Miss GE Jackson, Mr SR Platt Wirral University
ED Diagnosis of DVT or tools to rule out DVT in your ED
 ED Diagnosis of DVT or tools to rule out DVT in your ED Ralph Wang UCSF Department of Emergency Medicine 53 yo f c/o left leg swelling recent cholecystectomy its midnight how do you manage this patient?
ED Diagnosis of DVT or tools to rule out DVT in your ED Ralph Wang UCSF Department of Emergency Medicine 53 yo f c/o left leg swelling recent cholecystectomy its midnight how do you manage this patient?
Stroke Quality Measures. Kathy Wonderly RN, BSPA, CPHQ Performance Improvement Coordinator Developed: May, 2012 Most recently updated: December 2012
 1 Stroke Quality Measures Kathy Wonderly RN, BSPA, CPHQ Performance Improvement Coordinator Developed: May, 2012 Most recently updated: December 2012 2 Application of the Stroke Measure Set The stroke
1 Stroke Quality Measures Kathy Wonderly RN, BSPA, CPHQ Performance Improvement Coordinator Developed: May, 2012 Most recently updated: December 2012 2 Application of the Stroke Measure Set The stroke
Lack of Clinical Benefit of Thromboprophylaxis in Patients Hospitalized in a Medical Unit Over a 10-year Span
 Elmer Original Article ress Lack of Clinical Benefit of Thromboprophylaxis in Patients Hospitalized in a Medical Unit Over a 10-year Span Gabrielle Migner-Laurin a, Thomas St-Aubin b, Julie Lapointe b,
Elmer Original Article ress Lack of Clinical Benefit of Thromboprophylaxis in Patients Hospitalized in a Medical Unit Over a 10-year Span Gabrielle Migner-Laurin a, Thomas St-Aubin b, Julie Lapointe b,
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients. David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center
 DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention and Treatment of VTE in Patients Admitted to Hospital
 Please Note: This policy is currently under review and is still fit for purpose. Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention and Treatment of VTE in Patients Admitted to Hospital This procedural document supersedes
Please Note: This policy is currently under review and is still fit for purpose. Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevention and Treatment of VTE in Patients Admitted to Hospital This procedural document supersedes
Drug Use Criteria: Direct Oral Anticoagulants
 Texas Vendor Drug Program Drug Use Criteria: Oral Anticoagulants Publication History 1. Developed March 2017. 2. Revised February 2018. Notes: Information on indications for use or diagnosis is assumed
Texas Vendor Drug Program Drug Use Criteria: Oral Anticoagulants Publication History 1. Developed March 2017. 2. Revised February 2018. Notes: Information on indications for use or diagnosis is assumed
Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism
 Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Benjamin Hohlfelder Samuel Z. Goldhaber Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Cardiovascular Division Harvard Medical School Brigham and
Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Benjamin Hohlfelder Samuel Z. Goldhaber Handbook for Venous Thromboembolism Gregory Piazza Cardiovascular Division Harvard Medical School Brigham and
Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy. Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016
 Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016 Conflicts of Interest No conflicts of interest to report Objectives At the end of the program participants will be
Duration of Anticoagulant Therapy Linda R. Kelly PharmD, PhC, CACP September 17, 2016 Conflicts of Interest No conflicts of interest to report Objectives At the end of the program participants will be
Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in Department of Veterans Affairs Hospitals
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in Department of Veterans Affairs Hospitals Jerome Herbers, MD, MBA Susan Zarter, BSN Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of the Inspector General,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in Department of Veterans Affairs Hospitals Jerome Herbers, MD, MBA Susan Zarter, BSN Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of the Inspector General,
Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease
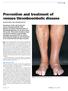 REVIEW Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease SUSAN McNEILL AND CATHERINE BAGOT Awareness of the risk factors for venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease and timely administration of thromboprophylaxis
REVIEW Prevention and treatment of venous thromboembolic disease SUSAN McNEILL AND CATHERINE BAGOT Awareness of the risk factors for venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease and timely administration of thromboprophylaxis
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Mismetti P, Laporte S, Pellerin O, Ennezat P-V, Couturaud F, Elias A, et al. Effect of a retrievable inferior vena cava filter plus anticoagulation vs anticoagulation alone
Supplementary Online Content Mismetti P, Laporte S, Pellerin O, Ennezat P-V, Couturaud F, Elias A, et al. Effect of a retrievable inferior vena cava filter plus anticoagulation vs anticoagulation alone
Use of combined oral contraceptives and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control studies using the QResearch and CPRD databases
 open access Use of combined oral contraceptives and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control studies using the and databases Yana Vinogradova, Carol Coupland, Julia Hippisley-Cox Division of
open access Use of combined oral contraceptives and risk of venous thromboembolism: nested case-control studies using the and databases Yana Vinogradova, Carol Coupland, Julia Hippisley-Cox Division of
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis After Major Orthopaedic Surgery: A Pooled Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
 Winner of the AAHKS Award Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis After Major Orthopaedic Surgery: A Pooled Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Greg A. Brown, MD, PhD The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 24
Winner of the AAHKS Award Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis After Major Orthopaedic Surgery: A Pooled Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Greg A. Brown, MD, PhD The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 24
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance on the recommended duration of anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism (VTE). BACKGROUND: Recurrent episodes of VTE
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM: DURATION OF TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide guidance on the recommended duration of anticoagulant therapy for venous thromboembolism (VTE). BACKGROUND: Recurrent episodes of VTE
Prophylaxis for Hospitalized and Non-Hospitalized Medical Patients
 Prophylaxis for Hospitalized and Non-Hospitalized Medical Patients An Educational Slide Set American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism Slide set authors: Eric
Prophylaxis for Hospitalized and Non-Hospitalized Medical Patients An Educational Slide Set American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for Management of Venous Thromboembolism Slide set authors: Eric
The diagnosis and prognosis of venous thromboembolism : variations on a theme Gibson, N.S.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The diagnosis and prognosis of venous thromboembolism : variations on a theme Gibson, N.S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Gibson, N. S.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The diagnosis and prognosis of venous thromboembolism : variations on a theme Gibson, N.S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Gibson, N. S.
Pharmacy Prior Authorization
 Pharmacy Prior Authorization AETA BETTER HEALTH EW JERSE (MEDICAID) Anticoagulant Injectable (Medicaid) This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review
Pharmacy Prior Authorization AETA BETTER HEALTH EW JERSE (MEDICAID) Anticoagulant Injectable (Medicaid) This fax machine is located in a secure location as required by HIPAA regulations. Complete/review
Drug Class Review Newer Oral Anticoagulant Drugs
 Drug Class Review Newer Oral Anticoagulant Drugs Final Original Report May 2016 The purpose of reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness and harms of different
Drug Class Review Newer Oral Anticoagulant Drugs Final Original Report May 2016 The purpose of reports is to make available information regarding the comparative clinical effectiveness and harms of different
Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. PE - Clinical
 Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
Key words: cardiac rehabilitation; coronary bypass; deep vein thrombosis; prevention; prophylaxis
 Deep Vein Thrombosis Among Patients Entering Cardiac Rehabilitation After Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery* Marco Ambrosetti, MD; Mario Salerno, MD; Mara Zambelli, MD; Filippo Mastropasqua, MD; Roberto Tramarin,
Deep Vein Thrombosis Among Patients Entering Cardiac Rehabilitation After Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery* Marco Ambrosetti, MD; Mario Salerno, MD; Mara Zambelli, MD; Filippo Mastropasqua, MD; Roberto Tramarin,
The PELICAN Study. Patient Experience of LIving with CANcer associated thrombosis
 The PELICAN Study Patient Experience of LIving with CANcer associated thrombosis Simon Noble: Clinical Reader in Palliative Medicine, Cardiff University & Honorary Consultant in Palliative Medicine, Aneurin
The PELICAN Study Patient Experience of LIving with CANcer associated thrombosis Simon Noble: Clinical Reader in Palliative Medicine, Cardiff University & Honorary Consultant in Palliative Medicine, Aneurin
Summary of Research and Writing Activities In Cardiovascular Disease
 Summary of Research and Writing Activities In Cardiovascular Disease Carole Alison Chrvala, PhD 919.545.2149 (Work) 919.951.5230 (Mobile) cchrvala@centurylink.net www.healthmattersmedwriting.com 1 Manuscripts
Summary of Research and Writing Activities In Cardiovascular Disease Carole Alison Chrvala, PhD 919.545.2149 (Work) 919.951.5230 (Mobile) cchrvala@centurylink.net www.healthmattersmedwriting.com 1 Manuscripts
