Atypical Kawasaki Disease Complicated by Kawasaki Disease Shock Syndrome in a 5-year-old Boy: A Case Report
|
|
|
- Miranda Morris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CASE REPORT Atypical Kawasaki Disease Complicated by Kawasaki Disease Shock Syndrome in a 5-year-old Boy: A Case Report Alyazia Al Hallami 1, Muna A. Al Dhaibani 1, Shamma Al Zaabi 1, Reem Albarguthi 1, Najla Al Kuwaiti 2, Aisha Alkhaaldi 3, Hossam Al Tatari 3 1 Department of Pediatric, Pediatric Residency Program, Tawam Hospital, Al-Ain, United Arab Emirates, 2 Department of Pediatric, Division of General Pediatrics, Tawam hospital, United Arab Emirates, 3 Department of Pediatric, Division of Infectious Diseases, Tawam hospital, United Arab Emirates ABSTRACT Diagnosing Kawasaki disease (KD) has always been challenging for physicians worldwide that might be related to the illdefined etiology along with unknown exact pathophysiology. It s an acute inflammatory process that strikingly affects small to medium vessels. It is known to mainly affect children younger than 5 years of age. Older children can also be affected, but the presentation seems to be more atypical with the older age groups. Kawasaki disease shock syndrome (KDSS) is one of the severe forms of KD that is often confused with toxic shock syndrome. This report discusses the case of a febrile child with atypical KD complicated by KDSS. Our aim is to delineate the challenges in diagnosis such severe atypical form of KD and its complication. Key words: Atypical Kawasaki disease, intravenous immunoglobulin, Kawasaki disease, Kawasaki disease shock syndrome BACKGROUND Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute febrile multisystem vasculitic syndrome of childhood, characterized by prolonged fever for more than 5 days along with other major criteria. [1] The syndrome derives its name from case reports presented by physician Kawasaki in [1] It is the most common vasculitic syndromes of unknown etiology, and it has been reported almost in all ethnic groups. In Japan, KD has 10 times higher incidences than other parts of the world, with the highest reported incidence of cases per 100,000 populations <5 years of age occurred in 2011 and per in This incidence was higher than United States incidence (20.8 cases/100,000 population) yearly for the same age group. [2-4] Moreover, KD has a higher tendency to occur in males compared to females.kd has emerged as a major cause of acquired heart disease among children throughout the developed world. If KD is left untreated, it can lead to significant coronary artery disease in 15 25% of cases. As a consequence, it may lead to myocardial infarction, and eventually sudden death. [3,5,6] Complete KD features include high-grade fever (temperature higher than 39 C or 102.2F) that persists for 5 days or more, with 4 of the clinical signs that are demonstrated in Table 1. In incomplete KD, patients lack sufficient clinical signs; therefore, the diagnosis will depend more on laboratory findings and/or cardiac echo findings to support the diagnosis. [7-11] Kawasaki disease shock syndrome (KDSS) is a new entity that was first described, in 2009, by Kanegaye et al. who defined it as sustained decrease in systolic blood pressure for age from baseline of 20% or clinical signs of poor perfusion in addition to KD features. [12,13] The exact mechanism is still unknown; however, previous reports illustrated that it might be due to capillary leakage as a result of vasculitis, myocardial Address for correspondence: Muna A. Al Dhaibani, Pediatric Residency Program, Tawam Hospital, P.O. Box 15258, Al-Ain, United Arab Emirate. Phone: ; mdhaibani89@gmail.com 2018 The Author(s). This open access article is distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) 4.0 license Clinical Research in Pediatrics Vol 1 Issue
2 dysfunction, and/or cytokines dysregulation. [14] It has been reported recently that patients with KDSS have higher inflammatory marker levels and they seem to be at a much higher risk of coronary artery aneurysm. [5,14] The mainstay of treatment in KD is intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), although some may display resistance to IVIG treatment and may require additional therapeutic measures. IVIG resistance is defined as persistent or recrudescent fever 36 h after completion of the IVIG infusion. [2,14] We are reporting an Emirati child who was diagnosed with incomplete KD and later on fulfilled the criteria of KDSS. We are highlighting his clinical presentation, risk factors, and the final outcome. CASE REPORT A 5-year-old boy, previously healthy, presented with high-grade fever of 5 days duration. On the 2 nd day of illness, he started to have a rash. The rash spread all over the body including palms and soles. The child also had bilateral red conjunctiva with watery discharges. In addition, he had deeply red tongue, sore throat, and generalized non-radiating abdominal pain. On admission, examination showed an alert boy; temperature was 40c, heart rate of 145 bpm, respiratory rate of 28 breaths/ min, and blood pressure of 93/45mmhg. He had a bilateral non-suppurative conjunctival injection, strawberry tongue and maculopapular rash over trunk and distal extremities, Table 1: Clinical diagnosis criteria as determined by the American Heart Association and laboratory criteria that may be used to help establish the diagnosis of KD Classical KD [17,24] : Fever persisting>5 days, plus at least four out of five of the following principal criteria: i. Changes in extremities, including indurative angioedema and desquamation ii. Polymorphous exanthema iii. Bilateral bulbar conjunctival injection without exudate iv. Changes to the lips and oral cavity, including pharyngeal injection, dry fissured lips, and/or strawberry tongue v. Acute nonpurulent cervical lymphadenopathy (>1.5 cm diameter) Atypical KD: Fever of>5 days associated with<4 principle criteria, with the following three or more criteria: i. Albumin<3 g/dl ii. C reactive protein>3 mg iii. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate>40 mm/h iv. Elevated alanine aminotransferase v. Leukocytosis: White cell count>15,000/mm vi. Normochromic, normocytic anemia for age vii. Sterile pyuria: >10 white blood cell/mm 3 Or Positive echocardiogram KD: Kawasaki disease with no palpable lymph nodes [Table 1a]. Remainder of his clinical examination was unremarkable. Initial investigations showed a normal white blood cell count, mild hypochromic microcytic anemia, and mild thrombocytopenia. There was the mild elevation of aminotransferases with indirect hyperbilirubinemia, low albumin level, and normal coagulation profile. He had a normal urinalysis and renal function test. C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate were markedly elevated [Table 1b]. Microbiological workup was non-contributory except for the detection of influenza B antigen in the nasopharyngeal aspirate. The history, clinical, and laboratory findings were supportive of the diagnosis of incomplete KD; therefore, intravenous immunoglobulin and high dose aspirin (100 mg/kg/24 h) were started. On the 2 nd day of admission, the patient s temperature decreased to 36.6c for 6 h, and he re-spiked fever again (38.9c) after 14 h of completing the IVIG infusion. He continued to have sinus tachycardia (Heart rate ranged between 124 and 147 bpm) with normal Table 1a: Patient s clinical features that fit with incomplete KD Classical KD: Fever persisting > 5 days+ i. Polymorphous exanthema ii. Bilateral bulbar conjunctival injection without exudate iii. Changes to the lips and oral cavity Atypical KD: Fever of > 5 days associated with < 4 principle criteria, with the following 4 more criteria: i. C reactive protein > 3 mg ii. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate > 40 mm/h iii. Elevated alanine aminotransferase iv. Sterile pyuria: >10 white blood cell/mm 3 KD: Kawasaki disease Table 1b: Patient s initial biochemical data Biochemical data [19,22] The patient Reference range WBCs /L Hgb 10.5 g/dl Platelets /L ALT 33 U/L AST 99 U/L Total bilirubin 507 mg/dl Direct bilirubin mg/dl Albumin 28 g/l CRP 105 mg/l 0 8 ESR 23 mm/h 0 10 CK MB 0.9 ng/ml Troponin I 0.02 ng/ml WBCs: White blood cells, ALT: Alanine aminotransferase, AST: Aspartate aminotransferase, CRP: C reactive protein, ESR: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, CK MB: Creatine kinase MB 2 Clinical Research in Pediatrics Vol 1 Issue
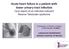
3 respiratory rate and blood pressure. At that point, acute myocarditis was highly suspected. Cardiac panel, including creatine kinase MB and troponin-i, was initially within normal limits [Table 1b]. Echocardiogram was performed on day 2 and showed normal findings including coronary arteries [Figure 1]. For precautions and to avoid the risk of influenza B associated Reye s syndrome, warfarin (1 mg/day) substituted aspirin and patient were started on oseltamivir. By next day, he continued to be febrile, irritable, and ill-looking. Physical examination revealed heart rate of 130bpm with a blood pressure of 81/40 mmhg (wide pulse pressure), warm extremities and Glasgow coma scale of 11 (opening eye spontaneously, cries, and withdraw to pain). At this stage, he was transferred to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU). Repeated cardiac enzymes were markedly increased this time [Table 2]. There were also some significant findings in the repeated echocardiogram with mildly depressed left ventricular function with ejection fraction of 47% and mild degree of mitral and tricuspid regurgitation with normal coronary artery dimensions and normal Z scores. Ultrasound study showed thickening of gallbladder wall, pericholecystic edema, and bilateral pleural effusions. Fluid resuscitation, inotropes, and broad-spectrum antibiotics were started for possible staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome (TSS). The patient was also complaining of neck stiffness and difficulty in swallowing. Examination of the neck showed rightsided tender cervical lymphadenopathy. Ultrasound confirmed enlargement of neck lymph node bilaterally. On the 5 th day of admission, the fever subsided after the second dose of IVIG and the overall clinical picture of the patient started to improve. He developed thrombocytosis (platelet: 569,000/mm³) on the 14 th day. Echocardiogram was normal on the 4 th week without coronary abnormalities. The patient has been following with cardiology clinic on low dose aspirin without any complications. The repeated echocardiographs were all normal. DISCUSSION KD remains to be of unclear etiology. To dates, there is no single pathognomonic clinical or laboratory finding to confirm the diagnosis. Our patient had incomplete KD, as he was not fulfilling the principle criteria. Furthermore, his condition got complicated by KDSS with hemodynamic instability. This clinical deterioration necessitated transfer to PICU for closer observation and inotropic support. In fact, there seem to be many similarities between KDSS and TSS. It has been speculated that a certain super-antigen mediates the interactions in both conditions. [15,16] The exact role of IVIG in KD is still not clearly understood, but it is known to have anti-inflammatory effects including reduction of fever, modulating cytokine levels, as well as downregulating antibodies synthesis. There have been many recent reports of IVIG failure or non-responsiveness in patients with KDSS. [17-19] On reviewing the temperature profile of the patient during IVIG infusion, his temperature subsided then re-appeared with a high grade in <24 Table 2: Repeated cardiac enzymes suggestive of acute myocarditis Cardiac enzymes The patient Reference range CK MB 11.2 ng/ml BNP 2107 pg/ml 0 35 Troponin I 2.38 ng/ml CK MB: Creatine kinase MB, BNP: B type natriuretic peptide Figure 1: Echocardiogram finding in the patient with normal coronaries vessels dimension. Normal coronary arteries with normal z-score: (1) Main left coronary artery (MLCA): 2.7 mm. (2) Left anterior descending artery (LAD): 1.9 mm. (3) Right coronary artery (RCA): 2.3 mm h. Therefore, he was labeled as partial non-responder to the initial treatment. [19] Several scores have been developed to predict the risk of IVIG resistance/failure. [20,21] Unfortunately, our patient scored high in all the three scores and indeed required a second dose of IVIG [Table 3]. KDSS, IVIG resistance, and acute myocarditis may exist together. Therefore, there was an interesting debate whether the sudden deterioration (hypotension, tachycardia, delayed capillary refill, etc.) was due to by KDSS or due to acute heart failure due to acute viral myocarditis secondary to influenza. Recent articles showed that patients with KDSS seem to be at higher risk for gastrointestinal manifestations, incomplete presentation, IVIG resistance, and myocardial infarction. [23,24] Interestingly, the child did not have any involvement of coronary arteries during acute, convalescent phase and follow-up, though he had the rare and the severe form of KD. Chen and Chi published a case-controlled study in 2015 that reviewed hospitalized patients ( ) who were diagnosed with KD and KDSS. They concluded that patients with KDSS presented with atypical features that could have been missed and were managed in the intensive care unit for hemodynamic support. [24] Another case report from Turkey by Is gu der et al. revealed that misdiagnosing KDSS is likely as pediatricians and intensive care unit practitioners are unaware of this condition and its damaging sequelae. [5] CONCLUSION While the role of IVIG in TSS is controversial, it continues to play a major role in the management of KDSS. Hence, it is prudent that pediatricians and intensivists become familiar Clinical Research in Pediatrics Vol 1 Issue
4 Table 3: Representative scoring systems for evaluating potential IVIG resistance IVIG resistance score Cutoff point Points The patient Point Kobayashi score ( 5 points; 76% Sodium 133 mmol/l sensitivity, 80% specificity) [17,20,21] Day of illness at initial IVIG (=KD diagnosed) Day 4 or earlier 1 2 nd day 1 AST 100 IU/L Neutrophil ratio 80% 2 80% 2 CRP 10 mg/dl Platelet counts /mm Age 12 months 1 5 years 0 Total 7 Egami score ( 3 points; 78% sensitivity, 76% specificity) ALT 80 IU/L Day of illness at initial IVI G (=KD diagnosed) Day 4 or earlier 1 2 nd day 1 CRP 8 mg/dl Platelet counts /mm Age 6 months years 0 Total 2 Sano score ( 2 points; 77% sensitivity, 86% specificity) AST 200 IU/L Total bilirubin 0.9 mg/dl CRP 7 mg/dl Total 2 IVIG: Intravenous immunoglobulin, KD: Kawasaki disease, ALT: Alanine aminotransferase, AST: Aspartate aminotransferase, CRP: C reactive protein with this entity to be able to reach an early diagnosis and start the appropriate therapy on time. REFERENCES 1. Kawasaki T. Infantile acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome with specific desquamation of the fingers and toes. Clinical observation of 50 cases. Jpn J Allerg 1967;16: McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW, Burns JC, Bolger AF, Gewitz M, et al. A scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association, diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease. Circulation 2017;135:e Gerding R. Kawasaki disease: A review. J Pediatr Health Care 2011;25: Uehara R, Belay ED. Epidemiology of Kawasaki disease in Asia. Eur United States J Epidemiol 2012;22: Is gu der R, Dokso z O, Bağ O, Ağın H, Mes e T, Karaarslan ÜU, et al Kawasaki disease shock syndrome: A severe form of Kawasaki disease. Turk J Pediatr 2013;55: Wood LE, Tulloh RM. Kawasaki disease in children. Heart 2009;95: Jamieson N, Singh-Grewal D. Kawasaki Disease: A Clinician s Update. DOI: /2013/ Sánchez-Manubens J, Bou R, Anton J. Diagnosis and classification of Kawasaki disease. J Autoimmun 2014;48-49:113e Greco A, De Virgilio A, Rizzo MI, Tombolini M, Gallo A. Susac syndrome: Microangiopathy of the retina, cochlea and brain. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2018;30: Fusconi M, Ruoppolo G, Pagliuca G, Martellucci S, de Vincentiis M. Kawasaki disease: An evolving paradigm. Autoimmun Rev 2015;14: Kawasaki T. Kawasaki disease. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 2006;82: Farley LF, Hodo LN. An 8-Year-Old Male with 4 Days of Fever, Abdominal Pain, and Jaundice. DOI: / Kanegaye JT, Wilder MS, Molkara D, Frazer JR, Pancheri J, Tremoulet AH, et al. Recognition of a kawasaki disease shock syndrome. Pediatrics 2009;123:e Çakan M, Gemici H, Aktay-Ayaz N, Keskindemirci G, Bornaun H, İkizoğlu T, et al. Kawasaki disease shock syndrome: A rare and severe complication of Kawasaki disease. Turk J Pediatr 2016;58: Gámez-González LB, Murata C, Muñoz-Ramírez M, Yamazaki-Nakashimada M. Clinical manifestations associated with Kawasaki disease shock syndrome in Mexican children. Eur J Pediatr 2013;172: Rowley AH, Kawasaki MD. Disease: Novel insights into etiology and genetic susceptibility. Annu Rev Med 4 Clinical Research in Pediatrics Vol 1 Issue
5 2011;62: To S, Yan C, Fong N, Leung C. Two cases of Kawasaki disease shock syndrome. HK J Paediatr 2016;21: Downie ML, Manlhiot C, Latino GA, Collins TH, Chahal N, Yeung RS, et al. Variability in Response to Intravenous Immunoglobulin in the Treatment of Kawasaki Disease. DOI: /j.jpeds Maggio MC, Corsello G, Prinzi E, Cimaz R. Kawasaki disease in Sicily: Clinical description and markers of disease severity. Italian J Pediatr 2016;42: Sleeper LA, Minich LL, McCrindle BM, Li JS, Mason W, Colan SD. Evaluation of kawasaki disease risk scoring systems for intravenous immunoglobulin resistance. J Pediatr 2011;158:831-5.e Kobayashi T, Inoue Y, Takeuchi K, Okada Y, Tamura K, Tomomasa T, et al. Prediction of intravenous immunoglobulin unresponsiveness in patients with Kawasaki disease. Circulation 2006;113: Parthasarathy P, Agarwal A, Chawla K, Tofighi T, Mondal TK. Upcoming biomarkers for the diagnosis of Kawasaki disease: A review. Clin Biochem 2015;48: Research Committee of the Japanese Society of Pediatric Cardiology. Guidelines for Medical Treatment of Acute Kawasaki Disease: Report of the Research Committee of the Japanese Society of Pediatric Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery (2012 revised version). Pediatr Int 2014;56: Chen P, Chi H, Huang FY, Peng CC, Chen MR, Chiu NC, et al. Clinical manifestations of Kawasaki disease shock syndrome: A case-control study. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2015;48: How to cite this article: Al Hallami A, Al Dhaibani M, Al Zaabi S, Albarguthi R, Al Kuwaiti N, Alkhaaldi A, Al Tatari H. Atypical Kawasaki Disease Complicated by Kawasaki Disease Shock Syndrome in a 5 Years Old Boy: Case Report. Clin Res Pediatr 2018;1(1):1-5. Clinical Research in Pediatrics Vol 1 Issue
Coronary artery status of patients with transient fever h after first IVIG infusion did not differ from that seen in responsive patients
 Baek et al. Pediatric Rheumatology (2018) 16:83 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12969-018-0301-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Coronary artery status of patients with transient fever 24 36 h after first IVIG infusion did
Baek et al. Pediatric Rheumatology (2018) 16:83 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12969-018-0301-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Coronary artery status of patients with transient fever 24 36 h after first IVIG infusion did
Kawasaki Disease. 1:45 2:30 p.m. James Nocton, MD Benjamin Goot, MD. Children s Specialty Group. All rights reserved.
 Kawasaki Disease 1:45 2:30 p.m. James Nocton, MD Benjamin Goot, MD Disclosures We have no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Objectives Describe the characteristic signs and symptoms of Kawasaki
Kawasaki Disease 1:45 2:30 p.m. James Nocton, MD Benjamin Goot, MD Disclosures We have no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Objectives Describe the characteristic signs and symptoms of Kawasaki
Clinical Characteristics of Kawasaki Disease in Infants Younger than Six Months: A Single-Center Study
 Original Article Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Clinical Characteristics of Kawasaki Disease in Infants Younger than Six Months: A Single-Center Study You Min Yoon,
Original Article Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Clinical Characteristics of Kawasaki Disease in Infants Younger than Six Months: A Single-Center Study You Min Yoon,
Clinical Manifestations of Kawasaki Disease: What Are the Significant Parameters?
 ASIAN PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY (2009) 27: 131-136 Clinical Manifestations of Kawasaki Disease: What Are the Significant Parameters? Kanoknaphat Chaiyarak 1, Kritvikrom Durongpisitkul 2,
ASIAN PACIFIC JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY (2009) 27: 131-136 Clinical Manifestations of Kawasaki Disease: What Are the Significant Parameters? Kanoknaphat Chaiyarak 1, Kritvikrom Durongpisitkul 2,
Kawasaki Disease: What you need to know from the 2017 Guidelines
 Kawasaki Disease: What you need to know from the 2017 Guidelines S. Kristen Sexson Tejtel, MD, PhD, MPH Pediatric Preventive Cardiology TCHAPP Conference April 4, 2019 No disclosures to report Outline
Kawasaki Disease: What you need to know from the 2017 Guidelines S. Kristen Sexson Tejtel, MD, PhD, MPH Pediatric Preventive Cardiology TCHAPP Conference April 4, 2019 No disclosures to report Outline
Kawasaki disease. Dr Laurence Lacroix
 Dr Laurence Lacroix 16.04.2014 1 2 DEFINITION: o Kawasaki disease(kd) is an acute febrile illness of childhood ovasculitisof medium-sized extraparenchymal arteries o Predilection for coronary arteries
Dr Laurence Lacroix 16.04.2014 1 2 DEFINITION: o Kawasaki disease(kd) is an acute febrile illness of childhood ovasculitisof medium-sized extraparenchymal arteries o Predilection for coronary arteries
Case Presentation. By Eman El Sharkawy Ass. Professor of cardiology Alexandria University
 Case Presentation By Eman El Sharkawy Ass. Professor of cardiology Alexandria University 6m old baby girl Past history : - At the age of 2m attack of fever, diarrhea, mouth ulcers, difficult breast feeding
Case Presentation By Eman El Sharkawy Ass. Professor of cardiology Alexandria University 6m old baby girl Past history : - At the age of 2m attack of fever, diarrhea, mouth ulcers, difficult breast feeding
Age-adjusted plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide level in Kawasaki disease
 Original article Jun Korean H, et J Pediatr al. Age-adjusted 2016;59(7):298-302 plasma NT-proBNP level and Kawasaki disease pissn 1738-1061 eissn 2092-7258 Korean J Pediatr Age-adjusted plasma N-terminal
Original article Jun Korean H, et J Pediatr al. Age-adjusted 2016;59(7):298-302 plasma NT-proBNP level and Kawasaki disease pissn 1738-1061 eissn 2092-7258 Korean J Pediatr Age-adjusted plasma N-terminal
Kawasaki Disease: Updates on Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management
 Kawasaki Disease: Updates on Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Kristin C. Lombardi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Clinical Educator The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Pediatric
Kawasaki Disease: Updates on Diagnosis, Treatment, and Management Kristin C. Lombardi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Clinical Educator The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Pediatric
Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for infants with Kawasaki diseaseyounger than 6 months
 IOSR Journal Of Pharmacywww.iosrphr.org (e)-issn: 220-303, (p)-issn: 239-29 Volume 6, Issue 2 Version. (Dec 206), PP. -6 Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for infants with Kawasaki diseaseyounger than
IOSR Journal Of Pharmacywww.iosrphr.org (e)-issn: 220-303, (p)-issn: 239-29 Volume 6, Issue 2 Version. (Dec 206), PP. -6 Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for infants with Kawasaki diseaseyounger than
Clinical Guidance. Kawasaki disease. Summary This guideline includes therapy and follow up including investigations (echocardiography, MRI).
 Clinical Guidance Kawasaki disease Summary This guideline includes therapy and follow up including investigations (echocardiography, MRI). Document Detail Document type Clinical Guideline Document name
Clinical Guidance Kawasaki disease Summary This guideline includes therapy and follow up including investigations (echocardiography, MRI). Document Detail Document type Clinical Guideline Document name
SUCCESSFUL HOME INR MONITORING FOLLOWING KAWASAKI DISEASE
 The West London Medical Journal 2013 Vol 5 No 2 pp 11-15 SUCCESSFUL HOME INR MONITORING FOLLOWING KAWASAKI DISEASE Bushra Ahmed ABSTRACT Camilla Sen Colin Michie Most paediatricians will encounter at least
The West London Medical Journal 2013 Vol 5 No 2 pp 11-15 SUCCESSFUL HOME INR MONITORING FOLLOWING KAWASAKI DISEASE Bushra Ahmed ABSTRACT Camilla Sen Colin Michie Most paediatricians will encounter at least
Medium-dose IVIG (1 g/kg) as an initial treatment of Kawasaki disease
 Original article Moon Korean KP, J Pediatr et al. 2016;59(4):178-182 Medium-dose IVIG (1 g/kg) as an initial treatment of Kawasaki disease pissn 1738-1061 eissn 2092-7258 Korean J Pediatr Prediction of
Original article Moon Korean KP, J Pediatr et al. 2016;59(4):178-182 Medium-dose IVIG (1 g/kg) as an initial treatment of Kawasaki disease pissn 1738-1061 eissn 2092-7258 Korean J Pediatr Prediction of
Non-Responders to Intravenous Immunoglobulin and Coronary Artery Dilatation in Kawasaki Disease: Predictive Parameters in Korean Children
 Original Article Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Non-Responders to Intravenous Immunoglobulin and Coronary Artery Dilatation in Kawasaki Disease: Predictive Parameters
Original Article Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Non-Responders to Intravenous Immunoglobulin and Coronary Artery Dilatation in Kawasaki Disease: Predictive Parameters
The Harada Score in the US Population of Children With Kawasaki Disease
 RESEARCH ARTICLE The Harada Score in the US Population of Children With Kawasaki Disease AUTHORS Helen Tewelde, MD, 1 Jeein Yoon, MD, 2 Wendy Van Ittersum, MD, 2 Sarah Worley, MS, 3 Tamar Preminger, MD,
RESEARCH ARTICLE The Harada Score in the US Population of Children With Kawasaki Disease AUTHORS Helen Tewelde, MD, 1 Jeein Yoon, MD, 2 Wendy Van Ittersum, MD, 2 Sarah Worley, MS, 3 Tamar Preminger, MD,
Reaction at the Bacillus CalmetteeGuérin Inoculation Site in Patients with Kawasaki Disease
 Pediatrics and Neonatology (2013) 54, 43e48 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: http://www.pediatr-neonatol.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reaction at the Bacillus CalmetteeGuérin Inoculation
Pediatrics and Neonatology (2013) 54, 43e48 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: http://www.pediatr-neonatol.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reaction at the Bacillus CalmetteeGuérin Inoculation
Diagnosis of Incomplete Kawasaki Disease in Infants Based on an Inflammation at the Bacille Calmette-Guérin Inoculation Site
 Original Article Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Diagnosis of Incomplete Kawasaki Disease in Infants Based on an Inflammation at the Bacille Calmette-Guérin Inoculation
Original Article Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Diagnosis of Incomplete Kawasaki Disease in Infants Based on an Inflammation at the Bacille Calmette-Guérin Inoculation
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute inflammatory
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Kawasaki Disease Risk Scoring System in a Single Center Experience from Japan Miho Ashiarai, Asami Shinbo, Kazuaki Matsumoto, Hisae Nakatani, Keiko Onda, Mari Okada, Masako
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of Kawasaki Disease Risk Scoring System in a Single Center Experience from Japan Miho Ashiarai, Asami Shinbo, Kazuaki Matsumoto, Hisae Nakatani, Keiko Onda, Mari Okada, Masako
DR.K.BALAGANESH DR.SHUBA DR.RAJAKUMAR PICU TEAM, SRMC
 DR.K.BALAGANESH DR.SHUBA DR.RAJAKUMAR PICU TEAM, SRMC 1 year old developmentally normal girl 2 nd born to non consanguineous parents presented with: Fever - 1 day 1 episode of vacant stare lasting for
DR.K.BALAGANESH DR.SHUBA DR.RAJAKUMAR PICU TEAM, SRMC 1 year old developmentally normal girl 2 nd born to non consanguineous parents presented with: Fever - 1 day 1 episode of vacant stare lasting for
Case Report Incomplete Kawasaki disease: The usefulness of BCG reactivation as a diagnostic tool
 Case Report Incomplete Kawasaki disease: The usefulness of BCG reactivation as a diagnostic tool Omer S.M. Suliman, Mohamed Abdelnasser Department of Paediatrics, AlRass General Hospital, Saudi Arabia
Case Report Incomplete Kawasaki disease: The usefulness of BCG reactivation as a diagnostic tool Omer S.M. Suliman, Mohamed Abdelnasser Department of Paediatrics, AlRass General Hospital, Saudi Arabia
Risk factors for persistence of coronary artery abnormalities in Turkish children with Kawasaki disease
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 248-253 Original Risk factors for persistence of coronary artery abnormalities in Turkish children with Kawasaki disease Murat Muhtar Yılmazer 1, Taliha Öner
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2015; 57: 248-253 Original Risk factors for persistence of coronary artery abnormalities in Turkish children with Kawasaki disease Murat Muhtar Yılmazer 1, Taliha Öner
Kawasaki disease: multiple giant coronary aneurysms intervention and pacemaker implantation due to complete heart block a case report
 Case Report Kawasaki disease: multiple giant coronary aneurysms intervention and pacemaker implantation due to complete heart block a case report Chunping Liu, Junxia Li, Zhenshuang Cui, Lili Niu, Junyu
Case Report Kawasaki disease: multiple giant coronary aneurysms intervention and pacemaker implantation due to complete heart block a case report Chunping Liu, Junxia Li, Zhenshuang Cui, Lili Niu, Junyu
Kawasaki disease (KD) is associated with
 Intravenous immunoglobulin 1 g/kg as the initial treatment for Kawasaki disease Hirohiko Shiraishi, Mayu Iino, Masaru Hoshina, Kou Ichihashi, Mariko Y Momoi Tochigi, Japan Background: Coronary artery lesion
Intravenous immunoglobulin 1 g/kg as the initial treatment for Kawasaki disease Hirohiko Shiraishi, Mayu Iino, Masaru Hoshina, Kou Ichihashi, Mariko Y Momoi Tochigi, Japan Background: Coronary artery lesion
ST - segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction complicating an atypical Kawasaki disease
 ST - segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction complicating an atypical Kawasaki disease Raluca PRISECARU, Marc VINCENT, Steven VERCAUTEREN Brussels Heart Center, Brussels, Belgium Disclosure None Clinical
ST - segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction complicating an atypical Kawasaki disease Raluca PRISECARU, Marc VINCENT, Steven VERCAUTEREN Brussels Heart Center, Brussels, Belgium Disclosure None Clinical
Relationship between serum sodium level and coronary artery abnormality in Kawasaki disease
 Original article Park Korean S, et J Pediatr al. Hyponatremia 7;():8- and coronary artery abnormality in Kawasaki disease pissn 78- eissn 9-758 Korean J Pediatr Relationship between serum sodium level
Original article Park Korean S, et J Pediatr al. Hyponatremia 7;():8- and coronary artery abnormality in Kawasaki disease pissn 78- eissn 9-758 Korean J Pediatr Relationship between serum sodium level
Kawasaki disease in infants
 Review article Korean J Pediatr Kawasaki disease in infants Jung Sook Yeom, MD, Hyang Ok Woo, MD, Ji Sook Park, MD, Eun Sil Park, MD, Ji-Hyun Seo, MD, Hee-Shang Youn, MD Department of Pediatrics, Gyeongsang
Review article Korean J Pediatr Kawasaki disease in infants Jung Sook Yeom, MD, Hyang Ok Woo, MD, Ji Sook Park, MD, Eun Sil Park, MD, Ji-Hyun Seo, MD, Hee-Shang Youn, MD Department of Pediatrics, Gyeongsang
The Relationship between Coronary Artery Aneurysm and QT Interval Dispersion in Acute Phase of Kawasaki Disease
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Jun 2011; Vol 21 (No 2), Pp: 220-224 The Relationship between Coronary Artery Aneurysm and QT Interval Dispersion in Acute Phase of Kawasaki Disease Abdolrazagh Kiani 1,
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Jun 2011; Vol 21 (No 2), Pp: 220-224 The Relationship between Coronary Artery Aneurysm and QT Interval Dispersion in Acute Phase of Kawasaki Disease Abdolrazagh Kiani 1,
Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis of Kawasaki Diseases
 11 th International Kawasaki Disease Symposium Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis of Kawasaki Diseases 2015 Feb 4 th Tai-Ming Ko Jer-Yuarn Wu, Yuan-Tsong Chen DISCLOSURES: None Biomarkers for human disease
11 th International Kawasaki Disease Symposium Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis of Kawasaki Diseases 2015 Feb 4 th Tai-Ming Ko Jer-Yuarn Wu, Yuan-Tsong Chen DISCLOSURES: None Biomarkers for human disease
KAWASAKI DISEASE IN GHANA: CASE REPORTS FROM KORLE BU TEACHING HOSPITAL
 KAWASAKI DISEASE IN GHANA: CASE REPORTS FROM KORLE BU TEACHING HOSPITAL E. V. BADOE 1, J. NEEQUAYE 1, J. O. OLIVER-COMMEY 1, J. AMOAH 2, A. OSAFO 2, I. ARYEE 2 and M. Y. NYARKO 3 1 Department of Child
KAWASAKI DISEASE IN GHANA: CASE REPORTS FROM KORLE BU TEACHING HOSPITAL E. V. BADOE 1, J. NEEQUAYE 1, J. O. OLIVER-COMMEY 1, J. AMOAH 2, A. OSAFO 2, I. ARYEE 2 and M. Y. NYARKO 3 1 Department of Child
CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II
 MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II Session 11 April 11, 2016 STUDENT COPY MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 2 CASE HISTORY 1 Chief complaint: Our baby
MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION MHD II Session 11 April 11, 2016 STUDENT COPY MHD II, Session 11, Student Copy Page 2 CASE HISTORY 1 Chief complaint: Our baby
Iron deficiency anemia as a predictor of coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki
 Iron deficiency anemia as a predictor of coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki disease Running title: Kawasaki disease with iron deficiency anemia Sohyun KIM, M.D., Lucy Youngmin EUN, M.D., Ph.D. Departments
Iron deficiency anemia as a predictor of coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki disease Running title: Kawasaki disease with iron deficiency anemia Sohyun KIM, M.D., Lucy Youngmin EUN, M.D., Ph.D. Departments
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated 2- infectious
IL-6) (Kawasaki disease) -α(tumor necrosis factor-α, TNF-α) -6(interleukin-6, ; 27: DOI: / [4] [5] [1,2] [6]
![IL-6) (Kawasaki disease) -α(tumor necrosis factor-α, TNF-α) -6(interleukin-6, ; 27: DOI: / [4] [5] [1,2] [6] IL-6) (Kawasaki disease) -α(tumor necrosis factor-α, TNF-α) -6(interleukin-6, ; 27: DOI: / [4] [5] [1,2] [6]](/thumbs/92/108301500.jpg) [] 57 1 林 2 1 540 107 5 5-7 10 2017; 27: 57-64 DOI: 10.3966/168232812017032701008 (Kawasaki disease) [1,2] 1967 [1] 1976 [3] -α(tumor necrosis factor-α, TNF-α)-6(interleukin-6, IL-6) [4] 10 5 19 [5] 1996
[] 57 1 林 2 1 540 107 5 5-7 10 2017; 27: 57-64 DOI: 10.3966/168232812017032701008 (Kawasaki disease) [1,2] 1967 [1] 1976 [3] -α(tumor necrosis factor-α, TNF-α)-6(interleukin-6, IL-6) [4] 10 5 19 [5] 1996
Vasculitis local: systemic
 Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Vasculitis Inflammation of the vessel wall. Signs and symptoms: 1- local: according to the involved tissue 2- systemic:(fever, myalgia, arthralgias, and malaise) Pathogenesis 1- immune-mediated inflammation
Early features of Kawasaki disease with pyuria in febrile infants younger than 6 months
 Yoon et al. BMC Pediatrics (2018) 18:389 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-018-1362-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Early features of Kawasaki disease with pyuria in febrile infants younger than 6 months Seo
Yoon et al. BMC Pediatrics (2018) 18:389 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-018-1362-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Early features of Kawasaki disease with pyuria in febrile infants younger than 6 months Seo
Kawasaki Disease: A Retrospective Study
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No. 2, June 2006 Kawasaki Disease: A Retrospective Study Z. Al-Mosawi, MBBCH, ABMS-Ped* A.M. Mohammad, MD, FAAP * A.N. Al-Saif, MD, FRCPI, DCH* A.R. Al Madhoob, MBBCH,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No. 2, June 2006 Kawasaki Disease: A Retrospective Study Z. Al-Mosawi, MBBCH, ABMS-Ped* A.M. Mohammad, MD, FAAP * A.N. Al-Saif, MD, FRCPI, DCH* A.R. Al Madhoob, MBBCH,
A walk through a STEMI
 A walk through a STEMI M.M. s Story Kim Robison Ashley Corcoran Situation M.M. is an 82 year old male brought in by private vehicle on 10/22/17 to the Emergency Department Pt. c/o left arm numbness, pain
A walk through a STEMI M.M. s Story Kim Robison Ashley Corcoran Situation M.M. is an 82 year old male brought in by private vehicle on 10/22/17 to the Emergency Department Pt. c/o left arm numbness, pain
DOI: /peds The online version of this article, along with updated information and services, is located on the World Wide Web at:
 Performance of 2004 American Heart Association Recommendations for Treatment of Kawasaki Disease Elizabeth S. Yellen, Kimberlee Gauvreau, Masato Takahashi, Jane C. Burns, Stanford Shulman, Annette L. Baker,
Performance of 2004 American Heart Association Recommendations for Treatment of Kawasaki Disease Elizabeth S. Yellen, Kimberlee Gauvreau, Masato Takahashi, Jane C. Burns, Stanford Shulman, Annette L. Baker,
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM. General Instructions: ID NUMBER: FORM NAME: H F A DATE: 10/13/2017 VERSION: CONTACT YEAR NUMBER:
 ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
How bout Them Steroids: The Role of Corticosteroids in Kawasaki Disease
 How bout Them Steroids: The Role of Corticosteroids in Kawasaki Disease Source: http://blog.timesunion.com/mdtobe/answer-to-medical-mystery-monday-65/1885/ Pharmacotherapy Grand Rounds Meenakshi R. Ramanathan,
How bout Them Steroids: The Role of Corticosteroids in Kawasaki Disease Source: http://blog.timesunion.com/mdtobe/answer-to-medical-mystery-monday-65/1885/ Pharmacotherapy Grand Rounds Meenakshi R. Ramanathan,
Hepatobiliary risk factors for clinical outcome of Kawasaki disease in children
 Yi et al. BMC Pediatrics 2014, 14:51 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Hepatobiliary risk factors for clinical outcome of Kawasaki disease in children Dae Yong Yi 1, Ji Young Kim 2, Eun Young Choi 1, Jung Yun
Yi et al. BMC Pediatrics 2014, 14:51 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Hepatobiliary risk factors for clinical outcome of Kawasaki disease in children Dae Yong Yi 1, Ji Young Kim 2, Eun Young Choi 1, Jung Yun
CASE 5 - Toy et al. CASE FILES: Obstetrics & Gynecology
 z CASE 5 - Toy et al. CASE FILES: Obstetrics & Gynecology A 28-year-old woman is brought into the emergency room with a blood pressure of 60/40. The patient s husband states that she had 2 days of nausea
z CASE 5 - Toy et al. CASE FILES: Obstetrics & Gynecology A 28-year-old woman is brought into the emergency room with a blood pressure of 60/40. The patient s husband states that she had 2 days of nausea
Case report. Open Access. Abstract
 Open Access Case report Incomplete, atypical kawasaki disease or evolving systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a case report Shakeel Shaikh 1, Sidra Ishaque 2 * and Taimur Saleem 2 Addresses: 1 Department
Open Access Case report Incomplete, atypical kawasaki disease or evolving systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a case report Shakeel Shaikh 1, Sidra Ishaque 2 * and Taimur Saleem 2 Addresses: 1 Department
KAWASAKI DISEASE New Paradigms Michael A. Portman
 KAWASAKI DISEASE New Paradigms Michael A. Portman Acute systemic vasculitis in children Predilection for the coronary arteries with aneurysm formation clot, stenosis Cause unknown 7000 cases per year in
KAWASAKI DISEASE New Paradigms Michael A. Portman Acute systemic vasculitis in children Predilection for the coronary arteries with aneurysm formation clot, stenosis Cause unknown 7000 cases per year in
Association of Sterile Pyuria and Coronary Artery Aneurysm in Kawasaki Syndrome
 ORIGINAL REPORT Association of Sterile Pyuria and Coronary Artery Aneurysm in Kawasaki Syndrome Mohsen Akhavan Sepahi 1, Reza Miri 2, and Hasan Taher Ahmadi 3 1 Department of Pediatric Nephrology, Qom
ORIGINAL REPORT Association of Sterile Pyuria and Coronary Artery Aneurysm in Kawasaki Syndrome Mohsen Akhavan Sepahi 1, Reza Miri 2, and Hasan Taher Ahmadi 3 1 Department of Pediatric Nephrology, Qom
Risk Factors of Resistance to Intravenous Immunoglobulin in patients with Kawasaki: A Cross-Sectional Study Over a 10 Year Period ( )
 Risk Factors of Resistance to Intravenous Immunoglobulin in patients with Kawasaki: A Cross-Sectional Study Over a 10 Year Period (2006-2016) Fariba Tarhani (1) Azadeh Jafrasteh (2) Mahshid Garmsiri (3)
Risk Factors of Resistance to Intravenous Immunoglobulin in patients with Kawasaki: A Cross-Sectional Study Over a 10 Year Period (2006-2016) Fariba Tarhani (1) Azadeh Jafrasteh (2) Mahshid Garmsiri (3)
Research Article Sonographic Gallbladder Abnormality Is Associated with Intravenous Immunoglobulin Resistance in Kawasaki Disease
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 2012, Article ID 485758, 5 pages doi:10.1100/2012/485758 The cientificworldjournal Research Article Sonographic Gallbladder Abnormality Is Associated with Intravenous
The Scientific World Journal Volume 2012, Article ID 485758, 5 pages doi:10.1100/2012/485758 The cientificworldjournal Research Article Sonographic Gallbladder Abnormality Is Associated with Intravenous
Uveitis as an important ocular sign to help early diagnosis in Kawasaki disease
 Original article Choi Korean HS, J et Pediatr al. Uveitis 2015;58(10):374-379 in Kawasaki disease pissn 1738-1061 eissn 2092-7258 Korean J Pediatr Uveitis as an important ocular sign to help early diagnosis
Original article Choi Korean HS, J et Pediatr al. Uveitis 2015;58(10):374-379 in Kawasaki disease pissn 1738-1061 eissn 2092-7258 Korean J Pediatr Uveitis as an important ocular sign to help early diagnosis
Chemistry Reference Ranges and Critical Values
 Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT, SGPT) 3-9 years 9-18 years 1-9 years 9-18 years 10-25 U/L 10-35 U/L 10-30 U/L 10-25 U/L 10-30 U/L 10-35 U/L 10-25 U/L 10-35 U/L 10-25 U/L 10-20 U/L 10-35 U/L Albumin 0-6
Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT, SGPT) 3-9 years 9-18 years 1-9 years 9-18 years 10-25 U/L 10-35 U/L 10-30 U/L 10-25 U/L 10-30 U/L 10-35 U/L 10-25 U/L 10-35 U/L 10-25 U/L 10-20 U/L 10-35 U/L Albumin 0-6
Chemistry Reference Ranges and Critical Values
 Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT, SGPT) 3-9 years 9-18 years 1-9 years 9-18 years 10-30 U/L 10-30 U/L 10-20 U/L Albumin 0-6 days 6 days - 37 months 37 months - 7 years 7-20 years 2.6-3.6 g/dl 3.4-4.2 g/dl
Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT, SGPT) 3-9 years 9-18 years 1-9 years 9-18 years 10-30 U/L 10-30 U/L 10-20 U/L Albumin 0-6 days 6 days - 37 months 37 months - 7 years 7-20 years 2.6-3.6 g/dl 3.4-4.2 g/dl
Kawasaki Disease: An Update
 Kawasaki Disease: An Update Mary Beth Son, MD Boston Children s Hospital September 23 rd, 2018 No disclosures relevant to this talk Outline of Talk Signs and Symptoms of KD Diagnosis Treatment knowns and
Kawasaki Disease: An Update Mary Beth Son, MD Boston Children s Hospital September 23 rd, 2018 No disclosures relevant to this talk Outline of Talk Signs and Symptoms of KD Diagnosis Treatment knowns and
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute febrile vasculitis that is usually observed in
 Original Article Iraj Mohammadzadeh (MD) 1 Somayyeh Noei (MD) 1 Kazem Babazadeh (MD) 1 Hassan Zamani (MD) 1 Rahim Barari-Savadkoohi (MD) 2 Reza Alizadeh-Navaei (MD) 3* 1. Non-Communicable Pediatric Research
Original Article Iraj Mohammadzadeh (MD) 1 Somayyeh Noei (MD) 1 Kazem Babazadeh (MD) 1 Hassan Zamani (MD) 1 Rahim Barari-Savadkoohi (MD) 2 Reza Alizadeh-Navaei (MD) 3* 1. Non-Communicable Pediatric Research
S u n g Yoon Ch o, M.D., Hye Kyu n g Cho, M.D., Ky You n g Ch o, M.D. Hae S oon Kim, M.D. an d S eju n g S ohn, M.D.
 DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2008.51.9.1023 Korean Journal of Pediatrics Vol. 51, No. 9, 2008 Case report 1)jtj Kawasaki disease presenting as retropharyngeal abscess S u n g Yoon Ch o, M.D., Hye Kyu n g Cho, M.D.,
DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2008.51.9.1023 Korean Journal of Pediatrics Vol. 51, No. 9, 2008 Case report 1)jtj Kawasaki disease presenting as retropharyngeal abscess S u n g Yoon Ch o, M.D., Hye Kyu n g Cho, M.D.,
KAWASAKI DISEASE. What is Kawasaki disease? Causes
 What is Kawasaki disease? Kawasaki disease is a form of vasculitis a family of rare disorders characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which can restrict blood flow and damage vital organs and
What is Kawasaki disease? Kawasaki disease is a form of vasculitis a family of rare disorders characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which can restrict blood flow and damage vital organs and
CASE REPORT: A THREE-MONTH-OLD BOY WITH INCOMPLETE KAWASAKI DISEASE AND EARLY SUPER-GIANT CORONARY ANEURYSM RESULTING IN DETRIMENTAL CARDIAC FUNCTION
 CASE REPORT: A THREE-MONTH-OLD BOY WITH INCOMPLETE KAWASAKI DISEASE AND EARLY SUPER-GIANT CORONARY ANEURYSM RESULTING IN DETRIMENTAL CARDIAC FUNCTION Prakul Chanthong, Pornrawee Plearntummakun, Chodchanok
CASE REPORT: A THREE-MONTH-OLD BOY WITH INCOMPLETE KAWASAKI DISEASE AND EARLY SUPER-GIANT CORONARY ANEURYSM RESULTING IN DETRIMENTAL CARDIAC FUNCTION Prakul Chanthong, Pornrawee Plearntummakun, Chodchanok
Usefulness intravenous immunoglobulin therapy
 Usefulness of initial single intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for Kawasaki disease Toshimasa Nakada Department of Pediatrics, Aomori Prefectural Central Hospital Kawasaki disease Kawasaki disease is
Usefulness of initial single intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for Kawasaki disease Toshimasa Nakada Department of Pediatrics, Aomori Prefectural Central Hospital Kawasaki disease Kawasaki disease is
ISPUB.COM. Kawasaki Disease: An Incomplete Presentation. G Gangadhara Rao, S Sadagopan, J Gnanapragasam CASE REPORT
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatology Volume 7 Number 1 G Gangadhara Rao, S Sadagopan, J Gnanapragasam Citation G Gangadhara Rao, S Sadagopan, J Gnanapragasam.. The Internet Journal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatology Volume 7 Number 1 G Gangadhara Rao, S Sadagopan, J Gnanapragasam Citation G Gangadhara Rao, S Sadagopan, J Gnanapragasam.. The Internet Journal
Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation Which of the following best describes the physical activity performed in my leisure time? A. I perform vigorous physical activity 3X/week for 20 minutes each time B.
Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation Which of the following best describes the physical activity performed in my leisure time? A. I perform vigorous physical activity 3X/week for 20 minutes each time B.
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute, self-limiting
 BNP and NT-pro BNP in KD B-type natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro-bnp in the acute phase of Kawasaki disease Satoru Iwashima, Takamichi Ishikawa Hamamatsu, Japan Background: This study was undertaken
BNP and NT-pro BNP in KD B-type natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro-bnp in the acute phase of Kawasaki disease Satoru Iwashima, Takamichi Ishikawa Hamamatsu, Japan Background: This study was undertaken
Coronary Artery Complications in Pediatric Patients with Kawasaki Disease: A 12-Year National Survey
 Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2013;29:357 365 Pediatric Cardiology Coronary Artery Complications in Pediatric Patients with Kawasaki Disease: A 12-Year National Survey Chun-Yen Chiang, 1 Chung-Han
Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2013;29:357 365 Pediatric Cardiology Coronary Artery Complications in Pediatric Patients with Kawasaki Disease: A 12-Year National Survey Chun-Yen Chiang, 1 Chung-Han
Pyuria is not always sterile in children with Kawasaki disease
 113..117 Pediatrics International (2010) 52, 113 117 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200X.2009.02884.x Original Articleped_2884 Pyuria is not always sterile in children with Kawasaki disease Sheng-Ling Jan, 1,2 Meng-Che
113..117 Pediatrics International (2010) 52, 113 117 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-200X.2009.02884.x Original Articleped_2884 Pyuria is not always sterile in children with Kawasaki disease Sheng-Ling Jan, 1,2 Meng-Che
Infection & Chemotherapy. Original Article. Hye Rim Park 1, Mi Young Han 2, Kyung Lim Yoon 2, Sung-Ho Cha 1, Sung Kyoung Moon 3, and Hae Woon Jung 1
 Original Article https://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2017.49.1.38 Infect Chemother 2017;49(1):38-43 ISSN 2093-2340 (Print) ISSN 2092-6448 (Online) Infection & Chemotherapy Mycoplasma Infection as a Cause of Persistent
Original Article https://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2017.49.1.38 Infect Chemother 2017;49(1):38-43 ISSN 2093-2340 (Print) ISSN 2092-6448 (Online) Infection & Chemotherapy Mycoplasma Infection as a Cause of Persistent
Recurrent Kawasaki disease: USA and Japan
 Recurrent Kawasaki disease: USA and Japan Ryan A. Maddox, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Robert C. Holman, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Ritei Uehara, Utsunomiya City Public Health
Recurrent Kawasaki disease: USA and Japan Ryan A. Maddox, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Robert C. Holman, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Ritei Uehara, Utsunomiya City Public Health
Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University
 Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University SHOCK Definition: Shock is a syndrome = inability to provide sufficient oxygenated blood to tissues. Oxygen
Pediatric emergencies (SHOCK & COMA) Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University SHOCK Definition: Shock is a syndrome = inability to provide sufficient oxygenated blood to tissues. Oxygen
Noncoronary Cardiac Abnormalities Are Associated With Coronary Artery Dilation and With Laboratory Inflammatory Markers in Acute Kawasaki Disease
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 57, No. 1, 2011 2011 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/$36.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2010.08.619
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 57, No. 1, 2011 2011 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/$36.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2010.08.619
Prenatal Exposure to Methyldopa Leading to Hypertensive Crisis and Cardiac Failure in a Neonate
 Prenatal Exposure to Methyldopa Leading to Hypertensive Crisis and Cardiac Failure in a Neonate abstract A 2-week-old infant with normal intracardiac anatomy presented to the emergency department in a
Prenatal Exposure to Methyldopa Leading to Hypertensive Crisis and Cardiac Failure in a Neonate abstract A 2-week-old infant with normal intracardiac anatomy presented to the emergency department in a
Acute heart failure in a patient with lower urinary tract infection Case report of an infection-induced Reverse Takotsubo syndrome
 Acute heart failure in a patient with lower urinary tract infection Case report of an infection-induced Reverse Takotsubo syndrome N.Μoschos, A.Dimitra, E.Tsakiri, D.Stavrianakis, A.Nouli CARDIOLOGY DEPARTMENT
Acute heart failure in a patient with lower urinary tract infection Case report of an infection-induced Reverse Takotsubo syndrome N.Μoschos, A.Dimitra, E.Tsakiri, D.Stavrianakis, A.Nouli CARDIOLOGY DEPARTMENT
Continuous Infusion of Cyclosporin A in Intravenous Immunoglobulin Resistant Kawasaki Disease Patients
 Case Report Continuous Infusion of Cyclosporin A in Intravenous Immunoglobulin Resistant Kawasaki Disease Patients Takaomi Minami, Hirohiko Shiraishi, Kensuke Oka, Jun Odaka, Tomoyuki Ishii, Akiko Takata,
Case Report Continuous Infusion of Cyclosporin A in Intravenous Immunoglobulin Resistant Kawasaki Disease Patients Takaomi Minami, Hirohiko Shiraishi, Kensuke Oka, Jun Odaka, Tomoyuki Ishii, Akiko Takata,
ARTICLE. Prevalence of Coronary Artery Lesions on the Initial Echocardiogram in Kawasaki Syndrome
 ARTICLE Prevalence of Coronary Artery Lesions on the Initial Echocardiogram in Kawasaki Syndrome Aryeh Z. Baer, MD; Lorry G. Rubin, MD; Craig A. Shapiro, BA; Sunil K. Sood, MD; Sujatha Rajan, MD; Yehuda
ARTICLE Prevalence of Coronary Artery Lesions on the Initial Echocardiogram in Kawasaki Syndrome Aryeh Z. Baer, MD; Lorry G. Rubin, MD; Craig A. Shapiro, BA; Sunil K. Sood, MD; Sujatha Rajan, MD; Yehuda
Comparison of Different Types and Regimens of Intravenous Immune Globulin (IVIG) in Patients with Kawasaki Disease
 Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2004;20:15 20 Pediatric Cardiology Comparison of Different Types and Regimens of Intravenous Immune Globulin (IVIG) in Patients with Kawasaki Disease Chi-Ming Liang, 1
Original Article Acta Cardiol Sin 2004;20:15 20 Pediatric Cardiology Comparison of Different Types and Regimens of Intravenous Immune Globulin (IVIG) in Patients with Kawasaki Disease Chi-Ming Liang, 1
Rare Refractory Kawasaki Disease in an Adolescent Boy With Cardiac and Diffuse Coronary Artery Involvement
 CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION 341 :341-5 Rare Refractory Kawasaki Disease in an Adolescent Boy With Cardiac and Diffuse Coronary Artery Involvement Rima Šileikienė 1, Jolanta Kudzytė 1, Antanas Jankauskas
CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION 341 :341-5 Rare Refractory Kawasaki Disease in an Adolescent Boy With Cardiac and Diffuse Coronary Artery Involvement Rima Šileikienė 1, Jolanta Kudzytė 1, Antanas Jankauskas
Immunoadsorption in Lupus
 Immunoadsorption in Lupus Myocarditis Griveas I. 1, Visvardis G. 1, Zarifis I. 2, Papadopoulou D. 1, Manou E. 1, Kyriklidou P. 1, Nouskas I. 2, Mitsopoulos E. 1, Sourgounis A. 2, Meimaridou D. 1, Ginikopoulou
Immunoadsorption in Lupus Myocarditis Griveas I. 1, Visvardis G. 1, Zarifis I. 2, Papadopoulou D. 1, Manou E. 1, Kyriklidou P. 1, Nouskas I. 2, Mitsopoulos E. 1, Sourgounis A. 2, Meimaridou D. 1, Ginikopoulou
Myocardial Infarction
 Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
AHA Scientific Statement
 AHA Scientific Statement Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term Management of Kawasaki Disease A Statement for Health Professionals From the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis and Kawasaki Disease,
AHA Scientific Statement Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term Management of Kawasaki Disease A Statement for Health Professionals From the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis and Kawasaki Disease,
Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician
 Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician Sepsis Continuum 1 Sepsis Continuum SIRS = 2 or more clinical criteria, resulting in Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Sepsis = SIRS + proven/suspected
Staging Sepsis for the Emergency Department: Physician Sepsis Continuum 1 Sepsis Continuum SIRS = 2 or more clinical criteria, resulting in Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome Sepsis = SIRS + proven/suspected
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Table S1: Number and percentage of patients by age category Distribution of age Age
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Table S1: Number and percentage of patients by age category Distribution of age Age
Two Cases of Super-Giant Coronary Aneurysms after Kawasaki Disease
 Case Report Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Two Cases of Super-Giant Coronary neurysms after Kawasaki Disease Joowon Lee, MD, Gi eom Kim, MD, o Sang Kwon, MD, Eun
Case Report Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Two Cases of Super-Giant Coronary neurysms after Kawasaki Disease Joowon Lee, MD, Gi eom Kim, MD, o Sang Kwon, MD, Eun
Severe Dengue Infection in ICU. Shirish Prayag MD, FCCM Pune, India
 Severe Dengue Infection in ICU Shirish Prayag MD, FCCM Pune, India Greetings from India Declaration Honararia from MSD, Astra Zenecea, Fresenius Kabi, Pfizer, Intas, Glenmark for conducting lectures. No
Severe Dengue Infection in ICU Shirish Prayag MD, FCCM Pune, India Greetings from India Declaration Honararia from MSD, Astra Zenecea, Fresenius Kabi, Pfizer, Intas, Glenmark for conducting lectures. No
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT
 HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
HEMORRHAGIC BULLOUS HENOCH- SCHONLEIN PURPURA: A CASE REPORT Nirmala Ponnuthurai, Sabeera Begum, Lee Bang Rom Paediatric Dermatology Unit, Institute of Paediatric, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia Abstract
Tables of Normal Values (As of February 2005)
 Tables of Normal Values (As of February 2005) Note: Values and units of measurement listed in these Tables are derived from several resources. Substantial variation exists in the ranges quoted as normal
Tables of Normal Values (As of February 2005) Note: Values and units of measurement listed in these Tables are derived from several resources. Substantial variation exists in the ranges quoted as normal
The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the cardiovascular system.
 LAB 3: THE MUSCLE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the cardiovascular system. The cases we will cover are: A. Atherosclerosis Refer to virtual slide p_8, should
LAB 3: THE MUSCLE AND CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of the cardiovascular system. The cases we will cover are: A. Atherosclerosis Refer to virtual slide p_8, should
5/9/2016. The Heart of a Child with Inflammatory Dilemmas. Header Text
 Header Text The Heart of a Child with Inflammatory Dilemmas Trudy A. Pierick, ARNP Pediatric Cardiology University of Iowa Children s Hospital No financial disclosures Objectives Identify similarities
Header Text The Heart of a Child with Inflammatory Dilemmas Trudy A. Pierick, ARNP Pediatric Cardiology University of Iowa Children s Hospital No financial disclosures Objectives Identify similarities
HISTORICAL ASPECTS CLINICAL FEATURES...405
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, July 1998, p. 405 414 Vol. 11, No. 3 0893-8512/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Kawasaki Syndrome ANNE H. ROWLEY 1 * AND
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, July 1998, p. 405 414 Vol. 11, No. 3 0893-8512/98/$04.00 0 Copyright 1998, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Kawasaki Syndrome ANNE H. ROWLEY 1 * AND
1 Week Followup 5/27/2014. Nursing Home/Assisted Care Hospice Another hospital Rehabilitation Facility Unknown
 1 Week Followup t Started Please answer all questions considering all time since the previous visit and current follow-up date. Print this Form Followup Status t Started Select one of the following Inpatient
1 Week Followup t Started Please answer all questions considering all time since the previous visit and current follow-up date. Print this Form Followup Status t Started Select one of the following Inpatient
Disclosure Information : No conflict of interest
 Intravenous nicorandil improves symptoms and left ventricular diastolic function immediately in patients with acute heart failure : a randomized, controlled trial M. Shigekiyo, K. Harada, A. Okada, N.
Intravenous nicorandil improves symptoms and left ventricular diastolic function immediately in patients with acute heart failure : a randomized, controlled trial M. Shigekiyo, K. Harada, A. Okada, N.
Juvenile Chronic Arthritis
 Juvenile Chronic Arthritis Dr. Christa Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK), Member Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Childhood Arthritis JCA/JIA/JRA Remember Acute rheumatic
Juvenile Chronic Arthritis Dr. Christa Visser MBChB MMed (Med Phys) Diploma Musculoskeletal Medicine (UK), Member Society of Orthopaedic Medicine (UK) Childhood Arthritis JCA/JIA/JRA Remember Acute rheumatic
Kawasaki syndrome (KS) is an acute, vasculitic
 Delayed Diagnosis of Kawasaki Syndrome: An Analysis of the Problem Marsha S. Anderson, MD; James K. Todd, MD; and Mary P. Glodé, MD ABSTRACT. Objective. Most pediatric providers in Colorado are familiar
Delayed Diagnosis of Kawasaki Syndrome: An Analysis of the Problem Marsha S. Anderson, MD; James K. Todd, MD; and Mary P. Glodé, MD ABSTRACT. Objective. Most pediatric providers in Colorado are familiar
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute systemic vasculitis of unknown etiology that primarily affects small- and mediumsized
 N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide and Risk of Coronary Artery Lesions and Resistance to Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Kawasaki Disease Ken Yoshimura, MD, Takahisa Kimata, MD, Kenji Mine, MD, Takamichi
N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide and Risk of Coronary Artery Lesions and Resistance to Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Kawasaki Disease Ken Yoshimura, MD, Takahisa Kimata, MD, Kenji Mine, MD, Takamichi
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO
 POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO Selection Examination for Enrolment to the in-service Training Programme in Postgraduate Certificate in Basic Laboratory Sciences leading to the
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO Selection Examination for Enrolment to the in-service Training Programme in Postgraduate Certificate in Basic Laboratory Sciences leading to the
Predictors of Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG) Resistance in Children with Kawasaki Disease in Calabria Region, Italy
 http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 9027-9036) Predictors of Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG) Resistance in Children with Kawasaki Disease in Calabria Region, Italy *Valentina Talarico 1,
http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Original Article (Pages: 9027-9036) Predictors of Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG) Resistance in Children with Kawasaki Disease in Calabria Region, Italy *Valentina Talarico 1,
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI).
 1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING
 AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING Diagnosis and Treatment Goals Aimee Borazanci, MD BNI Neuroimmunology Objectives Give an update on the causes for admission, clinical features, and outcomes of
AUTOIMMUNE DISORDERS IN THE ACUTE SETTING Diagnosis and Treatment Goals Aimee Borazanci, MD BNI Neuroimmunology Objectives Give an update on the causes for admission, clinical features, and outcomes of
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Clinical perspective It was recently discovered that small RNAs, called micrornas, circulate freely and stably in human plasma. This finding has sparked interest in the potential
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Clinical perspective It was recently discovered that small RNAs, called micrornas, circulate freely and stably in human plasma. This finding has sparked interest in the potential
Kawasaki Disease in the Older Child
 Kawasaki Disease in the Older Child Tarek Momenah, MBBS, DCH, FAAP, FRCP; Shubhayan Sanatani, BSc, MD, FRCP; Jim Potts, PhD; George G. S. Sandor, MB, ChB, DCH, FRCP, FACC; Derek G. Human, MA, BM, BCh,
Kawasaki Disease in the Older Child Tarek Momenah, MBBS, DCH, FAAP, FRCP; Shubhayan Sanatani, BSc, MD, FRCP; Jim Potts, PhD; George G. S. Sandor, MB, ChB, DCH, FRCP, FACC; Derek G. Human, MA, BM, BCh,
CLINICAL REVIEW. Kawasaki disease. Anthony Harnden, 1 Masato Takahashi, 2 David Burgner 3. For the full versions of these articles see bmj.
 For the full versions of these articles see bmj.com CLINICAL REVIEW Kawasaki disease Anthony Harnden, 1 Masato Takahashi, 2 David Burgner 3 1 Department of Primary Health Care, University of Oxford, Headington,
For the full versions of these articles see bmj.com CLINICAL REVIEW Kawasaki disease Anthony Harnden, 1 Masato Takahashi, 2 David Burgner 3 1 Department of Primary Health Care, University of Oxford, Headington,
Corticosteroids for the treatment of Kawasaki disease in children(review)
 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Corticosteroids for the treatment of Kawasaki disease in children(review) Wardle AJ, Connolly GM, Seager MJ, Tulloh RMR Wardle AJ, Connolly GM, Seager MJ, Tulloh
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Corticosteroids for the treatment of Kawasaki disease in children(review) Wardle AJ, Connolly GM, Seager MJ, Tulloh RMR Wardle AJ, Connolly GM, Seager MJ, Tulloh
PAEDIATRICS. Elis Lee Resident KK Hospital
 PAEDIATRICS Elis Lee Resident KK Hospital CASE 1 From the question: (1) Acute onset (two-day history) (2) One limb (right leg) (3) Pain APPROACH TO LIMB PAIN/LIMPING CHILD Trauma v.s. Non-trauma Joint
PAEDIATRICS Elis Lee Resident KK Hospital CASE 1 From the question: (1) Acute onset (two-day history) (2) One limb (right leg) (3) Pain APPROACH TO LIMB PAIN/LIMPING CHILD Trauma v.s. Non-trauma Joint
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP): important respiratory pathogen in children that cause many upper and lower respiratory tract diseases, including
 KHOA DICH VU HO HAP - Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP): important respiratory pathogen in children that cause many upper and lower respiratory tract diseases, including wheezing, coryza, bronchopneumonia. -
KHOA DICH VU HO HAP - Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP): important respiratory pathogen in children that cause many upper and lower respiratory tract diseases, including wheezing, coryza, bronchopneumonia. -
