King s Research Portal
|
|
|
- Joleen Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 King s Research Portal DOI: /j.artres Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Mills, C., Govoni, V., Casagrande, M. L., Faconti, L., Webb, A. J., & Cruickshank, J. K. (2015). Design and progress of a factorial trial testing the effect of spironolactone and inorganic nitrate on arterial function in people at risk of or with type 2 diabetes. Artery Research, 12, DOI: /j.artres Citing this paper Please note that where the full-text provided on King's Research Portal is the Author Accepted Manuscript or Post-Print version this may differ from the final Published version. If citing, it is advised that you check and use the publisher's definitive version for pagination, volume/issue, and date of publication details. And where the final published version is provided on the Research Portal, if citing you are again advised to check the publisher's website for any subsequent corrections. General rights Copyright and moral rights for the publications made accessible in the Research Portal are retained by the authors and/or other copyright owners and it is a condition of accessing publications that users recognize and abide by the legal requirements associated with these rights. Users may download and print one copy of any publication from the Research Portal for the purpose of private study or research. You may not further distribute the material or use it for any profit-making activity or commercial gain You may freely distribute the URL identifying the publication in the Research Portal Take down policy If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact librarypure@kcl.ac.uk providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. Download date: 15. Dec. 2017
2 *Manuscript Click here to view linked References Design and progress of a factorial trial testing the effect of spironolactone and inorganic nitrate on arterial function in people at risk of or with type 2 diabetes *Charlotte E Mills a,b, Virginia Govoni a,b, Maria Linda Casagrande a,b,, Luca Faconti a,b Andrew J Webb b,c, J Kennedy Cruickshank a,b a Cardiovascular Medicine group, Division of Diabetes and Nutritional Sciences, King s College, 4 th Floor Franklin Wilkins Building, London, UK b Biomedical Research Centre, Clinical Research Facility, 4 th Floor, North Wing, St Thomas Hospital, Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK c Department of Clinical Pharmacology, British Heart Foundation Centre, Cardiovascular Division, 4 th Floor, North Wing, St Thomas Hospital, King s College London, UK *Corresponding author: Charlotte E Mills; King s College London, 4 th floor Franklin Wilkins Building, Stamford Street, London. SE1 0NH; charlotte.1.mills@kcl.ac.uk; + 44 (0) Running title: Arterial function: VaSera trial design Funding acknowledgement: This work was funded by an unrestricted grant from Fukuda Denshi Co., Ltd. Clinical trial registration information: UK Clinical Research Network Portfolio Database:
3 Abstract Background Arterial stiffness (AS), as pulse wave velocity (PWV), is a powerful independent predictor of cardiovascular events and commonly complicates type 2 diabetes (T2D). This trial aims to test if AS, measured by the VaSera machine as cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI) and by Arteriograph measuring central PWV, can be reduced by spironolactone and/or inorganic nitrate from beetroot juice independently of blood pressure (BP) in those with or at risk of T2D. Methods A factorial design, double blind, randomised controlled trial in year old men and women clinically diagnosed with T2D or at risk of it (body mass index (BMI) > 27 kg.m -2, positive family history or glucose intolerance). The study lasts up to 36 weeks with daily intervention of either 50 mg spironolactone (intervention) or 16 mg doxazosin (control), and beetroot juice with 400 mg (9 mmol) inorganic nitrate (intervention) or placebo beetroot juice, 0 mg nitrate (control). Non-invasive AS measurements are carried out at baseline and then at 12-week intervals thereafter. Results To date, 95 participants have been consented and screened, 19 of these were not suitable or not willing to participate so that 73 have been randomised with 9 participants screened as eligible and awaiting randomisation. 53 participants have completed the study. Mean baseline and follow up measures of cardiac-ankle and cardiac-aortic bifurcation PWV and BP have been straightforward. Conclusion This is a proof-of-principle trial to alter AS independent of BP in a patient sample at high cardiovascular risk. [247 words]
4 Key words: Arterial stiffness; pulse wave velocity (PWV); cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI); spironolactone; beetroot; nitrate.
5 Background Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) is a chronic disease, possibly due to excess fat accumulation with inflammatory damage to blood vessels, currently diagnosed with elevated blood glucose. The rapid increase in T2D worldwide is due to both the obesity epidemic and the aging population [1]. Cardiovascular complications of T2D tend to emerge relatively early, with 54% of deaths in T2D patients being attributed to cardiovascular disease [2]. In these patients, deposition of collagen matrixes in the media of blood vessels is thought to cause arterial stiffening [3]. Aldosterone, the mineralocorticoid steroid hormone produced by the adrenal gland increasing salt and water retention, is involved in blood pressure (BP) regulation. Increasing evidence suggests that aldosterone causes collagen deposition in vascular walls [4, 5], hence promoting arterial stiffening. Spironolactone is a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist used primarily as a diuretic, but noted for its ability to control BP, although not formally licensed for this indication [6]. Although its BP lowering effects are established, the drug has also been shown to reduce arterial stiffening, measured as pulse wave velocity (PWV) in hypertensive diabetic patients in a small study (n= 10); however, how far this PWV effect was related to BP reduction is unclear [7]. A longer term study reported that spironolactone at 25 mg/day for 40 weeks reduced PWV independently of BP, although the latter still fell by 11 ± 12 mmhg, in addition to a reduction in left ventricular mass [8]. Improving vascular function by dietary means is becoming increasingly appealing for the public and clinicians alike. Foods rich in inorganic nitrate, such as spinach and beetroot have been shown to exhibit beneficial effects on the vascular system such as improving endothelial dysfunction [11], inhibiting platelet aggregation [9] and adhesion [10] in the endothelium and improving endothelial dysfunction [11]. Further,
6 nitrates are becoming an established means of reducing BP, as found in short term randomised controlled trials (RCTs) [12-15]. Nitrate containing foods are thought to work by uptake of their naturally occurring nitrate into the entero- salivary circulation and subsequent conversion via the nitrate- nitrite- nitric oxide (NO) pathway, with NO, the ubiquitous vasodilator from endothelium, mediating the reduction in BP. Less work, however, has investigated the effect of dietary nitrate on arterial stiffening; an acute investigation using a high nitrate spinach meal did not alter PWV in healthy volunteers [16], however a study in drug naive grade one hypertensive patients did show a reduction in PWV after beetroot juice ingestion [17]. PWV has long been an established technique of assessing arterial stiffness. While applanation tonometry has been the most widely used method to measure what is known as carotid-femoral (cf) PWV [18], as those vessel sites are used for measurement, other less intrusive means are now available. These cuff based measurements, Arteriograph and Mobil-o-graph (which measure central or aortic (ao) PWV) are becoming increasingly popular due to ease of application, the reduced amount of training required, comfort for patients and seemingly comparing well against other methods, including magnetic resonance (MR), once arterial path length is calibrated [19]. An alternative device, the VaSera machine (by Fukuda Denshi) measures cardio- ankle PWV, expressed as the cardio- ankle vascular index (CAVI) to reduce dependence from ambient BP [20]. Here, we describe the design of our VaSera trial, assessing the efficacy of spironolactone and dietary nitrate (as beetroot juice) to alter arterial stiffness, primarily as measured by CAVI, independently of BP. Study design and methods
7 Overall design The objective is to test, in a factorial designed RCT, whether spironolactone, up to 50mg/ day and/or dietary nitrate, up to 9 mmol nitrate per day as a 70mL shot of Beet-it or Beet-it Sport beetroot juice, (compared with up to 16mg/ day doxazosin and identical 70mL nitrate free juice respectively) reduces arterial stiffness after up to 6 months, measured as CAVI by the VaSera machine and as aopwv by the Arteriograph, in patients diagnosed with or at risk of T2D (see Table 1). After the initial consenting and screening/ familiarisation visit, visit 1 (V1), if the criteria were met (as below), patients were invited to return for a randomisation visit, visit 2 (V2), to be allocated to one of the four groups (Table 1). Participants and those running the study are blinded to the intervention allocation, which was block randomised in groups of six, performed and held by an independent party. At V2 baseline vascular measurements (CAVI, PWV and echocardiogram) are performed, in addition to baseline blood, spot urine and 24 hour urine collection for various biochemical assessments (HbA1c, glucose, renal function as well as a urinary steroid metabolite profile); 24 hour BP and PWV monitoring is also performed before the intervention is started. Study medication and juice is given at this visit; titrated up to 25 mg/ day spironolactone or 4 mg/ day doxazosin and beetroot juice with 4.5 mmol nitrate/ day or control 0 mmol nitrate/ day. A check up visit for renal function and well being occurs 2 weeks into the study (V3), then again with PWV and BP at 8 weeks after randomisation (V4). At 12 weeks post randomisation (V5) a further visit with vascular measures and detailed biochemical assessment and repeat 24 hour monitoring is carried out as at V2. At this visit, the medication dose should be doubled to 50 mg/ day (spironolactone) or 16 mg/ day (doxazosin) with a more concentrated beetroot juice (9 mmol nitrate /day or control, 0 mmol nitrate/ day), depending on biochemical
8 and BP data at check up visits. Visits 6 and 7 (V6, V7 at 24 and 36 weeks respectively), follow the same assessments as at V2 and V5; at one of these visits the study is terminated, depending on the length agreed with the participant at the start of the study, with study duration being shorter as recruitment nears its end (Figure 1). The study was reviewed and approved by Central London National Research Ethics Service (NRES). Participant eligibility We aim to randomise up to 120 people with or at risk of T2D from the local community (South London, UK) with a broad inclusion criteria for eligibility. Recruitment is carried out through referral from hypertension and diabetes clinics in secondary care, appropriate contact with local health centers and general practices and advertisements. The aim is to recruit approximately equal numbers of men and women and equal numbers with T2D and those at risk of T2D. The following inclusion and exclusion criteria are followed on recruitment of participants. Inclusion criteria: - Age years - Previously clinically diagnosed T2D or at risk of T2D (body mass index (BMI) 27 kg.m -2, a positive family history or glucose intolerance 2 hour after (75 g challenge) - Ability to understand the protocol and willingness to comply with it Exclusion criteria: - Chronic illness of any type that may interfere with participation - Previous adverse reaction to spironolactone or doxazosin - Known allergy to beetroot - Impaired renal function (egfr < 45 ml.min -1 )
9 - HbA1c > 11% or fasting random glucose > 12 mmol.l -1 - Being pregnant or breastfeeding for the duration of the study - Atrial fibrillation Arterial stiffness techniques AS is measured by a variety of devices, which have demonstrated good repeatability (between V1 and V2) at V1, V2, V5, V6, and V7 to assess the efficacy of the interventions on AS. Participants are measured using: i) The VaSera VS-1500N (Fukuda Denshi co., Ltd, Japan), a four- cuff device (placed over the upper arms, as with a standard BP cuff, and above both ankles) measuring stiffness from the heart to the ankles, using a microphone to detect aortic valve closure (the 2 nd heart sound) expressed as CAVI a value calculated from PWV using the stiffness parameter, β. The CAVI formula (Figure 2), which greatly reduces the dependence of PWV on ambient BP, aims to give a BP independent estimate of arterial stiffness. A change in CAVI is the primary outcome of the study. ii) The Arteriograph 24 TM (Tensiomed Kft. Hungary), which measures aopwv using a non invasive, one cuff method. The device uses the return time (difference between the first and reflected systolic peaks) and distance between sternal notch and symphsis to calculate aopwv. The device has been calibrated against cfpwv and MR derived PWV with length calibration [19]. iii) The Vicorder (SMT medical GmbH & Co. KG, Germany) is another non invasive cuff based technique to measure carotid-femoral cfpwv; one cuff, a small
10 band on the maximal carotid pulsation on one side of the neck only to detect carotid pulse waves (and easily striped off if the participant feels claustrophobic), the other around the upper thigh to detect femoral pulse waves. Hypothesis We hypothesise that between spironolactone and doxazosin (which both lower BP), spironolactone will further alter CAVI by 0.4 units and CAVI s cardiac-brachial PWV and aopwv by 0.5 ms -1 with a minimal difference in BP. Further, we anticipate that the oral inorganic nitrate supplement as the beetroot juice will promote longer term generation of vascular nitric oxide (measurable as increased circulating nitrite) and also, independently of the drug comparison arm, reduce PWV by 0.5 ms - 1, again after adjusting for any change in BP, compared with the effect of the control juice with no nitrate. We hypothesize that there will be an additive effect 1 ms -1 of both the spironolactone and nitrate in the combined arm, compared with neither on the assessed vascular parameters. Statistical considerations & power Sufficient data were not available from which to calculate sample sizes directly for CAVI only. Therefore to detect a reduction in CAVI, of 20% (± 8% standard deviation) with minimum 80% power, at p <0.05 over 6 months of on the study, we based calculations on previous short term studies on BP with beetroot juice [21, 22] and a long term study on aopwv and spironolactone [8], at similar power, and estimated that 24 participants per box of the 2x2 table are required. We therefore aim to recruit 30 patients per group based on a 20% drop out rate, to generate 25 people per box to finish the trial.
11 Results Participant descriptives On writing this manuscript, 95 patients had been consented, of which 7 were unsuitable due to uncontrolled diabetes, adverse reactions to the study interventions and being unable to commit. A dropout rate of 14% between consent and randomisation and 7% after randomisation has been observed, see CONSORT diagram, Figure 3. To that date, 53 participants have completed the entire study. The baseline descriptives of participants who entered to date at randomisation in Table 2 (n=73) show that we have recruited slightly more men than women, and more with clinically diagnosed T2D than those at risk. We classified ethnicity by local populations known to be at higher risk of diabetes (West African and African Caribbean, with relatively few South Asian people living locally). Considering the associations with vascular health, despite recruiting participants with or at risk of T2D the mean blood pressure is not elevated; our participants are not clinically defined as hypertensive. However, the mean PWV and CAVI of the participants, as measured by all methods suggest there is some stiffening of the arteries, for the men assessed this is even above the reference value considering their age [23]. Study interventions Of the 73 participants who have been randomised onto the study, there have been 103 reported adverse events (from 57 participants) post randomisation. Of these events 23 (from 12 participants) are considered to be attributed to the interventions, with
12 common reported events being dizziness/lethargy (13% of randomised participants), nausea/ sickness or diarrhoea (4%), incontinence (4%), rash (3%). No participants have dropped out of the study due to reported adverse effects from the interventions; all effects were controlled by reduction in dose or by stopping one of the interventions. In addition to these there have been six reported serious adverse events post randomisation with none of these being attributed to the interventions. Conclusions This study was designed to investigate the effect of inorganic nitrate from beetroot juice and spironolactone on arterial stiffness, independent of blood pressure in those with or at risk of T2D. To date this study has proven easy to recruit for with a low dropout rate (7% after randomisation). Participants have been happy taking the interventions with minimal consequential ill effects, and have generally been committed to the study for the duration. Conflict of interest statement JKC and AW report an unrestricted grant from Fukuda Denshi co. Ltd to support this work and JKC fees for lecturing. AW also reports a small share holding in Heartbeet Ltd. All other authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organisation or entity with financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
13 References 1. Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for Diabetes care 2004; 27(5): Morrish NJ, Wang SL, Stevens LK, Fuller JH, Keen H. Mortality and causes of death in the WHO Multinational Study of Vascular Disease in Diabetes. Diabetologia 2001; 44 Suppl 2: S Airaksinen KE, Salmela PI, Linnaluoto MK, Ikaheimo MJ, Ahola K, Ryhanen LJ. Diminished arterial elasticity in diabetes: association with fluorescent advanced glycosylation end products in collagen. Cardiovasc Res 1993; 27(6): Modena MG, Aveta P, Menozzi A, Rossi R. Aldosterone inhibition limits collagen synthesis and progressive left ventricular enlargement after anterior myocardial infarction. Am Heart J 2001; 141(1): Zhang L, Hao JB, Ren LS, Ding JL, Hao LR. The aldosterone receptor antagonist spironolactone prevents peritoneal inflammation and fibrosis. Laboratory Invest 2014; 94 (8): Chapman N, Dobson J, Wilson S, Dahlof B, Sever PS, Wedel H, et al. Effect of Spironolactone on Blood Pressure in Subjects With Resistant Hypertension. Hypertension 2007; 49: Davies J, Gavin A, Band M, Morris A, Struthers A. Spironolactone reduces brachial pulse wave velocity and PIIINP levels in hypertensive diabetic patients. Brit J Clin Pharmacol 2005; 59(5): Edwards NC, Steeds RP, Stewart PM, Ferro CJ, Townend JN. Effect of spironolactone on left ventricular mass and aortic stiffness in early-stage chronic kidney disease: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009; 54(6):
14 9. Bondonno CP, Yang X, Croft KD, Consindine MJ, Ward NC, Rich L et al. Flavonoid-rich apples and nitrate-rich spinach augment nitric oxide status and improve endothelial function in healthy men and women: a randomized controlled trial. Free Radical Bio Med 2012; 52(1): Radomski MW, Palmer RM and Moncada S. An L-arginine/nitric oxide pathway present in human platelets regulates aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1990; 87(13): Radomski MW, Palmer RM and Moncada S. Endogenous nitric oxide inhibits human platelet adhesion to vascular endothelium. Lancet 1987; 2(8567): Webb AJ, Patel N, Loukogeorgakis S, Okorie M, Aboud Z, Misra S et al. Acute blood pressure lowering, vasoprotective, and antiplatelet properties of dietary nitrate via bioconversion to nitrite. Hypertension 2008; 51(3): Coles L and Clifton P. Effect of beetroot juice on lowering blood pressure in free-living, disease-free adults: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr J 2012; 11: Kapil V, Milsom AB, Okorie M, Maleki- Toyserkani S, Akram F, Rehman F, et al. Inorganic nitrate supplementation lowers blood pressure in humans: role for nitritederived NO. Hypertension 2010; 56(2): Hobbs DA, Kaffa N, George TW, Methven L, Lovegrove J. Blood pressurelowering effects of beetroot juice and novel beetroot-enriched bread products in normotensive male subjects. Brit J Nutr 2012; 108(11): Liu AH, Bondonno CP, Croft KD, Puddey IB, Woodman RJ, Rich L, et al. Effects of a nitrate-rich meal on arterial stiffness and blood pressure in healthy volunteers. Nitric Oxide 2013; 35:
15 17. Ghosh SM, Kapil V, Fuentes-Calvo I, Bubb KJ, Pearl V, Milsom AB, et al. Enhanced vasodilator activity of nitrite in hypertension: Critical role for erythrocytic xanthine oxidoreductase and translational potential. Hypertension 2013; 61(5): Laurent S, Cockcroft J, Van Bortel L, Boutouyrie P, Giannattasio C, Hayoz D, et al. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur Heart J 2006; 27(21), Rezai MR, Wallace AM, Sattar N, Sattar N, Finn JD, Wu FC, et al. Ethnic differences in aortic pulse wave velocity occur in the descending aorta and may be related to vitamin D. Hypertension 2011; 58(2): Shirai K, Utino J, Otsuka K, Takata M., A novel blood pressure-independent arterial wall stiffness parameter; cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI). J Atheroscler Thromb, (2): p Kapil V, Milsom AB, Okorie M, Maleki- Toyserkani S, Akram F, Rehman F, et al. Inorganic nitrate supplementation lowers blood pressure in humans: role for nitritederived NO. Hypertension 2010; 56(2): Webb AJ, Patel N, Loukogeorgakis S, Okorie M, Aboud Z, Misra S, et al. Acute blood pressure lowering, vasoprotective, and antiplatelet properties of dietary nitrate via bioconversion to nitrite. Hypertension 2008; 51(3): Mattace-Raso F, Hoffman A, Verwoert GC, Wittemana JC, Wilkinson I, Cockcroft J, et al. Determinants of pulse wave velocity in healthy people and in the presence of cardiovascular risk factors: 'establishing normal and reference values'. Eur Heart J 2010; 31(9):
16 TABLES AND FIGURES Table 1. Factorial design of the VaSera trial, with number of participants to be randomised to each arm Nitrate juice (4.5 9 mmol nitrate/day) Placebo juice (0 mmol nitrate/day) Total (n) Spironolactone ( mg/day) Doxazosin (4-16 mg/ day) Total (n)
17 Table 2. Baseline characteristics of 52 participants randomised to date Parameter Men ± SD Women ± SD n (%) Age (years) 58 ± ± 11 Weight (kg) 96.3 ± ± 19.3 BMI (kg.m -2 ) 32 ± 6 34 ± 7 Waist circumference (cm) 109 ± ± 16 Type 2 diabetes (%) Ethnicity (%): European African Caribbean 4 18 West African 4 18 Other SBP (mm Hg) 133 ± ± 16 DBP (mm Hg) 78 ± ± 10 Pulse (BPM) 70 ± ± 12 aosbp (mm Hg) 128 ± ± 18 aoaix (%) 25 ± ± 14 aopwv (m.s -1 ) 9.21 ± ± 1.67 cfpwv (m.s -1 ) a 8.90 ± ± 1.37 CAVI (units) 8.40 ± ± 0.95
18 a men, n=27 and women, n=21 for this measurement BMI, body mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; BPM, beats per minute; ao, aortic (central); cf, carotid-femoral; ca, cardio-ankle; CAVI, cardio-ankle vascular index.
19 Figure 1. Study flow diagram a Multiple arterial stiffness measurements; central (ao) pulse wave velocity (PWV) by Arteriograph, carotid femoral (cf)pwv by Vicorder and cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI) by VaSera, in addition to echocardiogram and blood pressure monitoring. b One off aopwv by Arteriograph PWV; pulse wave velocity, BP; blood pressure Figure 2. Formulas to derive cardio- ankle vascular index (CAVI) β; stiffness parameter, Ps; systolic pressure, Pd; diastolic pressure, D; diameter, PWV; pulse wave velocity, P; pulse pressure, ρ; blood density, CAVI; cardio-ankle vascular index Figure 3. CONSORT (consolidated standards of reporting trials) diagram Based on inclusion/ exclusion criteria patients are diagnosed with or at risk of type 2 diabetes (with BMI 27 kg.m -2 or glucose intolerance). HbA1c are to be < 11% or fasting glucose <12 mmol.l -1 with good renal function (egfr> 45mL.min -1 )
20 Figure 1 Click here to download high resolution image
21 Figure 2 Click here to download high resolution image
22 Figure 3 Click here to download high resolution image
King s Research Portal
 King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.10.093 Document Version Early version, also known as pre-print Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA):
King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.10.093 Document Version Early version, also known as pre-print Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA):
King s Research Portal
 King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2016.03.102 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Giovannini, P., Howes,
King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1016/j.dib.2016.03.102 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Giovannini, P., Howes,
Allopurinol reduces left ventricular hypertrophy and endothelial dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease
 Allopurinol reduces left ventricular hypertrophy and endothelial dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease Michelle P Kao, Donald S Ang, Steve Gandy, Chim C Lang, Allan D Struthers Division of
Allopurinol reduces left ventricular hypertrophy and endothelial dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease Michelle P Kao, Donald S Ang, Steve Gandy, Chim C Lang, Allan D Struthers Division of
The Acute Effects of Beetroot Powder and Arginine Supplementation on Blood Pressure in Normotensive Adults
 Loma Linda University TheScholarsRepository@LLU: Digital Archive of Research, Scholarship & Creative Works Loma Linda University Research Reports 5-17-2017 The Acute Effects of Beetroot Powder and Arginine
Loma Linda University TheScholarsRepository@LLU: Digital Archive of Research, Scholarship & Creative Works Loma Linda University Research Reports 5-17-2017 The Acute Effects of Beetroot Powder and Arginine
Theoretical and practical questions in the evaluation of arterial function Miklós Illyés MD. Ph.D.
 Theoretical and practical questions in the evaluation of arterial function Miklós Illyés MD. Ph.D. TensioMed Arterial Stiffness Centre, Budapest Heart Institute, Faculty of Medicine, University of Pécs
Theoretical and practical questions in the evaluation of arterial function Miklós Illyés MD. Ph.D. TensioMed Arterial Stiffness Centre, Budapest Heart Institute, Faculty of Medicine, University of Pécs
Estimated Pulse Wave Velocity Calculated from Age and Mean Arterial Blood Pressure
 Received: August 19, 2016 Accepted after revision: November 4, 2016 Published online: December 1, 2016 2235 8676/16/0044 0175$39.50/0 Mini-Review Estimated Pulse Wave Velocity Calculated from Age and Mean
Received: August 19, 2016 Accepted after revision: November 4, 2016 Published online: December 1, 2016 2235 8676/16/0044 0175$39.50/0 Mini-Review Estimated Pulse Wave Velocity Calculated from Age and Mean
Clinical application of Arterial stiffness. pulse wave analysis pulse wave velocity
 Clinical application of Arterial stiffness pulse wave analysis pulse wave velocity Arterial system 1. Large arteries: elastic arteries Aorta, carotid, iliac, Buffering reserve: store blood during systole
Clinical application of Arterial stiffness pulse wave analysis pulse wave velocity Arterial system 1. Large arteries: elastic arteries Aorta, carotid, iliac, Buffering reserve: store blood during systole
Which method is better to measure arterial stiffness; augmentation index, pulse wave velocity, carotid distensibility? 전북의대내과 김원호
 Which method is better to measure arterial stiffness; augmentation index, pulse wave velocity, carotid distensibility? 전북의대내과 김원호 Arterial stiffness Arterial stiffness is inversely related to arterial
Which method is better to measure arterial stiffness; augmentation index, pulse wave velocity, carotid distensibility? 전북의대내과 김원호 Arterial stiffness Arterial stiffness is inversely related to arterial
CONCORD INTERNAL MEDICINE HYPERTENSION PROTOCOL
 CONCORD INTERNAL MEDICINE HYPERTENSION PROTOCOL Douglas G. Kelling Jr., MD Carmella Gismondi-Eagan, MD, FACP George C. Monroe, III, MD Revised, April 8, 2012 The information contained in this protocol
CONCORD INTERNAL MEDICINE HYPERTENSION PROTOCOL Douglas G. Kelling Jr., MD Carmella Gismondi-Eagan, MD, FACP George C. Monroe, III, MD Revised, April 8, 2012 The information contained in this protocol
Various Indices of Arterial Stiffness: Are They Closely Related or Distinctly Different?
 Received: October 19, 2016 Accepted after revision: February 8, 2017 Published online: April 7, 2017 Mini-Review Various Indices of Arterial Stiffness: Are They Closely Related or Distinctly Hirofumi Tanaka
Received: October 19, 2016 Accepted after revision: February 8, 2017 Published online: April 7, 2017 Mini-Review Various Indices of Arterial Stiffness: Are They Closely Related or Distinctly Hirofumi Tanaka
Arterial stiffness index: A new evaluation for arterial stiffness in elderly patients with essential hypertension
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UK GGIGeriatrics and Gerontology International1444-15862002 Blackwell Science Asia Pty Ltd 24December 2002 045 ASI in elderly hypertensive patients M Kaibe et al. 10.1046/j.1444-1586.2002.00045.x
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UK GGIGeriatrics and Gerontology International1444-15862002 Blackwell Science Asia Pty Ltd 24December 2002 045 ASI in elderly hypertensive patients M Kaibe et al. 10.1046/j.1444-1586.2002.00045.x
Relationship between Arterial Stiffness and the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Subjects with and without Metabolic Syndrome
 243 Original Article Hypertens Res Vol.30 (2007) No.3 p.243-247 Relationship between Arterial Stiffness and the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Subjects with and without Metabolic Syndrome Yutaka KOJI
243 Original Article Hypertens Res Vol.30 (2007) No.3 p.243-247 Relationship between Arterial Stiffness and the Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in Subjects with and without Metabolic Syndrome Yutaka KOJI
Special Lecture 11/08/2013. Hypertension Dr. HN Mayrovitz
 Special Lecture 11/08/2013 Hypertension Dr. HN Mayrovitz Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) Major Factors Summarized Sympathetic Hormones Arteriole MAP ~ Q x TPR + f (V / C) SV x HR Renal SBP Hypertension =
Special Lecture 11/08/2013 Hypertension Dr. HN Mayrovitz Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) Major Factors Summarized Sympathetic Hormones Arteriole MAP ~ Q x TPR + f (V / C) SV x HR Renal SBP Hypertension =
King s Research Portal
 King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1016/j.encep.2016.04.004 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Yang, H., & Young,
King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1016/j.encep.2016.04.004 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Yang, H., & Young,
Pulse wave velocity, augmentation index and arterial age in students
 Pulse wave velocity, augmentation index and arterial age in students IOANA MOZOS 1, SERBAN GLIGOR 2 1 Department of Functional Sciences Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara ROMANIA
Pulse wave velocity, augmentation index and arterial age in students IOANA MOZOS 1, SERBAN GLIGOR 2 1 Department of Functional Sciences Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara ROMANIA
Arterial Pressure in CKD5 - ESRD Population Gérard M. London
 Arterial Pressure in CKD5 - ESRD Population Gérard M. London INSERM U970 Paris 150 SBP & DBP by Age, Ethnicity &Gender (US Population Age 18 Years, NHANES III) 150 SBP (mm Hg) 130 110 80 Non-Hispanic Black
Arterial Pressure in CKD5 - ESRD Population Gérard M. London INSERM U970 Paris 150 SBP & DBP by Age, Ethnicity &Gender (US Population Age 18 Years, NHANES III) 150 SBP (mm Hg) 130 110 80 Non-Hispanic Black
ASSOCIATION OF SYSTEMIC INFLAMMATION WITH ARTERIAL STIFFNESS IN HYPERTENSION
 ASSOCIATION OF SYSTEMIC INFLAMMATION WITH ARTERIAL STIFFNESS IN HYPERTENSION Jung-Sun Kim a and Sungha Park a,b, a Division of Cardiology, b Cardiovascular Genome Center, Yonsei Cardiovascular Center,
ASSOCIATION OF SYSTEMIC INFLAMMATION WITH ARTERIAL STIFFNESS IN HYPERTENSION Jung-Sun Kim a and Sungha Park a,b, a Division of Cardiology, b Cardiovascular Genome Center, Yonsei Cardiovascular Center,
Nomogram of the Relation of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Blood Pressure
 801 Original Article Nomogram of the Relation of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Blood Pressure Akira YAMASHINA, Hirofumi TOMIYAMA, Tomio ARAI, Yutaka KOJI, Minoru YAMBE, Hiroaki MOTOBE, Zydem
801 Original Article Nomogram of the Relation of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Blood Pressure Akira YAMASHINA, Hirofumi TOMIYAMA, Tomio ARAI, Yutaka KOJI, Minoru YAMBE, Hiroaki MOTOBE, Zydem
Managing cardiovascular risk with SphygmoCor XCEL
 Managing cardiovascular risk with SphygmoCor XCEL Central pulse pressure better predicts outcome than does brachial pressure Roman et al., Hypertension, 2007; 50:197-203 Carotid to femoral Pulse Wave Velocity
Managing cardiovascular risk with SphygmoCor XCEL Central pulse pressure better predicts outcome than does brachial pressure Roman et al., Hypertension, 2007; 50:197-203 Carotid to femoral Pulse Wave Velocity
Chapter 01. General introduction and outline
 Chapter 01 General introduction and outline General introduction and outline Introduction Cardiovascular disease is the main cause of death in patients with hypertension and in patients with type-1 diabetes
Chapter 01 General introduction and outline General introduction and outline Introduction Cardiovascular disease is the main cause of death in patients with hypertension and in patients with type-1 diabetes
Special Lecture 10/28/2012
 Special Lecture 10/28/2012 HYPERTENSION Dr. HN Mayrovitz Special Lecture 10/28/2012 Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) - Definitions ABP Review Indirect Oscillographic Method Resistance (R), Compliance (C)
Special Lecture 10/28/2012 HYPERTENSION Dr. HN Mayrovitz Special Lecture 10/28/2012 Arterial Blood Pressure (ABP) - Definitions ABP Review Indirect Oscillographic Method Resistance (R), Compliance (C)
The EARNEST study : interarm blood pressure differences should also be recorded Moody, William; Ferro, Charles; Townend, Jonathan
 The EARNEST study : interarm blood pressure differences should also be recorded Moody, William; Ferro, Charles; Townend, Jonathan DOI: 10.1016/j.ahj.2014.05.006 License: None: All rights reserved Document
The EARNEST study : interarm blood pressure differences should also be recorded Moody, William; Ferro, Charles; Townend, Jonathan DOI: 10.1016/j.ahj.2014.05.006 License: None: All rights reserved Document
LabVIEW based Non-Invasive prototype device for cardiac diagnosis using Nadi Shastra
 Original Article LabVIEW based Non-Invasive prototype device for cardiac diagnosis using Nadi Shastra Parth Shah 1, A.V. Leio 1, Siddaram Mahajan* 1, Shaik Jameel 2 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Original Article LabVIEW based Non-Invasive prototype device for cardiac diagnosis using Nadi Shastra Parth Shah 1, A.V. Leio 1, Siddaram Mahajan* 1, Shaik Jameel 2 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
THE INFLUENCE OF WEIGHT LOSS ON ARTERIAL STIFFNESS IN OBESE AND OVERWEIGHT SUBJECTS
 2012 ILEX PUBLISHING HOUSE, Bucharest, Roumania http://www.jrdiabet.ro Rom J Diabetes Nutr Metab Dis. 19(4):353-360 doi: 10.2478/v10255-012-0041-1 THE INFLUENCE OF WEIGHT LOSS ON ARTERIAL STIFFNESS IN
2012 ILEX PUBLISHING HOUSE, Bucharest, Roumania http://www.jrdiabet.ro Rom J Diabetes Nutr Metab Dis. 19(4):353-360 doi: 10.2478/v10255-012-0041-1 THE INFLUENCE OF WEIGHT LOSS ON ARTERIAL STIFFNESS IN
King s Research Portal
 King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2016.03.028 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Eskandari, M.,
King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2016.03.028 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Eskandari, M.,
NO causes vasodilation by stimulating vascular smooth
 Clinical Treatment Clinical Potential of Combined Organic Nitrate and Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor in Treatment-Resistant Hypertension James J. Oliver, James W. Dear, David J. Webb Abstract NO donor
Clinical Treatment Clinical Potential of Combined Organic Nitrate and Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitor in Treatment-Resistant Hypertension James J. Oliver, James W. Dear, David J. Webb Abstract NO donor
How does obesity influence arterial stiffness in asymptomatic adults? Béla Benczúr the former President of HSAS
 How does obesity influence arterial stiffness in asymptomatic adults? Béla Benczúr the former President of HSAS Hetényi Géza County Hospital, Dept. of Cardiology Szolnok, HUNGARY Faculty Disclosure of
How does obesity influence arterial stiffness in asymptomatic adults? Béla Benczúr the former President of HSAS Hetényi Géza County Hospital, Dept. of Cardiology Szolnok, HUNGARY Faculty Disclosure of
Catherine Bondonno. School of Medicine and Pharmacology Faculty of Natural and Agricultural Sciences
 Catherine Bondonno School of Medicine and Pharmacology Faculty of Natural and Agricultural Sciences Catherine has had an extensive and varied career in science. Since graduating from the University of
Catherine Bondonno School of Medicine and Pharmacology Faculty of Natural and Agricultural Sciences Catherine has had an extensive and varied career in science. Since graduating from the University of
Hypertension: What s new since JNC 7. Harold M. Szerlip, MD, FACP, FCCP, FASN, FNKF
 Hypertension: What s new since JNC 7 Harold M. Szerlip, MD, FACP, FCCP, FASN, FNKF Disclosures Spectral Diagnostics Site investigator Eli Lilly Site investigator ACP IM ITE writing committee NBME Step
Hypertension: What s new since JNC 7 Harold M. Szerlip, MD, FACP, FCCP, FASN, FNKF Disclosures Spectral Diagnostics Site investigator Eli Lilly Site investigator ACP IM ITE writing committee NBME Step
APPLICATION OF PHYSICAL METHODS FOR DETERMINATION OF FUNCTIONAL PARAMETERS OF ARTERIES IN RHEUMATIC PATIENTS
 APPLICATION OF PHYSICAL METHODS FOR DETERMINATION OF FUNCTIONAL PARAMETERS OF ARTERIES IN RHEUMATIC PATIENTS Jolanta DADONIENE*, Alma CYPIENE**, Diana KARPEC***, Rita RUGIENE*, Sigita STROPUVIENE*, Aleksandras
APPLICATION OF PHYSICAL METHODS FOR DETERMINATION OF FUNCTIONAL PARAMETERS OF ARTERIES IN RHEUMATIC PATIENTS Jolanta DADONIENE*, Alma CYPIENE**, Diana KARPEC***, Rita RUGIENE*, Sigita STROPUVIENE*, Aleksandras
Hypertension. Hypertension, also referred to as high blood
 Hypertension Hypertension, also referred to as high blood pressure, is a condition in which the arteries have persistently elevated blood pressure. Every time the human heart beats, it pumps blood to the
Hypertension Hypertension, also referred to as high blood pressure, is a condition in which the arteries have persistently elevated blood pressure. Every time the human heart beats, it pumps blood to the
Central Pressures and Prehypertension
 Central Pressures and Prehypertension Charalambos Vlachopoulos Associate Professor of Cardiology 1 st Cardiology Dept Athens Medical School Central Pressures and Prehypertension Charalambos Vlachopoulos
Central Pressures and Prehypertension Charalambos Vlachopoulos Associate Professor of Cardiology 1 st Cardiology Dept Athens Medical School Central Pressures and Prehypertension Charalambos Vlachopoulos
Nielsen, Jane Hyldgård; Rotevatn, Torill Alise; Peven, Kimberly; Melendez-Torres, G. J.; Sørensen, Erik Elgaard; Overgaard, Charlotte
 Aalborg Universitet A realist review of the use of reminder systems for follow-up screening and early detection of type 2 diabetes in women with previous gestational diabetes Nielsen, Jane Hyldgård; Rotevatn,
Aalborg Universitet A realist review of the use of reminder systems for follow-up screening and early detection of type 2 diabetes in women with previous gestational diabetes Nielsen, Jane Hyldgård; Rotevatn,
Arterial Age and Shift Work
 340 Arterial Age and Shift Work Ioana Mozos 1*, Liliana Filimon 2 1 Department of Functional Sciences, Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Timisoara, Romania 2 Department of Occupational
340 Arterial Age and Shift Work Ioana Mozos 1*, Liliana Filimon 2 1 Department of Functional Sciences, Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Timisoara, Romania 2 Department of Occupational
5.2 Key priorities for implementation
 5.2 Key priorities for implementation From the full set of recommendations, the GDG selected ten key priorities for implementation. The criteria used for selecting these recommendations are listed in detail
5.2 Key priorities for implementation From the full set of recommendations, the GDG selected ten key priorities for implementation. The criteria used for selecting these recommendations are listed in detail
Introduction of diverse devices to measure arterial stiffness
 Slide 1 Introduction of diverse devices to measure arterial stiffness PARK, Jeong Bae, MD, PhD, Medicine/Cardiology, Samsung Cheil Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine 2005 5 27 일혈관연구회부산집담회,
Slide 1 Introduction of diverse devices to measure arterial stiffness PARK, Jeong Bae, MD, PhD, Medicine/Cardiology, Samsung Cheil Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine 2005 5 27 일혈관연구회부산집담회,
2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension.
 2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension Writing Group: Background Hypertension worldwide causes 7.1 million premature
2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension Writing Group: Background Hypertension worldwide causes 7.1 million premature
John Feely deceased. Received 21 October 2008 Revised 5 June 2009 Accepted 28 June 2009
 2186 Original article Assessment of arterial stiffness in hypertension: comparison of oscillometric (Arteriograph), piezoelectronic (Complior) and tonometric (SphygmoCor) techniques M Noor A. Jatoi, Azra
2186 Original article Assessment of arterial stiffness in hypertension: comparison of oscillometric (Arteriograph), piezoelectronic (Complior) and tonometric (SphygmoCor) techniques M Noor A. Jatoi, Azra
Effect of beetroot juice on lowering blood pressure in free-living, disease-free adults: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial
 Nutrition Journal This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Effect of beetroot juice
Nutrition Journal This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Effect of beetroot juice
INCREASED PULSE PRESSURE AND SYSTOLIC x HEART RATE DOUBLE PRODUCT AND CARDIOVASCULAR AUTONOMIC NEUROPATHY IN TYPE 2 DIABETIC PATIENTS
 INCREASED PULSE PRESSURE AND SYSTOLIC x HEART RATE DOUBLE PRODUCT AND CARDIOVASCULAR AUTONOMIC NEUROPATHY IN TYPE 2 DIABETIC PATIENTS A.J. Scheen, J.C. Philips, M. Marchand Division of Diabetes, Nutrition
INCREASED PULSE PRESSURE AND SYSTOLIC x HEART RATE DOUBLE PRODUCT AND CARDIOVASCULAR AUTONOMIC NEUROPATHY IN TYPE 2 DIABETIC PATIENTS A.J. Scheen, J.C. Philips, M. Marchand Division of Diabetes, Nutrition
SECONDARY HYPERTENSION
 HYPERTENSION Hypertension is the clinical term used to describe a high blood pressure of 140/90 mmhg or higher (National Institute of Health 1997). It is such a health risk the World Health Organisation
HYPERTENSION Hypertension is the clinical term used to describe a high blood pressure of 140/90 mmhg or higher (National Institute of Health 1997). It is such a health risk the World Health Organisation
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Retinal vessel analysis in dyslipidemia: The eye, a window to the body s microcirculation
 Project Summary SWISS LIPID RESEARCH AWARD 2017 SPONSORED BY AMGEN Retinal vessel analysis in dyslipidemia: The eye, a window to the body s microcirculation Matthias P. Nägele, M.D. 1, Jens Barthelmes,
Project Summary SWISS LIPID RESEARCH AWARD 2017 SPONSORED BY AMGEN Retinal vessel analysis in dyslipidemia: The eye, a window to the body s microcirculation Matthias P. Nägele, M.D. 1, Jens Barthelmes,
Arterial function and longevity Focus on the aorta
 Arterial function and longevity Focus on the aorta Panagiota Pietri, MD, PhD, FESC Director of Hypertension Unit Athens Medical Center Athens, Greece Secrets of longevity Secrets of longevity Unveiling
Arterial function and longevity Focus on the aorta Panagiota Pietri, MD, PhD, FESC Director of Hypertension Unit Athens Medical Center Athens, Greece Secrets of longevity Secrets of longevity Unveiling
Fondazione C.N.R./Regione Toscana G. Monasterio Pisa - Italy. Imaging: tool or toy? Aortic Compliance
 Fondazione C.N.R./Regione Toscana G. Monasterio Pisa - Italy massimo lombardi Imaging: tool or toy? Aortic Compliance 2011 ESC Paris Disclosure: Cardiovascular MR Unit is receiving research fundings from
Fondazione C.N.R./Regione Toscana G. Monasterio Pisa - Italy massimo lombardi Imaging: tool or toy? Aortic Compliance 2011 ESC Paris Disclosure: Cardiovascular MR Unit is receiving research fundings from
Endothelial function is impaired in women who had pre-eclampsia
 Endothelial function is impaired in women who had pre-eclampsia Christian Delles, Catriona E Brown, Joanne Flynn, David M Carty Institute of Cardiovascular and Medical Sciences University of Glasgow United
Endothelial function is impaired in women who had pre-eclampsia Christian Delles, Catriona E Brown, Joanne Flynn, David M Carty Institute of Cardiovascular and Medical Sciences University of Glasgow United
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Where a licence is displayed above, please note the terms and conditions of the licence govern your use of this document.
 Obstructive sleep apnoea and retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes Altaf, Quratul-ain; Dodson, Paul; Ali, Asad; Raymond, Neil T; Wharton, Helen; Hampshire- Bancroft, Rachel; Shah, Mirriam; Shepherd,
Obstructive sleep apnoea and retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes Altaf, Quratul-ain; Dodson, Paul; Ali, Asad; Raymond, Neil T; Wharton, Helen; Hampshire- Bancroft, Rachel; Shah, Mirriam; Shepherd,
WHAT IS AORTIC PULSE WAVE VELOCITY?
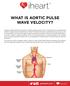 WHAT IS AORTIC PULSE WAVE VELOCITY? Imagine a single health metric able to identify people in their 20 s at increased risk for development of Heart Disease, Stroke and Dementia. What if this health indicator
WHAT IS AORTIC PULSE WAVE VELOCITY? Imagine a single health metric able to identify people in their 20 s at increased risk for development of Heart Disease, Stroke and Dementia. What if this health indicator
Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors
 Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Hypertension Management Controversies in the Elderly Patient
 Hypertension Management Controversies in the Elderly Patient Juan Bowen, MD Geriatric Update for the Primary Care Provider November 17, 2016 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure No financial relationships No
Hypertension Management Controversies in the Elderly Patient Juan Bowen, MD Geriatric Update for the Primary Care Provider November 17, 2016 2016 MFMER slide-1 Disclosure No financial relationships No
Younger adults with a family history of premature artherosclerotic disease should have their cardiovascular risk factors measured.
 Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Salt Sensitivity in Blacks
 ONLINE SUPPLEMENT Salt Sensitivity in Blacks Evidence That the Initial Pressor Effect of NaCl Involves Inhibition of Vasodilatation by Asymmetrical Dimethylarginine Olga Schmidlin 1, Alex Forman 1, Anna
ONLINE SUPPLEMENT Salt Sensitivity in Blacks Evidence That the Initial Pressor Effect of NaCl Involves Inhibition of Vasodilatation by Asymmetrical Dimethylarginine Olga Schmidlin 1, Alex Forman 1, Anna
ADVANCE post trial ObservatioNal Study
 Hot Topics in Diabetes 50 th EASD, Vienna 2014 ADVANCE post trial ObservatioNal Study Sophia Zoungas The George Institute The University of Sydney Rationale and Study Design Sophia Zoungas The George Institute
Hot Topics in Diabetes 50 th EASD, Vienna 2014 ADVANCE post trial ObservatioNal Study Sophia Zoungas The George Institute The University of Sydney Rationale and Study Design Sophia Zoungas The George Institute
King s Research Portal
 King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1016/j.tcm.2016.03.003 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Rinaldi, C. A. (2016).
King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1016/j.tcm.2016.03.003 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Rinaldi, C. A. (2016).
Managing anti-hypertensive treatment with SphygmoCor XCEL
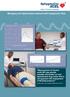 Managing anti-hypertensive treatment with SphygmoCor XCEL Measurement of Central aortic BP may provide valuable information on antihypertensive drug action that is not apparent with assessment of Brachial
Managing anti-hypertensive treatment with SphygmoCor XCEL Measurement of Central aortic BP may provide valuable information on antihypertensive drug action that is not apparent with assessment of Brachial
Vital Signs. Vital Signs. Pulse. Temperature. Respiration. Blood Pressure
 Vital Signs Jarvis, Chapter 9 Vital Signs Classic Vital Signs TPR/BP Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood Pressure Additional Vital Signs Height Weight BMI (Kg/m2) or (702Xlbs/in2) Supine, orthostatic
Vital Signs Jarvis, Chapter 9 Vital Signs Classic Vital Signs TPR/BP Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood Pressure Additional Vital Signs Height Weight BMI (Kg/m2) or (702Xlbs/in2) Supine, orthostatic
A Novel Blood Pressure-independent Arterial Wall Stiffness Parameter; Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index (CAVI)
 Original Article 1 A Novel Blood Pressure-independent Arterial Wall Stiffness Parameter; Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index () Kohji Shirai 1, Junji Utino, Kuniaki Otsuka 3, and Masanobu Takata 4 1 Internal Medicine,
Original Article 1 A Novel Blood Pressure-independent Arterial Wall Stiffness Parameter; Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index () Kohji Shirai 1, Junji Utino, Kuniaki Otsuka 3, and Masanobu Takata 4 1 Internal Medicine,
DISCLOSURES OUTLINE OUTLINE 9/29/2014 ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DISCLOSURES Editor-in-Chief- Nephrology- UpToDate- (Wolters Klewer) Richard J. Glassock, MD, MACP Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA 1 st Annual Internal
ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DISCLOSURES Editor-in-Chief- Nephrology- UpToDate- (Wolters Klewer) Richard J. Glassock, MD, MACP Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA 1 st Annual Internal
Using the New Hypertension Guidelines
 Using the New Hypertension Guidelines Kamal Henderson, MD Department of Cardiology, Preventive Medicine, University of North Carolina School of Medicine Kotchen TA. Historical trends and milestones in
Using the New Hypertension Guidelines Kamal Henderson, MD Department of Cardiology, Preventive Medicine, University of North Carolina School of Medicine Kotchen TA. Historical trends and milestones in
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. Blood Pressure Control role of specific antihypertensives
 Blood Pressure Control role of specific antihypertensives Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillian GUIDELINES a. Regimens that include angiotensin-converting enzyme
Blood Pressure Control role of specific antihypertensives Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillian GUIDELINES a. Regimens that include angiotensin-converting enzyme
King s Research Portal
 King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1017/S1352465814000290 Document Version Early version, also known as pre-print Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA):
King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1017/S1352465814000290 Document Version Early version, also known as pre-print Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA):
Citation for published version (APA): Luijendijk, P. (2014). Aortic coarctation: late complications and treatment strategies
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Aortic coarctation: late complications and treatment strategies Luijendijk, P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Luijendijk, P. (2014). Aortic
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Aortic coarctation: late complications and treatment strategies Luijendijk, P. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Luijendijk, P. (2014). Aortic
Preventing Early Vascular Ageing (EVA) and its hemodynamic changes
 Translational Research 31 st October 2013, Moscow Preventing Early Vascular Ageing (EVA) and its hemodynamic changes Peter M Nilsson, MD, PhD Department of Clinical Sciences Lund University University
Translational Research 31 st October 2013, Moscow Preventing Early Vascular Ageing (EVA) and its hemodynamic changes Peter M Nilsson, MD, PhD Department of Clinical Sciences Lund University University
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
abcd Clinical Study for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the clinical
Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care
 Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care Implementing NICE guidance August 2011 NICE clinical guideline 127 What this presentation covers Five clinical case scenarios, including: presentation
Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care Implementing NICE guidance August 2011 NICE clinical guideline 127 What this presentation covers Five clinical case scenarios, including: presentation
Effects of heart rate reduction with ivabradine on left ventricular remodeling and function:
 Systolic Heart failure treatment with the If inhibitor ivabradine Trial Effects of heart rate reduction with ivabradine on left ventricular remodeling and function: results of the SHIFT echocardiography
Systolic Heart failure treatment with the If inhibitor ivabradine Trial Effects of heart rate reduction with ivabradine on left ventricular remodeling and function: results of the SHIFT echocardiography
Guideline scope Hypertension in adults (update)
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Hypertension in adults (update) This guideline will update the NICE guideline on hypertension in adults (CG127). The guideline will be
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Hypertension in adults (update) This guideline will update the NICE guideline on hypertension in adults (CG127). The guideline will be
Causes of death in Diabetes
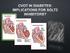 Rates of CV events in Diabetes patients Respiratory4.2 Cancer 7.6 Diabetes 1.3 CV disease 17.3 Causes of death in Diabetes 250 200 150 100 50 0 per 10,000 person-years 97 151 243 Framingham 5 X increase
Rates of CV events in Diabetes patients Respiratory4.2 Cancer 7.6 Diabetes 1.3 CV disease 17.3 Causes of death in Diabetes 250 200 150 100 50 0 per 10,000 person-years 97 151 243 Framingham 5 X increase
Departments of Cardiology and Vascular Surgery Michaelidion Cardiac Center University of Ioannina, Greece
 Departments of Cardiology and Vascular Surgery Michaelidion Cardiac Center University of Ioannina, Greece ARGYRIS Vassilis, PEROULIS Michalis, MATSAGKAS Miltiadis, BECHLIOULIS Aris, MICHALIS Lampros, NAKA
Departments of Cardiology and Vascular Surgery Michaelidion Cardiac Center University of Ioannina, Greece ARGYRIS Vassilis, PEROULIS Michalis, MATSAGKAS Miltiadis, BECHLIOULIS Aris, MICHALIS Lampros, NAKA
Micro Medical Limited. PO Box 6, Rochester Kent ME1 2AZ England T +44 (0) F +44 (0)
 Limited PO Box 6, Rochester Kent ME1 2AZ England T +44 (0) 1634 893500 F +44 (0) 1634 893600 Email micromedical@viasyshc.com http://www.micromedical.co.uk Contents What is PulseTrace?................................................
Limited PO Box 6, Rochester Kent ME1 2AZ England T +44 (0) 1634 893500 F +44 (0) 1634 893600 Email micromedical@viasyshc.com http://www.micromedical.co.uk Contents What is PulseTrace?................................................
Hypertension in the Elderly. John Puxty Division of Geriatrics Center for Studies in Aging and Health, Providence Care
 Hypertension in the Elderly John Puxty Division of Geriatrics Center for Studies in Aging and Health, Providence Care Learning Objectives Review evidence for treatment of hypertension in elderly Consider
Hypertension in the Elderly John Puxty Division of Geriatrics Center for Studies in Aging and Health, Providence Care Learning Objectives Review evidence for treatment of hypertension in elderly Consider
Interested parties (organisations or individuals) that commented on the draft document as released for consultation.
 23 June 2016 EMA/CHMP/345847/2015 Committee for Medicinal products for Human Use Overview of comments received on ''Guideline on clinical investigation of medicinal products in the treatment of hypertension'
23 June 2016 EMA/CHMP/345847/2015 Committee for Medicinal products for Human Use Overview of comments received on ''Guideline on clinical investigation of medicinal products in the treatment of hypertension'
Stephen G. Worthley 1, Gerard T. Wilkins 2, Mark W. Webster 3,Joseph K. Montarello 1, Paul T. Antonis 4, Robert J. Whitbourn 5, Roderic J.
 Six Month Results of First-in-Human Sympathetic Renal Artery Denervation Using a Next Generation Multi-Electrode Renal Artery Denervation System in Patients with Drug-Resistant Hypertension Stephen G.
Six Month Results of First-in-Human Sympathetic Renal Artery Denervation Using a Next Generation Multi-Electrode Renal Artery Denervation System in Patients with Drug-Resistant Hypertension Stephen G.
Arterial stiffness and central BP as goals for antihypertensive therapy in pre- and elderly. Piotr Jankowski
 Arterial stiffness and central BP as goals for antihypertensive therapy in pre- and elderly Piotr Jankowski I Department of Cardiology and Hypertension CM UJ, Kraków, Poland piotrjankowski@interia.pl Vienna,
Arterial stiffness and central BP as goals for antihypertensive therapy in pre- and elderly Piotr Jankowski I Department of Cardiology and Hypertension CM UJ, Kraków, Poland piotrjankowski@interia.pl Vienna,
The reproducibility of central aortic blood pressure measurements in healthy subjects using applanation tonometry and sphygmocardiography
 Journal of Human Hypertension (1999) 13, 625 629 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE The reproducibility of central aortic
Journal of Human Hypertension (1999) 13, 625 629 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE The reproducibility of central aortic
THE IMPACT OF CCB AND RAS INHIBITOR COMBINATION THERAPY TO PREVENT CKD INCIDENCE IN HYPERTENSION AND ADVANCED ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 THE IMPACT OF CCB AND RAS INHIBITOR COMBINATION THERAPY TO PREVENT CKD INCIDENCE IN HYPERTENSION AND ADVANCED ATHEROSCLEROSIS Daisuke MAEBUCHI, Yasuyuki SHIRAISHI, Hiroaki TANAKA, Yumiko INUI, Makoto TAKEI,
THE IMPACT OF CCB AND RAS INHIBITOR COMBINATION THERAPY TO PREVENT CKD INCIDENCE IN HYPERTENSION AND ADVANCED ATHEROSCLEROSIS Daisuke MAEBUCHI, Yasuyuki SHIRAISHI, Hiroaki TANAKA, Yumiko INUI, Makoto TAKEI,
Laser Doppler Vibrometry for Assessment of Pulse Wave Velocity
 Laser Doppler Vibrometry for Assessment of Pulse Wave Velocity Application in an Experimental Setup and in Living Subjects A. Campo, J. Dirckx, Laboratory of Biomedical Physics (Bimef), University of Antwerp
Laser Doppler Vibrometry for Assessment of Pulse Wave Velocity Application in an Experimental Setup and in Living Subjects A. Campo, J. Dirckx, Laboratory of Biomedical Physics (Bimef), University of Antwerp
King s Research Portal
 King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.01.015 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Valmaggia, L.
King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1016/j.psychres.2016.01.015 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Valmaggia, L.
High blood pressure (Hypertension)
 High blood pressure (Hypertension) Information for patients from the Department of Renal (Kidney) Medicine This leaflet is not meant to replace the information discussed between you and your doctor, but
High blood pressure (Hypertension) Information for patients from the Department of Renal (Kidney) Medicine This leaflet is not meant to replace the information discussed between you and your doctor, but
Effects of Renin-Angiotensin System blockade on arterial stiffness and function. Gérard M. LONDON Manhès Hospital Paris, France
 Effects of Renin-Angiotensin System blockade on arterial stiffness and function Gérard M. LONDON Manhès Hospital Paris, France Determinants of vascular overload (afterload) on the heart Peripheral Resistance
Effects of Renin-Angiotensin System blockade on arterial stiffness and function Gérard M. LONDON Manhès Hospital Paris, France Determinants of vascular overload (afterload) on the heart Peripheral Resistance
Relationship of Atherosclerotic Risk Factors with Pulmonary Age and Vascular Age. Masao Shimizu, Asako Okano, Masaki Adachi, Yoshiaki Maruyama
 Original Article 0000 ; 6 : 00 00 Relationship of Atherosclerotic Risk Factors with Pulmonary Age and Vascular Age Masao Shimizu, Asako Okano, Masaki Adachi, Yoshiaki Maruyama Abstract Background: Different
Original Article 0000 ; 6 : 00 00 Relationship of Atherosclerotic Risk Factors with Pulmonary Age and Vascular Age Masao Shimizu, Asako Okano, Masaki Adachi, Yoshiaki Maruyama Abstract Background: Different
Antialdosterone treatment in heart failure
 Update on the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure 2012 Antialdosterone treatment in heart failure 전남의대윤현주 Chronic Heart Failure Prognosis of Heart failure Cecil, Text book of Internal Medicine, 22 th edition
Update on the Treatment of Chronic Heart Failure 2012 Antialdosterone treatment in heart failure 전남의대윤현주 Chronic Heart Failure Prognosis of Heart failure Cecil, Text book of Internal Medicine, 22 th edition
King s Research Portal
 King s Research Portal Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Durrenberger, G., Hillert, L., Kandel, S., Oftedal, G., Rubin, G. J., van Rongen, E., &
King s Research Portal Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Durrenberger, G., Hillert, L., Kandel, S., Oftedal, G., Rubin, G. J., van Rongen, E., &
Cardiac Pathophysiology
 Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Association between arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk factors in a pediatric population
 + Association between arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk factors in a pediatric population Maria Perticone Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine University Magna Graecia of Catanzaro
+ Association between arterial stiffness and cardiovascular risk factors in a pediatric population Maria Perticone Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine University Magna Graecia of Catanzaro
Effects of coexisting hypertension and type II diabetes mellitus on arterial stiffness
 (2004) 18, 469 473 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of coexisting hypertension and type II diabetes mellitus on arterial
(2004) 18, 469 473 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of coexisting hypertension and type II diabetes mellitus on arterial
Managing HTN in the Elderly: How Low to Go
 Managing HTN in the Elderly: How Low to Go Laxmi S. Mehta, MD, FACC The Ohio State University Medical Center Assistant Professor of Clinical Internal Medicine Clinical Director of the Women s Cardiovascular
Managing HTN in the Elderly: How Low to Go Laxmi S. Mehta, MD, FACC The Ohio State University Medical Center Assistant Professor of Clinical Internal Medicine Clinical Director of the Women s Cardiovascular
Abdominal Aortic Doppler Waveform in Patients with Aorto-iliac Disease
 Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg (2010) 39, 714e718 Abdominal Aortic Doppler Waveform in Patients with Aorto-iliac Disease G. Styczynski a, *, C. Szmigielski a, J. Leszczynski b, A. Kuch-Wocial a, M. Szulc a a
Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg (2010) 39, 714e718 Abdominal Aortic Doppler Waveform in Patients with Aorto-iliac Disease G. Styczynski a, *, C. Szmigielski a, J. Leszczynski b, A. Kuch-Wocial a, M. Szulc a a
Η σημασία της αρτηριακής σκληρίας στην εκτίμηση της διαστολικής δυσλειτουργίας στην υπέρταση. Θεραπευτικές παρεμβάσεις
 Η σημασία της αρτηριακής σκληρίας στην εκτίμηση της διαστολικής δυσλειτουργίας στην υπέρταση. Θεραπευτικές παρεμβάσεις Ελένη Τριανταφυλλίδη Επιμελήτρια Α Β Πανεπιστημιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική Αττικό Νοσοκομείο
Η σημασία της αρτηριακής σκληρίας στην εκτίμηση της διαστολικής δυσλειτουργίας στην υπέρταση. Θεραπευτικές παρεμβάσεις Ελένη Τριανταφυλλίδη Επιμελήτρια Α Β Πανεπιστημιακή Καρδιολογική Κλινική Αττικό Νοσοκομείο
New Recommendations for the Treatment of Hypertension: From Population Salt Reduction to Personalized Treatment Targets
 New Recommendations for the Treatment of Hypertension: From Population Salt Reduction to Personalized Treatment Targets Sidney C. Smith, Jr. MD, FACC, FAHA Professor of Medicine/Cardiology University of
New Recommendations for the Treatment of Hypertension: From Population Salt Reduction to Personalized Treatment Targets Sidney C. Smith, Jr. MD, FACC, FAHA Professor of Medicine/Cardiology University of
Director of the Israeli Institute for Quality in Medicine Israeli Medical Association July 1st, 2016
 The differential effect of Atherosclerosis on end organ damage in adult and elderly patients with CVRF: New Algorithm for Hypertension Diagnosis and Treatment R. Zimlichman, FAHA, FASH, FESC, FESH Chief
The differential effect of Atherosclerosis on end organ damage in adult and elderly patients with CVRF: New Algorithm for Hypertension Diagnosis and Treatment R. Zimlichman, FAHA, FASH, FESC, FESH Chief
Pharmacological modulation of vascular structure and function. L. Van Bortel. Heymans Institute of Pharmacology, Ghent University
 Pharmacological modulation of vascular structure and function L. Van Bortel Heymans Institute of Pharmacology, Ghent University BHC 2015 Pharmacological modulation of Endothelial function CIMT Pulse wave
Pharmacological modulation of vascular structure and function L. Van Bortel Heymans Institute of Pharmacology, Ghent University BHC 2015 Pharmacological modulation of Endothelial function CIMT Pulse wave
Food and plant bioactives for reducing cardiometabolic disease: How does the evidence stack up?
 Food and plant bioactives for reducing cardiometabolic disease: How does the evidence stack up? Arrigo F.G. Cicero, MD, PhD Medical and Surgical Sciences Dept., University of Bologna, Italy Italian Nutraceutical
Food and plant bioactives for reducing cardiometabolic disease: How does the evidence stack up? Arrigo F.G. Cicero, MD, PhD Medical and Surgical Sciences Dept., University of Bologna, Italy Italian Nutraceutical
INTERNATIONAL REGISTRY FOR AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE AND ARTERIAL STIFFNESS TELEMONITORING
 INTERNATIONAL REGISTRY FOR AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE AND ARTERIAL STIFFNESS TELEMONITORING VASOTENS Registry Vascular health ASsessment Of The hypertensive patients Project Coordinator: Dr. Stefano Omboni
INTERNATIONAL REGISTRY FOR AMBULATORY BLOOD PRESSURE AND ARTERIAL STIFFNESS TELEMONITORING VASOTENS Registry Vascular health ASsessment Of The hypertensive patients Project Coordinator: Dr. Stefano Omboni
Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR
 Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Slide notes: References:
 1 2 3 Cut-off values for the definition of hypertension are systolic blood pressure (SBP) 135 and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) 85 mmhg for home blood pressure monitoring (HBPM) and daytime ambulatory
1 2 3 Cut-off values for the definition of hypertension are systolic blood pressure (SBP) 135 and/or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) 85 mmhg for home blood pressure monitoring (HBPM) and daytime ambulatory
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
