Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: two and a half years
|
|
|
- Hortense Harrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Accident and Emergency Medicine 99, 4-9 Correspondence: T.W. Wong, Consultant, Accident and Emergency Department, Kwong Wah Hospital, Waterloo Road, Yaumati, Kowloon, Hong Kong. Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: two and a half years experience of an accident and emergency department in Hong Kong T.W. WONG & K.C. YEUNG Accident & Emergency Department, Kwong Wah Hospital, Waterloo Road, Yaumati, Kowloon, Hong Kong SUMMARY The results are presented of / years of experience of patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrests who were resuscitated in an accident and emergency department (A&E) attached to an acute district hospital in Hong Kong. Out of 6 cases of out-ofhospital cardiac arrest as a result of a variety of causes only seven patients survived (%) and among the patients with cardiac aetiology only four survived (%). Ways to improve the outcome for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest are discussed. Key words: out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, survival rate. INTRODUCTION Since the publication by Kouwenhoven' of the usefulness of closed chest compression for cardiac arrest in the 96s, there has been great interest in the application of this knowledge. Community cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) programmes have flourished in many developed countries. In Hong Kong, both the St John Ambulance Association and the Red Cross offer many basic CPR courses for the public. Studies have shown that bystander CPR, when initiated early, improves survival of patients suffering from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Survival rates of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients vary widely (-6%).4, The purpose of this study is to report our experience over a / year period. STUDY SETTING Kwong Wah Hospital is situated in the densely populated city centre on the Kowloon Peninsular. The catchment area is about square kilometres with an estimated population of over 4. About % of patients are over 6 years old. The A&E department has an annual attendance of around. Hong Kong has a population of around 6 million and the male to female ratio is.4. The population is becoming older and in 99 % of the population were older than years. The death rate per population was 4. in 99 of which.4% were attributed to ischaemic heart disease (ICD 4-44). The proportion of citizens with basic CPR training is not known. During the study period our pre-hospital emergency medical system (EMS) was basically a onetier system staffed by ambulance personnel. The ambulance service is run by the Fire Service Department in Hong Kong. Citizens can gain access to the system by dialling '999'. The ambulance personnel are required to attend a 4-week training programme before being placed into active service. They are instructed to begin external cardiac massage and airway management in patients who have suffered out-of-hospital cardiac arrests. They are allowed to insert an oral airway and to ventilate patients with a pressure cycled Stephenson Minuteman ventilator using a CPR head. They are not allowed to intubate or to administer drugs, nor are they allowed to cease resuscitation efforts in the field. METHOD All out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients brought in by ambulance and resuscitated during the -month period from June 99 to November 99 were included. Patients who were clinically judged to be beyond resuscitation (e.g. rigor mortis, decomposition, dependent lividity) were certified as Death Before Arrival and were excluded from the present study. Standard record sheets were used for patients who were resuscitated in the department. This study was started before the Utstein style was promul- 99 Blackwell Science Ltd
2 Out of hospital gated. Terminology and definitions used in this cardiac arrest report conform to those recommended by the Utstein style as far as possible. Differences in definitions are specified below. Information collected included age, sex, initial rhythm on arrival, treatment given and (after December 99) whether the arrest was witnessed. The time when cardiac arrest occurred was difficult to ascertain reliably and was therefore not included. Records of time intervals before arrival in the A&E department were also not available. Initial rhythm was defined as the first rhythm recorded after arrival at the department since ECG monitors were usually unavailable in the ambulance. Patients who were admitted to the intensive care unit/ward after return of spontaneous circulation were followed up by the authors to determine the outcome. Causes of death were traced from the pathology department when post-mortem examinations were performed. Otherwise, the diagnoses stated on the death certificates were used. For patients who were certified dead in the A&E department, causes of death were ascertained by the forensic pathologist. Survival was defined as patients discharged alive to either their home or to some extended care facilities. -Data about cerebral performance at discharge were unavailable. RESULTS A total of 648 out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients were brought in by ambulance during the study period. Out of these 648 patients only 6 (4%) were resuscitated. Within this group ( %) had a cardiac aetiology for their arrest (Table ). For the group, which included all causes of death (all causes group), the average age was 64 years and 68% of the patients were male. For the group of patients with cardiac aetiology (cardiac causes group) the average age was 69. years with % of patients being male (Table ). Asystole was the most common initial rhythm monitored (around %). Ventricular fibrillation (VF) occurred in % in the all causes group and 9% in the cardiac causes group. Return of spontaneous circulation and admission to the ward was achieved in 4% patients in VF for the all causes group. For the cardiac causes group % of patients in VF were admitted. Patients presenting with other initial rhythms (mainly pulseless electrical activity) had the highest survival to admission rate of around % for both groups. This result was surprising and could be because of mis- classification of rhythm by the doctor on duty. No patient in the other rhythm group survived. Out of the total 6 patients presenting to the A&E department only seven (%) were discharged alive. Of the cases with a cardiac cause only four (%) survived. The circumstances of the arrest were known in 99 patients and among them 4 (%) were witnessed. Within this witnessed arrest group 8 (6%) presented with VF/VT on arrival; in the unwitnessed group only 8% were in VF/VT (P <.). Return of spontaneous circulation and admission to ward was achieved in (%) of patients in the witnessed arrest group as compared with (%) in the unwitnessed group (P <.) (Table ). DISCUSSION 99 Blackwell Science Ltd, Journal of Accident and Emergency Medicine, 4-9 Heart disease accounted for % of the out-ofhospital cardiac arrests in our study which is expected as this is the second major cause of death in Hong Kong after malignancy. Aneurysms are not a common cause of death in Hong Kong and it was interesting to note that all the cases were only diagnosed at post-mortem. Respiratory disease, notably obstructive airway disease, is also important as a cause of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Perhaps, more effort should be made by doctors to educate these patients on the warning signals of severe attacks. Trauma was an infrequent cause of death in this study, possibly because of the slow traffic in this very busy district. The survival rate for out-of-hospital cardic arrest, as reported in the literature, varies. In a study of 6 cases in Brighton there was only one survivor8 whereas, the survival rate was as high as 6%9 for the King County series, which consisted of 9 cases. One of the main variables that affects the success rate is the organization of the emergency medical system (EMS). The EMS, with one tier of emergency medical technicians (EMT) providing basic life support has the worst rate of success and systems with two tiers, consisting of EMT and paramedics providing advanced life support, have the best results.9 At the time of the present study our system belonged to the basic EMT classification. We compared our resuts with other countries with similar systems (Table 4) and the discharged alive rate for all rhythm groups was comparable. In a Chicago study of outcome for out-of-hospital arrest in cities with populations of over million, the survival rate was only % out of cases. An earlier study with cases in Los Angeles however,
3 T. W. Wong & K.C. Yeung Diagnosis Clinical Post-mortem Total (%) Table. Causes of death Heart Disease Myocardial infarction Ischemic heart disease Hypertensive heart disease Heart failure Cardiomyopathy Myocarditis Other Dissecting aneurysm Rupture aortic aneurysm Chronic obstructive airway disease Pneumonia Aspiration Tension pneumothorax Pulmonary embolism Stroke Epilepsy Malignancies Narcotic overdose Poisoning Electrocution Trauma Anaphylaxis Pending Unknown Miscellaneous Holt-Oram syndrome Chronic renal failure Pulmonary fibrosis Septicaemia Total 6 yielded a better result of %. Hong Kong is also plagued with all sorts of access problems, e.g. traffic jams, high rise buildings with a small lift or no lift at all etc. In a recent study in Arizona, it was reported that nearly half the on-scene time was spent accessing and removing patients. In Hong Kong, this could take even longer. Experts in the field of pre-hospital care have propounded the concept of 'chain of survival' in the understanding of successful resuscitation of out-of- 6 hospital cardiac arrests. The first chain is 'early access' which is the summation of the process of early recognition and prompt EMS response. According to a study of ambulance services in Hong Kong reported in 986, the call to despatch interval was estimated to be min. This was significantly longer than the min recommended. It was also reported that 9% of the destinations could be reached within 4 min and % could be reached within min from the call being received in Kowloon where the hospital is situated. In comparison with other places our average call-response 99 Blackwell Science Ltd, Journal of Accident and Emergency Medicine, 4-9
4 Out of hospital cardiac arrest Table. Comparison of results for all causes and cardiac causes of arrest All causes Number of cases 6 Cardiac causes Average age Male 8 (68%) 9 (%) Female 8 (%) 8 (8%) Initial rhythm Asystole 8 (69%) 9 (6%) V.F. (%) (9%) V.T. (%) (%) Other 46 (%) (%) Ward admission Asystole 4 (%) (%) V.F. (4%) 8 (%) V.T. (%) (%) Other (6%) (%) Discharged (%) 4 (%) Alive Table. Comparison of results for witnessed vs. unwitnessed arrest Ward admission Fail Survive Total Witnessed 6 4 Unwitnessed 66 8 *Total 6 99 Asystole VF/VT Other Total Witnessed Unwitnessed 6 8 **Total x =.694, P <. * =.4, P <. time of min was long4' (Table 4) and was certainly longer than the 4min recommended by experts. The despatch system of the Fire Service Department has recently been computerized and hopefully the call to despatch interval will shorten. Further decrease in response time is obviously desirable but costly. The second variable in the chain of survival is early CPR. Many studies have indicated the usefulness of immediate bystander CPR in improving the survival rate. In this present study we did not (, 99 Blackwell Science Ltd, Journal of Accident and Emergency Medicine, 4-9 systematically look into this factor but our impression was that bystander CPR was seldom practised in our patient population. This was reflected in our low initial VF rate (%) despite the fact that % of our cases were witnessed arrests (Table 4). Several approaches were suggested to improve the bystander CPR rate.9 The first was community-based CPR training as organized by the Red Cross etc. According to estimations made by the American Heart Association an adult CPR uptake rate of % in a community would be effective to decrease mortality and morbidity because of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. It was our impression that the uptake rate in Hong Kong was much lower when compared with the United States. The second approach is to target CPR training to those who are more likely to come across cardiac arrests, e.g. staff of old people's homes and spouses of cardiac patients. A third approach is despatcher-assisted CPR using a telephone link. The third factor in the chain of survival is early defibrillation.',4 Since January 99, some of our ambulances were equipped with automatic external defibrillators. In a preliminary study by Lo et al., there was no significant increase in the number of patients successfully resuscitated and admitted into hospital compared with ordinary ambulances without defibrillators. Brison6 likewise did not find a significant increase in survival after the introduction of defibrillators. Both papers stressed the importance of improvement in other elements in the chain of survival. The final variable in the chain of survival is early advanced care which includes intravenous access, endotracheal intubation and administration of emergency drugs. With an average call-response time of min and an average scene-to-hospital time of min the arrest-to-advanced cardiac life support time could be as long as min in our setting, which is obviously not desirable. A new batch of ambulance personnel have been upgraded to the North American equivalent of EMT-intermediate level. It will probably be a long time before ambulance staff are trained to paramedic level. On the other hand, an Edinburgh group has found a hospital-based flying squad to be a feasible and economical alternative to training paramedics. This option is probably worth considering in Hong Kong. Cost-effectiveness analyses are important when contemplating improvements in our pre-hospital emergency medical system.8'9 From overseas studies, the addition of a defibrillator operated by ambulance personnel was cost-effective. Further
5 T.W. Wong & K.C. Yeung 8 Average call- No. of Male Arrest response attempted Average patients witnessed interval Study CPR age (years) (%) (%) (min) Basic EMT K.W.H Durham/ Minnesota/ Vancouver/ Winnipeg/ Paramedic Los Angeles/ Chicago/ Ontario/ With No. in all No. in V.F. bystander rhythms No. in V.F. discharged Study CPR (%) discharged (%) (%) (%) Basic EMT K.W.H.? () () () Durham/844 (9) 6 (48) () Minnesota/864 () - - Vancouver/ (6) - - Winnipeg/84 - (4) 6 () 4 () Paramedic Los Angeles/84 () (4) 9 (4) Chicago/9 8 () 4 () 9 (4) Ontario/96 8 (.) - - decreases in the call-response time after a certain limit may not be as cost-effective. More local studies are required in order to find the most cost-effective method to improve survival. In the mean time health care professionals should take the lead to better educate the public on the early recognition of impending arrest and the importance of calling for help immediately. Community efforts to learn basic CPR should also be encouraged. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We would like to thank Dr Elaine Gwi (Consultant Pathologist, KWH) and Dr David Yip (Consultant Forensic Pathologist) for their assistance in identifying the causes of death of patients in this study. REFERENCES. Kouwenhoven W.B., Jude J.R. & Knickerbocker G.G. (96) Closed-chest cardiac massage. Journal of Table 4. Patient characteristics and survival from out-of hospital cardiac arrest with different systems American Medical Association, Cummins R.O. & Eisenberg M.S. (98) Prehospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation: Is it effective? Journal of American Medical Association, Spaite D.W., Criss A.E., Wright A.L., Keeley K.T. & Meislin H.W. (99) Pre-hospital cardiac arrest: The impact of witnessed collapse and bystander CPR in a metropolitan EMS system with short response times. Annals of Emergency Medicine 9, Eisenberg M.S., Horwood B.T., Cummins R.O., Reynolds-Haertle R. & Heame T.R. (99) Cardiac arrest and resuscitation: A tale of 9 cities. Annals of Emergency Medicine 9, Becker L.B., Ostrander M.P., Barrett J. & Kondos G.T. (99) Outcome of CPR in a large metropolitan area - Where are the survivors? Annals of Emergency Medicine, Hospital Authority (994) Hospital Authority Statistical Report 99/9.. Cummins R.O., Chamberlain D.A., Abramson N.S. et al. (99) Recommended guidelines for uniform reporting of data from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: The Utstein style. Circulation 84(), Blackwell Science Ltd, Journal of Accident and Emergency Medicine, 4-9
6 Out of hospital cardiac arrest 8. White N.M., Parker W.S., Binning R.A., et al. (9) Mobile coronary care provided by ambulance personnel. British Medical Journal, Cummins R.O., Eisenberg M.S., Hallstrom A.P. et al (98) Survival of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with early initiation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation. American Journal of Emergency Medicine, Cummins R.O., Ornato J.P., Thies W.H. & Pepe P.E. (99) Improving surival from sudden cardiac arrest: The 'chain of survival' concept. Circulation 8, Raitt B. & Vicary M. (986) Review of Hong Kong Ambulance Service, Final Report. Fire Service Department, Hong Kong Government.. Becker L.B. & Pepe P.E. (99) Ensuring effectiveness of community-wide emergency cardiac care. Annals of Emergency Medicine (), Weaver W.D., Hill D., Fahrenbruch C.E. et al (988) Use of the automatic external defibrillator in the management of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. New England Journal of Medicine 9, Cobbe S.M., Redmond M.J., Watson J.M., Hollingworth J. & Carrington D.J. (99) 'Heartstart Scotland' - initial experience of a national scheme for out of hospital defibrillation. British Medical Journal, -.. Lo Y.S.A., Hui W.K., Yeung S. & Au-yeung H.L. (99) All ambulance crew should receive full paramedic training - Defibrillation training is just a step forward. Hong Kong College of Cardiology Inaugural Scientific Congress Proceedings. 6. Brison R.J. et al. (99) Cardiac arrest in Ontario: circumstances, community response, role of prehospital defibrllation and predictor of survival. Canadian Medical Association Journal 4, Cusack S., Steedman D.J., Robertson C.D. & Little K. (99) Flying Squad response to out-of-hospital cardiac arrest - a decade of experience. Archives of Emergency Medicine 9(), Valenzuela T.D., Criss E.A., Spaite D., Meislin H.W. Wright A.L. & Clark L. (99) Cost-effectiveness analysis of paramedic emergency medical services in the treatment of prehospital cardiopulmonary arrest. Annals of Emergency Medicine 9, Anderson I.W.R., Black R.J., Ledingham I.M. et al (98) Early emergency care study: the potential and benefits of advanced prehospital care. British Medical Journal 94, 8-. J Accid Emerg Med: first published as.6/emj...4 on March 99. Downloaded from Blackwell Science Ltd, Journal of Accident and Emergency Medicine, 4-9 on 6 April 9 by guest. Protected by copyright.
hospital Effect of bystander initiated cardiopulmonary survival after witnessed cardiac arrest outside resuscitation on ventricular fibrillation and
 48 Division of Cardiology, Sahlgrenska Hospital, Gothenburg, Sweden J Herlitz L Ekstr6m B Wennerblom A Axelsson A BAng S Holmberg Correspondence to: Dr J Herlitz, Division of Cardiology, Sahlgrenska Hospital,
48 Division of Cardiology, Sahlgrenska Hospital, Gothenburg, Sweden J Herlitz L Ekstr6m B Wennerblom A Axelsson A BAng S Holmberg Correspondence to: Dr J Herlitz, Division of Cardiology, Sahlgrenska Hospital,
Over the last 3 decades, advances in the understanding of
 Temporal Trends in Sudden Cardiac Arrest A 25-Year Emergency Medical Services Perspective Thomas D. Rea, MD, MPH; Mickey S. Eisenberg, MD, PhD; Linda J. Becker, MA; John A. Murray, MD; Thomas Hearne, PhD
Temporal Trends in Sudden Cardiac Arrest A 25-Year Emergency Medical Services Perspective Thomas D. Rea, MD, MPH; Mickey S. Eisenberg, MD, PhD; Linda J. Becker, MA; John A. Murray, MD; Thomas Hearne, PhD
Early defibrillation in out-of-hospital sudden cardiac death: an Australian experience
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 10, 1-7 Early defibrillation in out-of-hospital sudden cardiac death: an Australian experience I. A. SCOTT & G. J. FITZGERALD Ipswich General Hospital, Ipswich, Queensland
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 10, 1-7 Early defibrillation in out-of-hospital sudden cardiac death: an Australian experience I. A. SCOTT & G. J. FITZGERALD Ipswich General Hospital, Ipswich, Queensland
Protocol. This trial protocol has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work.
 Protocol This trial protocol has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Protocol for: Hasselqvist-Ax I, Riva G, Herlitz J, et al. Early cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Protocol This trial protocol has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Protocol for: Hasselqvist-Ax I, Riva G, Herlitz J, et al. Early cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Strengthening links in the "chain of survival": a Singapore perspective
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Strengthening links in the "chain of survival": a Singapore perspective RA Charles, F Lateef, V Anantharaman Introduction: The concept of the chain of survival is
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Strengthening links in the "chain of survival": a Singapore perspective RA Charles, F Lateef, V Anantharaman Introduction: The concept of the chain of survival is
Outcomes from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in Detroit
 Resuscitation (2007) 72, 59 65 CLINICAL PAPER Outcomes from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in Detroit Robert B. Dunne a,, Scott Compton a,b,c,d, R.J. Zalenski b, Robert Swor c, Robert Welch d, Brooks F.
Resuscitation (2007) 72, 59 65 CLINICAL PAPER Outcomes from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in Detroit Robert B. Dunne a,, Scott Compton a,b,c,d, R.J. Zalenski b, Robert Swor c, Robert Welch d, Brooks F.
C ardiac arrest remains a leading cause of cardiovascular
 619 PREHOSPITAL CARE Surviving out of hospital cardiac arrest at home: a postcode lottery? R M Lyon, S M Cobbe, J M Bradley, N R Grubb... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to:
619 PREHOSPITAL CARE Surviving out of hospital cardiac arrest at home: a postcode lottery? R M Lyon, S M Cobbe, J M Bradley, N R Grubb... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to:
A mong patients who have an out-of-hospital cardiac
 1114 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Can we define patients with no chance of survival after outof-hospital cardiac arrest? J Herlitz, J Engdahl, L Svensson, M Young, K-A Ängquist, S Holmberg... See end of article
1114 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Can we define patients with no chance of survival after outof-hospital cardiac arrest? J Herlitz, J Engdahl, L Svensson, M Young, K-A Ängquist, S Holmberg... See end of article
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Hasegawa K, Hiraide A, Chang Y, Brown DFM. Association of prehospital advancied airway management with neurologic outcome and survival in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac
Supplementary Online Content Hasegawa K, Hiraide A, Chang Y, Brown DFM. Association of prehospital advancied airway management with neurologic outcome and survival in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac
Automated external defibrillators and survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest: early experience at an Australian teaching hospital
 Automated external defibrillators and survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest: early experience at an Australian teaching hospital Roger J Smith, Bernadette B Hickey and John D Santamaria Early defibrillation
Automated external defibrillators and survival after in-hospital cardiac arrest: early experience at an Australian teaching hospital Roger J Smith, Bernadette B Hickey and John D Santamaria Early defibrillation
But unfortunately, the first sign of cardiovascular disease is often the last. Chest-Compression-Only Resuscitation Gordon A.
 THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 1 THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 2 But unfortunately, the first sign of cardiovascular disease is often the last 3 4 1 5 6 7 8 2 Risk of Cardiac
THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 1 THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Sarver Heart Center 2 But unfortunately, the first sign of cardiovascular disease is often the last 3 4 1 5 6 7 8 2 Risk of Cardiac
WORKSHEET for Evidence-Based Review of Science for Veterinary CPCR
 RECOVER 2011 1 of 6 WORKSHEET for Evidence-Based Review of Science for Veterinary CPCR 1. Basic Demographics Worksheet author(s) James Barr Mailing address: 4474 TAMU Texas A&M University College Station,
RECOVER 2011 1 of 6 WORKSHEET for Evidence-Based Review of Science for Veterinary CPCR 1. Basic Demographics Worksheet author(s) James Barr Mailing address: 4474 TAMU Texas A&M University College Station,
Ontario Pre-hospital Advanced Life Support (OPALS) Study
 Ontario Pre-hospital Advanced Life Support (OPALS) Study February 2005 Ian G. Stiell, MD, MSc, FRCPC Funding Provided by: Canadian Health Services Research Foundation Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term
Ontario Pre-hospital Advanced Life Support (OPALS) Study February 2005 Ian G. Stiell, MD, MSc, FRCPC Funding Provided by: Canadian Health Services Research Foundation Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term
OTHER FEATURES SMART CPR
 SMART CPR Philips has augmented the HeartStart AED s well proven patient analysis logic with SMART CPR, a feature that provides a tool for Medical Directors and Administrators to implement existing or
SMART CPR Philips has augmented the HeartStart AED s well proven patient analysis logic with SMART CPR, a feature that provides a tool for Medical Directors and Administrators to implement existing or
Is public access defibrillation needed in Hong Kong?
 Key words: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation; Electric countershock; Emergency medical services; Heart arrest; Hong Kong!!"!"#!"#$!" CB Lo TW Wong KK Lai Hong Kong Med J 2003;9:113-8 Accident and Emergency
Key words: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation; Electric countershock; Emergency medical services; Heart arrest; Hong Kong!!"!"#!"#$!" CB Lo TW Wong KK Lai Hong Kong Med J 2003;9:113-8 Accident and Emergency
Outcomes of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Performed in Emergency Department, Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcomes of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Performed in Emergency Department, Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia K S Chew*, Z M Idzwan*, N A R Hisamuddin*, J Kamaruddin**, W A Wan Aasim**
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcomes of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Performed in Emergency Department, Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia K S Chew*, Z M Idzwan*, N A R Hisamuddin*, J Kamaruddin**, W A Wan Aasim**
Out-Of-Hospital Management and Outcomes of Sudden Cardiac Death Abdelouahab BELLOU, MD, PhD
 Out-Of-Hospital Management and Outcomes of Sudden Cardiac Death Abdelouahab BELLOU, MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine, Emergency Medicine, Therapeutics. Past President of the European Society for
Out-Of-Hospital Management and Outcomes of Sudden Cardiac Death Abdelouahab BELLOU, MD, PhD Professor of Internal Medicine, Emergency Medicine, Therapeutics. Past President of the European Society for
Key statistics from the National Cardiac Arrest Audit: Paediatric arrests April 2012 to March 2017
 Key statistics from the National Cardiac Arrest Audit: Paediatric arrests April 12 to March 17 Supported by Resuscitation Council (UK) and Intensive Care National Audit & Research Centre (ICNARC) Data
Key statistics from the National Cardiac Arrest Audit: Paediatric arrests April 12 to March 17 Supported by Resuscitation Council (UK) and Intensive Care National Audit & Research Centre (ICNARC) Data
A large proportion of patients who die from ischaemic
 25 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Factors associated with survival to hospital discharge among patients hospitalised alive after out of hospital cardiac arrest: change in outcome over 20 years in the community
25 CARDIOVASCULAR MEDICINE Factors associated with survival to hospital discharge among patients hospitalised alive after out of hospital cardiac arrest: change in outcome over 20 years in the community
Introduction To ACLS,1 18 April 2011 INTRODUCTION TO ACLS
 Introduction To ACLS,1 INTRODUCTION TO ACLS EPIDEMIOLOGY In Singapore, every year about 2,400 people suffer from an acute myocardial infarction. Of these about 900 die as a result of sudden cardiac arrest,
Introduction To ACLS,1 INTRODUCTION TO ACLS EPIDEMIOLOGY In Singapore, every year about 2,400 people suffer from an acute myocardial infarction. Of these about 900 die as a result of sudden cardiac arrest,
Cardiac Arrest Registry Database Office of the Medical Director
 Cardiac Arrest Registry Database 2010 Office of the Medical Director 1 Monthly Statistical Summary Cardiac Arrest, December 2010 Western Western Description Division Division % Totals Eastern Division
Cardiac Arrest Registry Database 2010 Office of the Medical Director 1 Monthly Statistical Summary Cardiac Arrest, December 2010 Western Western Description Division Division % Totals Eastern Division
Advanced Cardiac Life Support in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
 The new england journal of medicine original article Advanced Cardiac Life Support in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Ian G. Stiell, M.D., George A. Wells, Ph.D., Brian Field, A.C.P., M.B.A., Daniel W.
The new england journal of medicine original article Advanced Cardiac Life Support in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Ian G. Stiell, M.D., George A. Wells, Ph.D., Brian Field, A.C.P., M.B.A., Daniel W.
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrests in Helsinki: Utstein
 18 Heart 1996;76:18-23 Out-of-hospital cardiac arrests in Helsinki: Utstein style reporting M Kuisma, T Maatta Helsinki Emergency Medical Services System, Department of Health, Helsinki, Finland M Kuisma
18 Heart 1996;76:18-23 Out-of-hospital cardiac arrests in Helsinki: Utstein style reporting M Kuisma, T Maatta Helsinki Emergency Medical Services System, Department of Health, Helsinki, Finland M Kuisma
Portage County EMS Annual Skills Labs
 Portage County EMS Annual Skills Labs Scope: Provide skills labs for all Emergency Medical Responders and First Response EMTs to assure proficiency of skills and satisfy the Wisconsin State approved Operational
Portage County EMS Annual Skills Labs Scope: Provide skills labs for all Emergency Medical Responders and First Response EMTs to assure proficiency of skills and satisfy the Wisconsin State approved Operational
Consensus Paper on Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in England
 Consensus Paper on Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in England Date: 16 th October 2014 Revision Date: 16 th October 2015 Introduction The purpose of this paper is to bring some clarity to the analysis of
Consensus Paper on Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in England Date: 16 th October 2014 Revision Date: 16 th October 2015 Introduction The purpose of this paper is to bring some clarity to the analysis of
Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist
 Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist Introduction. Basic Life Support (BLS). Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death
Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist Introduction. Basic Life Support (BLS). Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death
THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS RELATE TO THE RESUSCITATION COUNCIL (UK) RESUSCITATION GUIDELINES 2005
 THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS RELATE TO THE RESUSCITATION COUNCIL (UK) RESUSCITATION GUIDELINES 2005 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care
THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS RELATE TO THE RESUSCITATION COUNCIL (UK) RESUSCITATION GUIDELINES 2005 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care
Chapter 19 Detection of ROSC in Patients with Cardiac Arrest During Chest Compression Using NIRS: A Pilot Study
 Chapter 19 Detection of ROSC in Patients with Cardiac Arrest During Chest Compression Using NIRS: A Pilot Study Tsukasa Yagi, Ken Nagao, Tsuyoshi Kawamorita, Taketomo Soga, Mitsuru Ishii, Nobutaka Chiba,
Chapter 19 Detection of ROSC in Patients with Cardiac Arrest During Chest Compression Using NIRS: A Pilot Study Tsukasa Yagi, Ken Nagao, Tsuyoshi Kawamorita, Taketomo Soga, Mitsuru Ishii, Nobutaka Chiba,
Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines
 Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines www.circ.ahajournals.org Elham Pishbin. M.D Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine MUMS C H E S Advanced Life Support
Management of Cardiac Arrest Based on : 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines www.circ.ahajournals.org Elham Pishbin. M.D Assistant Professor of Emergency Medicine MUMS C H E S Advanced Life Support
Cardiac Arrest Registry Database Office of the Medical Director
 Cardiac Arrest Registry Database 2010 Office of the Medical Director 1 Monthly Statistical Summary Cardiac Arrest, September 2010 Western Western Description Division Division % Totals Eastern Division
Cardiac Arrest Registry Database 2010 Office of the Medical Director 1 Monthly Statistical Summary Cardiac Arrest, September 2010 Western Western Description Division Division % Totals Eastern Division
Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest. Franz R. Eberli MD, FESC, FAHA Cardiology Triemli Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
 Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest Franz R. Eberli MD, FESC, FAHA Cardiology Triemli Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Conflict of Interest I have no conflict of interest to disclose regarding this presentation.
Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest Franz R. Eberli MD, FESC, FAHA Cardiology Triemli Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Conflict of Interest I have no conflict of interest to disclose regarding this presentation.
Advanced Resuscitation - Child
 C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02C Resuscitation 2017-03-23 1 up to 10 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Child Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Advanced Resuscitation - Adult
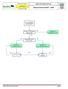 C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
C02A Resuscitation 2017-03-23 17 years & older Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adult Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia Algorithm
Recognition and Treatment of Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrests by Non-Emergency Ambulance Services in Singapore
 Original Article 445 Recognition and Treatment of Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrests by Non-Emergency Ambulance Services in Singapore Nausheen E Doctor, 1 MBBS (S pore), MMed, MRCSEd (A&E), Susan Yap, 1 RN,
Original Article 445 Recognition and Treatment of Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrests by Non-Emergency Ambulance Services in Singapore Nausheen E Doctor, 1 MBBS (S pore), MMed, MRCSEd (A&E), Susan Yap, 1 RN,
The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation
 The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation Introduction The ARREST (Amiodarone in out-of-hospital Resuscitation of REfractory Sustained
The ARREST Trial: Amiodarone for Resuscitation After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Due to Ventricular Fibrillation Introduction The ARREST (Amiodarone in out-of-hospital Resuscitation of REfractory Sustained
AUDIT. Condlusion-The impact of equipping. Wilma S Leslie, Bridie Fitzpatrick, Caroline E Morrison, Graham C M Watt, Hugh Tunstall-Pedoe
 Heart 1996;75:195-199 195 AUDIT MONICA Project Centre, Royal Infirmary, Glasgow W S Leslie C E Morrison Department of Social Policy, University of Glasgow, Glasgow B Fitzpatrick Department of General Practice,
Heart 1996;75:195-199 195 AUDIT MONICA Project Centre, Royal Infirmary, Glasgow W S Leslie C E Morrison Department of Social Policy, University of Glasgow, Glasgow B Fitzpatrick Department of General Practice,
Rural and remote cardiac outcomes: examination of a state-wide emergency medical service
 Rural and remote cardiac outcomes: examination of a state-wide emergency medical service Bronwyn Young, John Woodall, E Enraght-Moony, Vivienne Tippett, Louise Plug, Australian Centre for Prehospital Research
Rural and remote cardiac outcomes: examination of a state-wide emergency medical service Bronwyn Young, John Woodall, E Enraght-Moony, Vivienne Tippett, Louise Plug, Australian Centre for Prehospital Research
Factors modifying the effect of bystander cardiopulmonary resuscitation on survival in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients in Sweden
 European Heart Journal (2001) 22, 511 519 doi:10.1053/euhj.2000.2421, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Factors modifying the effect of bystander cardiopulmonary resuscitation on survival
European Heart Journal (2001) 22, 511 519 doi:10.1053/euhj.2000.2421, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Factors modifying the effect of bystander cardiopulmonary resuscitation on survival
Ethnic Differences in Sudden Cardiac Arrest. Joanna Ghobrial. A Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of
 Ethnic Differences in Sudden Cardiac Arrest Joanna Ghobrial A Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science University of Washington 2014 Committee: Susan
Ethnic Differences in Sudden Cardiac Arrest Joanna Ghobrial A Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science University of Washington 2014 Committee: Susan
ADVANCED LIFE SUPPORT
 ANSWERS IN ITALICS WITH REFERENCES 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care professionals equipped with a manual defibrillator, the providers
ANSWERS IN ITALICS WITH REFERENCES 1. The guidelines suggest that in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests, attended but unwitnessed by health care professionals equipped with a manual defibrillator, the providers
PANDUAN PENYELAMAT JANTUNG
 Improving survival from sudden cardiac arrest: the chain of survival concept. Sign In Sign-Up Bantuan Hidup Asas PANDUAN PENYELAMAT JANTUNG BUKU PANDUAN RESUSITASI KARDIOPULMONARI DAN PERTOLONGAN CEMAS
Improving survival from sudden cardiac arrest: the chain of survival concept. Sign In Sign-Up Bantuan Hidup Asas PANDUAN PENYELAMAT JANTUNG BUKU PANDUAN RESUSITASI KARDIOPULMONARI DAN PERTOLONGAN CEMAS
Rowan County EMS. I m p r o v i n g C a r d i a c A r r e s t S u r v i v a l. Christopher Warr NREMT-P Lieutenant.
 Rowan County EMS I m p r o v i n g C a r d i a c A r r e s t S u r v i v a l Christopher Warr NREMT-P Lieutenant Rowan County EMS christopher.warr@rowancountync.gov September 9, 2012 2:44 11:44:00 Mr.
Rowan County EMS I m p r o v i n g C a r d i a c A r r e s t S u r v i v a l Christopher Warr NREMT-P Lieutenant Rowan County EMS christopher.warr@rowancountync.gov September 9, 2012 2:44 11:44:00 Mr.
The Prognosis of Patients who Received Automated External Defibrillator Treatment in Hospital
 Original Article The Prognosis of Patients who Received Automated External Defibrillator Treatment in Hospital Isao Kato MD, Toru Iwa MD, Yasushi Suzuki MD, Takayuki Ito MD Division of Cardiology, Aichi
Original Article The Prognosis of Patients who Received Automated External Defibrillator Treatment in Hospital Isao Kato MD, Toru Iwa MD, Yasushi Suzuki MD, Takayuki Ito MD Division of Cardiology, Aichi
Victorian Ambulance Cardiac Arrest Registry (VACAR)
 Victorian Ambulance Cardiac Arrest Registry (VACAR) Dr Karen Smith (PhD) VACAR Chair Manager Research and Evaluation Ambulance Victoria Smith K, Bray J, Barnes V, Lodder M, Cameron P, Bernard S and Currell
Victorian Ambulance Cardiac Arrest Registry (VACAR) Dr Karen Smith (PhD) VACAR Chair Manager Research and Evaluation Ambulance Victoria Smith K, Bray J, Barnes V, Lodder M, Cameron P, Bernard S and Currell
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: incidence, process of care, and outcomes in an urban city, Korea
 Clin Exp Emerg Med 2014;1(2):94-100 http://dx.doi.org/10.15441/ceem.14.021 Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: incidence, process of care, and outcomes in an urban city, Korea Hanjin Cho 1, Sungwoo Moon 1,
Clin Exp Emerg Med 2014;1(2):94-100 http://dx.doi.org/10.15441/ceem.14.021 Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: incidence, process of care, and outcomes in an urban city, Korea Hanjin Cho 1, Sungwoo Moon 1,
Papers. Cost effectiveness and cost utility model of public place defibrillators in improving survival after prehospital cardiopulmonary arrest
 Cost effectiveness and cost utility model of public place defibrillators in improving survival after prehospital cardiopulmonary arrest Andrew Walker, Jane M Sirel, Andrew K Marsden, Stuart M Cobbe, Jill
Cost effectiveness and cost utility model of public place defibrillators in improving survival after prehospital cardiopulmonary arrest Andrew Walker, Jane M Sirel, Andrew K Marsden, Stuart M Cobbe, Jill
Overview and Latest Research on Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest
 L MODULE 1 Overview and Latest Research on Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Jamie Jollis, MD Co PI RACE CARS 2 Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest in U.S. 236 000 to 325 000 people in the United States each year
L MODULE 1 Overview and Latest Research on Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Jamie Jollis, MD Co PI RACE CARS 2 Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest in U.S. 236 000 to 325 000 people in the United States each year
Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in the 1990s: A Population-Based Study in the Maastricht Area on Incidence, Characteristics and Survival
 1500 JACC Vol. 30, No. 6 SUDDEN DEATH Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in the 1990s: A Population-Based Study in the Maastricht Area on Incidence, Characteristics and Survival JACQUELINE J. M. DE VREEDE-SWAGEMAKERS,
1500 JACC Vol. 30, No. 6 SUDDEN DEATH Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in the 1990s: A Population-Based Study in the Maastricht Area on Incidence, Characteristics and Survival JACQUELINE J. M. DE VREEDE-SWAGEMAKERS,
Paediatric out-of-hospital cardiac arrests: epidemiology and outcome
 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med J 2005; 46(6) : 289 Paediatric out-of-hospital cardiac arrests: epidemiology and outcome L P Tham, I Chan Department of Emergency Medicine KK Women s and Children
O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med J 2005; 46(6) : 289 Paediatric out-of-hospital cardiac arrests: epidemiology and outcome L P Tham, I Chan Department of Emergency Medicine KK Women s and Children
Mortality within hospital after resuscitation from ventricular fibrillation outside hospital
 334 Br Heart J 1992;67:334-8 Mortality within hospital after resuscitation from ventricular fibrillation outside hospital William Dickey, A A Jennifer Adgey Regional Medical Cardiology Centre, Royal Victoria
334 Br Heart J 1992;67:334-8 Mortality within hospital after resuscitation from ventricular fibrillation outside hospital William Dickey, A A Jennifer Adgey Regional Medical Cardiology Centre, Royal Victoria
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation
 Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
All under the division of cardiovascular medicine University of Minnesota
 The Team 1) Demetris Yannopoulos M.D. Medical Director, 2) Kim Harkins, Program Manager 3) Lucinda Klann, CARES Data Manager 4) Esther Almeida, Administrative Assistant All under the division of cardiovascular
The Team 1) Demetris Yannopoulos M.D. Medical Director, 2) Kim Harkins, Program Manager 3) Lucinda Klann, CARES Data Manager 4) Esther Almeida, Administrative Assistant All under the division of cardiovascular
Estimated Cost-Effectiveness of Dispatcher CPR Instruction via Telephone to Bystanders During Out-of-Hospital Ventricular Fibrillation
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Estimated Cost-Effectiveness of Dispatcher CPR Instruction via Telephone to Bystanders During Out-of-Hospital Ventricular Fibrillation Terence D. Valenzuela, MD, FACEP, FACP,1 Daniel
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Estimated Cost-Effectiveness of Dispatcher CPR Instruction via Telephone to Bystanders During Out-of-Hospital Ventricular Fibrillation Terence D. Valenzuela, MD, FACEP, FACP,1 Daniel
Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent
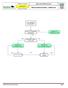 C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
C02B Resuscitation 2017-03-23 10 up to 17 years Office of the Medical Director Advanced Resuscitation - Adolescent Intermediate Advanced Critical From PRIMARY ASSESSMENT Known or suspected hypothermia
70% of OHCA Receiving PAD Has Cardiac Arrest EGC Waveform - An Analysis of the Initial Electrocardiogram upon EMS Arrivals -
 International Journal of Cardiovascular Diseases & Diagnosis Research Article 70% of OHCA Receiving PAD Has Cardiac Arrest EGC Waveform - An Analysis of the Initial Electrocardiogram upon EMS Arrivals
International Journal of Cardiovascular Diseases & Diagnosis Research Article 70% of OHCA Receiving PAD Has Cardiac Arrest EGC Waveform - An Analysis of the Initial Electrocardiogram upon EMS Arrivals
Johnson County Emergency Medical Services Page 23
 Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
Non-resuscitation Situations: Resuscitation should not be initiated in the following situations: Prolonged arrest as evidenced by lividity in dependent parts, rigor mortis, tissue decomposition, or generalized
CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health
 CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health Manual Subject Emergency Medical Services Administrative Policies and Procedures Table of Contents
CENTRAL CALIFORNIA EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES A Division of the Fresno County Department of Public Health Manual Subject Emergency Medical Services Administrative Policies and Procedures Table of Contents
Cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest (CA) occurs when the heart ceases to produce an effective pulse and circulate blood It includes four conditions:
 Basic Life Support: Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR). 2017 Lecture prepared by, Amer A. Hasanien RN, CNS, PhD Cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest (CA) occurs when the heart ceases to produce an effective
Basic Life Support: Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR). 2017 Lecture prepared by, Amer A. Hasanien RN, CNS, PhD Cardiac arrest Cardiac arrest (CA) occurs when the heart ceases to produce an effective
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation
 Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
Epinephrine Cardiovascular Emergencies Symposium 2018
 Epinephrine Cardiovascular Emergencies Symposium 218 Corey M. Slovis, M.D. Vanderbilt University Medical Center Metro Nashville Fire Department Nashville International Airport Nashville, TN High Quality
Epinephrine Cardiovascular Emergencies Symposium 218 Corey M. Slovis, M.D. Vanderbilt University Medical Center Metro Nashville Fire Department Nashville International Airport Nashville, TN High Quality
Wake County EMS System Peer Review/Clinical Data/System Performance
 P a g e 1 Wake County EMS System Peer Review/Clinical Data/System Performance Explanations and Definitions for Reports Wake County EMS engages in regular external review. The System makes quarterly reports
P a g e 1 Wake County EMS System Peer Review/Clinical Data/System Performance Explanations and Definitions for Reports Wake County EMS engages in regular external review. The System makes quarterly reports
CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY
 CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY The Effects of Sex on Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Outcomes Manabu Akahane, MD, PhD, a Toshio Ogawa, MSc, a Soichi Koike, MD, PhD, b Seizan Tanabe, MD, c Hiromasa Horiguchi, PhD,
CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY The Effects of Sex on Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Outcomes Manabu Akahane, MD, PhD, a Toshio Ogawa, MSc, a Soichi Koike, MD, PhD, b Seizan Tanabe, MD, c Hiromasa Horiguchi, PhD,
Minnesota Resuscitation Consortium
 Minnesota Resuscitation Consortium Dedicated to reducing deaths due to cardiac arrest in all of Minnesota How will we benchmark our success? What means will we pursue to reach this goal? American Heart
Minnesota Resuscitation Consortium Dedicated to reducing deaths due to cardiac arrest in all of Minnesota How will we benchmark our success? What means will we pursue to reach this goal? American Heart
TENNESSEE Project ADAM. Preventing Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD): Implementing your school s Public Access to Defibrillation (PAD) program.
 TENNESSEE Project ADAM Preventing Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD): Implementing your school s Public Access to Defibrillation (PAD) program. In Tennessee IT S THE LAW. All schools equipped with an AED must
TENNESSEE Project ADAM Preventing Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD): Implementing your school s Public Access to Defibrillation (PAD) program. In Tennessee IT S THE LAW. All schools equipped with an AED must
Developments in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Guidelines
 Developments in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Guidelines Bernd W. Böttiger Seite 1 To preserve human life by making high quality resuscitation available to all Outcome after CPR in Germany ROSC ( Return
Developments in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Guidelines Bernd W. Böttiger Seite 1 To preserve human life by making high quality resuscitation available to all Outcome after CPR in Germany ROSC ( Return
VARIOUS ASPECTS OF TREATMENT IN CARDIAC ARREST PRIOR TO HOSPITAL ARRIVAL
 From the Department of Clinical Science and Education, Södersjukhuset, Karolinska Institutet. VARIOUS ASPECTS OF TREATMENT IN CARDIAC ARREST PRIOR TO HOSPITAL ARRIVAL Per Nordberg Stockholm 2014 All previously
From the Department of Clinical Science and Education, Södersjukhuset, Karolinska Institutet. VARIOUS ASPECTS OF TREATMENT IN CARDIAC ARREST PRIOR TO HOSPITAL ARRIVAL Per Nordberg Stockholm 2014 All previously
EMS System Key Performance Indicator Data Quality Rules Clinical Group/ Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
 EMS System Key Performance Indicator Data Quality Rules 1. Critical Trauma Patient Management 1.1 Percent of Step 1 and Step 2 trauma patients with an EMS scene time of less than 10 minutes. (arrival-to-departure
EMS System Key Performance Indicator Data Quality Rules 1. Critical Trauma Patient Management 1.1 Percent of Step 1 and Step 2 trauma patients with an EMS scene time of less than 10 minutes. (arrival-to-departure
Nationwide Public-Access Defibrillation in Japan
 The new england journal of medicine original article Nationwide Public-Access Defibrillation in Japan Tetsuhisa Kitamura, M.D., Taku Iwami, M.D., Takashi Kawamura, M.D., Ken Nagao, M.D., Hideharu Tanaka,
The new england journal of medicine original article Nationwide Public-Access Defibrillation in Japan Tetsuhisa Kitamura, M.D., Taku Iwami, M.D., Takashi Kawamura, M.D., Ken Nagao, M.D., Hideharu Tanaka,
An Analysis of Continuous Chest Compression CPR for EMS Providers During Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest
 Illinois Wesleyan University Digital Commons @ IWU Honors Projects Psychology 2010 An Analysis of Continuous Chest Compression CPR for EMS Providers During Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Megan L. Gleason
Illinois Wesleyan University Digital Commons @ IWU Honors Projects Psychology 2010 An Analysis of Continuous Chest Compression CPR for EMS Providers During Out of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Megan L. Gleason
Tomohide Komatsu, Kosaku Kinoshita, Atsushi Sakurai, Takashi Moriya, Junko Yamaguchi, Atsunori Sugita, Rikimaru Kogawa, Katsuhisa Tanjoh
 Division of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Acute Medicine, Nihon University School of Medicine, Itabashi-ku, Tokyo, Japan Correspondence to Dr Atsushi Sakurai, Division of Emergency
Division of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Acute Medicine, Nihon University School of Medicine, Itabashi-ku, Tokyo, Japan Correspondence to Dr Atsushi Sakurai, Division of Emergency
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms. Introduction to the Algorithms
 Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Introduction to the Algorithms Cardiac Arrest Algorithms Prehospital Medication Profiles Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate
Emergency Cardiovascular Care: EMT-Intermediate Treatment Algorithms Introduction to the Algorithms Cardiac Arrest Algorithms Prehospital Medication Profiles Perspective regarding the EMT- Intermediate
The Role of Public Access Defibrillation in the Chain of Survival from Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
 The Role of Public Access Defibrillation in the Chain of Survival from Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Joseph P. Ornato, MD, FACP, FACC, FACEP Introduction Approximately 400-460,000 cardiac arrests occur
The Role of Public Access Defibrillation in the Chain of Survival from Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Joseph P. Ornato, MD, FACP, FACC, FACEP Introduction Approximately 400-460,000 cardiac arrests occur
Manual Defibrillation. CPR AGE: 18 years LOA: Altered HR: N/A RR: N/A SBP: N/A Other: N/A
 ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
ROC AMIODARONE, LIDOCAINE OR PLACEBO FOR OUT OF HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARREST DUE TO VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION OR TACHYCARDIA (ALPS) STUDY: MEDICAL CARDIAC ARREST MEDICAL DIRECTIVE An Advanced Care Paramedic
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL
 THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Journal of the New Zealand Medical Association Outcomes from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in the Wellington region of New Zealand. Does use of the Fire Service make a
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Journal of the New Zealand Medical Association Outcomes from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in the Wellington region of New Zealand. Does use of the Fire Service make a
Outcomes of Therapeutic Hypothermia in Cardiac Arrest. Saad Mohammed Shariff, MBBS Aravind Herle, MD, FACC
 Outcomes of Therapeutic Hypothermia in Cardiac Arrest Saad Mohammed Shariff, MBBS Aravind Herle, MD, FACC https://my.americanheart.org/idc/groups/ahamah-public/@wcm/@sop/@scon/documents/downloadable/ucm_427331.pdf
Outcomes of Therapeutic Hypothermia in Cardiac Arrest Saad Mohammed Shariff, MBBS Aravind Herle, MD, FACC https://my.americanheart.org/idc/groups/ahamah-public/@wcm/@sop/@scon/documents/downloadable/ucm_427331.pdf
Recommended guidelines for uniform reporting. abridged version) of data from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (new. The " Utstein Style"
 Br Heart J 1992;67:325-33 325 RESUSCITATION Recommended guidelines for uniform reporting of data from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (new abridged version) The " Utstein Style" Prepared by a task force
Br Heart J 1992;67:325-33 325 RESUSCITATION Recommended guidelines for uniform reporting of data from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (new abridged version) The " Utstein Style" Prepared by a task force
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Chan PS, Nallamothu BK, Krumholz HM, et al. Long-term outcomes
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Chan PS, Nallamothu BK, Krumholz HM, et al. Long-term outcomes
Science Behind Resuscitation. Vic Parwani, MD ED Medical Director CarolinaEast Health System August 6 th, 2013
 Science Behind Resuscitation Vic Parwani, MD ED Medical Director CarolinaEast Health System August 6 th, 2013 Conflict of Interest No Financial or Industrial Conflicts Slides: Drs. Nelson, Cole and Larabee
Science Behind Resuscitation Vic Parwani, MD ED Medical Director CarolinaEast Health System August 6 th, 2013 Conflict of Interest No Financial or Industrial Conflicts Slides: Drs. Nelson, Cole and Larabee
Automated External Defibrillation Principle of Early Defibrillation States that all BLS personnel be trained, equipped and allowed to operate a if
 1 2 3 4 5 6 Automated External Defibrillation Principle of Early Defibrillation States that all BLS personnel be trained, equipped and allowed to operate a if they are expected to respond to persons in
1 2 3 4 5 6 Automated External Defibrillation Principle of Early Defibrillation States that all BLS personnel be trained, equipped and allowed to operate a if they are expected to respond to persons in
Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular
 Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care 1 DR. Alireza Abootalebi Assistant Professor Of
Adult Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support 2015 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care 1 DR. Alireza Abootalebi Assistant Professor Of
Prof Gavin Perkins Co-Chair ILCOR
 Epidemiology of out of hospital cardiac arrest how to improve survival Prof Gavin Perkins Co-Chair ILCOR Chair, Community Resuscitation Committee, Resuscitation Council (UK) Conflict of interest Commercial
Epidemiology of out of hospital cardiac arrest how to improve survival Prof Gavin Perkins Co-Chair ILCOR Chair, Community Resuscitation Committee, Resuscitation Council (UK) Conflict of interest Commercial
5 Key EMS Articles for 2012
 5 Key EMS Articles for 2012 Corey M. Slovis, M.D. Vanderbilt University Medical Center Metro Nashville Fire Department Nashville International Airport Nashville, TN 5 Key Topics Cardiac Arrest Trauma
5 Key EMS Articles for 2012 Corey M. Slovis, M.D. Vanderbilt University Medical Center Metro Nashville Fire Department Nashville International Airport Nashville, TN 5 Key Topics Cardiac Arrest Trauma
Skills: Recall the incidence of seizures Recall the causes of seizures Describe types of seizures List signs and symptoms of seizure patients
 Medical 1 Resuscitation Describe the morbidity and mortality associated with sudden cardiac arrest List the chain of survival for sudden cardiac arrest as identified by the American Heart Association Discuss
Medical 1 Resuscitation Describe the morbidity and mortality associated with sudden cardiac arrest List the chain of survival for sudden cardiac arrest as identified by the American Heart Association Discuss
Resuscitation 82 (2011) Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. Resuscitation. journal homepage:
 Resuscitation 82 (2011) 277 284 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Resuscitation journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/resuscitation Clinical paper Variation in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest
Resuscitation 82 (2011) 277 284 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Resuscitation journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/resuscitation Clinical paper Variation in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest
Advanced Life Support
 Standard Operating Procedure 2.1 Advanced Life Support Position Responsible: Head of Operations CGC Approved: October 2017 Related Documents Further Information 1.0 Background Magpas Resuscitation Policy
Standard Operating Procedure 2.1 Advanced Life Support Position Responsible: Head of Operations CGC Approved: October 2017 Related Documents Further Information 1.0 Background Magpas Resuscitation Policy
Tissue Plasminogen Activator in In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest with Pulseless Electrical Activity
 Tissue Plasminogen Activator in In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest with Pulseless Electrical Activity Hannah Jordan A. Study Purpose and Rationale Pulseless electrical activity during cardiac arrest carries a
Tissue Plasminogen Activator in In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest with Pulseless Electrical Activity Hannah Jordan A. Study Purpose and Rationale Pulseless electrical activity during cardiac arrest carries a
Role of Non-Implantable Defibrillators in the Management of Patients at High Risk for Sudden Cardiac Death
 Role of Non-Implantable Defibrillators in the Management of Patients at High Risk for Sudden Cardiac Death 29 October 2011 Update in Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Zian H. Tseng, M.D., M.A.S. Associate
Role of Non-Implantable Defibrillators in the Management of Patients at High Risk for Sudden Cardiac Death 29 October 2011 Update in Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Zian H. Tseng, M.D., M.A.S. Associate
ILCOR Evidence Review
 ILCOR Evidence Review Task Force BLS 19-Apr-13 Question Status Pending Evidence Collection Short Title Dispatch CPR instructions PICO Question Evidence Reviewers ;#34;#Christian Vaillancourt;#177;#Manya
ILCOR Evidence Review Task Force BLS 19-Apr-13 Question Status Pending Evidence Collection Short Title Dispatch CPR instructions PICO Question Evidence Reviewers ;#34;#Christian Vaillancourt;#177;#Manya
The Automatic External Defibrillator in Cardiac Arrest
 Focus on CME at Memorial University of Newfoundland The Automatic External Defibrillator in Cardiac Arrest The recent release of new advanced cardiac life support guidelines have led to some changes in
Focus on CME at Memorial University of Newfoundland The Automatic External Defibrillator in Cardiac Arrest The recent release of new advanced cardiac life support guidelines have led to some changes in
LifeNet, Inc Annual Report on OUT-OF-HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARRESTS
 LifeNet, Inc. 7 Annual Report on OUT-OF-HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARRESTS 7 ANNUAL REPORT ON OUT-OF-HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARRESTS Prepared by LifeNet Clinical Services Team: Randy Bean, Paramedic Texarkana Daniel Stramp
LifeNet, Inc. 7 Annual Report on OUT-OF-HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARRESTS 7 ANNUAL REPORT ON OUT-OF-HOSPITAL CARDIAC ARRESTS Prepared by LifeNet Clinical Services Team: Randy Bean, Paramedic Texarkana Daniel Stramp
Clinical Investigation and Reports
 Clinical Investigation and Reports Comparison of Standard Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Versus the Combination of Active Compression-Decompression Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and an Inspiratory Impedance
Clinical Investigation and Reports Comparison of Standard Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Versus the Combination of Active Compression-Decompression Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and an Inspiratory Impedance
Don Eby, MD Local Medical Director, SWORBHP Lesley Pedlar, PCP Bruce County EMS Katie Gibbons, PCP Bruce County EMS
 PARAMEDIC ROUNDS Electrocution Sparking a Conversation about Medical Directives Don Eby, MD Local Medical Director, SWORBHP Lesley Pedlar, PCP Bruce County EMS Katie Gibbons, PCP Bruce County EMS Outline
PARAMEDIC ROUNDS Electrocution Sparking a Conversation about Medical Directives Don Eby, MD Local Medical Director, SWORBHP Lesley Pedlar, PCP Bruce County EMS Katie Gibbons, PCP Bruce County EMS Outline
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Community Chain-of-Survival Taiwan Perspective
 Community Chain-of-Survival Taiwan Perspective Matthew Huei-Ming Ma, MD, PhD Department of Emergency Medicine National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan COI Disclosure Matthew Huei-Ming Ma National Taiwan
Community Chain-of-Survival Taiwan Perspective Matthew Huei-Ming Ma, MD, PhD Department of Emergency Medicine National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan COI Disclosure Matthew Huei-Ming Ma National Taiwan
Development of an Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Surveillance Registry
 Development of an Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Surveillance Registry Bryan McNally, MD, MPH Executive Director CARES Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine Emory University School of Medicine Rollins
Development of an Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Surveillance Registry Bryan McNally, MD, MPH Executive Director CARES Associate Professor of Emergency Medicine Emory University School of Medicine Rollins
Sudden Cardiac Arrest
 Sudden Cardiac Arrest Amit Sharma, MD, FACP, FACC Interventional Cardiologist Rockledge Regional Medical Center Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Central Florida Disclosures No relevant financial
Sudden Cardiac Arrest Amit Sharma, MD, FACP, FACC Interventional Cardiologist Rockledge Regional Medical Center Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Central Florida Disclosures No relevant financial
Early Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
 Original Article Early Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Ingela Hasselqvist Ax, R.N., Gabriel Riva, M.D., Johan Herlitz, M.D., Ph.D., Mårten Rosenqvist, M.D., Ph.D., Jacob
Original Article Early Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Ingela Hasselqvist Ax, R.N., Gabriel Riva, M.D., Johan Herlitz, M.D., Ph.D., Mårten Rosenqvist, M.D., Ph.D., Jacob
Traumatic Cardiac Arrest Protocol
 Traumatic Cardiac Arrest Protocol Background: Major Trauma continues to be the leading worldwide cause of death in young adults. Mortality remains high but there are reports of good neurological outcomes
Traumatic Cardiac Arrest Protocol Background: Major Trauma continues to be the leading worldwide cause of death in young adults. Mortality remains high but there are reports of good neurological outcomes
Michigan Pediatric Cardiac Protocols. Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
 Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Date: November 15, 2012 Page 1 of 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Pediatric Asystole Section 4-1 Pediatric Bradycardia Section 4-2 Pediatric Cardiac Arrest General Section 4-3 Pediatric Narrow Complex Tachycardia
