UNDERSTANDING PACEMAKERS
|
|
|
- Moses Leonard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNDERSTANDING PACEMAKERS Living Well with a Pacemaker
2 Why You Need a Pacemaker Your heart has an electrical system that keeps it beating at the right speed. Problems with this system can make your heart beat too slowly. To correct this, your doctor may recommend a pacemaker. This booklet will tell you what a pacemaker is and how it s placed in the body. You ll also find out how a pacemaker can improve your health and help you lead a more active life. When You Have a Slow Heartbeat Blood carries oxygen throughout the body. When the heart beats too slowly, less oxygen gets to where it s needed. This can cause symptoms such as: Dizziness Lightheadedness Shortness of breath Fatigue Fainting spells (syncope) Common Causes of a Slow Heartbeat Changes in the heart due to aging Heart disease or previous heart surgery Taking medications that slow the heart, such as beta-blockers Heart defects present at birth Diagnosing the Problem Your doctor will ask about your symptoms and health history. You ll also have tests that check the speed and rhythm of your heartbeat. These include a painless test called an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). You may also be asked to wear a Holter monitor or an event recorder. These small devices record your heartbeat over a period of hours or days. 2
3 Older people are more likely to develop a slow heartbeat, but the problem can occur at any age. How a Pacemaker Can Help A pacemaker helps keep your heart from beating too slowly. This reduces symptoms of a slow heartbeat. It can also enable you to take medications that would otherwise slow your heartbeat too much. Best of all, a pacemaker can let you be more active. Your Role A pacemaker can make a big improvement in how you feel. But having one is a lifelong commitment. Work with your doctor to decide whether a pacemaker is right for you. You may have other options or things to consider. Know what you will need to do to care for the device and how often it needs to be checked and monitored. Be sure to mention concerns and get answers to any questions you have. By being informed, you can help your doctor ensure you get the care you need. 3
4 The Heart s Electrical System The heart is a muscle that pumps blood throughout the body. The heart s electrical system tells it when to contract (squeeze). If there s a problem with this electrical system, the heart may not beat as often as it should. This means that the heart can t pump the amount of blood that the body needs. Signals Tell the Heart to Beat Each heartbeat starts with an electrical signal. The signals are sent and received by special electrical cells in the heart called nodes. As the signals move through the heart, they tell the chambers that pump blood (called atria and ventricles) when to contract. With physical activity, the signals from the nodes speed up to pump blood faster. During rest, the signals return to a normal speed. The SA (sinoatrial, or sinus) node is the heart s natural pacemaker. It starts each heartbeat by sending an electrical signal that tells the atria to contract. The AV (atrioventricular) node receives the signal from the SA node after it passes through the atria. It then guides the signal to the ventricles. The bundle branches are pathways of cells that carry the signal through the ventricles. As the signal moves through the ventricles, they contract. The atria are the upper chambers where blood enters the heart. When the atria contract, blood is sent to the ventricles. The ventricles are the heart s lower chambers. They contract to pump blood out of the heart. 4
5 Normal heart rhythm is called sinus rhythm. Problems with Electrical Signals A slow heartbeat is often due to problems with the SA node or AV node. The heartbeat may be slow only once in a while or all the time. In some cases, the heartbeat doesn t speed up during physical activity. Sick Sinus Syndrome The main problem that affects the SA node is called sick sinus syndrome. It can cause: Sinus bradycardia. The SA node sends out signals too slowly. Sinus pause. The SA node fails to create a signal. Without With sinus pause, a signal, the atria don t contract. the SA node may fail Tachy-brady syndrome is a to create a signal. type of sick sinus syndrome. The heartbeat switches between very fast and too slow. AV Block ( Heart Block ) Heart block occurs when the AV node has problems passing on electrical signals from the SA node to the ventricles. It can be caused by problems with either the AV node or the bundle branches. If the ventricles don t receive a signal, they don t contract. This may happen only once in a while. Or, the signal may be blocked all the time. With heart block, the AV node or bundle branches fail to pass on signals to the ventricles. 5
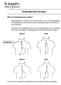
6 Understanding Pacemakers A pacemaker is a small, lightweight electronic device. It contains a tiny computer. It tracks the speed of the heartbeat. If the heart beats too slowly, it sends electrical signals to the heart. These signals pace the heart to keep the heartbeat at a minimum speed. Sensors in the pacemaker also keep track of the body s activity level and can adjust the signals as needed. The Parts of a Pacemaker The connector (header) is the part of the generator where the lead or leads are attached. The generator sends out electrical signals. It has a smooth, lightweight case that contains a tiny computer and battery. It is placed between your skin and chest muscle. Leads are wires covered by soft, flexible material. They are placed in a vein that goes to your heart. This lets them carry the generator s signals directly to the heart. Sensors on the leads also help the generator keep track of your heart s rhythm. Anchors on the tips of the leads attach the leads to the heart muscle. Leads Anchors Connector Generator 6
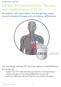
7 The pacemaker s leads are very thin and will not block blood flow through the veins. Types of Pacemakers You and your doctor will discuss the type of pacemaker that s best for you. Most pacemakers have one or two leads. If you have a condition called heart failure, you may be given a pacemaker with three leads instead. How a Pacemaker Adapts to Your Needs When you re active, your heart beats faster to meet the body s need for more blood and oxygen. Problems with the heart s electrical system can prevent the heart from speeding up. To address this problem, all pacemakers have a rate-responsive feature. This means they can automatically adjust your heart rate as needed. The pacemaker speeds up when you re active. It returns to a normal speed when you re resting. Right atrium Lead Right ventricle Leads Right atrium Right ventricle A single-chamber pacemaker has one lead. The lead is usually put into the right ventricle. The exact placement inside the ventricle may vary. A dual-chamber pacemaker has two leads. One is in the right atrium. The other is in the right ventricle. Having two leads helps coordinate the signals that tell these chambers when to contract. 7
8 The Implantation Procedure Placing a pacemaker inside the body is called implantation. This is not open heart surgery. It s a relatively minor procedure done in an operating room or cardiac catheterization lab. A pacemaker can be implanted in either side of the chest but is most often placed on the left side. The procedure usually takes 1 to 2 hours. Getting Ready for the Procedure Have tests that your doctor recommends. Tell your doctor about all prescribed medications you take. Be sure to mention medications to prevent blood clots. These include daily aspirin and drugs such as warfarin. Also be sure to mention diabetes medications such as insulin. You may be given special instructions for these. Also tell your doctor about all over-the-counter medications, herbal remedies, or supplements you use. Mention if you take pain relievers, such as NSAIDs. Talk to your doctor about which side of your chest the pacemaker is to be implanted in. Tell the doctor if you re left-handed or right-handed. Also mention if you often do activities that involve the chest and shoulder, such as shooting a rifle. Don t eat or drink anything as instructed before your procedure. Before Implantation On the day of your procedure, here s what to expect: You will be asked your name and procedure more than once. This is for your safety. An IV is put into your hand or arm to provide fluids and medication. You may be given medication to help you relax. Anesthesia is given to prevent pain and make you sleep during the procedure. You may be lightly asleep (conscious sedation) or in a state like deep sleep (general anesthesia). 8
9 During the Procedure The most common method for implanting a pacemaker is called endocardial ( inside the heart ) implantation. This means that the leads run directly from the generator to the inside of the heart. In rare cases, the leads are attached to the outside of the heart. To implant the pacemaker: Medications are given to prevent pain. A local anesthetic is used to numb the site where the pacemaker is implanted. You may also be given medications to help you relax or sleep. An incision is made beneath the collarbone. A small pocket for the generator is created between the skin and the chest muscle. The leads are put through the incision into a vein in the upper chest. The leads are guided into your heart. An x-ray monitor Collarbone Vein shows the leads as they move into place. Incision The leads are attached to the heart using small anchors on the tips of the leads. Electrical measurements are done to find the best placement for the leads. Right atrial lead Generator The generator is attached to the leads. Once the leads are secure, the generator is placed in the pocket beneath your skin. The incision is closed with sutures, Right surgical glue, or staples. You ll then ventricular lead be taken to a recovery area. Risks and Complications Like any procedure, pacemaker implantation has risks. These include: Bleeding or blood clots Infection Severe bruising or swelling at the incision site Puncture of the lung or heart muscle Tearing of the vein or artery wall Need to have leads or generator repositioned or replaced Heart attack, stroke, or death 9
10 After the Procedure You will likely stay in the hospital overnight. Before going home, you ll be given instructions for how to care for yourself. If you have questions, ask your doctor or nurse. To help your recovery, follow all of your doctor s instructions. In the Hospital After the procedure, nurses will monitor your heart signals and check your incision. They can also provide medications for pain. Be sure to tell the nurses if you have any chest pain, shortness of breath, twitching, or hiccups. Once you re stable, you ll be moved to a hospital room. There, your pacemaker s functions and settings may be checked. You ll also have a chest x-ray to ensure the leads are in the correct location. You can go home once your doctor says it s okay. Have an adult family member or friend ready to drive you. Recovering at Home You may be told to restrict how high you raise the arm on the side where the generator was implanted. Don t stop using the arm or shoulder completely. You can go back to normal use in time. You may have bruising at the incision site for about a month. This is normal. It will go away as the incision heals. It s normal to have some pain and stiffness around your incision for a few days. Over-the-counter pain medications can often help. If needed, your doctor may also prescribe pain medications. You can often get back to your normal routine soon after implantation. Ask your doctor when you can return to work. You may be instructed not to drive for a certain amount of time. Your doctor will tell you more about this. If you re told to limit raising your arm, ask for help reaching things above shoulder level. 10
11 Before you go home, be sure to know how to reach your doctor in case you have a problem. Caring for Your Incision Change or remove the dressing as instructed. Keep the incision clean and dry. You may be told to take sponge baths at first. You can begin showering when your doctor says it s okay. Don t scrub the incision as you bathe. Also, don t let water spray directly on the incision. Pat the incision dry. Don t use lotion, ointment, or powder on the incision while it heals. Call your doctor if you notice any changes in the incision, such as signs of infection (see below). When to Call the Doctor Call if you have any of the following after your procedure: Signs of infection at the incision site, such as increasing redness, swelling, warmth, or drainage Fever of F (38 C) or higher Pain around your pacemaker that gets worse, not better Bleeding or severe swelling of the incision site (bulging up like a golf ball) Swelling in the arm or hand on the side of the incision site Twitching chest or abdominal muscles Frequent or constant hiccups Chest pain or shortness of breath 11
12 Checking Your Pacemaker Your pacemaker s functions and battery will be checked regularly throughout the year. If needed, its settings can be adjusted. This helps ensure the pacemaker is always doing its best for your heart. Your pacemaker can be checked in person during follow-up visits and through remote checks from home. Reading the Pacemaker During follow-up visits, your doctor will check the information stored on your pacemaker s computer. This is done by placing an electronic wand over the skin where the pacemaker is implanted. It will not cause any pain. The battery inside the pacemaker is also checked. Making Adjustments Over time, the pacemaker s settings may need to be adjusted. At each visit, tell your doctor how the pacemaker is working for you. Are you able to do all the activities you want? Or do you often feel tired? To adjust the settings, your doctor uses a device called a programmer. This device reads the pacemaker s memory and adjusts the settings using radio signals. The pacemaker s settings are adjusted from outside your body. 12
13 Checking Your Pacemaker from Home You may be able to have your pacemaker checked from home. This is done using a special device. The device lets you send signals from your pacemaker over the phone line or wirelessly. Your doctor then reviews this information. He or she will let you know if you need to come in for an adjustment. If you have any symptoms of a slow heartbeat, be sure to tell your doctor. Replacing the Battery or Leads Be sure to keep your follow-up appointments and do home checks as often as directed. You may send your pacemaker readings to your doctor using a phone line or wireless connection. Most pacemaker batteries last for 5 to 10 years. If the battery begins to run low, the pacemaker sends out a signal that can be read. It may also have an alarm that sounds or vibrates to signal a low battery. In either case, there is plenty of time to replace the pacemaker. If the battery is low, the whole generator must be replaced. This is done with a procedure that is simpler and shorter than the first implantation. Leads rarely wear out. If they do need to be replaced, it is done during a procedure similar to the first implantation. 13
14 Living with a Pacemaker It s safe for you to do almost any activity you like. However, there are a few things that you ll need to keep in mind. If you have any questions about pacemaker safety, be sure to talk with your doctor. Your Pacemaker and Outside Signals Most machines and devices will NOT interfere with your pacemaker. For example, it s safe to use microwave ovens, computers, radios, and televisions. Hair dryers, electric blankets, and most power tools are also okay. However, use caution around certain devices (see below). If you re not sure whether a device is safe, ask your doctor or call the pacemaker manufacturer. Signals That Can Cause Problems Certain signals may interfere with your pacemaker. In general, they won t permanently damage your device or harm your heart. Contact your doctor if any of the following cause symptoms: Cellphones should not affect your pacemaker. To be safe, keep them 6 inches away from your generator. When talking, wear a headset or hold the cellphone to the ear on the opposite side of your pacemaker. Carry the phone on the opposite side as well. Electromagnetic antitheft systems are often found near store entrances and exits. Walking through one is okay. However, avoid standing near or leaning against one. Very strong magnets should be avoided. These include those in big speakers (such as those at concerts) and in handheld security wands. Talk to your doctor before scheduling an MRI (a test that uses strong magnets). Strong electrical fields can be created by radio towers and heavy-duty power equipment (such as an arc welder). Car engines also create an electrical field while they re running. Avoid leaning over the hood of a running car. When talking on a cellphone, wear a headset or hold the phone on the side opposite your pacemaker. 14
15 Ask your doctor if you should wear a medical alert bracelet. Carry an ID Card You ll receive an ID card that contains important information about your pacemaker. Show the ID card to any healthcare provider you visit. You may also need to show the card to security staff at times. This is because pacemakers tend to set off security devices. Be sure to show your card to security guards at the airport. They have special procedures to keep screening devices from interfering with your pacemaker. Exercise Regularly Having a pacemaker doesn t mean you can t be active. In fact, you may find that exercising is easier with a pacemaker. If you re not sure where to begin, ask your doctor for advice. He or she can help you design an exercise program that fits your needs. Most activities are fine. But talk with your doctor if you play contact sports or do weight lifting. In some cases, these could damage your pacemaker. Keep Seeing Your Doctor To get the best results from your pacemaker, keep seeing your doctor for regular checkups. If you have any symptoms that concern you, be sure to give your doctor a call right away. 15
16 Also available in Spanish Work with Your Doctor A pacemaker can help you have more energy. It can let you feel more confident about your heart and your health. But it s up to you to do your part. See your doctor for regular checkups. Ask for support in making changes and forming new habits. Also take good care of your heart. Then you can focus on the things in life that mean the most to you. For More Information If you want to learn more about pacemakers and heart rhythm problems, try these resources: American Heart Association Heart Rhythm Society TAKE OUR PATIENT SURVEY. Help us help other patients. Please visit to provide your feedback on this booklet. This booklet is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Only your doctor can diagnose and treat a medical problem. 2014, 2015 The StayWell Company, LLC All rights reserved. Made in the USA
IMPLANTABLE CARDIOVERTER DEFIBRILLATORS (ICDs)
 IMPLANTABLE CARDIOVERTER DEFIBRILLATORS (ICDs) Living Well with an ICD An ICD Could Save Your Life Your heart has an electrical system that keeps it beating at the right speed. Problems with this system
IMPLANTABLE CARDIOVERTER DEFIBRILLATORS (ICDs) Living Well with an ICD An ICD Could Save Your Life Your heart has an electrical system that keeps it beating at the right speed. Problems with this system
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs) How ICDs Treat Fast Heart Rhythms Before, During, and After Implantation Living Well with an ICD
 Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs) How ICDs Treat Fast Heart Rhythms Before, During, and After Implantation Living Well with an ICD An ICD Could Save Your Life Based on your health and medical
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs) How ICDs Treat Fast Heart Rhythms Before, During, and After Implantation Living Well with an ICD An ICD Could Save Your Life Based on your health and medical
X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary
 X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary Introduction A pacemaker is a device that regulates the heart beat. More than half a million Americans use a pacemaker. If your doctor recommends that you have a pacemaker,
X-Plain Pacemaker Reference Summary Introduction A pacemaker is a device that regulates the heart beat. More than half a million Americans use a pacemaker. If your doctor recommends that you have a pacemaker,
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) Heart Failure and Electrical Problems How CRT Helps Getting a Biventricular Pacemaker or ICD
 Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) Heart Failure and Electrical Problems How CRT Helps Getting a Biventricular Pacemaker or ICD What Is CRT? When you have heart failure, your heart is weakened and
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT) Heart Failure and Electrical Problems How CRT Helps Getting a Biventricular Pacemaker or ICD What Is CRT? When you have heart failure, your heart is weakened and
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES
 UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
You and your pacemaker
 You and your pacemaker You and your pacemaker Why do I need a pacemaker? A pacemaker will help improve your heart s rate. It is used to help your heart beat at a normal rate. What is a pacemaker? A pacemaker
You and your pacemaker You and your pacemaker Why do I need a pacemaker? A pacemaker will help improve your heart s rate. It is used to help your heart beat at a normal rate. What is a pacemaker? A pacemaker
There are different types of ICDs:
 Guidelines for Patients with Implantable Devices o Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) Your ICD is approximately the size of a pager and includes the following parts: The ICD: A battery powered
Guidelines for Patients with Implantable Devices o Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) Your ICD is approximately the size of a pager and includes the following parts: The ICD: A battery powered
Living With Your Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)
 Patient & Family Guide 2016 Living With Your Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) Aussi disponible en français : Vivre avec votre défibrillateur cardioverteur implantable (DCI) (FF85-1719) www.nshealth.ca
Patient & Family Guide 2016 Living With Your Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) Aussi disponible en français : Vivre avec votre défibrillateur cardioverteur implantable (DCI) (FF85-1719) www.nshealth.ca
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs) How ICDs Treat Fast Heart Rhythms Before, During, and After Implantation Living Well with an ICD
 Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs) How ICDs Treat Fast Heart Rhythms Before, During, and After Implantation Living Well with an ICD An ICD Could Save Your Life Based on your health and medical
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICDs) How ICDs Treat Fast Heart Rhythms Before, During, and After Implantation Living Well with an ICD An ICD Could Save Your Life Based on your health and medical
Catheter Ablation. Patient Education
 Catheter Ablation Patient Education Allina Health System Your heart has four chambers. Two upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). In order for the heart to pump, it requires
Catheter Ablation Patient Education Allina Health System Your heart has four chambers. Two upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). In order for the heart to pump, it requires
Care of Your Child with a Pacemaker
 Patient and Family Education Care of Your Child with a Pacemaker A pacemaker watches for slow heart rates. It can send signals to make the heart beat. Here is how to take care of your child s pacemaker.
Patient and Family Education Care of Your Child with a Pacemaker A pacemaker watches for slow heart rates. It can send signals to make the heart beat. Here is how to take care of your child s pacemaker.
Information for patients, parents and guardians. Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation.
 Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
About atrial fibrillation (AFib) Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) What is AFib? What s the danger? Who gets AFib?
 Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
This leaflet is intended for patients with permanent pacemakers and their parents.
 Permanent PACEMAKER This leaflet is intended for patients with permanent pacemakers and their parents. It serves as an information tool and a guide that offers some advice in order to live safely. General
Permanent PACEMAKER This leaflet is intended for patients with permanent pacemakers and their parents. It serves as an information tool and a guide that offers some advice in order to live safely. General
CORONARY ARTERY PROCEDURES
 CORONARY ARTERY PROCEDURES Cardiac Catheterization, Stenting, and Bypass Surgery Coronary Artery Disease Your doctor has told you that you may have coronary artery disease (CAD). Having CAD means that
CORONARY ARTERY PROCEDURES Cardiac Catheterization, Stenting, and Bypass Surgery Coronary Artery Disease Your doctor has told you that you may have coronary artery disease (CAD). Having CAD means that
LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR
 LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR Treating Your Hernia with Laparoscopy When You Have a Hernia Anyone can have a hernia. This is a weakness or tear in the wall of the abdomen. It often results from years of wear
LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR Treating Your Hernia with Laparoscopy When You Have a Hernia Anyone can have a hernia. This is a weakness or tear in the wall of the abdomen. It often results from years of wear
MIDDLE EAR SURGERY. For Better Health and Hearing
 MIDDLE EAR SURGERY For Better Health and Hearing Help for Ongoing Ear Problems Your doctor has found a problem with your middle ear. This is a part of the ear that you can t see. You may have taken medication,
MIDDLE EAR SURGERY For Better Health and Hearing Help for Ongoing Ear Problems Your doctor has found a problem with your middle ear. This is a part of the ear that you can t see. You may have taken medication,
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) and Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Defibrillator (CRT-D)
 How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections? Infection control is important to the well-being of our patients and for that reason we have infection control procedures in place. Keeping your
How can I help reduce healthcare associated infections? Infection control is important to the well-being of our patients and for that reason we have infection control procedures in place. Keeping your
LAPAROSCOPIC GALLBLADDER SURGERY
 LAPAROSCOPIC GALLBLADDER SURGERY Treating Gallbladder Problems with Laparoscopy A Common Problem If you ve had an attack of painful gallbladder symptoms, you re not alone. Gallbladder disease is very common.
LAPAROSCOPIC GALLBLADDER SURGERY Treating Gallbladder Problems with Laparoscopy A Common Problem If you ve had an attack of painful gallbladder symptoms, you re not alone. Gallbladder disease is very common.
ICD Implantation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm ICD Implantation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers (the right atrium
Melbourne Heart Rhythm ICD Implantation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers (the right atrium
Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
LUNG SURGERY. Treatment for Lung Problems
 LUNG SURGERY Treatment for Lung Problems When You Need Lung Surgery Your doctor is recommending surgery for your lung problem. Surgery alone may treat your problem. Or you may need other treatments as
LUNG SURGERY Treatment for Lung Problems When You Need Lung Surgery Your doctor is recommending surgery for your lung problem. Surgery alone may treat your problem. Or you may need other treatments as
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information Normal Heart Function The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Patient Information Normal Heart Function The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two
Yes, out of sight out of mind.
 Micra TRANSCATHETER PACING SYSTEM 25.9 mm Yes, out of sight out of mind. cardiocapsule Meet Micra The Invisible Pacemaker Micra is the world s smallest pacemaker 1. It leaves no bump under the skin, no
Micra TRANSCATHETER PACING SYSTEM 25.9 mm Yes, out of sight out of mind. cardiocapsule Meet Micra The Invisible Pacemaker Micra is the world s smallest pacemaker 1. It leaves no bump under the skin, no
Atrial Fibrillation. Damage to your heart caused by a heart attack or rheumatic heart disease
 Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
OVERCOMING FROZEN SHOULDER
 OVERCOMING FROZEN SHOULDER Treatment to Relieve Pain and Regain Movement When You Have Frozen Shoulder Is your shoulder stiff and painful? If so, you may have frozen shoulder (sometimes called adhesive
OVERCOMING FROZEN SHOULDER Treatment to Relieve Pain and Regain Movement When You Have Frozen Shoulder Is your shoulder stiff and painful? If so, you may have frozen shoulder (sometimes called adhesive
Cardiac Catheterization
 Cardiac Catheterization What is cardiac catheterization? Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat cardiovascular conditions. During cardiac catheterization, a long thin tube called
Cardiac Catheterization What is cardiac catheterization? Cardiac catheterization is a procedure used to diagnose and treat cardiovascular conditions. During cardiac catheterization, a long thin tube called
Lung Surgery: Thoracoscopy
 Lung Surgery: Thoracoscopy A Problem with Your Lungs Your doctor has told you that you need surgery called thoracoscopy for your lung problem. This surgery alone may treat your lung problem. Or you may
Lung Surgery: Thoracoscopy A Problem with Your Lungs Your doctor has told you that you need surgery called thoracoscopy for your lung problem. This surgery alone may treat your lung problem. Or you may
Arrhythmias. Pulmonary Artery
 Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
PROCEDURES FOR PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE
 PROCEDURES FOR PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE Improving Blood Flow and Relieving Pain Learning About PAD Your doctor has told you that you have peripheral arterial disease (PAD). This means the arteries in
PROCEDURES FOR PERIPHERAL ARTERIAL DISEASE Improving Blood Flow and Relieving Pain Learning About PAD Your doctor has told you that you have peripheral arterial disease (PAD). This means the arteries in
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease
 Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Appendicitis. Diagnosis and Surgery
 Appendicitis Diagnosis and Surgery What Is Appendicitis? Your side may hurt so much that you called your doctor. Or maybe you went straight to the hospital emergency room. If the symptoms came on quickly,
Appendicitis Diagnosis and Surgery What Is Appendicitis? Your side may hurt so much that you called your doctor. Or maybe you went straight to the hospital emergency room. If the symptoms came on quickly,
Parathyroidectomy. Surgery for Parathyroid Problems
 Parathyroidectomy Surgery for Parathyroid Problems Why You Need Parathyroid Surgery Has your doctor just recommended that you have parathyroid surgery? If so, you likely have many questions. What are the
Parathyroidectomy Surgery for Parathyroid Problems Why You Need Parathyroid Surgery Has your doctor just recommended that you have parathyroid surgery? If so, you likely have many questions. What are the
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator
 12:13:18 CTPALS067 V2_CTPALS01 25/04/2017 11:19 Page 1 Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator A device to help correct abnormal heart rhythms This leaflet has been written to provide information about
12:13:18 CTPALS067 V2_CTPALS01 25/04/2017 11:19 Page 1 Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator A device to help correct abnormal heart rhythms This leaflet has been written to provide information about
Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Definition of electrophysiology study and ablation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Electrophysiology Study and Ablation An electrophysiology, or EP, study is a test of the heart
Definition of electrophysiology study and ablation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Electrophysiology Study and Ablation An electrophysiology, or EP, study is a test of the heart
Ileal Conduit Diversion Surgery
 Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
Here are some words and pictures to help you understand this surgery: Bladder: the bladder stores urine that is made by the kidneys Bowels: the bowels are the parts of the body that digest food and fluids.
PNEUMONIA. Your Treatment and Recovery
 PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
PNEUMONIA Your Treatment and Recovery Understanding Pneumonia Symptoms of Pneumonia Do you feel feverish and tired, with a cough that won t go away? If so, you may have pneumonia. This is a lung infection
POST-OP PAIN MANAGEMENT
 POST-OP PAIN MANAGEMENT You re Part of the Team Pain Management After Surgery Having a procedure or surgery to address a health issue can result in post-op (postoperative) pain. This pain can and should
POST-OP PAIN MANAGEMENT You re Part of the Team Pain Management After Surgery Having a procedure or surgery to address a health issue can result in post-op (postoperative) pain. This pain can and should
Different indications for pacemaker implantation are the following:
 Patient Resources: ICD/Pacemaker Overview ICD/Pacemaker Overview What is a pacemaker? A pacemaker is a device that uses low energy electrical pulses to prompt the heart to beat whenever a pause in the
Patient Resources: ICD/Pacemaker Overview ICD/Pacemaker Overview What is a pacemaker? A pacemaker is a device that uses low energy electrical pulses to prompt the heart to beat whenever a pause in the
Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Definition of atrial fibrillation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disturbance that causes an irregular (and often
Definition of atrial fibrillation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disturbance that causes an irregular (and often
Deep brain stimulation
 About insertion of a deep brain stimulator The deep brain stimulator sends electrical impulses to the brain interrupting the abnormal signals that are causing the symptoms. The impulses are adjusted by
About insertion of a deep brain stimulator The deep brain stimulator sends electrical impulses to the brain interrupting the abnormal signals that are causing the symptoms. The impulses are adjusted by
After Your Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator (ICD) Generator Change
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION After Your Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator (ICD) Generator Change What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION After Your Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator (ICD) Generator Change What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Hemodialysis. A treatment option for kidney disease. Treatment Options for Kidney Disease
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Hemodialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and care of blood access. 2. Understand the purpose and basic principles of hemodialysis.
Electrophysiology Studies and Catheter Ablation. Electrophysiology Studies and Catheter Ablation
 Electrophysiology Studies Cardiac Conduction System. Mdmedicine.wordpress.com Patient Information Leaflet for: Electrophysiology Studies Available via Trust Docs Version: 6 Trust Docs ID: 10 Page 1 of
Electrophysiology Studies Cardiac Conduction System. Mdmedicine.wordpress.com Patient Information Leaflet for: Electrophysiology Studies Available via Trust Docs Version: 6 Trust Docs ID: 10 Page 1 of
Pacemaker Therapy (PPM)
 Patient information Pacemaker Therapy (PPM) i Important information for all patients requiring pacemaker therapy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk
Patient information Pacemaker Therapy (PPM) i Important information for all patients requiring pacemaker therapy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk
LUMBAR MICROSURGERY. Low Back Surgery to Reduce Your Pain
 LUMBAR MICROSURGERY Low Back Surgery to Reduce Your Pain Planning for Low Back Surgery Having a low back (lumbar) problem can be frustrating. You may have pain when you sit, stand, or walk. Even a simple
LUMBAR MICROSURGERY Low Back Surgery to Reduce Your Pain Planning for Low Back Surgery Having a low back (lumbar) problem can be frustrating. You may have pain when you sit, stand, or walk. Even a simple
After Your Pacemaker Generator Change
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION After Your Pacemaker Generator Change What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic at 206.598.4300. If you have
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION After Your Pacemaker Generator Change What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic at 206.598.4300. If you have
Caring for Your Pacemaker
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Caring for Your Pacemaker What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic at 206.598.4300. If you have a question
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Caring for Your Pacemaker What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic at 206.598.4300. If you have a question
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR)
 Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) Welcome to the Sanford Health Heart Clinic. It is a privilege to care for you. Your doctor has told you that you may need to have a TAVR procedure. TAVR stands
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) Welcome to the Sanford Health Heart Clinic. It is a privilege to care for you. Your doctor has told you that you may need to have a TAVR procedure. TAVR stands
THE THYROID BOOK. Medical and Surgical Treatment of Thyroid Problems
 THE THYROID BOOK Medical and Surgical Treatment of Thyroid Problems Trouble with Your Thyroid Gland The thyroid is a small gland in your neck that plays a big role in how your body functions. It impacts
THE THYROID BOOK Medical and Surgical Treatment of Thyroid Problems Trouble with Your Thyroid Gland The thyroid is a small gland in your neck that plays a big role in how your body functions. It impacts
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients Your doctor has determined that you have atrial fibrillation (AF), a common disturbance of the heart s rhythm. This pamphlet will answer many of your
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients Your doctor has determined that you have atrial fibrillation (AF), a common disturbance of the heart s rhythm. This pamphlet will answer many of your
UNDERSTANDING. Permanent Birth Control for Men
 UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
Lumbar Epidural Injections. Treatment to Reduce Pain
 Lumbar Epidural Injections Treatment to Reduce Pain What Is a Lumbar Epidural Injection? Your doctor may have suggested you have a lumbar epidural injection. This procedure can help relieve low back and
Lumbar Epidural Injections Treatment to Reduce Pain What Is a Lumbar Epidural Injection? Your doctor may have suggested you have a lumbar epidural injection. This procedure can help relieve low back and
Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps
 Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps Cardiology is the word in health care associated with heart, but the body s vascular system is also an important part of heart care. Your body has more than 60,000 miles
Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps Cardiology is the word in health care associated with heart, but the body s vascular system is also an important part of heart care. Your body has more than 60,000 miles
CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE
 CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist What Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition that affects nerves in the wrist and hand. CTS causes tingling and numbness
CARPAL TUNNEL RELEASE Relieving Pressure in Your Wrist What Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition that affects nerves in the wrist and hand. CTS causes tingling and numbness
GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
ICDs: Implantable. A Guide for Patients and Families 40 RUSKIN STREET, OTTAWA ON K1Y 4W7 T UOHI 75 (11/2014)
 ICDs: Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators A Guide for Patients and Families UOHI 75 (11/2014) 40 RUSKIN STREET, OTTAWA ON K1Y 4W7 T 613.696-7000 WWW.OTTAWAHEART.CA Patient Name PLEASE BRING THIS BOOK
ICDs: Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators A Guide for Patients and Families UOHI 75 (11/2014) 40 RUSKIN STREET, OTTAWA ON K1Y 4W7 T 613.696-7000 WWW.OTTAWAHEART.CA Patient Name PLEASE BRING THIS BOOK
Heart Valve Replacement
 Heart Valve Replacement Introduction Sometimes people have serious problems with the valves in their hearts. A heart valve repair or replacement surgery restores or replaces a defective heart valve. If
Heart Valve Replacement Introduction Sometimes people have serious problems with the valves in their hearts. A heart valve repair or replacement surgery restores or replaces a defective heart valve. If
Your Subcutaneous Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator (ICD)
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Your Subcutaneous Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator (ICD) What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic at 206-598-4300.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Your Subcutaneous Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator (ICD) What you need to know Who to Call If you have questions about your appointments, call the Cardiology Clinic at 206-598-4300.
Esophagectomy Surgery
 Esophagectomy Surgery What is esophagectomy surgery? Esophagectomy surgery is the removal part, or all, of the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that your food goes down on the way to your stomach.
Esophagectomy Surgery What is esophagectomy surgery? Esophagectomy surgery is the removal part, or all, of the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube that your food goes down on the way to your stomach.
Coronary angioplasty and stents
 Tests and Procedures Coronary angioplasty and stents By Mayo Clinic Staff Coronary angioplasty (AN-jee-o-plas-tee), also called percutaneous coronary intervention, is a procedure used to open clogged heart
Tests and Procedures Coronary angioplasty and stents By Mayo Clinic Staff Coronary angioplasty (AN-jee-o-plas-tee), also called percutaneous coronary intervention, is a procedure used to open clogged heart
Living with Your Heart Failure Device (CRT)*
 References 1 Zipes DP, Roberts D. Results of the international study of the implantable pacemaker cardioverter-defibrillator. A comparison of epicardial and endocardial lead systems. The Pacemaker-Cardioverter-
References 1 Zipes DP, Roberts D. Results of the international study of the implantable pacemaker cardioverter-defibrillator. A comparison of epicardial and endocardial lead systems. The Pacemaker-Cardioverter-
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Implantation A guide for patients and families
 Patient/Family Material Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Implantation A guide for patients and families Table of Contents Patient checklist. page 2 About Implantable
Patient/Family Material Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Implantation A guide for patients and families Table of Contents Patient checklist. page 2 About Implantable
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING
 ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
ANGIOPLASTY AND STENTING What is angioplasty and stenting? During an angioplasty, your vascular surgeon inflates a small balloon inside a narrowed blood vessel. This balloon helps to widen your blood vessel
Take control of your pain therapy. Getting started with Algovita SCS.
 Take control of your pain therapy. Getting started with Algovita SCS. The two-step approach to spinal cord stimulation therapy. You ve talked with your doctor. You ve discussed it with your family. You
Take control of your pain therapy. Getting started with Algovita SCS. The two-step approach to spinal cord stimulation therapy. You ve talked with your doctor. You ve discussed it with your family. You
Preparing for your Stereotactic Core Biopsy
 Preparing for your Stereotactic Core Biopsy For patients at the Rapid Diagnostic Centre Gattuso Rapid Diagnostic Centre Princess Margaret Cancer Centre 3rd floor, Breast Imaging 610 University Avenue Toronto,
Preparing for your Stereotactic Core Biopsy For patients at the Rapid Diagnostic Centre Gattuso Rapid Diagnostic Centre Princess Margaret Cancer Centre 3rd floor, Breast Imaging 610 University Avenue Toronto,
Newer pacemakers also can monitor your blood temperature, breathing, and other factors and adjust your heart rate to changes in your activity.
 Pacemakers & Defibrillators A pacemaker system consists of a battery, a computerized generator and wires with sensors called electrodes on one end. The battery powers the generator, and both are surrounded
Pacemakers & Defibrillators A pacemaker system consists of a battery, a computerized generator and wires with sensors called electrodes on one end. The battery powers the generator, and both are surrounded
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft
 Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Going home after an AV Fistula or AV Graft TGH Information for patients and families During your hospital stay, your surgeon created an: AV Fistula AV Graft Read this booklet to learn: how to care for
Heart catheterization for adults with congenital heart disease
 Heart catheterization for adults with congenital heart disease What is a heart catheterization? It is a procedure that provides details about your heart function and circulation. It helps your doctor make
Heart catheterization for adults with congenital heart disease What is a heart catheterization? It is a procedure that provides details about your heart function and circulation. It helps your doctor make
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Defibrillator (CRT-D)
 Patient information Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Defibrillator (CRT-D) i Important information for all patients requiring resynchronisation therapy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street
Patient information Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Defibrillator (CRT-D) i Important information for all patients requiring resynchronisation therapy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street
Neurostimulation. Spinal cord stimulators use electrodes placed in the space surrounding the spinal cord (epidural space).
 Neurostimulation.305145613.pdf 1 8/11/12 11:32 PM Neurostimulation Neurostimulation, also called electrostimulation, uses low-level electrical impulses to interfere with pain signals or block them from
Neurostimulation.305145613.pdf 1 8/11/12 11:32 PM Neurostimulation Neurostimulation, also called electrostimulation, uses low-level electrical impulses to interfere with pain signals or block them from
GETTING READY FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT
 GETTING READY FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Pre-Op Exercises for a Better Recovery Your Recovery Begins Now Even if your hip replacement surgery is weeks or months away, start getting ready now. People who
GETTING READY FOR TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT Pre-Op Exercises for a Better Recovery Your Recovery Begins Now Even if your hip replacement surgery is weeks or months away, start getting ready now. People who
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery Interoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging (imri)
 1 Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery Interoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging (imri) Patient Information Booklet What are the benefits and risks of this treatment for me? Am I a good candidate? What should
1 Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery Interoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging (imri) Patient Information Booklet What are the benefits and risks of this treatment for me? Am I a good candidate? What should
Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide
 Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Patient Resources: Syncope
 Patient Resources: Syncope Overview Syncope is the medical term for fainting or loss of consciousness. Fainting can occur for a few different reasons. The autonomic (involuntary) nervous system helps to
Patient Resources: Syncope Overview Syncope is the medical term for fainting or loss of consciousness. Fainting can occur for a few different reasons. The autonomic (involuntary) nervous system helps to
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation Todd J. Florin, M.D. Table of Contents The Normal Heart...1 What is Atrial Fibrillation...3 Risks of Afib: Stroke...5 Treatment Options...7 Radiofrequency Ablation...9
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation Todd J. Florin, M.D. Table of Contents The Normal Heart...1 What is Atrial Fibrillation...3 Risks of Afib: Stroke...5 Treatment Options...7 Radiofrequency Ablation...9
About Your Ventricular Assist Device (VAD) Surgery
 About Your Ventricular Assist Device (VAD) Surgery Why do I need surgery for a Heart Pump or Ventricular Assist Device (VAD)? VAD s may help you live longer. These electric powered heart pumps are put
About Your Ventricular Assist Device (VAD) Surgery Why do I need surgery for a Heart Pump or Ventricular Assist Device (VAD)? VAD s may help you live longer. These electric powered heart pumps are put
X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary
 X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate
X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate
What is a Small Bowel Capsule Endoscopy?
 What is a Small Bowel Capsule Endoscopy? Capsule endoscopy is a way for your doctor to see inside part of your digestive system. A small bowel capsule endoscopy looks at the lining of the small intestine.
What is a Small Bowel Capsule Endoscopy? Capsule endoscopy is a way for your doctor to see inside part of your digestive system. A small bowel capsule endoscopy looks at the lining of the small intestine.
Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias
 Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Atrial Fibrillation According to the American Heart Association, Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects an estimated 2.7 million
Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Atrial Fibrillation According to the American Heart Association, Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects an estimated 2.7 million
Having a cardiac resynchronisation therapy CRT-P device implanted
 Having a cardiac resynchronisation therapy CRT-P device implanted The aim of this leaflet is to answer any questions you may have about a cardiac resynchronisation therapy device (CRT-P). It explains what
Having a cardiac resynchronisation therapy CRT-P device implanted The aim of this leaflet is to answer any questions you may have about a cardiac resynchronisation therapy device (CRT-P). It explains what
Implantation of an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is an Implantable? Your doctor has recommended that you have an Implantable.
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is an Implantable? Your doctor has recommended that you have an Implantable.
THERAPY Baclofen Pump Program at Boston Children s Hospital
 BACLOFEN PUMP THERAPY Baclofen Pump Program at Boston Children s Hospital PAGER: 617-355-6369 and ask to page #7867 (PUMP) 1 Contents What is spasticity?... 3 What is baclofen?... 3 The evaluation for
BACLOFEN PUMP THERAPY Baclofen Pump Program at Boston Children s Hospital PAGER: 617-355-6369 and ask to page #7867 (PUMP) 1 Contents What is spasticity?... 3 What is baclofen?... 3 The evaluation for
WHAT TO EXPECT FOLLOWING MASTECTOMY AND IMMEDIATE RECONSTRUCTION WITH TISSUE EXPANDERS OR IMPLANTS
 WHAT TO EXPECT FOLLOWING MASTECTOMY AND IMMEDIATE RECONSTRUCTION WITH TISSUE EXPANDERS OR IMPLANTS Before Your Surgery 1 week before your surgery, please stop taking the following medications: o NSAIDs
WHAT TO EXPECT FOLLOWING MASTECTOMY AND IMMEDIATE RECONSTRUCTION WITH TISSUE EXPANDERS OR IMPLANTS Before Your Surgery 1 week before your surgery, please stop taking the following medications: o NSAIDs
Fistula for Hemodialysis
 St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton Kidney and Urinary Program Fistula for Hemodialysis What is a fistula? A fistula is the joining of an artery and a vein by a surgeon. The fistula is called an access. It
St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton Kidney and Urinary Program Fistula for Hemodialysis What is a fistula? A fistula is the joining of an artery and a vein by a surgeon. The fistula is called an access. It
Excisiona I Breast Biopsy
 Post-Surgery Instructions for: Excisiona I Breast Biopsy Orlando Health Surgical Group 14 West Gore Street Orlando, FL 32806 321-843-5001 Michael Kahky, MD, F.A.C.S Marc Demers, MD, F.A.C.S Jeffrey R.
Post-Surgery Instructions for: Excisiona I Breast Biopsy Orlando Health Surgical Group 14 West Gore Street Orlando, FL 32806 321-843-5001 Michael Kahky, MD, F.A.C.S Marc Demers, MD, F.A.C.S Jeffrey R.
Parkinson s disease, Essential Tremor and primary dystonia
 Parkinson s disease, Essential Tremor and primary dystonia What is Deep Brain Stimulation and how does it work? Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) uses one or two surgically implanted medical devices, similar
Parkinson s disease, Essential Tremor and primary dystonia What is Deep Brain Stimulation and how does it work? Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) uses one or two surgically implanted medical devices, similar
Patient Information for Consent
 Patient Information for Consent ER OS01 Total Hip Replacement Enhanced Recovery Expires end of February 2017 Issued June 2016 Local information If you need any more information please contact your BMI
Patient Information for Consent ER OS01 Total Hip Replacement Enhanced Recovery Expires end of February 2017 Issued June 2016 Local information If you need any more information please contact your BMI
Open Surgery for AAA
 Open Surgery for AAA A Weakened Blood Vessel What does it mean to have an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)? This is a balloon-like bulge in a major blood vessel, the aorta. The bulge forms at a weak place
Open Surgery for AAA A Weakened Blood Vessel What does it mean to have an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)? This is a balloon-like bulge in a major blood vessel, the aorta. The bulge forms at a weak place
Atrial Fibrillation and Options to Reduce Your Risk of Blood Clots and Stroke
 YOUR VALUES YOUR PREFERENCES YOUR CHOICE Atrial Fibrillation and Options to Reduce Your Risk of Blood Clots and Stroke Anticoagulant Medicine and Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Device Understanding Your
YOUR VALUES YOUR PREFERENCES YOUR CHOICE Atrial Fibrillation and Options to Reduce Your Risk of Blood Clots and Stroke Anticoagulant Medicine and Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion Device Understanding Your
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy with Defibrillation (CRT-D)
 A decision aid for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy with Defibrillation (CRT-D) For patients with heart failure who are getting cardiac resynchronization therapy and considering defibrillation CRT-D See
A decision aid for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy with Defibrillation (CRT-D) For patients with heart failure who are getting cardiac resynchronization therapy and considering defibrillation CRT-D See
12 Lead EKG. Brigham and Women's Hospital
 12 Lead EKG What is the heart? The heart is the organ that is responsible for pumping blood rich in oxygen to all parts of the body It is located in the center of the chest and is approximately the size
12 Lead EKG What is the heart? The heart is the organ that is responsible for pumping blood rich in oxygen to all parts of the body It is located in the center of the chest and is approximately the size
Heart Failure Overview
 Heart Failure Overview Help us make this guide better! Please fill out the brief survey at the back of the book or complete it online at heartandstroke.ca/feedback I Understanding Heart Failure The Basics
Heart Failure Overview Help us make this guide better! Please fill out the brief survey at the back of the book or complete it online at heartandstroke.ca/feedback I Understanding Heart Failure The Basics
MANAGING POST-OP PAIN AT HOME
 MANAGING POST-OP PAIN AT HOME Medicines and Self-Care After Surgery Managing Pain at Home Pain is expected after surgery. Know that you have a right to have this pain controlled. Managing pain helps you
MANAGING POST-OP PAIN AT HOME Medicines and Self-Care After Surgery Managing Pain at Home Pain is expected after surgery. Know that you have a right to have this pain controlled. Managing pain helps you
Ankle Arthroscopy. Removing Loose Bodies and Spurs
 Ankle Arthroscopy Removing Loose Bodies and Spurs What Is Arthroscopy? Your joints help you move freely. But living with a worn or injured joint can make an active lifestyle painful. Your orthopaedic surgeon
Ankle Arthroscopy Removing Loose Bodies and Spurs What Is Arthroscopy? Your joints help you move freely. But living with a worn or injured joint can make an active lifestyle painful. Your orthopaedic surgeon
What to expect when having a pacemaker implantation
 What to expect when having a pacemaker implantation Cardiology Department Patient information leaflet What is a pacemaker? A pacemaker is a small metal device which contains an electronic circuit and a
What to expect when having a pacemaker implantation Cardiology Department Patient information leaflet What is a pacemaker? A pacemaker is a small metal device which contains an electronic circuit and a
Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures
 Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed after you
Patient Education Cardiac Catheterization Lab Procedures This handout describes how cardiac catheterization works. It also explains how to prepare for your procedure and the self-care needed after you
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Pacemaker (CRT-P)
 Patient information Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Pacemaker (CRT-P) i Important information for all patients requiring resynchronisation therapy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank,
Patient information Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy Pacemaker (CRT-P) i Important information for all patients requiring resynchronisation therapy. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank,
Going home after breast surgery without drains
 Going home after breast surgery without drains Princess Margaret Information for patients and families Read this resource to learn: How to care for yourself when you go home What activities you can do
Going home after breast surgery without drains Princess Margaret Information for patients and families Read this resource to learn: How to care for yourself when you go home What activities you can do
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) For patients with tremor
 Patient Education Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) For patients with tremor Please read this handout before reading and signing the form Special Consent for Procedural Treatment. This handout describes how
Patient Education Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) For patients with tremor Please read this handout before reading and signing the form Special Consent for Procedural Treatment. This handout describes how
