thromboembolic disease deep vein thrombophlebitis superficial thrombophlebitis phlegmasia cereulea dolens pulmonary embolism
|
|
|
- Jonah Baker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 acute venous disease acute mitchell h. goldman md department of surgery the university of tennessee graduate school of medicine knoxville, tennessee
2 thromboembolic disease deep vein thrombophlebitis superficial thrombophlebitis phlegmasia cereulea dolens pulmonary embolism
3 some facts over 250,000/yr 000/yr die of pulmonary embolism 600, hospitalizations/yr ti for DVT 1-2% of hospitalized patients $ billion per yr.
4 risk factors Hx of dvt, p.e. sepsis prolonged sitting, congestive heart failure standing age >60 obesity recent surgery, trauma immobility paralysis malignancy hypercoaguable state smoking BCPs pregnancy (>3) venous insufficiency copd venous incompetence nephrotic syndrome
5 congenital disorders atiii deficiency protein c, s deficiency apc resistance (leiden mutation) prothrombin 20210a homocystinemia heparin cofactor II deficiency dysfibrinogenemia inc. factor VII decreased pa; increased pai g4 gene abnormal plasminogen
6 acquired risk factors heparin induced thrombocytopenia warfarin induced thrombosis antiphospholipid syndrome estrogens pregnancy diabetes mellitus
7 antithrombin three deficiency antithrombin inhibits factors IX a, X a, Xi a, and XII a, thrombin risk ik of fth thrombosis increases when functional activity is less than 80% decreased in liver disease, sepsis, dic, bcps heparin, ffp, atiii replacement, warfarin prophylaxis in prothrombotic events
8 protein c and s deficiency vitamin k dependant liver proteins activated by thrombin, bound to endothelial l cell thrombomodulin degrades factor V a and XIII a, decreases tissue pai protein s is a cofactor autosomal dominant 1:300
9 protein c and s deficiency-2 venous thrombosis at early age in heterozygotes (30-70% levels) prophylaxis with warfarin, heparin fresh frozen plasma to correct life long warfarin for thromboses warning!!! cutaneous necrosis on warfarin more likely
10 activated protein c resistance(factor V Leiden) most common inherited cause of thrombosis (3-15% caucasians) factor V resistance to degradation d by activated protein c 7 fold risk of venous thrombosis life long warfarin
11 homocystinemia increased risk of early onset dvt increased incidence of recurrent dvt platelet activation, increased factor VII and V, decreased protein c activity, mthfr mutation 39-50% of patients may have normal levels in fasting state folate (1-15mg/day), 15mg/day), B 12,B 6
12 prothrombin elevated levels of prothrombin nucleotide change (g to a transition) arterial thrombosis (coronary and cerebral), warfarin for early and recurrent thromboses
13 pregnancy 5 fold increased risk of dvt increase in factors I, VII, VIII, IX, X, XII, platlets, t pai-1,2 12 decrease in protein c and antithrombin rule out thrombophillic states prophylaxis for 2nd pregnancy
14 antiphospholipid syndrome acquired, drug induced 1-5% of the population 50% of pts over 80 lupus anticoagulants, anticardiolipin antibodies antibodies against B 2 glycoproteins, prothrombin, platlets, endothelial cells, protein c,s
15 antiphospholipid syndrome test for both anticardiolipin and lupus anticoagulant advise against oral contraception ti or pregnancy lifelong warfarin INR
16 combination of two factors=70-90% risk of vte
17 treatment goals prevent pulmonary embolism prevent propagation prevent postphlebitic sequellae
18 dvt diagnosis classic signs tumor-swelling, unilateral edema dolor-tenderness over the vein course in the thigh, calf muscles calor-not usually found rubor-if associated with svt Homans sign-present in 1/3 of patients with dvt and 1/2 of those without
19 diagnosis 2 clinical diagnosis is confirmed in 30-50%
20 differential diagnosis svt cellulitis/lymphangitis muscle or soft tissue injury achilles tendonitis asymmetric 2 0 edema baker s cyst arthritis post-phlebitic phlebitic syndrome
21 svt and dvt if you have svt in a patient with varicose veins, 4% chance of dvt without t varicose veins, 40% chance of concomitant dvt with proximal svt risk of dvt is 10%
22 duplex scan diagnostic tests d-dimerdimer venography mri/ct scan
23 acute dvt diagnosis ascending phlebography gold standard > 95% accurate least accurate in femoral, iliac or foot risks of p.e., causing dvt are low superficial vein filling preferentially site, adherence, extent, age observer error
24 phlebography dilution bubbles meniscus RR Tracks collateral
25 may-thurner syndrome a left iliac venous occlusion by left iliac venous occlusion by crossing rt. iliac artery
26 venography infiltration
27 doppler wave: continuous if hand held pulsed on duplex 5 MHZ probe, 60 degree angle listen for: spontaneous flow respiratory variation segmental tl augmentation tti competency of valves pulsatility
28 respiratory variation
29 augmentation position important evaluate tibials popliteal sfv cfv iliac saphenous
30 reflux
31 duplex scan Bmode MHZ linear array probe color to demonstrate flow grey scale to assess chronic changes assesses the iliac / vena cava better
32 duplex femoral vein
33 duplex scan criteria compressibility deep femoral superficial i femoral at adductor hiatus posterior tibialis at ankle augmentation competent phasic
34 compressibility
35 venous hemodynamics
36 dvt acute vs. chronic acute Less echogenic Vein distension i Homogeneity Free floating
37 dvt acute vs. chronic
38 dvt acute vs. chronic chronic echogenic vein retraction heterogeneity clot retraction collaterals recanalization
39 duplex rationale duplex least accurate in infrapopliteal veins incidence id of P.E. from infrapopliteal l veins low often don t treat calf thromboses incidence of progression >35% to popliteal in 24 hrs
40 duplex scan accuracy SENSITIVITY SPECIFICITY (%) (%) FEMORAL POPLITEAL POPLITEAL/UPPER CALF TIBIOPERONEAL
41 computed tomography THROMBUS-HALO
42 Hey you!! YEAH, YOU IN THE THIRD ROW!!!!!!!! WAKE UP!
43 d-dimerdi products of degradation of cross linked fibrin by plasmin up to 98% sensitive to diagnosis of DVT low as 38% specific malignancy, recent surgery, hospitalized for>3 days high Negative Predictive Value (if it s negative it high Negative Predictive Value (if it s negative it ain t there)
44 pre-testing stratification Clinical i l Feature Pts Active cancer 1 Paralysis, paresis, immobilization 1 Bed ridden >3days/Surgery<4 weeks 1 Tenderness along deep veins 1 Entire leg swollen 1 Swelling >3 cm vs other leg(10cm below tuberosity) 1 Pitting edema 1 Non-varicose superficial collateral veins 1 Alternative vediagnosis slikely minus 2 Probability: Low<0, Moderate 1-2, High>3 Lancet 350:1795, 97
45 diagnostic algorithm for outpatients Suspect Acute DVT Determine Pre-test Probability Low Moderate High D-Dimer D-Dimer Neg Pos Neg Pos Excludes Duplex Excludes Duplex DVT DVT Excludes: inpts, previous DVT, p anticoagulants, suspect PE
46 Prophylaxis-Hospitalized Low Risk Early and continuous ambulation, graduated stockings Moderate Risk Compression Device, s.c. low dose UFH or LMWH High Risk and/or low dose UFH or LMWH once or twice dil daily, or oral anticoagulant, t IPCD
47 dvt treatment tibio-peroneal fem-pop/iliofemoral recurrent phlegmasia cereulea dolens
48 tibio-peroneal dvt controversial to heparinize or not if you do, use outpt t therapy with LMWH if you don t, use nonsteroidals ambulation support hose restudy for propagation
49 ilio-fem fem-pop dvt 20% of popliteal untreated propagate LMWH or unfractionated heparin rate of propagation p and p.e. same ambulation early bed rest increases propagation p 20 to 1 swelling diminished sooner with ambulation and. support hose-class II early warfarin
50 recurrent dvt look for HCS or other reason if already on coumadin, add ASA/plavix retreat if not on anticoagulants consider lifelong coumadin Up to 20% recurrence
51 Differential Effects of UFH and LMWH on Factor Xa and Thrombin Hirsh J, Levine MN. Blood ; 79:
52 UFH vs LMWH high mw (15,000) low MW ( ) bioavailability b <30% >90% short t 1/2 low Anti-Xa/IIa drug interactions continuous/inpatient longer high Anti-Xa/IIa ratio fewer intermittent/outpatient
53 UFH vs LMWH recurrence (%) bleeding 1220(%) (%) death (%) HIT 1-2(%) 1-2
54 patients not suitable for outpatient severe liver disease thrombocytopenia renal disease high risk of falling acute p.e. therapy other reasons for hospitalization
55 LMWH or inpatient therapy continuous iv heparin by nomogram loading dose of U/kg U/kg/hr check aptt <35 sec rebolus and 4U/kg/hr sec ok >70 sec decrease or stop for 2 hrs
56 long term therapy start coumadin when aptt therapeutic or after 2 days of LMWH overlap of at least 5 days or until therapeutic INR of mo. reduces the frequency of recurrence over 1-2mo (6% vs 11-18%) 18%) check venous hemodynamics
57 alternatives to coumadin ximelagatran(oral iia ) max level l h hrs vte prophylaxis, decreased recurrent dvt vs lmwh +warfarin acute coronary syndrome with asa transient liver toxicity dabigatran (oral iia) vte prophylaxis phase iii equivalent to enoxaparin peak =2hrs; t ½ =15 hrs
58 alternatives to coumadin razaxaban factor xa inhibitor s.c. administration liver metabolized randomized knee replacement» dose dependant reduction in vte compared to lmwh» dose dependant increase in bleeding
59 HIT ufh acts as a hapten between platelet membrane and pf-4 uncommon in dialysis i pts-why? monitor pt ct every other day for 14 days lmwh 1/10 th incidence of hit 50% fall in platelets or below 150,000/ul argatroban (2.0 ug/kg/min)
60 argatroban direct thrombin (iia) inhibitor synthetic analog of hirudin (smaller molecule) l t ½ =30-60 mins. hepatic clearance i.v. administration monitor aptt
61 primary axillary/subclavian vein thrombosis (Paget-Schroetter) Sh 2 o to hypertrophy of the scalenus muscles or an abnormal rib duplex and venography, MVOV heparinization thrombylysis look for causes repair anticoagulation without repair-chronic problems and recurrence repair of anomalies should be done within a wk after lysis
62 Paget-Schroetter Syndrome TOS thoracic outlet diltd dilated superficial fiilveins cervical rib
63 Paget-Schroetter Straight Elevated
64 secondary axillary/subclavian vein thrombosis prevention-use I.J. preferentially avoid long termed central lines, pic lines surveillance thrombolysis early followed by anticoagulation catheter removal depends on necessity vs symptoms
65 phlegmasia iliofemoral thrombosis thrombectomy vs thrombolysis contraindication to lysis viability of limb (alba) popliteal approach for lysis with or without fistula post thrombotic sequellae anticoagulation
66 phlegmasia cereulea dolens
67 phlegmasia cereulea dolens if no P s Ps anticoagulate, elevate/ambulate, stockings P Pain Pallor Poikilothermia -Pulseless -PARESTHESIA -PARALYSIS even in the presence of arterial flow if the two big P s are present, thrombectomy and fasciotomy are necessary
68 thrombectomy
69 Thrombolysis systemic/regional better venous patency and less post thrombotic syndrome bleeding, long treatment times catheter directed patency and function improved over systemic possibly decreased bleeding life function better mechanical often needs thrombolytic therapy after
70 Thrombolysis pharmacomechanical seed with tpa mechanical thrombectomy increases clearing of clot fewer pts need regional or catheter thrombolysis for shorter times
71 phlegmasia-thrombolysis
72 Phlegmasia-thrombolysis popliteal access
73 adjunctive measures may-thurner
74 may-thurner after stent 90% 1 yr patency
75 Maximum Venous Outflow Velocity Evocative test measuring venous outflow velocity using a standardized thigh blood pressure cuff pressureand duplex obtained femoral vein velocities upon release to detect venous outflow obstruction. Lebow et al (UTMCK): MVOV is significantly decreased on the left side in a sample of normal female volunteers and can be used as a preliminary test to Dx functional venous outflow obstruction.
76 Left Venous Outflow Obstruction MVOV 82 cm/sec MVOV 40 cm/sec R L
77 amyth bed rest in acute dvt reduces the risk of pe, alleviates pain, and decreases swelling
78 no difference in pe between lmwh and bed rest and lmwh and d4h hrs ambulation a day and compression clinically asymptomatic pe was found by scan in ½ of pts at the time of dvt diagnosis ambulation and compression reduces stasis and thrombus propagation (26% vs 1%) ambulation blti and compression leads to faster pain relief lifand less swelling Reduces the frequency and severity of post thrombotic syndrome
79 Indications (classical) major p.e. p.e. on adequate anticoagulation loose clot ivc filters respiratory insufficiency can t anticoagulate 1-4% recurrence
80 ivc filters not so classical reasons cancer surgery and dvt hit trauma free floating morbid obesity surgery venous reconstruction, endovascular procedures
81 removable filters
82 removable filters Opt-Ease
83 rationale higher incidence of dvt after filter ivc thrombosis migration strut fracture ( ) Penetration ( ) Duodenum, ureter, aorta infection trauma pregnancy short termed prophylaxis
84 removable filter as yet, no clear-cut indications for use
85 summary-what s new since I last gave grand rounds on this subject over two years ago d-dimerdimer lmwh outpt therapy replacement for heparin-argatrobansargatrobans replacement for coumadin thrombolysis ct diagnosis of pe removable filters MVOV
86
87
Venous thrombosis is common and often occurs spontaneously, but it also frequently accompanies medical and surgical conditions, both in the community
 Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center
 Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Mabel Labrada, MD Miami VA Medical Center *1-Treatment for acute DVT with underlying malignancy is for 3 months. *2-Treatment of provoked acute proximal DVT can be stopped after 3months of treatment and
Disclosures. DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Questions To Ask. Dr. Susanna Shin - DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment. Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) None
 Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Disclosures DVT: Diagnosis and Treatment None Susanna Shin, MD, FACS Assistant Professor University of Washington Acute Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Risk factors for DVT. Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Anticoagulation (cont d) Diagnosis 1/5/2018. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Risk factors for DVT Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism. Ahmed Mahmoud, MD
 Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
Venous thrombosis & pulmonary embolism Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Risk factors for DVT Surgery ; post op especially for long cases, pelvic operations (THR), Trauma ; long bone fractures, pelvic fractures (posterior
DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO IMPROVING CLINICAL OUTCOMES
 DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO IMPROVING CLINICAL OUTCOMES Jose M. Borromeo M.D. Vascular Surgeon Iowa Heart Center Disclosures: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals Cook CVRx LeMaitre Vascular,
DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS A PRACTICAL APPROACH TO IMPROVING CLINICAL OUTCOMES Jose M. Borromeo M.D. Vascular Surgeon Iowa Heart Center Disclosures: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals Cook CVRx LeMaitre Vascular,
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT
 DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT): TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide an evidence-based approach to treatment of patients presenting with deep vein thrombosis (DVT). BACKGROUND: An estimated 45,000 patients in Canada
CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevalence Patho-physiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Management of DVT/PE Prevention VTE Patho-physiology
CHAPTER 2 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prevalence Patho-physiology Risk Factors Diagnosis Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Management of DVT/PE Prevention VTE Patho-physiology
Approach to Thrombosis
 Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
Approach to Thrombosis Theera Ruchutrakool, M.D. Division of Hematology Department of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Faculty of Medicine Mahidol University Approach to Thrombosis Thrombosis: thrombus formation
Surgical approach for DVT. Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine
 Surgical approach for DVT Seung-Kee Min Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine Treatment Options for Venous Thrombosis Unfractionated heparin &
Surgical approach for DVT Seung-Kee Min Division of Vascular Surgery Department of Surgery Seoul National University College of Medicine Treatment Options for Venous Thrombosis Unfractionated heparin &
Jordan M. Garrison, MD FACS, FASMBS
 Jordan M. Garrison, MD FACS, FASMBS Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Near or Complete obstruction of > 1 Peripheral Artery Peripheral Venous reflux Disease Varicose Veins Chronic Venous Stasis Ulcer Disease
Jordan M. Garrison, MD FACS, FASMBS Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) Near or Complete obstruction of > 1 Peripheral Artery Peripheral Venous reflux Disease Varicose Veins Chronic Venous Stasis Ulcer Disease
Dr. Riaz JanMohamed Consultant Haematologist The Hillingdon Hospital Foundation Trust
 MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) IN THE COMMUNITY SETTING & ANTICOAGULATION CLINICS THE PAST, PRESENT AND THE FUTURE Dr. Riaz JanMohamed Consultant Haematologist The Hillingdon Hospital
MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT) IN THE COMMUNITY SETTING & ANTICOAGULATION CLINICS THE PAST, PRESENT AND THE FUTURE Dr. Riaz JanMohamed Consultant Haematologist The Hillingdon Hospital
Thrombophilia. Diagnosis and Management. Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI
 Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
Thrombophilia Diagnosis and Management Kevin P. Hubbard, DO, FACOI Clinical Professor of Medicine Kansas City University of Medicine and Biosciences-College of Osteopathic Medicine Kansas City, Missouri
Venous interventions in DVT
 Venous interventions in DVT Sriram Narayanan Chief of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Tan Tock Seng Hospital A/Prof of Surgery, National University of Singapore ANTI-COAGULATION LMWH Warfarin x 6m Acute
Venous interventions in DVT Sriram Narayanan Chief of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Tan Tock Seng Hospital A/Prof of Surgery, National University of Singapore ANTI-COAGULATION LMWH Warfarin x 6m Acute
DOPPLER ULTRASOUND OF DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS
 TOKUDA HOSPITAL SOFIA DOPPLER ULTRASOUND OF DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS MILENA STANEVA, MD, PhD Department of vascular surgery and angiology Venous thromboembolic disease continues to cause significant morbidity
TOKUDA HOSPITAL SOFIA DOPPLER ULTRASOUND OF DEEP VENOUS THROMBOSIS MILENA STANEVA, MD, PhD Department of vascular surgery and angiology Venous thromboembolic disease continues to cause significant morbidity
Suspected Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Pathway for Non Pregnant patients Updated November 2016, with new D-dimer reference range
 Suspected Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Pathway for Non Pregnant patients Updated November 2016, with new D-dimer reference range Suspect a DVT? Complete a Two-level DVT Wells score on ICE system (see page
Suspected Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Pathway for Non Pregnant patients Updated November 2016, with new D-dimer reference range Suspect a DVT? Complete a Two-level DVT Wells score on ICE system (see page
Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach
 Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach Hae Giu Lee, MD Professor, Dept of Radiology Seoul St. Mary s Hospital The Catholic University of Korea Introduction Incidence High incidence: 250,000-1,000,000/year
Interventional Treatment VTE: Radiologic Approach Hae Giu Lee, MD Professor, Dept of Radiology Seoul St. Mary s Hospital The Catholic University of Korea Introduction Incidence High incidence: 250,000-1,000,000/year
Pulmonary Thromboembolism
 Pulmonary Thromboembolism James Allen, MD Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism 1,500,000 new cases per year in the United States Often asymptomatic 300,000 deaths per year DVT or PE present in 10% of ICU
Pulmonary Thromboembolism James Allen, MD Epidemiology of Pulmonary Embolism 1,500,000 new cases per year in the United States Often asymptomatic 300,000 deaths per year DVT or PE present in 10% of ICU
PE and DVT. Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP
 PE and DVT Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call +256777363201 Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP OBJECTIVES DEFINE DVT AND P.E PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DVT CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF DVT/PE INVESTIGATE DVT MANAGEMENT
PE and DVT Dr Anzo William Adiga WatsApp or Call +256777363201 Medical Officer/RHEMA MEDICAL GROUP OBJECTIVES DEFINE DVT AND P.E PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF DVT CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF DVT/PE INVESTIGATE DVT MANAGEMENT
Hemostasis. PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures
 Hemostasis PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures Disorders of Hemostasis - Hemophilia - von Willebrand Disease HEMOPHILIA A defect in the thrombin propagation phase
Hemostasis PHYSIOLOGICAL BLOOD CLOTTING IN RESPONSE TO INJURY OR LEAK no disclosures Disorders of Hemostasis - Hemophilia - von Willebrand Disease HEMOPHILIA A defect in the thrombin propagation phase
This chapter will describe the effectiveness of antithrombotic
 Antithrombotic Therapy for Venous Thromboembolic Disease The Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy Harry R. Büller, MD, Chair; Giancarlo Agnelli, MD; Russel D. Hull, MBBS,
Antithrombotic Therapy for Venous Thromboembolic Disease The Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy Harry R. Büller, MD, Chair; Giancarlo Agnelli, MD; Russel D. Hull, MBBS,
Optimal Utilization of Thrombolytics
 April 8-9, 2011 New York LaGuardia Marriott COMPLETE MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS DISEASE Optimal Utilization of Thrombolytics Anthony J. Comerota, MD, FACS, FACC Director, Jobst Vascular Institute Adjunct Professor
April 8-9, 2011 New York LaGuardia Marriott COMPLETE MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS DISEASE Optimal Utilization of Thrombolytics Anthony J. Comerota, MD, FACS, FACC Director, Jobst Vascular Institute Adjunct Professor
Not all Leg DVT s are the Same: Which Patients Benefit from Interventional Therapy? Case 1:
 12/16/2015 Not all Leg DVT s are the Same: Which Patients Benefit from Interventional Therapy? Constantino S.Peña, FSIR, FSCCT, FAHA Interventional Radiologist Medical Director, Vascular Imaging Miami
12/16/2015 Not all Leg DVT s are the Same: Which Patients Benefit from Interventional Therapy? Constantino S.Peña, FSIR, FSCCT, FAHA Interventional Radiologist Medical Director, Vascular Imaging Miami
DISORDERS OF VENOUS SYSTEM
 DISORDERS OF VENOUS SYSTEM Varicose Veins Any dilated, elongated and tortuous vein irrespective of size Varicose veins are common in the superficial veins of the leg which are subject to high pressure
DISORDERS OF VENOUS SYSTEM Varicose Veins Any dilated, elongated and tortuous vein irrespective of size Varicose veins are common in the superficial veins of the leg which are subject to high pressure
THERE IS NO ROLE FOR SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DVT
 THERE IS NO ROLE FOR SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DVT Tara D. Balint, MD FACS Sentara RMH Thursday, June 14, 2018 1 Objectives of treatment for DVT Prevent death from PE Prevent recurrent VTE Prevent post-thrombotic
THERE IS NO ROLE FOR SURGICAL THERAPY FOR DVT Tara D. Balint, MD FACS Sentara RMH Thursday, June 14, 2018 1 Objectives of treatment for DVT Prevent death from PE Prevent recurrent VTE Prevent post-thrombotic
DVT - initial management NSCCG
 Background information Information resources for patients and carers Updates to this care map Synonyms Below knee DVT and bleeding risks Patient with confirmed DVT Scan confirms superficial thrombophlebitis
Background information Information resources for patients and carers Updates to this care map Synonyms Below knee DVT and bleeding risks Patient with confirmed DVT Scan confirms superficial thrombophlebitis
Thrombosis. By Dr. Sara Mohamed Abuelgasim
 Thrombosis By Dr. Sara Mohamed Abuelgasim 1 Thrombosis Unchecked, blood coagulation would lead to dangerous occlusion of blood vessels if the protective mechanisms of coagulation factor inhibitors, blood
Thrombosis By Dr. Sara Mohamed Abuelgasim 1 Thrombosis Unchecked, blood coagulation would lead to dangerous occlusion of blood vessels if the protective mechanisms of coagulation factor inhibitors, blood
Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology
 Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology Iliac Vein Compression Syndrome Left CIV compressed by right CIA Virchow 1851: DVT L>R May and Thurner 1954: venous spurs Cockett and Thomas 1965:
Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology Iliac Vein Compression Syndrome Left CIV compressed by right CIA Virchow 1851: DVT L>R May and Thurner 1954: venous spurs Cockett and Thomas 1965:
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM. Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow
 CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
CURRENT & FUTURE THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Gordon Lowe Professor of Vascular Medicine University of Glasgow VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Common cause of death and disability 50% hospital-acquired
With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis
 BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital April
BRIGHAM AND WOMEN S HOSPITAL With All the New Drugs, This is How I Treat Acute DVT and Superficial Phlebitis Gregory Piazza, MD, MS Division of Cardiovascular Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital April
Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE)
 Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Whal Lee, M.D. Seoul National University Hospital Department of Radiology 2 nd EFORT Asia Symposium, 3 rd November 2010, Taipei DVT - Risk Factors Previous
Proper Diagnosis of Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Whal Lee, M.D. Seoul National University Hospital Department of Radiology 2 nd EFORT Asia Symposium, 3 rd November 2010, Taipei DVT - Risk Factors Previous
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information
 Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are both disorders of unwanted blood clotting. Unwanted blood clots can occur
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are both disorders of unwanted blood clotting. Unwanted blood clots can occur
Disclosures. What is a Specialty Vein Clinic? Prevalence of Venous Disease. Management of Venous Disease: an evidence based approach.
 Management of Venous Disease: an evidence based approach Disclosures Ed Boyle, MD Andrew Jones, MD Dr. Ed Boyle and Dr. Andrew Jones disclose Grants/research support: Medtronic, BTG International, Clearflow,
Management of Venous Disease: an evidence based approach Disclosures Ed Boyle, MD Andrew Jones, MD Dr. Ed Boyle and Dr. Andrew Jones disclose Grants/research support: Medtronic, BTG International, Clearflow,
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients. David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center
 DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
DVT Pathophysiology and Prophylaxis in Medically Hospitalized Patients David Liff MD Oklahoma Heart Institute Vascular Center Overview Pathophysiology of DVT Epidemiology and risk factors for DVT in the
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Outline of This Presentation
 Slide 1 Current Approaches to Venous Thromboembolism Prevention in Orthopedic Patients Hujefa Vora, MD Maria Fox, RN June 9, 2017 Slide 2 Slide 3 Outline of This Presentation Pathophysiology of venous
Slide 1 Current Approaches to Venous Thromboembolism Prevention in Orthopedic Patients Hujefa Vora, MD Maria Fox, RN June 9, 2017 Slide 2 Slide 3 Outline of This Presentation Pathophysiology of venous
Aggressive endovascular management of ilio-femoral DVT. thrombotic syndrome. is the key in preventing post
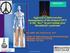 CACVS 2017 Aggressive endovascular management of ilio-femoral DVT is the key in preventing post thrombotic syndrome ALI AMIN MD, FACS,FACC, RVT CHIEF OF ENDOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS READING HEALTH SYSTEM
CACVS 2017 Aggressive endovascular management of ilio-femoral DVT is the key in preventing post thrombotic syndrome ALI AMIN MD, FACS,FACC, RVT CHIEF OF ENDOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS READING HEALTH SYSTEM
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
PULMONARY EMBOLISM (PE): DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OBJECTIVE: To provide a diagnostic algorithm and treatment options for patients with acute pulmonary embolism (PE). BACKGROUND: Venous thromboembolism (VTE)
BC Vascular Day. Contents. November 3, Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3. Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6. Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8
 BC Vascular Day Contents Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3 November 3, 2018 Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6 Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Conservative Management Risk factor modification
BC Vascular Day Contents Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm 2 3 November 3, 2018 Peripheral Arterial Disease 4 6 Deep Venous Thrombosis 7 8 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Conservative Management Risk factor modification
Treatment of acute thrombosis of axillo-subclavian vein
 Treatment of acute thrombosis of axillo-subclavian vein Yang Jin Park Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine CASE A 32-year-old male patient 3-day history of
Treatment of acute thrombosis of axillo-subclavian vein Yang Jin Park Vascular Surgery, Samsung Medical Center Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine CASE A 32-year-old male patient 3-day history of
NOTE: The first appearance of terms in bold in the body of this document (except titles) are defined terms please refer to the Definitions section.
 TITLE VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM PROPHYLAXIS SCOPE Provincial Acute and Sub-Acute Care Facilities APPROVAL AUTHORITY Alberta Health Services Executive Committee SPONSOR Vice President, Quality and Chief Medical
TITLE VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM PROPHYLAXIS SCOPE Provincial Acute and Sub-Acute Care Facilities APPROVAL AUTHORITY Alberta Health Services Executive Committee SPONSOR Vice President, Quality and Chief Medical
Implications from the ACCP 2012 Consensus Guidelines for the Management of Thrombosis: a case based approach
 Implications from the ACCP 2012 Consensus Guidelines for the Management of Thrombosis: a case based approach Prof. I. Baumgartner Head Clinical and Interventional Angiology About the ACCP guidelines Widely
Implications from the ACCP 2012 Consensus Guidelines for the Management of Thrombosis: a case based approach Prof. I. Baumgartner Head Clinical and Interventional Angiology About the ACCP guidelines Widely
4/23/2009. September 15, 2008
 The Current Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis: Are We Doing Enough? George H. Meier, MD Professor and Chief Division of Vascular Surgery University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio
The Current Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis: Are We Doing Enough? George H. Meier, MD Professor and Chief Division of Vascular Surgery University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Cincinnati, Ohio
Cancer and Thrombosis
 Cancer and Thrombosis The close relationship between venous thromboembolism and cancer has been known since at least the 19th century by Armand Trousseau. Thrombosis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality
Cancer and Thrombosis The close relationship between venous thromboembolism and cancer has been known since at least the 19th century by Armand Trousseau. Thrombosis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality
Treatment of Chronic DVT with EKOS: Reproducing ACCESS PTS Data in Every Day Clinical Practice
 Treatment of Chronic DVT with EKOS: Reproducing ACCESS PTS Data in Every Day Clinical Practice Mert Dumantepe, MD Acibadem Altunizade Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey Department of Cardiovascular Surgery Disclosure
Treatment of Chronic DVT with EKOS: Reproducing ACCESS PTS Data in Every Day Clinical Practice Mert Dumantepe, MD Acibadem Altunizade Hospital, Istanbul, Turkey Department of Cardiovascular Surgery Disclosure
THROMBOSIS RISK FACTOR ASSESSMENT
 Name: Procedure: Doctor: Date: THROMBOSIS RISK FACTOR ASSESSMENT CHOOSE ALL THAT APPLY EACH RISK FACTOR REPRESENTS 1 POINT Age 41 60 years Minor Surgery Planned History of Prior Major Surgery (< 1 month)
Name: Procedure: Doctor: Date: THROMBOSIS RISK FACTOR ASSESSMENT CHOOSE ALL THAT APPLY EACH RISK FACTOR REPRESENTS 1 POINT Age 41 60 years Minor Surgery Planned History of Prior Major Surgery (< 1 month)
Lower Limb Venous Ultrasound. Colin P. Griffin MSc, BSc (Hons)
 Lower Limb Venous Ultrasound Colin P. Griffin MSc, BSc (Hons) Peripheral Vessels Lower Limb Peripheral Vessels Lower Limb Venous Deep System Common Iliac External/Internal Iliac Common Femoral Femoral
Lower Limb Venous Ultrasound Colin P. Griffin MSc, BSc (Hons) Peripheral Vessels Lower Limb Peripheral Vessels Lower Limb Venous Deep System Common Iliac External/Internal Iliac Common Femoral Femoral
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT?
 How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
How long to continue anticoagulation after DVT? Dr. Nihar Ranjan Pradhan M.S., DNB (Vascular Surgery), FVES(UK) Consultant Vascular Surgeon Apollo Hospital, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad (Formerly Faculty in
Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders
 SURGICAL GRAND ROUNDS March 17 th, 2007 Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders Guillermo Escobar, M.D. LMWH vs UFH Jayer s sales pitch: FALSE LMW is
SURGICAL GRAND ROUNDS March 17 th, 2007 Low Molecular Weight Heparin for Prevention and Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Disorders Guillermo Escobar, M.D. LMWH vs UFH Jayer s sales pitch: FALSE LMW is
Copy Here. The Easy One.. What is the Role of Thrombus Removal in Acute Proximal DVT after ATTRACT? Deep Venous Thrombosis Spectrum
 What is the Role of Thrombus Removal in Acute Proximal DVT after ATTRACT? Mitchell J. Silver DO FACC FSVM RPVI Director, Center for Critical Limb Care Riverside Methodist Hospital Ohio Health Heart and
What is the Role of Thrombus Removal in Acute Proximal DVT after ATTRACT? Mitchell J. Silver DO FACC FSVM RPVI Director, Center for Critical Limb Care Riverside Methodist Hospital Ohio Health Heart and
Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis
 Approved by: Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Vice President and Chief Medical Officer; and Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: Date Approved January
Approved by: Venous Thromboembolism Prophylaxis Vice President and Chief Medical Officer; and Vice President and Chief Operating Officer Corporate Policy & Procedures Manual Number: Date Approved January
Objectives. Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis. Case VTE WHY DO IT? Question: Who Is At Risk?
 Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis Rishi Garg, MD Department of Medicine Identify patients at risk for VTE Options for VTE prophylaxis Current Recommendations (based on The Seventh ACCP
Objectives Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Prophylaxis Rishi Garg, MD Department of Medicine Identify patients at risk for VTE Options for VTE prophylaxis Current Recommendations (based on The Seventh ACCP
Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI
 Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI Cleveland Clinic Heart and Vascular Institute Heather L. Gornik, MD has the following relationships to disclose: CVR Global
Acute Versus Chronic DVT Imaging in the Vascular Lab Heather Gornik, MD, RVT, RPVI Cleveland Clinic Heart and Vascular Institute Heather L. Gornik, MD has the following relationships to disclose: CVR Global
Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism
 Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism Ethan Cumbler M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Hospitalist Medicine Section University of Colorado Denver May 2010 No Conflicts of Interest Objectives
Challenges in Anticoagulation and Thromboembolism Ethan Cumbler M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Hospitalist Medicine Section University of Colorado Denver May 2010 No Conflicts of Interest Objectives
Chronic Iliocaval Venous Occlusive Disease
 none Chronic Iliocaval Venous Occlusive Disease David Rigberg, M.D. Clinical Professor of Surgery Division of Vascular Surgery University of California Los Angeles Chronic Venous Occlusive Disease Chronic
none Chronic Iliocaval Venous Occlusive Disease David Rigberg, M.D. Clinical Professor of Surgery Division of Vascular Surgery University of California Los Angeles Chronic Venous Occlusive Disease Chronic
Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales
 Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales Merimbula, 6 th November 2010 University of Sydney Department of Surgery Westmead Hospital
Prevention and management of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) John Fletcher Wound Care Association of New South Wales Merimbula, 6 th November 2010 University of Sydney Department of Surgery Westmead Hospital
Deep Vein Thrombosis
 Deep Vein Thrombosis Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in a vein. This condition can affect men and women of any age and race. DVT is a potentially serious condition. If not treated,
Deep Vein Thrombosis Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in a vein. This condition can affect men and women of any age and race. DVT is a potentially serious condition. If not treated,
INDICATIONS FOR THROMBO-PROPHYLAXIS AND WHEN TO STOP ANTICOAGULATION BEFORE ELECTIVE SURGERY
 INDICATIONS FOR THROMBO-PROPHYLAXIS AND WHEN TO STOP ANTICOAGULATION BEFORE ELECTIVE SURGERY N.E. Pearce INTRODUCTION Preventable death Cause of morbidity and mortality Risk factors Pulmonary embolism
INDICATIONS FOR THROMBO-PROPHYLAXIS AND WHEN TO STOP ANTICOAGULATION BEFORE ELECTIVE SURGERY N.E. Pearce INTRODUCTION Preventable death Cause of morbidity and mortality Risk factors Pulmonary embolism
Management of Iliac and Femoral Thrombosis. Adam Lackey UCH Surgery Grand Rounds November 13, 2006
 Management of Iliac and Femoral Thrombosis Adam Lackey UCH Surgery Grand Rounds November 13, 2006 Overview Definitions/Anatomy Pathogenesis Prevalence Diagnosis Treatment/Prevention Definitions/Anatomy
Management of Iliac and Femoral Thrombosis Adam Lackey UCH Surgery Grand Rounds November 13, 2006 Overview Definitions/Anatomy Pathogenesis Prevalence Diagnosis Treatment/Prevention Definitions/Anatomy
Diagnostic Algorithms in VTE
 Diagnostic Algorithms in VTE Mark H. Meissner, MD Department of Surgery University of Washington School of Medicine Overutilization of Venous Duplex U/S 1983-1993 (Zweibel et al, Australasian Rad, 1995)
Diagnostic Algorithms in VTE Mark H. Meissner, MD Department of Surgery University of Washington School of Medicine Overutilization of Venous Duplex U/S 1983-1993 (Zweibel et al, Australasian Rad, 1995)
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS
 VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
A A U
 PVD Venous AUC Rating Sheet 2nd Round 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Median I NI MADM Rating Agree Disagree Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation Table 1. Venous Duplex of the Upper Extremities for Patency
PVD Venous AUC Rating Sheet 2nd Round 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Median I NI MADM Rating Agree Disagree Upper Extremity Venous Evaluation Table 1. Venous Duplex of the Upper Extremities for Patency
Updates in Medical Management of Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis. By: Justin Youtsey, Elliott Reiff, William Montgomery, Grant Finlan
 Updates in Medical Management of Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis By: Justin Youtsey, Elliott Reiff, William Montgomery, Grant Finlan Objectives Describe the prevalence of PE and DVT as it relates
Updates in Medical Management of Pulmonary Embolism and Deep Vein Thrombosis By: Justin Youtsey, Elliott Reiff, William Montgomery, Grant Finlan Objectives Describe the prevalence of PE and DVT as it relates
Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
 Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Diagnosis and Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Summary Number 68 Overview Venous thromboembolism
Misunderstandings of Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis
 Misunderstandings of Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis Veerendra Chadachan Senior Consultant Dept of General Medicine (Vascular Medicine and Hypertension) Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Case scenario
Misunderstandings of Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis Veerendra Chadachan Senior Consultant Dept of General Medicine (Vascular Medicine and Hypertension) Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore Case scenario
Starting with deep venous treatment
 Starting with deep venous treatment Carsten Arnoldussen, MD Interventional Radiologist Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht VieCuri Medical Centre, Venlo The Netherlands Background Maastricht
Starting with deep venous treatment Carsten Arnoldussen, MD Interventional Radiologist Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht VieCuri Medical Centre, Venlo The Netherlands Background Maastricht
Deep Vein Thrombosis
 Deep Vein Thrombosis from NHS (UK) guidelines Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in one of the deep veins in the body. Blood clots that develop in a vein are also known as venous thrombosis.
Deep Vein Thrombosis from NHS (UK) guidelines Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in one of the deep veins in the body. Blood clots that develop in a vein are also known as venous thrombosis.
What s New in DVT & PE
 What s New in DVT & PE Mark Buch MD CM CCFP(EM) Attending physician Emergency Department Jewish General Hospital Family Physician and Medical Director GMF Santé Mont-Royal Objectives: Review the diagnostic
What s New in DVT & PE Mark Buch MD CM CCFP(EM) Attending physician Emergency Department Jewish General Hospital Family Physician and Medical Director GMF Santé Mont-Royal Objectives: Review the diagnostic
Pulmonary Embolism Is it the Greatest Danger in Deep Vein Thrombosis?
 Difficult issues in Deep Vein Thrombosis: Pulmonary Embolism Is it the Greatest Danger in Deep Vein Thrombosis? Raluca Dulgheru; C Gherghinescu; B Dorobat; H Muresan; R Darabont; M Cinteza; D Vinereanu
Difficult issues in Deep Vein Thrombosis: Pulmonary Embolism Is it the Greatest Danger in Deep Vein Thrombosis? Raluca Dulgheru; C Gherghinescu; B Dorobat; H Muresan; R Darabont; M Cinteza; D Vinereanu
Resident Teaching Conference 3/12/2010
 Resident Teaching Conference 3/12/2010 Goals Definition and Classification of Acute Limb Ischemia Clinical Assessment of the Vascular Patient History and Physical Diagnostic Modalities Management of Acute
Resident Teaching Conference 3/12/2010 Goals Definition and Classification of Acute Limb Ischemia Clinical Assessment of the Vascular Patient History and Physical Diagnostic Modalities Management of Acute
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS. Pankaj Handa Department of General Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital
 CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS Pankaj Handa Department of General Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital My Talk Today 1.Introduction 2. Are All Cancer Patients at Risk of VTE? 3. Should All VTE Patients Be Screened
CANCER ASSOCIATED THROMBOSIS Pankaj Handa Department of General Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital My Talk Today 1.Introduction 2. Are All Cancer Patients at Risk of VTE? 3. Should All VTE Patients Be Screened
NOTE: Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Risk Factors
 Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is the formation of a blood clot, known as a thrombus, in the deep leg vein. It is a very serious condition that can cause permanent damage to the
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is the formation of a blood clot, known as a thrombus, in the deep leg vein. It is a very serious condition that can cause permanent damage to the
Complex Iliocaval Reconstruction PNEC. Seattle WA. Bill Marston MD Professor, Div of Vascular Surgery University of N.
 Complex Iliocaval Reconstruction 2017 PNEC. Seattle WA Bill Marston MD Professor, Div of Vascular Surgery University of N. Carolina DISCLOSURES William Marston, MD Consultant/Advisory Board: Veniti, Cardinal
Complex Iliocaval Reconstruction 2017 PNEC. Seattle WA Bill Marston MD Professor, Div of Vascular Surgery University of N. Carolina DISCLOSURES William Marston, MD Consultant/Advisory Board: Veniti, Cardinal
Thromboembolic Diseases
 Thromboembolic Diseases Incidence, Risk Factors, and Categories Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), together called venous thromboembolism (VTE), remain a serious health care problem.
Thromboembolic Diseases Incidence, Risk Factors, and Categories Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), together called venous thromboembolism (VTE), remain a serious health care problem.
Thursday, February 26, :00 am. Regulation of Coagulation/Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation HEMOSTASIS/THROMBOSIS III
 REGULATION OF COAGULATION Introduction HEMOSTASIS/THROMBOSIS III Regulation of Coagulation/Disseminated Coagulation necessary for maintenance of vascular integrity Enough fibrinogen to clot all vessels
REGULATION OF COAGULATION Introduction HEMOSTASIS/THROMBOSIS III Regulation of Coagulation/Disseminated Coagulation necessary for maintenance of vascular integrity Enough fibrinogen to clot all vessels
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM International Consensus Statement 2013 Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence Developed under the auspices of the: Cardiovascular Disease Educational
PREVENTION AND TREATMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM International Consensus Statement 2013 Guidelines According to Scientific Evidence Developed under the auspices of the: Cardiovascular Disease Educational
Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
 Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Catherine K. Chang, MD FACS Vascular Surgery San Diego Southern California Permanente Medical Group Acute Deep Venous Thrombosis Incidence & Outcomes
Iliofemoral DVT: Miminizing Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Catherine K. Chang, MD FACS Vascular Surgery San Diego Southern California Permanente Medical Group Acute Deep Venous Thrombosis Incidence & Outcomes
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine
 Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Venous thromboembolic diseases: diagnosis, management and thrombophilia testing (2012) NICE guideline CG144
 Venous thromboembolic diseases: diagnosis, management and thrombophilia testing (2012) NICE guideline CG144 Appendix A: Summary of new evidence from Summary of evidence from previous year Diagnosis Diagnostic
Venous thromboembolic diseases: diagnosis, management and thrombophilia testing (2012) NICE guideline CG144 Appendix A: Summary of new evidence from Summary of evidence from previous year Diagnosis Diagnostic
Venous Thrombosis. Magnitude of the Problem. DVT 2 Million PE 600,000. Death 60,000. Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year.
 Venous Thrombosis Magnitude of the Problem DVT 2 Million Postthrombotic Syndrome 800,000 PE 600,000 Death 60,000 Silent PE 1 Million Pulmonary Hypertension 30,000 Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year
Venous Thrombosis Magnitude of the Problem DVT 2 Million Postthrombotic Syndrome 800,000 PE 600,000 Death 60,000 Silent PE 1 Million Pulmonary Hypertension 30,000 Estimated Cost of VTE Care $1.5 Billion/year
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Evan C Lipsitz, MD Montefiore Medical Center and the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY DVT / VTE Magnitude of the Problem DVT 2 Million Post-thrombotic
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Evan C Lipsitz, MD Montefiore Medical Center and the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY DVT / VTE Magnitude of the Problem DVT 2 Million Post-thrombotic
A Brief Guide Treatment and Prevention
 A Brief Guide Treatment and Prevention Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism 08/18 Dear reader, This brochure provides you with information about deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. This
A Brief Guide Treatment and Prevention Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism 08/18 Dear reader, This brochure provides you with information about deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. This
Intervention for Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolus
 Intervention for Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolus Michael R. Jaff, DO Paul and Phyllis Fireman Endowed Chair in Vascular Medicine Massachusetts General Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard
Intervention for Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolus Michael R. Jaff, DO Paul and Phyllis Fireman Endowed Chair in Vascular Medicine Massachusetts General Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard
Blood Thinner Agent. Done by: Meznah Al-mutairi Pharm.D Candidate PNU Collage of Pharmacy
 Blood Thinner Agent Done by: Meznah Al-mutairi Pharm.D Candidate PNU Collage of Pharmacy Outline: Blood thinner agent definition. anticoagulants drugs. Thrombolytics. Blood thinner agent Therapeutic interference
Blood Thinner Agent Done by: Meznah Al-mutairi Pharm.D Candidate PNU Collage of Pharmacy Outline: Blood thinner agent definition. anticoagulants drugs. Thrombolytics. Blood thinner agent Therapeutic interference
Mutidisciplinary cooperation on VTE prevention and managment
 Mutidisciplinary cooperation on VTE prevention and managment TAO YANG Dpartment of vascular surgery Shanxi DAYI Hospita Tai yuan Shanxi China Disclosure Speaker name: Tao Yang... I have the following potential
Mutidisciplinary cooperation on VTE prevention and managment TAO YANG Dpartment of vascular surgery Shanxi DAYI Hospita Tai yuan Shanxi China Disclosure Speaker name: Tao Yang... I have the following potential
Rapid Fire-Top Articles You Need to Know
 Rapid Fire-Top Articles You Need to Know TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE- SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN FRANCISCO Financial Disclosures-NONE
Rapid Fire-Top Articles You Need to Know TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE- SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN FRANCISCO Financial Disclosures-NONE
Jessica Bryan, Natalia Evans, Karlyn Henderson, & Whitney Parks
 Jessica Bryan, Natalia Evans, Karlyn Henderson, & Whitney Parks 1. What is the most common cause of death in hospitalized patients? 1. Hospital-acquired infection 2. Pulmonary embolism 3. Myocardial infarction
Jessica Bryan, Natalia Evans, Karlyn Henderson, & Whitney Parks 1. What is the most common cause of death in hospitalized patients? 1. Hospital-acquired infection 2. Pulmonary embolism 3. Myocardial infarction
Suspected Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Assessment
 CHI no... First name... DOB... /... /... Last name... Sex: c M c F Address...... Telephone... or attach addressograph label here Hospital/Location: c Hairmyres c Monklands c Wishaw Other (specify)... Ward/Base...
CHI no... First name... DOB... /... /... Last name... Sex: c M c F Address...... Telephone... or attach addressograph label here Hospital/Location: c Hairmyres c Monklands c Wishaw Other (specify)... Ward/Base...
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK?
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK? Ayman El-Menyar (1), MD, Hassan Al-Thani (2),MD (1)Clinical Research Consultant, (2) Head of Vascular Surgery, Hamad General Hospital
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: IS THERE A LINK? Ayman El-Menyar (1), MD, Hassan Al-Thani (2),MD (1)Clinical Research Consultant, (2) Head of Vascular Surgery, Hamad General Hospital
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM
 VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Parker Truong, D.O. Interventional Cardiology Oklahoma Heart Hospital Physicians RELEVANT DISCLOSURE Under the Oklahoma State Medical Association CME guidelines disclosure must be
VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLISM Parker Truong, D.O. Interventional Cardiology Oklahoma Heart Hospital Physicians RELEVANT DISCLOSURE Under the Oklahoma State Medical Association CME guidelines disclosure must be
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in the Perioperative Patient
 ...PRESENTATIONS... Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in the Perioperative Patient Based on a presentation by James E. Muntz, MD Presentation Summary Approximately 500,000 cases of deep vein
...PRESENTATIONS... Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in the Perioperative Patient Based on a presentation by James E. Muntz, MD Presentation Summary Approximately 500,000 cases of deep vein
Epidemiology of Thrombosis in Patients with Malignancy. Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism. Chew HK, Arch Int Med, Feb Blom et al, JAMA, Feb 2005
 Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism Objectives 1. Epidemiology of thrombosis in patients with malignancy 2. Anticancer agents and thrombosis 3. Current treatment protocols at UHN 4. Prevention of DVT 5.
Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism Objectives 1. Epidemiology of thrombosis in patients with malignancy 2. Anticancer agents and thrombosis 3. Current treatment protocols at UHN 4. Prevention of DVT 5.
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin
 Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.019 10/15/2007 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 05/01/2016 Section: Prescription Drugs
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.019 10/15/2007 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 05/01/2016 Section: Prescription Drugs
Intended Learning Outcomes
 2011 Acute Limb Ischemia Definition, Etiology & Pathophysiology Clinical Evaluation Management Ali SABBOUR Prof. of Vascular Surgery, Ain Shams University Acute Limb Ischemia Intended Learning Outcomes
2011 Acute Limb Ischemia Definition, Etiology & Pathophysiology Clinical Evaluation Management Ali SABBOUR Prof. of Vascular Surgery, Ain Shams University Acute Limb Ischemia Intended Learning Outcomes
Anticoagulants. Pathological formation of a haemostatic plug Arterial associated with atherosclerosis Venous blood stasis e.g. DVT
 Haemostasis Thrombosis Phases Endogenous anticoagulants Stopping blood loss Pathological formation of a haemostatic plug Arterial associated with atherosclerosis Venous blood stasis e.g. DVT Vascular Platelet
Haemostasis Thrombosis Phases Endogenous anticoagulants Stopping blood loss Pathological formation of a haemostatic plug Arterial associated with atherosclerosis Venous blood stasis e.g. DVT Vascular Platelet
10/24/2013. Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy:
 Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy: Heparin-Induced (HIT) Michael H. Creer, MD Professor of Pathology Director, Clinical Laboratories, Medical Co- Director, Hematopathology and Chief, Division
Anticoagulation Management in ECMO Therapy: Heparin-Induced (HIT) Michael H. Creer, MD Professor of Pathology Director, Clinical Laboratories, Medical Co- Director, Hematopathology and Chief, Division
Percutaneous Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Iliofemoral DVT with the Aspirex Catheter: The Dijon Experience
 JFICV 2018, Beaune Percutaneous Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Iliofemoral DVT with the Aspirex Catheter: The Dijon Experience Prof. Romaric LOFFROY, MD, PhD, FCIRSE Chief, Department of Vascular and
JFICV 2018, Beaune Percutaneous Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Iliofemoral DVT with the Aspirex Catheter: The Dijon Experience Prof. Romaric LOFFROY, MD, PhD, FCIRSE Chief, Department of Vascular and
Deep vein thrombosis: diagnosis, prevention and treatment
 Deep vein thrombosis: diagnosis, prevention and treatment Catherine Bagot BSc, MD, MRCP, FRCPath and Campbell Tait BSc, FRCP, FRCPath Deep vein thrombosis can lead to significant morbidity and has well-recognised
Deep vein thrombosis: diagnosis, prevention and treatment Catherine Bagot BSc, MD, MRCP, FRCPath and Campbell Tait BSc, FRCP, FRCPath Deep vein thrombosis can lead to significant morbidity and has well-recognised
Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE
 Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE-SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN FRANCISCO Financial Disclosures-NONE
Updates in Diagnosis & Management of VTE TRACY MINICHIELLO, MD CHIEF, ANTICOAGULATION& THROMBOSIS SERVICE-SAN FRANCISCO VAMC PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN FRANCISCO Financial Disclosures-NONE
Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. Pulmonary Embolism. PE - Clinical
 Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
Pulmonary embolus - a practical approach to investigation and treatment Sam Janes Wellcome Senior Fellow and Respiratory Physician, University College London Background Diagnosis Treatment Common: 50 cases
Obesity, renal failure, HIT: which anticoagulant to use?
 Obesity, renal failure, HIT: which anticoagulant to use? Mark Crowther with thanks to Dr David Garcia and others. This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA 1 2 Drug choices The DOACs have
Obesity, renal failure, HIT: which anticoagulant to use? Mark Crowther with thanks to Dr David Garcia and others. This Photo by Unknown Author is licensed under CC BY-SA 1 2 Drug choices The DOACs have
