Chapter 29. Vital Signs
|
|
|
- Fay Collins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 29 Vital Signs
2 Vital Signs Temperature, pulse, respiratory rate, blood pressure Pain Oxygen saturation also frequently measured Vital signs are used to: Monitor patient s condition Identify problems Evaluate response to intervention
3 Guidelines for Measuring Vital Signs Ensure that equipment is functional and is appropriate for the size and age of the patient. Appropriately delegate measurement. Be able to understand and interpret values. Know the patient s usual range of vital signs. Determine the patient s medical history, therapies, and prescribed medications. Control or minimize environmental factors that affect vital signs.
4 Guidelines for Measuring Vital Signs (cont d) Use an organized, systematic approach when taking vital signs. Know the acceptable ranges for your patients before administering medications, and use vital sign measurements to determine indications for medication administration. Communicate findings. Accurately document findings. Analyze the results of vital sign measurement. Instruct the patient or family caregiver in vital sign assessment and the significance of findings.
5 Case Study Ms. Coburn is a 26-year-old schoolteacher. Her maternal grandparents immigrated to America from Brazil. She smokes one pack of cigarettes a day and has smoked since she was 16. She is 20 lbs overweight. She made an appointment because she started to have headaches and frequently felt tired.
6 Body Temperature Physiology Body temperature: Heat produced Heat lost Acceptable temperature range: 98.6 F to F or 36 C to 38 C Temperature sites: Oral, rectal, axillary, tympanic membrane, temporal artery, esophageal, pulmonary artery
7 Body Temperature Regulation Neural and vascular control Heat production Heat loss (radiation, conduction, convection, evaporation) Skin temperature regulation Behavioral control Thermoregulation
8 Case Study (cont d) Miguel is a 42-year-old Hispanic nurse who works at the clinic Ms. Coburn is visiting. He enjoys providing health-related teaching to the patients and has provided Mrs. Coburn care for 2 years. During the visit, Miguel assesses Ms. Coburn s symptoms. He asks her about her headache and fatigue, then takes her vital signs. Her temperature is 98 Fahrenheit.
9 Factors Affecting Body Temperature Age Exercise Hormonal level Circadian rhythm Environment Temperature alterations
10 Temperature Cycle
11 Temperature Alterations Pyrexia (fever): important defense mechanism Pyrogens Febrile/afebrile Fever of unknown origin (FUO) Hyperthermia Malignant hyperthermia Heatstroke (104 F or higher) Heat exhaustion Hypothermia Frostbite
12 Hypothalamic Temperature Control
13 Patterns of Fever Sustained Constant above 38 C (100.4 F) with little fluctuation Intermittent Fever spikes interspersed with usual temperature levels Remittent Fever spikes and falls without a return to normal temperature levels Relapsing Periods of febrile episodes and periods with acceptable temperature values
14 Nursing Process and Temperature Assessment Sites: advantages and disadvantages Core and surface Thermometers Electronic: oral, axillary, rectal, tympanic membrane, temporal artery Disposable: oral, axillary, rectal Fahrenheit or Celsius scale
15 Electronic Thermometer
16 Temporal Artery Thermometer
17 Chemical Dot Thermometer
18 Quick Quiz! 1.You have delegated vital signs to assistive personnel. The assistant informs you that the patient has just finished a bowl of hot soup. The nurse s most appropriate advice would be to A. Take a rectal temperature. B. Take the oral temperature as planned. C. Advise the patient to drink a glass of cold water. D. Wait 30 minutes and take an oral temperature.
19 Nursing Process: Temperature Diagnosis Risk for imbalanced body temperature Hyperthermia Hypothermia Ineffective thermoregulation Planning
20 Nursing Process: Temperature (cont d) Implementation Health promotion Consider activity, environment, and clothing. Acute care: treat pyrogen, antipyretics Heatstroke Hypothermia Restorative and continuing care Evaluation Get patient s perspective, compare actual with expected outcomes, and determine whether goals were met.
21 Pulse Physiology and Regulation Pulse = Palpable bounding of blood flow noted at various points on the body The indicator of circulatory status Pulse rate = Number of pulsing sensations in 1 minute Electrical impulses originate from the sinoatrial (SA) node. Cardiac output, heart rate, stroke volume Mechanical, neural, and chemical factors regulate ventricular contraction and stroke volume.
22 Assessment of Pulse Sites: temporal, carotid, apical, brachial, radial, ulnar, femoral, popliteal, posterior tibial, and dorsalis pedis Use of stethoscope Character of pulse: rate, rhythm, strength, and equality Nursing process and pulse determination
23 Parts of a Stethoscope
24 Use of a Stethoscope
25 Pulse Character Rate Apical rate: ID S1 and S2, lub + dub = 1 heartbeat Lub-dubs per minute = Rate Bradycardia Tachycardia Pulse deficit = Difference between radial and apical pulse rates Rhythm Dysrhythmia: regularly or irregularly irregular Strength: 4+, 3+, 2+ (normal), 1+, 0 Equality
26 Nursing Process and Pulse Determination Activity intolerance Anxiety Fear Decreased cardiac output Deficient/excess fluid volume Impaired gas exchange Hyperthermia Hypothermia Acute pain Ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion
27 Quick Quiz! 2. You notice that a teenager has an irregular pulse. The best action you should take includes A. Reading the history and physical. B. Assessing the apical pulse rate for 1 full minute. C. Auscultating for strength and depth of pulse. D. Asking whether the patient feels any palpitations or faintness of breath.
28 Respiration Ventilation = Movement of gases into and out of the lung. Diffusion= Movement of oxygen and carbon monoxide between alveoli and red blood cells. Perfusion = Distribution of red blood cells to and from the pulmonary capillaries. Physiological control; hypoxemia Mechanics of breathing; eupnea
29 Movements During Breathing
30 Assessment of Ventilation Easy to assess Respiratory rate: breaths/minute Ventilatory depth: deep, normal, shallow Ventilatory rhythm: regular/irregular Diffusion and perfusion Arterial oxygen saturation
31 Case Study (cont d) Miguel continues to take Ms. Coburn s vital signs. Ms. Coburn s respiratory rate is 14 breaths per minute, and her pulse is 86 beats per minute.
32 Factors Influencing Character of Respirations Exercise Anxiety Body position Neurological injury Acute pain Smoking Medications Hemoglobin function
33 Alterations in Breathing Pattern Bradypnea Tachypnea Hyperpnea Apnea Hyperventilation Hypoventilation Cheyne-Stokes respiration Kussmaul s respiration Biot s respiration
34 Assessment of Diffusion and Perfusion Measurement of arterial oxygen saturation (SaO 2 ), the percent of hemoglobin that is bound with oxygen in the arteries Usually 95% to 100% Pulse oximeter Probes: digit, earlobe, disposable
35 Pulse Oximeter
36 Nursing Process and Respiratory Vital Signs Nursing diagnosis Activity intolerance Ineffective airway clearance Anxiety Ineffective breathing pattern Impaired gas exchange Acute pain Ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion Dysfunctional ventilatory weaning response Planning, interventions, evaluation
37 Quick Quiz! 3. A postoperative patient is breathing rapidly. You should immediately A. Call the physician. B. Count the respirations. C. Assess the oxygen saturation. D. Ask the patient if he feels uncomfortable.
38 Arterial Blood Pressure Force exerted on the walls of an artery by pulsing blood under pressure from the heart Systolic = Maximum peak pressure during ventricular contraction Diastolic = Minimal pressure during ventricular relaxation Pulse pressure = Difference between systolic and diastolic pressures
39 Physiology of Arterial Blood Pressure Factors affecting arterial blood pressure: Cardiac output Peripheral resistance Blood volume Viscosity Elasticity
40 Factors Influencing Blood Pressure Age Stress Ethnicity Gender
41 Factors Influencing Blood Pressure (cont d) Daily variation Medications Activity, weight Smoking
42 Case Study (cont d) Ms. Coburn s blood pressure is 164/98 mm Hg. Ms. Coburn asks whether this means she is healthy.
43 Blood Pressure Cuff Size Guidelines
44 Hypertension versus Hypotension Hypertension More common than hypotension Thickening of walls Loss of elasticity Family history Risk factors Hypotension Systolic <90 mm Hg Dilation of arteries Loss of blood volume Decrease of blood flow to vital organs Orthostatic/postural
45 Case Study (cont d) Miguel responds, Ms. Coburn, your blood pressure is pretty high right now. After you see the nurse practitioner today, I am going to take your blood pressure again. We are also going to talk about the changes you can begin to make to help you be healthier and feel better.
46 Measurement of Blood Pressure Equipment Auscultation Children Ultrasonic stethoscope Palpation Lower extremity Electronic blood pressure
47 Sphygmomanometer
48 Alternate Methods of Measuring Blood Pressure
49 Patient Conditions Not Appropriate for Electronic Blood Pressure Measurement Irregular heart rate Peripheral vascular obstruction (e.g., clots, narrowed vessels) Shivering Seizures Excessive tremors Inability to cooperate Blood pressure less than 90 mm Hg systolic
50 Patient Measurement of BP Benefits Detection of new problems (prehypertension) Patients with hypertension can provide to their health care provider info about patterns of BP. Self-monitoring helps adherence to therapy. Disadvantages Improper use risks inaccurate readings. Unnecessary alarming of patient Patients may inappropriately adjust medications.
51 Nursing Process and Blood Pressure Determination Assessment of blood pressure and pulse evaluates the general state of cardiovascular health. Hypertension, hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, and narrow/wide pulse pressures are defining characteristics of certain nursing diagnoses.
52 Case Study (cont d) After caring for Ms. Coburn, Miguel sees the need to educate Ms. Coburn about the different types of vital signs. Miguel determines that the priority is to focus on hypertension and ways to prevent or control elevated BP. He states, We need to watch your blood pressure closely over the next few weeks. In the meantime, remember, you decided that you are going to walk for at least 15 minutes 3 days a week; you are also going to try to eat foods with less salt and think about not smoking anymore.
53 Quick Quiz! 4. When assessing the blood pressure of a school-aged child, using an adult cuff of normal size will affect the reading and produce a value that is A. Accurate. B. Indistinct. C. Falsely low. D. Falsely high.
54 Health Promotion and Vital Signs Monitor vital signs. Include age-related factors. Include environmental and activity factors.
55 Case Study (cont d) Ms. Coburn has purchased an electronic blood pressure device for home use. What evaluation strategies would you suggest for Miguel to use with Ms. Coburn?
56 Recording Vital Signs Record values on electronic or paper graphic. Record in nurses notes any accompanying or precipitating symptoms. Document interventions initiated on the basis of vital sign measurement. If a vital sign is outside anticipated outcomes, write a variance note to explain, along with the nursing course of action. In the nurse s variance note, address possible causes of a fever.
57 Safety Guidelines for Skills Cleaning devices between patients decreases the risk for infection. Rotating sites during repeated measurements of BP and pulse oximetry decreases the risk for skin breakdown. Analyze trends for vital signs, and report abnormal findings. Determine the appropriate frequency of measuring vital signs based on the patient s condition.
a central pulse located at the apex of the heart Apical pulse Apical-radial pulse a complete absence of respirations Apnea
 Afebrile absence of a fever Apical pulse a central pulse located at the apex of the heart Apical-radial pulse measurement of the apical beat and the radial pulse at the same time Apnea a complete absence
Afebrile absence of a fever Apical pulse a central pulse located at the apex of the heart Apical-radial pulse measurement of the apical beat and the radial pulse at the same time Apnea a complete absence
Chapter 15: Measuring Height, Weight, and Vital Signs. Copyright 2012 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 15: Measuring Height, Weight, and Vital Signs Height and Weight Weight Baseline measurement at patient s first visit Measured in kg or lbs Common types of scales Balance beam Dial Digital Height
Chapter 15: Measuring Height, Weight, and Vital Signs Height and Weight Weight Baseline measurement at patient s first visit Measured in kg or lbs Common types of scales Balance beam Dial Digital Height
Chapter 24 Vital Signs. Copyright 2011 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 24 Vital Signs Vital Signs Temperature Pulse Respiration Blood pressure When to Assess Vital Signs Upon admission to any healthcare agency Based on agency institutional policy and procedures Anytime
Chapter 24 Vital Signs Vital Signs Temperature Pulse Respiration Blood pressure When to Assess Vital Signs Upon admission to any healthcare agency Based on agency institutional policy and procedures Anytime
Measuring Vital Signs. Copyright 2014, 2009 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Measuring Vital Signs Copyright 2014, 2009 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Five Vital Signs Temperature, pulse, respiration, blood pressure, and pain Vital signs give indications
Measuring Vital Signs Copyright 2014, 2009 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Five Vital Signs Temperature, pulse, respiration, blood pressure, and pain Vital signs give indications
Vital Signs. 1. Define important words in this chapter. 2. Discuss the relationship of vital signs to health and well-being
 84 13 Vital Signs 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Discuss the relationship of vital signs to health and well-being 3. Identify factors that affect body temperature 4. List guidelines for taking
84 13 Vital Signs 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Discuss the relationship of vital signs to health and well-being 3. Identify factors that affect body temperature 4. List guidelines for taking
Measuring and Recording Temperature
 Measuring and Recording Temperature Measurement of balance between heat lost and produced by the body. Lost through: Perspiration Respiration Excretion Produced by: Metabolism of food Muscle and gland
Measuring and Recording Temperature Measurement of balance between heat lost and produced by the body. Lost through: Perspiration Respiration Excretion Produced by: Metabolism of food Muscle and gland
Vital Signs. Provide information about body function Include: Changes may be the first sign of disease Accuracy is imperative!
 Provide information about body function Include: temperature pulse respiration blood pressure Changes may be the first sign of disease Accuracy is imperative! 2 Temperature Measurement of the balance between
Provide information about body function Include: temperature pulse respiration blood pressure Changes may be the first sign of disease Accuracy is imperative! 2 Temperature Measurement of the balance between
Vital Signs. Vital Signs. Vital Signs
 Vital Signs Vital Signs Why do vital signs? Determine relative status of vital organs Establish baseline Monitor response to Rx, meds Observe trends Determine need for further evaluation, Rx, intervention
Vital Signs Vital Signs Why do vital signs? Determine relative status of vital organs Establish baseline Monitor response to Rx, meds Observe trends Determine need for further evaluation, Rx, intervention
Vital Signs. Temperature. Pulse. Respirations. Blood Pressure. O2 Saturation
 Vital Signs Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood Pressure O2 Saturation Vital Signs Temperature, pulse, respiration, blood pressure (B/P) & oxygen saturation are the most frequent measurements taken by
Vital Signs Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood Pressure O2 Saturation Vital Signs Temperature, pulse, respiration, blood pressure (B/P) & oxygen saturation are the most frequent measurements taken by
Chapter 21. Assisting With Assessment. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 21 Assisting With Assessment Vital Signs Vital signs reflect three body processes: Regulation of body temperature Breathing Heart function A person s vital signs: Vary within certain limits Are
Chapter 21 Assisting With Assessment Vital Signs Vital signs reflect three body processes: Regulation of body temperature Breathing Heart function A person s vital signs: Vary within certain limits Are
Chapter 29 1/8/2018. Vital Signs. Measuring and Reporting Vital Signs. Key Terms
 Chapter 29 Vital Signs Key Terms Blood pressure Body temperature Diastolic pressure Hypertension Hypotension Pulse Pulse rate Respiration Sphygmomanometer Stethoscope Systolic pressure Vital signs Measuring
Chapter 29 Vital Signs Key Terms Blood pressure Body temperature Diastolic pressure Hypertension Hypotension Pulse Pulse rate Respiration Sphygmomanometer Stethoscope Systolic pressure Vital signs Measuring
Aaron J. Katz, AEMT-P, CIC Outward signs of what is occurring inside the body
 Vital Signs Aaron J. Katz, AEMT-P, CIC www.es26medic.net 2013 Vital Signs Outward signs of what is occurring inside the body Also give valuable information about the patient s condition They are taken
Vital Signs Aaron J. Katz, AEMT-P, CIC www.es26medic.net 2013 Vital Signs Outward signs of what is occurring inside the body Also give valuable information about the patient s condition They are taken
Vital Signs and Oxygen Administration
 Vital Signs and Oxygen Administration By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Patient Care and Management (202) May-9-2010 Vital Signs and Oxygen Administration What are the vital signs? Why do we need to know them? How
Vital Signs and Oxygen Administration By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Patient Care and Management (202) May-9-2010 Vital Signs and Oxygen Administration What are the vital signs? Why do we need to know them? How
How To Measure Vital Signs
 How To Measure Vital Signs How to Use This Tutorial This tutorial is intended for healthcare providers or students to teach basic vital signs skills Use the navigation buttons below to move through the
How To Measure Vital Signs How to Use This Tutorial This tutorial is intended for healthcare providers or students to teach basic vital signs skills Use the navigation buttons below to move through the
VITAL SIGNS. Academic Success Center
 VITAL SIGNS Academic Success Center Because of the importance of these measurements they are referred to as Vital Signs. They are important indicators of the body s response to physical, environmental,
VITAL SIGNS Academic Success Center Because of the importance of these measurements they are referred to as Vital Signs. They are important indicators of the body s response to physical, environmental,
Pancreas: digestive enzymes Liver: bile-helps to digest fat, stored in gallblader; breaks down toxins, makes some parts of blood
 1 2 3 Pancreas: digestive enzymes Liver: bile-helps to digest fat, stored in gallblader; breaks down toxins, makes some parts of blood 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Highlights: - A pulse consists of two phases: contraction
1 2 3 Pancreas: digestive enzymes Liver: bile-helps to digest fat, stored in gallblader; breaks down toxins, makes some parts of blood 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Highlights: - A pulse consists of two phases: contraction
Vital Signs Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment
 Vital Signs Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Become a Data Gathering Machine The exam begins as soon as you see the patient o Appearance, demeanor, dress Well groomed, neat, disheveled, work
Vital Signs Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Become a Data Gathering Machine The exam begins as soon as you see the patient o Appearance, demeanor, dress Well groomed, neat, disheveled, work
Vital signs. Chapter 27. Ra'eda Almashagba 1
 Vital signs Chapter 27 Ra'eda Almashagba 1 Vital sign Vital sign are: a body temperature pulse respiration and blood pressure May add pulse oximetery and pain Monitoring a client vital sign should note
Vital signs Chapter 27 Ra'eda Almashagba 1 Vital sign Vital sign are: a body temperature pulse respiration and blood pressure May add pulse oximetery and pain Monitoring a client vital sign should note
Physiological Measurements Training for Care/Nursing & LD Small Group Home Staff
 Physiological Measurements Training for Care/Nursing & LD Small Group Home Staff CONTENTS 1. The National Early Warning Score 2. Respiratory Rate 3. Oxygen Saturations 4. Temperature 5. Blood Pressure
Physiological Measurements Training for Care/Nursing & LD Small Group Home Staff CONTENTS 1. The National Early Warning Score 2. Respiratory Rate 3. Oxygen Saturations 4. Temperature 5. Blood Pressure
Chapter 12. Vital Signs Assessment
 Chapter 12 Vital Signs Assessment Pre-Test 1. What are vital signs? 2. List as many vital signs as you know. Key Terms homeostasis: a state of equilibrium within the body maintained through the adaptation
Chapter 12 Vital Signs Assessment Pre-Test 1. What are vital signs? 2. List as many vital signs as you know. Key Terms homeostasis: a state of equilibrium within the body maintained through the adaptation
Vital Signs. Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment
 Vital Signs Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Become a Data Gathering Machine The exam begins as soon as you see the patient Appearance, demeanor, dress Well groomed, neat, disheveled, work
Vital Signs Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Become a Data Gathering Machine The exam begins as soon as you see the patient Appearance, demeanor, dress Well groomed, neat, disheveled, work
Unit 2: Vital signs. Outlines - Body temperature. - Pulse / heart rate. - Respiration. - Blood Pressure.
 Unit 2: Vital signs Outlines - Body temperature. - Pulse / heart rate. - Respiration. - Blood Pressure. Vital Signs Vital signs are measures of various physiological status, in order to assess the most
Unit 2: Vital signs Outlines - Body temperature. - Pulse / heart rate. - Respiration. - Blood Pressure. Vital Signs Vital signs are measures of various physiological status, in order to assess the most
Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History. Chapter 5
 Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Chapter 5 Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Assessment is the most complex skill EMT-Bs learn. During assessment you will: Gather key information. Evaluate
Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Chapter 5 Baseline Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Assessment is the most complex skill EMT-Bs learn. During assessment you will: Gather key information. Evaluate
MEASURING AND RECORDING PATIENT VITAL SIGNS
 MEASURING AND RECORDING PATIENT VITAL SIGNS ABSTRACT: Vital sign measurements are effective tools to assess if a patient is ill. They are quick, simple measurements and reliable indicators of a person
MEASURING AND RECORDING PATIENT VITAL SIGNS ABSTRACT: Vital sign measurements are effective tools to assess if a patient is ill. They are quick, simple measurements and reliable indicators of a person
Crucial Signs כל הזכויות שמורות למד"א מרחב ירושלים
 Crucial Signs Dan Drory, MDA Paramedic and Instructor, 2011 What are Signs? Sign Objective, measurable Symptom Subjective, evaluated by the patient ( Chest Pain, Difficulties Breathing, Headache ) Signs
Crucial Signs Dan Drory, MDA Paramedic and Instructor, 2011 What are Signs? Sign Objective, measurable Symptom Subjective, evaluated by the patient ( Chest Pain, Difficulties Breathing, Headache ) Signs
Techniques of Vital Signs. John Gazewood, MD, MSPH Department of Family Medicine
 Techniques of Vital Signs John Gazewood, MD, MSPH Department of Family Medicine Objectives Define normal in several ways. Describe correct technique of measuring vital signs. Describe correct technique
Techniques of Vital Signs John Gazewood, MD, MSPH Department of Family Medicine Objectives Define normal in several ways. Describe correct technique of measuring vital signs. Describe correct technique
Topic: Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill
 Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill Instructor Guide Session Reference: 1 Topic: Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill Level of Instruction: 2 Time Required: Three Hours Materials
Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill Instructor Guide Session Reference: 1 Topic: Baseline Vitals and Sample History Company Drill Level of Instruction: 2 Time Required: Three Hours Materials
BIOE221. Session 2. Vital Signs. Biosciences Dept.
 BIOE221 Session 2 Vital Signs Biosciences Dept. www.endeavour.edu.au Session Objectives cont o Understand the physiology related to the vital signs of temperature, pulse, respiration and blood pressure.
BIOE221 Session 2 Vital Signs Biosciences Dept. www.endeavour.edu.au Session Objectives cont o Understand the physiology related to the vital signs of temperature, pulse, respiration and blood pressure.
LEARNING OUTCOME The students will be able to elicit vital signs correctly on human volunteers/patients
 Vital signs (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, respiratory rate, pain) are physiological parameters that a healthcare professional requires when dealing with patients. Accurate measurement of vital signs
Vital signs (pulse, blood pressure, temperature, respiratory rate, pain) are physiological parameters that a healthcare professional requires when dealing with patients. Accurate measurement of vital signs
Chapter 12 - Vital_Signs_and_Monitoring_Devices
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 12.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 13 15, 17, 21 22, 26, 28, 30, 32 33, 35, 44, 47 48, 50, 55, 60 12.2 Identify the vital signs
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 12.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 13 15, 17, 21 22, 26, 28, 30, 32 33, 35, 44, 47 48, 50, 55, 60 12.2 Identify the vital signs
Dr.R.K.Yadava Associate Prof.&Head Department of kayachikitsa SRM Govt.Ayu.College&Hospital, Bareilly
 Dr.R.K.Yadava Associate Prof.&Head Department of kayachikitsa SRM Govt.Ayu.College&Hospital, Bareilly Email-drrky68@gmail.com General examination is most important aspect in clinical practice. Learn the
Dr.R.K.Yadava Associate Prof.&Head Department of kayachikitsa SRM Govt.Ayu.College&Hospital, Bareilly Email-drrky68@gmail.com General examination is most important aspect in clinical practice. Learn the
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: ASSESSMENT Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: ASSESSMENT Revised: 11/2013 DEFINITIONS General Impression - EMT develops a plan of action from the
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: ASSESSMENT Revised: 11/2013 DEFINITIONS General Impression - EMT develops a plan of action from the
Chapter 9 Vital Signs and SAMPLE History DOT Directory
 Chapter 9 Vital Signs and SAMPLE History U.S. Objectives U.S. Objectives are covered and/or supported by the PowerPoint Slide Program and Notes for Emergency Care, 11th Ed. Please see the Chapter 9 correlation
Chapter 9 Vital Signs and SAMPLE History U.S. Objectives U.S. Objectives are covered and/or supported by the PowerPoint Slide Program and Notes for Emergency Care, 11th Ed. Please see the Chapter 9 correlation
At the end of this chapter, the student should be able to: 2. Identify factors affecting changes in vital signs.
 Part III: Vital signs Lecture Outlines Body temperature. Pulse. Respiration. Blood Pressure. Learning Objectives At the end of this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. Discuss the concept of vital
Part III: Vital signs Lecture Outlines Body temperature. Pulse. Respiration. Blood Pressure. Learning Objectives At the end of this chapter, the student should be able to: 1. Discuss the concept of vital
Measuring body temperature, blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate and oxygen saturation
 Vital Signs Measuring body temperature, blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate and oxygen saturation Aims To ensure that students are able to demonstrate the safe and correct technique for setting up
Vital Signs Measuring body temperature, blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate and oxygen saturation Aims To ensure that students are able to demonstrate the safe and correct technique for setting up
How to Measure Vital Signs
 How to Measure Vital Signs Caregiving Series: Volume 10 Objectives Upon completion of this training, participants will understand: The definitions of temperature, pulse, respiration and blood pressure
How to Measure Vital Signs Caregiving Series: Volume 10 Objectives Upon completion of this training, participants will understand: The definitions of temperature, pulse, respiration and blood pressure
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pulse. Assess for the following:
 Vital Signs Overview LOC = AVPU Pulse Respiration's Blood Pressure Lung Sounds Skin: Color, Texture, Temperature Pupils = Equal, Reactive to Light with Accomodation Pulse Assess for the following: Rate
Vital Signs Overview LOC = AVPU Pulse Respiration's Blood Pressure Lung Sounds Skin: Color, Texture, Temperature Pupils = Equal, Reactive to Light with Accomodation Pulse Assess for the following: Rate
Cardiac Emergencies. Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington
 Cardiac Emergencies Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington The Heart -------Aorta Pulmonary Veins---- Superior Vena Cava------ Right Atrium-----
Cardiac Emergencies Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington The Heart -------Aorta Pulmonary Veins---- Superior Vena Cava------ Right Atrium-----
Chapter 26. Assisting With Oxygen Needs. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 26 Assisting With Oxygen Needs Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas. Oxygen Ø It has no taste, odor, or color. Ø It is a basic need required for life. Death occurs within minutes if breathing stops. Brain damage
Chapter 26 Assisting With Oxygen Needs Oxygen (O 2 ) is a gas. Oxygen Ø It has no taste, odor, or color. Ø It is a basic need required for life. Death occurs within minutes if breathing stops. Brain damage
Vital Signs and SAMPLE History
 CHAPTER 9 Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Overall Assessment Scheme Scene Size-Up Initial Assessment Trauma Physical Exam Vital Signs & SAMPLE History Medical SAMPLE History Physical Exam & Vital Signs
CHAPTER 9 Vital Signs and SAMPLE History Overall Assessment Scheme Scene Size-Up Initial Assessment Trauma Physical Exam Vital Signs & SAMPLE History Medical SAMPLE History Physical Exam & Vital Signs
Oxygenation. Chapter 45. Re'eda Almashagba 1
 Oxygenation Chapter 45 Re'eda Almashagba 1 Respiratory Physiology Structure and function Breathing: inspiration, expiration Lung volumes and capacities Pulmonary circulation Respiratory gas exchange: oxygen,
Oxygenation Chapter 45 Re'eda Almashagba 1 Respiratory Physiology Structure and function Breathing: inspiration, expiration Lung volumes and capacities Pulmonary circulation Respiratory gas exchange: oxygen,
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Vital Signs TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-23 LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Select from a list, three reasons why patients
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Vital Signs TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-23 LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Select from a list, three reasons why patients
INTERPRETATION OF VITAL SIGNS
 DIALYSIS MENTOR- DPSI-008/2011 INTERPRETATION OF VITAL SIGNS BY P.DAVID BALU G.PADMA PRABAKAR DIALYSIS PERSONNEL SOCIETY OF INDIA INTERPRETATION OF VITAL SIGNS VITAL SIGNS: Systemic inner vital organs
DIALYSIS MENTOR- DPSI-008/2011 INTERPRETATION OF VITAL SIGNS BY P.DAVID BALU G.PADMA PRABAKAR DIALYSIS PERSONNEL SOCIETY OF INDIA INTERPRETATION OF VITAL SIGNS VITAL SIGNS: Systemic inner vital organs
Vital Signs. Vital Signs. Pulse. Temperature. Respiration. Blood Pressure
 Vital Signs Jarvis, Chapter 9 Vital Signs Classic Vital Signs TPR/BP Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood Pressure Additional Vital Signs Height Weight BMI (Kg/m2) or (702Xlbs/in2) Supine, orthostatic
Vital Signs Jarvis, Chapter 9 Vital Signs Classic Vital Signs TPR/BP Temperature Pulse Respirations Blood Pressure Additional Vital Signs Height Weight BMI (Kg/m2) or (702Xlbs/in2) Supine, orthostatic
Ambulatory Services Orientation & Skill Review Skill Performance Checklist: Vital Signs. Name: Date:
 Evaluation Levels Behavior Level 3 Met Performed all skills competently. No behaviors omitted. Level 2 Satisfactory Omitted no more than three (3) non-critical behaviors. Level 1 Unsatisfactory Omitted
Evaluation Levels Behavior Level 3 Met Performed all skills competently. No behaviors omitted. Level 2 Satisfactory Omitted no more than three (3) non-critical behaviors. Level 1 Unsatisfactory Omitted
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Appendix E Choose the sign or symptom that best indicates severe respiratory distress.
 Appendix E-2 1. In Kansas EMT-B may monitor pulse oximetry: a. after they complete the EMT-B course b. when the service purchases the state approved pulse oximeters c. when the service director receives
Appendix E-2 1. In Kansas EMT-B may monitor pulse oximetry: a. after they complete the EMT-B course b. when the service purchases the state approved pulse oximeters c. when the service director receives
TEMPERATURE, PULSE, AND RESPIRATION
 TEMPERATURE, PULSE, AND RESPIRATION Course Principles of Health Science Unit X Vital Signs Course Health Science Unit VI CPR / AED & First Aid Essential Question Why is it important for health care providers
TEMPERATURE, PULSE, AND RESPIRATION Course Principles of Health Science Unit X Vital Signs Course Health Science Unit VI CPR / AED & First Aid Essential Question Why is it important for health care providers
Chapter 11. Objectives. Objectives 01/09/2013. Baseline Vital Signs, Monitoring Devices, and History Taking
 Chapter 11 Baseline Vital Signs, Monitoring Devices, and History Taking Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights
Chapter 11 Baseline Vital Signs, Monitoring Devices, and History Taking Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights
7/12/2014. Patient History and SAMPLE. Vital Signs, History Taking and Mechanism Of Injury (Class 7)
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Vital Signs, History Taking and Mechanism Of Injury (Class 7) Patient History and SAMPLE General Information Chief complaint Why EMS assistance was requested Should always be
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Vital Signs, History Taking and Mechanism Of Injury (Class 7) Patient History and SAMPLE General Information Chief complaint Why EMS assistance was requested Should always be
THERMOREGULATION 05 JUNE 2013
 THERMOREGULATION 05 JUNE 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Question the need to regulate body temperature in humans Examine the structure and functions of the different parts of the skin Look
THERMOREGULATION 05 JUNE 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Question the need to regulate body temperature in humans Examine the structure and functions of the different parts of the skin Look
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE. MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL (equ04)
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 2/80 7/17 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN, Patient Care Technician Multi-skilled
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE - MANUAL Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: 2/80 7/17 1 of 5 RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN, Patient Care Technician Multi-skilled
Lecture Notes. Chapter 2: Introduction to Respiratory Failure
 Lecture Notes Chapter 2: Introduction to Respiratory Failure Objectives Define respiratory failure, ventilatory failure, and oxygenation failure List the causes of respiratory failure Describe the effects
Lecture Notes Chapter 2: Introduction to Respiratory Failure Objectives Define respiratory failure, ventilatory failure, and oxygenation failure List the causes of respiratory failure Describe the effects
Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse. City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved
 Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved Course Content: Definition of Blood Pressure Normal Blood Pressure Readings Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
Taking and recording blood pressure and pulse City Gate Training Centre all rights reserved Course Content: Definition of Blood Pressure Normal Blood Pressure Readings Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Shock Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Shock Revised: 11/2013 DEFINITIONS Aerobic metabolism is energy using oxygen into cells. Anaerobic
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Basic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Shock Revised: 11/2013 DEFINITIONS Aerobic metabolism is energy using oxygen into cells. Anaerobic
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF SLEEP TECHNOLOGISTS TECHNICAL GUIDELINE FOR PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND VITAL SIGNS MEASUREMENT AND DOCUMENTATION
 AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF SLEEP TECHNOLOGISTS TECHNICAL GUIDELINE FOR PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND VITAL SIGNS MEASUREMENT AND DOCUMENTATION SUMMARY: Sleep technologists observe and monitor physical signs and
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION OF SLEEP TECHNOLOGISTS TECHNICAL GUIDELINE FOR PATIENT ASSESSMENT AND VITAL SIGNS MEASUREMENT AND DOCUMENTATION SUMMARY: Sleep technologists observe and monitor physical signs and
MA.A.1.2.c; I.C.5 6; affecting blood pressure. J. Describe the procedures for obtaining height, weight, and chest
 Chapter 24 Vital Signs and Measurements 691 CHAPTER 24 VITAL SIGNS AND MEASUREMENTS Overview Medical assisting students learn the theory and practice of taking vital signs, which will be one of the most
Chapter 24 Vital Signs and Measurements 691 CHAPTER 24 VITAL SIGNS AND MEASUREMENTS Overview Medical assisting students learn the theory and practice of taking vital signs, which will be one of the most
Foundation in Critical Care Nursing. Airway / Respiratory / Workbook
 Foundation in Critical Care Nursing Airway / Respiratory / Workbook Airway Anatomy: Please label the following: Tongue Larynx Epiglottis Pharynx Trachea Vertebrae Oesophagus Where is the ET (endotracheal)
Foundation in Critical Care Nursing Airway / Respiratory / Workbook Airway Anatomy: Please label the following: Tongue Larynx Epiglottis Pharynx Trachea Vertebrae Oesophagus Where is the ET (endotracheal)
Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to:
 Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to: Discuss the cardiovascular system Identify the normal changes that occur with ageing Explain the nurses role in the care of residents with
Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to: Discuss the cardiovascular system Identify the normal changes that occur with ageing Explain the nurses role in the care of residents with
Objectives of the Heart
 Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Essential Hypertension
 Essential Hypertension Introduction Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common condition that affects 1 out of every 3 adults. Hypertension is also called the Silent Killer because it often has
Essential Hypertension Introduction Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common condition that affects 1 out of every 3 adults. Hypertension is also called the Silent Killer because it often has
Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations
 ighapmlre33apg269_274 5/12/04 3:10 PM Page 269 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts: NAME Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations LAB TIME/DATE REVIEW SHEET exercise
ighapmlre33apg269_274 5/12/04 3:10 PM Page 269 impos03 302:bjighapmL:ighapmLrevshts:layouts: NAME Human Cardiovascular Physiology: Blood Pressure and Pulse Determinations LAB TIME/DATE REVIEW SHEET exercise
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
THE HEART THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM There are three primary closed cycles: 1) Cardiac circulation pathway of blood within the heart 2) Pulmonary circulation blood from the heart to lungs and back 3) Systemic
Anesthesia Monitoring. D. J. McMahon rev cewood
 Anesthesia Monitoring D. J. McMahon 150114 rev cewood 2018-01-19 Key Points Anesthesia Monitoring: - Understand the difference between guidelines & standards - ASA monitoring Standard I states that an
Anesthesia Monitoring D. J. McMahon 150114 rev cewood 2018-01-19 Key Points Anesthesia Monitoring: - Understand the difference between guidelines & standards - ASA monitoring Standard I states that an
Hypertension AN OVERVIEW
 AN OVERVIEW Hypertension Your doctor has determined that you have high blood pressure, or hypertension. Although high blood pressure is never really cured, it can be controlled by early detection, lifestyle
AN OVERVIEW Hypertension Your doctor has determined that you have high blood pressure, or hypertension. Although high blood pressure is never really cured, it can be controlled by early detection, lifestyle
Blood Pressure 1 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2011
 Blood Pressure 1 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2011 2 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Heart rate 3 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Heart rate is the rate at which your heart beats. It can be measured by taking a pulse. A pulse
Blood Pressure 1 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2011 2 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Heart rate 3 of 22 Boardworks Ltd 2011 Heart rate is the rate at which your heart beats. It can be measured by taking a pulse. A pulse
Capnography for Pediatric Procedural Sedation Learning Module Last revised: February 18, 2014
 Capnography for Pediatric Procedural Sedation Learning Module Last revised: February 18, 2014 Capnography 40 Non-invasive device that continually monitors EtCO 2 While pulse oximetry measures oxygen saturation,
Capnography for Pediatric Procedural Sedation Learning Module Last revised: February 18, 2014 Capnography 40 Non-invasive device that continually monitors EtCO 2 While pulse oximetry measures oxygen saturation,
Physical Fitness Biology Concepts of Biology 13.1
 Physical Fitness Biology 100 - Concepts of Biology 13.1 Name Instructor Lab Section Objectives: To gain an understanding of: What is meant by the term physical fitness Various tests used to measure an
Physical Fitness Biology 100 - Concepts of Biology 13.1 Name Instructor Lab Section Objectives: To gain an understanding of: What is meant by the term physical fitness Various tests used to measure an
Anesthesia Monitoring
 Anesthesia Monitoring Horatiu V. Vinerean, DVM, DACLAM Anesthesia Monitoring Anesthesia can be divided into four progressive phases. The signs relating to a certain phase are based upon the presence or
Anesthesia Monitoring Horatiu V. Vinerean, DVM, DACLAM Anesthesia Monitoring Anesthesia can be divided into four progressive phases. The signs relating to a certain phase are based upon the presence or
Function: Transportation of. Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases
 Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Can be felt where an artery passes near the skin surface and over a
 1 Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies 2 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since. Accounts for 1 of every 2.8 deaths Cardiovascular disease (CVD) claimed
1 Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies 2 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since. Accounts for 1 of every 2.8 deaths Cardiovascular disease (CVD) claimed
Rational Therapy of Fever in Children: Special Emphasis on Hydrotherapy
 Rational Therapy of Fever in Children: Special Emphasis on Hydrotherapy Piyush Gupta, MD, MAMS, FIAP Visiting Fellow, RCPCH, UK Professor of Pediatrics, University College of Medical Sciences, Delhi Myths
Rational Therapy of Fever in Children: Special Emphasis on Hydrotherapy Piyush Gupta, MD, MAMS, FIAP Visiting Fellow, RCPCH, UK Professor of Pediatrics, University College of Medical Sciences, Delhi Myths
ALCO Regulations. Protocol pg. 47
 For the EMT-Basic Objectives Understand ALCO regulations relative to monitoring pulse oximetry by the EMT-B Review the signs and symptoms of respiratory compromise. Understand the importance of adequate
For the EMT-Basic Objectives Understand ALCO regulations relative to monitoring pulse oximetry by the EMT-B Review the signs and symptoms of respiratory compromise. Understand the importance of adequate
*Monitor for significant side effects, especially symptoms of neurological or cardiovascular events.
 Assessment Prior to administration: Obtain complete health history including allergies, drug history, and possible drug reactions Assess reason for drug administration such as presence/history of anemia
Assessment Prior to administration: Obtain complete health history including allergies, drug history, and possible drug reactions Assess reason for drug administration such as presence/history of anemia
Source: Secondary Assessment
 Source: www.healthsciencetechnology.wikispaces.com Secondary Assessment Introduction A & P Review Components Assessment Source: www.healthsciencetechnology.wikispaces.com Introduction Must understand normal
Source: www.healthsciencetechnology.wikispaces.com Secondary Assessment Introduction A & P Review Components Assessment Source: www.healthsciencetechnology.wikispaces.com Introduction Must understand normal
science-u.org What affects blood Blood Pressure Directions You Will Need BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME Minutes
 What affects blood pressure? BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME 25-60 Minutes You Will Need Sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff) Stethoscope Blood pressure cuffs and stethoscopes can be found online
What affects blood pressure? BEST FOR GRADES 5-8 ESTIMATED TIME 25-60 Minutes You Will Need Sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff) Stethoscope Blood pressure cuffs and stethoscopes can be found online
LEFT HEART AND EXACERBATION OF LEFT HEART FAILURE
 LEFT HEART AND EXACERBATION OF LEFT HEART FAILURE Concept Map Aetiology: left heart failure is a severe fatal state in which the left side of the human heart fails to properly pump adequate amount of blood
LEFT HEART AND EXACERBATION OF LEFT HEART FAILURE Concept Map Aetiology: left heart failure is a severe fatal state in which the left side of the human heart fails to properly pump adequate amount of blood
VITAL SIGNS AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE CHEST Eve Bargmann, MD 9/22/03
 VITAL SIGNS AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE CHEST Eve Bargmann, MD 9/22/03 Objectives: 1. To understand normal 2. To introduce examination of vital signs, pulses and the chest 3. To relate anatomy to physical
VITAL SIGNS AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF THE CHEST Eve Bargmann, MD 9/22/03 Objectives: 1. To understand normal 2. To introduce examination of vital signs, pulses and the chest 3. To relate anatomy to physical
Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38
 Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38 Goals: 1. Compare closed and open circulatory systems. 2. Label the parts of the human heart. 3. Explain how blood travels through the heart; identify chambers
Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38 Goals: 1. Compare closed and open circulatory systems. 2. Label the parts of the human heart. 3. Explain how blood travels through the heart; identify chambers
UNDERSTANDING BLOOD PRESSURE
 UNDERSTANDING BLOOD PRESSURE A HANDY GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING WHAT BLOOD PRESSURE IS, HOW IT AFFECTS YOU, AND HOW TO MEASURE IT AT HOME Authored by the Texas Department of State Health Services Health Promotion
UNDERSTANDING BLOOD PRESSURE A HANDY GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING WHAT BLOOD PRESSURE IS, HOW IT AFFECTS YOU, AND HOW TO MEASURE IT AT HOME Authored by the Texas Department of State Health Services Health Promotion
Capnography 101. James A Temple BA, NRP, CCP
 Capnography 101 James A Temple BA, NRP, CCP Expected Outcomes 1. Gain a working knowledge of the physiology and science behind End-Tidal CO2. 2.Relate End-Tidal CO2 to ventilation, perfusion, and metabolism.
Capnography 101 James A Temple BA, NRP, CCP Expected Outcomes 1. Gain a working knowledge of the physiology and science behind End-Tidal CO2. 2.Relate End-Tidal CO2 to ventilation, perfusion, and metabolism.
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Performance Enhancement. Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance
 Performance Enhancement Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance Functions of the Cardiovascular System Deliver oxygen & nutrients to body tissues Carry wastes from the cells Anatomy
Performance Enhancement Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance Functions of the Cardiovascular System Deliver oxygen & nutrients to body tissues Carry wastes from the cells Anatomy
Hemodynamic Monitoring
 Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Perform Procedure And Interpret Results Hemodynamic Monitoring Tracheal Tube Cuff Pressure Dean R. Hess PhD RRT FAARC Hemodynamic Monitoring Cardiac Rate and Rhythm Arterial Blood Pressure Central Venous
Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since.
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since. Accounts for 1 of every 2.8 deaths Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since. Accounts for 1 of every 2.8 deaths Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Appendix D An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires:
 Answer Key Appendix D-2 1. An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires: a. oxygen given via nasal cannula b. immediate transport to a medical facility c.
Answer Key Appendix D-2 1. An unresponsive patient with shallow, gasping breaths at a rate of six per minute requires: a. oxygen given via nasal cannula b. immediate transport to a medical facility c.
Clinical Research Coordinator Skills Program
 Clinical Research Coordinator Skills Program Vital Signs This Skill Requires Provider direction Standard Precautions Using purell before and after contact with the patient or the patient s environment
Clinical Research Coordinator Skills Program Vital Signs This Skill Requires Provider direction Standard Precautions Using purell before and after contact with the patient or the patient s environment
Resident At Risk. The National Early Warning Score (NEWS) and Monitoring Vital Signs
 Resident At Risk The National Early Warning Score (NEWS) and Monitoring Vital Signs Schein et al 64 consecutive ward patients requiring CPR 84% clinical deterioration 8 hours before arrest Pathophysiology
Resident At Risk The National Early Warning Score (NEWS) and Monitoring Vital Signs Schein et al 64 consecutive ward patients requiring CPR 84% clinical deterioration 8 hours before arrest Pathophysiology
Circulatory System Notes
 Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
Understanding Blood Pressure. A handy guide to understanding what blood pressure is, how it affects you, and how to measure it at home
 Understanding Blood Pressure A handy guide to understanding what blood pressure is, how it affects you, and how to measure it at home Acknowledgments page Special thanks to the following individuals and
Understanding Blood Pressure A handy guide to understanding what blood pressure is, how it affects you, and how to measure it at home Acknowledgments page Special thanks to the following individuals and
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System
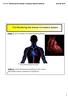 12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 5: Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 5.1 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 5: Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 5.1 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings
Hierarchy of Biological Organization
 Hierarchy of Biological Organization Transport & Exchange (Circulation & Respiration) Cardiovascular System - transports materials What materials? Components of Blood Read about The Components of the Blood
Hierarchy of Biological Organization Transport & Exchange (Circulation & Respiration) Cardiovascular System - transports materials What materials? Components of Blood Read about The Components of the Blood
After completing this chapter, you should be able to: Define and spell the terms for this chapter. 34.2
 M34_BEAM0202_04_SE_C34.indd Page 797 11/03/17 7:32 PM ganga /203/PH02957_R1/9780134420202_BEAMAN/BEAMAN_PEARSONS_COMPREHENSIVE_MEDICAL_ASSIST Chapter 34 Vital Signs Learning Objectives After completing
M34_BEAM0202_04_SE_C34.indd Page 797 11/03/17 7:32 PM ganga /203/PH02957_R1/9780134420202_BEAMAN/BEAMAN_PEARSONS_COMPREHENSIVE_MEDICAL_ASSIST Chapter 34 Vital Signs Learning Objectives After completing
