Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4): /ISSN: /IJCEP
|
|
|
- Maximilian Armstrong
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4): /ISSN: /IJCEP Original Article Acute cellular rejection and antibody-mediated rejection in endomyocardial biopsy after heart transplantation: a retrospective study from a single medical center Li Li 1, Xuejing Duan 1, Hongyue Wang 1, Qingzhi Wang 1, Yang Lu 1, Chaowu Yan 2, Hongyu Xu 1 Departments of 1 Pathology, 2 Radiology, Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, People s Republic of China Received January 18, 2017; Accepted February 22, 2017; Epub April 1, 2017; Published April 15, 2017 Abstract: Aims: Endomyocardial biopsy (EMB) is the routine procedure for monitoring the outcome of heart grafts. This article reports acute cellular rejection and antibody-mediated rejection after heart transplantation, as detected by EMB. Methods: We retrospectively evaluated 496 patients who underwent heart transplantation in Fuwai Hospital between August 2004 and June The EMB specimens were used for evaluating acute cellular rejection (ACR) and antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) by histopathology and immunohistochemistry. Results: Of 496 patients who underwent HTX, a total of 856 EMBs were performed in 261 patients. Among 850 myocardium biopsies, 425 (52.9%, 425/850) showed no evidence of ACR and AMR. ACR was seen in 345 EMBs (40.6%, 345/850) with mild rejection observed (grade 1R) in 318 cases (37.4%, 318/850), moderate rejection in 25 cases (2.9%, 25/850) EMBs and severe rejection (3R) in 2 cases (0.23%, 2/850). Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) was found in 8 EMBs, including 5 AMR alone and 3 AMR mixed with ACR. CD68 positive macrophages were found in all 8 EMBs with AMR and C4d staining was positive in 6 cases (75.0%). S6RP and ps6k were positive in 7 (87.5%) and 5 (62.5%) EMBs with AMR separately. Conclusions: Intravascular macrophages are a sign of microvascular inflammation and the earliest evidence of antibody-mediated allograft injury. Phosphorylated S6RP has the highest sensitivity in diagnosis of AMR, followed by C4d and ps6k. C4d is still a useful marker for AMR diagnosis. Keywords: Endomyocardial biopsy, cardiac transplantation, cellular rejection, antibody-mediated rejection Introduction Heart transplantation (HTX) is an established treatment for terminal heart failure [1, 2]. In 2010, a total of 3,892 heart transplants were reported to the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Registry [3]. Therefore, in managing affected patients, the close monitoring of lesions after HTX and during rejection, is a major challenge for cardiologists and heart surgeons. Many methods have been performed for rejection monitoring, and noninvasive methods such as cardiac echocardiography or MRI have been demonstrated not to retain the sensitivity and specificity [4]. Some serum immune circulating molecules such as anti-hla antibodies, anticardiac myosin or antiendothelial cell antigens, as well as plasma complement fragments C4d or C56-9, were proposed as biomarkers of graft rejection. However, no clear association between these molecules and heart rejection was confirmed [5]. Until now, endomyocardial biopsy (EMB) is still the most widely used routine procedure for monitoring the heart graft [6]. Acute cellular rejection (ACR) occurs most frequently and is characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells in the myocardium. It is classified into four grades: 0R, 1R, 2R and 3R [7]. Both the 2R and 3R grades require additional immunosuppressive treatment. ACR has been described precisely and the advent of immunosuppressants significantly lowered its frequency. Antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) is also drawing attention because of its role in cardiac allograft rejection and graft loss [8-10]. AMR is defined as allograft rejection caused by anti-
2 Figure 1. Morphologic and immunologic features of antibody-mediated rejection. A: Activated mononuclear cells fill and expand interstitial vessels (arrow shows). B-D: Immunologic features of AMR, B: CD68-positive macrophages fill vascular lumens. C: p-s6k strong and diffuse staining of capillaries. D: p-srp strong and diffuse staining of capillaries. Original magnification, 200. bodies directed against donor-specific human leukocyte antigen (HLA) molecules, blood group antigen (ABO)-isoagglutinins, or endothelial cell antigens [11]. AMR occurs in allosensitized individuals exposed to transfusion, gestations, transplants, or circulatory assistance devices [12]. The incidence of acute AMR may be as high as 15% during the first post-transplant year and confers a high risk for the later development of transplant coronary artery disease (TCAD) [12]. In 2011, based on an updated consensus, the AMR diagnosis was switched from a clinical to a pathological condition [13]. The diagnosis of AMR from biopsies was facilitated by the recognition of diffuse deposition of C4d, a breakdown product of the complement component C4, in capillaries [14]. In some c4d-negative AMR, the downstream effectors of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mtor), phosphorylated 70S6 kinase (S6K) and S6 ribosomal protein (S6RP), were detected in monitoring the proliferation of endothelia [15]. The present study reports EMB findings in patients who underwent heart transplantation between August 2004 and June 2015 at the Fuwai hospital. The study also investigates whether the signal transduction pathways involved in AMR have the potential to improve the diagnosis of cardiac AMR and guide the development of new therapeutic strategies for AMR. Materials and methods EMB and patients We analyzed all consecutive EMBs from patients who underwent an HTX at the Center for Heart Transplantation, between August 2004 and June A total of 496 patients underwent HTX during this 11-year study period, of which 261 patients underwent endomyocardial biopsies (EMB). EMBs at the interventricular septum on the side of the right ventricle were 4773 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):
3 obtained either as routine surveillance protocol biopsies or as a diagnostic tool in cases with allograft dysfunction and clinically suspected rejection. The regular biopsy schedule was as follows: every two weeks in the first month, every three months in the first years, and then every 6 months for the next 3 years. The patients clinical data including age, sex, primary heart disease and survival time after heart transplantation collected during the follow-up were reviewed. Cardiac allograft dysfunction after HTX was defined as left ventricular ejection fraction <50%, as measured by echocardiography, in the presence of signs and symptoms of heart failure such as cardiogenic shock, hypotension, decreased cardiac index and/or a rise in capillary wedge or pulmonary pressures [12]. The hospital ethics committee approved the study protocol. Diagnosis of rejection The biopsy specimens (usually 5 biopsy fragments) were fixed in 10% formalin and processed using a fast embedding program that yielded initial results within 12 hours. Sections were cut for hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) and Masson s Trichrome staining. Histological evaluation was performed by two pathologists in accordance with the ISHLT 2004 Working Formulation for Biopsy Diagnosis of Cardiac Allograft Rejection [7] and the ISHLT 2013 Working Formulation for the standardization of nomenclature in the pathologic diagnosis of antibody-mediated rejection in heart transplantation [13]. Accordingly, pamr was refined in 4 subcategories: pamr0 when no histopathologic and immunopathologic feature of AMR is seen on EMB; pamr1, or suspicious AMR, when only histopathologic [pamr1(h+)] or immunopathologic [(pamr1(i+)] features are present; pamr2 when both histopathologic and immunopathologic features occur simultaneously; and pamr3, or severe AMR, when additional signs of hemorrhage, intense inflammation, and endothelial cell pyknosis are evident [13]. C4d and CD68 immunostainings were performed in patients with histological or clinical suspicion of antibody-mediated rejection. Immunostainings for C4d and CD68 were performed using affinity-purified anti-human C4d and CD68 rabbit polyclonal antibodies (Biomedica Gruppe, Vienna). We considered C4d positivity in the setting of multifocal or diffuse (>50%) capillaries involvement and CD68 positivity when intravascular CD68-positive macrophages are present in >10% of capillaries (Figure 1) according to the new ISHLT classification [13]. Immunohistochemical analysis and grading of the phosphorylated S6 kinase and phosphorylated 70 S6-kinase protein Phosphorylated S6 kinase (S6RP) and 70 S6-kinase (S6K) protein immunostainings were performed in patients with histological or clinical suspicion of antibody-mediated rejection. The patients with only acute cellular rejection or no rejection were also selected for negative control. Immunohistochemical staining was performed as described elsewhere using antibodies against phospho-s6rp (Ser240/244, Catalog No ) and phospho-70s6-kinase protein (Thr421/Ser424, Catalog No. 9204), all purchased from Cell Signaling Technology Inc. (MA, USA). Briefly, endomyocardial biopsy sections were deparaffinized and rehydrated. Antigen was recovered in 10 mmol/l sodium citrate buffer (ph 6.0). Endogenous peroxidase activity was inhibited using 3% hydrogen peroxide in methanol for 15 minutes. The sections were then blocked with 10% normal goat serum in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). Sections were incubated with 100 µl diluted primary antibodies (1:50 for p-s6rp and p-70s6k) overnight at 4 C, followed by incubation with the IHC Detection Reagent (HRP, Rabbit. Cell Signaling Technology, Inc, CA) for 30 minutes at room temperature. The sections were then developed with a diaminobenzidine kit (DAB kit; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. MA, USA), and counter-stained with weak hematoxylin. Cardiac biopsies were scored by two study-blind cardiac pathologists. Positive EC staining results for phosphorylated forms of S6RP and SP70 was scored as follows: Grade 0 = no staining; Grade 1 = rare staining of single cells; Grade 2 = focal staining, several positive capillaries, but only in one region of the biopsy specimen and involving less than one third of the biopsy; and Grade 3 = multifocal to diffuse staining. A score 2 was considered positive [15]. Statistical analysis Continuous variables were expressed as means and standard deviations and categorical variables as counts and percentages. Sensitivity 4774 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):
4 Table 1. Patient characteristics Variables No. (%) or Mean ± SEM (n=261) Age in years 43.7±13.9 Male 211 (80.8) Primary heart disease Non-ischemic cardiomyopathy 199 (76.2) Ischemic cardiomyopathy 46 (17.6) Valvular heart disease 9 (3.4) Primary heart tumor 2 (0.8) Secondary heart disease* 5 (1.9) Retransplantation 2 (0.8) Time since transplant <2 years 34 (13.0) 2-5 years 47 (18.0) 6 years 180 (69.0) *Including: Duchenne myodystrophia, Behcet s aortitis and Marfan s syndrome. and specificity of Phosphorylated S6 kinase and 70 S6-kinase were determined by the Kappa test to compare categorical variables. The actual P values were calculated for small frequencies. P<0.05 was considered significant. Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS16.0 for Windows software (IBM Corporation; Armonk, NY). Results Acute cellular rejection In 261 patients, with an average age of 43.7±13.9 years (range, yrs), there were altogether 856 EMB events. The characteristics of these 261 patients included in the study are given in Table 1. Of 856 biopsies, six cases in which the harvested EMB fragments contained no myocardial tissue were excluded from the study. Among remaining 850 biopsies, 425 (52.9%, 425/850) showed no evidence of cellular rejection (scored grade 0R) or antibodymediated rejection. Acute cellular rejection was seen in 345 EMB (40.6%, 345/850) cases, including mild rejection (grade 1R) in 318 EMB (37.4%, 318/850) cases, moderate rejection in 25 (2.9%, 25/850) EMB cases and severe rejection (3R) in 2 (0.23%, 2/850) EMB cases. Antibody-mediated rejection and immunological features Of 850 EMBs, pathologic AMR (pamr) were observed in 8 EMBs including 5 AMR alone and 3 AMR accompanied by ACR. Typical histopathological features, such as swollen endothelial cells and intravascular macrophages, could be identified in all 8 EMBs, while interstitial edema was observed in three EMBs (Figure 1). The histopathological and immunological features of 8 EMBs with AMR are shown in Table 2. Diffuse C4d staining (>50%) was seen in 6 EMBs which were labeled C4d (+) AMR and focal C4d staining (<10%) in two which were labeled C4d (-) AMR. Diffuse CD68 staining (>10%) was seen in all 8 EMBs. To assess the cell-proliferation pathways activated in vivo by the HLA Class I molecules in the capillary endothelium, the expression of p-s6k and p-s6rp proteins was examined by immunohistochemistry on all 8 pamr 2 EMBs. Eight patients with clinical suspicion of AMR but no histological feature (pamr0) were also examined the expression of p-s6k and p-s6rp proteins. Figure 2 illustrates the staining pattern of positive p-s6k and p-s6rp in EMBs. The association between p-s6k and p-s6rp of capillary ECs and AMR, with or without C4d, is shown in Table 3. Seven of eight patients (87.5%, patient No. 1, 2, 4-8) with AMR demonstrated multifocal to diffuse capillary staining for p-s6rp, whereas only one patient (12.5%, patient No. 3) demonstrated focal staining (grade 1). Five of eight patients (62.5%, No. 1, 2, 4, 7, 8) with AMR showed multifocal to diffuse capillary staining of p-s6k, while three (37.5%, No. 3, 5, 6) exhibited focal staining (grade 1). All 8 patients with pamr0 were all negative immunity for p-s6k and p-s6rp with the specificity of 100% (Table 3). Time schedule of lesions Accordant to our biopsy time schedule, the frequency of EMB was the highest (231 EMB) in the first month, followed by EMBs performed in months 3 to 6 (156 EMB). The frequency of 1R rejection was higher during months 1-6 than during months 6-12 and >1 year period (41.7% vs 28.0% and 38.1%, P=0.033). The most grade 2R/3R rejections occurred during months 1-6 (n=17, 60.7%). Antibody-mediated rejection was seen in eight cases (5 AMR alone and 3 AMR accompanied with other lesions) and occurred in the first month (6) and months 1-3 as seen in Figure 2. Discussion This article represents a large, 11-year retrospective study of heart transplant cases from 4775 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):
5 Table 2. Histopathological and immunological features of seven biopsies with AMR No Sex Age Time after HTX Syndrome and signs Pathological diagnosis Histological features C4d (+) CD68 (+) Immunopathological features p-s6r (positive score) p-s6k (positive score) 1 M 47 y 6 d Hypotension LVEF43% ACR1R+AMR1 EC swollen, MC accumulation >50% >50% M 35 y 5 d Fatigue, LVEF 45% AMR1 EC swollen, MC accumulation, interstitial edema <10% >50% M 14 y 14 d IVS thicken ACR1R+AMR1 EC swollen, MC accumulation <10% >50% M 48 y 48 d Tachyarrthymia Hypotension AMR1 EC swollen, MC accumulation interstitial edema >50% >50% F 53 y 1 d NT-proBNP increase AMR1 EC swollen, MC accumulation >50% 10-50% M 45 y 12 d Hypotension AMR1 EC swollen, MC accumulation >50% >50% F 53 y 8 d Low cardiac output and hypotension AMR1 EC swollen, MC accumulation >50% >50% M 34 y 40 d BNP increase and Tachyarrthymia AMR1+ACR1R EC swollen, MC accumulation interstitial edema >50% >50% Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):
6 Figure 2. Time schedule of ACR and AMR after HTX. Table 3. Associations among capillary phosphorylation S6K, phosphorylation S6RP and classification of pamr Phosphorylated Immunity pamr0 pamr2 P value staining S6K positive 0 5 negative S6RP positive 0 7 negative the largest cardiovascular referral hospital in China, in which 850 right ventricle EMBs were analyzed. A lower incidence of moderate and severe acute cellular rejection (2.9% and 0.3%) was observed in this study in comparison to other studies (7.2%-26.6% and 1.3%) [16, 17]. The incidence of mild rejection (Grade 1R) in our study (40.6%) was similar to that observed in the other centers (45.1%) [16]. In a series of 1896 EMBs in Germany [16], mild (grade 1R), moderate (grade 2R) and severe (grade 3R) rejections were seen in 45.1%, 7.2% and 1.3% of EMBs, respectively. The low incidence of moderate and severe cellular rejection seen in the present study point to good compliance and effective anti-rejection therapy after transplantation. We also found that most 1R and 2R ACR cases occurred during the first 6 months. The time schedule of ACR was similar as in the other reports. In Strecker s report, the majority of 2R and 3R occurred within the first month [15]. Antibody-mediated rejection was rare in our study, with only 0.94% of 850 EMB. This preva- lence is slightly lower than reported in other studies (from 1.4- to 3%) [14, 17, 18]. This disparity can also be explained, in part, by the varying presence of risk factors in patient populations. AMR risk factors include female multiparity, a history of blood transfusion, prior transplantation, the use of left ventricular assist device, congenital heart disease and cytomegalovirus seropositivity, etc [8, 12, 19]. In the present study, these risk factors were not found, except in two patients with a history of prior heart transplantation (Table 1). In the present study, positive CD68 findings were observed in all EMBs, with a pathological diagnosis of AMR, including seven symptomatic and one asymptomatic patient. This result is in accordance with the previous observation of Fedrigo et al [19], who used CD68 immunostaining to evaluate the role of intravascular macrophages in the diagnosis of early and late AMR. In their study, in the early period, intravascular macrophages were more common in symptomatic (3 of 3, 100%) than asymptomatic (3 of 11, 27.3%) patients [19]. In the present study, one EMB had the obvious histological features of AMR, but the only immunohistochemical feature was the CD68 positive status. Therefore, it has been suggested that intravascular macrophages are a sign of microvascular inflammation and represent the earliest evidence of antibody-mediated allograft injury. If recognized early, before the complement deposition on tissue, it could represent a potential therapeutic target for prevention of consequent graft dysfunction and failure [19]. This study showed that ps6rp has the highest sensitivity in diagnosis of AMR, followed by C4d and ps6k (87.5%, 75.0% and 62.5%, respectively). This result is in accordance with the previous study by Lepin et al [20], but distinct from Li et al [15] and Tible et al [21]. In Lepin s study, nineteen of twenty (95%) patients with AMR showed multifocal or diffuse capillary staining for ps6rp. However, in Li s study, it seemed that ps6k has higher sensitivity compared to 4777 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):
7 ps6rp (53.1% vs 36.7%) in AMR. Tible and his colleagues also showed that ps6k and ps6rp are found with a higher frequency in pamr2 EMB specimens (77.8% and 55.6%, respectively) than in pamr0 (3.3% and 3.3%, respectively) and pamr1 (47.6% and 14.3%, respectively) [21]. This discrepancy may be partly ascribed to the differences in the number of patients. In our series, only eight patients had the histological features of AMR. In Li and Tible s studies, there were relatively large quantities of EMBs with AMR (49 and 37, respectively) [15, 21]. Recently, the sensitivity of C4d in diagnosis of AMR was questioned in renal [22] and cardiac AMR [21]. In the study of Tible and colleagues, C4d positive was found in only 22.2% of pathological AMR in cardiac AMR [21]. Unlike his report, the incidence of C4d positive was relatively high with 75.0% of AMR in our series. This result was in agreement with another study, in which Crespo-Leiro and his colleagues found that all six patients with clinical AMR were C4d positive [17]. Together with their study, our results strongly suggest that C4d is still a useful marker of AMR. Limitations Two limitations of the present study are the relatively small sample size and the absence of routine DSA testing in AMR patients. So the correlation of ps6rp and ps6k with DSA could not be evaluated in the present study. Further work and observation are warranted. Conclusions The incidence and severity of acute cellular rejection episodes were lower among the patients in our center in comparison to similar earlier reports. The incidence of antibody-mediated rejection was also very low. However, cardiologist and pathologist must still be aware of its potential role in graft dysfunction in AMR patients. Except for C4d and CD68, additional endothelium injury transcripts, such as ps6rp and ps6k, should be used to identify AMR. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study reporting EMBs pathology results in China from a single institution. Acknowledgements This study was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China ( ) and Peking Union Medical College Youth Fund ( ), Republic of People s Republic of China. Disclosure of conflict of interest None. Address correspondence to: Hongyue Wang, Departments of Pathology, Fuwai Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Peking Union Medical College, Beilishi Road, 167 Xicheng District, Beijing , People s Republic of China. hywangs@hotmail.com References [1] Frazier OH. Current status of cardiac transplantation and left ventricular assist devices. Tex Heart Inst J 2010; 37: [2] Vega JD, Moore J, Murray S, Chen JM, Johnson MR, Dyke DB. Heart transplantation in the United States, Am J Transplant 2009; 9: [3] Stehlik J, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, Benden C, Christie JD, Dipchand AI, Dobbels F, Kirk R, Rahmel AO, Hertz MI; International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation. The registry of the international society for heart and lung transplantation: 29 th official adult heart transplant report J Heart Lung Transplant 2012; 31: [4] Labarrere CA, Jaeger BR. Biomarkers of heart transplant rejection: the good, the bad, and the ugly! Transl Res 2012; 159: [5] Crescioli C. The role of immunological biomarkers in cardiac rejection. Curr Opin Organ Transplant 2013; 18: [6] Murphy J, Frantz R, Cooper L. Endomyocardial biopsy. In: Murphy J, Lloyd M, editors. Mayo Clinic Cardiology Concise Textbook. Minnesota: Rochester; pp [7] Stewart S, Winters GL, Fishbein MC, Berry GJ, Boehler A, Burke MM, Glanville A, Gould FK, Magro C, Marboe CC, McNeil KD, Reed EF, Reinsmoen NL, Scott JP, Studer SM, Tazelaar HD, Wallwork JL, Westall G, Zamora MR, Zeevi A, Yousem SA. Revision of the 1990 working formulation for the standardization of nomenclature in the diagnosis of heart rejection. J Heart Lung Transplant 2005; 24: [8] Fishbein GA, Fishbein MC. Morphologic and immunohistochemical findings in antibodymediated rejection of the cardiac allograft. Hum Immunol 2012; 73: [9] Hammond EH, Yowell RL, Nunoda S, Menlove RL, Renlund DG, Bristow MR, Gay WA Jr, Jones KW, O Connell JB. Vascular (humoral) rejection 4778 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):
8 in heart transplantation: pathologic observations and clinical implications. J Heart Transplant 1989; 8: [10] Lones MA, Cze LS, Trento A, Harasty D, Miller JM, Fishbein MC. Clinical-pathologic features of humoral rejection in cardiac allografts: a study in 81 consecutive patients. J Heart Lung Transplant 1995; 14: [11] Hsu CY, Chi NH, Chou NK, Shun CT, Chen YS, Huang SC, Yu HY, Wang SS. Antibody-mediated rejection after orthotopic heart transplantation: a 9-year single-institution experience. Transplant Proc 2013; 46: [12] Michaels PJ, Espejo ML, Kobashigawa J, Alejos JC, Burch C, Takemoto S, Reed EF, Fishbein MC. Humoral rejection in cardiac transplantation: risk factors, hemodynamic consequences and relationship to transplant coronary artery disease. J Heart Lung Transplant 2003; 22: [13] Berry G, Burke M, Andersen C, Bruneval P, Fedrigo M, Fishbein MC, Goddard M, Hammond EH, Leone O, Marboe C, Miller D, Neil D, Rassl D, Revelo MP, Rice A, Rene Rodriguez E, Stewart S, Tan CD, Winters GL, West L, Mehra MR, Angelini A. The 2013 international society for heart and lung transplantation working formulation for the standard of nomenclature in the pathologic diagnosis of antibody-mediated rejection in heart transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2013; 32: [14] Rodriguez ER, Skojec DV, Tan CD, Zachary AA, Kasper EK, Conte JV, Baldwin WM 3rd. Antibody-mediated rejection in human cardiac allografts: evaluation of immunoglobulins and complement activation products C4d and C3d as markers. Am J Transplant 2005; 5: [15] Li F, Wei Jennifer, Valenzuela NM, Zachary AA, Kasper EK, Conte JV, Baldwin WM 3rd. Phosohorylated S6 kinase and S6 ribosomal protein are diagnostic markers of antibody-mediated rejection in heart allografts. J Heart Lung Transplant 2015; 34: [16] Strecker T, Rosch J, Weyand M, Agaimy A. Endomyocardial biopsy for monitoring heart transplantation patients: 11-year-experience at a german heart center. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2013; 6: [17] Crespo-Leiro MG, Veiga-Barreiro A, Doménech N, Paniagua MJ, Piñón P, González-Cuesta M, Vázquez-Martul E, Ramirez C, Cuenca JJ, Castro-Beiras A. Humoral heart rejection (severe allograft dysfunction with no signs of cellular rejection or ischemia): incidence, management, and the value of C4d for diagnosis. Am J Transplant 2005; 5: [18] Yerly P, Rotman S, Nobile A, Aubert V, Tozzi P, Yarol N, Vogt P, Hullin R, Pascual M. Time-dependent specificity of immunopathologic (C4d- CD68) and histologic criteria of antibody-mediated rejection for donor-specific antibodies and allograft dysfunction in heart transplantation. Transplantation 2015; 99: [19] Fedrigo A, Feltrin G, Poli F, Frigo AC, Benazzi E, Gambino A, Tona F, Caforio AL, Castellani C, Toscano G, Gerosa G, Thiene G, Angelini A. Intravascular macrophages in cardiac allograft biopsies for diagnosis of early and late antibody-mediated rejection. J Heart Lung Transplant 2013; 32: [20] Lepin EJ, Zhang Q, Zhang X, Jindra PT, Hong LS, Ayele P, Peralta MV, Gjertson DW, Kobashigawa JA, Wallace WD, Fishbein MC, Reed EF. Phosphorylated S6 ribosomal protein: a novel biomarker of antibody-mediated rejection in heart allografts. Am J Transplant 2006; 6: [21] Tible M, Loupy A, Vernerey D, Suberbielle C, Beuscart T, Cazes A, Guillemain R, Amrein C, Pezzella V, Fabiani JN, Nochy D, Hill G, Empana JP, Jouven X, Charron D, Bruneval P, Duong Van Huyen JP. Pathologic classification of antibodymediated rejection correlates with donor. J Heart Lung Transplant 2013; 32: [22] Mengel M, Sis B, Haas M, Colvin RB, Halloran PF, Racusen LC, Solez K, Cendales L, Demetris AJ, Drachenberg CB, Farver CF, Rodriguez ER, Wallace WD, Glotz D. Banff 2011 meeting report: new concepts in antibody-mediated rejection. Am J Transplant 2012; 12: Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):
Intravascular macrophages in cardiac allograft biopsies for diagnosis of early and late antibody-mediated rejection
 http://www.jhltonline.org Intravascular macrophages in cardiac allograft biopsies for diagnosis of early and late antibody-mediated rejection Marny Fedrigo, MD, PhD, a Giuseppe Feltrin, MD, PhD, a Francesca
http://www.jhltonline.org Intravascular macrophages in cardiac allograft biopsies for diagnosis of early and late antibody-mediated rejection Marny Fedrigo, MD, PhD, a Giuseppe Feltrin, MD, PhD, a Francesca
Antibody Mediated Rejection (AMR) in Heart Transplantation Session
 Page 1 Antibody Mediated Rejection (AMR) in Heart Transplantation Session Dear Colleagues: The Heart session at Banff this year will be solely focused on AMR and besides the fact that many of us attending
Page 1 Antibody Mediated Rejection (AMR) in Heart Transplantation Session Dear Colleagues: The Heart session at Banff this year will be solely focused on AMR and besides the fact that many of us attending
Antibody Mediated Rejection (AMR) in LUNG TRANSPLANT Recipients
 Antibody Mediated Rejection (AMR) in LUNG TRANSPLANT Recipients Lorriana Leard, MD UCSF Transplant Pulmonologist Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine Vice Chief of Clinical Activities Pulmonary, Critical
Antibody Mediated Rejection (AMR) in LUNG TRANSPLANT Recipients Lorriana Leard, MD UCSF Transplant Pulmonologist Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine Vice Chief of Clinical Activities Pulmonary, Critical
No evidence of C4d association with AMR However, C3d and AMR correlated well
 C4d positivity Poor prognostic factor Reversal to C4d negativity did not change prognosis, with current therapy Prognostic factor for CAV Variable time line for CAV/death No correlation with cellular rejection
C4d positivity Poor prognostic factor Reversal to C4d negativity did not change prognosis, with current therapy Prognostic factor for CAV Variable time line for CAV/death No correlation with cellular rejection
Antibody-Mediated Rejection in the Lung Allograft. Gerald J Berry, MD Dept of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305
 Antibody-Mediated Rejection in the Lung Allograft Gerald J Berry, MD Dept of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305 Gerald J Berry, MD Professor of Pathology Stanford University, Stanford, CA
Antibody-Mediated Rejection in the Lung Allograft Gerald J Berry, MD Dept of Pathology Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305 Gerald J Berry, MD Professor of Pathology Stanford University, Stanford, CA
Endothelitis in cardiac allograft biopsy specimens: Possible relationship to antibody-mediated rejection
 http://www.jhltonline.org ORIGINAL CLINICAL SCIENCE Endothelitis in cardiac allograft biopsy specimens: Possible relationship to antibody-mediated rejection Fabio Tavora, MD, a Raghava Munivenkatappa,
http://www.jhltonline.org ORIGINAL CLINICAL SCIENCE Endothelitis in cardiac allograft biopsy specimens: Possible relationship to antibody-mediated rejection Fabio Tavora, MD, a Raghava Munivenkatappa,
ABSTRACT AJCP /ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Downloaded from by guest on 07 January 2019
 Correlation of Circulating Complement-Fixing Donor-Specific Antibodies Identified by the C1q Assay and Presence of C4d in Endomyocardial Biopsy Specimens Renee Frank, MD, 1 Priti Lal, MD, 1 Jane Kearns,
Correlation of Circulating Complement-Fixing Donor-Specific Antibodies Identified by the C1q Assay and Presence of C4d in Endomyocardial Biopsy Specimens Renee Frank, MD, 1 Priti Lal, MD, 1 Jane Kearns,
Meeting Report. Introduction
 American Journal of Transplantation 2017; 17: 42 53 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Meeting Report 2016 The Authors. American Journal of Transplantation published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American
American Journal of Transplantation 2017; 17: 42 53 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Meeting Report 2016 The Authors. American Journal of Transplantation published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American
Chronic injury to the microcirculation in EMB
 Chronic injury to the microcirculation in EMB Dylan V Miller MD M Patricia Revelo MD Disclosures Miller: None Revelo: None Goals & Objectives Characterize the tissue-level pathologic changes occurring
Chronic injury to the microcirculation in EMB Dylan V Miller MD M Patricia Revelo MD Disclosures Miller: None Revelo: None Goals & Objectives Characterize the tissue-level pathologic changes occurring
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Lefaucheur C, Loupy A, Vernerey D, et al. Antibody-mediated
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Lefaucheur C, Loupy A, Vernerey D, et al. Antibody-mediated
Research Article The Natural History of Biopsy-Negative Rejection after Heart Transplantation
 Transplantation Volume 2013, Article ID 236720, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/236720 Research Article The Natural History of Biopsy-Negative Rejection after Heart Transplantation Zhaoyi Tang,
Transplantation Volume 2013, Article ID 236720, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/236720 Research Article The Natural History of Biopsy-Negative Rejection after Heart Transplantation Zhaoyi Tang,
Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Individuals: With heart transplant
 Protocol Laboratory Tests for Heart Transplant Rejection (20168) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/14 Next Review Date: 05/18 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 05/13, 05/14, 05/15, 05/16, 05/17 This
Protocol Laboratory Tests for Heart Transplant Rejection (20168) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/14 Next Review Date: 05/18 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 05/13, 05/14, 05/15, 05/16, 05/17 This
Renal Pathology- Transplantation. Eva Honsova Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine Prague, Czech Republic
 Renal Pathology- Transplantation Eva Honsova Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine Prague, Czech Republic eva.honsova@ikem.cz Kidney has a limited number of tissue reactions by which the kidney
Renal Pathology- Transplantation Eva Honsova Institute for Clinical and Experimental Medicine Prague, Czech Republic eva.honsova@ikem.cz Kidney has a limited number of tissue reactions by which the kidney
Long-term efficacy and safety of conversion to tacrolimus in heart. transplant recipients with ongoing or recurrent acute cellular.
 Long-term efficacy and safety of conversion to tacrolimus in heart transplant recipients with ongoing or recurrent acute cellular rejection Blanka Skalická, Ivan Málek, Miloš Kubánek, Jevgenija Vymětalová,
Long-term efficacy and safety of conversion to tacrolimus in heart transplant recipients with ongoing or recurrent acute cellular rejection Blanka Skalická, Ivan Málek, Miloš Kubánek, Jevgenija Vymětalová,
Research Article The Diagnostic Value of Transcription Factors T-bet/GATA3 Ratio in Predicting Antibody-Mediated Rejection
 Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2013, Article ID 460316, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/460316 Research Article The Diagnostic Value of Transcription Factors T-bet/GATA3 Ratio in Predicting
Clinical and Developmental Immunology Volume 2013, Article ID 460316, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/460316 Research Article The Diagnostic Value of Transcription Factors T-bet/GATA3 Ratio in Predicting
Predictors of cardiac allograft vasculopathy in pediatric heart transplant recipients
 Pediatr Transplantation 2013: 17: 436 440 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Pediatric Transplantation DOI: 10.1111/petr.12095 Predictors of cardiac allograft vasculopathy in pediatric heart transplant recipients
Pediatr Transplantation 2013: 17: 436 440 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Pediatric Transplantation DOI: 10.1111/petr.12095 Predictors of cardiac allograft vasculopathy in pediatric heart transplant recipients
Posttransplant Human Leukocyte Antigen Antibodies in Stable Kidney Transplant Recipients
 Trends in Transplant. 2014;8:3-9 Gregor Bartel, Georg A. Böhmig: Alloantibodies and Graft Function Posttransplant Human Leukocyte Antigen Antibodies in Stable Kidney Transplant Recipients Gregor Bartel
Trends in Transplant. 2014;8:3-9 Gregor Bartel, Georg A. Böhmig: Alloantibodies and Graft Function Posttransplant Human Leukocyte Antigen Antibodies in Stable Kidney Transplant Recipients Gregor Bartel
Supplementary Appendix
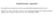 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Loupy A, Lefaucheur C, Vernerey D, et al. Complement-binding
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Loupy A, Lefaucheur C, Vernerey D, et al. Complement-binding
Pathological back-ground of renal transplant pathology and important mile-stones of the Banff classification
 Banff 1 Banff Pathological back-ground of renal transplant pathology and important mile-stones of the Banff classification Department of Nephrology, Japanese Red Cross Nagoya Daini Hospital Morozumi Kunio,
Banff 1 Banff Pathological back-ground of renal transplant pathology and important mile-stones of the Banff classification Department of Nephrology, Japanese Red Cross Nagoya Daini Hospital Morozumi Kunio,
Correspondence should be addressed to Tor Skibsted Clemmensen;
 Case Reports in Transplantation, Article ID 173589, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/173589 Case Report Case of Acute Graft Failure during Suspected Humoral Rejection with Preserved Ejection Fraction,
Case Reports in Transplantation, Article ID 173589, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/173589 Case Report Case of Acute Graft Failure during Suspected Humoral Rejection with Preserved Ejection Fraction,
Phosphorylated S6 Ribosomal Protein: A Novel Biomarker of Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Heart Allografts
 American Journal of Transplantation 2006; 6: 1560 1571 Blackwell Munksgaard C 2006 The Authors Journal compilation C 2006 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant
American Journal of Transplantation 2006; 6: 1560 1571 Blackwell Munksgaard C 2006 The Authors Journal compilation C 2006 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant
Biopsy Features of Kidney Allograft Rejection Banff B. Ivanyi, MD Department of Pathology, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary
 Biopsy Features of Kidney Allograft Rejection Banff 2017 B. Ivanyi, MD Department of Pathology, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary Treatment of allograft dysfunction should rely on the biopsy findings
Biopsy Features of Kidney Allograft Rejection Banff 2017 B. Ivanyi, MD Department of Pathology, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary Treatment of allograft dysfunction should rely on the biopsy findings
Interstitial Inflammation
 Interstitial Inflammation Currently considered to be T cell-mediated process Plasma cell rich acute rejection often associated with AMR Preliminary data suggests that interstitial follicular helper T cells
Interstitial Inflammation Currently considered to be T cell-mediated process Plasma cell rich acute rejection often associated with AMR Preliminary data suggests that interstitial follicular helper T cells
Antibody Mediated Rejection in Heart Transplantation
 Antibody Mediated Rejection in Heart Transplantation 2012 Teresa De Marco, MD, FACC Professor of Medicine & Surgery Director Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Program Medical Director, Heart Transplantation
Antibody Mediated Rejection in Heart Transplantation 2012 Teresa De Marco, MD, FACC Professor of Medicine & Surgery Director Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Program Medical Director, Heart Transplantation
3/6/2017. Prevention of Complement Activation and Antibody Development: Results from the Duet Trial
 Prevention of Complement Activation and Antibody Development: Results from the Duet Trial Jignesh Patel MD PhD FACC FRCP Medical Director, Heart Transplant Cedars-Sinai Heart Institute Disclosures Name:
Prevention of Complement Activation and Antibody Development: Results from the Duet Trial Jignesh Patel MD PhD FACC FRCP Medical Director, Heart Transplant Cedars-Sinai Heart Institute Disclosures Name:
Evaluation of Biopsy Classification for Rejection: Relation to Detection of Myocardial Damage by Monoclonal Antimyosin Antibody Imaging
 1357 HEART TRANSPLANT Evaluation of Biopsy Classification for Rejection: Relation to Detection of Myocardial Damage by Monoclonal Antimyosin Antibody Imaging MANEL BALLESTER, MD, RAMÓN BORDES, MD, HENRY
1357 HEART TRANSPLANT Evaluation of Biopsy Classification for Rejection: Relation to Detection of Myocardial Damage by Monoclonal Antimyosin Antibody Imaging MANEL BALLESTER, MD, RAMÓN BORDES, MD, HENRY
The Banff Classification for Diagnosis of Renal Allograft Rejection: Updates from the 2017 Banff Conference
 The Banff Classification for Diagnosis of Renal Allograft Rejection: Updates from the 2017 Banff Conference Mark Haas Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California, USA Statement of Disclosure Mark
The Banff Classification for Diagnosis of Renal Allograft Rejection: Updates from the 2017 Banff Conference Mark Haas Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California, USA Statement of Disclosure Mark
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence
 AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
AMR in Liver Transplantation: Incidence Primary AMR 1/3 to 1/2 of ABO-incompatible transplants Uncommon with ABO-compatible transplant Secondary AMR Unknown incidence: rarely tested Why is AMR uncommon
Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant Cardiology
 Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant Cardiology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills
Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant Cardiology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills
The new Banff vision of the role of HLA antibodies in organ transplantation: Improving diagnostic system and design of clinical trials
 The new Banff vision of the role of HLA antibodies in organ transplantation: Improving diagnostic system and design of clinical trials Carmen Lefaucheur 1 2 Banff 2015: Integration of HLA-Ab for improving
The new Banff vision of the role of HLA antibodies in organ transplantation: Improving diagnostic system and design of clinical trials Carmen Lefaucheur 1 2 Banff 2015: Integration of HLA-Ab for improving
Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD
 Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD Director, Renal Pathology Chapter Saudi Society of Nephrology & Transplantation Consultant Nephropathologist & Urological Pathologist Department of Pathology & Laboratory
Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD Director, Renal Pathology Chapter Saudi Society of Nephrology & Transplantation Consultant Nephropathologist & Urological Pathologist Department of Pathology & Laboratory
Incidence of Rejection in Renal Transplant Surgery in the LVHN Population Leading to Graft Failure: 6 Year Review
 Incidence of Rejection in Renal Transplant Surgery in the LVHN Population Leading to Graft Failure: 6 Year Review Jessica Ludolph 1 Lynsey Biondi, MD 1,2 and Michael Moritz, MD 1,2 1 Department of Surgery,
Incidence of Rejection in Renal Transplant Surgery in the LVHN Population Leading to Graft Failure: 6 Year Review Jessica Ludolph 1 Lynsey Biondi, MD 1,2 and Michael Moritz, MD 1,2 1 Department of Surgery,
Med Path Rads Conference Gurpreet Sodhi M.D.
 Med Path Rads Conference 5.10.13 Gurpreet Sodhi M.D. Objectives -Define and understand noncompaction cardiomyopathy -Briefly review normal intracardiac hemodynamic pressures and interpret a patient s pressures
Med Path Rads Conference 5.10.13 Gurpreet Sodhi M.D. Objectives -Define and understand noncompaction cardiomyopathy -Briefly review normal intracardiac hemodynamic pressures and interpret a patient s pressures
The multidisciplinary approach to AMR in lung transplantation: Reaching a consensus. Deborah Jo Levine Professor of Medicine University of Texas
 The multidisciplinary approach to AMR in lung transplantation: Reaching a consensus Deborah Jo Levine Professor of Medicine University of Texas Disclosures I have no financial relations with any relevant
The multidisciplinary approach to AMR in lung transplantation: Reaching a consensus Deborah Jo Levine Professor of Medicine University of Texas Disclosures I have no financial relations with any relevant
C4d Staining of Pulmonary Allograft Biopsies: An Immunoperoxidase Study
 C4d Staining of Pulmonary Allograft Biopsies: An Immunoperoxidase Study W. Dean Wallace, MD, a Elaine F. Reed, PhD, b David Ross, MD, c Charles R. Lassman, MD, PhD, a and Michael C. Fishbein, MD a Background:
C4d Staining of Pulmonary Allograft Biopsies: An Immunoperoxidase Study W. Dean Wallace, MD, a Elaine F. Reed, PhD, b David Ross, MD, c Charles R. Lassman, MD, PhD, a and Michael C. Fishbein, MD a Background:
Myocarditis in Infants and Children
 in Infants and Children Guideline of the German Society of Pediatric Cardiology Thomas Paul, Carsten Tschöpe, Reinhard Kandolf Children s Heart Center, Georg-August-University, Göttingen Department of
in Infants and Children Guideline of the German Society of Pediatric Cardiology Thomas Paul, Carsten Tschöpe, Reinhard Kandolf Children s Heart Center, Georg-August-University, Göttingen Department of
Post-Transplant Monitoring for the Development of Anti-Donor HLA Antibodies
 Post-Transplant Monitoring for the Development of Anti-Donor HLA Antibodies Lorita M Rebellato, Ph.D., D (ABHI) Associate Professor Department of Pathology The Brody School of Medicine at ECU Scientific
Post-Transplant Monitoring for the Development of Anti-Donor HLA Antibodies Lorita M Rebellato, Ph.D., D (ABHI) Associate Professor Department of Pathology The Brody School of Medicine at ECU Scientific
Statement of Disclosure
 Statement of Disclosure Mark Haas serves as a paid consultant on pathology adjudication committees for two industry-sponsored clinical trials: Shire ViroPharma Treatment of Acute ABMR AstraZeneca Treatment
Statement of Disclosure Mark Haas serves as a paid consultant on pathology adjudication committees for two industry-sponsored clinical trials: Shire ViroPharma Treatment of Acute ABMR AstraZeneca Treatment
Hemodynamics during Humoral Rejection Events with Total Versus Standard Orthotopic Heart Transplantation
 Original Article Hemodynamics during Humoral Rejection Events with Total Versus Standard Orthotopic Heart Transplantation Ivan Aleksic, MD, 1 Dov Freimark, MD, 2 Carlos Blanche, MD, 3 Lawrence SC Czer,
Original Article Hemodynamics during Humoral Rejection Events with Total Versus Standard Orthotopic Heart Transplantation Ivan Aleksic, MD, 1 Dov Freimark, MD, 2 Carlos Blanche, MD, 3 Lawrence SC Czer,
Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Individuals: With heart transplant. Comparators of interest are: Routine endomyocardial biopsy
 Protocol Laboratory Tests for Heart Transplant Rejection (20168) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/14 Next Review Date: 05/19 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 05/13, 05/14, 05/15, 05/16, 05/17, 05/18
Protocol Laboratory Tests for Heart Transplant Rejection (20168) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/14 Next Review Date: 05/19 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 05/13, 05/14, 05/15, 05/16, 05/17, 05/18
Role of Soluble ST2 as a Marker for Rejection after Heart Transplant
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/1.47/kcj.216.46.6.811 Print ISSN 1738-552 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Role of Soluble ST2 as a Marker for Rejection after Heart Transplant Ga Yeon
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/1.47/kcj.216.46.6.811 Print ISSN 1738-552 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Role of Soluble ST2 as a Marker for Rejection after Heart Transplant Ga Yeon
Management of Rejection
 Management of Rejection I have no disclosures Disclosures (relevant or otherwise) Deborah B Adey, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Center
Management of Rejection I have no disclosures Disclosures (relevant or otherwise) Deborah B Adey, MD Professor of Medicine University of California, San Francisco Kidney and Pancreas Transplant Center
The diffuse extent of peritubular capillaritis in renal allograft rejection is an independent risk factor for graft loss
 http://www.kidney-international.org 2015 International Society of Nephrology see commentary on page 218 The diffuse extent of peritubular capillaritis in renal allograft rejection is an independent risk
http://www.kidney-international.org 2015 International Society of Nephrology see commentary on page 218 The diffuse extent of peritubular capillaritis in renal allograft rejection is an independent risk
Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014
 Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014 Indications for cardiac catheterization Before a decision to perform an invasive procedure such
Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014 Indications for cardiac catheterization Before a decision to perform an invasive procedure such
Retransplant and Medical Therapy for Cardiac Allograft Vasculopathy: International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation Registry Analysis
 American Journal of Transplantation 2016; 16: 301 309 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Brief Communication C Copyright 2015 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons
American Journal of Transplantation 2016; 16: 301 309 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Brief Communication C Copyright 2015 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons
Review of Rituximab and renal transplantation. Dr.E Nemati. Professor of Nephrology
 Review of Rituximab and renal transplantation Dr.E Nemati Professor of Nephrology Introductio n Rituximab is a chimeric anti-cd20 monoclonal antibody. The CD20 antigen is a transmembrane nonglycosylated
Review of Rituximab and renal transplantation Dr.E Nemati Professor of Nephrology Introductio n Rituximab is a chimeric anti-cd20 monoclonal antibody. The CD20 antigen is a transmembrane nonglycosylated
Pros and cons for C4d as a biomarker
 review http://www.kidney-international.org & 2012 International Society of Nephrology Pros and cons for C4d as a biomarker Danielle Cohen 1, Robert B. Colvin 2, Mohamed R. Daha 3, Cinthia B. Drachenberg
review http://www.kidney-international.org & 2012 International Society of Nephrology Pros and cons for C4d as a biomarker Danielle Cohen 1, Robert B. Colvin 2, Mohamed R. Daha 3, Cinthia B. Drachenberg
Subject: Laboratory Tests for Heart and Kidney Transplant Rejection
 05-86000-24 Original Effective Date: 03/15/05 Reviewed: 12/06/18 Revised: 12/15/18 Subject: Laboratory Tests for Heart and Kidney Transplant Rejection THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION,
05-86000-24 Original Effective Date: 03/15/05 Reviewed: 12/06/18 Revised: 12/15/18 Subject: Laboratory Tests for Heart and Kidney Transplant Rejection THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION,
Le Rejet Humoral Chronique en 2010: Histoire naturelle et problématiques
 Le Rejet Humoral Chronique en 2010: Histoire naturelle et problématiques CAMR in 2010: natural history and perspectives Alexandre Loupy 1 Introduction 2 CAMR: the missing link 3 Natural history of CAMR
Le Rejet Humoral Chronique en 2010: Histoire naturelle et problématiques CAMR in 2010: natural history and perspectives Alexandre Loupy 1 Introduction 2 CAMR: the missing link 3 Natural history of CAMR
Kathryn J. Lindley, 1, 2 Ashwin K. Ravichandran, 1, 2 Joel Schilling, 1, 2, 3 and Susan M. Joseph 1, Introduction
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2012, Article ID 639284, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/639284 Case Report Antibody-Mediated Rejection of the Heart in the Setting of Autoimmune Demyelinating Polyneuropathy:
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2012, Article ID 639284, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/639284 Case Report Antibody-Mediated Rejection of the Heart in the Setting of Autoimmune Demyelinating Polyneuropathy:
Ventricular Tachycardia Ablation. Saverio Iacopino, MD, FACC, FESC
 Ventricular Tachycardia Ablation Saverio Iacopino, MD, FACC, FESC ü Ventricular arrhythmias, both symptomatic and asymptomatic, are common, but syncope and SCD are infrequent initial manifestations of
Ventricular Tachycardia Ablation Saverio Iacopino, MD, FACC, FESC ü Ventricular arrhythmias, both symptomatic and asymptomatic, are common, but syncope and SCD are infrequent initial manifestations of
BK virus infection in renal transplant recipients: single centre experience. Dr Wong Lok Yan Ivy
 BK virus infection in renal transplant recipients: single centre experience Dr Wong Lok Yan Ivy Background BK virus nephropathy (BKVN) has emerged as an important cause of renal graft dysfunction in recent
BK virus infection in renal transplant recipients: single centre experience Dr Wong Lok Yan Ivy Background BK virus nephropathy (BKVN) has emerged as an important cause of renal graft dysfunction in recent
Supplementary material 1. Definitions of study endpoints (extracted from the Endpoint Validation Committee Charter) 1.
 Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of the SIGNIFY trial: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ivabradine in patients with stable coronary artery disease without clinical
Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of the SIGNIFY trial: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ivabradine in patients with stable coronary artery disease without clinical
3/6/2017. Treatment of Detected Antibodies. I have financial relationship(s) with: Thoratec/St. Jude/Abbott Consultant CareDx Consultant/Speaker
 Treatment of Detected Antibodies Sean Pinney, MD Director, Advanced Heart Failure & Transplantation Mount Sinai Hospital New York, NY Sean Pinney, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Icahn School of Medicine
Treatment of Detected Antibodies Sean Pinney, MD Director, Advanced Heart Failure & Transplantation Mount Sinai Hospital New York, NY Sean Pinney, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Icahn School of Medicine
2017 BANFF-SCT Joint Scientific Meeting. BARCELONA March 2017
 2017 BANFF-SCT Joint Scientific Meeting BARCELONA 27-31 March 2017 Adriana Zeevi PhD (D) ABHI Professor of Pathology, Surgery and Immunology Director of Histocompatibility Laboratory University of Pittsburgh
2017 BANFF-SCT Joint Scientific Meeting BARCELONA 27-31 March 2017 Adriana Zeevi PhD (D) ABHI Professor of Pathology, Surgery and Immunology Director of Histocompatibility Laboratory University of Pittsburgh
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Laboratory Tests for Heart Transplant Rejection Page 1 of 13 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Laboratory Tests for Heart Transplant Rejection Professional
Laboratory Tests for Heart Transplant Rejection Page 1 of 13 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Laboratory Tests for Heart Transplant Rejection Professional
Heart Transplant: State of the Art. Dr Nick Banner
 Heart Transplant: State of the Art Dr Nick Banner Heart Transplantation What is achieved Current challenges Donor scarcity More complex recipients Long-term limitations Non-specific Pharmacological Immunosuppression
Heart Transplant: State of the Art Dr Nick Banner Heart Transplantation What is achieved Current challenges Donor scarcity More complex recipients Long-term limitations Non-specific Pharmacological Immunosuppression
Marta Farrero Torres₁, Marcelo Pando₂, Dolly Tyan₂, Hannah Valantine₃, Spenser Smith₃, Kiran Khush₃
 Development of HLA donor specific antibodies after heart transplantation: importance of a new method to detect the first component of the complement cascade Marta Farrero Torres₁, Marcelo Pando₂, Dolly
Development of HLA donor specific antibodies after heart transplantation: importance of a new method to detect the first component of the complement cascade Marta Farrero Torres₁, Marcelo Pando₂, Dolly
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients
 Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
HLA and Non-HLA Antibodies in Transplantation and their Management
 HLA and Non-HLA Antibodies in Transplantation and their Management Luca Dello Strologo October 29 th, 2016 Hystory I 1960 donor specific antibodies (DSA): first suggestion for a possible role in deteriorating
HLA and Non-HLA Antibodies in Transplantation and their Management Luca Dello Strologo October 29 th, 2016 Hystory I 1960 donor specific antibodies (DSA): first suggestion for a possible role in deteriorating
Introduction. Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats
 Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Laboratory Tests for Heart Transplant Rejection
 Laboratory Tests for Heart Transplant Rejection Policy Number: 2.01.68 Last Review: 6/2018 Origination: 6/2007 Next Review: 6/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Laboratory Tests for Heart Transplant Rejection Policy Number: 2.01.68 Last Review: 6/2018 Origination: 6/2007 Next Review: 6/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Acute cardiogenic shock with standing-still heart
 Acute cardiogenic shock with standing-still heart Ga Yeon Lee April, 21, 2017 Division of cardiology, Department of Medicine, Heart Vascular Stroke Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea
Acute cardiogenic shock with standing-still heart Ga Yeon Lee April, 21, 2017 Division of cardiology, Department of Medicine, Heart Vascular Stroke Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, South Korea
HLA Antibody Complement Based Assays. Howard M. Gebel, PhD, D(ABHI) Robert A. Bray, PhD, D(ABHI) Emory University Hospital Atlanta, GA
 HLA Antibody Complement Based Assays Howard M. Gebel, PhD, D(ABHI) Robert A. Bray, PhD, D(ABHI) Emory University Hospital Atlanta, GA Disclosure Neither presenter has any financial relationships related
HLA Antibody Complement Based Assays Howard M. Gebel, PhD, D(ABHI) Robert A. Bray, PhD, D(ABHI) Emory University Hospital Atlanta, GA Disclosure Neither presenter has any financial relationships related
Kidney Summary. Mark Haas Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California, USA
 Kidney Summary Mark Haas Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California, USA Key Issues to Address re: the Classification 1. Incorporation of i-ifta + tubulitis into the TCMR classification - Defining
Kidney Summary Mark Haas Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California, USA Key Issues to Address re: the Classification 1. Incorporation of i-ifta + tubulitis into the TCMR classification - Defining
Heart Transplantation
 Heart Transplantation Abbas Ardehali, M.D., F.A.C.S. Professor of Surgery and Medicine, Division of Cardiac Surgery William E. Connor Chair in Cardiothoracic Transplantation Director, UCLA Heart, Lung,
Heart Transplantation Abbas Ardehali, M.D., F.A.C.S. Professor of Surgery and Medicine, Division of Cardiac Surgery William E. Connor Chair in Cardiothoracic Transplantation Director, UCLA Heart, Lung,
Pulmonary AMR Therapeutic Options & Strategies: The Old and the New. Ramsey Hachem, MD March 28, 2017
 Pulmonary AMR Therapeutic Options & Strategies: The Old and the New Ramsey Hachem, MD March 28, 2017 Disclosures Ramsey Hachem I have no financial relations with any relevant commercial interests I will
Pulmonary AMR Therapeutic Options & Strategies: The Old and the New Ramsey Hachem, MD March 28, 2017 Disclosures Ramsey Hachem I have no financial relations with any relevant commercial interests I will
Evolution of the approaches toward grading and classifying chronic changes in the renal allograft: Banff classification updates III
 EDITORIAL Advance Access publication 24 February 2014 Evolution of the approaches toward grading and classifying chronic changes in the renal allograft: Banff classification updates III Histopathology
EDITORIAL Advance Access publication 24 February 2014 Evolution of the approaches toward grading and classifying chronic changes in the renal allograft: Banff classification updates III Histopathology
Immunopathology of T cell mediated rejection
 Immunopathology of T cell mediated rejection Ibrahim Batal MD Columbia University College of Physicians & Surgeons New York, NY, USA Overview Pathophysiology and grading of TCMR TCMR is still a significant
Immunopathology of T cell mediated rejection Ibrahim Batal MD Columbia University College of Physicians & Surgeons New York, NY, USA Overview Pathophysiology and grading of TCMR TCMR is still a significant
Kidney injury molecule-1 expression is closely associated with renal allograft damage
 Kidney injury molecule-1 expression is closely associated with renal allograft damage Lianlian Song 1,2, Lijuan Xue 1, Jinyu Yu 1, Jun Zhao 1, Wenlan Zhang 1, Yaowen Fu 1 * 1 Urology and Nephrology Center,
Kidney injury molecule-1 expression is closely associated with renal allograft damage Lianlian Song 1,2, Lijuan Xue 1, Jinyu Yu 1, Jun Zhao 1, Wenlan Zhang 1, Yaowen Fu 1 * 1 Urology and Nephrology Center,
The Banff Conferences on renal allograft pathology the latest 2013 report
 615245PSH0010.1177/2010105815615245Proceedings of Singapore HealthcareLoh research-article2015 Review Article PROCEEDINGS OF SINGAPORE HEALTHCARE The Banff Conferences on renal allograft pathology the
615245PSH0010.1177/2010105815615245Proceedings of Singapore HealthcareLoh research-article2015 Review Article PROCEEDINGS OF SINGAPORE HEALTHCARE The Banff Conferences on renal allograft pathology the
: A Study Examining the Prevalence of Transthyretin Mutations in Subjects Suspected of Having Cardiac Amyloidosis
 : A Study Examining the Prevalence of Transthyretin Mutations in Subjects Suspected of Having Cardiac Amyloidosis 02 November 2015 1 Background and Rationale Cardiac amyloidosis is caused by extracellular
: A Study Examining the Prevalence of Transthyretin Mutations in Subjects Suspected of Having Cardiac Amyloidosis 02 November 2015 1 Background and Rationale Cardiac amyloidosis is caused by extracellular
Effect of Acute Allograft Rejection on Exercise Hemodynamics in Patients Who
 Effect of Acute Allograft Rejection on Exercise Hemodynamics in Patients Who Have Undergone Cardiac Transplantation* John N. Nanas, MD; Maria I. Anastasiou-Nana, MD; Richard B. Sutton, MD; and Theofilos
Effect of Acute Allograft Rejection on Exercise Hemodynamics in Patients Who Have Undergone Cardiac Transplantation* John N. Nanas, MD; Maria I. Anastasiou-Nana, MD; Richard B. Sutton, MD; and Theofilos
Joint Banff/CST Program Committee Co-chairs: Dr. Alexandre Loupy and Dr. Prosanto Chaudhury. Joint Banff/CST Finance Committee
 2015 Banff/CST Meeting Organizing Corporation ( 2015 MOC ) Co-Directors: Dr. John Gill, Dr. Michael Mengel Members: Anthony Jevnikar, David Rush, Denis Glotz, Kim Solez, Marcelo Cantarovich, Mark Haas,
2015 Banff/CST Meeting Organizing Corporation ( 2015 MOC ) Co-Directors: Dr. John Gill, Dr. Michael Mengel Members: Anthony Jevnikar, David Rush, Denis Glotz, Kim Solez, Marcelo Cantarovich, Mark Haas,
Policy #: 212 Latest Review Date: June 2016
 Name of Policy: Heart Transplant Rejection Laboratory Testing Policy #: 212 Latest Review Date: June 2016 Category: Laboratory Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable
Name of Policy: Heart Transplant Rejection Laboratory Testing Policy #: 212 Latest Review Date: June 2016 Category: Laboratory Policy Grade: B Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable
Medical Policy. MP Laboratory Tests for Heart and Kidney Transplant Rejection
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.68 Last Review: 10/18/2018 Effective Date: 01/25/2019 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.04.130 ST2 Assay for Chronic Heart Failure and Heart Transplant Rejection
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.68 Last Review: 10/18/2018 Effective Date: 01/25/2019 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.04.130 ST2 Assay for Chronic Heart Failure and Heart Transplant Rejection
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
2015 SCVP Young Investigator Award Presentations
 2015 SCVP Young Investigator Award Presentations Md Shahrier Amin: Amyloidosis in Atrial Appendages Removed During the Cox Maze Procedure: A Study of 349 Consecutive Cases (2010 2014) with Clinical Implications.
2015 SCVP Young Investigator Award Presentations Md Shahrier Amin: Amyloidosis in Atrial Appendages Removed During the Cox Maze Procedure: A Study of 349 Consecutive Cases (2010 2014) with Clinical Implications.
Review Article Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Heart Transplantation: Case Presentation with a Review of Current International Guidelines
 Transplantation Volume 2011, Article ID 351950, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2011/351950 Review Article Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Heart Transplantation: Case Presentation with a Review of Current International
Transplantation Volume 2011, Article ID 351950, 7 pages doi:10.1155/2011/351950 Review Article Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Heart Transplantation: Case Presentation with a Review of Current International
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Laboratory Tests for Heart and Kidney Page 1 of 20 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Laboratory Tests for Heart and Kidney Transplant Rejection Professional
Laboratory Tests for Heart and Kidney Page 1 of 20 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Laboratory Tests for Heart and Kidney Transplant Rejection Professional
Why Do We Need New Immunosuppressive Agents
 Why Do We Need New Immunosuppressive Agents 1 Reducing acute rejection rates has not transplanted into better long-term graft survival Incidence of early acute rejection episodes by era Relative risk for
Why Do We Need New Immunosuppressive Agents 1 Reducing acute rejection rates has not transplanted into better long-term graft survival Incidence of early acute rejection episodes by era Relative risk for
Premier Health Plan considers Intravascular Ultrasound (IVUS) for Coronary Vessels medically necessary for the following indications:
 Premier Health Plan POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL MP.091.PH - Intravascular Ultrasound for Coronary Vessels This policy applies to the following lines of business: Premier Commercial Premier Employee Premier
Premier Health Plan POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL MP.091.PH - Intravascular Ultrasound for Coronary Vessels This policy applies to the following lines of business: Premier Commercial Premier Employee Premier
Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC-
 Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Solid Organ Transplant
 Solid Organ Transplant Lee R. Goldberg, MD, MPH, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Medical Director, Heart Failure and CardiacTransplant Program University of Pennsylvania Disclosures Thoratec Consulting
Solid Organ Transplant Lee R. Goldberg, MD, MPH, FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Medical Director, Heart Failure and CardiacTransplant Program University of Pennsylvania Disclosures Thoratec Consulting
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Laboratory Tests for Heart and Kidney Transplant Rejection File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: laboratory_tests_for_heart_and_kidney_transplant_rejection
Corporate Medical Policy Laboratory Tests for Heart and Kidney Transplant Rejection File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: laboratory_tests_for_heart_and_kidney_transplant_rejection
4/11/2017. Cardiomyopathy. John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart. Disclosures. No Conflicts. Cardiomyopathy. WHO Classification
 Cardiomyopathy John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart Disclosures No Conflicts Cardiomyopathy WHO Classification Anatomy & physiology of the LV 1. Dilated Enlarged Systolic dysfunction 2. Hypertrophic Thickened
Cardiomyopathy John Steuter, MD Bryan Heart Disclosures No Conflicts Cardiomyopathy WHO Classification Anatomy & physiology of the LV 1. Dilated Enlarged Systolic dysfunction 2. Hypertrophic Thickened
 http://researchoutput.csu.edu.au This is the author version of the paper published as: Author: T.-W. Sun, S.-Y. Zhang and L. Wang Author Address: lwang@csu.edu.au Title: Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide
http://researchoutput.csu.edu.au This is the author version of the paper published as: Author: T.-W. Sun, S.-Y. Zhang and L. Wang Author Address: lwang@csu.edu.au Title: Plasma B-type natriuretic peptide
U N I V E R S I T Ä T S M E D I Z I N B E R L I N CBF KARDIOLOGIE
 U N I V E R S I T Ä T S M E D I Z I N B E R L I N I have nothing to disclose. Case 2 A Case of acute heart failure 54 year old female Patient with acute heart failure and ventricular tachycardia 53 year
U N I V E R S I T Ä T S M E D I Z I N B E R L I N I have nothing to disclose. Case 2 A Case of acute heart failure 54 year old female Patient with acute heart failure and ventricular tachycardia 53 year
Antihuman leukocyte antigen (HLA) antibodies can be
 Antihuman Leukocyte Antigen Specific Antibody Strength Determined by Complement-Dependent or Solid-Phase Assays Can Predict Positive Donor-Specific Crossmatches Ibrahim Batal, MD; Adriana Zeevi, PhD; John
Antihuman Leukocyte Antigen Specific Antibody Strength Determined by Complement-Dependent or Solid-Phase Assays Can Predict Positive Donor-Specific Crossmatches Ibrahim Batal, MD; Adriana Zeevi, PhD; John
Microcirculation Inflammation Associates With Outcome in Renal Transplant Patients With De Novo Donor-Specific Antibodies
 American Journal of Transplantation 2013; 13: 485 492 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Brief Communication C Copyright 2012 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons
American Journal of Transplantation 2013; 13: 485 492 Wiley Periodicals Inc. Brief Communication C Copyright 2012 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons
PCI in Patients with Transplant Coronary Artery Disease. Michael S. Lee, MD, FACC, FSCAI Assistant Professor UCLA School of Medicine
 PCI in Patients with Transplant Coronary Artery Disease Michael S. Lee, MD, FACC, FSCAI Assistant Professor UCLA School of Medicine Faculty Disclosure Honararia for Boston Scientific, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo,
PCI in Patients with Transplant Coronary Artery Disease Michael S. Lee, MD, FACC, FSCAI Assistant Professor UCLA School of Medicine Faculty Disclosure Honararia for Boston Scientific, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo,
Gender-Based Analysis of Outcome After Heart Transplantation
 article Gender-Based Analysis of Outcome After Heart Transplantation Sandra Eifert, 1 Sieglinde Kofler, 2 Thomas Nickel, 2 Sophia Horster, 3 Amir Khosrow Bigdeli, 1 Andres Beiras-Fernandez, 1 Bruno Meiser,
article Gender-Based Analysis of Outcome After Heart Transplantation Sandra Eifert, 1 Sieglinde Kofler, 2 Thomas Nickel, 2 Sophia Horster, 3 Amir Khosrow Bigdeli, 1 Andres Beiras-Fernandez, 1 Bruno Meiser,
Objectives 3/6/2017. Impact of Non-HLA Antibodies in Lung Transplantation
 Impact of Non-HLA Antibodies in Lung Transplantation Nancy L. Reinsmoen, Ph.D., D(ABHI) Director, HLA and Immunogenetics Laboratory (Retired) Cedars Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Nancy L. Reinsmoen,
Impact of Non-HLA Antibodies in Lung Transplantation Nancy L. Reinsmoen, Ph.D., D(ABHI) Director, HLA and Immunogenetics Laboratory (Retired) Cedars Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, CA Nancy L. Reinsmoen,
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Case Report Fulminant Myocarditis Managed by Extracorporeal Life Support (Impella CP): A Rare Case
 Hindawi Volume 2017, Article ID 9231959, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9231959 Case Report Fulminant Myocarditis Managed by Extracorporeal Life Support (Impella CP): A Rare Case Henrik Fox, Martin
Hindawi Volume 2017, Article ID 9231959, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9231959 Case Report Fulminant Myocarditis Managed by Extracorporeal Life Support (Impella CP): A Rare Case Henrik Fox, Martin
Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the. impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood.
 Introduction: Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood. As of 2013, an estimated 5.8 million people in the United
Introduction: Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome that results in the impairment of the heart s ability to fill or to pump out blood. As of 2013, an estimated 5.8 million people in the United
Original Article TLR4 contributes to mechanical ventilation induced lung injury in the rabbits
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4700-4704 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0040416 Original Article TLR4 contributes to mechanical ventilation induced lung injury in the rabbits Hongmei Zhang 1, Pei
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4700-4704 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0040416 Original Article TLR4 contributes to mechanical ventilation induced lung injury in the rabbits Hongmei Zhang 1, Pei
Peritubular capillaries C4d deposits in renal allograft biopsies and anti HLA I/II alloantibodies screening Incidence and clinical importance
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Port J Nephrol Hypert 2008; 22(1): 37-42 Peritubular capillaries C4d deposits in renal allograft biopsies and anti HLA I/II alloantibodies screening Incidence and clinical importance Helena
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Port J Nephrol Hypert 2008; 22(1): 37-42 Peritubular capillaries C4d deposits in renal allograft biopsies and anti HLA I/II alloantibodies screening Incidence and clinical importance Helena
COMPETENCY CLASSES and MASTER CLASSES
 CORE COMPETENCY CLASSES and MASTER CLASSES ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACA ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT A
CORE COMPETENCY CLASSES and MASTER CLASSES ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACA ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT ACADEMY ISHLT A
Senior of Histopathology Department at Khartoum, Radiation and Isotopes Center
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 2/ May 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Immune Histochemical Evaluation of AMACR (P504S) in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. IV, Issue 2/ May 2016 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Immune Histochemical Evaluation of AMACR (P504S) in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma
