Life-threatening intestinal ischaemia and necrosis in a patient with cardiac arrest and atrial fibrillation
|
|
|
- Gervase Bond
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Grand Rounds Vol 16 pages 1 5 Specialities: Cardiology; Colorectal Surgery; Vascular Disease; Vascular Surgery Article Type: Case Report DOI: / ß 2016 e-med Ltd Life-threatening intestinal ischaemia and necrosis in a patient with cardiac arrest and atrial fibrillation Nouar Dia Alyonan Department of Cardiology, Odense University Hospital, Denmark Corresponding address: Department of Cardiology, Odense University Hospital, Denmark. nawar549@yahoo.com Date accepted for publication 13 February 2016 Abstract A 68-year old man was successfully resuscitated after sudden cardiac arrest. Following this event, the patient developed intestinal ischaemia and necrosis requiring surgical treatment. Our case report investigates the cause of the intestinal ischaemia and warns physicians to be aware of this rare but life-threatening condition. Keywords Cardiac arrest; superior mesenteric artery occlusion; intestinal ischaemia. Introduction Sudden cardiac arrest is a life-threatening condition causing death within minutes if not immediately and properly treated. It can be divided into out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and inhospital cardiac arrest, with survival rates of 9.5% and 23.9% in adults, respectively, which shows that this condition, even if treated immediately and in a hospital with trained medical personnel, has a low survival rate [1]. Patients who survive this condition are also at risk of neurological and other severe complications. In our case, the patient was successfully resuscitated and had spontaneous circulation within a few minutes after the cardiac arrest, but he then had unexplained abdominal symptoms, which required an urgent exploratory laparotomy to resolve. Case presentation A 68-year old man with known chronic coronary artery disease, a successful coronary bypass operation and femorofemoral crossover grafting 10 years previously, had a sudden cardiac arrest while out hunting, with no sentinel chest pain or other cardiac symptoms immediately before the event. A paramedic at the scene initiated immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and 2 min later an ambulance with a physician arrived at the scene and took over the CPR. The heart monitor revealed ventricular fibrillation and one shock of 360 J was administered, converting the This paper is available online at In the event of a change in the URL address, please use the DOI provided to locate the paper.
2 2 N. Dia Alyonan patient s heart rhythm from ventricular fibrillation into atrial fibrillation with a ventricular rate of 114 beats/min. The electrocardiogram (ECG) revealed ST segment depression in lead V2 V6. Following this the patient had a spontaneous pulse and circulation and the time to return of spontaneous circulation was only 15 min. The patient was thereafter awake, fully oriented, scored 15 on the Glasgow Coma Scale and his blood pressure was 161/80 mmhg. The patient s only complaint was chest pain accentuated by respiration, which was considered the result of possible rib fractures following the chest compressions during the CPR. The pain was relieved by low doses of intravenous morphine. The patient was subsequently transferred to the Department of Cardiology at the Regional University Hospital and underwent coronary arteriography, which was normal without any newly significant coronary artery stenosis, and this result could therefore not explain the patient s sudden cardiac arrest. Primary cardiac dysrhythmia was therefore suspected as the cause of the cardiac arrest. The patient was subsequently transferred to the cardiology ward, where he was carefully questioned and examined by the ward doctor. The patient only complained of pain from his ribs, and no other symptoms were present at that time. The ECG revealed atrial fibrillation with a ventricular rate of 100 beats/min, no ST segment changes and a normal QT interval. The patient had no previous history of atrial fibrillation and had no cardiac-related symptoms before the cardiac arrest, which made it difficult to estimate when the atrial fibrillation had begun. Bedside echocardiography revealed a near normal ejection fraction, no valvular abnormities and no pericardial effusion. There was a pre-existing hypokinetic area in the inferolateral segments known from earlier echocardiography 10 years previously after the coronary bypass operation. The first troponin I measurement taken at 17:30 h was 506 ng/l (reference level 525 ng/l), and the second troponin I measurement taken at 22:00 h was 1124 ng/l. Electrolytes (sodium, potassium and calcium) were all found to be in the normal range; the patient s creatinine measurement and blood sugar levels were also within the normal range. Blood pressure was 128/ 65 mmhg, pulse 80 beats/min and temperature 37.08C. A chest radiograph revealed two rib fractures but no signs of pneumothorax or pleural effusion. The patient complained of upper abdominal pain for the first time at 20:30 h. Physical examination carried out by the ward doctor revealed diffuse tenderness in the abdomen but no guarding, rebound or rigidity. The pain was relieved by low doses of intravenous morphine and was considered to be a result of the chest compressions during the CPR earlier that day. In the following hours the pain worsened and the patient had abdominal cramps and vomiting. An abdominal surgeon was informed but did not suspect any serious condition and also considered this to be a result of the chest compressions and rib fractures. The patient was needing intravenous morphine in progressively higher doses to relieve the pain, which was now more localized in the right upper part of the abdomen. At 23:30 h, arterial blood gas analysis revealed mild metabolic acidosis (Table 1).The ward doctor requested a contrastenhanced computer tomography (CT) of the patient s abdomen. This showed an abdominal aortic aneurysm 4.1 cm in diameter with mural thrombus, but no signs of aortic dissection (Fig. 1). It also revealed ischaemia of the ascending colon, several blood clots inside the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) (Fig. 2), and several atherosclerotic plaques in the proximal part of the SMA and coeliac trunk not causing significant stenosis. As the scan also suggested intestinal ischaemia consistent with the patient s abdominal symptoms, exploratory laparotomy was performed and subtotal colectomy of the ascending colon was necessary because of ischaemia and necrosis. The transverse and descending colon were both spared and an ileostomy was fashioned. Following this event, the patient recovered and during hospitalization there were several episodes of non-sustained ventricular tachycardia on continuous heart rate monitoring without concomitant clinical symptoms. Two weeks later the patient was discharged with an automated implantable cardioverter defibrillator. The ECG on the day of discharge revealed sinus rhythm but the patient was discharged on a treatment dose of the novel oral anticoagulant agent dabigatran and 100 mg metoprolol daily according to the national Danish guidelines [2]. At follow-up 2 months later, the patient was feeling well and had not experienced any cardiac or gastrointestinal symptoms since discharge. A vascular surgical opinion on the abdominal aortic aneurysm was sought and conservative management with annual surveillance ultrasonography was recommended.
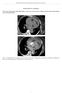
3 Intestinal ischaemia, necrosis and vascular disease 3 Table 1. The patient s blood gas analysis taken at 23:30 h on the day of hospitalization Patient s result Reference interval ph P a O kpa kpa P a CO kpa Base excess 6 mmol/l 2 to þ2 mmol/l 19.6 meq/l meq/l Lactic acid 1 mmol/l mmol/l Fig. 1. Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT of the patient in our case revealing an aortic aneurysm with a mural thrombus. There is no sign of aortic dissection. Fig. 2. Contrast-enhanced abdominal CT revealing the superior mesenteric artery (A) and the same almost occluded (B). Discussion Intestinal ischaemia may be caused by an acute reduction of the arterial blood supply to the intestines either due to embolism, thrombosis, poor cardiac output, blockage of the venous drainage or by a combination of two or several of these factors. Mesenteric embolism accounts for 25 30% of patients with intestinal ischaemia, and atrial fibrillation represents an important cause of embolism [3]. The presence of synchronous embolism and/or atrial fibrillation supports this diagnosis as a cause of the arterial occlusion. Thrombotic occlusions are more proximally located than embolic occlusions, result in more extensive intestinal infarction and are related to aortic wall thrombosis
4 4 N. Dia Alyonan or simply occlusion of the vessel secondary to narrowing [4]. Patients with thrombosis of the SMA are more likely to have a history of abdominal angina and the onset of symptoms is rarely sudden and dramatic as with an embolism. Embolisms tend to lodge just beyond the origin of the middle colic artery, where the calibre of the SMA narrows rapidly and ischaemia therefore spares the upper jejunum and transverse colon [5]. There are few case reports in the literature regarding ischaemia of the intestines in patients who survive cardiac arrest [6,7]. However in these cases, the intestinal ischaemia is a result of low blood flow within the visceral circulation due to hypotension, and not related to thrombotic or embolic occlusion of the SMA as suspected in our case report. Furthermore, these patients received vasoconstricting agents such as noradrenalin or vasopressin; our patient did not receive any vasoconstricting agent. Iraklis et al. [6] report a case of an 83-year old woman who had sudden in-hospital cardiac arrest, and following successful CPR was transferred intubated to the intensive care unit, where she was treated with the vasoconstricting agent norepinephrine to support her circulation. Several hours later she developed increasing abdominal distension and severe metabolic acidosis. Multidetector computer tomography (MDCT) revealed intestinal ischaemia and a subsequent exploratory laparotomy revealed ischaemia of the terminal ileum and extensive colonic necrosis. The scan did not show any endoluminal defect of mesenteric arteries or veins. The cause of the ischaemia in this case is thought to be the low cardiac output and hypotension despite the successful CPR. Stockman et al. [7] report a 38-year old woman who survived cardiac arrest following prolonged CPR but had ischaemia and necrosis of the colon, requiring subtotal colectomy of the ascending, transverse and descending colon. Pathological examination excluded arterial thrombosis as the cause. In this case, the patient had no spontaneous circulation for 84 min after her collapse, which might have contributed to a long period of hypotension and reduced blood flow in the visceral circulation leading to ischaemia of the intestines. Furthermore, the patient was treated with a vasopressin, which contributed to vasoconstriction of the intestinal arteries, poor tissue perfusion, ischaemia of the colon and necrosis [8]. A case where the cause of the intestinal ischaemia is related to embolism of the SMA is presented by Han et al. [9] who report on a 43-year old man admitted to the hospital 4 h after the onset of nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea. Contrast-enhanced CT and angiography revealed occlusion of the SMA. The patient in our case developed abdominal symptoms almost 4 h after his cardiac arrest, which was faster than the patients in the cases where hypotension was the suspected cause of the intestinal ischaemia [6,7] and similar to other cases where embolism was the suspected cause [5,9]. Furthermore, the contrast-enhanced abdominal CT of our patient revealed several endoluminal defects of the SMA suggesting blockage of this artery by either thrombosis or embolism. CPR was initiated immediately and the patient had spontaneous circulation 15 min after collapse when the patient s blood pressure was 161/80 mmhg. Therefore we do not believe that the intestinal ischaemia in our patient was related to hypotension during the cardiac arrest and the period of CPR. The most likely cause of the intestinal ischaemia in our patient is blockage of the SMA during the first hours of hospitalization, most likely due to an embolism. Atrial fibrillation was the predominant rhythm on the ECG following successful resuscitation, and continued to be so during the first few days of hospitalization. This is the most likely cause of the embolism. According to other studies in the literature [4], another source of embolism could be an aortic thrombus. Contrast-enhanced CT of the patient in our case confirmed an aortic aneurysm with an aortic thrombus (Fig. 1). Prior to the cardiac arrest, the patient had never complained of abdominal symptoms and did not have abdominal angina. Furthermore, the patient s symptoms were sudden in onset and dramatic as seen in patients with embolism of the SMA [5]. The only factor supporting the thrombosis theory is that the contrast-enhanced CT revealed several atherosclerotic plaques in the proximal part of the SMA and coeliac trunk. This, together with a history of chronic coronary artery disease suggests a tendency to generalized atherosclerosis. Plaque rupture in one of these plaques could have resulted in thrombosis of the SMA leading to ischaemia and necrosis of the intestines. It can be difficult and almost impossible to differentiate between these two causes of occlusion of the SMA as reported by Acosta et al. [4]. We agree with the authors in the above-mentioned cases [5 7,9] that once intestinal ischaemia is suspected the patient should undergo immediate medical imaging in the form of contrast-
5 Intestinal ischaemia, necrosis and vascular disease 5 enhanced CT or mesenteric angiography to determine the cause of the ischaemia and initiate immediate surgical or medical intervention. Conclusions In the present case, a 68-year old man with known chronic coronary artery disease survived sudden cardiac arrest following successful CPR, but subsequently had intestinal ischaemia and necrosis requiring surgical intervention. The cause of the ischaemia is most likely an embolism to the SMA. If patients develop atrial fibrillation and abdominal symptoms following successful resuscitation from a cardiac arrest, then intestinal ischaemia should be ruled out. However, atrial fibrillation, whether related to cardiac arrest or other factors, may cause an embolus and possible intestinal ischaemia. These patients must undergo immediate medical imaging, and physicians must initiate immediate treatment in order to reduce the high mortality rates of this condition. Teaching points First, our case warns physicians to be aware of this life-threatening condition (intestinal ischaemia and necrosis) as most of these patients may have concomitant medical conditions or diseases that tend to shift the light away from this. Second, patients with acute intestinal ischaemia are often not hospitalized in surgical wards but more likely in medical wards due to other concomitant internal medical diseases, therefore presenting a challenge to physicians in these wards, as its proven that the diagnosis of this condition in the early stages is difficult and often made too late for surgical intervention [10]. Anyone who develops abdominal pain following cardiac resuscitation should be suspected of having acute intestinal ischaemia and be investigated as a matter of urgency. Conflict of interest The author declares that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this article. References 1. Go A, Mozaffarian D, Roger V, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics Update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2013; 127: e6 e245. PMid: National Danish Guidelines. Atrial fibrillation Kevin GB, Anthony EY. The new Airds companion in surgical studies. 2nd ed.. Churchill Livingstone; 1998, p Acosta S, Ögren M, Sternby N-H, et al. Clinical implications for the management of acute thromboembolic occlusion of the superior mesenteric artery. Ann Surg 2005; 241: PMid: Basavanagowdappa H, Babu S, Kumar P, et al. Superior mesenteric artery embolism. J Assoc Physicians India 2008; 56: PMid: Katsoulis IE, Balanika A, Sakalidou M, et al. Extensive colonic necrosis following cardiac arrest and successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation: report of a case and literature review. World J Emerg Surg 2012; 7: 35. PMid: Stockman W, De Keyser J, Brabant S, et al. Colon ischemia and necrosis as a complication of prolonged but successful CPR. Resuscitation 2006; 71: PMid: Lambert M, de Peyer R, Muller AF, et al. Reversible ischemic colitis after intravenous vasopressor therapy. JAMA 1982; 247: PMid: Han Y, Liu ZG, Zhou XM, et al. Rare acute mesenteric artery embolism: a case report. EXCLI J 2006; 5: Acosta S, Ögren M, Sternby N, et al. Incidence of acute thrombo-embolic occlusion of the superior mesenteric artery a population-based study. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2004; 27: PMid:
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders
 C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders GENERAL ISSUES REGARDING MEDICAL FITNESS-FOR-DUTY 1. These medical standards apply to Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) employees
C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders GENERAL ISSUES REGARDING MEDICAL FITNESS-FOR-DUTY 1. These medical standards apply to Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) employees
OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY MESENTERIC ISCHAEMIA P Zwanepoel INTRODUCTION Mesenteric ischaemia results from hypoperfusion of the gut, most commonly due to occlusion, thrombosis or vasospasm.
OPEN ACCESS TEXTBOOK OF GENERAL SURGERY MESENTERIC ISCHAEMIA P Zwanepoel INTRODUCTION Mesenteric ischaemia results from hypoperfusion of the gut, most commonly due to occlusion, thrombosis or vasospasm.
Supplementary material 1. Definitions of study endpoints (extracted from the Endpoint Validation Committee Charter) 1.
 Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of the SIGNIFY trial: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ivabradine in patients with stable coronary artery disease without clinical
Rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of the SIGNIFY trial: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ivabradine in patients with stable coronary artery disease without clinical
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine
 Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
Dr. Rami M. Adil Al-Hayali Assistant Professor in Medicine Venous thromboembolism: pulmonary embolism (PE) deep vein thrombosis (DVT) 1% of all patients admitted to hospital 5% of in-hospital mortality
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 26 Caring for Clients with Coronary Heart Disease and Dysrhythmias Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Leading
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 26 Caring for Clients with Coronary Heart Disease and Dysrhythmias Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Leading
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Chest pain management. Ruvin Gabriel and Niels van Pelt August 2011
 Chest pain management Ruvin Gabriel and Niels van Pelt August 2011 Introduction Initial assessment Case 1 Case 2 and 3 Comparison of various diagnostic techniques Summary 1-2 % of GP consultations are
Chest pain management Ruvin Gabriel and Niels van Pelt August 2011 Introduction Initial assessment Case 1 Case 2 and 3 Comparison of various diagnostic techniques Summary 1-2 % of GP consultations are
Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist
 Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist Introduction. Basic Life Support (BLS). Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death
Hanna K. Al-Makhamreh, M.D., FACC Interventional Cardiologist Introduction. Basic Life Support (BLS). Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS). Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death
Common Codes for ICD-10
 Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
Common Codes for ICD-10 Specialty: Cardiology *Always utilize more specific codes first. ABNORMALITIES OF HEART RHYTHM ICD-9-CM Codes: 427.81, 427.89, 785.0, 785.1, 785.3 R00.0 Tachycardia, unspecified
AORTIC DISSECTION. DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or CLASSIFICATION
 DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or AORTIC DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION DeBakey classified aortic dissections into types I, II, and III :- Type I dissection the tear site originates in the ascending aorta,
DISSECTING ANEURYSMS OF THE AORTA or AORTIC DISSECTION CLASSIFICATION DeBakey classified aortic dissections into types I, II, and III :- Type I dissection the tear site originates in the ascending aorta,
General Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 2 General Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging 19 Peter G. Danias, Cardiovascular MRI: 150 Multiple-Choice Questions and Answers Humana Press 2008 20 Cardiovascular MRI: 150 Multiple-Choice Questions
2 General Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging 19 Peter G. Danias, Cardiovascular MRI: 150 Multiple-Choice Questions and Answers Humana Press 2008 20 Cardiovascular MRI: 150 Multiple-Choice Questions
Results of Ischemic Heart Disease
 Ischemic Heart Disease: Angina and Myocardial Infarction Ischemic heart disease; syndromes causing an imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply (inadequate myocardial blood flow) related to
Ischemic Heart Disease: Angina and Myocardial Infarction Ischemic heart disease; syndromes causing an imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply (inadequate myocardial blood flow) related to
REBEL. Platinum Chromium Coronary Stent System. Patient Information Guide
 REBEL Patient Information Guide REBEL PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE You have recently had a REBEL bare metal stent implanted in the coronary arteries of your heart. The following information is important for
REBEL Patient Information Guide REBEL PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE You have recently had a REBEL bare metal stent implanted in the coronary arteries of your heart. The following information is important for
Heart Disease. Signs and Symptoms
 Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Acute Coronary Syndrome. Emergency Department Updated Jan. 2017
 Acute Coronary Syndrome Emergency Department Updated Jan. 2017 Goals and Objectives To reduce mortality and morbidity for people who have cardiovascular disease, with a focus on those who experience an
Acute Coronary Syndrome Emergency Department Updated Jan. 2017 Goals and Objectives To reduce mortality and morbidity for people who have cardiovascular disease, with a focus on those who experience an
Acute arterial embolism
 Acute arterial embolism Definition Thrombus come from heart or blood vessel or other embolus such as tumor,air gas or fat flow with blood stream and occlude distal limb or visceral arteries which causes
Acute arterial embolism Definition Thrombus come from heart or blood vessel or other embolus such as tumor,air gas or fat flow with blood stream and occlude distal limb or visceral arteries which causes
MESENTERIC ISCHEMIA THE FORGOTTEN DIAGNOSIS. Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, Illinois
 MESENTERIC ISCHEMIA THE FORGOTTEN DIAGNOSIS Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, Illinois SCBT/MR 2010 San Diego, California March 8, 2010 16:00-16:10
MESENTERIC ISCHEMIA THE FORGOTTEN DIAGNOSIS Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, Illinois SCBT/MR 2010 San Diego, California March 8, 2010 16:00-16:10
Cardiovascular Disorders. Heart Disorders. Diagnostic Tests for CV Function. Bio 375. Pathophysiology
 Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Marie erna, Martin Kocher, Rohit Philip Thomas. cute aorta, overview of acute T findings and endovascular treatment options (doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.060) Fig. 1. : Non-enhanced T, hemopericardium
SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Marie erna, Martin Kocher, Rohit Philip Thomas. cute aorta, overview of acute T findings and endovascular treatment options (doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.060) Fig. 1. : Non-enhanced T, hemopericardium
Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship
 Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship CLINICAL PROBLEMS IN VASCULAR SURGERY 1. ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM A 70 year old man presents in the emergency department with
Learning Objectives for Rotations in Vascular Surgery Year 3 Basic Clerkship CLINICAL PROBLEMS IN VASCULAR SURGERY 1. ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM A 70 year old man presents in the emergency department with
Cardiology. Objectives. Chapter
 1:44 M age 1121 Chapter Cardiology Objectives art 1: Cardiovascular natomy and hysiology, ECG Monitoring, and Dysrhythmia nalysis (begins on p. 1127) fter reading art 1 of this chapter, you should be able
1:44 M age 1121 Chapter Cardiology Objectives art 1: Cardiovascular natomy and hysiology, ECG Monitoring, and Dysrhythmia nalysis (begins on p. 1127) fter reading art 1 of this chapter, you should be able
Severe Coronary Vasospasm Complicated with Ventricular Tachycardia
 Severe Coronary Vasospasm Complicated with Ventricular Tachycardia Göksel Acar, Serdar Fidan, Servet İzci and Anıl Avcı Kartal Koşuyolu High Specialty Education and Research Hospital, Cardiology Department,
Severe Coronary Vasospasm Complicated with Ventricular Tachycardia Göksel Acar, Serdar Fidan, Servet İzci and Anıl Avcı Kartal Koşuyolu High Specialty Education and Research Hospital, Cardiology Department,
Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014
 Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014 Indications for cardiac catheterization Before a decision to perform an invasive procedure such
Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014 Indications for cardiac catheterization Before a decision to perform an invasive procedure such
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiology. Self Learning Package. Module 5: Pharmacology: Treatment of Acute Coronary. Prevention
 Cardiology Self Learning Package Module 5: Pharmacology: Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndromes, Module 5: Pharmacology: Hyperlipidaemia, Treatment of Acute Coronary Hypertension, Symdrome, Hyperlipidaemia,
Cardiology Self Learning Package Module 5: Pharmacology: Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndromes, Module 5: Pharmacology: Hyperlipidaemia, Treatment of Acute Coronary Hypertension, Symdrome, Hyperlipidaemia,
Cardiac Imaging in abnormal rhythm Role of MDCT
 Cardiac Imaging in abnormal rhythm Role of MDCT Cardiac Imaging in abnormal rhythm Role of MDCT Scope of the problem CT in Atrial Fibrillation CT and pacing Ventricular arrhythmia Other applications 1
Cardiac Imaging in abnormal rhythm Role of MDCT Cardiac Imaging in abnormal rhythm Role of MDCT Scope of the problem CT in Atrial Fibrillation CT and pacing Ventricular arrhythmia Other applications 1
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies. V.Stoynova
 Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM
 REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
Cardiac Imaging Tests
 Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
Circulation and Cardiac Emergencies. Emergency Medical Response
 Circulation and Cardiac Emergencies Lesson 19: The Circulatory System and Cardiac Emergencies You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are called to the home of a 50-year-old man whose wife called 9-1-1
Circulation and Cardiac Emergencies Lesson 19: The Circulatory System and Cardiac Emergencies You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are called to the home of a 50-year-old man whose wife called 9-1-1
FastTest. You ve read the book now test yourself
 FastTest You ve read the book...... now test yourself To ensure you have learned the key points that will improve your patient care, read the authors questions below. The answers will refer you back to
FastTest You ve read the book...... now test yourself To ensure you have learned the key points that will improve your patient care, read the authors questions below. The answers will refer you back to
Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) is
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) is
Ischemic heart disease
 Ischemic heart disease Introduction In > 90% of cases: the cause is: reduced coronary blood flow secondary to: obstructive atherosclerotic vascular disease so most of the time it is called: coronary artery
Ischemic heart disease Introduction In > 90% of cases: the cause is: reduced coronary blood flow secondary to: obstructive atherosclerotic vascular disease so most of the time it is called: coronary artery
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplemental digital content 1, Appendix 1. Ischemic symptoms and electrocardiography
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental digital content 1, Appendix 1. Ischemic symptoms and electrocardiography findings 1. Ischemic symptoms included any of the following: chest discomfort, arm discomfort,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental digital content 1, Appendix 1. Ischemic symptoms and electrocardiography findings 1. Ischemic symptoms included any of the following: chest discomfort, arm discomfort,
General Data. 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性
 General Data 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性 Chief Complaint Vomiting twice this early morning Fever up to 38.9ºC was noted Present Illness (1) Old CVA with left side weakness for more than 10 years and with bed ridden
General Data 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性 Chief Complaint Vomiting twice this early morning Fever up to 38.9ºC was noted Present Illness (1) Old CVA with left side weakness for more than 10 years and with bed ridden
What is a myocardial infarction and how do we treat it? Paul Das Consultant Cardiologist North Wales Cardiac Centre Glan Clwyd Hospital
 What is a myocardial infarction and how do we treat it? Paul Das Consultant Cardiologist North Wales Cardiac Centre Glan Clwyd Hospital What is a myocardial infarction? THEY AINT WHAT THEY USED TO BE Case
What is a myocardial infarction and how do we treat it? Paul Das Consultant Cardiologist North Wales Cardiac Centre Glan Clwyd Hospital What is a myocardial infarction? THEY AINT WHAT THEY USED TO BE Case
10. Definition of cardiovascular disease 10.1 Nosologic definitions Acute myocardial infarction: myocardial cell death due to prolonged ischaemia 62.
 10. Definition of cardiovascular disease 10.1 Nosologic definitions Acute myocardial infarction: myocardial cell death due to prolonged ischaemia 62. Acute coronary syndrome: it is a big category which
10. Definition of cardiovascular disease 10.1 Nosologic definitions Acute myocardial infarction: myocardial cell death due to prolonged ischaemia 62. Acute coronary syndrome: it is a big category which
Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. in general practice. 22 BPJ Issue 39
 Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION in general practice 22 BPJ Issue 39 What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in primary care. It is often
Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION in general practice 22 BPJ Issue 39 What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in primary care. It is often
Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis?
 Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? December 19, 2017 Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? Indications for Thrombolytic Therapy in Patients with Acute Pulmonary Embolism Case Scenario A 28 year old woman
Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? December 19, 2017 Is Thrombolysis Only for a Crisis? Indications for Thrombolytic Therapy in Patients with Acute Pulmonary Embolism Case Scenario A 28 year old woman
EMT. Chapter 14 Review
 EMT Chapter 14 Review Review 1. All of the following are common signs and symptoms of cardiac ischemia, EXCEPT: A. headache. B. chest pressure. C. shortness of breath. D. anxiety or restlessness. Review
EMT Chapter 14 Review Review 1. All of the following are common signs and symptoms of cardiac ischemia, EXCEPT: A. headache. B. chest pressure. C. shortness of breath. D. anxiety or restlessness. Review
Detailed Order Request Checklists for Cardiology
 Next Generation Solutions Detailed Order Request Checklists for Cardiology 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue South Tower Suite 800 Chicago, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.com Appropriate.Safe.Affordable 2018
Next Generation Solutions Detailed Order Request Checklists for Cardiology 8600 West Bryn Mawr Avenue South Tower Suite 800 Chicago, IL 60631 www.aimspecialtyhealth.com Appropriate.Safe.Affordable 2018
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
IHCP bulletin INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS BT JANUARY 24, 2012
 IHCP bulletin INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS BT201203 JANUARY 24, 2012 The IHCP to reimburse implantable cardioverter defibrillators separately from outpatient implantation Effective March 1, 2012, the
IHCP bulletin INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS BT201203 JANUARY 24, 2012 The IHCP to reimburse implantable cardioverter defibrillators separately from outpatient implantation Effective March 1, 2012, the
Neurologic Recovery Following Prolonged Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest With Resuscitation Guided by Continuous Capnography
 CASE REPORT FULL RECOVERY AFTER PROLONGED CARDIAC ARREST AND RESUSCITATION WITH CAPNOGRAPHY GUIDANCE Neurologic Recovery Following Prolonged Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest With Resuscitation Guided by
CASE REPORT FULL RECOVERY AFTER PROLONGED CARDIAC ARREST AND RESUSCITATION WITH CAPNOGRAPHY GUIDANCE Neurologic Recovery Following Prolonged Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest With Resuscitation Guided by
Syncope: Ockham s Razor
 Syncope: Ockham s Razor Time/Place Wednesday, 25 th January 2006 10am-12pm Room 210, Wallace Wurth Building Facilitators Michael Grimm & Tony Grabs Aims Illustrate multiple possible causes for a common
Syncope: Ockham s Razor Time/Place Wednesday, 25 th January 2006 10am-12pm Room 210, Wallace Wurth Building Facilitators Michael Grimm & Tony Grabs Aims Illustrate multiple possible causes for a common
4 8mm warfarin potassium
 15 29 33 2006 1 4 10 44Marfan 1 2 2 15 29 33 2006 Marfan 4 10 Marfan 1 44Marfan 4 9 21 II + IIIb 4 10 8 Bentall Björk-Sheily 25mm + Hemashield 28mm graft Tel: 098-895-1168 903-0215207 2004 12 27 2005 11
15 29 33 2006 1 4 10 44Marfan 1 2 2 15 29 33 2006 Marfan 4 10 Marfan 1 44Marfan 4 9 21 II + IIIb 4 10 8 Bentall Björk-Sheily 25mm + Hemashield 28mm graft Tel: 098-895-1168 903-0215207 2004 12 27 2005 11
Pathophysiology. Tutorial 3 Hemodynamic Disorders
 Pathophysiology Tutorial 3 Hemodynamic Disorders ILOs Recall different causes of thrombosis. Explain different types of embolism and their predisposing factors. Differentiate between hemorrhage types.
Pathophysiology Tutorial 3 Hemodynamic Disorders ILOs Recall different causes of thrombosis. Explain different types of embolism and their predisposing factors. Differentiate between hemorrhage types.
Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings
 Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings Accogli S, Aringhieri G, Scalise P, Angelini G, Pancrazi F, Bemi P, Bartolozzi C Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University
Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings Accogli S, Aringhieri G, Scalise P, Angelini G, Pancrazi F, Bemi P, Bartolozzi C Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University
Chapter 29 - Chest_and_Abdominal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 29.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 18, 27 29.2 Describe mechanisms of injury commonly associated with chest injuries. Slides
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 29.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 18, 27 29.2 Describe mechanisms of injury commonly associated with chest injuries. Slides
1 7 central operation SMA SMA
 12 521 527 2003 198913 Stanford A 159 8 5.0 B 139 6 4.3 A SMA SMA A 8 1 7 central operation 3 1 SMA 1 1 5 1 14 8 3 38 B 6 1 5 2 +SMA 3 1 0 2910.3 SMA 3 50 A 5 B 5 SMA SMA SMA SMA SMA 12 521 527 2003 SMA
12 521 527 2003 198913 Stanford A 159 8 5.0 B 139 6 4.3 A SMA SMA A 8 1 7 central operation 3 1 SMA 1 1 5 1 14 8 3 38 B 6 1 5 2 +SMA 3 1 0 2910.3 SMA 3 50 A 5 B 5 SMA SMA SMA SMA SMA 12 521 527 2003 SMA
Cardiology/Cardiothoracic
 Cardiology/Cardiothoracic ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Code Mapper 800-334-5724 www.contexomedia.com 2013 ICD-9-CM 272.0 Pure hypercholesterolemia 272.2 Mixed hyperlipidemia 272.4 Other and hyperlipidemia 278.00
Cardiology/Cardiothoracic ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Code Mapper 800-334-5724 www.contexomedia.com 2013 ICD-9-CM 272.0 Pure hypercholesterolemia 272.2 Mixed hyperlipidemia 272.4 Other and hyperlipidemia 278.00
Objectives. Identify early signs and symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome Initiate proper protocol for ACS patient 10/2013 2
 10/2013 1 Objectives Identify early signs and symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome Initiate proper protocol for ACS patient 10/2013 2 Purpose of this Education Module: Chest Pain Center Accreditation involves
10/2013 1 Objectives Identify early signs and symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome Initiate proper protocol for ACS patient 10/2013 2 Purpose of this Education Module: Chest Pain Center Accreditation involves
(For items 1-12, each question specifies mark one or mark all that apply.)
 Form 121 - Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver. 9.2 COMMENTS -Affix label here- Member ID: - - To be completed by Physician Adjudicator Date Completed: - - (M/D/Y) Adjudicator Code: - Central Case No.:
Form 121 - Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver. 9.2 COMMENTS -Affix label here- Member ID: - - To be completed by Physician Adjudicator Date Completed: - - (M/D/Y) Adjudicator Code: - Central Case No.:
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a disorder seen
 This Just In... An Update on Arrhythmia What do recent studies reveal about arrhythmia? In this article, the authors provide an update on atrial fibrillation and ventricular arrhythmia. Beth L. Abramson,
This Just In... An Update on Arrhythmia What do recent studies reveal about arrhythmia? In this article, the authors provide an update on atrial fibrillation and ventricular arrhythmia. Beth L. Abramson,
Cardiovascular Disorders Lecture 3 Coronar Artery Diseases
 Cardiovascular Disorders Lecture 3 Coronar Artery Diseases By Prof. El Sayed Abdel Fattah Eid Lecturer of Internal Medicine Delta University Coronary Heart Diseases It is the leading cause of death in
Cardiovascular Disorders Lecture 3 Coronar Artery Diseases By Prof. El Sayed Abdel Fattah Eid Lecturer of Internal Medicine Delta University Coronary Heart Diseases It is the leading cause of death in
Chapter 14. Cardiovascular Emergencies
 Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies Introduction (1 of 2) Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since 1900. Accounts for 1 of every 2.8 deaths Introduction (2 of 2) EMS can help
Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies Introduction (1 of 2) Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since 1900. Accounts for 1 of every 2.8 deaths Introduction (2 of 2) EMS can help
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism
 Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Table S1: Number and percentage of patients by age category Distribution of age Age
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Table S1: Number and percentage of patients by age category Distribution of age Age
OCCULT PRESENTATIONS OF MESENTERIC INFARCT IN A KIDNEY TRANSPLANT RECIPIENT
 OCCULT PRESENTATIONS OF MESENTERIC INFARCT IN A KIDNEY TRANSPLANT RECIPIENT Yu-Tso Liao 1, Yen-Chun Hsu 2, Yu-Chang Yeh 2, Wing-Sum Chan 3 Abstract Mesenteric infarct is a critical disease; it would be
OCCULT PRESENTATIONS OF MESENTERIC INFARCT IN A KIDNEY TRANSPLANT RECIPIENT Yu-Tso Liao 1, Yen-Chun Hsu 2, Yu-Chang Yeh 2, Wing-Sum Chan 3 Abstract Mesenteric infarct is a critical disease; it would be
Complete Proximal Occlusion of All Three Main Coronary Arteries Complicated With a Left Main Coronary Aneurysm: A Case Report
 J Cardiol 2004 Nov; 44 5 : 201 205 Complete Proximal Occlusion of All Three Main Coronary Arteries Complicated With a Left Main Coronary Aneurysm: A Case Report Takatoshi Hiroshi Akira Takahiro Masayasu
J Cardiol 2004 Nov; 44 5 : 201 205 Complete Proximal Occlusion of All Three Main Coronary Arteries Complicated With a Left Main Coronary Aneurysm: A Case Report Takatoshi Hiroshi Akira Takahiro Masayasu
Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest. Franz R. Eberli MD, FESC, FAHA Cardiology Triemli Hospital Zurich, Switzerland
 Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest Franz R. Eberli MD, FESC, FAHA Cardiology Triemli Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Conflict of Interest I have no conflict of interest to disclose regarding this presentation.
Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest Franz R. Eberli MD, FESC, FAHA Cardiology Triemli Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Conflict of Interest I have no conflict of interest to disclose regarding this presentation.
Intended Learning Outcomes
 2011 Acute Limb Ischemia Definition, Etiology & Pathophysiology Clinical Evaluation Management Ali SABBOUR Prof. of Vascular Surgery, Ain Shams University Acute Limb Ischemia Intended Learning Outcomes
2011 Acute Limb Ischemia Definition, Etiology & Pathophysiology Clinical Evaluation Management Ali SABBOUR Prof. of Vascular Surgery, Ain Shams University Acute Limb Ischemia Intended Learning Outcomes
Cardiovascular Emergencies. Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular Emergencies Chapter 12 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease (CVD) claimed 931,108 lives in the US during 2001. 2,551 per day Almost two people per minute! CVD accounts for 38.5%
Cardiovascular Emergencies Chapter 12 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease (CVD) claimed 931,108 lives in the US during 2001. 2,551 per day Almost two people per minute! CVD accounts for 38.5%
Maternal Collapse Guideline
 Maternal Collapse Guideline Guideline Number: 664 Supersedes: Classification Clinical Version No: Date of EqIA: Approved by: Date Approved: Date made active: Review Date: 1 Obstetric Written Documentation
Maternal Collapse Guideline Guideline Number: 664 Supersedes: Classification Clinical Version No: Date of EqIA: Approved by: Date Approved: Date made active: Review Date: 1 Obstetric Written Documentation
General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]
![General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ] General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]](/thumbs/76/74079340.jpg) General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation
 Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
Update on Sudden Cardiac Death and Resuscitation Ashish R. Panchal, MD, PhD Medical Director Center for Emergency Medical Services Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Emergency Medicine The Ohio
When Should I Order a Stress Test or an Echocardiogram
 When Should I Order a Stress Test or an Echocardiogram Updates in Cardiology 2015 March 7, 2015 Donald L. Lappé, MD, FAHA, FACC Chairman, Cardiovascular Department Medical Director, Intermountain Cardiovascular
When Should I Order a Stress Test or an Echocardiogram Updates in Cardiology 2015 March 7, 2015 Donald L. Lappé, MD, FAHA, FACC Chairman, Cardiovascular Department Medical Director, Intermountain Cardiovascular
Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation Which of the following best describes the physical activity performed in my leisure time? A. I perform vigorous physical activity 3X/week for 20 minutes each time B.
Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation Which of the following best describes the physical activity performed in my leisure time? A. I perform vigorous physical activity 3X/week for 20 minutes each time B.
Automatic External Defibrillators
 Last Review Date: April 21, 2017 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC3v4 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Last Review Date: April 21, 2017 Number: MG.MM.DM.10dC3v4 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider must submit to EmblemHealth
Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year
![Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year Protocol Identifier Subject Identifier Visit Description. [Y] Yes [N] No. [Y] Yes [N] N. If Yes, admission date and time: Day Month Year](/thumbs/76/74263761.jpg) PAST MEDICAL HISTORY Has the subject had a prior episode of heart failure? o Does the subject have a prior history of exposure to cardiotoxins, such as anthracyclines? URGENT HEART FAILURE VISIT Did heart
PAST MEDICAL HISTORY Has the subject had a prior episode of heart failure? o Does the subject have a prior history of exposure to cardiotoxins, such as anthracyclines? URGENT HEART FAILURE VISIT Did heart
Chapter 16 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since 1900.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 Chapter 16 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since 1900. Accounts for of every 3 deaths Cardiovascular disease
1 2 3 4 5 6 Chapter 16 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since 1900. Accounts for of every 3 deaths Cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Session Guidelines This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff CNC holds webinars on the 3 rd Wednesday of each month to address topics related to risk adjustment
Cardiovascular Disease Session Guidelines This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff CNC holds webinars on the 3 rd Wednesday of each month to address topics related to risk adjustment
Unknown ECGs for the Clinician
 Unknown ECGs for the Clinician 2016 Bryan Heart Fall Cardiology Conference Andrew Merliss, MD, FACC, CDRS, FHRS Director of Cardiac Arrhythmia Service Bryan Heart Disclaimer Advisory Board for Medtronic
Unknown ECGs for the Clinician 2016 Bryan Heart Fall Cardiology Conference Andrew Merliss, MD, FACC, CDRS, FHRS Director of Cardiac Arrhythmia Service Bryan Heart Disclaimer Advisory Board for Medtronic
Descending aorta replacement through median sternotomy
 Descending aorta replacement through median sternotomy Mitrev Z, Anguseva T, Belostotckij V, Hristov N. Special hospital for surgery Filip Vtori Skopje - Makedonija June, 2010 Cardiosurgery - Skopje 1
Descending aorta replacement through median sternotomy Mitrev Z, Anguseva T, Belostotckij V, Hristov N. Special hospital for surgery Filip Vtori Skopje - Makedonija June, 2010 Cardiosurgery - Skopje 1
ARRHYTHMIAS AND DEVICE THERAPY
 Topic List A BASICS 1 History of Cardiology 2 Clinical Skills 2.1 History Taking 2.2 Physical Examination 2.3 Electrocardiography 2.99 Clinical Skills - Other B IMAGING 3 Imaging 3.1 Echocardiography 3.2
Topic List A BASICS 1 History of Cardiology 2 Clinical Skills 2.1 History Taking 2.2 Physical Examination 2.3 Electrocardiography 2.99 Clinical Skills - Other B IMAGING 3 Imaging 3.1 Echocardiography 3.2
Acute Mesenteric Ischemia. Michael Klein, MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center August 20, 2015
 Acute Mesenteric Ischemia Michael Klein, MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center August 20, 2015 85F www.downstatesurgery.org 5 months of intermittent diffuse abdominal pain Approximately 30-lb weight loss Abdominal
Acute Mesenteric Ischemia Michael Klein, MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center August 20, 2015 85F www.downstatesurgery.org 5 months of intermittent diffuse abdominal pain Approximately 30-lb weight loss Abdominal
Acute Type B dissection. Closure of the infra diaphragmatic tear: how and when?
 Acute Type B dissection. Closure of the infra diaphragmatic tear: how and when? Prof. Olgierd Rowiński II Department of Clinical Radiology Medical University of Warsaw Disclosure Speaker name: Olgierd
Acute Type B dissection. Closure of the infra diaphragmatic tear: how and when? Prof. Olgierd Rowiński II Department of Clinical Radiology Medical University of Warsaw Disclosure Speaker name: Olgierd
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy. Joseph L. Blackshear, MD Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida
 Takotsubo cardiomyopathy Joseph L. Blackshear, MD Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida 79 year old woman, pre chemo echo for esophageal cancer Post chemo, dehydration,
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy Joseph L. Blackshear, MD Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic College of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida 79 year old woman, pre chemo echo for esophageal cancer Post chemo, dehydration,
Rescue procedures in acute visceral ischemia
 Rescue procedures in acute visceral ischemia Yvonne Bausback Dept. Interventional Angiology Division of Internal Medicine, Neurology and Dermatology University of Leipzig, Germany Disclosure Speaker name:
Rescue procedures in acute visceral ischemia Yvonne Bausback Dept. Interventional Angiology Division of Internal Medicine, Neurology and Dermatology University of Leipzig, Germany Disclosure Speaker name:
Acute Coronary Syndrome
 ACUTE CORONOARY SYNDROME, ANGINA & ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION Administrative Consultant Service 3/17 Acute Coronary Syndrome Acute Coronary Syndrome has evolved as a useful operational term to refer to
ACUTE CORONOARY SYNDROME, ANGINA & ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION Administrative Consultant Service 3/17 Acute Coronary Syndrome Acute Coronary Syndrome has evolved as a useful operational term to refer to
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. A Surgeons Perspective Dr. Derek D. Muehrcke
 Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms A Surgeons Perspective Dr. Derek D. Muehrcke Aneurysm Definition The abnormal enlargement or bulging of an artery caused by an injury or weakness in the blood vessel wall A localized
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms A Surgeons Perspective Dr. Derek D. Muehrcke Aneurysm Definition The abnormal enlargement or bulging of an artery caused by an injury or weakness in the blood vessel wall A localized
When the learner has completed this module, she/he will be able to:
 Thrombolytics and Myocardial Infarction WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017
Thrombolytics and Myocardial Infarction WWW.RN.ORG Reviewed September 2017, Expires September 2019 Provider Information and Specifics available on our Website Unauthorized Distribution Prohibited 2017
AORTIC DISSECTIONS Current Management. TOMAS D. MARTIN, MD, LAT Professor, TCV Surgery Director UF Health Aortic Disease Center University of Florida
 AORTIC DISSECTIONS Current Management TOMAS D. MARTIN, MD, LAT Professor, TCV Surgery Director UF Health Aortic Disease Center University of Florida DISCLOSURES Terumo Medtronic Cook Edwards Cryolife AORTIC
AORTIC DISSECTIONS Current Management TOMAS D. MARTIN, MD, LAT Professor, TCV Surgery Director UF Health Aortic Disease Center University of Florida DISCLOSURES Terumo Medtronic Cook Edwards Cryolife AORTIC
WESTMEAD Cardiac QUESTIONS PRACTICE SAQ
 QUESTION 1 A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a history of palpitations. His vital signs are: BP 105/60 mmhg HR 156 beats/min RR 26 /min Temperature 36.2 o C His ECG is on the
QUESTION 1 A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a history of palpitations. His vital signs are: BP 105/60 mmhg HR 156 beats/min RR 26 /min Temperature 36.2 o C His ECG is on the
Ventricular Tachycardia Associated Syncope in a Patient of Variant Angina without Chest Pain
 Case Report Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Ventricular Tachycardia Associated Syncope in a Patient of Variant Angina without Chest Pain Soo Jin Kim, MD, Ji Young
Case Report Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Ventricular Tachycardia Associated Syncope in a Patient of Variant Angina without Chest Pain Soo Jin Kim, MD, Ji Young
Ischemic Heart Disease
 Ischemic Heart Disease Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Consideration Results from partial
Ischemic Heart Disease Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Division of Pathology University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Consideration Results from partial
Assessing Cardiac Risk in Noncardiac Surgery. Murali Sivarajan, M.D. Professor University of Washington Seattle, Washington
 Assessing Cardiac Risk in Noncardiac Surgery Murali Sivarajan, M.D. Professor University of Washington Seattle, Washington Disclosure None. I have no conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise. CME
Assessing Cardiac Risk in Noncardiac Surgery Murali Sivarajan, M.D. Professor University of Washington Seattle, Washington Disclosure None. I have no conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise. CME
Cardiac Emergencies. Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington
 Cardiac Emergencies Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington The Heart -------Aorta Pulmonary Veins---- Superior Vena Cava------ Right Atrium-----
Cardiac Emergencies Jim Bennett Paramedic and Clinical Education Coordinator American Medical Response Spokane, Washington The Heart -------Aorta Pulmonary Veins---- Superior Vena Cava------ Right Atrium-----
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM. General Instructions: ID NUMBER: FORM NAME: H F A DATE: 10/13/2017 VERSION: CONTACT YEAR NUMBER:
 ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
ARIC HEART FAILURE HOSPITAL RECORD ABSTRACTION FORM General Instructions: The Heart Failure Hospital Record Abstraction Form is completed for all heart failure-eligible cohort hospitalizations. Refer to
Arrhythmia 341. Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU
 Arrhythmia 341 Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU Objectives Epidemiology and Mechanisms of AF Evaluation of AF patients Classification of AF Treatment and Risk stratification of AF Identify other
Arrhythmia 341 Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU Objectives Epidemiology and Mechanisms of AF Evaluation of AF patients Classification of AF Treatment and Risk stratification of AF Identify other
Cardiac arrhythmias. Janusz Witowski. Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences. J. Witowski
 Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials
 Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials Sample size 500 # sites 70 (100 planned) 316 (500 planned) 196 (833 estimated) 206 (690 planned) 16 10 22 39 4 Treatment contrasts Baseline
Comparison of Five Major Recent Endovascular Treatment Trials Sample size 500 # sites 70 (100 planned) 316 (500 planned) 196 (833 estimated) 206 (690 planned) 16 10 22 39 4 Treatment contrasts Baseline
An Approach to the Patient with Syncope. Guy Amit MD, MPH Soroka University Medical Center Beer-Sheva
 An Approach to the Patient with Syncope Guy Amit MD, MPH Soroka University Medical Center Beer-Sheva Case presentation A 23 y.o. man presented with 2 episodes of syncope One during exercise,one at rest
An Approach to the Patient with Syncope Guy Amit MD, MPH Soroka University Medical Center Beer-Sheva Case presentation A 23 y.o. man presented with 2 episodes of syncope One during exercise,one at rest
Simultaneous Acute ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction And Acute Left Subclavian Artery Thrombosis
 Simultaneous Acute ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction And Acute Left Subclavian Artery Thrombosis Chee Yang CHIN, MBChB, MRCP(UK) C.W.L. Chin, P.T.L. Chiam, R.S. Tan National Heart Centre Singapore 26
Simultaneous Acute ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction And Acute Left Subclavian Artery Thrombosis Chee Yang CHIN, MBChB, MRCP(UK) C.W.L. Chin, P.T.L. Chiam, R.S. Tan National Heart Centre Singapore 26
WHI Form Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver (For items 1-11, each question specifies mark one or mark all that apply.
 WHI Form - Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver. 6. COMMENTS To be completed by Physician Adjudicator Date Completed: - - (M/D/Y) Adjudicator Code: OMB# 095-044 Exp: 4/06 -Affix label here- Clinical Center/ID:
WHI Form - Report of Cardiovascular Outcome Ver. 6. COMMENTS To be completed by Physician Adjudicator Date Completed: - - (M/D/Y) Adjudicator Code: OMB# 095-044 Exp: 4/06 -Affix label here- Clinical Center/ID:
ADVANCED CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING. Medical Knowledge. Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational
 Medical Knowledge Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational Know the basic principles of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including the role of the magnetic fields and gradient coil systems, generation
Medical Knowledge Goals and Objectives PF EF MF LF Aspirational Know the basic principles of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including the role of the magnetic fields and gradient coil systems, generation
Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction
 Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) occurs as a result of prolonged myocardial ischemia Atherosclerosis leads to endothelial rupture or erosion that
Diagnosis and Management of Acute Myocardial Infarction Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI) occurs as a result of prolonged myocardial ischemia Atherosclerosis leads to endothelial rupture or erosion that
Heart Rhythm Disorders. How do you quantify risk?
 Heart Rhythm Disorders How do you quantify risk? Heart Rhythm Disorders Scale of the Problem 1/2 population will have an episode of transient loss of consciousness (T-LOC) at some stage in their life.
Heart Rhythm Disorders How do you quantify risk? Heart Rhythm Disorders Scale of the Problem 1/2 population will have an episode of transient loss of consciousness (T-LOC) at some stage in their life.
