Calciphylaxis Responsive to Lanthanum
|
|
|
- Ashlynn Phelps
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Calciphylaxis Responsive to Lanthanum Carbonate (FOSRENOL) Therapy Micah R. Chan, MD, MPH; Alexander S. Yevzlin, MD; Molly Hinshaw, MD; Jonathan B. Jaffery, MD Abstract Calciphylaxis is a rare and debilitating vasculopathy predominantly seen in patients with renal failure. The proposed mechanism of injury is active vascular calcification with associated elevated parathyroid hormone, hypercalcemia, or hyperphosphatemia. With improved pharmacologic agents including non-calcium containing phosphate binders, vitamin D analogues, calcimimetics, and bisphosphonates, targeted therapy on the mineralization process has been tried with varied success. We report a case of biopsy-proven calciphylaxis in a patient with acute kidney injury requiring dialysis that had persistently elevated calcium-phosphorus product refractory to treatment. The patient, however, responded rapidly to the initiation of lanthanum carbonate therapy and modified dialysis. This is the first known case reported in the literature utilizing this new non-calcium-based phosphate binder in the setting of calciphylaxis. Introduction Calciphylaxis or calcific uremic arteriolopathy was first described by Bryant and White in 1898 in a child with renal failure. 1 In 1962, Hans Selye coined the term calciphylaxis with his animal studies of soft tissue calcium deposition that were sensitized to vitamin D, parathyroid hormone (PTH), high calcium and phosphorus and then challenged with iron salts and egg albumin. 2 The entity is a rare and debilitating vasculopathy predominantly seen in patients with renal failure, however also seen in patients without end-stage renal disease. 3 Although all of these cases possessed a proposed etiologic mechanism of injury and vascular calcification in the form of elevated serum PTH, hypercalcemia, and hypercoagulable state, the pathophysiology remains Author Affiliations: Section of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wis (Chan, Yevzlin, Jaffery); Department of Dermatology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, Wis (Hinshaw). Corresponding Author: Micah R. Chan, MD, MPH, Department of Medicine, Section of Nephrology, 3034 Fish Hatchery Rd, Suite B, Madison, WI 53713; phone ; fax ; e- mail mr.chan@hosp.wisc.edu. an elusive topic. The predominant theory is that it is a systemic syndrome that almost always affects the skin with characteristic calcification involving the media of small- to medium-sized arterioles. Much research and attention to date has focused on the internal milieu that causes the histologic findings of calcium-phosphate aggregation within blood vessels. In order to treat calciphylaxis, multiple case series and cohorts have targeted the ectopic or dystrophic calcification of injured tissue and vessels. Elevated calcium-phosphorus product has been a major focus of experimental studies and the pharmacologic management utilizing non-calcium-containing phosphate binders and vitamin D analogues. 4-5 Low-calcium dialysate and dietary modification, especially in patients on total parenteral nutrition and enteral feeding, have also been studied. 5-6 Parathyroidectomy in the past had been a successful strategy for treating calciphylaxis, however not until recently have results been controversial. 6-7 The extremely high mortality associated with the procedure and recent improved medical management of secondary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism has significantly diminished its role as a treatment regimen. Other novel and evolving treatment modalities cited in the literature include intravenous sodium thiosulfate, calcimimetics, bisphosphonates, tissue plasminogen activator, and hyperbaric oxygen. 8-9 We report a case of biopsy proven calciphylaxis in a patient with acute kidney injury requiring permanent hemodialysis that had persistently elevated calcium-phosphorus product recalcitrant to longer dialysis treatments and low-calcium dialysate. The patient interestingly responded rapidly to the initiation of lanthanum carbonate therapy and continued dialysis. This is the first case reported in the literature utilizing this new non-calcium-based phosphate binder in the setting of calciphylaxis. Case report A 64-year-old man with a history of cryptogenic cirrhosis was transferred to the trauma and life support unit after worsening liver failure, hypotension, renal failure, 335
2 Figure 1. Photograph of lower right leg showing violaceous necrotic skin lesions with black eschar. Figure 2. After 2 months of combination treatment with lanthanum and dialysis, there was significant healing with only superficial ulceration. and encephalopathy. Prior to transfer, the patient was started on empiric antibiotics for presumed spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and septic shock, given aggressive crystalloid and blood products for fluid resuscitation and correction of coagulopathy, and eventually started on vasopressors for hemodynamic instability. The patient was transferred for renal failure thought to be due to hepatorenal syndrome and evaluation for liver transplantation. On examination, the patient was diffusely jaundiced and had a pruritic, erythematous papular eruption over his trunk, abdomen, and lower extremities thought to be a drug eruption secondary to cephalosporin therapy he was receiving. He had pitting edema to his sacrum and no pain or hyperaesthesia over his lower extremities. Laboratory findings on admission included a blood urea nitrogren of 106mg/dL, creatinine 3.1mg/dL, total calcium 6.7mg/dL, phosphorus 4.8mg/dL, calcium- phosphorus product of 32.2mg 2 /dl 2, and an albumin of 1.3g/dL. The patient had numerous blood, urine, and peritoneal fluid cultures during his hospitalization that were negative. The patient was started on continuous venovenous hemofiltration (CVVHF) due to anuric renal failure, shock, and extreme volume overload that eventually necessitated intubation for hypoxemic respiratory failure due to pulmonary edema. Over the next several days, the patient continued on CVVHF with citrate regional anticoagulation secondary to a new internal capsule central nervous system bleed. Pre- and post-filter ionized calcium, as well as total calcium and phosphorus were managed without difficulty. The patient eventually was extubated, weaned off pressor agents, and tolerated intermittent hemodialysis 3 times weekly. Due to severe malnutrition and failed swallow studies, he necessitated nasogastric (NG) tube feeds with low phosphorus Nepro TM enteral nutrition. It was noted on day 20 of his admission that his calcium (uncorrected) and phosphorus was 10.3mg/dL and 7.1mg/dL respectively with a calcium-phosphorus product of 73.1 mg 2 / dl 2. A low dialysate calcium bath at 1.25meq/L was initiated from 2.5meq/L and dialysis time was increased from 3.5 hours to 4 hours and 4 times weekly. Despite these measures, over the next few days calcium and phosphorus levels did not show improvement. Calciumphosphorus product rose to a maximum of 135.7mg 2 / dl 2. An intact PTH was checked and normal at 26pg/ ml. Calcium-based phosphate binders such as calcium carbonate or calcium acetate (Phoslo ) could not be used because of increasing calcium serum levels and calciumphosphorus product. Sevelamer (Renagel ) could not be given due to the difficulty of crushing the tablets and the potential of obstructing the NG tube. Around this time, the patient developed extremely painful tears on the bilateral anterior lower legs. These lesions began as erythematous, indurated blisters/nodules that eventually ulcerated over approximately 2 weeks, resulting in necrotic eschar formation. Dermatology was then consulted (Figure 1) and a skin biopsy and cultures were performed. Since sevelamer could not be used, dialysis was continued and lanthanum carbonate therapy (1000mg) was started 3 times daily. He also continued on low phosphorus tube feeds and meticulous wound care. Over the next 8 weeks, the calcium and phosphorus levels were much more manageable, with a product averaging 35.5 mg 2 /dl 2. His nutritional status improved with an albumin level of 3.8g/dL, and his intact PTH was still within normal limits at 27pg/mL. The patient s skin lesions dramatically improved with these measures and the pain completely dissipated (Figure 2). The skin biopsy 336
3 revealed vascular calcification with intimal proliferation consistent with calciphylaxis (Figure 3). The patient s functional status has improved with physical therapy and receipt of a successful kidney and liver transplant. No side effects in this patient have been observed with continued therapy with lanthanum carbonate. Discussion Calciphylaxis has a prevalence rate of approximately 1%-4% in long-term hemodialysis patients, with 1-year survival of 45% and an 8-fold risk of death as compared to the general dialysis population. 10 Sepsis is the major cause of death in these patients. 11 Clinical suspicion and the evolvement of the classic skin lesion is the major clue to the diagnosis of this syndrome. Corresponding to the vascular nature of this disorder, patients typically present with a livedo reticularis pattern that progresses to exquisitely painful plaques. These plaques often have a stellate appearance, then ulcerate, and are covered in a black eschar. The lower extremities are the most common site of involvement. Risk factors reported in the literature range from obesity and female gender to hypoalbuminemia and protein C or S deficiency (Table 1). 3,7,12 These risk factors, in conjunction with key laboratory parameters of hyperparathyroidism, hypercalcemia, or hyperphosphatemia, should raise clinical suspicion of calciphylaxis. Levin et al described a mathematical formulation using some of these lab values as a surrogate in determining high-risk patients. 13 Unfortunately, this has not been validated in subsequent studies. Skin biopsy is still the gold standard for diagnosis and shows calcification of the media of small cutaneous blood vessels with intimal hyperplasia, vascular thrombosis, cutaneous ulceration, and necrosis. Recently bone scintigraphy has emerged as a highly sensitive tool in diagnosing calciphylaxis and as an adjunct to track prognosis in treated individuals. 14 Biomedical research has helped elucidate which cellular mechanisms are dysfunctional in patients with severe ectopic vascular calcification, ie, calciphylaxis. It has been shown that hyperparathyroidism is found in 82% of patients, hyperphosphatemia in 68%, hypercalcemia in 20%, and elevated calcium-phosphorus product in 33%. 12 What was once thought to be a passive deposition of calcium and phosphorus in blood vessels, now clearly points to an active and tightly regulated cell-mediated process. 3,7 Many groups have shown that a complex set of endogenous factors may induce the increased mineralization of vascular beds much like bone formation, whether by up-regulation of calcium or phosphorus Figure 3. Von kossa stain showing calcium deposition of intima and media of vessel wall. Table 1. Reported Risk Factors in Patients with Calciphylaxis Calcium carbonate and acetate Caucasian race Cirrhosis Corticosteroids Crohn s disease Diabetes mellitus Elevated calcium-phosphorus product Female gender Human immunodeficiency virus Hypercalcemia Hyperparathyroidism (primary, secondary, tertiary) Hyperphosphatemia Hypoalbuminemia Hypotension Iron overload Malignancy Obesity Protein C or S deficiency Renal transplantation Trauma Vitamin D Warfarin deposition or down-regulation of inhibitors. Matrix G1a protein (MGP), which originally was thought to promote calcification, has now been shown to be a potent inhibitor. In the MGP deficient mouse model, aggressive and uncontrolled vascular calcification occurs. 12 It has also been shown to be constitutively expressed in vascular smooth muscle cells and macrophages responsive to intimal injury. 5 Experimental evidence also suggests that vascular smooth muscle may differentiate into a phenotype capable of inducing proteins of osteoblastic type activity. Both osteopontin and osteocalcin expression has been demonstrated to be upregulated by a high phosphorus environment. 5 Ahmed et al demonstrated in a controlled study of calciphylaxis 337
4 patients that osteopontin expression by vascular smooth muscle was seen in the setting of high phosphorus and calcium-phosphorus product. 7 Moe et al further showed the importance of matrix Gla protein and α2-heremans- Schmid glycoprotein as inhibitors of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. α2-heremans-schmid glycoprotein is an endogenous inhibitor of calcification that has been observed to be significantly lower in calciphylaxis patients. 15 Based on experimental studies, elevated phosphorus levels seem to be the putative ion involved in elevation of calcium-phosphorus product and calciphylaxis. 7 Lathanum carbonate or FOSRENOL is a potent non-aluminum, non-calcium phosphate binder that was approved for use by the US Food and Drug Administration in October It is indicated to reduce serum phosphate levels in patients with end stage renal disease. It is not metabolized and is not a substrate or inhibitor of CYP450. It inhibits intestinal absorption of phosphate by forming highly insoluble complexes, thereby lowering serum phosphorus and calcium-phosphorus product. Well-designed studies have shown that doses of 375mg/day up to a maximum of 2250mg/day were effective in reducing phosphorus levels and calciumphosphorus product as compared to placebo. 16 Adverse effects were predominantly gastrointestinal, including nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, but in a majority of cases these doses were well tolerated. Pre-clinical data has shown minimal systemic absorption and, furthermore, bone biopsies in open-label active-controlled studies did not show differences in mineralization. 16 Our patient s calciphylaxis developed over the course of weeks with no history of previous chronic kidney disease. The patient s laboratory markers were not typical of classic calciphylaxis with elevated serum PTH, and therefore pharmacologic measures such as cinacalcet or bisphosphonates could not be tried due to risk of adynamic bone. The need to control his calcium and phosphorus levels were critical due to excruciating pain and high risk for secondary infection of his skin lesions. In contrast to conventional treatment, lanthanum carbonate in combination with low-calcium dialysate and longer duration/ frequency of dialysis provided a brisk response. More study is needed to determine whether the lanthanum carbonate was effective by decreasing the phosphorus levels or an active inhibitor of the mineralization process. Also, future therapeutic trials should investigate if treating an acute rise in phosphorus may mitigate potential detrimental effects such as vascular calcification. Conclusion In conclusion, our case report suggests an effective therapy for calciphylaxis in combination with modified hemodi- alysis and meticulous wound care. The rapid response to treatment may hold promise for many patients suffering from this deadly and debilitating syndrome. Lanthanum therefore offers an exciting and new option for health care professionals, but more studies need to determine whether it can be used safely and efficiently in all forms of this enigmatic disease. Funding/Support: None declared. Financial Disclosures: None declared. References 1. Bryant JH, White WH. A case of calcification of the arteries and obliterative endarteritis, associated with hydronephrosis, in a child aged 6 months. Guys Hospital Rep. 1898;55: Selye H. Calciphylaxis. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press; Couto FM, Chen H, Blank RD, Drezner MK. Calciphylaxis in the absence of end-stage renal disease. Endocr Pract. 2006;12: Campistol JM, Almirall J, Martin E, Torras A, Revert L. Calcium-carbonate-induced calciphylaxis. Nephron. 1989;51: Wilmer WA, Magro CM. Calciphylaxis: emerging concepts in prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Semin Dial. 2002;15: Don BR, Chin AI. A strategy for the treatment of calcific uremic arteriolopathy (calciphylaxis) employing a combination of therapies. Clin Nephrol. 2003;59: Ahmed S, O Neill KD, Hood AF, Evan AP, Moe SM. Calciphylaxis is associated with hyperphosphatemia and increased osteopontin expression by vascular smooth muscle cells. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;37: Guerra G, Shah RC, Ross EA. Rapid resolution of calciphylaxis with intravenous sodium thiosulfate and continuous venovenous haemofiltratio using low calcium replacement fluid: case report. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005;20: Monney P, Nguyen QV, Perroud H, Descombes E. Rapid improvement of calciphylaxis after intravenous pamidronate therapy in a patient with chronic renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2004;19: Mazhar AR, Johnson RJ, Gillen D, et al. Risk factors and mortality associated with calciphylaxis in end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. 2001;60: Roe SM, Graham LD, Brock WB, Barker DE. Calciphylaxis: early recognition and management. Am Surg. 1994;60: Guldbakke KK, Khachemoune A. Calciphylaxis. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46: Levin A, Mehta RL, Goldstein MB. Mathematical formulation to help identify the patient at risk of ischemic tissue necrosis a potentially lethal complication of chronic renal failure. Am J Nephrol. 1993;13: Han MM, Pan J, Shinkai K, Franc B, Hawkins R, Aparici CM. Calciphylaxis and bone scintigraphy: case report with histological confirmation and review of the literature. Ann Nucl Med. 2007;21: Moe SM, Reslerova M, Ketteler M, et al. Role of calcification inhibitors in the pathogenesis of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Kidney Int. 2005;67: Al-Baaj F, Speake M, Hutchison AJ. Control of serum phosphate by oral lanthanum carbonate in patients undergoing haemodialysis and continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis in a short-term, placebo-controlled study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005;20:
5 The mission of the Wisconsin Medical Journal is to provide a vehicle for professional communication and continuing education of Wisconsin physicians. The Wisconsin Medical Journal (ISSN ) is the official publication of the Wisconsin Medical Society and is devoted to the interests of the medical profession and health care in Wisconsin. The managing editor is responsible for overseeing the production, business operation and contents of Wisconsin Medical Journal. The editorial board, chaired by the medical editor, solicits and peer reviews all scientific articles; it does not screen public health, socioeconomic or organizational articles. Although letters to the editor are reviewed by the medical editor, all signed expressions of opinion belong to the author(s) for which neither the Wisconsin Medical Journal nor the Society take responsibility. The Wisconsin Medical Journal is indexed in Index Medicus, Hospital Literature Index and Cambridge Scientific Abstracts. For reprints of this article, contact the Wisconsin Medical Journal at or e- mail wmj@wismed.org Wisconsin Medical Society
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: Where are we now?
 Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: Where are we now? Dylan M. Barth, Pharm.D. PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident Mayo Clinic 2017 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Identify risk factors for the development of complications caused
Secondary Hyperparathyroidism: Where are we now? Dylan M. Barth, Pharm.D. PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident Mayo Clinic 2017 MFMER slide-1 Objectives Identify risk factors for the development of complications caused
Do We Do Too Many Parathyroidectomies in Dialysis? Sagar Nigwekar MD, MMSc Massachusetts General Hospital
 Do We Do Too Many Parathyroidectomies in Dialysis? Sagar Nigwekar MD, MMSc Massachusetts General Hospital E-mail: snigwekar@mgh.harvard.edu March 13, 2017 Disclosures statement: Consultant: Allena, Becker
Do We Do Too Many Parathyroidectomies in Dialysis? Sagar Nigwekar MD, MMSc Massachusetts General Hospital E-mail: snigwekar@mgh.harvard.edu March 13, 2017 Disclosures statement: Consultant: Allena, Becker
hypercalcemia of malignancy hyperparathyroidism PHPT the most common cause of hypercalcemia in the outpatient setting the second most common cause
 hyperparathyroidism A 68-year-old woman with documented osteoporosis has blood tests showing elevated serum calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels: 11.2 mg/dl (8.8 10.1 mg/dl) and 88 pg/ml (10-60),
hyperparathyroidism A 68-year-old woman with documented osteoporosis has blood tests showing elevated serum calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels: 11.2 mg/dl (8.8 10.1 mg/dl) and 88 pg/ml (10-60),
Vascular calcification in stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease patients on dialysis
 Vascular calcification in stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease patients on dialysis Seoung Woo Lee Div. Of Nephrology and Hypertension, Dept. of Internal Medicine, Inha Unv. College of Medicine, Inchon, Korea
Vascular calcification in stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease patients on dialysis Seoung Woo Lee Div. Of Nephrology and Hypertension, Dept. of Internal Medicine, Inha Unv. College of Medicine, Inchon, Korea
HYDROCHLORIDE FOR THE TREATMENT OF SECONDARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM IN PATIENTS WITH END-STAGE RENAL DISEASE ON MAINTENANCE DIALYSIS THERAPY
 UK RENAL PHARMACY GROUP SUBMISSION TO THE NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE on CINACALCET HYDROCHLORIDE FOR THE TREATMENT OF SECONDARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM IN PATIENTS WITH END-STAGE RENAL DISEASE
UK RENAL PHARMACY GROUP SUBMISSION TO THE NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE on CINACALCET HYDROCHLORIDE FOR THE TREATMENT OF SECONDARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM IN PATIENTS WITH END-STAGE RENAL DISEASE
Velphoro (sucroferric oxyhydroxide)
 STRENGTH DOSAGE FORM ROUTE GPID 500mg chewable tablet oral 36003 MANUFACTURER Fresenius Medical Care North America INDICATION(S) For the control of serum phosphorus levels in patients with chronic kidney
STRENGTH DOSAGE FORM ROUTE GPID 500mg chewable tablet oral 36003 MANUFACTURER Fresenius Medical Care North America INDICATION(S) For the control of serum phosphorus levels in patients with chronic kidney
CKD: Bone Mineral Metabolism. Peter Birks, Nephrology Fellow
 CKD: Bone Mineral Metabolism Peter Birks, Nephrology Fellow CKD - KDIGO Definition and Classification of CKD CKD: abnormalities of kidney structure/function for > 3 months with health implications 1 marker
CKD: Bone Mineral Metabolism Peter Birks, Nephrology Fellow CKD - KDIGO Definition and Classification of CKD CKD: abnormalities of kidney structure/function for > 3 months with health implications 1 marker
Normal kidneys filter large amounts of organic
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE - NEPHROLOGY Effect Of Lanthanum Carbonate vs Calcium Acetate As A Phosphate Binder In Stage 3-4 CKD- Treat To Goal Study K.S. Sajeev Kumar (1), M K Mohandas (1), Ramdas Pisharody (1),
ORIGINAL ARTICLE - NEPHROLOGY Effect Of Lanthanum Carbonate vs Calcium Acetate As A Phosphate Binder In Stage 3-4 CKD- Treat To Goal Study K.S. Sajeev Kumar (1), M K Mohandas (1), Ramdas Pisharody (1),
The Parsabiv Beginner s Book
 The Parsabiv Beginner s Book A quick guide to help you learn about your treatment with Parsabiv and what to expect Indication Parsabiv (etelcalcetide) is indicated for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism
The Parsabiv Beginner s Book A quick guide to help you learn about your treatment with Parsabiv and what to expect Indication Parsabiv (etelcalcetide) is indicated for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism
2017 KDIGO Guidelines Update
 2017 KDIGO Guidelines Update Clinic for Hemodialysis Clinical Center University of Sarajevo 13 th Congress of the Balkan cities Association of Nephrology, Dialysis, and Artificial Organs Transplantation
2017 KDIGO Guidelines Update Clinic for Hemodialysis Clinical Center University of Sarajevo 13 th Congress of the Balkan cities Association of Nephrology, Dialysis, and Artificial Organs Transplantation
Incorporating K/DOQI Using a Novel Algorithm Approach: Regina Qu Appelle s Experience
 Incorporating K/DOQI Using a Novel Algorithm Approach: Regina Qu Appelle s Experience Michael Chan, Renal Dietitian Regina Qu Appelle Health Region BC Nephrology Days There is a strong association among
Incorporating K/DOQI Using a Novel Algorithm Approach: Regina Qu Appelle s Experience Michael Chan, Renal Dietitian Regina Qu Appelle Health Region BC Nephrology Days There is a strong association among
Non-uremic calciphylaxis in alcoholic hepatitis
 Alnabelsi et al. 67 CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Non-uremic calciphylaxis in alcoholic hepatitis Talal Alnabelsi, Ramzi Mulki, Corrado Minimo, Janani Rangaswami ABSTRACT Introduction: Calciphylaxis
Alnabelsi et al. 67 CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Non-uremic calciphylaxis in alcoholic hepatitis Talal Alnabelsi, Ramzi Mulki, Corrado Minimo, Janani Rangaswami ABSTRACT Introduction: Calciphylaxis
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 28 March 2012
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 28 March 2012 OSVAREN 435 mg/235 mg, film-coated tablet Bottle of 180 (CIP: 382 886 3) Applicant: FRESENIUS MEDICAL
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 28 March 2012 OSVAREN 435 mg/235 mg, film-coated tablet Bottle of 180 (CIP: 382 886 3) Applicant: FRESENIUS MEDICAL
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 22 July 2009
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 22 July 2009 PHOSPHOSORB 660 mg, film-coated tablet Container of 200 (CIP: 381 466-0) Applicant: FRESENIUS MEDICAL
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 22 July 2009 PHOSPHOSORB 660 mg, film-coated tablet Container of 200 (CIP: 381 466-0) Applicant: FRESENIUS MEDICAL
Month/Year of Review: September 2012 Date of Last Review: September 2010
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Hyperparathyroidism: Operative Considerations. Financial Disclosures: None. Hyperparathyroidism. Hyperparathyroidism 11/10/2012
 Hyperparathyroidism: Operative Considerations Financial Disclosures: None Steven J Wang, MD FACS Associate Professor Dept of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of California, San Francisco
Hyperparathyroidism: Operative Considerations Financial Disclosures: None Steven J Wang, MD FACS Associate Professor Dept of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery University of California, San Francisco
Therapeutic golas in the treatment of CKD-MBD
 Therapeutic golas in the treatment of CKD-MBD Hemodialysis clinic Clinical University Center Sarajevo Bantao, 04-08.10.2017, Sarajevo Abbvie Satellite symposium 06.10.2017 Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral
Therapeutic golas in the treatment of CKD-MBD Hemodialysis clinic Clinical University Center Sarajevo Bantao, 04-08.10.2017, Sarajevo Abbvie Satellite symposium 06.10.2017 Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral
Phosphate binders and metabolic acidosis in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis sevelamer hydrochloride, calcium carbonate, and bixalomer
 Hemodialysis International 2015; 19:5459 Phosphate binders and metabolic acidosis in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis sevelamer hydrochloride, calcium carbonate, and bixalomer Toru SANAI, 1
Hemodialysis International 2015; 19:5459 Phosphate binders and metabolic acidosis in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis sevelamer hydrochloride, calcium carbonate, and bixalomer Toru SANAI, 1
Hyperphosphatemia is associated with a
 TREATMENT OPTIONS IN THE MANAGEMENT OF PHOSPHATE RETENTION * George A. Porter, MD, FACP, and Hartmut H. Malluche, MD, FACP ABSTRACT Hyperphosphatemia is an independent risk factor for mortality and cardiovascular
TREATMENT OPTIONS IN THE MANAGEMENT OF PHOSPHATE RETENTION * George A. Porter, MD, FACP, and Hartmut H. Malluche, MD, FACP ABSTRACT Hyperphosphatemia is an independent risk factor for mortality and cardiovascular
2.0 Synopsis. Paricalcitol Capsules M Clinical Study Report R&D/15/0380. (For National Authority Use Only)
 2.0 Synopsis AbbVie Inc. Name of Study Drug: ABT-358/Zemplar (paricalcitol) Capsules Name of Active Ingredient: paricalcitol Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For National
2.0 Synopsis AbbVie Inc. Name of Study Drug: ABT-358/Zemplar (paricalcitol) Capsules Name of Active Ingredient: paricalcitol Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For National
Kobe University Repository : Kernel
 Title Author(s) Citation Issue date 2009-09 Resource Type Resource Version DOI URL Kobe University Repository : Kernel Marked increase in bone formation markers after cinacalcet treatment by mechanisms
Title Author(s) Citation Issue date 2009-09 Resource Type Resource Version DOI URL Kobe University Repository : Kernel Marked increase in bone formation markers after cinacalcet treatment by mechanisms
Cardiovascular Mortality: General Population vs ESRD Dialysis Patients
 Cardiovascular Mortality: General Population vs ESRD Dialysis Patients Annual CVD Mortality (%) 100 10 1 0.1 0.01 0.001 25-34 35-44 45-54 55-64 66-74 75-84 >85 Age (years) GP Male GP Female GP Black GP
Cardiovascular Mortality: General Population vs ESRD Dialysis Patients Annual CVD Mortality (%) 100 10 1 0.1 0.01 0.001 25-34 35-44 45-54 55-64 66-74 75-84 >85 Age (years) GP Male GP Female GP Black GP
Clinical Guideline Bone chemistry management in adult renal patients on dialysis
 Clinical Guideline Bone chemistry management in adult renal patients on dialysis This guidance covers how to: Maintain serum phosphate 0.8 to 1.7mmol/L 1 Maintain serum corrected calcium 2.1 to 2.5mmol/L
Clinical Guideline Bone chemistry management in adult renal patients on dialysis This guidance covers how to: Maintain serum phosphate 0.8 to 1.7mmol/L 1 Maintain serum corrected calcium 2.1 to 2.5mmol/L
Sensipar (cinacalcet)
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.PMN.04 Effective Date: 11.15.17 Last Review Date: 05.18 Line of Business: Commercial, Medicaid Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.PMN.04 Effective Date: 11.15.17 Last Review Date: 05.18 Line of Business: Commercial, Medicaid Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important
( ) , (Donabedian, 1980) We would not choose any treatment with poor outcomes
 ..., 2013 Amgen. 1 ? ( ), (Donabedian, 1980) We would not choose any treatment with poor outcomes 1. :, 2. ( ): 3. :.,,, 4. :, [Biomarkers Definitions Working Group, 2001]., (William M. Bennet, Nefrol
..., 2013 Amgen. 1 ? ( ), (Donabedian, 1980) We would not choose any treatment with poor outcomes 1. :, 2. ( ): 3. :.,,, 4. :, [Biomarkers Definitions Working Group, 2001]., (William M. Bennet, Nefrol
Calciphylaxis: a still unmet challenge
 THOROUGH CRITICAL APPRAISALS JN EPHROL 24( DOI:10.5301/JN.2011.6366 Calciphylaxis: a still unmet challenge Vincent M. Brandenburg 1, Mario Cozzolino 2, Markus Ketteler 3 1 Department of Cardiology, University
THOROUGH CRITICAL APPRAISALS JN EPHROL 24( DOI:10.5301/JN.2011.6366 Calciphylaxis: a still unmet challenge Vincent M. Brandenburg 1, Mario Cozzolino 2, Markus Ketteler 3 1 Department of Cardiology, University
Literature Scan: Phosphate Binders
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Parsabiv the control of calcimimetic delivery you ve always wanted, the sustained lowering of shpt lab values your patients deserve 1
 Parsabiv the control of calcimimetic delivery you ve always wanted, the sustained lowering of shpt lab values your patients deserve 1 Not an actual Parsabiv vial. The displayed vial is for illustrative
Parsabiv the control of calcimimetic delivery you ve always wanted, the sustained lowering of shpt lab values your patients deserve 1 Not an actual Parsabiv vial. The displayed vial is for illustrative
Month/Year of Review: May 2014 Date of Last Review: September New Drug Evaluation: Sucrofferic Oxyhydroxide (Velphoro )
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35, Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
CKD FOR INTERNISTS. Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College
 CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
Pre-uremic Calciphylaxis
 KIDNEY DISEASES Pre-uremic Calciphylaxis Ali Nayer, 1 Sharad Virmani, 1 Maria Gonzalez-Suarez, 1 Elvia Goez-Gutierrez, 2 Andrew E Rosenberg, 2 Loay Salman, 1 Arif Asif 3 1 Division of Nephrology, University
KIDNEY DISEASES Pre-uremic Calciphylaxis Ali Nayer, 1 Sharad Virmani, 1 Maria Gonzalez-Suarez, 1 Elvia Goez-Gutierrez, 2 Andrew E Rosenberg, 2 Loay Salman, 1 Arif Asif 3 1 Division of Nephrology, University
Calcium x phosphate product
 Date written: August 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Carmel Hawley Calcium x phosphate product GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence SUGGESTIONS FOR CLINICAL
Date written: August 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Carmel Hawley Calcium x phosphate product GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence SUGGESTIONS FOR CLINICAL
Effects of Diabetes Mellitus, Age, and Duration of Dialysis on Parathormone in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients. Hamid Nasri 1, Soleiman Kheiri 2
 Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant 2008;19(4):608-613 2008 Saudi Center for Organ Transplantation Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation Original Article Effects of Diabetes Mellitus, Age, and
Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant 2008;19(4):608-613 2008 Saudi Center for Organ Transplantation Saudi Journal of Kidney Diseases and Transplantation Original Article Effects of Diabetes Mellitus, Age, and
Persistent post transplant hyperparathyroidism. Shiva Seyrafian IUMS-97/10/18-8/1/2019
 Persistent post transplant hyperparathyroidism Shiva Seyrafian IUMS-97/10/18-8/1/2019 normal weight =18-160 mg In HPT= 500-1000 mg 2 Epidemiology Mild 2 nd hyperparathyroidism (HPT) resolve after renal
Persistent post transplant hyperparathyroidism Shiva Seyrafian IUMS-97/10/18-8/1/2019 normal weight =18-160 mg In HPT= 500-1000 mg 2 Epidemiology Mild 2 nd hyperparathyroidism (HPT) resolve after renal
Case Report Calciphylaxis: Temporal Artery Calcification Preceding Widespread Skin Lesions and Penile Necrosis
 Case Reports in Nephrology Volume 2012, Article ID 309727, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/309727 Case Report Calciphylaxis: Temporal Artery Calcification Preceding Widespread Skin Lesions and Penile Necrosis
Case Reports in Nephrology Volume 2012, Article ID 309727, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/309727 Case Report Calciphylaxis: Temporal Artery Calcification Preceding Widespread Skin Lesions and Penile Necrosis
Improved Assessment of Aortic Calcification in Japanese Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improved Assessment of Aortic Calcification in Japanese Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis Masaki Ohya 1, Haruhisa Otani 2,KeigoKimura 3, Yasushi Saika 4, Ryoichi Fujii 4, Susumu
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Improved Assessment of Aortic Calcification in Japanese Patients Undergoing Maintenance Hemodialysis Masaki Ohya 1, Haruhisa Otani 2,KeigoKimura 3, Yasushi Saika 4, Ryoichi Fujii 4, Susumu
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University
 RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
RENAL FAILURE IN CHILDREN Dr. Mai Mohamed Elhassan Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES By the end of this lecture each student should be able to: Define acute & chronic kidney disease(ckd)
Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral Bone Disease
 NHS Logo here Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral Bone Disease (CKD-MBD) Patient Information Health & care information you can trust The Information Standard Certified Member Working together for better patient
NHS Logo here Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral Bone Disease (CKD-MBD) Patient Information Health & care information you can trust The Information Standard Certified Member Working together for better patient
Calcific uremic arteriolopathy (CUA), also called
 R e s i d e n t G r a n d R o u n d s Series Editor: Mark A. Perazella, MD Calcific Uremic Arteriolopathy Christopher L. Stout, MD Macram Ayoub, MD, FRCS(Edin), FRCS(Eng), FACS A 50-year-old African-American
R e s i d e n t G r a n d R o u n d s Series Editor: Mark A. Perazella, MD Calcific Uremic Arteriolopathy Christopher L. Stout, MD Macram Ayoub, MD, FRCS(Edin), FRCS(Eng), FACS A 50-year-old African-American
CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test. AKI & CRRT Conference 2018
 CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test AKI & CRRT Conference 2018 Question 1 Which ONE of the following statements regarding solute clearance in CRRT is MOST correct? A. Convective and diffusive solute
CRRT Fundamentals Pre- and Post- Test AKI & CRRT Conference 2018 Question 1 Which ONE of the following statements regarding solute clearance in CRRT is MOST correct? A. Convective and diffusive solute
Tenapanor, a gastrointestinal NHE3 inhibitor, reduces serum phosphate in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5D and hyperphosphatemia
 , a gastrointestinal NHE3 inhibitor, reduces serum phosphate in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5D and hyperphosphatemia Geoffrey A Block, 1 David P Rosenbaum, 2 Maria Leonsson-Zachrisson, 3
, a gastrointestinal NHE3 inhibitor, reduces serum phosphate in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5D and hyperphosphatemia Geoffrey A Block, 1 David P Rosenbaum, 2 Maria Leonsson-Zachrisson, 3
CKD-Mineral Bone Disorder (MBD) Pathogenesis of Metabolic Bone Disease. Grants: NIH, Abbott, Amgen, OPKO, Shire
 Pathogenesis of Metabolic Bone Disease Stuart M. Sprague, D.O. Chief, Division of Nephrology and Hypertension Professor of Medicine NorthShore University HealthSystem University of Chicago Pritzker School
Pathogenesis of Metabolic Bone Disease Stuart M. Sprague, D.O. Chief, Division of Nephrology and Hypertension Professor of Medicine NorthShore University HealthSystem University of Chicago Pritzker School
Ramzi Vareldzis, MD Avanelle Jack, MD Dept of Internal Medicine Section of Nephrology and Hypertension LSU Health New Orleans September 13, 2016
 Ramzi Vareldzis, MD Avanelle Jack, MD Dept of Internal Medicine Section of Nephrology and Hypertension LSU Health New Orleans September 13, 2016 1 MBD + CKD in Elderly patients Our focus for today: CKD
Ramzi Vareldzis, MD Avanelle Jack, MD Dept of Internal Medicine Section of Nephrology and Hypertension LSU Health New Orleans September 13, 2016 1 MBD + CKD in Elderly patients Our focus for today: CKD
CKD-MBD CKD mineral bone disorder
 CKD Renal bone disease Dr Mike Stone University Hospital Llandough Affects 5 10 % of population Increasingly common Ageing, diabetes, undetected hypertension Associated with: Cardiovascular disease Premature
CKD Renal bone disease Dr Mike Stone University Hospital Llandough Affects 5 10 % of population Increasingly common Ageing, diabetes, undetected hypertension Associated with: Cardiovascular disease Premature
Should cinacalcet be used in patients who are not on dialysis?
 Should cinacalcet be used in patients who are not on dialysis? Jorge B Cannata-Andía and José Luis Fernández-Martín Affiliations: Bone and Mineral Research Unit. Hospital Universitario Central de Asturias.
Should cinacalcet be used in patients who are not on dialysis? Jorge B Cannata-Andía and José Luis Fernández-Martín Affiliations: Bone and Mineral Research Unit. Hospital Universitario Central de Asturias.
A case series and clinical update on calciphylaxis
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2016) 24, 184-190 Review Article A case series and clinical update on calciphylaxis Calciphylaxis is a rare disorder characterised by microvascular calcification and thrombosis
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2016) 24, 184-190 Review Article A case series and clinical update on calciphylaxis Calciphylaxis is a rare disorder characterised by microvascular calcification and thrombosis
CRRT Fundamentals Pre-Test. AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT
 CRRT Fundamentals Pre-Test AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT Question 1 A 72-year-old man with HTN presents to the ED with slurred speech, headache and weakness after falling at home. He
CRRT Fundamentals Pre-Test AKI & CRRT 2017 Practice Based Learning in CRRT Question 1 A 72-year-old man with HTN presents to the ED with slurred speech, headache and weakness after falling at home. He
A rare presentation of calciphylaxis in normal renal function
 www.edoriumjournals.com case REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS A rare presentation of calciphylaxis in normal renal function Parin Rimtepathip, David Cohen ABSTRACT Introduction: Calciphylaxis is a rare
www.edoriumjournals.com case REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS A rare presentation of calciphylaxis in normal renal function Parin Rimtepathip, David Cohen ABSTRACT Introduction: Calciphylaxis is a rare
Sensipar. Sensipar (cinacalcet) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.30.46 Subject: Sensipar Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: June 22, 2018 Sensipar Description Sensipar (cinacalcet)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.30.46 Subject: Sensipar Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: June 22, 2018 Sensipar Description Sensipar (cinacalcet)
The impact of improved phosphorus control: use of sevelamer hydrochloride in patients with chronic renal failure
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2002) 17: 340 345 The impact of improved phosphorus control: use of sevelamer hydrochloride in patients with chronic renal failure Naseem Amin Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA,
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2002) 17: 340 345 The impact of improved phosphorus control: use of sevelamer hydrochloride in patients with chronic renal failure Naseem Amin Genzyme Corporation, Cambridge, MA,
Effect of lanthanum carbonate and calcium acetate in the treatment of hyperphosphatemia in patients of chronic kidney disease
 Research Article Effect of lanthanum and calcium acetate in the treatment of hyperphosphatemia in patients of chronic kidney disease P. Thomas Scaria, Reneega Gangadhar 1, Ramdas Pisharody 2 ABSTRACT Departments
Research Article Effect of lanthanum and calcium acetate in the treatment of hyperphosphatemia in patients of chronic kidney disease P. Thomas Scaria, Reneega Gangadhar 1, Ramdas Pisharody 2 ABSTRACT Departments
Hypocalcemia 6/8/12. Normal value. Physiologic functions. Nephron a functional unit of kidney. Influencing factors in Calcium and Phosphate Balance
 Normal value Hypocalcemia Serum calcium Total mg/dl Ionized mg/dl Cord blood 9.0 ~ 11.5 5.0 ~ 6.o New born (1 st 24 hrs) 9.0 ~ 10.6 4.3 ~ 5.1 24~ 48 hrs 7.0 ~12.0 4.0 ~4.7 Child 8.8 ~10.8 4.8 ~4.92 There
Normal value Hypocalcemia Serum calcium Total mg/dl Ionized mg/dl Cord blood 9.0 ~ 11.5 5.0 ~ 6.o New born (1 st 24 hrs) 9.0 ~ 10.6 4.3 ~ 5.1 24~ 48 hrs 7.0 ~12.0 4.0 ~4.7 Child 8.8 ~10.8 4.8 ~4.92 There
NOTTINGHAMSHIRE AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE SHARED CARE PROTOCOL AGREEMENT
 NOTTINGHAMSHIRE AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE SHARED CARE PROTOCOL AGREEMENT Phosphate Binders for the Treatment of Hyperphosphataemia in adults with Chronic Kidney Disease OBJECTIVES To outline referral
NOTTINGHAMSHIRE AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE SHARED CARE PROTOCOL AGREEMENT Phosphate Binders for the Treatment of Hyperphosphataemia in adults with Chronic Kidney Disease OBJECTIVES To outline referral
Approach to a patient with hypercalcemia
 Approach to a patient with hypercalcemia Ana-Maria Chindris, MD Division of Endocrinology Mayo Clinic Florida 2013 MFMER slide-1 Background Hypercalcemia is a problem frequently encountered in clinical
Approach to a patient with hypercalcemia Ana-Maria Chindris, MD Division of Endocrinology Mayo Clinic Florida 2013 MFMER slide-1 Background Hypercalcemia is a problem frequently encountered in clinical
Lanthanum Carbonate Reduces Urine Phosphorus Excretion: Evidence of High-Capacity Phosphate Binding
 Renal Failure, 34(3): 263 270, (2012) Copyright Informa Healthcare USA, Inc. ISSN 0886-022X print/1525-6049 online DOI: 10.3109/0886022X.2011.649657 Lanthanum Carbonate Reduces Urine Phosphorus Excretion:
Renal Failure, 34(3): 263 270, (2012) Copyright Informa Healthcare USA, Inc. ISSN 0886-022X print/1525-6049 online DOI: 10.3109/0886022X.2011.649657 Lanthanum Carbonate Reduces Urine Phosphorus Excretion:
End-Stage Renal Disease. Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology
 End-Stage Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology ESRD : Life with renal replacement therapy CASE: 18 month old male with HUS develops ESRD PD complicated
End-Stage Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology ESRD : Life with renal replacement therapy CASE: 18 month old male with HUS develops ESRD PD complicated
Corporate Presentation January 2013
 Corporate Presentation January 2013 0 Forward-Looking Statements Certain statements and information included in this presentation are forwardlooking statements under the Private Securities Litigation Reform
Corporate Presentation January 2013 0 Forward-Looking Statements Certain statements and information included in this presentation are forwardlooking statements under the Private Securities Litigation Reform
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 29, 2013
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 29, 2013 Takeyuki Hiramatsu, 1 Takahiro Hayasaki, 1 Akinori Hobo, 1 Shinji Furuta, 1 Koki Kabu, 2 Yukio Tonozuka, 2 Yoshiyasu Iida 1 Icodextrin Eliminates Phosphate
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 29, 2013 Takeyuki Hiramatsu, 1 Takahiro Hayasaki, 1 Akinori Hobo, 1 Shinji Furuta, 1 Koki Kabu, 2 Yukio Tonozuka, 2 Yoshiyasu Iida 1 Icodextrin Eliminates Phosphate
PROs for Drug Development. Melanie Blank, MD
 PROs for Drug Development in Chronic Kidney Disease Melanie Blank, MD Disclaimer The views expressed here represent my opinions and do not necessarily represent the views of the FDA. Overview Stagnation
PROs for Drug Development in Chronic Kidney Disease Melanie Blank, MD Disclaimer The views expressed here represent my opinions and do not necessarily represent the views of the FDA. Overview Stagnation
Calcific uraemic arteriolopathy A mini-review
 MINI-REVIEW Port J Nephrol Hypert 2016; 30(2): 108-112 Advance Access publication 20 May 2016 Filipa Brito Mendes 1, Sofia Couto Rocha 2, Rodica Agapii 2, Ana Silva 1,3, André Fragoso 1, Teresa Jerónimo
MINI-REVIEW Port J Nephrol Hypert 2016; 30(2): 108-112 Advance Access publication 20 May 2016 Filipa Brito Mendes 1, Sofia Couto Rocha 2, Rodica Agapii 2, Ana Silva 1,3, André Fragoso 1, Teresa Jerónimo
Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Dietetic Management Protocol
 Nutrition and Dietetic Service Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Dietetic Management Protocol Authors Hilary Mathieson, Renal Dietitian Paul McKeveney, Consultant Nephrologist
Nutrition and Dietetic Service Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Dietetic Management Protocol Authors Hilary Mathieson, Renal Dietitian Paul McKeveney, Consultant Nephrologist
Contents. Authors Name: Christopher Wong: Consultant Nephrologist Anne Waddington: Renal Pharmacist Eimear Fegan : Renal Dietitian
 Cheshire and Merseyside Renal Units Guidelines on the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease - Mineral Bone Disorder (adapted from Greater Manchester) Authors Name: Christopher Wong: Consultant Nephrologist
Cheshire and Merseyside Renal Units Guidelines on the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease - Mineral Bone Disorder (adapted from Greater Manchester) Authors Name: Christopher Wong: Consultant Nephrologist
Ca, Phos and Vitamin D Metabolism in Pre-Dialysis Patients
 Ca, Phos and Vitamin D Metabolism in Pre-Dialysis Patients A. WADGYMAR, MD Credit Valley Hospital, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada. June 1, 2007 1 Case: 22 y/o referred to Renal Clinic Case: A.M. 29 y/o Man
Ca, Phos and Vitamin D Metabolism in Pre-Dialysis Patients A. WADGYMAR, MD Credit Valley Hospital, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada. June 1, 2007 1 Case: 22 y/o referred to Renal Clinic Case: A.M. 29 y/o Man
Cinacalcet treatment in advanced CKD - is it justified?
 Cinacalcet treatment in advanced CKD - is it justified? Goce Spasovski ERBP Advisory Board member University of Skopje, R. Macedonia TSN Congress October 21, 2017, Antalya Session Objectives From ROD to
Cinacalcet treatment in advanced CKD - is it justified? Goce Spasovski ERBP Advisory Board member University of Skopje, R. Macedonia TSN Congress October 21, 2017, Antalya Session Objectives From ROD to
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. Biochemical Targets. Calcium GUIDELINES
 Date written: August 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Carmel Hawley Biochemical Targets CARMEL HAWLEY (Woolloongabba, Queensland) GRAHAME ELDER (Westmead, New South Wales) Calcium GUIDELINES
Date written: August 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Carmel Hawley Biochemical Targets CARMEL HAWLEY (Woolloongabba, Queensland) GRAHAME ELDER (Westmead, New South Wales) Calcium GUIDELINES
Treatment of Calciphylaxis: A Case for Oral Sodium Thiosulfate
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 32, 2016 Anupkumar Shetty, Jeffrey Klein Treatment of Calciphylaxis: A Case for Oral Sodium Thiosulfate Calciphylaxis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 32, 2016 Anupkumar Shetty, Jeffrey Klein Treatment of Calciphylaxis: A Case for Oral Sodium Thiosulfate Calciphylaxis is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in
Tenapanor, a gastrointestinal NHE3 inhibitor, reduces serum phosphate in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5D and hyperphosphatemia
 , a gastrointestinal NHE3 inhibitor, reduces serum phosphate in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5D and hyperphosphatemia Geoffrey A Block, 1 David P Rosenbaum, 2 Maria Leonsson- Zachrisson,
, a gastrointestinal NHE3 inhibitor, reduces serum phosphate in patients with chronic kidney disease stage 5D and hyperphosphatemia Geoffrey A Block, 1 David P Rosenbaum, 2 Maria Leonsson- Zachrisson,
Drugs for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism and hyperphosphataemia
 NSW Therapeutic Advisory Group Level 5, 376 Victoria Street PO Box 766 Darlinghurst NSW 2010 Phone: 61 2 8382 2852 Fax: 61 2 8382 3529 Email: nswtag@stvincents.com.au www.nswtag.org.au Drugs for the treatment
NSW Therapeutic Advisory Group Level 5, 376 Victoria Street PO Box 766 Darlinghurst NSW 2010 Phone: 61 2 8382 2852 Fax: 61 2 8382 3529 Email: nswtag@stvincents.com.au www.nswtag.org.au Drugs for the treatment
Systemic Calciphylaxis: Diffuse Cutaneous Involvement and Ischemic Optic Neuropathy a case report.
 Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2017; 13 (4): 126-130 Systemic Calciphylaxis: Diffuse Cutaneous Involvement and Ischemic Optic Neuropathy a case report. Nurshazwani MAT SALLEH 1, Yin Ping LIEW 2 1 Department
Case Report Brunei Int Med J. 2017; 13 (4): 126-130 Systemic Calciphylaxis: Diffuse Cutaneous Involvement and Ischemic Optic Neuropathy a case report. Nurshazwani MAT SALLEH 1, Yin Ping LIEW 2 1 Department
Glycaemic control and serum intact parathyroid hormone levels in diabetic patients on haemodialysis therapy
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2008) 23: 315 320 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm639 Advance Access publication 23 October 2007 Original Article Glycaemic control and serum intact parathyroid hormone levels in diabetic
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2008) 23: 315 320 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm639 Advance Access publication 23 October 2007 Original Article Glycaemic control and serum intact parathyroid hormone levels in diabetic
Level 1 Strong We recommendyshould A High Moderate Level 2 Weak We suggestymight C Low Very low. K Hyperphosphatemia has been associated with poor
 chapter 4.1 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2009 KDIGO Chapter 4.1: Treatment of CKD MBD targeted at lowering high serum phosphorus and maintaining serum calcium ; doi:10.1038/ki.2009.192 Grade for
chapter 4.1 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2009 KDIGO Chapter 4.1: Treatment of CKD MBD targeted at lowering high serum phosphorus and maintaining serum calcium ; doi:10.1038/ki.2009.192 Grade for
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. Serum phosphate GUIDELINES
 Date written: August 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Carmel Hawley Serum phosphate GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence SUGGESTIONS FOR CLINICAL CARE (Suggestions
Date written: August 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Carmel Hawley Serum phosphate GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence SUGGESTIONS FOR CLINICAL CARE (Suggestions
Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Dietetic Management Protocol
 This is an official Northern Trust policy and should not be edited in any way Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Dietetic Management Protocol Reference Number: NHSCT/12/553 Target
This is an official Northern Trust policy and should not be edited in any way Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Dietetic Management Protocol Reference Number: NHSCT/12/553 Target
Calciphylaxis. Smeeta Sinha Consultant Renal Physician & Honorary Senior Lecturer Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust
 Calciphylaxis Smeeta Sinha Consultant Renal Physician & Honorary Senior Lecturer Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust The Oxford Advanced Pain and Symptom Management Course Declaration of interests UK Calciphylaxis
Calciphylaxis Smeeta Sinha Consultant Renal Physician & Honorary Senior Lecturer Salford Royal NHS Foundation Trust The Oxford Advanced Pain and Symptom Management Course Declaration of interests UK Calciphylaxis
Once considered rare, calcific uremic arteriolopathy
 Sodium Thiosulfate Treatment for Calcific Uremic Arteriolopathy in Children and Young Adults Carlos E. Araya, Robert S. Fennell, Richard E. Neiberger, and Vikas R. Dharnidharka Division of Pediatric Nephrology,
Sodium Thiosulfate Treatment for Calcific Uremic Arteriolopathy in Children and Young Adults Carlos E. Araya, Robert S. Fennell, Richard E. Neiberger, and Vikas R. Dharnidharka Division of Pediatric Nephrology,
Hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of calciphylaxis: a case series
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2001) 16: 2176 2180 Original Article Hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of calciphylaxis: a case series Tiina Podymow 1, Chris Wherrett 2 and Kevin D. Burns 1 1 Division of Nephrology,
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2001) 16: 2176 2180 Original Article Hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of calciphylaxis: a case series Tiina Podymow 1, Chris Wherrett 2 and Kevin D. Burns 1 1 Division of Nephrology,
Parsabiv (etelcalcetide) NEW PRODUCT SLIDESHOW
 Parsabiv (etelcalcetide) NEW PRODUCT SLIDESHOW Introduction Brand name: Parsabiv Generic name: Etelcalcetide Pharmacological class: Calcimimetic Strength and Formulation: 2.5mg/0.5mL, 5mg/mL, 10mg/2mL;
Parsabiv (etelcalcetide) NEW PRODUCT SLIDESHOW Introduction Brand name: Parsabiv Generic name: Etelcalcetide Pharmacological class: Calcimimetic Strength and Formulation: 2.5mg/0.5mL, 5mg/mL, 10mg/2mL;
Medicines for anaemia and mineral bone disease
 Patient Information: Medicines NHS Logo here Medicines for anaemia and mineral bone disease Health & care information you can trust The Information Standard Certified Member Working together for better
Patient Information: Medicines NHS Logo here Medicines for anaemia and mineral bone disease Health & care information you can trust The Information Standard Certified Member Working together for better
Dialyzing challenging patients: Patients with hepato-renal conditions
 Dialyzing challenging patients: Patients with hepato-renal conditions Nidyanandh Vadivel MD Medical Director for Living kidney Donor and Pancreas Transplant Programs Swedish Organ Transplant, Seattle Acute
Dialyzing challenging patients: Patients with hepato-renal conditions Nidyanandh Vadivel MD Medical Director for Living kidney Donor and Pancreas Transplant Programs Swedish Organ Transplant, Seattle Acute
Clinical benefits of an adherence monitoring program in the management of secondary hyperparathyroidism with cinacalcet:
 Clinical benefits of an adherence monitoring program in the management of secondary hyperparathyroidism with cinacalcet: Results of a prospective randomized controlled study Forni Valentina¹, Pruijm Menno¹,
Clinical benefits of an adherence monitoring program in the management of secondary hyperparathyroidism with cinacalcet: Results of a prospective randomized controlled study Forni Valentina¹, Pruijm Menno¹,
Improvement in Pittsburgh Symptom Score Index After Initiation of Peritoneal Dialysis
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 24, 2008 Matthew J. Novak, 1 Heena Sheth, 2 Filitsa H. Bender, 1 Linda Fried, 1,3 Beth Piraino 1 Improvement in Pittsburgh Symptom Score Index After Initiation of
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 24, 2008 Matthew J. Novak, 1 Heena Sheth, 2 Filitsa H. Bender, 1 Linda Fried, 1,3 Beth Piraino 1 Improvement in Pittsburgh Symptom Score Index After Initiation of
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Prevalence and Pattern of Mineral Bone Disorder in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Using Serum
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Prevalence and Pattern of Mineral Bone Disorder in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Using Serum
New Medicines Profile. December 2013 Issue No. 13/04. Colestilan
 New Medicines Profile December 2013 Issue. 13/04 Concise evaluated information to support the managed entry of new medicines in the NHS Summary (BindRen ) is an oral, non-absorbed, non-calcium, nonmetallic
New Medicines Profile December 2013 Issue. 13/04 Concise evaluated information to support the managed entry of new medicines in the NHS Summary (BindRen ) is an oral, non-absorbed, non-calcium, nonmetallic
Variable Included. Excluded. Included. Excluded
 Table S1. Baseline characteristics of patients included in the analysis and those excluded patients because of missing baseline serumj bicarbonate levels, stratified by dialysis modality. Variable HD patients
Table S1. Baseline characteristics of patients included in the analysis and those excluded patients because of missing baseline serumj bicarbonate levels, stratified by dialysis modality. Variable HD patients
Decision making in acute dialysis
 Decision making in acute dialysis Geoffrey Bihl MB.BCh M.MED FCP(SA) Nephrologist and Director Winelands Kidney and Dialysis Centre Somerset West South Africa Important questions in AKI What is the cause?
Decision making in acute dialysis Geoffrey Bihl MB.BCh M.MED FCP(SA) Nephrologist and Director Winelands Kidney and Dialysis Centre Somerset West South Africa Important questions in AKI What is the cause?
chapter 1 & 2009 KDIGO
 http://www.kidney-international.org chapter 1 & 2009 DIGO Chapter 1: Introduction and definition of CD MBD and the development of the guideline statements idney International (2009) 76 (Suppl 113), S3
http://www.kidney-international.org chapter 1 & 2009 DIGO Chapter 1: Introduction and definition of CD MBD and the development of the guideline statements idney International (2009) 76 (Suppl 113), S3
Supplementary Table 1. Details of the components of the primary composite endpoint
 Supplementary Table 1. Details of the components of the primary composite endpoint 1. Death The cause of death will be defined by the underlying cause, not the immediate mode of death. Death will be classified
Supplementary Table 1. Details of the components of the primary composite endpoint 1. Death The cause of death will be defined by the underlying cause, not the immediate mode of death. Death will be classified
Nutritional Cases with CKD HEMODIALYSIS
 Nutritional Cases with CKD HEMODIALYSIS S. Muge DEGER, MD, FISN Yuksek Ihtisas University Faculty of Medicine, Koru Hospital Department of Nephrology Ankara, TURKEY CASE-1 BC, is a 60- year- old Caucasian
Nutritional Cases with CKD HEMODIALYSIS S. Muge DEGER, MD, FISN Yuksek Ihtisas University Faculty of Medicine, Koru Hospital Department of Nephrology Ankara, TURKEY CASE-1 BC, is a 60- year- old Caucasian
TABLE OF CONTENTS T-1. A-1 Acronyms and Abbreviations. S-1 Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
 A-1 Acronyms and Abbreviations TABLE OF CONTENTS S-1 Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Chapter 1: Nutrition Assessment Charts, Tables and Formulas 1-2 Practical Steps to Nutrition Assessment Adult
A-1 Acronyms and Abbreviations TABLE OF CONTENTS S-1 Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Chapter 1: Nutrition Assessment Charts, Tables and Formulas 1-2 Practical Steps to Nutrition Assessment Adult
Protocol GTC : A Randomized, Open Label, Parallel Design Study of Sevelamer Hydrochloride (Renagel ) in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients.
 Protocol GTC-68-208: A Randomized, Open Label, Parallel Design Study of Sevelamer Hydrochloride (Renagel ) in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. These results are supplied for informational purposes only.
Protocol GTC-68-208: A Randomized, Open Label, Parallel Design Study of Sevelamer Hydrochloride (Renagel ) in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. These results are supplied for informational purposes only.
CCRN Review - Renal. CCRN Review - Renal 10/16/2014. CCRN Review Renal. Sodium Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l
 CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
Calciphylaxis (cal-ci-phy-lax-is)
 Calciphylaxis (cal-ci-phy-lax-is) Renal Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about a condition called calciphylaxis. It will give you a better understanding of the condition and
Calciphylaxis (cal-ci-phy-lax-is) Renal Unit Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is about a condition called calciphylaxis. It will give you a better understanding of the condition and
BONE AND MINERAL METABOLISM in the PD PATIENT
 BONE AND MINERAL METABOLISM in the PD PATIENT John Burkart, MD Professor of Medicine/Nephrology Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center Chief Medical Officer Health Systems Management Maria V. DeVita,
BONE AND MINERAL METABOLISM in the PD PATIENT John Burkart, MD Professor of Medicine/Nephrology Wake Forest University Baptist Medical Center Chief Medical Officer Health Systems Management Maria V. DeVita,
The Effect of Residual Renal Function at the Initiation of Dialysis on Patient Survival
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2009.24.1.55 The Effect of Residual Renal Function at the Initiation of Dialysis on Patient Survival Seoung Gu Kim 1 and Nam Ho Kim 2 Department of Internal Medicine,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2009.24.1.55 The Effect of Residual Renal Function at the Initiation of Dialysis on Patient Survival Seoung Gu Kim 1 and Nam Ho Kim 2 Department of Internal Medicine,
ELECTROLYTES RENAL SHO TEACHING
 ELECTROLYTES RENAL SHO TEACHING Metabolic Alkalosis 2 factors are responsible for generation and maintenance of metabolic alkalosis this includes a process that raises serum bicarbonate and a process that
ELECTROLYTES RENAL SHO TEACHING Metabolic Alkalosis 2 factors are responsible for generation and maintenance of metabolic alkalosis this includes a process that raises serum bicarbonate and a process that
PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM
 PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM HYPERPARATHYROIDISM Inappropriate excess secretion of Parathyroid Hormone in Primary Hyperparathyroidism Appropriate Hypersecretion in Secondary Hyperparathyroidism PTH and
PRIMARY HYPERPARATHYROIDISM HYPERPARATHYROIDISM Inappropriate excess secretion of Parathyroid Hormone in Primary Hyperparathyroidism Appropriate Hypersecretion in Secondary Hyperparathyroidism PTH and
Case 4 Generalised bone pain
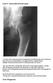 Case 4 Generalised bone pain C A 34- year- old woman presented complaining of multifocal pain in her chest and legs. The pain was intermittent, was aggravated by weight bearing. Initially was alleviated
Case 4 Generalised bone pain C A 34- year- old woman presented complaining of multifocal pain in her chest and legs. The pain was intermittent, was aggravated by weight bearing. Initially was alleviated
Disclosures. Topics. Staging and GFR. K-DOQI Staging of Chronic Kidney Disease. Definition of Chronic Kidney Disease. Chronic Kidney Disease
 Disclosures Chronic Kidney Disease Consultant: Baxter Healthcare J. Kevin Tucker, M.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Massachusetts General Hospital Topics Staging of chronic kidney disease (CKD) How to
Disclosures Chronic Kidney Disease Consultant: Baxter Healthcare J. Kevin Tucker, M.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Massachusetts General Hospital Topics Staging of chronic kidney disease (CKD) How to
