Marfan syndrome and cardiovascular complications: results of a family investigation
|
|
|
- Madeline Wilcox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sarr et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2017) 17:193 DOI /s CASE REPORT Marfan syndrome and cardiovascular complications: results of a family investigation Open Access Simon Antoine Sarr 1*, Siddikatou Djibrilla 1, Fatou Aw 1, Malick Bodian 1, Kana Babaka 1, Aliou Alassane Ngaidé 2, Momar Dioum 3 and Serigne Abdou Ba 1 Abstract Background: Cardiovascular complications in Marfan syndrome (MFS) make all its seriousness. Taking as a basis the Ghent criteria, we conducted a family screening from an index case. The objective was to describe the clinical characteristics of MFS anomalies and to detect cardiovascular complications in our patients. Case presentation: Six subjects were evaluated. Patients had to be in the same uterine siblings of the index case or be a descendant. The objective was to search for MFS based on the diagnostic criteria of Ghent and, subsequently, detecting cardiovascular damage. The average age was 24 years. The examination revealed three cases of sudden death in a context of chest pain. Five subjects had systemic involvement with a score 7 that allowed to the diagnosis of MFS. Two patients had simultaneously ectopia lentis and myopia. In terms of cardiovascular damage, there were three cases of dilatation of the aortic root, two cases of aortic dissection of Stanford s type A with severe aortic regurgitation in one case and moderate in the other. There were three patients with moderate mitral regurgitation with a case by valve prolapse. Conclusion: The family screening is crucial in Marfan syndrome. It revealed serious cardiovascular complications including sudden death and aortic dissection. Background Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a genetic disease with autosomal dominant transmission, usually related to a mutation in the fibrillin gene type 1. The possibility of cardiovascular complications justifies a systematic family screening when a case is discovered [1]. This syndrome is characterized by musculoskeletal, cardiovascular and ocular damages. Its diagnosis is based on the Ghent criteria [2] which are of great importance in a context where the genetic study is inaccessible, expensive with a long waiting time of results. Taking as a base the new Ghent criteria [2], we conducted a family screening from an index patient in whom the diagnosis of MFS was made. The objectives were to look for clinical anomalies characteristics of MFS and detect cardiovascular complications related, in the family. * Correspondence: sarrsimantoine@yahoo.fr 1 Department of Cardiology, Teaching Hospital Aristide Le Dantec, PO Box 6003, Dakar Etoile, Sénégal Full list of author information is available at the end of the article Case presentation We were interested in relatives of a patient with MFS and cardiovascular damage, at the Teaching Hospital Aristide Le Dantec in Dakar, from January to March Patients had to be in the same uterine siblings of the index case. Their descendants were also included. Relatives who refused to participate in the study were not included. We identified the siblings of the index case and had made a briefing on the MFS and its complications. The objectives of the work were specified and the consent of the subjects required. Subsequently, subjects were examined clinically and complementary explorations carried out. Computed tomography was made in a case of anomaly indicating namely the dilation of an aortic segment or the existence of an aortic dissection. Ethical considerations This study showed no risk for participants, its purpose was clear to them so they can give their consent. A sheet The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Sarr et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2017) 17:193 Page 2 of 6 was prepared for this. The results were communicated to them and support was offered. Parameters studied The clinical evaluation focused on: Search of functional signs, The following constants and anthropometric data: weight, height, body mass index, waist circumference, blood pressure in both arms, the arm span on height ratio, the upper segment on the lower segment (US / LS). A complete physical examination, which was particularly interested in cardiovascular, morphoskeletal, and ocular abnormalities in search of new diagnostic criteria of Ghent. The diagnosis was selected according to the following different possibilities [3]: In the absence of family history. 1. Aortic root dilatation (Z score 2) or aortic dissection and ectopia Lentis = Marfan syndrome. 2. Aortic root dilatation (Z score 2) or aortic dissection and FBN1 = Marfan syndrome. 3. Aortic root dilatation (Z score 2) or aortic dissection and systemic score 7 points = Marfan syndrome. 4. Ectopia lentis and FBN1 with known aortic root dilatation or aortic dissection = Marfan syndrome. In the presence of family history. 5. Ectopia lentis and family history of Marfan syndrome (as defined above) = Marfan syndrome. 6. A systemic score 7 points and family history of Marfan syndrome = Marfan syndrome. 7. Aortic Root Dilatation (Z score 2 above 20 years old, 3 below 20 years old) or aortic dissection + family history of Marfan syndrome = Marfan syndrome. All subjects had been consulted by an ophthalmologist (research lens dislocation, myopia...) The paraclinical evaluation consisted of achieving: A resting electrocardiogram (ECG) The analysis clarified the nature of rhythm, looking for abnormal rhythm or conduction disturbances of repolarization or signs of atrial or ventricular hypertrophy. A transthoracic echocardiography The review was done by a single operator who was looking for dilation, with or without aortic dissection. The measurements were carried out successively in longitudinal section major axis (aortic root), in the suprasternal cut (butt) and sectional subcostal (abdominal aorta). We also were interested in valvular structures in search of ballooning or prolapse, valvular leakage. Cavitary dimensions were also appreciated as the systolic function of both ventricles. Radiological examinations - The chest X-ray was looking for pneumothorax. - The pelvis X-ray was looking for acetabular protrusion. - The chest computed-tomography was done in a case of abnormalities of the aorta Doppler echocardiography. It specified dimensions of the aorta, the existence and extent of aortic dissection as well as its complications. After the collection of clinical and laboratory data, we calculated the systemic involvement score (Table 1). After clinical evaluation and paraclinical, according to found damages, they were offered medical care and / or surgical. Epidemiological aspects In total, six subjects were screened. All were male. The average age was 24 years, with extremes of 14 and 42 years. We reported three cases of sudden death in the family: mother and two half-brothers of the index case. Among these, the deaths had occurred in a context of physical effort and preceded by chest pain. One of the subjects was an active smoker of 6 packs per year. They were of low socioeconomic status and had no support. Table 1 Systemic score of Marfan syndrom Systemic involvement Points Wrist and thumb sign 3 Wrist or thumb sign 1 Pectus carinatum deformity 2 Pectus excavatum or chest asymmetry 1 Hindfoot deformity 2 Plain flat foot 1 Spontaneous pneumothorax 2 Dural ectasia 2 Protusio acetabuli 2 Scoliosis or thoracolumbar kyphosis 1 Reduced elbow extension 1 3 of 5 facial features 1 Skin striae 1 Severe myopia (> 3 diopters) 1 Mitral valve prolapse 1 Reduced upper segment / lower segment 1 (US/LS) and increased arm span / height (Facial features: dolicocephaly, malar hypoplasia, enophthalmos, retrognathia, and down-slanting palpebral fissures) Maximum total: 20 points; a score 7 is considered a positive systemic score
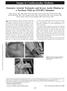
3 Sarr et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2017) 17:193 Page 3 of 6 Three of them were students, two were fishermen and one was a gardener. Clinical aspects The size was an average of 179 cm with extremes of 168 and 192 cm. Two patients (2/6) had functional signs: one had palpitations, and the other had episodic precordialgia not related to effort. Two patients had a heart murmur. It was in one, a diastolic murmur latero-sternal 3/6, and, in the other, an apical systolic murmur 2/6. Five patients (5/6) had systemic involvement with a score 7 (Fig. 1). The ocular examination showed ectopia lentis and coexisting myopia in two patients (2/6) (Table 2). Paraclinical aspects The echocardiography highlighted dilation of the aortic root in two cases. There were two cases of aortic dissection of Stanford s type A with severe aortic regurgitation in one and moderate in the other (Fig. 2). There were also three cases of moderate mitral regurgitation with a case of mitral valve prolapse. The aortic abnormalities were confirmed by computed tomography. Various anomalies are summarized in Table 3. The application of the Ghent criteria supported the findings of MFS in 5 of 6 cases as shown in Table 4. Therapeutic aspects All patients in whom the diagnosis of MFS was retained ha a beta blocker. A subject (1 subject) had a surgical repair of aortic dissection by Bentall procedure with a good result in more than a year now. He is, moreover, under effective anticoagulation. The second case of aortic dissection (about 4) could not be operated until now for lack of funds. Annual monitoring clinical and paraclinical (aortic root, changes in valvular heart disease). Subjects 1 and 3 are awaiting surgical treatment of the eye. Discussion and conclusion MFS is characterized by various musculoskeletal violations. They are at the forefront of clinical expression. These include, among other things, the dolichostenomelia using the arm span on height ratio. This ratio normally equal to 1, is around 1.03 in 80% of patients and becomes a criterion from 1.05 [3]. In our work, this ratio was increased in 4/6 subjects. Signs of the thumb and wrist are the witnesses of the arachnodactyly as well as ligamentous laxity. [3] Regarding chest deformities, 2 subjects had kyphosis (subjects 4 and 5). Subjects with Fig. 1 Clinical anomalies of a patient. a arachnodactyly; b: plain flat foot (c) dolicocephaly and malar hypoplasia; d High arched palate
4 Sarr et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2017) 17:193 Page 4 of 6 Table 2 Summary of clinical features of the patients Parameters P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 Total Height Mean 1.79 Arm span/height ratio > 1, 05 yes yes yes yes no no 4 Reduced US/LS yes yes yes yes yes no 5 Face: - Dolicocephaly yes yes yes yes yes no 5 - Enophtalmos yes yes yes yes yes no 5 - Down-slanting palpebral fissures yes no no no yes no 1 - Malar hypoplasia yes yes yes yes yes no 5 - Retrognathia yes yes yes yes yes no 5 Pectus carinatum no no no no no no 0 Pectus excavatum yes yes yes no yes no 4 Thumb sign yes yes no yes yes no 4 Wrist thumb yes yes no no yes no 3 Scoliosis no no no no no no 0 Thoracolumbar kyphosis no no no yes yes no 2 Plain plat foots yes yes yes yes yes no 5 Reduced elbow extension yes no yes no no no 2 Skin striae yes yes yes yes yes no 5 P patient US/LS upper segment/lower segment ratio Fig. 2 Images of aortic dissection of a patient. a Transthoracic echocardiography parasternal long axis view showing the dilation of aorta and the intimal flap; b Transthoracic echocardography parasternal long axis view showing a mitral valve prolapse; c Computed-tomography scan showing an aortic dissection; d Cardiac surgery of the patient
5 Sarr et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2017) 17:193 Page 5 of 6 Table 3 Summary of paraclinical features Anomalies P1 (index case) P2 P3 P4 P5 P 6 Number Left ventricular hypertrophia yes no no no no no 1 Left ventricular dilatation yes no no no no no 1 Aortic dissection yes no no yes no no 2 Aortic dilatation yes yes no yes no no 3 Aortic regurgitation yes no no yes no no 2 Mitral valve prolapse no no no no yes no 1 Mitral regurgitation no yes yes no yes no 3 Protrusio acetabulae no yes no yes no no 2 P patient MFS have valgus flat feet since childhood [3, 4], a result of laxity. This sign was standing in the subjects studied. Acetabular protrusion was found in 2 subjects. Kwang find them in 77% of reported cases. However, its presence does not have an impact on the final diagnosis because of its etiology which is variable and does not correlate to the presence of ectopia lentis or aortic disease [5]. Cardiovascular damage will determine the vital prognosis due to the risk of aortic dissection, often preceded by dilation and valvular disease [6]. They were described in 1943 by Bear, Tausig and Oppenheimer who reported two cases of sudden death in young adults with two dolichostenomelia and fusiform aneurysm of the ascending aorta. The histological examination had revealed the causal lesion of cardiovascular events like medial necrosis described by Gsell and Erdhein [7]. Acute aortic dissection is the most dangerous complication and the most common cause of death. The risk of dissection of the ascending aorta increases with the degree of aortic dilatation. The dilatation of the ascending aorta is observed in 60 80% of patients with MFS. It also represents a major diagnostic criterion. Conventionally it interests the sinus of Valsalva realizing expansion in onion bulb and the proximal portion of the ascending aorta [8]. This dilatation can affect the descending aorta in a minority of patients [9]. Aortic dissection usually occurs in the ascending aorta, but can extend at the butt of the neck vessels and the descending aorta [10]. It is more likely to occur if: - The dilatation is important: it is considered that the risk is low (though not zero) when the aortic diameter at the sinuses of Valsalva remains below 50 mm. Similarly, it is outstanding in the absence of dilation. The aortic diameter is regarded as the most powerful predictor of aortic dissection [11]; - The dilatation is fast: the examination has to be repeated to confirm the value by another imaging technique; - Aortic dilatation is diffuse and extends beyond the sino-tubular junction. - A parent who experienced aortic dissection without significant dilatation; - The existence of high blood pressure. The dissection of the descending aorta without ascending aortic dissection is rare because it is usually an extension of the ascending dissection [9]. This damage of the aorta exposes to his break and thus to sudden death. This complication is one of the assumptions in cases of sudden death recorded (2 cases). A valve disease can also be observed in the MFS. The aortic type may be related to the dilation of the aortic root in the absence of valvular structural abnormality. There is, in fact, a misalignment of the semilunar aortic valve by the deformation of the aortic root. Aortic regurgitation can also complicate a proximal aortic dissection [12]. The mitral involvement is common but is generally limited to prolapse with minimal or moderate leakage. It was noted in three cases in our work. There was a case of valve prolapse. Table 4 Ghent criteria for our patients P1 (index case) P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 Ascending aorta Dilatation yes: Z score 3,01 yes no yes no no Dissection yes no no yes no no Ectopia lentis yes no yes no no no Systemic involvement yes yes yes yes yes no Family history no yes yes yes yes yes Diagnosis of Marfan syndrom retained yes yes yes yes yes no P patients
6 Sarr et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2017) 17:193 Page 6 of 6 Moreover, it seems that the prevalence of ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias was higher in patients with MFS than in the general population, even in the absence of valvular leakage [13]. Rare cases of cardiac dilatation unrelated to a possible regurgitation were reported as a few cases of conduction disturbances. They might reflect a primary abnormality of the heart muscle [6, 14]. The indication for surgery was put in 2 patients for aortic dissection of Stanford s type A (subjects 1 and 4). Only about 1 had a Bentall procedure, this after a fundraiser. This is an expensive procedure, therefore, inaccessible to our subjects of low socioeconomic level. The surgery was life-saving for patients with MFS. Indeed, the average life expectancy which was 32 years is now close to that of the general population due to early surgery [15]. This prognostic improvement is the fact of several parameters. These include a better understanding of the disease, family screening but also the most accurate assessment of aortic risk authorized by imaging techniques such as transthoracic echocardiography and cardiac magnetic resonance imaging [15]. The family screening is crucial in Marfan syndrom. Diagnostic criteria have helped to detect the disease in 5 patients of 6. Similarly, it has revealed serious cardiovascular complications including sudden death and aortic dissection. Abbreviation MFS: Marfan syndrome Acknowledgements MBN, MD, AM, AK are the members of the supervising team of the department of cardiology of teaching hospital Aristide Le Dantec. SAB is the chief of department. Funding There is no funding for this study. Availability of data and materials The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Authors contributions SAS initiated this study, was the operator who made the transthoracic echocardiography of all the patients and wrote this article. SD analyzed the results of this study, made the review of literature and wrote the article. FA and MB analyzed the results of the study, and helped for the screening of the family and other exams and interpretation. KB made the review of literature with SD, analyzed the results of this study with SD, did the translation of this article in English, made final corrections, submitted this article according to the review criteria and made the corrections after the reviewer comments. AAN and MD did the review of litterature, corrected this article and made contributions. SAB did the final corrections before the article be submitted. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Ethics approval and consent to participate This study has the agreement of the local committee of university in Dakar. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor of this journal. Consent for publication Consent for publication is obtained by subjects. Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of clinical information and clinical images. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. The authors declare that they have no financial competing interest. Author details 1 Department of Cardiology, Teaching Hospital Aristide Le Dantec, PO Box 6003, Dakar Etoile, Sénégal. 2 Department of Cardiology, General Hospital of Grand Yoff, Dakar, Sénégal. 3 Department of Cardiology, Fann Teaching Hospital, Dakar, Sénégal. Received: 29 October 2016 Accepted: 12 July 2017 References 1. McBride A, Gargan M. Marfan syndrome. Curr Orthopaed. 2006;20: De Paepe A, Devereux RB, Dietz HC, Hennekam RC, Pyeritz RE. Revised diagnostic criteria for the Marfan syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 1996;62: Le Parc JM, Moclard S, Tubach F, Boileau C, Jondeau G, Muti C, et al. Le syndrome de Marfan et les fibrillinopathies. Rev Rhum. 2000;67(8): Stheneur C, Oberkampf B, Chevallier B. Syndrome de Marfan : critères diagnostiques et apport de la biologie moléculaire. Arch Pediatr. 2008; 15(5): McBride MT, Muldoon MP, Santore RF, Trousdale RT, Wenger DR. Protrusio acetabuli: diagnosis and treatment. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2001;9: Murdoch JL, Walker BA, Halpern BL, Kuzma JW, McKusick VA. Life expectancy and causes of death in the Marfan syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1972;286: Leu HJ. Erdheim-Gsell medial necrosis and mucoid degeneration of the media as a cause of aorto-arterial aneurysm. Pathologico-anatomical analysis of 150 excised vessels. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1988;118(18): Devereux RB, Roman MJ. Aortic disease in Marfan s syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(17): DE Backer J, Loeys B, De Paepe A. Marfan and Marfan-like syndromes. Artery Res. 2009;3: Crawford ES, Coselli JS, Svensson LG, Safi HJ, Hess KR. Diffuse aneurysmal disease (chronic aortic dissection, Marfan and mega aorta syndrome) and multiple aneurysm. Ann Surg. 1990;211: Gott VL, Greene PS, Alejo DE, Cameron DE, Naftel DC, Miller C, et al. Replacement of the aortic root in patients with Marfan s syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1999;340: Meuleman C, Jondeau G. Atteinte aortique dans le syndrome de Marfan. MT cardio. 2005;1(6): Yetman AT, Bornemeier RA, MMccrindle BW. Long-term outcome in patients with Marfan syndrome: is aortic dissection the only cause of sudden death? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003;41(2): Savolainen A, Kupari M, Toivonen L, Kaitila I, Vitasalo M. Abnormal ambulatory electrocardiographic findings in patients with the Marfan syndrome. J Intern Med. 1997;241: Silverman DI, Burton KJ, Gray J, Bosner MS, Kouchoukos NT, Roman MJ, et al. Life expectancy in the Marfan syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 1995;75: Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and we will help you at every step: We accept pre-submission inquiries Our selector tool helps you to find the most relevant journal We provide round the clock customer support Convenient online submission Thorough peer review Inclusion in PubMed and all major indexing services Maximum visibility for your research Submit your manuscript at
Case report. Open Access. Abstract
 Open Access Case report Late diagnosis of Marfan syndrome with fatal outcome in a young male patient: a case report Aurora Bakalli 1 *, Tefik Bekteshi 1, Merita Basha 2, Afrim Gashi 3, Afërdita Bakalli
Open Access Case report Late diagnosis of Marfan syndrome with fatal outcome in a young male patient: a case report Aurora Bakalli 1 *, Tefik Bekteshi 1, Merita Basha 2, Afrim Gashi 3, Afërdita Bakalli
CLINICAL INFORMATION SHEET
 CLINICAL INFORMATION SHEET Marfan syndrome and related aortic aneurysm syndromes Patient information Name: First Name(s): Sex: M F Date of Birth (dd/mm/yyyy): / / Address: Referring Physician: Referring
CLINICAL INFORMATION SHEET Marfan syndrome and related aortic aneurysm syndromes Patient information Name: First Name(s): Sex: M F Date of Birth (dd/mm/yyyy): / / Address: Referring Physician: Referring
A Case Of Marfan Syndrome With Ascending And Arch Of Aorta Aneurysm Presenting With Type A- Dissection Of Aorta.
 A Case Of Marfan Syndrome With Ascending And Arch Of Aorta Aneurysm Presenting With Type A- Dissection Of Aorta. Dr E Srikanth, Dr Ravi Srinivas MD.DM, Dr O Adikesava Naidu MD.DM, FACC,FESC. Dr Y V Subba
A Case Of Marfan Syndrome With Ascending And Arch Of Aorta Aneurysm Presenting With Type A- Dissection Of Aorta. Dr E Srikanth, Dr Ravi Srinivas MD.DM, Dr O Adikesava Naidu MD.DM, FACC,FESC. Dr Y V Subba
A growth disturbance and not a disorder with ligamentous laxity
 Marfan Syndrome A growth disturbance and not a disorder with ligamentous laxity 1 in 5,000-10,000 extensive phenotypic variability Fibrillin-1 abnormality Chromsome no. 15 Different forms of mutations
Marfan Syndrome A growth disturbance and not a disorder with ligamentous laxity 1 in 5,000-10,000 extensive phenotypic variability Fibrillin-1 abnormality Chromsome no. 15 Different forms of mutations
Diseases of the aorta: Pediatric and adult clinical presentation of the main syndromes. Birgit Donner Universitäts-Kinderspital beider Basel
 Diseases of the aorta: Pediatric and adult clinical presentation of the main syndromes Birgit Donner Universitäts-Kinderspital beider Basel Seite 2 Pubmed Results >10.000 publications/10 yrs Seite 3 Which
Diseases of the aorta: Pediatric and adult clinical presentation of the main syndromes Birgit Donner Universitäts-Kinderspital beider Basel Seite 2 Pubmed Results >10.000 publications/10 yrs Seite 3 Which
Clinical Characteristics of Marfan Syndrome in Korea
 Original Article Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Clinical Characteristics of Marfan Syndrome in Korea A Young Lim, MD 1, Ju Sun Song, MD 2, Eun Kyoung Kim, MD 1,
Original Article Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Clinical Characteristics of Marfan Syndrome in Korea A Young Lim, MD 1, Ju Sun Song, MD 2, Eun Kyoung Kim, MD 1,
MARFANS SYNDROME-A CASE REPORT
 TJPRC:International Journal of Cardiology, Echocardiography & Cardiovascular Medicine (TJPRC:IJCECM) Vol. 1, Issue 1 Jun 2015 1-6 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. MARFANS SYNDROME-A CASE REPORT MEENA, PRAVEENA, PRIYA &
TJPRC:International Journal of Cardiology, Echocardiography & Cardiovascular Medicine (TJPRC:IJCECM) Vol. 1, Issue 1 Jun 2015 1-6 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd. MARFANS SYNDROME-A CASE REPORT MEENA, PRAVEENA, PRIYA &
Marfan s Syndrome Meraj Ud Din Shah MD, DM, FICC
 91 Marfan s Syndrome Meraj Ud Din Shah MD, DM, FICC Case Report: A 2 year male child was having routine check up for respiratory infection and was detected to have grade 3/6 murmur in precordium. Patient
91 Marfan s Syndrome Meraj Ud Din Shah MD, DM, FICC Case Report: A 2 year male child was having routine check up for respiratory infection and was detected to have grade 3/6 murmur in precordium. Patient
(i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at
 1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
1 Supplementary Note Clinical descriptions of families (i) Family 1. The male proband (1.III-1) from European descent was referred at age 14 because of scoliosis. He had normal development. Physical evaluation
Random Pearls in Dysmorphology and Genetics
 Random Pearls in Dysmorphology and Genetics Marilyn C. Jones Professor of Clinical Pediatrics, UCSD Wellesley College, BA Columbia University P&S, MD Pediatric Residency and Fellowship in Dysmorphology,
Random Pearls in Dysmorphology and Genetics Marilyn C. Jones Professor of Clinical Pediatrics, UCSD Wellesley College, BA Columbia University P&S, MD Pediatric Residency and Fellowship in Dysmorphology,
The Prevalence of Marfan Syndrome in Korea
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epidemiology, Occupation & Environmental Medicine https://doi.org/.6/jkms.7...76 J Korean Med Sci 7; : 76-8 The of Marfan Syndrome in Korea Shin Yi Jang, Su Ra Seo, Seung Woo Park, and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epidemiology, Occupation & Environmental Medicine https://doi.org/.6/jkms.7...76 J Korean Med Sci 7; : 76-8 The of Marfan Syndrome in Korea Shin Yi Jang, Su Ra Seo, Seung Woo Park, and
Marfan syndrome: diagnosis and management. JCS Dean Consultant and Honorary Reader, Department of Medical Genetics, Medical School, Aberdeen, Scotland
 PAPER 2007 Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh Consultant and Honorary Reader, Department of Medical Genetics, Medical School, Aberdeen, Scotland ABSTRACTThe diagnosis of Marfan syndrome requires
PAPER 2007 Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh Consultant and Honorary Reader, Department of Medical Genetics, Medical School, Aberdeen, Scotland ABSTRACTThe diagnosis of Marfan syndrome requires
Marfan syndrome affecting four generations of a family without ocular involvement
 Postgrad Med J (1991) 67, 538 542 The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1991 Marfan syndrome affecting four generations of a family without ocular involvement A.B. Bridges, M. Faed', M. Boxer', W.M.
Postgrad Med J (1991) 67, 538 542 The Fellowship of Postgraduate Medicine, 1991 Marfan syndrome affecting four generations of a family without ocular involvement A.B. Bridges, M. Faed', M. Boxer', W.M.
Marfan syndrome: Report of two cases with review of literature
 Case Report Marfan syndrome: Report of two cases with review of literature AK Randhawa, C Mishra 1, SB Gogineni 2, S Shetty 2 Departments of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Luxmi Bai Institute of Dental Sciences
Case Report Marfan syndrome: Report of two cases with review of literature AK Randhawa, C Mishra 1, SB Gogineni 2, S Shetty 2 Departments of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Luxmi Bai Institute of Dental Sciences
Triathlon Canada Pre-Participation Medical Exam
 Triathlon Canada Pre-Participation Medical Exam This letter is to outline the guidelines for Triathlon Canada s policy for Athlete Pre-Participation Medical Clearance. Guidance to doctors As a member nation
Triathlon Canada Pre-Participation Medical Exam This letter is to outline the guidelines for Triathlon Canada s policy for Athlete Pre-Participation Medical Clearance. Guidance to doctors As a member nation
Congenital Aortopathies Marfans, Loeys-Dietz, ACTA 2, etc. DATE: October 9 th, 2017 PRESENTED BY: Cristina Fuss, MD
 Congenital Aortopathies Marfans, Loeys-Dietz, ACTA 2, etc. DATE: October 9 th, 2017 PRESENTED BY: Cristina Fuss, MD 24 yof present with SoB 9/4/2017 2 24yo F Presenting to local ED with SoB No other pertinent
Congenital Aortopathies Marfans, Loeys-Dietz, ACTA 2, etc. DATE: October 9 th, 2017 PRESENTED BY: Cristina Fuss, MD 24 yof present with SoB 9/4/2017 2 24yo F Presenting to local ED with SoB No other pertinent
Neonatal Marfan Syndrome: Report of Two Cases
 Case Report Iran J Pediatr Feb 2013; Vol 23 (No 1), Pp: 113-117 Neonatal Marfan Syndrome: Report of Two Cases Ghandi, Yazdan 1, MD; Zanjani, Keyhan S. 1,2 *, MD; Mazhari-Mousavi, Seyed-Eshagh 1, MD; Parvaneh,
Case Report Iran J Pediatr Feb 2013; Vol 23 (No 1), Pp: 113-117 Neonatal Marfan Syndrome: Report of Two Cases Ghandi, Yazdan 1, MD; Zanjani, Keyhan S. 1,2 *, MD; Mazhari-Mousavi, Seyed-Eshagh 1, MD; Parvaneh,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Marfan syndrome: Getting to the root of the problem Franken, Romy. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Marfan syndrome: Getting to the root of the problem Franken, Romy Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Franken, R. (2016). Marfan syndrome: Getting
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Marfan syndrome: Getting to the root of the problem Franken, Romy Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Franken, R. (2016). Marfan syndrome: Getting
Effect of Angiotensine II Receptor Blocker vs. Beta Blocker on Aortic Root Growth in pediatric patients with Marfan Syndrome
 Effect of Angiotensine II Receptor Blocker vs. Beta Blocker on Aortic Root Growth in pediatric patients with Marfan Syndrome Goetz Christoph Mueller University Heart Center Hamburg Paediatric Cardiology
Effect of Angiotensine II Receptor Blocker vs. Beta Blocker on Aortic Root Growth in pediatric patients with Marfan Syndrome Goetz Christoph Mueller University Heart Center Hamburg Paediatric Cardiology
Dr Tracy Dudding Clinical Geneticist Hunter Genetics
 Dr Tracy Dudding Clinical Geneticist Hunter Genetics Genetic testing -Why? Confirm a clinical diagnosis and mode of inheritance Clarify management Identification of at risk family members Family planning
Dr Tracy Dudding Clinical Geneticist Hunter Genetics Genetic testing -Why? Confirm a clinical diagnosis and mode of inheritance Clarify management Identification of at risk family members Family planning
A 23 year old woman with Marfan syndrome and spine deformity (RCD code: I-2A.1)
 Journal of Rare Cardiovascular Diseases 2013; 1 (3): 122 128 www.jrcd.eu CASE REPORT Rare diseases of systemic circulation A 23 year old woman with Marfan syndrome and spine deformity (RCD code: I-2A.1)
Journal of Rare Cardiovascular Diseases 2013; 1 (3): 122 128 www.jrcd.eu CASE REPORT Rare diseases of systemic circulation A 23 year old woman with Marfan syndrome and spine deformity (RCD code: I-2A.1)
ROUTINE SURVEILLANCE FOR INDIVIDUALS WITH DOWN SYNDROME
 ROUTINE SURVEILLANCE FOR INDIVIDUALS WITH DOWN SYNDROME NEONATAL (Birth - 1 Month) Review parental concerns. Chromosomal karyotype; genetic counseling, if necessary. If vomiting or absence of stools, check
ROUTINE SURVEILLANCE FOR INDIVIDUALS WITH DOWN SYNDROME NEONATAL (Birth - 1 Month) Review parental concerns. Chromosomal karyotype; genetic counseling, if necessary. If vomiting or absence of stools, check
Inheritable Connective Tissue Diseases: Or It s Probably Not Marfan s. RJ Willes 4/23/2018
 Inheritable Connective Tissue Diseases: Or It s Probably Not Marfan s RJ Willes 4/23/2018 This pretty much sums it up. Inheritable Connective tissues diseases A homogenous collection of varied syndromes
Inheritable Connective Tissue Diseases: Or It s Probably Not Marfan s RJ Willes 4/23/2018 This pretty much sums it up. Inheritable Connective tissues diseases A homogenous collection of varied syndromes
Scoliotic curve patterns in patients with Marfan syndrome
 J Child Orthop (2008) 2:211 216 DOI 10.1007/s11832-008-0095-z ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Scoliotic curve patterns in patients with Marfan syndrome Yann Glard Æ Franck Launay Æ Grégory Edgard-Rosa Æ Patrick
J Child Orthop (2008) 2:211 216 DOI 10.1007/s11832-008-0095-z ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Scoliotic curve patterns in patients with Marfan syndrome Yann Glard Æ Franck Launay Æ Grégory Edgard-Rosa Æ Patrick
강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예
 대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
مارفان متلازمة = syndrome Marfan Friday, 15 October :19 - Last Updated Thursday, 11 November :07
 1 / 8 MARFAN SYNDROME Epidemiology Marfan syndrome is a generalized connective tissue disease affecting approximately 1 in 5000 to 10,000 individuals, with no racial, gender, or geographic predilection.
1 / 8 MARFAN SYNDROME Epidemiology Marfan syndrome is a generalized connective tissue disease affecting approximately 1 in 5000 to 10,000 individuals, with no racial, gender, or geographic predilection.
Marfan s Disease in Pregnancy. A Review Of Five Recent Cases and a Consideration of Guidelines. Dr Len Kliman.
 Marfan s Disease in Pregnancy A Review Of Five Recent Cases and a Consideration of Guidelines. Dr Len Kliman. Antoine Bernard-Jean Marfan (1858-1942). Son of a provincial medical practitioner who discouraged
Marfan s Disease in Pregnancy A Review Of Five Recent Cases and a Consideration of Guidelines. Dr Len Kliman. Antoine Bernard-Jean Marfan (1858-1942). Son of a provincial medical practitioner who discouraged
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Marfan Syndrome, Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms and File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_marfan_syndrome_thoracic_aortic_aneurysms_and_dissections_and_relat
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Marfan Syndrome, Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms and File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_marfan_syndrome_thoracic_aortic_aneurysms_and_dissections_and_relat
UK Genetic Testing Network Marfan syndrome testing guideline workshop
 UK Genetic Testing Network Marfan syndrome testing guideline workshop Executive summary 5 th September 2012, 10.30-3.15pm Royal College of Physicians, London Meeting report The UK Genetic Testing Network
UK Genetic Testing Network Marfan syndrome testing guideline workshop Executive summary 5 th September 2012, 10.30-3.15pm Royal College of Physicians, London Meeting report The UK Genetic Testing Network
Marfan's Syndrome : Natural History and Long-Term Follow-Up of Cardiovascular Involvement
 4 JACC Vol. 14, No. August 1989 :4-8 Marfan's Syndrome : Natural History and Long-Term Follow-Up of Cardiovascular Involvement DOMINIC L. MARSALESE, MD, DOUGLAS S. MOODIE, MD, FACC, MICHAEL VACANTE, DO,
4 JACC Vol. 14, No. August 1989 :4-8 Marfan's Syndrome : Natural History and Long-Term Follow-Up of Cardiovascular Involvement DOMINIC L. MARSALESE, MD, DOUGLAS S. MOODIE, MD, FACC, MICHAEL VACANTE, DO,
Summers, Kim, West, Jennifer, Peterson, Madelyn, Stark, Denis, McGill, James J., West, Malcolm
 Challenges in the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome Author Summers, Kim, West, Jennifer, Peterson, Madelyn, Stark, Denis, McGill, James J., West, Malcolm Published 2006 Journal Title Medical Journal of Australia
Challenges in the diagnosis of Marfan syndrome Author Summers, Kim, West, Jennifer, Peterson, Madelyn, Stark, Denis, McGill, James J., West, Malcolm Published 2006 Journal Title Medical Journal of Australia
Case Report Marfan Syndrome: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 595343, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/595343 Case Report Marfan Syndrome: A Case Report Rajendran Ganesh, Rajendran Vijayakumar, and Haridoss Selvakumar Department
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 595343, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/595343 Case Report Marfan Syndrome: A Case Report Rajendran Ganesh, Rajendran Vijayakumar, and Haridoss Selvakumar Department
Sports Participation in Patients with Inherited Diseases of the Aorta
 Sports Participation in Patients with Inherited Diseases of the Aorta Yonatan Buber, MD Adult Congenital Heart Service Leviev Heart Center Safra Childrens Hospital Disclosures None Patient Presentation
Sports Participation in Patients with Inherited Diseases of the Aorta Yonatan Buber, MD Adult Congenital Heart Service Leviev Heart Center Safra Childrens Hospital Disclosures None Patient Presentation
Marfan s Disease: Tricuspid and Mitral Valve Insufficiency with a Normal Aortic root
 Case Reports Marfan s Disease: Tricuspid and Mitral Valve Insufficiency with a Normal Aortic root Jacques Heibig, MD, FACC, FCCP,* Charles Robinson, MD, FRCP(C) and Mohammed E. Fawzy, MB, MRCP* * Consultant
Case Reports Marfan s Disease: Tricuspid and Mitral Valve Insufficiency with a Normal Aortic root Jacques Heibig, MD, FACC, FCCP,* Charles Robinson, MD, FRCP(C) and Mohammed E. Fawzy, MB, MRCP* * Consultant
Prognostic Significance of the Pattern of Aortic Root Dilation in the Marfan Syndrome
 1470 JACC Vol. 22, No. 5 November 1. 1993 :1470-6 VASCULAR DISEASE Prognostic Significance of the Pattern of Aortic Root Dilation in the Marfan Syndrome MARY J. ROMAN, MD, FACC, STACEY E. RICHARD B. DEVEREUX,
1470 JACC Vol. 22, No. 5 November 1. 1993 :1470-6 VASCULAR DISEASE Prognostic Significance of the Pattern of Aortic Root Dilation in the Marfan Syndrome MARY J. ROMAN, MD, FACC, STACEY E. RICHARD B. DEVEREUX,
Pregnancy, Heart Disease and Imaging. Hemodynamics. Decreased systemic vascular resistance. Physiology anemia
 Pregnancy, Heart Disease and Imaging Sangeeta Shah, MD, FASE, FACC Associate Professor, Ochsner Clinical School of Medicine Advanced CV Imaging and Adult Congenital Heart Disease New Orleans, LA Hemodynamics
Pregnancy, Heart Disease and Imaging Sangeeta Shah, MD, FASE, FACC Associate Professor, Ochsner Clinical School of Medicine Advanced CV Imaging and Adult Congenital Heart Disease New Orleans, LA Hemodynamics
Marfan syndrome is a variable, autosomal dominant connective tissue disorder, affecting
 c MAKING Correspondence to: Dr John CS Dean, Department of Medical Genetics, Medical School, Foresterhill, Aberdeen AB25 9ZD, UK; j.dean@abdn.ac.uk General cardiology MANAGEMENT OF MARFAN SYNDROME John
c MAKING Correspondence to: Dr John CS Dean, Department of Medical Genetics, Medical School, Foresterhill, Aberdeen AB25 9ZD, UK; j.dean@abdn.ac.uk General cardiology MANAGEMENT OF MARFAN SYNDROME John
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Likes ML, Johnston TA. Gastric pseudoaneurysm in the setting of Loey s Dietz Syndrome. Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2012;14(3):1-5
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Likes ML, Johnston TA. Gastric pseudoaneurysm in the setting of Loey s Dietz Syndrome. Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2012;14(3):1-5 University of Washington, Pediatrics, Seattle
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Likes ML, Johnston TA. Gastric pseudoaneurysm in the setting of Loey s Dietz Syndrome. Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2012;14(3):1-5 University of Washington, Pediatrics, Seattle
Pre-participation Screening for the Prevention of sudden Cardiac Death in Young Athletes. Thomas W. Allen, DO, MPH
 Pre-participation Screening for the Prevention of sudden Cardiac Death in Young Athletes Thomas W. Allen, DO, MPH Cardiovascular disorders are the leading cause of sudden death in young athletes accounting
Pre-participation Screening for the Prevention of sudden Cardiac Death in Young Athletes Thomas W. Allen, DO, MPH Cardiovascular disorders are the leading cause of sudden death in young athletes accounting
The transition of pediatric Marfan patients to adult care: a challenge and its risks
 Original Article The transition of pediatric Marfan patients to adult care: a challenge and its risks Veronika C. Stark 1, Katrin Doering 1, Yskert von Kodolitsch 2, Rainer Kozlik-Feldmann 1, Götz C. Mueller
Original Article The transition of pediatric Marfan patients to adult care: a challenge and its risks Veronika C. Stark 1, Katrin Doering 1, Yskert von Kodolitsch 2, Rainer Kozlik-Feldmann 1, Götz C. Mueller
University of Groningen. Marfan syndrome and related connective tissue disorders Aalberts, Jan
 University of Groningen Marfan syndrome and related connective tissue disorders Aalberts, Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Marfan syndrome and related connective tissue disorders Aalberts, Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The heart in Down syndrome Vis, J.C. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The heart in Down syndrome Vis, J.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Vis, J. C. (2011). The heart in Down syndrome General rights It is
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) The heart in Down syndrome Vis, J.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Vis, J. C. (2011). The heart in Down syndrome General rights It is
CRANIOFACIAL CHARACTERIZATION OF PATIENTS WITH MARFAN SYNDROME. Christian M. Johnson. Chapel Hill 2017
 CRANIOFACIAL CHARACTERIZATION OF PATIENTS WITH MARFAN SYNDROME Christian M. Johnson A thesis submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements
CRANIOFACIAL CHARACTERIZATION OF PATIENTS WITH MARFAN SYNDROME Christian M. Johnson A thesis submitted to the faculty at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of the requirements
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Marfan syndrome: Getting to the root of the problem Franken, Romy. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Marfan syndrome: Getting to the root of the problem Franken, Romy Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Franken, R. (2016). Marfan syndrome: Getting
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Marfan syndrome: Getting to the root of the problem Franken, Romy Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Franken, R. (2016). Marfan syndrome: Getting
Seminar. Marfan s syndrome
 Marfan s syndrome Daniel P Judge, Harry C Dietz Marfan s syndrome is a systemic disorder of connective tissue caused by mutations in the extracellular matrix protein fibrillin 1. Cardinal manifestations
Marfan s syndrome Daniel P Judge, Harry C Dietz Marfan s syndrome is a systemic disorder of connective tissue caused by mutations in the extracellular matrix protein fibrillin 1. Cardinal manifestations
Problems in Pediatrics: Pediatric Cardiology Cases
 Problems in Pediatrics: Pediatric Cardiology Cases Kristin C. Lombardi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Clinical Educator The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Pediatric Cardiologist,
Problems in Pediatrics: Pediatric Cardiology Cases Kristin C. Lombardi, M.D. Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Clinical Educator The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University Pediatric Cardiologist,
Evolving phenotype of Marfan s syndrome
 Archives of Disease in Childhood 1997;76:41 46 41 Evolving phenotype of Marfan s syndrome Department of Medical Genetics, St Mary s Hospital, Manchester K J Lipscomb J Clayton-Smith R Harris Correspondence
Archives of Disease in Childhood 1997;76:41 46 41 Evolving phenotype of Marfan s syndrome Department of Medical Genetics, St Mary s Hospital, Manchester K J Lipscomb J Clayton-Smith R Harris Correspondence
Case Report Anomalous Coronary Artery Origin in a Young Patient with Marfan Syndrome
 Hindawi Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2017, Article ID 3861923, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3861923 Case Report Anomalous Coronary Artery Origin in a Young Patient with Marfan Syndrome S.
Hindawi Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2017, Article ID 3861923, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3861923 Case Report Anomalous Coronary Artery Origin in a Young Patient with Marfan Syndrome S.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2008 October 3.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2007 March ; 4(3): 167 171. doi:10.1038/ncpcardio0797. Severe aortic and arterial aneurysms associated
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2007 March ; 4(3): 167 171. doi:10.1038/ncpcardio0797. Severe aortic and arterial aneurysms associated
WEST AFRICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
 WEST AFRICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE ORIGINAL ARTICLE Marfan Syndrome: A Study of a Nigerian Family and Review of Current Cardiovascular Management Syndrome de Marfan: A Study of a Family nigérian et de l
WEST AFRICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE ORIGINAL ARTICLE Marfan Syndrome: A Study of a Nigerian Family and Review of Current Cardiovascular Management Syndrome de Marfan: A Study of a Family nigérian et de l
EARLY ONSET MARFAN SYNDROME: ATYPICAL CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF TWO CASES
 18 (1), 2015 71-76 DOI: 10.1515/bjmg-2015-0008 ORIGINAL ARTICLE EARLY ONSET MARFAN SYNDROME: ATYPICAL CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF TWO CASES Ozyurt A 1,*, Baykan A 2, Argun M 2, Pamukcu O 2, Halis H 3, Korkut
18 (1), 2015 71-76 DOI: 10.1515/bjmg-2015-0008 ORIGINAL ARTICLE EARLY ONSET MARFAN SYNDROME: ATYPICAL CLINICAL PRESENTATION OF TWO CASES Ozyurt A 1,*, Baykan A 2, Argun M 2, Pamukcu O 2, Halis H 3, Korkut
Marfan syndrome and related heritable aortic disease
 Marfan syndrome and related heritable aortic disease Julie De Backer, MD, hd Department of Cardiology and Center for Medical Genetics University Hospital Ghent, Belgium 1 Overview Definition and Diagnostic
Marfan syndrome and related heritable aortic disease Julie De Backer, MD, hd Department of Cardiology and Center for Medical Genetics University Hospital Ghent, Belgium 1 Overview Definition and Diagnostic
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Marfan Syndrome AHS M2144 Notification File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: marfan_syndrome 01/01/2019 N/A 01/01/2020 01/01/2019 Description of
Corporate Medical Policy Marfan Syndrome AHS M2144 Notification File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: marfan_syndrome 01/01/2019 N/A 01/01/2020 01/01/2019 Description of
The revised Ghent nosology for the Marfan syndrome
 The revised Ghent nosology for the Marfan syndrome Bart L Loeys, Harry C Dietz, Alan C Braverman, Bert L Callewaert, Julie De Backer, Richard B Devereux, Yvonne Hilhorst-Hofstee, Guillaume Jondeau, Laurence
The revised Ghent nosology for the Marfan syndrome Bart L Loeys, Harry C Dietz, Alan C Braverman, Bert L Callewaert, Julie De Backer, Richard B Devereux, Yvonne Hilhorst-Hofstee, Guillaume Jondeau, Laurence
Oral manifestations of a rare variant of Marfan syndrome
 CASE REPORT Oral manifestations of a rare variant of Marfan syndrome Abhishek Sinha 1, Sandeep Kaur 2, Syed Ahmed Raheel 3, Kirandeep Kaur 4, Mohammed Alshehri 5 & Omar Kujan 3,6 1 Department of Orthodontics,
CASE REPORT Oral manifestations of a rare variant of Marfan syndrome Abhishek Sinha 1, Sandeep Kaur 2, Syed Ahmed Raheel 3, Kirandeep Kaur 4, Mohammed Alshehri 5 & Omar Kujan 3,6 1 Department of Orthodontics,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Marfan syndrome: Getting to the root of the problem Franken, Romy. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Marfan syndrome: Getting to the root of the problem Franken, Romy Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Franken, R. (2016). Marfan syndrome: Getting
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Marfan syndrome: Getting to the root of the problem Franken, Romy Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Franken, R. (2016). Marfan syndrome: Getting
Mitral Regurgitation in a Patient with the Madan Syndrome
 Mitral Regurgitation in a Patient with the Madan Syndrome I BERNARD SEGAL, M.D.,* HRATCH KASPARIAN, M.D.,** AND WILLIAM LIKOFF, M.D., F.C.C.P,t N 1896, MARFAN DESCRIBED THE GROSS skeletal manifestations
Mitral Regurgitation in a Patient with the Madan Syndrome I BERNARD SEGAL, M.D.,* HRATCH KASPARIAN, M.D.,** AND WILLIAM LIKOFF, M.D., F.C.C.P,t N 1896, MARFAN DESCRIBED THE GROSS skeletal manifestations
Pregnancy and aortic root growth in the Marfan syndrome: a prospective study
 European Heart Journal (2005) 26, 914 920 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehi103 Clinical research Pregnancy and aortic root growth in the Marfan syndrome: a prospective study Lilian J. Meijboom 1, Frederiek E.
European Heart Journal (2005) 26, 914 920 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehi103 Clinical research Pregnancy and aortic root growth in the Marfan syndrome: a prospective study Lilian J. Meijboom 1, Frederiek E.
Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Marfan syndrome
 Dormand and Mohiaddin Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2013, 15:33 REVIEW Open Access Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Marfan syndrome Helen Dormand 1 and Raad H Mohiaddin 2* Abstract This
Dormand and Mohiaddin Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2013, 15:33 REVIEW Open Access Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Marfan syndrome Helen Dormand 1 and Raad H Mohiaddin 2* Abstract This
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY DATA REPORT FORM
 Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
Patient ID Patient Study ID AVM - - Date of form completion / / 20 Initials of person completing the form mm dd yyyy Study period Preoperative Postoperative Operative 6-month f/u 1-year f/u 2-year f/u
Surgical Management of Mitral Regurgitation in Patients with Marfan Syndrome during Infancy and Early Childhood
 Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2015;48:7-12 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2015.48.1.7 Surgical Management of Mitral Regurgitation in
Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2015;48:7-12 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2015.48.1.7 Surgical Management of Mitral Regurgitation in
Progress in Pediatric Cardiology
 Progress in Pediatric Cardiology 34 (2012) 9 14 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Progress in Pediatric Cardiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ppedcard Marfan syndrome: Progress
Progress in Pediatric Cardiology 34 (2012) 9 14 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Progress in Pediatric Cardiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ppedcard Marfan syndrome: Progress
HTAD PATIENT PATHWAY
 HTAD PATIENT PATHWAY Strategy for Diagnosis and Initial Management of patients and families with (suspected) Heritable Thoracic Aortic Disease (HTAD) DISCLAIMER This document is an opinion statement reflecting
HTAD PATIENT PATHWAY Strategy for Diagnosis and Initial Management of patients and families with (suspected) Heritable Thoracic Aortic Disease (HTAD) DISCLAIMER This document is an opinion statement reflecting
CORRELATIONS BETWEEN SYSTEMIC FEATURES AND DENTAL ABNORMALITIES IN MITRAL VALVE PROLAPSE SYNDROME
 CORRELATIONS BETWEEN SYSTEMIC FEATURES AND DENTAL ABNORMALITIES IN MITRAL VALVE PROLAPSE SYNDROME Paloma Manea 1*, Cristina Maria Gavrilescu 1, Crînguţa Paraschiv 1, Irina Cotea 1, Dragoş Munteanu 1, Răzvan
CORRELATIONS BETWEEN SYSTEMIC FEATURES AND DENTAL ABNORMALITIES IN MITRAL VALVE PROLAPSE SYNDROME Paloma Manea 1*, Cristina Maria Gavrilescu 1, Crînguţa Paraschiv 1, Irina Cotea 1, Dragoş Munteanu 1, Răzvan
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS. Health Supervision for Children With Marfan Syndrome
 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS Health Supervision for Children With Marfan Syndrome Committee on Genetics ABSTRACT. This set of guidelines is designed to assist the pediatrician in caring for children
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS Health Supervision for Children With Marfan Syndrome Committee on Genetics ABSTRACT. This set of guidelines is designed to assist the pediatrician in caring for children
IMAGING the AORTA. Mirvat Alasnag FACP, FSCAI, FSCCT, FASE June 1 st, 2011
 IMAGING the AORTA Mirvat Alasnag FACP, FSCAI, FSCCT, FASE June 1 st, 2011 September 11, 2003 Family is asking $67 million in damages from two doctors Is it an aneurysm? Is it a dissection? What type of
IMAGING the AORTA Mirvat Alasnag FACP, FSCAI, FSCCT, FASE June 1 st, 2011 September 11, 2003 Family is asking $67 million in damages from two doctors Is it an aneurysm? Is it a dissection? What type of
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a
 CLINICIAN UPDATE Treatment of Aortic Disease in Patients With Marfan Syndrome Dianna M. Milewicz, MD, PhD; Harry C. Dietz, MD; D. Craig Miller, MD Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a heritable disorder of the connective
CLINICIAN UPDATE Treatment of Aortic Disease in Patients With Marfan Syndrome Dianna M. Milewicz, MD, PhD; Harry C. Dietz, MD; D. Craig Miller, MD Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a heritable disorder of the connective
Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (heds) vs. Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD): What s the Difference?
 Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (heds) vs. Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD): What s the Difference? There has been a major revision in the approach to joint hypermobility (JH) as a whole. To recognize
Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (heds) vs. Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD): What s the Difference? There has been a major revision in the approach to joint hypermobility (JH) as a whole. To recognize
The new Ghent criteria for Marfan syndrome: what do they change?
 The new Ghent criteria for Marfan syndrome: what do they change? G Faivre, Gwenaëlle Collod-Béroud, A Adès, A Arbustini, C Child, C Callewaert, B Loeys, C. Binquet, G Gautier, M. Mayer, et al. To cite
The new Ghent criteria for Marfan syndrome: what do they change? G Faivre, Gwenaëlle Collod-Béroud, A Adès, A Arbustini, C Child, C Callewaert, B Loeys, C. Binquet, G Gautier, M. Mayer, et al. To cite
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS. Health Supervision for Children With Marfan Syndrome
 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS Health Supervision for Children With Marfan Syndrome Committee on Genetics ABSTRACT. This set of guidelines is designed to assist the pediatrician in caring for children
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF PEDIATRICS Health Supervision for Children With Marfan Syndrome Committee on Genetics ABSTRACT. This set of guidelines is designed to assist the pediatrician in caring for children
University of Groningen. Marfan syndrome and related connective tissue disorders Aalberts, Jan
 University of Groningen Marfan syndrome and related connective tissue disorders Aalberts, Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Marfan syndrome and related connective tissue disorders Aalberts, Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Inferior vena cava stenosis: Echocardiographic diagnosis in Marfan syndrome
 OPEN ACCESS Images in cardiology Inferior vena cava stenosis: Echocardiographic diagnosis in Marfan syndrome Sami Nimer Ghazal*, Shady G Ouf Cardiology Division, Internal Medicine Department, King Fahd
OPEN ACCESS Images in cardiology Inferior vena cava stenosis: Echocardiographic diagnosis in Marfan syndrome Sami Nimer Ghazal*, Shady G Ouf Cardiology Division, Internal Medicine Department, King Fahd
Mitral Valve Disease. Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna
 Mitral Valve Disease Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna Fall 2008 Mitral Valve Stenosis Lecture Outline Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical features Diagnostic testing
Mitral Valve Disease Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna Fall 2008 Mitral Valve Stenosis Lecture Outline Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical features Diagnostic testing
WHAT IS MARFAN SYNDROME?
 THIS IS MY SON LIAM, HE DIED 4 YEARS AGO, AT THE AGE OF 27, HIS DEATH, A RUPTURE OF HIS MAIN HEART VALVE HAS BEEN ATTRIBUTED TO MARFANS SYNDROME. MY FATHER ALSO DIED AT THE AGE OF 27, WHEN I WAS ONLY 3
THIS IS MY SON LIAM, HE DIED 4 YEARS AGO, AT THE AGE OF 27, HIS DEATH, A RUPTURE OF HIS MAIN HEART VALVE HAS BEEN ATTRIBUTED TO MARFANS SYNDROME. MY FATHER ALSO DIED AT THE AGE OF 27, WHEN I WAS ONLY 3
Natural history of cardiovascular manifestations in Marfan syndrome
 Arch Dis Child 01;84:129 137 129 Department of Paediatrics H3-0, Emma Children s Hospital, Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, Meibergdreef 9, AZ Amsterdam, Netherlands CDMvanKarnebeek MSJNaeV
Arch Dis Child 01;84:129 137 129 Department of Paediatrics H3-0, Emma Children s Hospital, Academic Medical Center, University of Amsterdam, Meibergdreef 9, AZ Amsterdam, Netherlands CDMvanKarnebeek MSJNaeV
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW
 PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
PROSTHETIC VALVE BOARD REVIEW The correct answer D This two chamber view shows a porcine mitral prosthesis with the typical appearance of the struts although the leaflets are not well seen. The valve
S. Bruce Greenberg, MD FNASCI and President, NASCI Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences
 S. Bruce Greenberg, MD FNASCI and President, NASCI Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences No financial disclosures Aorta Congenital aortic stenosis/insufficiency
S. Bruce Greenberg, MD FNASCI and President, NASCI Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences No financial disclosures Aorta Congenital aortic stenosis/insufficiency
PREGNANCY AND CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE
 PREGNANCY AND CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE SIDDHARTH JADHAV M.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology E.B. Singleton Department of Pediatric Radiology Texas Children's Hospital COMMERCIAL DISCLOSURE - None Objectives
PREGNANCY AND CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE SIDDHARTH JADHAV M.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology E.B. Singleton Department of Pediatric Radiology Texas Children's Hospital COMMERCIAL DISCLOSURE - None Objectives
Very late recurrence of sinus of Valsalva aneurysm rupture after patch repair
 Lin et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:73 CASE REPORT Open Access Very late recurrence of sinus of Valsalva aneurysm rupture after patch repair Ting-Tse Lin 1, Hsiao-En Tsai 2, Lin Lin 1, Tsung-Yan Chen 2, Cheng-Pin
Lin et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:73 CASE REPORT Open Access Very late recurrence of sinus of Valsalva aneurysm rupture after patch repair Ting-Tse Lin 1, Hsiao-En Tsai 2, Lin Lin 1, Tsung-Yan Chen 2, Cheng-Pin
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial
 An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
An aneurysm is a localized abnormal dilation of a blood vessel or the heart Types: 1-"true" aneurysm it involves all three layers of the arterial wall (intima, media, and adventitia) or the attenuated
Surgical Procedures and Complications
 Radiological Society of North America, RSNA 2013 Refresher Course Program: Vascular Track Surgical Procedures and Complications Learning objectives Outline RC 112 : Key Concepts: Surgical Procedures and
Radiological Society of North America, RSNA 2013 Refresher Course Program: Vascular Track Surgical Procedures and Complications Learning objectives Outline RC 112 : Key Concepts: Surgical Procedures and
The Heart of the Matter
 The Heart of the Matter Is the Heart the Matter? --Chest pain in the Pediatric Patient-- 19th Interregional Symposium November 2, 2018 Session A, 9:35-10:50 am John-Charles Loo, MD Pediatric Cardiology,
The Heart of the Matter Is the Heart the Matter? --Chest pain in the Pediatric Patient-- 19th Interregional Symposium November 2, 2018 Session A, 9:35-10:50 am John-Charles Loo, MD Pediatric Cardiology,
Images in Cardiovascular Medicine
 Images in Cardiovascular Medicine Extensive Arterial Tortuosity and Severe Aortic Dilation in a Newborn With an EFEMP2 Mutation Maria Iascone, BSc, PhD; Maria Elena Sana, PhD; Laura Pezzoli, BSc; Paolo
Images in Cardiovascular Medicine Extensive Arterial Tortuosity and Severe Aortic Dilation in a Newborn With an EFEMP2 Mutation Maria Iascone, BSc, PhD; Maria Elena Sana, PhD; Laura Pezzoli, BSc; Paolo
Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms with a Genetic Basis
 Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms with a Genetic Basis Aws Hamid 1, Elizabeth Lee 1, Maryam Ghadimi Mahani 1, Brian Smiley 1, Jimmy C Lu 1,2, Adam L Dorfman 1,2, Prachi P Agarwal 1 Department of Radiology, University
Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms with a Genetic Basis Aws Hamid 1, Elizabeth Lee 1, Maryam Ghadimi Mahani 1, Brian Smiley 1, Jimmy C Lu 1,2, Adam L Dorfman 1,2, Prachi P Agarwal 1 Department of Radiology, University
Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease
 Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease Michael Vogel Kinderherz-Praxis München CHD missed in childhood Subsequent lesions after repaired CHD Follow-up of cyanotic heart disease CHD missed in
Echocardiography in Adult Congenital Heart Disease Michael Vogel Kinderherz-Praxis München CHD missed in childhood Subsequent lesions after repaired CHD Follow-up of cyanotic heart disease CHD missed in
Familial aggregation studies indicate that up to 20% of
 Mapping a Locus for Familial Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms and Dissections (TAAD2) to 3p24 25 Sumera N. Hasham, PhD; Marcia C. Willing, MD, PhD; Dong-chuan Guo, PhD; Ann Muilenburg, MA; Rumin He, MD; Van T.
Mapping a Locus for Familial Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms and Dissections (TAAD2) to 3p24 25 Sumera N. Hasham, PhD; Marcia C. Willing, MD, PhD; Dong-chuan Guo, PhD; Ann Muilenburg, MA; Rumin He, MD; Van T.
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Loeys-Dietz Syndrome OMIM number for disease 609192; 608967; 610380; 610168 Disease
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Loeys-Dietz Syndrome OMIM number for disease 609192; 608967; 610380; 610168 Disease
Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery
 Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery Dr. Amira Esmat, El Tantawy, MD Professor of Pediatrics Consultant Pediatric Cardiac Interventionist Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 23/2/2017
Debate in Management of native COA; Balloon Versus Surgery Dr. Amira Esmat, El Tantawy, MD Professor of Pediatrics Consultant Pediatric Cardiac Interventionist Faculty of Medicine Cairo University 23/2/2017
PECTUS EXCAVATUM WITH SPONTANEOUS TYPE 1 ECG BRUGADA PATTERN OR BRUGADA LIKE PHENOTYPE: ANOTHER BRUGADA ECG PHENOCOPY
 PECTUS EXCAVATUM WITH SPONTANEOUS TYPE 1 ECG BRUGADA PATTERN OR BRUGADA LIKE PHENOTYPE: ANOTHER BRUGADA ECG PHENOCOPY ANDRÉS RICARDO PÉREZ RIERA MD Chief of the Sector of Electro-Vectocardiography of the
PECTUS EXCAVATUM WITH SPONTANEOUS TYPE 1 ECG BRUGADA PATTERN OR BRUGADA LIKE PHENOTYPE: ANOTHER BRUGADA ECG PHENOCOPY ANDRÉS RICARDO PÉREZ RIERA MD Chief of the Sector of Electro-Vectocardiography of the
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
New Cardiovascular Devices and Interventions: Non-Contrast MRI for TAVR Abhishek Chaturvedi Assistant Professor. Cardiothoracic Radiology
 New Cardiovascular Devices and Interventions: Non-Contrast MRI for TAVR Abhishek Chaturvedi Assistant Professor Cardiothoracic Radiology Disclosure I have no disclosure pertinent to this presentation.
New Cardiovascular Devices and Interventions: Non-Contrast MRI for TAVR Abhishek Chaturvedi Assistant Professor Cardiothoracic Radiology Disclosure I have no disclosure pertinent to this presentation.
Aortic Regurgitation & Aorta Evaluation
 VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Regurgitation Valvular Lessions 2017 Aortic Regurgitation & Aorta Evaluation Jorge Eduardo Cossío-Aranda MD, FACC Chairman of Outpatient Care Department Instituto Nacional de Cardiología
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Regurgitation Valvular Lessions 2017 Aortic Regurgitation & Aorta Evaluation Jorge Eduardo Cossío-Aranda MD, FACC Chairman of Outpatient Care Department Instituto Nacional de Cardiología
Diseases of the Aorta
 Diseases of the Aorta ASE Review 2018 Susan E Wiegers, MD, FASE, FACC Professor of Medicine My great friend Dr. Roberto Lang Disclosure None related to this presentation 1 Objectives Aneurysm Dissection
Diseases of the Aorta ASE Review 2018 Susan E Wiegers, MD, FASE, FACC Professor of Medicine My great friend Dr. Roberto Lang Disclosure None related to this presentation 1 Objectives Aneurysm Dissection
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: Michael Shea, M.D., 2008 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Author: Michael Shea, M.D., 2008 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/
Marfan s S drome: Combined Composite Valve GrAeplacement of the Aortic Root and Transaortic Mihal Valve Replacement
 Marfan s S drome: Combined Composite Valve GrAeplacement of the Aortic Root and Transaortic Mihal Valve Replacement E. Stanley Crawford, M.D., and Joseph S. Coselli, M.D. ABSTRACT Echocardiographic studies
Marfan s S drome: Combined Composite Valve GrAeplacement of the Aortic Root and Transaortic Mihal Valve Replacement E. Stanley Crawford, M.D., and Joseph S. Coselli, M.D. ABSTRACT Echocardiographic studies
The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery
 Accepted Manuscript Chronic type A dissection: when to operate? Francois Dagenais, MD PII: S0022-5223(18)33131-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.11.032 Reference: YMTC 13781 To appear in: The
Accepted Manuscript Chronic type A dissection: when to operate? Francois Dagenais, MD PII: S0022-5223(18)33131-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.11.032 Reference: YMTC 13781 To appear in: The
Interventions of interest are: Testing for genes associated with connective tissue diseases
 Genetic Testing for Marfan Syndrome, Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms (204129) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/15 Next Review Date: 05/18 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 05/15, 05/16, 05/17 Preauthorization
Genetic Testing for Marfan Syndrome, Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms (204129) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/15 Next Review Date: 05/18 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 05/15, 05/16, 05/17 Preauthorization
