A Beginner's Guide to Brain CT in Acute Stroke
|
|
|
- Phillip Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Beginner's Guide to Brain CT in Acute Stroke Poster No.: C-2524 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. E. A. Noeman; Güstrow/DE Keywords: Ischemia / Infarction, Embolism / Thrombosis, Thrombolysis, CTAngiography, CT, Neuroradiology brain DOI: /ecr2012/C-2524 Any information contained in this pdf file is automatically generated from digital material submitted to EPOS by third parties in the form of scientific presentations. References to any names, marks, products, or services of third parties or hypertext links to thirdparty sites or information are provided solely as a convenience to you and do not in any way constitute or imply ECR's endorsement, sponsorship or recommendation of the third party, information, product or service. ECR is not responsible for the content of these pages and does not make any representations regarding the content or accuracy of material in this file. As per copyright regulations, any unauthorised use of the material or parts thereof as well as commercial reproduction or multiple distribution by any traditional or electronically based reproduction/publication method ist strictly prohibited. You agree to defend, indemnify, and hold ECR harmless from and against any and all claims, damages, costs, and expenses, including attorneys' fees, arising from or related to your use of these pages. Please note: Links to movies, ppt slideshows and any other multimedia files are not available in the pdf version of presentations. Page 1 of 34
2 Learning objectives The purpose of this exhibit is: 1- To have a systematic approach in evaluating brain CT. 2- To recognize and describe the early signs of acute ischemic stroke. 3- To exclude lesions that mimic acute ischemic stroke. Background Even in the era of diffusion and perfusion-weighted MRI, cranial computed tomography (CCT) remains the first-line diagnostic test - after physical examination- for the emergency evaluation of early ischemic stroke having the advantages of being available in most hospitals, available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, performed fast, easily performed in severely ill patients who are dependent on support and monitoring devices and above all CCT is sensitive for detection of intracranial hemorrhage. Stroke is considered the third most common cause of death and one of the leading causes of adult disability in North America, Europe, and Asia. Thrombolytic therapy with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-pa) is the treatment of choice for ischemic stroke provided that there is no contraindication to this treatment. However, the benefit of intravenous thrombolysis decreases steadily over time from symptom onset, so that the time window for intervention can be as narrow as 3 hours (19). "Time is brain", therefore having frontline radiologists to be proficient in interpreting the emergency CCT scan improves the efficiency of the whole pathway of care and is potentially life saving. Stroke can be defined as a rapid loss of brain function(s) due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. There are two major types of stroke: Page 2 of 34
3 a) ischemic (lack of blood flow) caused by blockage (thrombosis, arterial embolism) (nearly 80%). b) or a hemorrhage (leakage of blood) (20%). The goal of CT imaging in a patient with acute stroke is (4): 1- to exclude lesions that mimic stroke like intracranial hemorrhage, subdural hematoma, cerebritis etc.. 2- to define the extension of the ischemic brain tissues. 3- to identify the presence of stenosis or occlusion of major extra and intracranial arteries. The key principle behind successful interpretation when dealing with ischemic stroke is knowing "where" to look and "what" to look for (5). Imaging findings OR Procedure details Systematic approach to interpretation: (8) 1- Check the scout image. May see a fracture or gross abnormality. 2- A quick 'first pass' is recommend, noting gross pathology, followed by a more detailed analysis of the images. 3- Use the mnemonic 'ABBCS' to remember important structures. 4- Finally, extend search pattern to include orbits, sinuses, oropharynx, ears, craniocervical junction, face, vault and scalp. The "ABBCS System": A: Asymmetry: comparing one side with another. B: Blood:acute hemorrhage --> hyperdense compared to brain (Figure 1). Page 3 of 34
4 Fig. 1: Axial non-enhanced CT scan of the brain shows acute intracranial hemorrhage "hyperdense" (red arrows) in the right frontal lobe with perifocal edema "hypodense"(blue arrows). References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY B: Brain: * Abnormal density: - Hyperdensity: acute blood, tumour, bone, contrast media. Page 4 of 34
5 - Hypodensity: edema/infarct, air and tumour (Figure 2). Fig. 2: A- Axial non-enhanced brain CT demonstrates finger-like focal edema in the left parietal lobe with compression of the left lateral ventricle and displacement of the interhemispheric fissure towards the right side. B- After administration of contrast media, it revealed a solitary intra-axial supratentorial focal lesion with ringenhancement "blue arrows" which turned to be brain metastases. References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY * Displacement: - Midline shift (Figure 3). - Midline structures (falx cerebri, pituitary & pineal glands). - Asymmetry of CSF spaces. - Effacement of the basal cisterns and tonsillar herniation. * Grey/white matter differentiation (see later in early signs of infarction). Page 5 of 34
6 Fig. 3: Axial non-enhanced brain CT demonstrates extensive intracranial bleeding (red arrows) after brain contusion. Notice the total compression of the left lateral ventricle (yellow arrows) and the displacement of the midline towards the right side (blue arrows). Page 6 of 34
7 References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY C: CSF spaces: Cisterns, sulci and ventricles. * Sizes of the ventricles and sulci, in proportion to each other and the brain parenchyma. * Normal cisterns (quadrigeminal plate, suprasellar and the mid brain region) and fissures (interhemispheric and Sylvian). * Pathology may be primary, within a ventricle, or may result from secondary compression from adjacent brain pathology. * Diffuse brain swelling can result in ventricular compression and reduced conspicuity of the normal sulcal/gyral pattern. S: Skull and scalp: Assess the scalp for soft tissue injury. * Useful in patients where a full history is absent. * Help to localise coup and contracoup injuries. * Assess the bony vault underlying a soft tissue injury for evidence of a fracture (Figure 4). * Assess the bony vault for shape, symmetry and mineralisation. * Adjust windowing to optimise bony detail. Page 7 of 34
8 Fig. 4: Axial non-enhanced brain CT with (bone window) demonstrates longitudinal fracture of the right petrous bone (red arrow). Notice the hypodene material (blue arrow)(most probably blood) in the middle ear. References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY Main arterial blood supply of the brain: (Figure 5) Anterior cerebral artery (ACA): Supplies the medial part of the frontal and the parietal lobe and the anterior portion of the corpus callosum, basal ganglia and internal capsule. Middle cerebral artery (MCA): Page 8 of 34
9 Supplies the lateral surface of the hemisphere, except for the medial part of the frontal and the parietal lobe (ACA), and the inferior part of the temporal lobe (PCA). Posterior cerebral artery (PCA): Supplies parts of the midbrain, subthalamic nucleus, basal nucleus, thalamus, mesial inferior temporal lobe, and occipital and occipitoparietal cortices. Also supplies inferomedial part of the temporal lobe, occipital pole, visual cortex, and splenium of the corpus callosum. Besides, it is an important sources of collateral circulation for the middle cerebral artery (MCA) territory (18). Page 9 of 34
10 Fig. 5: Cerebral Arterial Territory: ACA: Anterior cerebral Artery, MCA: Middle cerebral Artery, PCA: Posterior cerebral Artery. References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY Page 10 of 34
11 Early Signs of Stroke 1- Hypodensity of the brain tissue: Hypodensity = irreversible ischemic brain damage * Appearance: - It appears as area(s) of hypoattenuation compared to nearby normal brain tissues (Figure 6, 7). * Value: - It is highly specific for irreversible ischemic brain damage when detected within first 6 hours. - Patients who present with symptoms of stroke and who demonstrate hypodensity on CT within first six hours were proven to have larger infarct volumes, more severe symptoms, less favorable clinical courses and they even have a higher risk of hemorrhage. - The presence of hypoattenuation affecting more than one-third of the MCA territory is a contraindication for revascularization because it has been demonstrated that hemorrhagic complications are associated with larger established infarcted lesions before treatment (1). * Explanation: - The reason we see hypodensity on CT is that an ischemia cytotoxic edema develops as a result of failure of the ion-pumps. - These fail due to an inadequate supply of ATP. Page 11 of 34
12 Fig. 6: A- Axial non-enhanced brain CT shows a large area of hypoattenuation in the territory of the right MCA (red arrows), after 24 hours of onset of clinical symptoms. BSame patient after 48 hours. Notice the well-demarcation of the Infarction. References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY Page 12 of 34
13 Fig. 7: Axial non-enhanced CT scans show: A) Hypodensity in the middle 1/3 of the territory of the left MCA (parietal lobe). B) Hypodensity in the posterior 1/3 of the territory of the right MCA (temporal lobe). C) Hypodensity in the territory of the right ACA (frontal lobe). D) Hypodensity in the territory of the left PCA (occipital lobe). References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY 2- The insular ribbon sign: Page 13 of 34
14 * Anatomy: - The insula or island of Reil is an "island" of cortex that lies at the base of the sylvian fissure, overlying the extreme capsule and claustrum. - The insular ribbon refers to the island of Reil, extreme capsule, and claustrum. * Appearance: - It is the loss of graywhite interface definition, reflects cytotoxic edema and relates to specificity of arterial anatomy. * Explanation: - The insular ribbon is supplied exclusively by the insular segment of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) and its claustral branches. - With interruption of MCA flow, the insular ribbon becomes the region most distal from the anterior and posterior cerebral collateral circulations (17,20). Fig. 17: Insular ribbon sign on the left in axial non contrast CT images, obtained in a 58-year-old man (a) 3 and (b) 26 hours after the onset of symptoms. References: G. Krumina; MR, CT and US centre, Medical Academy of Latvia, Riga, LATVIA 3- Disappearing basal ganglia sign: Page 14 of 34
15 * Anatomy (Figure 8): - The basal ganglia include the caudate nucleus, amygdala, claustrum, internal capsule, external capsule, extreme capsule, and lentiform nucleus. - The lentiform nucleus comprises the globus pallidus and putamen. - The caudate nucleus, globus pallidus, and putamen are collectively referred to as the corpora striatum. Page 15 of 34
16 Fig. 8: Anatomy of the basal ganglia References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY * Appearance: Page 16 of 34
17 - It appears as a loss of the normal delineation of the basal ganglia, with the affected basal ganglia exhibiting abnormal morphologic features (Figure 9). - This is best appreciated when a comparison is made between the affected basal ganglia and the contralateral side of the brain. * Explanation: - Normally, the lentiform nucleus and caudate nucleus are slightly hyperattenuated when compared with the surrounding white matter. When present, a vascular insult will usually manifest at CT as areas of hypoattenuation (Figure 10). - Is caused by MCA occlusion proximally to lenticulostriate arteries. Involvement of the lenticulostriate territory indicates that a proximal M1 occlusion must have been present (7,12). * DD considerations: - Include arterial dissection, trauma, vasculitis, and hemolytic uremic syndrome (7,12). Page 17 of 34
18 Fig. 9: Axial non-enhanced brain CT demonstrates the disappearance of the lateral border of the left basal ganglia in acute stroke patient. References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY Page 18 of 34
19 Fig. 10: Axial non-enhanced brain CT demonstrates well-demarcated infarction of the right basal ganglia (red arrows) in acute stroke patient. References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY 4- Loss of grey/white differentiation: * Appearance: Page 19 of 34
20 - Appears as loss of the normal distinction between the grey matter and the white matter (Figure 11). * Explanation: - White matter is of slightly reduced attenuation compared to grey matter due to increased fatty myelin content. - In an early infarct, oedema leads to loss of this differentiation. Fig. 11: A) Axial non-enhanced brain CT of acute stroke patient demonstrating loss of grey/white matter differentiation in the posterior 1/3 of the territory of the right MCA (red arrows) as an early sign of infarction compared to normal brain tissues on the normal left side (blue arrow). Note the old posterior infarction on the left side (green arrows). B) Axial non-enhanced brain CT demonstrates loss of grey/white matter differentiation in the territory of right MCA (blue arrows). References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY 5- Hyperdense artery sign: The hyperdense artery sign represents stasis of flow due to arterial thrombus, most frequently seen in MCA. a) Hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign (HMCAS)(Figure 12, 13): * Incidence: Page 20 of 34
21 - It has been reported that HAS in MCA is present in 75% of the infarctions in the first 90 minutes and in 15% from hour 12 to hour 24 (9). * Value: - The presence or absence of (HMCAS) on NCCT can predict also the thrombus volume. - Thrombus volumes are significantly larger in patients with HMCAS than in those without HMCAS in ICA and M1 occlusions. - An association between a hyperattenuating MCA sign and the location of infarction has also been found. Patients with a proximal hyperattenuating MCA sign developed cortical and larger deep MCA infarctions more often(10). * DD: - False positive sign have been documented in patients with calcified atherosclerosis or high hematocrit levels (10). Fig. 12: a) Axial non-enhanced brain CT image shows hyperattenuation in the proximal (M1) segment of the left MCA "hyperdense MCA-Sign"(red arrow). b) reformatted images from CT-angiography of the same patient show the apparent absence of the same vessel segment(red arrows) compared to the normal vessel right MCA (blue arrows). References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY Page 21 of 34
22 Fig. 13: A) Axial non-enhanced brain CT demonstrates "hyperdense MCA sign" of the left MCA. B) 3D-Reconstruction image of the intracranial circulation demonstrates the occlusion of the left MCA confirming the diagnosis. References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY b) Hyperdense dot sign (Figure 14, 15): It is a variant of the hyperdense vessel sign and is relatively recent added symptom on non contrast CT in the setting of suspected acute stroke. * Definition: - It is a punctate focus of hyperattenuation located in the sylvian fissure and is seen on a noncontrast CT (2). - To be properly applied, the MCA dot sign should have a higher attenuation than any other visible vessel. * Explanation: - It represents a thromboembolus within a segmental branch of the MCA located within the sylvian fissure (M2 or M3 segment). - The sign appears when this highattenuation structure is viewed in cross section, since the occluded vessel courses in a plane perpendicular to the transverse plane of imaging (14). * Value: Page 22 of 34
23 - MCA dot sign is important for the thrombolytic therapy selection and prognosis. Patients with MCA dot sign are good candidates for thrombolysis, as it reflects more distal vessel occlusion and therefore suggests a smaller territory at risk (15). * DD: - Calcification associated with intracranial atherosclerosis, however, these smaller-caliber intracranial vessels are less likely to be affected by atherosclerosis than larger intracranial vessels (13). Fig. 14: Axial non-enhanced brain CT demonstrates: a) Hyperdense dot sign in the right sylvian fissure. b) Same patient after 8 hours with demarcated infarct in the territory of the right MCA. References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY Page 23 of 34
24 Fig. 15: Axial non-enhanced brain CT demonstrates "hyperdense dot sign" typically in the left sylvian fissure as an early sign of acute stroke. References: M. E. A. Noeman; Radiology Department, Akademishes Lehrkrankenhaus der Universitäts Rostock, Güstrow, GERMANY c) Hyperdense posterior artery sign (HPCA): Page 24 of 34
25 * Definition: - It is a hyperdensity seen within the ambient cistern, medial to the tentorium cerebelli (Figure 16). - Is typically visualized in 1 or 2 adjacent slices and can extend into the quadrigeminal cistern. - Is a marker of acute ischemia in the posterior cerebral artery (PCA) territory. * Incidence: - This sign is detected with good interobserver reliability in more than one third of all patients with PCA ischemia (6). * Value: - The sign is often associated with thalamic infarction, large PCA territory ischemia, more severe neurological symptomatology, and a higher risk of hemorrhagic transformation. - Therefore, it may not only be helpful in the early diagnosis of PCA infarction but might also act as a prognostic marker in acute PCA territory ischemic stroke (6). Fig. 16: Axial non contrast CT images, obtained in a 64-year-old female 7 hours after the onset of symptoms: hyperdense posterior artery sign a, black arrow ), corresponding large PCA territory ischemia (b). References: G. Krumina; MR, CT and US centre, Medical Academy of Latvia, Riga, LATVIA Page 25 of 34
26 Images for this section: Fig. 5: Cerebral Arterial Territory: ACA: Anterior cerebral Artery, MCA: Middle cerebral Artery, PCA: Posterior cerebral Artery. Page 26 of 34
27 Fig. 6: A- Axial non-enhanced brain CT shows a large area of hypoattenuation in the territory of the right MCA (red arrows), after 24 hours of onset of clinical symptoms. BSame patient after 48 hours. Notice the well-demarcation of the Infarction. Page 27 of 34
28 Fig. 8: Anatomy of the basal ganglia Page 28 of 34
29 Fig. 12: a) Axial non-enhanced brain CT image shows hyperattenuation in the proximal (M1) segment of the left MCA "hyperdense MCA-Sign"(red arrow). b) reformatted images from CT-angiography of the same patient show the apparent absence of the same vessel segment(red arrows) compared to the normal vessel right MCA (blue arrows). Page 29 of 34
30 Fig. 13: A) Axial non-enhanced brain CT demonstrates "hyperdense MCA sign" of the left MCA. B) 3D-Reconstruction image of the intracranial circulation demonstrates the occlusion of the left MCA confirming the diagnosis. Page 30 of 34
31 Conclusion Stroke is usually encountered by young radiologists, with ischemic stroke accounting for nearly 80% of cases. Thrombolytic therapy with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator (rt-pa) is the treatment of choice for ischaemic stroke presenting within 3 hours of clinical onset, provided that there is no contraindication to this treatment, including exclusion of intracranial haemorrhage by CT. Thus, recognition of early features is vitally important as it minimises morbidity and mortality. CT of the brain remains the modality of choice and the gold standard for initial assessment of acute stroke in most institutions being rapid, reliable, readily-available tool and can distinguish between stroke and its clinical mimics - potentially reducing the risk of postthrombolysis complications. Personal Information Mohammed Noeman Radiology Resident Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology KMG Klinikum Güstrow Academic Teaching Hospital of the University of Rostock Güstrow - Germany dr_noman99@hotmail.com Images for this section: Page 31 of 34
32 Fig. 18: Diagnostic and Interventional Department KMG Klinikum Güstrow Page 32 of 34
33 References (1) Acute stroke: usefulness of early CT findings before thrombolytic therapy by R von Kummer et al. Radiology 1997, Vol 205, , (2) Barber PA, Demchuk AM, Hudon ME, Pexman JH, Hill MD, Buchan AM. Hyperdense sylvian fissure MCA "dot" sign: a CT marker of acute ischemia. Stroke 2001;32: (3) Bogousslavsky J, Kaste M, Skyhoj Olsen T, et al. Risk factors and stroke prevention: European Stroke Initiative (EUSI). Cerebrovasc Dis 2000; 10:12-21 (4) Brain Ischemia - Imaging in Acute Stroke, by Majda Thurnher Department of Radiology, Medical University of Vienna (online) (5) Brain CT in Clinical Practice: Usiakimi Igbaseimokumo, Springer e-isbn (6) Brandt T, Steinke W, Thie A, Pessin MS, Caplan L. Posterior cerebral artery territory infarcts: clinical features, infarct topography, causes and outcome. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2000;10: (7) Dahnert W. Radiology review manual. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2000; 197. (8) Interpretation of Emergency Head CT, A Practical Handbook, Erskine J. Holmes, MRCS (9) G. Krumina; CT or MRI in the acute ischemic stroke? Poster No.: A-273, ECR 2010 (10) Kharitonova T, Thorén M, Ahmed N, Wardlaw J M, von Kummer R, Thomassen L, Wahlgren N. Disappearing hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign in ischaemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis: clinical course and prognostic significance. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2009;80: (11) Latchaw R, Alberts M, Lev M, Connors J, Harbaugh R, Higashida R, Hobson R, Kidwell C, Koroshetz W, Mathews V, Villablanca P, Warach S, Walters B. Page 33 of 34
34 Recommendations for Imaging of Acute Ischemic Stroke. A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Stroke. 2009;40:3646 (12) Osborn A, Tong K. Handbook of neuroradiology: brain and skull. St Louis, Mo: Mosby, 1996; 52-53, (13) Rauch RA, Bazan C 3rd, Larsson EM, Jinkins JR. Hyperdense middle cerebral arteries identified on CT as a false sign of vascular occlusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1993;14: (14) Rutgers DR, van der Grond J, Jansen GH, Somford DM, Mali WP. Radiologicpathologic correlation of the hyperdense middle cerebral artery sign: a case report. Acta Radiol 2001;42: (15) Somford DM, Nederkoorn PJ, Rutgers DR, Kappelle LJ, Mali WP, van der Grond J. Proximal and distal hyperattenuating middle cerebral artery signs at CT: different prognostic implications. Radiology 2002;223: (16) State-of-the-Art Imaging of Acute Stroke by Ashok Srinivasan et al RadioGraphics 2006;26:S75-S95 (17) Tanriover N, Rhoton AL, Kawashima M, Ulm AJ, Yasda A. Microsurgical anatomy of the insula and the sylvian fissure. J Neurosurg May;100(5): (18) The vascular territories of the carotid and vertebrobasilar systems. Diagrams based on CT studies of infarcts. by Savoiardo M. Ital J Neurol Sci Aug;7(4): (19) Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-pa Stroke Study Group. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: (20) Truwit CL, Barkovich AJ, Gean-Marton A, Hibri N, Norman D. Loss of the insular ribbon: another early CT sign of acute middle cerebral artery infarction. Radiology, 1990 Sep;176(3):801-6 Page 34 of 34
Translent CT hyperattenuation after intraarterial thrombolysis in stroke. Contrast extravasation or hemorrhage
 Translent CT hyperattenuation after intraarterial thrombolysis in stroke. Contrast extravasation or hemorrhage Poster No.: C-0053 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Losa Palacios,
Translent CT hyperattenuation after intraarterial thrombolysis in stroke. Contrast extravasation or hemorrhage Poster No.: C-0053 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Losa Palacios,
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
The "filling defect" sign helps localise the site of intracranial aneurysm rupture on an unenhanced CT
 The "filling defect" sign helps localise the site of intracranial aneurysm rupture on an unenhanced CT Poster No.: C-3380 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit Neuro
The "filling defect" sign helps localise the site of intracranial aneurysm rupture on an unenhanced CT Poster No.: C-3380 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit Neuro
Duret hemorraghe caused by traumatic brain injury: what the radiologist should know.
 Duret hemorraghe caused by traumatic brain injury: what the radiologist should know. Poster No.: C-1270 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Dewachter 1, T. Vanderhasselt 1, K. De Smet
Duret hemorraghe caused by traumatic brain injury: what the radiologist should know. Poster No.: C-1270 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Dewachter 1, T. Vanderhasselt 1, K. De Smet
Extra- and intracranial tandem occlusions in the anterior circulation - clinical outcome of endovascular treatment in acute major stroke.
 Extra- and intracranial tandem occlusions in the anterior circulation - clinical outcome of endovascular treatment in acute major stroke. Poster No.: C-1669 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Extra- and intracranial tandem occlusions in the anterior circulation - clinical outcome of endovascular treatment in acute major stroke. Poster No.: C-1669 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit
"Ultrasound measurements of the lateral ventricles in neonates: A comparison of multiple measurements methods."
 "Ultrasound measurements of the lateral ventricles in neonates: A comparison of multiple measurements methods." Poster No.: C-1557 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit I.
"Ultrasound measurements of the lateral ventricles in neonates: A comparison of multiple measurements methods." Poster No.: C-1557 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit I.
Chronology of normal brain myelination in newborns with MR imaging
 Chronology of normal brain myelination in newborns with MR imaging Poster No.: C-0577 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit F. Fernandez Usagre; Sevilla/ES Neuroradiology
Chronology of normal brain myelination in newborns with MR imaging Poster No.: C-0577 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit F. Fernandez Usagre; Sevilla/ES Neuroradiology
Thrombus hounsfield unit on CT predicts vascular recanalization in stroke patients
 Thrombus hounsfield unit on CT predicts vascular recanalization in stroke patients Poster No.: C-2616 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: H. F.Termes, J. Puig, J. Daunis-i-Estadella,
Thrombus hounsfield unit on CT predicts vascular recanalization in stroke patients Poster No.: C-2616 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: H. F.Termes, J. Puig, J. Daunis-i-Estadella,
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases
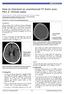 How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
A pictorial review of normal anatomical appearences of Pericardial recesses on multislice Computed Tomography.
 A pictorial review of normal anatomical appearences of Pericardial recesses on multislice Computed Tomography. Poster No.: C-1787 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Ahmed 1, G. Avery
A pictorial review of normal anatomical appearences of Pericardial recesses on multislice Computed Tomography. Poster No.: C-1787 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Ahmed 1, G. Avery
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence
 A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence Poster No.: C-1347 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Hodel, A. GUILLONNET, M. Rodallec, S. GERBER, R. 1
A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence Poster No.: C-1347 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Hodel, A. GUILLONNET, M. Rodallec, S. GERBER, R. 1
Assessment of Vasospasm and Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Current concepts and Value of CT Perfusion and CT Angiography
 Assessment of Vasospasm and Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Current concepts and Value of CT Perfusion and CT Angiography Poster No.: C-2563 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
Assessment of Vasospasm and Delayed Cerebral Ischemia after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Current concepts and Value of CT Perfusion and CT Angiography Poster No.: C-2563 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational
Acute stroke. Ischaemic stroke. Characteristics. Temporal classification. Clinical features. Interpretation of Emergency Head CT
 Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign
 Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign Poster No.: C-1095 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Goldstein, K. Jhaveri; Toronto, ON/CA Keywords: Abdomen,
Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign Poster No.: C-1095 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Goldstein, K. Jhaveri; Toronto, ON/CA Keywords: Abdomen,
Radiographic and statistical analysis of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations.
 Radiographic and statistical analysis of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Poster No.: C-0996 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. E. Rodriguez 1, A. Lopez Moreno 1, D. Sánchez Paré
Radiographic and statistical analysis of Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Poster No.: C-0996 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. E. Rodriguez 1, A. Lopez Moreno 1, D. Sánchez Paré
High density thrombi of pulmonary embolism on precontrast CT scan: Is it dangerous?
 High density thrombi of pulmonary embolism on precontrast CT scan: Is it dangerous? Poster No.: C-1753 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit B. Y. Lee, H. R. KIM, J. I. Jung,
High density thrombi of pulmonary embolism on precontrast CT scan: Is it dangerous? Poster No.: C-1753 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit B. Y. Lee, H. R. KIM, J. I. Jung,
CT assessment of acute coalescent mastoiditis.
 CT assessment of acute coalescent mastoiditis. Poster No.: C-1794 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Head and Neck Authors: A. Thomson, S. J. Thomas, A. Hutchings, E. Tilley; Portsmouth/UK
CT assessment of acute coalescent mastoiditis. Poster No.: C-1794 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Head and Neck Authors: A. Thomson, S. J. Thomas, A. Hutchings, E. Tilley; Portsmouth/UK
Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum
 Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum Poster No.: C-2705 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: P. S. Naphade, M. D. Agrawal, S. S. Sankhe, K. M. Siva, B. K. Jain; Mumbai/IN
Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum Poster No.: C-2705 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: P. S. Naphade, M. D. Agrawal, S. S. Sankhe, K. M. Siva, B. K. Jain; Mumbai/IN
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT
 Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
Mechanical thrombectomy with stent retriever in acute ischemic stroke: first results.
 Mechanical thrombectomy with stent retriever in acute ischemic stroke: first results. Poster No.: C-0829 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. H. J. Voormolen, T. Van der Zijden, I. Baar,
Mechanical thrombectomy with stent retriever in acute ischemic stroke: first results. Poster No.: C-0829 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. H. J. Voormolen, T. Van der Zijden, I. Baar,
Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma
 Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma Poster No.: C-0123 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: X. Han, J. Chen, K. Shi; Haikou/CN Keywords: Neuroradiology
Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma Poster No.: C-0123 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: X. Han, J. Chen, K. Shi; Haikou/CN Keywords: Neuroradiology
Whole brain CT perfusion maps with paradoxical low mean transit time to predict infarct core
 Whole brain CT perfusion maps with paradoxical low mean transit time to predict infarct core Poster No.: B-292 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Topic: Neuro Authors: S. Chakraborty, M. E. Ahmad,
Whole brain CT perfusion maps with paradoxical low mean transit time to predict infarct core Poster No.: B-292 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Topic: Neuro Authors: S. Chakraborty, M. E. Ahmad,
What to expect on post mechanical thrombectomy CT - a guide to correct diagnosis.
 What to expect on post mechanical thrombectomy CT - a guide to correct diagnosis. Poster No.: C-2257 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. Buende Tchokouako, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, A.
What to expect on post mechanical thrombectomy CT - a guide to correct diagnosis. Poster No.: C-2257 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. Buende Tchokouako, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, A.
Intracranial Lesions: MRI Signs for Localization
 Intracranial Lesions: MRI Signs for Localization Poster No.: C-1574 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Cucos, A. Puiu, S. Manole ; Cluj-Napoca/RO, Cluj napoca/ RO Keywords: Cerebrospinal
Intracranial Lesions: MRI Signs for Localization Poster No.: C-1574 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Cucos, A. Puiu, S. Manole ; Cluj-Napoca/RO, Cluj napoca/ RO Keywords: Cerebrospinal
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
Artifact in Head CT Images Due to Air Bubbles in X-Ray Tube Oil
 Artifact in Head CT Images Due to Air Bubbles in X-Ray Tube Oil Poster No.: C-0671 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Patel 1, W. Liu 2, J. DeSanto 2, S. Meagher 2, M. Zagardo 2,
Artifact in Head CT Images Due to Air Bubbles in X-Ray Tube Oil Poster No.: C-0671 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Patel 1, W. Liu 2, J. DeSanto 2, S. Meagher 2, M. Zagardo 2,
CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease
 CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. C. Lam, C. P. Tsang, K. K. Wong, R. LEE ; HK, Hong Kong/HK Keywords: Hemodynamics / Flow dynamics,
CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. C. Lam, C. P. Tsang, K. K. Wong, R. LEE ; HK, Hong Kong/HK Keywords: Hemodynamics / Flow dynamics,
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 4
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 4 Strokes and infarcts K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 4 Strokes and infarcts K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
The tale of global hypoxic ischaemic injury
 The tale of global hypoxic ischaemic injury Poster No.: C-0400 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. M. Zammit, R. Grech ; Paola/MT, Dublin 9/IE Keywords: CNS, CT, MR, Education, Computer
The tale of global hypoxic ischaemic injury Poster No.: C-0400 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. M. Zammit, R. Grech ; Paola/MT, Dublin 9/IE Keywords: CNS, CT, MR, Education, Computer
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings
 Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
Brainstem diffuse gliomas: radiologic findings.
 Brainstem diffuse gliomas: radiologic findings. Poster No.: C-2220 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. GARCIA MARTINEZ 1, D. H. Jiménez 1, L. Navarro Vilar 2, C. P. Fernandez Ruiz
Brainstem diffuse gliomas: radiologic findings. Poster No.: C-2220 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. GARCIA MARTINEZ 1, D. H. Jiménez 1, L. Navarro Vilar 2, C. P. Fernandez Ruiz
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
Monophasic versus biphasic contrast application in CT of patients with head and neck tumour
 Monophasic versus biphasic contrast application in CT of patients with head and neck tumour Poster No.: C-3331 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit Head and Neck G.
Monophasic versus biphasic contrast application in CT of patients with head and neck tumour Poster No.: C-3331 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit Head and Neck G.
The role of abdominal CT and MRI in detection of complications after transplantations of liver, kidney and pancreas.
 The role of abdominal CT and MRI in detection of complications after transplantations of liver, kidney and pancreas. Poster No.: C-1319 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Muslimov,
The role of abdominal CT and MRI in detection of complications after transplantations of liver, kidney and pancreas. Poster No.: C-1319 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Muslimov,
Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists.
 Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists. Poster No.: C-1844 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Kecler - Pietrzyk, W. Torreggiani ; Dublin/IE,
Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists. Poster No.: C-1844 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Kecler - Pietrzyk, W. Torreggiani ; Dublin/IE,
Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution
 Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution Poster No.: C-2104 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Hernandez Castro, M. D. Monedero
Oligodendroglioma: imaging findings, radio-pathological correlation and evolution Poster No.: C-2104 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Hernandez Castro, M. D. Monedero
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING
 ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression
 MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression Poster No.: C-1281 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nishihara 1, T. Noguchi 1, H. Irie 1, K. Sasaguri
MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression Poster No.: C-1281 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nishihara 1, T. Noguchi 1, H. Irie 1, K. Sasaguri
Imaging characterization of renal clear cell carcinoma
 Imaging characterization of renal clear cell carcinoma Poster No.: C-0327 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Ballester 1, A. Gaser 2, M. Dotta 1, M. F. CAPPA 1, F. Hammar 1 ; 1 2
Imaging characterization of renal clear cell carcinoma Poster No.: C-0327 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Ballester 1, A. Gaser 2, M. Dotta 1, M. F. CAPPA 1, F. Hammar 1 ; 1 2
CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors
 CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors Poster No.: C-0060 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. V. V. P. Costa, L. Nascimento, T. Bilhim ; Estoril/PT, PT, 1 2 3 1 2 3 Lisbon/PT
CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors Poster No.: C-0060 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. V. V. P. Costa, L. Nascimento, T. Bilhim ; Estoril/PT, PT, 1 2 3 1 2 3 Lisbon/PT
Valsalva-manoeuvre or prone belly position for computed tomography (CT) scan when an orbita varix is suspected: a single-case study.
 Valsalva-manoeuvre or prone belly position for computed tomography (CT) scan when an orbita varix is suspected: a single-case study. Poster No.: C-0512 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI:
Valsalva-manoeuvre or prone belly position for computed tomography (CT) scan when an orbita varix is suspected: a single-case study. Poster No.: C-0512 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI:
Persistent ankle pain after inversion lesions: what the radiologist must look for
 Persistent ankle pain after inversion lesions: what the radiologist must look for Poster No.: P-0118 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Poster R. Leao, L. C. Zattar-Ramos, E.
Persistent ankle pain after inversion lesions: what the radiologist must look for Poster No.: P-0118 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Poster R. Leao, L. C. Zattar-Ramos, E.
Curious case of Misty Mesentery
 Curious case of Misty Mesentery Poster No.: C-1385 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit T. Simelane 1, H. Khosa 2, N. Ramesh 2 ; 1 Dublin/IE, 2 Portlaoise/IE Abdomen, Anatomy,
Curious case of Misty Mesentery Poster No.: C-1385 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit T. Simelane 1, H. Khosa 2, N. Ramesh 2 ; 1 Dublin/IE, 2 Portlaoise/IE Abdomen, Anatomy,
NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE
 1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
Normal and abnormal meningeal enhancement: MRI features
 Normal and abnormal meningeal enhancement: MRI features Poster No.: C-3381 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: I. Hasni Bouraoui, W. Gamaoun, N. Mama, H. Moulahi, A. Daadoucha,
Normal and abnormal meningeal enhancement: MRI features Poster No.: C-3381 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: I. Hasni Bouraoui, W. Gamaoun, N. Mama, H. Moulahi, A. Daadoucha,
Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods
 Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit
64-MDCT imaging of the pancreas: Scan protocol optimisation by different scan delay regimes
 64-MDCT imaging of the pancreas: Scan protocol optimisation by different scan delay regimes Poster No.: C-051 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Abdominal and Gastrointestinal Authors:
64-MDCT imaging of the pancreas: Scan protocol optimisation by different scan delay regimes Poster No.: C-051 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Abdominal and Gastrointestinal Authors:
Computed tomography in the evaluation of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
 Computed tomography in the evaluation of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis Poster No.: C-0090 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit J. Avsenik, K. Surlan Popovic; Ljubljana/SI
Computed tomography in the evaluation of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis Poster No.: C-0090 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit J. Avsenik, K. Surlan Popovic; Ljubljana/SI
Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia.
 Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia. Poster No.: C-1577 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Manso Garcia, M. J. Velasco Marcos,
Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia. Poster No.: C-1577 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Manso Garcia, M. J. Velasco Marcos,
Spinal injury is very common in Ireland: 19 per 100,000 (1). It poses a significant disease burden.
 MRI in traumatic spinal cord injury: a single national spinal centre experience and study of imaging features with clinical correlation with ASIA score and outcome Poster No.: C-1235 Congress: ECR 2011
MRI in traumatic spinal cord injury: a single national spinal centre experience and study of imaging features with clinical correlation with ASIA score and outcome Poster No.: C-1235 Congress: ECR 2011
Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment
 Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment Poster No.: C-1854 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. G. Trigo,
Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment Poster No.: C-1854 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. G. Trigo,
Sicle-cell disease and silent cerebral infarcts evaluated with magnetic resonance imaging
 Sicle-cell disease and silent cerebral infarcts evaluated with magnetic resonance imaging Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Solomou, A. Rigopoulou, P. Kraniotis,
Sicle-cell disease and silent cerebral infarcts evaluated with magnetic resonance imaging Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Solomou, A. Rigopoulou, P. Kraniotis,
Diffuse high-attenuation within mediastinal lymph nodes on non-enhanced CT scan: Usefulness in the prediction of benignancy
 Diffuse high-attenuation within mediastinal lymph nodes on non-enhanced CT scan: Usefulness in the prediction of benignancy Poster No.: C-1785 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Diffuse high-attenuation within mediastinal lymph nodes on non-enhanced CT scan: Usefulness in the prediction of benignancy Poster No.: C-1785 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Intracranial haemorrhage on phase images of SWI (susceptibility weighted image)
 Intracranial haemorrhage on phase images of SWI (susceptibility weighted image) Poster No.: C-1088 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: Y. J. LEE, H. S. Choi, B.-Y. Kim, J. Jang, S. L.
Intracranial haemorrhage on phase images of SWI (susceptibility weighted image) Poster No.: C-1088 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: Y. J. LEE, H. S. Choi, B.-Y. Kim, J. Jang, S. L.
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases
 White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
Cierny-Mader classification of chronic osteomyelitis: Preoperative evaluation with cross-sectional imaging
 Cierny-Mader classification of chronic osteomyelitis: Preoperative evaluation with cross-sectional imaging Poster No.: C-590 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal Authors:
Cierny-Mader classification of chronic osteomyelitis: Preoperative evaluation with cross-sectional imaging Poster No.: C-590 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Topic: Educational Exhibit Musculoskeletal Authors:
Dynamic CT Assessment of Distal Radioulnar Instability
 Dynamic CT Assessment of Distal Radioulnar Instability Poster No.: P-0114 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Educational Poster Authors: S. Dumonteil, M. A. Shah, A. Srikanthan, V. Ejindu, N. Papadakos; London/UK
Dynamic CT Assessment of Distal Radioulnar Instability Poster No.: P-0114 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Educational Poster Authors: S. Dumonteil, M. A. Shah, A. Srikanthan, V. Ejindu, N. Papadakos; London/UK
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
The "whirl sign". Diagnostic accuracy for intestinal volvulus.
 The "whirl sign". Diagnostic accuracy for intestinal volvulus. Poster No.: C-0670 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Pire, M. Marti, A. Borobia, A. Verón; Madrid/ES Keywords: Abdomen,
The "whirl sign". Diagnostic accuracy for intestinal volvulus. Poster No.: C-0670 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Pire, M. Marti, A. Borobia, A. Verón; Madrid/ES Keywords: Abdomen,
Role of 3D T2 weighted imaging at 3T in evaluation of cranial nerve pathologies - An overview
 Role of 3D T2 weighted imaging at 3T in evaluation of cranial nerve pathologies - An overview Poster No.: C-1153 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Kasi Arunachalam 1, R. Renganathan
Role of 3D T2 weighted imaging at 3T in evaluation of cranial nerve pathologies - An overview Poster No.: C-1153 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Kasi Arunachalam 1, R. Renganathan
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI)
 Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect!
 MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
Presence and severity of carotid siphon calcification on computed tomography images in mild cognitive impairment
 Presence and severity of carotid siphon calcification on computed tomography images in mild cognitive impairment Poster No.: C-2117 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Rutkauskas, S.
Presence and severity of carotid siphon calcification on computed tomography images in mild cognitive impairment Poster No.: C-2117 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Rutkauskas, S.
Bolus administration of esmolol allows for safe and effective heart rate control during coronary computed tomography angiography
 Bolus administration of esmolol allows for safe and effective heart rate control during coronary computed tomography angiography Poster No.: C-1342 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Bolus administration of esmolol allows for safe and effective heart rate control during coronary computed tomography angiography Poster No.: C-1342 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD): Brain MRI findings in patients at our institution and literature review.
 Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD): Brain MRI findings in patients at our institution and literature review. Poster No.: C-0817 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. I. MICHELIN,
Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD): Brain MRI findings in patients at our institution and literature review. Poster No.: C-0817 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. I. MICHELIN,
Overview of physiological post-mortem alterations in totalbody imaging of 100 in-hospital deceased patients
 Overview of physiological post-mortem alterations in totalbody imaging of 100 in-hospital deceased patients Poster No.: C-1234 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: I. Wagensveld, W. Oosterhuis,
Overview of physiological post-mortem alterations in totalbody imaging of 100 in-hospital deceased patients Poster No.: C-1234 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: I. Wagensveld, W. Oosterhuis,
Non-calculus causes of renal colic on CT KUB
 Non-calculus causes of renal colic on CT KUB Poster No.: C-1341 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary Authors: A. Afaq, E. L. Leen; London/UK Keywords: renal colic, CT KUB, appendicitis
Non-calculus causes of renal colic on CT KUB Poster No.: C-1341 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary Authors: A. Afaq, E. L. Leen; London/UK Keywords: renal colic, CT KUB, appendicitis
Pulmonary infarction semiology in CT. Revision of 80 cases.
 Pulmonary infarction semiology in CT. Revision of 80 cases. Poster No.: C-0369 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. González Vázquez, D. Castellon, J. Calatayud, N. Silva 1 2 1 1 1 1
Pulmonary infarction semiology in CT. Revision of 80 cases. Poster No.: C-0369 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. González Vázquez, D. Castellon, J. Calatayud, N. Silva 1 2 1 1 1 1
Anatomical Variations of the Levator Scapulae Muscle - an MR Imaging Study
 Anatomical Variations of the Levator Scapulae Muscle - an MR Imaging Study Poster No.: R-0016 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Au, A. Webb, G. Buirski, P. Smith, M. Pickering, D.
Anatomical Variations of the Levator Scapulae Muscle - an MR Imaging Study Poster No.: R-0016 Congress: 2015 ASM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Au, A. Webb, G. Buirski, P. Smith, M. Pickering, D.
A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome
 A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome Poster No.: C-2780 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: E. Tavernaraki,
A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome Poster No.: C-2780 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: E. Tavernaraki,
Long bones manifestations of congenital syphilis
 Long bones manifestations of congenital syphilis Poster No.: C-0139 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. F. de Souza 1, P. P. Collier 1, E. J. M. Bronzatto 1, G. L. P. Keywords: DOI:
Long bones manifestations of congenital syphilis Poster No.: C-0139 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. F. de Souza 1, P. P. Collier 1, E. J. M. Bronzatto 1, G. L. P. Keywords: DOI:
BRAIN DEATH - The contribution of cerebral angiography. A 5-years experience.
 BRAIN DEATH - The contribution of cerebral angiography. A 5-years experience. Poster No.: C-1170 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Georgiou 1, V. KARTSOUNI 2, G. STAINHAUER 3, N.
BRAIN DEATH - The contribution of cerebral angiography. A 5-years experience. Poster No.: C-1170 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Georgiou 1, V. KARTSOUNI 2, G. STAINHAUER 3, N.
Identification and numbering of lumbar vertebrae using various anatomical landmarks on MRI of lumbosacral spine
 Identification and numbering of lumbar vertebrae using various anatomical landmarks on MRI of lumbosacral spine Poster No.: C-2125 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit S. patil 1, A. M.
Identification and numbering of lumbar vertebrae using various anatomical landmarks on MRI of lumbosacral spine Poster No.: C-2125 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit S. patil 1, A. M.
Seemingly isolated greater trochanter fractures do not exist
 Seemingly isolated greater trochanter fractures do not exist Poster No.: B-0950 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: D. Dunker, J. H. Göthlin, M. Geijer ; Gothenburg/SE, Lund/SE Keywords:
Seemingly isolated greater trochanter fractures do not exist Poster No.: B-0950 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: D. Dunker, J. H. Göthlin, M. Geijer ; Gothenburg/SE, Lund/SE Keywords:
Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage: Initial and Follow-up HRCT Features
 Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage: Initial and Follow-up HRCT Features Poster No.: E-0037 Congress: ESTI 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: Scientific Exhibit M. Y. Kim; Seoul/KR Lung, CT-High Resolution, CT, Computer
Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage: Initial and Follow-up HRCT Features Poster No.: E-0037 Congress: ESTI 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: Scientific Exhibit M. Y. Kim; Seoul/KR Lung, CT-High Resolution, CT, Computer
Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia.
 Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia. Poster No.: C-1577 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Manso Garcia, M. J. Velasco Marcos,
Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia. Poster No.: C-1577 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Manso Garcia, M. J. Velasco Marcos,
Educational Exhibit Authors:
 Endoleaks in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Endoprosthesis: What radiologists need to know about Diagnostic, Characterization and Basic Management Strategies Poster No.: C-0150 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational
Endoleaks in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Endoprosthesis: What radiologists need to know about Diagnostic, Characterization and Basic Management Strategies Poster No.: C-0150 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational
Ultrasonic evaluation of superior mesenteric vein in cancer of the pancreatic head
 Ultrasonic evaluation of superior mesenteric vein in cancer of the pancreatic head Poster No.: C-1430 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E. Fisenko, N. Vetsheva, E. Pershina;
Ultrasonic evaluation of superior mesenteric vein in cancer of the pancreatic head Poster No.: C-1430 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E. Fisenko, N. Vetsheva, E. Pershina;
Diagnostic accuracy of MRI in detecting posterior ligamentous complex injury in thoracolumbar vertebral fractures
 Diagnostic accuracy of MRI in detecting posterior ligamentous complex injury in thoracolumbar vertebral fractures Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. Aguirre, P.
Diagnostic accuracy of MRI in detecting posterior ligamentous complex injury in thoracolumbar vertebral fractures Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. Aguirre, P.
Purpose. Methods and Materials. Results
 Prevalence and significance of hypoattenuating hepatic lesions deemed too small to characterise: How are we following up these lesions and what are the outcomes? Poster No.: C-014 Congress: ECR 2009 Type:
Prevalence and significance of hypoattenuating hepatic lesions deemed too small to characterise: How are we following up these lesions and what are the outcomes? Poster No.: C-014 Congress: ECR 2009 Type:
STROKE - IMAGING. Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli.
 STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
AFib is the most common cardiac arrhythmia and its prevalence and incidence increases with age (Fuster V. et al. Circulation 2006).
 Feasibility, image quality and radiation dose of coronary CT angiography (CCTA) in patients with atrial fibrillation using a new generation 256 multi-detector CT (MDCT) Poster No.: C-2378 Congress: ECR
Feasibility, image quality and radiation dose of coronary CT angiography (CCTA) in patients with atrial fibrillation using a new generation 256 multi-detector CT (MDCT) Poster No.: C-2378 Congress: ECR
Basal ganglia and thalamus in Parkinson disease: structural and connectivity associated changes
 Basal ganglia and thalamus in Parkinson disease: structural and connectivity associated changes Poster No.: C-0851 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Onu, L. Badea,
Basal ganglia and thalamus in Parkinson disease: structural and connectivity associated changes Poster No.: C-0851 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Onu, L. Badea,
Audit of CT Pulmonary Angiogram in suspected pulmonary embolism patients
 Audit of CT Pulmonary Angiogram in suspected pulmonary embolism patients Poster No.: C-2511 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. D. Gupta, M. K. Heir, P. Bradding; Leicester/UK Keywords:
Audit of CT Pulmonary Angiogram in suspected pulmonary embolism patients Poster No.: C-2511 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. D. Gupta, M. K. Heir, P. Bradding; Leicester/UK Keywords:
Idiopathic dilatation of the pulmonary artery : radiographic and MDCT features in 6 cases
 Idiopathic dilatation of the pulmonary artery : radiographic and MDCT features in 6 cases Poster No.: P-0075 Congress: ESTI 2014 Type: Authors: Educational Poster J. J. Woo 1, K. Y. Lee 2, Y. Cho 1, J.
Idiopathic dilatation of the pulmonary artery : radiographic and MDCT features in 6 cases Poster No.: P-0075 Congress: ESTI 2014 Type: Authors: Educational Poster J. J. Woo 1, K. Y. Lee 2, Y. Cho 1, J.
Stroke School for Internists Part 1
 Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when?
 Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when? Poster No.: P-0157 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E. Ilieva, V. Tasseva,
Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when? Poster No.: P-0157 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E. Ilieva, V. Tasseva,
The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological
 The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological Poster No.: P-0104 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: M. Bartocci 1, C. Dell'atti 2, E. Federici 1, V. Martinelli
The posterolateral corner of the knee: the normal and the pathological Poster No.: P-0104 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: M. Bartocci 1, C. Dell'atti 2, E. Federici 1, V. Martinelli
Even in the era of diffusion and perfusion-weighted MRI,
 The Hyperdense Posterior Cerebral Artery Sign A Computed Tomography Marker of Acute Ischemia in the Posterior Cerebral Artery Territory Timo Krings, MD; Dagmar Noelchen, MD; Michael Mull, MD; Klaus Willmes,
The Hyperdense Posterior Cerebral Artery Sign A Computed Tomography Marker of Acute Ischemia in the Posterior Cerebral Artery Territory Timo Krings, MD; Dagmar Noelchen, MD; Michael Mull, MD; Klaus Willmes,
Cervical spine degenerative disease: a comparative study between computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings
 Cervical spine degenerative disease: a comparative study between computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings Poster No.: C-2517 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. Papavasilopoulou,
Cervical spine degenerative disease: a comparative study between computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging findings Poster No.: C-2517 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. Papavasilopoulou,
ACUTE STROKE IMAGING
 ACUTE STROKE IMAGING Mahesh V. Jayaraman M.D. Director, Inter ventional Neuroradiology Associate Professor Depar tments of Diagnostic Imaging and Neurosurger y Alper t Medical School at Brown University
ACUTE STROKE IMAGING Mahesh V. Jayaraman M.D. Director, Inter ventional Neuroradiology Associate Professor Depar tments of Diagnostic Imaging and Neurosurger y Alper t Medical School at Brown University
Differentiation of osteoporosis from metastasis in the vertebral fracture using chemical shift and diffusion weighted imaging
 Differentiation of osteoporosis from metastasis in the vertebral fracture using chemical shift and diffusion weighted imaging Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H.
Differentiation of osteoporosis from metastasis in the vertebral fracture using chemical shift and diffusion weighted imaging Poster No.: C-0444 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H.
Spinal meningioma imaging
 Spinal meningioma imaging Poster No.: C-0448 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Smoljan, D. Zadravec ; Zagreb/HR, Zageb/HR Keywords: Neoplasia, Imaging sequences, Education, MR, CT,
Spinal meningioma imaging Poster No.: C-0448 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Smoljan, D. Zadravec ; Zagreb/HR, Zageb/HR Keywords: Neoplasia, Imaging sequences, Education, MR, CT,
Knee ultrasound in pediatric patients - anatomy, diagnostic pitfalls, common pathologies.
 Knee ultrasound in pediatric patients - anatomy, diagnostic pitfalls, common pathologies. Poster No.: C-2434 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. M. Olchowy, M. Lasecki, M. Inglot,
Knee ultrasound in pediatric patients - anatomy, diagnostic pitfalls, common pathologies. Poster No.: C-2434 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. M. Olchowy, M. Lasecki, M. Inglot,
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors
 Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke. Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV
 The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV Patient CR 62 yo F w/ 2 wk h/o altered mental status Presents to ED w/ confusion following a fall 1 day prior New onset left facial droop
The Role of Neuroimaging in Acute Stroke Bradley Molyneaux, HMS IV Patient CR 62 yo F w/ 2 wk h/o altered mental status Presents to ED w/ confusion following a fall 1 day prior New onset left facial droop
CT INTERPRETATION COURSE
 CT INTERPRETATION COURSE Refresher Course ASTRACAT October 2012 Stroke is a Clinical Diagnosis A clinical syndrome characterised by rapidly developing clinical symptoms and/or signs of focal loss of cerebral
CT INTERPRETATION COURSE Refresher Course ASTRACAT October 2012 Stroke is a Clinical Diagnosis A clinical syndrome characterised by rapidly developing clinical symptoms and/or signs of focal loss of cerebral
