Títle: Efficacy of high-flow oxygen and active humidification in a patient with acute respiratory failure of neuromuscular origin.
|
|
|
- Helena Shields
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Títle: Efficacy of high-flow oxygen and active humidification in a patient with acute respiratory failure of neuromuscular origin. Authors: Díaz- Lobato S, MD, PhD; Folgado MA*, MD; Chapa A*, MD; Mayoralas S, MD, PhD. Centre: Pneumological Department. Ramón y Cajal Hospital. Madrid. Spain. * Emergency Departament. Virgen de la Concha Hospital. Zamora. Spain. Correspondence: Salvador Díaz-Lobato. Pneumological Department. Ramón y Cajal Hospital. Carretera de Colmenar Viejo, Km 9, MADRID. Tfno sdiazlobato@gmail.com
2 Abstract The treatment of choice for patients with respiratory failure of neuromuscular origin, especially in situations of hypercapnic respiratory acidosis, is noninvasive ventilation (NIV). Endotracheal intubation and invasive ventilation are indicated for patients with severe respiratory compromise or failure of NIV. In recent years high-flow oxygen therapy and active humidification devices have been introduced in the medical practice. They are emerging evidence that high-flow may be effective in different clinical settings: such as acute respiratory failure, after cardiac surgery, during sedation and analgesia, in acute heart failure, in hypoxemic respiratory distress, in Do-Not-Intubate patients, in the case of patients with chronic cough and copious secretions, pulmonary fibrosis or cancer, both in critical areas or in the emergency department. We have studied a patient suffering from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) who arrived at the emergency department with acute hypercapnic respiratory failure, which was treated successfully with a heated, humidified high-flow oxygen therapy device (HFNC). The patient did not tolerate NIV and we decided to try the HFNC as an alternative to intubation, since the patient had also rejected the application of invasive measures. An ABG performed after an hour of treatment showed a trend for improvement of both the ph, and the PCO2, and also improved the level of awareness of the patient. Respiratory acidosis was corrected and the patient could be discharged after 5 days of hospitalization. The response to HFNC was similar to that expected with NIV. We discuss the mechanisms of action of heated, humidified high-flow oxygen therapy and the need for research on this in the future. Keywords: High flow oxygen therapy; non-invasive ventilation; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
3 Non invasive ventilation (NIV) is the treatment of choice for patients with respiratory failure of neuromuscular origin, especially in situations of hypercapnic respiratory acidosis (1,2). Endotracheal intubation and invasive ventilation are indicated for patients with severe respiratory compromise or NIV failure. In patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), respiratory muscle weakness represents the major cause of mortality. As a result, NIV is an important part of disease management (3). Randomized controlled trials have indicated that therapy with long-term NIV improves survival in ALS patients. It can also improve patient symptoms and health-related quality of life (4). NIV has been shown to be effective in correcting respiratory failure, probably by acting to a greater or lesser extent on muscle fatigue, the mechanical properties of the respiratory apparatus, the control of ventilation, the alterations in gas exchange during the night leading to loss of sensitivity of central and peripheral chemoreceptors, and the degree of dysfunction of the upper airways (5). In recent years heated, humidified high-flow oxygen therapy (HFNC) has been introduced in the medical practice (6). They are emerging evidence that HFNC could be an effective treatment in different clinical settings: such as acute respiratory failure (7-9), after cardiac surgery (10,11), during sedation and analgesia (12), in acute heart failure (13), in hypoxemic respiratory distress, in Do-Not-Intubate patients (14), in the case of patients with chronic cough and copious secretions (15), pulmonary fibrosis (16) or cancer (17), both in critical areas (18) or in the emergency department (19). We have studied a patient suffering from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) who arrived at the emergency department with acute hypercapnic respiratory failure, which was treated successfully with HFNC. Clinical case
4 A 65 years old woman was diagnosed with ALS 6 months earlier, although she had no other past medical history. Usually she had no dyspnea, decubitus intolerance or other respiratory symptoms. From a functional point of view, the patient had a recent spirometry showing FVC 2450 ml (78 %), FEV ml (75 %), FEV1/FVC 0.7. The maximum inspiratory/expiratory pressure was normal, above 80 cm H2O. The patient went to the hospital emergency department, complaining of progressive dyspnea and decreased level of consciousness over two days. She had no fever, cough or expectoration. On physical examination the patient was drowsy, had a blood pressure of 140/70, a heart rate of 110 bpm, a respiratory rate of 13 breaths per minute, and a temperature of 36.8 C, showing an overall of breath sounds at cardiopulmonary auscultation. The remaining physical examination was of irrelevant interest. Laboratory tests showed hemoglobin 16 g/dl, hematocrit 50.6%, WBC /ml with 87% neutrophils, INR 0.9. Biochemistry was normal with a creatinine of 0.59 mg/dl. Arterial blood gases (ABG) performed with 50% oxygen by venturi mask showed: ph 7.27, PCO2 90 mmhg, PO2 88 mmhg, HCO3 40 mmol/l. Chest radiography showed left costophrenic angle obliteration without any other findings of interest. Her husband related the onset of symptoms with a catarrhal process. A hypercapnic respiratory acidosis without infiltrates secondary to a respiratory infection in a patient with ALS was diagnosed. She was treated with antibiotic and steroids. NIV by a bilevel pressure ventilator (Trilogy 100, Philips Respironics, Murrisville, Pensylvania) through an oronasal mask and a passive circuit was then started. The ventilator was adjusted using the following parameters in a ST mode: inspiratory pressure: 16 cm H2O, expiratory pressure: 6 cm H2O; backup rate: 15 breaths per minute; trigger sensitivity: 2; and rise time: 2. Oxygen was added at 5 lpm and the arterial saturation and heart rate was monitored. A severe intolerance was shown by the patient, so NIV was withdrawn after
5 5 minutes from starting. The patient was agitated, restless, and wanting to remove the mask. Arterial oxygen saturation was of 80 %. Then, a heated, humidified high-flow oxygen therapy device (Optiflow cannula with humidification by an MR880 heated humidifier, both from Fisher & Paykel Healthcare, Auckland, New Zealand) (Figure 1) setting at 45 L/min and a 0.26 fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2), was applied. After an hour of treatment, the patient showed a clinical improvement and was more awake. ABG showed: ph 7.31, PCO2 74 mmhg, PO2 51 mmhg, HCO3 36 mmol/l. The patient was admitted to the respiratory ward. Three hours later, an ABG showed ph 7.40, PCO2 61 mmhg, PO2 62 mmhg, HCO3 41 mmol/l. The patient gradually improved and was discharged after 5 days of hospital admission. The HFNC device was used during the length of hospitalization. A later chest radiography showed similar left costophrenic angle obliteration without any other findings of interest. On the day of discharge, we put the patient on conventional oxygen therapy by nasal prongs at 1,5 lpm for 5 hours in the morning. An ABG showed ph 7,39, PCO2 48 mmhg, PO2 68 mmhg, CO3H 35 mmol/l. A Domiciliary oxygen therapy by nasal prongs at 1,5 lpm was recommended. Discussion In the present case, an ALS patient with hypercapnic acidosis without infiltrates was successfully treated with HFNC. She had not tolerated NIV and also had rejected the application of invasive measures. We decided to try HFNC as an alternative to intubation. Patient management was similar to that of a patient with a COPD exacerbation and respiratory hypercapnic acidosis, using a low FiO2 aimed to maintain an arterial saturation slightly higher than 90 % to prevent greater hypoventilation. We monitored the patient as if she was receiving NIV and an ABG was performed at the first hour of treatment. The ABG showed a trend for improvement of both the ph and
6 the PCO2, and also improved the level of awareness of the patient. Respiratory acidosis was corrected and the patient was discharged after 5 days of hospitalization. The response to HFNC was similar to that expected with NIV. Basically, we applied the same criteria used for acute COPD patients. Heated, humidified high flow nasal cannula oxygen is a technique that can deliver up to 100 % heated and humidified oxygen at a maximum flow of 60 L/min of gas via nasal prongs or cannula. The benefits of HFNC are related to a number of physiological properties (20). One of the main effects of delivering high gas flows directly in the nasopharynx is to wash CO2, whereby reducing CO2 rebreathing and providing a reservoir of fresh gas. This reduces dead space and increases the alveolar ventilation over minute ventilation ratio (21). Because high flow devices can generate flows that match or exceed patients peak inspiratory demand, it is thought that high flow nasal oxygen minimizes the nasopharyngeal resistance so decreasing resistive work of breathing. In the same line of reasoning, it was speculated that the use of high flows generated a certain amount of positive airway pressure as have been demonstrated by several authors (22-24). The pressures reached are not very high, estimated in 1 cm H2O of pressure for every 10 L/min of flow. These devices cannot be considered as CPAP devices, but we cannot forget this feature, responsible for some beneficial effects on respiratory mechanics. On the other hand, Corley et al (25) have demonstrated in patients with acute respiratory failure that part at least of the improvement in oxygenation observed is due to alveolar recruitment. Finally, high flow oxygen therapy showed a great tolerance by the patient related to the heat and humidity supplied by the device, the use of nasal prongs instead of face mask and reduction of work of breathing. Correction of hypoxemia may also play a role (26).
7 Its usefulness in critically ill patients, weaning and as an alternative to intubation, is being investigated and we have promising evidence in the literature (27, 28). The dead space washout, the nasopharyngeal resistance reduction, the positive pharyngeal pressure, the alveolar recruitment, the oxygen dilution reduction, the decreased work of breathing secondary to these mechanisms, the comfort provided by the temperature and humidity the patient receives and an excellent patient tolerance with this technique, may explain the clinical and gasometric improvement in our patient. Respiratory acidosis was corrected and the patient could be discharged from the hospital. Our experience opens up a field of research in which perhaps some patients with acute respiratory failure and hypercapnic acidosis can be treated with high-flow oxygen therapy and active humidification as an alternative to conventional techniques of NIV. The simplicity of the technique, the lower cost of equipment and greater tolerance by patients, can provide an added benefit to the clinical efficacy of great importance in an era where efficiency should be prioritized. Future research is necessary to clarify these issues. References 1. Ambrosino N, Carpenè N, Gherardi M. Chronic respiratory care for neuromuscular diseases in adults. Eur Respir J 2009;34(2): Consensus Clinical indications for noninvasive positive pressure ventilation in chronic respiratory failure due to restrictive lung disease, COPD, and nocturnal hypoventilation--a consensus conference report. Chest. 1999;116(2): Vitacca M, Vianello A; on behalf of the Scientific Group on Respiratory Intensive Care of the Italian Association of Hospital Pulmunologists. Respiratory Outcomes Of Patients With Als: An Italian Nationwide Survey. Respir Care [Epub ahead of print] 4. Bourke SC, Bullock RE, Williams TL, Shaw PJ, Gibson GJ. Noninvasive ventilation in ALS: indications and effect on quality of life. Neurology 2003;61(2): Díaz-Lobato S, Ruiz-Cobos A, García Río FJ, Villamor-León J.Physiopathology of respiratory insufficiency of neuromuscular origin. Rev Neurol 2001;32(1): Roca O, Riera J, Torres F, Masclans JR. High-flow oxygen therapy in acute respiratory failure. Respir Care 2010;55(4):
8 7. Parke RL, McGuinness SP, Eccleston ML. A preliminary randomized controlled trial to assess effectiveness of nasal high-flow oxygen in intensive care patients. Respir Care 2011;56(3): Sztrymf B, Messika J, Mayot T, Lenglet H, Dreyfuss D, Ricard JD. Impact of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy on intensive care unit patients with acute respiratory failure: a prospective observational study. J Crit Care 2012;27(3): Sztrymf B, Messika J, Bertrand F, Hurel D, Leon R, Dreyfuss D, Ricard JD. Beneficial effects of humidified high flow nasal oxygen in critical care patients: a prospective pilot study. Intensive Care Med 2011;37(11): Parke RL, McGuinness SP, Dixon R, Jull A. Protocol for a randomised controlled trial of nasal high flow oxygen therapy compared to standard care in patients following cardiac surgery: the HOT-AS study. Int J Nurs Stud 2012;49(3): Nicolet J, Poulard F, Baneton D, Rigal JC, Blanloeil Y. High-flow nasal oxygen for severe hypoxemia after cardiac surgery. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim. 2011;30(4): Deitch K, Chudnofsky CR, Dominici P, Latta D, Salamanca Y. The utility of high-flow oxygen during emergency department procedural sedation and analgesia with propofol: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Emerg Med 2011;58(4): Carratalá Perales JM, Llorens P, Brouzet B, Albert Jiménez AR, Fernández- Cañadas JM, Carbajosa Dalmau J, et al. High-Flow therapy via nasal cannula in acute heart failure. Rev Esp Cardiol 2011;64(8): Peters SG, Holets SR, Gay PC. Nasal High Flow Oxygen Therapy in Do-Not- Intubate Patients With Hypoxemic Respiratory Distress. Respir Care (2012, in press). 15. Díaz Lobato S, Mayoralas Alises S. Effectiveness of high-flow oxygen therapy with warm humidification in a COPD patient with chronic cough. Arch Bronconeumol 2011;47(8): Boyer A, Vargas F, Delacre M, Saint-Léger M, Clouzeau B, Hilbert G, Gruson D. Prognostic impact of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen supply in an ICU patient with pulmonary fibrosis complicated by acute respiratory failure. Intensive Care Med 2011;37(3): Epstein AS, Hartridge-Lambert SK, Ramaker JS, Voigt LP, Portlock CS. Humidified high-flow nasal oxygen utilization in patients with cancer at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center. J Palliat Med 2011;14(7): Wattier BA, Ward JJ. High-flow nasal cannula oxygen in critically ill adults: do the nose or lungs know there's a difference? Respir Care 2011;56(3): Lenglet H, Sztrymf B, Leroy C, Brun P, Dreyfuss D, Ricard JD. Humidified High Flow Nasal Oxygen During Respiratory Failure in the Emergency Department: Feasibility and Efficacy. Respir Care (2012, in press). 20. Ricard JD. High flow nasal oxygen in acute respiratory failure. Minerva Anestesiol 2012;78(7): Dysart K, Miller T, Wolfson MR, Shaffer TH. Research in high flow therapy: mechanisms of action. Respir Med 2009;103(10): Parke RL, Eccleston ML, McGuinness SP. The effects of flow on airway pressure during nasal high-flow oxygen therapy. Respir Care 2011;56(8):
9 23. Ritchie JE, Williams AB, Gerard C, Hockey H. Evaluation of a humidified nasal high-flow oxygen system, using oxygraphy, capnography and measurement of upper airway pressures. Anaesth Intensive Care 2011;39(6): Urbano J, del Castillo J, López-Herce J, Gallardo JA, Solana MJ, Carrillo Á. High-flow oxygen therapy: pressure analysis in a pediatric airway model. Respir Care 2012;57(5): Corley A, Caruana LR, Barnett AG, Tronstad O, Fraser JF. Oxygen delivery through high-flow nasal cannulae increase end-expiratory lung volume and reduce respiratory rate in post-cardiac surgical patients. Br J Anaesth 2011;107(6): Cuquemelle E, Pham T, Papon JF, Louis B, Danin PE, Brochard L. Heated and Humidified High-Flow Oxygen Therapy Reduces Discomfort During Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure. Respir Care 2012;57(10): Ward JJ. High-flow oxygen administration by nasal cannula for adult and perinatal patients. Respir Care 2013; 58(1): El-Khatyb MF. High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy during hypoxemic respiratory failure. Respir Care 2012 Oct;57(10): Legend Figure 1 This picture shows the various components of the high-flow oxygen therapy and active humidification device: the platform with the flow source MaxVenturi (1) and the humidifier MR850 (2); the delivery system with the humidification chamber and the breathing circuit (3); and the interface F&P Optiflow TM Nasal Cannula (4).
10 For Peer Review
PRESSURES DELIVERED BY NASAL HIGH FLOW THERAPY DURING
 PRESSURES DELIVERED BY NASAL HIGH FLOW THERAPY DURING ALL PHASES OF THE RESPIRATORY CYCLE Rachael L. Parke, RN, MHSc (Hons) Cardiothoracic and Vascular Intensive Care Unit Auckland City Hospital Private
PRESSURES DELIVERED BY NASAL HIGH FLOW THERAPY DURING ALL PHASES OF THE RESPIRATORY CYCLE Rachael L. Parke, RN, MHSc (Hons) Cardiothoracic and Vascular Intensive Care Unit Auckland City Hospital Private
High-Flow Nasal Cannula in a Mixed Adult ICU
 High-Flow Nasal Cannula in a Mixed Adult ICU Kristina A Gaunt MD, Sarah K Spilman MA, Meghan E Halub MD, Julie A Jackson RRT-ACCS, Keith D Lamb RRT-ACCS, and Sheryl M Sahr MD MSc BACKGROUND: Humidified,
High-Flow Nasal Cannula in a Mixed Adult ICU Kristina A Gaunt MD, Sarah K Spilman MA, Meghan E Halub MD, Julie A Jackson RRT-ACCS, Keith D Lamb RRT-ACCS, and Sheryl M Sahr MD MSc BACKGROUND: Humidified,
High-Flow Nasal Cannula in a Mixed Adult ICU
 High-Flow Nasal Cannula in a Mixed Adult ICU Kristina A Gaunt MD, Sarah K Spilman MA, Meghan E Halub MD, Julie A Jackson RRT-ACCS, Keith D Lamb RRT-ACCS, and Sheryl M Sahr MD MSc BACKGROUND: Humidified,
High-Flow Nasal Cannula in a Mixed Adult ICU Kristina A Gaunt MD, Sarah K Spilman MA, Meghan E Halub MD, Julie A Jackson RRT-ACCS, Keith D Lamb RRT-ACCS, and Sheryl M Sahr MD MSc BACKGROUND: Humidified,
Adult Nasal High Flow: Clinical Paper Summaries
 Adult Nasal High Flow: Clinical Paper Summaries Table of Contents KEY REFERENCES THERAPY OVERVIEW Research in high flow therapy (Dysart).. S1 SPECIFIC PATIENT POPULATION High-flow nasal cannulae in post-cardiac
Adult Nasal High Flow: Clinical Paper Summaries Table of Contents KEY REFERENCES THERAPY OVERVIEW Research in high flow therapy (Dysart).. S1 SPECIFIC PATIENT POPULATION High-flow nasal cannulae in post-cardiac
Nasal High Flow Humidification with or without Oxygen for COPD Management. Shereen Bailey, RCP, RRT, NPS
 Nasal High Flow Humidification with or without Oxygen for COPD Management Shereen Bailey, RCP, RRT, NPS Objectives How it works COPD Management today The role of NHFC Evidence Research/Case Studies Types
Nasal High Flow Humidification with or without Oxygen for COPD Management Shereen Bailey, RCP, RRT, NPS Objectives How it works COPD Management today The role of NHFC Evidence Research/Case Studies Types
Use of High-Flow Nasal Cannula for Acute Dyspnea and Hypoxemia in the Emergency Department
 Use of High-Flow Nasal Cannula for Acute Dyspnea and Hypoxemia in the Emergency Department Nuttapol Rittayamai MD, Jamsak Tscheikuna MD, Nattakarn Praphruetkit MD, and Sunthorn Kijpinyochai MD BACKGROUND:
Use of High-Flow Nasal Cannula for Acute Dyspnea and Hypoxemia in the Emergency Department Nuttapol Rittayamai MD, Jamsak Tscheikuna MD, Nattakarn Praphruetkit MD, and Sunthorn Kijpinyochai MD BACKGROUND:
High flow nasal oxygen in acute respiratory failure J.-D. RICARD 1, 2, 3
 This document is protected by international copyright laws. No additional reproduction is authorized. It is permitted for personal use to download and save only one file and print only one copy of this
This document is protected by international copyright laws. No additional reproduction is authorized. It is permitted for personal use to download and save only one file and print only one copy of this
Efficacy of High-Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy in Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure: Decreased Use of Mechanical Ventilation
 Efficacy of High-Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy in Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure: Decreased Use of Mechanical Kazuma Nagata MD, Takeshi Morimoto MD PhD MPH, Daichi Fujimoto MD, Takehiro Otoshi MD, Atsushi
Efficacy of High-Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy in Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure: Decreased Use of Mechanical Kazuma Nagata MD, Takeshi Morimoto MD PhD MPH, Daichi Fujimoto MD, Takehiro Otoshi MD, Atsushi
What you need to know about: High flow nasal oxygen therapy
 What you need to know about: High flow nasal oxygen therapy Main introduction Adequate oxygenation is essential in many disorders, and this article will discuss the physiology, practicalities and indications
What you need to know about: High flow nasal oxygen therapy Main introduction Adequate oxygenation is essential in many disorders, and this article will discuss the physiology, practicalities and indications
Effectiveness of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy for acute respiratory failure with hypercapnia
 Original Article Effectiveness of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy for acute respiratory failure with hypercapnia Eun Sun Kim, Hongyeul Lee, Se Joong Kim, Jisoo Park, Yeon Joo Lee, Jong Sun Park,
Original Article Effectiveness of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy for acute respiratory failure with hypercapnia Eun Sun Kim, Hongyeul Lee, Se Joong Kim, Jisoo Park, Yeon Joo Lee, Jong Sun Park,
Effect of Very-High-Flow Nasal Therapy on Airway Pressure and End-Expiratory Lung Impedance in Healthy Volunteers
 Effect of Very-High-Flow Nasal Therapy on Airway Pressure and End-Expiratory Lung Impedance in Healthy Volunteers Rachael L Parke RN PhD, Andreas Bloch MD, and Shay P McGuinness MB ChB BACKGROUND: Previous
Effect of Very-High-Flow Nasal Therapy on Airway Pressure and End-Expiratory Lung Impedance in Healthy Volunteers Rachael L Parke RN PhD, Andreas Bloch MD, and Shay P McGuinness MB ChB BACKGROUND: Previous
Policy Specific Section: October 1, 2010 January 21, 2013
 Medical Policy Bi-level Positive Airway Pressure (BPAP/NPPV) Type: Medical Necessity/Not Medical Necessity Policy Specific Section: Durable Medical Equipment Original Policy Date: Effective Date: October
Medical Policy Bi-level Positive Airway Pressure (BPAP/NPPV) Type: Medical Necessity/Not Medical Necessity Policy Specific Section: Durable Medical Equipment Original Policy Date: Effective Date: October
Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification
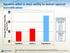 Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation in Children ศ.พญ.อร ณวรรณ พฤทธ พ นธ หน วยโรคระบบหายใจเด ก ภาคว ชาก มารเวชศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร โรงพยาบาลรามาธ บด
 Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation in Children ศ.พญ.อร ณวรรณ พฤทธ พ นธ หน วยโรคระบบหายใจเด ก ภาคว ชาก มารเวชศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร โรงพยาบาลรามาธ บด Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation Provide support without
Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation in Children ศ.พญ.อร ณวรรณ พฤทธ พ นธ หน วยโรคระบบหายใจเด ก ภาคว ชาก มารเวชศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร โรงพยาบาลรามาธ บด Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation Provide support without
The use of high-flow nasal cannula in acute decompensated heart failure: ready for prime time yet?
 Perspective Page 1 of 5 The use of high-flow nasal cannula in acute decompensated heart failure: ready for prime time yet? Mui Teng Chua 1, Win Sen Kuan 1,2 1 Emergency Medicine Department, National University
Perspective Page 1 of 5 The use of high-flow nasal cannula in acute decompensated heart failure: ready for prime time yet? Mui Teng Chua 1, Win Sen Kuan 1,2 1 Emergency Medicine Department, National University
Haut debit nasal ou BiPAP? Laurent Brochard Toronto
 Haut debit nasal ou BiPAP? Laurent Brochard Toronto Conflicts of interest Our clinical research laboratory has received research grants for clinical trials from the following companies: General Electric
Haut debit nasal ou BiPAP? Laurent Brochard Toronto Conflicts of interest Our clinical research laboratory has received research grants for clinical trials from the following companies: General Electric
Bi-Level Therapy: Boosting Comfort & Compliance in Apnea Patients
 Bi-Level Therapy: Boosting Comfort & Compliance in Apnea Patients Objectives Describe nocturnal ventilation characteristics that may indicate underlying conditions and benefits of bilevel therapy for specific
Bi-Level Therapy: Boosting Comfort & Compliance in Apnea Patients Objectives Describe nocturnal ventilation characteristics that may indicate underlying conditions and benefits of bilevel therapy for specific
What is the next best step?
 Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
High Flow Humidification Therapy, Updates.
 High Flow Humidification Therapy, Updates. Bernardo Selim, M.D. I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Assistant Professor, Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, Mayo Clinic What
High Flow Humidification Therapy, Updates. Bernardo Selim, M.D. I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose. Assistant Professor, Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, Mayo Clinic What
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE
 Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Non-invasive ventilation in immunocompromised patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure
 Perspective Non-invasive ventilation in immunocompromised patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure Lorenzo Del Sorbo 1, Angela Jerath 2,3, Martin Dres 4, Matteo Parotto 2,3 1 Interdepartmental
Perspective Non-invasive ventilation in immunocompromised patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure Lorenzo Del Sorbo 1, Angela Jerath 2,3, Martin Dres 4, Matteo Parotto 2,3 1 Interdepartmental
Sample Case Study. The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on
 Sample Case Study The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on February 25 th with a chief complaint of shortness of breath and a deteriorating pulmonary status along with
Sample Case Study The patient was a 77-year-old female who arrived to the emergency room on February 25 th with a chief complaint of shortness of breath and a deteriorating pulmonary status along with
Disclosure. Learning Objectives. Bernadette Zelaya, RRT. Area Clinical Manager
 High Velocity Nasal Insufflation An Important Therapeutic Approach for Use in the Emergency Department Presented by Vapotherm Accredited for 1 CEU by the American Association for Respiratory Care Provider
High Velocity Nasal Insufflation An Important Therapeutic Approach for Use in the Emergency Department Presented by Vapotherm Accredited for 1 CEU by the American Association for Respiratory Care Provider
NON INVASIVE LIFE SAVERS. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV)
 Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
High Flow Oxygen Therapy in Acute Respiratory Failure. Laurent Brochard Toronto
 High Flow Oxygen Therapy in Acute Respiratory Failure Laurent Brochard Toronto Conflicts of interest Our clinical research laboratory has received research grants for clinical research projects from the
High Flow Oxygen Therapy in Acute Respiratory Failure Laurent Brochard Toronto Conflicts of interest Our clinical research laboratory has received research grants for clinical research projects from the
Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither?
 Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither? Robert Kempainen, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Hennepin County Medical Center University of Minnesota School of Medicine Objectives Summarize
Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither? Robert Kempainen, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Hennepin County Medical Center University of Minnesota School of Medicine Objectives Summarize
Improving Care & Outcomes
 Improving Care & Outcomes Macquarie Technology Day, 20 October 2011 1 Improving Care & Outcomes The Care Continuum - Matthew Payton F&P Optiflow - Matthew Payton F&P Info Technologies - Lewis Gradon ICON
Improving Care & Outcomes Macquarie Technology Day, 20 October 2011 1 Improving Care & Outcomes The Care Continuum - Matthew Payton F&P Optiflow - Matthew Payton F&P Info Technologies - Lewis Gradon ICON
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. This online publication has been corrected. The corrected
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. This online publication has been corrected. The corrected
Effect of High-Flow Nasal Cannula on Thoraco-Abdominal Synchrony in Adult Critically Ill Patients
 Effect of High-Flow Nasal Cannula on Thoraco-Abdominal Synchrony in Adult Critically Ill Patients Taiga Itagaki MD, Nao Okuda MD, Yumiko Tsunano MD, Hisakazu Kohata MD, Emiko Nakataki MD PhD, Mutsuo Onodera
Effect of High-Flow Nasal Cannula on Thoraco-Abdominal Synchrony in Adult Critically Ill Patients Taiga Itagaki MD, Nao Okuda MD, Yumiko Tsunano MD, Hisakazu Kohata MD, Emiko Nakataki MD PhD, Mutsuo Onodera
Case Report High-Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy in a Patient with Reperfusion Pulmonary Edema following Percutaneous Transluminal Pulmonary Angioplasty
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Pulmonology Volume 2014, Article ID 837612, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/837612 Case Report High-Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy in a Patient with Reperfusion
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Pulmonology Volume 2014, Article ID 837612, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/837612 Case Report High-Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy in a Patient with Reperfusion
Tissue is the Issue. PEEP CPAP FiO2 HFNC PSV HFNC. DO 2 = CO [(Hb x 1.34) SaO PaO 2 ] perfusione
![Tissue is the Issue. PEEP CPAP FiO2 HFNC PSV HFNC. DO 2 = CO [(Hb x 1.34) SaO PaO 2 ] perfusione Tissue is the Issue. PEEP CPAP FiO2 HFNC PSV HFNC. DO 2 = CO [(Hb x 1.34) SaO PaO 2 ] perfusione](/thumbs/79/78902905.jpg) Tissue is the Issue perfusione PEEP CPAP FiO2 HFNC PSV HFNC DO 2 = CO [(Hb x 1.34) SaO 2 + 0.003 PaO 2 ] O2 HFNC PEEP CPAP PSV ARF ACPE HIGH FLOW NASAL CANNULA High and Exact FiO2, High Flow heating and
Tissue is the Issue perfusione PEEP CPAP FiO2 HFNC PSV HFNC DO 2 = CO [(Hb x 1.34) SaO 2 + 0.003 PaO 2 ] O2 HFNC PEEP CPAP PSV ARF ACPE HIGH FLOW NASAL CANNULA High and Exact FiO2, High Flow heating and
Ron Hosp, MS-HSA, RRT Regional Respiratory Specialist. This program has been approved for 1 hour of continuing education credit.
 Ron Hosp, MS-HSA, RRT Regional Respiratory Specialist This program has been approved for 1 hour of continuing education credit. Course Objectives Identify at least four goals of home NIV Identify candidates
Ron Hosp, MS-HSA, RRT Regional Respiratory Specialist This program has been approved for 1 hour of continuing education credit. Course Objectives Identify at least four goals of home NIV Identify candidates
High-flow nasal oxygen therapy and noninvasive ventilation in the management of acute hypoxemic respiratory failure
 Review Article Page 1 of 8 High-flow nasal oxygen therapy and noninvasive ventilation in the management of acute hypoxemic respiratory failure Jean-Pierre Frat 1,2,3, Rémi Coudroy 1,2,3, Nicolas Marjanovic
Review Article Page 1 of 8 High-flow nasal oxygen therapy and noninvasive ventilation in the management of acute hypoxemic respiratory failure Jean-Pierre Frat 1,2,3, Rémi Coudroy 1,2,3, Nicolas Marjanovic
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION
 CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
POLICY. Number: Title: APPLICATION OF NON INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE. Authorization
 POLICY Number: 7311-60-024 Title: APPLICATION OF NON INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Authorization [ ] President and CEO [ x ] Vice President, Finance and Corporate Services Source:
POLICY Number: 7311-60-024 Title: APPLICATION OF NON INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE Authorization [ ] President and CEO [ x ] Vice President, Finance and Corporate Services Source:
Case Scenarios. Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC. Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity
 Case Scenarios Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Case 1 A 36 year male with cirrhosis and active GI bleeding is intubated to protect his airway,
Case Scenarios Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Case 1 A 36 year male with cirrhosis and active GI bleeding is intubated to protect his airway,
10/17/2016 OXYGEN DELIVERY: INDICATIONS AND USE OF EQUIPMENT COURSE OBJECTIVES COMMON CAUSES OF RESPIRATORY FAILURE
 OXYGEN DELIVERY: INDICATIONS AND USE OF EQUIPMENT J U L I E Z I M M E R M A N, R N, M S N C L I N I C A L N U R S E S P E C I A L I S T E L O I S A C U T L E R, R R T, B S R C C L I N I C A L / E D U C
OXYGEN DELIVERY: INDICATIONS AND USE OF EQUIPMENT J U L I E Z I M M E R M A N, R N, M S N C L I N I C A L N U R S E S P E C I A L I S T E L O I S A C U T L E R, R R T, B S R C C L I N I C A L / E D U C
ERJ Express. Published on August 9, 2012 as doi: /
 ERJ Express. Published on August 9, 2012 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00076912 Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in a non intubated patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) Olaf Wiesner, *
ERJ Express. Published on August 9, 2012 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00076912 Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in a non intubated patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) Olaf Wiesner, *
Average volume-assured pressure support
 Focused review Average volume-assured pressure support Abdurahim Aloud MD Abstract Average volume-assured pressure support (AVAPS) is a relatively new mode of noninvasive positive pressure ventilation
Focused review Average volume-assured pressure support Abdurahim Aloud MD Abstract Average volume-assured pressure support (AVAPS) is a relatively new mode of noninvasive positive pressure ventilation
Physiologic Effects of High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen in Critical Care Subjects
 Physiologic Effects of High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen in Critical Care Subjects Frederic Vargas MD PhD, Mélanie Saint-Leger MD, Alexandre Boyer MD PhD, Nam H Bui MD, and Gilles Hilbert MD PhD INTRODUCTION:
Physiologic Effects of High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen in Critical Care Subjects Frederic Vargas MD PhD, Mélanie Saint-Leger MD, Alexandre Boyer MD PhD, Nam H Bui MD, and Gilles Hilbert MD PhD INTRODUCTION:
(To be filled by the treating physician)
 CERTIFICATE OF MEDICAL NECESSITY TO BE ISSUED TO CGHS BENEFICIAREIS BEING PRESCRIBED BILEVEL CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BI-LEVEL CPAP) / BI-LEVEL VENTILATORY SUPPORT SYSTEM Certification Type
CERTIFICATE OF MEDICAL NECESSITY TO BE ISSUED TO CGHS BENEFICIAREIS BEING PRESCRIBED BILEVEL CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BI-LEVEL CPAP) / BI-LEVEL VENTILATORY SUPPORT SYSTEM Certification Type
Gestione della dispnea nell insufficienza respiratoria end-stage
 Gestione della dispnea nell insufficienza respiratoria end-stage Salvatore M. Maggiore, MD, PhD salvatore.maggiore@unich.it Anesthesia and Intensive Care SS. Annunziata Hospital Gabriele d Annunzio University
Gestione della dispnea nell insufficienza respiratoria end-stage Salvatore M. Maggiore, MD, PhD salvatore.maggiore@unich.it Anesthesia and Intensive Care SS. Annunziata Hospital Gabriele d Annunzio University
Rachael L Parke MHSc, Shay P McGuinness, and Michelle L Eccleston RN
 Original Research A Preliminary Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess Effectiveness of Nasal High-Flow Oxygen in Intensive Care Patients Rachael L Parke MHSc, Shay P McGuinness, and Michelle L Eccleston
Original Research A Preliminary Randomized Controlled Trial to Assess Effectiveness of Nasal High-Flow Oxygen in Intensive Care Patients Rachael L Parke MHSc, Shay P McGuinness, and Michelle L Eccleston
Transnasal Humidified Rapid Insufflation Ventilatory Exchange (THRIVE): An Optimal Method of Preoxygenation for General Anaesthesia in Obstetrics
 Transnasal Humidified Rapid Insufflation Ventilatory Exchange (THRIVE): An Optimal Method of Preoxygenation for General Anaesthesia in Obstetrics Dr E McMaster, Dr E Gent, Dr T Mahendrayogam, Dr A Surendran
Transnasal Humidified Rapid Insufflation Ventilatory Exchange (THRIVE): An Optimal Method of Preoxygenation for General Anaesthesia in Obstetrics Dr E McMaster, Dr E Gent, Dr T Mahendrayogam, Dr A Surendran
Oxygen & High flow nasal Oxygen therapy. Learning points. Why? 18/07/
 Oxygen & High flow nasal Oxygen therapy 13.07.2017 Learning points Update on BTS guidance May 2017 Help you understand the mechanism of action of high flow nasal oxygen therapy Help you think about the
Oxygen & High flow nasal Oxygen therapy 13.07.2017 Learning points Update on BTS guidance May 2017 Help you understand the mechanism of action of high flow nasal oxygen therapy Help you think about the
NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP)
 Introduction NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a method of delivering oxygen by positive pressure mask that allows for the prevention or postponement of invasive
Introduction NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a method of delivering oxygen by positive pressure mask that allows for the prevention or postponement of invasive
Oxygen and ABG. Dr Will Dooley
 Oxygen and ABG G Dr Will Dooley Oxygen and ABGs Simply in 10 cases Recap of: ABG interpretation Oxygen management Some common concerns A-a gradient Base Excess Anion Gap COPD patients CPAP/BiPAP First
Oxygen and ABG G Dr Will Dooley Oxygen and ABGs Simply in 10 cases Recap of: ABG interpretation Oxygen management Some common concerns A-a gradient Base Excess Anion Gap COPD patients CPAP/BiPAP First
Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo
 Instant dowload and all chapters Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-pilbeams-mechanical-ventilation-physiologicalclinical-applications-6th-edition-cairo/
Instant dowload and all chapters Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-pilbeams-mechanical-ventilation-physiologicalclinical-applications-6th-edition-cairo/
Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor
 Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC. Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand
 786 High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand Disclaimer I was a scep@c un@l I used it Now I am a firm believer HFNC The Fisher and Paykel
786 High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand Disclaimer I was a scep@c un@l I used it Now I am a firm believer HFNC The Fisher and Paykel
Objectives. Health care significance of ARF 9/10/15 TREATMENT OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE OF VARIABLE CAUSES: INVASIVE VS. NON- INVASIVE VENTILATION
 TREATMENT OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE OF VARIABLE CAUSES: INVASIVE VS. NON- INVASIVE VENTILATION Louisa Chika Ikpeama, DNP, CCRN, ACNP-BC Objectives Identify health care significance of acute respiratory
TREATMENT OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY FAILURE OF VARIABLE CAUSES: INVASIVE VS. NON- INVASIVE VENTILATION Louisa Chika Ikpeama, DNP, CCRN, ACNP-BC Objectives Identify health care significance of acute respiratory
NI 60. Non-invasive ventilation without compromise. Homecare Pneumology Neonatology Anaesthesia. Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support
 NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without compromise Homecare Pneumology Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without
NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without compromise Homecare Pneumology Neonatology Anaesthesia INTENSIVE CARE VENTILATION Sleep Diagnostics Service Patient Support NI 60 Non-invasive ventilation without
Index. sleep.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acquired central hypoventilation syndrome, NPPV in children with, 475 Acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema, PAP therapy in, 394 395 Adaptive
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acquired central hypoventilation syndrome, NPPV in children with, 475 Acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema, PAP therapy in, 394 395 Adaptive
NIV in Acute Respiratory Failure: Where we fail? Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity
 NIV in Acute Respiratory Failure: Where we fail? Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Use of NIV 1998-2010 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1998
NIV in Acute Respiratory Failure: Where we fail? Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Use of NIV 1998-2010 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1998
Positive End-Expiratory Pressure Effect of 3 High-Flow Nasal Cannula Devices
 Positive End-Expiratory Pressure Effect of 3 High-Flow Nasal Cannula Devices Jing-chao Luo MD, Mei-shan Lu RN, Zhi-hong Zhao MD, Wei Jiang MD, Biao Xu MD, Li Weng MD, Tong Li MD, and Bin Du MD BACKGROUND:
Positive End-Expiratory Pressure Effect of 3 High-Flow Nasal Cannula Devices Jing-chao Luo MD, Mei-shan Lu RN, Zhi-hong Zhao MD, Wei Jiang MD, Biao Xu MD, Li Weng MD, Tong Li MD, and Bin Du MD BACKGROUND:
High-flow nasal cannula use in a paediatric intensive care unit over 3 years
 High-flow nasal cannula use in a paediatric intensive care unit over 3 years Tracey I Wraight and Subodh S Ganu Respiratory illness and/or distress is the commonest reason for non-elective paediatric intensive
High-flow nasal cannula use in a paediatric intensive care unit over 3 years Tracey I Wraight and Subodh S Ganu Respiratory illness and/or distress is the commonest reason for non-elective paediatric intensive
IICU Staff Meeting Minutes May 15 and 16, 2013 IICU Conference Room
 IICU Staff Meeting Minutes May 15 and 16, 2013 IICU Conference Room 1) Decreasing Telemetry Alarms Janice Marlett, BSN, RN, Nursing Staff Educator To decrease tele alarms: Properly prep the skin Shave
IICU Staff Meeting Minutes May 15 and 16, 2013 IICU Conference Room 1) Decreasing Telemetry Alarms Janice Marlett, BSN, RN, Nursing Staff Educator To decrease tele alarms: Properly prep the skin Shave
High-Flow Therapy Literature list
 High-Flow Therapy Literature list Tables of contents Categories 1 Therapy overview / Reviews 8 12 13 14 15 28 29 76 2 Mechanisms of action / Physiological Benefits of high flow oxygen therapy Flushing
High-Flow Therapy Literature list Tables of contents Categories 1 Therapy overview / Reviews 8 12 13 14 15 28 29 76 2 Mechanisms of action / Physiological Benefits of high flow oxygen therapy Flushing
Non-Invasive Ventilation
 Khusrav Bajan Head Emergency Medicine, Consultant Intensivist & Physician, P.D. Hinduja National Hospital & M.R.C. 112 And the Lord God formed man of the dust of the ground and breathed into his nostrils
Khusrav Bajan Head Emergency Medicine, Consultant Intensivist & Physician, P.D. Hinduja National Hospital & M.R.C. 112 And the Lord God formed man of the dust of the ground and breathed into his nostrils
FAILURE OF NONINVASIVE VENTILATION FOR DE NOVO ACUTE HYPOXEMIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE: ROLE OF TIDAL VOLUME
 FAILURE OF NONINVASIVE VENTILATION FOR DE NOVO ACUTE HYPOXEMIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE: ROLE OF TIDAL VOLUME Guillaume CARTEAUX, Teresa MILLÁN-GUILARTE, Nicolas DE PROST, Keyvan RAZAZI, Shariq ABID, Arnaud
FAILURE OF NONINVASIVE VENTILATION FOR DE NOVO ACUTE HYPOXEMIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE: ROLE OF TIDAL VOLUME Guillaume CARTEAUX, Teresa MILLÁN-GUILARTE, Nicolas DE PROST, Keyvan RAZAZI, Shariq ABID, Arnaud
Prone ventilation revisited in H1N1 patients
 International Journal of Advanced Multidisciplinary Research ISSN: 2393-8870 www.ijarm.com DOI: 10.22192/ijamr Volume 5, Issue 10-2018 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijamr.2018.05.10.005 Prone
International Journal of Advanced Multidisciplinary Research ISSN: 2393-8870 www.ijarm.com DOI: 10.22192/ijamr Volume 5, Issue 10-2018 Case Report DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22192/ijamr.2018.05.10.005 Prone
Mechanical Ventilation of the Patient with Neuromuscular Disease
 Mechanical Ventilation of the Patient with Neuromuscular Disease Dean Hess PhD RRT Associate Professor of Anesthesia, Harvard Medical School Assistant Director of Respiratory Care, Massachusetts General
Mechanical Ventilation of the Patient with Neuromuscular Disease Dean Hess PhD RRT Associate Professor of Anesthesia, Harvard Medical School Assistant Director of Respiratory Care, Massachusetts General
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Non-Invasive Ventilation in Pediatric Medicine. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Non-Invasive Ventilation in Pediatric Medicine. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key
Oxygen: Is there a problem? Tom Heaps Acute Physician
 Oxygen: Is there a problem? Tom Heaps Acute Physician Case 1 79-year-old female, diabetic, morbidly obese Admitted with LVF Overnight Reduced GCS?cause 15l NRB in situ ABG showed ph 6.9, pco 2 15.9kPa
Oxygen: Is there a problem? Tom Heaps Acute Physician Case 1 79-year-old female, diabetic, morbidly obese Admitted with LVF Overnight Reduced GCS?cause 15l NRB in situ ABG showed ph 6.9, pco 2 15.9kPa
GE Healthcare. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator. Relief, Relax, Recovery
 GE Healthcare Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator Relief, Relax, Recovery COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world, and further increases in the prevalence
GE Healthcare Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator Relief, Relax, Recovery COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world, and further increases in the prevalence
INDICATIONS FOR RESPIRATORY ASSISTANCE A C U T E M E D I C I N E U N I T P - Y E A R M B B S 4
 INDICATIONS FOR RESPIRATORY ASSISTANCE A C U T E M E D I C I N E U N I T P - Y E A R M B B S 4 RESPIRATORY FAILURE Acute respiratory failure is defined by hypoxemia with or without hypercapnia. It is one
INDICATIONS FOR RESPIRATORY ASSISTANCE A C U T E M E D I C I N E U N I T P - Y E A R M B B S 4 RESPIRATORY FAILURE Acute respiratory failure is defined by hypoxemia with or without hypercapnia. It is one
Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices
 Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices Dr LAU Chun Wing Arthur Department of Intensive Care Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital 6 October 2009 In this lecture, you will learn Major concepts
Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices Dr LAU Chun Wing Arthur Department of Intensive Care Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital 6 October 2009 In this lecture, you will learn Major concepts
Concerns and Controversial Issues in NPPV. Concerns and Controversial Issues in Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation
 : Common Therapy in Daily Practice Concerns and Controversial Issues in Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation Rongchang Chen Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Disease as the first choice of mechanical
: Common Therapy in Daily Practice Concerns and Controversial Issues in Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation Rongchang Chen Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Disease as the first choice of mechanical
Over the last several years various national and
 Recommendations for the Management of COPD* Gary T. Ferguson, MD, FCCP Three sets of guidelines for the management of COPD that are widely recognized (from the European Respiratory Society [ERS], American
Recommendations for the Management of COPD* Gary T. Ferguson, MD, FCCP Three sets of guidelines for the management of COPD that are widely recognized (from the European Respiratory Society [ERS], American
Intensive Care Medicine Experimental. Yu Onodera * , Ryo Akimoto, Hiroto Suzuki, Masayuki Okada, Masaki Nakane and Kaneyuki Kawamae
 Onodera et al. Intensive Care Medicine Experimental (2018) 6:7 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40635-018-0172-7 Intensive Care Medicine Experimental RESEARCH Open Access A high-flow nasal cannula system with
Onodera et al. Intensive Care Medicine Experimental (2018) 6:7 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40635-018-0172-7 Intensive Care Medicine Experimental RESEARCH Open Access A high-flow nasal cannula system with
Tissue Hypoxia and Oxygen Therapy
 Tissue Hypoxia and Oxygen Therapy ก ก ก ก ก ก 1. ก ก 2. ก ก 3. tissue hypoxia 4. ก ก ก 5. ก ก ก 6. ก กก ก 7. ก ก tissue hypoxia ก ก ก ก 1. Pathway of oxygen transport 2. Causes of tissue hypoxia 3. Effect
Tissue Hypoxia and Oxygen Therapy ก ก ก ก ก ก 1. ก ก 2. ก ก 3. tissue hypoxia 4. ก ก ก 5. ก ก ก 6. ก กก ก 7. ก ก tissue hypoxia ก ก ก ก 1. Pathway of oxygen transport 2. Causes of tissue hypoxia 3. Effect
Basics of NIV. Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC. Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity
 Basics of NIV Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Objectives: Definitions Advantages and Disadvantages Interfaces Indications Contraindications
Basics of NIV Dr Shrikanth Srinivasan MD,DNB,FNB,EDIC Consultant, Critical Care Medicine Medanta, The Medicity Objectives: Definitions Advantages and Disadvantages Interfaces Indications Contraindications
NIV use in ED. Dr. Khalfan AL Amrani Emergency Resuscitation Symposium 2 nd May 2016 SQUH
 NIV use in ED Dr. Khalfan AL Amrani Emergency Resuscitation Symposium 2 nd May 2016 SQUH Outline History & Introduction Overview of NIV application Review of proven uses of NIV History of Ventilation 1940
NIV use in ED Dr. Khalfan AL Amrani Emergency Resuscitation Symposium 2 nd May 2016 SQUH Outline History & Introduction Overview of NIV application Review of proven uses of NIV History of Ventilation 1940
Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) include both hereditary and acquired diseases of the peripheral neuromuscular system. They are diseases of the
 Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) include both hereditary and acquired diseases of the peripheral neuromuscular system. They are diseases of the peripheral nerves (neuropathies and anterior horn cell diseases),
Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) include both hereditary and acquired diseases of the peripheral neuromuscular system. They are diseases of the peripheral nerves (neuropathies and anterior horn cell diseases),
Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet
 Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet 1. Name of Guideline / Policy/ Procedure 2. Purpose of Procedure/ Guidelines/ Protocol Guideline for
Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet 1. Name of Guideline / Policy/ Procedure 2. Purpose of Procedure/ Guidelines/ Protocol Guideline for
Challenging Cases in Pediatric Polysomnography. Fauziya Hassan, MBBS, MS Assistant Professor Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep
 Challenging Cases in Pediatric Polysomnography Fauziya Hassan, MBBS, MS Assistant Professor Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Conflict of Interest None pertaining to this topic Will be using some slides from
Challenging Cases in Pediatric Polysomnography Fauziya Hassan, MBBS, MS Assistant Professor Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Conflict of Interest None pertaining to this topic Will be using some slides from
High Flow Nasal Cannula in Children During Sleep. Brian McGinley M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics University of Utah
 High Flow Nasal Cannula in Children During Sleep Brian McGinley M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics University of Utah Disclosures Conflicts of Interest: None Will discuss a product that is commercially
High Flow Nasal Cannula in Children During Sleep Brian McGinley M.D. Associate Professor of Pediatrics University of Utah Disclosures Conflicts of Interest: None Will discuss a product that is commercially
Nasal high-flow oxygen therapy system for improving sleep-related hypoventilation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a case report
 Okuda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:341 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Nasal high-flow oxygen therapy system for improving sleep-related hypoventilation in chronic
Okuda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:341 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Nasal high-flow oxygen therapy system for improving sleep-related hypoventilation in chronic
Recent Advances in Respiratory Medicine
 Recent Advances in Respiratory Medicine Dr. R KUMAR Pulmonologist Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) NIV Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) refers to the administration of ventilatory support without using an invasive
Recent Advances in Respiratory Medicine Dr. R KUMAR Pulmonologist Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) NIV Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) refers to the administration of ventilatory support without using an invasive
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Motor neurone disease: the use of non-invasive ventilation in the management of motor neurone disease 1.1 Short title Motor
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Motor neurone disease: the use of non-invasive ventilation in the management of motor neurone disease 1.1 Short title Motor
Youfeng Zhu 1, Haiyan Yin 1, Rui Zhang 1 and Jianrui Wei 2*
 Zhu et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2017) 17:201 DOI 10.1186/s12890-017-0525-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy versus conventional oxygen therapy in patients with acute
Zhu et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2017) 17:201 DOI 10.1186/s12890-017-0525-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy versus conventional oxygen therapy in patients with acute
Chris Cameron Clinical pharmacologist & General Physician CCDHB. Oxygen- A prescribing Blindspot?
 Chris Cameron Clinical pharmacologist & General Physician CCDHB Oxygen- A prescribing Blindspot? Ms J, 70yo Lives with partner, who has a recent diagnosis of breast cancer Works 3 days a week Weight 46kg
Chris Cameron Clinical pharmacologist & General Physician CCDHB Oxygen- A prescribing Blindspot? Ms J, 70yo Lives with partner, who has a recent diagnosis of breast cancer Works 3 days a week Weight 46kg
(Non)-invasive ventilation: transition from PICU to home. Christian Dohna-Schwake
 (Non)-invasive ventilation: transition from PICU to home Christian Dohna-Schwake Increased use of NIV in PICUs over last 15 years First choice of respiratory support in many diseases Common temporary indications:
(Non)-invasive ventilation: transition from PICU to home Christian Dohna-Schwake Increased use of NIV in PICUs over last 15 years First choice of respiratory support in many diseases Common temporary indications:
5. What is the cause of this patient s metabolic acidosis? LACTIC ACIDOSIS SECONDARY TO ANEMIC HYPOXIA (HIGH CO LEVEL)
 Self-Assessment RSPT 2350: Module F - ABG Analysis 1. You are called to the ER to do an ABG on a 40 year old female who is C/O dyspnea but seems confused and disoriented. The ABG on an FiO 2 of.21 show:
Self-Assessment RSPT 2350: Module F - ABG Analysis 1. You are called to the ER to do an ABG on a 40 year old female who is C/O dyspnea but seems confused and disoriented. The ABG on an FiO 2 of.21 show:
County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System
 County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System Policy #700-M12: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE Effective: February 8, 2013TBD Replaces: NewFebruary 8,
County of Santa Clara Emergency Medical Services System Policy #700-M12: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE Effective: February 8, 2013TBD Replaces: NewFebruary 8,
High flow nasal Oxygen therapy. Learning points. Part 1: Oxygen 21/06/ Oxford Advanced Course: Newcastle
 High flow nasal Oxygen therapy 15.06.2017 Oxford Advanced Course: Newcastle Learning points Update on BTS guidance May 2017 Help you understand the mechanism of action of high flow nasal oxygen therapy
High flow nasal Oxygen therapy 15.06.2017 Oxford Advanced Course: Newcastle Learning points Update on BTS guidance May 2017 Help you understand the mechanism of action of high flow nasal oxygen therapy
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device
 I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
RESPIRATORY FAILURE. Dr Graeme McCauley KGH
 RESPIRATORY FAILURE Dr Graeme McCauley KGH Definitions Failure to oxygenate-pao2 < 60 Failure to clear CO2-PaCO2 > 50 Acute vs Chronic Hypoxemic failure- type l Hypercapneic failure- type ll Causes of
RESPIRATORY FAILURE Dr Graeme McCauley KGH Definitions Failure to oxygenate-pao2 < 60 Failure to clear CO2-PaCO2 > 50 Acute vs Chronic Hypoxemic failure- type l Hypercapneic failure- type ll Causes of
Non-invasive Ventilation protocol For COPD
 NHS LANARKSHIRE MONKLANDS HOSPITAL Non-invasive Ventilation protocol For COPD April 2017 S Baird Review Date: Oct 2019 Approved by Medical Directorate Indications for Non-Invasive Ventilation (NIV) NIV
NHS LANARKSHIRE MONKLANDS HOSPITAL Non-invasive Ventilation protocol For COPD April 2017 S Baird Review Date: Oct 2019 Approved by Medical Directorate Indications for Non-Invasive Ventilation (NIV) NIV
BTS Guideline for Home Oxygen use in adults Appendix 9 (online only) Key Questions - PICO 10 December 2012
 BTS Guideline for Home Oxygen use in adults Appendix 9 (online only) Key Questions - PICO 10 December 2012 Evidence base for Home Oxygen therapy in COPD, non-copd respiratory disease and nonrespiratory
BTS Guideline for Home Oxygen use in adults Appendix 9 (online only) Key Questions - PICO 10 December 2012 Evidence base for Home Oxygen therapy in COPD, non-copd respiratory disease and nonrespiratory
Dyspnea: Should we use BIPAP?
 Dyspnea: Should we use BIPAP? Thomas R. Gildea MD, MS FCCP Head Section of Bronchoscopy Respiratory Institute Transplant Center Disclosure SuperDimension Inc. PI for single center study Others: Aeris,
Dyspnea: Should we use BIPAP? Thomas R. Gildea MD, MS FCCP Head Section of Bronchoscopy Respiratory Institute Transplant Center Disclosure SuperDimension Inc. PI for single center study Others: Aeris,
Images have been removed from the PowerPoint slides in this handout due to copyright restrictions.
 Arterial Blood Gas Interpretation Routine Assessment Inspection Palpation Auscultation Labs Na 135-145 K 3.5-5.3 Chloride 95-105 CO2 22-31 BUN 10-26 Creat.5-1.2 Glu 80-120 Arterial Blood Gases WBC 5-10K
Arterial Blood Gas Interpretation Routine Assessment Inspection Palpation Auscultation Labs Na 135-145 K 3.5-5.3 Chloride 95-105 CO2 22-31 BUN 10-26 Creat.5-1.2 Glu 80-120 Arterial Blood Gases WBC 5-10K
Learning Objectives. 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence
 Learning Objectives 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence Pre-hospital Non-invasive vventilatory support Marc Gillis, MD Imelda Bonheiden Our goal out there
Learning Objectives 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence Pre-hospital Non-invasive vventilatory support Marc Gillis, MD Imelda Bonheiden Our goal out there
Non-invasive Ventilation
 Non-invasive Ventilation 163 29 Non-invasive Ventilation AM BHAGWATI Artificial ventilatory support has became an integral component in the management of critically ill patients in the intensive care units.
Non-invasive Ventilation 163 29 Non-invasive Ventilation AM BHAGWATI Artificial ventilatory support has became an integral component in the management of critically ill patients in the intensive care units.
COPD Challenge CASE PRESENTATION
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations may make up more than 10% of acute medical admissions [1], and they are increasingly recognised as a cause of significant morbidity and mortality
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbations may make up more than 10% of acute medical admissions [1], and they are increasingly recognised as a cause of significant morbidity and mortality
NIV and Aerosoltherapy
 NIV and Aerosoltherapy Workshop Jean-Bernard Michotte (Lausanne-CH) Simone Gambazza (Milano-IT) Jean-Bernard Michotte Haute Ecole de Santé Vaud, 1011 Lausanne - Suisse Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc,
NIV and Aerosoltherapy Workshop Jean-Bernard Michotte (Lausanne-CH) Simone Gambazza (Milano-IT) Jean-Bernard Michotte Haute Ecole de Santé Vaud, 1011 Lausanne - Suisse Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc,
OXYGEN USE IN PHYSICAL THERAPY PRACTICE. Rebecca H. Crouch, PT,DPT,MS,CCS,FAACVPR
 OXYGEN USE IN PHYSICAL THERAPY PRACTICE Rebecca H. Crouch, PT,DPT,MS,CCS,FAACVPR Supplemental Oxygen Advantages British Medical Research Council Clinical Trial Improved survival using oxygen 15 hrs/day
OXYGEN USE IN PHYSICAL THERAPY PRACTICE Rebecca H. Crouch, PT,DPT,MS,CCS,FAACVPR Supplemental Oxygen Advantages British Medical Research Council Clinical Trial Improved survival using oxygen 15 hrs/day
Respiratory Pathophysiology Cases Linda Costanzo Ph.D.
 Respiratory Pathophysiology Cases Linda Costanzo Ph.D. I. Case of Pulmonary Fibrosis Susan was diagnosed 3 years ago with diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. She tries to continue normal activities,
Respiratory Pathophysiology Cases Linda Costanzo Ph.D. I. Case of Pulmonary Fibrosis Susan was diagnosed 3 years ago with diffuse interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. She tries to continue normal activities,
A study of non-invasive ventilation in acute respiratory failure
 Original Research Article A study of non-invasive ventilation in acute respiratory failure Nilima Manohar Mane 1, Jayant L. Pednekar 2, Sangeeta Pednekar 3* 1 Consultant Physician and Diabetologist, Apollo
Original Research Article A study of non-invasive ventilation in acute respiratory failure Nilima Manohar Mane 1, Jayant L. Pednekar 2, Sangeeta Pednekar 3* 1 Consultant Physician and Diabetologist, Apollo
Bilevel positive airway pressure nasal mask ventilation in patients with acute hypercapnic respiratory failure
 Bilevel positive airway pressure nasal mask ventilation in patients with acute hypercapnic respiratory failure CK Chan, KS Lau, HC Fan, CW Lam The efficacy and complications of bilevel positive airway
Bilevel positive airway pressure nasal mask ventilation in patients with acute hypercapnic respiratory failure CK Chan, KS Lau, HC Fan, CW Lam The efficacy and complications of bilevel positive airway
