(10) Patent No.: US 6,836,684 B1
|
|
|
- Earl Williams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (12) United States Patent Rijkhoff et al. US B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,836,684 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 28, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (51) (52) (58) (56) METHOD TO CONTROLAN OVERACTIVE BLADDER Inventors: Nico J. M. Rijkhoff, Aalborg (DK); Thomas Sinkjaer, Gistrup (DK); Saso Jezernik, Zurich (CH); Warren Grill, Cleveland Heights, OH (US) Assignee: Neurocon ApS, Aalborg O (DK) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by 0 days. Appl. No.: 09/830,666 PCT Fed: Oct. 29, 1999 PCT No.: PCT/DK99/00589 S371 (c)(1), (2), (4) Date: Jul. 30, 2001 PCT Pub. No.: WO00/25859 PCT Pub. Date: May 11, 2000 Int. Cl... A61N 1/08 U.S. Cl /40 Field of Search /363, 377; 607/40, 41, 115, 116 References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 3,662,758. A 5/1972 Glover /40 3,870,051 A 3/1975 Brindley /422 4, A 9/1983 Horwinski et al /422 4,607,639 A 8/1986 Tanagho et al /419 E 5,188,104 A * 2/1993 Wernicke et al /40 5, A * 4/1993 Fang et al /419 E 6,354,991 B1 3/2002 Gross et al /29 6,505,074 B2 * 1/2003 Boveja et al /41 6,587,725 B1 * 7/2003 Durand et al /42 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS WO 95/ /1995 OTHER PUBLICATIONS Sengupta et al.; Mechanosensitive Properties of Pelvic Nerve Afferent Fibers Innervating the Urinary Bladder of the Rat; Journal of Neurophysiology, vol. 72, No. 5, 1994, Vodusek et al.; Detrusor Inhibition on Selective Pudendal Nerve Stimulation in the Perineum; Neurourology and Uro dynamics; 6: , Wiart et al., The effects of capsaicin on the neurogenic hyperreflexic detrusor. A double blind placebo controlled Study in patients with Spinal cord disease. Preliminary results; Spinal Cord (1998), 36: Binard et al.; Intermittent Catheterization the Right Way! (Volume vs. Time-Directed); The Journal of Spinal Cord Medicine; vol. 19, No. 3, Rijkhoff et al.; Acute Animal Studies on the Use of an Anodal Block to Reduce Urethral Resistance in Sacral Root Stimulation; IEEE Transactions on Rehabilitation Engineer ing, vol. 2, No. 2, 1994; (List continued on next page.) Primary Examiner Jeffrey R. Jastrzab Assistant Examiner Frances P. Oropeza (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Jacobson Holman PLLC (57) ABSTRACT A method to control an overactive bladder and to estimate bladder Volume using an implanted Sensor having at least one nerve electrode to Sense electrical Signals. The method includes detecting events from nerve signals, generating electrical pulses for Stimulating nerves, and Stimulating the nerves to inhibit detrusor contraction. Bladder volume may also be estimated based on the amplitude of the detected nerve signals and/or the time between two detected nerve Signals from consecutive detrusor contractions. 13 Claims, 2 Drawing Sheets Signal Processing Urit Stinuator
2 US 6,836,684 B1 Page 2 OTHER PUBLICATIONS Rijkhoff et al.; Selective detrusor activation by Sacral ventral nerve-root Stimulation: results of intraoperative testing in humans during implantation of a Finetech-Brindley System; World J Urol (1998) 16: Koldewijn et al.; Bladder Pressure Sensors in an Animal Model; Journal of Urology, 151, , Wheeler, Jr. et al.; Bladder Inhibition by Penile Nerve Stimulation in Spinal Cord Injury Patients; The Journal of Urology, vol. 147, , Van Kerrebroeck et al., Intradural Sacral rhizotomies and implantation of an anterior Sacral root Stimulator in the treatment of neurogenic bladder dysfunction after Spinal cord injury. Surgical technique and complications, World Journal of Urology, 9: , Koldewijn et al.; Bladder Compliance After Posterior Sacral Root Rhizotomies and Anterior Sacral Root Stimulation; Journal of Urology, 151, , Sidi et al.; Augmentation Enterocystoplasty for the Manage ment of Voiding Dysfunction in Spinal Cord Injury Patients; The Journal of Urology, vol. 143, pp , Lefurge et al., Chronically Implanted Intrafascicular Recording Electrodes, Annals of Biomedical Engineering; vol. 19, 1991, pp * cited by examiner
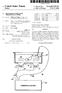
3 U.S. Patent Dec. 28, 2004 Sheet 1 of 2 US 6,836,684 B1 FIG. 1 1 O Signol processor Stimulator Peripheral sensory eye Amplifier Peripheroi nerve FG Signol processor Tronsmitter Receiver Actuator Amplifier Peripheral sensory nerve
4 U.S. Patent Dec. 28, 2004 Sheet 2 of 2 US 6,836,684 B1 FIG 3 Signo Processing Unit Stimuotor
5 1 METHOD TO CONTROLAN OVERACTIVE BLADDER BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Field of the Invention This application concerns a method to control an overac tive bladder and to estimate bladder Volume, comprising an implanted Sensor, which Sensor comprises at least one nerve electrode to Sense electrical Signals, means for Stimulation of nerves to inhibit detrusor contraction, an electronic unit to detect events from nerve signals and generate electrical pulses for Stimulating nerves. 2. Description of the Related Art U.S. Pat. No. 4,406,228 discloses a system that purport edly conditions pelvic floor musculature by means of neu rostimulation for the purpose of controlling urinary loss. Such System includes Stimulation apparatus for applying electrical pulses to electrodes implanted in the abdominal region or to a plug positioned in an anus. The plug contacts the Spincter muscle of the anus for the alleged purpose of inhibiting bladder contraction in response to excitation of the plug. In this way the bladder volume is not measured, which can lead to bladder over distensions, and can lead to bladder rupture. The Storage phase of the micturition cycle requires a stable bladder with high compliance (i.e. a relaxed bladder) and closed urethral outlet. However, due to the feedback System the bladder may easily become unstable. Any Stimu lus that elicits a small burst of impulses in the mechanore ceptor afferents, Such as coughing and jumping, may trigger an involuntary micturition reflex and cause urine leakage. To prevent this from happening, the neural control System is equipped with Several inhibitory circuits, both at Spinal and Supraspinal levels, which prevent the detrusor muscle from contracting. However, these inhibitory circuits are Suscep tible to a variety of neurologic disorders. Therefore, patients with neurologic disorders frequently Suffer from urinary incontinence due to involuntary detrusor contractions. The impaired Storage function could in principle be improved by methods that decrease the sensitivity of the bladder afferents, decrease the activity of the bladder effer ents or increase the bladder Volume/capacity. Available treatment options are therefore: Surgical augmentation of the bladder Sidi et al., 1990), Surgical deafferentation of the bladder Koldewijn et al., 1994), the use of anticholinergic drugs and the use of intravesical capsaicin Wiart et al., 1998). Bladder inhibition by electrical stimulation has been described before e.g. Vodusek et al., 1988; Wheeler et al., 1992 but only continuous stimulation was used, i.e. stimu lation is permanent except during voiding. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION The objects of the invention are: 1) treatment of involuntary loss of urine (incontinence) due to involuntary detrusor contractions (detrusor overactivity) 2) estimation of bladder volume. This finds particular application in patients who use aids to empty their bladder e.g. intermittent catherisation or electrical Stimulation. The invention finds particular application in patients where the involuntary detrusor contraction is associated with a neurologic disorder. US 6,836,684 B Treatment of detrusor overactivity and estimation of blad der volume can be achieved by a method as described in the first paragraph using a closed loop Stimulation System to allow event-driven inhibition of the bladder where stimula tion is only applied when an undesired bladder contraction occurs, and an implanted Sensor comprising at least one nerve electrode to Sense electrical Signals from nerves innervating the bladder. Sensing electrical Signals related to mechanical bladder activity via Said Sensor, the method detects the onset of a bladder contraction and estimates bladder Volume using Signal processing methods, activating an inhibitory neural circuit by Stimulating afferent nerve fibers. By this method no nerves have to be cut, and no irrevers ible Surgery has to be done. Stimulation of neural tissue only takes place when needed, and the Volume of the bladder is monitored. The present invention uses electrical Stimulation to inhibit the bladder. Inhibition of the bladder by electrical Stimulation is possible Since, besides the mentioned neural inhibitory circuits, additional Spinal inhibitory circuits exist to prevent involuntary leakage during, e.g., defecation, coi tus and physical activity. Activation of the afferent paths of these neural circuits has two effects: they activate the in hibitory sympathetic neurons to the bladder and they provide central inhibition of the preganglionic detrusor-motoneurons through a direct route in the Spinal cord. These additional inhibitory reflexes are not Suppressed during micturition, which means that they are quite capable of interrupting a detrusor contraction. Activation of these reflexes by electri cal Stimulation is a nondestructive alternative method for patients who are refractory to drugs, cannot tolerate the Side effects or for other reasons do not accept a drug treatment. Primarily, the recorded nerve signals come from afferents innervating mechanoreceptors located in the bladder wall. By detecting the onset of the bladder contraction, the Stimu lator can be activated only when contraction occurs, and continuous Stimulation is not necessary. This minimises the risk of neural damage due to the Stimulation. In addition, if the patient can Sense the Stimulation, the duration of Stimu lation should be minimised to minimise the discomfort. The Step of implanting a Sensor might comprise the Step of implanting a nerve cuff electrode. The intrafasicular electrode is flexible and Small, and may be preferred in locations where limited Space is available. The Step of implanting a Sensor might comprise the Step of implanting an intrafasicular electrode Lefurge et al., 1991). The intrafasicular electrode is flexible and smaller, and might be preferred in locations where limited Space is available. The electrodes can be used to detect efferent or afferent nerve activity. The same electrode could be used to record both types of nerve Signals. The electrode can be placed on a nerve that contains afferent nerve fibres innervating mechanoreceptors located in the bladder. In this way information about the status of the bladder can be obtained. The electrode can be located at the intradural or extradural dorsal Sacral nerve roots. In this way the electrodes can be placed at a mechanically stable position, and the nerve roots are relatively long, which enables easy placement of elec trodes. The electrode can be placed on a nerve that contains efferent nerve fibres innervating the bladder, so bladder activation can be monitored. The electrode can be located at the intradural or extradural Ventral Sacral nerve roots. In this way the electrodes can be placed at a mechanically stable position, and the nerve roots are relatively long, which enables easy placement of elec trodes.
6 3 The electrode might be located at at least one of the preganglionic pelvic nerve branches and postganglionic nerve branches. In this way nerve signals from the bladder can be recorded more Selectively without contamination with Signals from other organs. Preferably two different nerve signals can be used to detect a detrusor contraction, where the first signal comes from afferent nerves innervating the bladder, and the Second Signal comes from efferent nerves innervating the detrusor muscle. In this way the detrusor contraction can be detected more reliably. Activating a neural circuit that inhibits the bladder con traction can be done by Stimulating afferent nerve fibres, innervating mechanoreceptors, located in the glans of the penis or clitoris. In this way an ongoing detrusor contraction can be aborted or Stopped and leakage of urine will be prevented. The bladder volume can be derived from the amplitude of the recorded afferent Signal. By measuring of the bladder volume the patient can be informed about his/her bladder Volume. The bladder volume can be derived from the time between two consecutive detrusor contractions. By measuring of the bladder volume, the patient can be informed about his/her bladder volume. The bladder volume can be derived from both the ampli tude of the recorded nerve Signal and the time between two consecutive detrusor contractions. This way the bladder Volume can be estimated in a more reliable way. In the following the invention will be detailed described partly with reference to drawings. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 shows a block diagram of event driven stimulation System to treat an overactive bladder. FIG. 2 shows a block diagram of a bladder volume monitoring System. FIG.3 shows schematically how the invention is applied. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS Further scope of applicability of the present invention will become apparent from the detailed description given here inafter. However, it should be understood that the detailed description and Specific examples, while indicating pre ferred embodiments of the invention, are given by way of illustration only, Since various changes and modifications within the spirit and scope of the invention will become apparent to those skilled in the art from this detailed descrip tion. Mechanoreceptors located in the bladder wall act as tension receptors and respond in graded fashion to increases in bladder Volume and intravesical pressure. It has been shown that a close relationship between afferent nerve activity and the pattern of intravesical pressure changes is best observed when the activity of many afferent nerve fibres is Summed. Sensor 14 comprises an implantable nerve cuff electrode. This type of electrode Surrounds the Selected nerve in close proximity So currents generated by the nerve fibres result in Sufficiently large Voltage differences in the volume within the cuff so that they can be detected by the electrode. However, other electrode configurations Such as intrafasicular electrodes could also be used to detect the efferent nerve activity. The electrode needs to be placed on a peripheral nerve 15 that contains afferent nerve fibres innervating mechanoreceptors located in the bladder. Pos US 6,836,684 B sible locations for the electrode are therefore: intradural dorsal Sacral nerve roots (S2-S4), extradural Sacral nerve roots (S2-S4), preganglionic pelvic nerve branches and postganglionic nerve branches. An alternative method to detect a bladder contraction is to record from the efferent nerve fibres that innervate the detrusor muscle. An increase in the efferent Signal results in a detrusor contraction So an increased efferent Signal indicates a detrusor contraction. Possible locations for the electrode to record efferent signals from peripheral nerve 15 are: intradural ventral sacral nerve roots (S2-S4), extradural sacral nerve roots (S2-S4), preganglionic pelvic nerve branches and postganglionic nerve branches. The output of the sensor 14 is passed through a circuit 13 that includes an amplifier and a filter. The output of circuit 13 is passed to circuit 10, which contains a detection algorithm that allows the detection of the onset of a Sudden rise in intravesical pressure or a detrusor contraction. The detection algorithm takes place in a signal processor 10, which will pass a trigger Signal to Stimulator 11 when it detects Such a pressure rise. The Stimulator 11 includes one or more electrodes placed on peripheral Sensory nerves 12. The Stimulator 11 produces, in response to the trigger Signal from circuit 10, an electrical potential difference, which will result in an electrical current through the electrode and adjacent nervous tissue. A rapid change in this electrical current activates or Stimulates nerve fibres causing the production of action potentials in peripheral nerve 12. It has been shown that activation of afferent nerve fibres, inner Vating mechanoreceptors located in the glans of the penis or clitoris, has a strong inhibitory effect on the bladder. To obtain the desired effect of bladder inhibition upon stimu lation the afferents should be Stimulated Somewhere along their course from mechanoreceptors to the Sacral Spinal cord. This means that possible locations for the electrode to be placed on peripheral nerve 12 are: dorsal penile/clitoris nerve, pudendal nerve, extradural Sacral nerve roots (S2-S4) and intradural dorsal sacral nerve roots (S2-S4). A System for monitoring the bladder Volume is shown in FIG. 2. Mechanoreceptors located in the bladder wall act as tension receptors and respond in graded fashion to increases in bladder Volume and intravesical pressure. It has been shown that a close relationship exist between afferent nerve activity and bladder volume. In addition, bladder volume could be estimated from the time between two consecutive hyperreflexic bladder contractions Since the number of con tractions per time unit is proportional to the bladder Volume. The preferred nerve electrode 25 for this purpose is an implantable nerve cuff electrode, although other electrode configurations could also be used. The Sensor 25 comprises an electrode, which needs to be placed on a peripheral Sensory nerve 26 that contains afferent nerve fibres inner Vating mechanoreceptors located in the bladder. Possible locations for the sensor 25 are therefore: intradural dorsal Sacral nerve roots (S2-S4), extradural Sacral nerve roots (S2-S4), preganglionic pelvic nerve branches and postgan glionic nerve branches. Sensor 25 could be the same one as sensor 14 so the systems of FIG. 1 and FIG. 2 share the same electrode. The output of the sensor 25 is passed through a circuit 24 that includes an amplifier and a filter. The output of circuit 24 is passed to Signal processing unit 20, which contains an estimation algorithm that allows estimation of bladder vol ume. If the estimated volume exceeds the volume threshold then a trigger Signal will be passed to transmitter 21. Upon receiving a trigger, transmitter 21 Sends a Signal to receiver 22 using radio waves. Receiver 22 is placed outside the body
7 S and will, upon receiving a Signal from transmitter 21, pass a signal to actuator 23. Actuator 23 will alert the user that the bladder volume exceeded the volume threshold. Various devices could be used as actuator Such as a buzzer, a Vibrator, etc. FIG. 3 shows in detail the elements of the invention. A bladder 31 with a closing mechanism comprising a Sphincter 32 together with the innervating peripheral nerves, which comprises intradural dorsal Sacral root 34, intradural Ventral Sacral root 35, extradural Sacral root 36, preganglionic pelvic nerve 37, postganglionic pelvic nerve 38 and pudendal nerve 39. In addition, the dorsal penile/clitoral nerve 40 is shown. These nerves relay information to and from the Spinal cord 33. A recording electrode 41 senses information from the nerves 37, and electrical information is transmitted through an electrode lead 43 to a signal processing unit 44, which is connected to a stimulator 45. The signal from the stimulator 45 is transmitted through an electrode lead 43 to a stimu lation electrode 42, which stimulates nerve 40. The invention being thus described, it will be apparent that the same may be varied in many ways. Such variations are not to be regarded as a departure from the Spirit and Scope of the invention, and all Such modifications as would be recognized by one skilled in the art are intended to be included within the Scope of the following claims. What is claimed is: 1. A method for controlling an overactive bladder, com prising the Steps: detecting nerve Signals from nerves innervating the blad der; detecting a bladder event from the nerve signals; generating electrical pulses in response to the detected event, Stimulating afferent nerves using the generated electrical pulses in order to inhibit detrusor contraction of the bladder. 2. A method as defined in claim 1, wherein the detected nerve Signals primarily come from afferent nerve fibres innervating mechanoreceptors in the bladder wall. 3. A method as defined in claim 1, wherein the detected nerve Signals come from efferent nerve fibres innervating the bladder. 4. A method as defined in claim 1, wherein two different Signals are used to detect detrusor contractions, a first signal coming from afferent nerves innervating the bladder, and a US 6,836,684 B Second Signal coming from efferent nerves innervating the detrusor muscle. 5. A method as defined in claim 1, wherein neural circuits inhibiting bladder contraction are Stimulated by activating an inhibitory Spinal reflex by Stimulating afferent nerve fibres innervating mechanoreceptors located in the glans of the penis or clitoris. 6. A method as defined in claim 5, wherein a stimulation electrode is located at a nerve belonging to the group consisting of a dorsal penile/clitoris nerve, a pudendal nerve, an extradural Sacral nerve root and an intradural dorsal Sacral nerve root. 7. A method as defined in claim 1, wherein both a detecting electrode and a stimulation electrode are located at either the intradural dorsal Sacral nerve roots or the extra dural Sacral nerve root. 8. A method as defined in claim 7, wherein the dorsal Sacral nerve roots belong to the group S2-S4. 9. The method as set forth in claim 1, further comprising the Step of estimating bladder Volume in response to the detected Signals using Signal-processing methods. 10. The method as set forth in claim 9, wherein said step of estimating is performed using an amplitude of the detected nerve Signals. 11. The method as set forth in claim 9, wherein said step of estimating is performed using a time between two detected nerve signals derived from two consecutive detru Sor contractions. 12. The method as set forth in claim 9, wherein said step of estimating is performed using an amplitude of the detected nerve signals and a time between two detected nerve signals derived from two consecutive detrusor con tractions. 13. The method as set forth in claim 9, further comprising the Steps of: transmitting, from a transmitter placed inside a user's body, a Signal when a predetermined threshold value for bladder volume has been exceeded; receiving the Signal with a receiver located outside the user's body; actuating an alert in response to the received signal for alerting the user that the threshold value has been reached.
8 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE CERTIFICATE OF CORRECTION PATENT NO. : 6,836,684 B1 Page 1 of 1 DATED : December 28, 2004 INVENTOR(S) : Rijkhoffet al. It is certified that error appears in the above-identified patent and that said Letters Patent is hereby corrected as shown below: Title page, Insert Foreign Application Priority Data Oct. 30, 1998 (DK) O Signed and Sealed this Seventh Day of June, 2005 WDJ JON W. DUDAS Director of the United States Patent and Trademark Office
Technologies and architectures" Stimulator, electrodes, system flexibility, reliability, security, etc."
 March 2011 Introduction" Basic principle (Depolarization, hyper polarization, etc.." Stimulation types (Magnetic and electrical)" Main stimulation parameters (Current, voltage, etc )" Characteristics (Muscular
March 2011 Introduction" Basic principle (Depolarization, hyper polarization, etc.." Stimulation types (Magnetic and electrical)" Main stimulation parameters (Current, voltage, etc )" Characteristics (Muscular
Stimulation of the Sacral Anterior Root Combined with Posterior Sacral Rhizotomy in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury. Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.58 Stimulation of the Sacral Anterior Root Combined with Posterior Sacral Rhizotomy in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Medical Policy Section Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review
MP 7.01.58 Stimulation of the Sacral Anterior Root Combined with Posterior Sacral Rhizotomy in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Medical Policy Section Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review
Electrostimulation Part 3: Bladder dysfunctions
 GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux Intelligents Electrostimulation Part 3: Bladder dysfunctions Mohamad Sawan et al Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim!!! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! mohamad.sawan@polymtl.ca!
GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux Intelligents Electrostimulation Part 3: Bladder dysfunctions Mohamad Sawan et al Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim!!! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! mohamad.sawan@polymtl.ca!
GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux Intelligents. Electrostimulation. Part 3: Bladder dysfunctions
 GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux Intelligents Electrostimulation Part 3: Bladder dysfunctions Mohamad Sawan et al Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim!!! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! mohamad.sawan@polymtl.ca!
GBM8320 Dispositifs Médicaux Intelligents Electrostimulation Part 3: Bladder dysfunctions Mohamad Sawan et al Laboratoire de neurotechnologies Polystim!!! http://www.cours.polymtl.ca/gbm8320/! mohamad.sawan@polymtl.ca!
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,691,578 B1
 USOO6691578B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,691,578 B1 Puskas (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS FOR 4,710,233 A 12/1987 Hohmann et al.... 205/701 ULTRASOUND
USOO6691578B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,691,578 B1 Puskas (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 17, 2004 (54) MEASUREMENT SYSTEMS FOR 4,710,233 A 12/1987 Hohmann et al.... 205/701 ULTRASOUND
(12) United States Patent
 US007043040B2 (12) United States Patent Westerkull (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) HEARING AID APPARATUS (75) Inventor: Patrick Westerkull, Hovås (SE) (73) Assignee: P&B Research
US007043040B2 (12) United States Patent Westerkull (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2006 (54) HEARING AID APPARATUS (75) Inventor: Patrick Westerkull, Hovås (SE) (73) Assignee: P&B Research
Physiologic Anatomy and Nervous Connections of the Bladder
 Micturition Objectives: 1. Review the anatomical organization of the urinary system from a physiological point of view. 2. Describe the micturition reflex. 3. Predict the lines of treatment of renal failure.
Micturition Objectives: 1. Review the anatomical organization of the urinary system from a physiological point of view. 2. Describe the micturition reflex. 3. Predict the lines of treatment of renal failure.
Minimal invasive electrode implantation for conditional stimulation of the dorsal genital nerve in neurogenic detrusor overactivity
 (2011) 49, 566 572 & 2011 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/11 $32.00 www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE Minimal invasive electrode implantation for conditional stimulation of the dorsal
(2011) 49, 566 572 & 2011 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/11 $32.00 www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE Minimal invasive electrode implantation for conditional stimulation of the dorsal
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US006319006B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,319,006 B1 Scherer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2001 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCINGA DRILL 5,967,777 * 10/1999 Klein 5 a1...... 433/75 ASSISTANCE
(12) United States Patent US006319006B1 (10) Patent N0.: US 6,319,006 B1 Scherer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 20, 2001 (54) METHOD FOR PRODUCINGA DRILL 5,967,777 * 10/1999 Klein 5 a1...... 433/75 ASSISTANCE
Renal Physiology: Filling of the Urinary Bladder, Micturition, Physiologic Basis of some Renal Function Tests. Amelyn R.
 Renal Physiology: Filling of the Urinary Bladder, Micturition, Physiologic Basis of some Renal Function Tests Amelyn R. Rafael, MD 1 Functions of the Urinary Bladder 1. storage of urine 150 cc 1 st urge
Renal Physiology: Filling of the Urinary Bladder, Micturition, Physiologic Basis of some Renal Function Tests Amelyn R. Rafael, MD 1 Functions of the Urinary Bladder 1. storage of urine 150 cc 1 st urge
NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS
 NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS Introduction The pelvic floor is highly complex structure made up of skeletal and striated muscle, support and suspensory ligaments, fascial coverings and an intricate
NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS Introduction The pelvic floor is highly complex structure made up of skeletal and striated muscle, support and suspensory ligaments, fascial coverings and an intricate
1 ADJUSTMENT THRESHOLD-N. United States Patent (19) Donehoo et al. 5,660,184. Aug. 26, 1997 PATIENT'S HEARTBEAT PACEMAKEREVENT QRS DETECTION THRESHOLD
 United States Patent (19) Donehoo et al. US00566O184A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,660,184 Aug. 26, 1997 54 PACEMAKER PULSE DETECTION AND ARTIFACT REJECTION 75 Inventors: Robert F. Donehoo, Lutz;
United States Patent (19) Donehoo et al. US00566O184A 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 5,660,184 Aug. 26, 1997 54 PACEMAKER PULSE DETECTION AND ARTIFACT REJECTION 75 Inventors: Robert F. Donehoo, Lutz;
Regulation of the Urinary Bladder Chapter 26
 Regulation of the Urinary Bladder Chapter 26 Anatomy 1. The urinary bladder is smooth muscle lined internally by transitional epithelium and externally by the parietal peritoneum. Contraction of the smooth
Regulation of the Urinary Bladder Chapter 26 Anatomy 1. The urinary bladder is smooth muscle lined internally by transitional epithelium and externally by the parietal peritoneum. Contraction of the smooth
Objectives. Key Outlines:
 Objectives! Iden8fy and describe the Func8onal Anatomy of Urinary Bladder! Describe the mechanism of filling and emptying of the urinary bladder! Cystometrogram! Appreciate neurogenic control of the mechanism
Objectives! Iden8fy and describe the Func8onal Anatomy of Urinary Bladder! Describe the mechanism of filling and emptying of the urinary bladder! Cystometrogram! Appreciate neurogenic control of the mechanism
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kimber et al. USOO6565529B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,565,529 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 20, 2003 (54) TAMPEREVIDENT SYRINGE DESIGN (75) Inventors: Michael Browning Kimber, New South
(12) United States Patent Kimber et al. USOO6565529B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,565,529 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 20, 2003 (54) TAMPEREVIDENT SYRINGE DESIGN (75) Inventors: Michael Browning Kimber, New South
Aalborg Universitet. Published in: Journal of Urology. DOI (link to publication from Publisher): /01.ju b
 Aalborg Universitet Treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity in spinal cord injured patients by conditional electrical stimulation Hansen, John; Media, S.; Nøhr, M.; Biering-Sørensen, F.; Sinkjær,
Aalborg Universitet Treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity in spinal cord injured patients by conditional electrical stimulation Hansen, John; Media, S.; Nøhr, M.; Biering-Sørensen, F.; Sinkjær,
The Neurogenic Bladder
 The Neurogenic Bladder Outline Brandon Haynes, MD Resident Physician Department of Urology Jelena Svircev, MD Assistant Professor Department of Rehabilitation Medicine Anatomy and Bladder Physiology Bladder
The Neurogenic Bladder Outline Brandon Haynes, MD Resident Physician Department of Urology Jelena Svircev, MD Assistant Professor Department of Rehabilitation Medicine Anatomy and Bladder Physiology Bladder
Neural Control of Lower Urinary Tract Function. William C. de Groat University of Pittsburgh Medical School
 Neural Control of Lower Urinary Tract Function William C. de Groat University of Pittsburgh Medical School Disclosures Current funding: NIH Grants, DK093424, DK-091253, DK-094905, DK-090006. Other financial
Neural Control of Lower Urinary Tract Function William C. de Groat University of Pittsburgh Medical School Disclosures Current funding: NIH Grants, DK093424, DK-091253, DK-094905, DK-090006. Other financial
The Praxis FES System and Bladder/Bowel Management in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury
 The Praxis FES System and Bladder/Bowel Management in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Brian J. Benda 1, Thierry Houdayer 2, Graham Creasey 3, Randal R. Betz 1, Brian T. Smith 1 *, Therese E. Johnston
The Praxis FES System and Bladder/Bowel Management in Patients with Spinal Cord Injury Brian J. Benda 1, Thierry Houdayer 2, Graham Creasey 3, Randal R. Betz 1, Brian T. Smith 1 *, Therese E. Johnston
Spinal Cord Injury. R Hamid Consultant Neuro-Urologist London Spinal Injuries Unit, Stanmore & National Hospital for Neurology & Neurosurgery, UCLH
 Spinal Cord Injury R Hamid Consultant Neuro-Urologist London Spinal Injuries Unit, Stanmore & National Hospital for Neurology & Neurosurgery, UCLH SCI 800 1000 new cases per year in UK Car accidents 35%
Spinal Cord Injury R Hamid Consultant Neuro-Urologist London Spinal Injuries Unit, Stanmore & National Hospital for Neurology & Neurosurgery, UCLH SCI 800 1000 new cases per year in UK Car accidents 35%
75 Inventors: Ulrik Nosted, Lyngby; Jan Torstensen, 55. o1. Rho 206/364
 US006059107A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,059,107 Nosted et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2000 54). URINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY WITH A 3,967,728 7/1976 Gordon et al.. READY-TO-USE CATHETER
US006059107A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,059,107 Nosted et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2000 54). URINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY WITH A 3,967,728 7/1976 Gordon et al.. READY-TO-USE CATHETER
Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction
 Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction (Text update March 2009) M. Stöhrer (chairman), B. Blok, D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier- Kastler, P. Denys, G. Kramer, J. Pannek, G. del Popolo, P.
Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction (Text update March 2009) M. Stöhrer (chairman), B. Blok, D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier- Kastler, P. Denys, G. Kramer, J. Pannek, G. del Popolo, P.
EE 791 Lecture 10. FES April 1, EE 791 Lecture 10 1
 EE 791 Lecture 10 FES April 1, 2013 EE 791 Lecture 10 1 Normal Functional Control EE 791 Lecture 10 2 Current uses of FES Cardiovascular Exercise Breathing assist Grasping and Reaching Transfer and Standing
EE 791 Lecture 10 FES April 1, 2013 EE 791 Lecture 10 1 Normal Functional Control EE 791 Lecture 10 2 Current uses of FES Cardiovascular Exercise Breathing assist Grasping and Reaching Transfer and Standing
Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS
 Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS OhioHealth, Columbus Ohio Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the role of a pelvic floor therapist in
Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS OhioHealth, Columbus Ohio Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the role of a pelvic floor therapist in
Chapter 23. Micturition and Renal Insufficiency
 Chapter 23 Micturition and Renal Insufficiency Voiding Urine Between acts of urination, the bladder is filling. detrusor muscle relaxes urethral sphincters are tightly closed accomplished by sympathetic
Chapter 23 Micturition and Renal Insufficiency Voiding Urine Between acts of urination, the bladder is filling. detrusor muscle relaxes urethral sphincters are tightly closed accomplished by sympathetic
IIII. United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,776,150 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998
 United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 54) SUTURE ASSIST DEVICE 75) Inventors: Leo J. Nolan; John P. Measamer, both of Cincinnati; James D. Staley, Jr., Loveland; Robert F. Welch, Maineville, all of Ohio
United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 54) SUTURE ASSIST DEVICE 75) Inventors: Leo J. Nolan; John P. Measamer, both of Cincinnati; James D. Staley, Jr., Loveland; Robert F. Welch, Maineville, all of Ohio
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,282,443 B1
 USOO6282443B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,282,443 B1 Mann et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2001 (54) METHOD OF TREATMENT OF (56) References Cited DYSMENORRHEA OR RELIEVING MENSTRUAL
USOO6282443B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,282,443 B1 Mann et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 28, 2001 (54) METHOD OF TREATMENT OF (56) References Cited DYSMENORRHEA OR RELIEVING MENSTRUAL
Urodynamic and electrophysiological investigations in neuro-urology
 Urodynamic and electrophysiological investigations in neuro-urology Pr. Gerard Amarenco Neuro-Urology and Pelvic-Floor Investigations Department Tenon Hospital, Assistance Publique Hôpitaux de Paris, Er6,
Urodynamic and electrophysiological investigations in neuro-urology Pr. Gerard Amarenco Neuro-Urology and Pelvic-Floor Investigations Department Tenon Hospital, Assistance Publique Hôpitaux de Paris, Er6,
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial Tahereh Eftekhar 1, Nastaran Teimoory 1, Elahe Miri 1, Abolghasem Nikfallah 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial Tahereh Eftekhar 1, Nastaran Teimoory 1, Elahe Miri 1, Abolghasem Nikfallah 2,
Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence
 Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
NEUROGENIC BLADDER. Dr Harriet Grubb Dr Alison Seymour Dr Alexander Joseph
 NEUROGENIC BLADDER Dr Harriet Grubb Dr Alison Seymour Dr Alexander Joseph OUTLINE Definition Anatomy and physiology of bladder function Types of neurogenic bladder Assessment and management Complications
NEUROGENIC BLADDER Dr Harriet Grubb Dr Alison Seymour Dr Alexander Joseph OUTLINE Definition Anatomy and physiology of bladder function Types of neurogenic bladder Assessment and management Complications
(12) United States Patent
 USOO951 0624B2 (12) United States Patent Li et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,510,624 B2 Dec. 6, 2016 (54) DISPOSABLE ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (75) Inventors: Yonghai Li, Shenzhen (CN); Zhongli
USOO951 0624B2 (12) United States Patent Li et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,510,624 B2 Dec. 6, 2016 (54) DISPOSABLE ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (75) Inventors: Yonghai Li, Shenzhen (CN); Zhongli
Neural control of the lower urinary tract in health and disease
 Neural control of the lower urinary tract in health and disease Jalesh N. Panicker MD, DM, FRCP Consultant Neurologist and Clinical lead in Uro-Neurology The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery
Neural control of the lower urinary tract in health and disease Jalesh N. Panicker MD, DM, FRCP Consultant Neurologist and Clinical lead in Uro-Neurology The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery
6/16/2016 IOM APPROACHES TO THE PUDENDAL NERVE TEAL TAYLOR, REEGT/REPT/CNIM EVOKES, LLC A SENSITIVE SUBJECT: I DON T WANT TO WEAR A DIAPER
 IOM APPROACHES TO THE PUDENDAL NERVE TEAL TAYLOR, REEGT/REPT/CNIM EVOKES, LLC A SENSITIVE SUBJECT: I DON T WANT TO WEAR A DIAPER In IOM we continuously work to protect the Sensory and Motor Function of
IOM APPROACHES TO THE PUDENDAL NERVE TEAL TAYLOR, REEGT/REPT/CNIM EVOKES, LLC A SENSITIVE SUBJECT: I DON T WANT TO WEAR A DIAPER In IOM we continuously work to protect the Sensory and Motor Function of
Neural control of the lower urinary tract
 Neural control of the lower urinary tract Jalesh N. Panicker Consultant Neurologist and Honorary Senior Lecturer The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery and UCL Institute of Neurology Queen
Neural control of the lower urinary tract Jalesh N. Panicker Consultant Neurologist and Honorary Senior Lecturer The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery and UCL Institute of Neurology Queen
(12) United States Patent
 USOO94462B2 (12) United States Patent Su et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Sep. 20, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) () () (51) (52) (58) LOW FREQUENCY ELECTRICAL STMULATION THERAPY FOR PELVC
USOO94462B2 (12) United States Patent Su et al. () Patent No.: () Date of Patent: Sep. 20, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) () () (51) (52) (58) LOW FREQUENCY ELECTRICAL STMULATION THERAPY FOR PELVC
New Neurostimulation and Blockade Strategy to. Enhance Bladder Voiding in Paraplegics
 Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 3, 2010, no. 7, 321-337 New Neurostimulation and Blockade Strategy to Enhance Bladder Voiding in Paraplegics Fayçal Mounaïm 1, Ehab Elzayat 2, Mohamad Sawan 1, Jacques
Contemporary Engineering Sciences, Vol. 3, 2010, no. 7, 321-337 New Neurostimulation and Blockade Strategy to Enhance Bladder Voiding in Paraplegics Fayçal Mounaïm 1, Ehab Elzayat 2, Mohamad Sawan 1, Jacques
Storage is accomplished through the following mechanisms:
 NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 13, 2017 Examples of Coordinated Autonomic and Motor Responses and Return to the Cardiovascular System 1) Micturition Micturition, or the process of emptying
NROSCI/BIOSC 1070 and MSNBIO 2070 September 13, 2017 Examples of Coordinated Autonomic and Motor Responses and Return to the Cardiovascular System 1) Micturition Micturition, or the process of emptying
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701 65099A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0165099 A1 Buddharaju (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2017 (54) CONDOM CATHETER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A61F 5/453
(19) United States US 201701 65099A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0165099 A1 Buddharaju (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2017 (54) CONDOM CATHETER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A61F 5/453
Review Article. TENS: A Treatment Option for Bladder Dysfunction. International Urogynecology Journal
 Int Urogynecol J (1996) 7:185-190 9 1996 The International Urogynecology Journal International Urogynecology Journal Review Article TE: A Treatment Option for Bladder Dysfunction S. E. Bristow 1'2, S.
Int Urogynecol J (1996) 7:185-190 9 1996 The International Urogynecology Journal International Urogynecology Journal Review Article TE: A Treatment Option for Bladder Dysfunction S. E. Bristow 1'2, S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 2004O23O254A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0230254A1 Harrison et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 18, 2004 (54) HYBRID IMPLANTABLE COCHLEAR STIMULATOR HEARING
(19) United States US 2004O23O254A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0230254A1 Harrison et al. (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 18, 2004 (54) HYBRID IMPLANTABLE COCHLEAR STIMULATOR HEARING
Recommandations de prise en charge des vessies neurogènes EAU 2006
 Annexe 4-1 Recommandations de prise en charge des vessies neurogènes EAU 2006 (Version courte) 685 686 GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION M. Stöhrer (chairman), D. Castro-Diaz, E.
Annexe 4-1 Recommandations de prise en charge des vessies neurogènes EAU 2006 (Version courte) 685 686 GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION M. Stöhrer (chairman), D. Castro-Diaz, E.
TEPZZ _ 849 A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ _ 849 A_T (11) EP 3 138 493 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 08.03.17 Bulletin 17/ (21) Application number: 786271. (22)
(19) TEPZZ _ 849 A_T (11) EP 3 138 493 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 3(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 08.03.17 Bulletin 17/ (21) Application number: 786271. (22)
GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION
 GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION M. Stöhrer (chairman), D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier-Kastler, G. Kramer, A. Mattiasson, J-J. Wyndaele Introduction NLUTD (neurogenic lower urinary
GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION M. Stöhrer (chairman), D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier-Kastler, G. Kramer, A. Mattiasson, J-J. Wyndaele Introduction NLUTD (neurogenic lower urinary
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 US007052479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,052.479 B2 Drennan (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 2006 (54) TRACTION DEVICE 3,762.405 A * 10/1973 De George... 602/23 3,771,519 A * 11/1973 Haake......
US007052479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,052.479 B2 Drennan (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 2006 (54) TRACTION DEVICE 3,762.405 A * 10/1973 De George... 602/23 3,771,519 A * 11/1973 Haake......
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Updates in the nonpharmacological. treatment on overactive bladder
 Updates in the nonpharmacological treatment on overactive bladder Overactive Bladder Also known as urgency-frequency syndrome Symptoms Urgency Daytime frequency Nocturia Urge urinary incontinence Sudden
Updates in the nonpharmacological treatment on overactive bladder Overactive Bladder Also known as urgency-frequency syndrome Symptoms Urgency Daytime frequency Nocturia Urge urinary incontinence Sudden
URINARY SYSTEM. Urinary System
 URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
URINARY SYSTEM Urinary System Kidney Functions Excretion Regulation of blood volume and pressure Regulation of electrolyte and ph levels Kidney Structure Gross Anatomy Fibrous Capsule Renal Cortex Renal
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN
 Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070050.058A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0050058 A1 Zuziak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) PLACEMAT FOR CALCULATING AND Related U.S. Application
US 20070050.058A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0050058 A1 Zuziak et al. (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 1, 2007 (54) PLACEMAT FOR CALCULATING AND Related U.S. Application
Refractory Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
 Sacral Neuromodulation for Treatment of Refractory Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Alex Kavanagh, PGY3 Mar 30/2011 Goals 1. Define sacral neuromodulation (SNM) and review the clinical implementation 2. Provide
Sacral Neuromodulation for Treatment of Refractory Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Alex Kavanagh, PGY3 Mar 30/2011 Goals 1. Define sacral neuromodulation (SNM) and review the clinical implementation 2. Provide
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,351,671 B1
 USOO6351671B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Myklebust et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2002 (54) SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AND WO WO OO/27464 + 5/2000 ANALYZING CARDIO-PULMONARY RESUSCITATION
USOO6351671B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Myklebust et al. (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 26, 2002 (54) SYSTEM FOR MEASURING AND WO WO OO/27464 + 5/2000 ANALYZING CARDIO-PULMONARY RESUSCITATION
Development of mathematical model for lower urinary tract dysfunctions
 Development of mathematical model for lower urinary tract dysfunctions Mohanad A.Deaf 1, Mohamed A.A.Eldosoky 1, Ahmed M. El-Garhy 2, Hesham W.Gomma 2, Ahmed S.El-Azab 3 Dept. of Biomedical Engineering,
Development of mathematical model for lower urinary tract dysfunctions Mohanad A.Deaf 1, Mohamed A.A.Eldosoky 1, Ahmed M. El-Garhy 2, Hesham W.Gomma 2, Ahmed S.El-Azab 3 Dept. of Biomedical Engineering,
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
 Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
Service: Urology Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered What is OAB? An overactive bladder or OAB is where a person regularly gets a sudden and compelling need or
03/13/18. A. Symptoms lasting for greater than or equal to 12 months that have resulted to significant impairment in activities of daily living; and
 Reference #: MC/I008 Page: 1 of 5 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) Non-ERISA PreferredOne Community Health Plan
Reference #: MC/I008 Page: 1 of 5 PRODUCT APPLICATION: PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) ERISA PreferredOne Administrative Services, Inc. (PAS) Non-ERISA PreferredOne Community Health Plan
Normal micturition involves complex
 NEW TARGET FOR INTERVENTION: THE NEUROUROLOGY CONNECTION * Donald R. Ostergard, MD, FACOG ABSTRACT Urine storage and release are under the control of the parasympathetic, sympathetic, and somatic nervous
NEW TARGET FOR INTERVENTION: THE NEUROUROLOGY CONNECTION * Donald R. Ostergard, MD, FACOG ABSTRACT Urine storage and release are under the control of the parasympathetic, sympathetic, and somatic nervous
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Figone et al. 11 Patent Number: 4,834,212 (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 1989 54) (76) 21) 22 (51) (52) (58) SOUND MUFFLER FOR COVERING THE MOUTH Inventors: Moira J. Figone; Frank
United States Patent (19) Figone et al. 11 Patent Number: 4,834,212 (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 1989 54) (76) 21) 22 (51) (52) (58) SOUND MUFFLER FOR COVERING THE MOUTH Inventors: Moira J. Figone; Frank
Electrical pelvic floor stimulation: a possible alternative treatment for reflex urinary incontinence in patients with spinal cord injury
 Spinal Cord (1996)34 411-415 @ 1996 International Medical Society of Paraplegia ll rights reserved 1362-4393/96 $1200 lectrical pelvic floor stimulation a possible alternative treatment for reflex urinary
Spinal Cord (1996)34 411-415 @ 1996 International Medical Society of Paraplegia ll rights reserved 1362-4393/96 $1200 lectrical pelvic floor stimulation a possible alternative treatment for reflex urinary
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Neurogenic bladder. Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder.
 Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0020415A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0020415 A1 Reno (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOMETRIC EXERCISE EQUIPMENT WITH Publication Classification PORTABLE
US 2005.0020415A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0020415 A1 Reno (43) Pub. Date: (54) ISOMETRIC EXERCISE EQUIPMENT WITH Publication Classification PORTABLE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150273 183A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0273183 A1 Foley et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2015 (54) INTERMITTENTURINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY AND ANADAPTER
(19) United States US 20150273 183A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0273183 A1 Foley et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2015 (54) INTERMITTENTURINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY AND ANADAPTER
(12) United States Patent Clapp et al. US 7,206,386 B2 Apr. 17, 2007 US B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 US007206386B2 (12) United States Patent Clapp et al. (io) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,206,386 B2 Apr. 17, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION WITH THE HEARING IMPAIRED (75)
US007206386B2 (12) United States Patent Clapp et al. (io) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,206,386 B2 Apr. 17, 2007 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATION WITH THE HEARING IMPAIRED (75)
y 2. (12) United States Patent VbOt W N 35 (10) Patent No.: US 8,855,348 B2 HAD CIRCUIT ACTIVE TELECOIL (45) Date of Patent: Oct.
 USOO8855348B2 (12) United States Patent Johnson (54) TELECOIL INA DETACHABLE DIRECT AUDIO INPUT ACCESSORY (75) Inventor: Andrew Joseph Johnson, Edina, MN (US) (73) Assignee: Starkey Laboratories, Inc.,
USOO8855348B2 (12) United States Patent Johnson (54) TELECOIL INA DETACHABLE DIRECT AUDIO INPUT ACCESSORY (75) Inventor: Andrew Joseph Johnson, Edina, MN (US) (73) Assignee: Starkey Laboratories, Inc.,
United States Patent (19) Groesch et al.
 United States Patent (19) Groesch et al. 54 DUMMY FOR CAR CRASH TESTING 75) Inventors: Lothar Groesch; Gabriel Netzer, both of Stuttgart; Lothar Kassing, Nufringen, all of Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Groesch et al. 54 DUMMY FOR CAR CRASH TESTING 75) Inventors: Lothar Groesch; Gabriel Netzer, both of Stuttgart; Lothar Kassing, Nufringen, all of Fed. Rep. of Germany 73) Assignee:
Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know. A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury
 Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about managing your bladder After SCI, you may
Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about managing your bladder After SCI, you may
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0289446 A1 Stone et al. US 2013 02894.46A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) (51) BLADDERFULLNESS LEVEL INDICATION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0289446 A1 Stone et al. US 2013 02894.46A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) (51) BLADDERFULLNESS LEVEL INDICATION
Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz
 Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz 54 year old female presenting with: Dragging sensation Urinary incontinence Some faecal incontinence HPC Since May 14 had noticed a mass protruding from the vagina when going
Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz 54 year old female presenting with: Dragging sensation Urinary incontinence Some faecal incontinence HPC Since May 14 had noticed a mass protruding from the vagina when going
Accessible Incontinence Control Device
 Accessible Incontinence Control Device GROUP 8 Maroun Bousleiman, Erica Kramer, Yamalia Roberts, Zack Smith Roberts Sponsored by RERC Sponsored by RERC-AMI National Student Design AMI National Student
Accessible Incontinence Control Device GROUP 8 Maroun Bousleiman, Erica Kramer, Yamalia Roberts, Zack Smith Roberts Sponsored by RERC Sponsored by RERC-AMI National Student Design AMI National Student
(12) United States Patent
 US009 138575B2 (12) United States Patent Osypka (54) (71) BALLOON CATHETER Applicant: Peter Osypka Stiftung, Grenzach-Wyhlen (DE) (72) Inventor: Peter Osypka, Grenzach-Wyhlen (DE) (73) Assignee: Peter
US009 138575B2 (12) United States Patent Osypka (54) (71) BALLOON CATHETER Applicant: Peter Osypka Stiftung, Grenzach-Wyhlen (DE) (72) Inventor: Peter Osypka, Grenzach-Wyhlen (DE) (73) Assignee: Peter
Signal transduction underlying the control of urinary bladder smooth muscle tone Puspitoayu, E.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Signal transduction underlying the control of urinary bladder smooth muscle tone Puspitoayu, E. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Puspitoayu,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Signal transduction underlying the control of urinary bladder smooth muscle tone Puspitoayu, E. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Puspitoayu,
GUIDELINES ON NEURO-UROLOGY
 GUIDELINES ON NEURO-UROLOGY (Text update pril 2014) J. Pannek (co-chair), B. Blok (co-chair), D. Castro-Diaz, G. del Popolo, J. Groen, G. Karsenty, T.M. Kessler, G. Kramer, M. Stöhrer Eur Urol 2009 Jul;56(1):81-8
GUIDELINES ON NEURO-UROLOGY (Text update pril 2014) J. Pannek (co-chair), B. Blok (co-chair), D. Castro-Diaz, G. del Popolo, J. Groen, G. Karsenty, T.M. Kessler, G. Kramer, M. Stöhrer Eur Urol 2009 Jul;56(1):81-8
Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve
 Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve Stefan De Wachter, MD, PhD, FEBU Professor of Urology University of Antwerpen, Belgium Chairman dept of Urology, UZA Disclosures Consultant speaker: Astellas, Medtronic,
Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve Stefan De Wachter, MD, PhD, FEBU Professor of Urology University of Antwerpen, Belgium Chairman dept of Urology, UZA Disclosures Consultant speaker: Astellas, Medtronic,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1
 (19) United States US 20060074454A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0074454 A1 Freeberg (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR SELECTION OF CARDAC PACING ELECTRODE CONFIGURATIONS
(19) United States US 20060074454A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0074454 A1 Freeberg (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR SELECTION OF CARDAC PACING ELECTRODE CONFIGURATIONS
Neurourology, especially the video urodynamic
 NEUROUROLOGIC FINDINGS WITH APPLICABILITY TO INCONTINENCE AND URETHRAL FUNCTION * Edward J. McGuire, MD ABSTRACT Neurourology is applicable to urinary incontinence and obstructive uropathy in the general
NEUROUROLOGIC FINDINGS WITH APPLICABILITY TO INCONTINENCE AND URETHRAL FUNCTION * Edward J. McGuire, MD ABSTRACT Neurourology is applicable to urinary incontinence and obstructive uropathy in the general
Original Article. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine INTRODUCTION
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(3):342-346 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.3.342 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Phasic Changes in Bladder Compliance
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(3):342-346 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.3.342 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Phasic Changes in Bladder Compliance
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective. Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado
 Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
United States Patent (19) Hensel
 United States Patent (19) Hensel - 54 75 73 1 51 5 58 56) FLUID BEARNG CONSTRUCTION EMPLOYING THRUST PLATE WITH PRESSURE COMPENSATION PORTS Inventor: Robert J. Hensel, Gaston, Oreg. Assignee: Synektron
United States Patent (19) Hensel - 54 75 73 1 51 5 58 56) FLUID BEARNG CONSTRUCTION EMPLOYING THRUST PLATE WITH PRESSURE COMPENSATION PORTS Inventor: Robert J. Hensel, Gaston, Oreg. Assignee: Synektron
Various Types. Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG
 Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
What is the role for neurophysiology in the evaluation of patients with uro-genito-anal dysfunction?
 London, 2016 What is the role for neurophysiology in the evaluation of patients with uro-genito-anal dysfunction? David B. Vodušek Medical Faculty, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia vodusek.david.b@gmail.com
London, 2016 What is the role for neurophysiology in the evaluation of patients with uro-genito-anal dysfunction? David B. Vodušek Medical Faculty, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia vodusek.david.b@gmail.com
EAU GUIDELINES ON NEURO-UROLOGY
 EAU GUIDELINES ON NEURO-UROLOGY (Limited text update March 2016) B. Blok (Co-chair), J. Pannek (Co-chair) D. Castro-Diaz, G. del Popolo, J. Groen, R. Hamid, G. Karsenty, T.M. Kessler. Guidelines Associates:
EAU GUIDELINES ON NEURO-UROLOGY (Limited text update March 2016) B. Blok (Co-chair), J. Pannek (Co-chair) D. Castro-Diaz, G. del Popolo, J. Groen, R. Hamid, G. Karsenty, T.M. Kessler. Guidelines Associates:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O1 OO694A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0100694 A1 PELLETER (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) KNEE PILLOW Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
US 2016O1 OO694A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0100694 A1 PELLETER (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) KNEE PILLOW Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
This Special Report supplement
 ...INTRODUCTION... Overactive Bladder: Defining the Disease Alan J. Wein, MD This Special Report supplement to The American Journal of Managed Care features proceedings from the workshop, Overactive Bladder:
...INTRODUCTION... Overactive Bladder: Defining the Disease Alan J. Wein, MD This Special Report supplement to The American Journal of Managed Care features proceedings from the workshop, Overactive Bladder:
ParasymPathetic Nervous system. Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
We have heard a great deal about "overactive" bladder recently. But what
 BLADDER DYSFUNCTION Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Impaired Bladder Emptying Naoki Yoshimura, MD, PhD, Michael B. Chancellor, MD Department of Urology, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine,
BLADDER DYSFUNCTION Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Impaired Bladder Emptying Naoki Yoshimura, MD, PhD, Michael B. Chancellor, MD Department of Urology, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine,
URINARY TRACT NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS: DRUG THERAPY REVIEW
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk URINARY TRACT NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS: DRUG THERAPY REVIEW Author : Ian Battersby Categories : Vets Date : August 3, 2009
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk URINARY TRACT NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS: DRUG THERAPY REVIEW Author : Ian Battersby Categories : Vets Date : August 3, 2009
Management of OAB. Lynsey McHugh. Consultant Urological Surgeon. Lancashire Teaching Hospitals
 Management of OAB Lynsey McHugh Consultant Urological Surgeon Lancashire Teaching Hospitals Summary Physiology Epidemiology Definitions NICE guidelines Evaluation Conservative management Medical management
Management of OAB Lynsey McHugh Consultant Urological Surgeon Lancashire Teaching Hospitals Summary Physiology Epidemiology Definitions NICE guidelines Evaluation Conservative management Medical management
(12) United States Patent
 US008556757B2 (12) United States Patent Kilshaw (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2013 (54) BICYCLE GEAR MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Richard J. Kilshaw, Lake Oswego, OR (US) *) Notice: Subject
US008556757B2 (12) United States Patent Kilshaw (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2013 (54) BICYCLE GEAR MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Richard J. Kilshaw, Lake Oswego, OR (US) *) Notice: Subject
SELECTIVE BLOCK TECHNIQUES OF URETHRAL SPHINCTER CONTRACTIONS IN SACRAL ANTERIOR ROOT STIMULATION
 SELECTIVE BLOCK TECHNIQUES OF URETHRAL SPHINCTER CONTRACTIONS IN SACRAL ANTERIOR ROOT STIMULATION S. Schumacher, S. Bross*, J.R. Scheepe*, G. Böhler*, K.P. Jünemann*, S.C. Müller and P. Alken* Department
SELECTIVE BLOCK TECHNIQUES OF URETHRAL SPHINCTER CONTRACTIONS IN SACRAL ANTERIOR ROOT STIMULATION S. Schumacher, S. Bross*, J.R. Scheepe*, G. Böhler*, K.P. Jünemann*, S.C. Müller and P. Alken* Department
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: percutaneous_tibial_nerve_stimulation_for_voiding_dysfunction
Corporate Medical Policy Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: percutaneous_tibial_nerve_stimulation_for_voiding_dysfunction
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090305855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0305855A1 Terre (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) ABDOMINAL EXERCISE MACHINE (57) ABSTRACT An abdominal exercise
(19) United States US 20090305855A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0305855A1 Terre (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 10, 2009 (54) ABDOMINAL EXERCISE MACHINE (57) ABSTRACT An abdominal exercise
TREATMENT METHODS FOR DISORDERS OF SMALL ANIMAL BLADDER FUNCTION
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk TREATMENT METHODS FOR DISORDERS OF SMALL ANIMAL BLADDER FUNCTION Author : SIMONA T RADAELLI Categories : Vets Date : July
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk TREATMENT METHODS FOR DISORDERS OF SMALL ANIMAL BLADDER FUNCTION Author : SIMONA T RADAELLI Categories : Vets Date : July
Module 3 Causes Of Urinary Incontinence
 Causes Of Urinary Incontinence V4: Last Reviewed September 2017 Learning Outcomes Appreciate the numerous requirements and skills necessary for the person to achieve and maintain urinary continence Discuss
Causes Of Urinary Incontinence V4: Last Reviewed September 2017 Learning Outcomes Appreciate the numerous requirements and skills necessary for the person to achieve and maintain urinary continence Discuss
PHYSIOLOGICAL SOCIETY SYMPOSIUM: THE PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF THE LOWER URINARY TRACT THE ACTIVATION OF BLADDER WALL AFFERENT NERVES
 Experimental Physiology (1999). 84, 131-136 Printed in Great Britain PHYSIOLOGICAL SOCIETY SYMPOSIUM: THE PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF THE LOWER URINARY TRACT THE ACTIVATION OF BLADDER WALL AFFERENT
Experimental Physiology (1999). 84, 131-136 Printed in Great Britain PHYSIOLOGICAL SOCIETY SYMPOSIUM: THE PHYSIOLOGY AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF THE LOWER URINARY TRACT THE ACTIVATION OF BLADDER WALL AFFERENT
Neurons Chapter 7 2/19/2016. Learning Objectives. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System
 Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
The Nervous System PART A
 7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
7 The Nervous System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Structural Classification
Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2
 NAME PER DATE Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2 Matching: 1. afferent nerves 2. autonomic nervous system 3. cell body 4. central nervous system (CNS) 5. dendrites 6. efferent nerves 7. myelin sheath
NAME PER DATE Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2 Matching: 1. afferent nerves 2. autonomic nervous system 3. cell body 4. central nervous system (CNS) 5. dendrites 6. efferent nerves 7. myelin sheath
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation
 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.025 01/01/2015 Lines of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2015 Section: Medicine Place(s)
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.025 01/01/2015 Lines of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2015 Section: Medicine Place(s)
