Urinalysis (UA) provides information about the urinary
|
|
|
- Damian Robinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Today s TeChniCian PEER REVIEWED URINALYSIS IN COMPANION ANIMALS Part 1: Collection, Sample Handling, & Initial Evaluation Theresa E Rizzi, DVM, Diplomate ACVP (Clinical Pathology) Oklahoma State University Urinalysis (UA) provides information about the urinary system as well as other body systems. It is usually performed in-clinic rather than being sent to an outside laboratory, which is why it is important for the veterinary team to be able to effectively evaluate a complete UA. The UA is designed to provide information needed to pursue a particular clinical problem or as part of a health screen. Therefore, it is usually included as part of the minimum database of diagnostic tests, along with a complete blood count (CBC) and clinical biochemistry profile. The UA should be performed to (Table 1): Evaluate any animal with clinical signs related to the urinary tract Assess an animal with systemic illness Monitor response to treatment. COLLECTION OF URINE Method of collection is important to know because it can influence the interpretation of results. The 3 ways to collect urine for analysis are (Table 2): 1. Free catch 2. Catheterization 3. Cystocentesis. Free-Catch Collection Free-catch samples are easy to obtain. Urine should be collected in a clean container with a tight fitting lid that is available from medical supply companies (Figure 1). Discourage owners from using containers from home, which may contain contaminants, such as detergent, food, and medications, that may alter chemistry results. Table 1. indications for Performing a Urinalysis as part of diagnostic minimum database azotemia dysuria/stranguria hematuria Pigmenturia Pollakiuria Polyuria/polydipsia monitor response to urinary tract disease treatment Urinary incontinence 64
2 Figure 1. Secure clean container with lid for routine urinalysis. Today s Technician Samples can be obtained via normal voiding or by manual compression of the urinary bladder. A midstream sample is preferred. The disadvantage of a voided free-catch sample is potential contamination with cells, bacteria, and debris from the distal urethra, genital tract, and external skin. Free-catch samples that are positive for white cells, bacteria, and protein will necessitate sampling via cystocentesis (or catheter) in small animal patients. Catheterization Catheterization of the urinary bladder is performed using a sterile urinary catheter; the external genital area and distal urethral opening are aseptically prepared; however, contamination of the sample may still occur. In addition, catheterization may cause iatrogenic urinary tract infections by introducing bacteria into the urinary bladder, and is more likely to add red cells and transitional cells to the sample due to mild trauma that results as the catheter passes through the urethra. Urinalysis in Companion Animals FREE CATCH Advantages Disadvantages Table 2. Advantages & Disadvantages of Sampling Methods Normal voiding: No risk and pet owners can obtain samples Manual compression: Distended urinary bladder compressed at convenience of collector Both methods: Samples are often contaminated Manual compression: (1) Urinary bladder may be traumatized, (2) infected urine may be forced into ureters, kidneys, and prostate, (3) technique cannot be used immediately post cystotomy, and may be uncomfortable in other postoperative laparotomy patients CATHETERIZATION Advantages Bladder does not have to be distended Disadvantages Can only be performed by trained personnel Risk for iatrogenic infection, blood and cellular contaminants Risk for trauma or perforation of the urethra or urinary bladder Not possible if there is urethral obstruction CYSTOCENTESIS Advantages Less risk for iatrogenic infection and contaminants Localizes source of cells and/or bacteria Disadvantages Can only be performed by trained personnel Must have sufficient amount of urine in bladder to perform Risk for microscopic hematuria Inadvertent intestinal sampling Urinary bladder tear (very rare), leakage of urine into abdomen (usually only a very small amount that is not clinically important, but risk is greatest in animals with severe bladder distension due to urethral obstruction, or those with severe disease of the bladder wall) Contraindicated in the presence of a coagulopathy or anti-coagulant therapy March/April 2014 Today s Veterinary Practice 65
3 Today s Technician STEP-BY-STEP: Cystocentesis Bladder Isolation Technique Equipment Needed 6- to 12-mL syringe 22-gauge needle, 1 to 1.5 inches (dependent on animal size) Ethanol 1. Assemble equipment and attach needle to syringe. 2. Restrain the animal in lateral recumbency. In some dogs, the bladder may be easily palpated while standing. 3. Palpate the urinary bladder, located in the caudal abdomen, to determine if bladder contains enough urine. 4. Clean the caudal abdomen skin with ethanol. 5. Gently isolate the bladder between the fingers of one hand. 6. Once the bladder is isolated, insert the needle without applying negative pressure, at an approximate 45-degree angle. 7. At the appropriate depth, slowly draw back the syringe plunger to aspirate the desired volume of urine. 8. When the desired volume of urine is obtained, release the syringe plunger and withdraw the needle. Ultrasound-Guided Technique Equipment Needed As listed above Ultrasound unit 1. Assemble equipment and attach needle to syringe. 2. Restrain the animal in dorsal or lateral recumbency and spray the caudal abdomen skin with ethanol. 3. Apply the ultrasound transducer to the surface of the abdomen and visualize the urinary bladder. 4. While visualizing the urinary bladder, insert the needle as previously described to aspirate the desired volume of urine. 5. When the desired volume of urine is obtained, release the syringe plunger and withdraw the needle. Cystocentesis Cystocentesis of the urinary bladder is generally easy to perform in small animals. It is the preferred method of urine collection when evaluating the significance of cells or bacteria in the urine or obtaining urine for culture. Mild blood contamination may be seen in cystocentesis-obtained urine samples. Although urine leak or hemorrhage is possible following cystocentesis, the incidence of these complications is exceedingly rare and should not deter the practitioner from performing cystocentesis in the vast majority of patients. See Step-by-Step: Cystocentesis Bladder Isolation Technique. SAMPLE HANDLING Once a sample is collected, UA should be performed within the hour to avoid artifactual changes that occur as cells and casts deteriorate. If the urine cannot be examined within that time, or will be shipped to a laboratory, the lid should be tightly secured and the sample refrigerated to slow the rate of artifactual changes. Refrigerated and sealed samples are valid up to approximately 6 hours. Most laboratories suggest shipping the sample with a cold pack to delay onset of artifactual changes (Table 3). Samples that will be: Tested in-house are typically collected in a clean container, free of disinfectants that can alter the results of chemistry tests Shipped to an outside laboratory for biochemical analysis or cytologic examination should contain several mls of urine sent in a clean, secured collection container for routine biochemical analysis and sediment evaluation, or in an EDTA tube for cytologic evaluation of the the sediment. Alternately, an air-dried slide of sediment can be sent for staining and evaluation by a veterinary clinical pathologist if suspected cellular atypia is present. Table 3. Artifactual Changes of Delayed Examination 1 Bacterial (real or contaminant) overgrowth Color changes Decreased bilirubin Decreased glucose Decreased ketones Deterioration of casts Deterioration of cells Dissolution of crystals (dependent on type and urine ph) Formation of crystals (dependent on type, storage temperature, and urine ph) Increased odor Increased turbidity Increased urine ph 66
4 Shipped for culture should be obtained by cystocentesis, which is the preferred method. Samples obtained via mid-stream free catch or aseptic catheterization are acceptable if a quantitative culture is performed so that contamination can be ruled out. When urine is obtained by cystocentesis, the needle should be changed before placing the urine in a vacuum tube. Most laboratories prefer at least 1 ml of urine sent in a sterile red top tube with an accompanying cold pack to keep the sample cool. Bacterial proliferation occurs in urine stored at room temperature, thus urine should be refrigerated until shipped. Today s Technician Urinalysis in Companion Animals EDTA preserves cell morphology, which is particularly important since cells deteriorate rapidly in urine, and will prevent clotting in samples containing blood. It also has bacteriostatic properties that inhibit bacterial overgrowth in samples containing bacteria. EXAMINATION OF URINE The components of a complete UA are: 1. Evaluation of the urine sample s physical appearance 2. Specific gravity (USG) 3. Urine chemical properties 4. Microscopic examination of urine sediment. Part 1 of this article will discuss evaluation of the sample s physical appearance and USG, while Part 2, which will be published in the next issue of Today s Veterinary Practice, will address evaluation of urine chemistry and sediment. PHYSICAL APPEARANCE Color The normal color of urine is pale yellow, yellow, or amber (Figure 2). Abnormal urine color may be the reason clients seek veterinary attention for their pets (Table 4). There are many reasons for abnormal urine color, including issues related to diet, medications, and the pet s environment. It is important to recognize that pigmenturia may interfere with the color change results on the urine chemistry reagent strip test pads. Turbidity Urine is typically clear. Cloudy urine samples may be caused by suspended material, including cells, crystals, bacteria, lipids, and mucus. Causes of turbidity can be further investigated by examining the urine sediment under a microscope, which will be discussed in part 2 of this article. Figure 2. Normal range of urine color (3 samples on left); sample on right is abnormal color. Table 4. Causes of Abnormal Urine Color ABNORMAL COLOR Red Red-brown Brown to black Yelloworange Yellow-green Yellow-brown CAUSE Erythrocytes, hemoglobin, myoglobin Erythrocytes, hemoglobin, myoglobin, methemoglobin Methemoglobin from hemoglobin or myoglobin Bilirubin Bilirubin or biliverdin Bilirubin or biliverdin URINE SPECIFIC GRAVITY USG indicates the solute concentration of the urine, and is an indicator of the kidneys ability to concentrate or dilute urine, providing valuable information about one of the kidneys primary functions. Measurement USG is measured by a refractometer (Figure 3). Refractometers are calibrated for the species being tested and many types are available, including digital refractometers. A drop of urine is placed on the glass under the plastic cover; then held up to a light source while the examiner looks through the eyepiece. March/April 2014 Today s Veterinary Practice 67
5 Today s Technician Table 5. Select Factors that Decrease Urine Specific Gravity Figure 3. Handheld refractometer Diuretic administration Glucocorticoid administration (including topical) Feline hyperthyroidism Fluid therapy Hyperadrenocorticism Hypercalcemia Hypoadrenocorticism Hypokalemia Hyponatremia/hypochloremia Liver failure Psychogenic water drinking Pyometra USG is recorded at the light/dark interface on the scale visualized through the eyepiece. When complete, it is important to wipe the glass without scratching the surface. Scratches on the glass may interfere with USG reading and invalidate results. Interpretation Interpretation of USG is dependent on several factors: Hydration status Electrolyte concentrations Serum creatinine and urea nitrogen concentrations Administration of fluids and/or medications. Several clinical entities may also alter the kidneys ability to concentrate urine (Table 5). Hyposthenuria (USG < 1.007) is dilute urine, indicating a specific gravity lower than plasma and glomerular filtrate. Isosthenuria (USG ) indicates a specific gravity equal to plasma and glomerular filtrate. A dehydrated animal with healthy kidney function should excrete a small amount of highly concentrated urine, increasing the USG. If the USG indicates isosthenuria (USG < in a dog and < in a cat), a detailed history to determine recent medication administration and evaluation of serum creatinine and urea nitrogen concentrations are indicated. The maximum urine dilution in most domestic animals is 1.001, and maximum urine concentrating ability is > in cats, > in dogs, and > in horses and cattle. 1 Normal reference intervals for USG may be misleading since there are many variables that contribute to USG. Therefore, the interpretation of USG is always based on the clinical status of the patient and consideration of factors that are known to alter USG. n Read Part 2 of this article Evaluation of Urine Chemistry & Sediment in the next issue of Today s Veterinary Practice. CBC = complete blood count; UA = urinalysis; USG = urine specific gravity References 1. Osborne CA, Stevens JB. Biochemical analysis of urine: Indications, methods, interpretation. urine sediment: Under the microscope. Urinalysis: A Clinical Guide to Compassionate Patient Care. Pittsburgh: Bayer Corporation, 1999, pp 58, Suggested Reading Chew DJ, DiBartola SP. Sample handling, preparation, and analysis. Interpretation of Canine and Feline Urinalysis. Wilmington, DE: Ralston Purina Company Clinical Handbook Series, 1998, p 10. Stockham S, Scott M. Urinary. Fundamentals of Veterinary Clinical Pathology, 2nd ed. Ames, Iowa: Blackwell Publishing, pp Theresa E. Rizzi, DVM, Diplomate ACVP (Clinical Pathology), is a clinical associate professor at Oklahoma State University s Center for Veterinary Health Sciences. Her clinical interests include cytauxzoon infection in cats, hematology, and diagnostic cytology. Dr. Rizzi teaches select classes in the clinical pathology core curriculum. 68
A. SAP is the D-Lab's name for a specific set of serum biochemical tests.
 Understanding CBC, SAP, UA/Laura J. Steadman, DVM I. CBC - Complete Blood Count A. Three major types of cells are counted 1. Red Blood Cells 2. White Blood Cells 3. Platelets B. Cells are counted at the
Understanding CBC, SAP, UA/Laura J. Steadman, DVM I. CBC - Complete Blood Count A. Three major types of cells are counted 1. Red Blood Cells 2. White Blood Cells 3. Platelets B. Cells are counted at the
Taking a dip into urinalysis
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Taking a dip into urinalysis Author : Christine Jameison Categories : RVNs Date : July 1, 2009 Christine Jameison RVN, probes
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Taking a dip into urinalysis Author : Christine Jameison Categories : RVNs Date : July 1, 2009 Christine Jameison RVN, probes
Assessment of urine of a bovine patient
 Commonwealth of Australia Copyright regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been copied and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Adelaide pursuant of Part VB of the Copyright Act
Commonwealth of Australia Copyright regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been copied and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Adelaide pursuant of Part VB of the Copyright Act
Proceeding of the ACVP Annual Meeting
 http://www.ivis.org Proceeding of the ACVP Annual Meeting Oct.17-21, 2015 Minneapolis, MN, USA Next Meeting: Dec. 3-7, 2016 - New Orleans, LA, USA Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the
http://www.ivis.org Proceeding of the ACVP Annual Meeting Oct.17-21, 2015 Minneapolis, MN, USA Next Meeting: Dec. 3-7, 2016 - New Orleans, LA, USA Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the
The Minimum Diagnostic Database: Urinalysis
 The Minimum Diagnostic Database: Urinalysis Jeff Niziolek, DVM Professional Services Veterinarian IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. 208 Bay Meadows Drive Holland, MI 49424 The minimum database includes three types
The Minimum Diagnostic Database: Urinalysis Jeff Niziolek, DVM Professional Services Veterinarian IDEXX Laboratories, Inc. 208 Bay Meadows Drive Holland, MI 49424 The minimum database includes three types
Assisting in the Analysis of Urine. Copyright 2011, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Assisting in the Analysis of Urine Urinalysis Why is Urine is analyzed? To detect extrinsic conditions those in which the kidney is functioning normally, but abnormal end-products of metabolism are excreted
Assisting in the Analysis of Urine Urinalysis Why is Urine is analyzed? To detect extrinsic conditions those in which the kidney is functioning normally, but abnormal end-products of metabolism are excreted
It s not just water! What is Urinalysis?
 It s not just water! An introduction to Urinalysis What is Urinalysis? Urinalysis or the analysis of urine is one of the oldest laboratory procedures in the practice of medicine. It is a good test for
It s not just water! An introduction to Urinalysis What is Urinalysis? Urinalysis or the analysis of urine is one of the oldest laboratory procedures in the practice of medicine. It is a good test for
A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today
 III. THE ROUTINE URINALYSIS A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today 1. Cave man noted change in urine properties associated with disease 2. Babylonians and Egyptians noted
III. THE ROUTINE URINALYSIS A. History Urinalysis is the oldest lab test still being performed today 1. Cave man noted change in urine properties associated with disease 2. Babylonians and Egyptians noted
SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats
 SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats These SOPs were developed by the Office of the University Veterinarian and reviewed by Virginia Tech IACUC to provide a reference and guidance to investigators during
SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats These SOPs were developed by the Office of the University Veterinarian and reviewed by Virginia Tech IACUC to provide a reference and guidance to investigators during
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE
 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND DETECTION OF NORMAL CONSTITUENTS OF URINE - OBJECTIVES: 1- The simple examination of urine. 2- To detect some of the normal organic constituents of urine. 3- To detect some of the
GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS)
 GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS) Physiology Lab-8 December, 2018 Lect. Asst. Zakariya A. Mahdi MSc Pharmacology Background Urine (from Latin Urina,) is a typically sterile liquid by-product of
GENERAL URINE EXAMINATION (URINE ANALYSIS) Physiology Lab-8 December, 2018 Lect. Asst. Zakariya A. Mahdi MSc Pharmacology Background Urine (from Latin Urina,) is a typically sterile liquid by-product of
Light yellow to dark golden yellow Clear ph range Specific gravity Sediments
 #11 Objectives: Understand specific gravity and identify normal specific gravity values for urine Learn to use a urine hydrometer to measure specific gravity Define specific gravity and identify normal
#11 Objectives: Understand specific gravity and identify normal specific gravity values for urine Learn to use a urine hydrometer to measure specific gravity Define specific gravity and identify normal
Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
 Barger both02.tex V3-07/08/2015 7:05 P.M. Page 1 Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Chapter 1 Getting Started with Clinical Pathology 1. Which component of the microscope should be adjusted when evaluating
Barger both02.tex V3-07/08/2015 7:05 P.M. Page 1 Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Chapter 1 Getting Started with Clinical Pathology 1. Which component of the microscope should be adjusted when evaluating
Bacterial urinary tract infections
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Bacterial urinary tract infections Author : CATHERINE F LE BARS Categories : Vets Date : February 11, 2008 CATHERINE F LE
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Bacterial urinary tract infections Author : CATHERINE F LE BARS Categories : Vets Date : February 11, 2008 CATHERINE F LE
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg. Session Outline. Routine Urinalysis a historical perspective. Unit 2; Session 8
 Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 8 Session Outline Historical perspective Importance of testing Basic urine composition Types of collection Timing of collection Urine preservatives Urinalysis
Urinalysis and Body Fluids CRg Unit 2; Session 8 Session Outline Historical perspective Importance of testing Basic urine composition Types of collection Timing of collection Urine preservatives Urinalysis
EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE
 EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Skills: 30 points Objectives: 1. State the specimen of choice for chemical analysis of urine. 2. List two macroscopic observations of urine and
EXERCISE 11: MACROSCOPIC AND CHEMICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Skills: 30 points Objectives: 1. State the specimen of choice for chemical analysis of urine. 2. List two macroscopic observations of urine and
Purpose Provide instructions for collection of optimal urine specimens to ensure accurate test results.
 Policy S:PC-2110 Page 1 Fairview Health Services Department Laboratory / Nursing Section Acute Care: Collection Category Provision of Care Subject URINE COLLECTION, RANDOM/CATHETER/OTHER Purpose Provide
Policy S:PC-2110 Page 1 Fairview Health Services Department Laboratory / Nursing Section Acute Care: Collection Category Provision of Care Subject URINE COLLECTION, RANDOM/CATHETER/OTHER Purpose Provide
Patient Preparation Unique patient preparation requirements are listed under each test in the Test Directory.
 Specimen Collection Lab results are only as good as the specimen provided. Patient preparation, venipuncture technique, specimen handling, and transportation can all affect the quantity of results. Health
Specimen Collection Lab results are only as good as the specimen provided. Patient preparation, venipuncture technique, specimen handling, and transportation can all affect the quantity of results. Health
Lecture 7. The Urinary System
 Lecture 7 The Urinary System Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning The Urinary System The urinary system removes wastes from the body The urinary system also maintains homeostasis or a constant internal
Lecture 7 The Urinary System Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning The Urinary System The urinary system removes wastes from the body The urinary system also maintains homeostasis or a constant internal
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Urinary System Diseases/Disorders. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Urinary System Diseases/Disorders LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Identify the purposes
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Urinary System Diseases/Disorders LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Identify the purposes
Application Note. Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1
 Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Author: Carl Zeiss
Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Application Note Light Microscopic Analysis of Urine ZEISS Primo Star and ZEISS Axio Lab.A1 Author: Carl Zeiss
Topic Objectives. Physical Examination LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE. Appearance. Odor Specific Gravity Volume
 LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Topic Objectives 1. Identify the colors which commonly associated with abnormal urine. 2. State two possible causes for urine turbidity in a sample that
LECTURE MODULE 3; PHYSICAL EXAMINATION OF URINE Topic Objectives 1. Identify the colors which commonly associated with abnormal urine. 2. State two possible causes for urine turbidity in a sample that
LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis
 LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis Notes 1. This lab combines the objectives and activities of the macroscopic and microscopic lab activities. Students are expected to review those labs for reference.
LABORATORY 5: The Complete Urinalysis Notes 1. This lab combines the objectives and activities of the macroscopic and microscopic lab activities. Students are expected to review those labs for reference.
The Urinary System. 1. Define important words in this chapter. 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system
 109 16 The Urinary System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system 3. Discuss changes in the urinary system due to aging 4. List normal qualities
109 16 The Urinary System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system 3. Discuss changes in the urinary system due to aging 4. List normal qualities
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS
 PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
PRINCIPLE OF URINALYSIS Vanngarm Gonggetyai Objective Can explain : the abnormalities detected in urine Can perform : routine urinalysis Can interprete : the results of urinalysis Examination of urine
URINANLYSIS. Pre-Lab Guide
 URINANLYSIS Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions on
URINANLYSIS Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions on
URINE DIPSTICK AND SULPHOSALICYLIC ACID TEST. Špela Borštnar UREX 2015, Ljubljana, Slovenia
 URINE DIPSTICK AND SULPHOSALICYLIC ACID TEST Špela Borštnar UREX 2015, Ljubljana, Slovenia KIDNEY DISEASE? severity of kidney disease = estimating GFR cause of kidney disease = urinalysis URINE EXAMINATION
URINE DIPSTICK AND SULPHOSALICYLIC ACID TEST Špela Borštnar UREX 2015, Ljubljana, Slovenia KIDNEY DISEASE? severity of kidney disease = estimating GFR cause of kidney disease = urinalysis URINE EXAMINATION
Routine urine examination
 Routine urine examination 尿常规检查 Huawei Liang, PhD E-mail: hwliang99@163.com Objectives To examine urine for the presence of normal and abnormal constituents by routine urine analysis Principles Urine formation
Routine urine examination 尿常规检查 Huawei Liang, PhD E-mail: hwliang99@163.com Objectives To examine urine for the presence of normal and abnormal constituents by routine urine analysis Principles Urine formation
Sources Tips for Writing Tests. Rules, tips, and errors when writing examination questions. Before you start writing: Before you start writing:
 Rules, tips, and errors when writing examination questions Steven L. Stockham, D.V.M., M.S. Diplomate, A.C.V.P, Honorary Diplomate, E.C.V.C.P. Professor and Director of Clinical Pathology Laboratory College
Rules, tips, and errors when writing examination questions Steven L. Stockham, D.V.M., M.S. Diplomate, A.C.V.P, Honorary Diplomate, E.C.V.C.P. Professor and Director of Clinical Pathology Laboratory College
Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats (Struvite Stones in the Urinary Tract of Cats) Basics
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Struvite Urolithiasis in Cats (Struvite Stones in the Urinary Tract of Cats) Basics
Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis
 Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis Reviewed & ratified by: Dr V Taylor-Jones & Ms C Tierney. Urinalysis Aims and Objectives Aim: For the student to be able to safely conduct a urinalysis on
Year 1 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Urinalysis Reviewed & ratified by: Dr V Taylor-Jones & Ms C Tierney. Urinalysis Aims and Objectives Aim: For the student to be able to safely conduct a urinalysis on
Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care
 Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care Table of Contents 1 What is a catheter?... 2 2 Why does the child need a catheter?... 2 3 Normal Urine... 2 4 How to do a clean urethral catheterization
Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care Table of Contents 1 What is a catheter?... 2 2 Why does the child need a catheter?... 2 3 Normal Urine... 2 4 How to do a clean urethral catheterization
Role of Quantitative MA Testing in Everyday Practice
 Print PDF Save PDF Sign Up for Newsletter Past Editions August/September 2012 Focus: Renal Disease Diagnostics Role of Quantitative MA Testing in Everyday Practice Interview with Brenda Harai, DVM, MS,
Print PDF Save PDF Sign Up for Newsletter Past Editions August/September 2012 Focus: Renal Disease Diagnostics Role of Quantitative MA Testing in Everyday Practice Interview with Brenda Harai, DVM, MS,
CPT Code: Serum Urea Nitrogen, Urine Urea Nitrogen in mg/dl, 24 hour Urine Urea Nitrogen, Urea Clearance
 UREA CLEARANCE UREACL Specimen Required: 2.5 ml blood, gel tube and total collection 24 hour urine Special Instructions: Refrigerate urine during collection. Provide starting date and time, and ending
UREA CLEARANCE UREACL Specimen Required: 2.5 ml blood, gel tube and total collection 24 hour urine Special Instructions: Refrigerate urine during collection. Provide starting date and time, and ending
Sub Flush Kit A Special Flush Kit with T-FloLoc TM for use with the SUB System
 NORFOLK VET PRODUCTS Specialty Medical Devices For The Veterinary Community the Sub Flush Kit A Special Flush Kit with T-FloLoc TM for use with the SUB System Instructions For Use provided by Drs. Allyson
NORFOLK VET PRODUCTS Specialty Medical Devices For The Veterinary Community the Sub Flush Kit A Special Flush Kit with T-FloLoc TM for use with the SUB System Instructions For Use provided by Drs. Allyson
VetScan UA Urine Analyzer Clinical Performance Larry Lem, PhD & Andrew Rosenfeld, DVM, ABVP
 VetScan UA Urine Analyzer Clinical Performance Larry Lem, PhD & Andrew Rosenfeld, DVM, ABVP Abstract Background: The VetScan UA urine strip reader is an analyzer designed to provide semi-quantitative and
VetScan UA Urine Analyzer Clinical Performance Larry Lem, PhD & Andrew Rosenfeld, DVM, ABVP Abstract Background: The VetScan UA urine strip reader is an analyzer designed to provide semi-quantitative and
Functional Renal Physiology and Urine Production
 Functional Renal Physiology and Urine Production Urinalysis can provide insight into hydration status, renal function or dysfunction, systemic disease, and toxic insults. Accurate interpretation of urinalysis
Functional Renal Physiology and Urine Production Urinalysis can provide insight into hydration status, renal function or dysfunction, systemic disease, and toxic insults. Accurate interpretation of urinalysis
General Guidelines for Sample Submissions
 HISTORY General Guidelines for Sample Submissions (See the Client Handbook for specific test requirements.) The history of the animal is very important, including treatments, vaccinations and feeding,
HISTORY General Guidelines for Sample Submissions (See the Client Handbook for specific test requirements.) The history of the animal is very important, including treatments, vaccinations and feeding,
Role of Quantitative MA Testing in Everyday Practice
 Print PDF Save PDF Sign Up for Newsletter Past Editions August/September 2012 Focus: Renal Disease Diagnostics Role of Quantitative MA Testing in Everyday Practice Interview with Brenda Harai, DVM, MS,
Print PDF Save PDF Sign Up for Newsletter Past Editions August/September 2012 Focus: Renal Disease Diagnostics Role of Quantitative MA Testing in Everyday Practice Interview with Brenda Harai, DVM, MS,
BCH472 [Practical] 1
![BCH472 [Practical] 1 BCH472 [Practical] 1](/thumbs/89/98494556.jpg) BCH472 [Practical] 1 Physical Examination Chemical Examination 2 ph Color Specific Gravity Volume Odor Appearance Acidic: -Diabetic Ketoacidosis. -Starvation. -UTIs (E. coli). Alkaline: -UTIs (ureasplitting
BCH472 [Practical] 1 Physical Examination Chemical Examination 2 ph Color Specific Gravity Volume Odor Appearance Acidic: -Diabetic Ketoacidosis. -Starvation. -UTIs (E. coli). Alkaline: -UTIs (ureasplitting
The Urinary System. Lab Exercise 38. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Urinary System Objectives - Be able to identify the structures of the urinary system and give their function - Be able to recognize the gross anatomy of the kidney - Identify the components
Lab Exercise The Urinary System Objectives - Be able to identify the structures of the urinary system and give their function - Be able to recognize the gross anatomy of the kidney - Identify the components
What s Your Diagnosis??? Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012
 Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012 What s Your Diagnosis??? Signalment Emma, a 9 year old, Female, Spayed, Domestic Short Haired Feline Presenting Complaint Weight loss, vomited the morning of her visit,
Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012 What s Your Diagnosis??? Signalment Emma, a 9 year old, Female, Spayed, Domestic Short Haired Feline Presenting Complaint Weight loss, vomited the morning of her visit,
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Microscopic Examination of Urine
 Download http://www.vetlab.com/kova.htm Definition of urine sediment: all solid materials suspended in the urine - a semiquantative evaluation of the urine sediment Significance of formed elements in the
Download http://www.vetlab.com/kova.htm Definition of urine sediment: all solid materials suspended in the urine - a semiquantative evaluation of the urine sediment Significance of formed elements in the
Instruction Guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization for Parents of Boys Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Instruction Guide to Sterile Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Men Using the Cure Catheter Closed System
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Chapter 23. Composition and Properties of Urine
 Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers DIFFUSE
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers DIFFUSE
Specimen Collection Policies
 Specimen Collection Policies Purpose Great River Medical Center Laboratory is a hospital-based and outreach laboratory with specific standards of excellence. To best serve our patients, all specimens will
Specimen Collection Policies Purpose Great River Medical Center Laboratory is a hospital-based and outreach laboratory with specific standards of excellence. To best serve our patients, all specimens will
Steve Garnett, DVM, DACVS-SA Dogs and Cats Veterinary Referral and Emergency April 30, 2017
 Steve Garnett, DVM, DACVS-SA Dogs and Cats Veterinary Referral and Emergency April 30, 2017 Overview Anatomy review Cystotomy Urethrotomy Urethrostomy What s New! Anatomy Anatomy Cystotomy Indications
Steve Garnett, DVM, DACVS-SA Dogs and Cats Veterinary Referral and Emergency April 30, 2017 Overview Anatomy review Cystotomy Urethrotomy Urethrostomy What s New! Anatomy Anatomy Cystotomy Indications
4/7/2017. Ultrasound of the Urinary Bladder. Indications for Bladder Ultrasound. Patient Preparation. Transition Adjustments.
 Indications for Bladder Ultrasound Ultrasound of the Urinary Bladder Hematuria, pyuria, or other UA abnormality Abnormal transitional cells Pollakuria, dysuria, stranguria, periuria History of urinary
Indications for Bladder Ultrasound Ultrasound of the Urinary Bladder Hematuria, pyuria, or other UA abnormality Abnormal transitional cells Pollakuria, dysuria, stranguria, periuria History of urinary
NONGYNECOLOGICAL CYTOLOGY FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION SPECIMENS
 NONGYNECOLOGICAL CYTOLOGY FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION SPECIMENS I. Purpose Fine needle aspiration of mass lesions is commonly utilized in the detection and characterization of a variety of malignant diseases.
NONGYNECOLOGICAL CYTOLOGY FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION SPECIMENS I. Purpose Fine needle aspiration of mass lesions is commonly utilized in the detection and characterization of a variety of malignant diseases.
31 August 2016 Urinalysis - a review
 31 August 2016 Urinalysis - a review Bradley Galgut, BVSc (Hons), DACVP Specialist Veterinary Clinical Pathologist Urinalysis A Review Bradley Galgut, BVSc (Hons), DACVP Specialist Veterinary Clinical
31 August 2016 Urinalysis - a review Bradley Galgut, BVSc (Hons), DACVP Specialist Veterinary Clinical Pathologist Urinalysis A Review Bradley Galgut, BVSc (Hons), DACVP Specialist Veterinary Clinical
Ch17-18 Urinary System
 Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
Ch17-18 Urinary System Main Function: Filter the blood Other Functions: maintain purity and consistency of internal fluids eliminates nitrogenous wastes, toxins, and drugs from the body regulates blood
APPENDIX E COLLECTION AND SUBMISSION OF SPECIMENS FOR TB TESTING
 APPENDIX E COLLECTION AND SUBMISSION OF SPECIMENS FOR TB TESTING For additional information about the collection, transport or submission of specimens for AFB examination, contact BC Public Health & Microbiology
APPENDIX E COLLECTION AND SUBMISSION OF SPECIMENS FOR TB TESTING For additional information about the collection, transport or submission of specimens for AFB examination, contact BC Public Health & Microbiology
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists. Membership Examination. Small Animal Medicine Paper 1
 Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2018 Small Animal Medicine Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal Answer
Australian and New Zealand College of Veterinary Scientists Membership Examination June 2018 Small Animal Medicine Paper 1 Perusal time: Fifteen (15) minutes Time allowed: Two (2) hours after perusal Answer
Case Log Number(s) Veterinarian or VTS Accurately report test results, using appropriate units of measurement Quality Control/Assurance Date Mastered
 AVCPT Skills List Candidate: Understanding of test methodology, techniques and ability to perform testing must be applied to each skill. The overall goal is to provide accurate and valid results to assist
AVCPT Skills List Candidate: Understanding of test methodology, techniques and ability to perform testing must be applied to each skill. The overall goal is to provide accurate and valid results to assist
Controls (positive and negative) for quality assessment-located in central laboratory Note: See central lab UA procedure for QC. Read strips visually.
 ACTION DATE INITIAL Adopted Reviewed 2/8/16 KLW Reviewed 12/12/16 KLW Reviewed Reviewed Revised 5/11/10 MAS Supersedes 2/6/08 name change from Bayer to Siemens TITLE: URINALYSIS TESTING USING Siemens MULTISTIX
ACTION DATE INITIAL Adopted Reviewed 2/8/16 KLW Reviewed 12/12/16 KLW Reviewed Reviewed Revised 5/11/10 MAS Supersedes 2/6/08 name change from Bayer to Siemens TITLE: URINALYSIS TESTING USING Siemens MULTISTIX
Michelle Moy, MAd Ed, MT(ASCP)SC Program Director Clinical Laboratory Science Program Loyola University Chicago, Illinois
 Reviewers Lorraine Doucette, MS, MLS(ASCP)CM Associate Professor and Medical Laboratory Technician Program Coordinator Anne Arundel Community College Arnold, Maryland Pamela B. Lonergan, MS, MT(ASCP)SC
Reviewers Lorraine Doucette, MS, MLS(ASCP)CM Associate Professor and Medical Laboratory Technician Program Coordinator Anne Arundel Community College Arnold, Maryland Pamela B. Lonergan, MS, MT(ASCP)SC
Squamous epithelial cells in urine 0-5
 Toggle navigation Squamous epithelial cells in urine 0-5 13-10-2017 Finding epithelial cells in urine is a diagnostic result found during urinalysis and may raise some red flags for physicians to several
Toggle navigation Squamous epithelial cells in urine 0-5 13-10-2017 Finding epithelial cells in urine is a diagnostic result found during urinalysis and may raise some red flags for physicians to several
TREATMENT METHODS FOR DISORDERS OF SMALL ANIMAL BLADDER FUNCTION
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk TREATMENT METHODS FOR DISORDERS OF SMALL ANIMAL BLADDER FUNCTION Author : SIMONA T RADAELLI Categories : Vets Date : July
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk TREATMENT METHODS FOR DISORDERS OF SMALL ANIMAL BLADDER FUNCTION Author : SIMONA T RADAELLI Categories : Vets Date : July
THE PREVALENCE OF HEMATURIA IN DOGS AND CATS
 Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LXIII (2) ISSN 2065-1295; ISSN 2343-9394 (CD-ROM); ISSN 2067-3663 (Online); ISSN-L 2065-1295 THE PREVALENCE OF HEMATURIA IN DOGS AND CATS Alexandra
Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LXIII (2) ISSN 2065-1295; ISSN 2343-9394 (CD-ROM); ISSN 2067-3663 (Online); ISSN-L 2065-1295 THE PREVALENCE OF HEMATURIA IN DOGS AND CATS Alexandra
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA LEARNING OBJECTIVES DEFINITION. KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer
 MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF ABDOMINAL TRAUMA. LUIS H. TELLO MV, MS, DVM, COS Portland Hospital Classic International Medical Advisor Banfield Pet Hospital
 MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF ABDOMINAL TRAUMA LUIS H. TELLO MV, MS, DVM, COS Portland Hospital Classic International Medical Advisor Banfield Pet Hospital ABDOMINAL TRAUMA 70-80% of multiple trauma patients 55%
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF ABDOMINAL TRAUMA LUIS H. TELLO MV, MS, DVM, COS Portland Hospital Classic International Medical Advisor Banfield Pet Hospital ABDOMINAL TRAUMA 70-80% of multiple trauma patients 55%
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
A general approach to canine urinary tract disorders: origin to treatment
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk A general approach to canine urinary tract disorders: origin to treatment Author : Fernando Reina Categories : RVNs Date :
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk A general approach to canine urinary tract disorders: origin to treatment Author : Fernando Reina Categories : RVNs Date :
Associated Terms: Bladder Stones, Ureteral Stones, Kidney Stones, Cystotomy, Urolithiasis, Cystic Calculi
 Associated Terms: Bladder Stones, Ureteral Stones, Kidney Stones, Cystotomy, Urolithiasis, Cystic Calculi The term "ACVS Diplomate" refers to a veterinarian who has been board certified in veterinary surgery.
Associated Terms: Bladder Stones, Ureteral Stones, Kidney Stones, Cystotomy, Urolithiasis, Cystic Calculi The term "ACVS Diplomate" refers to a veterinarian who has been board certified in veterinary surgery.
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female)
 Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female) Refer to National Infection Prevention and Control Manual for information on aseptic technique/cleaning equipment. Equipment
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female) Refer to National Infection Prevention and Control Manual for information on aseptic technique/cleaning equipment. Equipment
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Women Using the Extra Long Cure Medical Pocket Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
SHASTA PATHOLOGY ASSOCIATES CYTOLOGY SPECIMEN COLLECTION
 SHASTA PATHOLOGY ASSOCIATES CYTOLOGY SPECIMEN COLLECTION I. PRINCIPLE: Proper collection and handling of all cytology specimens helps ensure the most accurate results possible from the specimen. Cytology
SHASTA PATHOLOGY ASSOCIATES CYTOLOGY SPECIMEN COLLECTION I. PRINCIPLE: Proper collection and handling of all cytology specimens helps ensure the most accurate results possible from the specimen. Cytology
Patient Information Publications Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health
 Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health What is a subcutaneous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous
Warren Grant Magnuson Clinical Center National Institutes of Health What is a subcutaneous injection? A subcutaneous injection is given in the fatty layer of tissue just under the skin. A subcutaneous
Urine bench. Urine test for: SARAH Sugar
 Urine bench Urine test for: Sugar It's normal to occasionally have a small amount of sugar in your urine during pregnancy, but if you have elevated levels at a couple of prenatal visits in a row or a very
Urine bench Urine test for: Sugar It's normal to occasionally have a small amount of sugar in your urine during pregnancy, but if you have elevated levels at a couple of prenatal visits in a row or a very
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Women Using the Cure Twist
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Urinalysis (Macroscopic Physical Tests) Urinalysis. Basic Urinalysis 12/22/2012. Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari DCLS, PhD
 Urinalysis (Macroscopic Physical Tests) Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari DCLS, PhD Urinalysis Basic Urinalysis CLSI: U/A is the testing of urine with procedures commonly performed in an expeditious, reliable, accurate,
Urinalysis (Macroscopic Physical Tests) Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari DCLS, PhD Urinalysis Basic Urinalysis CLSI: U/A is the testing of urine with procedures commonly performed in an expeditious, reliable, accurate,
Clinical Laboratory Science: Urinalysis
 Clinical Laboratory Science: Urinalysis Urine is produced by the kidney to maintain constant plasma osmotic concentration; to regulate ph, electrolyte and fluid balances and to excrete some 50 grams of
Clinical Laboratory Science: Urinalysis Urine is produced by the kidney to maintain constant plasma osmotic concentration; to regulate ph, electrolyte and fluid balances and to excrete some 50 grams of
VOIDING UROHYDROPROPULSION
 CANINE UROLITHIASIS 0195-5616/99 $8.00 +.00 VOIDING UROHYDROPROPULSION Lessons From 5 Years of Experience Jody P. Lulich, DVM, PhD, Carl A. Osborne, DVM, PhD, Sherry L. Sanderson, DVM, Lisa K. Ulrich,
CANINE UROLITHIASIS 0195-5616/99 $8.00 +.00 VOIDING UROHYDROPROPULSION Lessons From 5 Years of Experience Jody P. Lulich, DVM, PhD, Carl A. Osborne, DVM, PhD, Sherry L. Sanderson, DVM, Lisa K. Ulrich,
More than 100 different tests can be done on urine. A regular urinalysis often includes the following tests:
 Urine Test Table of Contents Test Overview Why It Is Done How To Prepare How It Is Done How It Feels Risks Results What Affects the Test What To Think About References Credits Test Overview A urine test
Urine Test Table of Contents Test Overview Why It Is Done How To Prepare How It Is Done How It Feels Risks Results What Affects the Test What To Think About References Credits Test Overview A urine test
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter
 Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter Equipment required collect prior to procedure Perform this procedure as an aseptic technique to minimise the risk of introducing Clean the
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter Equipment required collect prior to procedure Perform this procedure as an aseptic technique to minimise the risk of introducing Clean the
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN)
 Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Non-protein nitrogenous substances (NPN) A simple, inexpensive screening test a routine urinalysis is often the first test conducted if kidney problems are suspected. A small, randomly collected urine
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Women Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Physical Characteristics of
 Physical Characteristics of Urine Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The urinary system s ability to filter the blood resides in about 2 to 3 million tufts of specialized capillaries the glomeruli distributed more or
Physical Characteristics of Urine Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The urinary system s ability to filter the blood resides in about 2 to 3 million tufts of specialized capillaries the glomeruli distributed more or
Color: BROWN/WHITE. Protein test is performed and confirmed by the sulfosalicylic acid test.
 5/8/2014 L 29 UA/Microscopy results from IDEXX Reference GLUCOSE NEGATIVE BILIRUBIN NEGATIVE KETONES NEGATIVE BLOOD NEGATIVE PH 6.5 SP GRAVITY 1.031 PROTEIN NEGATIVE UROB NORMAL WBC NONE SEEN HPF 0-5 RBC
5/8/2014 L 29 UA/Microscopy results from IDEXX Reference GLUCOSE NEGATIVE BILIRUBIN NEGATIVE KETONES NEGATIVE BLOOD NEGATIVE PH 6.5 SP GRAVITY 1.031 PROTEIN NEGATIVE UROB NORMAL WBC NONE SEEN HPF 0-5 RBC
5. Use of antibiotics, which disturbs balance of normal flora. 6. Poor nutritional status.
 Microbiology Chapter 5 Introduction to Pathogens 5:1 Changing Patterns of Disease In the past 100 years, since the discovery of the Germ Theory of Disease was accepted: We have learned that microbes cause
Microbiology Chapter 5 Introduction to Pathogens 5:1 Changing Patterns of Disease In the past 100 years, since the discovery of the Germ Theory of Disease was accepted: We have learned that microbes cause
Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis (Calcium Oxalate Stones in the Urinary Tract) Basics
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Calcium Oxalate Urolithiasis (Calcium Oxalate Stones in the Urinary Tract) Basics
Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents. Amal Alamri
 Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents Amal Alamri Lecture Over view Abnormal constituent of urine Urine analysis Experiments Physical Chemical Micro/Macro 1-Detection of some abnormal
Detection and Estimation of Some Abnormal Constituents Amal Alamri Lecture Over view Abnormal constituent of urine Urine analysis Experiments Physical Chemical Micro/Macro 1-Detection of some abnormal
Providence Medford Medical Center Pathology Department
 Providence Medford Medical Center Pathology Department Anatomic pathology services including histology, cytology and autopsies are offered through Providence Medford Medical Center Pathology Department.
Providence Medford Medical Center Pathology Department Anatomic pathology services including histology, cytology and autopsies are offered through Providence Medford Medical Center Pathology Department.
A step-by-step preparation guide
 A step-by-step preparation guide For needle and needle-free systems This guide provides detailed instructions on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of VELETRI. It is intended to be used after your
A step-by-step preparation guide For needle and needle-free systems This guide provides detailed instructions on the reconstitution, dilution, and storage of VELETRI. It is intended to be used after your
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Ostruction (Blockage of the Extrahepatic or Common Bile Duct) Basics
 Extrahepatic Bile Duct Ostruction (Blockage of the Extrahepatic or Common Bile Duct) Basics OVERVIEW The liver is the largest gland in the body; it has many functions, including production of bile (a fluid
Extrahepatic Bile Duct Ostruction (Blockage of the Extrahepatic or Common Bile Duct) Basics OVERVIEW The liver is the largest gland in the body; it has many functions, including production of bile (a fluid
Science of Veterinary Medicine. Urinary System Unit Handouts
 Science of Veterinary Medicine Urinary System Unit Handouts Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Regulate aspects of homeostasis Organs of the Urinary system The
Science of Veterinary Medicine Urinary System Unit Handouts Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Regulate aspects of homeostasis Organs of the Urinary system The
A Technician s Guide to Feline Urethral Obstruction. Jennie Schade, RVT November 5, 2017
 A Technician s Guide to Feline Urethral Obstruction Jennie Schade, RVT November 5, 2017 Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease A variety of conditions affecting the bladder and the urethra Symptoms Causes
A Technician s Guide to Feline Urethral Obstruction Jennie Schade, RVT November 5, 2017 Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease A variety of conditions affecting the bladder and the urethra Symptoms Causes
advice on prevention
 Women & Children s Directorate Urinary Tract Infection advice on prevention information for children and their families 2 Urinary tract infection (UTI for short) is one of the commonest bacterial diseases
Women & Children s Directorate Urinary Tract Infection advice on prevention information for children and their families 2 Urinary tract infection (UTI for short) is one of the commonest bacterial diseases
Urologic investigations
 Urologic investigations د. Laboratory studies EXAMINATION OF URINE Urinalysis: Urinalysis is one of the most important and useful urologic tests available. Reasons for inadequate urinalyses include: (1)
Urologic investigations د. Laboratory studies EXAMINATION OF URINE Urinalysis: Urinalysis is one of the most important and useful urologic tests available. Reasons for inadequate urinalyses include: (1)
Instruction Guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization for Parents of Girls Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
A&P of the Urinary System
 A&P of the Urinary System Week 44 1 Objectives Identify the organs of the urinary system, from a Identify the parts of the nephron (the functional unit List the characteristics of a normal urine specimen.
A&P of the Urinary System Week 44 1 Objectives Identify the organs of the urinary system, from a Identify the parts of the nephron (the functional unit List the characteristics of a normal urine specimen.
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Men Using the Hydrophilic Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter
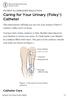 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
SAMPLE. Collecting a faeces specimen
 7. Perform steps 10 16 of the common steps (see pp. 39 43). Evidence base: PHE (2014a) To ensure that: the patient is safe and comfortable. the specimen has been correctly collected and documented in the
7. Perform steps 10 16 of the common steps (see pp. 39 43). Evidence base: PHE (2014a) To ensure that: the patient is safe and comfortable. the specimen has been correctly collected and documented in the
TISSUE COLLECTION. SCPA 603- Histopathological Techniques for Routine and Research
 TISSUE COLLECTION SCPA 603- Histopathological Techniques for Routine and Research Somphong Narkpinit, MD. Department of Pathobiology Faculty of Science, Mahidol University somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th Learning
TISSUE COLLECTION SCPA 603- Histopathological Techniques for Routine and Research Somphong Narkpinit, MD. Department of Pathobiology Faculty of Science, Mahidol University somphong.nar@mahidol.ac.th Learning
Media Fill Test Kits. Manufactured by. Making USP <797> compliance easy!
 Media Fill Test Kits Manufactured by Making USP compliance easy! Compliance was never so easy! Microbial Contamination Testing for CSPs Hardy Diagnostics offers all the products you need to easily
Media Fill Test Kits Manufactured by Making USP compliance easy! Compliance was never so easy! Microbial Contamination Testing for CSPs Hardy Diagnostics offers all the products you need to easily
