Single-Port Laparoscopic Parastomal Hernia Repair with Modified Sugarbaker Technique
|
|
|
- Nickolas Erick Todd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Single-Port Laparoscopic Parastomal Hernia Repair with Modified Sugarbaker Technique Hanh Tran, MD, Isidro Turingan, RN, Marta Zajkowska, RN, Kim Tran ABSTRACT Introduction: Laparoscopic parastomal hernia repair with modified Sugarbaker technique has become increasingly the operation of choice because of its low recurrence rates. This study aimed to assess feasibility, safety, and efficiency of performing the same operation with single-incision laparoscopic surgery. Materials and Methods: All patients referred from March 2010 to February 2013 were considered for single-port laparoscopic repair with modified Sugarbaker technique. A SILS port (Covidien, Norwalk, Connecticut, USA) was used together with conventional straight dissecting instruments and a 5.5- mm/52-cm/30 laparoscope. Important technical aspects include modified dissection techniques, namely, inline and chopsticks to overcome loss of triangulation, insertion of a urinary catheter into an ostomy for ostomy limb identification, safe adhesiolysis by avoiding electocautery, saline -jet dissection to demarcate tissue planes, dissection of an entire laparotomy scar to expose incidental incisional hernias, adequate mobilization of an ostomy limb for lateralization, and wide overlapping of defect with antiadhesive mesh. Results: Of 6 patients, 5 underwent single-port laparoscopic repair, and 1 (whose body mass index [BMI] of 39.4 kg/m 2 did not permit SILS port placement) underwent multiport repair. Mean defect size was 10 cm, and mean mesh size was 660 cm 2 with 4 patients having incidental incisional hernias repaired by the same mesh. Mean operation time was 270 minutes, and mean hospital stay was 4 days. Appliance malfunction ceased immediately, and pain associated with parastomal hernia disappeared. There was no recurrence with a follow-up of 2 to 36 months. Discipline of Surgery, Sydney Medical School, University of Sydney, Westmead Hospital, Westmead, NSW, Australia (Dr. Tran). The Sydney Hernia Specialists Clinic, Sydney, NSW, Australia (Mr. Turingan, Ms. Zajkowska, Ms. Tran). Address correspondence to: Hahn Tran, FRACS, The Sydney Hernia Specialists Clinic, Level 2, 195 Macquarie St, Sydney NSW 2000, Australia, Tel: Fax: , info@sydneyherniaspecialists.com.au DOI: / X by JSLS, Journal of the Society of Laparoendoscopic Surgeons. Published by the Society of Laparoendoscopic Surgeons, Inc. Conclusion: Compared with multiport repair, single-port laparoscopic parastomal repair with modified Sugarbaker technique is safe and efficient, and it may eventually become the standard of care. Key Words: Parastomal hernia, Single-incision laparoscopic surgery (SILS), Modified Sugarbaker technique. INTRODUCTION Parastomal hernias have been shown to occur in up to 48% of patients with a colostomy or 36% for patients with an ileostomy, with the rate rising the longer the followup. 1,2 This is not surprising given the fact that the stoma is essentially a hernia (Figure 1). The best treatment for a parastomal hernia is, of course, reversal of the ostomy. However, for patients with a terminal ostomy, this reversal is not an option, and surgical options up to now have proven disappointing. For this reason, the indications for repair have been narrow. Indications for the repair include incarceration causing pain, obstruction, bleeding, and stoma appliance malfunction. The latter can be extremely distressing to some patients, have negative psychological effects, and destroy the patient s relationships. Until now, surgical options have been limited, in addition to having significant morbidity and high recurrence rates. Because most parastomal hernias are still being repaired via a laparotomy incision, this type of repair alone implies a lifetime risk of an incisional hernia formation of up to 30%. Basically, treatment options include resiting the ostomy, which has a recurrence rate of up to 76%; however, there is an added risk of an incisional hernia at the ostomy site and onlay mesh repair with recurrence rates up to 70%. 3,4 Open techniques involving placement of the mesh intraperitoneally with a hole for the stoma suffer from an intrinsic fault that the hole will allow herniation sooner or later, especially given that all meshes will shrink to some extent with time, further enlarging the hole and thus encouraging herniation. 5,6 In 1980, Sugarbaker 7 described a technique for parastomal hernia repair via a laparotomy in which a nonslit polypro- 34
2 Figure 1. Typical patient with a large parastomal hernia after an anterior resection complicated by an anastomotic leak resulting in a Hartman s procedure 5 years ago, with insets showing computed tomography scans in coronal section (left) and sagittal section (right). pylene mesh is placed intraperitoneally over the hernia with lateralization of the bowel. He reported a series of 7 patients with no recurrence with a follow-up at 4 years. Parallel with recent advances in laparoscopic ventral hernia repair, laparoscopic parastomal hernia repair with a modified Sugarbaker technique compared with the keyhole technique has offered these patients real hope of a permanent solution. 9,10 Laparoscopic repair of a parastomal hernia with a modified Sugarbaker technique is the laparoscopic repair of the stomal hernia with a nonslit mesh covering the hernia defect with at least a 5-cm overlap; with lateralization of the colon/ileum going into the stoma, that treatment has been shown to have the lowest rates of recurrence. 11,12 In an attempt to further reduce parietal trauma, singleincision laparoscopic surgery (SILS) has become increasingly popular in many surgical disciplines, including herniology, although conclusive evidence of its superiority over conventional multiport surgery still awaits prospective randomized controlled studies. Our unit began to perform single-incision laparoscopic repair routinely for virtually all inguinal and ventral hernias since December We aimed to evaluate the feasibility, safety, and success with single-incision laparoscopic parastomal hernia repair using the modified Sugarbaker technique. The Independent Review Board of Holroyd Private Hospital approved this study for the purpose of data collection and follow-up of patients. MATERIALS AND METHODS Figure 2. Position of the SILS port (Covidien, Norwalk, Connecticut, USA), surgeons, scrub nurse, and equipment for laparoscopic repair of a parastomal hernia with modified Sugarbaker technique of a left-sided ostomy; insert (of another patient) showing insertion of a urinary catheter to assist with identification of the ostomy limb during laparoscopy. All referred patients with parastomal hernias from March 2010 to February 2013 underwent single-incision laparoscopic repair. Preoperatively all patients were bowelprepped as for colonoscopy or colon resection. A single dose of cefazolin and metronidazole was given during induction of anesthesia. Nasogastric intubation and urinary catheterization (for nonurostomy patients) were standard intraoperative procedures. Additionally, a 16-F urinary catheter was placed inside the ostomy, and water (5 ml for urostomy and 10 ml for colostomy) was injected into the balloon to ensure that it could be tugged gently without dislodging it (Figure 2). This procedure assisted with intraoperative identification of the ostomy limb as it exited the skin. Patients were placed supine with both arms tucked in along the sides to allow monitors to be placed close to the 35
3 Single-Port Laparoscopic Parastomal Hernia Repair with Modified Sugarbaker Technique, Tran H et al. patient. Because of the possibility of extensive adhesions and the lateral nature of mesh placement, the patients were restrained at the chest and pelvis so that the operating table could be tilted. All patients were always preoperatively marked on the opposite site of the abdomen by a stoma nurse in case the stoma had to be resited. The patients were prepped widely with iodine, dried, draped, and covered with iodine-impregnated plastic drape. This is the standard preparation for all our patients undergoing laparoscopic ventral hernia repair. The positioning of the surgeon, assistant, scrub nurse, and video equipment for a left-sided stoma is shown in Figure 2. A SILS port (Covidien, Norwalk, Connecticut, USA) was inserted in the upper outer quadrant, opposite to the ostomy, in the anterior axillary line, just inferior to the ninth rib, with an open technique under direct vision with a muscle-splitting incision. Initially, one 10-mm trocar and two 5-mm trocars were placed with a 10-mm/30 videoscope introduced anteriorly. This process allowed clear visualization and inspection of abdominal contents, in particular, where the adhesiolysis needed to be performed. During the dissection, the 10-mm trocar was replaced by a 5-mm trocar for insertion of a 5.5-mm laparoscope because this decreased the clashing of dissecting instruments and increased maneuverability. In addition, the use of dissecting instruments of different lengths further minimized clashing of the handles (Figure 3). The most difficult part of any laparoscopic parastomal/ ventral hernia repair is the safe division of adhesions, and extreme care must taken to avoid electrocautery. Liberal use of sharp dissection under direct vision, clipping of bleeding points, as well as the use of saline-jet dissection, which helps with demarcating tissue planes when bowel adhesions are encountered, must be included in this part of the procedure. For SILS, modified dissection techniques, namely, inline and chopstix, were used to overcome the relative lack of triangulation. Because of the nature of previous major surgery in the formation of the ostomy, dense adhesions were to be expected; hence meticulous dissection with division of adhesions strand by strand and in millimeter increments played in favor of SILS owing to its relative lack of triangulation. According to our routine practice in laparoscopic ventral hernia repairs, if the adhesions were deemed too dense, we would not hesitate to perform a mini-laparotomy to safely divide the adhesions, and then the laparotomy wound would be closed before recommencing the laparoscopic hernia repair. The entire midline laparotomy wound was dissected free to allow identification of incidental incisional hernias (Figure 3) because these can be covered with the same mesh, which must have a margin of at least 5 cm larger than the defect. The content of the hernial sac was reduced, and the ostomy limb and its mesentery must be dissected free enough for lateraliza- Figure 3. A, SILS port (Covidien, Norwalk, Connecticut, USA) with an extralong laparoscope that keeps the side arm away from the handles of straight dissecting instruments of different lengths to overcome clashing of the handles. B, Extensive omental and small bowel adhesions. C, Parastomal defect with ileal conduit. D, Three incidental incisional hernias in the midline wound. 36
4 tion without a kink or tension as the ostomy limb entered into the tunnel. The catheter balloon helped with identification of the ostomy limb as it exited the skin as it can be tugged externally (Figure 4). Another useful maneuver was to place a temporary Vessiloop (Getz Bros, Chicago, Illinois, USA) around the most inferior aspect of the ostomy limb as it entered into the tunnel, with the loop pulled outside the skin with suture passer (Figure 4). This helped to ensure sufficient laxity of the lateralized limb and to assist with mesh placement (see below). Sizing of the mesh to be used is an inexact science and is helped with the use of a spinal needle, and the abdomen deflates to 4 mm Hg to minimize the chance that too large a mesh may be used. As with laparoscopic ventral hernia repair, only microporous or coated meshes should be used. We used a microporous eptfe mesh (Gore-Tex Dualmesh Plus, WL Gore, Flagstaff, Arizona, USA) in 5 patients, and C-QUR mesh (Atrium Medical Corporation, Hudson, New Hampshire, USA) was used in 1 patient. Orientation marks were placed on the medial and superior aspects of the mesh. Most parastomal hernias that caused symptoms were large; the mesh that was used was correspondingly large. Placement of the mesh into the peritoneal cavity usually meant either temporary removal of the SILS port (Covidien) when the mesh could be inserted under direct vision with a pair of Rampleys sponge forceps and the SILS port would then be reintroduced, or placement of a 15-mm port into the SILS port after having partially withdrawn one 5-mm trocar to increase the space within the SILS port. When the latter method was used, a 5.5-mm laparoscope was placed in the remaining 5-mm port for direct visualization of mesh entry into the peritoneal cavity. Transfascial O PDS sutures (Ethicon, Inc, Radnor, Pennsylvania, USA) were placed well away from the stoma medially, superiorly, and inferiorly. As with laparoscopic ventral hernia repair, a double-crown technique was used. Unlike laparoscopic ventral hernia repair procedures in which the outer crown was placed first, in laparoscopic parastomal hernia repair, the inner crown was placed first. Unlike laparoscopic ventral hernia repair, where there is no bowel anterior to the mesh and the mesh can be stapled without negative effects, extreme care must be taken with every staple (Protack, Autosutures, Tyco Health Care Group, Norwalk, Connecticut, USA) that was placed on the inner crown to avoid accidental stapling into the ostomy limb. To aid the handling of a potentially large piece of mesh, usually at least a 20- to 30-cm piece of mesh, the mesh was rolled, with the smooth/coated peritoneal side inward, and temporary sutures are placed at 5-cm intervals. This process allowed the mesh to be flipped upward more easily so Figure 4. A, Balloon of urinary catheter in ostomy limb for ease of identification. B, Vessiloop (Getz Bros, Chicago, Illinois, USA) around ostomy limb to aid its lateralization. C, Extensive overlapping of the parastomal hernia defect with mesh. D, ostomy limb in tunnel under mesh and fibrin sealant sprayed along mesh ostomy interface, periphery of mesh, and staples. 37
5 Single-Port Laparoscopic Parastomal Hernia Repair with Modified Sugarbaker Technique, Tran H et al. that the bowel could clearly be seen before a staple was placed. The inner crown was done sequentially on both sides, placing the bowel in the tunnel, and the temporary sutures keeping the mesh rolled up were cut to allow further unrolling of the mesh. This process was repeated until the bowel had been adequately lateralized (Figure 4). The outer crown was then completed, and additional transfascial sutures were placed. Herniation of bowel loops into the tunnel and adhesions to the periphery of the mesh and staples could be minimized by application of 4 ml of fibrin sealant (Tisseel Duo, Baxter AG, Vienna, Austria), which was sprayed copiously along the mesh ostomy interface and sparsely along the periphery of the mesh and the staple line (Figure 4). The upper quadrant wound was closed in layers with No. O PDS sutures (Ethicon) and dissolvable sutures subcutaneously and subcuticularly. RESULTS There were 6 patients between March 2010 and February 2013: 2 with paracolostomal hernias and 4 with paraurostomal hernias (1 patient had had two previous open repairs). Of the latter patients, 1 had originally had a Hartman s procedure, cystectomy, and formation of ileal conduit due to colon cancer invading the bladder. The colostomy was subsequently closed, but the patient also developed an incisional hernia at this site. This hernia was repaired as an open procedure, but it soon recurred. The mean diameter of the defects was 10 cm (range 6 15 cm), and the mean mesh size was 660 cm 2 (range cm 2 ). Half of the patients also had incidental midline incisional hernias that were repaired with the same mesh. The mean operation time was 270 minutes (range minutes). However, the mean time to complete the division of adhesions and free the ostomy limb for lateralization was 180 minutes (range minutes). The mean length of hospital stay was 4 days (range 1 9 days); 2 of the 6 patients stayed in hospital only overnight. In the 3 patients with paracolostomal hernias, stomaappliance malfunctioning resulting in fecal soiling stopped immediately. The pain related to the bulge had also disappeared, and the bulge had almost disappeared in all patients (Figure 5), and the ostomy diameter decreased from a mean of 45 mm (range mm) preoperatively to 35 mm (range mm) postoperatively. There was no evidence of a recurrence with a mean follow-up of 12 months (range 1 36 months). There was no morbidity or mortality. Figure 5. Preoperative appearance of patient with parastomal hernia (top photos) compared with appearance 6 months postoperatively (bottom photos) after single-incision laparoscopic repair with modified Sugarbaker technique. 38
6 DISCUSSION The natural progression of hernias including parastomal hernias is one of progressive enlargement with time. Parastomal hernias can cause typical problems, including incarceration, obstruction, and a cosmetically unpleasant bulge. However, as the parastomal hernias enlarge during the day during periods of mobility, the ostomy appliance when applied during this period tends to become dislodged at nighttime when some or all of the parastomal hernia contents reduce. This circumstance causes highly unpleasant fecal/urinary soiling in bed, which can lead to psychological distress and relationship problems. This aspect of parastomal hernia complications is often underappreciated. Until now, the treatment options and results have been extremely limited and poor. Consequently, although ventral/incisional hernias are being repaired routinely to prevent complications, the laparoscopic repair has revolutionized repair practices by significantly reducing complications and improving success rates to 95%. 13,14 The poor results of conventional surgical options, including resiting and open underlay or onlay mesh repair with a slit technique, mean that most surgeons would contemplate parastomal hernia repair only for significant symptoms as mentioned above. Guzman-Valdivia et al 15 reported a series of an anterior onlay mesh repair in 25 patients with parastomal hernias with a recurrence of 8.8% with a follow-up period of just 12 months, surgical wound infection of 8%, and seroma formation of 8%. Safadi 16 reported a series of 9 patients undergoing laparoscopic repair with the keyhole technique. He reported an operation time of 243 minutes (range minutes), an average range of hospital stay of 4.7 days (range 2 7 days), morbidity of 33.3%, recurrence of 44.4%, and a prolapsed stoma in 1 patient; all of these failures occurred within 6 months of the operation. In 1980, Sugarbaker 7 first reported his series of 7 patients; his technique remained unused for 20 years, until the advent of laparoscopic hernia repair. The laparoscopic repair of parastomal hernias using the modified Sugarbaker technique with a nonslit mesh and lateralization of the bowel has shown great promise. Stelzner et al 8 reported a recurrence rate of 15% with a 3.5-year follow-up using a modified Sugarbaker technique. Craft et al 17 reported their study of a series of 21 patients treated by this method and reported a recurrence of just 5%, which parallels the best results obtainable for laparoscopic ventral/ incisional hernia repair. 12 A recent multi-institutional series (Mancini et al 11 ) involving 5 highly experienced surgeons in laparoscopic ventral hernia repair over a period of 5 years with 25 patients showed a recurrence in just 1 patient (4%) with a follow-up of 19 months (range 2 38 months). There was, however, one death and the morbidity was 23%, with one mesh infection requiring removal. Such results have been replicated by Le Blanc et al 18 and Hansson et al. 12 The latter authors have also shown that the slit mesh repair resulted in significant higher recurrence rates compared with the nonslit mesh repair. Our experience with 6 patients over a 3-year period represents a significant workload of parastomal hernias, given that most highly experienced laparoscopic hernia surgeons would perform only one to two parastomal hernia repairs per year. 19 Despite the fact that SILS is still in its relative infancy, we have demonstrated operation times similar to those involving conventional multiport nonslit mesh repair. Most of the operation time was in fact spent on the safe division of adhesions, given that a previous major surgery was required to perform the ostomy. The relative loss of triangulation was overcome easily by modified dissection techniques, the use of a smaller and longer laparoscope, as well as the use of dissecting instruments with different lengths. Sharp dissection with avoidance of electocautery and use of a saline jet allowed safe division of adhesions without the need to perform a laparotomy. Identification of the ostomy limb was facilitated by the insertion of a urinary catheter into the ostomy, and the use of a temporary sling across the ostomy limb, together with sequential unrolling of the mesh, allowed safe mesh fixation. These important techniques allowed us to achieve success that was similar to that of multiport surgery, with no recurrence to date and with no morbidity or mortality. An important advantage of SILS is that the dissecting instruments are inserted in-line with the laparoscope with little fear of accidental damage to bowel loops as the laparoscope is merely pulled slightly out, and then it follows the instruments in. In contrast, safe insertion of dissecting instruments in multiport surgery requires direct visualization every time, especially when the patient is tilted over to the port side, and that can be time-consuming. CONCLUSION Single-incision laparoscopic repair of parastomal hernia using the modified Sugarbaker technique is safe and efficient. In addition, it represents a natural progression and extension of the increasingly popular technique of SILS. This represents the next level of technical innovation in laparoscopic surgery in minimizing parietal trauma while 39
7 Single-Port Laparoscopic Parastomal Hernia Repair with Modified Sugarbaker Technique, Tran H et al. achieving the same success rates as those achieved by conventional multiport laparoscopic repair. We predict that the rate of parastomal hernia repair will rise significantly as hernia specialists become more involved with parastomal hernia treatment and as colorectal surgeons learn to master skills in laparoscopic ventral/parastomal hernia repair. References: 1. Carne PWG, Robertson GM, Frizelle FA. Parastomal hernia. Br J Surg. 2003;90: Pearl RK. Parastomal hernias. World J Surg. 1994;13: Janes A, Cengiz Y, Israelsson LA. Randomized clinical trial of the use of a prosthetic mesh to prevent parastomal hernia. Br J Surg. 2004;91: van Sprundel TC. Gerritsen van der Hoop A. Modified technique for parastomal hernia repair in patients with intractable stoma-care problems. Colorectal Dis. 2005;7(5): Lüning TH, Spilllenaar-Bilge EJ. Parastomal hernia: complications of extra-peritoneal onlay mesh placement. Hernia. 2009; 13(5): Vijayasekar C, Marimuthu K, Jadhav V, Mathew G. Parastomal hernia: is prevention better than cure? Use of preperitoneal polypropylene mesh at the time of stoma formation. Tech Coloproctol. 2008;12(4): Sugarbaker PH. Prosthetic mesh repair of large hernias at the site of colonic stomas. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1980;150: Stelzner S, Hellmich G, Ludwig K. Repair of paracolostomy hernias with a prosthetic mesh in the intraperitoneal onlay position: modified Sugarbaker technique. Dis Colon Rectum. 2004; 47: Bickel A, Shinkarevsky E, Eitan AJ. Laparoscopic repair of paracolostomy hernia. Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 1999;9: García-Vallejo L, Concheiro P, Mena E, Baltar J, Baamonde I, Folgar L. Parastomal hernia repair: laparoscopic ventral hernia meshplasty with stoma relocation. The current state and a clinical case presentation. Hernia. 2011;15(1): Mancini GJ, McClusky DA III, Khaitan L, et al. Laparoscopic parastomal hernia repair using a non-slit mesh technique. Surg Endosc. 2007;21(9): Hansson BM, Slater NJ, van der Velden AS, et al. Surgical techniques for parastomal hernia repair: a systematic review of the literature. Ann Surg. 2012;255(4): Henniford BT, Park A, Ramshaw BJ, Voeller G. Laparoscopic repair of ventral hernias: nine years experience with 850 consecutive cases. Ann Surg. 2003;238(3): Kaoutzanis C, Leichtle SW, Mouawad NJ, et al. Postoperative surgical site infections after ventral/incisional hernia repair: a comparison of open and laparoscopic outcomes. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27(6): Guzmán-Valdivia G, Guerrero TS, Laurrabaquio HV. Parastomal hernia-repair using mesh and an open technique. World J Surg. 2008;32(3): Safadi B. Laparoscopic repair of parastomal hernias: early results. Surg Endosc. 2004;12(4): Craft RO, Huguet KL, McLemore EC, Harold KL. Laparoscopic parastomal hernia repair. Hernia. 2007;12(2): Le Blanc KA, Bellanger DE, Whitaker JM, Hausmann MG. Laparoscopic parastomal hernia repair. Hernia. 2005;9: Banerjee A, Beck C, Narula VK, et al. Laparoscopic ventral hernia repair: does primary repair in addition to placement of mesh decrease recurrence? Surg Endosc. 2012;26(5):
LAPAROCELI: LAPAROSCOPY LIVE SURGERY PARASTOMAL HERNIA: WHAT TO DO? OSPEDALE DI PORTOGRUARO U.O.C. CHIRURGIA GENERALE FRANCESCO FIDANZA
 LAPAROCELI: LAPAROSCOPY LIVE SURGERY PARASTOMAL HERNIA: WHAT TO DO? OSPEDALE DI PORTOGRUARO U.O.C. CHIRURGIA GENERALE FRANCESCO FIDANZA PARASTOMAL HERNIA Some degree of herniation around a colostomy is
LAPAROCELI: LAPAROSCOPY LIVE SURGERY PARASTOMAL HERNIA: WHAT TO DO? OSPEDALE DI PORTOGRUARO U.O.C. CHIRURGIA GENERALE FRANCESCO FIDANZA PARASTOMAL HERNIA Some degree of herniation around a colostomy is
STOMA SITING & PARASTOMAL HERNIA MANAGEMENT
 STOMA SITING & PARASTOMAL HERNIA MANAGEMENT Professor Hany S. Tawfik Head of the Department of Surgery & Chairman of Colorectal Surgery Unit Benha University Disclosure No financial affiliation to disclose
STOMA SITING & PARASTOMAL HERNIA MANAGEMENT Professor Hany S. Tawfik Head of the Department of Surgery & Chairman of Colorectal Surgery Unit Benha University Disclosure No financial affiliation to disclose
Parastomal Hernia Repair: a Single Center Experience
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Parastomal Hernia Repair: a Single Center Experience Danielle M. Pastor, DO, Eric M. Pauli, MD, Walter A. Koltun, MD, Randy S. Haluck, MD, Timothy R. Shope, MD, Lisa S. Poritz, MD ABSTRACT
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Parastomal Hernia Repair: a Single Center Experience Danielle M. Pastor, DO, Eric M. Pauli, MD, Walter A. Koltun, MD, Randy S. Haluck, MD, Timothy R. Shope, MD, Lisa S. Poritz, MD ABSTRACT
Single-Port Onlay Mesh Repair of Recurrent Inguinal Hernias after Failed Anterior and Laparoscopic Repairs
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Single-Port Onlay Mesh Repair of Recurrent Inguinal Hernias after Failed Anterior and Laparoscopic Repairs Hanh Tran, MD, Kim Tran, Marta Zajkowska, RN, Vincent Lam, MD, Wayne J. Hawthorne,
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Single-Port Onlay Mesh Repair of Recurrent Inguinal Hernias after Failed Anterior and Laparoscopic Repairs Hanh Tran, MD, Kim Tran, Marta Zajkowska, RN, Vincent Lam, MD, Wayne J. Hawthorne,
Safety and Efficacy of Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery for Abdominal Wall Hernias
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Safety and Efficacy of Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery for Abdominal Wall Hernias Hanh Tran, MD, FRACS ABSTRACT Background: Laparoendoscopic single-site surgery has rapidly progressed
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Safety and Efficacy of Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery for Abdominal Wall Hernias Hanh Tran, MD, FRACS ABSTRACT Background: Laparoendoscopic single-site surgery has rapidly progressed
Keyhole Laparoscopic Hernia Repairs: What s the Benefit for Your Patients?
 InTouch ARTICLE Keyhole Laparoscopic Hernia Repairs: What s the Benefit for Your Patients? Author: Mr Steve Warren Date: Mary 2015 17 19 View Road, Highgate, London, N6 4DJ Tel. 020 8341 4182 Email. enquiries@highgatehospital.co.uk
InTouch ARTICLE Keyhole Laparoscopic Hernia Repairs: What s the Benefit for Your Patients? Author: Mr Steve Warren Date: Mary 2015 17 19 View Road, Highgate, London, N6 4DJ Tel. 020 8341 4182 Email. enquiries@highgatehospital.co.uk
7/2/2015. Incidence. *Mudge M et al, Br. J. Surg, 1985, 72:70-71
 Ventral Hernia Repair: Revisonal Surgery Natan Zundel MD FACS Professor of Surgery Vice-Chairman Department of Surgery FIU Herbert Wertheim College of Medicine. Miami Florida DISCLOSURE Ethicon Endosurgery
Ventral Hernia Repair: Revisonal Surgery Natan Zundel MD FACS Professor of Surgery Vice-Chairman Department of Surgery FIU Herbert Wertheim College of Medicine. Miami Florida DISCLOSURE Ethicon Endosurgery
Inadvertent Enterotomy in Minimally Invasive Abdominal Surgery
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Inadvertent Enterotomy in Minimally Invasive Abdominal Surgery Steven J. Binenbaum, MD, Michael A. Goldfarb, MD ABSTRACT Background: Inadvertent enterotomy (IE) in laparoscopic abdominal
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Inadvertent Enterotomy in Minimally Invasive Abdominal Surgery Steven J. Binenbaum, MD, Michael A. Goldfarb, MD ABSTRACT Background: Inadvertent enterotomy (IE) in laparoscopic abdominal
The laparoscopic modified Sugarbaker technique is safe and has a low recurrence rate: a multicenter cohort study
 Surg Endosc (2013) 27:494 500 DOI 10.1007/s00464-012-2464-4 and Other Interventional Techniques The laparoscopic modified Sugarbaker technique is safe and has a low recurrence rate: a multicenter cohort
Surg Endosc (2013) 27:494 500 DOI 10.1007/s00464-012-2464-4 and Other Interventional Techniques The laparoscopic modified Sugarbaker technique is safe and has a low recurrence rate: a multicenter cohort
Repeat Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery after Primary Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery for Colorectal Disease
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 2234-778X eissn 2234-5248 J Minim Invasive Surg 2018;21(1):38-42 Journal of Minimally Invasive Surgery Repeat Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery after Primary Single Incision Laparoscopic
ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn 2234-778X eissn 2234-5248 J Minim Invasive Surg 2018;21(1):38-42 Journal of Minimally Invasive Surgery Repeat Single Incision Laparoscopic Surgery after Primary Single Incision Laparoscopic
Hernias Umbilical Hernia When to See a Surgeon? What Are Symptoms of an Umbilical Hernia? How is Repair Performed?
 Hernias Umbilical Hernia An umbilical hernia occurs when part of the intestine protrudes through the umbilical opening in the abdominal muscles. Umbilical hernias are common and typically harmless. They
Hernias Umbilical Hernia An umbilical hernia occurs when part of the intestine protrudes through the umbilical opening in the abdominal muscles. Umbilical hernias are common and typically harmless. They
Colostomy & Ileostomy
 Colostomy & Ileostomy Indications, problems and preference By Waleed Omar Professor of Colorectal surgery, Mansoura University. Disclosure I have no disclosures. Presentation outline Stoma: Definition
Colostomy & Ileostomy Indications, problems and preference By Waleed Omar Professor of Colorectal surgery, Mansoura University. Disclosure I have no disclosures. Presentation outline Stoma: Definition
Single-Incision Laparoscopic Surgery Versus Standard Laparoscopic Surgery for Unroofing of Hepatic Cysts
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Single-Incision Laparoscopic Surgery Versus Standard Laparoscopic Surgery for of s Shuodong Wu, MD, Yongnan Li, MM, Yu Tian, MD, Min Li, MM ABSTRACT Background and Objectives: The aim
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Single-Incision Laparoscopic Surgery Versus Standard Laparoscopic Surgery for of s Shuodong Wu, MD, Yongnan Li, MM, Yu Tian, MD, Min Li, MM ABSTRACT Background and Objectives: The aim
Title at a Single Institution. Issue Date Right.
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Laparoscopic Repair of a Ventral He at a Single Institution. Ono, Shinichiro; Kawashita, Yujo; K Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia, 57(2), p Issue Date
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Laparoscopic Repair of a Ventral He at a Single Institution. Ono, Shinichiro; Kawashita, Yujo; K Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia, 57(2), p Issue Date
Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form.
 : Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Surgery doi: To be assigned Early view version published: November
: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Surgery doi: To be assigned Early view version published: November
Abdominal Wall Modification for the Difficult Ostomy
 Abdominal Wall Modification for the Difficult Ostomy David E. Beck, M.D. 1 ABSTRACT A select group of patients with major stomal problems may benefit from operative modification of the abdominal wall.
Abdominal Wall Modification for the Difficult Ostomy David E. Beck, M.D. 1 ABSTRACT A select group of patients with major stomal problems may benefit from operative modification of the abdominal wall.
INGUINAL HERNIA REPAIR PROCEDURE GUIDE
 ROOM CONFIGURATION The following figure shows an overhead view of the recommended OR configuration for a da Vinci Inguinal Hernia Repair (Figure 1). NOTE: Configuration of the operating room suite is dependent
ROOM CONFIGURATION The following figure shows an overhead view of the recommended OR configuration for a da Vinci Inguinal Hernia Repair (Figure 1). NOTE: Configuration of the operating room suite is dependent
Prevention and Surgical management of Parastomal hernias; When to treat?
 Prevention and Surgical management of Parastomal hernias; When to treat? Sabry A. Mahmoud (MD) Prof of General & Colorectal Surgery Mansoura University It is an incisional hernia that develops at the site
Prevention and Surgical management of Parastomal hernias; When to treat? Sabry A. Mahmoud (MD) Prof of General & Colorectal Surgery Mansoura University It is an incisional hernia that develops at the site
Single-incision laparoscopic parastomal hernia repair employing fascial defect closure and sandwich technique
 Case Report on Gastrointestinal Surgery Page 1 of 6 Single-incision laparoscopic parastomal hernia repair employing fascial defect closure and sandwich technique Akira Umemura 1, Takayuki Suto 1, Hisataka
Case Report on Gastrointestinal Surgery Page 1 of 6 Single-incision laparoscopic parastomal hernia repair employing fascial defect closure and sandwich technique Akira Umemura 1, Takayuki Suto 1, Hisataka
Case Report. XCM Biologic Tissue Matrix. Components separation using sandwich technique for reconstruction of abdominal wall defect.
 Case Report XCM Biologic Tissue Matrix. Components separation using sandwich technique for reconstruction of abdominal wall defect. XCM Biologic Tissue Matrix. Components separation using sandwich technique
Case Report XCM Biologic Tissue Matrix. Components separation using sandwich technique for reconstruction of abdominal wall defect. XCM Biologic Tissue Matrix. Components separation using sandwich technique
This information is intended as an overview only
 This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
Laparoscopic Repair of Incisional and Other Complex Abdominal Wall Hernias
 credits available for this article see page 95. Laparoscopic Repair of Incisional and Other Complex Abdominal Wall Hernias Randall O Craft, MD Kristi L Harold, MD Abstract Incisional hernia is one of the
credits available for this article see page 95. Laparoscopic Repair of Incisional and Other Complex Abdominal Wall Hernias Randall O Craft, MD Kristi L Harold, MD Abstract Incisional hernia is one of the
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 1 2013 Article 8 ISSUE 1 Single Incision Laparoscopic Colectomy: A Series of Five Patients, Lessons Learned Elyssa Feinberg David O Connor Diego Camacho
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 1 2013 Article 8 ISSUE 1 Single Incision Laparoscopic Colectomy: A Series of Five Patients, Lessons Learned Elyssa Feinberg David O Connor Diego Camacho
Life Science Journal 2017;14(1) Single port versus multiport laparoscopic trans abdominal preperitoneal hernia repair.
 Single port versus multiport laparoscopic trans abdominal preperitoneal hernia repair. Hany Mohamed El-Barbary, FRCS, FACS, Department of General Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Ain shams university (ASU)
Single port versus multiport laparoscopic trans abdominal preperitoneal hernia repair. Hany Mohamed El-Barbary, FRCS, FACS, Department of General Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Ain shams university (ASU)
Laparoscopic reversal of Hartmann's procedure
 J Korean Surg Soc 2012;82:256-260 http://dx.doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2012.82.4.256 CASE REPORT JKSS Journal of the Korean Surgical Society pissn 2233-7903 ㆍ eissn 2093-0488 Laparoscopic reversal of Hartmann's
J Korean Surg Soc 2012;82:256-260 http://dx.doi.org/10.4174/jkss.2012.82.4.256 CASE REPORT JKSS Journal of the Korean Surgical Society pissn 2233-7903 ㆍ eissn 2093-0488 Laparoscopic reversal of Hartmann's
Research Article Parastomal Hernia Repair with Intraperitoneal Mesh
 Hindawi Surgery Research and Practice Volume 2017, Article ID 8597463, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8597463 Research Article Parastomal Hernia Repair with Intraperitoneal Mesh PiaNäsvall, 1,2 JörgenRutegård,
Hindawi Surgery Research and Practice Volume 2017, Article ID 8597463, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8597463 Research Article Parastomal Hernia Repair with Intraperitoneal Mesh PiaNäsvall, 1,2 JörgenRutegård,
Laparoscopic Repair of Incisional and Parastomal Hernias after Major Genitourinary or Abdominal Surgery
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 15, Number 2, March 2001 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Laparoscopic Repair of Incisional and Parastomal Hernias after Major Genitourinary or Abdominal Surgery PAUL M. KOZLOWSKI,
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 15, Number 2, March 2001 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Laparoscopic Repair of Incisional and Parastomal Hernias after Major Genitourinary or Abdominal Surgery PAUL M. KOZLOWSKI,
Colorectal procedure guide
 Colorectal procedure guide Illustrations by Lisa Clark Biodesign ADVANCED TISSUE REPAIR cookmedical.com 2 INDEX Anal fistula repair Using the Biodesign plug with no button.... 4 Anal fistula repair Using
Colorectal procedure guide Illustrations by Lisa Clark Biodesign ADVANCED TISSUE REPAIR cookmedical.com 2 INDEX Anal fistula repair Using the Biodesign plug with no button.... 4 Anal fistula repair Using
3/21/2011. Advances in laparoscopic ventral hernia repair. Laparoscopic approach well-suited for simple hernias:
 Advances in laparoscopic ventral hernia repair Topics Technique of laparoscopic ventral hernia repair Patient selection Is laparoscopic any better than open? Recent advances (or, should we say, advances?)
Advances in laparoscopic ventral hernia repair Topics Technique of laparoscopic ventral hernia repair Patient selection Is laparoscopic any better than open? Recent advances (or, should we say, advances?)
Troubleshooting the Dysfunctional PD Catheter
 Troubleshooting the Dysfunctional PD Catheter ASDIN Annual Scientific Meeting Phoenix, Arizona February, 2014 Corporate Relationships in PD Area-Dr. Ash Developed Y-Tec System for placing PD catheters
Troubleshooting the Dysfunctional PD Catheter ASDIN Annual Scientific Meeting Phoenix, Arizona February, 2014 Corporate Relationships in PD Area-Dr. Ash Developed Y-Tec System for placing PD catheters
Single-Port Parastomal Hernia Repair by Using 3-D Textile Implants
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Single-Port Parastomal Hernia Repair by Using 3-D Textile Implants Gernot Köhler, MD, Klaus Emmanuel, MD, Rudolf Schrittwieser, MD ABSTRACT Background: Parastomal hernias (PSHs) are a
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Single-Port Parastomal Hernia Repair by Using 3-D Textile Implants Gernot Köhler, MD, Klaus Emmanuel, MD, Rudolf Schrittwieser, MD ABSTRACT Background: Parastomal hernias (PSHs) are a
34 yo M presented in ER of KCH at 7/06/10 Painful lump lt groin + vomiting Pain started 2 hrs before presentation. PMH known left inguinal hernia PSH
 Case Presentation 34 yo M presented in ER of KCH at 7/06/10 Painful lump lt groin + vomiting Pain started 2 hrs before presentation. PMH known left inguinal hernia PSH negative NKDA Case Presentation VS:
Case Presentation 34 yo M presented in ER of KCH at 7/06/10 Painful lump lt groin + vomiting Pain started 2 hrs before presentation. PMH known left inguinal hernia PSH negative NKDA Case Presentation VS:
Hernia. emoryhealthcare.org
 Hernia Have you noticed a bulge or pain in your abdominal wall or groin? If so you may have a hernia. You may be in the process of confirming this diagnosis with your Primary Care Physician or already
Hernia Have you noticed a bulge or pain in your abdominal wall or groin? If so you may have a hernia. You may be in the process of confirming this diagnosis with your Primary Care Physician or already
Surgery and Crohn s. Crohn s Disease 70 % Why Operate? Complications of Disease. The Gastrointestinal Tract. Surgery for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 The Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Jonathan Chun, MD The regon Clinic Gastrointestinal and Minimally Invasive Surgery Crohn s Disease Can affect anywhere in the GI tract,
The Gastrointestinal Tract Surgery for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Jonathan Chun, MD The regon Clinic Gastrointestinal and Minimally Invasive Surgery Crohn s Disease Can affect anywhere in the GI tract,
Ventral Hernia Repair
 Ventral Hernia Repair Ventrio ST Hernia Patch Ventrio Hernia Patch Technique Guide Open and Laparoscopic Ventral Hernia Repair SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product. Right Outcome. This Technique
Ventral Hernia Repair Ventrio ST Hernia Patch Ventrio Hernia Patch Technique Guide Open and Laparoscopic Ventral Hernia Repair SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product. Right Outcome. This Technique
PD catheter implantation (double-cuff straight Tenckhoff catheter) 基隆長庚一般外科卓世川
 PD catheter implantation (double-cuff straight Tenckhoff catheter) 基隆長庚一般外科卓世川 Successful assess of PD Various techniques for various designs of peritoneal catheters. Access of catheter placement is the
PD catheter implantation (double-cuff straight Tenckhoff catheter) 基隆長庚一般外科卓世川 Successful assess of PD Various techniques for various designs of peritoneal catheters. Access of catheter placement is the
Diagnosis and Management of Parastomal Hernias
 RESIDENT S CORNER Diagnosis and Management of Parastomal Hernias CASE SUMMARY: A 63-year-old woman with history of stage II rectal adenocarcinoma status postneoadjuvant chemoradiation and subsequent abdominoperineal
RESIDENT S CORNER Diagnosis and Management of Parastomal Hernias CASE SUMMARY: A 63-year-old woman with history of stage II rectal adenocarcinoma status postneoadjuvant chemoradiation and subsequent abdominoperineal
Rectal Cancer. About the Colon and Rectum. Symptoms. Colorectal Cancer Screening
 Patient information regarding care and surgery associated with RECTAL CANCER by Robert K. Cleary, M.D., John C. Eggenberger, M.D., Amalia J. Stefanou., M.D. location: Michigan Heart and Vascular Institute,
Patient information regarding care and surgery associated with RECTAL CANCER by Robert K. Cleary, M.D., John C. Eggenberger, M.D., Amalia J. Stefanou., M.D. location: Michigan Heart and Vascular Institute,
LESS Laparosc Endosc Surg Sci 2016;23(2):34-38 DOI: /less
 LESS Laparosc Endosc Surg Sci 2016;23(2):34-38 DOI: 10.14744/less.2013.69775 Original Article Lumbar hernia repair: Myth or reality? Aziz Sümer, 1 Ediz Altınlı, 2 Ersan Eroğlu, 2 Mehmet Ali Uzun, 3 Serkan
LESS Laparosc Endosc Surg Sci 2016;23(2):34-38 DOI: 10.14744/less.2013.69775 Original Article Lumbar hernia repair: Myth or reality? Aziz Sümer, 1 Ediz Altınlı, 2 Ersan Eroğlu, 2 Mehmet Ali Uzun, 3 Serkan
Needlescopic Surgery Versus Single-port Laparoscopy for Inguinal Hernia
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Needlescopic Surgery Versus Single-port Laparoscopy for Inguinal Hernia Yi-Wei Chan, MD, MSc, Christian Hollinsky, MD ABSTRACT Background and Objectives: In recent years, 2 modifications
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Needlescopic Surgery Versus Single-port Laparoscopy for Inguinal Hernia Yi-Wei Chan, MD, MSc, Christian Hollinsky, MD ABSTRACT Background and Objectives: In recent years, 2 modifications
HARTMANNS PROCEDURE. Patient information Leaflet
 HARTMANNS PROCEDURE Patient information Leaflet April 2017 WHAT IS A HARTMANNS PROCEDURE? This operation is necessary to remove the area of bowel that is diseased. The operation removes a piece of your
HARTMANNS PROCEDURE Patient information Leaflet April 2017 WHAT IS A HARTMANNS PROCEDURE? This operation is necessary to remove the area of bowel that is diseased. The operation removes a piece of your
Farah S, Kiyingi A, Leinkram C. The Melbourne Hernia Clinic Masada Hospital 26 Balaclava Road St Kilda East Victoria, Australia 3168.
 Medium to Long term results following open intra-abdominal repair of large incisional hernias with a new composite polypropylene and silicone mesh, without components separation. Farah S, Kiyingi A, Leinkram
Medium to Long term results following open intra-abdominal repair of large incisional hernias with a new composite polypropylene and silicone mesh, without components separation. Farah S, Kiyingi A, Leinkram
Complications of laparoscopic protective loop ileostomy in patients with colorectal cancer
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 19 Number 2 Complications of laparoscopic protective loop ileostomy in patients with colorectal cancer F Puccio, M Solazzo, G Pandolfo, P Marcianò Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 19 Number 2 Complications of laparoscopic protective loop ileostomy in patients with colorectal cancer F Puccio, M Solazzo, G Pandolfo, P Marcianò Citation
Parastomal Hernia Is a Problem Yet to Be Solved
 Elmer ress Review J Curr Surg. 2015;5(2-3):151-156 Parastomal Hernia Is a Problem Yet to Be Solved Hagar Mizrahi a, c, Nissim Geron a, Michael C. Parker b Abstract Parastomal hernia is a common surgical
Elmer ress Review J Curr Surg. 2015;5(2-3):151-156 Parastomal Hernia Is a Problem Yet to Be Solved Hagar Mizrahi a, c, Nissim Geron a, Michael C. Parker b Abstract Parastomal hernia is a common surgical
REVERSAL OF ILEOSTOMY. Patient information Leaflet
 REVERSAL OF ILEOSTOMY Patient information Leaflet April 2017 WHAT IS A REVERSAL OF ILEOSTOMY? A reversal of ileostomy is an operation to close your temporary ileostomy. Your surgeon will make a cut in
REVERSAL OF ILEOSTOMY Patient information Leaflet April 2017 WHAT IS A REVERSAL OF ILEOSTOMY? A reversal of ileostomy is an operation to close your temporary ileostomy. Your surgeon will make a cut in
-primarily by apposition of the anterior rectus
 2 Component separation Cop HARVEY CHIM, KAREN KIM EVANS, AND SAMIR MARDINI Mater al Introduction 7 Preoperative markings 7 Intraoperative details 9 Technique modification: Component separation with preservation
2 Component separation Cop HARVEY CHIM, KAREN KIM EVANS, AND SAMIR MARDINI Mater al Introduction 7 Preoperative markings 7 Intraoperative details 9 Technique modification: Component separation with preservation
The Emergency Hernia or The call you don t want at 2:00 a.m.*
 or The call you don t want at 2:00 a.m.* *Or even at 8:00 a.m. Michael G. Sarr, MD Professor of Surgery Mayo Clinic South Canada WEST CANADA EAST CANADA Clinical talk Hernias Inguinal Umbilical Incisional
or The call you don t want at 2:00 a.m.* *Or even at 8:00 a.m. Michael G. Sarr, MD Professor of Surgery Mayo Clinic South Canada WEST CANADA EAST CANADA Clinical talk Hernias Inguinal Umbilical Incisional
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of reinforcement of a permanent stoma with mesh to prevent a parastomal hernia A
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of reinforcement of a permanent stoma with mesh to prevent a parastomal hernia A
Index. Note: Page numbers of article title are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article title are in boldface type. A Abscess(es) in Crohn s disease, 168 169 IPAA and, 110 114 as unexpected finding in colorectal surgery, 46 Adhesion(s) trocars-related laparoscopy
Index Note: Page numbers of article title are in boldface type. A Abscess(es) in Crohn s disease, 168 169 IPAA and, 110 114 as unexpected finding in colorectal surgery, 46 Adhesion(s) trocars-related laparoscopy
First Transumbilical Transabdominal Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair in the Middle East
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 25 Number 1 First Transumbilical Transabdominal Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair in the Middle East A Al-Dowais Citation A Al-Dowais. First Transumbilical
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 25 Number 1 First Transumbilical Transabdominal Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair in the Middle East A Al-Dowais Citation A Al-Dowais. First Transumbilical
Anus,Rectum and Colon
 JOURNAL OF THE Anus,Rectum and Colon dx.doi.org/1.23922/jarc.216-14 http://journal-arc.jp ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Laparoscopic versus Open stoma creation: A retrospective analysis Kengo Hayashi, Masanori
JOURNAL OF THE Anus,Rectum and Colon dx.doi.org/1.23922/jarc.216-14 http://journal-arc.jp ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Laparoscopic versus Open stoma creation: A retrospective analysis Kengo Hayashi, Masanori
Technique Guide. Bard MK Hernia Repair. Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh SOFT TISSUE REPAIR. Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair
 Bard MK Hernia Repair Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh Technique Guide Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product. Right Outcome. The opinions
Bard MK Hernia Repair Featuring Modified Onflex Mesh Technique Guide Anterior Approach to a Preperitoneal Inguinal Hernia Repair SOFT TISSUE REPAIR Right Procedure. Right Product. Right Outcome. The opinions
Facing a Hernia Repair?
 Facing a Hernia Repair? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery www.olarts.com The Condition: Hernia A hernia happens when part of an internal organ or tissue bulges through a hole or weak area
Facing a Hernia Repair? Learn about minimally invasive da Vinci Surgery www.olarts.com The Condition: Hernia A hernia happens when part of an internal organ or tissue bulges through a hole or weak area
Laparoscopic Bladder-Preserving Surgery for Enterovesical Fistula Complicated with Benign Gastrointestinal Disease
 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the article
This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the article
Reduced port laparoscopic surgery for colon cancer in a patient with tuberculous kyphosis and dwarfism: a rare case and literature review
 Case report Videosurgery Reduced port laparoscopic surgery for colon cancer in a patient with tuberculous kyphosis and dwarfism: a rare case and literature review Si-Yuan Yao, Atsushi Ikeda, Yoichiro Tada
Case report Videosurgery Reduced port laparoscopic surgery for colon cancer in a patient with tuberculous kyphosis and dwarfism: a rare case and literature review Si-Yuan Yao, Atsushi Ikeda, Yoichiro Tada
Laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal repair.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 12 Ver. IX (Dec. 2015), PP 26-30 www.iosrjournals.org Laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 12 Ver. IX (Dec. 2015), PP 26-30 www.iosrjournals.org Laparoscopic transabdominal preperitoneal
Transabdominal pre peritoneal (TAPP) vs totally extraperitoneal (TEP) laparoscopic techniques for inguinal hernia repair
 Transabdominal pre peritoneal (TAPP) vs totally extraperitoneal (TEP) laparoscopic techniques for inguinal hernia repair An inguinal hernia (hernia of the groin) is a weakness in the wall of the abdominal
Transabdominal pre peritoneal (TAPP) vs totally extraperitoneal (TEP) laparoscopic techniques for inguinal hernia repair An inguinal hernia (hernia of the groin) is a weakness in the wall of the abdominal
The incidence of incisional hernias following ileostomy reversal in colorectal cancer patients treated with anterior resection
 GENERAL SURGERY Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2017; 99: 319 324 doi 10.1308/rcsann.2016.0347 The incidence of incisional hernias following ileostomy reversal in colorectal cancer patients treated with anterior
GENERAL SURGERY Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2017; 99: 319 324 doi 10.1308/rcsann.2016.0347 The incidence of incisional hernias following ileostomy reversal in colorectal cancer patients treated with anterior
Parastomal hernia mesh repair, variant of surgical technique without stoma relocation
 , pp.157 161 Parastomal hernia mesh repair, variant of surgical technique without stoma relocation Guriță RE*, Popa F**, Bălălău C**, Scăunașu Răzvan*** *General Surgery Department, Sf. Pantelimon Emergency
, pp.157 161 Parastomal hernia mesh repair, variant of surgical technique without stoma relocation Guriță RE*, Popa F**, Bălălău C**, Scăunașu Răzvan*** *General Surgery Department, Sf. Pantelimon Emergency
SINGLE INCISION LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY
 SINGLE INCISION LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY DR ADEWALE ADISA CONSULTANT MINIMAL ACCESS SURGEON & SENIOR LECTURER DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY, OBAFEMI AWOLOWO UNIVERSITY, & OBAFEMI AWOLOWO UNIVERSITY TEACHING HOSPITALS
SINGLE INCISION LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY DR ADEWALE ADISA CONSULTANT MINIMAL ACCESS SURGEON & SENIOR LECTURER DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY, OBAFEMI AWOLOWO UNIVERSITY, & OBAFEMI AWOLOWO UNIVERSITY TEACHING HOSPITALS
A comparative study of open versus laparoscopic incisional hernia repair
 International Surgery Journal Bathalapalli JMR et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Mar;4(3):916-920 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20170428
International Surgery Journal Bathalapalli JMR et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Mar;4(3):916-920 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20170428
Medieval times in surgery Still no solution for:
 Medieval times in surgery Still no solution for: The most frequent complications of the abdominal surgeon: Adhesions Postoperative ileus Incisional hernia Anastomotic leakage Wound infection Incidence
Medieval times in surgery Still no solution for: The most frequent complications of the abdominal surgeon: Adhesions Postoperative ileus Incisional hernia Anastomotic leakage Wound infection Incidence
Surgery has been proven to be beneficial for selected patients
 Thoracoscopic Lung Volume Reduction Surgery Robert J. McKenna, Jr, MD Surgery has been proven to be beneficial for selected patients with severe emphysema. Compared with medical management, lung volume
Thoracoscopic Lung Volume Reduction Surgery Robert J. McKenna, Jr, MD Surgery has been proven to be beneficial for selected patients with severe emphysema. Compared with medical management, lung volume
The use of peritoneal flaps in the repair of large incisional hernia
 The use of peritoneal flaps in the repair of large incisional hernia Marc Huyghe MD GZA St Augustinus Hospital (Antwerp) Mesh 2017 - Paris Peritoneal flap in the repair of incisional hernia - definition
The use of peritoneal flaps in the repair of large incisional hernia Marc Huyghe MD GZA St Augustinus Hospital (Antwerp) Mesh 2017 - Paris Peritoneal flap in the repair of incisional hernia - definition
LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR
 LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR Treating Your Hernia with Laparoscopy When You Have a Hernia Anyone can have a hernia. This is a weakness or tear in the wall of the abdomen. It often results from years of wear
LAPAROSCOPIC HERNIA REPAIR Treating Your Hernia with Laparoscopy When You Have a Hernia Anyone can have a hernia. This is a weakness or tear in the wall of the abdomen. It often results from years of wear
One hundred percent fascial approximation with sequential abdominal closure of the open abdomen
 The American Journal of Surgery 192 (2006) 238 242 HowIdoit One hundred percent fascial approximation with sequential abdominal closure of the open abdomen C. Clay Cothren, M.D. a,b, *, Ernest E. Moore,
The American Journal of Surgery 192 (2006) 238 242 HowIdoit One hundred percent fascial approximation with sequential abdominal closure of the open abdomen C. Clay Cothren, M.D. a,b, *, Ernest E. Moore,
Laparoscopic umbilical herniorrhaphy: a novel technique of hernia neck closure and outcomes in the first 19 cases
 Original Article Page 1 of 7 Laparoscopic umbilical herniorrhaphy: a novel technique of hernia neck closure and outcomes in the first 19 cases Cheyenne Vetter 1, Yagan Pillay 2 1 Department of Family Medicine,
Original Article Page 1 of 7 Laparoscopic umbilical herniorrhaphy: a novel technique of hernia neck closure and outcomes in the first 19 cases Cheyenne Vetter 1, Yagan Pillay 2 1 Department of Family Medicine,
Motility Disorders. Pelvic Floor. Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 701) January 2010 November 2011
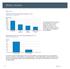 Motility Disorders Pelvic Floor Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 71) January 21 November 211 New Patients 35 3 25 2 15 1 5 Constipation Fecal Incontinence Rectal Prolapse Digestive-Genital
Motility Disorders Pelvic Floor Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 71) January 21 November 211 New Patients 35 3 25 2 15 1 5 Constipation Fecal Incontinence Rectal Prolapse Digestive-Genital
Case Study Review #2!
 1 Case Study Review #2! Based on your feedback for more SCQR-specific education, we are offering this common case scenario with frequently asked SCQR questions and misinterpreted variables. The case study
1 Case Study Review #2! Based on your feedback for more SCQR-specific education, we are offering this common case scenario with frequently asked SCQR questions and misinterpreted variables. The case study
Positioning System. Laparoscopic ventral hernia repair KEY BENEFITS SOFT TISSUE REPAIR
 Echo PS Positioning System with Ventralight ST Mesh or Composix L/P Mesh Laparoscopic ventral hernia repair Echo PS Positioning System with Ventralight ST Mesh Echo PS Positioning System with Composix
Echo PS Positioning System with Ventralight ST Mesh or Composix L/P Mesh Laparoscopic ventral hernia repair Echo PS Positioning System with Ventralight ST Mesh Echo PS Positioning System with Composix
2015 General Surgery Survival Guide
 2015 General Surgery Survival Guide Chapter 10: Hernia Repair Know What to Look for When Coding Hernia Repair Reporting hernia repair can be tricky. But if you know what to look for then half the work
2015 General Surgery Survival Guide Chapter 10: Hernia Repair Know What to Look for When Coding Hernia Repair Reporting hernia repair can be tricky. But if you know what to look for then half the work
SCIENTIFIC PAPER ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION METHODS
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Adhesion Formation After Laparoscopic Ventral Incisional Hernia Repair With Polypropylene Mesh: A Study Using Abdominal Ultrasound Juliane Bingener, MD, George B. Kazantsev, MD, Shailendra
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Adhesion Formation After Laparoscopic Ventral Incisional Hernia Repair With Polypropylene Mesh: A Study Using Abdominal Ultrasound Juliane Bingener, MD, George B. Kazantsev, MD, Shailendra
Urinary stoma. This is the simplest and most straightforward form of
 This is the simplest and most straightforward form of urinary drainage following surgery to remove the bladder (cystectomy). You may see it referred to as a urostomy, an ileal conduit or urinary diversion.
This is the simplest and most straightforward form of urinary drainage following surgery to remove the bladder (cystectomy). You may see it referred to as a urostomy, an ileal conduit or urinary diversion.
Laparoscopic Resection Of Colon & Rectal Cancers. R Sim Centre for Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery, TTSH
 Laparoscopic Resection Of Colon & Rectal Cancers R Sim Centre for Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery, TTSH Feasibility and safety Adequacy - same radical surgery as open op. Efficacy short term benefits and
Laparoscopic Resection Of Colon & Rectal Cancers R Sim Centre for Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery, TTSH Feasibility and safety Adequacy - same radical surgery as open op. Efficacy short term benefits and
DIVERTICULAR DISEASE. Dr. Irina Murray Casanova PGY IV
 DIVERTICULAR DISEASE Dr. Irina Murray Casanova PGY IV Diverticular Disease Colonoscopy Abdpelvic CT Scan Surgical Indications Overall, approximately 20% of patients with diverticulitis require surgical
DIVERTICULAR DISEASE Dr. Irina Murray Casanova PGY IV Diverticular Disease Colonoscopy Abdpelvic CT Scan Surgical Indications Overall, approximately 20% of patients with diverticulitis require surgical
SAGES guidelines for laparoscopic ventral hernia repair
 Surg Endosc (2016) 30:3163 3183 DOI 10.1007/s00464-016-5072-x and Other Interventional Techniques GUIDELINES SAGES guidelines for laparoscopic ventral hernia repair David Earle 1 J. Scott Roth 1 Alan Saber
Surg Endosc (2016) 30:3163 3183 DOI 10.1007/s00464-016-5072-x and Other Interventional Techniques GUIDELINES SAGES guidelines for laparoscopic ventral hernia repair David Earle 1 J. Scott Roth 1 Alan Saber
SPIGELIAN HERNIA Anastasia Ussia
 SPIGELIAN HERNIA Anastasia Ussia 34 years old woman 2010 : Operated for endometriosis and afterwards severe pain mainly in the right fossa ; extending up to umbilicus and radiating to upper right thigh
SPIGELIAN HERNIA Anastasia Ussia 34 years old woman 2010 : Operated for endometriosis and afterwards severe pain mainly in the right fossa ; extending up to umbilicus and radiating to upper right thigh
Outcomes of Colostomy Reversal Procedures in Two Teaching Hospitals in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia A. Bekele, B. Kotisso, H. Biluts Correspondence to
 East and Central African Journal of Surgery http://www.bioline.org.br/js 9 Outcomes of Colostomy Reversal Procedures in Two Teaching Hospitals in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia A. Bekele, B. Kotisso, H. Biluts
East and Central African Journal of Surgery http://www.bioline.org.br/js 9 Outcomes of Colostomy Reversal Procedures in Two Teaching Hospitals in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia A. Bekele, B. Kotisso, H. Biluts
A comparative study between laparoscopic intraperitoneal onlay mesh hernioplasty and open underlay mesh hernioplasty for ventral hernias
 International Surgery Journal Rao ASN et al. Int Surg J. 2015 Aug;2(3):352-360 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20150498
International Surgery Journal Rao ASN et al. Int Surg J. 2015 Aug;2(3):352-360 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20150498
Open Tension-Free Mesh Repair for Adult Inguinal Hernia: Eight Years of Experience in a Community Hospital
 Original Articles Asian Journal of Surgery Excerpta Medica Asia Ltd Open Tension-Free Mesh Repair for Adult Inguinal Hernia: Eight Years of Experience in a Community Hospital Shunji Yamamoto, Toshiki Maeda,
Original Articles Asian Journal of Surgery Excerpta Medica Asia Ltd Open Tension-Free Mesh Repair for Adult Inguinal Hernia: Eight Years of Experience in a Community Hospital Shunji Yamamoto, Toshiki Maeda,
Perhaps the most controversial of new laparoscopic operations is the repair of the inguinal hernia. The
 JOURNAL OF LAPAROENDOSCOPIC SURGERY Volume 2, Number 6, 1992 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., Publishers Extraperitoneal Endoscopie Inguinal Hernia Repair GEORGE S. FERZLI, M.D., F.A.C.S., AZIZ MASSAD, M.D., and
JOURNAL OF LAPAROENDOSCOPIC SURGERY Volume 2, Number 6, 1992 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., Publishers Extraperitoneal Endoscopie Inguinal Hernia Repair GEORGE S. FERZLI, M.D., F.A.C.S., AZIZ MASSAD, M.D., and
The lateral incisional hernia: anatomical considerations for a standardized retromuscular sublay repair
 Hernia (2009) 13:293 297 DOI 10.1007/s10029-009-0479-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The lateral incisional hernia: anatomical considerations for a standardized retromuscular sublay repair M. Stumpf J. Conze A. Prescher
Hernia (2009) 13:293 297 DOI 10.1007/s10029-009-0479-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The lateral incisional hernia: anatomical considerations for a standardized retromuscular sublay repair M. Stumpf J. Conze A. Prescher
Robot Assisted Rectopexy
 1. Abdominal cavity approach 1A Trocars Introduce Introduce five trocars to gain access to the abdominal cavity (in da Vinci Si type; In Xi type the trocar placement may differ slightly). First the camera
1. Abdominal cavity approach 1A Trocars Introduce Introduce five trocars to gain access to the abdominal cavity (in da Vinci Si type; In Xi type the trocar placement may differ slightly). First the camera
GS12 Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair (TAPP)
 GS12 Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair (TAPP) What is an inguinal hernia? An inguinal hernia is a common type of hernia, causing a lump and sometimes pain in the groin. Your surgeon has recommended a
GS12 Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair (TAPP) What is an inguinal hernia? An inguinal hernia is a common type of hernia, causing a lump and sometimes pain in the groin. Your surgeon has recommended a
Dr Candice Silverman MBBS (HONS) FRACS General & Laparoscopic Surgeon
 Dr Candice Silverman MBBS (HONS) FRACS General & Laparoscopic Surgeon Core Specialist Group Suite 5G, John Flynn Medical Centre 42 Inland Drive TUGUN QLD 4224 Tel: 07 5598 0955 Write questions or notes
Dr Candice Silverman MBBS (HONS) FRACS General & Laparoscopic Surgeon Core Specialist Group Suite 5G, John Flynn Medical Centre 42 Inland Drive TUGUN QLD 4224 Tel: 07 5598 0955 Write questions or notes
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair, Indications, Superiority and Outcome
 Laparoscopic Hernia Repair, Indications, Superiority and Outcome Mr. Amir Morgan MBBCh; MSc; MD; FICS; JAG; FRCS Consultant Laparoscopic Colorectal & General Surgeon Lead of medical education and surgical
Laparoscopic Hernia Repair, Indications, Superiority and Outcome Mr. Amir Morgan MBBCh; MSc; MD; FICS; JAG; FRCS Consultant Laparoscopic Colorectal & General Surgeon Lead of medical education and surgical
Port Site Hernia after Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 Human Journals Research Article November 2018 Vol.:13, Issue:4 All rights are reserved by Ridha Turki Jasim et al. Port Site Hernia after Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Keywords: Port site hernia, port closure,
Human Journals Research Article November 2018 Vol.:13, Issue:4 All rights are reserved by Ridha Turki Jasim et al. Port Site Hernia after Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Keywords: Port site hernia, port closure,
Ventralex ST Hernia Patch featuring Sepra Technology
 Ventralex ST Hernia Patch featuring Sepra Technology Proven Sepra Technology in a Low Profile, Lightweight Mesh Sepra Technology An extensively studied barrier with more than 10 publications and used clinically
Ventralex ST Hernia Patch featuring Sepra Technology Proven Sepra Technology in a Low Profile, Lightweight Mesh Sepra Technology An extensively studied barrier with more than 10 publications and used clinically
A Comparative Study between Onlay and Pre Peritoneal Mesh Repair in Management of Ventral Hernias
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. II (December. 2016), PP 63-67 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study between Onlay
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. II (December. 2016), PP 63-67 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study between Onlay
Comparative Study Of Laparoscopic Versus Open Peptic Perforation Closure
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 Comparative Study Of Laparoscopic Versus Open Peptic Perforation Closure M Porecha, S Mehta, D Udani, P Mehta, K Patel, S Nagre Citation M Porecha,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 Comparative Study Of Laparoscopic Versus Open Peptic Perforation Closure M Porecha, S Mehta, D Udani, P Mehta, K Patel, S Nagre Citation M Porecha,
Transitioning to Single-Incision Laparoscopic Inguinal Herniorrhaphy
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Transitioning to Single-Incision Laparoscopic Inguinal Herniorrhaphy Danny A. Sherwinter, MD ABSTRACT Background: Laparoendoscopic single-site surgery (LESS) offers cosmetic benefits and
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Transitioning to Single-Incision Laparoscopic Inguinal Herniorrhaphy Danny A. Sherwinter, MD ABSTRACT Background: Laparoendoscopic single-site surgery (LESS) offers cosmetic benefits and
Laparoscopic colon resection for colon cancer
 Laparoscopic colon resection for colon cancer Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we
Laparoscopic colon resection for colon cancer Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we
Can Robotics be useful to a General Surgeon Performing Colorectal Surgery? Curtis L. Peery MD April 27 th 2018 Throckmorton Surgical Society
 Can Robotics be useful to a General Surgeon Performing Colorectal Surgery? Curtis L. Peery MD April 27 th 2018 Throckmorton Surgical Society 1.Intuitive Surgical 2.C-Sats 3.Virtual Incision Study comparing
Can Robotics be useful to a General Surgeon Performing Colorectal Surgery? Curtis L. Peery MD April 27 th 2018 Throckmorton Surgical Society 1.Intuitive Surgical 2.C-Sats 3.Virtual Incision Study comparing
Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Placement. Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Placement. Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Placement
 ASDIN Advanced Techniques Pre-course Feb. 24, 2012 New Orleans, La Randall L. Rasmussen, MD Special thank you to Drs. Rajeev Narayan, San Antonio, Tx and Hemant Dhingra, Fresno Ca for lending me slides
ASDIN Advanced Techniques Pre-course Feb. 24, 2012 New Orleans, La Randall L. Rasmussen, MD Special thank you to Drs. Rajeev Narayan, San Antonio, Tx and Hemant Dhingra, Fresno Ca for lending me slides
Ultrapro Hernia System Bi Layer Dr Cosmas Gora T SpB-KBD. dffdfdfxxgfxgfxgffxgxgxg
 Bi Layer Dr Cosmas Gora T SpB-KBD dffdfdfxxgfxgfxgffxgxgxg Why UHS? Lightweight Mesh Covering entire myopectineal orifices with underlay mesh in preperitoneal space (posterior repair) Covering the inguinal
Bi Layer Dr Cosmas Gora T SpB-KBD dffdfdfxxgfxgfxgffxgxgxg Why UHS? Lightweight Mesh Covering entire myopectineal orifices with underlay mesh in preperitoneal space (posterior repair) Covering the inguinal
SINGLE INCISION ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY (SIES)
 EAES CONSENSUS CONFERENCE SINGLE INCISION ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY (SIES) STATEMENTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS EAES appreciates your input! Please give your opinion on the below statements and recommendations of the
EAES CONSENSUS CONFERENCE SINGLE INCISION ENDOSCOPIC SURGERY (SIES) STATEMENTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS EAES appreciates your input! Please give your opinion on the below statements and recommendations of the
The pillars defining our quality care. We Care!
 The pillars defining our quality care We Care! 1 An umbilical hernia occurs when a tissue bulges out through an opening in time muscles on the abdomen near the navel or belly button (umbilicus). About
The pillars defining our quality care We Care! 1 An umbilical hernia occurs when a tissue bulges out through an opening in time muscles on the abdomen near the navel or belly button (umbilicus). About
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 03 Page March 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i3.65 Comparative Study of Onlay and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i3.65 Comparative Study of Onlay and
Echo PS Positioning System with Ventralight ST Mesh or Composix L/P Mesh
 Ventralight ST Mesh with Echo PS Positioning System Catalog Number Shape Mesh Size 5955450 Circle 4.5" (11.4 cm) 5955460 Ellipse 4" x 6" (10.2 cm x 15.2 cm) 5955600 Circle 6" (15.2 cm) 5955680 Ellipse
Ventralight ST Mesh with Echo PS Positioning System Catalog Number Shape Mesh Size 5955450 Circle 4.5" (11.4 cm) 5955460 Ellipse 4" x 6" (10.2 cm x 15.2 cm) 5955600 Circle 6" (15.2 cm) 5955680 Ellipse
Geoffrey Axiak M.Sc. Nursing (Manch.), B.Sc. Nursing, P.G. Dip. Nutrition & Dietetics Clinical Nutrition Practice Nurse
 The Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Geoffrey Axiak M.Sc. Nursing (Manch.), B.Sc. Nursing, P.G. Dip. Nutrition & Dietetics Clinical Nutrition Practice Nurse What is a P.E.G.? Percutaneous Endoscopic
The Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy Geoffrey Axiak M.Sc. Nursing (Manch.), B.Sc. Nursing, P.G. Dip. Nutrition & Dietetics Clinical Nutrition Practice Nurse What is a P.E.G.? Percutaneous Endoscopic
