RCOG Urogynaecolgy Curriculum 2014
|
|
|
- Dustin Merritt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists RCOG Urogynaecolgy Curriculum 2014 Approved by the GMC as of 14 January GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
2 Introduction The programme consists of seven modules. One is common to all subspecialty programmes (Generic Module) and the other six are specific to urogynaecology. Aside from the modules, the trainee must also demonstrate that they have achieved a thorough understanding of the anatomy, physiology and pharmacology of the lower urinary tract and the impact of pregnancy, parturition, menopause and ageing on lower urinary tract function. They must also be aware of the effects of disease, both mental and physical upon the pelvic organs. The conditions that the trainee must be familiar with are listed below. An understanding of these is expanded upon within the modules. Conditions to be familiar with: Urodynamic stress incontinence Detrusor overactivity Trauma and congenital abnormalities resulting in incontinence Voiding disorders and urinary retention Overactive bladder syndrome Pelvic pain Lower urinary tract and lower gastointestinal tract fistulae Pelvic organ prolapse, both primary and recurrent Painful bladder syndrome Urethral lesions, e.g. diverticulae Effects of pelvic surgery and irradiation on the lower bowel urinary tract and pelvic floor Urinary disorders in pregnancy Evaluation and care of the elderly Lesions of the central nervous system affecting urinary, faecal control and pelvic floor Difficult defaecation Disorders of lower gastro-intestinal tract function including incontinence and motility Obstetric anal sphincter injury (OASIS) Urinary disorders in childhood; The physically or mentally handicapped Sexually transmitted diseases Emotional and behavioural disorders Hormone deficiency states Urinary problems secondary to medical disorders and drugs Symptoms associated with sexual intercourse, e.g. coital incontinence. 2GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
3 1.1 History Learning outcomes: Module 1: General Urogynaecology Assessment To demonstrate the know ledge skills and attitudes required to make an appropriate clinical assessment of an urogynaecological patient. To understand the different facets of obtaining a history of the w oman s condition: - obtain a general history - obtain a urinary/prolapse/bow el and sexual history - use standardised questionnaires - use quality of life (QoL) questionnaires Knowledge criteria GMP Clinical competency GMP Professional skills and attitudes GMP Training support Evidence/assessment Symptoms Relationships with other medical conditions How standardised questionnaires are devised Meaning of QoL questionnaires Understanding of how questionnaires are validated 1 Take an appropriate history Present relevant history for patients with either urinary, prolapse, sexual or faecal problems Use of appropriate standardized QoL 1,3,4 Ability to take an appropriate history Ability to use appropriate standardised questionnaires and to analyse them Ability to use appropriate QoL questionnaires and to analyse them 1,2 Tailored clinical experience Observation of, assisting and discussion with senior medical staff Personal study Appropriate postgraduate education courses Feedback from trainer Mini-CEX Logbook of competences and experience Annual subspecialty assessment Evidence of attendance at appropriate courses 3GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
4 1.2 Examination Learning outcomes: To be able to carry out a competent examination: - undertake a general examination - undertake a pelvic examination, including standardised methods of assessment - undertake a relevant neurological examination Knowledge criteria GMP Clinical competency GMP Professional skills and attitudes GMP Training support Evidence/assessment Examination findings relevant to lower urinary tract disorders Examination findings relevant to women with prolapse Neurological findings in women with denervation of the pelvic floor and neurological conditions affecting the lower urinary tract (e.g. multiple sclerosis) 1 Carry out an appropriate general, pelvic floor and neurological examination 1,3,4 Ability to: Carry out an appropriate general examination, especially abdominal Carry out an appropriate pelvic examination, including usage of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Quantification (POPQ) system or new assessments methods as they are introduced into clinical practice Carry out an appropriate neurological examination, especially pelvic floor innervation 1,2 Tailored clinical experience Observation of, assisting and discussion with senior medical staff Personal study Appropriate postgraduate education courses Feedback from trainer Mini-CEX Logbook of competences and experience 2GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
5 1.3 Investigations Learning outcomes: To be able to select appropriate tests and carry out the test proficiently and w here appropriate interpret results Knowledge criteria GMP Clinical competency GMP Professional skills and attitudes GMP Training support Evidence/assessment Investigations of lower urinary tract: Urinalysis Urine culture and cytology Frequency/volume charts Pad test Bladder scan Uroflowmetry Cystometry Videocystourethrography Ambulatory urodynamics Urethral function studies Cystourethroscopy: rigid/flexible Bladder Biopsy 1 Initiates investigations, understands and interprets results 1,3,4 Ability to understand impact of results on clinical management Ability to select appropriate tests and carry out the test proficiently (investigations for lower urinary tract) and interpret the results (investigations for lower and upper urinary tract, neurourology, pelvic floor investigation and colorectal investigations) 1,2 Direct observation Attendance at multidisciplinary team meetings Log book of competences and experience Annual subspecialty assessment OSATS: Urodynamics Cystoscopy Bladder Biopsy Investigations of upper urinary tract: Renal ultrasound Abdominal X-ray Intravenous urogram / CT Urogram / MRI Urogram Micturating Cystogram Isotope renography (e.g. Mag 3) Neurourology: Pelvic floor electromyography Pelvic floor investigation: Magnetic resonance imaging Ultrasound of pelvic floor Colorectal: Anorectal function studies Barium enema Contrast CT colon / Colonoscopy Defaecating proctogram Endoanal ultrasound 3GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
6 Module 1: General Urogynaecological Assessment Competence level Not required Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Date Signature Date Signature Date Signature History Take full urogynaecology history Take history of sexual dysfunction Interpret quality-of-life questionnaires Examination Appropriate abdominal examination Appropriate pelvic examination (including cough stress test) Assess pelvic floor tone Perform pelvic organ prolapse scoring Appropriate neurological examination Investigations Frequency Volume chart 4GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
7 Module 1: General Urogynaecological Assessment (continued) Competence level Not required Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Date Signature Date Signature Date Signature Pad Test Uroflow metry Perform bladder scan Perform dual channel subtracted cystometry Perform videocystometry Perform ambulatory urodynamics Perform urethral pressure profilometry Cystourethroscopy (rigid) Cystourethroscopy (flexible) Bladder biopsy at cystoscopy Renal ultrasound Abdominal Xray 5GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
8 Competence level Not required Module 1: General Urogynaecological Assessment (continued) Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Date Signature Date Signature Date Signature Intravenous urogram / CT urogram / MRI urogram Micturating cystogram Isotope renography Pelvic floor electromyography Ultrasound of the pelvic floor MRI scan of the pelvic floor Anorectal function studies Barium enema Contrast CT / Colonsocpoy Defaecating proctogram Endoanal ultrasound 6GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
9 Authorisation of signatures (to be completed by the clinical trainers) Name of clinical trainer (please print) Signature of clinical trainer 7GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
10 OSATS Urodynamics Each OSATS should be successfully completed for Independent Practice on 3 occasions before the module can be signed off Date Date Date Signature Signature Signature Cystoscopy (+/-Biopsy) Date Date Date Signature Signature Signature COMPLETION OF MODULE 1 I confirm that all components of the module have been successfully completed: Date Name of subspecialty training programme supervisor Signature of subspecialty training programme supervisor 8GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
11 Module 2: Conservative Management of Urogynaecological Conditions Learning outcomes: To demonstrate a thorough understanding of the evaluation and treatment of low er urinary tract disorders using conservative measures (including recommendations of the International Consultation on Incontinence) - Anatomy and function of low er urinary tract and pelvis - Fluid management - Physical therapies - Pharmacological therapies - Catheters and drug therapies for voiding difficulties - Pessaries for prolapse - Other therapies Knowledge criteria GMP Clinical competency GMP Professional skills and attitudes GMP Training support Evidence/assessment Anatomy, physiology and pathophysiology of lower urinary tract and pelvis Effects of abnormal anatomy, physiological events and systemic disease Related symptoms and clinical findings Principles of pharmacology and mode of action of substances acting on pelvic organs and lower urinary tract Indications for different types of catheters, insertion of catheters and intermittent self-catheterisation Indications for and fitting of ring, shelf and other pessaries 1 Take a history and carry out appropriate examination Analyse charts (frequency, frequency/volume, input/output) and give advice from the recordings presented Assess pelvic floor strength Insert catheters Teach intermittent self-catheterisation Fit and change pessaries 1,3,4 Ability to apply knowledge of anatomy, physiology and function to the clinical situation Ability to tailor treatment, taking into consideration underlying condition Ability to take a history, including standardised questionnaire, QoL Ability to demonstrate how recommendations to the patient depend on charts provided Ability to perform an appropriate general, pelvic floor and neurological examination Ability to implement drug management for incontinence 1,2 Appropriate courses/training days Observation of, assisting and discussion with senior medical staff Personal study Tailored clinical Experience Discussions with Physiotherapists Working with continence nurse specialist Demonstrates adequate exposure during training Logbook of competences and experience Feedback from trainer Annual subspecialty assessment Mini-CEX Use of different charts to assess intake and/or output and to assess and treat women with excessive voiding patterns Ability to insert a suprapubic catheter Ability to change a permanent suprapubic catheter 9GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
12 Knowledge criteria GMP Clinical competency GMP Professional skills and attitudes GMP Training support Evidence/assessment Pharmacology, including mechanism of action, adverse effects and interaction, for treatment of: Overactive bladder syndrome Nocturnal frequency and nocturia Stress urinary incontinence Painful bladder syndrome Use of hormone replacement therapy 1 1,3,4 Ability to teach intermittent selfcatheterisation Ability to fit and change non-ring pessaries and manage pessary problems 1,2 Effects of drugs used in other conditions on the lower urinary tract system Principles of different modalities of pelvic floor exercises: Cones Electrical therapy Magnetic stimulator Biofeedback Overactive bladder syndrome: Principles of and possible indications for treatment: o Biofeedback o Acupuncture o Hypnotherapy o Psychotherapy. 10GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
13 Module 2: Conservative Management of Urogynaecology Conditions Competence level Not required Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Date Signature Date Signature Date Signature Teaching of Pelvic Floor Exercises Teach clean intermittent self-catheterisation Insert suprapubic catheter Change suprapubic catheter Select and fit pessaries (ring, gellhorn and other non-ring pessaries) Medical management of detrusor overactivity Medical management of stress incontinence 11GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
14 Authorisation of signatures (to be completed by the clinical trainers) Name of clinical trainer (please print) Signature of clinical trainer COMPLETION OF MODULE 2 I confirm that all components of the module have been successfully completed: Date Name of subspecialty training programme supervisor Signature of subspecialty training programme supervisor 12GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
15 Module 3: Surgical Treatments Learning outcomes: To demonstrate the knowledge and skills to understand the indications for and the ability to carry out the required surgical procedures. This includes the skills and attitudes to counsel patients appropriately, to have an understanding of potential surgical complications and how to deal with them when they occur Knowledge criteria GMP Clinical competency GMP Professional skills and attitudes GMP Training support Evidence/assessment Urodynamic stress incontinence: Colposuspension (open and/or laparoscopic) Midurethral slings Bladder-neck injections Secondary surgery for urodynamic stress incontinence Detrusor overactivity Botulinum toxin injections Sacral nerve stimulation Voiding difficulties: Urethral dilatation Postoperative problems Advantages/disadvantages of different techniques Pelvic organ prolapse: Anterior and posterior repairs Paravaginal repair Vaginal hysterectomy Uterosacral plication or McCall culdoplasty for vault support at hysterectomy Mesh repair Vault prolapse: Sacrospinous fixation Sacrocolpopexy (open and laparoscopic) Other vaginal procedures 1 Counsel patients appropriately Perform procedures for treatment of urodynamic stress incontinence: Midurethral slings: - transobturator - retropubic Bladder neck injections Secondary surgery for urodynamic stress incontinence Management of mid-uretrhal tape mesh complecations involving bladder or urethra Perform urethral dilatation Perform repair of pelvic organ prolapse: Anterior repair Paravaginal repairs Vaginal hysterectomy Posterior repair Uterosacral plication or McCalls culdoplasty for vault support at hysterectomy Mesh repairs Perform repair of vault prolapse: Sacrospinous fixation Sacrocolpopexy (open and/or laparoscopic) Other vaginal procedures. Manage complications of surgical procedures Counsel patients with failed previous surgery Management of postoperative voiding dysfunction including obstructive causes Instruct patients in techniques for treatment of voiding difficulties 1,3,4 Ability to perform procedures for treatment of urodynamic stress incontinence: Midurethral slings Autologous slings and / or bladder neck injections Secondary surgery for urodynamic stress incontinence Ability to manage vaginal / bladder/ urethral / mesh erosion post mid-urethral tape Ability to perform urethral dilatation Ability to perform repair of pelvic organ prolapse: Anterior repair Vaginal hysterectomy Posterior repair Uterosacral plication Mesh repairs Ability to perform repair of vault prolapse: Sacrospinous fixation Sacrocolpopexy (open and/or laparoscopic) Other vaginal procedures Ability to work and communicate with other professionals Ability to counsel patients Ability to formulate a management plan and modify if necessary 1,2 Direct observation/ supervision Training programme Logbook of competences and experience Feedback from trainer 13GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust OSATS: Midurethral slings Vaginal hysterectomy and anterior repair Posterior repair Sacrospinous fixation Sacrolpopexy Annual subspecialty assessment Attendance at multiprofessional team meetings
16 Module 3: Surgical Treatments Competence level Not required Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Date Signature Date Signature Date Signature Bladder biopsy Bladder neck Injection Cysyoscopy w ith botulinum injections Colposuspension Transobturator midurethral sling Retropubic midurethral sling Urethral dilatation Urethrotomy Management of mid-urethral tape mesh complications involving bladder or urethra Anterior repair 14GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
17 Competence level Not required Module 3: Surgical Treatments (continued) Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Date Signature Date Signature Date Signature Posterior repair Hysterectomy for prolapse Uterus-conserving uterine prolapse surgery Mesh prolapse repair McCall Culdoplasty or uterosacral plication at vaginal hysterectomy Sacrospinous fixation Sacrocolpopexy (open or laparoscopic) Other prolapse operations, e.g. colpocleisis Management of intraoperative bladder injury 15GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
18 Authorisation of signatures (to be completed by the clinical trainers) Name of clinical trainer (please print) Signature of clinical trainer 16GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
19 OSATS Midurethral slings Each OSATS should be successfully completed for Independent Practice on 3 occasions before the module can be signed off Date Date Date Signature Signature Signature Vaginal hysterectomy and anterior repair Posterior repair Date Date Date Signature Signature Signature Date Date Date Signature Signature Signature Sacrospinous fixation Date Date Date Signature Signature Signature Sacrocolpopexy Date Date Date Signature Signature Signature COMPLETION OF MODULE 3 I confirm that all components of the module have been successfully completed: Date Name of subspecialty training programme supervisor Signature of subspecialty training programme supervisor 17GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
20 Module 4: Urology Learning outcomes: To understand and demonstrate a know ledge of specialist surgical treatments for urodynamic stress incontinence and detrusor overactivity To understand fistula management and be able to diagnose and treat urethral diverticula To be able to diagnose ureteric problems and use stents appropriately To understand the principles of ureteric reimplantation, anastomosis and nephrostomy Knowledge criteria GMP Clinical competency GMP Professional skills and attitudes GMP Training support Evidence/assessment Surgical principles for the treatment of complex urodynamic stress incontinence and detrusor overactivity: Fascial slings Artificial urinary sphincters Augmentation cytoplasty Urinary diversion procedures Botulinum toxin injections Fistulae (vesicovaginal, ureterovaginal, urethrovaginal): Investigation and diagnostic criteria Surgical principles of fistula repair and complications that may occur Urethral diverticula 1 Determine correct indications for referral for urodynamic stress incontinence and detrusor overactivity Undertake investigations and counsel patients appropriately Diagnose fistulae and order appropriate investigations Diagnose and treat urethral diverticula Insert appropriate ureteric stents 1,3,4 Ability to determine correct indications for referral for urodynamic stress incontinence and detrusor overactivity Ability to assess patients and counsel appropriately Ability to understand and use upper renal tract investigations appropriately Ability to manage ureteric injury and obstruction Ability to insert appropriate ureteric stents 1,2 Observation, assisting and discussion with senior medical staff Personal study Appropriate postgraduate education courses Feedback from trainer Work with clinicians in other disciplines e.g. urologists Case-based discussions Logbook of competences and experience Annual subspecialty assessment Treatments for ureteric obstruction and ureteric injury: Ureteric stents (double J stents or ureteric catheters) Surgical principles of ureteric reanastomosis and reimplantation techniques Tailored clinical experience Attachment to radiology department 18GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
21 Module 4: Specialist Urology Competence level Not required Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Date Signature Date Signature Date Signature Fascial sling Artificial sphincter Clam cystoplasty Urinary diversion Vesicovaginal fistula repair Urethrovaginal fistula repair Urethral diverticulum Nephrostomy Ureteric stenting Ureteric reimplantation Ureteric reanastomosis 19GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
22 Competence level Not required Module 4: Specialist Urology (continued) Observation Direct Supervision Independent Practice Date Signature Date Signature Date Signature 20GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
23 Authorisation of signatures (to be completed by the clinical trainers) Name of clinical trainer (please print) Signature of clinical trainer COMPLETION OF MODULE 4 I confirm that all components of the module have been successfully completed: Date Name of subspecialty training programme supervisor Signature of subspecialty training programme supervisor 21GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
24 Module 5: Colorectal Learning outcomes: To develop the know ledge, skills and attitudes appropriate to understanding the methods of investigations and principles of treatment of patients w ith colorectal problems Knowledge criteria GMP Clinical competency GMP Professional skills and attitudes GMP Training support Evidence/assessment Methods of investigations and principles of treatment of incontinence: Secondary anal sphincter repair Bulking agents Pelvic floor exercises Surgical management of rectal prolapse such as delormes, rectopexy Use of constipating agents Methods of investigations and principles of treatment for emptying problems: Use of laxatives / conservative therpies Transanal repair of rectocele Transanal resection (STARR) 1 Understand indications for investigations and interpret results Understand principles of management Repair anal sphincter Appropriate counseling 1,3,4 Ability to observe/undertake investigations and explained rationale Ability to work and communicate with other professionals Ability to counsel patients Ability to formulate a management plan and modify if necessary Ability to repair anal sphincter Ability to work in a multidisciplinary team 1,2 Tailored clinical experience May need to rotate to other departments / hospital Anal sphincter repair course Appropriate rotation on training programme Logbook Annual subspecialty assessment Attendance at appropriate course Feedback from multidisciplinary team meetings Attendance at perineal or nurse-led biofeedback clinics Methods of investigations and principles of treatment for urgency: Biofeedback Drug treatment Behavioural modification Attendance at anorectal physiology investigation clinics Investigations and principles of treatment of enteric fistulae, including those involving bladder, vagina, anus or perenium 22GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
25 Module 5: Specialist Colorectal Competence level Not required Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Date Signature Date Signature Date Signature Secondary anal sphincter repair Trans-anal repair of rectocele Recto-vaginal fistula repair Stapled transanal rectal resection procedure Rectopexy Delormes precedure 23GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
26 Authorisation of signatures (to be completed by the clinical trainers) Name of clinical trainer (please print) Signature of clinical trainer COMPLETION OF MODULE 5 I confirm that all components of the module have been successfully completed: Date Name of subspecialty training programme supervisor Signature of subspecialty training programme supervisor 24GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
27 Learning outcomes: Module 6: Neurology To understand the effects of neurological conditions on the lower urinary tract To understand and have knowledge of the principles of specialist assessm ent and treatments for bladder dysfunction Knowledge criteria GMP Clinical competency GMP Professional skills and attitudes GMP Training support Evidence/assessment Effects of neurological conditions on lower urinary tract function Lower urinary tract manifestations of: Spina bifida Multiple sclerosis Parkinson s disease Spinal cord injury Lower motor neuropathy Stroke Pelvic floor electromyogram: Use of sacral nerve stimulators Tibial nerve stimulation 1 Carry out an appropriate neurological examination and order appropriate investigations Interpret pelvic floor electromyogram results Manage patients with neurological conditions affecting the bladder Observation of / direct supervision for sacral neuromodulation 1,3,4 Ability to assess patients and counsel appropriately Ability to understand relationship between neurological conditions and lower urinary tract function Ability to carry out an appropriate neurological examination and order appropriate investigations 1,2 Tailored clinical experience Observation of, assisting and discussion with senior medical staff Personal study Appropriate postgraduate education courses Work with other disciplines e.g. neurology Logbook Annual subspecialty assessment 25GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
28 Module 6 Neurology Competence level Not required Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Date Signature Date Signature Date Signature Manage patients w ith neurological conditions affecting the bladder Sacral nerve modulation Posterior tibial nerve stimulation 26GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
29 Authorisation of signatures (to be completed by the clinical trainers) Name of clinical trainer (please print) Signature of clinical trainer COMPLETION OF MODULE 6 I confirm that all components of the module have been successfully completed: Date Name of subspecialty training programme supervisor Signature of subspecialty training programme supervisor 27GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain 1: Knowledge, ski lls and Performance Domain 2: Safety and quality Domain 3: Communication, Partnership and Teamwork. Domain 4: Maintaining Trust
RCOG Urogynaecology Curriculum 2017
 Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists RCOG Urogynaecology Curriculum 207 Approved by the GMC on 0 July 207 and implemented by RCOG February 208 GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists RCOG Urogynaecology Curriculum 207 Approved by the GMC on 0 July 207 and implemented by RCOG February 208 GMC Good Medical Practice (GMP) Domains: Domain
Clinical Curriculum: Urogynecology
 Updated July 201 Clinical Curriculum: Urogynecology GOAL: The primary goal of the Urogynecology rotation at the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) is to train physicians to have a broad knowledge
Updated July 201 Clinical Curriculum: Urogynecology GOAL: The primary goal of the Urogynecology rotation at the University of Alabama at Birmingham (UAB) is to train physicians to have a broad knowledge
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence. Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations
 The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
NICE guideline Published: 2 April 2019 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng123
 Urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse in women: management NICE guideline Published: 2 April 2019 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng123 NICE 2019. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse in women: management NICE guideline Published: 2 April 2019 nice.org.uk/guidance/ng123 NICE 2019. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights (https://www.nice.org.uk/terms-and-conditions#notice-ofrights).
Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery
 Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery APPLICATION FOR NEW FELLOWSHIP Name of Institution: McGill University Location: Royal Victoria Hospital (Glen Site), St Mary s Hospital Centre Type of Fellowship:
Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery APPLICATION FOR NEW FELLOWSHIP Name of Institution: McGill University Location: Royal Victoria Hospital (Glen Site), St Mary s Hospital Centre Type of Fellowship:
Urogynecology: Evidence-Based Clinical Practice
 Urogynecology: Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Kate H. Moore Urogynecology: Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Second Edition Kate H. Moore, MBBS, FRCOG, FRANZCOG, MD, CU Department Obstetrics & Gynaecology
Urogynecology: Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Kate H. Moore Urogynecology: Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Second Edition Kate H. Moore, MBBS, FRCOG, FRANZCOG, MD, CU Department Obstetrics & Gynaecology
Tertiary, regional and local pelvic floor service providers: the future. model? Andrew Williams
 Tertiary, regional and local pelvic floor service providers: the future Andrew Williams model? Pelvic Floor Unit Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust Background 23% women suffer at least one pelvic
Tertiary, regional and local pelvic floor service providers: the future Andrew Williams model? Pelvic Floor Unit Guy s and St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust Background 23% women suffer at least one pelvic
John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student
 John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student Prolapse/incontinence You need to know: Pelvic floor anatomy in relation to uterovaginal support and continence The classification of uterovaginal
John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student Prolapse/incontinence You need to know: Pelvic floor anatomy in relation to uterovaginal support and continence The classification of uterovaginal
2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL)
 2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL) SECTION B PART 1 - SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No. Service
2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL) SECTION B PART 1 - SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No. Service
A. Service Specifications
 A. Service Specifications SCHEDULE 2 THE SERVICES Service Specification No: Service Commissioner Lead Specialised Complex Surgery for Urinary Incontinence and Vaginal and Uterine Prolapse For local completion
A. Service Specifications SCHEDULE 2 THE SERVICES Service Specification No: Service Commissioner Lead Specialised Complex Surgery for Urinary Incontinence and Vaginal and Uterine Prolapse For local completion
Urogynaecology. Colm McAlinden
 Urogynaecology Colm McAlinden Definitions Urinary incontinence compliant of any involuntary leakage of urine with many different causes Two main types: Stress Urge Definitions Nocturia: More than a single
Urogynaecology Colm McAlinden Definitions Urinary incontinence compliant of any involuntary leakage of urine with many different causes Two main types: Stress Urge Definitions Nocturia: More than a single
IUGA guidelines for training in female pelvic medicine and reconstructive pelvic surgery (FPM-RPS)
 Int Urogynecol J (2010) 21:1445 1453 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1225-y IUGA GUIDELINES IUGA guidelines for training in female pelvic medicine and reconstructive pelvic surgery (FPM-RPS) Updated Guidelines
Int Urogynecol J (2010) 21:1445 1453 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1225-y IUGA GUIDELINES IUGA guidelines for training in female pelvic medicine and reconstructive pelvic surgery (FPM-RPS) Updated Guidelines
Incontinence in neurological disease
 nice bulletin Incontinence in neurological disease NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised NICE Bulletin - Incontinence in neurological disease.indd
nice bulletin Incontinence in neurological disease NICE provided the content for this booklet which is independent of any company or product advertised NICE Bulletin - Incontinence in neurological disease.indd
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583
 Sacrocolpopexy using mesh to repair vaginal vault prolapse Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583 Your responsibility This guidance represents the view of
Sacrocolpopexy using mesh to repair vaginal vault prolapse Interventional procedures guidance Published: 28 June 2017 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg583 Your responsibility This guidance represents the view of
Urogynecology Curriculum for the PGY III and IV Resident
 Urogynecology Curriculum for the PGY III and IV Resident Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Maryland Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology I. Educational Purpose: The dedicated Urogynecology rotation is intended
Urogynecology Curriculum for the PGY III and IV Resident Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Maryland Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology I. Educational Purpose: The dedicated Urogynecology rotation is intended
Prolapse & Urogynaecology. Hester Mannion and Fabi Sica
 Prolapse & Urogynaecology Hester Mannion and Fabi Sica Take home messages Prolapse and associated incontinence is very common It has a devastating effect on the QoL of the patient and their partner Strategies
Prolapse & Urogynaecology Hester Mannion and Fabi Sica Take home messages Prolapse and associated incontinence is very common It has a devastating effect on the QoL of the patient and their partner Strategies
Content. Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management
 Prolapse Content Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management Terminology Prolapse Descent of pelvic organs into the vagina Cystocele ant. vaginal wall involving bladder Uterine
Prolapse Content Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management Terminology Prolapse Descent of pelvic organs into the vagina Cystocele ant. vaginal wall involving bladder Uterine
1) What conditions is vaginal mesh used to commonly treat? Vaginal mesh is used to treat two different health issues in women:
 Vaginal Mesh Frequently Asked Questions 1) What conditions is vaginal mesh used to commonly treat? Vaginal mesh is used to treat two different health issues in women: a) stress urinary incontinence (SUI)
Vaginal Mesh Frequently Asked Questions 1) What conditions is vaginal mesh used to commonly treat? Vaginal mesh is used to treat two different health issues in women: a) stress urinary incontinence (SUI)
Urogynaecology & Prolapse. Alexander Denning and Leifa Jennings
 + Urogynaecology & Prolapse Alexander Denning and Leifa Jennings + Contents What even is prolapse / urogynaecology? Pelvic floor anatomy Prolapse Urinary incontinence Prevention The end (woot) + Urogynaecology
+ Urogynaecology & Prolapse Alexander Denning and Leifa Jennings + Contents What even is prolapse / urogynaecology? Pelvic floor anatomy Prolapse Urinary incontinence Prevention The end (woot) + Urogynaecology
By:Dr:ISHRAQ MOHAMMED
 By:Dr:ISHRAQ MOHAMMED Protrusion of an organ or structure beyond its normal confines. Prolapses are classified according to their location and the organs contained within them. 1-Anterior vaginal wall
By:Dr:ISHRAQ MOHAMMED Protrusion of an organ or structure beyond its normal confines. Prolapses are classified according to their location and the organs contained within them. 1-Anterior vaginal wall
Various Types. Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG
 Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Prolapse & Stress Incontinence
 Advanced Pelvic Floor Course Prolapse & Stress Incontinence OVERVIEW Day One and morning of Day Two- Pelvic Organ Prolapse The Prolapse component covers the detailed anatomy of POP including the DeLancey
Advanced Pelvic Floor Course Prolapse & Stress Incontinence OVERVIEW Day One and morning of Day Two- Pelvic Organ Prolapse The Prolapse component covers the detailed anatomy of POP including the DeLancey
Clinical guideline Published: 8 August 2012 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg148
 Urinary incontinence in neurological disease: assessment and management Clinical guideline Published: 8 August 2012 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg148 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights
Urinary incontinence in neurological disease: assessment and management Clinical guideline Published: 8 August 2012 nice.org.uk/guidance/cg148 NICE 2018. All rights reserved. Subject to Notice of rights
Pelvic Floor Disorders. Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon
 Pelvic Floor Disorders Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon What is Pelvic Floor Disorder Surgical perspective symptoms of RED, FI or prolapse on the background
Pelvic Floor Disorders Amir Darakhshan MD FRCS (Gen Surg) Consultant Colorectal and General Surgeon What is Pelvic Floor Disorder Surgical perspective symptoms of RED, FI or prolapse on the background
2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL)
 E10d 2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL) SECTION B PART 1 - SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No.
E10d 2012/13 NHS STANDARD CONTRACT FOR ACUTE, AMBULANCE, COMMUNITY AND MENTAL HEALTH AND LEARNING DISABILITY SERVICES (MULTILATERAL) SECTION B PART 1 - SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS Service Specification No.
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence in women
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence in women
Update Guidelines IUGA Guidelines for Training in Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Pelvic Surgery (FPMRPS)
 1 Update Guidelines IUGA Guidelines for Training in Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Pelvic Surgery (FPMRPS) IUGA Educational Committee Introduction The first IUGA Educational Guidelines were
1 Update Guidelines IUGA Guidelines for Training in Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Pelvic Surgery (FPMRPS) IUGA Educational Committee Introduction The first IUGA Educational Guidelines were
We welcome comments and corrections which will be used to improve the system annually.
 ACGME Case Log Instructions: Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery (FPMRS) Review Committees for Obstetrics and Gynecology, and Urology Updated July 2013 BACKGROUND The ACGME Case Log System
ACGME Case Log Instructions: Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery (FPMRS) Review Committees for Obstetrics and Gynecology, and Urology Updated July 2013 BACKGROUND The ACGME Case Log System
URODYNAMICS. Special Skills Training Module. June Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists
 Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Special Skills Training Module URODYNAMICS In collaboration with the British Society of Urogynaecology June 2002 Published by the RCOG Press at the Royal
Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists Special Skills Training Module URODYNAMICS In collaboration with the British Society of Urogynaecology June 2002 Published by the RCOG Press at the Royal
Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction
 Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction (Text update March 2009) M. Stöhrer (chairman), B. Blok, D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier- Kastler, P. Denys, G. Kramer, J. Pannek, G. del Popolo, P.
Guidelines on Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction (Text update March 2009) M. Stöhrer (chairman), B. Blok, D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier- Kastler, P. Denys, G. Kramer, J. Pannek, G. del Popolo, P.
Disease Management. Incontinence Care. Chan Sau Kuen Continence Nurse Consultant United Christian Hospital 14/11/09
 Disease Management in Incontinence Care Chan Sau Kuen Continence Nurse Consultant United Christian Hospital 14/11/09 What is incontinence? Definition of Incontinence - Is the compliant of any involuntary
Disease Management in Incontinence Care Chan Sau Kuen Continence Nurse Consultant United Christian Hospital 14/11/09 What is incontinence? Definition of Incontinence - Is the compliant of any involuntary
Incontinence; Lets talk about it. Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery
 Incontinence; Lets talk about it Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Select the most appropriate subtitle for this talk A: Bladders gone wild! B: There s no such thing
Incontinence; Lets talk about it Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Select the most appropriate subtitle for this talk A: Bladders gone wild! B: There s no such thing
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal mesh background of, 84 85 Age as factor in PFDs, 8 Anal plugs in FI management in women, 107 Anterior compartment native tissue
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal mesh background of, 84 85 Age as factor in PFDs, 8 Anal plugs in FI management in women, 107 Anterior compartment native tissue
Ralph & Berryl Goldman Fellowship in Neuro urology, voiding dysfunction and bladder reconstruction
 Ralph & Berryl Goldman Fellowship in Neuro urology, voiding dysfunction and bladder reconstruction Length of fellowship: A 1 year Fellowship: This fellowship has been designed for Urology or Gynecology
Ralph & Berryl Goldman Fellowship in Neuro urology, voiding dysfunction and bladder reconstruction Length of fellowship: A 1 year Fellowship: This fellowship has been designed for Urology or Gynecology
Prolapse and Urogynae. By Sarah Rangan & Daniel Warrell
 Prolapse and Urogynae By Sarah Rangan & Daniel Warrell Anatomy and physiology of the pelvic supports The pelvic floor supports the pelvic viscera and vaginal, urethral and rectal openings Endopelvic fascial
Prolapse and Urogynae By Sarah Rangan & Daniel Warrell Anatomy and physiology of the pelvic supports The pelvic floor supports the pelvic viscera and vaginal, urethral and rectal openings Endopelvic fascial
Objectives. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
 URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566
 Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse
 Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse Genital(utero-vaginal )prolapse is extremely common, with an estimated 11% of women undergoing at least one operation for this condition. Definition: A
Gynecology Dr. Sallama Lecture 3 Genital Prolapse Genital(utero-vaginal )prolapse is extremely common, with an estimated 11% of women undergoing at least one operation for this condition. Definition: A
Urogynaecology Update. Andrew Tapp Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Shrewsbury & Telford Hospital NHS Trust
 Urogynaecology Update Andrew Tapp Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Shrewsbury & Telford Hospital NHS Trust Urogynaecology Training Core module 18. ATSM. Sub-specialty training. Urogynaecology
Urogynaecology Update Andrew Tapp Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Shrewsbury & Telford Hospital NHS Trust Urogynaecology Training Core module 18. ATSM. Sub-specialty training. Urogynaecology
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE. Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence 2 Background a) The National
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence 2 Background a) The National
Subspecialty Procedural Volume Guidelines
 Subspecialty Review Committee for Obstetrics and Gynecology In response to requests from program directors, and in an effort to be transparent, the Review Committee for Obstetrics and Gynecology has elected
Subspecialty Review Committee for Obstetrics and Gynecology In response to requests from program directors, and in an effort to be transparent, the Review Committee for Obstetrics and Gynecology has elected
University of Alberta Reconstructive Urology Fellowship
 University of Alberta Reconstructive Urology Fellowship 1. Overview 2. Eligibility Requirements 3. Funding 4. Clinical Expectations 5. Academic Expectations 6. Objectives of Training 7. Teaching Methods
University of Alberta Reconstructive Urology Fellowship 1. Overview 2. Eligibility Requirements 3. Funding 4. Clinical Expectations 5. Academic Expectations 6. Objectives of Training 7. Teaching Methods
GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION
 GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION M. Stöhrer (chairman), D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier-Kastler, G. Kramer, A. Mattiasson, J-J. Wyndaele Introduction NLUTD (neurogenic lower urinary
GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION M. Stöhrer (chairman), D. Castro-Diaz, E. Chartier-Kastler, G. Kramer, A. Mattiasson, J-J. Wyndaele Introduction NLUTD (neurogenic lower urinary
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence. Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa
 Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
Advanced Care for Female Overactive Bladder & Urinary Incontinence Department of Urology Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Goals Participants will: Review normal urinary tract anatomy and function Understand
Urinary Incontinence. Lora Keeling and Byron Neale
 Urinary Incontinence Lora Keeling and Byron Neale Not life threatening. Introduction But can have a huge impact on quality of life. Two main types of urinary incontinence (UI). Stress UI leakage on effort,
Urinary Incontinence Lora Keeling and Byron Neale Not life threatening. Introduction But can have a huge impact on quality of life. Two main types of urinary incontinence (UI). Stress UI leakage on effort,
EAU GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE
 EU GUIDELINES ON URINRY INONTINENE (Limited text update March 2017) F.. urkhard (hair), J.L.H.R. osch, F. ruz, G.E. Lemack,.K. Nambiar, N. Thiruchelvam,. Tubaro Guidelines ssociates: D. mbühl, D. edretdinova,
EU GUIDELINES ON URINRY INONTINENE (Limited text update March 2017) F.. urkhard (hair), J.L.H.R. osch, F. ruz, G.E. Lemack,.K. Nambiar, N. Thiruchelvam,. Tubaro Guidelines ssociates: D. mbühl, D. edretdinova,
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Understanding Pelvic Organ Prolapse. Stephanie Pickett, MD, MS Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery
 Understanding Pelvic Organ Prolapse Stephanie Pickett, MD, MS Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery Disclosures None I am the daughter of a physician assistant. Objectives List types of pelvic
Understanding Pelvic Organ Prolapse Stephanie Pickett, MD, MS Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery Disclosures None I am the daughter of a physician assistant. Objectives List types of pelvic
Neurogenic bladder. Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder.
 Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
Management of Female Stress Incontinence
 Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence. Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes
 Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes 66 year old woman with incontinence PC: 7 year Hx of urgency, frequency, nocturia (incl. incontinence at night), and stress incontinence
Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes 66 year old woman with incontinence PC: 7 year Hx of urgency, frequency, nocturia (incl. incontinence at night), and stress incontinence
Post operative voiding dysfunction and the Value of Urodynamics. Dr Salwan Al-Salihi Urogynaecologist Obstetrician and Gynaecologist
 Post operative voiding dysfunction and the Value of Urodynamics Dr Salwan Al-Salihi Urogynaecologist Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Learning objectives: v Pathophysiology of post op voiding dysfunction.
Post operative voiding dysfunction and the Value of Urodynamics Dr Salwan Al-Salihi Urogynaecologist Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Learning objectives: v Pathophysiology of post op voiding dysfunction.
4. Know how to examine and name relevant test performed on patients
 Chapter 18 Female Urinary lncontinence Dr Zeelha Abdool Ed ucational Objectives : After completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Understand the pathophysiology of incontinence 2. Define and
Chapter 18 Female Urinary lncontinence Dr Zeelha Abdool Ed ucational Objectives : After completion of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Understand the pathophysiology of incontinence 2. Define and
EAU GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE
 EU GUIDELINES ON URINRY INONTINENE (Partial text update March 2016) F.. urkhard (hair), M.G. Lucas, L.. erghmans, J.L.H.R. osch, F. ruz, G.E. Lemack,.K. Nambiar,.G. Nilsson, R. Pickard,. Tubaro Guidelines
EU GUIDELINES ON URINRY INONTINENE (Partial text update March 2016) F.. urkhard (hair), M.G. Lucas, L.. erghmans, J.L.H.R. osch, F. ruz, G.E. Lemack,.K. Nambiar,.G. Nilsson, R. Pickard,. Tubaro Guidelines
MIDLAND MEMORIAL HOSPITAL Delineation of Privileges FEMALE PELVIC MEDICINE AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY (UROGYNECOLOGY)
 MIDLAND MEMORIAL HOSPITAL Delineation of Privileges FEMALE PELVIC MEDICINE AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY (UROGYNECOLOGY) Physician Name: Your home for healthcare Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive
MIDLAND MEMORIAL HOSPITAL Delineation of Privileges FEMALE PELVIC MEDICINE AND RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY (UROGYNECOLOGY) Physician Name: Your home for healthcare Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive
Recommandations de prise en charge des vessies neurogènes EAU 2006
 Annexe 4-1 Recommandations de prise en charge des vessies neurogènes EAU 2006 (Version courte) 685 686 GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION M. Stöhrer (chairman), D. Castro-Diaz, E.
Annexe 4-1 Recommandations de prise en charge des vessies neurogènes EAU 2006 (Version courte) 685 686 GUIDELINES ON NEUROGENIC LOWER URINARY TRACT DYSFUNCTION M. Stöhrer (chairman), D. Castro-Diaz, E.
Hong Kong College of Surgical Nursing
 Hong Kong College of Surgical Nursing Higher Surgical Nursing Training: Part B Specialty - Urological Nursing Curriculum TABLE OF CONTENTS No. Contents Page. Introduction. Aims. Learning Objectives 4.
Hong Kong College of Surgical Nursing Higher Surgical Nursing Training: Part B Specialty - Urological Nursing Curriculum TABLE OF CONTENTS No. Contents Page. Introduction. Aims. Learning Objectives 4.
University of Alberta Reconstructive Urology Fellowship
 FACULTY OF MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY DIVISION OF UROLOGY Keith Rourke, MD, FRCSC Reconstructive Urology Professor Chair of Academic Urology Reconstructive Urology Fellowship Director
FACULTY OF MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY DIVISION OF UROLOGY Keith Rourke, MD, FRCSC Reconstructive Urology Professor Chair of Academic Urology Reconstructive Urology Fellowship Director
Module 5 Management Of Urinary Incontinence
 Management Of Urinary Incontinence V3: Last Reviewed September 2017 Learning Outcomes Outline conservative management options Discover the options available to manage the different types of incontinence
Management Of Urinary Incontinence V3: Last Reviewed September 2017 Learning Outcomes Outline conservative management options Discover the options available to manage the different types of incontinence
Stop Coping. Start Living. Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy
 Stop Coping. Start Living Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy Did you know? One in three women will suffer from a pelvic health condition in her lifetime. Four of the most
Stop Coping. Start Living Talk to your doctor about pelvic organ prolapse and sacrocolpopexy Did you know? One in three women will suffer from a pelvic health condition in her lifetime. Four of the most
Morbidity Audit and Logbook Tool SNOMED Board Reporting Terms for SET and IMG Urology ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT
 ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT Cystolitholapaxy Cystoscopic removal of foreign body from bladder Cystoscopic removal of ureteric stent Cystoscopy and cystodiathermy Cystoscopy and transurethral biopsy
ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT Cystolitholapaxy Cystoscopic removal of foreign body from bladder Cystoscopic removal of ureteric stent Cystoscopy and cystodiathermy Cystoscopy and transurethral biopsy
Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence
 Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Introduction/Learning Objectives. Incontinence: Natural History. Course Outline 10/14/2016. Urinary Incontinence: Conservative Measures
 Management of Urinary Complications after Prostatectomy Course Faculty: Introduction/Learning Objectives Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Associate Attending Urologist Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial Sloan
Management of Urinary Complications after Prostatectomy Course Faculty: Introduction/Learning Objectives Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Associate Attending Urologist Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial Sloan
Stress Incontinence. Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS
 Stress Incontinence Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS Definitions Prevalence Assessment Investigation Treatment Surgery Men International Continence Society define as the complaint of any involuntary leakage
Stress Incontinence Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS Definitions Prevalence Assessment Investigation Treatment Surgery Men International Continence Society define as the complaint of any involuntary leakage
CONTINENCE MODULE 1 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMALE LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS
 CONTINENCE MODULE 1 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMALE LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS The minimum standards required to initiate specialised conservative
CONTINENCE MODULE 1 MIMIMUM STANDARDS FOR THE SPECIALIST ASSESSMENT & CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT OF FEMALE LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS The minimum standards required to initiate specialised conservative
Fecal Incontinence. What is fecal incontinence?
 Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
Scan for mobile link. Fecal Incontinence Fecal incontinence is the inability to control the passage of waste material from the body. It may be associated with constipation or diarrhea and typically occurs
GUIDELINES ON NEURO-UROLOGY
 GUIDELINES ON NEURO-UROLOGY (Limited text update March 2015) B. Blok (Co-chair), J. Pannek (Co-chair), D. Castro Diaz, G. del Popolo, J. Groen, T. Gross (Guidelines ssociate), R. Hamid, G. Karsenty, T.M.
GUIDELINES ON NEURO-UROLOGY (Limited text update March 2015) B. Blok (Co-chair), J. Pannek (Co-chair), D. Castro Diaz, G. del Popolo, J. Groen, T. Gross (Guidelines ssociate), R. Hamid, G. Karsenty, T.M.
Surgical repair of vaginal wall prolapse using mesh
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Surgical repair of vaginal wall prolapse using mesh Vaginal wall prolapse happens when the normal support
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Surgical repair of vaginal wall prolapse using mesh Vaginal wall prolapse happens when the normal support
Overactive bladder can result from one or more of the following causes:
 Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Royal Free NHS Trust Barnet Hospital
 Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Royal Free NHS Trust Barnet Hospital Pelvic Organ Prolapse (POP)- herniation of pelvic organs into vaginal walls Common Huge impact on daily activities
Moneli Golara Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist Royal Free NHS Trust Barnet Hospital Pelvic Organ Prolapse (POP)- herniation of pelvic organs into vaginal walls Common Huge impact on daily activities
GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE
 GUIDELINES ON URINRY INONTINENE (Text update pril 2014) M.G. Lucas (chair), D. edretdinova, J.L.H.R. osch, F. urkhard, F. ruz, D.J.M.K. de Ridder,. Nambiar,.G. Nilsson,. Tubaro, R.S. Pickard This pocket
GUIDELINES ON URINRY INONTINENE (Text update pril 2014) M.G. Lucas (chair), D. edretdinova, J.L.H.R. osch, F. urkhard, F. ruz, D.J.M.K. de Ridder,. Nambiar,.G. Nilsson,. Tubaro, R.S. Pickard This pocket
Pelvic organ prolapse
 Page 1 of 11 Pelvic organ prolapse Introduction The aim of this leaflet is to give you information about a pelvic organ prolapse, its causes and available treatments but does not replace advice given by
Page 1 of 11 Pelvic organ prolapse Introduction The aim of this leaflet is to give you information about a pelvic organ prolapse, its causes and available treatments but does not replace advice given by
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN
 Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Overactive Bladder Syndrome
 Overactive Bladder Syndrome behavioural modifications to pharmacological and surgical treatments Dr Jos Jayarajan Urologist Austin Health, Eastern Health Warringal Private, Northpark Private, Epworth Overactive
Overactive Bladder Syndrome behavioural modifications to pharmacological and surgical treatments Dr Jos Jayarajan Urologist Austin Health, Eastern Health Warringal Private, Northpark Private, Epworth Overactive
GUIDELINES ON NEURO-UROLOGY
 GUIDELINES ON NEURO-UROLOGY (Text update pril 2014) J. Pannek (co-chair), B. Blok (co-chair), D. Castro-Diaz, G. del Popolo, J. Groen, G. Karsenty, T.M. Kessler, G. Kramer, M. Stöhrer Eur Urol 2009 Jul;56(1):81-8
GUIDELINES ON NEURO-UROLOGY (Text update pril 2014) J. Pannek (co-chair), B. Blok (co-chair), D. Castro-Diaz, G. del Popolo, J. Groen, G. Karsenty, T.M. Kessler, G. Kramer, M. Stöhrer Eur Urol 2009 Jul;56(1):81-8
Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS
 Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS OhioHealth, Columbus Ohio Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the role of a pelvic floor therapist in
Pelvic Floor Therapy for the Neurologic Client Carina Siracusa, PT, DPT, WCS OhioHealth, Columbus Ohio Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe the role of a pelvic floor therapist in
Module Title: GENITO-URINARY TRACT Date: May 2013 Module Rationale and Competencies
 Module Title: Date: May 2013 Module Rationale and Competencies A paediatric surgeon is required to have a thorough understanding of normal anatomy and physiology, pathophysiology, investigations, differential
Module Title: Date: May 2013 Module Rationale and Competencies A paediatric surgeon is required to have a thorough understanding of normal anatomy and physiology, pathophysiology, investigations, differential
Introduction to GYN Specialties
 Outline Introduction to GYN Specialties Gynecologic Oncology* Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery* Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility* Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology** Family
Outline Introduction to GYN Specialties Gynecologic Oncology* Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery* Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility* Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology** Family
WEDNESDAY MARCH 8 th. Prevention of Perineal Trauma. Advanced urodynamic course. Marketing. Room Nursing school. Room TURQUESA 5.
 WEDNESDAY MARCH 8 th 08:00h-10:00h TURQUESA 1 TURQUESA 2 TURQUESA 3 TURQUESA 4 TURQUESA 5 TUQUESA 6 Nursing school USP Workshop 5: Demystifying and promoting the adherence of Clean Intermittent Catheterization
WEDNESDAY MARCH 8 th 08:00h-10:00h TURQUESA 1 TURQUESA 2 TURQUESA 3 TURQUESA 4 TURQUESA 5 TUQUESA 6 Nursing school USP Workshop 5: Demystifying and promoting the adherence of Clean Intermittent Catheterization
Injection of Urethral Bulking Agents
 Injection of Urethral Bulking Agents Department of Gynaecology Patient Information What are urethral bulking agents? Urethral bulking agents are substances that are injected to support the bladder neck.
Injection of Urethral Bulking Agents Department of Gynaecology Patient Information What are urethral bulking agents? Urethral bulking agents are substances that are injected to support the bladder neck.
Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed defaecation syndrome
 Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed Issued: June 2010 www.nice.org.uk/ipg351 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed Issued: June 2010 www.nice.org.uk/ipg351 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Paediatric Urotherapy Training
 Paediatric Urotherapy Training Frances Shit NS, MSc (Hons), ET, Dept. of Surgery, PWH, CUHK HKSAR Urinary Incontinence in Children Urine leakage in a child from 5 years of age Leakage occurs on a regular
Paediatric Urotherapy Training Frances Shit NS, MSc (Hons), ET, Dept. of Surgery, PWH, CUHK HKSAR Urinary Incontinence in Children Urine leakage in a child from 5 years of age Leakage occurs on a regular
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Index. Cyclical pelvic pain, 37 Cystocele, 22, 23, 25, 48, 51, 52, 54, 56, 124, 148, 160
 A Abdominal approach, 141 Abdominal hernia s surgery, 123, 124 Abdominal sacrocolpopexy (ASC), 116, 117 Abnormal uterine bleeding, 96 Anterior compartment repair, 101, 102 Apical compartment repair, 96
A Abdominal approach, 141 Abdominal hernia s surgery, 123, 124 Abdominal sacrocolpopexy (ASC), 116, 117 Abnormal uterine bleeding, 96 Anterior compartment repair, 101, 102 Apical compartment repair, 96
Urodynamics in women. Aims of Urodynamics in women. Why do Urodynamics?
 Urodynamics in women Chendrimada Madhu MD, MA, MRCOG Subspecialty Trainee in Urogynaecology Southmead Hospital 2013 Aims of Urodynamics in women n Confirmation of incontinence and its cause n Definition
Urodynamics in women Chendrimada Madhu MD, MA, MRCOG Subspecialty Trainee in Urogynaecology Southmead Hospital 2013 Aims of Urodynamics in women n Confirmation of incontinence and its cause n Definition
Tools for Evaluation. Urodynamics Case Studies. Case 1. Evaluation. Case 1. Bladder Diary SUI 19/01/2018
 Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
An Undergraduate Syllabus for Urology. Produced on behalf of the British Association of Urological Surgeons. March 2012
 An Undergraduate Syllabus for Urology Produced on behalf of the British Association of Urological Surgeons March 2012 Authors H Hashim, P Jones, KJ O Flynn, I Pearce, J Royle, M Shaw, AM Sinclair Correspondence
An Undergraduate Syllabus for Urology Produced on behalf of the British Association of Urological Surgeons March 2012 Authors H Hashim, P Jones, KJ O Flynn, I Pearce, J Royle, M Shaw, AM Sinclair Correspondence
PRACTICE BULLETIN Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery Volume 23, Number 4, July/August 2017
 PRACTICE BULLETIN Number 176, April 2017 (Replaces Committee Opinion Number 513, December 2011) Pelvic Organ Prolapse Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is a common, benign condition in women. For many women
PRACTICE BULLETIN Number 176, April 2017 (Replaces Committee Opinion Number 513, December 2011) Pelvic Organ Prolapse Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is a common, benign condition in women. For many women
NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS
 NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS Introduction The pelvic floor is highly complex structure made up of skeletal and striated muscle, support and suspensory ligaments, fascial coverings and an intricate
NEUROMODULATION FOR UROGYNAECOLOGISTS Introduction The pelvic floor is highly complex structure made up of skeletal and striated muscle, support and suspensory ligaments, fascial coverings and an intricate
A Strategy for Increasing Standards of Care in Female, Neurological and Urodynamic Urology
 British Association of Urological Surgeons Section of Female, Neurological and Urodynamic Urology A Strategy for Increasing Standards of Care in Female, Neurological and Urodynamic Urology Prepared by
British Association of Urological Surgeons Section of Female, Neurological and Urodynamic Urology A Strategy for Increasing Standards of Care in Female, Neurological and Urodynamic Urology Prepared by
LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR
 LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR Dr. R. K. Mishra Elements comprising the Pelvis Bones Ilium, ischium and pubis fusion Ligaments Muscles Obturator internis muscle Arcus tendineus levator ani or white
LAPAROSCOPIC REPAIR OF PELVIC FLOOR Dr. R. K. Mishra Elements comprising the Pelvis Bones Ilium, ischium and pubis fusion Ligaments Muscles Obturator internis muscle Arcus tendineus levator ani or white
Imaging of Pelvic Floor Weakness. Dr Susan Kouloyan-Ilic Radiologist Epworth Medical Imaging The Women s, Melbourne
 Imaging of Pelvic Floor Weakness Dr Susan Kouloyan-Ilic Radiologist Epworth Medical Imaging The Women s, Melbourne Outline Overview and Epidemiology Risk Factors, Causes and Results Review of Relevant
Imaging of Pelvic Floor Weakness Dr Susan Kouloyan-Ilic Radiologist Epworth Medical Imaging The Women s, Melbourne Outline Overview and Epidemiology Risk Factors, Causes and Results Review of Relevant
BEST PRACTICE ADVOCACY CENTRE NEW ZEALAND SCOPE. Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women
 BEST PRACTICE ADVOCACY CENTRE NEW ZEALAND SCOPE 1 Guideline title Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 2 Guideline Contextualisation This is a contextualisation
BEST PRACTICE ADVOCACY CENTRE NEW ZEALAND SCOPE 1 Guideline title Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 2 Guideline Contextualisation This is a contextualisation
Mr. GIT KAH ANN. Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur.
 Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment
 Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Incontinence. When I was given this topic in urology to discuss with you today I
 Incontinence When I was given this topic in urology to discuss with you today I was slightly disappointed. I personally see mostly men for problems such as stones, benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostate
Incontinence When I was given this topic in urology to discuss with you today I was slightly disappointed. I personally see mostly men for problems such as stones, benign prostatic hyperplasia, prostate
Motility Disorders. Pelvic Floor. Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 701) January 2010 November 2011
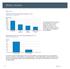 Motility Disorders Pelvic Floor Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 71) January 21 November 211 New Patients 35 3 25 2 15 1 5 Constipation Fecal Incontinence Rectal Prolapse Digestive-Genital
Motility Disorders Pelvic Floor Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 71) January 21 November 211 New Patients 35 3 25 2 15 1 5 Constipation Fecal Incontinence Rectal Prolapse Digestive-Genital
INCONTINENCE AND OTHER UROLOGICAL DILEMMAS DR. ANNA LAWRENCE UROLOGIST AUCKLAND HOSPITAL 161 UROLOGY
 INCONTINENCE AND OTHER UROLOGICAL DILEMMAS DR. ANNA LAWRENCE UROLOGIST AUCKLAND HOSPITAL 161 UROLOGY COVERING INCONTINENCE BE ON JUST NAPPIES CATHETERS TYPES AVAILABLE AND WHEN TO USE THEM JJ STENTS???
INCONTINENCE AND OTHER UROLOGICAL DILEMMAS DR. ANNA LAWRENCE UROLOGIST AUCKLAND HOSPITAL 161 UROLOGY COVERING INCONTINENCE BE ON JUST NAPPIES CATHETERS TYPES AVAILABLE AND WHEN TO USE THEM JJ STENTS???
NEUROGENIC BLADDER. Dr Harriet Grubb Dr Alison Seymour Dr Alexander Joseph
 NEUROGENIC BLADDER Dr Harriet Grubb Dr Alison Seymour Dr Alexander Joseph OUTLINE Definition Anatomy and physiology of bladder function Types of neurogenic bladder Assessment and management Complications
NEUROGENIC BLADDER Dr Harriet Grubb Dr Alison Seymour Dr Alexander Joseph OUTLINE Definition Anatomy and physiology of bladder function Types of neurogenic bladder Assessment and management Complications
