Understanding evidence and basic intermittent catheterisation techniques
|
|
|
- Jemima Benson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pocket guide for healthcare professionals Understanding evidence and basic intermittent catheterisation techniques CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 1 17/08/ :20
2 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 1 17/08/ :20
3 Understanding evidence and basic intermittent catheterisation (IC) techniques Pocket guide for healthcare professionals (HCP) Table of contents Introduction 2 Neurogenic bladder characteristics 3 Non-surgical management of chronic urinary retention 4 Evidence-based benefits of IC 5 Choosing catheters for IC 6 Uncoated and coated 6 IC best practice regimen 7 Applying best practice in IC 8 How to perform IC 9 Hand hygiene 9 Quick guide to IC 11 Risk of UTI 16 Overcoming barriers to IC 17 Patient-related concerns 17 Helping patients in wheelchairs to catheterise after discharge from hospital 18 Summary 19 Bibliography 20 1 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 1 17/08/ :20
4 Introduction This pocket guide briefly summarises the clinical evidence supporting the use of intermittent catheterisation (IC) in patients with chronic urinary retention in general and spinal cord injury (SCI) specifically. It provides an overview of information on how to perform the IC technique correctly and gives advice on the best ways to teach patients about IC. Topics you will need to discuss with your patients include the importance of healthy bladder management; the benefits of IC and the optimal IC regimen. You will also need to understand when IC should be used, how to assess the patient s home; and how to overcome barriers to effective IC practices. The use of IC is recommended by international guidelines and is considered the gold standard (the ideal option based on clinical evidence and best practice) for managing urinary incontinence in patients with chronic urinary retention. 1 The aim of IC is to: Restore continence Prevent urine retention Minimise the risk of urinary tract complications Healthy bladder management is essential to avoid long-term complications and can improve the person s physical health and quality of life (QoL). 2 You should use this pocket guide in conjunction with other Coloplast Care Education Programme materials. 2 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 2 17/08/ :20
5 Neurogenic bladder characteristics The term neurogenic bladder describes impaired function of the bladder and sphincters, caused by damage to nerves that control urination. SCI is a common cause of neurogenic bladder It is important that your patients with SCI regularly empty their bladders In patients who have an SCI above T6 an overfull bladder can trigger a rare, but potentially life-threatening, overactivity of the nervous system (known as autonomic dysreflexia). 3,4 Symptoms include headache, throbbing, sweating, nausea and red patches on the skin The main aims of neurogenic bladder management are to: 3 Re-establish continence Enhance QoL Allow better planning and control of bladder emptying Prevent urine retention Minimise the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs) and other complications Prevent kidney damage 3 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 3 17/08/ :20
6 Non-surgical management of chronic urinary retention Catheterisation is a non-surgical option for managing urinary retention. Techniques include IC, indwelling urethral and suprapubic catheterisation. 2 Guidelines regard IC as the gold standard for managing chronic urinary retention. 1,5 7 Table 1. Indications and contraindications for IC Indications for IC 7 Bladder capacity >200 ml Capable of adhering to the correct routine for bladder emptying using IC Sufficient hand dexterity and cognitive function Contraindications 1 Urethral abnormalities Acute infection of urogenital tract 4 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 4 17/08/ :20
7 Evidence-based benefits of IC IC is the safest method of bladder management for patients with chronic urinary retention, compared with alternative bladder management options, including indwelling catheterisation and suprapubic catheterisation. 8 Table 2. IC minimises urinary tract complications and can improve your patient s QoL 9 27 Providing relief from lower urinary tract symptoms Urgency, frequency and incontinence Urinary retention The need to wake up and urinate during the night Promoting independence Allowing the person to take control of their bladder and their life Removing the need to wear external appliances, such as indwelling catheters and drainage bags Reducing the risk of complications Urinary tract infections (UTIs) Urethral inflammation, trauma and bleeding Bladder and kidney stones Damage to their bladder and kidney Optimising lifestyle Increasing their ability to take part in social or sporting activities Increasing their sense of security, freedom, self-esteem Enhancing sexuality and fertility 5 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 5 17/08/ :20
8 Choosing catheters for IC There are a wide variety of catheters to choose from. If the patient is pleased with their choice of catheter they are more likely to continue using IC to drain the bladder and to do so regularly in accordance with recommendations. Therefore, it is important to take the time to find the right catheter for the individual patient; sometimes one patient may even need a selection of different catheters in order to fit catheterisation into their daily life. Uncoated and coated Catheters for IC can be broadly grouped into two main types: 1. Uncoated catheters requiring gel lubricant prior to use 2. Hydrophilic-coated catheters which can be divided into those that: Require an external water source to activate the surface lubrication Are pre-packaged in saline solution, so are ready to use anywhere A hydrophilic coating binds and absorbs water to form a smooth, slippery surface that helps insertion of the catheter Hydrophilic-coated catheters for IC are associated with fewer UTIs, compared with conventional uncoated catheters Hydrophilic-coated catheters are patients preferred option for IC 20, CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 6 17/08/ :20
9 IC best practice regimen Emphasis should be placed on motivating patients to establish and maintain a healthy bladder management regimen Establishing relationships with community HCPs can help your patients to maintain healthy bladder management when they are living at home Table 3. A healthy IC regimen Component Clean technique 10,35,36 Single-use hydrophilic-coated catheters 28 Repeat catheterisation 4 6 times a day 5,38 to maintain collected volumes of <400 ml 10,36 Use antibiotics sparingly to treat symptomatic UTIs 36 Patient education and follow-up 36 Reason Minimise risk of contamination and infection 36 Indwelling catheters are associated with UTIs and long-term complications 37 Less frequent catheterisation can lead to an overfull bladder and a build-up of pressure affecting the kidneys 11,39 More frequent catheterisations increase cross-infection risk 5,38 Asymptomatic bacteriuria is common in patients performing IC and does not justify the use of antibiotics 36 Patients experiencing recurrent UTIs should use a sterile technique To monitor progress with IC over the long-term and identify potential factors that may predict non-adherence 36 For further information see the Coloplast Care Education Programme training guide 7 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 7 17/08/ :20
10 Applying best practice in IC You should tell your patients about the benefits of IC. Restoring continence with this technique allows them to take control of their bladder management, provides them with a greater freedom to do what they want and helps to improve their overall QoL. Help your patients to make IC part of their daily routine. They could catheterise on waking up, at lunch time, at dinner time and at bedtime. Table 4. The three steps to explaining healthy bladder management 1. Why has my bladder changed? Explain how their bladder worked before Explain what s different with their bladder now Reassure your patient that there is a solution to their problem 2. Why IC? Explain the evidence supporting IC as the technique of choice Remember to use the Coloplast Care Education Programme materials, if you need more information 3. Optimal IC regimen Explain the benefits of good technique Tell them about the benefits of using IC Teach them how to perform IC correctly Help your patients to stay motivated as long as is required 8 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 8 17/08/ :20
11 How to perform IC During hospitalisation, guidelines recommend that you use a sterile IC technique on your patients. However, clean IC has been shown to be an effective and safe technique when patients perform IC themselves. 11,35,40 The following section shows you how to perform sterile IC. It also contains notes to discuss with your patient regarding the differences between sterile and clean IC. Hand hygiene Good hand hygiene is essential in IC to limit the risk of getting a UTI. The hand hygiene technique can be applied when washing your hands with soap and water, as well as when using a bactericidal alcohol scrub. The directions for hand hygiene when washing with soap and water are shown in Figure 1. Demonstrating this hand hygiene technique to your patients is important to minimise the risk of infection when they perform IC themselves. 9 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 9 17/08/ :20
12 Figure 1. The WHO hand hygiene technique with soap and water Wet hands with water Apply enough soap to cover all hand surfaces Rub hands palm to palm Right palm over left dorsum with interlaced fingers and vice versa Palm to palm with fingers interlaced Backs of fingers to opposing palms with fingers interlocked Rotational rubbing of left thumb clasped in right palm and vice versa Rotational rubbing, backwards and forwards with clasped fingers of right hand in left palm and vice versa Rinse hands with water Dry hands thoroughly with a single use towel Use towel to turn off faucet Your hands are now safe 'Based on the 'How to Handwash', URL: World Health Organization All rights reserved. 10 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 10 17/08/ :20
13 Quick guide to IC 1. Obtain informed patient consent. 2. Catheterisation can be carried out with the patient sitting on the toilet or in their wheelchair (if they are a wheelchair user) or lying on their back. Make sure that the patient is comfortable. Your patient s clothes and underwear should be lowered. Clean IC: Women When learning to catheterise themselves women will normally lie down. Female patients might find it helpful to attach a mirror to their thigh to help them see what they are doing. Men When performing IC themselves, men do not need to lie down. If sitting, they can use a pantler to hold their clothes in place during IC. 3. Make sure you have everything you need. Clean your hands thoroughly and follow the WHO hand hygiene technique (Figure 1). Place the wipes in the disinfectant. Clean IC: Patients do not need to use disinfectant, soap and water is fine. 4. Prepare the catheter and urine bag if needed. This step will differ depending on the type of catheter you use, either coated or uncoated. 11 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 11 17/08/ :20
14 Clean IC: When teaching your patients to catheterise, you should discuss the different sizes and lengths of catheter available. For a ready-to-use hydrophilic-coated catheter, place the catheter vertically within easy reach of the patient s bedside. Only peel the pouch open until you see all of the funnel connector For a hydrophilic-coated catheter, open the package and fill it with water. Place the catheter within easy reach of the patient s bedside. Wait the recommended amount of time to lubricate the catheter If required open the packaging of the urine bag Put on sterile non-latex gloves. 42 For an uncoated catheter, lubricate the tip of the catheter using a suitable lubricant jelly (Vaseline or mineral oils damage the catheter) Clean IC: When the patient performs clean IC themselves they will not need to use a pair of sterile gloves after washing their hands. You should remind your patients they should make sure their catheter is properly lubricated before they use it. 5. If needed, connect a urine bag to the funnel connector of the catheter and place the urine bag in a secure position. 12 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 12 17/08/ :20
15 Women 6. With your non-dominant hand separate the labia and locate the opening of the urethra. Use forceps or your gloved hand to take the wipes from the disinfectant. Drain any excess disinfectant and clean the labia with a single downward stroke. Use each wipe once. Clean IC: Patients can use soapy water or water alone to clean the labia and then clean the urethral opening with a single downward stroke. 7. Still keeping the labia apart take the catheter in your dominant hand and slowly insert the catheter into the opening of the urethra, 2 3 cm at a time until the urine starts to flow. Then insert the catheter a further 1 2 cm. Any non-sterile contact with the catheter means that the catheter should be exchanged for a new one. Clean IC: Remind your patients of the need to be careful and gentle when they perform clean IC. You will need to tell them how to insert and remove the catheter. 8. When the flow of urine stops, you can withdraw the catheter by 1 cm. If you are using a catheter with a straight tip rotate it before it is withdrawn further. This helps ensure complete emptying of the bladder. Continue to step CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 13 17/08/ :20
16 Men 6. Place a sterile drape under the penis. Hold and lift the penis using sterile gauze in your non-dominant hand and retract the foreskin (if present). Use forceps or your gloved hand to take the wipes from the disinfectant. Drain any excess disinfectant and clean the head and shaft of the penis. Clean the opening of the urethra with a downward stroke away from the urethra. Use each wipe once. Clean IC: Patients can use warm soapy water to clean the penis and then clean the urethral opening with a single outward stroke. They should remember to only use each wipe once. 7. Take the catheter in your dominant hand. Holding the penis at a 45 angle from the stomach, slowly insert the catheter into the opening of the urethra. Insert about 2 3 cm at a time until the urine starts to flow. Continue to carefully insert the catheter for a further 2 3 cm. You might meet some resistance when the catheter reaches the urethral sphincter and prostate. Any non-sterile contact with the catheter means that the catheter should be exchanged for a new one. 8. When the flow of urine stops, you can withdraw the catheter in small cm-by-cm steps. If you are using a catheter with a straight tip rotate it before it is withdrawn further. This helps ensure complete emptying of the bladder. Continue to step CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 14 17/08/ :20
17 9. Once the catheter has been removed you can dispose of it in the clinical waste. Clean the area around the opening of the urethra as previously described Wash your hands using the WHO hand hygiene technique (Figure 1) 41 Clean IC: Because patients do not wear gloves when performing clean IC, it is very important to remind them of the importance of good hygiene during the procedure. 10. Record the following information where relevant: Date and time Urine volume Catheter type, length and size Patient challenges (if they had any) HCP challenges (if you had any) Instructions adapted from EAUN guidelines 1 15 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 15 17/08/ :20
18 Risk of UTI Make sure your patients know how to reduce their risk of getting a UTI. The correct IC technique and frequency will minimise this risk. However, it is also important to tell your patients about the warning signs of a UTI (Figure 2). 43 If your patients understand the signs of an infection, it can be treated earlier. This reduces the risk of more serious complications. Figure 2. Risk factors (grey rectangles) and symptoms (blue squares) of UTIs in patients using IC Poor hygiene 44 Poor technique 38,45 Not catheterising 4 6 times per day 38 Continuing presence of blood in the urine Urethral discharge Rapid breathing and heart rate UTI Cloudy, dark or foul-smelling urine Fever and/ or chills Feeling tired, shaky or confused Vomiting 16 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 16 17/08/ :20
19 Overcoming barriers to IC Patient-related concerns Some patients will have concerns about starting IC. You can help reduce their anxiety by answering their questions clearly and giving them the relevant information which will in turn give them confidence. Table 5. Overcoming patient-related concerns The challenge The solution Patient worries about having insufficient help and support to overcome the problems they face 46 Patients fear of feeling pain or discomfort and the possibility of causing damage when they insert the catheter 46 Patients worry about loss of body image 46 Patients do not understand the benefits of IC Patients who are embarrassed by having a nurse of the opposite sex catheterise and train them Empower and encourage your patients at every step by giving them the right information when they need it Let them know they are not alone and that they can always ask you or other medical staff questions Let them know about the patient materials available as part of the Coloplast Care Education Programme Tell the patient about local and national spinal injury support groups Help and support patients who may be experiencing technical difficulties with IC Evidence shows us that the majority of patients find IC causes them no or minimal pain 19 and discomfort 34 IC can improve the person s self-esteem compared with other bladder management options 19 Use the information in this booklet to show them the benefits of IC IC is the best option for long-term health Reassure patients that the highest professional standards will be maintained and, if they prefer, arrange for a same sex nurse to carry out IC or train the patient Promote self-ic 17 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 17 17/08/ :20
20 Helping patients in wheelchairs to catheterise after discharge from hospital The homes of wheelchair users will often need to be adapted to make sure they are safe, comfortable and practical for them to live in. Each patient will have different needs and the changes must fit with how they want to live their lives. You will need to discuss these general changes with each individual. A checklist to help you and your patient think about some of the likely changes that may need to be made to their home and any issues they should consider is included in the Coloplast Care Education Programme training guide. Questions to discuss with your patient include: Where are they most likely to perform IC at home? Where will they keep their catheters at home? Where will they keep their catheters when they are not at home? Have they thought about where they will carry out IC when they are not at home? This will depend on how much privacy the patient feels they need Where will they dispose of their catheters when they are not at home or will they bring them home to dispose of? Have they thought about hygiene when they are not at home? Where will they get their supply of catheters from? Do they need someone to help them? Does their carer and/or family understand how to carry out IC? 18 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 18 17/08/ :20
21 Summary The use of IC is recommended by international guidelines and is considered the gold standard approach for managing chronic urinary retention. The benefits of IC are supported by clinical evidence. Adhering to the correct IC technique and frequency of catheterisations helps ensure that your patients can successfully maintain healthy long-term bladder management. It is important that you educate and motivate your patients to maintain healthy bladder management. You have a crucial role to play in helping your patients with chronic urinary retention to: Gain a better understanding of their condition Understand how to best manage their condition to minimise the risk of urinary tract complications Know how they can maintain a healthy bladder over time Understand the rationale for maintaining a healthy bladder management regimen To ensure you provide the right level of information to each patient and at the right time, it is important to assess factors such as your patient s standard of education and knowledge; cognitive function; emotional and functional status; personal and social environment; and personal priorities. 19 CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 19 17/08/ :20
22 Bibliography 1. Geng V, et al. European Association of Urology Nurses Benevento BT, Sipski ML. Phys Ther 2002;82(6): Merck. Neurogenic bladder. The Merck Manuals Online Medical Library for Healthcare Professionals 2007; Genitourinary Disorders Section. 4. Kewalramani LS. Am J Phys Med 1980;59(1): Stohrer M, et al. Eur Urol 2009;56(1): Royal College of Nursing. Catheter care: RCN guidance for nurses Consortium for Spinal Cord Medicine. J Spinal Cord Med 2006;29(5): Weld KJ, Dmochowski RR. J Urol 2000;163(3): Turi MH, et al. J Pak Med Assoc 2006;56(9): Bakke A, et al. Br J Urol 1997;79(1): Nazarko L. Br J Nurs 2009;18(2): Verpoorten C, Buyse GM. Pediatr Nephrol 2008;23(5): van Gool JD, et al. Monatsschr Kinderheilkd 1991;139(9): Chai T, et al. Paraplegia 1995;33(3): Vaidyananthan S, et al. Spinal Cord 1998;36(6): Getliffe K, et al. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs 2007;34(3): Robinson J. Nurs Stand 2007;21(29):48 56;quiz Esclarin De Ruz A, et al. J Urol 2000;164(4): Kessler TM, et al. Neurourol Urodyn 2009;28(1): Pascoe G, Clovis S. Br J Nurs 2001;10(5): Naik R, et al. Gynecol Oncol 2005;99(2): Oakeshott P, Hunt GM. Br J Gen Pract 1992;42(359): Wyndaele JJ, et al. Eur Urol 1980;6(2): Shaw C, et al. J Adv Nurs 2008;61(6): Igawa Y, et al. Int J Urol 2008;15(6): Pilloni S, et al. Age Ageing 2005;34(1): Luoto E, et al. Sairaanhoitaja 1993(1): De Ridder DJ, et al. Eur Urol 2005;48(6): Vapnek JM, et al. J Urol 2003;169(3): Cindolo L, et al. Urol Int 2004;73(1): CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 20 17/08/ :20
23 31. Diokno AC, et al. J Urol 1995;153(2): Sutherland RS, et al. J Urol 1996;156(6): van Kuppevelt HJM, et al. Poster presented at ISCoS. 2004;P Lopez Pereira P, et al. Actas Urol Esp 2001;25(10): Perrouin-Verbe B, et al. Paraplegia 1995;33(11): Bonniaud V, et al. Presse Med 2009;38(3): Chao R, et al. Urology 1993;42(3): Wyndaele JJ. Spinal Cord 2002;40(10): Jamison J, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2004(2):CD Wyndaele JJ. Spinal Cord 2002;40(9): World Health Organization. WHO guidelines on hand hygiene in health care. WHO Press, Geneva, Switzerland Newman DK. Nurs Manage 2009;40(7): Tenke P, et al. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2008;31: Neal DE, et al. Int Urogynecol J 1993;4(1): Shekelle PG, et al. J Spinal Cord Med 1999;22(4): van Achterberg T, et al. J Clin Nurs 2008;17(3): CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 21 17/08/ :20
24 Coloplast develops products and services that make life easier for people with very personal and private medical conditions. Working closely with the people who use our products, we create solutions that are sensitive to their special needs. We call this intimate healthcare. Our business includes ostomy care, urology and continence care and wound and skin care. We operate globally and employ more than 7,000 people. The Coloplast logo is a registered trademark of Coloplast A/S. [ ] All rights reserved Coloplast A/S, 3050 Humlebæk, Denmark. Coloplast A/S Holtedam Humlebæk Denmark CP_Intermittent catheterisation_training guide_a6 Pocket Guide_AW.indd 22 17/08/ :20
Instruction Guide to Sterile Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Men Using the Cure Catheter Closed System
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Instruction Guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization for Parents of Boys Using the Hydrophilic Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Instruction Guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization for Parents of Boys Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Men Using the Hydrophilic Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization. Nova Scotia Rehabilitation Centre
 2014 Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Nova Scotia Rehabilitation Centre Why do I need to do this? Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Your bladder may not empty completely when you go to the
2014 Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Nova Scotia Rehabilitation Centre Why do I need to do this? Intermittent Clean Self-Catheterization Your bladder may not empty completely when you go to the
Instruction Guide to Sterile Intermittent Catheterization For Parents of Girls Using the Cure Catheter Closed System
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Instruction Guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization for Parents of Girls Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Women Using the Extra Long Cure Medical Pocket Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Looking after your suprapubic catheter. Information for patients
 Looking after your suprapubic catheter Information for patients What is a suprapubic catheter? A catheter is a soft hollow tube, which is used to drain urine from the bladder. The catheter is inserted
Looking after your suprapubic catheter Information for patients What is a suprapubic catheter? A catheter is a soft hollow tube, which is used to drain urine from the bladder. The catheter is inserted
Sterile Intermittent Catheterization for Women
 INSTRUCTION GUIDE A note about our preferred catheter: Comfort Medical s preferred A note about our catheter is called the Cure preferred catheter: Catheter, manufactured by Cure Medical. Cure ofers irepolished
INSTRUCTION GUIDE A note about our preferred catheter: Comfort Medical s preferred A note about our catheter is called the Cure preferred catheter: Catheter, manufactured by Cure Medical. Cure ofers irepolished
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Women Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Achieving Independence
 Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization Achieving Independence Introduction This brochure is provided by Bard, a leading provider of urology products since 1907. The best
Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization Achieving Independence Introduction This brochure is provided by Bard, a leading provider of urology products since 1907. The best
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Women Using the Cure Twist
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Intermittent self-catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Spinal Injuries
 Intermittent self-catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Spinal Injuries page 2 of 12 What is clean intermittent self-catheterisation (CISC)? Urinary catheterisation is a procedure used to drain
Intermittent self-catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Spinal Injuries page 2 of 12 What is clean intermittent self-catheterisation (CISC)? Urinary catheterisation is a procedure used to drain
Wellness education. The basics of intermittent self-catheterization
 Wellness education The basics of intermittent self-catheterization Coloplast Consumer Care Advisors can assist you with your intimate healthcare needs. They are available Monday through Friday from 7 a.m.
Wellness education The basics of intermittent self-catheterization Coloplast Consumer Care Advisors can assist you with your intimate healthcare needs. They are available Monday through Friday from 7 a.m.
NHS GREATER GLASGOW & CLYDE CONTROL OF INFECTION COMMITTEE STANDARD OPERATING PROCEDURE (SOP) INSERTION & MAINTENANCE OF INDWELLING
 Page Page 1 of 6 AIM STATEMENT REQUIREMENTS LOCATION TIMING PROCEDURE To minimise the risk of secondary infection as a result of urinary catheterisation. A urinary catheter bypasses the body s normal defence
Page Page 1 of 6 AIM STATEMENT REQUIREMENTS LOCATION TIMING PROCEDURE To minimise the risk of secondary infection as a result of urinary catheterisation. A urinary catheter bypasses the body s normal defence
Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care
 Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care Table of Contents 1 What is a catheter?... 2 2 Why does the child need a catheter?... 2 3 Normal Urine... 2 4 How to do a clean urethral catheterization
Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care Table of Contents 1 What is a catheter?... 2 2 Why does the child need a catheter?... 2 3 Normal Urine... 2 4 How to do a clean urethral catheterization
Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC)
 Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
CLEAN INTERMITTENT SELF CATHETERISATION
 CLEAN INTERMITTENT SELF CATHETERISATION INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Catheter size :-... Regime:-......... Follow up appointment... UROLOGY SYDNEY Level 1, St George Medical Centre, 1 South Street, Kogarah
CLEAN INTERMITTENT SELF CATHETERISATION INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Catheter size :-... Regime:-......... Follow up appointment... UROLOGY SYDNEY Level 1, St George Medical Centre, 1 South Street, Kogarah
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls
 Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow
Guide for Use. Advance Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System
 Advance Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Hollister Advance Plus intermittent catheter features Touch Free technique enabling users to catheterize with confidence virtually anytime,
Advance Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Hollister Advance Plus intermittent catheter features Touch Free technique enabling users to catheterize with confidence virtually anytime,
Guide for Use. Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System
 Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Touch free, sterile, and self-contained, Hollister Apogee Plus intermittent catheter empowers you to maintain your independence and live
Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Touch free, sterile, and self-contained, Hollister Apogee Plus intermittent catheter empowers you to maintain your independence and live
Managing your suprapubic catheter
 Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Managing your suprapubic catheter What you need to know The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery. Not all of the content will apply to
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter
 Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter Equipment required collect prior to procedure Perform this procedure as an aseptic technique to minimise the risk of introducing Clean the
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of a supra pubic catheter Equipment required collect prior to procedure Perform this procedure as an aseptic technique to minimise the risk of introducing Clean the
CLEANINTERMITTENT CATHETERISATION FORFEMALES. PatientInformation ~~~ Canterbury. DistrictHealth Board. Te Poari Hauora (5Waitaha
 CLEANINTERMITTENT CATHETERISATION FORFEMALES PatientInformation ~~~ Canterbury DistrictHealth Board Te Poari Hauora (5Waitaha What is clean intermittent catheterisation? Clean intermittent catheterisation
CLEANINTERMITTENT CATHETERISATION FORFEMALES PatientInformation ~~~ Canterbury DistrictHealth Board Te Poari Hauora (5Waitaha What is clean intermittent catheterisation? Clean intermittent catheterisation
Catheter Passport. Guide for male and female patients and their carers. Please keep it safe.
 Catheter Passport Guide for male and female patients and their carers Please keep it safe. 20 1 Introduction The purpose of this booklet is to give you advice on looking after your urinary catheter. If
Catheter Passport Guide for male and female patients and their carers Please keep it safe. 20 1 Introduction The purpose of this booklet is to give you advice on looking after your urinary catheter. If
Guide for Use. Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System
 Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Touch free, sterile, and self-contained, Hollister Apogee Plus intermittent catheter empowers you to maintain your independence and live
Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Touch free, sterile, and self-contained, Hollister Apogee Plus intermittent catheter empowers you to maintain your independence and live
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Boys
 Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Boys What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow plastic
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Boys What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow plastic
ISC. (Intermittent self-catheterisation) Patient Information. Women and Children Gynaecology
 44 ISC (Intermittent self-catheterisation) Patient Information Women and Children Gynaecology The purpose of this leaflet is to give a brief explanation of what intermittent catheterisation is and how
44 ISC (Intermittent self-catheterisation) Patient Information Women and Children Gynaecology The purpose of this leaflet is to give a brief explanation of what intermittent catheterisation is and how
Experience the difference. GentleCath Hydrophilic Catheters Help reduce the risk of infection with no-touch catheterization 1 2
 Experience the difference GentleCath Hydrophilic Catheters Help reduce the risk of infection with no-touch catheterization 1 2 INTERMITTENT URINARY CATHETER TM Live the difference What is intermittent
Experience the difference GentleCath Hydrophilic Catheters Help reduce the risk of infection with no-touch catheterization 1 2 INTERMITTENT URINARY CATHETER TM Live the difference What is intermittent
Inserting Your Own Urinary Catheter Self-Catheterization Instructions for Women
 CCO/ Clker-Free-Vector-Images/Pixabay.com Inserting Your Own Urinary Catheter Self-Catheterization Instructions for Women Your family practitioner (family doctor or nurse practitioner) has told you that
CCO/ Clker-Free-Vector-Images/Pixabay.com Inserting Your Own Urinary Catheter Self-Catheterization Instructions for Women Your family practitioner (family doctor or nurse practitioner) has told you that
Stricture guide. Urology department. yeovilhospital.nhs.uk
 Stricture guide Urology department 01935 384 394 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is a urethral stricture? A urethral stricture is a narrowing or restriction of the urethra (the tube from your bladder through
Stricture guide Urology department 01935 384 394 yeovilhospital.nhs.uk What is a urethral stricture? A urethral stricture is a narrowing or restriction of the urethra (the tube from your bladder through
Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters
 Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters This leaflet provides you with information and instructions on caring for clients who have an indwelling
Information and instruction for Home Helps caring for clients with indwelling urinary catheters This leaflet provides you with information and instructions on caring for clients who have an indwelling
Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems
 If you require this leaflet in any other format, e.g., large print, please telephone 01935 384256 Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems Useful organisations Ms Society Helpline Tel: 0808 800
If you require this leaflet in any other format, e.g., large print, please telephone 01935 384256 Indwelling Urinary Catheters And Drainage systems Useful organisations Ms Society Helpline Tel: 0808 800
Types of Intermittent Catheters and Access to Urological Supplies
 Types of Intermittent Catheters and Access to Urological Supplies Anna Markiewicz; Sr Reimbursement Specialist Hollister Incorporated Lydia Cannady; Sr Product Manager Hollister Incorporated Why Catheterize?
Types of Intermittent Catheters and Access to Urological Supplies Anna Markiewicz; Sr Reimbursement Specialist Hollister Incorporated Lydia Cannady; Sr Product Manager Hollister Incorporated Why Catheterize?
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female)
 Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female) Refer to National Infection Prevention and Control Manual for information on aseptic technique/cleaning equipment. Equipment
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female) Refer to National Infection Prevention and Control Manual for information on aseptic technique/cleaning equipment. Equipment
Intermittent Self-Catheterization
 Intermittent Self-ization Create Medic Co.,Ltd. Marketing Department Suzuki Masaru If the bodily function emptying bladder, a physiological phenomenon in daily life, is impaired due to some kind of disease,
Intermittent Self-ization Create Medic Co.,Ltd. Marketing Department Suzuki Masaru If the bodily function emptying bladder, a physiological phenomenon in daily life, is impaired due to some kind of disease,
University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street. Urinary sheaths. Urology Directorate
 University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street Urinary sheaths Urology Directorate If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter, contact
University College Hospital at Westmoreland Street Urinary sheaths Urology Directorate If you would like this document in another language or format, or require the services of an interpreter, contact
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e. For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries
 B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
B l a d d e r & B o w e l C a r e For Patients with Spinal Cord Injuries 1 Bladder Specific Care Intermittent Catheterization (IC) is used to empty the bladder with a catheter. A catheter is a tube that
TOWN OF FAIRFIELD PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING
 TOWN OF FAIRFIELD PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING PROGRAM: School Health APPROVED BY: Board of Health School Medical Advisor POLICY & PROCEDURE: Clean Intermittent Catheterization DATE: 5/9/94 DEFINITION: POLICY
TOWN OF FAIRFIELD PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING PROGRAM: School Health APPROVED BY: Board of Health School Medical Advisor POLICY & PROCEDURE: Clean Intermittent Catheterization DATE: 5/9/94 DEFINITION: POLICY
Self Catheterisation for Men
 Intermittent Self Catheterisation for Men www.fittleworth.com Opening Hours: 8 am to 8 pm Monday to Friday 9 am to 1 pm Saturday National: 0800 378 846 Scotland: 0800 783 7148 Intermittent Self Catheterisation
Intermittent Self Catheterisation for Men www.fittleworth.com Opening Hours: 8 am to 8 pm Monday to Friday 9 am to 1 pm Saturday National: 0800 378 846 Scotland: 0800 783 7148 Intermittent Self Catheterisation
Designed for fast* and convenient cathing. * No additional waiting time once the catheter has been wetted
 Designed for fast* and convenient cathing * No additional waiting time once the catheter has been wetted Getting started For some men, starting intermittent catheterization or cathing can be a time of
Designed for fast* and convenient cathing * No additional waiting time once the catheter has been wetted Getting started For some men, starting intermittent catheterization or cathing can be a time of
Indwelling urinary catheter
 Indwelling urinary catheter Information for patients and carers RDaSH leading the way with care What is a catheter? A catheter is a hollow flexible tube designed to drain urine from the bladder. Following
Indwelling urinary catheter Information for patients and carers RDaSH leading the way with care What is a catheter? A catheter is a hollow flexible tube designed to drain urine from the bladder. Following
gentle catheter clip USER GUIDE optimum medical support optimummedical independence with confidence
 independence with confidence optimum medical support Have you visited the patient support area of our website? Designed to fix and support urethral and suprapubic catheters at the catheter bifurcation
independence with confidence optimum medical support Have you visited the patient support area of our website? Designed to fix and support urethral and suprapubic catheters at the catheter bifurcation
My urinary catheter passport DRAFT
 My urinary catheter passport Contents Personal information Purpose of the catheter passport Patient information Why do I need a catheter? Daily catheter care Leg bag care Healthy bladder and bowel Self-help
My urinary catheter passport Contents Personal information Purpose of the catheter passport Patient information Why do I need a catheter? Daily catheter care Leg bag care Healthy bladder and bowel Self-help
Achieving Independence. A Guide to Self-Catheterization with the Bard Touchless Plus Intermittent Catheter System
 Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization with the Bard Touchless Plus Intermittent Catheter System Achieving Independence Introducing the Bard Touchless Plus Catheter One
Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization with the Bard Touchless Plus Intermittent Catheter System Achieving Independence Introducing the Bard Touchless Plus Catheter One
User Appreciation of the VaPro Intermittent Catheter Characteristics and Packaging
 User Appreciation of the VaPro Intermittent Catheter Characteristics and Packaging B. Wachs 1, MD, I. Clesson 2, MSN, J. Perley 3, MD, F. Bernier 4, PhD, RNC, E. Livesley 4 1) Atlantic Urology Medical
User Appreciation of the VaPro Intermittent Catheter Characteristics and Packaging B. Wachs 1, MD, I. Clesson 2, MSN, J. Perley 3, MD, F. Bernier 4, PhD, RNC, E. Livesley 4 1) Atlantic Urology Medical
How to Change a. Foley catheter. Patient Education Rehabilitation Nursing. Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver
 Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives step-bystep instructions for changing a Foley catheter, which is a tube in your bladder to
Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives step-bystep instructions for changing a Foley catheter, which is a tube in your bladder to
Male and Female Catheterisation
 Male and Female Catheterisation Practical Skills Teaching Year 3 Medical Students MB BCh 2012-2013 Contents Introduction to workshop... 3 Overall Session Aim... 4 Intended Learning Outcomes... 4 Workshop
Male and Female Catheterisation Practical Skills Teaching Year 3 Medical Students MB BCh 2012-2013 Contents Introduction to workshop... 3 Overall Session Aim... 4 Intended Learning Outcomes... 4 Workshop
LoFric catheters: PROVING THEMSELVES DAY IN, DAY OUT. wellspect.com
 LoFric catheters: PROVING THEMSELVES DAY IN, DAY OUT wellspect.com LoFric catheters proven over time Introduced in 1983, LoFric was the world s first hydrophilic urinary catheter for clean intermittent
LoFric catheters: PROVING THEMSELVES DAY IN, DAY OUT wellspect.com LoFric catheters proven over time Introduced in 1983, LoFric was the world s first hydrophilic urinary catheter for clean intermittent
Patient Urinary Catheter Passport
 Useful contact details Name Contact Number Produced by Adapted from Worth by Michelle Pickering, Continence Specialist Practitioner Hambleton and Richmondshire Locality Continence Advisory Service and
Useful contact details Name Contact Number Produced by Adapted from Worth by Michelle Pickering, Continence Specialist Practitioner Hambleton and Richmondshire Locality Continence Advisory Service and
Intermittent catheterization for women. Easy for beginners. Great for long-term use. Right from. the start
 Intermittent catheterization for women. Easy for beginners. Great for long-term use. Right from the start Get it right from the start A good start to catheterization is vital for many reasons. Your bladder
Intermittent catheterization for women. Easy for beginners. Great for long-term use. Right from the start Get it right from the start A good start to catheterization is vital for many reasons. Your bladder
Ethan. H Activities H How - to Instructions for boys. H Story. Can Cath!
 Ethan Can Cath! H Story H Activities H How - to Instructions for boys Ethan and Emma's Field Trip By Angela Ruzicka Author of Wendy on Wheels Illustrated by Elizabeth Gearhart One day, Ethan and Emma s
Ethan Can Cath! H Story H Activities H How - to Instructions for boys Ethan and Emma's Field Trip By Angela Ruzicka Author of Wendy on Wheels Illustrated by Elizabeth Gearhart One day, Ethan and Emma s
Instruction For Use for All Silicon Foley Catheter
 General Description: All Silicone Foley Catheter for single use is a thin, is a flexible tube passed through the urethra and into the bladder to drain urine. It is the most common type of indwelling urinary
General Description: All Silicone Foley Catheter for single use is a thin, is a flexible tube passed through the urethra and into the bladder to drain urine. It is the most common type of indwelling urinary
Caring for your indwelling urinary catheter
 Caring for your indwelling urinary catheter Information for patients This information is produced by the Continence, Urology and Colorectal Service Leeds Community Healthcare NHS Trust Having a urinary
Caring for your indwelling urinary catheter Information for patients This information is produced by the Continence, Urology and Colorectal Service Leeds Community Healthcare NHS Trust Having a urinary
Bladder Management. Why is a Bladder Program so Important?
 Bladder Management A clear understanding of the principles and skills involved in bladder management will help you prevent complications such as a urinary tract infection. Before your injury, waste products
Bladder Management A clear understanding of the principles and skills involved in bladder management will help you prevent complications such as a urinary tract infection. Before your injury, waste products
Intermittent self catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Gynaecology
 Intermittent self catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Gynaecology page 2 of 8 What is ISC? Intermittent self catheterisation (ISC) is a simple technique where a narrow tube (catheter) is inserted
Intermittent self catheterisation (ISC) Information for patients Gynaecology page 2 of 8 What is ISC? Intermittent self catheterisation (ISC) is a simple technique where a narrow tube (catheter) is inserted
Teaching Intermittent Catheterisation. Liz Croxon Clinical Facilitator National Rehabilitation Hospital Dunlaoghaire
 Teaching Intermittent Catheterisation Liz Croxon Clinical Facilitator National Rehabilitation Hospital Dunlaoghaire Aim of Workshop To provide knowledge of the principles and practises of teaching a client
Teaching Intermittent Catheterisation Liz Croxon Clinical Facilitator National Rehabilitation Hospital Dunlaoghaire Aim of Workshop To provide knowledge of the principles and practises of teaching a client
Continence Promotion. CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS
 Continence Promotion. 1 CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS CHARACTERISTICS OF URINE 2 A liquid excrement consisting of water, salts, and urea, which is made in the kidneys then released through
Continence Promotion. 1 CATHETER CARE CONTINENCE CARE CONVEENS STOMAS CHARACTERISTICS OF URINE 2 A liquid excrement consisting of water, salts, and urea, which is made in the kidneys then released through
My urinary catheter passport
 My urinary catheter passport Please take your urinary catheter passport with you to all your healthcare appointments, on hospital admissions and when you travel. Emergency contact details: Special instructions
My urinary catheter passport Please take your urinary catheter passport with you to all your healthcare appointments, on hospital admissions and when you travel. Emergency contact details: Special instructions
Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know. A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury
 Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about managing your bladder After SCI, you may
Neurogenic Bladder: What You Should Know A Guide for People with Spinal Cord Injury Why Is This Information Important? Before SCI, you didn t have to think about managing your bladder After SCI, you may
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
Be you. with NEW LoFric Origo
 Be you with NEW LoFric Origo ac h. The one choice that is always k. g out. n. tio ca va. town n Out o n the Hangin O ho. me or be w the With friends. NEW LoFric Origo the catheter designed to make life
Be you with NEW LoFric Origo ac h. The one choice that is always k. g out. n. tio ca va. town n Out o n the Hangin O ho. me or be w the With friends. NEW LoFric Origo the catheter designed to make life
Self-Catheterization for Females
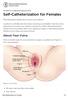 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Self-Catheterization for Females This information explains how to insert your catheter. A catheter is a flexible tube that drains urine from your bladder. Your doctor has
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Self-Catheterization for Females This information explains how to insert your catheter. A catheter is a flexible tube that drains urine from your bladder. Your doctor has
Intermittent Catheterisation
 Intermittent Catheterisation Your personal guide to Male Intermittent Catheterisation With over 35 years experience in the design, development and manufacture of medical devices, Flexicare has developed
Intermittent Catheterisation Your personal guide to Male Intermittent Catheterisation With over 35 years experience in the design, development and manufacture of medical devices, Flexicare has developed
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag
 Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder.
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder.
Self Dilatation. Intermittent. for Women. National: Scotland:
 Intermittent Self Dilatation for Women www.fittleworth.com Opening Hours: 8 am to 8 pm Monday to Friday 9 am to 1 pm Saturday National: 0800 378 846 Scotland: 0800 783 7148 Reason for using intermittent
Intermittent Self Dilatation for Women www.fittleworth.com Opening Hours: 8 am to 8 pm Monday to Friday 9 am to 1 pm Saturday National: 0800 378 846 Scotland: 0800 783 7148 Reason for using intermittent
Looking after your bladder
 Looking after your bladder A guide for men after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Regional Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people
Looking after your bladder A guide for men after spinal cord injury Spinal Cord Injury Regional Rehabilitation Program This booklet has been written by the health care providers who provide care to people
Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces
 Rationale Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces These guidelines are to provide the required information for designated registered nurses, health care assistants and bank support workers to perform
Rationale Guidelines for the Manual Evacuation of Faeces These guidelines are to provide the required information for designated registered nurses, health care assistants and bank support workers to perform
Indwelling Urinary Catheter Template for Care Plan Development Problem No: be a last resort when all suprapubic catheter in CAUTI
 Indwelling Urinary Catheter Template for Care Plan Development Problem No: Name: DOB Address: Indwelling Urinary Catheter (Urethral/ Suprapubic) Date Assessed Need GOAL INTERVENTION Evaluation of intervention/
Indwelling Urinary Catheter Template for Care Plan Development Problem No: Name: DOB Address: Indwelling Urinary Catheter (Urethral/ Suprapubic) Date Assessed Need GOAL INTERVENTION Evaluation of intervention/
sleeve leg bag holder
 independence with confidence optimum medical support Have you visited the patient support area of our website? It s been created to help you understand more about the procedures you experience, and the
independence with confidence optimum medical support Have you visited the patient support area of our website? It s been created to help you understand more about the procedures you experience, and the
NHS Urinary Catheter Passport
 South Sefton Care Home Innovation Programme (CHIP) PROTOCOL 07:Urinary Catheter Passport NHS Urinary Catheter Passport Information for patients and carers The passport is a hand held patient document for
South Sefton Care Home Innovation Programme (CHIP) PROTOCOL 07:Urinary Catheter Passport NHS Urinary Catheter Passport Information for patients and carers The passport is a hand held patient document for
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME
 CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
CARING FOR YOUR CATHETER AT HOME After surgery (radical prostatectomy) for prostate cancer you will have a urinary catheter for a short period of time and will need to go home with the catheter still in
Suprapubic and Mitrofanoff Catheter Care
 Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
Urinary catheters are tubes that drain urine from your child s bladder. There are many different types of urinary catheters. Your nurse will teach you how to care for these catheters. Here is information
Patient Urinary Catheter Passport
 Useful contact details: Continence Service (Community) 01724 298325 Continence Service (Goole) 01482 336951 Continence Service (SGH) 01724 282282 Ext 2823 Continence Service (DPOW) 01472 874111 Infection
Useful contact details: Continence Service (Community) 01724 298325 Continence Service (Goole) 01482 336951 Continence Service (SGH) 01724 282282 Ext 2823 Continence Service (DPOW) 01472 874111 Infection
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter
 Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
Catheter Care How to Care for a Urinary Catheter Ensure patient/client is provided with any available product specific instructions along with this booklet. About Your Catheter Your urinary catheter allows
CATHETER PASSPORT. Looking after your Urinary Catheter. The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter.
 CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
Your catheter. Information for patients and carers. NHS Grampian Continence Service
 Your catheter Information for patients and carers NHS Grampian Continence Service Healthcare professional details Name: Contact number:. GP: Telephone number: Reason for catheterisation:... Date of initial
Your catheter Information for patients and carers NHS Grampian Continence Service Healthcare professional details Name: Contact number:. GP: Telephone number: Reason for catheterisation:... Date of initial
Chapter 18. Assisting With Urinary Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 18 Assisting With Urinary Elimination The urinary system: The Urinary System Removes waste products from the blood Maintains the body s water balance 2 Normal Urination The healthy adult produces
Chapter 18 Assisting With Urinary Elimination The urinary system: The Urinary System Removes waste products from the blood Maintains the body s water balance 2 Normal Urination The healthy adult produces
Right from. the start. Intermittent catheterization for men. Easy for beginners. Great for long-term use.
 Right from the start Intermittent catheterization for men. Easy for beginners. Great for long-term use. Get it right from the start A good start to catheterization is vital for many reasons. Your bladder
Right from the start Intermittent catheterization for men. Easy for beginners. Great for long-term use. Get it right from the start A good start to catheterization is vital for many reasons. Your bladder
Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home
 Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South Tyneside and Sunderland. Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home The purpose
Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home Providing a range of NHS services in Gateshead, South Tyneside and Sunderland. Managing your bladder with a Supra-pubic catheter at home The purpose
Acknowledgement goes to WHO for use of their hand washing technique
 How to administer third party insulin injections safely with a pen device, safety pen needle and syringe 1 Hand washing It takes at least 15 seconds to wash your hands. This is about how long it takes
How to administer third party insulin injections safely with a pen device, safety pen needle and syringe 1 Hand washing It takes at least 15 seconds to wash your hands. This is about how long it takes
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Urinary System Diseases/Disorders. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Urinary System Diseases/Disorders LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Identify the purposes
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Urinary System Diseases/Disorders LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Identify the purposes
Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter
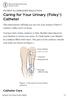 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Caring for Your Urinary (Foley ) Catheter This information will help you care for your urinary (Foley ) catheter while you re at home. You have had a Foley catheter (a thin,
limbsandthings.com Advanced Catheterisation Trainer User Guide For more skills training products visit Limbs & Things Ltd.
 Advanced Catheterisation Trainer Product No: 60150 User Guide For more skills training products visit limbsandthings.com Limbs & Things Ltd. Sussex Street, St Philips Bristol, BS2 0RA, UK sales@limbsandthings.com
Advanced Catheterisation Trainer Product No: 60150 User Guide For more skills training products visit limbsandthings.com Limbs & Things Ltd. Sussex Street, St Philips Bristol, BS2 0RA, UK sales@limbsandthings.com
Urinary Catheters. Prevalence of Infections
 Urinary Catheterisation Urinary catheterisation is defined as an intervention to enable the emptying of the bladder by insertion of a catheter. Catheters can be short term less than 28 days or long term
Urinary Catheterisation Urinary catheterisation is defined as an intervention to enable the emptying of the bladder by insertion of a catheter. Catheters can be short term less than 28 days or long term
The Urinary System. 1. Define important words in this chapter. 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system
 109 16 The Urinary System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system 3. Discuss changes in the urinary system due to aging 4. List normal qualities
109 16 The Urinary System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system 3. Discuss changes in the urinary system due to aging 4. List normal qualities
Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS
 Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS Information for Patients and Carers F:\CONTINENCE\Acute Urianary Retention\04-12\005- Indwelling Urinary Cathter Leaflet - A4-13-02-09.doc
Shropshire s Continence Advisory Service INDWELLING URINARY CATHETERS Information for Patients and Carers F:\CONTINENCE\Acute Urianary Retention\04-12\005- Indwelling Urinary Cathter Leaflet - A4-13-02-09.doc
My urinary catheter passport
 My urinary catheter passport Please take your urinary catheter passport with you to all your healthcare appointments, on hospital admissions and when you travel. Emergency contact details: Special instructions
My urinary catheter passport Please take your urinary catheter passport with you to all your healthcare appointments, on hospital admissions and when you travel. Emergency contact details: Special instructions
Intermittent Self-Catheterization. A Guide for Men and Women
 Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Men and Women 1986 2013 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon,
Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide for Men and Women 1986 2013 Contributors: Jennifer Skelly, Paula Eyles, Linda Hilts, Jane Worral, Linda Campbell & Janice North Artwork by: Elizabeth McMahon,
In addition to the indications stated above catheterisation may be carried out in female patients for two further reasons:
 Urinary Catheterisation This is the process of inserting a specially designed tube into the urinary bladder using an aseptic technique, for the purpose of draining urine, removing clots and/or debris and
Urinary Catheterisation This is the process of inserting a specially designed tube into the urinary bladder using an aseptic technique, for the purpose of draining urine, removing clots and/or debris and
Hand Hygiene. For everyone
 Hand Hygiene For everyone Preventing Infections Most infections that can be passed from person to person are passed on people s hands, either directly, from one person to another, or indirectly via contact
Hand Hygiene For everyone Preventing Infections Most infections that can be passed from person to person are passed on people s hands, either directly, from one person to another, or indirectly via contact
Urinary Catheter Passport SAMPLE COPY. A guide to looking after a urinary catheter. (for service users and healthcare workers) 2nd Edition
 Urinary Catheter Passport A guide to looking after a urinary catheter (for service users and healthcare workers) 2nd Edition Contact details Urinary Catheter Passport Service user Name Address Postcode
Urinary Catheter Passport A guide to looking after a urinary catheter (for service users and healthcare workers) 2nd Edition Contact details Urinary Catheter Passport Service user Name Address Postcode
WHAT TYPES OF CONTINENCE PRODUCTS ARE THERE?
 15 CAN HELP MANAGE WHAT ARE? Continence products help manage the symptoms of poor bladder and bowel control. They may be used for a short time during treatment. They can also be used long term if poor
15 CAN HELP MANAGE WHAT ARE? Continence products help manage the symptoms of poor bladder and bowel control. They may be used for a short time during treatment. They can also be used long term if poor
2.0 Scope All Cheshire services where the practice of intermittent urinary catheterisation occurs.
 Status: Standard Procedure: Specifies the procedures to be followed, only in exceptional circumstances should these not be followed. Page 1 of 5 Title: Standard Procedure for Intermittent Urinary Catheterisation
Status: Standard Procedure: Specifies the procedures to be followed, only in exceptional circumstances should these not be followed. Page 1 of 5 Title: Standard Procedure for Intermittent Urinary Catheterisation
Urinary Catheter Passport
 Urinary Catheter Passport Catheter Change Record and Looking After Your Urinary Catheter Please take this booklet with you if you are admitted to hospital or have an appointment Patient details Name Address
Urinary Catheter Passport Catheter Change Record and Looking After Your Urinary Catheter Please take this booklet with you if you are admitted to hospital or have an appointment Patient details Name Address
Implementing Clean Intermittent Catheterisation (CIC)
 Implementing Clean Intermittent Catheterisation (CIC) Julie Dicker (Spina Bifida CNC) Kids Rehab The Children s Hospital at Westmead Reasons for CIC: Neurogenic Bladder CIC is the gold standard for this
Implementing Clean Intermittent Catheterisation (CIC) Julie Dicker (Spina Bifida CNC) Kids Rehab The Children s Hospital at Westmead Reasons for CIC: Neurogenic Bladder CIC is the gold standard for this
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
My Urinary Catheter Passport Looking after my urinary catheter
 Feedback We welcome your comments. If you have any ideas about how we could do something better or feedback about positive aspects of the service please let us know. If you have a complaint please let
Feedback We welcome your comments. If you have any ideas about how we could do something better or feedback about positive aspects of the service please let us know. If you have a complaint please let
