Short-term evaluation of the adjustable bulbourethral male sling for post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence
|
|
|
- Megan Patterson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Received: 26 September 2017 Revised: 9 March 2018 Accepted: 23 April 2018 DOI: /luts ORIGINAL ARTICLE Short-term evaluation of the adjustable bulbourethral male sling for post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence Samer Shamout 1 Yu Qing Huang 2 Hani Kabbara 3 Jacques Corcos 1 Lysanne Campeau 1 1 Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Jewish General Hospital, McGill University, Montreal, Canada 2 Faculty of Medicine, McGill University, Montreal, Canada 3 StatRAC Statistical Research and Analysis Consultancy Firm, Montreal, Canada Correspondence Lysanne Campeau, Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Lady Davis Institute for Medical Research, McGill University, Jewish General Hospital, E959, 3755 C.te Ste- Catherine Road, Montreal, QC, Canada, H3T 1E2. lysanne.campeau@mcgill.ca Objective: The Argus perineal sling is a minimally invasive surgical option to treat postprostatectomy stress urinary incontinence (PPSUI). This study retrospectively evaluated the short-term clinical outcomes with the Argus sling for PPSUI management and determined the effects of potential preoperative parameters on intraoperative retrograde leak point pressure (RLPP). Methods: In this retrospective review of 16 men with various degrees of stress incontinence after prostatic surgery who underwent Argus sling, PPSUI was evaluated by pad usage, urodynamics, 24-hour pad weight, and validated questionnaires. Findings before and a minimum of 6 months after sling placement were compared. Cure was defined as no pad usage or the use of 1 pad for security; improvement was defined as a reduction in daily pad use by >50%. Results: After a mean (SD) follow-up of months, 62.5% of patients were cured, 18.75% were improved, and 18.75% were still incontinent. Preoperative 24-hour pad weight was positively correlated with RLPP (P =.0121, r = ). Mean RLPP was cmh 2 O. During follow-up, 44% of men had transient perineal or scrotal pain managed conservatively. Sling explantation, reported in 3 of 16 patients, was associated with urethral erosion or previous radiation therapy. Conclusion: The Argus male sling can lead to satisfactory results in carefully selected patients. Increased stress urinary incontinence severity based on 24-hour pad weight required higher RLPP to achieve continence. Favorable satisfaction variables and quality of life scores are affected by appropriate intraoperative tensioning pressure. KEYWORDS male sling, prostatectomy, urinary stress incontinence 1 INTRODUCTION Stress urinary incontinence (SUI) remains a major complication following radical prostatectomy despite improvements in surgical techniques and implementation of minimally invasive procedures. The reported incidence of SUI after prostate surgery is widely variable, ranging from <10% to >80%. 1,2 Surgical therapy is often required in patients who are persistently incontinent despite conservative treatment. Current surgical options include the artificial urinary sphincter (AUS), considered as the gold standard, and various commercially available male perineal slings. Even though AUS has well-recognized superior long-term outcomes, several patients would prefer a minimally invasive non-mechanical sling device. 3 Previous studies have shown that the Argus male perineal sling has good early results with a reasonably low complication rate, and that it could be an alternative surgical option for patients suffering from mild to moderate post-prostatectomy incontinence. 4,5 Adjustable bulbourethral male perineal slings do not require manipulation before voiding, making them an appealing surgical option. 6 In addition, the Argus sling system can have its tension adjusted intraoperatively or in follow-up clinic visits if outcomes of continence are not initially achieved. Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. 2018;1 6. wileyonlinelibrary.com/journal/luts 2018 John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd 1
2 2 SHAMOUT ET AL. To implement the Argus adjustable perineal sling system, surgeons have to consider the intraoperative retrograde leak point pressure (RLPP) for appropriate adjustment. An RLPP of cmh 2 Ois recommended by standards for male slings because it corresponds with the normal physiological pressure exerted on the urinary sphincter. 4,7,8 If the sling is not tightened enough, the patient may remain incontinent. Therefore, the optimal RLPP could be adjusted from measures of the severity of a patient s incontinence prior to the procedure. Herein we describe our experience at a single institution with the Argus male sling and evaluate its short-term efficacy and complication rates. In addition, we determined whether any preoperative parameters were predictive of the intraoperative RLPP. 2 METHODS 2.1 Population We conducted a retrospective chart review identifying all consecutive men who underwent a male Argus adjustable sling at Jewish General Hospital in Canada from February 2013 to August The study was approved by the ethics board of the tertiary care center in which it was conducted. The incontinence was a result of radical prostatectomy in all patients included, except 1 who underwent laser transurethral resection of the prostate. To be eligible for the study, patients had to have had mild to moderate SUI for more than 1 year after surgery. Incontinence severity in the present study was categorized on the basis of 24-hour pad weight, as described previously, 3 as mild Post Prostatectomy Incontinence (PPI) (<100 g/24 h), moderate ( g/24 h), or severe (>400 g/24 h). All patients had failed adequate trial of conservative management for 1 year (all patients had pelvic floor muscle training, with or without electrical stimulation therapy) and required more than 1 incontinence pad per day. Patients with urethral strictures or bladder neck contracture were excluded from the study, as well as those with bladder outlet obstruction or decreased compliance during urodynamic evaluation. All patients were informed regarding risks and benefits of both the Argus sling and AUS and offered the opportunity for AUS implantation as the gold standard treatment of post-prostatectomy SUI (PPSUI). Moreover, patients were instructed concerning the possibility of additional surgical procedures if they were still incontinent after device implantation. Information regarding all baseline characteristics and preoperative evaluation parameters was collected. The evaluation prior to implantation of the sling included a medical history, previous treatments for SUI, history of pelvic irradiation, physical examination, a urodynamic evaluation, a 24-hour pad weight, pad count, and a diagnostic cystoscopy of the bladder, bladder neck, and urethra. All patients were requested to complete validated questionnaires preoperatively and during follow-up. 2.2 Surgical procedure The Argus male perineal sling (Promedon, Cordoba, Argentina) was implanted by 2 experienced surgeons at 1 hospital, as described previously. 4 The Foley catheter was left in situ at the end of the procedure and removed the following morning. Patients are usually discharged from the hospital on Postoperative Day 1. In the current series, the adjustment pressure was manipulated intraoperatively for each subject using a simple standing column manometer and arterial line tubing. The Argus sling is gradually adjusted by tightening the silicone columns through the washers to achieve continence. Correct sling tension was arbitrated if cystoscopy demonstrated coaptation of the bulbar urethra with a discontinuation of water drip. To avoid persistent pain, urethral atrophy and erosion while maintaining efficacy, the sling was positioned with an RLPP in the range cmh 2 O. 2.3 Follow-up Postoperatively, patients were evaluated at 6 weeks, 6 months, 12 months, and yearly thereafter. The primary outcome was evaluated according to pad count over a 24-hour period at the last followup visit. Patients were categorized as either cured if they were not using any pads or were using 1 dry pad for security reasons or as improved if daily pad use was reduced by >50%. Otherwise, the procedure was classified as a treatment failure. Secondary efficacy outcomes were patient response scores on the Overactive Bladder Symptom Score (OABSS), International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire - Short Form (ICIQ-SF), and Incontinence Impact Questionnaire (IIQ-7) questionnaires. On the OABSS, scores can range from 0 to 28, with higher scores representing worse symptoms; 9 the ICIQ- SF is measured over the range 0 (minimal symptoms) to 21 (maximum symptoms); 10 and IIQ-7 scores range from 0 to 100, with higher scores representing worse quality of life (QoL). 11 All three tools are valid and reliable self-report questionnaires used to assess patients satisfaction and QoL. Postoperative complications and revision procedures were also recorded. 2.4 Statistical analysis For continuous data, data are presented as the mean SD. To assess outcomes, pre- and postoperative findings were compared using 2-tailed paired t-tests, with P <.05 taken to indicate significant improvements in a given parameter. No imputation was performed to replace missing values; patients with missing values were excluded from the regression analysis. Spearman s rank correlation was used to investigate univariate associations between continuous variables. Factors independently related to variability in RLPP and postoperative questionnaires scores were established through multiple stepwise regression analysis. Statistical analyses were performed using SAS v.9.2 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). 3 RESULTS 3.1 Patient characteristics In all, 16 male patients were identified with iatrogenic SUI treated with the male perineal sling Argus adjustable system. Mean patient age was 68 6 years (range years) and the mean follow-up duration was months (range 6 18 months). The vast
3 SHAMOUT ET AL. 3 TABLE 1 Patient characteristics majority of patients had mild (37.5%) or moderate (56.25%) incontinence at baseline; 1 patient had severe urinary incontinence. Mean 24-hour pad weight was 155 g (range g), whereas the mean number of pads used per day was 2.4 (range 1 6). Most (93.75%) of the patients included in the present study were incontinent after radical prostatectomy. The mean duration between prostatectomy and insertion of the Argus male sling was 3.2 years (range 1 16 years); of these men, 2 (12.5%) received radiotherapy for local recurrence of prostate cancer before sling implantation. One patient received intravesical Botox injections twice before implantation due to refractory detrusor overactivity (Table 1). Preoperative urodynamic data indicated normal maximal flow and post-void residual (PVR) values with efficient bladder emptying. Three patients (18.75%) had evidence of associated detrusor overactivity. The mean Valsalva leak point pressure (VLPP) and bladder capacity were cmh 2 O and 349 ml, respectively. 3.2 Efficacy outcomes No. patients 16 Age (y) Mean SD 68 6 Range Follow-up period (mo) Mean SD Range 6 18 Body mass index (kg/m 2 ) Mean SD 28 4 Range Prostatectomy Robotic radical prostatectomy 8 (50) Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy 4 (25) Retropubic radical prostatectomy 3 (19) TURP (laser) 1 (6) Previous pelvic irradiation 2 (13) No. pads used/d Mean SD 2.4 Range h pad weight (g) Mean SD Range Time between prostatectomy and sling procedure (y) Mean SD 3.2 Range 1 16 Previous treatment for incontinence a 1 (6) Pretreatment incontinence severity Mild (<100 g/24 h) 8 (50) Moderate ( g/24 h) 8 (50) Severe (>400 g/24 h) 0 (0) Unless indicated otherwise, data are given as the mean SD or as n (%). TURP, transurethral resection of the prostate. a Intravesical Botox injection. PPSUI are desired to determine the true clinical utility of RLPP in these patient populations when treated with an Argus sling system. 3.3 Safety There were no intraoperative complications reported in the patient cohort. The type and incidence of postoperative complications are Overall success rate (defined as patients who were cured and improved) was 87.5% at the first and second assessments 6 and 12 weeks postoperatively. Mean follow-up was 9.75 months (range 6 18 months). The success rate remained constant up to the 6-month follow-up. After this point 13 of 16 patients (81.25%) were noted as being cured or improved: 10 patients (62.5%) were completely dry (cured), 3 (18.75%) had a >50% reduction in daily pad usage (improved), and the procedure was considered a failure in 3 patients (18.75%). The mean pad count decreased from 2.4 (range 1 6) before surgery to 0.5 (range 0 2.5) at the last follow-up (P <.001). The success rates per degree of incontinence are shown in Figure 1. In terms of patient satisfaction and QoL, symptom scores indicated significant improvements in all questionnaires used. The baseline and postoperative outcomes are listed in Table 2. The sling was positioned at a mean intraoperative RLPP of cmh 2 O (range cmh 2 O). Only preoperative 24-hour pad weight was positively correlated with the RLPP attained to achieve continence (P =.0121, r = ). In contrast, body mass index (BMI; P =.558), age (P =.106), and VLPP (P =.1539) had no effect on RLPP. Simple and multiple linear regression analyses were performed to examine whether potential preoperative factors (age, BMI, 24-hour pad test, history of pelvic irradiation, previous incontinence treatment, satisfaction variables, VLPP, maximum cystometric capacity, and bladder compliance) contributed significantly to explain the variability in RLPP. In an attempt to overcome the small sample size, which resulted in the study being underpowered to identify predictive factors, a multiple linear regression model examining the predictive ability of pooled preoperative parameters was used, and showed that pretreatment pad weight with ICIQ-SF score were together significant predictors of the tension required intraoperatively during sling placement, as measured by RLPP (R 2 = 0.44; P =.032; Table 3). However, in the univariable analysis, neither pad weight nor questionnaire score were independent predictors of RLPP in this patient subset. Further studies with long-term data correlating RLPP with treatment outcomes for FIGURE 1 Overall success rate of the Argus sling and success rates stratified according to the degree of incontinence based on 24-h pad weight
4 4 SHAMOUT ET AL. TABLE 2 Efficacy outcomes following the placement of the Argus sling Preoperative At last follow-up ΔScore change (MID) Mean SD Range Mean SD Range P-value Mean SD Range Daily pad count <.001 ICIQ-SF score < IIQ-7 score < OABSS score < P-values were calculated using two-tailed t-tests. ICIQ-SF, International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire - Short Form; IIQ-7, Incontinence Impact Questionnaire; MID, minimum important difference; OABSS, Overactive Bladder Symptom Score. TABLE 3 Coefficients for linear regression models in which the dependent variable was retrograde leak point pressure Unstandardized coefficients Standardized coefficients Model β 95% CI β t R 2 P-value Predictors (constant) h pad weight , Preoperative ICIQ-SF score , ICIQ-SF, International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire - Short Form. given in Table 4. The most common complication was transient perineal or scrotal pain (44%); this complaint resolved within 4 6 weeks of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory treatment. The 3 sling explantations were performed because of infection associated with urethral erosion in 1 patient and because of failed treatment in the other 2 patients. After complete healing of the erosion following sling explantation, an AUS implantation was performed, which was also complicated by infection that necessitated device removal. Adjustment was necessary in 1 patient with an unsatisfactory outcome after a period of 100 days; this patient required sling tightening under local anesthesia, and the adjustment pressure was increased to 41 cmh 2 O. This patient had a history of pelvic irradiation and preoperative 24-hour pad weight of 311 g. Despite sling tension readjustment, the patient was still using 2 3 pads per day, compared with 4 before initial implantation of the sling. Eventually this patient was planned for AUS placement and sling removal. With regard to the 2nd patient with a poor outcome, at the 6-month follow-up this patient was still leaking urine and using 3 pads per day; he had reported a preoperative count of 4 pads per day and a 24-hour pad weight of 266 g, and his initial sling tightening pressure was 40 cmh 2 O. This patient was offered tension readjustment or AUS placement, but was later lost to follow-up. The mortality rate associated with Argus sling placement was 0%. 4 DISCUSSION Male continence is maintained primarily by the external rhabdosphincter converging around the membranous urethra, thereby preventing urinary leakage during stress maneuvers. Male slings use this concept by applying tension to create a slight, permanent urethral resistance to achieve continence. Considering the risk of overtensioning leading to pain and obstruction or undertensioning reducing the efficacy of the procedure, individualized optimization of intraoperative tensioning with RLPP may improve the success rate of male perineal slings. The TABLE 4 Postoperative complications after Argus sling implantation in the 16 patients in the present study Complication No. (%) Mild perineal or scrotal pain 7 (44) Revision for persistent SUI 2 (13) Erosion/infection 1 (6) De novo urge 1 (6) Total no. complications 11 (69) SUI, stress urinary incontinence. intraoperative RLPP measures the degree of tension placed on the urethra for optimal tensioning and subsequent adjustment. In the present study, several potential preoperative assessment variables were analyzed that may contribute to the prediction of the optimal intraoperative tensioning pressure. We demonstrated that a high 24-hour pad weight predicts more tension required to adjust the sling intraoperatively. This result needs to be interpreted with caution due to the study s small sample size and the lack of comparator group. Kumar et al. 3 recently reported that most patients (92%), when given a choice, prefer treatment with a non-mechanical device. In addition, the sling is much less expensive than the AUS, allowing the patient to maintain physiologic voiding. Therefore, an adjustable male sling is a valuable treatment option for mild to moderate PPSUI in patients who wish to avoid a mechanical device. Nevertheless, longterm randomized control trials are needed to prove long-term durability (8 10 years) of male perineal slings compared with the AUS. The lack of standard definitions for efficacy outcomes and severe PPSUI makes it challenging to compare results between studies. In 2009, Romano et al. 12 published long-term results after Argus male sling implantation, reporting a cure rate of 66% and a social continence rate of 79% after a minimum follow-up of 3 years. 12 In the Argus series by Hübner et al., 13 despite a cure rate of 79.2%, sling adjustment was necessary in almost 39% of patients. In their experience of 100 patients treated with the Argus sling system, Bochove- Overgaauw and Schrier 14 reported a cure rate of 54% after a median follow-up of 27 months. The sparse literature on the Argus sling
5 SHAMOUT ET AL. 5 system, with data on 278 patients and an average follow-up of 33 months, shows an overall cure rate ranging from 54% to nearly 79%; 15 despite best practices and a clear attempt to select appropriate patients, results still vary widely. This could be explained by the broad heterogeneity in study populations, definitions of outcome measures, and sling adjustment pressure. Furthermore, there was considerable variation in the rate of tension adjustments, ranging from 16% to 90%. 15 Another important aspect to be noted is the prior history of radiotherapy and/or refractory detrusor overactivity in the present study cohort, making careful patient selection of greatest importance. The functional effect of the Argus sling is created by a passive increase in intraurethral pressure, sufficient to achieve mucosal coaptation at cmh 2 O. 14 This is estimated from the voiding pressure required to overcome urethral resistance. Bladder contraction strength can be measured from the isometric detrusor contraction pressure (P iso ). The P iso needs to be greater or of equal to the RLPP set intraoperatively to overcome the resistance applied by a compressive sling. 16 This pressure can be simply adjusted by tightening or loosening the sling. The results of the present study indicate similar continence results compared with other male slings, such as the AdVance (AdVance, American Medical Systems, Minnetonka, MN, USA) transobturator male sling and the bone-anchored suburethral synthetic sling. 15,17 In a recent study, Hübner et al. 13 reported a mean sling tightening pressure of 37 cmh 2 O (range cmh 2 O) in a series of 101 patients, findings that are corroborated by the results for the present study cohort, as evidenced by a relatively parallel mean tightening pressure. The present study confirms the earlier efficacy results reported by Hübner et al. 13 of a 79.2% continence rate after a mean follow-up of 2.1 years, based on both the 20-minute pad-weight tests and Urinary Incontinence Quality of Life Scale (I-QoL) questionnaire scores that obviously improved compared with baseline (P <.001). Hübner et al. 13 also established that an average RLPP of 37 cm H 2 O is an appropriate degree of tension to avoid erosion and enable easier sling adjustment. In another study of 100 patients who received an Argus adjustable male sling for the treatment of SUI of varying degrees SUI, Bochove-Overgaauw and Schrier 14 reported an overall success rate (cure and improvement) of 72% after a median follow-up of 27 months and a 55% complication rate. Most complications were of Clavien Grade I II, with significant improvements of visual analog scale and in QoL. 14 In the present study, intraoperative RLPP >37 cm H 2 O led to more favorable patient-reported outcomes of the Argus sling based on ICIQ-SF scores (P <.05), but this result needs to be confirmed in a larger patient population, simultaneously with several validated subjective and objective assessment tools and a parallel comparative tension measurement technique. Hübner et al. 13 preferred a mean RLPP of 37 cmh 2 O, although they initially tightened the sling to 45 cmh 2 O. Until recently, the minimum tension pressure required to achieve continence and diminish adverse events remained a poorly understood component of the continence mechanism. The pressure required to achieve continence and avoid chronic perineal pain remains unknown. In the present study, a significantly higher intraoperative tension was required in patients with a more severe form of incontinence, as measured by 24-hour pad weight before implantation (P =.0121). This finding is in line with a number of previous studies. 19,20 This correlation may be related to surgeon bias, because knowing the severity of incontinence may lead the surgeon to achieve a higher RLPP intraoperatively. No statistically significant association was found for other factors evaluated. The results of the present study do not demonstrate a significant correlation between Abdominal leak point pressure (ALPP) and efficacy outcomes. Sanchez-Ortiz et al. 21 reported that ALPP has been useful in predicting treatment outcome of collagen injection for post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence. However, Nitti et al. 22 reported that ALPP is a relatively poor predictor for the actual evaluation of post-prostatectomy incontinence. In the present study, some patients were slightly more complex; 2 patients (13%) received pelvic irradiation, and another patient had 2 intravesical Botox injections (6%). These procedures could potentially affect efforts to achieve satisfactory results following any surgical intervention for SUI. Despite such challenges, the Argus sling succeeded with a continence rate of 81.25% at a mean follow-up of 9.75 months. We realize that the follow-up period in the present study is relatively short, but most failures were detectable within the first 3 6 months. A longer follow-up period is required to validate claims regarding the durability of the Argus sling. The small sample size is a limitation of the present retrospective study, as is the lack of a comparator group using a different sling tensioning technique. Urodynamic studies and 24-hour pad weight were performed only preoperatively for all patients included in the present study. Furthermore, we did not measure preoperative RLPP during the urodynamic assessment. These values would have been of interest to correlate with intraoperative RLPP prior to tensioning. Finally, in the literature, the Argus sling has been reported to have a mean success rate of only 71%, combined with high explant rate of 17%, over approximately 33 months of follow-up; therefore, it is probably not competitive to either the AUS or AdVance systems. 15 In conclusion, adjustable bulbourethral male slings could be a valuable option for treating male SUI and may be considered in carefully selected patients. Increased severity of SUI based on 24-hour pad weight was associated with a higher RLPP to achieve continence. Ultimately, intraoperative tensioning pressure was positively correlated with postoperative evaluation of patient satisfaction, based on ICIQ-SF results. Better patient selection and an appropriate degree of tension may lead to positive outcomes in this specific group of patients. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS None. Conflicts of interest None declared. ORCID Samer Shamout Lysanne Campeau
6 6 SHAMOUT ET AL. REFERENCES 1. Stanford JL, Feng Z, Hamilton AS, et al. Urinary and sexual function after radical prostatectomy for clinically localized prostate cancer: the Prostate Cancer Outcomes Study. JAMA. 2000;283: Goluboff ET, Saidi JA, Mazer S, et al. Urinary continence after radical prostatectomy: the Columbia experience. J Urol. 1998;159: Kumar A, Litt ER, Ballert KN, Nitti VW. Artificial urinary sphincter versus male sling for post-prostatectomy incontinence what do patients choose? J Urol. 2009;181: Romano SV, Metrebian SE, Vaz F, et al. An adjustable male sling for treating urinary incontinence after prostatectomy: a Phase III multicentre trial. BJU Int. 2006;97: Lim B, Kim A, Song M, Chun JY, Park J, Choo MS. Comparing Argus sling and artificial urinary sphincter in patients with moderate post-prostatectomy incontinence. J Exerc Rehabil. 2014;10: Comiter CV, Sullivan MP, Yalla SV. Correlation among maximal urethral closure pressure, retrograde leak point pressure, and abdominal leak point pressure in men with postprostatectomy stress incontinence. Urology. 2003;62: Herschorn S, Bruschini H, Comiter C, et al. Surgical treatment of stress incontinence in men. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010;29: Caremel R, Corcos J. Incontinence after radical prostatectomy: anything new in its management? Can Urol Assoc J. 2014;8: Blaivas JG, Panagopoulos G, Weiss JP, Somaroo C. Validation of the overactive bladder symptom score. The Journal of urology. 2007;178 (2): Avery K, Donovan J, Peters TJ, Shaw C, Gotoh M, Abrams P. ICIQ: a brief and robust measure for evaluating the symptoms and impact of urinary incontinence. Neurourology and urodynamics. 2004;23(4): Uebersax JS, Wyman JF, Shumaker SA, McClish DK. Short forms to assess life quality and symptom distress for urinary incontinence in women: the Incontinence Impact Questionnaire and the Urogenital Distress Inventory. Neurourology and urodynamics. 1995;14(2): Romano SV, Metrebian SE, Vaz F, et al. Long-term results of a Phase III multicentre trial of the adjustable male sling for treating urinary incontinence after prostatectomy: minimum 3 years. Actas Urol Esp. 2009;33: (in Spanish). 13. Hübner WA, Gallistl H, Rutkowski M, Huber ER. Adjustable bulbourethral male sling: experience after 101 cases of moderate-to-severe male stress urinary incontinence. BJU Int. 2011;107: Bochove-Overgaauw DM, Schrier BP. An adjustable sling for the treatment of all degrees of male stress urinary incontinence: retrospective evaluation of efficacy and complications after a minimal followup of 14 months. J Urol. 2011;185: Van Bruwaene S, De Ridder D, Van der Aa F. The use of sling vs sphincter in post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence. BJU Int. 2015; 116: Comiter CV, Dobberfuhl AD. The artificial urinary sphincter and male sling for postprostatectomy incontinence: which patient should get which procedure? Invest Clin Urol. 2016;57: Crivellaro S, Singla A, Aggarwal N, Frea B, Kocjancic E. Adjustable continence therapy (ProACT) and bone anchored male sling: comparison of two new treatments of post prostatectomy incontinence. Int J Urol. 2008;15: Cornu JN, Sebe P, Ciofu C, et al. The AdVance transobturator male sling for postprostatectomy incontinence: clinical results of a prospective evaluation after a minimum follow-up of 6 months. Eur Urol. 2009;56: Fischer MC, Huckabay C, Nitti VW. The male perineal sling: assessment and prediction of outcome. J Urol. 2007;177: Rehder P, Haab F, Cornu JN, Gozzi C, Bauer RM. Treatment of postprostatectomy male urinary incontinence with the transobturator retroluminal repositioning sling suspension: 3-year follow-up. Eur Urol. 2012;62: Sanchez-Ortiz RF, Broderick GA, Chaikin DC, et al. Collagen injection therapy for post-radical retropubic prostatectomy incontinence: role of Valsalva leak point pressure. J Urol. 1997;158: Twiss C, Fleischmann N, Nitti VW. Correlation of abdominal leak point pressure with objective incontinence severity in men with post-radical prostatectomy stress incontinence. Neurourol Urodyn. 2005;24: How to cite this article: Shamout S, Huang YQ, Kabbara H, Corcos J, Campeau L. Short-term evaluation of the adjustable bulbourethral male sling for post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence. Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. 2018; org/ /luts.12227
Deirdre M. Bochove-Overgaauw* and Bart Ph. Schrier
 An Adjustable Sling for the Treatment of All Degrees of Male Stress Urinary Incontinence: Retrospective Evaluation of Efficacy and Complications After a Minimal Followup of 14 Months Deirdre M. Bochove-Overgaauw*
An Adjustable Sling for the Treatment of All Degrees of Male Stress Urinary Incontinence: Retrospective Evaluation of Efficacy and Complications After a Minimal Followup of 14 Months Deirdre M. Bochove-Overgaauw*
AdVance Male Sling System
 AdVance Male Sling System Clinical study summary This document is a compilation and summary of several AdVance Male Sling System peer-reviewed journal articles. The information presented here is taken
AdVance Male Sling System Clinical study summary This document is a compilation and summary of several AdVance Male Sling System peer-reviewed journal articles. The information presented here is taken
Department of Urology, University Hospital Ulm, Prittwitzstrasse 43, D Ulm, Germany
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 304205, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/304205 Clinical Study The Retrourethral Transobturator Sling Suspension in the Treatment of
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 304205, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/304205 Clinical Study The Retrourethral Transobturator Sling Suspension in the Treatment of
I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling
 I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling The CL Medical I-STOP TOMS sling for male stress urinary incontinence was developed in France where it is widely used and is the market leader. It is constructed with
I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling The CL Medical I-STOP TOMS sling for male stress urinary incontinence was developed in France where it is widely used and is the market leader. It is constructed with
A transobturator adjustable system for male incontinence: 30-month follow-up of a multicenter study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 40 (6): 781-789, November - December, 2014 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.06.09 A transobturator adjustable system for male incontinence: 30-month follow-up of a multicenter study
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 40 (6): 781-789, November - December, 2014 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.06.09 A transobturator adjustable system for male incontinence: 30-month follow-up of a multicenter study
Urodynamic study before and after radical porstatectomy 가톨릭의대성바오로병원김현우
 Urodynamic study before and after radical porstatectomy 가톨릭의대성바오로병원김현우 Introduction Radical prostatectomy - treatment of choice for patients with localized prostate cancer. Urinary incontinence and/or
Urodynamic study before and after radical porstatectomy 가톨릭의대성바오로병원김현우 Introduction Radical prostatectomy - treatment of choice for patients with localized prostate cancer. Urinary incontinence and/or
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF POST-PROSTATECTOMY INCONTINENCE
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF POST-PROSTATECTOMY INCONTINENCE Arthi Satyanarayan, Ryan Mooney, *Nirmish Singla Department of Urology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas, USA *Correspondence
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF POST-PROSTATECTOMY INCONTINENCE Arthi Satyanarayan, Ryan Mooney, *Nirmish Singla Department of Urology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas, USA *Correspondence
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 56 (2009)
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 56 (2009) 923 927 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Platinum Priority Incontinence Editorial by Drogo K. Montague on pp. 934 935 of this issue
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 56 (2009) 923 927 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Platinum Priority Incontinence Editorial by Drogo K. Montague on pp. 934 935 of this issue
Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT
 Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT Hong Sup Kim Konkuk University TURP & MIT TURP : Gold standard MIT TUIP TUNA TUMT HIFU LASER Nd:YAG, ILC, HoLRP, KTP LUTS after TURP and MIT Improved : about 70% Persistent
Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT Hong Sup Kim Konkuk University TURP & MIT TURP : Gold standard MIT TUIP TUNA TUMT HIFU LASER Nd:YAG, ILC, HoLRP, KTP LUTS after TURP and MIT Improved : about 70% Persistent
Outcome and complications of adjustable continence therapy (ProACT ) after radical prostatectomy: 10 years experience in 143 patients
 Received: 16 August 2017 Accepted: 13 November 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23463 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Outcome and complications of adjustable continence therapy (ProACT ) after radical prostatectomy: 10
Received: 16 August 2017 Accepted: 13 November 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23463 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Outcome and complications of adjustable continence therapy (ProACT ) after radical prostatectomy: 10
Four-year follow-up on a Zephyr Surgical Implants 375 artificial urinary sphincter for male urinary incontinence from one urological centre in Poland
 320 O R I G I N A L P A P E R FUNCTIONAL UROLOGY Four-year follow-up on a Zephyr Surgical Implants 375 artificial urinary sphincter for male urinary incontinence from one urological centre in Poland Ireneusz
320 O R I G I N A L P A P E R FUNCTIONAL UROLOGY Four-year follow-up on a Zephyr Surgical Implants 375 artificial urinary sphincter for male urinary incontinence from one urological centre in Poland Ireneusz
Comparison of bone-anchored male sling and collagen implant for the treatment of male incontinence
 Blackwell Publishing AsiaMelbourne, AustraliaIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722006 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd???2006130012071211Original ArticleComparison of male sling and collagen implant
Blackwell Publishing AsiaMelbourne, AustraliaIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722006 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd???2006130012071211Original ArticleComparison of male sling and collagen implant
Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI Family Physiotherapy Centre of London
 Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI blandry@fpclondon.com Family Physiotherapy Centre of London Objectives To describe the scope of post-prostatectomy incontinence To describe what s been done To provide
Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI blandry@fpclondon.com Family Physiotherapy Centre of London Objectives To describe the scope of post-prostatectomy incontinence To describe what s been done To provide
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566
 Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion
 Are the Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion the Same for Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence with or without Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency? A Retrospective Study in Hong Kong
Are the Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion the Same for Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence with or without Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency? A Retrospective Study in Hong Kong
Impact of the Midurethral Sling Procedure on Quality of Life in Women with Urinary Incontinence
 www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.2.122 Voiding Dysfunction Impact of the Midurethral Sling Procedure on Quality of Life in Women with Urinary Incontinence Hwa Su Lim, Jong Min Kim, Phil Hyun Song,
www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.2.122 Voiding Dysfunction Impact of the Midurethral Sling Procedure on Quality of Life in Women with Urinary Incontinence Hwa Su Lim, Jong Min Kim, Phil Hyun Song,
The role of synthetic slings in male stress incontinence
 Arab Journal of Urology (2011) 9, 129 134 Arab Journal of Urology (Official Journal of the Arab Association of Urology) www.sciencedirect.com URODYNAMICS/FEMALE UROLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE The role of synthetic
Arab Journal of Urology (2011) 9, 129 134 Arab Journal of Urology (Official Journal of the Arab Association of Urology) www.sciencedirect.com URODYNAMICS/FEMALE UROLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE The role of synthetic
Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011
 Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 Treatment, Urinary Stress Incontinence, Transurethral Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0359 Revision Date: Code(s): 53860 Transurethral
Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 Treatment, Urinary Stress Incontinence, Transurethral Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0359 Revision Date: Code(s): 53860 Transurethral
REVIEW ARTICLE. Accepted for publication 21 April 2011
 BJUI REVIEW ARTICLE The male sling for post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence: a review of contemporary sling designs and outcomes Blayne K. Welk and Sender Herschorn Division of Urology, Sunnybrook Health
BJUI REVIEW ARTICLE The male sling for post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence: a review of contemporary sling designs and outcomes Blayne K. Welk and Sender Herschorn Division of Urology, Sunnybrook Health
Incontinence after radical prostatectomy: Anything new in its management?
 Original review research Incontinence after radical prostatectomy: Anything new in its management? Romain Caremel, MD; Jacques Corcos, MD, FRCSC Department of Urology, Jewish General Hospital, McGill University,
Original review research Incontinence after radical prostatectomy: Anything new in its management? Romain Caremel, MD; Jacques Corcos, MD, FRCSC Department of Urology, Jewish General Hospital, McGill University,
Introduction. Keywords Male urinary incontinence Artificial urinary sphincter Compressive adjustable slings
 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2523-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of adjustable male slings and artificial urinary sphincter in the treatment of male urinary incontinence: a retrospective analysis
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2523-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of adjustable male slings and artificial urinary sphincter in the treatment of male urinary incontinence: a retrospective analysis
Urodynamic findings in women with insensible incontinence
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
Tomonori Yamanishi,* Tomoya Mizuno, Miho Watanabe, Mikihiko Honda and Ken-Ichiro Yoshida
 Randomized, Placebo Controlled Study of Electrical Stimulation With Pelvic Floor Muscle Training for Severe Urinary Incontinence After Radical Prostatectomy Tomonori Yamanishi,* Tomoya Mizuno, Miho Watanabe,
Randomized, Placebo Controlled Study of Electrical Stimulation With Pelvic Floor Muscle Training for Severe Urinary Incontinence After Radical Prostatectomy Tomonori Yamanishi,* Tomoya Mizuno, Miho Watanabe,
Evaluating the impact of radiation therapy on patient quality of life following primary artificial urinary sphincter placement
 Original Article Evaluating the impact of radiation therapy on patient quality of life following primary artificial urinary sphincter placement Jason P. Joseph, Marcelino E. Rivera, Brian J. Linder, Boyd
Original Article Evaluating the impact of radiation therapy on patient quality of life following primary artificial urinary sphincter placement Jason P. Joseph, Marcelino E. Rivera, Brian J. Linder, Boyd
Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy. Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester
 Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester Themes Can we predict urinary morbidity? Prevention of urinary morbidity
Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester Themes Can we predict urinary morbidity? Prevention of urinary morbidity
Single institution experience with the transobturator sling suspension system AdVance in the treatment of male urinary incontinence: mid-term results
 Clinical Urology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (4): 488-494, July - August, 2011 Single institution experience with the transobturator sling suspension system AdVance in the treatment of male urinary
Clinical Urology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (4): 488-494, July - August, 2011 Single institution experience with the transobturator sling suspension system AdVance in the treatment of male urinary
Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh Repair: A Prospective Study of 105 Cases
 International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
Efficacy of High-frequency Magnetic Stimulation of the Sacral Root in Patients with Urinary Incontinence Following a Radical Prostatectomy
 LUTS (2011) 3, 10 14 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy of High-frequency Magnetic Stimulation of the Sacral Root in Patients with Urinary Incontinence Following a Radical Prostatectomy Nobuyuki KAI, 1 Masakazu
LUTS (2011) 3, 10 14 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy of High-frequency Magnetic Stimulation of the Sacral Root in Patients with Urinary Incontinence Following a Radical Prostatectomy Nobuyuki KAI, 1 Masakazu
Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence. Goals of presentation. Preoperative evaluation: Urodynamic Testing? Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D.
 Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence Goals of presentation Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D. Director of Urogynecology The Permanente Medical Group Kaiser, San Francisco Review preoperative care & evaluation
Operative Approach to Stress Incontinence Goals of presentation Michelle Y. Morrill, M.D. Director of Urogynecology The Permanente Medical Group Kaiser, San Francisco Review preoperative care & evaluation
Fan Zhang 1,2 and Limin Liao 1,2*
 Zhang and Liao BMC Urology (018) 18:3 DOI 10.1186/s1894-018-0314-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Artificial urinary sphincter implantation: an important component of complex surgery for urinary tract reconstruction
Zhang and Liao BMC Urology (018) 18:3 DOI 10.1186/s1894-018-0314-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Artificial urinary sphincter implantation: an important component of complex surgery for urinary tract reconstruction
Review Article Male Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Review of Surgical Treatment Options and Outcomes
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 287489, 13 pages doi:10.1155/2012/287489 Review Article Male Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Review of Surgical Treatment Options
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 287489, 13 pages doi:10.1155/2012/287489 Review Article Male Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Review of Surgical Treatment Options
q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE
 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 2 What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Urinary
493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 1 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT YOUR DIAGNOSIS OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE 493495.q7:480499_P0 6/5/09 10:23 AM Page 2 What is Stress Urinary Incontinence? Urinary
Efficacy of the InVance TM Male Sling in Men with Stress Urinary Incontinence
 european urology 51 (2007) 498 503 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Reconstructive Urology Efficacy of the InVance TM Male Sling in Men with Stress Urinary Incontinence
european urology 51 (2007) 498 503 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Reconstructive Urology Efficacy of the InVance TM Male Sling in Men with Stress Urinary Incontinence
Artificial urinary sphincter revision for urethral atrophy: comparing single cuff downsizing and tandem cuff placement
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 43 (2): 264-270, March - April, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0240 Artificial urinary sphincter revision for urethral atrophy: comparing single cuff downsizing and tandem
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 43 (2): 264-270, March - April, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0240 Artificial urinary sphincter revision for urethral atrophy: comparing single cuff downsizing and tandem
INJINTERNATIONAL. Original Article INTRODUCTION. Int Neurourol J 2017;21: pissn eissn
 Official Journal of Korean Continence Society / Korean Society of Urological Research / The Korean Children s Continence and Enuresis Society / The Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and
Official Journal of Korean Continence Society / Korean Society of Urological Research / The Korean Children s Continence and Enuresis Society / The Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and
Management of Post-Prostatectomy Urinary Incontinence and Sexual Dysfunction
 Management of Post-Prostatectomy Urinary Incontinence and Sexual Dysfunction Robert C. Eyre, MD, FACS Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery (Urology) Harvard Medical School Post-prostatectomy Incontinence
Management of Post-Prostatectomy Urinary Incontinence and Sexual Dysfunction Robert C. Eyre, MD, FACS Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery (Urology) Harvard Medical School Post-prostatectomy Incontinence
Post- prostatectomy Incontinence - PPI
 Post- prostatectomy Incontinence - PPI Dr. Kolombo Ivan, MD, FEBU Assoc.Prof. Popken Gralf MD, PhD, Assoc.Prof. Otčenášek Michal MD, PhD, Dr. Klézl Petr MD, MBA, Dr. Kolombová Jitka MD, MBA, Assoc.Prof.
Post- prostatectomy Incontinence - PPI Dr. Kolombo Ivan, MD, FEBU Assoc.Prof. Popken Gralf MD, PhD, Assoc.Prof. Otčenášek Michal MD, PhD, Dr. Klézl Petr MD, MBA, Dr. Kolombová Jitka MD, MBA, Assoc.Prof.
Practical urodynamics What PA s need to know. Gary E. Lemack, MD Professor of Urology and Neurology
 Practical urodynamics What PA s need to know Gary E. Lemack, MD Professor of Urology and Neurology Urodynamics essential elements Urethral catheter Fill rate Catheter size Intravesical pressure measurements
Practical urodynamics What PA s need to know Gary E. Lemack, MD Professor of Urology and Neurology Urodynamics essential elements Urethral catheter Fill rate Catheter size Intravesical pressure measurements
Detrusor underactivity is prevalent after radical prostatectomy: a urodynamic study including risk factors
 original research Detrusor underactivity is prevalent after radical prostatectomy: a urodynamic study including risk factors Doreen E. Chung, MD, FRCSC; * Benjamin Dillon, MD; Jordan Kurta, MD; Alexandra
original research Detrusor underactivity is prevalent after radical prostatectomy: a urodynamic study including risk factors Doreen E. Chung, MD, FRCSC; * Benjamin Dillon, MD; Jordan Kurta, MD; Alexandra
A.M.I. ATOMS System. Hydraulic system substitutes urinary sphincter function in incontinent males
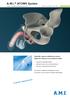 A.M.I. ATOMS System Product Group Urology Issue 11/2016 ATOMS = Adjustable TransObturator Male System Hydraulic system substitutes urinary sphincter function in incontinent males Long-term, adjustable
A.M.I. ATOMS System Product Group Urology Issue 11/2016 ATOMS = Adjustable TransObturator Male System Hydraulic system substitutes urinary sphincter function in incontinent males Long-term, adjustable
What should we consider before surgery? BPH with bladder dysfunction. Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Sung Luck Hee
 What should we consider before surgery? BPH with bladder dysfunction Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Sung Luck Hee Diagnostic tests in three categories Recommendation: there is evidence to support
What should we consider before surgery? BPH with bladder dysfunction Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Sung Luck Hee Diagnostic tests in three categories Recommendation: there is evidence to support
Urinary Adverse Events after Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer
 Urinary Adverse Events after Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Sexual Medicine Society of North America Scottsdale, Arizona 2016 Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial Sloan
Urinary Adverse Events after Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer Sexual Medicine Society of North America Scottsdale, Arizona 2016 Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial Sloan
Bard: Continence Therapy. Stress Urinary Incontinence. Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle.
 Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem and one that can be resolved by working
Bard: Continence Therapy Stress Urinary Incontinence Regaining Control. Restoring Your Lifestyle. Stress Urinary Incontinence Urinary incontinence is a common problem and one that can be resolved by working
Sep \8958 Appell Dmochowski.ppt LMF 1
 Surgical Outcomes (How did we get ourselves into this mess?) Roger R. Dmochowski, MD, FACS Department of Urologic Surgery Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Nashville, Tennessee Considerations Evaluation
Surgical Outcomes (How did we get ourselves into this mess?) Roger R. Dmochowski, MD, FACS Department of Urologic Surgery Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Nashville, Tennessee Considerations Evaluation
Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence
 Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Effective Date: December 21, 2016 Subject: Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Background: Urinary incontinence (the involuntary
Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Effective Date: December 21, 2016 Subject: Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Background: Urinary incontinence (the involuntary
Introduction/Learning Objectives. Incontinence: Natural History. Course Outline 10/14/2016. Urinary Incontinence: Conservative Measures
 Management of Urinary Complications after Prostatectomy Course Faculty: Introduction/Learning Objectives Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Associate Attending Urologist Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial Sloan
Management of Urinary Complications after Prostatectomy Course Faculty: Introduction/Learning Objectives Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Associate Attending Urologist Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial Sloan
A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes
 Neurourology and Urodynamics 19:127 135 (2000) A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes Asnat Groutz, Jerry G. Blaivas,* and Jarrod E. Rosenthal Weill Medical College,
Neurourology and Urodynamics 19:127 135 (2000) A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes Asnat Groutz, Jerry G. Blaivas,* and Jarrod E. Rosenthal Weill Medical College,
Conclusions. Keywords
 Functional Urology Outcomes of single- vs double-cuff artificial urinary sphincter insertion in low- and high-risk profile male patients with severe stress urinary incontinence Sascha A. Ahyai*, Tim A.
Functional Urology Outcomes of single- vs double-cuff artificial urinary sphincter insertion in low- and high-risk profile male patients with severe stress urinary incontinence Sascha A. Ahyai*, Tim A.
Long-term results of the implantation of the AMS 800 artificial sphincter for post-prostatectomy incontinence: a single-center experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 44 (1): 114-120, January - February, 2018 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0165 Long-term results of the implantation of the AMS 800 artificial sphincter for post-prostatectomy incontinence:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 44 (1): 114-120, January - February, 2018 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0165 Long-term results of the implantation of the AMS 800 artificial sphincter for post-prostatectomy incontinence:
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC
 PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC STUDIES: IS THERE VALUE IN PREDICTING POST-OPERATIVE STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN UNDERGOING PROLAPSE SURGERY? Dr K Janse van Rensburg Dr JA van Rensburg INTRODUCTION POP
PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC STUDIES: IS THERE VALUE IN PREDICTING POST-OPERATIVE STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN UNDERGOING PROLAPSE SURGERY? Dr K Janse van Rensburg Dr JA van Rensburg INTRODUCTION POP
Virtue male sling for post-prostatectomy stress incontinence: a prospective evaluation and mid-term outcomes
 Virtue male sling for post-prostatectomy stress incontinence: a prospective evaluation and mid-term outcomes Matteo Ferro*, Danilo Bottero*, Carolina D Elia, Deliu Victor Matei*, Antonio Cioffi*, Gabriele
Virtue male sling for post-prostatectomy stress incontinence: a prospective evaluation and mid-term outcomes Matteo Ferro*, Danilo Bottero*, Carolina D Elia, Deliu Victor Matei*, Antonio Cioffi*, Gabriele
Information for men considering a male sling procedure UHB is a no smoking Trust
 Information for men considering a male sling procedure UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Information for men considering a male sling procedure UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Urinary Incontinence Following Surgery for bph: the Role of Aging on the Incidence of Bladder Dysfunction
 Neurology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (3): 380-387, May - June, 2011 doi: 10.1590/S1677-55382011000300012 Urinary Incontinence Following Surgery for bph: the Role of Aging on the Incidence of Bladder
Neurology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (3): 380-387, May - June, 2011 doi: 10.1590/S1677-55382011000300012 Urinary Incontinence Following Surgery for bph: the Role of Aging on the Incidence of Bladder
Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary Retention
 Advances in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 797854, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/797854 Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary
Advances in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 797854, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/797854 Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary
Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence
 Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Patient Information English Glossary of terms Urinary Incontinence Anaesthesia (general, spinal, or local) Before a procedure you will get medication to make sure that you don t feel pain. Under general
Outcomes of Midurethral Slings in Women with Concomitant Preoperative Severe Lower Urinary Tract Voiding Symptoms
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH The Ochsner Journal 15:223 227, 2015 Ó Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Outcomes of Midurethral Slings in Women with Concomitant Preoperative Severe Lower Urinary Tract
ORIGINAL RESEARCH The Ochsner Journal 15:223 227, 2015 Ó Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Outcomes of Midurethral Slings in Women with Concomitant Preoperative Severe Lower Urinary Tract
A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence
 A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence Q: What is SUI? A: Stress urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary leakage of urine. The problem afflicts approximately 18 million
A PATIENT GUIDE TO Understanding Stress Urinary Incontinence Q: What is SUI? A: Stress urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary leakage of urine. The problem afflicts approximately 18 million
Suburethral sling at the time of radical prostatectomy in patients at high risk of postoperative incontinence
 Original Article IMMEDIATE SLING DURING RP IN HIGH-RISK PATIENTS WESTNEY et al. Suburethral sling at the time of radical prostatectomy in patients at high risk of postoperative incontinence O. LENAINE
Original Article IMMEDIATE SLING DURING RP IN HIGH-RISK PATIENTS WESTNEY et al. Suburethral sling at the time of radical prostatectomy in patients at high risk of postoperative incontinence O. LENAINE
The Safety and Efficacy of a New Adjustable Single Incision Sling for Treatment of Female. Stress Urinary Incontinence Through 12-months of Follow-up
 Manuscript (Submit in MS Word; include Title Page and Abstract; Tables and Figures should NOT be included but attached separately) Runninghead: ALTIS SINGLE INCISION SLING The Safety and Efficacy of a
Manuscript (Submit in MS Word; include Title Page and Abstract; Tables and Figures should NOT be included but attached separately) Runninghead: ALTIS SINGLE INCISION SLING The Safety and Efficacy of a
INJ. Original Article INTRODUCTION. Int Neurourol J 2010;14: doi: /inj pissn eissn
 Original Article Int Neurourol J 21;14:267-271 pissn 293-4777 eissn 293-6931 International Neurourology Journal The Influence of Preoperative Bladder Outlet Obstruction on Continence and Satisfaction in
Original Article Int Neurourol J 21;14:267-271 pissn 293-4777 eissn 293-6931 International Neurourology Journal The Influence of Preoperative Bladder Outlet Obstruction on Continence and Satisfaction in
Transcorporal artificial urinary sphincter in radiated and non - radiated compromised urethra. Assessment with a minimum 2 year follow-up
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (3): 494-500, May - June, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2015.0329 Transcorporal artificial urinary sphincter in radiated and non - radiated compromised urethra. Assessment
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (3): 494-500, May - June, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2015.0329 Transcorporal artificial urinary sphincter in radiated and non - radiated compromised urethra. Assessment
Effect of Transurethral Resection of the Prostate Based on the Degree of Obstruction Seen in Urodynamic Study
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.12.840 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection of the Prostate Based on the Degree of Obstruction Seen in Urodynamic
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.12.840 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection of the Prostate Based on the Degree of Obstruction Seen in Urodynamic
Predictors of Postoperative Voiding Dysfunction following Transobsturator Sling Procedures in Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Voiding Dysfunction INJ 2010;14:26-33 Predictors of Postoperative Voiding Dysfunction following Transobsturator Sling Procedures in Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence Sung-Tae Cho, Hyeong-Cheol
Voiding Dysfunction INJ 2010;14:26-33 Predictors of Postoperative Voiding Dysfunction following Transobsturator Sling Procedures in Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence Sung-Tae Cho, Hyeong-Cheol
UroToday International Journal. Volume 4 - June 2011
 UroToday International Journal Paulo Palma, 1 Cassio Riccetto, 1 Rodrigo Castro, 2 Sebastian Altuna, 3 Viviane Herrmann, 1 Ricardo Miyaoka 1 1 Division of Female Urology, State University of Campinas (UNICAMP),
UroToday International Journal Paulo Palma, 1 Cassio Riccetto, 1 Rodrigo Castro, 2 Sebastian Altuna, 3 Viviane Herrmann, 1 Ricardo Miyaoka 1 1 Division of Female Urology, State University of Campinas (UNICAMP),
Efficacy and safety of a readjustable midurethral sling (Remeex system) for stress urinary incontinence with female voiding dysfunction
 Original Article - Female Urology pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Efficacy and safety of a readjustable midurethral sling (Remeex system) for stress urinary incontinence with female voiding dysfunction
Original Article - Female Urology pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Efficacy and safety of a readjustable midurethral sling (Remeex system) for stress urinary incontinence with female voiding dysfunction
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics
 International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics COMMITTEE FOR UROGYNAECOLOGY AND PELVIC FLOOR MEMBER: TSUNG-HSIEN (CHARLES) SU, CHAIR (TAIWAN) DAVID RICHMOND, CO-CHAIR (UK) CHITTARANJAN PURANDARE,
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics COMMITTEE FOR UROGYNAECOLOGY AND PELVIC FLOOR MEMBER: TSUNG-HSIEN (CHARLES) SU, CHAIR (TAIWAN) DAVID RICHMOND, CO-CHAIR (UK) CHITTARANJAN PURANDARE,
Long-Term Outcome of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Female Urinary Incontinence: A 6-Year Follow-Up
 www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.6.409 Voiding Dysfunction Long-Term Outcome of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Female Urinary Incontinence: A 6-Year Follow-Up Jun Hyung Lee, Min Chul
www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2010.51.6.409 Voiding Dysfunction Long-Term Outcome of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Female Urinary Incontinence: A 6-Year Follow-Up Jun Hyung Lee, Min Chul
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control SURGERY TO TREAT URINARY INCONTINENCE AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is Urinary Incontinence? Urinary incontinence
BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control SURGERY TO TREAT URINARY INCONTINENCE AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is Urinary Incontinence? Urinary incontinence
UroToday International Journal. Volume 4 - February 2011
 UroToday International Journal Scott Serels, 1 Sandy B Nosseir, 2 Lawrence R Lind, 2 Harvey A Winkler 2 1 Bladder Control Center of Norwalk and Section of Urogynecology, Norwalk Hospital, Norwalk, CT,
UroToday International Journal Scott Serels, 1 Sandy B Nosseir, 2 Lawrence R Lind, 2 Harvey A Winkler 2 1 Bladder Control Center of Norwalk and Section of Urogynecology, Norwalk Hospital, Norwalk, CT,
Blue Ridge Urogynecology
 Surgery for Stress Urinary Incontinence Surgery has proved to be a very effective treatment for stress incontinence. The best surgical procedures improve or cure the incontinence in 85 to 90 percent of
Surgery for Stress Urinary Incontinence Surgery has proved to be a very effective treatment for stress incontinence. The best surgical procedures improve or cure the incontinence in 85 to 90 percent of
Post-prostatectomy Incontinence Initial Evaluation
 Post-prostatectomy Incontinence Initial Evaluation 2 Raveen Syan and Victor W. Nitti Post-prostatectomy Incontinence: Introduction Incidence Urinary incontinence is a relatively common complication following
Post-prostatectomy Incontinence Initial Evaluation 2 Raveen Syan and Victor W. Nitti Post-prostatectomy Incontinence: Introduction Incidence Urinary incontinence is a relatively common complication following
Resolution of urge urinary incontinence with midurethral sling surgery in patients with mixed incontinence and low-pressure urethra
 Gynecol Surg (2012) 9:427 432 DOI 10.1007/s10397-012-0735-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Resolution of urge urinary incontinence with midurethral sling surgery in patients with mixed incontinence and low-pressure
Gynecol Surg (2012) 9:427 432 DOI 10.1007/s10397-012-0735-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Resolution of urge urinary incontinence with midurethral sling surgery in patients with mixed incontinence and low-pressure
Fix your incontinence Find your happiness. Restore your normalcy. Renew your confidence. Male stress urinary incontinence
 Fix your incontinence Find your happiness. Restore your normalcy. Renew your confidence. Male stress urinary incontinence Understanding your condition What is incontinence? Incontinence is defined as any
Fix your incontinence Find your happiness. Restore your normalcy. Renew your confidence. Male stress urinary incontinence Understanding your condition What is incontinence? Incontinence is defined as any
Management of recurrent stress urinary incontinence and urinary retention following midurethral sling insertion in women
 UROLOGY doi 10.1308/003588412X13373405385610 Management of recurrent stress urinary incontinence and urinary retention following midurethral sling H Hashim 1, TR Terry 2 1 North Bristol NHS Trust, UK 2
UROLOGY doi 10.1308/003588412X13373405385610 Management of recurrent stress urinary incontinence and urinary retention following midurethral sling H Hashim 1, TR Terry 2 1 North Bristol NHS Trust, UK 2
The Significance of Beaking Sign on Cystography in Stress Urinary Incontinence 1
 The Significance of Beaking Sign on Cystography in Stress Urinary Incontinence 1 Jae Won Kim, M.D., Jeong Kon Kim, M.D., Seung Soo Lee, M.D., Yu-Ri Kahng, M.D., Myung-Soo Choo, M.D. 2, Kyoung-Sik Cho,
The Significance of Beaking Sign on Cystography in Stress Urinary Incontinence 1 Jae Won Kim, M.D., Jeong Kon Kim, M.D., Seung Soo Lee, M.D., Yu-Ri Kahng, M.D., Myung-Soo Choo, M.D. 2, Kyoung-Sik Cho,
Efficacy and Adverse Effects of Monarc Versus Tension-free Vaginal Tape Obturator: a Retrospective One-year Follow-up Study
 Efficacy and Adverse Effects of Monarc Versus Tension-free Vaginal Tape Obturator: a Retrospective One-year Follow-up Study Yvonne KY CHENG MBChB, MRCOG William WK TO MBBS, M Phil, FRCOG, FHKAM (O&G) HX
Efficacy and Adverse Effects of Monarc Versus Tension-free Vaginal Tape Obturator: a Retrospective One-year Follow-up Study Yvonne KY CHENG MBChB, MRCOG William WK TO MBBS, M Phil, FRCOG, FHKAM (O&G) HX
Outpatient mid-urethral tissue fixation system sling for urodynamic stress urinary incontinence: 3-year surgical and quality of life results
 Int Urogynecol J (2017) 28:1733 1738 DOI 10.1007/s00192-017-3341-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outpatient mid-urethral tissue fixation system sling for urodynamic stress urinary incontinence: 3-year surgical and
Int Urogynecol J (2017) 28:1733 1738 DOI 10.1007/s00192-017-3341-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outpatient mid-urethral tissue fixation system sling for urodynamic stress urinary incontinence: 3-year surgical and
Francesca Manassero, 1 * Cinzia Traversi, 1 Valeria Ales, 1 Donatella Pistolesi, 1 Erica Panicucci, 2 Francesca Valent, 3 and Cesare Selli 1
 Neurourology and Urodynamics 26:985 989 (2007) Contribution of Early Intensive Prolonged Pelvic Floor Exercises on Urinary Continence Recovery After Bladder Neck-Sparing Radical Prostatectomy: Results
Neurourology and Urodynamics 26:985 989 (2007) Contribution of Early Intensive Prolonged Pelvic Floor Exercises on Urinary Continence Recovery After Bladder Neck-Sparing Radical Prostatectomy: Results
Surgical treatment of post-prostatectomy stress urinary incontinence in adult men: Report from the 6th International Consultation on Incontinence
 Received: 18 July 2018 Accepted: 10 September 2018 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23845 REVIEW ARTICLE Surgical treatment of post-prostatectomy stress urinary incontinence in adult men: Report from the 6th International
Received: 18 July 2018 Accepted: 10 September 2018 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23845 REVIEW ARTICLE Surgical treatment of post-prostatectomy stress urinary incontinence in adult men: Report from the 6th International
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence. Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations
 The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
Tension-free Vaginal Tape for Urodynamic Stress Incontinence
 Long-term Results of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion for Urodynamic Stress Incontinence in Chinese Women at Eight-year Follow-up: a Prospective Study YM CHAN MBBS, MRCOG, FHKAM (O&G), DCG, DCH, DFM,
Long-term Results of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion for Urodynamic Stress Incontinence in Chinese Women at Eight-year Follow-up: a Prospective Study YM CHAN MBBS, MRCOG, FHKAM (O&G), DCG, DCH, DFM,
This information is intended as an overview only
 This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
This information is intended as an overview only Please refer to the INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE included with this device for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions and other important information
Urodynamics in women. Aims of Urodynamics in women. Why do Urodynamics?
 Urodynamics in women Chendrimada Madhu MD, MA, MRCOG Subspecialty Trainee in Urogynaecology Southmead Hospital 2013 Aims of Urodynamics in women n Confirmation of incontinence and its cause n Definition
Urodynamics in women Chendrimada Madhu MD, MA, MRCOG Subspecialty Trainee in Urogynaecology Southmead Hospital 2013 Aims of Urodynamics in women n Confirmation of incontinence and its cause n Definition
University of Alberta Reconstructive Urology Fellowship
 University of Alberta Reconstructive Urology Fellowship 1. Overview 2. Eligibility Requirements 3. Funding 4. Clinical Expectations 5. Academic Expectations 6. Objectives of Training 7. Teaching Methods
University of Alberta Reconstructive Urology Fellowship 1. Overview 2. Eligibility Requirements 3. Funding 4. Clinical Expectations 5. Academic Expectations 6. Objectives of Training 7. Teaching Methods
Leak point pressures: how useful are they?
 REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Leak point pressures: how useful are they? Helena Burden, Katherine Warren, and Paul Abrams Purpose of review The present article reviews the literature from the last 12 months
REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Leak point pressures: how useful are they? Helena Burden, Katherine Warren, and Paul Abrams Purpose of review The present article reviews the literature from the last 12 months
Jennifer Locke UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Resident Year 3 October 12, Learning Objectives
 Artificial Urinary Sphincter after 40 Years of Use: Indications, Techniques and Outcomes Jennifer Locke UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Resident Year 3 October 12, 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Identify
Artificial Urinary Sphincter after 40 Years of Use: Indications, Techniques and Outcomes Jennifer Locke UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Resident Year 3 October 12, 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Identify
Incidence and Risk Factors of Postoperative De Novo Voiding Dysfunction following Midurethral Sling Procedures
 Incidence and Risk Factors of Postoperative De Novo Voiding Dysfunction following Midurethral Sling Procedures Hoon Ah Jang, Jae Hyun Bae, Jeong Gu Lee From the Department of Urology, College of Medicine,
Incidence and Risk Factors of Postoperative De Novo Voiding Dysfunction following Midurethral Sling Procedures Hoon Ah Jang, Jae Hyun Bae, Jeong Gu Lee From the Department of Urology, College of Medicine,
Effects of the REMEEX System in Female Patients with Intrinsic Sphincteric Deficiency and Recurrent Urinary Incontinence: 3-Year Outcomes
 LUTS (2012) 4, 120 125 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of the REMEEX System in Female Patients with Intrinsic Sphincteric Deficiency and Recurrent Urinary Incontinence: 3-Year Outcomes Phil H. SONG, Chang H.
LUTS (2012) 4, 120 125 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of the REMEEX System in Female Patients with Intrinsic Sphincteric Deficiency and Recurrent Urinary Incontinence: 3-Year Outcomes Phil H. SONG, Chang H.
University of Alberta Reconstructive Urology Fellowship
 FACULTY OF MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY DIVISION OF UROLOGY Keith Rourke, MD, FRCSC Reconstructive Urology Professor Chair of Academic Urology Reconstructive Urology Fellowship Director
FACULTY OF MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY DIVISION OF UROLOGY Keith Rourke, MD, FRCSC Reconstructive Urology Professor Chair of Academic Urology Reconstructive Urology Fellowship Director
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 57 (2010)
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 57 (2010) 430 436 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Surgery in Motion Transrectal Ultrasound Guided Implantation of Adjustable Continence Therapy
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 57 (2010) 430 436 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Surgery in Motion Transrectal Ultrasound Guided Implantation of Adjustable Continence Therapy
Impact of urethral catheterization on uroflow during pressure-flow study
 Research Report Impact of urethral catheterization on uroflow during pressure-flow study Journal of International Medical Research 2016, Vol. 44(5) 1034 1039! The Author(s) 2016 Reprints and permissions:
Research Report Impact of urethral catheterization on uroflow during pressure-flow study Journal of International Medical Research 2016, Vol. 44(5) 1034 1039! The Author(s) 2016 Reprints and permissions:
Video-urodynamics. P J R Shah Institute of Urology and UCH
 Video-urodynamics P J R Shah Institute of Urology and UCH Bladder Function Storage Capacity and Pressure Emptying Pressure/flow/emptying URODYNAMIC INVESTIGATIONS Free urine flow rate Urethral pressure
Video-urodynamics P J R Shah Institute of Urology and UCH Bladder Function Storage Capacity and Pressure Emptying Pressure/flow/emptying URODYNAMIC INVESTIGATIONS Free urine flow rate Urethral pressure
Evidence Summary: The inflow Urinary Prosthesis FDA De Novo Approval DEN130044
 Evidence Summary: The inflow Urinary Prosthesis FDA De Novo Approval DEN130044 Unique alternative to urinary catheters for women with permanent urinary retention Therapeutic benefits o Highly effective
Evidence Summary: The inflow Urinary Prosthesis FDA De Novo Approval DEN130044 Unique alternative to urinary catheters for women with permanent urinary retention Therapeutic benefits o Highly effective
Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction.
 Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Posted online 2015.11.26 pissn 2005-6737 eissn 2005-6745 Urodynamic assessment of bladder and urethral function among men with lower urinary tract symptoms
Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Posted online 2015.11.26 pissn 2005-6737 eissn 2005-6745 Urodynamic assessment of bladder and urethral function among men with lower urinary tract symptoms
URINARY INCONTINENCE
 Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Center for Continence Care and Pelvic Medicine What is urinary incontinence? URINARY INCONTINENCE Urinary incontinence is the uncontrollable loss of urine. The amount of urine leaked can vary from only
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline
 Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion
Risk Factors of Voiding Dysfunction and Patient Satisfaction After Tension-free Vaginal Tape Procedure
 J Korean Med Sci 2005; 20: 1006-10 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Risk Factors of Voiding Dysfunction and Patient Satisfaction After Tension-free Vaginal Tape Procedure
J Korean Med Sci 2005; 20: 1006-10 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences Risk Factors of Voiding Dysfunction and Patient Satisfaction After Tension-free Vaginal Tape Procedure
Tools for Evaluation. Urodynamics Case Studies. Case 1. Evaluation. Case 1. Bladder Diary SUI 19/01/2018
 Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
