In the 1960s, silicone rubber was found to be less irritating
|
|
|
- Donald McKenzie
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proceedings of the ISPD 2006 The 11th Congress of the ISPD /07 $ August 25 29, 2006, Hong Kong Copyright 2007 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 27 (2007), Supplement 2 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. RATIONAL CHOICE OF PERITONEAL DIALYSIS CATHETER Roberto Dell Aquila, Stefano Chiaramonte, Maria Pia Rodighiero, Emilia Spano, Pierluigi Di Loreto, Catalina Ocampo Kohn, Dinna Cruz, Natalia Polanco, Dingwei Kuang, Valentina Corradi, Massimo De Cal, and Claudio Ronco Department of Nephrology, Dialysis, and Transplantation, St. Bortolo Hospital, Vicenza, Italy In the 1960s, silicone rubber was found to be less irritating to the peritoneal membrane than other plastics were, and in 1968, Tenckhoff and Schechter used a polyester-felt cuff to safely seal the catheter to the tissues, reducing the occurrence of leakage. This innovation was the most important in the history of peritoneal access devices. The Tenckhoff catheter became the gold standard of peritoneal access. Some of the original recommendations for catheter insertion such as an arcuate subcutaneous tunnel and downward direction of both the intraperitoneal and external exits are still considered very important elements of catheter implantation. From 1968 to the present time, many attempts have been made to reduce catheter-related complications such as displacement, catheter survival, cuff extrusion, leakage, exit-site infection, and peritonitis (Table 1); however, none of the devices currently used is troublefree. The peritoneal catheter should be a permanent and safe access to the peritoneal cavity. Catheter-related problems are often the cause of permanent transfer to hemodialysis (HD) in up to 20% of peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients; in some cases, these problems require a temporary period on HD. Advances in connectology have reduced the incidence of peritonitis, and so catheter-related complications during PD have become a major concern. In the last few years, novel techniques have emerged in the field of PD: new dialysis solutions, better connectology, and cyclers for automated PD. However, extracorporeal dialysis has continued to improve in terms of methods and patient survival, but PD has failed to do so. The main reason is that peritoneal access has remained problematical. The peritoneal catheter is the major obstacle to widespread use of PD. Overcoming catheter-related problems means giving a real chance to development of the peritoneal technique. Catheters should be as efficient, safe, and acceptable as possible. Since its introduction in the mid-1960s, the Tenckhoff catheter has not become obsolete: dozens of new models have been proposed, but none has significantly reduced the predominance of the first catheter. No convincing prospective data demonstrate the superiority of any peritoneal catheter, and so it seems that factors other than choice of catheter are what affect survival and complication rates. Efforts to improve peritoneal catheter survival and complication rates should probably focus on factors other than the choice of catheter. The present article provides an overview of the characteristics of the best-known peritoneal catheters. Perit Dial Int 2007; 27(S2):S119 S125 KEY WORDS: Peritoneal catheter; survival; peritonitis; continuous flow peritoneal dialysis; dislocation; exitsite infection; complications; catheter removal. Corresondence to: R. Dell Aquila, Department of Nephrology, Dialysis, and Transplantation, St. Bortolo Hospital, 37 Rodolfi Avenue, Vicenza Italy. roberto.dellaquila@ulssvicenza.it TABLE 1 The Most Commonly Used Catheters, by Inner and Outer Shaft Shape Straight and coiled Tenckhoff catheters Straight Straight with discs (TWH) Straight with weight (Di Paolo) Straight short (Vicenza Cath) Coiled Baloon (Valli) T-fluted (Ash) Swan-neck catheters Swan-neck abdominal catheters Swan-neck Tenckhoff straight and coiled Swan-neck Missouri straight and coiled Moncrief Popovich catheter Swan-neck presternal catheter Swan-neck Missouri catheter S119
2 PROCEEDINGS OF THE 11TH CONGRESS OF THE ISPD JUNE 2007 VOL. 27, SUPPL 2 PDI CHRONIC PERITONEAL CATHETERS Currently, the method of catheter placement has more effect on outcome than does choice of catheter (1). Four designs characterize the intraperitoneal portion of various catheters (2): Straight Tenckhoff, with an 8- or 16-cm portion containing side holes (the 16-cm with or without a 12-g tungsten weight at the tip) Coiled Tenckhoff, with a coiled 16-cm portion containing side holes Straight Tenckhoff, with perpendicular silicone discs [Toronto Western Hospital (TWH) or Oreopoulos Zellerman catheter] T-fluted catheter [Ash Advantage (Ash Advantage Technology, Lafayette, IN, U.S.A.)], a T-shaped catheter with grooved limbs positioned against the parietal peritoneum The subcutaneous portion of the catheter between the muscle wall and the skin exit site takes one of three basic shapes: Straight or straight with a gentle curve A permanent 150-degree bend or arc (swan-neck catheter) A permanent 90-degree bend, with another 90-degree bend at the peritoneal surface (Cruz catheter) Three positions and designs are seen for the polyester cuffs: Single cuff around the catheter, usually placed in the rectus muscle, but sometimes on the anterior surface of the rectus (depending on the procedure used to implant the catheter) Dual cuffs around the catheter, one in the rectus muscle and the other in subcutaneous tissue Disc-ball deep cuff, with parietal peritoneum and posterior rectus sheath sewn between a polyester disc and a silicone ball, and a second subcutaneous cuff (TWH and Missouri catheters) Adult PD catheters have three possible internal diameters, all with an outer diameter of approximately 5 mm (Figure 1): 2.6 mm, the standard size of the Tenckhoff catheter, swan-neck catheter, Missouri swan-neck catheter, and TWH catheter 3.1 mm (Cruz catheter) S120 A B C D Figure 1 Comparison of cross-sectional dimensions of the intraperitoneal portions of several peritoneal catheters. (A) Flex-Neck Tenckhoff catheter, silicone (Medigroup, Oswego, IL, U.S.A.); (B) Cruz Tenckhoff catheter, polyurethane; (C) Standard Tenckhoff catheter, silicone; (D) One intraperitoneal limb of the T-fluted catheter (Ash Advantage: Ash Advantage Technology, Lafayette, IN, U.S.A.), silicone. From S. Ash, with permission. 3.5 mm [Flex-Neck (Medigroup, Oswego, IL, U.S.A.) and Ash Advantage catheters] Two main materials are used in catheter construction: Silicone rubber (nearly all catheters) Polyurethane (Cruz catheter) A study by Nielson demonstrated a longer 3-year survival for coiled Tenckhoff catheters than for the straight models (3). If properly placed, dual-cuff Tenckhoff catheters have a lower incidence of exit-site infection and a longer lifespan than do single-cuff catheters (4). Coiled Tenckhoff catheters have a lower incidence of outflow failure than do straight catheters. Swan-neck catheters appear to have a lower incidence of exit-site infection than do those with straight subcutaneous segments (5). The Swan-Neck Presternal Catheter: The swan-neck presternal catheter is composed of two silicone rubber tubes joined by a titanium connector. The exit site is located in the parasternal area. The catheter location on the chest was designed to reduce the incidence of exit-site infection, and presternal catheters tend to perform better than swan-neck abdominal catheters do with regard to exit-site and tunnel infection. Useful in obese patients [body mass index (BMI) > 35], with rates of infectious complications and of survival superior to those of other catheters, the 2-year and 3-year survival rates of these catheters are 95% and 86% respectively. Recurrent peritonitis tends to be the only cause of failure. However, the implantation technique is more challenging than for single-piece abdominal catheters (6). The Ash Advantage Catheter: The Ash Advantage catheter (Figure 2) assures a stable position without extrusion of the deep cuff or exit-site erosion (7,8) and demonstrates a 1-year survival of 90%. During follow-
3 PDI JUNE 2007 VOL. 27, SUPPL 2 PROCEEDINGS OF THE 11TH CONGRESS OF THE ISPD Figure 2 The Ash Advantage catheter (Ash Advantage Technology, Lafayette, IN, U.S.A.). From S. Ash, with permission. up of 42 patients with Ash Advantage catheters in place for up to 4 years, only 1 patient developed a pericatheter leak and no patient developed a pericatheter hernia or late exit-site infection. The PD fluid outflow rate is, on average, equal to the best-functioning Tenckhoff catheters (including the large internal diameter Flex- Neck catheters). Negative aspects of the Ash Advantage catheter include a somewhat more complicated insertion procedure and a potential for blockage of the small openings between the fluted limbs and the central T-portion if the peritoneal fluid contains a considerable amount of blood or fibrin. The Ronco Catheter for Continuous Flow Peritoneal Dialysis: Continuous-flow PD (CFPD) may represent a new dialysis option, especially for patients with limited chances on standard continuous ambulatory PD or automated PD schedules. The CFPD technique permits an exploration of the effects of high-dose PD treatment with new and potentially beneficial effects (1,9 15). Double-lumen catheters with one short and one long branch in straight and spiral shapes were originally designed. Ash and coworkers designed a T-shape catheter to maximize the distance between the tips of the two lumens. Recently Ronco, Dell Aquila, Gloukhoff Wentling, Amerling, Cruz, and Levin designed a novel catheter for CFPD (16,17) with a double cuff and a thin-walled silicone diffuser to gently diffuse the inflow dialysate into the peritoneum. To eliminate the problem of recirculation, the diffuser design and hole locations (Figure 3) disperse the high-flow dialysate fluid at 360 degrees, reducing trauma to the peritoneal walls and allowing the dialysate to mix into the peritoneal cavity. The infused fluid so dispersed is then drained through the second lumen, whose tip is placed into the lower Douglas cavity. Additional design elements include a new tunnelizer and a removable hub with two spikes (adapted to the Figure 3 The Ronco catheter for continuous flow peritoneal dialysis. double-lumen cannula) to be applied after the catheter has been extracted from the skin through an adequate small hole. The results so far achieved seem to offer advantages in terms of high flows, minimal-pressure regimes, and negligible recirculation. This novel catheter was tested against other catheters to determine whether the new design had improved flow versus gravity and recirculation. Average recirculation was measured at 1.5%, and average flow at about 350 ml/min. The catheter was authorized for compassionate use in a 86-year-old man and produced encouraging results in terms of urea and creatinine clearances. Importantly, after its use in CFPD, this catheter can easily be used for automated PD by employing just one of the two lumens, suggesting that this catheter could theoretically be placed in every patient and be used for CFPD only when needed. The TWH Catheter: In a recent work by Sikaneta et al. (18), 192 patients receiving PD therapy with a TWH catheter were studied. With catheter removal being considered a failed or a censored event depending on whether the reason for the removal was peritonitis or another reason, the 1- and 3-year actuarial survival rates were and , and and respectively. No difference in the survival rate was observed between diabetic and non-diabetic patients, between men and women, and between patients older or younger than 65 years. A total of 349 catheter complications occurred during catheter months of follow-up. Two or more episodes of peritonitis were seen with 38 of the catheters. Recurrent, refractory, fungal, or tuberculous S121
4 PROCEEDINGS OF THE 11TH CONGRESS OF THE ISPD JUNE 2007 VOL. 27, SUPPL 2 PDI peritonitis led to the removal of 27 catheters. Two or more exit-site infections occurred with 26 of the catheters. A total of 67 catheters became obstructed, with 7 catheters developing obstructions more than once. After intervention failed to relieve an obstruction, 9 catheters had to be replaced; intervention was successful for the other 57 catheters. Malfunction was diagnosed and led to catheter replacement in 8 cases. The leaks that occurred in 5 catheters developed at an average of 30.9 months after catheter insertion. The authors concluded that most studies have shown results similar to those of TWH catheters (19,20). It therefore seems likely that factors other than catheter choice are what affect survival and complication rates. Indeed, the absence of convincing prospective data demonstrating superiority for any peritoneal catheter has led some authors to suggest that practical considerations such as cost or availability be the factors that govern catheter choice (21). The Self-Locating Catheter: The self-locating catheter, designed by Di Paolo, has been increasingly used in Italy and elsewhere since Currently, about a thousand patients are implanted with this catheter every year. Twelve grams of tungsten inserted in the tip of the conventional Tenckhoff catheter (Figure 4) keep the tip firmly in the Douglas cavity (22 25). A multicenter controlled study lasting 24 months was conducted in 16 Italian nephrology departments with 962 uremic patients on PD, 216 of whom (representing 2678 patient months) were implanted with Tenckhoff catheters and 746 of whom (representing 10,444 patient months) received self-locating catheters (26). The annual number of displacements, the catheter life in months, and the annual number of cuff extrusions, leakages, exit-site infections, peritonitis episodes, and peritoneal sclerosis events were assessed. The results showed a statistically significant reduction in displacements, peritonitis, tunnel infection, cuff extrusion, obstruction, and early and late leakage with the self-locating catheter. The Vicenza Short Peritoneal Catheter: The Vicenza catheter (Figure 5) is a modified double-cuff straight Tenckhoff catheter with a inner shaft 8 cm in length instead of the normal 15 cm (27,28). From 1985 until the end of 2005, our group implanted a total of 726 Vicenza catheters. In a recent study, 701 catheters were evaluated in terms of removal rate for infection, removal rate for infection in obese patients, catheter dislocation, body image acceptance, and catheter wearability (29). From among the 701 catheters, a prospective analysis was carried out on 233 catheters implanted during , with particular regard to catheter survival at 5 years. Catheter survival was 94.3% and 91.5% at 2 and 5 years respectively. This high survival rate is probably attributable to our meticulous attention to exit-site care and early antibiotic treatment of infections. Furthermore, to prevent major complications, routine ultrasound examination of the exit-site and subcutaneous tunnel are performed [Figure 6(a,b)]. From 1985 to 2005, annual infections per patient decreased to 0.2 from 0.7 and catheter removals per patient year decreased to 0.03 from These data demonstrate that promotion of good exit-site care is one of the most important factors in reducing the incidence of infectious complications and catheter removal (30). All patients with a BMI > 35 underwent catheter removal. An explanation may be that the subcutaneous cuff in these patients was located in fat tissue where the fibroblastic process is absent. For that reason, we recently modified the Vicenza catheter (Figure 7) to create a 20-cm distance between the two cuffs. To the time of writing, we had implanted only one of these new devices, Figure 4 Di Paolo self locating peritoneal dialysis catheter. S122 Figure 5 The Vicenza short catheter compared with the classical Tenckhoff.
5 PDI JUNE 2007 VOL. 27, SUPPL 2 PROCEEDINGS OF THE 11TH CONGRESS OF THE ISPD A B Figure 6 Ultrasound examination of the subcutaneous cuff of a Vicenza catheter in place: (A) longitudinal section; (B) cross section. Note the presence of hypo-echogenic areas. and more data are needed to determine if the modified catheter achieves longer survival in obese patients. In 1986, our 26 prevalent patients had a catheter dislocation rate of 22%; in 2005, we encountered only 4% displacements in 102 prevalent patients. Three years before the time of writing, we had evaluated 27 abdominal X-ray examinations of malfunctioning devices and observed that catheters with an exit site on the patient s left abdomen had a higher rate of migration (18/27) than did those with an exit site on the patient s right abdomen (9/27). In the latter cases of displacement, repositioning was easier after enhancement of peristalsis: the clockwise direction of the peristalsis helped to reposition the tip of the catheter. Figure 8(a,b) shows the best result we obtained. These findings explain the trend displayed over the last 3 years. Figure 7 Modified Vicenza catheter for obese patients: the distance between the cuffs is 20 cm. A B Figure 8 Abdominal X-ray of a displaced Vicenza catheter (A) before and (B) after enhancement of peristalsis (31). The exit site was placed on the patient s right side. S123
6 PROCEEDINGS OF THE 11TH CONGRESS OF THE ISPD JUNE 2007 VOL. 27, SUPPL 2 PDI Finally, we conducted a survey of patient satisfaction and quality of life: because of the catheter insertion position, patients declared good body image acceptance (98%) and excellent wearability (100%). CONCLUSIONS Even if certain catheter shapes have demonstrated better performance in terms of survival and reduction of displacements, peritonitis, tunnel infection, cuff extrusion, obstruction, and early and late leakage, none of the catheters discussed here and most commonly used in practice are completely free from complications. Some authors emphasize the importance of catheter design, but other conditions are probably leading to the reported complications. Special attention must be given to care of the catheter in the hospital and at home. Patients must be well trained in self-care and the medical and nursing staff must pay attention to the implantation technique, the construction of the tunnel and exit site, and the early care of catheter and exit site. REFERENCES 1. Gokal R, Alexander S, Ash S, Chen TW, Danielson A, Holmes C, et al. Peritoneal catheters and exit site practice: toward optimum peritoneal access: 1998 update. Perit Dial Int 1998; 18: Ash SR. Chronic peritoneal dialysis catheters: effects of catheter design, materials and location. Semin Dial 1990; 3: Nielsen PK, Hemmingsen C, Friis SU, Ladefoged J, Olgaard K. Comparison of straight and curled Tenckhoff peritoneal dialysis catheters implanted by percutaneous technique: a prospective randomized study. Perit Dial Int 1995; 15: Kim D, Burke D, Izatt S, Mathews R, Wu G, Khanna R, et al. Single- or double-cuff peritoneal catheters? A prospective comparison. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs 1984; 30: Eklund BH, Honkanen EO, Kala AR, Kyllonen LE. Peritoneal dialysis access: prospective randomized comparison of the swan neck and Tenckhoff catheters. Perit Dial Int 1995; 15: Twardowski ZJ. Presternal peritoneal catheter. Adv Ren Replace Ther 2002; 9: Ash SR, Janle EM. T-Fluted peritoneal dialysis catheter. Adv Perit Dial 1993; 9: Ash SR, Sutton JM, Mankus RA, Rossman J, de Ridder V, Nassvi MS, et al. Clinical trials of the T-fluted (Ash Advantage) peritoneal dialysis catheter. Adv Ren Replace Ther 2002; 9: Ronco C, Gloukhoff A, Dell Aquila R, Levin NW. Catheter design for continuous flow peritoneal dialysis. Blood Purif S ; 20: Cruz C, Melendez A, Gotch F, Folden T, Levin NW, Crawford T, et al. Continuous flow peritoneal dialysis (CFPD): preliminary clinical experience (Abstract). Perit Dial Int 2000; 20(Supp 1):S Raj DSC, Self M, Work J. Hybrid dialysis: recirculation peritoneal dialysis revisited. Am J Kidney Dis 2000; 36: Mineshima M, Suzuki S, Sato Y, Ishimori I, Ishida K, Kaneko I, et al. Solute removal characteristics of continuous recirculating peritoneal dialysis in experimental and clinical studies. ASAIO J 2000; 46: Diaz Buxo JA. Continuous flow peritoneal dialysis. Nephrol News Issues 2001; 15: Ronco C, Diaz Buxo JA. Automated peritoneal dialysis. Revisitation of the past or beginning of a new PD era? Nephron 2001; 87: Amerling R, Glezerman I, Savransky E, Dubrow A, Ronco C. Continuous flow peritoneal dialysis: current perspectives. Contrib Nephrol 2003; 140: Ronco C, Dell Aquila R, Bonello M, Gloukhoff A, Amerling R, Cruz C, et al. Continuous flow peritoneal dialysis: a new double lumen catheter. Int J Artif Organs 2003; 26: Ronco C, Wentling AG, Amerling R, Cruz C, Levin NW. New catheter design for continuous flow peritoneal dialysis. Contrib Nephrol 2004; 142: Sikaneta T, Cheung KM, Abdolell M, Tam P, Ting R, Fung J, et al. The Toronto Western Hospital catheter: one center s experience and review of the literature. Int J Artif Organs 2006; 29: Ortiz AM, Fernandez MA, Troncoso PA, Guzmán S, Del Campo F, Morales RA. Outcome of peritoneal dialysis: Tenckhoff catheter survival in a prospective study. Adv Perit Dial 2004; 20: Ash SR. Chronic peritoneal dialysis catheters: procedures for placement, maintenance, and removal. Semin Nephrol 2002; 22: Piraino B. Which catheter is the best buy? Perit Dial Int 1995; 15: Di Paolo N, Petrini G, Garosi G, Buoncristiani U, Berardi S, Monaci G. A new self-locating peritoneal catheter. Perit Dial Int 1996; 16: Di Paolo N, Gaggiotti E. The self-locating peritoneal catheter. Int J Artif Organs 2004; 27: Di Paolo N, Manganelli A, Strappaveccia F, De Mia M, Gaggiotti E. A new technique for insertion of the Tenckhoff peritoneal catheter. Nephron 1985; 40: Di Paolo N, De Mia M, Gaggiotti E, Capotondo L, Rossi P, Sansoni E. A simple and safe method of positioning the permanent peritoneal catheter. In: La Greca G, ed. Peritoneal Dialysis. Milan: Wichtig Editore; 1985: Di Paolo N, Capotondo L, Sansoni E, Romolini V, Simola M, Gaggiotti E, et al. The self-locating catheter: clinical experience and follow-up. Perit Dial Int 2004; 24: Tenckhoff H, Schechter H. A bacteriologically safe peritoneal access device. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs 1968;
7 PDI JUNE 2007 VOL. 27, SUPPL 2 PROCEEDINGS OF THE 11TH CONGRESS OF THE ISPD XIV: Chiaramonte S, Feriani M, Biasoli S, Bragantini L, Brendolan A, Dell Aquila R, et al. Clinical experience with short peritoneal dialysis catheters. Proc Eur Dial Transplant Assoc Eur Ren Assoc 1985; 22: Dell Aquila R, Chiaramonte S, Rodighiero MP, Di Loreto P, Spanò E, Nalesso F, et al. The Vicenza short peritoneal catheter: a twenty years experience. Int J Artif Organs 2006; 29: Dell Aquila R, Rodighiero MP, Bonello M, Ronco C. Conditions leading to catheter removal or substitution. Contrib Nephrol 2004; 142: Twardowski ZJ. Presternal peritoneal catheter. Adv Ren Replace Ther 2002; 9: S125
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australians with Renal Impairment. Guidelines
 6. Type of peritoneal dialysis Date written: February 2003 Final submission: May 2004 Guidelines No peritoneal dialysis has proven to be superior to the two cuff standard Tenckhoff in the prevention of
6. Type of peritoneal dialysis Date written: February 2003 Final submission: May 2004 Guidelines No peritoneal dialysis has proven to be superior to the two cuff standard Tenckhoff in the prevention of
6. Type of peritoneal dialysis catheter
 Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKNEPNephrology1320-53582004 Asian Pacific Society of NephrologyOctober 20049S3S59S64MiscType of peritoneal dialysis The CARI Guidelines NEPHROLOGY 2004; 9, S59 S64 Date written:
Blackwell Science, LtdOxford, UKNEPNephrology1320-53582004 Asian Pacific Society of NephrologyOctober 20049S3S59S64MiscType of peritoneal dialysis The CARI Guidelines NEPHROLOGY 2004; 9, S59 S64 Date written:
Presternal Catheter Design An Opportunity to Capitalize on Catheter Immobilization
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 26, 2010 Dale G. Zimmerman Presternal Catheter Design An Opportunity to Capitalize on Catheter Immobilization Effective immobilization of the peritoneal catheter has
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 26, 2010 Dale G. Zimmerman Presternal Catheter Design An Opportunity to Capitalize on Catheter Immobilization Effective immobilization of the peritoneal catheter has
Innovation in Technology II: Changed and Improved Design. PD Catheters- designs. Bharat Sachdeva MD LSU Shreveport
 Innovation in Technology II: Changed and Improved Design PD Catheters- designs Bharat Sachdeva MD LSU Shreveport What s at risk? Why Is Material/Design Important? Reduce risk for transfer to HD Displacement
Innovation in Technology II: Changed and Improved Design PD Catheters- designs Bharat Sachdeva MD LSU Shreveport What s at risk? Why Is Material/Design Important? Reduce risk for transfer to HD Displacement
II 12, 2017, 4:45-5:15 PM
 Page 1 Choosing the Most Appropriate PD Catheter by Preoperative Mapping PD Nursing Fundamentals II Sunday, March 12, 2017, 4:45-5:15 PM by John H. Crabtree, MD Since patients come in all sizes and shapes
Page 1 Choosing the Most Appropriate PD Catheter by Preoperative Mapping PD Nursing Fundamentals II Sunday, March 12, 2017, 4:45-5:15 PM by John H. Crabtree, MD Since patients come in all sizes and shapes
New Dimensions in Medical Technology
 New Dimensions in Medical Technology MEDIONICS INTERNATIONAL INC. Table of Contents Adult Tenckhoff... pg. 1 Paediatric Tenckhoff... pg. 2 Neonatal Tenckhoff... pg. 2 Adult Coil... pg. 3 Paediatric Coil...
New Dimensions in Medical Technology MEDIONICS INTERNATIONAL INC. Table of Contents Adult Tenckhoff... pg. 1 Paediatric Tenckhoff... pg. 2 Neonatal Tenckhoff... pg. 2 Adult Coil... pg. 3 Paediatric Coil...
Troubleshooting the Dysfunctional PD Catheter
 Troubleshooting the Dysfunctional PD Catheter ASDIN Annual Scientific Meeting Phoenix, Arizona February, 2014 Corporate Relationships in PD Area-Dr. Ash Developed Y-Tec System for placing PD catheters
Troubleshooting the Dysfunctional PD Catheter ASDIN Annual Scientific Meeting Phoenix, Arizona February, 2014 Corporate Relationships in PD Area-Dr. Ash Developed Y-Tec System for placing PD catheters
PERITONEOSCOPIC PLACEMENT OF THE TENCKHOFF CATHETER: FURTHER CLINICAL EXPERIENCE
 PERITONEOSCOPIC PLACEMENT OF THE TENCKHOFF CATHETER: FURTHER CLINICAL EXPERIENCE Stephen R. Ash*,*** Alan E. Handt** Richard Bloch*** SUMMARY In the past two and one-half years, 80 Tenckhoff peritoneal
PERITONEOSCOPIC PLACEMENT OF THE TENCKHOFF CATHETER: FURTHER CLINICAL EXPERIENCE Stephen R. Ash*,*** Alan E. Handt** Richard Bloch*** SUMMARY In the past two and one-half years, 80 Tenckhoff peritoneal
Money or Patient well-being
 John A. Navis President, Janin Group Inc john@janingroup.com TEL: 630-554-5533 CELL: 630-240-3710 Money or Patient well-being 2 3 4 Continual decisions by you and everyone involved focusing on the goal
John A. Navis President, Janin Group Inc john@janingroup.com TEL: 630-554-5533 CELL: 630-240-3710 Money or Patient well-being 2 3 4 Continual decisions by you and everyone involved focusing on the goal
02/27/2018. About half million people in the US with ESRD. HD is currently more prevalent than PD
 Anil S. Paramesh, MD, FACS Professor of Surgery, Urology and Pediatrics Tulane University School of Medicine Transplant Advisor, ESRD Network 13 First described in the 1920s Chronic PD initiated in 1960s
Anil S. Paramesh, MD, FACS Professor of Surgery, Urology and Pediatrics Tulane University School of Medicine Transplant Advisor, ESRD Network 13 First described in the 1920s Chronic PD initiated in 1960s
Hepatorenal Syndrome Treated for Eight Months with Continuous-Flow Peritoneal Dialysis
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 29, 2013 Elliot Charen, 1 Kobena Dadzie, 1 Nijal Sheth, 1 Hira Siktel, 1 Alan Dubrow, 1 Nikolas Harbord, 1 James Winchester, 1 Claudio Ronco, 2 Richard Amerling 1
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 29, 2013 Elliot Charen, 1 Kobena Dadzie, 1 Nijal Sheth, 1 Hira Siktel, 1 Alan Dubrow, 1 Nikolas Harbord, 1 James Winchester, 1 Claudio Ronco, 2 Richard Amerling 1
ASDIN 9th Annual Scientific Meeting
 Can Interventional Programs (IN) Help Popularize Home Dialysis Therapies? Gerald Beathard State of the Art Lecture ASDIN Washington, DC February 16, 2013 Stephen R. Ash, MD, FACP Indiana University Health
Can Interventional Programs (IN) Help Popularize Home Dialysis Therapies? Gerald Beathard State of the Art Lecture ASDIN Washington, DC February 16, 2013 Stephen R. Ash, MD, FACP Indiana University Health
This is the published version of a paper published in Medicine (Baltimore, Md.). Citation for the original published paper (version of record):
 http://www.diva-portal.org This is the published version of a paper published in Medicine (Baltimore, Md.). Citation for the original published paper (version of record): Stegmayr, B G., Sperker, W., Nilsson,
http://www.diva-portal.org This is the published version of a paper published in Medicine (Baltimore, Md.). Citation for the original published paper (version of record): Stegmayr, B G., Sperker, W., Nilsson,
Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Placement. Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Placement. Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Placement
 ASDIN Advanced Techniques Pre-course Feb. 24, 2012 New Orleans, La Randall L. Rasmussen, MD Special thank you to Drs. Rajeev Narayan, San Antonio, Tx and Hemant Dhingra, Fresno Ca for lending me slides
ASDIN Advanced Techniques Pre-course Feb. 24, 2012 New Orleans, La Randall L. Rasmussen, MD Special thank you to Drs. Rajeev Narayan, San Antonio, Tx and Hemant Dhingra, Fresno Ca for lending me slides
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 23, 2007
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 23, 2007 Antonios H. Tzamaloukas, 1,2 Aideloje Onime, 1,2 Dominic S.C. Raj, 2 Glen H. Murata, 1 Dorothy J. VanderJagt, 3 Karen S. Servilla 1,2 Computation of the Dose
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 23, 2007 Antonios H. Tzamaloukas, 1,2 Aideloje Onime, 1,2 Dominic S.C. Raj, 2 Glen H. Murata, 1 Dorothy J. VanderJagt, 3 Karen S. Servilla 1,2 Computation of the Dose
Strategies to Prevent Peritoneal Dialysis Failure
 Strategies to Prevent Peritoneal Dialysis Failure Constantinos J. Stefanidis, MD, PhD P & A Kyriakou Children s Hospital, Athens, Greece Technique failure Drop-out Transfer to HD Technique failure rate
Strategies to Prevent Peritoneal Dialysis Failure Constantinos J. Stefanidis, MD, PhD P & A Kyriakou Children s Hospital, Athens, Greece Technique failure Drop-out Transfer to HD Technique failure rate
The peritoneal equilibration test (PET) was developed THE SHORT PET IN PEDIATRICS. Bradley A. Warady and Janelle Jennings
 Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 27, pp. 441 445 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/07 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2007 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis THE SHORT PET IN PEDIATRICS
Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 27, pp. 441 445 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/07 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2007 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis THE SHORT PET IN PEDIATRICS
Adequate and permanent access to the peritoneal
 Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 23, pp. 242 248 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/03 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2003 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis EXPERIENCE USING PRESTERNAL
Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 23, pp. 242 248 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/03 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2003 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis EXPERIENCE USING PRESTERNAL
Mini-laparoscopic placement of peritoneal dialysis catheter: New technique
 Blackwell Publishing AsiaMelbourne, AustraliaASHSurgical Practice1744-1625 2006 The Authors; Journal compilation 2006 College of Surgeons of Hong Kong? 20071113640Surgical TechniqueMini-laparoscopic placement
Blackwell Publishing AsiaMelbourne, AustraliaASHSurgical Practice1744-1625 2006 The Authors; Journal compilation 2006 College of Surgeons of Hong Kong? 20071113640Surgical TechniqueMini-laparoscopic placement
5. Indications for the use of urokinase in peritoneal dialysis associated peritonitis
 5. Indications for the use of urokinase in peritoneal dialysis associated peritonitis Date written: February 2003 Final submission: July 2004 Guidelines (Include recommendations based on level I or II
5. Indications for the use of urokinase in peritoneal dialysis associated peritonitis Date written: February 2003 Final submission: July 2004 Guidelines (Include recommendations based on level I or II
Outcome of Immediate Use of the Permanent Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter in Children with Acute and Chronic Renal Failure
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Apr 2013; Vol 23 (No 2), Pp: 171-176 Outcome of Immediate Use of the Permanent Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter in Children with Acute and Chronic Renal Failure Ahmad-Ali Nikibakhsh,
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Apr 2013; Vol 23 (No 2), Pp: 171-176 Outcome of Immediate Use of the Permanent Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter in Children with Acute and Chronic Renal Failure Ahmad-Ali Nikibakhsh,
3/21/2017. Solute Clearance and Adequacy Targets in Peritoneal Dialysis. Peritoneal Membrane. Peritoneal Membrane
 3/21/2017 Solute Clearance and Adequacy Targets in Peritoneal Dialysis Steven Guest MD Director, Medical Consulting Services Baxter Healthcare Corporation Deerfield, IL, USA Peritoneal Membrane Image courtesy
3/21/2017 Solute Clearance and Adequacy Targets in Peritoneal Dialysis Steven Guest MD Director, Medical Consulting Services Baxter Healthcare Corporation Deerfield, IL, USA Peritoneal Membrane Image courtesy
Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
 Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS St George Hospital Renal Department, reviewed 2017 St George Hospital Renal Department RENAL SELF LEARNING PACKAGE INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL
Renal Self Learning Package INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL DIALYSIS St George Hospital Renal Department, reviewed 2017 St George Hospital Renal Department RENAL SELF LEARNING PACKAGE INTRODUCTION TO PERITONEAL
Fistula First? Vascular Symposium 4/28/18
 Fistula First? Vascular Symposium 4/28/18 Disclosure I have no financial interest to disclose connected to any of the information presented in this discussion Objectives Scope of Problem Benefits of PD
Fistula First? Vascular Symposium 4/28/18 Disclosure I have no financial interest to disclose connected to any of the information presented in this discussion Objectives Scope of Problem Benefits of PD
Peritoneal dialysis. Overview. Preparing for dialysis. Links to sections in topic Other topics available on website
 Peritoneal dialysis This infokid topic is for parents and carers about children s kidney conditions. Visit www.infokid.org.uk to find more topics about conditions, tests & diagnosis, treatments and supporting
Peritoneal dialysis This infokid topic is for parents and carers about children s kidney conditions. Visit www.infokid.org.uk to find more topics about conditions, tests & diagnosis, treatments and supporting
Comparison of temporary and permanent catheters for acute peritoneal dialysis
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1988, 63, 827-831 Comparison of temporary and permanent for acute peritoneal dialysis S N WONG AND D F GEARY Division of Nephrology, Department of Paediatrics, Hospital
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1988, 63, 827-831 Comparison of temporary and permanent for acute peritoneal dialysis S N WONG AND D F GEARY Division of Nephrology, Department of Paediatrics, Hospital
Training for Fluoroscopic Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Placement. Rajeev Narayan MD San Antonio Kidney Disease Center San Antonio, TX
 Training for Fluoroscopic Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Placement Rajeev Narayan MD San Antonio Kidney Disease Center San Antonio, TX Disclosures No financial conflicts of interest to disclose. My comments
Training for Fluoroscopic Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Placement Rajeev Narayan MD San Antonio Kidney Disease Center San Antonio, TX Disclosures No financial conflicts of interest to disclose. My comments
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION. Peritoneal Dialysis. A treatment option for kidney disease. There are 2 types of PD: continuous ambulatory
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peritoneal Dialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and basic principles of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). 2.
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Peritoneal Dialysis A treatment option for kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand the purpose and basic principles of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). 2.
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Disclaimer. PD Catheter Placement in Urgent and Emergent Peritoneal Dialysis. Catheter design and outcomes CATHETER DESIGN AND OUTCOME
 ASDIN 2014 Scientific Meeting Disclaimer PD Catheter Placement in Urgent and Emergent Peritoneal Dialysis Bharat Sachdeva M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine/Nephrology Interventional Nephrology Division
ASDIN 2014 Scientific Meeting Disclaimer PD Catheter Placement in Urgent and Emergent Peritoneal Dialysis Bharat Sachdeva M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine/Nephrology Interventional Nephrology Division
The key to successful chronic peritoneal dialysis (PD)
 Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 25, pp. 132 139 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/05 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2005 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis PERITONEAL CATHETERS
Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 25, pp. 132 139 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/05 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2005 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis PERITONEAL CATHETERS
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients have increased
 Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 23, pp. 249 254 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/03 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2003 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis RISK FACTORS FOR ABDOMINAL
Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 23, pp. 249 254 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/03 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2003 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis RISK FACTORS FOR ABDOMINAL
Managing Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter Complications. (A Two-Part Series) Part 1: Mechanical Complications of Peritoneal Dialysis
 Home Therapies Participant Guide Institute Managing Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter (A Two-Part Series) Part 1: Mechanical John H. Crabtree, MD Visiting Clinical Faculty, Division of Nephrology and Hypertension
Home Therapies Participant Guide Institute Managing Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter (A Two-Part Series) Part 1: Mechanical John H. Crabtree, MD Visiting Clinical Faculty, Division of Nephrology and Hypertension
BAPN 2016 Audit of dialysis access and complications in UK children
 BAPN 2016 Audit of dialysis access and complications in UK children Version 2, 8 th Dec 2015 Yincent Tse, BAPN audit committee member, yincenttse@nhs.net Introduction For children on dialysis, their access
BAPN 2016 Audit of dialysis access and complications in UK children Version 2, 8 th Dec 2015 Yincent Tse, BAPN audit committee member, yincenttse@nhs.net Introduction For children on dialysis, their access
PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST. AR. Merrikhi. MD. Isfahan University of Medical Sciences
 PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST AR. Merrikhi. MD. Isfahan University of Medical Sciences INTRODUCTION The peritoneal equilibration test (PET) is a semiquantitative assessment of peritoneal membrane transport
PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST AR. Merrikhi. MD. Isfahan University of Medical Sciences INTRODUCTION The peritoneal equilibration test (PET) is a semiquantitative assessment of peritoneal membrane transport
Peritoneal Dialysis. Life Improved
 Peritoneal Dialysis Life Improved Peritoneal Dialysis Flex-Neck ExxTended Upper Chest The Flex-Neck Adult catheter has an internal diameter of 3.5 mm, allowing up to 30% higher flow rates than other catheters
Peritoneal Dialysis Life Improved Peritoneal Dialysis Flex-Neck ExxTended Upper Chest The Flex-Neck Adult catheter has an internal diameter of 3.5 mm, allowing up to 30% higher flow rates than other catheters
PROGRESS IN NEPHROLOGY, DIALYSIS AND TRANSPLANTATION
 PROGRESS IN NEPHROLOGY, DIALYSIS AND TRANSPLANTATION PD catheters: evolution towards optimal design Zbylut J. Twardowski University of Missouri, Columbia, MO, USA Corresponding Author: Prof. dr hab. n.
PROGRESS IN NEPHROLOGY, DIALYSIS AND TRANSPLANTATION PD catheters: evolution towards optimal design Zbylut J. Twardowski University of Missouri, Columbia, MO, USA Corresponding Author: Prof. dr hab. n.
2018 HEMODIALYSIS CATHETERS CODING AND REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE
 2018 HEMODIALYSIS CATHETERS CODING AND REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE Contents Overview of Central Venous Access s for Hemodialysis 2 Procedures Using Hemodialysis s 2 Physician Reimbursement for Hemodialysis s 3
2018 HEMODIALYSIS CATHETERS CODING AND REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE Contents Overview of Central Venous Access s for Hemodialysis 2 Procedures Using Hemodialysis s 2 Physician Reimbursement for Hemodialysis s 3
Resumption of Peritoneal Dialysis by Externalization of the Embedded Catheter: A Case Report
 15 Case Report J. St. Marianna Univ. Vol. 7, pp. 15 19, 2016 Resumption of Peritoneal Dialysis by Externalization of the Embedded Catheter: A Case Report Nagayuki Kaneshiro 1, Tsutomu Sakurada 2, Mikako
15 Case Report J. St. Marianna Univ. Vol. 7, pp. 15 19, 2016 Resumption of Peritoneal Dialysis by Externalization of the Embedded Catheter: A Case Report Nagayuki Kaneshiro 1, Tsutomu Sakurada 2, Mikako
Cateteri venosi per emodialisi nel 2017: lo stato dell arte Maurizio Gallieni
 Cateteri venosi per emodialisi nel 2017: lo stato dell arte Maurizio Gallieni Nephrology and Dialysis Unit Ospedale S. Carlo Borromeo, ASST Santi Paolo e Carlo, University of Milano, Milano, Italy Kidney
Cateteri venosi per emodialisi nel 2017: lo stato dell arte Maurizio Gallieni Nephrology and Dialysis Unit Ospedale S. Carlo Borromeo, ASST Santi Paolo e Carlo, University of Milano, Milano, Italy Kidney
Objectives. Certification Review Course. Peritoneal Dialysis. Peritoneal Membrane. 010e Certification Review Course: Peritoneal Dialysis - Kennedy
 Certification Review Course Peritoneal Dialysis Ray Agnello, MSN, RN, CNN Quality Management Specialist Saint Joseph s Regional Medical Center Paterson, New Jersey To provide attendees with a summarized
Certification Review Course Peritoneal Dialysis Ray Agnello, MSN, RN, CNN Quality Management Specialist Saint Joseph s Regional Medical Center Paterson, New Jersey To provide attendees with a summarized
Chapter 2 Peritoneal Equilibration Testing and Application
 Chapter 2 Peritoneal Equilibration Testing and Application Francisco J. Cano Case Presentation FW, a recently diagnosed patient with CKD Stage 5, is a 6-year-old boy who has been recommended to initiate
Chapter 2 Peritoneal Equilibration Testing and Application Francisco J. Cano Case Presentation FW, a recently diagnosed patient with CKD Stage 5, is a 6-year-old boy who has been recommended to initiate
for the ideal insertion of peritoneal dialysis catheter (patent pending)
 for the ideal insertion of peritoneal dialysis catheter (patent pending) CAUTION: U.S. federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a properly licensed practitioner. DEVICE DESCRIPTION
for the ideal insertion of peritoneal dialysis catheter (patent pending) CAUTION: U.S. federal law restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a properly licensed practitioner. DEVICE DESCRIPTION
THE THIRD NATIONAL KIDNEY FOUNDATION LECTURE CAPD
 VOLUME 26, NO 6, OCT 1985 THE THIRD NATIONAL KIDNEY FOUNDATION LECTURE CAPD - 1985 L H Nielson K D Nolph University of Missouri - Columbia M472 Health Sciences Center One Hospital Drive Columbia, Missouri
VOLUME 26, NO 6, OCT 1985 THE THIRD NATIONAL KIDNEY FOUNDATION LECTURE CAPD - 1985 L H Nielson K D Nolph University of Missouri - Columbia M472 Health Sciences Center One Hospital Drive Columbia, Missouri
SIMULTANEOUS CATHETER REPLACEMENT FOR INFECTIOUS AND MECHANICAL COMPLICATIONS WITHOUT INTERRUPTION OF PERITONEAL DIALYSIS
 Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 36, pp. 182 187 www.pdiconnect.com 0896-8608/16 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2016 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis SIMULTANEOUS CATHETER REPLACEMENT FOR INFECTIOUS
Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 36, pp. 182 187 www.pdiconnect.com 0896-8608/16 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2016 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis SIMULTANEOUS CATHETER REPLACEMENT FOR INFECTIOUS
Accidental Insertion of a Peritoneal Dialysis Catheter in the Urinary Bladder
 Published online: April 26, 2018 2018 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC) (http://www.karger.com/services/openaccesslicense).
Published online: April 26, 2018 2018 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC) (http://www.karger.com/services/openaccesslicense).
DISCOVER NEW HORIZONS IN FLUID DRAINAGE. Bringing Safety and Convenience to Fluid Drainage Management
 DISCOVER NEW HORIZONS IN FLUID DRAINAGE Bringing Safety and Convenience to Fluid Drainage Management DRAIN ASEPT Pleural and Peritoneal Drainage Catheter System 600mL or 1,000mL Evacuated Drainage Bottle
DISCOVER NEW HORIZONS IN FLUID DRAINAGE Bringing Safety and Convenience to Fluid Drainage Management DRAIN ASEPT Pleural and Peritoneal Drainage Catheter System 600mL or 1,000mL Evacuated Drainage Bottle
Sichol sooksee,rn. Hemodialysis Unit Rajavej Chiang Mai Hospital
 Sichol sooksee,rn. Hemodialysis Unit Rajavej Chiang Mai Hospital Button hole or Ladder?? Vascular Access Cannulation It s a Life Line of Hemodialysis patient Arterio-venous fistula(avf) is the K/DOQI
Sichol sooksee,rn. Hemodialysis Unit Rajavej Chiang Mai Hospital Button hole or Ladder?? Vascular Access Cannulation It s a Life Line of Hemodialysis patient Arterio-venous fistula(avf) is the K/DOQI
Disinfection by Sodium Hypochlorite: Dialysis Applications
 Disinfection by Sodium Hypochlorite: Dialysis Applications Contributions to Nephrology Vol. 154 Series Editor Claudio Ronco Vicenza Disinfection by Sodium Hypochlorite: Dialysis Applications Volume Editors
Disinfection by Sodium Hypochlorite: Dialysis Applications Contributions to Nephrology Vol. 154 Series Editor Claudio Ronco Vicenza Disinfection by Sodium Hypochlorite: Dialysis Applications Volume Editors
PD catheter implantation (double-cuff straight Tenckhoff catheter) 基隆長庚一般外科卓世川
 PD catheter implantation (double-cuff straight Tenckhoff catheter) 基隆長庚一般外科卓世川 Successful assess of PD Various techniques for various designs of peritoneal catheters. Access of catheter placement is the
PD catheter implantation (double-cuff straight Tenckhoff catheter) 基隆長庚一般外科卓世川 Successful assess of PD Various techniques for various designs of peritoneal catheters. Access of catheter placement is the
St George & Sutherland Hospitals PERITONEAL DIALYSIS UNIT RENAL DEPARTMENT Workplace Instruction (Renal_SGH_WPI_097)
 PERITONEAL DIALYSIS (PD) PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST (PET) Cross references NSW Health PD2007_036 - Infection Control Policy SGH-TSH CLIN027 - Aseptic Technique - Competency and Education Requirements
PERITONEAL DIALYSIS (PD) PERITONEAL EQUILIBRATION TEST (PET) Cross references NSW Health PD2007_036 - Infection Control Policy SGH-TSH CLIN027 - Aseptic Technique - Competency and Education Requirements
SURGICAL OUTCOME OF PERITONEAL DIALYSIS IN ELDERLY PATIENTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SURGICAL OUTCOME OF PERITONEAL DIALYSIS IN ELDERLY PATIENTS Xin-Yi Ng 1, Chien-Liang Liu 1,2, Tsang-Pai Liu 1,2, Wen-Ching Ko 1,2, Shih-Ping Cheng 1, Chih-Jen Wu 2,3,4, Jie-Jen Lee 1,5
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SURGICAL OUTCOME OF PERITONEAL DIALYSIS IN ELDERLY PATIENTS Xin-Yi Ng 1, Chien-Liang Liu 1,2, Tsang-Pai Liu 1,2, Wen-Ching Ko 1,2, Shih-Ping Cheng 1, Chih-Jen Wu 2,3,4, Jie-Jen Lee 1,5
Case Report A Novel Technique for Laparoscopic Salvage of CAPD Catheter Malfunction and Migration: The Santosh-PGI Hanging Loop Technique
 Case Reports in Nephrology Volume 2015, Article ID 684976, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/684976 Case Report A Novel Technique for Laparoscopic Salvage of CAPD Catheter Malfunction and Migration:
Case Reports in Nephrology Volume 2015, Article ID 684976, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/684976 Case Report A Novel Technique for Laparoscopic Salvage of CAPD Catheter Malfunction and Migration:
4th self-care dialysis symposium 6th & 7th June 2018
 Seasonal morbidity variations on PD Data of French Language PD Registry (RDPLF) Christian Verger, RDPLF Pontoise (France) 4th self-care dialysis symposium 6th & 7th June 2018 Background Few studies on
Seasonal morbidity variations on PD Data of French Language PD Registry (RDPLF) Christian Verger, RDPLF Pontoise (France) 4th self-care dialysis symposium 6th & 7th June 2018 Background Few studies on
What Does Peritoneal Thickness in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients Tell Us?
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 23, 2007 Soner Duman, 1 Suha Sureyya Ozbek, 2 Ebru Sevinc Gunay, 1 Devrim Bozkurt, 1 Gulay Asci, 1 Savas Sipahi, 1 Fatih Kirçelli, 1 Muhittin Ertilav, 1 Mehmet Özkahya,
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 23, 2007 Soner Duman, 1 Suha Sureyya Ozbek, 2 Ebru Sevinc Gunay, 1 Devrim Bozkurt, 1 Gulay Asci, 1 Savas Sipahi, 1 Fatih Kirçelli, 1 Muhittin Ertilav, 1 Mehmet Özkahya,
Treatment Options Not Not access
 Treatment Options Treatment options for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) CKD is a permanent condition. Treatment will: Help the patient feel better Not cure the disease Not make the kidneys start working again
Treatment Options Treatment options for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) CKD is a permanent condition. Treatment will: Help the patient feel better Not cure the disease Not make the kidneys start working again
STUDIES ON ULTRAFILTRATION IN PERITONEAL DIALYSIS: INFLUENCE OF PLASMA PROTEINS AND CAPILLARY BLOOD FLOW
 STUDIES ON ULTRAFILTRATION IN PERITONEAL DIALYSIS: INFLUENCE OF PLASMA PROTEINS AND CAPILLARY BLOOD FLOW ABSTRACT Claudio Ronco Alessandra Brendolan Luisa Bragantini Stefano Chiaramonte Mariano Feriani
STUDIES ON ULTRAFILTRATION IN PERITONEAL DIALYSIS: INFLUENCE OF PLASMA PROTEINS AND CAPILLARY BLOOD FLOW ABSTRACT Claudio Ronco Alessandra Brendolan Luisa Bragantini Stefano Chiaramonte Mariano Feriani
Maintaining Peritoneal Dialysis Adequacy: The Process of Incremental Prescription
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 34, 2018 Susie Q. Lew Maintaining Peritoneal Dialysis Adequacy: The Process of Incremental Prescription Urea kinetics (weekly Kt/V) greater than 1.7 generally define
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 34, 2018 Susie Q. Lew Maintaining Peritoneal Dialysis Adequacy: The Process of Incremental Prescription Urea kinetics (weekly Kt/V) greater than 1.7 generally define
Enhancement of convective transport by internal filtration in a modified experimental hemodialyzer Technical Note
 Kidney International, Vol. 54 (1998), pp. 979 985 Enhancement of convective transport by internal filtration in a modified experimental hemodialyzer Technical Note CLAUDIO RONCO, GIANCARLO ORLANDINI, ALESSANDRA
Kidney International, Vol. 54 (1998), pp. 979 985 Enhancement of convective transport by internal filtration in a modified experimental hemodialyzer Technical Note CLAUDIO RONCO, GIANCARLO ORLANDINI, ALESSANDRA
Dialysis, personalized. More options for your patients well being.
 Dialysis, personalized. More options for your patients well being. Discover the advanced peritoneal dialysis (PD) system with improved features for added control and convenience during your patients treatment
Dialysis, personalized. More options for your patients well being. Discover the advanced peritoneal dialysis (PD) system with improved features for added control and convenience during your patients treatment
Update on home dialysis
 Update on home dialysis dr. Karlien François Nefrologie, UZ Brussel Let s start with the good news on PD! Tx All HD = PD ERA EDTA Annual Report 2014 ...despite we don t do it so often ERA EDTA Annual Report
Update on home dialysis dr. Karlien François Nefrologie, UZ Brussel Let s start with the good news on PD! Tx All HD = PD ERA EDTA Annual Report 2014 ...despite we don t do it so often ERA EDTA Annual Report
Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index, home hemodialysis outcomes 131
 Subject Index Aksys PHD system 113 Anemia, home outcomes 111, 172, 173 Automated peritoneal dialysis dialysis comparison 17, 18 selection factors 18, 19 telemedicine system 19 21 Blood pressure -peritoneal
Subject Index Aksys PHD system 113 Anemia, home outcomes 111, 172, 173 Automated peritoneal dialysis dialysis comparison 17, 18 selection factors 18, 19 telemedicine system 19 21 Blood pressure -peritoneal
Appendix E: Overview of Vascular
 Appendix E: Overview of Vascular 56 Peripheral Short Catheter, less than 3 inches (7.5 cm) in length; over-the-needle catheter is most common. Inserted by percutaneous venipuncture, generally into a hand
Appendix E: Overview of Vascular 56 Peripheral Short Catheter, less than 3 inches (7.5 cm) in length; over-the-needle catheter is most common. Inserted by percutaneous venipuncture, generally into a hand
Claudio Ronco, MD Dipartimento di Nefrologia, Dialisi & Trapianto Renale International Renal Research Institute Ospedale San Bortolo - Vicenza
 Claudio Ronco, MD Dipartimento di Nefrologia, Dialisi & Trapianto Renale International Renal Research Institute Ospedale San Bortolo - Vicenza Four Areas where telemedicine can be useful in Nephrology
Claudio Ronco, MD Dipartimento di Nefrologia, Dialisi & Trapianto Renale International Renal Research Institute Ospedale San Bortolo - Vicenza Four Areas where telemedicine can be useful in Nephrology
Fluoroscopic Manipulation of Peritoneal Dialysis Catheters: Outcomes and Factors Associated with Successful Manipulation
 Article Fluoroscopic Manipulation of Peritoneal Dialysis Catheters: Outcomes and Factors Associated with Successful Manipulation Matthew Miller,* Brendan McCormick, Susan Lavoie, Mohan Biyani, and Deborah
Article Fluoroscopic Manipulation of Peritoneal Dialysis Catheters: Outcomes and Factors Associated with Successful Manipulation Matthew Miller,* Brendan McCormick, Susan Lavoie, Mohan Biyani, and Deborah
Automated peritoneal dialysis (APD) has, in recent
 VIIth International Course on Peritoneal Dialysis May 23 26, 2000, Vicenza, Italy Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 20, Suppl. 2 0896-8608/00 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2000 International Society for Peritoneal
VIIth International Course on Peritoneal Dialysis May 23 26, 2000, Vicenza, Italy Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 20, Suppl. 2 0896-8608/00 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2000 International Society for Peritoneal
Kidney Disease Treatment Options
 Page 1 Fact sheet The kidneys play a number of important roles in your body such as: extracting excess water to make urine (wee) controlling your blood pressure filtering waste products and toxins from
Page 1 Fact sheet The kidneys play a number of important roles in your body such as: extracting excess water to make urine (wee) controlling your blood pressure filtering waste products and toxins from
Home Dialysis. Peritoneal Dialysis. Home Hemodialysis
 Home Dialysis The information provided is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. A licensed healthcare professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and
Home Dialysis The information provided is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice. A licensed healthcare professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and
Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter
 Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter Instructions For Use Access Systems Product Description: The Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid
Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter Instructions For Use Access Systems Product Description: The Aspira* Peritoneal Drainage Catheter is a tunneled, long-term catheter used to drain accumulated fluid
Galt Medical Corp. A leader in vascular and interventional medical devices. part of the GaltNeedleTech TM Family
 Galt Medical Corp. A leader in vascular and interventional medical devices. part of the GaltNeedleTech TM Family MICRO-INTRODUCERS Micro-Introducer Kits Galt s Micro-Introducer Kits with smooth transition,
Galt Medical Corp. A leader in vascular and interventional medical devices. part of the GaltNeedleTech TM Family MICRO-INTRODUCERS Micro-Introducer Kits Galt s Micro-Introducer Kits with smooth transition,
Instructions for Use. IJ Catheter Ultrasound Model Version 2400 Series
 Instructions for Use IJ Catheter Ultrasound Model Version 2400 Series 3601 Sagamore Parkway North, Suite B Lafayette, IN 47904 Phone 765.742.4813 www.hemocleanse.com Instructions Revision 3.0 2014 Table
Instructions for Use IJ Catheter Ultrasound Model Version 2400 Series 3601 Sagamore Parkway North, Suite B Lafayette, IN 47904 Phone 765.742.4813 www.hemocleanse.com Instructions Revision 3.0 2014 Table
Protecting Patients. Preserving Access.
 MAHURKAR * Family of Acute Care Catheters Protecting Patients. Preserving Access. The Gold Standard Mahurkar * Acute Care Catheter Family Ease of insertion. Optimal flow rates. Patient comfort. A variety
MAHURKAR * Family of Acute Care Catheters Protecting Patients. Preserving Access. The Gold Standard Mahurkar * Acute Care Catheter Family Ease of insertion. Optimal flow rates. Patient comfort. A variety
The low ph of conventional peritoneal dialysis (PD) solutions,
 Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 29, pp. 158 162 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/09 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2009 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis EFFECTS OF IONIZED SODIUM
Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 29, pp. 158 162 Printed in Canada. All rights reserved. 0896-8608/09 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2009 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis EFFECTS OF IONIZED SODIUM
Predictive Value of Dialysate Cell Counts in Peritonitis Complicating Peritoneal Dialysis
 Predictive Value of Dialysate Cell Counts in Peritonitis Complicating Peritoneal Dialysis Kai Ming Chow,* Cheuk Chun Szeto,* Kitty Kit-Ting Cheung,* Chi Bon Leung,* Sunny Sze-Ho Wong, Man Ching Law,* Yiu
Predictive Value of Dialysate Cell Counts in Peritonitis Complicating Peritoneal Dialysis Kai Ming Chow,* Cheuk Chun Szeto,* Kitty Kit-Ting Cheung,* Chi Bon Leung,* Sunny Sze-Ho Wong, Man Ching Law,* Yiu
Update in Peritoneal dialysis
 Update in Peritoneal dialysis Matthew Jose MBBS, FRACP, PhD, FASN, AFRACMA Royal Hobart Hospital FACULTY OF HEALTH I pay my respects to the traditional owners of this land, the Larrakia people, and to
Update in Peritoneal dialysis Matthew Jose MBBS, FRACP, PhD, FASN, AFRACMA Royal Hobart Hospital FACULTY OF HEALTH I pay my respects to the traditional owners of this land, the Larrakia people, and to
Well-trained interventional physicians can readily
 Ten Lessons Learned in Peritoneal Dialysis Expert observations aimed at improving quality of care and outcomes related to the use of peritoneal dialysis catheters. BY PETER B. HATHAWAY, MD Well-trained
Ten Lessons Learned in Peritoneal Dialysis Expert observations aimed at improving quality of care and outcomes related to the use of peritoneal dialysis catheters. BY PETER B. HATHAWAY, MD Well-trained
Introduction To The Peritoneal Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Pattern Study
 Introduction To The Peritoneal Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Pattern Study Western Canada PD Days Friday February 8, 2013 Vancouver, British Columbia Jeffrey Perl MD SM FRCP(C) Division of Nephrology
Introduction To The Peritoneal Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Pattern Study Western Canada PD Days Friday February 8, 2013 Vancouver, British Columbia Jeffrey Perl MD SM FRCP(C) Division of Nephrology
Unit 11. Objectives. Indications for IV Therapy. Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids. 3 categories. Maintenance Replacement Restoration
 Unit 11 Fluids, Electrolytes and Acid Base Imbalances Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids Objectives Review the purpose and types of intravenous (IV) therapy. Recall the nursing care related
Unit 11 Fluids, Electrolytes and Acid Base Imbalances Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids Objectives Review the purpose and types of intravenous (IV) therapy. Recall the nursing care related
Protecting Patients. Preserving Access.
 MAHURKAR * Family of Acute Care Catheters Protecting Patients. Preserving Access. A full spectrum of acute care catheters for use in hemodialysis, apheresis, infusion and renal replacement therapy The
MAHURKAR * Family of Acute Care Catheters Protecting Patients. Preserving Access. A full spectrum of acute care catheters for use in hemodialysis, apheresis, infusion and renal replacement therapy The
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (994) 9: 399-403 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Nocturnal intermittent peritoneal dialysis G. Woodrow, J. H. Turney, J. A. Cook, J. Gibson, S. Fletcher, A.
Nephrol Dial Transplant (994) 9: 399-403 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Nocturnal intermittent peritoneal dialysis G. Woodrow, J. H. Turney, J. A. Cook, J. Gibson, S. Fletcher, A.
Designed to Reduce the Risk of Occlusion (1)
 Designed to Reduce the Risk of Occlusion (1) more efficient flushing better outcomes The Vortex* ports feature the Vortex Technology for a more efficient flushing. The Vortex Technology sets up efficient
Designed to Reduce the Risk of Occlusion (1) more efficient flushing better outcomes The Vortex* ports feature the Vortex Technology for a more efficient flushing. The Vortex Technology sets up efficient
PERSISTENT SYMPTOMATIC INTRA-ABDOMINAL COLLECTION AFTER CATHETER REMOVAL FOR PD-RELATED PERITONITIS
 Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 31, pp. 34-38 doi:10.3747/pdi.2009.00185 0896-8608/11 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2011 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis PERSISTENT SYMPTOMATIC INTRA-ABDOMINAL
Peritoneal Dialysis International, Vol. 31, pp. 34-38 doi:10.3747/pdi.2009.00185 0896-8608/11 $3.00 +.00 Copyright 2011 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis PERSISTENT SYMPTOMATIC INTRA-ABDOMINAL
You can sleep while I dialyze
 You can sleep while I dialyze Nocturnal Peritoneal Dialysis Dr. Suneet Singh Medical Director, PD, VGH Division of Nephrology University of British Columbia Acknowledgements Melissa Etheridge You can sleep
You can sleep while I dialyze Nocturnal Peritoneal Dialysis Dr. Suneet Singh Medical Director, PD, VGH Division of Nephrology University of British Columbia Acknowledgements Melissa Etheridge You can sleep
PD In Acute Kidney Injury. February 7 th -9 th, 2013
 PD In Acute Kidney Injury February 7 th -9 th, 2013 Objectives PD as a viable initial therapy PD in AKI PD versus dhd PD versus CVVHD Why not PD first PD for AKI Early days (1970 s) PD was the option of
PD In Acute Kidney Injury February 7 th -9 th, 2013 Objectives PD as a viable initial therapy PD in AKI PD versus dhd PD versus CVVHD Why not PD first PD for AKI Early days (1970 s) PD was the option of
Peritoneal Dialysis Prescriptions: A Primer for Nurses
 Peritoneal Dialysis Prescriptions: A Primer for Nurses A Primer ABCs of PD R x Betty Kelman RN-EC MEd CNeph (C) Toronto General Hospital University Health Network Toronto, Ontario, Canada A moment to remember
Peritoneal Dialysis Prescriptions: A Primer for Nurses A Primer ABCs of PD R x Betty Kelman RN-EC MEd CNeph (C) Toronto General Hospital University Health Network Toronto, Ontario, Canada A moment to remember
Phosphate Clearance in Peritoneal Dialysis: Automated PD Compared with Continuous Ambulatory PD
 Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 28, 2012 Dixie-Ann Sawin, Rainer Himmele, Jose A. Diaz Buxo Phosphate Clearance in Peritoneal Dialysis: Automated PD Compared with Continuous Ambulatory PD Although
Advances in Peritoneal Dialysis, Vol. 28, 2012 Dixie-Ann Sawin, Rainer Himmele, Jose A. Diaz Buxo Phosphate Clearance in Peritoneal Dialysis: Automated PD Compared with Continuous Ambulatory PD Although
Received: Accepted:
 Received: 1.12.2010 Accepted: 5.3.2011 Original Article Comparing the outcomes of open surgical procedure and percutaneously peritoneal dialysis catheter (PDC) insertion using laparoscopic needle: A two
Received: 1.12.2010 Accepted: 5.3.2011 Original Article Comparing the outcomes of open surgical procedure and percutaneously peritoneal dialysis catheter (PDC) insertion using laparoscopic needle: A two
Drug Use in Dialysis
 (Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Drug Use in Dialysis Drambarean, B. (2017). Drug Use in Dialysis. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. DIALYSIS
(Last Updated: 08/22/2018) Created by: Socco, Samantha Drug Use in Dialysis Drambarean, B. (2017). Drug Use in Dialysis. Lecture presented at PHAR 503 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy, Chicago. DIALYSIS
Arteriovenous fistula cannulation by buttonhole technique using dull needle
 Original Article Arteriovenous fistula cannulation by buttonhole technique using dull needle Authors Manuel Carlos Martins de Castro 1 Celina de Fátima e Silva 1 João Marcos Rodrigues de Souza 1 Maria
Original Article Arteriovenous fistula cannulation by buttonhole technique using dull needle Authors Manuel Carlos Martins de Castro 1 Celina de Fátima e Silva 1 João Marcos Rodrigues de Souza 1 Maria
Acute Therapy Systems. provencare Catheter Sets
 Acute Therapy Systems provencare Catheter Sets Catheter Sets Contents provencare Catheter Sets 4 provencare Product Features and Accessories 6 provencare Single Lumen Catheter Sets 8 provencare Paediatric
Acute Therapy Systems provencare Catheter Sets Catheter Sets Contents provencare Catheter Sets 4 provencare Product Features and Accessories 6 provencare Single Lumen Catheter Sets 8 provencare Paediatric
Aus Artificial Uretheral Sphincter Port System
 NORFOLK VET PRODUCTS the AUS for the long-term relief of incontinence in dogs and cats making life easier for pets Speciality Medical Devices For The Veterinary Community the Aus Artificial Uretheral Sphincter
NORFOLK VET PRODUCTS the AUS for the long-term relief of incontinence in dogs and cats making life easier for pets Speciality Medical Devices For The Veterinary Community the Aus Artificial Uretheral Sphincter
LLL Session - Nutritional support in renal disease
 ESPEN Congress Leipzig 2013 LLL Session - Nutritional support in renal disease Peritoneal dialysis D. Teta (CH) Nutrition Support in Patients undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) Congress ESPEN, Leipzig
ESPEN Congress Leipzig 2013 LLL Session - Nutritional support in renal disease Peritoneal dialysis D. Teta (CH) Nutrition Support in Patients undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) Congress ESPEN, Leipzig
End-Stage Renal Disease. Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology
 End-Stage Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology ESRD : Life with renal replacement therapy CASE: 18 month old male with HUS develops ESRD PD complicated
End-Stage Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology ESRD : Life with renal replacement therapy CASE: 18 month old male with HUS develops ESRD PD complicated
Proceedings of the ISPD 2006 The 11th Congress of the ISPD /07 $ MAXIMIZING THE SUCCESS OF PERITONEAL DIALYSIS IN HIGH TRANSPORTERS
 Proceedings of the ISPD 2006 The 11th Congress of the ISPD 0896-8608/07 $3.00 +.00 August 25 29, 2006, Hong Kong Copyright 2007 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis Peritoneal Dialysis International,
Proceedings of the ISPD 2006 The 11th Congress of the ISPD 0896-8608/07 $3.00 +.00 August 25 29, 2006, Hong Kong Copyright 2007 International Society for Peritoneal Dialysis Peritoneal Dialysis International,
Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care. The High-Flow Port Designed for Apheresis
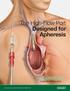 Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care The High-Flow Port Designed for Apheresis Optimized for Long Device Life Bench Tested up to 1,000 Accesses 1 Bard is proud to introduce the first and only
Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care The High-Flow Port Designed for Apheresis Optimized for Long Device Life Bench Tested up to 1,000 Accesses 1 Bard is proud to introduce the first and only
Petite Wound Drainage System. 13mm CWV Drainage System. CWSump. CWV with Trocar
 CWVDrain Designed to assure optimum cosmetic results Tapered, hubless design provides atraumatic insertion and removal Internal ribs prevent collapsing or kinking Large 150cc capacity reservoir decreases
CWVDrain Designed to assure optimum cosmetic results Tapered, hubless design provides atraumatic insertion and removal Internal ribs prevent collapsing or kinking Large 150cc capacity reservoir decreases
PERITONEAL DIALYSIS PRESCRIPTION MANAGEMENT QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE
 PERITONEAL DIALYSIS PRESCRIPTION MANAGEMENT QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE This quick reference guide will help serve as a reference tool for clinicians setting a patient s Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) prescription.
PERITONEAL DIALYSIS PRESCRIPTION MANAGEMENT QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE This quick reference guide will help serve as a reference tool for clinicians setting a patient s Peritoneal Dialysis (PD) prescription.
Vincenzo La Milia 1, Giuseppe Pontoriero 1, Giovambattista Virga 2 and Francesco Locatelli 1
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2015) 30: 1741 1746 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv275 Advance Access publication 16 July 2015 Ionic conductivity of peritoneal dialysate: a new, easy and fast method of assessing peritoneal
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2015) 30: 1741 1746 doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv275 Advance Access publication 16 July 2015 Ionic conductivity of peritoneal dialysate: a new, easy and fast method of assessing peritoneal

 '} I c.
'} I c.