The incidence of acute urinary retention secondary to BPH is increasing among California men
|
|
|
- Ronald Webb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Disease (2013) 16, & 2013 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved /13 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The incidence of acute urinary retention secondary to BPH is increasing among California men HK Groves 1,2, D Chang 1,3, K Palazzi 1, S Cohen 1 and JK Parsons 1 BACKGROUND: Current epidemiological patterns of adverse events of clinical BPH remain unclear. We investigated trends in acute urinary retention (AUR) associated with BPH in a large, population-based cohort. METHODS: We utilized the California Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development Database to examine emergency room (ER) visits in California among men aged X 50 years from 2007 to Outcomes included AUR for which BPH was the primary diagnosis, AUR for which BPH was a secondary diagnosis and urethral catheterization for AUR. We generated adjusted odds ratios (OR adj ) using multivariate logistic regression to determine longitudinal trends. RESULTS: A total of men presented with a diagnosis of BPH-associated AUR, the unadjusted incidence of which increased from 4.00 per 1000 ER visits in 2007 to 5.23 per 1000 ER visits in 2010 (Po0.001). In adjusted analyses, primary AUR (OR adj ¼ 1.25; 95% confidence interval (CI), ; Po0.001) and secondary AUR (OR adj ¼ 1.80; 95% CI, ; Po0.001) increased 25% and 80%, respectively. Urethral catheterization for primary (OR adj ¼ 1.30; 95% CI, ; Po0.001) and secondary (OR adj ¼ 1.82; 95% CI, ; Po0.001) AUR increased 30% and 82%, respectively. Asian race (Po0.001), Hispanic race (Po0.001) and commercial insurance (Po0.001) were associated with significantly increased risks of AUR and urethral catheterization. CONCLUSIONS: Between 2007 and 2010, the observed incidence of BPH-associated AUR increased substantially in a large and ethnically diverse male population of the United States. Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Disease (2013) 16, ; doi: /pcan ; published online 7 May 2013 Keywords: urinary retention; BPH; incidence; lower urinary tract symptoms; a-blocker; five a-reductase inhibitor INTRODUCTION Clinical BPH affects as many as 75% of men by age 70 years and generates at least $4 billion in treatment costs annually in the United States. 1,2 Clinical BPH usually presents with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), which in older men are independently associated with increased risks of mortality, falls and diminished quality of life. 3 6 Sequelae of advanced BPH, including acute urinary retention (AUR) and renal failure, are associated with significantly increased morbidity and mortality. 7 The most common treatment for BPH is oral therapy. 2 Oral therapy is highly effective for alleviating LUTS and decreasing the risks of AUR, urinary infection, surgery and renal failure. 8,9 The advent of oral therapy transformed BPH from a surgical disease into a chronic medical condition and coincided with a decreased population incidence of adverse events secondary to BPH. 2 However, formal Phase 4 studies of a-blocker and five a-reductase inhibitor therapy were not performed, and longerterm epidemiological trends in adverse events of BPH during the oral therapy era remain unclear. 10 Notably, recent epidemiological data suggest that adverse events of BPH have either increased or persisted in hospitalized patients over the past decade. An analysis of the Nationwide Inpatient Sample observed that hospitalizations in the United States for acute renal failure secondary to BPH increased more than 400% between 1998 and 2008; concomitantly, the frequency of hospitalizations for AUR and urinary infection remained stable. 11 Diagnosis and treatment for BPH occurs primarily in the outpatient setting. 2 Further epidemiological studies of adverse events of BPH identified in outpatient venues, therefore, would inform BPH treatment and health policy by providing insight into current population trends in BPH severity. AUR, which occurs in B3% of BPH patients followed for 5 years, 8 is a readily measurable outcome and a robust marker of advanced BPH. Therefore, we evaluated trends in the incidence of AUR among men with BPH presenting to California emergency rooms (ERs). MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population: the California Office of Health Planning and Development ER database The State of California Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development (Healthcare Quality and Analysis Division) provides ER discharge data for the years The State of California government requires all licensed ERs to submit data on all discharged patients every 6 months. These records thus comprise a 100% sample of all non-federal (that is, non-veterans Administration) ER discharges in the state of California. All data are de-identified and include demographic information, including age, gender, race, information on primary and concomitant diagnoses recorded and procedures performed, discharge information (for example, hospital admission and death) and administrative information (for example, payer information). As individual patients are not identified in this multicenter registry report, the need for consent and institutional review board approval was waived at the University of California San Diego. 1 Division of Urologic Oncology, Section of Urology, Department of Surgery, UC San Diego Moores Cancer Center, VA San Diego Medical Center, La Jolla, CA, USA; 2 University of California, San Diego School of Medicine, La Jolla, CA, USA and 3 UC San Diego Health System, San Diego, CA, USA. Correspondence: Dr JK Parsons, Division of Urologic Oncology, UC San Diego Moores Cancer Center, 3855 Health Sciences Drive 0987, La Jolla, CA , USA. k0parsons@ucsd.edu Received 14 January 2013; revised 20 February 2013; accepted 23 February 2013; published online 7 May 2013
2 Case selection We performed a cross-sectional analysis from 2007 to 2010 for men X 50 years of age and identified BPH patients using ICD-9 codes ( , and ). We used ICD-9 codes , and for urinary retention. We excluded men with a diagnosis of urinary strictures (598.8), neurogenic bladder (344.61, ), presence of neuropacemaker or other electronic device (V45.89), bladder cancer ( , V10.51), prostate cancer (185, V10.46) and kidney cancer (189.0, V10.52). We began our analysis in 2007 to avoid potential confounding from a diagnostic coding change for BPH that occurred in October Outcomes: AUR and urethral catheterization The primary outcomes were BPH-associated AUR and urethral catheterization for BPH-associated AUR. We classified AUR into two different categories to distinguish encounters for which BPH was the presenting problem from those in which BPH occurred in the setting of another disorder. Primary AUR (BPH was the presenting problem) consisted of a primary code of AUR with an associated BPH code in a secondary position or a primary code of BPH with an associated AUR code in a secondary position. Secondary AUR (BPH occurred with another disorder) consisted of AUR and BPH codes in secondary positions. To examine urethral catheterization, we identified urinary catheter insertion occurring with primary and secondary AUR using CPT codes 51701, and for insertion of urethral catheter. Exposure variables included insurance status, race, age and diabetes mellitus (identified by ICD-9 code ). We determined three categories for insurance status based on the expected source of payment variable: commercial insurance, Medicare and limited (which included Medicaid and other assistance programs). Statistical analysis We tested statistical significance of the outcome variable for bivariate analysis using w 2 -test and two-tailed significance of Pp0.05. Demographic variables were compared with ER patients without BPH-associated AUR and between primary AUR and secondary AUR. Median age was compared using Mann Whitney s U-test. We performed multivariate analysis using binary logistical regression adjusted for age, race, diabetes and insurance status, and was expressed as the odds ratio with 95% confidence interval (CI). We determined the significance of the year-to-year trend using a linear time model and expressed as P-trend. The year-to-year trend in AUR incidence among subsets of Black, White, Asian and Hispanic men with commercial insurance and men with limited insurance were compared using multivariate logistic regression to assess for homogeneity. We also compared year-to-year trends in primary AUR incidence with secondary AUR incidence among elderly patients (older than 85 years) and younger patients (age years) to examine the relationship between age and AUR subtype. All analyses were performed using Stata v 11.1 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA). RESULTS Analytic cohort We included ER visits in this analysis (Figure 1). The median age of the final analytic cohort was 61 years (interquartile range 54 73). Men with primary AUR (median 74 years, interquartile range 64 82, Po0.001) and secondary AUR (median 75 years, interquartile range 65 83, Po0.001) were significantly older than men without AUR. Of all ER visits during the period of study, 0.46% included a diagnosis of BPH-associated AUR. The incidence of AUR steadily increased from 2007 to 2010 (Table 1). Primary AUR occurred four times as often as secondary AUR. Compared with non-aur ER encounters, men with AUR were less likely to be Black, more likely to be Hispanic and more likely to be insured by Medicare (Table 1). Acute urinary retention On multivariate analysis, there was a 36% increase in the incidence of overall AUR in 2010 compared with that in The incidence of primary AUR increased 25%, whereas the incidence of Eligible (n= 3,839,108) --Men > 50 years old presenting to the ER Analyzed (n= 3,724,016) Excluded (n=115,092) -- Neurogenic bladder (n= 1,928) -- Malignant neoplasm of bladder, kidney, or prostate (n= 25,126) -- History of malignancy of bladder, kidney or prostate (n= 52,726) -- Urethral stricture (n= 303) -- Post procedure state (n= 37,454) Figure 1. Composition of the analytic cohort: the California Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development (OSHPD) emergency room (ER) database, secondary AUR increased 80%. Variables associated with increased risk of AUR included older age, Hispanic and Asian race and commercial insurance. Diabetes was associated with decreased risk of overall, primary and secondary AUR (Table 2). Urethral catheterization Primary AUR and secondary AUR were associated with urethral catheterization in 64% and 44% of cases, respectively. On multivariate analyses, there were significant increases in the incidence of urethral catheterization for primary (30%) and secondary (82%). Older age, Hispanic and Asian race and commercial insurance were associated with increased risk; diabetes and African American race was associated with decreased risk (Table 3). Sensitivity analyses To examine potential residual confounding by age, we performed subset analyses to examine the increase of primary and secondary AUR among the elderly. Among men older than 85 years, the incidence of primary AUR increased 22% (adjusted odds ratio (OR adj ¼ 1.22; 95% CI, ), whereas the incidence of secondary AUR increased 201% (OR adj ¼ 2.01; 95% CI, ). Findings among the youngest age category men aged years were similar to those for the primary analysis (data not shown). We also performed sensitivity analyses to test for homogeneity of the trend in increasing incidence of AUR among demographic subsets. There were no significant differences in the rates of increased incidence among Black and White race or among limited and commercial insurance (data not shown). DISCUSSION In this study, one of the largest population analyses to date of BPH complications, we observed substantial increases in both incident AUR and urethral catheterization for AUR among a large and ethnically diverse male population of the United States. Commercial insurance coverage and Hispanic and Asian race were each associated with increased risks of AUR and urethral catheterization. Collectively, our results suggest that the incidence of BPHassociated AUR is increasing in California and, consistent with recent data among BPH patients hospitalized for acute renal failure, 11 could indicate a rising incidence and prevalence of clinically advanced BPH in the US population. Prior studies of longitudinal trends in AUR indicated a decreasing incidence from the 1990s through the early 2000s; after 2000, rates generally stabilized. From 1994 to 2000, according to observational data from the Urologic Diseases of America Project, the number of men presenting to ERs with BPH as the primary diagnosis decreased by 34%. 2 Similarly, the 261 & 2013 Macmillan Publishers Limited Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Disease (2013),
3 262 Table 1. Characteristics of men presenting to non-federal California ERs with and without BPH-associated AUR: the California OSHPD ER database, Demographics of analytic cohort Total ER patients All AUR Primary AUR Secondary AUR Variable N (%) N/1000 ER visits N/1000 ER visits N/1000 ER visits Calendar year Age (%), years (58.8) 1.92 (24.8) a 1.58 (26.5) a 0.35 (19.2) a,b (18.8) 7.44 (30.5) 5.92 (31.7) 1.52 (26.7) (14.8) 9.14 (29.6) 6.85 (28.9) 2.29 (31.7) 85 þ (7.7) 9.03 (15.2) 5.91 (12.9) 3.12 (22.5) Race (%) White (64.2) 4.44 (61.3) a 3.33 (60.1) a 1.11 (64.9) a,b Black (10.4) 2.72 (6.08) 2.06 (6.0) 0.66 (6.2) Hispanic (18.0) 5.71 (22.1) 4.44 (22.5) 1.27 (20.7) Asian (4.1) 7.61 (6.7) 6.31 (7.3) 1.30 (4.8) Other (3.4) 5.37 (3.9) 4.28 (4.1) 1.10 (0.1) Insurance (%) Limited (28.4) 2.29 (14.0) a 1.83 (14.7) a 0.46 (11.9) a,b Commercial (27.8) 3.55 (21.3) 2.86 (22.5) 0.69 (17.6) Medicare (43.8) 6.84 (64.6) 5.09 (62.9) 1.75 (70.4) Diabetes Mellitus (%) (13.9) 3.89 (11.9) a 2.81 (11.2) a 1.08 (14.1), NS b Urethral Catheter (%) (2.4) (58.9) a (63.6) a (43.6) a,b Abbreviations: AUR, acute urinary retention; ER, emergency room; OSHPD, Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development; NS, not significant. a w 2 -Test comparing AUR subtype with ER patients without BPH-associated AUR. Significant Po0.001 level. b w 2 -Test comparing primary AUR with secondary AUR. Significant Po0.001 level. Hospital Episode Statistics database in England showed that primary AUR incidence decreased by 7% between 1998 and 2003 although, notably, the incidence of recurrent AUR increased by 20%. 12 Finally, between 1998 and 2008, hospitalizations for AUR in the United States remained stable. 11 Although Canadian investigators observed a substantial rise in the percentage of TURP patients presenting with AUR from 1988 (22.9%) to 2008 (42.9%), this result most likely reflected changes in the types of patients undergoing TURP rather than changes in population incidence. 13 To the best of our knowledge the present analysis is the first to describe incident AUR after 2008 and, within the context of prior studies, suggests a U-shaped AUR incidence curve with a steady decrease in the 1990s, a nadir in the early 2000s and a substantial increase after There are at least three potential explanations for these observations. First, these data could indicate an increase in the number of men with clinically advanced BPH, possibly resulting from the aging population. Alternatively, increasing numbers of BPH patients may now be presenting with clinically advanced disease after prolonged medical suppression of LUTS. The rapid transition to medical therapy during the 1990s occurred in the absence of randomized clinical trials comparing surgery with medication, models analyzing the import such a paradigm shift might have on future BPH population trends, or longer-term Phase 4 studies of medication utilization in a community. 10 A large proportion of BPH patients now undergo treatment in the primary care setting, and most of these patients receive a-blocker monotherapy. 14,15 Both the Medical Therapy of Prostate Symptoms and a combination of Avodart and Tamsulosin trials demonstrated that a-blocker monotherapy is inferior to five a-reductase inhibitor alone or to combination therapy in preventing AUR, 8,9 and five a-reductase inhibitor prescription rates are inversely and a-blocker prescription rates are directly associated with risk of BPH surgery. 16 It is possible that a-blocker monotherapy masks LUTS while allowing for subclinical biological progression, delaying the clinical onset of late-stage BPH without altering its longer-term natural history or reducing the overall incidence of adverse sequelae. The positive association of commercial insurance coverage with increased risk of AUR in this cohort supports this interpretation; patients with commercial insurance coverage presumably had greater access to oral BPH medications. Second, rather than reflecting actual changes in AUR incidence, these data may instead indicate alterations in claimsbased diagnostic coding aimed at increasing reimbursements. 17,18 As the similar patterns in AUR and urethral catheterization suggest cases in which bladder drainage was clinically indicated, temporal changes in claims-based data would likely represent a correction in rather than a misrepresentation of estimates of actual disease prevalence, with providers submitting claims (that is, for urethral catheterization) that previously had not been captured in the billing process. In this scenario, incidence would be expected to eventually stabilize at a new, higher frequency. The insurance status association is consistent with this interpretation, as providers would be more motivated to seek additional reimbursement for patients with commercial insurance coverage. Finally, these results may reveal evolutions in the management of AUR. It is possible, for example, that health care providers over time are more aggressively diagnosing and treating AUR, or that Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Disease (2013), & 2013 Macmillan Publishers Limited
4 Table 2. OR adj with 95% CI of BPH-associated AUR among men presenting to non-federal California ERs: the California OSHPD ER database, AUR Variable All AUR Primary AUR Secondary AUR OR adj (±95% CI) P-value OR adj (±95% CI) P-value OR adj (±95% CI) P-value Calendar year 2007 (reference) ( ) ( ) ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o0.001 P-trend o0.001 o0.001 o0.001 Age (years) (reference) ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o þ 5.57 ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o0.001 Race White (reference) Black 0.93 ( ) ( ) ( ) 0.98 Hispanic 1.65 ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o0.001 Asian 1.60 ( ) o ( ) o ( ) 0.3 Other 1.46 ( ) o ( ) o ( ) Insurance Limited (reference) Commercial 1.34 ( ) o ( ) o ( ) Medicare 1.03 ( ) ( ) ( ) 0.63 Diabetes mellitus Non-diabetic (reference) Diabetic 0.72 ( ) o ( ) o ( ) Abbreviations: AUR, acute urinary retention; CI, confidence interval; ER, emergency room; OD adj, adjusted odds ratio; OSHPD, Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development. Adjusted for race, age, race, insurance status, and concurrent diagnosis of diabetes. P-value indicates significance of year-to-year trend in an adjusted linear time model. AUR patients previously catheterized in clinic are increasingly being sent to the ER. This latter interpretation raises issues related to resource utilization and the appropriateness of sending AUR patients to the ER for further procedures. Notably, the insurance status association is not consistent with this interpretation, as providers would presumably be more apt to send underfunded, rather than funded, patients to the ER. We also found that the increases in incident secondary AUR cases for which the primary diagnosis was non-urologic, but the patient had a concomitant diagnosis of BPH were greater in magnitude than those for primary AUR, with an 80% adjusted increase in risk from 2007 to As older age was more strongly associated with secondary AUR, and BPH patients with concomitant diagnoses of COPD and cardiac disease are at increased risk of AUR, 19,20 a likely explanation is an aging population with a higher prevalence of both BPH and comorbid conditions. With the global population aging, these data portend a growing burden of AUR and associated health care costs in this setting, particularly as Foley catheter insertion is already a considerable source of morbidity that affects estimated tens of thousands of US men annually. 21,22 In this cohort, the higher risk of AUR for Hispanic and Asian men, and the lower risk for African American men, may indicate differences in community prevalence of advanced BPH among these groups. However, prior published data on associations of BPH and race have been conflicting, likely due, at least in part, to differences in clinical definitions of BPH and LUTS. 26 In addition, insurance status and treatment seeking may also have influenced these observations. The inverse associations of AUR with diabetes conflict with prior studies supporting increased risks of BPH 27 and BPH with urinary retention 20 with a diagnosis of diabetes. It is possible that in this case diabetic men with BPH and urinary retention were less likely to be evaluated in the ER. A major strength of this study is the large and ethnically diverse analytic cohort. California is the most populous state in the United States, with a population approaching 40 million individuals ( Both its size and high proportion of non-white residents contribute to the robustness and external validity of the findings. Moreover, the analytic cohort included a nearly 100% sample of all California ER visits during this time period. A potential limitation of this analysis is that it did not incorporate detailed patient-level data, including BPH medication use, surgical history or ER bladder-scan data. Still, there is no evidence to suggest that variations in patient-level parameters would have been differential by year with respect to the primary study outcomes. It is also possible that misclassification bias, secondary to inaccurate coding by providers, occurred. To limit the potential for BPH misclassification bias, we stratified AUR by primary and secondary BPH and, importantly, AUR incidence significantly increased in both categories. Moreover, it is highly unlikely that inaccurate coding for BPH systematically generated an apparent association of year with incident AUR. In conclusion, between 2007 and 2010, the incidences of BPH-associated AUR and urethral catheterization increased & 2013 Macmillan Publishers Limited Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Disease (2013),
5 264 Table 3. OR adj with 95% CI of urethral catheterization for BPH-associated AUR among men presenting to non-federal California ERs: the California OSHPD ER database, Urethral catheterization Variable All AUR þ urethral catheterization Primary AUR þ urethral catheterization Secondary AUR þ urethral catheterization OR adj (±95% CI) P-value OR adj (±95% CI) P-value OR adj (±95% CI) P-value Calendar year 2007 (reference) ( ) o ( ) ( ) ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o0.001 P-trend o0.001 o0.001 o0.001 Age (years) (reference) ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o þ 5.38 ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o0.001 Race White (reference) Black 0.81 ( ) o ( ) o ( ) Hispanic 1.51 ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o0.001 Asian 1.78 ( ) o ( ) o ( ) Other 1.35 ( ) o ( ) o ( ) 0.40 Insurance Limited (reference) Commercial 1.69 ( ) o ( ) o ( ) o0.001 Medicare 1.26 ( ) o ( ) o ( ) Diabetes mellitus Non-diabetic (reference) Diabetic 0.70 ( ) o ( ) o ( ) Abbreviations: AUR, acute urinary retention; CI, confidence interval; ER, emergency room; OD adj, adjusted odds ratio; OSHPD, Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development. Adjusted for race, age, race, insurance status and concurrent diagnosis of diabetes. P-value indicates significance of year-to-year trend in an adjusted linear time model. substantially in a large and ethnically diverse male population of the United States. Potential explanations which merit further study include an increased population prevalence of clinically advanced BPH, temporal changes in provider billing procedures and alterations in practice patterns for management of AUR. CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflict of interest. REFERENCES 1 Saigal CS, Joyce G. Economic costs of benign prostatic hyperplasia in the private sector. J Urol 2005; 173: Wei JT, Calhoun E, Jacobsen SJ. Urologic diseases in America project: benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 2005; 173: Engstrom G, Henningsohn L, Steineck G, Leppert J. Self-assessed health, sadness and happiness in relation to the total burden of symptoms from the lower urinary tract. BJU Int 2005; 95: Taylor BC, Wilt TJ, Fink HA, Lambert LC, Marshall LM, Hoffman AR et al. Prevalence, severity, and health correlates of lower urinary tract symptoms among older men: the MrOS study. Urology 2006; 68: Parsons JK, Mougey J, Lambert L, Wilt TJ, Fink HA, Garzotto M et al. Lower urinary tract symptoms increase the risk of falls in older men. BJU Int 2009; 104: Kupelian V, Fitzgerald MP, Kaplan SA, Norgaard JP, Chiu GR, Rosen RC. Association of nocturia and mortality: results from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J Urol 2011; 185: Armitage JN, Sibanda N, Cathcart PJ, Emberton M, van der Meulen JH. Mortality in men admitted to hospital with acute urinary retention: database analysis. BMJ 2007; 335: McConnell JD, Roehrborn CG, Bautista OM, Andriole Jr GL, Dixon CM, Kusek JW et al. The long-term effect of doxazosin, finasteride, and combination therapy on the clinical progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Eng J Med 2003; 349: Roehrborn CG, Siami P, Barkin J, Damiao R, Major-Walker K, Nandy I et al. The effects of combination therapy with dutasteride and tamsulosin on clinical outcomes in men with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: 4-year results from the CombAT study. Eur Urol 2010; 57: Parsons JK. Commentary on BPH and public health--have we lost the forest through the trees? J Urol 2008; 179(5 Suppl): S Stroup SP, Palazzi-Churas K, Kopp RP, Parsons JK. Trends in adverse events of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in the USA, 1998 to BJU Int 2012; 109: Cathcart P, van der Meulen J, Armitage J, Emberton M. Incidence of primary and recurrent acute urinary retention between 1998 and 2003 in England. J Urol 2006; 176: Izard J, Nickel JC. Impact of medical therapy on transurethral resection of the prostate: two decades of change. BJU Int 2011; 108: Wei JT, Miner MM, Steers WD, Rosen RC, Seftel AD, Pasta DJ et al. Benign prostatic hyperplasia evaluation and management by urologists and primary care physicians: practice patterns from the observational BPH registry. J Urol 2011; 186: Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Disease (2013), & 2013 Macmillan Publishers Limited
6 15 Miner MM. Primary care physician versus urologist: how does their medical management of LUTS associated with BPH differ? Curr Urol Rep 2009; 10: Sung JC, Curtis LH, Schulman KA, Albala DM. Geographic variations in the use of medical and surgical therapies for benign prostatic hyperplasia. J Urol 2006; 175(3 Pt 1): Abelson R, Creswell J, Palmer G. Medicare Bills Rise as Records Turn Electronic. New York Times The New York Times Company: New York, Abelson R, Creswell J. U.S. Warning to Hospitals on Medicare Bill Abuses. New York Times. The New York Times Company: New York, Stephenson A, Seitz D, Bell CM, Gruneir A, Gershon AS, Austin PC et al. Inhaled anticholinergic drug therapy and the risk of acute urinary retention in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a population-based study. Arch Intern Med 2011; 171: Woldrich JM, Palazzi-Churas K, Lakin C, Albo M, Parsons JK. Prostate laser vaporization in men with urinary retention. BJU Int 2011; 108: Kashefi C, Messer K, Barden R, Sexton C, Parsons JK. Incidence and prevention of iatrogenic urethral injuries. J Urol 2008; 179: Leuck AM, Wright D, Ellingson L, Kraemer L, Kuskowski MA, Johnson JR. Complications of foley catheters-is infection the greatest risk? J Urol 2012; 187: Platz EA, Kawachi I, Rimm EB, Willett WC, Giovannucci E. Race, ethnicity and benign prostatic hyperplasia in the health professionals follow-up study. J Urol 2000; 163: Van Den Eeden SK, Shan J, Jacobsen SJ, Aaronsen D, Haque R, Quinn VP et al. Evaluating racial/ethnic disparities in lower urinary tract symptoms in men. J Urol 2012; 187: Howard DL, Taylor YJ, Ross LE. Differences in lower urinary tract symptoms, treatment and mortality among African-American and white elderly men. J Natl Med Assoc 2008; 100: Parsons JK. Modifiable risk factors for benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms: new approaches to old problems. J Urol 2007; 178: Sarma AV, Parsons JK, McVary K, Wei JT. Diabetes and benign prostatic hyperplasia/lower urinary tract symptoms--what do we know? J Urol 2009; 182(6 Suppl): S32 S & 2013 Macmillan Publishers Limited Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Disease (2013),
REPORTS. Clinical and Economic Outcomes in Patients Treated for Enlarged Prostate
 Clinical and Economic Outcomes in Patients Treated for Enlarged Prostate Michael James Naslund, MD, MBA; Muta M. Issa, MD, MBA; Amy L. Grogg, PharmD; Michael T. Eaddy, PharmD, PhD; and Libby Black, PharmD
Clinical and Economic Outcomes in Patients Treated for Enlarged Prostate Michael James Naslund, MD, MBA; Muta M. Issa, MD, MBA; Amy L. Grogg, PharmD; Michael T. Eaddy, PharmD, PhD; and Libby Black, PharmD
Evaluation of Recent Trends in Treatment Patterns Among Men With Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
 469245JMHXXX10.1177/1557988312469245A merican Journal of Men s HealthKruep et al. Article Evaluation of Recent Trends in Treatment Patterns Among Men With Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia American Journal
469245JMHXXX10.1177/1557988312469245A merican Journal of Men s HealthKruep et al. Article Evaluation of Recent Trends in Treatment Patterns Among Men With Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia American Journal
Increasing Awareness, Diagnosis, and Treatment of BPH, LUTS, and EP
 Introduction to Enlarged Prostate E. David Crawford, MD Professor of Surgery (Urology) and Radiation Oncology Head, Urologic Oncology E. David Crawford Endowed Chair in Urologic Oncology University of
Introduction to Enlarged Prostate E. David Crawford, MD Professor of Surgery (Urology) and Radiation Oncology Head, Urologic Oncology E. David Crawford Endowed Chair in Urologic Oncology University of
The Clinical and Economic Benefit of Early Avodart Use vs Early Finasteride Use (Study: 8AVO027HO)
 The Clinical and Economic Benefit of Early Avodart Use vs Early Finasteride Use (Study: 8AVO027HO) November 2011 (Revised May 2012) Prepared for: GlaxoSmithKline Please direct comments and questions to:
The Clinical and Economic Benefit of Early Avodart Use vs Early Finasteride Use (Study: 8AVO027HO) November 2011 (Revised May 2012) Prepared for: GlaxoSmithKline Please direct comments and questions to:
α-blocker Monotherapy and α-blocker Plus 5-Alpha-Reductase Inhibitor Combination Treatment in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia; 10 Years Long-Term Results
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.4.248 Voiding Dysfunction α-blocker Monotherapy and α-blocker Plus 5-Alpha-Reductase Inhibitor Combination Treatment in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia;
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.4.248 Voiding Dysfunction α-blocker Monotherapy and α-blocker Plus 5-Alpha-Reductase Inhibitor Combination Treatment in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia;
Treating BPH: Comparing Rezum UroLift and HoLEP
 Treating BPH: Comparing Rezum UroLift and HoLEP Scott M. Cheney MD Mayo Clinic Arizona 2018 MFMER slide-1 Welcome to AZ 2018 MFMER slide-2 Outline Background on BPH, Rezum, Urolift, HoLEP AUA Guideline
Treating BPH: Comparing Rezum UroLift and HoLEP Scott M. Cheney MD Mayo Clinic Arizona 2018 MFMER slide-1 Welcome to AZ 2018 MFMER slide-2 Outline Background on BPH, Rezum, Urolift, HoLEP AUA Guideline
The Risk of Fracture with Taking Alpha Blockers for Treating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
 J Prev Med Public Health 2009;42(3):165-170 DOI: 103961/jpmph2009423165 The Risk of Fracture with Taking Alpha Blockers for Treating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Joongyub Lee 1) Nam-Kyoung Choi 13) Sun-Young
J Prev Med Public Health 2009;42(3):165-170 DOI: 103961/jpmph2009423165 The Risk of Fracture with Taking Alpha Blockers for Treating Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Joongyub Lee 1) Nam-Kyoung Choi 13) Sun-Young
Title of Research Thesis:
 Eastern Michigan University By Fatai Osinowo Adviser s Name: Dr. Stephen Sonstein, PhD Title of Research Thesis: A sub-analyses from the Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Registry and Patient survey:
Eastern Michigan University By Fatai Osinowo Adviser s Name: Dr. Stephen Sonstein, PhD Title of Research Thesis: A sub-analyses from the Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Registry and Patient survey:
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD
 Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Over half of patients from the Medicare 5% sample (restricted to age 65 and older) have a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease (), cardiovascular disease,
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Over half of patients from the Medicare 5% sample (restricted to age 65 and older) have a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease (), cardiovascular disease,
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD
 Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients in the Medicare 5% sample (aged 65 and older) had at least one of three diagnosed chronic conditions chronic kidney disease
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients in the Medicare 5% sample (aged 65 and older) had at least one of three diagnosed chronic conditions chronic kidney disease
The Evolution of Combination Therapy. US men eligible for BPH treatment * with projected population changes
 The Management of BPH & The Impact of Combination Therapy Results Combination of Avodart and Tamsulosin (CombAT) Medical Therapy of Prostate Symptoms (MTOPS) Dr. Jack Barkin, md, fics, facs, dabu, Mcert
The Management of BPH & The Impact of Combination Therapy Results Combination of Avodart and Tamsulosin (CombAT) Medical Therapy of Prostate Symptoms (MTOPS) Dr. Jack Barkin, md, fics, facs, dabu, Mcert
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients with CKD
 Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients with CKD Over half of patients in the Medicare 5% sample (aged 65 and older) had at least one of three diagnosed chronic conditions chronic kidney disease
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients with CKD Over half of patients in the Medicare 5% sample (aged 65 and older) had at least one of three diagnosed chronic conditions chronic kidney disease
Influence of body mass index on Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia-related complications in patients undergoing prostatectomy
 Mosli and Mosli SpringerPlus 2013, 2:537 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Influence of body mass index on Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia-related complications in patients undergoing prostatectomy
Mosli and Mosli SpringerPlus 2013, 2:537 a SpringerOpen Journal CASE STUDY Open Access Influence of body mass index on Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia-related complications in patients undergoing prostatectomy
The Journal of International Medical Research 2012; 40:
 The Journal of International Medical Research 2012; 40: 899 908 Comparison of α-blocker Monotherapy and α-blocker Plus 5α-Reductase Inhibitor Combination Therapy Based on Prostate Volume for Treatment
The Journal of International Medical Research 2012; 40: 899 908 Comparison of α-blocker Monotherapy and α-blocker Plus 5α-Reductase Inhibitor Combination Therapy Based on Prostate Volume for Treatment
GSK Clinical Study Register
 In February 2013, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) announced a commitment to further clinical transparency through the public disclosure of GSK Clinical Study Reports (CSRs) on the GSK Clinical Study Register. The
In February 2013, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) announced a commitment to further clinical transparency through the public disclosure of GSK Clinical Study Reports (CSRs) on the GSK Clinical Study Register. The
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Introduction The examination of care in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a significant challenge, as most large datasets
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Introduction The examination of care in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a significant challenge, as most large datasets
Medical Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Present and Future Impact
 REPORTS Medical Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Present and Future Impact Muta M. Issa, MD, MBA; Timothy S. Regan, BPharm, RPh, CPh Abstract The purpose of this manuscript is to provide clinicians,
REPORTS Medical Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Present and Future Impact Muta M. Issa, MD, MBA; Timothy S. Regan, BPharm, RPh, CPh Abstract The purpose of this manuscript is to provide clinicians,
Abstract. Key words Trial without catheter, Acute urinary retention, Benign prostatic hyperplasia, Introduction
 The role of sustained-released alfuzosin in the treatment of acute urinary retention Mohamed Fawzi Ahmed. Department of Surgery, Ninevah College of Medicine, University of Mosul. Abstract To see whether
The role of sustained-released alfuzosin in the treatment of acute urinary retention Mohamed Fawzi Ahmed. Department of Surgery, Ninevah College of Medicine, University of Mosul. Abstract To see whether
BPH: a present and future perspective on health impact
 BPH: a present and future perspective on health impact Burden of disease in men with moderate LUTS Dalibor Pacík This presentation is financially supported by GlaxoSmithKline. CZ/DUTT/0019/12 Men with
BPH: a present and future perspective on health impact Burden of disease in men with moderate LUTS Dalibor Pacík This presentation is financially supported by GlaxoSmithKline. CZ/DUTT/0019/12 Men with
Index. urologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablative therapies, transurethral needle ablation, Adverse events, sexual side effects of BPH Aging, and incidence of BPH associated with
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablative therapies, transurethral needle ablation, Adverse events, sexual side effects of BPH Aging, and incidence of BPH associated with
Korean Urologist s View of Practice Patterns in Diagnosis and Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Nationwide Survey
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.2.248 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(2):248-252, 2010 Korean Urologist s View of Practice Patterns in Diagnosis and Management of Benign Prostatic
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.2.248 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 51(2):248-252, 2010 Korean Urologist s View of Practice Patterns in Diagnosis and Management of Benign Prostatic
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Important Papers / Landmark. Vijayan Manogran
 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Important Papers / Landmark Studies Vijayan Manogran MTOPS & CombAT PLESS SMART ALTESS ALF-ONE VA PREDICT EPICS Landmark Studies MTOPS Medical Therapy of Prostatic Symptoms
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Important Papers / Landmark Studies Vijayan Manogran MTOPS & CombAT PLESS SMART ALTESS ALF-ONE VA PREDICT EPICS Landmark Studies MTOPS Medical Therapy of Prostatic Symptoms
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Jay Lee, MD, FRCSC Clinical Associate Professor University of Calgary
 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Jay Lee, MD, FRCSC Clinical Associate Professor University of Calgary Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied,
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Jay Lee, MD, FRCSC Clinical Associate Professor University of Calgary Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied,
Finland and Sweden and UK GP-HOSP datasets
 Web appendix: Supplementary material Table 1 Specific diagnosis codes used to identify bladder cancer cases in each dataset Finland and Sweden and UK GP-HOSP datasets Netherlands hospital and cancer registry
Web appendix: Supplementary material Table 1 Specific diagnosis codes used to identify bladder cancer cases in each dataset Finland and Sweden and UK GP-HOSP datasets Netherlands hospital and cancer registry
Prostate Gland Volume and Its Relationship to Complications of Benign Prostatic Enlargement
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 6 Ver. II (Jun. 2015), PP 33-37 www.iosrjournals.org Prostate Gland Volume and Its Relationship
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 6 Ver. II (Jun. 2015), PP 33-37 www.iosrjournals.org Prostate Gland Volume and Its Relationship
Prostatitis refers to several clinical syndromes, including
 Prostatitis Michel A. Pontari,* Geoffrey F. Joyce, Matthew Wise, Mary McNaughton-Collins and the Urologic Diseases in America Project From the Department of Urology, Temple University School of Medicine,
Prostatitis Michel A. Pontari,* Geoffrey F. Joyce, Matthew Wise, Mary McNaughton-Collins and the Urologic Diseases in America Project From the Department of Urology, Temple University School of Medicine,
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH):
 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Evidence Based Guidelines for Primary Care Providers Jeanne Martin, DNP, ANP-BC Objectives 1. Understand the pathophysiology and prevalence of BPH 2. Select the appropriate
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Evidence Based Guidelines for Primary Care Providers Jeanne Martin, DNP, ANP-BC Objectives 1. Understand the pathophysiology and prevalence of BPH 2. Select the appropriate
FEP Medical Policy Manual
 FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: April 15, 2018 Related Policies: None Prostatic Urethral Lift Description Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition in older individuals that can
FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: April 15, 2018 Related Policies: None Prostatic Urethral Lift Description Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition in older individuals that can
How Do New Data from Clinical Trials Allow Us to Optimise the Assessment and Treatment of Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia?
 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com How Do New Data from Clinical Trials Allow Us to Optimise the Assessment and Treatment of Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia?
available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com How Do New Data from Clinical Trials Allow Us to Optimise the Assessment and Treatment of Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia?
Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.39 Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
MP 7.01.39 Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
NOTE: This policy is not effective until April 1, Transurethral Water Vapor Thermal Therapy of the Prostate
 NOTE: This policy is not effective until April 1, 2019. Medical Policy Manual Surgery, Policy No. 210 Transurethral Water Vapor Thermal Therapy of the Prostate Next Review: December 2019 Last Review: December
NOTE: This policy is not effective until April 1, 2019. Medical Policy Manual Surgery, Policy No. 210 Transurethral Water Vapor Thermal Therapy of the Prostate Next Review: December 2019 Last Review: December
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM
 USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients from the Medicare 5 percent sample have either a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients from the Medicare 5 percent sample have either a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease
Chapter 5: Acute Kidney Injury
 Chapter 5: Acute Kidney Injury Introduction In recent years, acute kidney injury (AKI) has gained increasing recognition as a major risk factor for the development of chronic kidney disease (CKD). The
Chapter 5: Acute Kidney Injury Introduction In recent years, acute kidney injury (AKI) has gained increasing recognition as a major risk factor for the development of chronic kidney disease (CKD). The
Subject: Temporary Prostatic Stent and Prostatic Urethral Lift
 02-54000-21 Original Effective Date: 03/15/05 Reviewed: 09/27/18 Revised: 10/15/18 Subject: Temporary Prostatic Stent and Prostatic Urethral Lift THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION,
02-54000-21 Original Effective Date: 03/15/05 Reviewed: 09/27/18 Revised: 10/15/18 Subject: Temporary Prostatic Stent and Prostatic Urethral Lift THIS MEDICAL COVERAGE GUIDELINE IS NOT AN AUTHORIZATION,
Evidence-based guidelines in lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia and variation in care
 REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Evidence-based guidelines in lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia and variation in care Seth A. Strope Purpose of review Guidelines have been developed
REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Evidence-based guidelines in lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia and variation in care Seth A. Strope Purpose of review Guidelines have been developed
Associations of obesity, physical activity and diet with benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms
 REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Associations of obesity, physical activity and diet with benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms Omer A. Raheem a and J. Kellogg Parsons a,b,c Purpose of review
REVIEW C URRENT OPINION Associations of obesity, physical activity and diet with benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary tract symptoms Omer A. Raheem a and J. Kellogg Parsons a,b,c Purpose of review
Introduction to PAE. Rational / Animal. Francisco Cesar Carnevale MD, PhD. University of Sao Paulo Medical School - Brazil
 Introduction to PAE Rational / Animal Francisco Cesar Carnevale MD, PhD University of Sao Paulo Medical School - Brazil Francisco Carnevale, M.D. No relevant financial relationship reported Bladder Outlet
Introduction to PAE Rational / Animal Francisco Cesar Carnevale MD, PhD University of Sao Paulo Medical School - Brazil Francisco Carnevale, M.D. No relevant financial relationship reported Bladder Outlet
Alameda County Public Health Department. Adult Preventable Hospitalizations: Examining Impacts, Trends, and Disparities by Group
 Adult Preventable Hospitalizations: Examining Impacts, Trends, and Disparities by Group Abstract Preventable hospitalizations occur when persons are hospitalized for a medical condition that could have
Adult Preventable Hospitalizations: Examining Impacts, Trends, and Disparities by Group Abstract Preventable hospitalizations occur when persons are hospitalized for a medical condition that could have
FEP Medical Policy Manual
 FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: January 15, 2019 Related Policies: None Prostatic Urethral Lift Description Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition in older individuals that
FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: January 15, 2019 Related Policies: None Prostatic Urethral Lift Description Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition in older individuals that
Management of LUTS. Simon Woodhams February 2012
 Management of LUTS Simon Woodhams February 2012 The management of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in men Implementing NICE guidance May 2010 NICE clinical guideline 97 Background Lower urinary tract
Management of LUTS Simon Woodhams February 2012 The management of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) in men Implementing NICE guidance May 2010 NICE clinical guideline 97 Background Lower urinary tract
Chapter 6: Healthcare Expenditures for Persons with CKD
 Chapter 6: Healthcare Expenditures for Persons with CKD In this 2017 Annual Data Report (ADR), we introduce information from the Optum Clinformatics DataMart for persons with Medicare Advantage and commercial
Chapter 6: Healthcare Expenditures for Persons with CKD In this 2017 Annual Data Report (ADR), we introduce information from the Optum Clinformatics DataMart for persons with Medicare Advantage and commercial
EAU GUIDELINES POCKET EDITION 3
 EAU GUIDELINES POCKET EDITION 3 CONTENTS: BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA URINARY INCONTINENCE UROLITHIASIS 2 3 EAU POCKET GUIDELINES POCKET EDITION 3 This is one of a series of convenient pocket size books
EAU GUIDELINES POCKET EDITION 3 CONTENTS: BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA URINARY INCONTINENCE UROLITHIASIS 2 3 EAU POCKET GUIDELINES POCKET EDITION 3 This is one of a series of convenient pocket size books
Ankle fractures are one of
 Elevated Risks of Ankle Fracture Surgery in Patients With Diabetes Nelson F. SooHoo, MD, Lucie Krenek, MD, Michael Eagan, MD, and David S. Zingmond, MD, PhD Ankle fractures are one of the most common types
Elevated Risks of Ankle Fracture Surgery in Patients With Diabetes Nelson F. SooHoo, MD, Lucie Krenek, MD, Michael Eagan, MD, and David S. Zingmond, MD, PhD Ankle fractures are one of the most common types
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Urol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 May 4.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Urol. 2009 December ; 182(6): 2819 2824. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2009.08.086. Intravesical Prostatic Protrusion in Men in Olmsted County,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Urol. 2009 December ; 182(6): 2819 2824. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2009.08.086. Intravesical Prostatic Protrusion in Men in Olmsted County,
The Enlarged Prostate Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
 The Enlarged Prostate Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment MAC00031-01 Rev G Financial support for this seminar has been provided by NeoTract, Inc., the manufacturer of the UroLift System. 1 Today s Agenda
The Enlarged Prostate Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment MAC00031-01 Rev G Financial support for this seminar has been provided by NeoTract, Inc., the manufacturer of the UroLift System. 1 Today s Agenda
Zhao Y Y et al. Ann Intern Med 2012;156:
 Zhao Y Y et al. Ann Intern Med 2012;156:560-569 Introduction Fibrates are commonly prescribed to treat dyslipidemia An increase in serum creatinine level after use has been observed in randomized, placebocontrolled
Zhao Y Y et al. Ann Intern Med 2012;156:560-569 Introduction Fibrates are commonly prescribed to treat dyslipidemia An increase in serum creatinine level after use has been observed in randomized, placebocontrolled
Therapeutic Strategies for Managing BPH Progression
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 997 1003 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Therapeutic Strategies for Managing BPH Progression John M. Fitzpatrick a, *,
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 997 1003 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Therapeutic Strategies for Managing BPH Progression John M. Fitzpatrick a, *,
PATIENT INFORMATION 2017 NeoTract, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA. MAC Rev A
 PATIENT INFORMATION OVER 70% OF MEN IN THEIR 60s HAVE SYMPTOMS OF BPH 1 BPH affects more than 500 million men worldwide, with many men suffering from symptoms of enlarged prostate. 1 You no longer have
PATIENT INFORMATION OVER 70% OF MEN IN THEIR 60s HAVE SYMPTOMS OF BPH 1 BPH affects more than 500 million men worldwide, with many men suffering from symptoms of enlarged prostate. 1 You no longer have
Chapter 5: Acute Kidney Injury
 Chapter 5: Acute Kidney Injury In 2015, 4.3% of Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries experienced a hospitalization complicated by Acute Kidney Injury (AKI); this appears to have plateaued since 2011
Chapter 5: Acute Kidney Injury In 2015, 4.3% of Medicare fee-for-service beneficiaries experienced a hospitalization complicated by Acute Kidney Injury (AKI); this appears to have plateaued since 2011
Can men with prostates sized 80 ml or larger be managed conservatively?
 Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:359-364. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Can men with prostates sized 80 ml or larger be managed conservatively? Alvin Lee,
Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:359-364. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Can men with prostates sized 80 ml or larger be managed conservatively? Alvin Lee,
Chapter 3: Morbidity and Mortality in Patients with CKD
 Chapter 3: Morbidity and Mortality in Patients with CKD In this 2017 Annual Data Report (ADR) we introduce analysis of a new dataset. To provide a more comprehensive examination of morbidity patterns,
Chapter 3: Morbidity and Mortality in Patients with CKD In this 2017 Annual Data Report (ADR) we introduce analysis of a new dataset. To provide a more comprehensive examination of morbidity patterns,
Treatment Patterns in Alpha-Blocker Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
 510732JMHXXX10.1177/1557988313510732American Journal of Men s HealthSchoenfeld et al. research-article2013 Article Treatment Patterns in Alpha-Blocker Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia American
510732JMHXXX10.1177/1557988313510732American Journal of Men s HealthSchoenfeld et al. research-article2013 Article Treatment Patterns in Alpha-Blocker Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia American
Key Findings. Mortality Rates
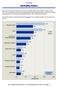 Mortality Rates Statewide in-hospital mortality rates showed a statistically significant decrease from to in nine of the 15 conditions reported. The largest decrease was in, where the mortality rate decreased
Mortality Rates Statewide in-hospital mortality rates showed a statistically significant decrease from to in nine of the 15 conditions reported. The largest decrease was in, where the mortality rate decreased
Will Medical Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Result in Better or Worse Sexual Function in Men?
 Urol Sci 2011;22(1):14 18 MINI REVIEW Will Medical Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Result in Better or Worse Sexual Function in Men? Thomas I.S. Hwang 1,2,3 * 1 Shin Kong WHS Hospital, Taipei,
Urol Sci 2011;22(1):14 18 MINI REVIEW Will Medical Management of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Result in Better or Worse Sexual Function in Men? Thomas I.S. Hwang 1,2,3 * 1 Shin Kong WHS Hospital, Taipei,
Control & confidence. You deserve both. YOUR GUIDE TO THE TREATMENT OF BPH
 Control & confidence. You deserve both. YOUR GUIDE TO THE TREATMENT OF BPH The more you know, the better you ll feel. You ve likely had a discussion with your doctor about BPH 1. What follows are some
Control & confidence. You deserve both. YOUR GUIDE TO THE TREATMENT OF BPH The more you know, the better you ll feel. You ve likely had a discussion with your doctor about BPH 1. What follows are some
Control & confidence. You deserve both.
 Learn more about BPH and Plasma therapy Control & confidence. You deserve both. YOUR GUIDE TO THE TREATMENT OF BPH Your doctor is always happy to offer all the guidance you need so that you feel completely
Learn more about BPH and Plasma therapy Control & confidence. You deserve both. YOUR GUIDE TO THE TREATMENT OF BPH Your doctor is always happy to offer all the guidance you need so that you feel completely
POLICIES AND PROCEDURE MANUAL
 POLICIES AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Policy: MP048 Section: Medical Benefit Policy Subject: Surgical and Minimally Invasive Therapies for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy I. Policy: Surgical and
POLICIES AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Policy: MP048 Section: Medical Benefit Policy Subject: Surgical and Minimally Invasive Therapies for the Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy I. Policy: Surgical and
HEALTH CARE EXPENDITURES ASSOCIATED WITH PERSISTENT EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT USE: A MULTI-STATE ANALYSIS OF MEDICAID BENEFICIARIES
 HEALTH CARE EXPENDITURES ASSOCIATED WITH PERSISTENT EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT USE: A MULTI-STATE ANALYSIS OF MEDICAID BENEFICIARIES Presented by Parul Agarwal, PhD MPH 1,2 Thomas K Bias, PhD 3 Usha Sambamoorthi,
HEALTH CARE EXPENDITURES ASSOCIATED WITH PERSISTENT EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT USE: A MULTI-STATE ANALYSIS OF MEDICAID BENEFICIARIES Presented by Parul Agarwal, PhD MPH 1,2 Thomas K Bias, PhD 3 Usha Sambamoorthi,
Ambulatory Try off Catheter (ATOC) Program for the Patient with Acute Retention of Urine Outpatient Service
 Ambulatory Try off Catheter (ATOC) Program for the Patient with Acute Retention of Urine Outpatient Service Mr. Tang, Chi Chiu Kevin (APN) Urology Center Department of Surgery Kwong Wah Hospital Redevelopment
Ambulatory Try off Catheter (ATOC) Program for the Patient with Acute Retention of Urine Outpatient Service Mr. Tang, Chi Chiu Kevin (APN) Urology Center Department of Surgery Kwong Wah Hospital Redevelopment
National Incidence and Impact of Noninfectious Urethral Catheter Related Complications on the Surgical Care Improvement Project
 National Incidence and Impact of Noninfectious Urethral Catheter Related Complications on the Surgical Care Improvement Project David S. Aaronson,* Alex K. Wu, Sarah D. Blaschko, Jack W. McAninch and Maurice
National Incidence and Impact of Noninfectious Urethral Catheter Related Complications on the Surgical Care Improvement Project David S. Aaronson,* Alex K. Wu, Sarah D. Blaschko, Jack W. McAninch and Maurice
Chapter 3: Morbidity and Mortality
 Chapter 3: Morbidity and Mortality Introduction In this chapter we evaluate the morbidity and mortality of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients continuously enrolled in Medicare. Each year s analysis
Chapter 3: Morbidity and Mortality Introduction In this chapter we evaluate the morbidity and mortality of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients continuously enrolled in Medicare. Each year s analysis
a guide to Reimbursement of Intermittent Catheters Know your options M2116N 04.08
 a guide to Reimbursement of Intermittent Catheters 1 Know your options Coloplast Corp. Minneapolis, MN 55411 1.800.533.0464 usmedweb@coloplast.com www.us.coloplast.com is a registered trademark of Coloplast
a guide to Reimbursement of Intermittent Catheters 1 Know your options Coloplast Corp. Minneapolis, MN 55411 1.800.533.0464 usmedweb@coloplast.com www.us.coloplast.com is a registered trademark of Coloplast
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM
 USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 10: Dialysis Providers In 2013, collectively the three large dialysis organizations treated 71% of patients in 67% of all dialysis units. In the Small Dialysis
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 10: Dialysis Providers In 2013, collectively the three large dialysis organizations treated 71% of patients in 67% of all dialysis units. In the Small Dialysis
Last Review Status/Date: December Summary
 Section: Surgery Effective Date: January 15, 2016 Subject: Prostatic Urethral Lift Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Status/Date: December 2015 Summary Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition in
Section: Surgery Effective Date: January 15, 2016 Subject: Prostatic Urethral Lift Page: 1 of 9 Last Review Status/Date: December 2015 Summary Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition in
Tennessee Department of Health in collaboration with Tennessee State University and University of Tennessee Health Science Center
 Tennessee Department of Health in collaboration with Tennessee State University and University of Tennessee Health Science Center 2006 Tennessee Department of Health 2006 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS CONTRIBUTING
Tennessee Department of Health in collaboration with Tennessee State University and University of Tennessee Health Science Center 2006 Tennessee Department of Health 2006 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS CONTRIBUTING
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript World J Urol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 February 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: World J Urol. 2011 February ; 29(1): 11 14. doi:10.1007/s00345-010-0625-4. Significance of preoperative PSA velocity in men with low
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: World J Urol. 2011 February ; 29(1): 11 14. doi:10.1007/s00345-010-0625-4. Significance of preoperative PSA velocity in men with low
Prevalence of Mental Illness
 Section 1 Prevalence of Mental Illness The prevalence of mental health problems or mental illness appears to be quite stable over time. Full epidemiological surveys of prevalence, reported using complex
Section 1 Prevalence of Mental Illness The prevalence of mental health problems or mental illness appears to be quite stable over time. Full epidemiological surveys of prevalence, reported using complex
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance SCOPE The UroLift system for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia 1
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance SCOPE The UroLift system for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms secondary to benign prostatic hyperplasia 1
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Lee JS, Nsa W, Hausmann LRM, et al. Quality of care for elderly patients hospitalized for pneumonia in the United States, 2006 to 2010. JAMA Intern Med. Published online September
Supplementary Online Content Lee JS, Nsa W, Hausmann LRM, et al. Quality of care for elderly patients hospitalized for pneumonia in the United States, 2006 to 2010. JAMA Intern Med. Published online September
DrugTreatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Hospital Admission for BPH-Related Surgery
 European Urology European Urology 43 (2003) 528 534 DrugTreatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Hospital Admission for BPH-Related Surgery P.C. Souverein a,*, J.A. Erkens b, J.J.M.C.H. de la Rosette
European Urology European Urology 43 (2003) 528 534 DrugTreatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia and Hospital Admission for BPH-Related Surgery P.C. Souverein a,*, J.A. Erkens b, J.J.M.C.H. de la Rosette
Population based studies in Pancreatic Diseases. Satish Munigala
 Population based studies in Pancreatic Diseases Satish Munigala 1 Definition Population-based studies aim to answer research questions for defined populations 1 Generalizable to the whole population addressed
Population based studies in Pancreatic Diseases Satish Munigala 1 Definition Population-based studies aim to answer research questions for defined populations 1 Generalizable to the whole population addressed
Voluntary Mental Health Treatment Laws for Minors & Length of Inpatient Stay. Tori Lallemont MPH Thesis: Maternal & Child Health June 6, 2007
 Voluntary Mental Health Treatment Laws for Minors & Length of Inpatient Stay Tori Lallemont MPH Thesis: Maternal & Child Health June 6, 2007 Introduction 1997: Nearly 300,000 children were admitted to
Voluntary Mental Health Treatment Laws for Minors & Length of Inpatient Stay Tori Lallemont MPH Thesis: Maternal & Child Health June 6, 2007 Introduction 1997: Nearly 300,000 children were admitted to
Department of Urology, Nippon Medical School Chiba Hokusou Hospital, Chiba, Japan. Department of Urology, Nippon Medical School, Tokyo, Japan
 Original Treatment Results of Transurethral Resection of the Prostate by Non-Japanese Board-Certified Urologists for Benign Prostate Hyperplasia: Analysis by Resection Volume Yasutomo Suzuki 1,2, Yuka
Original Treatment Results of Transurethral Resection of the Prostate by Non-Japanese Board-Certified Urologists for Benign Prostate Hyperplasia: Analysis by Resection Volume Yasutomo Suzuki 1,2, Yuka
Index. urologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablation, of prostate, holmium laser, 485 495 African prune tree (Pygeum africanum), 454 455 Alfuzosin, 445 446 Alpha-adrenergic agonists,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablation, of prostate, holmium laser, 485 495 African prune tree (Pygeum africanum), 454 455 Alfuzosin, 445 446 Alpha-adrenergic agonists,
The role of bladder diverticula in the prevalence of acute urinary retention in patients with BPH who are candidates
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 44 (x): 2018 March 3.[Ahead of print] doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0605 The role of bladder diverticula in the prevalence of acute urinary retention in patients with BPH who
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 44 (x): 2018 March 3.[Ahead of print] doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0605 The role of bladder diverticula in the prevalence of acute urinary retention in patients with BPH who
Low Incidence of Acute Urinary Retention in the General Male Population: TheTriumph Project
 European Urology European Urology 47 (2005) 494 498 Low Incidence of Acute Urinary Retention in the General Male Population: TheTriumph Project K.M.C. Verhamme a,b, *, J.P. Dieleman a, M.A.M. van Wijk
European Urology European Urology 47 (2005) 494 498 Low Incidence of Acute Urinary Retention in the General Male Population: TheTriumph Project K.M.C. Verhamme a,b, *, J.P. Dieleman a, M.A.M. van Wijk
2017 USRDS ANNUAL DATA REPORT KIDNEY DISEASE IN THE UNITED STATES S611
 Healthy People 2020 In this chapter, we examine data for 11 Healthy People 2020 (HP2020) objectives 10 for CKD and one for diabetes spanning 20 total indicators for which the USRDS serves as the official
Healthy People 2020 In this chapter, we examine data for 11 Healthy People 2020 (HP2020) objectives 10 for CKD and one for diabetes spanning 20 total indicators for which the USRDS serves as the official
Hyoung Woo Kim, Dae Geun Moon, Hyun Min Kim, Jong Ho Hwang, Soon Chan Kim, Sam Geuk Nam, Jun Tag Park
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2011.52.10.681 Voiding Dysfunction Effect of Shifting from Combination Therapy to Monotherapy of α-blockers or 5α-Reductase Inhibitors on Prostate Volume
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2011.52.10.681 Voiding Dysfunction Effect of Shifting from Combination Therapy to Monotherapy of α-blockers or 5α-Reductase Inhibitors on Prostate Volume
Literature Scan: Drugs for BPH
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
PROSTATIC EMBOLIZATION FOR BENIGN HYPERPLASIA
 St. Louis Hospital PROSTATIC EMBOLIZATION FOR BENIGN HYPERPLASIA INITIAL CLINICAL RESULTS Faculty of Medical Sciences New University of Lisbon JOÃO PISCO LUÍS CAMPOS PINHEIRO TIAGO BILHIM HUGO RIO TINTO
St. Louis Hospital PROSTATIC EMBOLIZATION FOR BENIGN HYPERPLASIA INITIAL CLINICAL RESULTS Faculty of Medical Sciences New University of Lisbon JOÃO PISCO LUÍS CAMPOS PINHEIRO TIAGO BILHIM HUGO RIO TINTO
Evaluation of Sexual Dysfunction in Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms/Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Patients
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/10 Evaluation of Sexual Dysfunction in Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms/Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Patients N. Narayanamoorthy,
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/10 Evaluation of Sexual Dysfunction in Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms/Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Patients N. Narayanamoorthy,
Impact of Changing Trends in Medical Therapy on Surgery for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Over Two Decades
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.1.23 Voiding Dysfunction Impact of Changing Trends in Medical Therapy on Surgery for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Over Two Decades Se Young Choi,
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.1.23 Voiding Dysfunction Impact of Changing Trends in Medical Therapy on Surgery for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Over Two Decades Se Young Choi,
Key words: Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (LUTS), Prostatic Hyperplasia, Alpha-1 Adrenoceptor Antagonists, Tamsulosin, Terazosin.
 The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.17957/TPMJ/17.4102 ORIGINAL PROF-4102 PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA; COMPARISON BETWEEN TAMSULOSIN AND TERAZOSIN FOR EFFICACY IN MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF LOWER URINARY TRACT
The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.17957/TPMJ/17.4102 ORIGINAL PROF-4102 PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA; COMPARISON BETWEEN TAMSULOSIN AND TERAZOSIN FOR EFFICACY IN MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF LOWER URINARY TRACT
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM
 USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 6: Medicare Expenditures for Persons With CKD Medicare spending for patients with CKD aged 65 and older exceeded $50 billion in 2013, representing 20% of all
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 6: Medicare Expenditures for Persons With CKD Medicare spending for patients with CKD aged 65 and older exceeded $50 billion in 2013, representing 20% of all
Webinar Series: Diabetes Epidemic & Action Report (DEAR) for Washington State - How We Are Doing and How We Can Improve.
 Webinar Series: Diabetes Epidemic & Action Report (DEAR) for Washington State - How We Are Doing and How We Can Improve April 22, 2015 Qualis Health A leading national population health management organization
Webinar Series: Diabetes Epidemic & Action Report (DEAR) for Washington State - How We Are Doing and How We Can Improve April 22, 2015 Qualis Health A leading national population health management organization
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Update on Innovative Current Treatments
 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Update on Innovative Current Treatments Michael Ferrandino, MD As.soc Professor Director of Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery Division of Urologic Surgery Duke University
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Update on Innovative Current Treatments Michael Ferrandino, MD As.soc Professor Director of Minimally Invasive Urologic Surgery Division of Urologic Surgery Duke University
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. Department of Public Health Sciences
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Public Health Sciences THE LENGTH OF STAY AND READMISSIONS IN MASTECTOMY PATIENTS A Thesis in Public Health Sciences by Susie Sun 2015
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Public Health Sciences THE LENGTH OF STAY AND READMISSIONS IN MASTECTOMY PATIENTS A Thesis in Public Health Sciences by Susie Sun 2015
Medical Coverage Policy Prostatic Urethral Lifts
 Medical Coverage Policy Prostatic Urethral Lifts EFFECTIVE DATE:12 01 2018 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 10 03 2017 OVERVIEW Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a common condition in older men that can lead to increased
Medical Coverage Policy Prostatic Urethral Lifts EFFECTIVE DATE:12 01 2018 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 10 03 2017 OVERVIEW Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a common condition in older men that can lead to increased
Key Findings. Mortality Rates
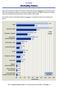 Mortality Rates Statewide in-hospital mortality rates showed a statistically significant decrease from federal fiscal year to federal fiscal year in 12 of the 15 conditions reported. The largest decrease
Mortality Rates Statewide in-hospital mortality rates showed a statistically significant decrease from federal fiscal year to federal fiscal year in 12 of the 15 conditions reported. The largest decrease
Exploring the Relationship Between Substance Abuse and Dependence Disorders and Discharge Status: Results and Implications
 MWSUG 2017 - Paper DG02 Exploring the Relationship Between Substance Abuse and Dependence Disorders and Discharge Status: Results and Implications ABSTRACT Deanna Naomi Schreiber-Gregory, Henry M Jackson
MWSUG 2017 - Paper DG02 Exploring the Relationship Between Substance Abuse and Dependence Disorders and Discharge Status: Results and Implications ABSTRACT Deanna Naomi Schreiber-Gregory, Henry M Jackson
Transurethral Prostatic Resection for Acute Urinary Retention in Patients with Prostate Cancer
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transurethral Prostatic Resection for Acute Urinary Retention in Patients with Prostate Cancer Chang-Chi Chang, Junne-Yih Kuo*, Kuang-Kuo Chen, Alex Tong-Long Lin, Yen-Hwa Chang, Howard
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transurethral Prostatic Resection for Acute Urinary Retention in Patients with Prostate Cancer Chang-Chi Chang, Junne-Yih Kuo*, Kuang-Kuo Chen, Alex Tong-Long Lin, Yen-Hwa Chang, Howard
ACO #44 Use of Imaging Studies for Low Back Pain
 Measure Information Form (MIF) DATA SOURCE Medicare Claims Medicare beneficiary enrollment data MEASURE SET ID ACO #44 VERSION NUMBER AND EFFECTIVE DATE Version 1, effective 01/01/18 CMS APPROVAL DATE
Measure Information Form (MIF) DATA SOURCE Medicare Claims Medicare beneficiary enrollment data MEASURE SET ID ACO #44 VERSION NUMBER AND EFFECTIVE DATE Version 1, effective 01/01/18 CMS APPROVAL DATE
Chapter 10: Dialysis Providers
 Chapter 10: Dialysis Providers In 2014 the two largest dialysis organizations, Fresenius and DaVita, collectively treated 69% of patients in 65% of all dialysis units (Figure 10.2). Nearly 90% of all dialysis
Chapter 10: Dialysis Providers In 2014 the two largest dialysis organizations, Fresenius and DaVita, collectively treated 69% of patients in 65% of all dialysis units (Figure 10.2). Nearly 90% of all dialysis
Mini-Invasive Treatment in Urological Diseases Dott. Alberto Saita Responsabile Endourologia Istituto Clinico Humanitas - Rozzano
 Dipartimento di Urologia Direttore Prof. Giorgio Guazzoni Mini-Invasive Treatment in Urological Diseases Dott. Alberto Saita Responsabile Endourologia Istituto Clinico Humanitas - Rozzano alberto.saita@humanitas.it
Dipartimento di Urologia Direttore Prof. Giorgio Guazzoni Mini-Invasive Treatment in Urological Diseases Dott. Alberto Saita Responsabile Endourologia Istituto Clinico Humanitas - Rozzano alberto.saita@humanitas.it
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Toyoda N, Chikwe J, Itagaki S, Gelijns AC, Adams DH, Egorova N. Trends in infective endocarditis in California and New York State, 1998-2013. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.4287
Supplementary Online Content Toyoda N, Chikwe J, Itagaki S, Gelijns AC, Adams DH, Egorova N. Trends in infective endocarditis in California and New York State, 1998-2013. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.4287
Chapter 4: Research and Future Directions
 Chapter 4: Research and Future Directions Introduction Many of the future research needs listed in the 1994 Agency for Health Care Policy and Research (AHCPR) clinical practice guideline Benign Prostatic
Chapter 4: Research and Future Directions Introduction Many of the future research needs listed in the 1994 Agency for Health Care Policy and Research (AHCPR) clinical practice guideline Benign Prostatic
PROSTATIC ARTERY EMBOLISATION (PAE) FOR BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA. A Minimally Invasive Innovative Treatment
 PROSTATIC ARTERY EMBOLISATION (PAE) FOR BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA A Minimally Invasive Innovative Treatment What is the prostate? The prostate is an accessory organ of the male reproductive system.
PROSTATIC ARTERY EMBOLISATION (PAE) FOR BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA A Minimally Invasive Innovative Treatment What is the prostate? The prostate is an accessory organ of the male reproductive system.
Prevalence of vertebral fractures on chest radiographs of elderly African American and Caucasian women
 Osteoporos Int (2011) 22:2365 2371 DOI 10.1007/s00198-010-1452-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of vertebral fractures on chest radiographs of elderly African American and Caucasian women D. Lansdown & B.
Osteoporos Int (2011) 22:2365 2371 DOI 10.1007/s00198-010-1452-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prevalence of vertebral fractures on chest radiographs of elderly African American and Caucasian women D. Lansdown & B.
Combination Drug Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
 The Annals of African Surgery www.sskenya.org Combination Drug Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Author: Oliech J.S. FRCS, Affiliation: Department of Surgery, University of Nairobi. P.O. Box
The Annals of African Surgery www.sskenya.org Combination Drug Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) Author: Oliech J.S. FRCS, Affiliation: Department of Surgery, University of Nairobi. P.O. Box
