1. Spell and define the key terms 2. List and describe the disorders of the. the urinary system and the male reproductive
|
|
|
- Peter Lambert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 34 Urology Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define the key terms 2. List and describe the disorders of the urinary system and the male reproductive system 3. Describe and explain the purpose of various diagnostic procedures associated with the urinary system 4. Discuss the role of the medical assistant in diagnosing and treating disorders of the urinary system and the male reproductive system 5. Identify common pathologies related to each body system 6. Describe implications for treatment related to pathology Psychomotor Domain 1. Perform a female urinary catheterization (Procedure 34-1) 2. Perform a male urinary catheterization (Procedure 34-2) 3. Instruct a male patient on the testicular self-examination (Procedure 34-3) 4. Assist physician with patient care 5. Prepare a patient for procedures and/or treatments 6. Practice standard precautions 7. Document patient care 8. Document patient education 9. Practice within the standard of care for a medical assistant Affective Domain 1. Apply critical thinking skills in performing patient assessment and care 2. Use language/verbal skills that enable patients understanding 3. Demonstrate empathy in communicating with patients, family, and staff 4. Use appropriate body language and other nonverbal skills in communicating with patients, family, and staff 5. Demonstrate awareness of the territorial boundaries of the person with whom you are communicating 6. Demonstrate sensitivity appropriate to the message being delivered 7. Demonstrate recognition of the patient s level of understanding in communications 8. Recognize and protect personal boundaries in communicating with others 9. Demonstrate respect for individual diversity, incorporating awareness of one s own biases in areas including gender, race, religion, age, and economic status 10. Apply active listening skills 11. Apply local, state, and federal health care legislation and regulation appropriate to the medical assisting practice setting 629
2 630 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant ABHES Competencies 1. Assist the physician with the regimen of diagnostic and treatment modalities as they relate to each body system 2. Comply with federal, state, and local health laws and regulations 3. Communicate on the recipient s level of comprehension 4. Serve as a liaison between the physician and others 5. Show empathy and impartiality when dealing with patients 6. Document accurately
3 CHAPTER 34 Urology 631 Name: Date: Grade: COG MULTIPLE CHOICE Circle the letter preceding the correct answer. 1. Cystoscopy is: a. an inflammation of the urinary bladder. b. the direct visualization of the bladder and urethra. c. a procedure used to help patients pass calculi. d. the treatment used for men with an inguinal hernia. e. the use of a small camera inserted into the rectum. 2. Which of the following might contribute to psychogenic impotence? a. Disease in any other body system b. Injury to pelvic organs c. Medication d. Exhaustion e. Cardiovascular problems 3. Before scheduling a patient for an IVP or a retrograde pyelogram, you must check for a(n): a. protein allergy. b. lubricant allergy. c. iodine allergy. d. rubber allergy. e. latex allergy. 4. A procedure that cleanses the blood of waste products and excess fluid is: a. oliguria. b. lithotripsy. c. proteinuria. d. cystoscopy. e. dialysis. 5. Young girls are prone to urethritis because they: a. forget to practice good hand-washing technique. b. have a short urethra. c. don t take enough baths. d. urinate too frequently. e. wipe from front to back. 6. Which of the following instructions would be helpful for a patient trying to pass a stone? a. Eat a large amount of fiber. b. Get plenty of bed rest and relaxation. c. Drink lots of water. d. Go to the hospital when the stone passes. e. Do not consume anything until the stone has passed. 7. Orchiopexy is surgery to correct: a. undescended testes. b. enlarged prostate. c. inguinal hernia. d. impotence. e. hydrocele. 8. One common urinary disorder in females is: a. benign prostatic hyperplasia. b. nocturia. c. hydrocele. d. cryptorchidism. e. urinary tract infection. Scenario for questions 9 and 10: An elderly patient comes in for a routine checkup, and the physician discovers his prostate gland is very enlarged. 9. What is a blood test you can run to look for prostate cancer? a. PSA test b. Proteinuria c. Snellen test d. Digital rectal exam e. Dialysis
4 632 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant 10. A urinary condition that might indicate an enlarged prostate gland is: a. proteinuria. b. oliguria. c. nocturia. d. hematuria. e. pyuria. 11. Seventy-five percent of men with prostate cancer are over age: a. 15 years. b. 30 years. c. 34 years. d. 50 years. e. 75 years. 12. What kind of juice is recommended to patients to acidify urine? a. Tomato juice b. Orange juice c. Grape juice d. Cranberry juice e. Grapefruit juice 13. A patient should be given a catheter when: a. the patient suffers from nocturia. b. the patient has a urinary tract infection. c. the patient s urine has high PSA levels. d. the patient has calculi. e. the patient has dysuria. 14. Which of the following instruments is used to view the bladder and urethra? a. Catheter b. Cystoscope c. Dialysis machine d. Ultrasound e. Pyelogram 15. Which of the following patients is most likely to develop a urinary tract infection? a. A young boy who frequently urinates b. A teenaged girl who takes bubble baths c. An elderly woman who only wears loose-fitting dresses d. An adult woman who showers immediately after sexual intercourse e. A middle-aged man who does not wash his hands very often 16. Which of the following is the initial step in catheterization of a patient? a. Wash your hands. b. Open the catheterization kit. c. Put on sterile gloves. d. Use antiseptic swabs to clean area. e. Assist patient to assume position. 17. What is a symptom of hydronephrosis? a. Proteinuria b. Chills c. Swollen prostate d. Back pain e. High PSA levels 18. Which of the following is true for catheterizing both men and women? a. Tray may be placed on patient s lap for easy access to tools. b. Patient s position is on his or her back, legs apart. c. Catheter is inserted 5 inches. d. Nondominant hand is contaminated. e. Coudé catheter may be used.
5 CHAPTER 34 Urology Which of the following is a cause of organic impotence? a. Exhaustion b. Anxiety c. Depression d. Stress e. Endocrine imbalance 20. Ultrasonography can be used to treat which of the following? a. Renal failure b. Hydronephrosis c. Calculi d. Urinary tract infection e. Inguinal hernia COG MATCHING Grade: Place the letter preceding the defi nition on the line next to the term. Key Terms Definitions 21. anuria 22. blood urea nitrogen 23. catheterization 24. cystoscopy 25. dialysis 26. dysuria 27. enuresis 28. hematuria 29. impotence 30. incontinence 31. intravenous pyelogram (IVP) 32. lithotripsy 33. nephrostomy 34. nocturia 35. oliguria 36. prostate-specific antigen 37. proteinuria a. an inability to achieve or maintain an erection b. painful or difficult urination c. crushing a stone with sound waves d. the removal of waste in blood not filtered by kidneys by passing fluid through a semipermeable barrier that allows normal electrolytes to remain, either with a machine with circulatory access or by passing a balanced fluid through the peritoneal cavity e. excessive urination at night f. a blood test to determine the amount of nitrogen in blood or urea, a waste product normally excreted in urine g. of psychological origin h. a normal protein produced by the prostate that usually elevates in the presence of prostate cancer i. the density of a liquid, such as urine, compared with water j. radiography using contrast medium to evaluate kidney function k. direct visualization of the urinary bladder through a cystoscope inserted through the urethra l. an examination of the physical, chemical, and microscopic properties of urine m. failure of kidneys to produce urine n. blood in the urine o. the presence of large quantities of protein in the urine; usually a sign of renal dysfunction p. scant urine production q. the urge to urinate occurring more often than is required for normal bladder elimination r. a surgical opening to the outside of the body from the ureter to facilitate drainage of urine from an obstructed kidney
6 634 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant 38. psychogenic 39. pyuria 40. retrograde pyelogram 41. specific gravity 42. ureterostomy 43. urinalysis s. pus in the urine t. bed wetting u. the placement of a catheter in the kidney pelvis to drain urine from an obstructed kidney v. the inability to control elimination of urine, feces, or both w. a procedure for introducing a flexible tube into the body x. an x-ray of the urinary tract using contrast medium injected through the bladder and ureters; useful in diagnosing obstructions 44. urinary frequency COG SHORT ANSWER Grade: 45. What is the difference between hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis? 46. What are calculi? 47. List five microorganisms that may cause epididymitis. a. b. c. d. e.
7 CHAPTER 34 Urology What are the symptoms of a possible tumor in the urinary system? 49. Are stones more likely to form when urine is alkaline or acidic? 50. Why is a woman more likely to have cystitis than a man? 51. Why are infections in the male urinary tract likely to spread to the reproductive system? 52. What are the three characteristics of the prostate that the physician is checking when performing a digital rectal examination?
8 636 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant 53. An older adult male patient with prostatic hypertrophy must be given a catheter in order to obtain a urine sample. What is the best type of catheter to use, and why? 54. List three suggestions to help patients avoid urinary tract infections. 55. What is the difference between an intravenous pyelogram and a retrograde pyelogram? What might the medical assistant be responsible for with regards to the physician order for an intravenous pyelogram and retrograde pyelogram? COG TRUE OR FALSE? Grade: Indicate whether the statements are true or false by placing the letter T (true) or F (false) on the line preceding the statement. 56. Orchiopexy refers to either one or both undescended testes. 57. A nephrologist is a physician who specializes in the physical characteristics of the urinary system. 58. No other form of birth control is needed after a man receives a vasectomy. 59. Your office is obligated to notify a patient if a procedure or medication is still in clinical trials, but likely to be approved.
9 CHAPTER 34 Urology 637 COG AFF CASE STUDIES FOR CRITICAL THINKING Grade: 1. A middle-aged patient in good shape comes in complaining of some pain in his groin. The physician suspects he might have an inguinal hernia. What is the procedure to diagnosis this, and how is it corrected? 2. An older adult patient has been diagnosed with renal failure and will need to undergo dialysis. However, he is not sure if hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis would be better for his lifestyle. What information can you tell him about the two different processes, including the advantages and disadvantages of each? 3. The physician asks you to give information to one of the patients about passing small calculi. What would you tell the patient about calculi, and what suggestions would you give to help the patient pass the stones? 4. A man in his early 20s has come in for his physical, and the physician has instructed you to teach him about testicular disease. You will also need to teach him how to perform a self-examination. However, the man is shy and embarrassed about the procedure. What can you say to him to help him overcome his discomfort?
10 638 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant 5. An older adult woman has chronic renal failure, and the physician decides that she will need a catheter for peritoneal dialysis. The woman is upset that she needs this, because she believes that it will limit her movement and ability to participate in activities she likes. What can you tell her about catheters and how her lifestyle will change that might put her more at ease?
11 CHAPTER 34 Urology 639 PSY PROCEDURE 34-1 Perform a Female Urinary Catheterization Name: Date: Time: Grade: EQUIPMENT/SUPPLIES: Straight catheterization tray that includes a #14 or #16 French catheter, a sterile tray, sterile gloves, antiseptic, a specimen cup with a lid, lubricant, and a sterile drape; an examination light; an anatomically correct female torso model for performing the catheterization; a biohazard container STANDARDS: Given the needed equipment and a place to work the student will perform this skill with % accuracy in a total of minutes. (Your instructor will tell you what the percentage and time limits will be before you begin.) KEY : 4 = Satisfactory 0 = Unsatisfactory NA = this step is not counted PROCEDURE STEPS SELF PARTNER INSTRUCTOR 1. Wash your hands. 2. Identify the patient. a. Explain the procedure and have the patient disrobe from the waist down. b. Provide adequate gowning and draping materials. 3. Place the patient in the dorsal recumbent or lithotomy position. a. Drape carefully to prevent unnecessary exposure. b. Open the tray and place it between the patient s legs. c. Adjust examination light to allow adequate visualization of the perineum. 4. Remove the sterile glove package and put on the sterile gloves. 5. Remove sterile drape and place it under the patient s buttocks. 6. Open the antiseptic swabs and place them upright inside the catheter tray. 7. Open the lubricant and squeeze a generous amount onto the tip of the catheter. 8. Remove the sterile urine specimen cup and lid and place them to the side of the tray. 9. Using your nondominant hand, carefully expose the urinary meatus. 10. Using your sterile dominant hand, use antiseptic swabs to cleanse the urinary meatus by starting at the top and moving the swab down each side of the urinary meatus and down the middle, using a new swab for each side and the middle. Do not contaminate the glove on this hand.
12 640 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant 11. Pick up the catheter with the sterile, dominant hand and: a. Carefully insert the lubricated tip into the urinary meatus approximately 3 inches. b. Leave the other end of the catheter in the tray. 12. Once the urine begins to flow into the catheter tray, hold the catheter in position with your nondominant hand. 13. Use your dominant hand to direct the flow of urine into the specimen cup. 14. Remove catheter when urine flow slows or stops or 1,000 ml has been obtained. 15. Wipe the perineum carefully with the drape that was placed under the buttocks. 16. Dispose of urine appropriately and discard supplies in a biohazard container. a. Label the specimen container and complete the necessary laboratory requisition. b. Process the specimen according to the guidelines of the laboratory. 17. Remove your gloves and wash your hands. 18. Instruct patient to dress and give any follow-up information. 19. Document the procedure in the patient s medical record. CALCULATION Total Possible Points: Total Points Earned: Multiplied by 100 = Divided by Total Possible Points = % PASS FAIL COMMENTS: Student s signature Date Partner s signature Date Instructor s signature Date
13 CHAPTER 34 Urology 641 PSY PROCEDURE 34-2 Perform a Male Urinary Catheterization Name: Date: Time: Grade: EQUIPMENT/SUPPLIES: Straight catheterization tray that includes a #14 or #16 French catheter, a sterile tray, sterile gloves, antiseptic, a specimen cup with a lid, lubricant, and a sterile drape; an examination light; an anatomically correct male torso model for performing the catheterization; a biohazard container STANDARDS: Given the needed equipment and a place to work the student will perform this skill with % accuracy in a total of minutes. (Your instructor will tell you what the percentage and time limits will be before you begin.) KEY : 4 = Satisfactory 0 = Unsatisfactory NA = this step is not counted PROCEDURE STEPS SELF PARTNER INSTRUCTOR 1. Wash your hands. 2. Identify the patient. a. Explain the procedure and have the patient disrobe from the waist down. b. Provide adequate gowning and draping materials. 3. Place the patient in the supine position. a. Drape carefully to prevent unnecessary exposure. b. Open the tray and place it to the side or on the patient s thighs. c. Adjust examination light to allow adequate visualization of the perineum. 4. Remove the sterile glove package and put on the sterile gloves. 5. Carefully remove the sterile drape and place it under the glans penis. 6. Open the antiseptic swabs and place them upright inside the catheter tray. 7. Open lubricant and squeeze a generous amount onto the tip of the catheter. 8. Remove sterile urine specimen cup and lid and place them to the side of the tray. 9. Using your nondominant hand, pick up the penis to expose the urinary meatus. 10. Using your sterile dominant hand, use antiseptic swabs to cleanse the urinary meatus by starting at the top and moving the swab around each side of the urinary meatus and down the middle, using a new swab for each side and the middle. Do not contaminate the glove on this hand.
14 642 PART III The Clinical Medical Assistant 11. Using your sterile dominant hand, pick up the catheter. a. Carefully insert the lubricated tip into the meatus approximately 4 to 6 inches. b. The other end of the catheter should be left in the tray. 12. Once the urine begins to flow into the catheter tray, hold the catheter in position. 13. Use your dominant hand to direct the flow of urine into the specimen cup. 14. Remove the catheter when urine flow slows or stops or 1,000 ml has been obtained. 15. Wipe the glans penis carefully with the drape that was placed under the buttocks. 16. Dispose of urine appropriately and discard supplies in a biohazard container. 17. Label the specimen container and complete the necessary laboratory requisition. 18. Process specimen according to the guidelines of the laboratory. 19. Remove your gloves and wash your hands. 20. Instruct patient to dress and give any follow-up information. 21. Document the procedure in the patient s medical record. CALCULATION Total Possible Points: Total Points Earned: Multiplied by 100 = Divided by Total Possible Points = % PASS FAIL COMMENTS: Student s signature Partner s signature Instructor s signature Date Date Date
15 CHAPTER 34 Urology 643 PSY PROCEDURE 34-3 Instruct a Male Patient on the Self-Testicular Examination Name: Date: Time: Grade: EQUIPMENT/SUPPLIES: A patient instruction sheet if available; a testicular examination model or pictures STANDARDS: Given the needed equipment and a place to work the student will perform this skill with % accuracy in a total of minutes. (Your instructor will tell you what the percentage and time limits will be before you begin.) KEY : 4 = Satisfactory 0 = Unsatisfactory NA = This step is not counted PROCEDURE STEPS SELF PARTNER INSTRUCTOR 1. Wash your hands. 2. Identify the patient and explain the procedure. 3. Using the testicular model or pictures, explain the procedure. a. Tell the patient to examine each testicle by gently rolling between the fingers and the thumb with both hands. b. Check for lumps or thickenings. 4. Explain that the epididymis is located on top of each testicle. a. Palpate to avoid incorrectly identifying it as an abnormal growth or lump. b. Instruct patient to report abnormal lumps or thickenings to the physician. 5. Allow the patient to ask questions related to the testicular self-examination. 6. Document the procedure in the patient s medical record. CALCULATION Total Possible Points: Total Points Earned: Multiplied by 100 = Divided by Total Possible Points = % PASS FAIL COMMENTS: Student s signature Partner s signature Instructor s signature Date Date Date
16
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Urinary System Diseases/Disorders. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Urinary System Diseases/Disorders LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Identify the purposes
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Urinary System Diseases/Disorders LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-8. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 4-1. Identify the purposes
Questions and Answers About the Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
 CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Questions and Answers
CANCER FACTS N a t i o n a l C a n c e r I n s t i t u t e N a t i o n a l I n s t i t u t e s o f H e a l t h D e p a r t m e n t o f H e a l t h a n d H u m a n S e r v i c e s Questions and Answers
Guide for Use. Advance Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System
 Advance Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Hollister Advance Plus intermittent catheter features Touch Free technique enabling users to catheterize with confidence virtually anytime,
Advance Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Hollister Advance Plus intermittent catheter features Touch Free technique enabling users to catheterize with confidence virtually anytime,
Guide for Use. Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System
 Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Touch free, sterile, and self-contained, Hollister Apogee Plus intermittent catheter empowers you to maintain your independence and live
Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Touch free, sterile, and self-contained, Hollister Apogee Plus intermittent catheter empowers you to maintain your independence and live
Endocrinology. Learning Outcomes. Cognitive Domain. Psychomotor Domain. ABHES Competencies. Affective Domain
 CHAPTER 36 Endocrinology Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define key terms 2. Identify abnormal conditions of the thyroid, pancreas, adrenal, and pituitary glands 3. Describe the tests commonly
CHAPTER 36 Endocrinology Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define key terms 2. Identify abnormal conditions of the thyroid, pancreas, adrenal, and pituitary glands 3. Describe the tests commonly
Guide for Use. Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System
 Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Touch free, sterile, and self-contained, Hollister Apogee Plus intermittent catheter empowers you to maintain your independence and live
Apogee Plus Touch Free Intermittent Catheter System Guide for Use Touch free, sterile, and self-contained, Hollister Apogee Plus intermittent catheter empowers you to maintain your independence and live
You have been booked for a. Flexible Cystoscopy. Under Local Anaesthetic
 You have been booked for a Flexible Cystoscopy Under Local Anaesthetic 1 WHAT IS A FLEXIBLE CYSTOSCOPY A flexible cystoscopy is a test to examine the uretha (waterpipe) and bladder using a thin, lighted
You have been booked for a Flexible Cystoscopy Under Local Anaesthetic 1 WHAT IS A FLEXIBLE CYSTOSCOPY A flexible cystoscopy is a test to examine the uretha (waterpipe) and bladder using a thin, lighted
The prostate can be affected by three conditions that may cause problems for men as they get older.
 The Prostate Gland The Prostate gland specific to males only, located in the pelvis between the bladder and rectum. It is about the shape and size of a walnut or satsuma and gets bigger as you get older.
The Prostate Gland The Prostate gland specific to males only, located in the pelvis between the bladder and rectum. It is about the shape and size of a walnut or satsuma and gets bigger as you get older.
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System
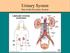 Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
URINARY SYSTEM. MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Chapter Six HIT #141. Anatomy
 URINARY SYSTEM MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Chapter Six HIT #141 Anatomy Kidneys = bean-shaped organs, located on each side of the spinal column, removal of waste from the blood. Nephron = microscopic located in
URINARY SYSTEM MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY Chapter Six HIT #141 Anatomy Kidneys = bean-shaped organs, located on each side of the spinal column, removal of waste from the blood. Nephron = microscopic located in
The Urinary System. 1. Define important words in this chapter. 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system
 109 16 The Urinary System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system 3. Discuss changes in the urinary system due to aging 4. List normal qualities
109 16 The Urinary System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the urinary system 3. Discuss changes in the urinary system due to aging 4. List normal qualities
Bladder Management. Why is a Bladder Program so Important?
 Bladder Management A clear understanding of the principles and skills involved in bladder management will help you prevent complications such as a urinary tract infection. Before your injury, waste products
Bladder Management A clear understanding of the principles and skills involved in bladder management will help you prevent complications such as a urinary tract infection. Before your injury, waste products
Endoscopy. Flexible Cystoscopy. Information
 Endoscopy Flexible Cystoscopy Information What is a Flexible Cystoscopy? This is a test for both men and women to examine the inside of your bladder either to help make a diagnosis or to make sure that
Endoscopy Flexible Cystoscopy Information What is a Flexible Cystoscopy? This is a test for both men and women to examine the inside of your bladder either to help make a diagnosis or to make sure that
Urinary System. Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system
 Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Urinary System Analyze the Anatomy and Physiology of the urinary system Kidney Bean-shaped Located between peritoneum and the back muscles (retroperitoneal) Renal pelvis funnelshaped structure at the beginning
Haematuria Clinic. Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST
 Haematuria Clinic Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST The Haematuria Clinic You have been referred to the Haematuria Clinic as
Haematuria Clinic Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST The Haematuria Clinic You have been referred to the Haematuria Clinic as
Cystoscopy. Your cystoscopy is scheduled at the Ambulatory Procedure Center at Altru Clinic - Main, 4-south waiting room.
 Improving Health, Enriching Life Cystoscopy Your cystoscopy is scheduled at the Ambulatory Procedure Center at Altru Clinic - Main, 4-south waiting room. Arrival Time: Appointment Date: Normal Female Urinary
Improving Health, Enriching Life Cystoscopy Your cystoscopy is scheduled at the Ambulatory Procedure Center at Altru Clinic - Main, 4-south waiting room. Arrival Time: Appointment Date: Normal Female Urinary
Instruction Guide to Sterile Intermittent Catheterization For Parents of Girls Using the Cure Catheter Closed System
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
How to Change a. Foley catheter. Patient Education Rehabilitation Nursing. Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver
 Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives step-bystep instructions for changing a Foley catheter, which is a tube in your bladder to
Patient Education How to Change a Foley Catheter Step-by-step instructions for the caregiver This handout gives step-bystep instructions for changing a Foley catheter, which is a tube in your bladder to
Flexible Cystoscopy. Patient Information
 Flexible Cystoscopy Patient Information 05/11/2012 Mehul Pankaj Raithatha 3 rd Year Medical Student Barts and the London - School of Medicine and Dentistry INTRODUCTION The urinary bladder is the organ
Flexible Cystoscopy Patient Information 05/11/2012 Mehul Pankaj Raithatha 3 rd Year Medical Student Barts and the London - School of Medicine and Dentistry INTRODUCTION The urinary bladder is the organ
Instruction Guide to Sterile Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Men Using the Cure Catheter Closed System
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care
 Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care Table of Contents 1 What is a catheter?... 2 2 Why does the child need a catheter?... 2 3 Normal Urine... 2 4 How to do a clean urethral catheterization
Complex Care Hub Manual: Urethral Catheter Care Table of Contents 1 What is a catheter?... 2 2 Why does the child need a catheter?... 2 3 Normal Urine... 2 4 How to do a clean urethral catheterization
Instruction Guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization for Parents of Girls Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Instruction Guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization for Parents of Boys Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Achieving Independence. A Guide to Self-Catheterization with the Bard Touchless Plus Intermittent Catheter System
 Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization with the Bard Touchless Plus Intermittent Catheter System Achieving Independence Introducing the Bard Touchless Plus Catheter One
Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization with the Bard Touchless Plus Intermittent Catheter System Achieving Independence Introducing the Bard Touchless Plus Catheter One
Achieving Independence
 Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization Achieving Independence Introduction This brochure is provided by Bard, a leading provider of urology products since 1907. The best
Bard: Intermittent Self-Catheterization A Guide to Self-Catheterization Achieving Independence Introduction This brochure is provided by Bard, a leading provider of urology products since 1907. The best
Apogee. Intermittent Catheter Guide for Use
 Apogee Intermittent Catheter Guide for Use Personal Care Plan This is your Personal Care Plan, which should be completed by your healthcare professional. Name: Telephone Number: Clinician (Doctor/Nurse):
Apogee Intermittent Catheter Guide for Use Personal Care Plan This is your Personal Care Plan, which should be completed by your healthcare professional. Name: Telephone Number: Clinician (Doctor/Nurse):
HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases
 HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases Urine production Core elements: Glomerulus, proximal and distal convoluted tube, loop of Henle, collecting tubules, ureters, bladder, sphincter, uretra, and out
HMM 4401 Genito-urinary tract diseases Urine production Core elements: Glomerulus, proximal and distal convoluted tube, loop of Henle, collecting tubules, ureters, bladder, sphincter, uretra, and out
Urinary System. Unit 6.12 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.12 (7 th Edition)
 Urinary System Unit 6.12 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.12 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the urinary system and their functions. Explain the major functions of the kidneys.
Urinary System Unit 6.12 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.12 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the major organs of the urinary system and their functions. Explain the major functions of the kidneys.
THE UROLOGY GROUP
 THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
Prostate Cancer Screening. A Decision Guide
 Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate Cancer Screening A Decision Guide This booklet was developed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Is screening right for you?
Prostate surgery. What is the prostate? What is a TURP? Why is a TURP operation necessary? Deciding to have a TURP operation.
 What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows
What is the prostate? The prostate is a gland about the size of a walnut that is only present in men. It is located just below the bladder and surrounds the urethra, the tube through which urine flows
Having a flexible cystoscopy
 Having a flexible cystoscopy Information for you Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa Visit our website: www.nhsaaa.net All our publications are available in other
Having a flexible cystoscopy Information for you Follow us on Twitter @NHSaaa Find us on Facebook at www.facebook.com/nhsaaa Visit our website: www.nhsaaa.net All our publications are available in other
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls
 Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow
Clean Intermittent Catheterization in Girls What is Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC)? Clean Intermittent Catheterization (CIC) is a way to empty your child s bladder using a catheter (a hollow
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urinary Tract Infections
 Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
Urinary Tract Infections Introduction A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. Infections are caused by microbes, including bacteria, fungi and viruses. Microbes are organisms
The Urinary System. Maintenance Systems Unit 5
 The Urinary System Maintenance Systems Unit 5 Basic Functions of the Urinary System Regulates the composition and volume of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of water and solutes. Eliminates
The Urinary System Maintenance Systems Unit 5 Basic Functions of the Urinary System Regulates the composition and volume of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of water and solutes. Eliminates
SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats
 SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats These SOPs were developed by the Office of the University Veterinarian and reviewed by Virginia Tech IACUC to provide a reference and guidance to investigators during
SOP: Urinary Catheter in Dogs and Cats These SOPs were developed by the Office of the University Veterinarian and reviewed by Virginia Tech IACUC to provide a reference and guidance to investigators during
Reproductive System: Male
 Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
Reproductive System Reproductive System: Male Produces new life Same types of organs for males and females Gonads, or sex glands Male organs located mainly outside of body Testes The male gonads Located
UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Urinary System Test Bank
 UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Urinary System Test Bank Objective 5.05 Describe the basic functions of the urinary system. 1. Which of the following is NOT a function of the urinary system? a. Maintain body
UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Urinary System Test Bank Objective 5.05 Describe the basic functions of the urinary system. 1. Which of the following is NOT a function of the urinary system? a. Maintain body
Urinary System. Dr. Thorson
 Urinary System Dr. Thorson Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, students should be able to Define and spell the terms to learn for this chapter. Describe the purpose and function of the urinary
Urinary System Dr. Thorson Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, students should be able to Define and spell the terms to learn for this chapter. Describe the purpose and function of the urinary
M E D I C A L T E R M I N O L O G Y
 URINARY SYSTEM M E D I C A L T E R M I N O L O G Y Is the organ system which produces, stores and eliminates waste. Is responsible for waste excretion in the form of urine Fluid Intake Is necessary in
URINARY SYSTEM M E D I C A L T E R M I N O L O G Y Is the organ system which produces, stores and eliminates waste. Is responsible for waste excretion in the form of urine Fluid Intake Is necessary in
Pulmonary Medicine. 1. Spell and define the key terms 2. Identify the primary defense mechanisms
 CHAPTER 30 Pulmonary Medicine Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define the key terms 2. Identify the primary defense mechanisms of the respiratory system 3. Identify common pathology related
CHAPTER 30 Pulmonary Medicine Learning Outcomes Cognitive Domain 1. Spell and define the key terms 2. Identify the primary defense mechanisms of the respiratory system 3. Identify common pathology related
A word about incontinence
 A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
A word about incontinence When you re continent, you have control over your urine. You feel the need to urinate, and you can hold it until you get to a bathroom. When you re incontinent, you may urinate
TYPES OF PROSTATITIS There are three types of prostatitis-type presentations:
 SPECIALIZED UROLOGIC CONSULTANTS, SC 10400 Southwest Hwy 16632 S. 107 th Ct. Chicago Ridge, IL 60453 Orland Park, IL 60467 Tel (708) 423-8706 Tel (708) 349-6350 PROSTATITIS - REVIEW Prostatitis is an inflammation
SPECIALIZED UROLOGIC CONSULTANTS, SC 10400 Southwest Hwy 16632 S. 107 th Ct. Chicago Ridge, IL 60453 Orland Park, IL 60467 Tel (708) 423-8706 Tel (708) 349-6350 PROSTATITIS - REVIEW Prostatitis is an inflammation
Day 1 Bell Work We will be discussing one of FIVE excretory organs in the human body. We have already studied four of them. The kidneys are considered
 URINARY SYSTEM 1 Day 1 Bell Work We will be discussing one of FIVE excretory organs in the human body. We have already studied four of them. The kidneys are considered the main organ in the excretory system.
URINARY SYSTEM 1 Day 1 Bell Work We will be discussing one of FIVE excretory organs in the human body. We have already studied four of them. The kidneys are considered the main organ in the excretory system.
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
Instruction Guide to Clean Intermittent Catheterization for Parents of Boys Using the Hydrophilic Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Urodynamic Testing National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the urinary tract? The urinary tract
Urodynamic Testing National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is the urinary tract? The urinary tract
Dr. Aso Urinary Symptoms
 Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Women Using the Extra Long Cure Medical Pocket Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
THE UROLOGY GROUP
 THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
Patient and Family Education. Bladder Exstrophy. What is bladder exstrophy? How common is bladder exstrophy? What causes bladder exstrophy?
 Patient and Family Education Bladder Exstrophy What is bladder exstrophy? Bladder exstrophy (x-tro-fee) is a bladder that is not formed right. The bladder and genitals are split in half, turned inside
Patient and Family Education Bladder Exstrophy What is bladder exstrophy? Bladder exstrophy (x-tro-fee) is a bladder that is not formed right. The bladder and genitals are split in half, turned inside
Saving. Kidneys. Benign Prostate Disease
 Saving Kidneys 9 Benign Prostate Disease This booklet will tell you more about the prostate gland. Its functions and benign hyperplasia have been defined in a simple way. Ways to prevent and treat this
Saving Kidneys 9 Benign Prostate Disease This booklet will tell you more about the prostate gland. Its functions and benign hyperplasia have been defined in a simple way. Ways to prevent and treat this
Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE)
 Service: Imaging Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions The team delivering your healthcare want to encourage you to become as involved as possible
Service: Imaging Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions The team delivering your healthcare want to encourage you to become as involved as possible
Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer
 Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer Introduction This leaflet is written for patients and their family. It provides information on prostate cryotherapy for prostate cancer which has not previously
Cryotherapy for localised prostate cancer Introduction This leaflet is written for patients and their family. It provides information on prostate cryotherapy for prostate cancer which has not previously
1: : Lifetime risk for prostate cancer 1:27. Lifetime risk for. testicular cancer. Lifetime risk for. penile cancer
 *Based on the National Cancer Registry of 2010 Lifetime risk for prostate cancer 1:27 Lifetime risk for testicular cancer Lifetime risk for penile cancer 1:2 040 1:1 114 Prostate cancer 1 in 27 South African
*Based on the National Cancer Registry of 2010 Lifetime risk for prostate cancer 1:27 Lifetime risk for testicular cancer Lifetime risk for penile cancer 1:2 040 1:1 114 Prostate cancer 1 in 27 South African
Bladder Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging
 Bladder Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
Bladder Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and Staging Detection and Diagnosis Catching cancer early often allows for more treatment options. Some early cancers may have signs and symptoms that can be
TOWN OF FAIRFIELD PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING
 TOWN OF FAIRFIELD PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING PROGRAM: School Health APPROVED BY: Board of Health School Medical Advisor POLICY & PROCEDURE: Clean Intermittent Catheterization DATE: 5/9/94 DEFINITION: POLICY
TOWN OF FAIRFIELD PUBLIC HEALTH NURSING PROGRAM: School Health APPROVED BY: Board of Health School Medical Advisor POLICY & PROCEDURE: Clean Intermittent Catheterization DATE: 5/9/94 DEFINITION: POLICY
THE UROLOGY GROUP
 THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
THE UROLOGY GROUP www.urologygroupvirginia.com 1860 Town Center Drive Suite 150/160 Reston, VA 20190 703-480-0220 19415 Deerfield Avenue Suite 112 Leesburg, VA 20176 703-724-1195 224-D Cornwall Street,
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Women Using the Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Drinking fluids and how they affect your bladder
 www.olarts.com Drinking fluids and how they affect your bladder Contact us Patient Advice and Liaison Service (PALS) To make comments or raise concerns about the Trust s services, please contact PALS.
www.olarts.com Drinking fluids and how they affect your bladder Contact us Patient Advice and Liaison Service (PALS) To make comments or raise concerns about the Trust s services, please contact PALS.
Effective Date: August 31, 2006
 COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 416 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: ENEMAS 1. PURPOSE: A. To relieve distention and gas by absorption,
COALINGA STATE HOSPITAL NURSING POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL SECTION - Treatments POLICY NUMBER: 416 Effective Date: August 31, 2006 SUBJECT: ENEMAS 1. PURPOSE: A. To relieve distention and gas by absorption,
Instruction Guide to Clean Self-Intermittent Catheterization For Men Using the Hydrophilic Cure Catheter
 Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Cure Medical donates 10% of net income to medical research in pursuit of a cure for spinal cord injuries and central nervous system disorders. For information on scientific advancements, visit www.curemedical.com.
Continuous Bladder Irrigation
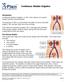 Continuous Bladder Irrigation Introduction Continuous bladder irrigation, or CBI, is the infusion of a sterile solution into the urinary bladder. The purpose of CBI is to prevent the formation of blood
Continuous Bladder Irrigation Introduction Continuous bladder irrigation, or CBI, is the infusion of a sterile solution into the urinary bladder. The purpose of CBI is to prevent the formation of blood
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Urinary System Objectives
 Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 12-Urinary System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health and Human
Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 12-Urinary System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health and Human
flow resulting from damage to blood vessels can also contribute to sexual dysfunction.
 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Troublesome bladder symptoms and changes in sexual function are common health problems as people age. Having diabetes can mean
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Troublesome bladder symptoms and changes in sexual function are common health problems as people age. Having diabetes can mean
Inserting an antegrade ureteric stent. Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England.
 Inserting an antegrade ureteric stent Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained
Inserting an antegrade ureteric stent Brought to you in association with EIDO Healthcare and endorsed by the Royal College of Surgeons England. Discovery has made every effort to ensure that we obtained
WJ UROGENITAL SYSTEM. UROLOGY
 WJ UROGENITAL SYSTEM. UROLOGY 1 Societies 11 History Include all aspects 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible 15 Classification.
WJ UROGENITAL SYSTEM. UROLOGY 1 Societies 11 History Include all aspects 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible 15 Classification.
P ROLIEVE. Thermodilatation System. The Prolieve System Patient Information is Directed to You, the Patient. A Transurethral Microwave Therapy Device
 P ROLIEVE Thermodilatation System A Transurethral Microwave Therapy Device The Prolieve System Patient Information is Directed to You, the Patient. Contents Why am I being treated with the Prolieve Thermodilatation
P ROLIEVE Thermodilatation System A Transurethral Microwave Therapy Device The Prolieve System Patient Information is Directed to You, the Patient. Contents Why am I being treated with the Prolieve Thermodilatation
advice on prevention
 Women & Children s Directorate Urinary Tract Infection advice on prevention information for children and their families 2 Urinary tract infection (UTI for short) is one of the commonest bacterial diseases
Women & Children s Directorate Urinary Tract Infection advice on prevention information for children and their families 2 Urinary tract infection (UTI for short) is one of the commonest bacterial diseases
CATHETER PASSPORT. Looking after your Urinary Catheter. The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter.
 CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
CATHETER PASSPORT Looking after your Urinary Catheter The Catheter Passport should be given to all patients with a urinary catheter. Health care staff should ensure that page 10 is completed. This document
My Urinary Catheter Passport Looking after my urinary catheter
 Feedback We welcome your comments. If you have any ideas about how we could do something better or feedback about positive aspects of the service please let us know. If you have a complaint please let
Feedback We welcome your comments. If you have any ideas about how we could do something better or feedback about positive aspects of the service please let us know. If you have a complaint please let
4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007)
 4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007) I. Genitourinary Trauma: 1. Goal: The student will be able to demonstrate a basic clinical approach to the management & diagnosis of
4 th Year Urology Core Objectives Keith Rourke (Revised June 1, 2007) I. Genitourinary Trauma: 1. Goal: The student will be able to demonstrate a basic clinical approach to the management & diagnosis of
Chapter 47 1/8/2018. Urinary System Disorders. Urinary Tract Infections. Treatment
 Chapter 47 Urinary System Disorders Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common Infection in one area can involve the entire system Microbes enter through the urethra. Catheterization,
Chapter 47 Urinary System Disorders Urinary Tract Infections Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common Infection in one area can involve the entire system Microbes enter through the urethra. Catheterization,
Chapter 18: Glossary
 Chapter 18: Glossary Sutter Health Cancer Service Line: Prostate Committee Advanced cancer: When the cancer has spread to other parts of the body (including lymph nodes, bones, or other organs) and is
Chapter 18: Glossary Sutter Health Cancer Service Line: Prostate Committee Advanced cancer: When the cancer has spread to other parts of the body (including lymph nodes, bones, or other organs) and is
Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC)
 Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Saint Mary s Hospital & Trafford General Hospital Uro-gynaecology Service Information for Patients Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterisation (CISC) What is catheterisation? Catheterisation involves passing
Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James
 PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James This handout tells you how to care for your nephrostomy catheter. If you have any questions about this information,
PATIENT EDUCATION patienteducation.osumc.edu Home Care for Your Nephrostomy Catheter - The James This handout tells you how to care for your nephrostomy catheter. If you have any questions about this information,
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
RATIONALE: The organs making up the urinary system consist of the kidneys, bladder, urethra, and ureters.
 Chapter 12 Section Review 12.1 1. A. Kidneys RATIONALE: The renal pelvis receives urine from the kidney, travels through the ureters on the way to the bladder, but urine is formed in the kidney. 2. C.
Chapter 12 Section Review 12.1 1. A. Kidneys RATIONALE: The renal pelvis receives urine from the kidney, travels through the ureters on the way to the bladder, but urine is formed in the kidney. 2. C.
Introduction. Growths in the prostate can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer).
 This information was taken from urologyhealth.org. Feel free to explore their website to learn more. Another trusted website with good information is the national comprehensive cancer network (nccn.org).
This information was taken from urologyhealth.org. Feel free to explore their website to learn more. Another trusted website with good information is the national comprehensive cancer network (nccn.org).
Nephrostomy. Radiology Department. Patient information leaflet
 Nephrostomy Radiology Department Patient information leaflet This leaflet informs you about the procedure known as a nephrostomy. It explains what is involved and the possible risks. The benefits and risks
Nephrostomy Radiology Department Patient information leaflet This leaflet informs you about the procedure known as a nephrostomy. It explains what is involved and the possible risks. The benefits and risks
Patient information leaflet. Royal Surrey County Hospital. NHS Foundation Trust. Nephrostomy. Radiology
 Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Nephrostomy Radiology This leaflet informs you about the procedure known as a nephrostomy. It explains what is involved and
Patient information leaflet Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Nephrostomy Radiology This leaflet informs you about the procedure known as a nephrostomy. It explains what is involved and
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options
 AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
AFTER DIAGNOSIS: PROSTATE CANCER Understanding Your Treatment Options INTRODUCTION This booklet describes how prostate cancer develops, how it affects the body and the current treatment methods. Although
Urinary incontinence. Urology Department. Patient Information Leaflet
 Urinary incontinence Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with urinary incontinence. It contains information about the bladder,
Urinary incontinence Urology Department Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet is for people who have been diagnosed with urinary incontinence. It contains information about the bladder,
BLADDER PROSTATE PENIS TESTICLES BE YO ND YO UR CA NC ER
 BLADDER PROSTATE PENIS TESTICLES THE PROSTATE IS A SMALL, WALNUT-SIZED GLAND THAT IS PART OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. IT RESTS BELOW THE BLADDER, IN FRONT OF THE RECTUM AND SURROUNDS PART OF THE URETHRA.
BLADDER PROSTATE PENIS TESTICLES THE PROSTATE IS A SMALL, WALNUT-SIZED GLAND THAT IS PART OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM. IT RESTS BELOW THE BLADDER, IN FRONT OF THE RECTUM AND SURROUNDS PART OF THE URETHRA.
Lecture 7. The Urinary System
 Lecture 7 The Urinary System Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning The Urinary System The urinary system removes wastes from the body The urinary system also maintains homeostasis or a constant internal
Lecture 7 The Urinary System Copyright 2006 Thomson Delmar Learning The Urinary System The urinary system removes wastes from the body The urinary system also maintains homeostasis or a constant internal
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female)
 Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female) Refer to National Infection Prevention and Control Manual for information on aseptic technique/cleaning equipment. Equipment
Procedure for removal and reinsertion of an indwelling urethral catheter (female) Refer to National Infection Prevention and Control Manual for information on aseptic technique/cleaning equipment. Equipment
What to do about infertility?
 What to do about infertility? Dr. M.A. Fischer Section Head, Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton,
What to do about infertility? Dr. M.A. Fischer Section Head, Division of Urology, Department of Surgery Assistant Clinical Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Hamilton Health Sciences, Hamilton,
Urology. Flexible Cystoscopy
 Urology Flexible Cystoscopy The Urology service offers a comprehensive range of adult urologic care to patients, including advanced diagnostic, medical and surgical care for men and women. Our team of
Urology Flexible Cystoscopy The Urology service offers a comprehensive range of adult urologic care to patients, including advanced diagnostic, medical and surgical care for men and women. Our team of
Collection of Specimen
 Collection of Specimen Purpose This procedure helps the student nurse to identify different types of specimen and their purposes. Objectives At the end of this procedure, the student nurse should be able
Collection of Specimen Purpose This procedure helps the student nurse to identify different types of specimen and their purposes. Objectives At the end of this procedure, the student nurse should be able
Patient Urinary Catheter Passport
 Useful contact details: Continence Service (Community) 01724 298325 Continence Service (Goole) 01482 336951 Continence Service (SGH) 01724 282282 Ext 2823 Continence Service (DPOW) 01472 874111 Infection
Useful contact details: Continence Service (Community) 01724 298325 Continence Service (Goole) 01482 336951 Continence Service (SGH) 01724 282282 Ext 2823 Continence Service (DPOW) 01472 874111 Infection
Chapter 18. Assisting With Urinary Elimination. Elsevier items and derived items 2014, 2010 by Mosby, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 18 Assisting With Urinary Elimination The urinary system: The Urinary System Removes waste products from the blood Maintains the body s water balance 2 Normal Urination The healthy adult produces
Chapter 18 Assisting With Urinary Elimination The urinary system: The Urinary System Removes waste products from the blood Maintains the body s water balance 2 Normal Urination The healthy adult produces
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag
 Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder.
Going Home with a Urinary Catheter and an All in One Day/Night Drainage Bag Doctor: Phone Number: About Your Catheter A urinary catheter is a small tube that goes through your urethra and into your bladder.
Trans urethral resection of prostate (TURP)
 Trans urethral resection of prostate (TURP) Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST What is the prostate? Only men have a prostate
Trans urethral resection of prostate (TURP) Information for patients Urology PROUD TO MAKE A DIFFERENCE SHEFFIELD TEACHING HOSPITALS NHS FOUNDATION TRUST What is the prostate? Only men have a prostate
Radiological insertion of a nephrostomy and ureteric stent. An information guide
 TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Radiological insertion of a nephrostomy and ureteric stent An information guide Radiological Insertion of Nephrostomy and Ureteric Stent
TO PROVIDE THE VERY BEST CARE FOR EACH PATIENT ON EVERY OCCASION Radiological insertion of a nephrostomy and ureteric stent An information guide Radiological Insertion of Nephrostomy and Ureteric Stent
UNDERSTANDING. Permanent Birth Control for Men
 UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
UNDERSTANDING VASECTOMY Permanent Birth Control for Men Is Vasectomy for You? Vasectomy is a simple, safe procedure that makes a man sterile (unable to father a child). It s the most effective birth control
Getting Ready. My Child Is Having A VCUG
 Getting Ready My Child Is Having A VCUG Welcome to Inova Fairfax Hospital for Children. Your child is going to have a voiding cystourethrogram,a diagnostic test commonly referred to as a VCUG. It is very
Getting Ready My Child Is Having A VCUG Welcome to Inova Fairfax Hospital for Children. Your child is going to have a voiding cystourethrogram,a diagnostic test commonly referred to as a VCUG. It is very
Chapter 7. Male Reproductive System. Copyright 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 7 Male Reproductive System Chapter 7 Objective 1: Pronounce organs and anatomic structures of the male reproductive system. Organs (1 of 2) The organs of the male reproductive system include the
Chapter 7 Male Reproductive System Chapter 7 Objective 1: Pronounce organs and anatomic structures of the male reproductive system. Organs (1 of 2) The organs of the male reproductive system include the
